
NSERIES
F4G TIER 3
Agricultural applications (Hyundai)
F4GE9484F*J608
F4GE9454J*J604
Technical and Repair manual

This publication contains data, features, instructions and
methods for performing repair interventions on the assembly
and its components.
This publication is addressed to qualified, specialised personnel.
Check that you have the publication related to the assembly
on which you are about to work available before you start.
Make sure that you have all the necessary safety apparatuses,
suchas,forexample,protectiveeyewear,helmet,gloves,footwear, etc. Check that the working, lifting and transport equipment etc. is available and in working order. Make sure that the
group is prepared and secured.
Proceed by carefully observing the instructions contained
herein and use the indicated specific tools to ensure correct
repair procedures, observance of time schedules and safety of
operators.
All repair interventions are aimed at restoring the conditions
of operation, efficiency and safety contemplated by FPT.
All on-group interventions, aimed at implementing changes,
alterations or other not authorised by FPT will relieve FPT
from responsibility. Specifically, the warranty (where applicable) will be immediately cancelled.
FPT cannot be held responsible for repair interventions.
FPT is available to provide any additional information needed
for performing the inventions and indications in the cases and
situations not contemplated in this publication.
The data contained in this publication may not be up-to-date
if changes are made by the manufacturer at any time for technical or commercial reasons or if required to meet legal requirements of countries worldwide.
Contact a FPT dealership before proceedingin the event of differences between the contents of this publication and the
actual assembly.
Reproduction, even partial, of this text and the illustrations
contained herein is prohibited.
Publication edited by
FIAT Powertrain Technologies
Mkt. Advertising & Promotion
Viale dell’Industria, 15/17
20010 Pregnana Milanese
Milano (Italy)
Print P2D32N010 E -1
st
Ed. 02.2009
Produced by:
B.U. TECHNICAL PUBLISHING
Iveco Technical Publications
Lungo Stura Lazio, 15/19
10156 Turin - Italy
F4GE N SERIES
1
F4GE N SERIES
F4GE N Series Part 1
-

2
F4GE N SERIES
-

F4GE N SERIES
INTRODUCTION 1
Introduction
Page
PREFACE TO USER’S GUIDELINE MANUAL 3....
SYMBOLS 5...............................
- Warnings 3.............................
- Service operations 3......................
GENERAL WARNINGS 5.....................
GENERAL WARNINGS
ON THE ELECTRIC SYSTEM 7...............
- Bonding and screening 8...................
CONVERSIONS BETWEEN THE MAIN UNITS
OF MEASUREMENT OF THE INTERNATIONAL
SYSTEM AND MOST USED DERIVED
QUANTITIES 9...........................
KEY OF LECTURE OF THE HEADINGS
AND FOOTNOTES 10.....................
-

2
INTRODUCTION
F4GE N SERIES
-

F4GE N SERIES
INTRODUCTION 3
PREFACE TO USER’S GUIDELINE MANUAL
Manuals for repairs are split into Parts and Sections, each one of which is marked by a numeral; the contents of these sections are
indicated in the general table of contents.
The sections dealing with things mechanic introduce the specifications, tightening torque values, tool lists, assembly
detaching/reattaching operations, bench overhauling operations, diagnosis procedures and maintenance schedules.
The sections (or parts) of the electric/electronic system include the descriptions of the electric network and the assembly’s
electronic systems, wiring diagrams, electric features of components, component coding and the diagnosis procedures for the
control units peculiar to the electric system.
Section 1 describes the engine illustrating its features and working in general.
Section 2 describes the type of fuel feed.
Section 3 relates to the specific duty and is divided in four separate parts:
1. Mechanical part, related to the engine overhaul, limited to those components with different characteristics based on the relating
specific duty.
2. Electrical part, concerning wiring harness, electrical and electronic equipment with different characteristics based on the relating
specific duty.
3. Maintenance planning and specific overhaul.
4. Troubleshooting part dedicated to the operators who, being entitled to provide technical assistance, shall have simple and direct
instructions to identify the cause of the major inconveniences.
Sections 4 and 5 illustrate the overhaul operations of the engine overhaul on stand and the necessary equipment to execute such
operations.
The appendix contains a list of the general safety regulations to be respected by all installation and maintenance engineers in order
to prevent serious accidents taking place.
The manual uses proper symbols in its descriptions; the purpose of these symbols is to classify contained information. In particular,
there have been defined a set of symbols to classify warnings and a set for assistance operations.
SYMBOLS - Warnings
Danger for persons
Missing or incomplete observance of these prescriptions can cause serious danger for persons’ safety.
Danger of serious damage for the assembly
Failure to comply, both fully or in part, with such prescriptions will involve serious damage to the assembly and may
sometimes cause the warranty to become null and void.
General danger
!
It includes the dangers of above described signals.
Environment protection
Moreover, it describes the correct actions to be taken to ensure that the assembly is used in such a way so as to protect
the environment as much as possible.
NOTE
It indicates an additional explanation for a piece of information.
Service operations
Example
∅
Ø 1 = housing for connecting rod small end bush
1
Ø 2 = housing for connecting rod bearings
∅
2
Tighten to torque
Tighten to torque + angular value
α
-
4
INTRODUCTION
F4GE N SERIES
Removal
Disconnection
Refitting
Connection
Removal
Disassembly
Fitting in place
Assembly
Tighten to torque
ρ
Intake
Exhaust
Operation
Compression ratio
Tolerance
Weight difference
Tighten to torque + angle value Rolling torque
α
Press or caulk Rotation
Regulation
Adjustment
Angle
Angular value
Visual inspection
Fitting position check
Preload
Measurement
Value to find
Number of revolutions
Check
Equipment Temperature
Surface for machining
Machine finish
Interference
Strained assembly
Thickness
Clearance
Lubrication
Damp
Grease
Sealant
Adhesive
bar
Pressure
Oversized
Higher than….
Maximum, peak
Undersized
Less than….
Minimum
Selection
Classes
Oversizing
Temperature < 0 °C
Cold
Winter
Temperature > 0 °C
Air bleeding
Hot
Summer
-

F4GE N SERIES
GENERAL WARNINGS
Warnings shown cannot be representative of all danger situationspossibly occurring. Therefore, it is suggested to contact
immediate superiors where a danger situation occurs which is not described.
!
Use both specific and general-purpose toolings according to the prescriptions contained in respective use and
maintenance handbooks. Check use state and suitability of tools not subjected to regular check.
The manual handling of loads must be assessed in advance because it also depends, besides weight, on its size and on
the path.
Handling by mechanical means must be with hoisters proper as for weight as well as for shape and volume. Hoisters,
ropes and hooks used must contain clear indications on maximum carrying capacity acceptable. The use of said means
is compulsorily permitted to authorised personnel only. Stay duly clear of the load, and, anyhow, never under it.
