Page 1
INSTRUCTION MANUAL
IM116R04
4" Submersible Pumps
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
Page 2

Owner’s Information
Owner’s Information
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Pump Model #:
Pump Serial #:
Motor Model #:
Motor Serial #:
Dealer:
Dealer Telephone:
Purchase Date:
Installation Date:
Volts:
Amps:
SUBJECT PAGE
Safety Instructions ................... 3 & 4
Pump Protection Devices .................4
Installation Checklist ....................... 5
1.0 Typical Installations ................... 6
2.0 Piping and Tank ......................... 7
3.0 Wire Sizing, Splicing and
Power Supply ............................... 9
4.0 Wiring the Controls and
Switch ......................................... 9
5.0 Starting the Pump ....................12
6.0 Paperwork and IOM ...............12
CentriPro 4" 1 Ph Motor Data ......13
Single Phase Wire Sizing Charts ....14
PumpSaver Schematics ..................14
Three Phase Motor Data ............... 15
Three Phase Motor
Electrical Data ...........................16
Three Phase Motor
Wire Chart ................................17
Resistance and Generator Data .....18
Wiring Diagrams ................. 19 & 20
Three Phase Starters ...................... 21
Troubleshooting ............................. 22
Limited Warranty .......................... 66
2
Page 3
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
WARNING
WARNING
TO AVOID SERIOUS OR FATAL PERSONAL INJURY OR MAJOR
PROPERTY DAMAGE, READ AND FOLLOW ALL SAFETY
INSTRUCTIONS IN MANUAL AND ON PUMP.
THIS MANUAL IS INTENDED TO ASSIST IN THE INSTALLATION AND
OPERATION OF THIS UNIT AND MUST BE KEPT WITH THE PUMP.
This is a SAFETY ALERT SYMBOL. When you see this
symbol on the pump or in the manual, look for one of the
following signal words and be alert to the potential for
personal injury or property damage.
DANGER
WARNING
CAUTION
Warns of hazards that WILL cause serious personal injury,
death or major property damage.
Warns of hazards that CAN cause serious personal injury,
death or major property damage.
Warns of hazards that CAN cause personal injury or property
damage.
NOTICE: INDICATES SPECIAL INSTRUCTIONS WHICH ARE VERY
IMPORTANT AND MUST BE FOLLOWED.
THOROUGHLY REVIEW ALL INSTRUCTIONS AND WARNINGS
PRIOR TO PERFORMING ANY WORK ON THIS PUMP.
MAINTAIN ALL SAFETY DECALS.
Important notice: Read safety instructions before proceeding with any wiring
All electrical work must be performed by a qualified
technician. Always follow the National Electrical Code (NEC),
or the Canadian Electrical Code, as well as all local, state and provincial
codes. Code questions should be directed to your local electrical inspector.
Failure to follow electrical codes and OSHA safety standards may result
in personal injury or equipment damage. Failure to follow manufacturer’s
installation instructions may result in electrical shock, fire hazard, personal
injury or death, damaged equipment, provide unsatisfactory performance,
and may void manufacturer’s warranty.
Standard units are not designed for use in swimming pools,
open bodies of water, hazardous liquids, or where flammable
gases exist. Well must be vented per local codes. See specific pump catalog
bulletins or pump nameplate for all agency Listings.
Disconnect and lockout electrical power before installing or
servicing any electrical equipment. Many pumps are equipped
with automatic thermal overload protection which may allow an overheated
pump to restart unexpectedly.
Never over pressurize the tank, piping or system to a pressure
higher than the tank's maximum pressure rating. This will
damage the tank, voids the warranty and may create a serious hazard.
Protect tanks from excessive moisture and spray as it will cause
the tank to rust and may create a hazard. See tank warning
labels and IOM for more information.
3
Page 4
CAUTION
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
DANGER
WARNING
CAUTION
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS (continued)
CAUTION
CAUTION
Do not lift, carry or hang pump by the electrical cables.
Damage to the electrical cables can cause shock,
burns or death.
Use only stranded copper wire to pump/motor and ground.
The ground wire must be at least as large as the power supply
wires. Wires should be color coded for ease of maintenance
and troubleshooting.
Install wire and ground according to the National Electrical
Code (NEC), or the Canadian Electrical Code, as well as all
local, state and provincial codes.
Install an all leg disconnect switch where required
by code.
The electrical supply voltage and phase must match all equipment requirements. Incorrect voltage or phase can cause fire,
motor and control damage, and voids the warranty.
All splices must be waterproof. If using splice kits follow
manufacturer’s instructions.
Select the correct type and NEMA grade junction box for the
application and location. The junction box must insure dry,
safe wiring connections.
All motors require a minimum 5' submergence for proper refill
check valve operation.
Failure to permanently ground the pump, motor and controls
before connecting to power can cause shock, burns or death.
All three phase (3Ø) controls for submersible pumps must
provide Class 10, quick-trip, overload protection.
4" motors ≥ 2 HP require a minimum flow rate of .25 ft/sec.
or 7.62 cm/sec. past the motor for proper motor cooling.
The following are the minimum flows in GPM per well
diameter required for cooling: 1.2 GPM/4", 7 GPM/5",
13 GPM/6", 20 GPM/7", 30 GPM/8" or 50 GPM in a 10"
well.
Pumps ≥ 2 HP installed in large tanks should be installed in a
flow inducer sleeve to create the needed cooling flow or velocity past the motor.
This pump has been evaluated for use with Water Only.
PUMP PROTECTION
We recommend using SymCom’s PumpSaver to protect the system from low
water, rapid cycling, high/low voltage, dead heading/flow restriction and
overcurrent.
4
Page 5

INSTALLATION CHECK LIST
• Enter the pump and motor information and other requested data on the front
of this manual.
• Inspect all components for shipping damage, report damage to the distributor
immediately.
• Verify that motor HP and pump HP match.
• Match power supply voltage and phase to motor and control specications.
• Select a dry, shaded location in which to mount the controls.
• Make all underwater and underground splices with waterproof splice
connections.
• Hold the pump at the discharge head when installing threaded pipe or an
adapter fitting as most pumps have left hand threads which will be loosened
if you hold the pump anyplace except the discharge head.
• Check all plumbing connections to insure they are tight and sealed with
Teflon tape.
• Verify that the pipe pressure rating is higher than pump shut-off pressure.
• Install a pressure relief valve on any system capable of creating over 75 PSI.
The system pressure cannot exceed the tank's maximum pressure rating.
• Locating the tank and controls in an area protected from rain, spray and
other environmental factors may prolong their useful life. Especially in areas
with acid rain and saline water.
• Locate the pressure switch within 4' of the pressure tank to prevent switch
chatter.
• Adjust tank pre-charge to 2 PSI below the system cut-in pressure setting, ex.
28 on a 30/50 system.
• Set the pump 10' above the well bottom to keep above sediment and debris.
• Insure that main power is disconnected, turned OFF, before wiring any com-
ponents.
• Wiring should be performed only by qualied technicians.
• Wiring and Grounding must be in compliance with national and local codes.
• Restrict the ow with a ball or globe valve, 1/3 open, before starting pump
for first time.
• Open a faucet or discharge valve on start-up to keep dirty water from entering the tank.
• Turn main breaker or disconnect ON.
• Run through several on/off cycles to verify proper switch operation.
• Check amps and enter the data on the front of this manual.
• Leave the manual with the owner or at the job site.
5
Page 6
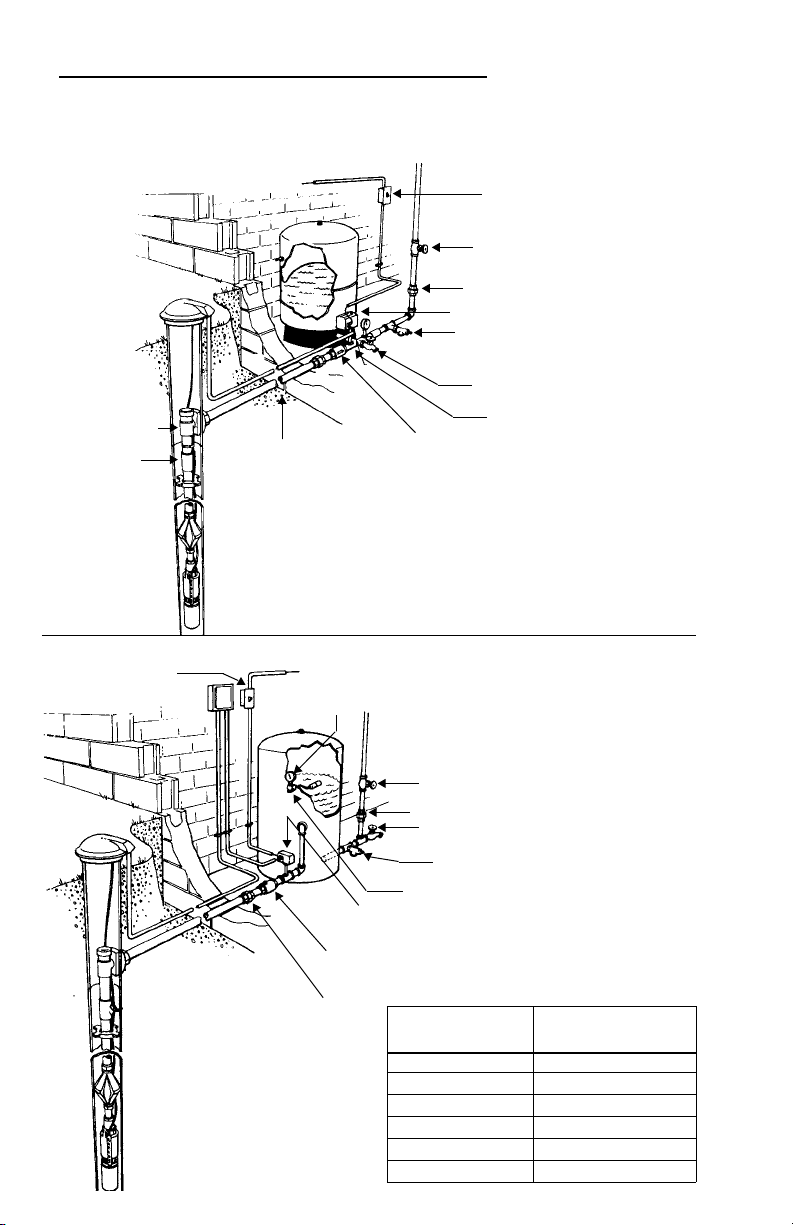
1.0 TYPICAL INSTALLATIONS
1.0 TYPICAL INSTALLATIONS
CAPTIVE AIR TANK INSTALLATION
NOTICE: TANK PRE-CHARGE PRESSURE CHANGES MUST BE
MADE USING THE AIR VALVE ON TOP OF THE TANK.
To House Piping
Disconnect Switch
Shut-off Valve
Union
Pressure Switch
Pressure Relief Valve
Drain Tap
Tank Tee
Check Valve ②
Pitless Adapter ①
Check Valve ①
Protected Power Supply
Frost Level
① On installations with a pitless adapter the top check
valve should be below the pitless, not at the tank, as the
discharge line should be pressurized back to the pitless.
② On installations with well seals or well pits it is allowable
to locate the top check valve near the tank.
Figure 1
GALVANIZED TANK INSTALLATION
Disconnect Switch
Control Box
Protected Power Supply
Pressure
Gauge
To House
Piping
Shut-off Valve
Union
Drain Tap
Pressure Relief Valve
Air Escape Control
Pressure Switch
Pitless Adapter
Drain and Y Fitting
Line Check Valve with Snifter
Approximate Drain Fitting Setting
Union
Distance Drain and “Y”
Tank Capacity Fitting Below the Line Check
42 gallon (159 L) 7 feet (2.1m)
82 gallon (310 L) 10 feet (3m)
120 gallon (454 L) 15 feet (4.6m)
220 gallon (833 L) 15 feet (4.6m)
315 gallon (1192 L) 20 feet (6.1m)
Figure 2
525 gallon (1981 L) 20 feet (6.1m)
6
Page 7
DANGER
2.0 PIPING
2.0 PIPING
Notice: Most 4" submersibles have
left-hand discharge head threads,
hold the pump only at the
“discharge head” when installing
fittings or threaded pipe.
CAUTION
2.1 General
The pump discharge
piping should be sized for
Hazardous pressure can
cause personal injury or
property damage.
efficient pump operation.
Use the Friction Loss
Tables to calculate total
dynamic head using different pipe
sizes. As a rule of thumb, use 1" for
up to 10 gpm, 1¼" for up to 30 gpm,
1½" for up to 45 gpm, and 2" for up
to 80 gpm. In the case of long pipe
runs it is best to increase pipe size.
Some pumps are capable of very high
discharge pressures, please select pipe
accordingly. Consult with your pipe
supplier to determine the best type of
pipe for each installation.
2.2 Pressure Tank,
Pressure Switch
and Pressure
Relief Valve
Do not install tank where
it will be subjected to
spray from irrigation
systems. Exposure to such
spray could result in
corrosion of the tank,
eventually leading to an
explosion which can cause
property damage, serious
personal injury or death.
and pressure relief valve. The tank
should be located in an area where a
leak will not damage property.
The pressure switch should be
located at the tank cross tee and
never more than 4' from the tank.
Locating the switch more than
4' from the tank will cause
switch chatter.
Do not install valves, filters, or high
loss fittings between the switch and
the tank(s) as switch chatter may
result. As an example, a 1¼" spring
check valve has friction loss equal to
12' of pipe, placing the valve between
Select a dry location in
which the ambient temperature is always above 34º
F (1º C) in which to install
the tank, pressure switch,
the pressure switch and the pressure
tank is the same as moving the pressure switch 12' away from the tank. It
will create switch chatter.
On multiple tank installations the
switch should be as close to the center of the tanks as possible. Multiple
tank installations should have a manifold pipe at least 1½ times the size of
the supply pipe from the pump. This
will reduce the Friction Head in the
manifold and reduce the possibility
of switch chatter.
Pressure relief valves are required on
any system that is capable of
producing 100 psi or 230' TDH. If
blow-off may damage property,
connect a drain line to the pressure
relief valve and run it to a suitable
drain.
2.3 Adjusting Tank
Pre-Charge
Insure that the tank is empty of
water. Use a high quality pressure
gauge to check the tank pre-charge
pressure. The pressure should be 2 psi
below the pump cut-in pressure. As
an example, a 30-50 psi system would
use a tank pre-charge of 28 psi.
2.4 Discharge Pipe
Note: Most discharge heads are
threaded into the casing with lefthand threads. Hold the pump only
at the discharge head when installing
fittings. Failure to hold the discharge
head will loosen it and pump damage
will result on start-up.
If your pipe requires an adapter we
strongly recommend using stainless steel. Galvanized fittings or pipe
should never be connected directly to
a stainless steel discharge head as
galvanic corrosion may occur. Plastic
or brass pumps can use any
material for this connection. Barb
type connectors should always be
double clamped.
7
Page 8

The pump discharge head has a loop
for attaching a safety cable. The use
of a safety cable is recommended
when using poly pipe as the pipe
stretches when under pressure and
filled with water.
2.5 Installing Pump in Well
If using a torque arrestor, install it
per the manufacturer’s installation
instructions. Consult the seller for
information on torque arrestors and
for installation instructions.
Connect the discharge pipe to the
discharge head or adapter. Barb
style connectors should be double
clamped. Install the pump into the
well using a pitless adapter or similar
device at the wellhead. Consult the
fitting manufacturer or pitless
supplier for specific installation
instructions.
Using waterproof electrical tape,
fasten the wires to the drop pipe at
10' intervals. Pump suppliers also sell
clip-on style wire connectors that
attach to the drop pipe.
2.6 Special Piping For
Galvanized Tank
Systems
When using a galvanized tank install
an AV11 Drain & Y fitting in the well
and a check valve with snifter valve
at the tank. This will add air to the
tank and prevent water logging the
tank. Use an AA4 Air Escape on the
tank to allow excess air to escape.
The distance between the AV11
and check valve with snifter valve
determines the amount of air introduced on each cycle. See the table for
recommended settings. See Figure 2
in Sec 1.0.
Gaseous wells should use galvanized
or glass lined steel tanks with AA4
air escapes to vent off excess air and
prevent “spurting” at the faucets.
Methane and other explosive or
dangerous gases require special water
treatment for safe removal. Consult a
water treatment specialist to address
these issues.
Installations with top feeding wells
should use flow sleeves on the pump.
2.7 Check Valves
Our pumps use four different styles of
check valves. We recommend check
valves as they prevent back-spinning
the pump and motor which will
cause premature bearing wear. Check
valves also prevent water hammer and
upthrust damage. Check valves should
be installed every 200' in the vertical
discharge pipe. See notes 1 & 2 on
Figure 1 for other check valve placement recommendations.
If you wish to disable a check valve
for a drain back system, you should
use other means to prevent water
hammer and upthrust damage:
• Built-in stainless steel valves have a
flat which is easily drilled through
using an electric drill and a ¼" or
3
⁄8" drill bit to disable the valve.
• Poppet style check valves which
are threaded in from the top of
the discharge head can be easily
removed using a ½" nut driver or
deep socket. The hex hub is visible
and accessible from the top.
• Internal Flomatic™ design plastic
poppet style valves must be
removed from inside which
requires pump disassembly.
• Built-in plastic poppet style valves
with a stem through the top may
be removed from discharge head
by pulling on the stem with pliers.
8
Page 9
WARNING
Hazardous voltage
can shock, burn or
cause death.
3.0 WIRE
3.0 WIRE
SIZING,
SIZING,
SPLICING and
SPLICING and
POWER SUPPLY
POWER SUPPLY
Always follow the National Electric
Code (N.E.C.), Canadian Electrical
Code, and any state, provincial, or
local codes.
We suggest using only copper wire.
Size wire from the charts found in
the Technical Data section of this
manual, MAID manual, or an
N.E.C. (National Electric Code)
code book. If discrepancies exist the
N.E.C. book takes precedence over a
manufacturer’s recommendations.
3.1 Splicing Wire to
Motor Leads
When the drop cable must be spliced
or connected to the motor lead, it is
necessary that the splice be watertight. The splice can be done with
heat shrink kits or waterproof tape.
A. Heat Shrink Splice Instructions
To use a typical heat shrink kit: strip
½" from the motor wires and drop
cable wires; it is best to stagger the
splices. Place the heat shrink tubes
on the wires. Place the crimps on the
wires and crimp the ends. Slide the
heat shrink tubes over the crimps and
heat from the center outward. The
sealant and adhesive will ooze out
the ends when the tube shrinks. The
tube, crimps, sealant, and adhesive
create a very strong, watertight seal.
B. Taped Splice Instructions
A) Strip individual conductor of
insulation only as far as
necessary to provide room for a
stake type connector. Tubular
connectors of the staked type are
preferred. If connector O.D. is
not as large as cable insulation,
build-up with rubber electrical
tape.
B) Tape individual joints with
rubber electrical tape, using two
layers; the first extending two
inches beyond each end of the
conductor insulation end, the
second layer two inches beyond
the ends of the first layer. Wrap
tightly, eliminating air spaces as
much as possible.
C) Tape over the rubber electrical
tape with #33 Scotch electrical
tape, or equivalent, using two
layers as in step "B" and making
each layer overlap the end of the
preceding layer by at least two
inches.
In the case of a cable with three
conductors encased in a single outer
sheath, tape individual conductors as
described, staggering joints.
Total thickness of tape should be no
less than the thickness of the conductor insulation.
WARNING
Hazardous voltage
can shock, burn or
cause death.
4.0 WIRING
4.0 WIRING
THE
THE
CONTROLS and
CONTROLS and
SWITCH
SWITCH
4.1 Mounting the Motor
Control Box
Single phase 3-wire control boxes
meet U.L. requirements for Type
3R enclosures. They are suitable for
vertical mounting in indoor and outdoor locations. They will operate at
temperatures between 14ºF (-10ºC)
and 122ºF (50ºC). Select a shaded,
dry place to mount the box. Insure
that there is enough clearance for the
cover to be removed.
9
Page 10
4.2 Verify Voltage and Turn
Supply Power Off
Insure that your motor voltage and
power supply voltage are the same.
Place the circuit breaker or disconnect switch in the OFF position to
prevent accidentally starting the
pump before you are ready.
Three-phase starter coils are very
voltage sensitive; always verify actual
supply voltage with a voltmeter.
High or low voltage, greater than
±10%, will damage motors and
controls and is not covered under
warranty.
4.3 Connecting Motor Leads
to Motor Control Box,
Pressure Switch or
Starter
WARNING
Hazardous voltage
can shock, burn or
cause death.
connecting the pressure switch line
leads to the power supply. Follow
all local and national codes. Use a
disconnect where required by code.
A. Three-Wire Single Phase Motor
Connect the color coded motor leads
to the motor control box terminals
- Y (yellow), R (red), and B (black);
and the Green or bare wire to the
green ground screw.
Connect wires between the Load
terminals on the pressure switch
and control box terminals L1 and
L2. Run a ground wire between the
switch ground and the control box
ground. See Figure 4 or 5.
B. Two-Wire Single Phase Motor
Connect the black motor leads to the
Load terminals on the pressure switch
and the green or bare ground wire
to the green ground screw. CentriPro
Caution Do not power the
unit or run the pump until
all electrical and plumbing
connections are completed.
Verify that the disconnect
or breaker is OFF before
2-wire motors will not work with
Franklin Electric PumpTec. Use a
PumpSaver. See Figure 3.
C. Three phase motors
Connect the motor leads to T1, T2,
and T3 on the 3 phase starter. Connect the ground wire to the ground
screw in the starter box. Follow
starter manufacturers instructions
for connecting pressure switch or
see Figure 6.
4.4 Connect To
WARNING
Hazardous voltage
can shock, burn or
cause death.
or disconnect where used.
Three phase - make the connections
between L1, L2, L3, and ground on
the starter to the disconnect switch
and then to the circuit breaker panel.
Three phase installations must be
checked for motor rotation and
phase unbalance. To reverse motor
rotation, switch (reverse) any two
leads. See the instructions for checking three phase unbalance in section
4.6. Failure to check phase unbalance
can cause premature motor failure
and nuisance overload tripping. If
using a generator, see Technical Data
for generators.
Power Supply
Complete the wiring by
making the connection
from the single phase pressure switch Line terminals
to the circuit breaker panel
4.5 Three Phase Overload
Protection
Use only Class 10, quick-trip overload protection on three-phase
submersible motors. See Definite
Purpose Starters in this manual.
Call the pump manufacturer’s
Customer Service group for selection
assistance.
10
Page 11

4.6 Three Phase Power Unbalance
A full three phase supply consisting of three individual transformers
or one three phase transformer is
recommended. “Open” delta or wye
connections using only two transformers can be used, but are more
likely to cause poor performance,
overload tripping or early motor
failure due to current unbalance.
Check the current in each of the three
motor leads and calculate the current
unbalance as explained below.
If the current unbalance is 2% or
less, leave the leads as connected.
If the current unbalance is more
than 2%, current readings should
be checked on each leg using each
of the three possible hook-ups. Roll
the motor leads across the starter in
the same direction to prevent motor
reversal.
To calculate percent of current
unbalance:
A. Add the three line amp values
together.
B. Divide the sum by three, yield-
ing average current.
C. Pick the amp value which is
furthest from the average current
(either high or low).
D. Determine the difference
between this amp value (furthest
from average) and the average.
E. Divide the difference by the
average.
Multiply the result by 100 to
determine percent of
unbalance.
Current unbalance should not exceed
5%. If the unbalance cannot be corrected by rolling leads, the source of
the unbalance must be located and
corrected. If, on the three possible
hookups, the leg farthest from the
average stays on the same power
lead, most of the unbalance is coming
from the power source.
Contact your local power company
to resolve the imbalance.
Hookup 1 Hookup 2 Hookup 3
Starter Terminals L1 L2 L3 L1 L2 L3 L1 L2 L3
Motor Leads R B Y Y R B B Y R
T3 T1 T2 T2 T3 T1 T1 T2 T3
Example:
T3-R = 51 amps T2-Y = 50 amps T1-B = 50 amps
T1-B = 46 amps T3-R = 48 amps T2-Y = 49 amps
T2-Y = 53 amps T1-B = 52 amps T3-R = 51 amps
Total = 150 amps Total = 150 amps Total = 150 amps
÷ 3 = 50 amps ÷ 3 = 50 amps ÷ 3 = 50 amps
– 46 = 4 amps – 48 = 2 amps – 49 = 1 amps
4 ÷ 50 = .08 or 8% 2 ÷ 50 = .04 or 4% 1 ÷ 50 = .02 or 2%
11
Page 12

