Alcatel-Lucent OMNIACCESS User Manual

OmniAccess RNTM
User Guide
i
OmniAccess RN: User Guide
Copyright
Copyright © 2005 Alcatel Internetworking, Inc. All rights reserved.
Specifications in this manual are subject to change without notice.
Originated in the USA.
Trademarks
AOS-W, Alcatel 4308, Alcatel 4324, Alcatel 6000, Alcatel 60/61, Alcatel 70, and Alcatel 52 are trademarks of Alcatel Internetworking, Inc. in the United States and certain other countries.
Any other trademarks appearing in this manual are the property of their respective companies.
Legal Notice
The use of Alcatel Internetworking Inc. switching platforms and software, by all individuals or corporations, to terminate Cisco or Nortel VPN client devices constitutes complete acceptance of liability by that individual or corporation for this action and indemnifies, in full, Alcatel Internetworking Inc. from any and all legal actions that might be taken against it with respect to infringement of copyright on behalf of Cisco Systems or Nortel Networks.
ii |
Part 031650-00 |
May 2005 |
|
|
|

Contents
Preface |
xi |
Document Organization . . . . . . . . . . xi Related Documents . . . . . . . . . . . . . xii Text Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xii Contacting Alcatel . . . . . . . . . . . . . xiii
Chapter 1 Deploying Access Points . . . . |
1 |
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. 1 |
Getting Started . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. 1 |
Chapter 2 Secure Remote Access |
|
Points . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
11 |
Deploying a Branch Office/Home |
|
Office Solution . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
11 |
Securing Communications . . . . . . . . . |
12 |
How the Secure Remote Access |
|
Point Service Works . . . . . . . . . . |
12 |
Configuring the Secure Remote |
|
Access Point Service . . . . . . . . . . |
14 |
Double Encryption . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
22 |
Managing Software Feature |
|
Licenses |
1 |
Alcatel Software Licenses . . . . . . . . . |
. 1 |
Software License Types . . . . . . . . |
. 1 |
Obtaining a Software License . . . . . |
. 2 |
The Software Licensing Process . . . . . |
. 2 |
Software License Certificates . . . . . |
. 2 |
The System Serial Number. . . . . . . |
. 3 |
The Alcatel License Management |
|
Web Site . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. 4 |
Applying The License Key . . . . . . . |
. 4 |
Contents iii
OmniAccess RN: User Guide
Additional Software License Information . 5
Permanent Licenses . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Evaluation Licenses . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Deleting a License Key . . . . . . . . . 7
Moving Licenses . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Switch Resetting . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
License Fraud Management . . . . . . . 8
Getting Help with Licenses . . . . . . . . . 8
Chapter 3 Configuring Network Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Conceptual Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 Network Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . 9 Create/Edit a VLAN. . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Configuring a Port to Be an
Access Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Configuring a Trunk Port . . . . . . . 12
Configuring Static Routes . . . . . . . 14
Modifying the Loopback IP Address . 14
Chapter 4 Configuring Redundancy . . . . |
17 |
Conceptual Overview . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Redundancy Configuration . . . . . . . . 18
Configuring Local Switch Redundancy 18
Master Switch Redundancy. . . . . . 22
Master-Local Switch Redundancy . . 26
Chapter 5 Adding a Local Switch . . . . . . 31
Configuring Local Switches . . . . . . . . 32
Configuring the Local Switch . . . . . 32
Configuring the L2 / L3 Settings . . . 35
Configuring Trusted Ports. . . . . . . 35
Configure the APs . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Reboot the APs . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Chapter 6 Configuring Wireless LANs . . 39
Conceptual Overview . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Configuring Wireless LAN—802.11
Networks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Pre-requisites . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Configuring Wireless LANs—Radio
Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Configuring Wireless LANs—Advanced . 49
Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
iv |
Part 031650-00 |
May 2005 |
|
|
|

Adaptive Radio Management. . . . . . . . 53
Deciding the Channel Setting . . . . . 54
Deciding Power Settings . . . . . . . . 54
Advantages of Using ARM . . . . . . . 54
Configuring ARM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Chapter 7 The External Services |
|
Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
57 |
Understanding ESI. . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Load Balancing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Configuring the Alcatel ESI . . . . . . . . . 59
Configuring the ESI servers . . . . . . 60
Configuring the User Policy . . . . . . 62
Chapter 8 Configuring Firewall Roles |
|
and Policies . . . . . . . . . . . . |
65 |
Configuring Policies . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66 Creating a New Policy . . . . . . . . . 66 Editing an Existing Policy . . . . . . . . 73 Applying the Policy to a User Role. . . 74
Chapter 9 Configuring AAA Servers . . . |
81 |