In disassembling operations, always observe provided prescriptions; prevent mechanical parts being taken out from
accidentally striking workshop personnel.
Workshop jobs performed in pairs must always be performed in maximum safety; avoid operations which could be
dangerous for the co-operator because of lack of visibility or of his/her not correct position.
Keep personnel not authorised to operations clear of working area.
You shall get familiar with the operating and safety instructions for the assembly prior to operating on the latter. Strictly
follow all the safety indications found on the assembly.
INTRODUCTION 5
Do not leave the running assembly unattended when making repairs.
When carrying out work on the assembly lifted off the ground, verify that the assembly is firmly placed on its supporting
stands, and that the manual/automatic safety devices have been actuated in the event that the assembly is to be lifted
by means of a hoist.
When you have to operate on assemblies powered by natural gas, follow the instructions contained in the document,
as well as all the specific safety standards provided for.
Only remove radiator cap when the engine is cold by cautiously unscrewing it in order to let system residual pressure
out.
Inflammable fuel and all inflammable fluids and liquids must be handled with care, according to what contained on harmful
materials 12-point c ards. Refuelling must be performed outdoors with the engine off, avoiding lit cigarettes, free flames
or sparks in order to prevent sudden fires/bursts. Adequately store inflammable, corrosive and polluting fluids and liquids
according to what provided by regulations in force. Compulsorily avoid to use food containers to store harmful liquids.
Avoid to drill or bore pressurised containers, and throw cloths impregnated with inflammable substances into suitable
containers.
Worn out, damaged or consumable parts must be replaced by original spares.
During workshopactivity, always keep the work place clean; timely clear or clean floors from accidental liquid or oil spots.
Electric sockets and electric equipment necessary to perform r epair interventions must meet safety rules.
-
6
INTRODUCTION
F4GE N SERIES
Put on, where required by the intervention, garments and protections provided in accident prevention rules; contact
with moving parts can cause serious injuries. Use suitable, preferably tight-fitted garments, and avoid to use jewels,
scarves, etc.
Do not leave the engine in motion at workshop locations not provided with a pipe to scavenge exhaust gas outside.
Avoid to breathe fumes coming from heating or from paint welding because they can cause damages to health; operate
outdoors or in suitably ventilated areas. Put on proper inspirator if paint powder is present.
Avoid contact with hot water or steam coming from the engine, radiator and pipings because they could cause serious
burns. Avoid direct c ontact with liquids and fluids present in vehicle systems; where an accidental contact has occurred,
refer to 12-point cards for provisions to make.
Clean the assemblies and carefully verify that they are intact prior to overhauling. Tidy up detached or disassembled
parts with their securing elements (screws, nuts, etc.) into special containers.
Check for the integrity of the parts which prevent screws from being unscrewed: broken washers, dowels, clips, etc.
Self-locking nuts with an insert made of nylon must always be replaced.
Avoid contact of rubber parts with diesel oil, petrol or other not compatible substances.
Before washing under pressure mechanical parts, protect electric connectors, and central units, if present.
Tightening screws and nuts must always be according to prescriptions; FPT commercial and assistance network is
available to give all clarifications necessary to perform repair interventions not provided in this document.
Before welding:
- Disconnect all electronic central units, take power cable off battery positive terminal (connect it to chassis bonding)
and detach connectors.
- Remove paint by using proper solvents or paint removers and clean relevant surfices with soap and water.
- Await about 15 minutes before welding.
- Equip with suitable fire resistant protections to protect hoses or other components where fluids or other materials
flow which may catch fire easily on welding.
Should the vehicle be subjected to temperatures exceeding 80°C (dryer ovens), disassemble drive electronic central
units.
The disposal of all liquids and fluids must be performed with full observance of specific rules in force.
-
F4GE N SERIES
GENERALWARNINGS O N THE ELECTRIC SYSTEM
If an intervention has to be made on the electric/electronic system, disconnect batteries from the system; in this case,
!
always disconnect, as a first one, the chassis bonding cable from batteries negative terminal.
Before connecting the batteries to the system, make sure that the system is well isolated.
Disconnect the external recharging apparatus from the public utility network before taking apparatus pins off battery
terminals.
Do not cause sparks to be generated in checking if the circuit is energised.
Do not use a test lamp in checking circuit continuity, but only use proper control apparatuses.
Make sure that the electronic devices wiring harnesses (length, lead type, location, strapping, connection to screening
braiding, bonding, etc.) comply with FPT system and are carefully recovered after repair or maintenance interventions.
Measurements in drive electronic central units, plugged connections and electric connections to components can only
be made on proper testing lines with special plugs and plug bushes. Never use improper means like wires, screwdrivers,
clips and the like in order to avoid the danger of causing a short circuit, as well as of damaging plugged connections, which
would later cause contact problems.
INTRODUCTION 7
To start up the engine, do not use fast chargers. Start up must only be performed with either separate batteries or special
truck.
A wrong polarisation of supply voltage in drive electronic central units (for instance, a wrong polarisation of batteries)
can cause them to be destroyed.
Disconnect the batteries from the system during their recharging with an external apparatus.
On connecting, only screw up connector (temperature sensors, pressure sensors etc.) nuts at prescribed tightening
torque.
Before disconnecting the junction connector from an electronic central unit, isolate the system.
Do not directly supply electronic central units servo components at nominal vehicle voltage.
Cables must be arranged such as to result to be parallel to reference plane, i.e. as close as possible to chassis/body
structure.
Once the intervention on the electric system has been completed, recover connectors and wiring harnesses according
to original arrangement.
NOTE
Connectors present must be seen from cable side. Connectors views contained in the manual are representative of cable
side.