5.0 STARTING
5.0 STARTING
THE PUMP
THE PUMP
CAUTION
5.1 Install a Valve
and Run the Pump To
Clear the Water
Hazardous pressure can
cause personal injury or
property damage.
with the valve 1⁄3 open, pump the well
until the water begins to run clear.
Open the valve slowly to check flow
and when the water runs clear turn
the pump Power Off.
Remove the ball or globe valve and
connect the pump discharge to the
house plumbing, pressure tank and
switch. Turn Power On. Run a few
cycles through the tank to rinse it
out and to verify proper pump and
switch operation. Use this time to
check all fittings for leaks.
CAUTION: If the well has a high
static level, please see next section
for important pump protection
information.
CAUTION
On a new well - Install a
ball or globe valve on the
pump discharge line and
5.2 Throttling A
High Static
Level Well To
Hazardous pressure can
cause personal injury or
property damage.
pump to operate off the curve to the
right or outside the “Recommended
Range” shown on the pump curve.
We recommend using a “Dole” flow
restrictor or throttling with a ball
valve to prevent upthrust damage to
Prevent Upthrust
Any well with a high static
water level may allow the
the pump and motor. The maximum
flow must be restricted to be within
the pumps recommended operating
range. If you use a ball valve, set it,
remove the handle, tape the handle
to the pipe, and tag the valve with a
note saying, “Do not open this valve
or pump may be damaged”. The
easiest way to “set” the flow is to fill
a 5 gallon bucket and time how long
it takes to produce 5 gallons. Calculate the flow in gpm based on this
value. As the water level drops in the
well the flow will be reduced due to
increased head and the valve will not
interfere with performance.
6.0 PAPERWORK
6.0 PAPERWORK
and IOM
and IOM
Please give this filled-in IOM and
your business card to the owner.
A sticker with your name and phone
number on the tank or control box is
a great sales tool for future business!
We now provide an extra pump label
which you can affix to the IOM, put
on a 3-wire control box or locate
near the tank and pressure switch for
future pump identification.
12
Page 13
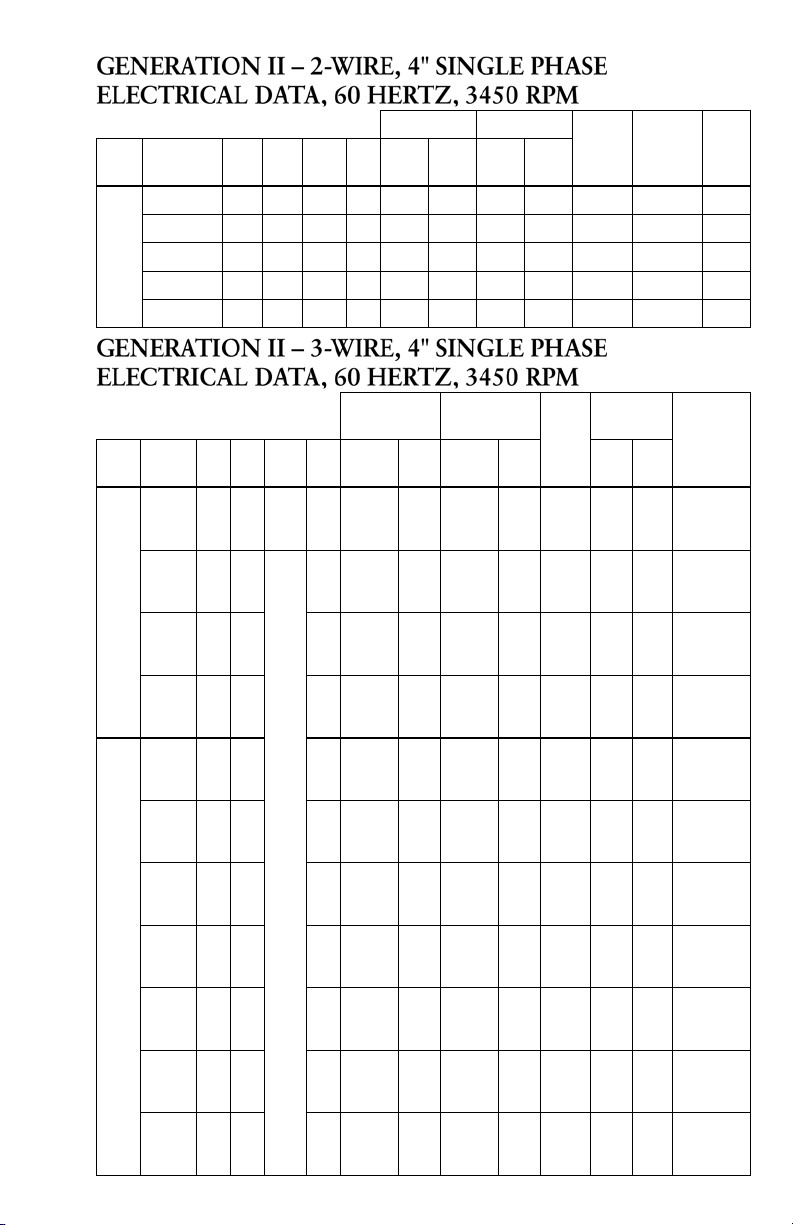
GENERATION II – 2-WIRE, 4" SINGLE PHASE
ELECTRICAL DATA, 60 HERTZ, 3450 RPM
Full Load Service Factor
CentriPro
Type
Order No.
M05421 0.5 0.37 115 1.6 7.9 910 9.8 1120 28 1.4-2.0 H
M05422 0.5 0.37 230 1.6 4.0 845 4.7 1050 16 6.1-7.2 J
2-
Wire
M07422 0.75 0.55 230 1.5 5.0 1130 6.2 1400 18 5.9-6.9 F
(PSC)
M10422 1.0 0.75 230 1.4 6.7 1500 8.1 1800 24 4.2-5.2 F
M15422 1.5 1.1 230 1.3 9.0 2000 10.4 2350 43 1.8-2.4 H
HP KW Volts SF Amps Watts Amps Watts
Locked
Rotor
Amps
Winding
Resis-
tance
GENERATION II – 3-WIRE, 4" SINGLE PHASE
ELECTRICAL DATA, 60 HERTZ, 3450 RPM
Rotor
Amps
Winding
Resistance
Main
Start
(B-Y)
(R-Y)
1.0-
2.5-
1.4
3.1
5.1-
12.4-
6.1
13.7
2.6-
10.4-
3.3
11.7
2.0-
9.3-
2.6
10.4
1.0-
2.5-
1.4
3.1
5.1-
12.4-
6.1
13.7
2.6-
10.4-
3.3
11.7
2.0-
9.3-
2.6
10.4
1.6-
10.8-
2.2
12.0
1.1-
2.0-
1.4
2.5
.62-
1.36-
.76
1.66
Full Load Service Factor
Order
Type
3-
Wire
with
Q.D.
Cap.
Start
Box
3-
Wire
with
CSCR
(CR)
or
Mag-
netic
Contac-
tor
(MC)
Control
Box
¹ A CSCR control box with a CR suffix can be replaced by a Magnetic Contactor model ending in MC.
HP KW Volts SF Amps Watts Amps Watts
No.
1.6
Y – 8.8
B – 8.8
R – 0
Y – 5.3
B – 5.3
R – 0
Y – 6.6
B – 6.6
R – 0
Y – 8.1
B – 8.1
R – 0
Y – 4.2
B – 4.1
R – 1.8
Y – 4.8
B – 4.4
R – 2.5
Y – 6.1
B – 5.2
R – 2.7
Y – 9.1
B – 8.2
R – 1.2
Y – 9.9
B – 9.1
R – 2.6
Y – 14.3
B – 12.0
R – 5.7
Y – 24.0
B – 19.1
R – 10.2
M05411 0.5 0.37 115 1.6
M05412 0.5 0.37
M07412 0.75 0.55 1.5
M10412 1.0 0.75 1.4
M05412 0.5 0.37 1.6
M07412 0.75 0.55 1.5
230
M10412 1.0 0.75 1.4
M15412 1.5 1.1 1.3
M20412 2 1.5 1.25
M30412 3 2.2 1.15
M50412 5 3.7 1.15
675
740
970
1215
715
940
1165
1660
2170
3170
5300
Y – 10.9
B – 10.9
R – 0
Y – 6.1
B – 6.1
R – 0
Y – 7.8
B – 7.8
R – 0
Y – 9.4
B – 9.4
R – 0
Y – 4.8
B – 4.3
R – 1.8
Y – 6.0
B – 4.9
R – 2.3
Y – 7.3
B – 5.8
R – 2.6
Y – 10.9
B – 9.4
R – 1.1
Y – 12.2
B – 11.7
R – 2.6
Y – 16.5
B – 13.9
R – 5.6
Y – 27.0
B – 22.0
R – 10.0
Locked
980 44
1050 21
1350 32
1620 41
960 21
1270 32
1540 41
2130 49
2660 49
3620 76
6030 101
KVA
Code
Required
Control
1
Box
CB05411
CB05412
CB07412
CB10412
CB05412CR
CB07412CR
CB10412CR
CB15412CR
or
CB15412MC
CB20412CR
or
CB20412MC
CB30412CR
or
CB30412MC
CB50412CR
or
CB50412MC
13
Page 14
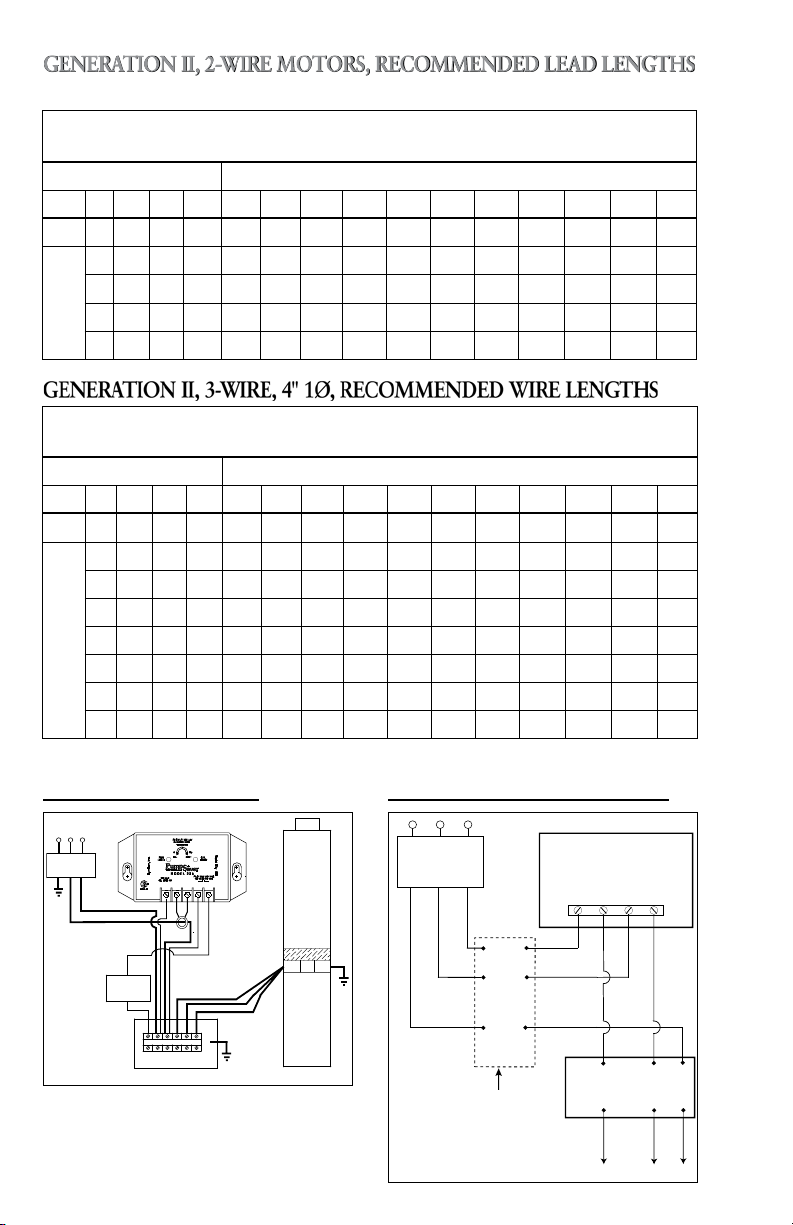
GENERATION II, 2-WIRE MOTORS, RECOMMENDED LEAD LENGTHS
Released for Sale in November/December 2011
CentriPro Motor Lead Lengths - 2 Wire Motors, 1Ø, 4" Motors
Based on Service Factor Amps, 30º C Ambient and 5% Voltage Drop
Motor Rating 60º C and 75º C Insulation - AWG Copper Wire Size
Volts HP kW FLA S FA 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 1/0 2/0 3/0 4/0
115 ½ 0.37 7.9 9.8 112 178 284 449 699 1114 1769 2814 3550 4481 5646
½ 0.37 4.0 4.7 466 742 1183 1874 2915 4648 7379 11733
¾ 0.55 5.0 6.2 353 562 897 1420 2210 3523 5594 8895 11222
230
1 0.75 6.7 8.1 271 430 686 1087 1692 2697 4281 6808 8590 10843
1½ 1.1 9.0 10.4 211 335 535 847 1318 2100 3335 5303 6690 8445
GENERATION II, 3-WIRE, 4" 1Ø, RECOMMENDED WIRE LENGTHS
CentriPro 3-Wire Motors – Recommended Motor Lead Lengths
Based on Service Factor Amps, 30º C Ambient and 5% Voltage Drop
Motor Rating 60º C and 75º C Insulation - AWG Copper Wire Size
Volts HP kW FLA SFA 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 1/0 2/0 3/0 4/0
115 ½ 0.37 8.8 10.9 101 160 255 404 629 1002 1591 2530 3192 4029 5076
½ 0.37 5.3 6.1 359 571 912 1444 2246 3581 5685 9040 - - -
¾ 0.55 6.6 7.8 281 447 713 1129 1757 2800 4446 7070 8920 - -
1 0.75 8.1 9.4 233 371 592 937 1458 2324 3689 5867 7402 - -
230
1½ 1.1 9.1 10.9 201 320 510 808 1257 2004 3182 5059 6383 - -
2 1.5 9.9 12.2 180 286 456 722 1123 1790 2843 4520 5703 - -
3 2.2 14.3 16.5 133 211 337 534 830 1324 2102 3342 4217 5323 -
5 3.7 24 27 - - 206 326 507 809 1284 2042 2577 3253 -
PUMPSAVER 235
PUMPSAVER 235
GND L2 L1
FUSED DISCONNECT
OR CIRCUIT BREAKER
L1
L2
PRESSURE SWITCH
OR
OTHER CONTROL
L1 CT1 CT2 L2 IN L2 OUT
CT
L1SW L2 YEL BLK RED
DELUXE CONTROL BOX
14
TO PUMP
PUMP
PUMP
MOTOR
PUMPSAVER 111 / 233
PUMPSAVER 111 / 233
L1 L2
GND
FUSED DISCONNECT
OR CIRCUIT BREAKER
L1
L2
PRESSURE
SWITCH
OR OTHER
GND
PRESSURE SWITCH MAY BE INSTALLED
AHEAD OF THE PUMPSAVER WHEN
RAPID CYCLE PROTECTION IS
NOT REQUIRED
CONTROL
PUMPSAVER
L1INL1
L1
L2
GND
L1
L1
TO MOTOR OR CONTROL BOX
111 / 233
OUTL2IN OUT
PRESSURE SWITCH
OR OTHER CONTROL
L2
GND
L2
GND
L2
Page 15