Authentication Timers. . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Accessing the Configuration page. . . 81
Authentication Servers . . . . . . . . . . . 83
RADIUS Server Configuration . . . . . 83
Editing an Existing Entry . . . . . . . . 85
Deleting an Existing Entry . . . . . . . 85
Advanced AAA Settings . . . . . . . . . . 86
Selecting the Right Server . . . . . . . 87
Configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Example Deployment . . . . . . . . . . 88
LDAP Server Settings . . . . . . . . . . 89
Editing an Existing Entry . . . . . . . . 91
Deleting an Existing Entry . . . . . . . 92
Internal Database . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Editing an Existing Entry . . . . . . . . 95
Deleting an Entry . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Configuring Server Rules . . . . . . . . . . 95
Example. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Chapter 10 Configuring the Captive |
|
Portal. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
99 |
Configuring Captive Portals for |
|
Contents v
OmniAccess RN: User Guide
Guest Logon . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Configuring Captive Portal for
User Logon . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
Configuring the AAA Server for
Captive Portal. . . . . . . . . . . 108
Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
Personalizing the Captive Portal Page . 111
Chapter 11 Configuring 802.1x Security 117 |
|
Default Open Ports . . . . . . . . . . . . |
118 |
Configuring Wireless User |
|
Authentication Only . . . . . . . . . |
118 |
Configuring the Authentication |
|
Servers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
121 |
Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
124 |
Configuring User and Machine |
|
Authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . |
126 |
Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
130 |
Configuring MAC-based |
|
Authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . |
133 |
Configuring the Switch . . . . . . . |
133 |
Configuring Users . . . . . . . . . . |
135 |
Configuring 802.1x for Wired Users . . |
137 |
Modifying the 802.1x Settings . . . |
138 |
Resetting the 802.1x Settings . . . |
138 |
Advanced Configuration Options |
|
of 802.1x . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
139 |
Chapter 12 Configuring Virtual Private
Networks. . . . . . . . . . . . . 143
VPN Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . 143 Enabling VPN Authentication . . . . 143 Configuring VPN with L2TP IPSec . 145 Enabling Src NAT. . . . . . . . . . . 147 IKE Shared Secrets . . . . . . . . . . 147 IKE Policies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
Configuring Alcatel Dialer Example . 150
Examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
Chapter 13 Intrusion Detection . . . . . . . |
163 |
vi |
Part 031650-00 |
May 2005 |
|
|
|

Rogue/Interfering AP Detection . . . . . 163
Denial of Service Detection . . . . . . 164
Man-In-The-Middle Detection . . . . 164
Signature Detection . . . . . . . . . . 165
Wireless LAN Policies . . . . . . . . . 165
Configuring Rogue AP Detection . . 166
Configuring Denial of Service
Attack Detection. . . . . . . . . . 168
Configuring Man-In-The-Middle
Attack Detection. . . . . . . . . . 171
Configuring Signature Detection. . . 173
Adding a New Signature Pattern. . . 175
Configuring Wireless LAN Policies . 178
Configuring Wireless Bridge
Detection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179
Chapter 14 System and Network
Management 185
Configuring SNMP for the Alcatel
Mobility Controller. . . . . . . . . . . 185
Configuring SNMP for the Access
Points . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 189
SNMP Traps from the Switch . . . . . . 196
SNMP traps from Access Point/Air
Monitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 198
Configuring Logging. . . . . . . . . . . . 202
Chapter 15 Configuring Quality of |
|
|
|
Service for Voice |
|
|
Applications . . . . . . . . . . |
207 |
|
Configuring QoS for SVP . . . . . . . . . |
208 |
|
Configuring QoS for SIP . . . . . . . . . |
213 |
Chapter 16 |
Topology Example One . . . . |
219 |
Chapter 17 |
Topology Example Two . . . |
227 |
Chapter 18 |
Topology Example Three . . |
239 |
Chapter 19 |
Topology Example Four . . . |
253 |
|
Topology Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . |
255 |
|
Topology Description . . . . . . . . . |
255 |
Contents vii
OmniAccess RN: User Guide
viii |
Part 031650-00 |
May 2005 |
|
|
|

Preface
This preface includes the following information:
zAn overview of the sections in this manual
zA list of related documentation for further reading
zA key to the various text conventions used throughout this manual
zAlcatel support and service information
Document Organization
This user guide includes instructions and examples for commonly used, basic wireless LAN (Wireless LAN) switch configurations such as Virtual Private Networks (VPNs), firewalls, and redundancy. This guide shows you how to configure your environment with the most commonly needed features and services.
To use this guide effectively, apply the configuration or configurations required and skip the rest. Unless otherwise indicated, chapters are not dependent on each other. That is, you do not need to configure a feature in an earlier chapter before you can configure a feature in a subsequent chapter. Chapter order is not significant.
For information on parameters and settings on the WebUI, refer to the Alcatel AOS-W Reference Guide.