-
8
INTRODUCTION
F4GE N SERIES
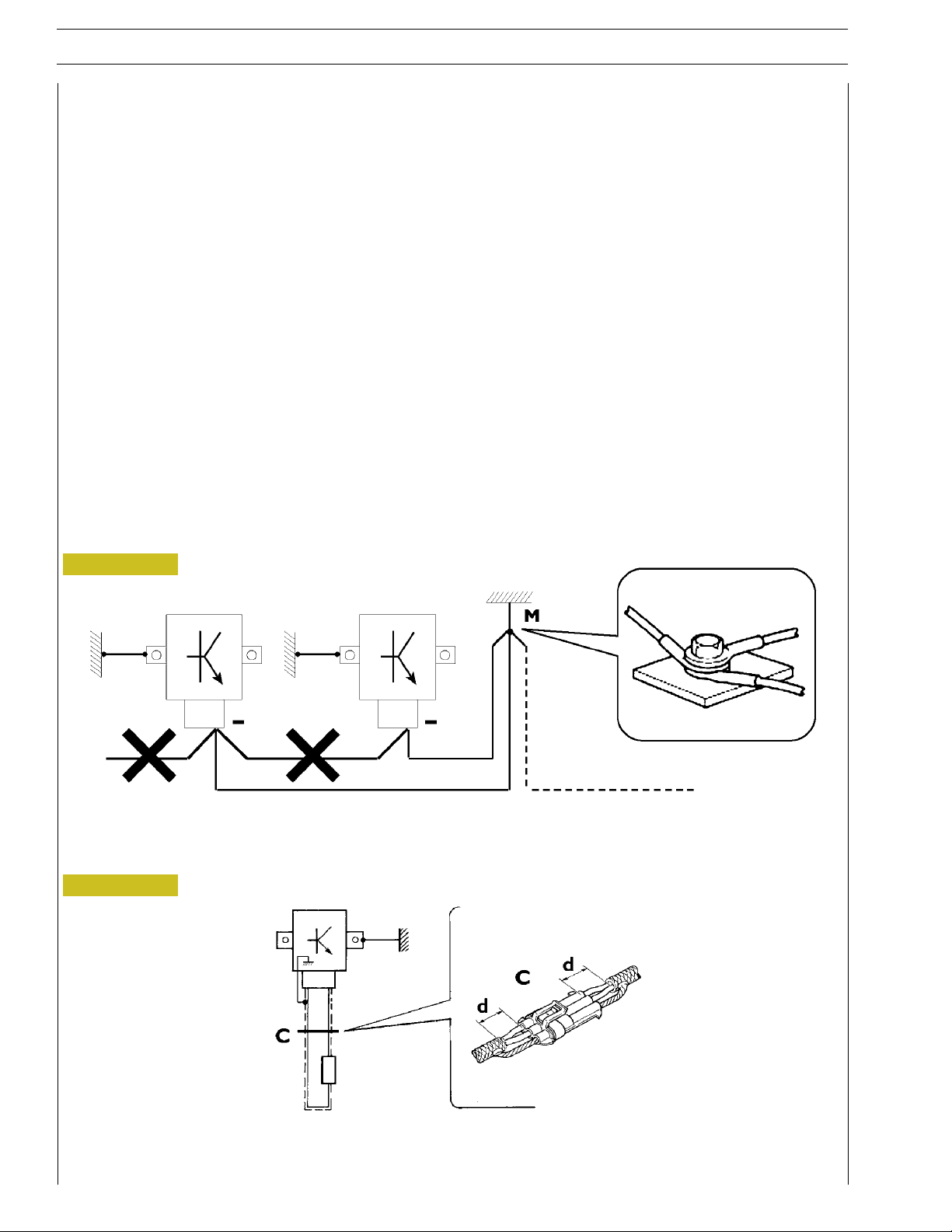
Bonding and screening
Negative leads connected to a system bonded point must be both as short and possible and “star“-connected to each other, trying
then to have their centering tidily and properly made (Figure 1, re. M).
Further, following warnings are to be compulsorily observed for electronic components:
- Electronic central units must be connected to system bonding when they are provided with a metallic shell.
- Electronic central units negative cables must be connected both to a system bonding point such as the dashboard opening
bonding (avoiding “serial“ or “chain“ connections), and to battery negative terminal.
- Analog bonding (sensors), although not connected to battery negative system/terminal bonding, must have optimal isolation.
Consequently, particularly considered must be parasitic resistances in lugs: oxidising, clinching defects, etc.
- Screened circuits braiding must only electrically contact the end towards the central unit entered by the signal (Figure 2).
- If junction connectors are present, unscreened section d, near them, must be as short as possible (Figure 2).
- Cables must be arranged such as to result to be parallel to reference plane, i.e. as close as possible to chassis/body structure.
Figure 1
1. NEGATIVE CABLES “STAR“ CONNECTION TO SYSTEM BONDING M
Figure 2
2. SCREENING THROUGH METALLIC BRAIDING OF A CABLE TO AN ELECTRONIC COMPONENT — C. CONNECTOR
d. DISTANCE ! 0
-
88039

F4GE N SERIES
INTRODUCTION 9
CONVERSIONS BETWEEN THE MAIN UNITS OF MEASUREMENT OF THE
INTERNATIONAL SYSTEM AND MOST USED DERIVED QUANTITIES
Power
1 kW = 1.36 metric HP
1 kW = 1.34 HP
1 metric HP = 0.736 kW
1 metric HP = 0.986 HP
1 HP = 0.746 kW
1 HP = 1.014 metric HP
Torque
1 Nm = 0.1019 kgm
1 kgm = 9.81 Nm
Revolutions per time unit
1 rad/s = 1 rpm x 0.1046
1 rpm = 1 rad/s x 9.5602
Pressure
Pa
2
2
according to ratio 1:1
1 bar = 1.02 kg/cm
1 kg/cm
1bar = 10
2
= 0.981 bar
5
Where accuracy is not particularly needed:
- Nm unit is for the sake of simplicity converted into kgm according to ratio 10:1
1 kgm = 10 Nm;
- bar unit is for the sake of simplicity converted into kg/cm
2
1 kg/cm
=1bar.
Temperature
0° C=32° F
1° C = (1 x 1.8 + 32) ° F
-
10
INTRODUCTION
KEY OF LECTURE OF THE HEADINGS AND FOOTNOTES
F4GE N SERIES
Type of
vehicle
Section
title
Page
number
Printout
number
-
Language
Publication
Basic edition referred to
month - year editorial
phase closing
When month - year update
is present (revi) to the
basic edition

F4GE N SERIES
1
Part 1
F4GE N SERIES
Section
General specifications
Fuel 2
Agricultural applications 3
Overhaul and technical specifications 4
Tools 5
Safety prescriptions Appendix
1
-

2
F4GE N SERIES
-
F4GE N SERIES
UPDATING
Section Description Page Date of revision
3
-

4
F4GE N SERIES
-

F4GE N SERIES
SECTION 1 - GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS 1
SECTION 1
General Specifications
Page
LUBRICATION 3............................
OIL VAPOUR RECIRCULATING SYSTEM 4.......
COOLING SYSTEM 5........................
AIR INDUCTION BOOST DIAGRAM 6..........
- Boosting version engines 6.................
- Description 6...........................
- Inter-cooled engine version 7...............
- Description 7...........................