CENTRIPRO THREE PHASE, 4", MOTOR DATA
EFFICIENCY, THRUST RATING, FUSE/CIRCUIT BREAKER, KVA CODES
Efficiency %
Thrust
Model
M05430 0.5
M07430 0.75 69 74 R 15 15 10 15 10 15
M10430 1 66 70 M 15 20 10 10 10 15
M15430 1.5 72 74 L 20 25 10 15 15 20
M20430 2 74 75
M30430 3 77 77 K 35 40 20 25 30 35
M50430 5 76 76
M75430 7.5 74 74 J 80 90 50 60 70 80
M05432 0.5
M07432 0.75 66 71 R 6 15 6 10 6 10
M10432 1 69 72 M 10 15 6 10 10 15
M15432 1.5 75 76 K 15 20 10 15 15 20
M20432 2 75 75
M30432 3 77 77 J 25 35 15 20 25 30
M50432 5 76 76
M75432 7.5 75 75 J 70 80 45 50 60 70
M05434 0.5
M07434 0.75 69 73 R 3 10 6 6 3 6
M10434 1 65 69 M 6 10 3 6 6 10
M15434 1.5 72 73 K 10 10 6 6 6 10
M20434 2 74 75
M30434 3 76 77 J 15 20 10 10 15 15
M50434 5 77 77
M75434 7.5 76 76 L 40 50 25 30 30 35
M100434 10 79 80 K 45 60 25 35 35 45
M15437 1.5
M20437 2 78 78
M30437 3 78 78 J 10 15 10 10 10 15
M50437 5 74 75
M75437 7.5 77 77 J 25 35 20 20 25 30
HP Volts F.L. S.F.
#
200
230
460
575
62 68
61 68
61 68
73 74 700 # J 6 10 3 6 6 10
Rat-
ing
700 #
900 #
1500 #
700 #
900 #
1500 #
700 #
900 #
1500 #
900 #
1500 #
Standard
Fuse
KVA
Meets
Code
NEC
Value
based
based
FLA
R 10 15 6 10 10 10
K 25 30 15 20 20 25
J 60 70 35 40 50 60
R 6 10 6 6 6 10
K 15 25 15 15 20 20
J 45 60 30 35 40 45
R 3 6 3 3 3 6
L 15 15 6 10 10 10
J 25 30 15 20 15 25
M 10 10 6 6 10 10
M 20 25 15 15 20 20
Max.
SFA
DE-TD Fuse
Meets
NEC
based
FLA
Max.
Value
based
SFA
Circuit
Breaker
Meets
NEC
based
FLA
Max.
Value
based
SFA
15
Page 16
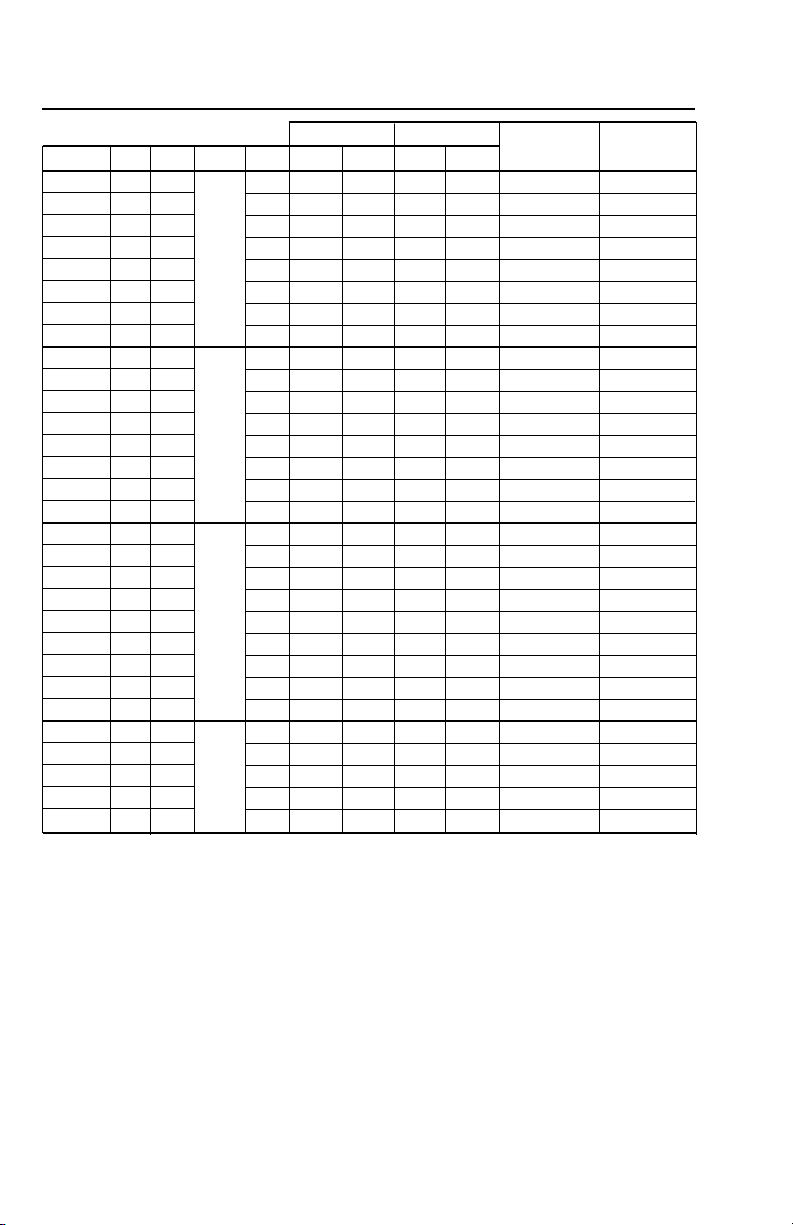
THREE PHASE, 4" MOTOR DATA
THREE PHASE 4" MOTOR DATA
Electrical Data, 60 Hz, 3450 RPM
Electrical Data, 60 Hz, 3450 RPM
Full Load Service Factor
Model # HP kW Volts SF Amps Watts Amps Watts
M05430 0.5 0.37 1.6 2.9 600 3.4 870 22 4.1-5.2
M07430 0.75 0.55 1.5 3.8 812 4.5 1140 32 2.6-3.0
M10430 1 0.75 1.4 4.6 1150 5.5 1500 29 3.4-3.9
M15430 1.5 1.1
M20430 2 1.5 1.25 7.5 2015 8.8 2490 51 1.4-2.0
M30430 3 2.2 1.15 10.9 2890 12.0 3290 71 0.9-1.3
M50430 5 3.7 1.15 18.3 4850 20.2 5515 113 0.4-0.8
M75430 7.5 5.5 1.15 27.0 7600 30.0 8800 165 0.5-0.6
M05432 0.5 0.37 1.6 2.4 610 2.9 880 17.3 5.7-7.2
M07432 0.75 0.55 1.5 3.3 850 3.9 1185 27 3.3-4.3
M10432 1 0.75 1.4 4.0 1090 4.7 1450 26.1 4.1-5.1
M15432 1.5 1.1
M20432 2 1.5 1.25 6.5 1990 7.6 2450 44 1.8-2.4
M30432 3 2.2 1.15 9.2 2880 10.1 3280 58.9 1.3-1.7
M50432 5 3.7 1.15 15.7 4925 17.5 5650 93 .85-1.25
M75432 7.5 5.5 1.15 24 7480 26.4 8570 140 .55-.85
M05434 0.5 0.37 1.6 1.3 610 1.5 875 9 23.6-26.1
M07434 0.75 0.55 1.5 1.7 820 2.0 1140 14 14.4-16.2
M10434 1 0.75 1.4 2.2 1145 2.5 1505 13 17.8-18.8
M15434 1.5 1.1 1.3 2.8 1560 3.2 1980 16.3 12.3-13.1
M20434 2 1.5 460 1.25 3.3 2018 3.8 2470 23 8.0-8.67
M30434 3 2.2 1.15 4.8 2920 5.3 3320 30 5.9-6.5
M50434 5 3.7 1.15 7.6 4810 8.5 5530 48 3.58-4.00
M75434 7.5 5.5 1.15 12.2 7400 13.5 8560 87 1.9-2.3
M100434 10 7.5 1.15 15.6 9600 17.2 11000 110 1.8-2.2
M15437 1.5 1.1 1.3 2.0 1520 2.4 1950 11.5 19.8-20.6
M20437 2 1.5 1.25 2.7 1610 3.3 2400 21 9.4-9.7
M30437 3 2.2 575 1.15 3.7 2850 4.1 3240 21.1 9.4-9.7
M50437 5 3.7 1.15 7.0 5080 7.6 5750 55 3.6-4.2
M75437 7.5 5.5 1.15 9.1 7260 10.0 8310 55 3.6-4.2
1.3 6.3 1560 7.2 1950 40 1.9-2.5
200
1.3 5.2 1490 6.1 1930 32.4 2.8-3.4
230
Locked
Rotor Amps Resistance
Line - Line
16
Page 17
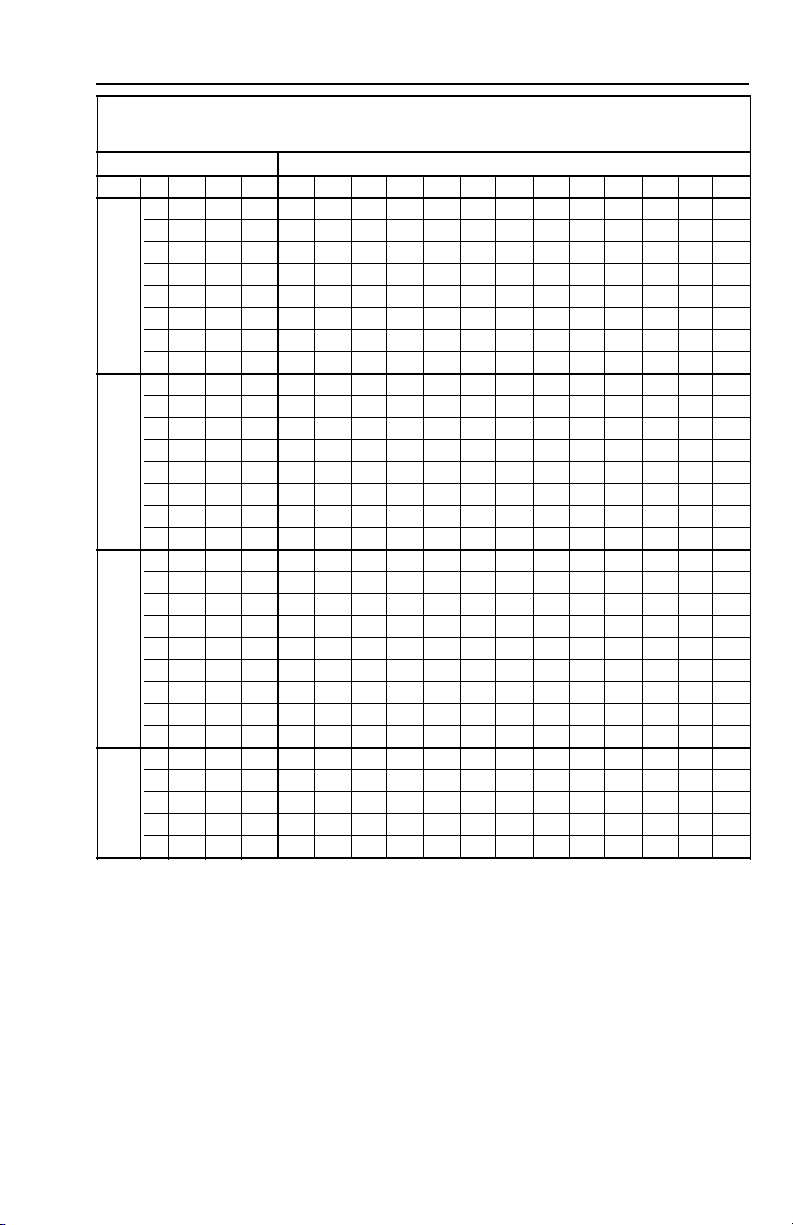
THREE PHASE, 4" MOTOR WIRE CHART
THREE PHASE 4" MOTOR WIRE CHART
Motor Lead Lengths – 3-Phase Motors –
Based on Service Factor Amps, 30º C Ambient and 5% Voltage Drop
Motor Rating 60º C and 75º C Insulation - AWG Copper Wire Size
Volts HP kW FLA SFA 14 12 10 8 6 4 3 2 1 1/0 2/0 3/0 4/0
.5 .37 3.8 2.9 657 1045 1667 2641 4109
.75 .55 3.8 4.5 423 674 1074 1702 2648
1 .75 4.6 5.5 346 551 879 1392 2166 3454 4342
1.5 1.1 6.3 7.2 265 421 672 1064 1655 2638 3317
200
2 1.5 7.5 8.8 217 344 549 870 1354 2158 2714 3427 4317 5449
3 2.2 10.9 12.0 159 253 403 638 993 1583 1990 2513 3166 3996
5 3.7 18.3 20.2 94 150 239 379 590 940 1182 1493 1881 2374 2995 3781 4764
7.5 5.5 27.0 30.0 64 101 161 255 397 633 796 1005 1266 1598 2017 2546 3207
.5 .37 2.4 2.9 756 1202 1917 3037 4725 7532 9469
.75 .55 3.3 3.9 562 894 1426 2258 3513 5601 7041 8892
1 .75 4 4.7 466 742 1183 1874 2915 4648 5843 7379
1.5 1.1 5.2 6.1 359 571 912 1444 2246 3581 4502 5685 7162 9040
230
2 1.5 6.5 7.6 288 459 732 1159 1803 2874 3613 4563 5748 7256 9155
3 2.2 9.2 10.1 217 345 551 872 1357 2163 2719 3434 4326 5460 6889 8696 10956
5 3.7 15.7 17.5 318 503 783 1248 1569 1982 2496 3151 3976 5019 6323
7.5 5.5 24 26.4 334 519 827 1040 1314 1655 2089 2635 3327 4192
.5 .37 1.3 1.5 2922 4648 7414
.75 .55 1.7 2.0 2191 3486 5560 8806
1 .75 2.2 2.5 1753 2789 4448 7045
1.5 1.1 2.8 3.2 1370 2179 3475 5504
460 2 1.5 3.3 3.8 1153 1835 2926 4635 7212
3 2.2 4.8 5.3 827 1315 2098 3323 5171
5 3.7 7.6 8.5 516 820 1308 2072 3224 5140
7.5 5.5 12.2 13.5 325 516 824 1305 2030 3236 4068 5138 6472
10 7.5
1.5 1.1 2.0 2.4 2283 3631 5792
2 1.5 2.7 3.3 1660 2641 4212 6671
575 3 2.2 3.7 4.1 1336 2126 3390 5370
5 3.7 7.0 7.6 721 1147 1829 2897 4507
7.5 5.5 9.1 10.0 548 871 1390 2202 3426
17
Page 18
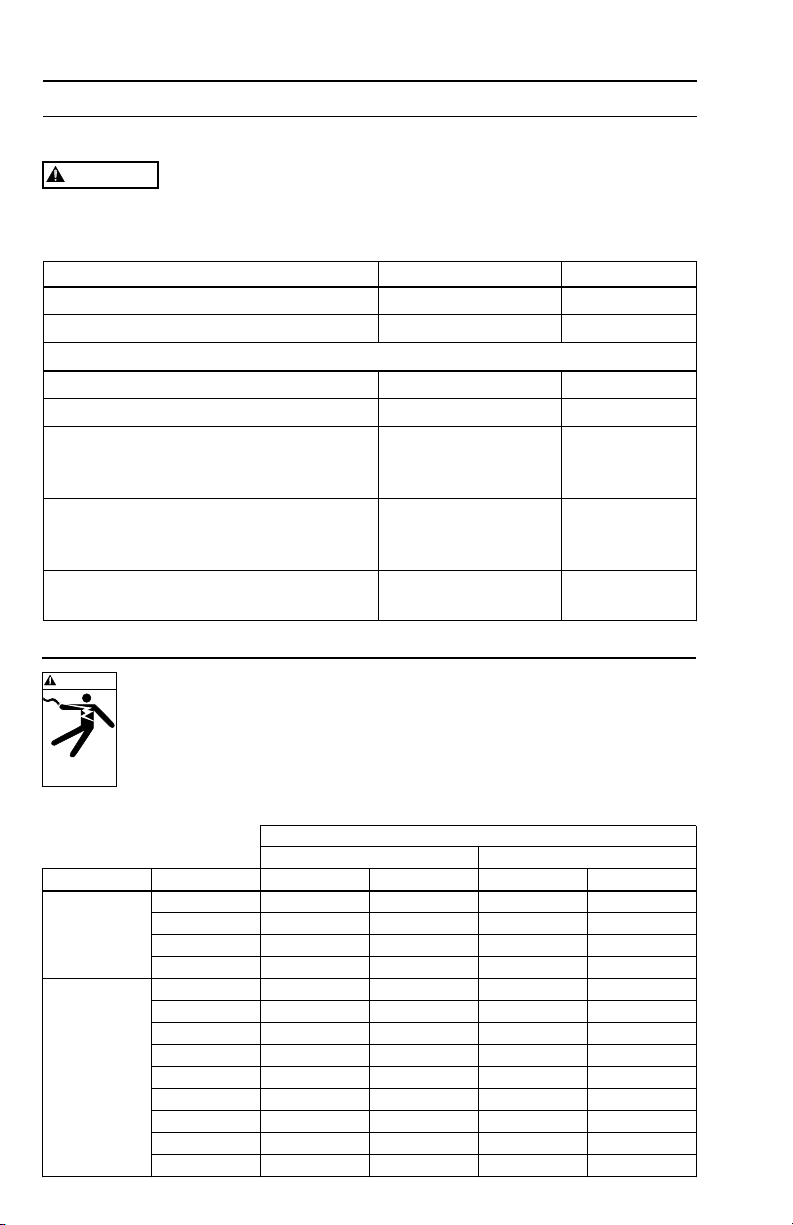
Technical Data
CAUTION
Technical Data
MOTOR INSULATION RESISTANCE READINGS
Normal Ohm/Megohm readings, ALL motors, between all leads and ground
To perform insulation resistance test, open breaker and
disconnect all leads from QD control box or pressure switch.
Connect one ohmmeter lead to any motor lead and one to metal drop pipe
or a good ground. R x 100K Scale
Condition of Motor and Leads OHM Value Megohm Value
New motor, without power cable 20,000,000 (or more) 20.0
Used motor, which can be reinstalled in well 10,000,000 (or more) 10.0
Motor in well – Readings are power cable plus motor
New motor 2,000,000 (or more) 2.0
Motor in reasonably good condition 500,000 to 2,000,000 0.5 – 2.0
Motor which may be damaged or have
damaged power cable 20,000 to 500,000 0.02 – 0.5
Do not pull motor for these reasons
Motor definitely damaged or with
damaged power cable 10,000 to 20,000 0.01 – 0.02
Pull motor and repair
Failed motor or power cable
Pull motor and repair
Generator Operation
Generator Operation
WARNING
FAILURE TO USE A MANUAL OR AUTOMATIC
Less than 10,000 0 – 0.01
TRANSFER SWITCH WHEN GENERATOR IS USED AS
STANDBY OR BACKUP CAN CAUSE SHOCK, BURNS
OR DEATH. FOLLOW THE GENERATOR MANUFACTURER’S
Hazardous voltage
can shock, burn or
cause death.
INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY. TWO WIRE DATA IS ONLY FOR
PSC TYPE MOTORS, SPLIT PHASE 2 WIRE SHOULD BE 50%
LARGER THAN 3 WIRE GENERATOR RATING.
Minimum Generator Rating
Externally Regulated Internally Regulated
Motor HP KW KVA KW KVA
.5 2.5 3.1 1.8 2.2
2 Wire
.75 3.5 4.4 2.5 3.1
1Ø
1 5 6.3 3.2 4
PSC Only
1.5 6 7.5 4 5
.5 2 2.5 1.5 1.9
.75 3 3.8 2 2.5
1 4 5 2.5 3.2
1.5 5 6.3 3 3.8
3 Wire
2 7.5 9.4 4 5
1Ø or 3Ø
3 10 12.5 5 6.3
5 15 18.8 7.5 9.4
7.5 20 25 10 12.5
10 30 37.5 15 18.8
18
Page 19
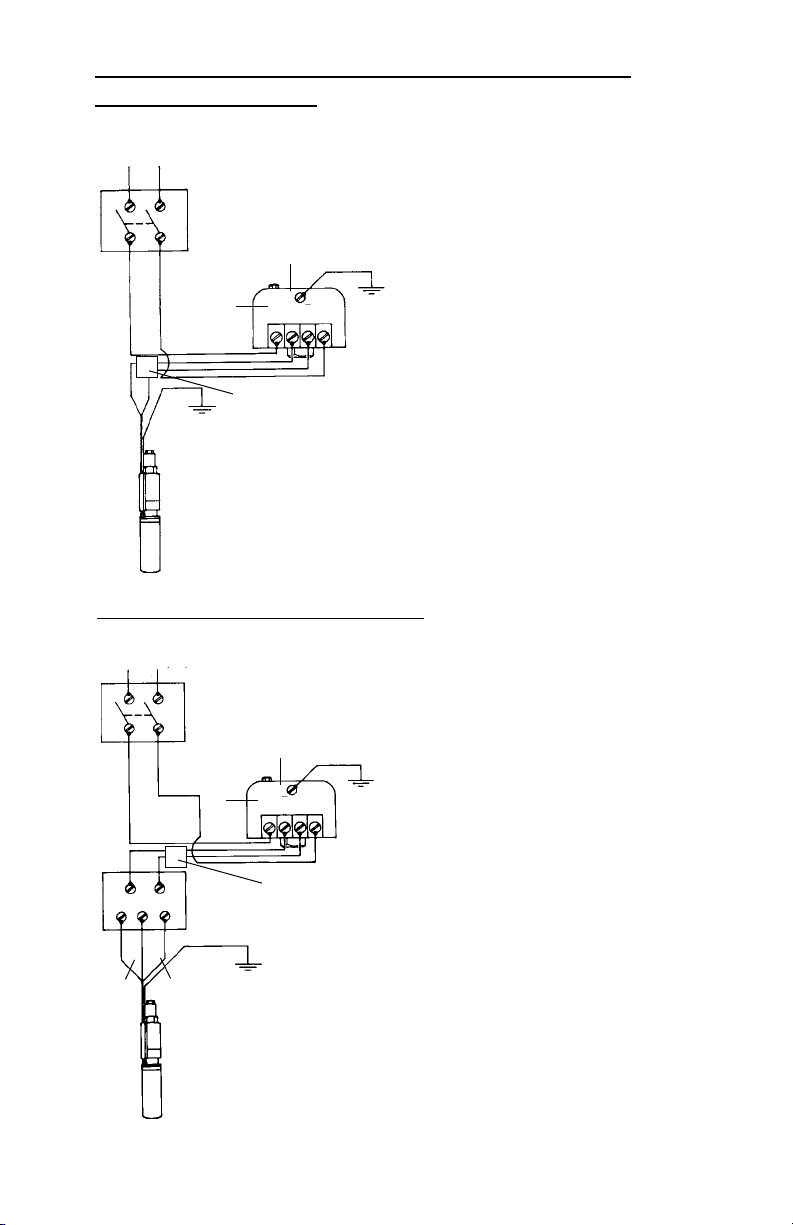
Wiring Diagrams — Esquemas de conexión —
Wiring Diagrams — Esquemas de conexión —
Schémas de câblage
Schémas de câblage
Incoming Supply from Fuse Box or
L1 L2
Circuit Breaker (1)
Disconnect
Switch (2)
(4)
1. Suministro de entrada de la caja de fusibles o del
cortacircuitos
2. Interruptor de desconexión
3. Línea
4. Carga
(3)
NOTE: PumpSaver
Two Wire – Direct Connected to
Bifilar – conectado directamente al
interruptor por caída de presión
Moteur à deux fils – connecté
directement au pressostat
Figure (Figura) 3
Incoming Supply from Fuse Box or
L1 L2
R Y Blk
Red
(8)
(9)
L1 L2
Circuit Breaker (1)
Disconnect
Switch (2)
(3)
Three Wire
Control Box
Black
Yellow
(10)
Three Wire – Direct Connected to Pressure
Trifilar – conectado directamente al interruptor
Moteur à trois fils – connecté directement
por caída de presión
Line
Load
Load
Line
Pressure Switch
(4)
Line
Load
Load
Line
NOTE: PumpSaver (6)
(7)
Switch
au prossostat
Pressure
Switch (5)
(6)
Pressure
Switch
5. Interruptor por caída de presión
6. NOTA: PumpSaver
7. Caja de control trifilar
8. Rojo
9. Amarillo
10. Negro
1. Courant d’entrée provenant de la boîte à fusibles
ou du disjoncteur
2.
Sectionneur
3.
Ligne
4.
Charge
5.
Pressostat
6.
Protection PumpSaver
(5)
7.
Boîte de commande à trois fils
8.
Rouge
9.
Jaune
10.
Noir
Figure (Figura) 4
19
Page 20
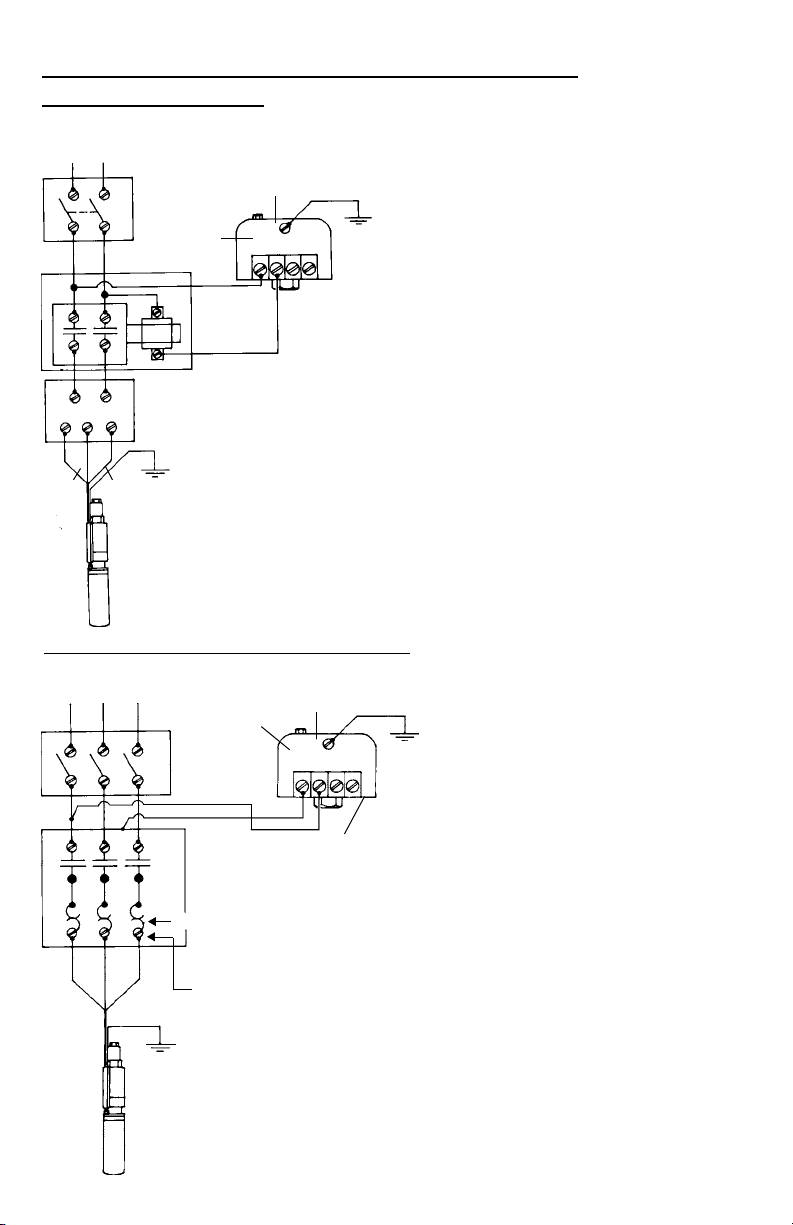
Wiring Diagrams — Esquemas de conexión —
Wiring Diagrams — Esquemas de conexión —
Schémas de câblage
Schémas de câblage
Incoming Supply from Fuse Box or
L1 L2
T1 T2
L1 L2
Circuit Breaker (1)
Disconnect
Switch (2)
(3)
Magnetic
Contactor
(6)
Three Wire Control Box (7)
L1 L2
R Y Blk
(4)
Line
Load
Load
Line
Pressure
Switch (5)
1. Suministro de entrada de la caja de
fusibles o del cortacircuitos
2. Interruptor de desconexión
3. Línea
4. Carga
5. Interruptor por caída de presión
6. Contactador magnético
7. Caja de control trifilar
8. Rojo
Red
Yellow
(8)
(9)
(10)
Incoming Supply from Fuse Box or
L1 L2 L3
T1 T2 T3
20
Black
Three Wire – Connected through
Magnetic Contactor
Trifilar – conectado a través del
contactador magnético
Moteur à trois fils – relié au pressostat par un
contacteur magnétique
Figure (Figura) 5
Circuit Breaker (1)
(3)
Disconnect
Switch (2)
3
Heaters (11)
Ambient Compensated
Magnetic Starter with
Quick-Trip Heaters
(12) or ESP100 Class 10
overloads
Three Phase Connections
Tres conexiones de fase
Circuit triphasé
Line
Pressure Switch
Figure (Figura) 6
(4)
Load
Load
Line
(5)
9. Amarillo
10. Negro
11. Calentadores
12. Arrancador magnético con compensación
ambiental con calentadores de disparo
rápido
1. Courant d’entrée provenant de la boîte à
fusibles ou du disjoncteur
2. Sectionneur
3. Ligne
4. Charge
5. Pressostat
6. Contacteur magnétique
7. Boîte de commande à trois fils
8. Rouge
9. Jaune
10. Noir
11. Dispositifs de protection contre la
surcharge (DPS)
12. Démarreur magnétique compensé
(température ambiante) avec DPS à
déclenchement rapide rapide ou limiteurs
de surcharge ESP100 de classe 10
Page 21
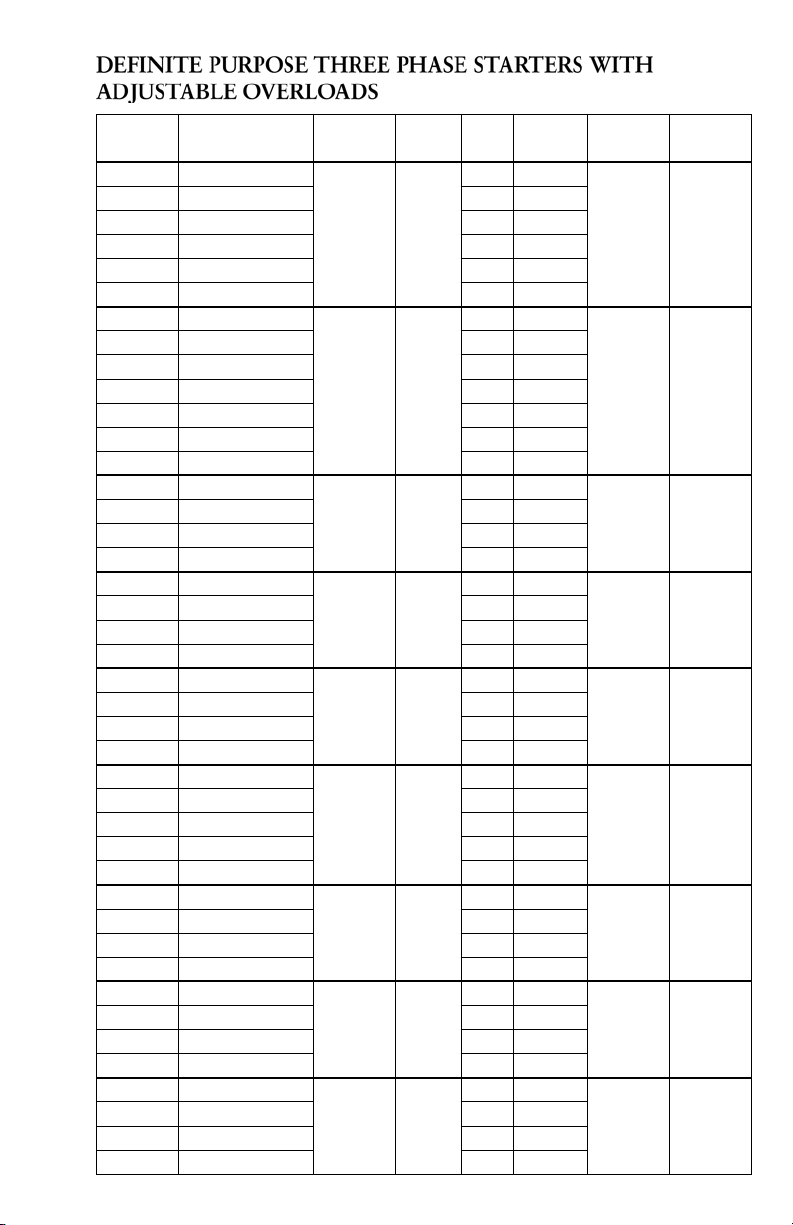
DEFINITE PURPOSE THREE PHASE STARTERS WITH
ADJUSTABLE OVERLOADS
CentriPro
Order No.
DP25D2 A27CGC25BA2P4
DP25E2 A27CGC25BA004 E 2.4-4
DP25F2 A27CGC25BA006 F 4-6
DP25G2 A27CGC25BA010 G 6-10
DP25H2 A27CGC25BA016 H 10-16
DP25J2 A27CGC25BA024 J 16-24
DP25C4 A27CGC25CA1P6
DP25D4 A27CGC25CA2P4 D 1.6-2.4
DP25E4 A27CGC25CA004 E 2.4-4
DP25F4 A27CGC25CA006 F 4-6
DP25G4 A27CGC25CA010 G 6-10
DP25H4 A27CGC25CA016 H 10-16
DP25J4 A27CGC25CA024 J 16-24
DP25E5 A27CGC25DA004
DP25F5 A27CGC25DA006 F 4-6
DP25G5 A27CGC25DA010 G 6-10
DP25H5 A27CGC25DA016 H 10-16
DP30L2 A27CGE30BA010
DP30M2 A27CGE30BA016 M 10-16
DP30N2 A27CGE30BA024 N 16-24
DP30P2 A27CGE30BA040 P 24-40
DP30L4 A27CGE30CA010
DP30M4 A27CGE30CA016 M 10-16
DP30N4 A27CGE30CA024 N 16-24
DP30P4 A27CGE30CA040 P 24-40
DP30L5 A27CGE30DA010
DP30M5 A27CGE30DA016 M 10-16
DP30N5 A27CGE30DA024 N 16-24
DP30P5 A27CGE30DA040 P 24-40
DP30R5 A27CGE30DA057 R 40-57
DP40L2 A27CGE40BA010
DP40M2 A27CGE40BA016 M 10-16
DP40N2 A27CGE40BA024 N 16-24
DP40P2 A27CGE40BA040 P 24-40
DP40L4 A27CGE40CA010
DP40M4 A27CGE40CA016 M 10-16
DP40N4 A27CGE40CA024 N 16-24
DP40P4 A27CGE40CA040 P 24-40
DP40L5 A27CGE40DA010
DP40M5 A27CGE40DA016 M 10-16
DP40N5 A27CGE40DA024 N 16-24
DP40P5 A27CGE40DA040 P 24-40
Eaton Reference
Number
Maximum
Amps
25 208-230
25 460
25 575
30 208-230
30 460
30 575
40 208-230
40 460
40 575
Supply
Voltage
O.L.
Overload
Relay
D 1.6-2.4
C 1-1.6
E 2.4-4
L 6-10
L 6-10
L 6-10
L 6-10
L 6-10
L 6-10
Range
Maximum
LRA
150 .5 - 5
125 .5 - 10
100 1.5 - 10
180 1.5 - 7.5
150 5 - 20
120 5 - 15
240 1.5 - 10
200 5 - 20
160 5 - 20
Typical HP
Range
21
Page 22

Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
WARNING
DISCONNECT AND LOCKOUT ELECTRICAL POWER BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY SERVICE. FAILURE TO DO SO CAN
CAUSE SHOCK, BURNS OR DEATH.
Hazardous voltage
can shock, burn or
cause death.
Symptom Probable Cause Recommended Action
PUMP MOTOR
NOT RUNNING
1. Motor thermal protector tripped
a. Incorrect control box
b. Incorrect or faulty electrical
connections
1. Allow motor to cool, thermal
protector will automatically reset
a – e. Have a qualified electrician
inspect and repair, as required
c. Faulty thermal protector
d. Low voltage
e. Ambient temperature of control
box/starter too high
f. Pump bound by foreign matter
g. Inadequate submergence
2. Open circuit breaker or blown fuse
f. Pull pump, clean, adjust set
depth as required
g. Confirm adequate unit
submergence in pumpage
2. Have a qualified electrician inspect
and repair, as required
3. Power source inadequate for load
4. Power cable insulation damage
5. Faulty power cable splice
3. Check supply or generator capacity
4 – 5. Have a qualified electrician
inspect and repair, as required
LITTLE OR
NO LIQUID
DELIVERED
BY PUMP
22
1. Faulty or incorrectly installed
check valve
2. Pump air bound
3. Lift too high for pump
4. Pump bound by foreign matter
5. Pump not fully submerged
6. Well contains excessive amounts
of air or gases
7. Excessive pump wear
8. Incorrect motor rotation
– three phase only.
1. Inspect check valve, repair as
required
2. Successively start and stop pump
until flow is delivered
3. Review unit performance, check
with dealer
4. Pull pump, clean, adjust set depth
as required
5. Check well recovery, lower pump
if possible
6. If successive starts and stops does
not remedy, well contains excessive
air or gases
7. Pull pump and repair as required
8. Reverse any two motor electrical
leads
Page 23

MANUAL DE INSTRUCCIÓN
IM116R04
Bomba sumergible
de 4 pulg.
INSTALACIÓN, OPERACIÓN Y MANUAL DEL MANTENIMIENTO
23
Page 24

Información del propietario
Información del propietario
Índice
Índice
Número de modelo de la bomba:
Número de serie de la bomba:
Número de modelo del motor:
Número de serie del motor:
Agente:
No. telefónico del agente:
Fecha de compra:
Fecha de instalación:
Voltios:
Amperios:
TEMA PÁGINA
Instrucciones de seguridad ......... 25-26
Dispositivos de protección de la
bomba ............................................. 28
Lista de verificación
de la instalación .......................... 28
1.0 Instalaciones típicas ................... 29
2.0 Tuberías y tanque ...................... 30
3.0 Tamaño y empalme de alambres y
fuente de alimentación .............. 32
4.0 Cómo conectar los controles y
el interruptor .............................. 33
5.0 Cómo arrancar la bomba .......... 36
6.0 Documentación y el manuel de
instrucciones (IOM) .................... 36
Datos del motor monofásico
CentriPro de 4"............................ 37
Cuadros de tamaños de cable
monofásico ................................. 37
Diagrama del PumpSaver ................ 37
Datos del motor trifásico ...........38-40
Datos de resistencia y generador..... 41
Diagramas de cableado ..............19-20
Datos Técnicos .............................. 41
Arrancadores trifásicos ..................42
Identificación y resolución de
problemas .................................... 43
Garantía limitada ............................ 66
24
Page 25

ADVERTENCIA
ADVERTENCIA
INSTRUCCIONES DE SEGURIDAD
ADVERTENCIA
PRECAUCIÓN
ADVERTENCIA
PARA EVITAR LESIONES PERSONALES GRAVES O AÚN FATALES Y
SERIOS DAÑOS MATERIALES, LEA Y SIGA TODAS LAS INSTRUCCIONES DE SEGURIDAD EN EL MANUAL Y EN LA BOMBA.
ESTE MANUAL HA SIDO CREADO COMO UNA GUÍA PARA LA INSTALACIÓN Y OPERACIÓN DE ESTA UNIDAD Y SE DEBE CONSERVAR JUNTO A LA BOMBA.
Éste es un SÍMBOLO DE ALERTA DE SEGURIDAD.
Cuando vea este símbolo en la bomba o en el manual, busque
una de las siguientes palabras de señal y esté alerta a la
probabilidad de lesiones personales o daños materiales.
PELIGRO
AVISO: INDICA INSTRUCCIONES ESPECIALES QUE SON MUY
IMPORTANTES Y QUE SE DEBEN SEGUIR DE
RETROCESO DE DRENAJE; ESTOS SISTEMAS DEBEN
UTILIZAR OTROS MEDIOS FRANKLIN ELECTRIC O EN
UN MANUAL DEL CÓDIGO N.E.C. (CÓDIGO ELÉCTRICO
NACIONAL DE LOS ESTADOS UNIDOS).
EXAMINE BIEN TODAS LAS INSTRUCCIONES Y ADVERTENCIAS
ANTES DE REALIZAR CUALQUIER TRABAJO EN ESTA BOMBA.
MANTENGA TODAS LAS CALCOMANÍAS DE SEGURIDAD.
Advierte los peligros que CAUSARÁN graves lesiones
personales, la muerte o daños materiales mayores.
Advierte los peligros que PUEDEN causar graves lesiones
personales, la muerte o daños materiales mayores.
Advierte los peligros que PUEDEN causar lesiones personales
o daños materiales.
Aviso importante: Lea las instrucciones de seguridad antes de proseguir con el cableado.
Todo el trabajo eléctrico debe ser realizado por un técnico
calificado. Siempre siga el Código Eléctrico Nacional (NEC) o
el Código Eléctrico Canadiense, además de todos los códigos locales, estatales
y provinciales. Las preguntas acerca del código deben ser dirigidas al inspector
eléctrico local. Si se hace caso omiso a los códigos eléctricos y normas de seguridad de OSHA, se pueden producir lesiones personales o daños al equipo.
Si se hace caso omiso a las instrucciones de instalación del fabricante, se puede
producir electrochoque, peligro de incendio, lesiones personales o incluso
la muerte, daños al equipo, rendimiento insatisfactorio y podría anularse la
garantía del fabricante.
Las unidades estándar no fueron diseñadas para su uso en
piscinas, cuerpos abiertos de agua, líquidos peligrosos o donde
existan gases inflamables. El pozo debe contar con ventilación de acuerdo
con los códigos locales. Vea los boletines de catálogos de bombas específicos
o la placa de nombre de la bomba para todas las listas de agencias.
Desconecte y bloquee la corriente eléctrica antes de instalar o dar
servicio a cualquier equipo eléctrico. Muchas bombas están equi-
padas con protección automática contra la sobrecarga térmica, la cual podría
permitir que una bomba demasiado caliente rearranque inesperadamente.
25
Page 26

26
ADVERTENCIA
ADVERTENCIA
ADVERTENCIA
ADVERTENCIA
ADVERTENCIA
ADVERTENCIA
ADVERTENCIA
PELIGRO
ADVERTENCIA
PRECAUCIÓN
PRECAUCIÓN
PRECAUCIÓN
PRECAUCIÓN
ADVERTENCIA
ADVERTENCIA
Nunca presurice demasiado el tanque, las tuberías o el sistema
a una presión superior a la clasificación de presión máxima del
tanque. El hacerlo dañará el tanque, anula la garantía y puede
crear un peligro grave.
Proteja a los tanques contra humedad y pulverización excesivas, ya
que oxidarán al tanque y pueden crear un peligro. Vea las etiquetas
de advertencia o el manual del tanque para más información.
No levante ni transporte ni cuelgue la bomba de los cables eléctricos. El daño a los cables eléctricos puede producir electrochoque,
quemaduras o aún la muerte.
Use únicamente alambre trenzado de cobre para la bomba/motor
y la conexión a tierra. El alambre de conexión a tierra debe ser al
menos del mismo tamaño que los alambres de la fuente de alimentación. Los alambres deben codificarse con colores para facilitar el
mantenimiento y la identificación y resolución de problemas.
Instale los cables y la conexión a tierra de acuerdo con el Código
Eléctrico Nacional de EE.UU. (NEC) o el Código Eléctrico Canadiense, además de los códigos locales, estatales y provinciales.
Instale un desconectador de todos los circuitos donde el código lo
requiera.
La tensión y fase de la fuente de alimentación deben corresponder
con todos los requerimientos del equipo. La tensión o fase incorrecta puede producir incendio, daño al motor o a los controles y
anula la garantía.
Todos los empalmes deben ser impermeables. Si utiliza juegos de
empalme, siga las instrucciones del fabricante.
Seleccione una caja de conexiones NEMA del tipo correcto para
la aplicación y ubicación. La caja de conexiones debe garantizar
conexiones de cableado seguras y secas.
Todos los motores requieren una sumersión de 5' para que la
válvula de verificación de llenado funcione correctamente.
La falla de conectar a tierra permanentemente la bomba, el motor
y los controles, antes de conectar la corriente eléctrica, puede
causar electrochoque, quemaduras o la muerte.
Todos los controles trifásicos (3Ø) para bombas sumergibles deben incluir protección contra sobrecarga de Clase 10, de disparo
rápido.
Los motores de 4 pulg. ≥ 2 caballos de fuerza requieren una
velocidad de flujo mínima de 0.25 pies/seg o 7.62 cm/seg más allá
del motor para producir un enfriamiento apropiado del mismo.
Los flujos mínimos en GPM por diámetro de pozo requeridos
para el enfriamiento son los siguientes: 1.2 GPM/4 pulg., 7
GPM/5 pulg., 13 GPM/6 pulg., 20 GPM/7 pulg., 30 GPM/8
pulg. o 50 GPM en un pozo de 10 pulg.
Las bombas ≥ 2 caballos de fuerza instaladas en tanques grandes
se deben instalar en una camisa de inducción de flujo para crear el
flujo de enfriamiento o la velocidad necesaria más allá del motor.
Esta bomba se evaluó para uso con Agua Únicamente.
Page 27

PROTECCIÓN DE LA BOMBA
Recomendamos el uso del PumpSaver de SymCom para proteger al sistema
contra bajo nivel de agua, ciclaje rápido, voltaje alto/bajo, funcionamiento de
la bomba sin succión/restricción de flujo y sobretensión.
LISTA DE VERIFICACIÓN DE LA INSTALACIÓN
• Anote la información de la bomba y del motor y otros datos solicitados en la
portada de este manual.
• Inspeccione todos los componentes para detectar daños de envío; notique los
daños de inmediato al distribuidor.
• Verique la correspondencia de los caballos de fuerza del motor y de la bomba.
• Haga corresponder la tensión y fase de la fuente de alimentación con las especi-
caciones de control y del motor.
• Seleccione un lugar sombreado y seco en el cual montar los controles.
• Las conexiones de todos los empalmes sumergidos y subterráneos deben ser
impermeables.
• Sujete la bomba en la cabeza de descarga cuando instale tubo roscado o un
accesorio adaptador, ya que la mayoría de las bombas tienen roscas de mano
izquierda que se aflojarán si sujeta la bomba de cualquier otra parte.
• Revise todas las conexiones de plomería para vericar que estén ajustadas y selladas con cinta de Teflon.
• Verique que la clasicación de presión del tubo sea más alta que la presión de
paro de la bomba.
• Instale una válvula de alivio de presión en todo sistema capaz de crear más de 75
PSI.
• Sitúe el interruptor por caída de presión a menos de 4 pies del tanque de presión
para evitar el chasquido del interruptor.
• Ajuste la precarga del tanque 2 PSI por debajo de la presión de conexión del
sistema, por ejemplo 28 en un sistema de 30/50.
• Instale la bomba 10 pies más arriba del fondo del pozo para mantenerla lejos de
los sedimentos y residuos.
• Verique que el suministro eléctrico principal esté desconectado y APAGADO
antes de cablear los componentes.
• El cableado debe ser realizado por técnicos calicados únicamente.
• El cableado y la puesta a tierra deben cumplir con los códigos nacionales y locales.
• Restrinja el ujo con una válvula de bola o de globo, 1/3 abierta, antes de arrancar
la bomba por primera vez.
• Abra un grifo o una válvula de descarga durante la puesta en marcha para evitar
que entre agua sucia al tanque.
• ENCIENDA el cortacircuitos principal o el desconectador.
• Active/desactive varias veces para vericar el funcionamiento correcto del inter-
ruptor.
• Verique los amperios y anote los datos en la portada de este manual.
• Entregue el manual al propietario en el sitio de la obra.
27
Page 28

1.0 INSTALACIONES TÍPICAS
1.0 INSTALACIONES TÍPICAS
INSTALACIÓN DEL TANQUE CAPTIVE AIR
AVISO: LOS CAMBIOS DE PRESIÓN DE PRECARGA DEL TANQUE
DEBEN HACERSE CON LA VÁLVULA NEUMÁTICA EN EL EXTREMO
SUPERIOR DEL TANQUE.
Fuente de alimentación protegida
Adaptador sin
fosa ①
Válvula de
retención ①
Nivel de helada
① En instalaciones con un adaptador sin fosa, la válvula de
A la cañería de la casa
Interruptor de desconexión
Válvula de cierre
Unión
Interruptor por caída de presión
Válvula de alivio de presión
Derivación de drenaje
T del tanque
Válvula de retención ②
retención superior debe situarse debajo del área sin fosa y no
en el tanque, ya que la línea de descarga se debe presurizar de
regreso al área sin fosa.
② En instalaciones con sellos de pozo o fosas de pozo, está
permitido situar la válvula de retención superior cerca del
Figura 1
tanque.
INSTALACIÓN DE TANQUE GALVANIZADO
Interruptor de desconexión
Caja de control
Fuente de alimentación protegida
Indicador de
presión
A la cañería de
la casa
28
Adaptador sin cavidad
Accesorio de drenaje y en Y
Figura 2
Válvula de cierre
Unión
Derivación de drenaje
Válvula de alivio de presión
Control de escape de aire
Interruptor por caída de presión
Válvula de retención de línea con desahogo
Posición aproximada del accesorio de drenaje
Unión
Distancia del accesorio de
Capacidad del tanque drenaje y en “Y” por debajo de
la válvula de retención de línea
159 L (42 galones) 7 pies (2.1m)
310 L (82 galones) 10 pies (3m)
454 L (120 galones) 15 pies (4.6m)
833 L (220 galones) 15 pies (4.6m)
1192 L (315 galones) 20 pies (6.1m)
1981 L (525 galones) 20 pies (6.1m)
Page 29

2.0 TUBERÍA
2.0 TUBERÍA
Aviso: La mayoría de las bombas
sumergibles de 4 pulg. tienen roscas
de mano izquierda en la cabeza de
descarga; sujete la bomba sólo en la
“cabeza de descarga” con una llave
cuando instale accesorios o tubo
roscado.
PRECAUCI N
2.1 Generalidades
La tubería de descarga de
la bomba debe dimensio-
Niveles de presi n
peligrosos pueden causar
lesiones personales o
da os materiales.
narse para producir un
funcionamiento eficiente
de la bomba. Utilice las
Tablas de pérdida por fricción para
calcular la carga dinámica total empleando tubos de tamaños diferentes.
Como regla práctica, utilice 1 pulg.
para hasta 10 gpm, 1¼ pulg. para
hasta 30 gpm, 1½ pulg. para hasta
45 gpm y 2 pulg. para hasta 80 gpm.
En el caso de secciones largas de
tubería es mejor aumentar el tamaño
de la tubería.
Algunas bombas son capaces de
producir presiones de descarga muy
altas; por lo tanto, seleccione el tubo
que corresponda. Consulte con su
proveedor de tubería para determinar
el mejor tipo para cada instalación.
PELIGRO
2.2 Tanque de
presión, interruptor
por caída de presión
y válvula de alivio
No instale el tanque donde
esté sujeto a pulverización
de sistemas de irrigación.
La exposición a dicha
pulverización podría
causar la corrosión del
tanque y, a la larga, una
explosión que puede
causar daños a la propiedad, lesiones personales
graves o muerte.
a 34º F (1º C) para instalar el tanque,
el interruptor de presión y la válvula
de alivio de presión. Se debe ubicar el
tanque en un área en la que una pérdida no causaría daños a la propiedad.
El interruptor por caída de presión
debe estar situado en la doble T del
tanque y nunca a más de 4 pies del
tanque. Si el interruptor se sitúa a
de presión
Elija una ubicación seca en
la que la temperatura am-
biente sea siempre superior
más de 4 pies del tanque, emitirá un
chasquido.
No instale válvulas, filtros o
conexiones de alta absorción entre el
interruptor y el/los tanque(s), ya que
puede provocar el fallo del interruptor. Como ejemplo, una válvula de
verificación de resorte de 1¼" tiene
una pérdida de fricción equivalente
a 12' de caño, colocar la válvula
entre el interruptor de presión y el
tanque de presión equivale a alejar al
interruptor de presión 12' del tanque.
Esto provocará un fallo en el
interruptor.
En instalaciones de varios tanques,
el interruptor debe situarse lo más
cerca posible del centro del tanque.
Las instalaciones de varios tanques
deben tener un tubo de distribución
cuyo tamaño sea al menos 1½ veces
el tamaño del tubo de suministro de
la bomba. Esto reducirá la carga por
fricción en el tubo de distribución y
disminuirá la posibilidad de
chasquido del interruptor.
Se requieren válvulas de alivio de
presión en cualquier sistema que
sea capaz de producir 100 lbs./
pulg. cuadrada o 230 pies de carga
dinámica total. Si ésta es una área
donde una purga o fuga de agua
podría dañar la propiedad, conecte
una línea de drenaje a la válvula
de alivio de presión. Tiéndala a un
drenaje adecuado o a un área donde
el agua no dañará la propiedad.
2.3 Cómo ajustar la precarga
del tanque
Asegúrese de que no haya nada de
agua en el tanque. Utilice un indicador de presión de alta calidad para
medir la presión de precarga del
tanque. La presión debe ser 2 lbs./
pulg. cuadrada menos que la presión
de conexión de la bomba. Como
ejemplo, un sistema de 30-50 lbs./
pulg. cuadrada utilizaría una precarga
del tanque de 28 lbs./pulg. cuadrada.
29
Page 30

2.4 Tubería de descarga y
válvula de retención
Nota: La mayoría de las cabezas de
descarga se atornillan en la carcasa
con roscas de mano izquierda. Sólo
sujete la bomba en la cabeza de descarga cuando instale los accesorios.
Si no se sujeta la cabeza de descarga,
ésta se aflojará y se dañará la bomba
al ponerla en marcha.
Si la tubería necesita un adaptador,
recomendamos enfáticamente utilizar
acero inoxidable. Los accesorios o
tuberías galvanizadas nunca deben
conectarse directamente a una cabeza
de descarga de acero inoxidable ya
que podría producirse corrosión
galvánica. Se puede utilizar cualquier material para esta conexión
en el caso de bombas de plástico o
de latón. Los conectores tipo arpón
siempre deben sujetarse con doble
abrazadera.
El cabezal de descarga de la bomba
tiene un ojal para sujetar un cable de
seguridad. Se recomienda el uso de
un cable de seguridad al usar tuberías
de poliuretano, ya que la tubería
se estira cuando está bajo presión y
llena de agua.
2.5 Cómo instalar la bomba
en el pozo
Si está utilizando un mecanismo
antitorsión, instálelo de acuerdo con
las instrucciones de instalación del
fabricante. Solicite información al
proveedor sobre mecanismos antitorsión e instrucciones de instalación.
Conecte la tubería de descarga a la
cabeza de descarga o al adaptador
que instaló previamente. Los conectores tipo arpón siempre deben
sujetarse con doble abrazadera.
Instale la bomba en el interior del
pozo utilizando un adaptador sin fosa
o dispositivo similar en el cabezal
del pozo. Consulte con el fabricante
del accesorio o con el proveedor del
adaptador con respecto a instrucciones específicas de instalación.
Utilice cinta aislante impermeable
para sujetar los alambres al tubo
de bajada a intervalos de 10 pies.
Asegúrese de que la cinta no se desprenda ya que bloqueará la succión
de la bomba si cae dentro del pozo.
Los proveedores de bombas también
venden conectores de alambre estilo
presilla para sujetar el alambre al
tubo de bajada.
2.6 Tubería especial para
sistemas de tanques
galvanizados
Cuando utilice un tanque galvanizado, debe instalar un accesorio de
drenaje e “Y” AV11 en el pozo y
una válvula de retención con válvula de desahogo en el tanque. Esto
introducirá aire al tanque con cada
arranque de la bomba y evitará el
estancamiento del agua en el tanque.
Utilice un escape de aire AA4 en el
tanque para permitir el escape del exceso de aire. La distancia entre AV11
y la válvula de desahogo determina
la cantidad de aire que entra en cada
ciclo. Consulte la tabla con respecto
a los valores recomendados. Consulte
la Fig. 2 en la Sección 1.0.
En el caso de pozos de gas, deben
utilizarse tanques galvanizados con
escapes de aire AA4 para ventear el
exceso de aire y evitar la “salida de
agua por chorros” en las llaves.
El metano y otros gases explosivos o
peligrosos requieren un tratamiento
especial del agua para extraerlos en
forma segura. Consulte con un especialista de tratamiento de agua para
considerar estos asuntos.
En las instalaciones con pozo de
alimentación superior se deben usar
camisas de flujo en la bomba.
30
Page 31

2.7 Válvulas de retención
Nuestras bombas utilizan cuatro estilos distintos de válvulas de retención.
Recomendamos el uso de válvulas
de retención ya que evitan el giro
inverso de la bomba y motor que
producirá un desgaste prematuro de
los cojinetes. Además, las válvulas
de retención evitan que se produzca
ariete hidráulico o daños por empuje
hacia arriba. Las válvulas de retención se deben instalar cada 200 - 250
pies en la tubería de descarga vertical.
La siguiente información es para
clientes que desean desactivar una
válvula de retención para un sistema
de retroceso de drenaje; estos sistemas deben utilizar otros medios para
impedir el ariete hidráulico o los
daños por empuje hacia arriba:
• Las válvulas de acero inoxidable
incorporadas tienen un área plana
que se puede perforar con facilidad con un taladro eléctrico y una
broca de ¼ pulg. o 3⁄8 pulg. para
desactivar la válvula.
• Las válvulas de retención estilo
aguja que están atornilladas desde
arriba de la cabeza de descarga se
pueden retirar con facilidad utilizando un entuercador de
12 pulg. o una boquilla profunda.
El cubo hexagonal es visible y
accesible desde arriba.
• Las válvulas internas estilo aguja
de plástico de diseño Flomatic™ se
deben retirar desde adentro, para
lo cual es necesario desarmar la
bomba.
• Las válvulas estilo aguja de plástico
incorporadas con un vástago a
través del extremo superior se
pueden retirar de la cabeza de
descarga tirando el vástago con
alicates.
PELIGRO
La tensión peligrosa
puede causar choques,
quemaduras o
la muerte.
3.0 TAMAÑO
3.0 TAMAÑO
Y EMPALME DE
Y EMPALME DE
ALAMBRES y
ALAMBRES y
FUENTE DE ALI-
FUENTE DE ALI-
MENTACIÓN
MENTACIÓN
Siempre siga el Código Eléctrico de
los Estados Unidos (N.E.C.)
el Código Eléctrico del Canadá y
cualquier código estatal o local.
Sugerimos usar únicamente cable de
cobre. Utilice el tamaño de cable que
figura en la sección de Datos Técnicos
de este manual, el manual MAID, o
un manual de Código Eléctrico Nacional (N.E.C. – National Electric Code).
En caso de discrepancias, el libro del
N.E.C. prevalecerá con respecto a las
recomendaciones de un fabricante.
3.1 Empalme de alambre a los
conductores del motor
Cuando deba empalmarse o conectarse un cable de bajada al conductor del motor, es necesario que
el empalme sea impermeable. El
empalme puede realizarse con juegos
de contracción por calor o cinta
impermeable.
A. Instrucciones de empalme con
juego de contracción por calor
Para utilizar un juego típico de contracción por calor: pele ½ pulgada de
los alambres del motor y de los alambres del cable de bajada; es mejor
escalonar los empalmes. Coloque los
tubos de contracción por calor sobre
los alambres. Coloque los plegadores
sobre los alambres y pliegue los extremos. Deslice los tubos de contracción por calor sobre los plegadores y
caliéntelos desde el centro hacia afuera. El sellador y el adhesivo saldrán
por los extremos cuando el tubo se
contrae. El tubo, los plegadores, el
sellador y el adhesivo crearán un sello
impermeable muy resistente.
31
Page 32

B. Instrucciones de empalme
con cinta
A) Pele el aislamiento del conductor
individual sólo lo necesario para
dejar espacio para un conector
tipo estaca. Se prefieren los
conectores tubulares tipo estaca.
Si el D.E. del conector no es tan
grande como el aislamiento del
cable, auméntelo con cinta
aislante de caucho.
B) Encinte las juntas individuales
con cinta aislante de caucho,
empleando dos capas; la primera
extendiéndose dos pulgadas más
allá de cada extremo de
aislamiento del conductor,
la segunda capa extendiéndose
dos pulgadas más allá de la
primera capa. Envuelva en forma
apretada, eliminando los espacios
de aire lo más posible.
C) Aplique cinta aislante Scotch
#33 o equivalente sobre la cinta
aislante de caucho, empleando
dos capas como en el paso “B” y
haciendo que cada capa se
superponga al menos dos
pulgadas al extremo de la capa
anterior.
En el caso de un cable con tres
conductores recubiertos con un solo
revestimiento exterior, encinte los
conductores individuales en la forma
descrita, alternando las juntas.
El espesor total de la cinta no debe
ser inferior al espesor del aislamiento
del conductor.
PELIGRO
La tensión peligrosa
puede causar choques,
quemaduras o
la muerte.
4.0 CÓMO
4.0 CÓMO
CONECTAR LOS
CONECTAR LOS
CONTROLES y EL
CONTROLES y EL
INTERRUPTOR
INTERRUPTOR
4.1 Cómo montar la caja de
control del motor
Las cajas de control monofásicas trifilares cumplen con los requerimientos
de U.L. para las cubiertas tipo 3R.
Son adecuadas para montaje vertical en lugares interiores y exteriores.
Funcionarán a temperaturas entre
14ºF (-10ºC) y 122ºF (50ºC). Seleccione un lugar sombreado y seco para
montar la caja. Asegure que haya suficiente espacio para quitar la tapa.
4.2 Verifique la tensión y
apague la fuente de
alimentación
Asegure que la tensión del motor y
la tensión de la fuente de alimentación sean iguales.
Coloque el cortacircuitos o interruptor de desconexión en la posición
OFF (de apagado) para evitar arrancar la bomba accidentalmente antes
de que esté listo.
Las bobinas de arrancadores trifásicos
son muy sensibles a la tensión; siempre verifique la tensión de suministro
real con un voltímetro.
La alta o baja tensión, de más de
±10%, dañará los motores y controles y eso no está cubierto por la
garantía.
32
Page 33