Preface ix

OmniAccess RN: User Guide
Related Documents
The following items are part of the complete documentation set for the Alcatel system:
zAlcatel Mobility Controller Installation Guides
zAlcatel AP Installation Guides
zAlcatel AOS-W Reference Guide
Text Conventions
The following conventions are used throughout this manual to emphasize important concepts:
TABLE P-1 Text Conventions
Type Style |
Description |
|
|
|
|
Italics |
This style is used to emphasize important terms and to |
|
|
mark the titles of books. |
|
|
|
|
System items |
This fixed-width font depicts the following: |
|
|
z |
Sample screen output |
|
z |
System prompts |
|
z Filenames, software devices, and certain commands |
|
|
|
when mentioned in the text. |
|
|
|
Commands |
In the command examples, this bold font depicts text |
|
|
that the user must type exactly as shown. |
|
|
|
|
<Arguments> |
In the command examples, italicized text within angle |
|
|
brackets represents items that the user should replace |
|
|
with information appropriate to their specific situation. |
|
|
For example: |
|
|
|
# send <text message> |
|
In this example, the user would type “send” at the |
|
|
system prompt exactly as shown, followed by the text of |
|
|
the message they wish to send. Do not type the angle |
|
|
brackets. |
|
|
|
|
[ Optional ] |
In the command examples, items enclosed in brackets |
|
|
are optional. Do not type the brackets. |
|
{ Item A | Item B } In the command examples, items within curled braces and separated by a vertical bar represent the available choices. Enter only one choice. Do not type the braces or bars.
x |
Part 031650-00 |
May 2005 |
|
|
|

Contacting Alcatel
Web Site
z |
Main Site |
http://www.alcatel.com |
|
z |
Support |
http://www.alcatel.com/enterprise |
|
Telephone Numbers |
|
||
z |
Main US/Canada |
(800) 995-2612 |
|
z |
Main Outside US |
(818) 880-3500 |
|
Preface xi
OmniAccess RN: User Guide
xii |
Part 031650-00 |
May 2005 |
|
|
|

CHAPTER 1
Deploying Access Points
This chapter outlines the recommended methods used to deploy and provision Alcatel Access Points (APs) in an enterprise network environment, detailing the various provisioning options and steps required.
Overview
Alcatel wireless APs (also applicable to APs deployed as Air Monitors (AMs) are designed to be low-touch configuration devices that require only minimal provisioning to make them fully operational on an Alcatel-enabled Wireless LAN network. Once the AP has established Layer-3 communication with its host Alcatel Mobility Controller, advanced configuration and provisioning may be applied either to individual APs or globally across the entire wireless network centrally using the WebUI of the Master Alcatel Switch.
Getting Started
1.Planning
Decide where you wish to locate the APs in advance of physical installation. Alcatel RF Plan can be utilized to provide an AP placement map relative to a building floor plan to ensure optimal RF coverage. (For more information on RF Plan, see the Alcatel RF Plan for Windows User Guide.)
When deploying APs, note the AP MAC address and serial number against the physical location. This will be useful in assigning location code identifiers to APs (see “Assigning AP Location Codes” below), which will greatly enhance location-based services and wireless network calibration.
Deploying Access Points 1
OmniAccess RN: User Guide
2Provisioning the Network for AP-Switch Communications
There are deployment prerequisites that must be met before deploying APs in a live network environment. These prerequisites ensure that the APs are able to discover and attach to a host Alcatel Mobility Controller (defined as the
master). This also relieves the administrator from the need to manually configure each AP.
NOTE—Alcatel APs can only obtain their software image and configuration from a master Alcatel Mobility Controller.
The deployment prerequisites for Alcatel APs are:
zA Valid IP Address
Alcatel APs require a unique IP address on a subnet that has routable Layer-3 connectivity to a master Alcatel Mobility Controller. Alcatel recommends assigning the AP an IP address via DHCP (either from an existing network server or directly from an Alcatel Mobility Controller configured with a DHCP server).
To configure the AP IP address, go to“Assigning the IP Address to the AP”.