EXHAUST GAS RE-CIRCULATION SYSTEM (EGR) 8
-

2
SECTION 1 - GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
F4GE N SERIES
-
F4GE N SERIES
SECTION 1 - GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS 3
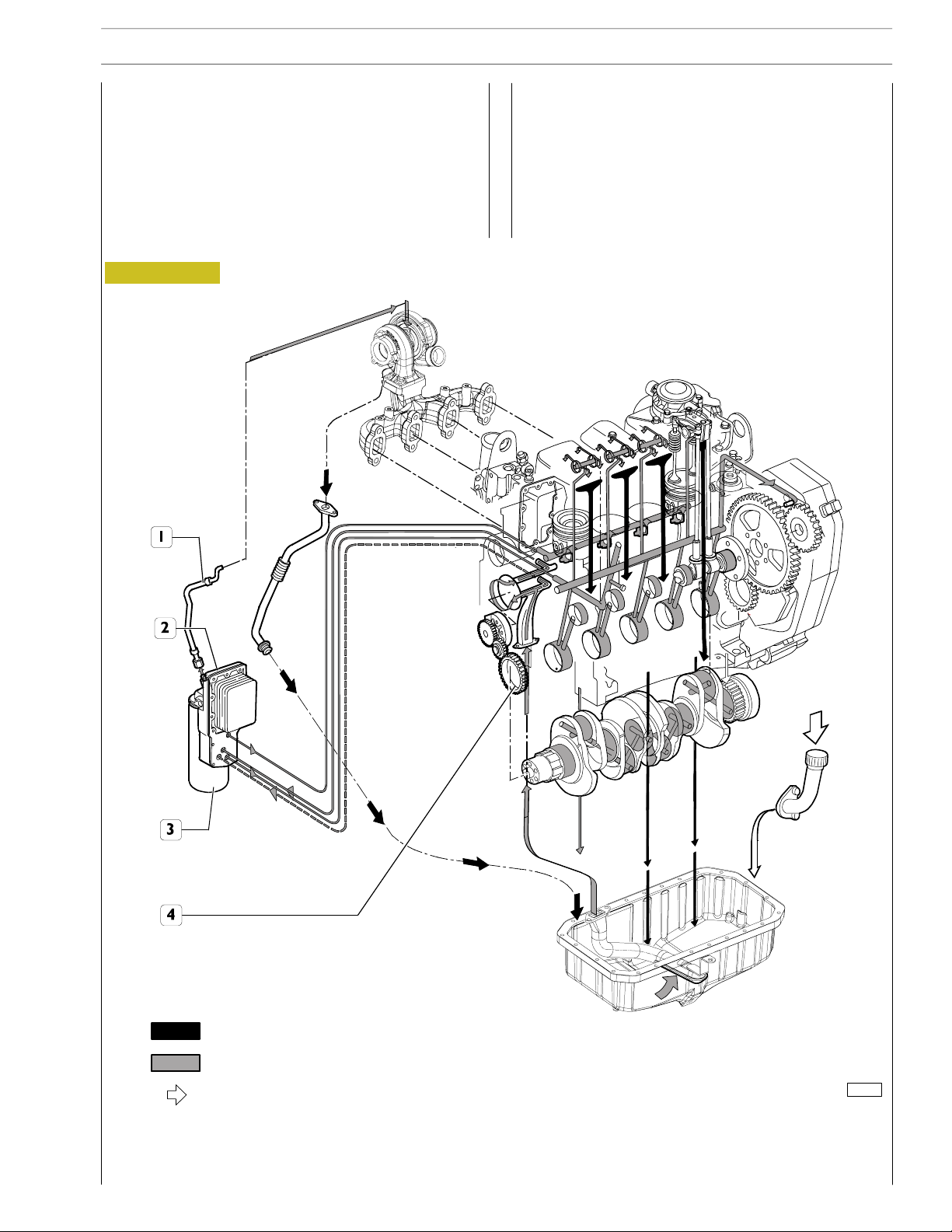
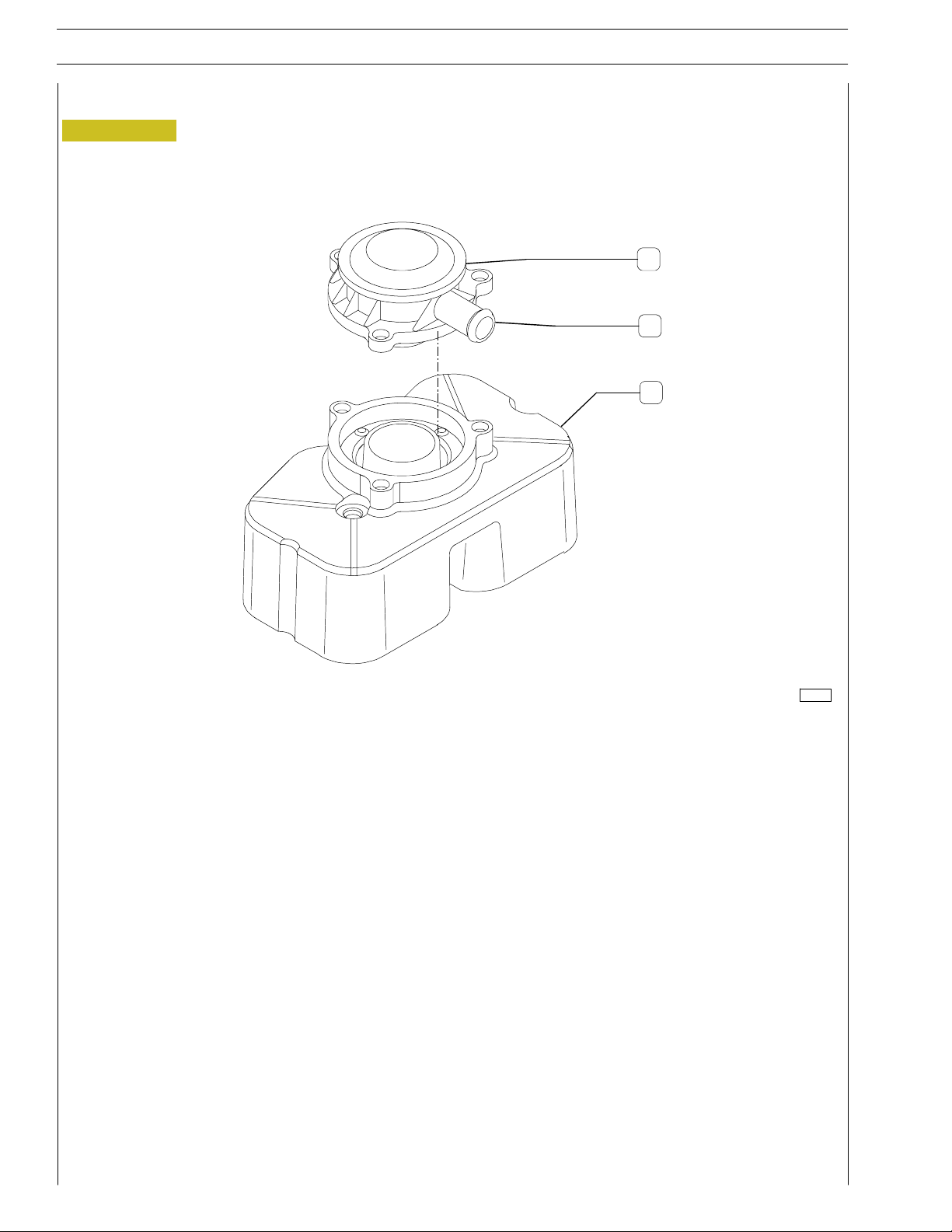
LUBRICATION
Lubrication by forced circulation is achieved through oil rotary
expansion pump, placed in the front part of the basement,
driven by the straight-tooth gear splined to the shaft’s bar hold.