4.3 Cómo conectar los
conductores del motor a
la caja de control del
motor, interruptor por
caída de presión o
arrancador
PELIGRO
La tensión peligrosa
puede causar choques,
quemaduras o
la muerte.
o cortacircuitos esté APAGADO antes
de conectar los conductores de la línea
del interruptor por caída de presión a
la fuente de alimentación. Siga todos
los códigos locales y nacionales. Utilice
un desconector cuando el código así lo
requiera.
A. Motor monofásico trifilar
Conecte los conductores del motor
codificados con colores a los terminales de la caja de control del motor -
Y (amarillo), R (rojo) y B (negro) y el
alambre verde o desnudo al tornillo
verde de puesta a tierra.
Conecte los alambres entre los terminales de carga en el interruptor por
caída de presión y los terminales L1
y L2 de la caja de control. Conecte
un alambre de puesta a tierra entre la
tierra del interruptor y la tierra de la
caja de control. Consulte la Figura
4 ó 5
B. Motor monofásico bifilar
Conecte los conductores negros del
motor a los terminales de carga en el
interruptor por caída de presión y el
alambre verde o desnudo de puesta
a tierra al tornillo verde de puesta a
tierra. El motor CentriPro de dos hilos
no funcionará con un PumpTec de
Franklin Electric. Use un PumpSaver.
Consulte la Figura 3
C. Motores trifásicos
Conecte los conductores del motor a
T1, T2 y T3 en el arrancador trifásico.
Conecte el alambre de puesta a tierra
al tornillo de puesta a tierra en la caja
Precaución No energice la
unidad ni haga funcionar
la bomba hasta que haya
completado todas las conexiones eléctricas y de tuberías.
Verifique que el desconector
del arrancador. Siga las instrucciones
del fabricante del arrancador para
conectar el interruptor por caída de
presión o consulte la Figura 6.
4.4 Conexión a la fuente de
alimentación
PELIGRO
La tensión peligrosa
puede causar choques,
quemaduras o
la muerte.
desconector en caso que se utilice.
Instalaciones trifásicas – haga las
conexiones entre L1, L2, L3 y tierra
en el arrancador al desconector y
luego al panel de cortacircuitos.
Deben verificarse las instalaciones
trifásicas con respecto a la rotación
del motor y al desbalance de fase.
Para invertir la rotación del motor,
cambie (invierta) dos conductores
cualquiera. Consulte las instrucciones
para identificar el desbalance trifásico
en la Sección Técnica de este manual.
Si no se revisa el desbalance de fase,
se puede producir una falla prematura
del motor o un disparo por sobrecarga falso. Si está utilizando un generador, consulte los Datos Técnicos para
generadores.
Complete el cableado
haciendo la conexión desde
los terminales de línea del
interruptor por caída de
presión monofásico hasta el
panel de cortacircuitos o el
4.5 Protección contra las
sobrecargas en unidades
trifásicas
Sólo use la protección de Clase 10, de
disparo rápido contra las sobrecargas
en los motores sumergibles trifásicos.
Vea los arrancadores definidos del
propósito en este manual.
Llame al grupo de Servicio al Cliente
del fabricante de la bomba para pedir
asistencia para la selección.
33
Page 34

4.6 Desbalance de potencia
trifásica
Se recomienda un suministro trifásico
completo, lo que incluye tres
transformadores individuales o un
transformador trifásico. Se pueden
usar conexiones en estrella o en
triángulo “abierto” empleando sólo
dos transformadores, pero hay más
posibilidad de que produzcan un
rendimiento inadecuado, disparo
por sobrecarga o falla prematura
del motor debido al desbalance de
corriente.
Mida la corriente en cada uno de los
tres conductores del motor y calcule
el desbalance de corriente en la forma
que se explica abajo.
Si el desbalance de corriente es del
2% o menos, deje los conductores tal
como están conectados.
Si el desbalance de corriente es de
más del 2%, hay que verificar las
lecturas de corriente en cada derivación empleando cada una de las
tres conexiones posibles. Enrolle los
conductores del motor en el arrancador en la misma dirección para evitar
una inversión del motor.
Para calcular el porcentaje de
desbalance de corriente:
A. Sume los tres valores de corriente
de línea.
B. Divida la suma por tres, con lo cual
se obtiene la corriente promedio.
C. Seleccione el valor de corriente
más alejado de la corriente
promedio (ya sea alto o bajo).
D. Determine la diferencia entre este
valor de corriente (más alejado del
promedio) y el promedio.
E. Divida la diferencia por el promedio.
Multiplique el resultado por 100 para
determinar el porcentaje de desbalance.
El desbalance de corriente no debe
exceder el 5% a la carga del factor de
servicio o el 10% a la carga de entrada
nominal. Si el desbalance no puede
corregirse enrollando los conductores,
la causa del desbalance debe
determinarse y corregirse. Si, en las
tres conexiones posibles, la derivación
más alejada del promedio está en el
mismo conductor de potencia, entonces la mayoría del desbalance proviene
de la fuente de potencia.
Contacte a la compañía de electricidad
local para solucionar el desbalance.
Conexión 1 Conexión 2 Conexión 3
Terminales del L1 L2 L3 L1 L2 L3 L1 L2 L3
arrancador
Conductores R B Y Y R B B Y R
del motor T3 T1 T2 T2 T3 T1 T1 T2 T3
Ejemplo:
T3-R = 51 amperios T2-Y = 50 amperios T1-B = 50 amperios
T1-B = 46 amps T3-R = 48 amps T2-Y = 49 amps
T2-Y = 53 amps T1-B = 52 amps T3-R = 51 amps
Total = 150 amperios Total = 150 amperios Total = 150 amperios
÷ 3 = 50 amps ÷ 3 = 50 amps ÷ 3 = 50 amps
— 46 = 4 amps — 48 = 2 amps — 49 = 1 amps
4 ÷ 50 = .08 ó 8% 2 ÷ 50 = .04 ó 4% 1 ÷ 50 = .02 ó 2%
34
Page 35

5.0 CÓMO ARRANCAR
5.0 CÓMO ARRANCAR
LA BOMBA
LA BOMBA
PRECAUCI N
5.1 Instale una
válvula y haga
funcionar la bomba
Niveles de presi n
peligrosos pueden causar
lesiones personales o
da os materiales.
una válvula esférica o de globo en la
línea de descarga de la bomba y con la
válvula 1⁄3 abierta, bombee el pozo hasta
que el agua salga limpia. Abra la válvula lentamente para verificar el flujo
y, cuando el agua salga limpia, apague
la bomba.
Retire la válvula esférica o de globo
y conecte la descarga de la bomba a
cañería de la casa, el tanque de presión
y el interruptor. Encienda la bomba.
Permita que la bomba funcione varios
ciclos para que se enjuague y para
verificar que la bomba y el interruptor
funcionen correctamente. Aproveche
este tiempo para fijarse si las conexiones presentan pérdidas.
CUIDADO: Si el pozo tiene un nivel
estático alto, vea la próxima sección
con información importante para la
protección de la bomba.
PRECAUCI N
para limpiar el agua
En un pozo nuevo - Instale
5.2 Estrangulación
de un pozo de alto
nivel estático para
Niveles de presi n
peligrosos pueden causar
lesiones personales o
da os materiales.
alto nivel estático de agua podría
permitir que la bomba funcione fuera
de la curva a la derecha o fuera del
“intervalo recomendado” mostrado
en la curva de la bomba. Recomendamos utilizar un restrictor de flujo
“Dole” o estrangular con una válvula
de bola para evitar el daño por empuje hacia arriba a la bomba y al motor. Debe restringirse el flujo máximo
para que esté dentro del intervalo de
funcionamiento recomendado de la
bomba. Si utiliza una válvula de bola,
evitar el empuje hacia
arriba
Cualquier pozo con un
ajústela, quite la manija, encinte la
manija al tubo y etiquete la válvula
con una nota que diga “No abra esta
válvula o podría dañarse la bomba”.
La manera más fácil de “ajustar” el
flujo es llenar un cubo de 5 galones
y medir el tiempo que lleva producir
5 galones. Calcule el flujo en gpm
de acuerdo con este valor. A medida
que el nivel de agua disminuye en el
pozo, se reducirá el flujo debido al
aumento de la carga y la válvula no
interferirá con el rendimiento.
6.0 DOCUMENTACIÓN y
6.0 DOCUMENTACIÓN y
EL MANUAL DE
EL MANUAL DE
INSTRUCCIONES
INSTRUCCIONES
(IOM)
(IOM)
Entregue este manual de instrucciones y su tarjeta al propietario.
¡Una etiqueta con su nombre y
número de teléfono en el tanque o
en la caja de control es una buena
herramienta de venta para los
negocios futuros!
Actualmente, proveemos una etiqueta
adicional de bomba que usted puede
fijar en el IOM, colocar en una
caja de control de 3 hilos o ubicar
cerca del tanque y del interruptor de
presión para identificación futura de
la bomba.
35
Page 36

GENERACIÓN II - DE 2-HILOS, 4 PULG. DATOS
ELÉCTRICOS LA MONOFÁSICO, 60 HERTZ, 3450 RPM
Carga plena
CP No. de
Tipo
orden
M05421 0.5 0.37 115 1.6 7.9 910 9.8 1120 28 1.4-2.0 H
PSC
M05422 0.5 0.37 230 1.6 4.0 845 4.7 1050 16 6.1-7.2 J
de
M07422 0.75 0.55 230 1.5 5.0 1130 6.2 1400 18 5.9-6.9 F
2-
M10422 1.0 0.75 230 1.4 6.7 1500 8.1 1800 24 4.2-5.2 F
hilos
M15422 1.5 1.1 230 1.3 9.0 2000 10.4 2350 43 1.8-2.4 H
HP KW
Voltios
SF Amps Watts Amps Watts
Factor de servicio
Amperaje
del rotor
bloqueado
Winding
Resis-
tance
Có-
digo
KVA
GENERACIÓN II - DE 3-HILOS, 4 PULG. DATOS
ELÉCTRICOS LA MONOFÁSICO, 60 HERTZ, 3450 RPM
Carga plena
CP No.
Tipo
de orden
3-hilos
M05411 0.5 0.37 115 1.6
con
Q.D.
rectán-
M05412 0.5 0.37
gulo
del
co-
M07412 0.75 0.55 1.5
mienzo
del con-
densa-
M10412 1.0 0.75 1.4
dor
M05412 0.5 0.37 1.6
M07412 0.75 0.55 1.5
3-hilos
con
CSCR
M10412 1.0 0.75 1.4
(CR)
o el
rectán-
gulo de
M15412 1.5 1.1 1.3
control
magnético del
M20412 2 1.5 1.25
contac-
tor
(MC)
M30412 3 2.2 1.15
M50412 5 3.7 1.15
¹ Un rectángulo de control de CSCR con un sufijo del CR se puede substituir por una conclusión magnética del modelo del contactor en MC.
HP KW
Voltios
SF Amps Watts Amps Watts
Y – 8.8
B – 8.8
R – 0
Y – 5.3
1.6
B – 5.3
R – 0
Y – 6.6
B – 6.6
R – 0
Y – 8.1
B – 8.1
R – 0
Y – 4.2
B – 4.1
R – 1.8
Y – 4.8
B – 4.4
230
R – 2.5
Y – 6.1
B – 5.2
R – 2.7
Y – 9.1
B – 8.2
R – 1.2
Y – 9.9
B – 9.1
R – 2.6
Y – 14.3
B – 12.0
R – 5.7
Y – 24.0
B – 19.1
R – 10.2
675
740
970
1215
715
940
1165
1660
2170
3170
5300
Factor de servicio
Y – 10.9
B – 10.9
R – 0
Y – 6.1
B – 6.1
R – 0
Y – 7.8
B – 7.8
R – 0
Y – 9.4
B – 9.4
R – 0
Y – 4.8
B – 4.3
R – 1.8
Y – 6.0
B – 4.9
R – 2.3
Y – 7.3
B – 5.8
R – 2.6
Y – 10.9
B – 9.4
R – 1.1
Y – 12.2
B – 11.7
R – 2.6
Y – 16.5
B – 13.9
R – 5.6
Y – 27.0
B – 22.0
R – 10.0
980 44
1050 21
1350 32
1620 41
960 21
1270 32
1540 41
2130 49
2660 49
3620 76
6030 101
Ampe-
raje del
rotor blo-
queado
Winding
Resistance
Prin-
Ar-
ciple
ranque
(B-Y)
(R-Y)
1.0-
2.5-
1.4
3.1
5.1-
12.4-
6.1
13.7
2.6-
10.4-
3.3
11.7
2.0-
9.3-
2.6
10.4
1.0-
2.5-
1.4
3.1
5.1-
12.4-
6.1
13.7
2.6-
10.4-
3.3
11.7
2.0-
9.3-
2.6
10.4
1.6-
10.8-
2.2
12.0
1.1-
2.0-
1.4
2.5
.62-
1.36-
.76
1.66
Caja de
control
requerida
CB05411
CB05412
CB07412
CB10412
CB05412CR
CB07412CR
CB10412CR
CB15412CR o
CB15412MC
CB20412CR o
CB20412MC
CB30412CR o
CB30412MC
CB50412CR o
CB50412MC
1
36
Page 37

GENERACIÓN II, MOTORES DE DOS HILOS, RECOMENDADOS LON-
GITUDES DEL TERMINAL DE COMPONENTE
Release/versión para venta en noviembre/el diciembre de 2011
Largos de conductores del motor - Motores de 2 hilos CentriPro -
con base en Amps de Factor de Servicio, temperatura ambiente 30°C y caída de voltaje del 5%
Clasificación de motor 60°C y 75° aislamiento - tamaño de cable de cobre AWG
Voltios
HP kW FLA SFA 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 1/0 2/0 3/0 4/0
115 ½ 0.37 7.9 9.8 112 178 284 449 699 1114 1769 2814 3550 4481 5646
½ 0.37 4.0 4.7 466 742 1183 1874 2915 4648 7379 11733
¾ 0.55 5.0 6.2 353 562 897 1420 2210 3523 5594 8895 11222
230
1 0.75 6.7 8.1 271 430 686 1087 1692 2697 4281 6808 8590 10843
1½ 1.1 9.0 10.4 211 335 535 847 1318 2100 3335 5303 6690 8445
GENERACIÓN II, 3-ALAMBRE, 4" 1Ø, RECOMENDADO LONGITUDES DEL ALAMBRE
Largos de conductores del motor - Motores de 3 hilos CentriPro (CSIR) -
con base en Amps de Factor de Servicio, temperatura ambiente 30°C y caída de voltaje del 5%
Clasificación de motor 60°C y 75° aislamiento - tamaño de cable de cobre AWG
Voltios
HP kW FLA SFA 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 1/0 2/0 3/0 4/0
115 ½ 0.37 8.8 10.9 101 160 255 404 629 1002 1591 2530 3192 4029 5076
½ 0.37 5.3 6.1 359 571 912 1444 2246 3581 5685 9040 - - -
¾ 0.55 6.6 7.8 281 447 713 1129 1757 2800 4446 7070 8920 - -
1 0.75 8.1 9.4 233 371 592 937 1458 2324 3689 5867 7402 - -
230
1½ 1.1 9.1 10.9 201 320 510 808 1257 2004 3182 5059 6383 - -
2 1.5 9.9 12.2 180 286 456 722 1123 1790 2843 4520 5703 - -
3 2.2 14.3 16.5 133 211 337 534 830 1324 2102 3342 4217 5323 -
5 3.7 24 27 - - 206 326 507 809 1284 2042 2577 3253 -
PUMPSAVER 235
PUMPSAVER 235
GND L2 L1
DESCONECTOR CON
FUSIBLES O DISYUNTOR
L1
L2
INTERRUPTOR DE PRESIÓN
U OTRO CONTROL
L1 CT1 CT2 L2 IN L2 OUT
CT
L1INT. L2 AMAR LK ROJO
CAJA DE CONTROL DE LUJO
A BOMBA
BOMBA
MOTOR DE
LA BOMBA
PUMPSAVER 111 / 233
PUMPSAVER 111 / 233
L1 L2
TIERRA
DESCONECTOR CON
FUSIBLES O
DISYUNTOR
L1
L2
TIERRA
SE PUEDE INSTALAR EL INTERRUPTOR
DE PRESIÓN ANTES DEL PUMPSAVER
CUANDO NO SE REQUIERA
PROTECCIÓN DE CICLO RÁPIDO
INTERRUP
PRESIÓN U
CONTROL
TOR DE
OTRO
PUMPSAVER
L1
ENTRADA
L1
L2
TIERRA
L1
L1
A MOTOR O CAJA DE CONTROL
111 / 233
L1
ENTRADASALIDA
CAJA DE CONTROL
DE LUJO
L2
L2
SALIDA
TIERRA
L2
TIERRA
L2
37
Page 38

CENTRIPRO TRIFÁSICO, 4", DATOS DEL MOTOR
EFICACIA, GRADO DEL EMPUJE, FUSIBLE/CORTA-CIRCUITO, CÓDIGOS DEL KVA
No. de.
Modelo
HP
Voltios
Eficacia %
F.L. S.F.
Grado
del
em-
puje
Codi-
KVA
go
Fusible
estándar
El NEC
de las
reuniones
máximo
basó FLA
M05430 0.5
M07430 0.75 69 74 R 15 15 10 15 10 15
M10430 1 66 70 M 15 20 10 10 10 15
M15430 1.5 72 74 L 20 25 10 15 15 20
M20430 2 74 75
M30430 3 77 77 K 35 40 20 25 30 35
M50430 5 76 76
M75430 7.5 74 74 J 80 90 50 60 70 80
M05432 0.5
M07432 0.75 66 71 R 6 15 6 10 6 10
M10432 1 69 72 M 10 15 6 10 10 15
M15432 1.5 75 76 K 15 20 10 15 15 20
M20432 2 75 75
M30432 3 77 77 J 25 35 15 20 25 30
M50432 5 76 76
M75432 7.5 75 75 J 70 80 45 50 60 70
M05434 0.5
M07434 0.75 69 73 R 3 10 6 6 3 6
M10434 1 65 69 M 6 10 3 6 6 10
M15434 1.5 72 73 K 10 10 6 6 6 10
M20434 2 74 75
M30434 3 76 77 J 15 20 10 10 15 15
M50434 5 77 77
M75434 7.5 76 76 L 40 50 25 30 30 35
M100434 10 79 80 K 45 60 25 35 35 45
M15437 1.5
M20437 2 78 78
M30437 3 78 78 J 10 15 10 10 10 15
M50437 5 74 75
M75437 7.5 77 77 J 25 35 20 20 25 30
62 68
700 #
200
900 #
1500 #
61 68
700 #
230
900 #
1500 #
61 68
700 #
460
73 74 700 # J 6 10 3 6 6 10
575
900 #
1500 #
900 #
1500 #
R 10 15 6 10 10 10
K 25 30 15 20 20 25
J 60 70 35 40 50 60
R 6 10 6 6 6 10
K 15 25 15 15 20 20
J 45 60 30 35 40 45
R 3 6 3 3 3 6
L 15 15 6 10 10 10
J 25 30 15 20 15 25
M 10 10 6 6 10 10
M 20 25 15 15 20 20
El valor
basó
SFA
Fusible de
DE-TD
El NEC
de las
reuniones
basó FLA
El valor
máximo
basó
SFA
Corta-circuito
El NEC
El valor
de las
máximo
reuniones
basó FLA
basó
SFA
38
Page 39

DATOS DEL MOTOR DE 4" TRIFÁSICO
DATOS DEL MOTOR DE 4" TRIFÁSICO
DATOS ELÉCTRICOS, 60 HZ, 3450 RPM
DATOS ELÉCTRICOS, 60 HZ, 3450 RPM
Carga plena Factor de servicio
No. de
Modelo bloqueado línea
M05430 0.5 0.37 1.6 2.9 600 3.4 870 22 4.1 - 5.2
M07430 0.75 0.55 1.5 3.8 812 4.5 1140 32 2.6-3.0
M10430 1 0.75 1.4 4.6 1150 5.5 1500 29 3.4-3.9
M15430 1.5 1.1
M20430 2 1.5 1.25 7.5 2015 8.8 2490 51 1.4-2.0
M30430 3 2.2 1.15 10.9 2890 12.0 3290 71 0.9-1.3
M50430 5 3.7 1.15 18.3 4850 20.2 5515 113 0.4-0.8
M75430 7.5 5.5 1.15 27.0 7600 30.0 8800 165 0.5-0.6
M05432 0.5 0.37 1.6 2.4 610 2.9 880 17.3 5.7 - 7.2
M07432 0.75 0.55 1.5 3.3 850 3.9 1185 27 3.3 - 4.3
M10432 1 0.75 1.4 4.0 1090 4.7 1450 26.1 4.1-5.1
M15432 1.5 1.1
M20432 2 1.5 1.25 6.5 1990 7.6 2450 44 1.8-2.4
M30432 3 2.2 1.15 9.2 2880 10.1 3280 58.9 1.3-1.7
M50432 5 3.7 1.15 15.7 4925 17.5 5650 93 .85-1.25
M75432 7.5 5.5 1.15 24 7480 26.4 8570 140 .55-.85
M05434 0.5 0.37 1.6 1.3 610 1.5 875 9 23.6 - 26.1
M07434 0.75 0.55 1.5 1.7 820 2.0 1140 14 14.4 - 16.2
M10434 1 0.75 1.4 2.2 1145 2.5 1505 13 17.8 - 18.8
M15434 1.5 1.1
M20434 2 1.5 1.25 3.3 2018 3.8 2470 23 8.0 - 8.67
M30434 3 2.2 1.15 4.8 2920 5.3 3320 30 5.9-6.5
M50434 5 3.7 1.15 7.6 4810 8.5 5530 48 3.58-4.00
M75434 7.5 5.5 1.15 12.2 7400 13.5 8560 87 1.9-2.3
M100434 10 7.5 1.15 15.6 9600 17.2 11000 110 1.8-2.2
M15437 1.5 1.1 1.3 2.0 1520 2.4 1950 11.5 19.8-20.6
M20437 2 1.5 1.25 2.7 1610 3.3 2400 21 9.4-9.7
M30437 3 2.2 575 1.15 3.7 2850 4.1 3240 21.1 9.4-9.7
M50437 5 3.7 1.15 7.0 5080 7.6 5750 55 3.6-4.2
M75437 7.5 5.5 1.15 9.1 7260 10.0 8310 55 3.6-4.2
HP kW Voltios SF Amps Vatios Amps Vatios
1.3 6.3 1560 7.2 1950 40 1.9-2.5
200
1.3 5.2 1490 6.1 1930 32.4 2.8-3.4
230
1.3 2.8 1560 3.2 1980 16.3 12.3 - 13.1
460
Amperaje Línea –
del Rotor Resistencia
39
Page 40

CUADRO DE CABLE DEL MOTOR DE 4” TRIFÁSICO
CUADRO DE CABLE DEL MOTOR DE 4” TRIFÁSICO
Largos de conductores de motor – Motores trifásicos - Con base en amperes de
factor de servicio, temperatura ambiente 30°C y caída de tensión del 5%
Clasificación de motor 60°C y 75°C aislamiento - tamaño de cable de cobre AWG
Voltios HP kW FLA SFA 14 12 10 8 6 4 3 2 1 1/0 2/0 3/0 4/0
.5 .37 3.8 2.9 657 1045 1667 2641 4109
.75 .55 3.8 4.5 423 674 1074 1702 2648
1 .75 4.6 5.5 346 551 879 1392 2166 3454 4342
1.5 1.1 6.3 7.2 265 421 672 1064 1655 2638 3317
200
2 1.5 7.5 8.8 217 344 549 870 1354 2158 2714 3427 4317 5449
3 2.2 10.9 12.0 159 253 403 638 993 1583 1990 2513 3166 3996
5 3.7 18.3 20.2 94 150 239 379 590 940 1182 1493 1881 2374 2995 3781 4764
7.5 5.5 27.0 30.0 64 101 161 255 397 633 796 1005 1266 1598 2017 2546 3207
.5 .37 2.4 2.9 756 1202 1917 3037 4725 7532 9469
.75 .55 3.3 3.9 562 894 1426 2258 3513 5601 7041 8892
1 .75 4 4.7 466 742 1183 1874 2915 4648 5843 7379
1.5 1.1 5.2 6.1 359 571 912 1444 2246 3581 4502 5685 7162 9040
230
2 1.5 6.5 7.6 288 459 732 1159 1803 2874 3613 4563 5748 7256 9155
3 2.2 9.2 10.1 217 345 551 872 1357 2163 2719 3434 4326 5460 6889 8696 10956
5 3.7 15.7 17.5 318 503 783 1248 1569 1982 2496 3151 3976 5019 6323
7.5 5.5 24 26.4 334 519 827 1040 1314 1655 2089 2635 3327 4192
.5 .37 1.3 1.5 2922 4648 7414
.75 .55 1.7 2.0 2191 3486 5560 8806
1 .75 2.2 2.5 1753 2789 4448 7045
1.5 1.1 2.8 3.2 1370 2179 3475 5504
460 2 1.5 3.3 3.8 1153 1835 2926 4635 7212
3 2.2 4.8 5.3 827 1315 2098 3323 5171
5 3.7 7.6 8.5 516 820 1308 2072 3224 5140
7.5 5.5 12.2 13.5 325 516 824 1305 2030 3236 4068 5138 6472
10 7.5
1.5 1.1 2.0 2.4 2283 3631 5792
2 1.5 2.7 3.3 1660 2641 4212 6671
575 3 2.2 3.7 4.1 1336 2126 3390 5370
5 3.7 7.0 7.6 721 1147 1829 2897 4507
7.5 5.5 9.1 10.0 548 871 1390 2202 3426
40
Page 41