zMaster Alcatel Mobility Controller/loopback IP Address
This is the IP address from which the AP will attach to and obtain its software image and configuration. The master Alcatel Mobility Controller/loopback IP address can be provided to an Alcatel AP using one of the following methods:
DNS Server |
Alcatel APs are factory configured with |
Configuration |
Alcatel-master as the DNS host name. A DNS server |
|
on the network can be configured with an entry for |
|
Alcatel-master with the master Alcatel Mobility |
|
Controller/loopback IP address as the resolution. |
|
To configure this option see “DNS Server-derived AP |
|
Provisioning ”. |
|
|
DHCP Server |
A DHCP server on the same subnet as the AP can be |
Configuration |
configured to not only provide the AP its own IP |
|
address, but also provide the IP address of a master |
|
Alcatel Mobility Controller to which the AP should |
|
attach. This is achieved by configuring the DHCP |
|
standard vendor specific option (attribute 43) in the |
|
DHCP server, with the desired master Alcatel Mobility |
|
Controller/loopback IP address. When the DHCP |
|
server returns its offer to the AP, this attribute will be |
|
returned with it. |
|
To configure this option see “DHCP Server-derived |
|
AP Provisioning ”. |
|
|
2 |
Part 031650-00 |
May 2005 |
|
|
|

Chapter 1
Alcatel Discovery |
Alcatel APs are factory configured with ADP, a |
Protocol (ADP) - Plug |
feature that allows plug and play provisioning for APs |
and Play |
connected via Layer 2/3 to a master Alcatel Mobility |
|
Controller on an ADP-enabled network. |
|
ADP equipped APs send out periodic multicast and |
|
broadcast queries to locate a master Alcatel Mobility |
|
Controller. If an Alcatel switch is present in the same |
|
broadcast domain as the APs, it will respond with the |
|
switch/loopback IP address of the master switch. |
|
If the APs and Alcatel switch reside in different |
|
broadcast domains, the APs can discover the Alcatel |
|
master switch using IP multicast (IP multicast must |
|
be enabled in the network for this to function). The |
|
ADP multicast queries are sent to the IP multicast |
|
group address 224.0.82.11. |
|
Alternatively, you can configure a master Alcatel |
|
Mobility Controller address as the IP Helper/relay |
|
address on any Layer-3 switch on the same |
|
broadcast domain as the APs, thus mitigating the |
|
need to enable multicast in the network. |
|
ADP also functions for APs connected directly to |
|
Ethernet ports on a master Alcatel Mobility |
|
Controller. To configure this option see “Alcatel |
|
Discovery Protocol (ADP)”. |
|
|
Deploying Access Points 3
OmniAccess RN: User Guide
Step 2a.Assigning the IP Address to the AP
Either configure a DHCP server in the same subnet where the APs will be connected to the network, or configure a device in the same subnet to act as a relay agent for a DHCP server on a different subnet that can provide the AP with its IP information.
If you are planning on using a network-based DHCP server, skip to “AP-Master Switch Provisioning”.
If the APs are on the same subnet as the master Alcatel Mobility Controller, the Alcatel switch can be used as a DHCP server to manage IP address assignment to APs. (The Alcatel Mobility Controller must be the only DHCP server for this subnet.)
To enable DHCP server capability on an Alcatel switch:
zNavigate to the Configuration > DHCP Server page.
zCreate a DHCP server pool configuration.
zCreate an excluded address range.
zClick Apply to apply the configuration to the switch.
zClick Start to start the on-switch DHCP server.
Step 2b.AP-Master Switch Provisioning
It is imperative that the administrator chooses one of the aforementioned options to provide the Access Points with the master Alcatel Mobility Controller/loopback IP address. To configure each of these options see below:
DNS Server-derived AP Provisioning
When DNS server-derived provisioning is the chosen option to provide the AP with the master Alcatel Mobility Controller/loopback IP address, verify
that the DNS server used by the AP (usually supplied by DHCP) has an entry configured for the standard name Alcatel-master.
NOTE—The APs request for DNS resolution is for the Fully Qualified Domain Name Alcatel-master so make sure that this name is configured. After initial
provisioning, if the default domain name values are changed, make sure the AP and switch domain name settings match.
Alcatel recommends DNS server-derived AP configuration because it involves minimal changes to the network and offers the greatest flexibility in placement of APs.
If you select this option, skip the remainder of this section and proceed to “Deploying APs in the Network”.
4 |
Part 031650-00 |
May 2005 |
|
|
|

Chapter 1
DHCP Server-derived AP Provisioning
When DHCP server-derived provisioning is the chosen option to provide the AP with the master Alcatel Mobility Controller/loopback IP address, make sure the DHCP server is configured to return the Alcatel vendor-specific attribute information in its DHCP offer to the AP.
Configure the DHCP server to send the Alcatel master switch IP address
within the DHCP vendor-specific attribute option 43. The vendor class identifier used to identify DHCP requests from Alcatel APs is AlcatelAP.
NOTE—DHCP requires the format and contents of the vendor class identifier to be correct (AlcatelAP).
If you select this option, skip the remainder of this section and proceed to “Deploying APs in the Network”.
Alcatel Discovery Protocol (ADP)
NOTE—When APs are NOT on the same broadcast domain as the master Alcatel Mobility Controller, you must enable multicast or employ IP Helper to relay broadcast messages across the network for ADP to function correctly.
If ADP is the preferred option to provide the AP with the master Alcatel Mobility Controller/loopback IP address, and the APs are on the same broadcast domain as any master Alcatel Mobility Controller, no additional network configuration is required. APs will send broadcast queries to which a master Alcatel Mobility Controller will respond, along with its switch/loopback IP address, and the APs will boot to this switch.