From the pan, the lubrication oil flows to the driving shaft, to
the camshaft and to the valve drive.
Figure 1
Lubrication involves the heat exchanger and the turboblower.
All these components may often vary according to the specific
duty.
Routing of oil under
pressure
Routing of oil return
by gravity to sump
Introduction of oil
LUBRICATION SYSTEM LAYOUT
1. Lubrication oil pipe to supercharger - 2. Heat exchanger body - 3. Oil rotary expansion pump - 4. Oil filter.
132102
-
4
SECTION 1 - GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
OIL VAPOUR RECIRCULATING SYSTEM
Figure 2
F4GE N SERIES
1
2
3
3240t
1. Valve - 2. Breather pipe - 3. Tappet Cap
On the tappet cap (3) there is a valve (1) whose duty is to condense oil vapour inducing these to fall down because of gravity,
to the Tappet cap underneath.
The remaining non-condensed vapours shall be properly conveyed through the breather pipe (2), by suction as an example (connection towards these vapours shall be designed by the Engineer).
-
F4GE N SERIES
SECTION 1 - GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS 5
COOLING SYSTEM
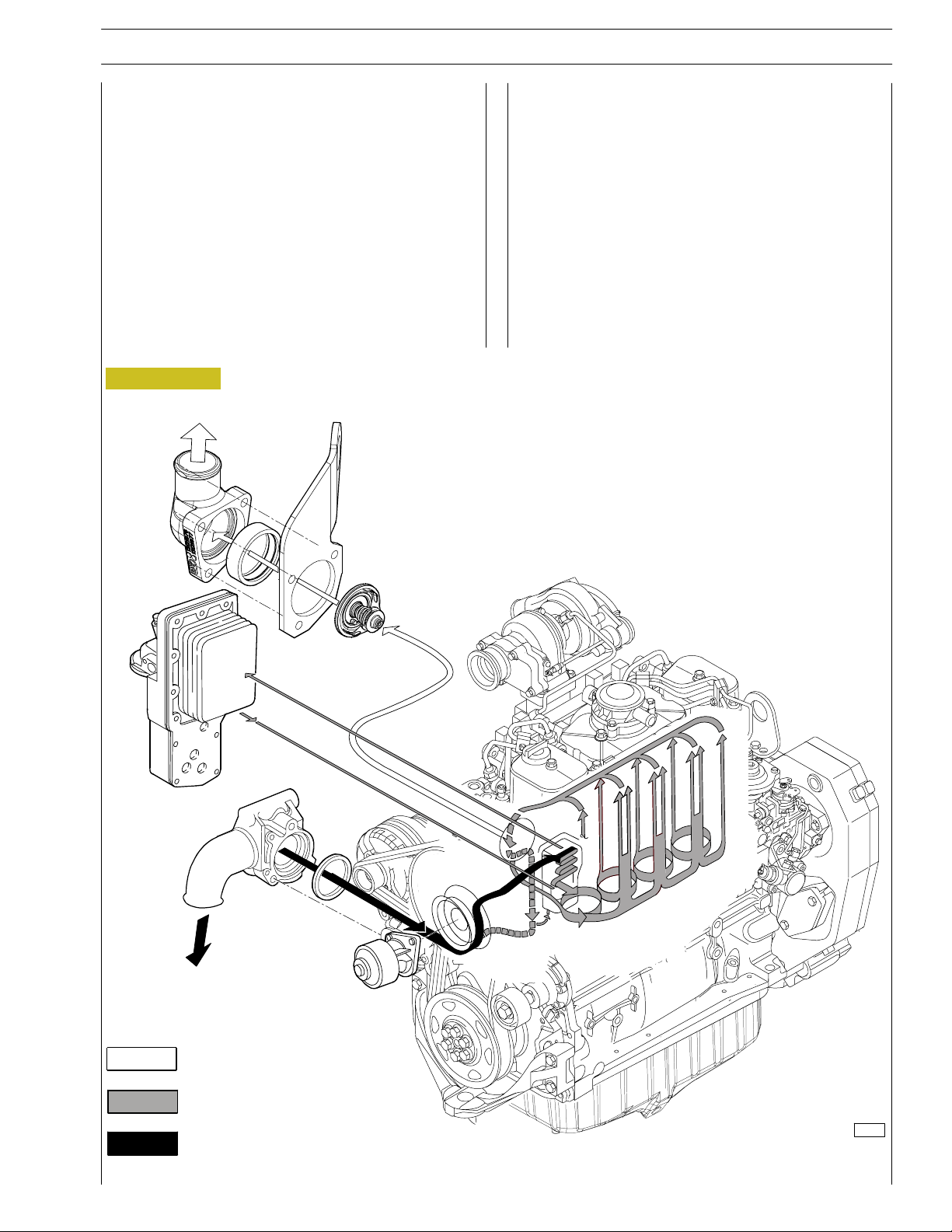
The engine cooling system, closed circuit forced circulation
type, generally incorporates the following components:
- Expansion tank; placement, shape and dimensions are
subject to change according to the engine’s equipment.
- Radiator, which has the duty to dissipate the heat
subtracted to the engine by the cooling liquid. Also this
component will have specific peculiarities based on the
equipment developed, both for what concerns the
placement and the dimensions.
- Visc pusher fan, having the duty to increase the heat
dissipating power of the radiator. This component as well
will be specifically equipped based on the engine’s
development.
Figure 3
TO RADIATOR
- Heat exchanger to cool the lubrication oil: even this
component is part of the engine’s specific equipment.
- Centrifugal water pump, placed in the front part of the
engine block.
- Thermostat regulating the circulation of the cooling liquid.
