Page 1

Technical Manual
Functional Safety (FS)
NC Software
606 420-01 SP 05
606 421-01 SP 05
July 2011
Page 2

Page 3

Subject
1 Update Information
1.1 General Information............................................................................7
1 Update Information No. 01 –
Functional Safety
1.1 Overview..............................................................................................9
1.1.1 Released service packs ...........................................................9
1.2 NC Software 606 42x-01 SP 05 ........................................................10
1.2.1 Important notes.....................................................................10
1.3 New Safety Functions ......................................................................11
2Introduction
2.1 Meaning of the Symbols Used in this Manual...............................13
2.2 Warnings............................................................................................14
2.3 Proper Operation...............................................................................17
2.4 Trained Personnel .............................................................................17
2.5 General Information..........................................................................18
2.6 Overview of FS Components...........................................................23
2.6.1 List of approved control components....................................24
2.6.2 List of approved inverter components...................................27
2.6.3 Differences between systems with and without
functional safety (FS)...........................................................29
3 Directives and Standards
3.1 Applicable Directives ........................................................................31
3.2 Basis for Testing................................................................................32
3.3 Requirements on Safety Integrity...................................................35
3.4 SIL and Target Failure Measures.....................................................35
3.5 Storage and Operating Temperatures............................................35
3.6 Limit Values for EM Noise Immunity..............................................35
3.7 Mission Time .....................................................................................35
July 2011 3
Page 4

4 Realization and Safety Functions
4.1 Glossary .............................................................................................37
4.2 Realization of the HEIDENHAIN Safety System.............................41
4.3 Activation of Functional Safety (FS) ...............................................41
4.4 (S)PLC Programs ...............................................................................42
4.5 SPLC ...................................................................................................43
4.6 SKERN................................................................................................45
4.7 Cross Comparison.............................................................................46
4.8 Description of the Safety/Monitoring Functions...........................47
4.8.1 Overview of the safety functions ..........................................47
4.8.2 Overview of monitoring functions .........................................49
4.8.3 Safe stop 0 (SS0)...................................................................50
4.8.4 Safe stop 1 (SS1) – Fastest possible stopping ......................51
4.8.5 Safe stop 1D (SS1D) – Delayed SS1......................................54
4.8.6 Safe stop 1F (SS1F) – Fastest possible stopping ..................54
4.8.7 Safe stop 2 (SS2) – Controlled stopping ................................55
4.8.8 Summary of the stop reactions .............................................58
4.8.9 Safe torque off (STO).............................................................60
4.8.10 Safe operating stop (SOS) .....................................................62
4.8.11 Safely limited speed (SLS).....................................................63
4.8.12 Safely limited position (SLP)..................................................64
4.8.13 Safe brake control (SBC)........................................................66
4.8.14 Safely limited increment (SLI)................................................67
4.8.15 Nominal-actual value comparison..........................................67
4.8.16 Nominal-actual value comparison of position values .............68
4.8.17 Nominal-actual value comparison of speed values................68
4.8.18 Protection against unexpected start-up.................................69
4.8.19 dv/dt monitoring of the braking processes............................69
4.8.20 Response times, definitions, demand rates ..........................70
4.8.21 Safe status bits......................................................................75
4.8.22 Fault reaction to safe status bits ...........................................78
4.8.23 Behavior when a fault is detected.........................................80
4.8.24 Stop reactions depending on the fault situations ..................82
4.9 Special Features of Software Version 606 42x-01 .........................88
4.10 Requirements the Application Must Meet .....................................92
4.11 Remaining Risks................................................................................94
5 Safety-Related MPs and Signals
5.1 Safety-Related Machine Parameters (SMPs)..................................95
5.2 SMP Commissioning ......................................................................112
5.3 Acceptance Test..............................................................................119
5.4 Safety-Related Hardware Signals..................................................120
5.5 Entries in the OEM.SYS File...........................................................124
4 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Page 5

6 Safety-Related Operating Modes and
Interfaces
6.1 Operating Modes (SOM Safe Operating Modes).........................125
6.1.1 Operating mode 1 (SOM_1) ................................................126
6.1.2 Operating mode 2 (SOM_2) ................................................127
6.1.3 Operating mode 3 (SOM_3) ................................................129
6.1.4 Operating mode 4 (SOM_4) ................................................131
6.1.5 Operating mode – restricted spindle operation (SOM_S)....133
6.1.6 Operating mode selection – inputs......................................134
6.1.7 Configuration of axis groups................................................136
6.1.8 Magazine axes.....................................................................138
6.1.9 Non-safe axes and spindles.................................................139
6.1.10 Electronic handwheel ..........................................................140
6.1.11 Use of several operating units.............................................142
6.2 Safety-Related Hardware Interfaces .............................................143
6.2.1 Interfaces of the SPL...........................................................143
6.2.2 Interfaces of the SMOP.......................................................152
6.2.2.1 Interfaces of the handwheel (HR)........................................155
7 Safety-Related Tests and Forced
Dynamic Sampling
7.1 Safety Self-Test...............................................................................157
7.2 Self-Test Sequence .........................................................................159
7.3 Test of the Cut-Out Channels ........................................................162
7.4 Test of Machine Control Voltage...................................................162
7.5 Test of the Chain of Normally Closed Contacts...........................163
7.6 Test of the Guard Doors.................................................................163
7.7 Test of the Motor Brake Control....................................................164
7.8 Motor Brake Test ............................................................................166
7.8.1 Brake test for synchronized axes ........................................168
7.9 Test of the Machine Configuration................................................175
7.10 Test of the Machine Keys and Permissive Buttons/Keys............175
7.11 Test of the Emergency-Stop Circuit..............................................175
July 2011 5
Page 6