ADP is enabled on all Alcatel Mobility Controllers by factory default. However, to ensure that ADP discovery is enabled on your switch use the following command:
(Alcatel4324) #show adp config
ADP Configuration
-----------------
key |
value |
--- |
----- |
discoveryenable igmp-joinenable
If ADP discovery is not enabled, use the following command to enable it:
(Alcatel4324) (config) #adp discovery enable
When APs are connected to Alcatel switches indirectly (via an IP-routed network), the administrator needs to make sure that multicast routing is enabled in the network, and that all routers are configured to listen for IGMP joins from the master Alcatel Mobility Controller and to route these multicast packets.
Make sure both ADP discovery and IGMP-join options are enabled. Verify using the show adp config command as shown above.
Should ADP discovery or IGMP-join options not be enabled:
Deploying Access Points 5
OmniAccess RN: User Guide
zEnable ADP discovery by entering:
(Alcatel4324) (config) #adp discovery enable
zEnable IGMP join by entering:
(Alcatel4324) (config) #adp igmp-join enable
zProceed to “Deploying APs in the Network” below.
3Deploying APs in the Network
You are now ready to physically install the APs and attach them to the network. (For information on mounting and powering options please refer to the AP hardware installation guide that shipped with the AP.)
When deploying APs, note the AP MAC address and serial number against the physical location. This will be useful in assigning location code identifiers to APs (see “Assigning AP Location Codes” below), which will greatly enhance location-based services and wireless network calibration.
zPhysically install the Access Point in the desired location.
zConnect the Access Point to the network port.
zMake sure power is available to the AP using 802.3af-compliant
Power over Ethernet (PoE) or via the optionally available AC power adapter kits. (The POWER and ENET LEDs on the AP will respectively indicate power/network link states.)
zAPs will now attempt to locate their master Alcatel Mobility Controller in the network.
4Assigning AP Location Codes
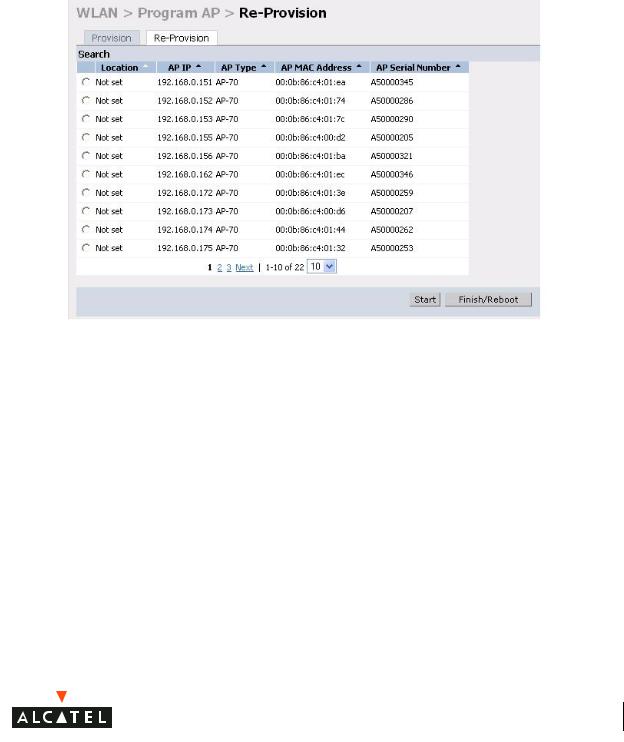
Now the APs are provisioned on the network, the final step in Access Point deployment is to configure (re-provision) each AP with a unique location code, which is used for location service capability. This location code is numerical and in the format 1.2.3 (where 1=building, 2=floor, 3=location). This can be configured for each AP in the network using the WebUI of the master Alcatel Mobility Controller.
To configure an AP with a unique location code:
zNavigate to the Maintenance > Program AP > Re-provision page.
This page displays a list of APs that have registered with the Master switch with either their default location code (-1.-1.-1) or their currently configured location code (if the AP has been provisioned already).
6 |
Part 031650-00 |
May 2005 |
|
|
|
Chapter 1
zSelect the AP that is to be configured from the list. This can be
selected by using the MAC address of the AP or the serial number of the AP. Click Enable to start provisioning the AP.
Deploying Access Points 7
OmniAccess RN: User Guide
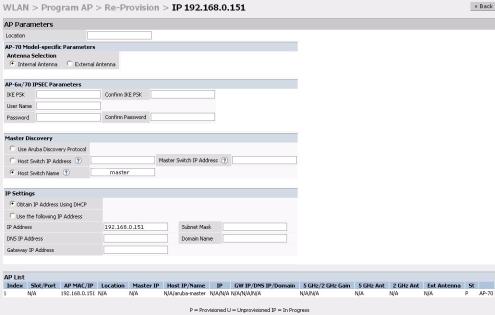
zEnter the location code in the format explained above.
zIf the AP being provisioned is a model with detachable antenna capability (such as an Alcatel AP-60) enter the antenna gain in dBi, for example 4.0. This is mandatory for all detachable antenna models as the AP will not will bring up its radio interface or function as an AP without it.
zClick Apply to apply the configuration to the AP.