Datos técnicos
Datos técnicos
LECTURAS DE RESISTENCIA DEL AISLAMIENTO DEL MOTOR
Lecturas normales en ohmios/megaohmios, TODOS los motores, entre todos
los conductores y tierra
PRECAUCIÓN
Para realizar la prueba de resistencia de aislamiento, abra el
cortacircuitos y desconecte todos los conductores de la caja
de control QD o del interruptor por caída de presión. Conecte un conductor
del ohmímetro a cualquier conductor del motor y otro a un tubo de bajada de
metal o a una tierra adecuada. Escala R x 100K
Condición del motor y los conductores Valor en OHMIOS Valor en Megaohmios
Motor nuevo, sin cable de alimentación 20,000,000 (o más) 20.0
Motor usado, el cual puede reinstalarse en el pozo 10,000,000 (o más) 10.0
Motor en el pozo – lecturas del cable de alimentación más el motor
Motor nuevo 2,000,000 (o más) 2.0
El motor está en relativamente buenas condiciones de 500,000 a 2,000,000 0.5 – 2.0
El motor podría estar dañado o con cable
de alimentación dañado de 20,000 a 500,000 0.02 – 0.5
No retire el motor por estas razones
Motor definitivamente dañado o con cable
de alimentación dañado de 10,000 a 20,000 0.01 – 0.02
Retire y repare el motor
Falla del motor o del cable de alimentación
Retire y repare el motor
Operación del generador
Operación del generador
PELIGRO
SI NO SE USA UN INTERRUPTOR DE TRANSFERENCIA MANUAL
menos de 10,000 0 – 0.01
O AUTOMÁTICO CUANDO EL GENERADOR SE UTILIZA COMO
UNIDAD DE RESERVA, SE PUEDE PRODUCIR ELECTROCHOQUE,
QUEMADURAS O LA MUERTE. LOS DATOS DE DOS HILOS SON
La tensión peligrosa
puede causar choques,
quemaduras o
la muerte.
Clasificación mínima del generador
Regulado externamente Regulado internamente
Motor HP KW KVA KW KVA
0,5 2,5 3,1 1,8 2,2
0,75 3,5 4,4 2,5 3,1
1 5 6,3 3,2 4
1,5 6 7,5 4 5
0,5 2 2,5 1,5 1,9
0,75 3 3,8 2 2,5
1 4 5 2,5 3,2
1,5 5 6,3 3 3,8
2 7,5 9,4 4 5
3 10 12,5 5 6,3
5 15 18,8 7,5 9,4
7,5 20 25 10 12,5
10 30 37,5 15 18,8
SOLO PARA MOTORES DEL TIPO PSC; 2 CABLES CON FASE DIVIDIDA
DEBEN SER UN 50% MÁS GRANDES QUE LA CLASIFICACIÓN DE
GENERADOR DE 3 HILOS.
2 hilos
1Ø
Solo PSC
3 hilos
1Ø o 3
41
Page 42

ARRANCADORES TRIFÁSICOS DEL PROPÓSITO DEFINIDO
CON SOBRECARGAS AJUSTABLES
Orden de
CentriPro no.
DP25D2 A27CGC25BA2P4
DP25E2 A27CGC25BA004 E 2.4-4
DP25F2 A27CGC25BA006 F 4-6
DP25G2 A27CGC25BA010 G 6-10
DP25H2 A27CGC25BA016 H 10-16
DP25J2 A27CGC25BA024 J 16-24
DP25C4 A27CGC25CA1P6
DP25D4 A27CGC25CA2P4 D 1.6-2.4
DP25E4 A27CGC25CA004 E 2.4-4
DP25F4 A27CGC25CA006 F 4-6
DP25G4 A27CGC25CA010 G 6-10
DP25H4 A27CGC25CA016 H 10-16
DP25J4 A27CGC25CA024 J 16-24
DP25E5 A27CGC25DA004
DP25F5 A27CGC25DA006 F 4-6
DP25G5 A27CGC25DA010 G 6-10
DP25H5 A27CGC25DA016 H 10-16
DP30L2 A27CGE30BA010
DP30M2 A27CGE30BA016 M 10-16
DP30N2 A27CGE30BA024 N 16-24
DP30P2 A27CGE30BA040 P 24-40
DP30L4 A27CGE30CA010
DP30M4 A27CGE30CA016 M 10-16
DP30N4 A27CGE30CA024 N 16-24
DP30P4 A27CGE30CA040 P 24-40
DP30L5 A27CGE30DA010
DP30M5 A27CGE30DA016 M 10-16
DP30N5 A27CGE30DA024 N 16-24
DP30P5 A27CGE30DA040 P 24-40
DP30R5 A27CGE30DA057 R 40-57
DP40L2 A27CGE40BA010
DP40M2 A27CGE40BA016 M 10-16
DP40N2 A27CGE40BA024 N 16-24
DP40P2 A27CGE40BA040 P 24-40
DP40L4 A27CGE40CA010
DP40M4 A27CGE40CA016 M 10-16
DP40N4 A27CGE40CA024 N 16-24
DP40P4 A27CGE40CA040 P 24-40
DP40L5 A27CGE40DA010
DP40M5 A27CGE40DA016 M 10-16
DP40N5 A27CGE40DA024 N 16-24
DP40P5 A27CGE40DA040 P 24-40
Número de refer-
encia de Eaton
Máximo
amperios
25 208-230
25 460
25 575
30 208-230
30 460
30 575
40 208-230
40 460
40 575
Voltaje de
fuente
O.L.
Rango de la
Relevo
sobrecarga
D 1.6-2.4
C 1-1.6
E 2.4-4
L 6-10
L 6-10
L 6-10
L 6-10
L 6-10
L 6-10
42
Máximo
LRA
típico de HP
150 .5 - 5
125 .5 - 10
100 1.5 - 10
180 1.5 - 7.5
150 5 - 20
120 5 - 15
240 1.5 - 10
200 5 - 20
160 5 - 20
Rango
Page 43

Identificación y resolución de problemas
Identificación y resolución de problemas
PELIGRO
DESCONECTE Y BLOQUEE LA CORRIENTE ELÉCTRICA
ANTES INTENTAR DAR SERVICIO. DE LO CONTRARIO, SE
PUEDE PRODUCIR ELECTROCHOQUE, QUEMADURAS O LA
La tensión peligrosa
puede causar choques,
quemaduras o
la muerte.
MUERTE.
Síntoma Causa probable Acción recomendada
EL MOTOR DE
LA BOMBA NO
ESTÁ
FUNCIONADO
1. Se disparó el protector térmico del
motor
a. Caja de control incorrecta
b. Conexiones eléctricas incorrectas
o defectuosas
c. Protector térmico defectuoso
d. Baja tensión
e. La temperatura ambiente de
la caja de control/arrancador es
demasiado alta
f. La bomba está atascada con
materias extrañas
g. Sumersión inadecuada
2. Cortacircuitos abierto o fusible
quemado
3. La fuente de energía es inadecuada
para la carga
4. Daño del aislamiento del cable de
alimentación
5. Empalme defectuoso del cable de
alimentación
LA BOMBA
ENTREGA POCO
O NADA DE
1. Válvula de retención defectuosa o
instalada incorrectamente
2. La bomba está atascada con aire
LÍQUIDO
3. Elevación demasiado alta para la
bomba
4. La bomba está atascada con materias
extrañas
5. La bomba no está completamente
sumergida
6. El pozo contiene demasiado aire o
gases
7. Desgaste excesivo de la bomba
8. Rotación incorrecta del motor – uni-
dades trifásicas únicamente.
1. Deje que el motor se enfríe, el protector
térmico se reposicionará
automáticamente
a – e. Solicite que un electricista
calificado inspeccione y repare,
según sea requerido.
f. Retire la bomba, límpiela, ajústela,
fije la profundidad según sea
requerido
g. Confirme la sumersión adecuada de
la unidad en el agua bombeada
2. Solicite que un electricista calificado
inspeccione y repare, según
sea requerido.
3. Verifique el suministro o
la capacidad del generador
4 – 5. Solicite que un electricista califi-
cado inspeccione y repare, según sea
requerido.
1. Inspeccione la válvula de retención,
repárela según sea necesario
2. Arranque y detenga la bomba sucesiva-
mente hasta que haya flujo
3. Verifique el rendimiento de la unidad,
consulte con agente
4. Retire la bomba, límpiela ajústela, fije la
profundidad según sea requerido
5. Verifique la recuperación del pozo, baje
la bomba si es posible
6. Si los arranques y paradas sucesivos
no solucionan el problema, el pozo
contiene demasiado aire o gases
7. Retire y repare la bomba, según sea
necesario
8. Invierta dos conductores eléctricos
cualesquiera del motor
43
Page 44

MANUEL D'UTILISATION
IM116R04
Pompes submersibles
de 4 po
DIRECTIVES D’INSTALLATION, D’UTILISATION ET D’ENTRETIEN
44
Page 45

Informations pour le
Informations pour le
propriétaire
propriétaire
Nº de modèle de la pompe :
Nº de série de la pompe :
Nº de modèle du moteur :
Nº de série du moteur :
Détaillant :
Nº de téléphone du détaillant :
Date d’achat :
Date d’installation :
Tension (V) :
Intensité (A) :
Table des matières
Table des matières
SUJET PAGE
Consignes de sécurité ....................46
Protection de la pome ....................47
Préparatifs d’installation ................ 48
1. Installations types ...................... 49
2. Tuyauterie et réservoir ............... 50
3. Alimentation électrique,
câblage et jonction ...................52
4. Connexion de la boîte de
commande et du pressostat ....... 53
5. Mise en service de la pompe ......56
6. Documentation et manuel ......... 56
Données sur les moteurs
CentriPro de 1 Ø, de 4 po .......... 57
Calibres de fil des moteurs
CentriPro de 1 Ø, à 2 ou 3 fils ...58
PumpSaver .....................................58
Schémas de câblage ...................19-20
Données sur les moteurs CentriPro
de 3 Ø, 60 Hz .......................59-60
Longueur maximale des câbles
de moteur de 3 Ø ....................... 61
Données techniques .......................62
Valeurs de résistance d'isolement
du moteur .................................. 62
Utilisation d'une génératrice .......... 63
Démarreurs triphasés .....................64
Diagnostic de anomalies ................ 65
Garantie limitée ............................. 67
45
Page 46

AVERTISSEMENT
AVERTISSEMENT
AVERTISSEMENT
CONSIGNES DE SÉCURITÉ
AVERTISSEMENT
AFIN DE PRÉVENIR LES BLESSURES GRAVES OU MORTELLES ET LES
DOMMAGES MATÉRIELS IMPORTANTS, SUIVRE CHAQUE CONSIGNE DE
SÉCURITÉ FIGURANT DANS LE MANUEL ET SUR LA POMPE.
LE PRÉSENT MANUEL A POUR BUT DE FACILITER L’INSTALLATION ET
L’UTILISATION DE LA POMPE ET DOIT ÊTRE CONSERVÉ PRÈS DE CELLE-CI.
Le symbole ci-contre est un SYMBOLE DE SÉCURITÉ
employé pour signaler les mots-indicateurs dont on trouvera
la description ci-dessous. Sa présence sert à attirer l’attention
afin d’éviter les blessures et les dommages matériels.
DANGER
AVERTISSEMENT
ATTENTION
AVIS : SERT À ÉNONCER LES DIRECTIVES SPÉCIALES DE
GRANDE IMPORTANCE QUE L’ON DOIT SUIVRE.
LIRE SOIGNEUSEMENT CHAQUE DIRECTIVE ET AVERTISSEMENT
AVANT D’EFFECTUER TOUT TRAVAIL SUR LA POMPE.
N’ENLEVER AUCUNE DÉCALCOMANIE DE SÉCURITÉ.
Avis important : lire les consignes de sécurité avant de procéder au câblage.
du code provincial ou national de l’électricité pertinent et les règlements locaux. Adresser toute question relative au code à un inspecteur en électricité.
Le non-respect du code et des politiques de santé et de sécurité au travail
peut entraîner des blessures et des dommages matériels. L’inobservation des
directives d’installation fournies par le fabricant peut se traduire par un choc
électrique, un incendie, des blessures ou la mort, ainsi que par des dommages matériels, des performances non satisfaisantes et l’annulation de la
garantie du fabricant.
Aérer le puits selon les codes locaux. La plaque signalétique de la pompe et
les feuillets du catalogue de pompes listent les organismes de normalisation.
Le protecteur thermique de certains moteurs coupe le courant lorsqu'il y a
surcharge thermique et le rétablit automatiquement, redémarrant ainsi la
pompe inopinément.
de ne pas l'endommager, annuler la garantie ni constituer un grave danger.
Prévient des risques qui VONT causer des blessures graves,
la mort ou des dommages matériels importants.
Prévient des risques qui PEUVENT causer des blessures
graves, la mort ou des dommages matériels importants.
Prévient des risques qui PEUVENT causer des blessures ou
des dommages matériels.
L’installation électrique doit être entièrement effectuée par
un technicien qualifié. Il faut toujours suivre les prescriptions
Les pompes standard ne sont pas conçues pour les piscines,
l'eau libre, les liquides dangereux ni les gaz inflammables.
Verrouiller la source de courant en position hors circuit
avant l’installation ou l’entretien des dispositifs électriques.
Pour le système et le réservoir, ne jamais utiliser une pression
excédant la pression nominale maximale de ce dernier, afin
46
Page 47

ATTENTION
AVERTISSEMENT
Protéger le réservoir des éclaboussures et des excès d'humidité
DANGER
ATTENTION
AVERTISSEMENT
AVERTISSEMENT
AVERTISSEMENT
AVERTISSEMENT
AVERTISSEMENT
AVERTISSEMENT
AVERTISSEMENT
ATTENTION
ATTENTION
AVERTISSEMENT
pour prévenir la corrosion et les risques. Lire les étiquettes du
réservoir et le manuel pour plus de détails.
Ne pas lever, transporter ni suspendre la pompe par le câble
d’alimentation : l’endommagement du câble pourrait causer
un choc électrique, des brûlures ou la mort.
N’utiliser que du fil de cuivre torsadé pour l’alimentation et la
mise à la terre du moteur et de la pompe. Le calibre du fil de
terre doit être au moins égal à celui des fils d’alimentation. Les fils devraient
tous être chromocodés pour faciliter l’entretien et le diagnostic des anomalies.
Poser le fil de terre et les autres fils suivant les prescriptions
du code provincial ou national de l’électricité pertinent et les
règlements locaux.
Installer un sectionneur tout conducteur si le code l’exige.
Le nombre de phases et la tension d’alimentation doivent
convenir à tout l’équipement. Un nombre de phases et une
tension inappropriés annulent la garantie et peuvent causer un incendie et des
dommages au moteur et aux commandes.
Chaque jonction de fils doit être étanche. Si l’on emploie un
nécessaire de jonction (« kit »), suivre les directives du fabricant.
Choisir la boîte de jonction du type et de la classe NEMA
convenant au type et au lieu d’utilisation. La boîte doit assurer
une jonction de fils sûre et étanche.
Pour que la pompe fonctionne correctement, en immerger le
clapet de non-retour à une profondeur minimale de 5 pi.
Omettre la mise à la terre permanente de la pompe, du
moteur et des commandes avant le branchement à la source de
courant peut causer un choc électrique, des brûlures ou la mort.
Les commandes triphasées des pompes submersibles doivent
assurer une protection rapide de classe 10 contre la surcharge.
Pour bien refroidir tout moteur de 4 po de 2 hp et plus,
s’assurer que la vitesse d’écoulement minimale de l’eau autour
du moteur est de 0,25 pi/s (7,62 cm/s). Donc, le débit minimal nécessaire au
refroidissement du moteur en fonction du calibre du tubage devrait être :
1,2 gal US/min pour 4 po ; 7 pour 5 po ; 13 pour 6 po ; 20 pour 7 po ;
30 pour 8 po et 50 pour 10 po.
Si une pompe de 2 hp et plus est utilisée dans un grand réser-
voir, on devrait la placer dans un manchon d’accélération pour
obtenir la vitesse d’écoulement ou le débit nécessaires au bon refroidissement
du moteur.
La pompe submersible de 4 po a été évaluée pour le pompage
de l’eau seulement.
PROTECTION DE LA POMPE — La protection PumpSaver de SymCom est recommandée contre les : bas niveau d'eau, fonctionnement cyclique rapide, débit
restreint ou nul, surtension, sous-tension et surintensité.
47
Page 48

PRÉPARATIFS D’INSTALLATION
• Inscrire en deuxième page les informations pour le propriétaire au sujet de la
pompe, du moteur, etc.
• Inspecter tous les composants pour s’assurer qu’ils n’ont pas été endommagés
durant le transport. S’ils l’ont été, en aviser le distributeur immédiatement.
• Vérier si la puissance du moteur (en hp) convient à la pompe.
• S’assurer que la tension d’alimentation et le nombre de phases sont appropriés
au moteur et aux commandes.
• Installer les commandes dans un endroit sec et ombragé.
• Effectuer la jonction des ls immergés ou enfouis avec des connecteurs étanches.
• Étant donné que la tête de refoulement de la plupart des pompes est vissée à
gauche, immobiliser la tête et non la pompe pour éviter de dévisser la tête au
moment d’y fixer le tuyau ou le raccord-adaptateur.
• S’assurer que tous les raccords et accessoires de plomberie sont bien serrés et
étanchés avec du ruban de Téflon.
• Vérier si la pression nominale de la tuyauterie est supérieure à la pression
d’arrêt de la pompe.
• Si la pression du système peut dépasser 75 lbf/po2, poser une soupape de
décharge. La pression ne peut excéder la pression nominale max. du réservoir.
• L'emplacement du réservoir et de la commande en un lieu protégé des pluies
acides, de l'air salin et des éclaboussures peut en augmenter la durée.
• Pour empêcher le cliquetis répétitif du pressostat, ne pas le poser à plus de
4 pi du réservoir à pression.
• Régler la pression de l’air précomprimé du réservoir à 2 lbf/po
2
de moins que
la pression de démarrage de la pompe, soit à 28 lbf/po2 pour une plage de
pression de service de 30 à 50 lbf/po2 par exemple.
• L'emplacement du réservoir et de la commande en un lieu protégé des pluies
acides, de l'air salin et des éclaboussures peut en augmenter la durée.
• Placer la pompe à au moins 10 pi du fond du puits pour prévenir l’aspiration de
sédiments et de débris.
• S’assurer que le disjoncteur principal ou le sectionneur sont HORS circuit avant
de câbler les composants.
• Le câblage devrait être effectué uniquement par un technicien qualié.
• Le câblage et la mise à la terre doivent être conformes au code provincial ou
national pertinent et aux règlements locaux.
• Diminuer la section de passage du tuyau avec un robinet à tournant sphérique
ou à soupape ouvert à peu près au tiers (1⁄3) avant de mettre la pompe en
marche pour la première fois.
• Ouvrir un robinet de puisage ou de vidange au moment du démarrage de la
pompe pour purger l’eau sale afin qu’elle ne puisse entrer dans le réservoir.
• Mettre le disjoncteur principal ou le sectionneur EN circuit.
• Faire fonctionner la pompe durant quelques cycles pour vérier le
fonctionnement du pressostat.
• Vérier l’intensité (A) du courant et l’inscrire en deuxième page.
• Remettre le manuel au propriétaire ou le laisser près de la pompe.
48
Page 49

1. INSTALLATIONS TYPES
1. INSTALLATIONS TYPES
INSTALLATION À RÉSERVOIR À AIR CAPTIF
AVIS : ON DOIT UTILISER LA VALVE À AIR COMPRIMÉ SITUÉE SUR LE
DESSUS DU RÉSERVOIR POUR RÉGLER LA PRESSION D’AIR DE CELUI-CI.
Alimentation électrique protégée
Adaptateur
de tête de puits①
Clapet de nonretour①
Ligne de gel
① Dans les installations munies d’un adaptateur de tête de puits, le
Vers la tuyauterie de la maison
Sectionneur
Robinet de sectionnement
Raccord union
Pressostat (manostat)
Soupape de décharge
Robinet de vidange
Té
Clapet de non-retour②
clapet de non-retour supérieur devrait être en amont de (avant)
l’adaptateur et non près du réservoir, afin de maintenir l’adaptateur
sous pression.
② Dans les installations à joint de puits ou à fosse d’aspiration, il est
permis de poser le clapet de non-retour près du réservoir.
Figure 1
INSTALLATION À RÉSERVOIR GALVANISÉ
Sectionneur
Boîte de commande
Alimentation électrique protégée
Manomètre
Vers la tuyauterie
de la maison
Adaptateur de tête
de puits
Raccord de vidange
en Y
Figure 2
Robinet de sectionnement
Raccord union
Robinet de vidange
Soupape de décharge
Commande d’échappement d’air
Pressostat (manostat)
Clapet de non-retour à reniflard
Raccord
union
Position approx. du raccord de vidange en Y
Distance entre le raccord en Y
Volume total du réservoir
159 L (42 gal US) 2,1 m (7 pi)
310 L (82 gal US) 3 m (10 pi)
454 L (120 gal US) 4,6 m (15 pi)
833 L (220 gal US) 4,6 m (15 pi)
1 192 L (315 gal US) 6,1 m (20 pi)
1 987 L (525 gal US) 6,1 m (20 pi)
et le clapet de non-retour
49
Page 50

2. Tuyauterie et réservoir
DANGER
2. Tuyauterie et réservoir
Avis : la tête de refoulement de la
majorité des pompes submersibles de
4 po est vissée à gauche. Immobiliser
la pompe uniquement par la « tête de
refoulement » pour y fixer tout
raccord ou tuyau fileté.
ATTENTION
2.1. Généralités
Le calibre de la tuyauterie
de refoulement devrait être
Les pressions dangereuses
peuvent causer des
blessures et des
dommages matériels.
choisi pour permettre le
rendement optimal de
la pompe. Calculer la hauteur
manométrique totale en tenant
compte des divers calibres de tuyau
figurant dans les tables de perte de
charge. En règle générale, on choisit
le débit maximal selon le calibre :
10 gal US/min pour 1 po, 30 pour
1¼ po, 45 pour 1½ po et 80 pour
2 po. Si la tuyauterie est longue, il
vaut mieux accroître le calibre.
Étant donné que certaines pompes
produisent une pression de
refoulement très élevée, choisir le
tuyau en conséquence. Consulter un
fournisseur de tuyaux pour
déterminer le meilleur type de
tuyau pour chaque installation.
2.2. Réservoir à
pression,
pressostat et
soupape de
Ne pas placer le réservoir
en un lieu non protégé
du jet d'un système
d'irrigation, car il en
résulterait la corrosion
du réservoir et tôt ou
tard l'explosion de
celui-ci, pouvant causer
des dommages
matériels, de graves
blessures, voire la mort.
choisir un endroit sec où la température dépassera toujours 1 °C (34 °F) et
où aucune fuite ne pourra causer de
dommages matériels.
décharge
Pour l'installation du
réservoir, du pressostat et
de la soupape de décharge,
Pour empêcher le cliquetis répétitif
du pressostat, on devrait le poser près
du té du réservoir, mais jamais à plus
de 4 pi de celui-ci.
Ne poser entre le pressostat et le
réservoir ni robinet, ni clapet de nonretour, ni filtre, ni raccord produisant
une perte de charge (par frottement)
élevée. Par exemple, la perte de
charge d'un clapet à ressort de
1¼ po équivaut à une longueur de
tuyau additionnelle de 12 pi. Donc,
placer le clapet entre un réservoir et
un pressostat reviendrait à les écarter
de 12 pi de plus et à causer le cliquetis répétitif de ce dernier.
Dans les installations à réservoirs
multiples, on devrait poser le pressostat aussi près que possible du centre
des réservoirs. Afin de réduire la
hauteur équivalente de perte de
charge (par frottement) dans le tuyau
collecteur-répartiteur et d’empêcher
le pressostat de cliqueter à répétition,
on devrait employer un collecteurrépartiteur de calibre 1½ fois supérieur à celui du tuyau de refoulement
de la pompe.
Une soupape de décharge est requise
dans tout système ayant une pression supérieure à 100 lbf/po
2
ou
une HMT supérieure à 230 pi. Si
l'éjection de fluide par la soupape
peut causer des dommages, en relier
la sortie à un tuyau d'évacuation approprié avec une conduite.
50
Page 51