FROM RADIATOR
Water coming out from thermostat
Water recirculating in engine
Water coming into pump
127129
COOLING SYSTEM LAYOUT
-
6
SECTION 1 - GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
AIRINDUCTION BOOST DIAGRAM
Boosting version engines
Figure 4
F4GE N SERIES
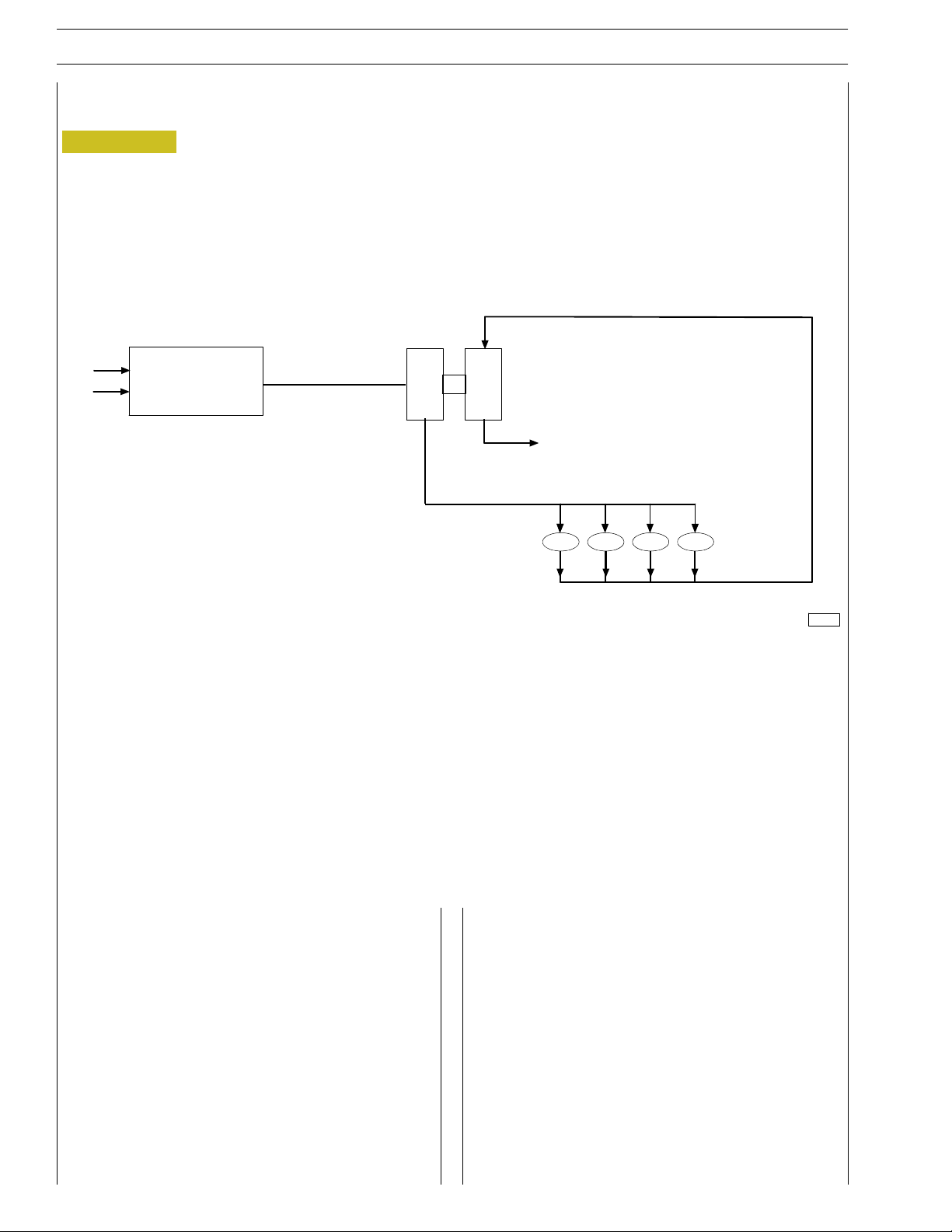
AIR FILTER
TURBOCHARGER
EXHAUST
88208
Description
The turbocharger is composed by the following main parts:
one turbine, one transforming valve to regulate the boost
feeding pressure , one main body and one compressor.
During engine working process, the exhaust emission flow
through the body of the turbine, provoking the turbine disk
wheel’s rotation.
The compressor rotor, being connected by shaft to the
turbine disk wheel, rotates as long as this last one rotates,
compressing the sucked air through the air filter.
The air coming out of the compressor is sent via the intake
manifold directly to the pistons.
-
The turbocharger is equipped with a transforming valve to
regulate the pressure , that is l ocated on the exhaust collector
before the turbine and connected by piping to the induction
collector.
It’s duty is to choke the exhaust of the emissions , releasing part
of them directly to the exhau st tube when the boost feeding
pressure, over the compressor, reaches the prescribed bar
value.
The cooling process and the lubrication of the turbocharger
and of the bearings is made by the oil of the engine.
F4GE N SERIES
Inter-cooled engine version
Figure 5
SECTION 1 - GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS 7
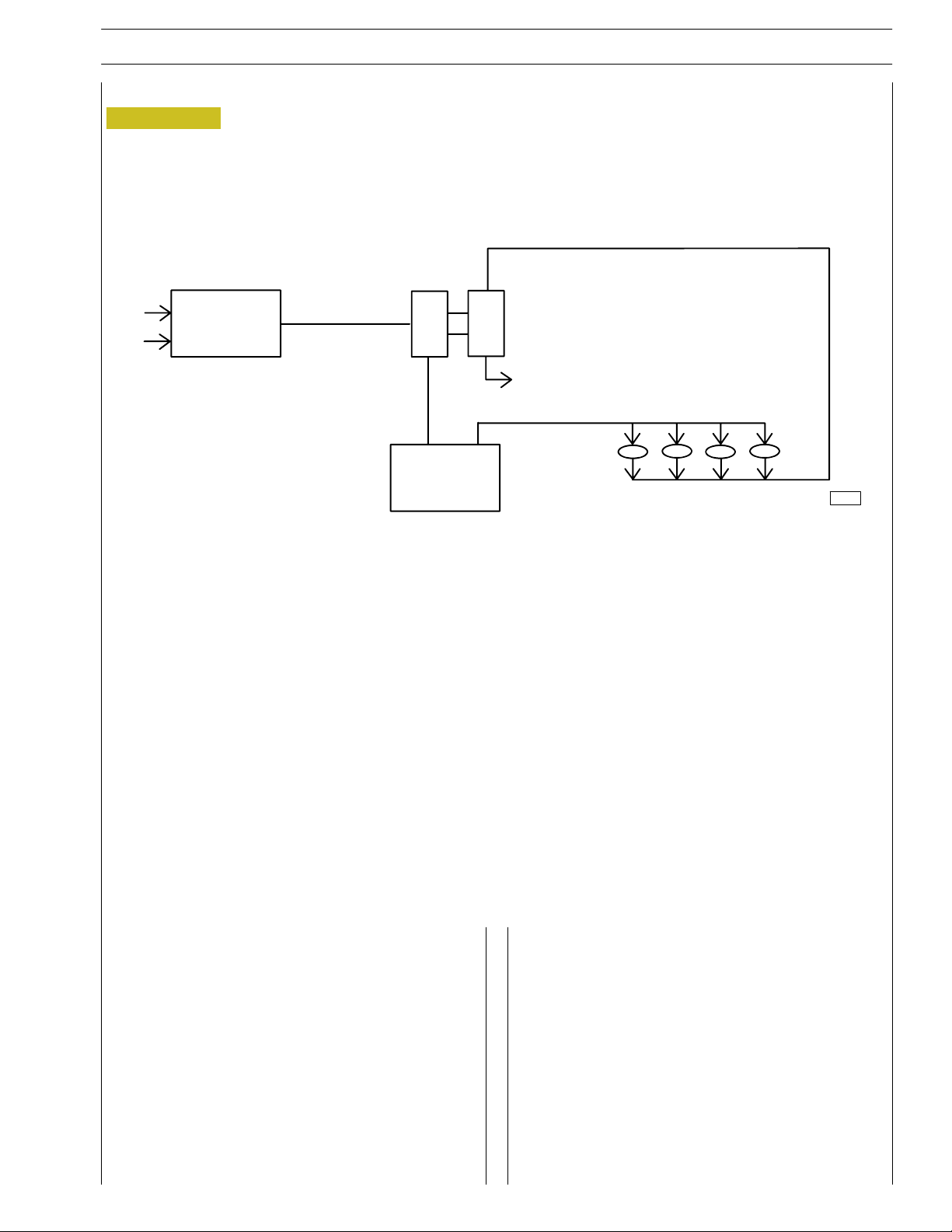
AIR FILTER
TURBOCHARGER
EXHAUST
RADIATOR
74195
4 cylinders version
Description
The turbocharger is composed by the following main parts:
one turbine, one transforming valve to regulate the boost
feeding pressure , one main body and one compressor.