NOTE—The configuration does not take effect until the AP is rebooted.
zNavigate to the Maintenance > Reboot AP page.
zSelect the AP from the list of the APs and click Reboot to reboot the AP.
zNavigate to the Maintenance > Program AP > Re-provision page to confirm that the new settings have taken effect.
8 |
Part 031650-00 |
May 2005 |
|
|
|

Chapter 1
Deploying Access Points 9
OmniAccess RN: User Guide
10 |
Part 031650-00 |
May 2005 |
|
|
|

CHAPTER 2
Secure Remote Access Points
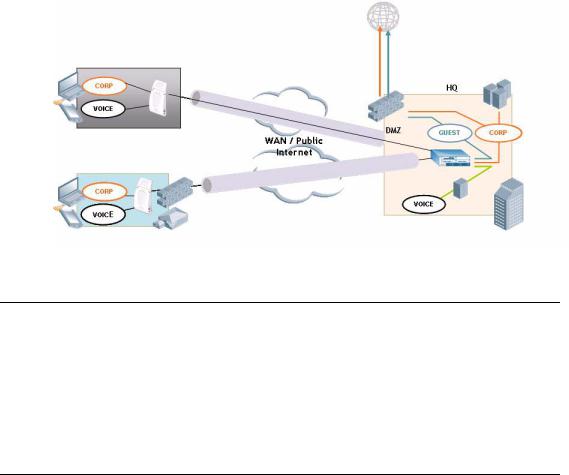
The Secure Remote Access Point Service allows users to connect APs on remote sites over the Internet to an Alcatel Mobility Controller. This capability allows remote locations equipped with Remote Access Points to connect to a corporate office, for example, over the Internet.
The Remote AP uses L2TP/IPSEC to connect to the Alcatel Mobility Controller with NAT-T (UDP port 4500 only) support. All of the AP control traffic and 802.11 data are carried through this tunnel to the Switch.
Since the Internet is involved, securing data between the AP and switch becomes key. Also most branch/home office deployments sit behind a firewall or a NAT device. In case of Remote AP, all traffic between the switch and the Remote AP is VPN encapsulated, and all control traffic between the switch and AP is encrypted. Administrators have a choice of encrypting the data in addition to the control traffic as additional security.
The advantage of using the Secure Remote Access Point Service as a Remote Access Point is the corporate office is now extended to the Remote Site. The users can enjoy similar feature sets as the corporate office users, VoIP application can be extended to remote sites while the servers and the PBX sit securely in the corporate office. The corporate network is virtually extended to the remote user.
Deploying a Branch Office/Home Office Solution
To deploy the Remote AP in a branch office or home office as shown in the illustration below, the following requirements need to be met:
Secure Remote Access Points 11
OmniAccess RN: User Guide
zThe Wireless LAN environment should be a single switch environment. Future releases of the code are planned to enable multi-switch support and redundancy.
Securing Communications
The Remote Access Point configurations can also be used to secure control traffic between the AP and the switch in a corporate environment. In this case, the AP and switch are in the company’s private address space. The Remote AP will be similar to the Alcatel AP while tunneling and encrypting all data and control traffic to the switch.
How the Secure Remote Access Point Service
Works
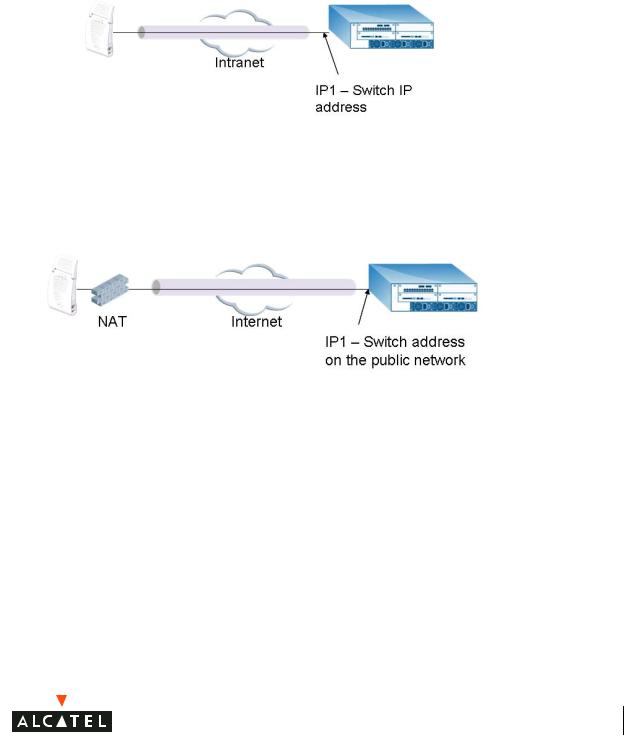
The Secure Remote Access Point Service APs can be deployed in one of the following ways:
1. The Remote Access Point and switch in a private network which is used to secure AP-to-switch communication. (Alcatel recommends this deployment when AP-to-switch communications need to be secured.)