2.3. Réglage de la pression de
l’air précomprimé du
réservoir
S’assurer que le réservoir est vide.
Utiliser un manomètre de haute
qualité pour vérifier la pression de
l’air précomprimé du réservoir.
Celle-ci devrait être inférieure de
2 lbf/po2 à la pression de démarrage
de la pompe. Par exemple, elle serait
de 28 lbf/po2 dans un système dont la
pression de service est de 30 à
50 lbf/po2.
2.4. Tuyau de refoulement et
clapet de non-retour
Nota : la plupart des têtes de refoulement sont vissées à gauche. Pour fixer
un raccord ou un tuyau sur la pompe,
n'immobiliser celle-ci que par la tête
de refoulement pour ne pas desserrer
la pompe et risquer de l'abîmer au
démarrage.
Si le tuyau de refoulement requiert
un adaptateur, il est fortement
recommandé d’en poser un en inox.
Pour prévenir la corrosion galvanique, on ne devrait jamais fixer de
raccords, de tuyaux ni d’accessoires
de tuyauterie galvanisés directement
sur la tête de refoulement. À ce sujet,
aucun matériau de fabrication n’est
interdit pour les têtes de refoulement
en plastique ou en laiton. Les raccords à barbillons devraient toujours
être assujettis avec deux colliers de
serrage.
La tête de refoulement possède un
œil de fixation pour câble de sécurité.
Le câble est recommandé quand on
utilise un tuyau en polypropylène,
qui s'allonge lorsqu'il est sous pression ou plein d'eau.
2.5. Mise en place de
la pompe
Si l’on emploie un dispositif
antitorsion, le poser selon les
directives du fabricant du dispositif.
Pour plus de détails, consulter le
vendeur du dispositif.
Raccorder le tuyau de refoulement à
l’adaptateur ou à la tête de
refoulement de la pompe. Les raccords à barbillons devraient toujours
être assujettis avec deux colliers
de serrage. Poser un adaptateur
de tête de puits ou autre dispositif
du même type pour y raccorder le
tuyau de refoulement de la pompe.
S’adresser au fabricant ou au vendeur
de l’adaptateur ou du dispositif en
question pour obtenir les directives
d’installation pertinentes.
Avec du ruban isolant (chatterton)
étanche, fixer les fils d’alimentation
au tuyau de refoulement à tous les
10 pi. Les fournisseurs de pompes
vendent des attaches encliquetables à
cette fin.
2.6. Accessoires de tuyauterie
spéciaux pour systèmes à
réservoir galvanisé
Lorsque l’on utilise un réservoir
galvanisé, on devrait poser un
raccord de vidange en Y AV11 dans
le puits et un clapet de non-retour à
reniflard au réservoir. On permettra
ainsi l’entrée d’air dans le réservoir
pour empêcher le réservoir de trop
s’emplir d’eau. Poser une commande
d’échappement d’air AA4 sur le
réservoir pour en laisser sortir l’excès
d’air. La distance entre l'AV11 et
le clapet de non-retour à reniflard
détermine la quantité d’air admise à
chaque démarrage. Voir la distance
recommandée dans la figure 2.
51
Page 52

Si le puits dégage du gaz, il est pré-
DANGER
Les tensions dangereuses
peuvent causer un choc
électrique, des brûlures ou
la mort.
férable de munir le réservoir en acier
vitrifié ou galvanisé d’une commande
d’échappement d’air AA4 pour
évacuer le surplus d’air et en prévenir
le « jaillissement » du robinet.
On doit soumettre l’eau contenant du
méthane ou tout gaz explosif ou dangereux à un traitement spécial permettant d’éliminer le gaz en question
sans danger. À cet effet, consulter un
spécialiste du traitement de l’eau.
Quant aux puits alimentés par le
haut, il faudrait poser un manchon
d’accélération de l’écoulement de
l’eau autour de la pompe.
• Clapets de non-retour à ressort
vissés sur la tête de refoulement
— leur obturateur peut s’enlever
facilement de son moyeu à l’aide
d’une douille ou d’un tournevis à
douille de ½ po, que l’on introduit
par le haut.
• Clapets de non-retour internes en
plastique du type FlomaticMC à
ressort — ils doivent être enlevés
et requièrent donc le démontage
de la pompe.
• Clapets de non-retour intégrés en
plastique à tige accessible par le
haut de la tête de refoulement —
on peut les enlever en tirant sur
leur tige avec une pince.
2.7 Clapets de non-retour
Quatre types de clapets de nonretour sont utilisés. Ces clapets sont
recommandés pour empêcher le
liquide de redescendre dans la pompe
et de faire ainsi tourner le moteur
et la pompe en sens inverse, ce qui
en provoquerait l’usure prématurée
des roulements et des coussinets.
En outre, les clapets préviennent les
dommages dus aux coups de bélier
et aux poussées axiales. Un clapet de
non-retour supplémentaire devrait
être posé à tous les 200 pi sur le tronçon vertical du tuyau de refoulement.
Voir les textes 1 et 2 de la figure 1
pour les autres positions recommandées.
Si l'on veut mettre un clapet de nonretour hors service pour vidanger le
système, on devrait employer un
autre moyen, et ce, afin de prévenir
les dommages dus aux coups de
bélier et aux poussées axiales :
• Clapets de non-retour intégrés en
inox — ils possèdent une surface
plane que l’on peut facilement
perforer avec une perceuse
électrique et un foret de ¼ ou
de 3⁄8 po.
3. ALIMENTATION
3. ALIMENTATION
ÉLECTRIQUE,
ÉLECTRIQUE,
CÂBLAGE
CÂBLAGE
ET JONCTION
ET JONCTION
On doit toujours suivre les prescriptions du code provincial ou national
de l’électricité pertinent et les règlements locaux.
Il est suggéré de n'utiliser que du fil
de cuivre. En choisir le calibre à l'aide
des tables appropriées ci-dessous, du
manuel MAID (Motor Application
and Installation Data) ou du code
provincial ou national de l'électricité.
En cas de divergence, le code de
l'électricité pertinent prévaut.
3.1. Jonction du câble
d’alimentation aux fils de
moteur
Il est nécessaire que la jonction des
fils de moteur au câble d’alimentation
soit étanche. Le joint peut être
effectué avec une gaine isolante thermorétrécissables ou du ruban isolant
étanche.
52
Page 53

DANGER
Les tensions dangereuses
peuvent causer un choc
électrique, des brûlures ou
la mort.
A. Joints à gaine isolante
thermorétrécissable
Pour employer le nécessaire de
jonction type à gaines
thermorétrécissables : dénuder les
fils sur une longueur de ½ po (il vaut
mieux échelonner les joints), y enfiler
une gaine isolante (une par joint),
joindre les fils de moteur aux fils de
câble d’alimentation correspondants
avec un raccord à sertir, sertir les
extrémités de chaque raccord, puis
recouvrir celui-ci avec la gaine et
chauffer cette dernière à partir du
centre. Les gaines contiennent un
produit d’étanchéité et une colle dont
l’excédent sortira par les extrémités
de la gaine pendant son rétrécissement. L’ensemble forme un joint
étanche, très résistant.
B. Joints à ruban isolant étanche
a) Dénuder les fils sur une longueur
suffisante pour y poser un raccord
tubulaire (type préférable). Si le
raccord est trop mince, l’épaissir
en y enroulant du chatterton en
caoutchouc jusqu’à ce qu’il ait le
même diamètre que la gaine du fil.
b) Enrouler chaque joint de deux
couches de chatterton en
caoutchouc : enrouler le ruban de
façon aussi serrée que possible
pour empêcher la formation de
bulles d’air, la première couche
dépassant de deux pouces chaque
extrémité de la gaine isolante, et
la seconde, de deux pouces
chaque extrémité de la première
couche de chatterton.
c) Enrouler deux couches —
comme à l’étape b) précédente —
de chatterton Scotch nº 33 ou
l’équivalent sur le chatterton en
caoutchouc, chaque couche
dépassant la précédente d’au
moins deux pouces.
S’il s’agit d’un câble d’alimentation
trifilaire (à 3 fils) à gaine unique,
séparer chaque fil de façon à échelonner les joints, puis isoler ceux-ci avec
du ruban de la manière précitée.
L’épaisseur totale du ruban isolant ne
devrait pas être inférieure à celle de
la gaine du fil.
4. CONNEXION DE
4. CONNEXION DE
LA BOÎTE DE
LA BOÎTE DE
COMMANDE ET
COMMANDE ET
DU PRESSOSTAT
DU PRESSOSTAT
4.1. Pose de la boîte
de commande
Les boîtes de commande trifilaires
monophasées satisfont aux exigences UL relatives aux boîtiers du
type 3R. Elles peuvent être montées
à la verticale, à l’intérieur comme à
l’extérieur, et fonctionnent entre
– 10 et 50 ºC (14 et 122 ºF). Choisir
un endroit ombragé, sec et suffisamment dégagé pour permettre la
dépose du couvercle.
4.2. Vérification de la tension
et mise hors tension du
système
S’assurer que la tension d’entrée du
moteur et la tension d’alimentation
sont identiques.
Mettre le disjoncteur ou le sectionneur HORS circuit pour prévenir le
démarrage accidentel de la pompe
avant qu’elle soit prête à mettre en
service.
Les bobines de démarreur triphasé
sont très sensibles à la tension. On
doit donc toujours vérifier la tension
d’alimentation réelle avec un voltmètre.
Une basse ou une haute tension de
variation supérieure à ± 10 %
endommagera le moteur et les
commandes et n’est pas couverte par
la garantie.
53
Page 54

DANGER
Les tensions dangereuses
peuvent causer un choc
électrique, des brûlures ou
la mort.
4.3. Connexion des fils de
DANGER
Les tensions dangereuses
peuvent causer un choc
électrique, des brûlures ou
la mort.
moteur à la boîte de
commande, au pressostat
ou au démarreur
Mise en garde : ne pas
brancher l’appareil au
secteur ni mettre la pompe
en marche tant que les
connexions électriques
et hydrauliques n’ont pas
toutes été effectuées. S’assurer que
le disjoncteur ou le sectionneur
est HORS circuit avant de connecter les fils du pressostat à la source
d’alimentation électrique. Suivre
toutes les prescriptions du code
provincial ou national de l’électricité
pertinent. Employer un sectionneur
quand le code l’exige.
A. Moteurs monophasés à trois fils
Brancher les fils de moteur
chromocodés sur les bornes de la
boîte de commande comme suit : le
jaune sur Y, le rouge sur R, le noir
sur B et le vert (ou le fil dénudé) sur
la vis de terre (verte).
Connecter les fils reliant les bornes
« Charge » du pressostat aux bornes
L1 et L2 de la boîte de commande.
Relier la borne de terre du pressostat
à celle de la boîte de commande par
un fil de terre. Voir la figure 4 ou 5.
B. Moteurs monophasés à deux fils
Connecter les fils de moteur noirs
aux bornes « Charge » et le vert (ou le
fil dénudé) à la vis de terre (verte) du
pressostat. La PumpTec (F.E.) ne peut
servir avec les CentriPro à 2 fils. Utiliser une PumpSaver. Voir la figure 3.
C. Moteurs triphasés
Brancher les fils de moteur sur les
bornes T1, T2 et T3 du démarreur
triphasé. Connecter le fil de terre à la
borne de terre (dans le démarreur).
Pour brancher le pressostat, suivre les
directives du fabricant du démarreur
ou voir la figure 6.
4.4. Connexion à la source
d’alimentation
électrique
S’il s’agit d’une alimentation monophasée, finir
le câblage en reliant les
bornes « Ligne » du pressostat à celles du panneau de
disjoncteurs ou du sectionneur, selon
le cas.
Alimentation triphasée — relier les
bornes L1, L2, L3 et de terre du
démarreur à celles du sectionneur,
puis au panneau de disjoncteurs.
Dans les installations à moteur
triphasé, on doit vérifier si le moteur
tourne dans le bon sens et s’il y a
différence de phases. Pour inverser le
sens de rotation, intervertir deux fils
de moteur. Voir les directives de vérification du déséquilibre du courant
triphasé à 4.6. La non-vérification
de la différence de phases peut causer
la défaillance prématurée du moteur
et le déclenchement intempestif du
limiteur de surcharge. Si l’on emploie
une génératrice, voir les données
techniques sur son utilisation.
4.5 Protection contre la
surcharge en triphasé
Employer uniquement des protections contre la surcharge rapides de
classe 10 avec les moteurs submersibles triphasés. Voir les démarreurs
définis de but en ce manuel.
Si l'on a besoin d'aide pour choisir la
protection, s'adresser au fabricant de
la pompe.
54
Page 55

4.6. Déséquilibre du courant
triphasé
Un circuit d’alimentation électrique
entièrement triphasé est recommandé.
Il peut être constitué de trois
transformateurs distincts ou d’un
transformateur triphasé. On peut aussi
utiliser deux transformateurs montés
en étoile ou en triangle « ouverts »,
mais il est possible qu’un tel montage
crée un déséquilibre de courant se
traduisant par des performances médiocres, le déclenchement intempestif
du limiteur de surcharge et la
défaillance prématurée du moteur.
Vérifier l’intensité du courant sur
chacun des trois fils de moteur, puis
calculer le déséquilibre du courant.
Si le déséquilibre est de 2 % ou moins,
ne pas changer la connexion des fils.
S’il dépasse 2 %, on devrait vérifier
l’intensité du courant sur chaque
conducteur, dans les trois montages
possibles ci-dessous. Afin de maintenir le sens de rotation du moteur,
suivre l’ordre numérique indiqué
dans chaque montage pour la connexion des fils de moteur.
Pour calculer le pourcentage de
déséquilibre du courant :
A. Faire l’addition des trois intensi-
tés mesurées sur les conducteurs.
B. Diviser le total par 3 pour
obtenir l’intensité moyenne.
C. Prendre l’écart d’intensité le plus
grand par rapport à la moyenne.
D. Soustraire cet écart de la
moyenne.
E. Diviser la différence par la
moyenne, puis multiplier le
résultat par 100 pour obtenir le
pourcentage de déséquilibre.
Le déséquilibre de courant ne devrait
pas excéder 5 %. Si le déséquilibre
persiste en connectant les fils de
moteur dans l’ordre numérique
indiqué, on doit en trouver la cause
et l’éliminer. Si, dans les trois montages, l’écart d’intensité le plus grand
par rapport à la moyenne est toujours
mesuré sur le même conducteur, la
cause du déséquilibre vient surtout de
la source d’alimentation.
On s’adressera alors à la société
d’électricité pour rectifier le
déséquilibre de courant.
1er montage 2e montage 3e montage
Bornes de démarreur L1 L2 L3 L1 L2 L3 L1 L2 L3
Fils de moteur R B Y Y R B B Y R
T3 T1 T2 T2 T3 T1 T1 T2 T3
Exemples :
T3-R = 51 A T2-Y = 50 A T1-B = 50 A
T1-B = 46 A T3-R = 48 A T2-Y = 49 A
T2-Y = 53 A T1-B = 52 A T3-R = 51 A
Total = 150 A Total = 150 A Total = 150 A
÷3 = 50 A ÷3 = 50 A ÷3 = 50 A
– 46 A = 4 A – 48 A = 2 A – 49 A = 1 A
4 ÷50 = 0,08 ou 8 % 2 ÷50 = 0,04 ou 4 % 1 ÷50 = 0,02 ou 2 %
55
Page 56

5. MISE EN SERVICE
5. MISE EN SERVICE
DE LA POMPE
DE LA POMPE
ATTENTION
5.1 Pose d'un robinet et clarification de
l'eau
Les pressions dangereuses
peuvent causer des
blessures et des
dommages matériels.
ment un robinet à soupape ou à
tournant sphérique, l'entrouvrir au
tiers, pomper l'eau jusqu'à ce qu'elle
devienne plus claire, ouvrir le robinet
lentement pour vérifier le débit et,
une fois l'eau devenue limpide,
arrêter la pompe.
Déposer le robinet et raccorder le
tuyau de refoulement à la tuyauterie
de la maison, au réservoir à pression
et au pressostat. Faire fonctionner la
pompe durant quelques cycles pour
rincer l'intérieur du réservoir, vérifier
le bon fonctionnement de la pompe
et du pressostat et s'assurer que
tous les joints de la tuyauterie sont
étanches.
MISE EN GARDE : si le niveau
statique du puits est élevé, voir les
informations sur la protection de la
pompe à 5.2.
ATTENTION
Nouveau puits — Poser
sur le tuyau de refoule-
5.2. Étranglement
prévenant les
poussées axiales
Les pressions dangereuses
peuvent causer des
blessures et des
dommages matériels.
Tout puits ayant un niveau statique élevé peut entraîner le fonctionnement de la pompe en dehors
de la « plage de performances
recommandée ». Il est donc suggéré d’employer un réducteur de
débit Dole ou un robinet à tournant
sphérique pour étrangler la section
de passage du tuyau de refoulement et empêcher les dommages
à la pompe et au moteur dus aux
poussées axiales. On doit maintenir
le débit maximal dans la plage de
avec un niveau
statique élevé
fonctionnement recommandée de
la pompe. Si l’on utilise un robinet
à tournant sphérique, en régler
l’ouverture, en enlever la poignée
et l’attacher au tuyau avec du ruban
adhésif, puis fixer au robinet une
étiquette volante portant la mention :
« Ne pas ouvrir ce robinet, car cela
pourrait endommager la pompe. » La
manière la plus simple de « régler »
le débit est de remplir un contenant de 5 gallons US, de mesurer le
temps nécessaire à son remplissage,
puis de se baser sur ce temps pour
calculer le débit (en gal US/min). À
mesure que le niveau du puits baisse,
la hauteur de charge augmente,
réduisant le débit et neutralisant
l’effet d’étranglement pouvant altérer
les performances.
6. DOCUMENTATION
6. DOCUMENTATION
ET MANUEL
ET MANUEL
Remplir la section « Informations
pour le propriétaire » en deuxième
page, puis remettre le présent manuel
au propriétaire, ainsi qu’une carte
d’affaires. La pose d’un autocollant portant le nom et le numéro
de téléphone du détaillant sur le
réservoir ou la boîte de commande
est un excellent outil de promotion
des affaires !
Une nouvelle étiquette fournit les
informations sur la pompe. On peut
l'apposer au manuel ou à une boîte
de commande à 3 fils, ou bien la
placer près du réservoir ou du
pressostat.
56
Page 57

GÉNÉRATION II - À 2 FILS, 4 po DONNÉES
ÉLECTRIQUES MONOPHASÉ, 60 HERTZ, 3450 T/MN
À pleine charge
Type
(PSC)
No de
catalogue
M05421 0,5 0,37 115 1,6 7,9 910 9,8 1120 28 1,4-2,0 H
M05422 0,5 0,37 230 1,6 4,0 845 4,7 1050 16 6,1-7,2 J
2-
fils
M07422 0,75 0,55 230 1,5 5,0 1130 6,2 1400 18 5,9-6,9 F
M10422 1,0 0,75 230 1,4 6,7 1500 8,1 1800 24 4,2-5,2 F
M15422 1,5 1,1 230 1,3 9,0 2000 10,4 2350 43 1,8-2,4 H
hp kW V FS A W A W
Avec FS*
A avec
rotor
bloqué
Résistance
d'enroule-
ment
GÉNÉRATION II - À 3 FILS, 4 po DONNÉES
ÉLECTRIQUES MONOPHASÉ, 60 HERTZ, 3450 T/MN
À pleine charge
No de
Type
catalogue
3-fils
avec le
cadre
rapide
de
début
de con-
densa-
teur
3-fils
avec
CSCR
(CR) ou
boîte
de con-
trôle
mag-
nétique
de
con-
tacteur
(MC)
¹ Une boîte de contrôle de CSCR avec un suffixe de CR peut être remplacée par une fin magnétique de modèle de contacteur dans MC.
J = fil jaune, N = fil noir, R = fil rouge
hp kW V FS A W A W
1,6
J (8,8)
N (8,8)
R (0)
J (5,3)
N (5,3)
R (0)
J (6,6)
N (6,6
R (0)
J (8,1)
N (8,1)
R ( 0)
J (4,2)
N (4,1)
R (1,8)
J (4,8)
N (4,4)
R (2,5
J (6,1)
N (5,2)
R (2,7)
J (9,1)
N (8,2)
R (1,2)
J (9,9)
N (9,1)
R (2,6)
J (14,3)
N (12,0)
R (5,7)
J (24,0)
N (19,1)
R (10,2)
M05411 0,5 0,37 115 1,6
M05412 0,5 0,37
M07412 0,75 0,55 1,5
M10412 1,0 0,75 1,4
M05412 0,5 0,37 1,6
M07412 0,75 0,55 1,5
230
M10412 1,0 0,75 1,4
M15412 1,5 1,1 1,3
M20412 2 1,5 1,25
M30412 3 2,2 1,15
M50412 5 3,7 1,15
675
740
970
1215
715
940
1165
1660
2170
3170
5300
Avec FS*
J (10,9)
N (10,9)
R (0)
J (6,1)
N (6,1)
R (0)
J (7,8)
N (7,8)
R (0)
J (9,4)
N (9,4)
R (0)
J (4,8)
N (4,3)
R (1,8)
J (6,0)
N (4,9)
R (2,3)
J (7,3)
N (5,8)
R (2,6)
J (10,9)
N (9,4)
R (1,1)
J (12,2)
N (11,7)
R (2,6)
J (16,5)
N (13,9)
R (5,6)
J (27,0)
N (22,0)
R (10,0)
980 44
1050 21
1350 32
1620 41
960 21
1270 32
1540 41
2130 49
2660 49
3620 76
6030 101
A avec
rotor
bloqué
Résistance d'-
enroulement
Enroul.
Enroul.
princ.
démarr.,
N-J ()
R-J ()
1,0-
2,5-
1,4
3,1
5,1-
12,4-
6,1
13,7
2,6-
10,4-
3,3
11,7
2,0-
9,3-
2,6
10,4
1,0-
2,5-
1,4
3,1
5,1-
12,4-
6,1
13,7
2,6-
10,4-
3,3
11,7
2,0-
9,3-
2,6
10,4
1,6-
10,8-
2,2
12,0
1,1-
2,0-
1,4
2,5
,62-
1,36-
,76
1,66
Boîte de
requise
CB05412CR
CB07412CR
CB10412CR
CB15412CR
CB15412MC
CB20412CR
CB20412MC
CB30412CR
CB30412MC
CB50412CR
CB50412MC
Code
kV·A
comm.
CB05411
CB05412
CB07412
CB10412
or
or
or
or
1
57
Page 58

GÉNÉRATION II, MOTEURS À 2 FILS, RECOMMANDÉS LONGUEURS DE FIL DE SORTIE
Libéré pour vente en novembre/décembre 2011
Longueur des fils de moteur CentriPro CAP à 2 fils, fondée sur :
A avec facteur de surcharge, chute de tension de 5 % et température ambiante de 30 °C
Moteur Calibre AWG, fils en cuivre, isolation pour 60 °C et 75 °C
V hp kW FLA AFS 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 1/0 2/0 3/0 4/0
115 ½ 0,37 7,9 9,8 112 178 284 449 699 1114 1769 2814 3550 4481 5646
½ 0,37 4,0 4,7 466 742 1183 1874 2915 4648 7379 11733
¾ 0,55 5,0 6,2 353 562 897 1420 2210 3523 5594 8895 11222
230
1 0,75 6,7 8,1 271 430 686 1087 1692 2697 4281 6808 8590 10843
1½ 1,1 9,0 10,4 211 335 535 847 1318 2100 3335 5303 6690 8445
GÉNÉRATION II, 3-FILE=S, 4" 1Ø, RECOMMANDÉ LONGUEURS DE FIL
Longueur des fils de moteur CentriPro ICD à 3 fils, fondée sur :
A avec facteur de surcharge, chute de tension de 5 % et température ambiante de 30 °C
Moteur Calibre AWG, fils en cuivre, isolation pour 60 °C et 75 °C
V hp kW FLA AFS 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 1/0 2/0 3/0 4/0
115 ½ 0,37 8,8 10,9 101 160 255 404 629 1002 1591 2530 3192 4029 5076
½ 0,37 5,3 6,1 359 571 912 1444 2246 3581 5685 9040 - - -
¾ 0,55 6,6 7,8 281 447 713 1129 1757 2800 4446 7070 8920 - -
1 0,75 8,1 9,4 233 371 592 937 1458 2324 3689 5867 7402 - -
230
1½ 1,1 9,1 10,9 201 320 510 808 1257 2004 3182 5059 6383 - -
2 1,5 9,9 12,2 180 286 456 722 1123 1790 2843 4520 5703 - -
3 2,2 14,3 16,5 133 211 337 534 830 1324 2102 3342 4217 5323 -
5 3,7 24 27 - - 206 326 507 809 1284 2042 2577 3253 -
AFS = courant avec facteur de surcharge
PUMPSAVER 235
PUMPSAVER 235
TERRE L2 L1
DISJONCTEUR OU
SECTIONNEUR À
FUSIBLE(S)
L1
L2
PRESSOSTAT
OU AUTRE
COMMANDE
L1 CT1 CT2 L2 IN L2 OUT
TC
PR.L1 L2 JNR
BOÎTE DE COMMANDE DE LUXE
58
VERS POMPE
POMPE
MOTEUR
PUMPSAVER 111 / 233
PUMPSAVER 111 / 233
L1 L2
TERRE
DISJONCTEUR OU
SECTIONNEUR À
FUSIBLE(S)
L1
L2
PRESSOSTAT
OU AUTRE
COMMANDE
TERRE
PRESSOSTAT INSTALLABLE EN AMONT
DE LA PUMPSAVER SI PROTECTION NON
REQUISE CONTRE FONCTIONNEMENT
CYCLIQUE RAPIDE
PUMPSAVER
111 / 233
SORTIE
L2
L1
L1
ENTRÉE
ENTRÉE
L1
L2
TERRE
L1
PRESSOSTAT OU
AUTRE
COMMANDE
L1
VERS MOTEUR OU BOÎTE DE COMMANDE
SORTIE
L2
L2
L2
TERRE
TERRE
Page 59