During engine working process, the exhaust emission flow
through the body of the turbine, provoking the turbine disk
wheel’s rotation.
The compressor rotor, being connected by shaft to the
turbine disk wheel, rotates as long as this last one rotates,
compressing the sucked air through the air filter.
The above mentioned air is then cooled by the radiator and
flown through the piston induction collector.
The turbocharger is equipped with a transforming valve to
regulate the pressure , that is l ocated on the exhaust collector
before the turbine and connected by piping to the induction
collector.
It’s duty is to choke the exhaust of the emissions , releasing part
of them directly to the exhau st tube when the boost feeding
pressure, over the compressor, reaches the prescribed bar
value.
The cooling process and the lubrication of the turbocharger
and of the bearings is made by the oil of the engine.
-
8
SECTION 1 - GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
F4GE N SERIES
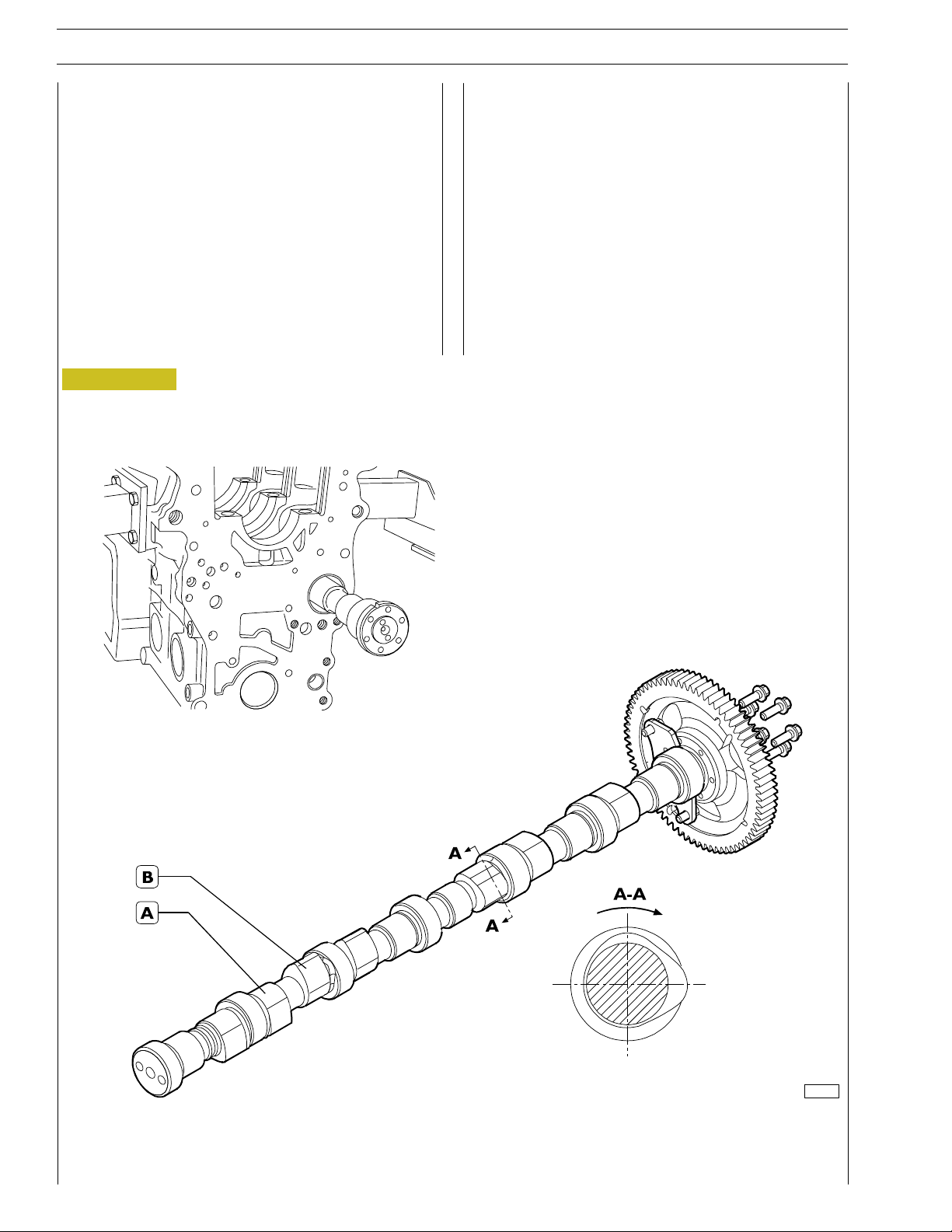
EXHAUST GAS RE-CIRCULATION SYSTEM
(EGR)
In the TIER 3 version, the profile of the exhaust cam has been
modified in order to allow the partial opening of the relative
valve during the aspiration phase (re-circulation of EGR
exhaust gas) with the subsequent re-introduction of part of
the exhaust gas into the engine cylinders.
The exhaust gases can partially be re-directed into the
cylinders so as to reduce the maximum combustion
temperature values responsible for the production of nitric
acid (NO
The exhaust gas re-circulation system (EGR), reducing the
combustion temperature by means of the diminishing of the
concentration of oxygen in the combustion chamber,
represents therefore an efficient control system of the
emission of NO
).
x
Figure 6
.
x
The internal EGR system is not equipped with any
electronically controlled elements: the system is always active.