12 |
Part 031650-00 |
May 2005 |
|
|
|
Chapter 2
2The Remote Access Point is on the public network or behind a NAT device and the switch is on the public network
3The Remote Access Point is on the public network or behind a NAT device and the switch is also behind a NAT device. (Alcatel recommends this deployment for remote access.)
Secure Remote Access Points 13
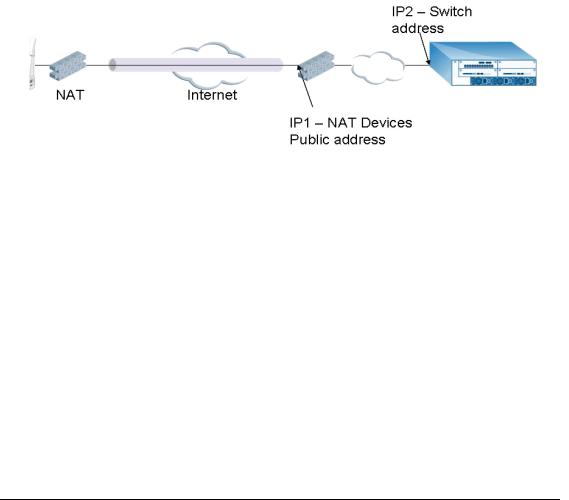
OmniAccess RN: User Guide
The basic operation for each of these deployments is the same, differing only slightly in configuration details. The difference in configuration for each of these deployments will be highlighted in the steps below.
The Secure Remote Access Point Service APs have to be configured with the tunnel termination address, and address IP1 in the above figures. This address would be the switch’s IP address, or the NAT device’s public address, depending on the deployment scenario.
In the case where the switch is behind a NAT device (as in deployment scenario 3), NAT-T (UDP 4500 port only) needs to be enabled, and all packets from the NAT device on UDP port 4500 should be forwarded to the Alcatel Mobility Controller.
The AP uses IP1 to establish a VPN/ IPSec tunnel with the switch. Once the VPN tunnel is established, the AP bootstraps and becomes operational.
Configuring the Secure Remote Access Point
Service
To configure the Secure Remote Gird Point Service (refer to the three deployment illustrations above):
zConfigure the AP as a Remote AP with the master address, the LMP IP, IKE PSK, and the username and password for authentication.
zConfigure IPSec VPN tunnels on the switch the AP will use before it bootstraps.
zConfigure the Secure Remote Access Point Service user role and permissions.
14 |
Part 031650-00 |
May 2005 |
|
|
|

Chapter 2
zAdd the entry for the username/password used for authentication by Secure Remote Access Point Service to the authentication server.
Configure the NAT device to which the switch connects (deployment scenario 3 only).
These steps are explained below:
1. Configure the AP with the master address, username and password authentication.
All AP60/61 and AP70 Alcatel Access Points can be provisioned to offer Secure Remote Access Point Services. The easiest way is to use the Program AP Web configuration page to configure the AP settings.
zOnce the AP boots up, it will appear as an un-provisioned AP if it is a new AP. If the AP is an already provisioned AP which has to be re-con-
figured to provide Secure Access Point Services, continue with the next step. Otherwise, navigate to the Wireless LAN > Program AP > Provision AP page and provision the AP as you would a regular AP with its location and master IP. Apply the changes and reload the AP. This step ensures that the AP now boots with the 2.4 code (or higher) that supports this feature.
Deployment Scenario |
Master IP Address Value while |
|
Provisioning the AP |
||
|
||
Deployment 1 |
Alcatel Mobility Controller IP address |
|
Deployment 2 |
Alcatel Mobility Controller public IP address |
|
Deployment 3 |
Public address of the NAT device to which the |
|
|
Alcatel Mobility Controller is connected. |
Secure Remote Access Points 15
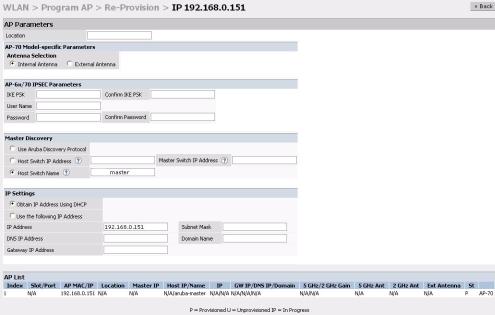
OmniAccess RN: User Guide
zSelect the AP that needs to be configured to provide Secure Access Point Services on the Program AP > Reprovision page. Configure the AP username and password, and the IKE PSK for the IPSec settings. Set the master IP to the public IP address if the AP is connected to the switch over the Internet.
zRegardless of the deployment type, Alcatel recommends that the LMS-IP of the AP be set to the switch IP address, (either the loopback address of the switch or the VLAN 1 IP address).
zNavigate to the Configuration > Wireless LAN > Advanced page. Select the AP to be configured as a Remote Access Point. Configure the LMS-IP to the Alcatel Wireless LAN switch IP address.