CENTRIPRO TRIPHASÉ, 4 po, DONNÉES DE MOTEUR
EFFICACITÉ, ESTIMATION DE POUSSÉE, FUSIBLE/DISJONCTEUR, CODES DE KVA
Efficacité %
Modèle hp V F.L.
Facteur
de sur-
charge
Esti-
ma-
tion
de
pous-
sée
Code
kV·A
Fusible
standard
La NEC
de ras-
semble-
ments
a basé
La valeur
FLA
M05430 0,5
M07430 0,75 69 74 R 15 15 10 15 10 15
M10430 1 66 70 M 15 20 10 10 10 15
M15430 1,5 72 74 L 20 25 10 15 15 20
M20430 2 74 75
M30430 3 77 77 K 35 40 20 25 30 35
M50430 5 76 76
M75430 7,5 74 74 J 80 90 50 60 70 80
M05432 0,5
M07432 0,75 66 71 R 6 15 6 10 6 10
M10432 1 69 72 M 10 15 6 10 10 15
M15432 1,5 75 76 K 15 20 10 15 15 20
M20432 2 75 75
M30432 3 77 77 J 25 35 15 20 25 30
M50432 5 76 76
M75432 7,5 75 75 J 70 80 45 50 60 70
M05434 0,5
M07434 0,75 69 73 R 3 10 6 6 3 6
M10434 1 65 69 M 6 10 3 6 6 10
M15434 1,5 72 73 K 10 10 6 6 6 10
M20434 2 74 75
M30434 3 76 77 J 15 20 10 10 15 15
M50434 5 77 77
M75434 7,5 76 76 L 40 50 25 30 30 35
M100434 10 79 80 K 45 60 25 35 35 45
M15437 1,5
M20437 2 78 78
M30437 3 78 78 J 10 15 10 10 10 15
M50437 5 74 75
M75437 7,5 77 77 J 25 35 20 20 25 30
62 68
200
1500 #
61 68
230
1500 #
61 68
460
1500 #
73 74 700 # J 6 10 3 6 6 10
575
1500 #
R 10 15 6 10 10 10
700 #
K 25 30 15 20 20 25
900 #
J 60 70 35 40 50 60
R 6 10 6 6 6 10
700 #
K 15 25 15 15 20 20
900 #
J 45 60 30 35 40 45
R 3 6 3 3 3 6
700 #
900 #
900 #
L 15 15 6 10 10 10
J 25 30 15 20 15 25
M 10 10 6 6 10 10
M 20 25 15 15
maximale
a basé
SFA
Fusible de
DE-TD
La NEC
La valeur
de ras-
semble-
ments
a basé
FLA
maxi-
male
a basé
SFA
Disjoncteur
La NEC
La valeur
de ras-
maxi-
semble-
male
ments
a basé
a basé
FLA
20 20
SFA
59
Page 60

MOTEURS TRIPHASÉS DE 4 po
MOTEURS TRIPHASÉS DE 4 po
Données électriques — 60 Hz, 3 450 r/min
Données électriques — 60 Hz, 3 450 r/min
À pleine charge Avec FS*
Modèle hp kW V FS* A W A W
M05430 0,5 0,37 1,6 2,9 600 3,4 870 22 4,1 à 5,2
M07430 0,75 0,55 1,5 3,8 812 4,5 1 140 32 2,6 à 3,0
M10430 1 0,75 1,4 4,6 1 150 5,5 1 500 29 3,4 à 3,9
M15430 1,5 1,1
M20430 2 1,5 1,25 7,5 2 015 8,8 2 490 51 1,4 à 2,0
M30430 3 2,2 1,15 10,9 2 890 12,0 3 290 71 0,9 à 1,3
M50430 5 3,7 1,15 18,3 4 850 20,2 5 515 113 0,4 à 0,8
M75430 7,5 5,5 1,15 27 7 600 30,0 8 800 165 0,5 à 0,6
M05432 0,5 0,37 1,6 2,4 610 2,9 880 17,3 5,7 à 7,2
M07432 0,75 0,55 1,5 3,3 850 3,9 1 185 27 3,3 à 4,3
M10432 1 0,75 1,4 4,0 1 090 4,7 1 450 26,1 4,1 à 5,1
M15432 1,5 1,1
M20432 2 1,5 1,25 6,5 1 990 7,6 2 450 44 1,8 à 2,4
M30432 3 2,2 1,15 9,2 2 880 10,1 3 280 58,9 1,3 à 1,7
M50432 5 3,7 1,15 15,7 4 925 17,5 5 650 93 0,85 à 1,25
M75432 7,5 5,5 1,15 24 7 480 26,4 8 570 140 0,55 à 0,85
M05434 0,5 0,37 1,6 1,3 610 1,5 875 9 23,6 à 26,1
M07434 0,75 0,55 1,5 1,7 820 2,0 1 140 14 14,4 à 16,2
M10434 1 0,75 1,4 2,2 1 145 2,5 1 505 13 17,8 à 18,8
M15434 1,5 1,1
M20434 2 1,5 1,25 3,3 2 018 3,8 2 470 23 8,0 à 8,67
M30434 3 2,2 1,15 4,8 2 920 5,3 3 320 30 5,9 à 6,5
M50434 5 3,7 1,15 7,6 4 810 8,5 5 530 48 3,58 à 4,00
M75434 7,5 5,5 1,15 12,2 7 400 13,5 8 560 87 1,9 à 2,3
M100434 10 7,5 1,15 15,6 9600 17,2 11000 110 1,8-2,2
M15437 1,5 1,1 1,3 2,0 1 520 2,4 1 950 11,5 19,8 à 20,6
M20437 2 1,5 1,25 2,7 1 610 3,3 2 400 21 9,4 à 9,7
M30437 3 2,2 575 1,15 3,7 2 850 4,1 3 240 21,1 9,4 à 9,7
M50437 5 3,7 1,15 7,0 5 080 7,6 5 750 55 3,6 à 4,2
M75437 7,5 5,5 1,15 9,1 7 260 10,0 8 310 55 3,6 à 4,2
* FS = facteur de surcharge
1,3 6,3 1 560 7,2 1 950 40 1,9 à 2,5
200
1,3 5,2 1 490 6,1 1 930 32,4 2,8 à 3,4
230
1,3 2,8 1 560 3,2 1 980 16,3 12,3 à 13,1
460
A avec rotor
bloqué
Ligne à
ligne ()
60
Page 61

CALIBRES DE FIL DES MOTEURS TRIPHASÉS DE 4 po
CALIBRES DE FIL DES MOTEURS TRIPHASÉS DE 4 po
Longueur des fils de moteurs triphasés fondée sur : A avec facteur
de surcharge, chute de tension de 5 % et température ambiante de 30 °C
Moteur Calibre AWG, fils en cuivre, isolation pour 60 °C et 75 °C
V hp kW APC* AFS* 14 12 10 8 6 4 3 2 1 0 00 000 0000
0,5 0,37 3,8 2,9 657 1 045 1 667 2 641 4 109
0,75 0,55 3,8 4,5 423 674 1 074 1 702 2 648
1 0,75 4,6 5,5 346 551 879 1 392 2 166 3 454 4 342
1,5 1,1 6,3 7,2 265 421 672 1 064 1 655 2 638 3 317
200
2 1,5 7,5 8,8 217 344 549 870 1 354 2 158 2 714 3 427 4 317 5 449
3 2,2 10,9 12,0 159 253 403 638 993 1 583 1 990 2 513 3 166 3 996
5 3,7 18,3 20,2 94 150 239 379 590 940 1 182 1 493 1 881 2 374 2 995 3 781 4 764
7,5 5,5 27 30,0 64 101 161 255 397 633 796 1 005 1 266 1 598 2 017 2 546 3 207
0,5 0,37 2,4 2,9 756 1 202 1 917 3 037 4 725 7 532 9 469
0,75 0,55 3,3 3,9 562 894 1 426 2 258 3 513 5 601 7 041 8 892
1 0,75 4 4,7 466 742 1 183 1 874 2 915 4 648 5 843 7 379
1,5 1,1 5,2 6,1 359 571 912 1 444 2 246 3 581 4 502 5 685 7 162 9 040
230
2 1,5 6,5 7,6 288 459 732 1 159 1 803 2 874 3 613 4 563 5 748 7 256 9 155
1
3 2,2 9,2 10,1 217 345 551 872 1 357 2 163 2 719 3 434 4 326 5 460 6 889 8 696
5 3,7 15,7 17,5 318 503 783 1 248 1 569 1 982 2 496 3 151 3 976 5 019 6 323
7,5 5,5 24 26,4 334 519 827 1 040 1 314 1 655 2 089 2 635 3 327 4 192
0,5 0,37 1,3 1,5 2 922 4 648 7 414
0,75 0,55 1,7 2,0 2 191 3 486 5 560 8 806
1 0,75 2,2 2,5 1 753 2 789 4 448 7 045
1,5 1,1 2,8 3,2 1 370 2 179 3 475 5 504
460 2 1,5 3,3 3,8 1 153 1 835 2 926 4 635 7 212
3 2,2 4,8 5,3 827 1 315 2 098 3 323 5 171
5 3,7 7,6 8,5 516 820 1 308 2 072 3 224 5 140
7,5 5,5 12,2 13,5 325 516 824 1 305 2 030 3 236 4 068 5 138 6 472
10 7,5
1,5 1,1 2,0 2,4 2 283 3 631 5 792
2 1,5 2,7 3,3 1 660 2 641 4 212 6 671
575 3 2,2 3,7 4,1 1 336 2 126 3 390 5 370
5 3,7 7,0 7,6 721 1 147 1 829 2 897 4 507
7,5 5,5 9,1 10,0 548 871 1 390 2 202 3 426
* AFS courant (A) avec facteur de surcharge, APC = courant (A) à pleine charge.
0 956
61
Page 62

Données techniques
DANGER
Les tensions dangereuses
peuvent causer un choc
électrique, des brûlures ou
la mort.
ATTENTION
Données techniques
VALEURS DE RÉSISTANCE D’ISOLEMENT DU MOTEUR
Valeurs mesurées normalement en ohms et en mégohms entre chaque fil de
moteur et le fil de terre, et ce, pour TOUS les moteurs.
Pour mesurer la résistance d’isolement, mettre le disjoncteur hors circuit et
débrancher tous les fils du pressostat ou de la boîte de commande (à
déconnexion rapide). Brancher un fil de l’ohmmètre à un fil de moteur et l’autre, au tuyau de
refoulement en métal descendant dans le puits ou à une bonne prise de terre. Échelle « R x 100K »
État du moteur et des fils Ohms Mégohms
Moteur neuf, sans câble d’alimentation 20 000 000 (et plus) 20,0
Moteur usagé réutilisable (en puits) 10 000 000 (et plus) 10,0
Moteur en puits — valeurs mesurées : câble d’alimentation plus moteur
Moteur neuf 2 000 000 (et plus) 2,0
Moteur dans un état raisonnablement bon 500 000 à 2 000 000 0,5 à 2,0
Moteur ou câble d’aliment. peut-être endommagé
Ne pas sortir la pompe du puits pour cela.
Moteur ou câble d’alimentation endommagé
Sortir la pompe du puits et effectuer les réparations.
Moteur ou câble d’alimentation défectueux
Sortir la pompe du puits et effectuer les réparations.
Utilisation d’une génératrice
Utilisation d’une génératrice
20 000 à 500 000 0,02 à 0,5
10 000 à 20 000 0,01 à 0,02
Moins de 10 000 0 à 0,01
AVEC LES GÉNÉRATRICES DE SECOURS OU DE RÉSERVE,
UTILISER UN COMMUTATEUR DE TRANSFERT MANUEL
OU AUTOMATIQUE POUR PRÉVENIR LES CHOCS ÉLECTRIQUES, LES BRÛLURES ET LA MORT. SUIVRE LES DIRECTIVES DU FABRICANT. LES DONNÉES « 2 FILS... » VISENT
LES MOTEURS À CAP. LES 2 FILS DE MOTEUR À ENROULEMENT AUXILIAIRE DE DÉMARRAGE DEVRAIENT ÊTRE 50 % PLUS
GROS QUE LE CALIBRE NOMINAL POUR LES « 3 FILS... ».
Puissance nominale minimale de la génératrice
À régulation externe À régulation interne
Moteur hp kW kV·A kW kV·A
0,5 2,5 3,1 1,8 2,2
2 fils, 1 Ø, à CAP
0,75 3,5 4,4 2,5 3,1
(condensat. auxi-
1 5 6,3 3,2 4
liaire permanent)
1,5 6 7,5 4 5
0,5 2 2,5 1,5 1,9
0,75 3 3,8 2 2,5
1 4 5 2,5 3,2
1,5 5 6,3 3 3,8
2 7,5 9,4 4 5
3 fils,
1 Ø ou 3 Ø
3 10 12,5 5 6,3
5 15 18,8 7,5 9,4
7,5 20 25 10 12,5
10 30 37,5 15 18,8
62
Page 63

DÉMARREURS TRIPHASÉS DE BUT DÉFINI AVEC DES
SURCHARGES RÉGLABLES
Ordre de
CentriPro Nº
DP25D2 A27CGC25BA2P4
DP25E2 A27CGC25BA004 E 2.4-4
DP25F2 A27CGC25BA006 F 4-6
DP25G2 A27CGC25BA010 G 6-10
DP25H2 A27CGC25BA016 H 10-16
DP25J2 A27CGC25BA024 J 16-24
DP25C4 A27CGC25CA1P6
DP25D4 A27CGC25CA2P4 D 1.6-2.4
DP25E4 A27CGC25CA004 E 2.4-4
DP25F4 A27CGC25CA006 F 4-6
DP25G4 A27CGC25CA010 G 6-10
DP25H4 A27CGC25CA016 H 10-16
DP25J4 A27CGC25CA024 J 16-24
DP25E5 A27CGC25DA004
DP25F5 A27CGC25DA006 F 4-6
DP25G5 A27CGC25DA010 G 6-10
DP25H5 A27CGC25DA016 H 10-16
DP30L2 A27CGE30BA010
DP30M2 A27CGE30BA016 M 10-16
DP30N2 A27CGE30BA024 N 16-24
DP30P2 A27CGE30BA040 P 24-40
DP30L4 A27CGE30CA010
DP30M4 A27CGE30CA016 M 10-16
DP30N4 A27CGE30CA024 N 16-24
DP30P4 A27CGE30CA040 P 24-40
DP30L5 A27CGE30DA010
DP30M5 A27CGE30DA016 M 10-16
DP30N5 A27CGE30DA024 N 16-24
DP30P5 A27CGE30DA040 P 24-40
DP30R5 A27CGE30DA057 R 40-57
DP40L2 A27CGE40BA010
DP40M2 A27CGE40BA016 M 10-16
DP40N2 A27CGE40BA024 N 16-24
DP40P2 A27CGE40BA040 P 24-40
DP40L4 A27CGE40CA010
DP40M4 A27CGE40CA016 M 10-16
DP40N4 A27CGE40CA024 N 16-24
DP40P4 A27CGE40CA040 P 24-40
DP40L5 A27CGE40DA010
DP40M5 A27CGE40DA016 M 10-16
DP40N5 A27CGE40DA024 N 16-24
DP40P5 A27CGE40DA040 P 24-40
Numéro de ré-
férence d'Eaton
Maximum
ampères
25 208-230
25 460
25 575
30 208-230
30 460
30 575
40 208-230
40 460
40 575
Tension d'
alimentation
O.L.
Chaîne de
Relais
D 1.6-2.4
C 1-1.6
E 2.4-4
L 6-10
L 6-10
L 6-10
L 6-10
L 6-10
L 6-10
surcharge
Maximum
LRA
150 .5 - 5
125 .5 - 10
100 1.5 - 10
180 1.5 - 7.5
150 5 - 20
120 5 - 15
240 1.5 - 10
200 5 - 20
160 5 - 20
Intervalle
typique de HP
63
Page 64

DANGER
Les tensions dangereuses
peuvent causer un choc
électrique, des brûlures ou
la mort.
Diagnostic de anomalies
Diagnostic de anomalies
OMETTRE LE VERROUILLAGE DU DISJONCTEUR DU CIRCUIT ÉLECTRIQUE EN POSITION OUVERTE (HORS CIRCUIT) AVANT D’EFFECTUER TOUT TRAVAIL D’ENTRETIEN
SUR LA POMPE PEUT CAUSER UN CHOC ÉLECTRIQUE, DES
BRÛLURES ET LA MORT.
Anomalies Causes probables Correctifs recommandés
NONFONCTIONNEMENT
DU MOTEUR DE
LA POMPE
DÉBIT DE
REFOULEMENT
FAIBLE OU NUL
1. Protecteur thermique du moteur
déclenché
a) Boîte de commande inappropriée
b) Connexions électriques défectueuses
ou incorrectes
c) Protecteur thermique défectueux
d) Basse tension électrique
e) Température ambiante trop élevée pour
la boîte de commande ou le démarreur
f) Pompe bloquée par un corps étranger
g) Hauteur d’immersion inappropriée
2. Disjonsteur ouvert ou fusible sauté
3. Alimentation électrique inappropriée à
la charge
4. Gaine du câble d’alimentation
endommagée
5. Jonction du câble d’alimentation
défectueuse
1. Clapet de non-retour défectueux ou
mal posé
2. Poche d’air dans la pompe
3. Hauteur d’aspiration trop élevée pour
la pompe
4. Pompe bloquée par un corps étranger
5. Pompe non entièrement immergée
6. Présence excessive d’air ou de gaz dans
le puits
7. Usure excessive de la pompe
8. Mauvais sens de rotation du moteur (en
triphasé seulement)
1. Laisser le moteur refroidir, et le protecteur
thermique s’enclenchera de nouveau
automatiquement.
a) à e) Faire inspecter l’appareil par un
électricien et effecttuer les réparations
requises.
f) Sortir la pompe du puits, la nottoyer et
la redescendre à la hauteur d’immersion
requise.
g) Confirmer la bonne hauteur d’immersion
dans le liquide pompé.
2. Faire inspecter l’appareil par un électricien
et effectuer les réparations requises.
3. Vérifier la puissance électrique du circuit
d’alimentation ou de la génératrice.
4. et 5. Faire inspecter l’appareil par un électricien et effectuer les répararions requises.
1. Inspecter le clapet de non-retour et le
réparer au besoin.
2. Démarrer et arrêter la pompe à répétition
jusqu’à ce que son débit soit bon.
3. Vérifier les performances de l’appareil et
consulter le détaillant.
4. Sortir la pompe du puits, la nettoyer et
la redescendre à la hauteur d’immersion
requise.
5. Vérifier la remontée du niveau du puits
et immerger la pompe davantage si c’est
possible.
6. Si le démarrage et l’arrêt répétitifs de la
pompe ne résolvent pas le problème, il y
a trop d’air ou de gaz dans le puits.
7. Retirer la pompe du puits et effectuer les
réparations requises.
8. Intervertir deux fils du moteur.
64
Page 65

65
Page 66

RED JACKET WATER PRODUCTS LIMITED WARRANTY
The warranty period for RJWP standard construction submersible pumps used with CentriPro motors and
controls shall be thirty-six (36) months from date of installation or forty-two (42) months from date of
manufacture, whichever period is shorter.
Any part or parts found to be defective within the warranty period shall be replaced at no charge to the
dealer during the warranty period.
A dealer who believes that a warranty claim exists must contact the authorized Red Jacket Water Products
distributor from whom the pump was purchased and furnish complete details regarding the claim. The
distributor is authorized to adjust any warranty claims utilizing the Red Jacket Water Products Customer
Service Department.
The warranty excludes:
(a) Labor, transportation and related costs incurred by the dealer;
(b) Reinstallation costs of repaired equipment;
(c) Reinstallation costs of replacement equipment;
(d) Consequential damages of any kind; and,
(e) Reimbursement for loss caused by interruption of service.
For purposes of this warranty, the following terms have these definitions:
(1) “Distributor” means any individual, partnership, corporation, association, or other legal relationship that
stands between Red Jacket Water Products and the dealer in purchases, consignments or contracts for
sale of the subject pumps.
(2) “Dealer” means any individual, partnership, corporation, association, or other legal relationship which
engages in the business of selling or leasing pumps to customers.
(3) “Customer” means any entity who buys or leases the subject pumps from a dealer. The “customer” may
mean an individual, partnership, corporation, limited liability company, association or other legal entity
which may engage in any type of business.
THIS WARRANTY EXTENDS TO THE DEALER ONLY.
GARANTÍA LIMITADA DE RED JACKET WATER PRODUCTS
El periodo de garantía para las bombas sumergibles de construcción estándar RJWP utilizadas con motores y
controles CentriPro será de treinta y seis (36) meses a partir de la fecha de instalación o cuarenta y dos (42)
meses a partir de la fecha de fabricación, de los anteriores, el periodo que sea más corto.
Toda parte o partes que resulten defectuosas dentro del período de garantía serán reemplazadas sin cargo
para el comerciante durante dicho período de garantía.
Todo comerciante que considere que existe lugar a un reclamo de garantía deberá ponerse en contacto con
el distribuidor autorizado de Red Jacket Water Products del cual adquiriera la bomba, y ofrecer información
detallada con respecto al reclamo. El distribuidor está autorizado a liquidar todos los reclamos por garantía a
través del Departamento de Servicios a Clientes de Red Jacket Water Products.
La presente garantía excluye:
(a) La mano de obra, el transporte y los costos relacionados en los que incurra el comerciante;
(b) los costos de reinstalación del equipo reparado;
(c) los costos de reinstalación del equipo reemplazado;
(d) daños emergentes de cualquier naturaleza; y
(e) el reembolso de cualquier pérdida causada por la interrupción del servicio.
A los fines de esta garantía, los términos “Distribuidor”, “Comerciante” y “Cliente” se definen como sigue:
(1) “Distribuidor” es aquel individuo, sociedad, corporación, asociación u otra entidad jurídica que opera
entre Red Jacket Water Products y el comerciante para la compra, consignación o contratos de venta de
las bombas en cuestión.
(2) “Comerciante” es todo individuo, sociedad, corporación, asociación u otra entidad jurídica que realiza
negocios de venta o alquiler-venta (leasing) de bombas a clientes.
(3) “Cliente” es toda entidad que compra o que adquiere bajo la modalidad de leasing las bombas en cuestión
de un comerciante. El término “cliente” puede significar un individuo, una sociedad, una corporación,
una sociedad de responsabilidad limitada, una asociación o cualquier otra entidad jurídica con actividades en cualquier tipo de negocios.
LA PRESENTE GARANTÍA SE EXTIENDE AL COMERCIANTE ÚNICAMENTE
66
Page 67

GARANTIE LIMITÉE DE RED JACKET WATER PRODUCTS
Les pompes submersibles standard de RJWP munies d’un moteur et d’une commande CentriPro seront garanties selon la période suivante expirant la première : trente-six (36) mois à compter de la date d’installation
ou quarante-deux (42) mois à partir de la date de fabrication.
Toute pièce se révélant défectueuse sera remplacée sans frais pour le détaillant durant la période de garantie
pertinente.
Le détaillant qui, aux termes de la présente garantie, désire effectuer une demande de règlement doit
s’adresser au distributeur Red Jacket Water Products agréé chez lequel la pompe a été achetée et fournir tous
les détails à l’appui de sa demande. Le distributeur est autorisé à régler toute demande par le biais du service
à la clientèle de Red Jacket Water Products.
La garantie ne couvre pas :
a) les frais de main-d’œuvre ou de transport ni les frais connexes encourus par le détaillant ;
b) les frais de réinstallation de l’équipement réparé ;
c) les frais de réinstallation de l’équipement de remplacement ;
d) les dommages indirects de quelque nature que ce soit ;
e) ni les pertes découlant de la panne.
Aux fins de la garantie, les termes ci-dessous sont définis comme suit :
1) « Distributeur » signifie une personne, une société de personnes, une société de capitaux, une association
ou autre entité juridique servant d’intermédiaire entre Red Jacket Water Products et le détaillant pour les
achats, les consignations ou les contrats de vente des pompes en question.
2) « Détaillant » veut dire une personne, une société de personnes, une société de capitaux, une association ou
autre entité juridique dont les activités commerciales sont la vente ou la location de pompes à des clients.
3) « Client » signifie une entité qui achète ou loue les pompes en question chez un détaillant. Le « client » peut
être une personne, une société de personnes, une société de capitaux, une société à responsabilité limitée,
une association ou autre entité juridique se livrant à quelque activité que ce soit.
LA PRÉSENTE GARANTIE SE RAPPORTE AU DÉTAILLANT SEULEMENT.
67
Page 68

Xylem, Inc.
2881 East Bayard Street Ext., Suite A
Seneca Falls, NY 13148
Phone (Teléfono/Téléphone): (866) 325-4210
Fax (Télécopie): (888) 322-5877
www.xyleminc.com/brands/redjacketwaterproducts
Red Jacket Water Products is a trademark of Xylem Inc. or one of its subsidiaries. Red
Jacket Water Products es una marca registrada de Xylem Inc. o una de sus filiales. Red
Jacket Water Products est une marque déposée de Xylem, Inc. ou de ses filiales.
© 2012 Xylem Inc. IM116 Revision Number 4
September (Septiembre/Septembre) 2012
 Loading...
Loading...