8 SPLC – Safety-Related PLC
8.1 General Information........................................................................177
8.2 Safe Software Structure.................................................................178
8.3 Software Structure of PLC / SPLC.................................................178
8.4 Glossary ...........................................................................................179
8.5 SPLC Development Tool.................................................................181
8.6 PLC and SPLC Programs.................................................................182
8.7 Safety of the SPLC Program ..........................................................183
8.8 Requirements to Be Met by the SPLC Program...........................184
8.8.1 Axis groups / working spaces for an example milling
machine.............................................................................184
8.8.2 Moving the axes with open guard doors .............................184
8.9 Interfaces of the SPLC ....................................................................185
8.9.1 The splcapimarker.def definition file....................................185
8.9.2 Safety-related inputs, FS inputs...........................................187
8.9.3 Safety-related outputs, FS outputs......................................188
8.9.4 SKERN --> SPLC programming interface ............................190
8.9.5 SPLC --> SKERN programming interface ............................193
8.9.6 PLC --> SPLC programming interface .................................194
8.9.7 SPLC --> PLC programming interface .................................195
8.9.8 Diagnosis of the SPLC operands.........................................195
8.10 Tasks of the SPLC Program............................................................196
8.10.1 Operation with open guard door..........................................196
8.10.2 Selecting a safety-related operating mode (SOM)...............197
8.10.3 Requirements to be met by SPLC outputs..........................197
8.10.4 Requirements on the data of the ApiToSafety structure.....200
8.10.5 Filtering of inputs.................................................................219
8.11 Sample Cases ..................................................................................221
8.11.1 Movement of NC axes and spindle .....................................221
8.11.2 Movement of the axes of the tool magazine.......................228
6 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Page 7

1 Update Information
1.1 General Information
Update Information for the Functional Safety Technical Manual appears at
irregular intervals, often as part of a new software version. This is preliminary
information in PDF format, containing brief descriptions of new software
functions as well as new hardware components. After the Update Information
has been published, the new items are included in the Functional Safety
Technical Manual.
The Technical Manual and each Update Information are saved in the
HEIDENHAIN FileBase on the Internet, where registered users can access
them at http://portal.heidenhain.de.
Registered users of the HEIDENHAIN FileBase on the Internet receive an
e-mail notification when a new Update Information appears.
This version of the Technical Manual includes all Update Information
notifications up to and including number 01, meaning that the contents of this
Functional Safety (FS) Technical Manual correspond to the scope of functions
of software version 606 42x-01 with Service Pack 05.
July 2011 1.1 General Information 7
Page 8

8 HEIDENHAIN Functional Safety Technical Manual
Page 9

1 Update Information No. 01 – Functional Safety
1.1 Overview
1.1.1 Released service packs
The following service packs were released for 606 42x-01:
Service pack 01: August 2010
Service pack 02: December 2010
Service pack 03: February 2011
Service pack 04: March 2011 (not for functional safety)
Service pack 05: May 2011 (full version)
July 2011 1.1 Overview 9
Page 10

1.2 NC Software 606 42x-01 SP 05
Attention
1.2.1 Important notes
New test of the safe outputs:
Service pack 05 expands the safety selftest as regards the safe outputs. This
new safety test for safe PL outputs is necessary for certification of the
functional safety.
During the test all safe, dual-channel PL outputs are specifically switched off.
This state is checked to ensure that all dual-channel outputs assume this state
(= 0) and remain in it.
However, the PLD-H 04-08-00FS modules with ID 727 219-01 do not fulfill the
requirements of this test yet, and must therefore be modified. Other PL
modules already support this test.
If PLD modules with ID 727 219-01 are in the electrical cabinet when the new
test is performed, the test is aborted with the error message "E031 error
xxxxxxxx…".
Further procedure:
HEIDENHAIN started building the PLD-H 04-08-00FS modules with the
appropriate modification in April 2011, and changed the variant to 02
(ID 727 219-02).
Starting immediately, please ship all machines with HSCI and functional safety
only with the 02 variant of PLD-H 04-08-00FS PL modules. The modules must
also be exchanged for affected machines already in the field, so that the test
can be performed. Please get in touch with your contact partner at
HEIDENHAIN first, in order to coordinate the exchange action in the best
possible manner.
The test can be deactivated via SMP560 bit 12 = 1 until the PL modules have
been exchanged. The test must be reactivated once the modules have been
exchanged!
On machines with PLD-H 04-08-00FS (ID 727 219-02) PL modules, or
without PLD-H 04-08-00FS, the test must be activated with SMP560 bit
12 = 0.
10 HEIDENHAIN Functional Safety Technical Manual
Page 11