2Configure the IPSec VPN settings on the switch by navigating to the Configuration > Security > VPN Settings > IPSec page.
16 |
Part 031650-00 |
May 2005 |
|
|
|
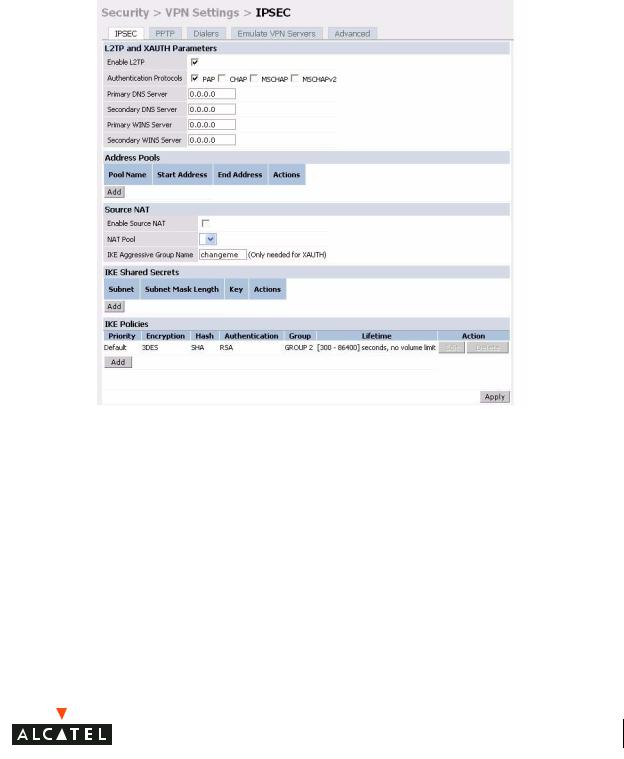
Chapter 2
To configure PAP authentication for L2TP:
Make sure that PAP Authentication Protocol is selected. Click Apply, to apply the configuration changes made.
From the CLI enter:
(Alcatel4324)# config t
(Alcatel4324) (config)# vpdn group l2tp
(Alcatel4324) (config-vpdn-l2tp)# ppp authentication PAP (Alcatel4324) (config-vpdn-l2tp)# exit
(Alcatel4324) (config)#
To configure the L2TP IP pool:
Secure Remote Access Points 17
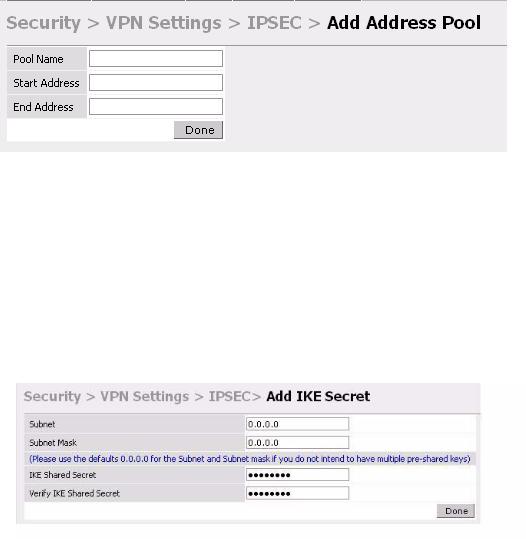
OmniAccess RN: User Guide
Click Add in the Address Pools panel. Configure the L2TP pool from which the APs will be assigned addresses.
From the CLI enter:
(Alcatel4324)# config t
(Alcatel4324) (config)# ip local pool l2tppool1 192.168.69.1 192.168.69.254
(Alcatel4324) (config)#
To configure an ISAKMP encrypted subnet and pre-share key:
Click Add in the IKE Shared Secrets panel and configure the pre-shared key and the address pool. For more details, refer to “Configuring Virtual Private Networks” on page 143.
From the CLI enter:
(Alcatel4324)# configure t
(Alcatel4324) (config)# crypto isakmp key testkey address 0.0.0.0 netmask 0.0.0.0
(Alcatel4324) (config)#
To create an ISAKMP policy:
18 |
Part 031650-00 |
May 2005 |
|
|
|
 Loading...
Loading...