Its configuration does not need additional elements
i.e.checking valves, piping or heat exchangers.
The exhaust cam (B) has another lobe apart from the major
lobe (see Section. A-A fig.) with respects to the configur ation
without EGR.
The additional lobe, during the aspiration phase in the cylinder
in question, allows a brief opening of the exhaust valve
generating re-circulation due to the intake of the exhaust gases
caused by depression which is created in the aspiration phase
inside the cylinder.
114789
A. Aspiration valve control - B. Exhaust valve control.
-
F4GE N SERIES
SECTION 2 - FUEL 1
SECTION 2
Fuel
Page
4-CYLINDER ENGINES WITH BOSCH VE 4/12 F
ROTARY MECHANICAL PUMP 3............
- General information 3.....................
- Description of working principles 4...........
FEED PUMP 5..............................
- Example of identification 5.................
PRIMING PUMP 6...........................
FUEL FILTER 7..............................
-

2
SECTION 2 - FUEL
F4GE N SERIES
-

F4GE N SERIES
ase-February2009
SECTION 2 - FUEL
4-CYLINDER ENGINES WITH BOSCH VE 4/12 F ROTARY MECHANICAL PUMP
General information
Fuel feed system is composed by:
- Fuel tank (placed on the machine)
- Fuel delivery and back-flow to tank
- Fuel pre-filter (if available, it is usually placed close to the engine on the machine frame)
- Priming pump, assembled to the engine and driven by the camshaft
- Fuel filter (assembled to the engine in different positions ac cording to equipment application and duty)
- Fuel feed rotary pump
- Injec t or feed pipeline (from fuel feed pump to injectors)
- Injectors
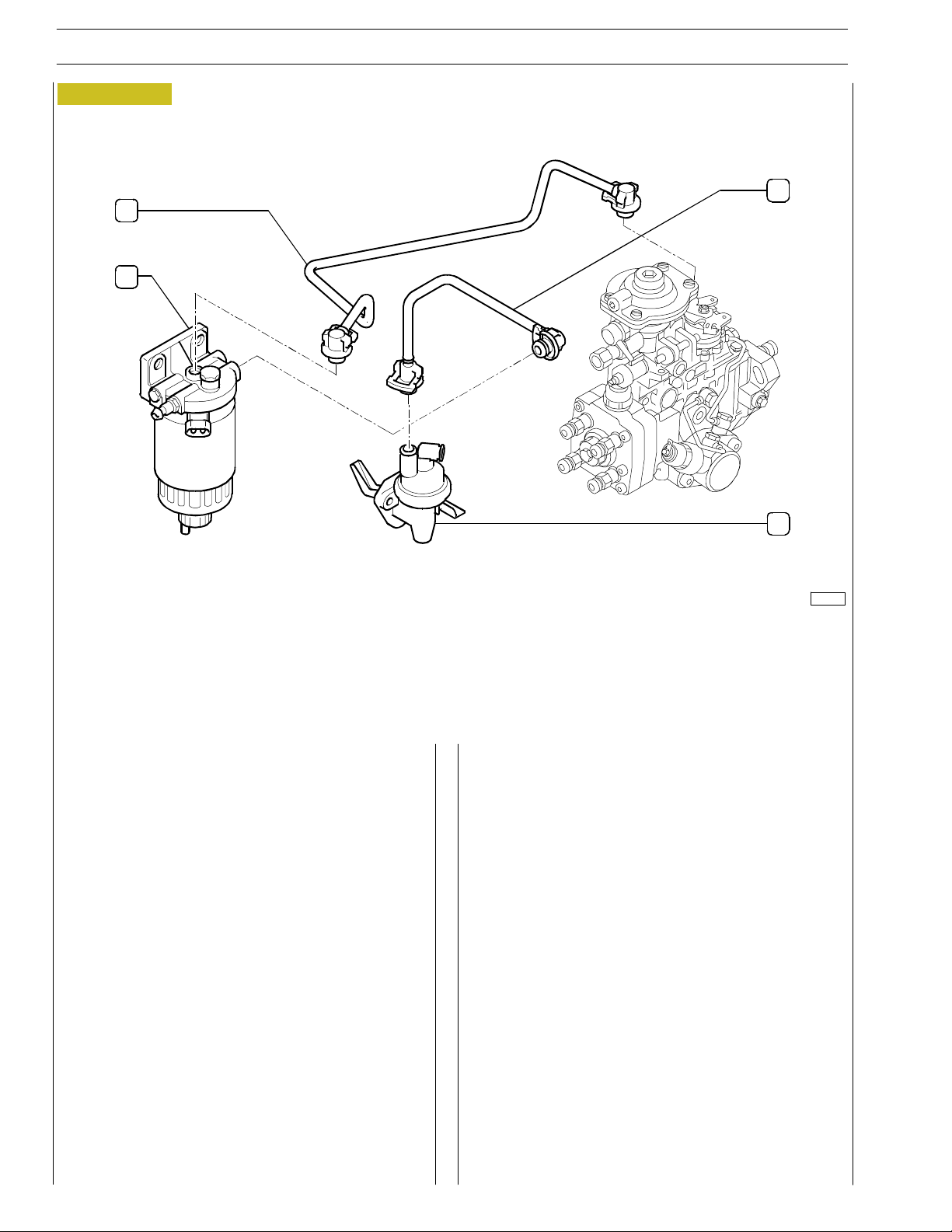
Figure 1
3
2
1
4
7
5
3
6
74168
1. Injector feed pipes - 2. Fuel exhaust pipes from injectors - 3. Fuel feed rotary pump - 4. Connector for LDA pressure
gauge pipe within suction c ollector - 5. KSB thermal bulb - 6. Electro-valve - 7. Injector.
PrintP2D32N010E B
4
ase-February2009Print
Figure 2
SECTION 2 - FUEL
2
1
F4GE N SERIES
3
1. Fuel filter - 2. Feed pipeline from filter to fuel pump - 3. Feed pipeline from priming pump to filter - 4. Priming pump.
Description of working principles
Fuel is sucked from the fuel tank by the priming pump. This
last one is placed on the engine basement and is driven by
the camshaft.
Throughout the filter, the fuel is piped to the union fitting
vacuum c hamber of the transfer pump. (For applications to
be equipped in cold climate areas, the fuel filter is provided
with heater).
Transfer pump is placed inside the feed pump, and is bladed
type; its duty is to increase fuel pressure in c orrespondence
with the increase of the number of revolutions.
The fuel arrives therefore to the valve gauging the pressure
inside feed pump.
The distribution plunger further increases this pressure and
delivers fuel throughout the delivery pipe fitting to the
injectors.
The fuel drawing from the injectors is recovered and delivered
to the tank again.
4
75807
B
P2D32N010E
 Loading...
Loading...