1.3 New Safety Functions
dv/dt monitoring of
the spindle
dv/dt monitoring of the spindle during SS1 reaction
dv/dt monitoring of the spindle is being introduced as a new safety function in
service pack 05. The safety function monitors braking of the spindle during an
SS1 reaction.
After an SS1 reaction has been initiated, the SKERN monitors the spindle
speed to ensure that it continually decreases. Should the monitoring
determine that the speed remains constant or even increases, an SS0 reaction
is initiated for the spindle. SS1F is initiated for all other axes. This monitoring
can be deactivated with SMP560 bit 11 for commissioning purposes.
However, this monitoring is essential to the HEIDENHAIN safety strategy, and
must be reactivated after commissioning.
Input for SMP560 bit 11:
0: dv/dt monitoring of the spindle active
1: dv/dt monitoring of the spindle inactive
July 2011 1.3 New Safety Functions 11
Page 12

12 HEIDENHAIN Functional Safety Technical Manual
Page 13

2 Introduction
Danger
Attention
Note
2.1 Meaning of the Symbols Used in this Manual
Failure to comply with this information could result in most serious or fatal
injuries, and/or in substantial material damage.
Failure to comply with this information could result in injuries and
interruptions of operation, including material damage.
Tips and tricks for operation as well as important information, for example
about standards and regulations as well as for better understanding of the
document.
July 2011 2.1 Meaning of the Symbols Used in this Manual 13
Page 14

2.2 Warnings
Danger
The functional safety as provided by HEIDENHAIN only handles the safety
functions stated and described in this manual. Functional safety can reduce
the inherent risks of machine tools. However, it is impossible to implement
safety measures that ensure that nothing will ever go wrong with a
machine tool.
In order for functional safety to take effect, the machine manufacturer
must:
verify the theoretical and actual setup of the machine tool, the necessary
(S)PLC programs and the machine-parameter settings with a thoroughly
documented acceptance test. This acceptance test must be performed
by qualified personnel.
thoroughly understand the information contained in this manual and
other documentation for the control and other electronic components
being used (such as inverters and motors), as well as understand and
enforce the safety instructions, constraints and relevant standards.
draw up a risk analysis, as required by the EC machinery directive.
implement all measures deemed necessary based on the risk analysis of
the machine. These measures may be implemented as a part of
functional safety, or with other suitable equipment or procedures. All
measures must be validated.
14 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Page 15
Danger
Many safety-related machine parameters (SMP) and the safety-related PLC
Attention
program (SPLC program) are important for ensuring the safety of the
machine when it is controlled by an iTNC 530 with integrated safety
strategy.
Changing these safety-related machine parameters or the SPLC program
can result in loss of the machine safety as specified in the applicable
standards!
Safety-related machine parameters are therefore protected by a special
OEM password that is only known to the machine manufacturer.
Changes to the safety-related machine parameters and the SPLC program
may only be performed by trained personnel of the OEM. He is responsible
for the safety of the machine and compliance with the applicable standards,
in particular with EN 12417.
The HEIDENHAIN safety strategy cannot detect erroneous
parameterization or programming by the OEM. The necessary level of
safety can only be achieved with thorough acceptance testing of the
machine.
When exchanging a power module or motor, the same type must be used,
since otherwise the settings of the machine parameters could lead to
different reactions by the safety functions. If an encoder is exchanged, the
affected axis must be recalibrated.
Hardware components of the machine tool may only be exchanged by
trained personnel.
Prior to the initial operation or shipping of a machine tool, the
machine manufacturer must conduct a complete acceptance test.
All of the machine's safety functions must be tested. Furthermore, the
input values of the safety-related machine parameters and the entire SPLC
program must be checked for correctness.
If the SPLC program is changed subsequently, the entire acceptance
test must be repeated.
If individual machine parameters are changed subsequently, a partial
acceptance test is required.
Upon subsequent changes the safety functions affected by the respective
change must be tested. The changes and the necessary acceptance tests
may only be performed by trained personnel of the OEM.
July 2011 2.2 Warnings 15
Page 16

Attention
The machine tool is not in a safe state until after it has booted completely
and the safety self-test was passed successfully!
During start-up or the reset phase, the control is not in a safe state (e.g.
installation of a service pack). Axes and spindles are without torque
during this time!
When exchanging hardware components, also use the same model. If an
encoders is exchanged, then the motor affected must be referenced and
tested again.
Depending on the changes during an exchange or update of the
software, either a partial or complete acceptance test becomes
necessary. The following must be ensured before or during an exchange
or update of the software:
• All openings (e.g. doors) to the working space must be closed
• Emergency stop must be activated
• There must be no tools in the spindle
• Vertical axes must be protected against falling
• No persons are permitted in the danger zone
The control must be shut down correctly before the machine is switched
off via the main switch. Should this not be possible due to an error, an
emergency stop is to be initiated via the man switch before removing
power from the machine.
16 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Page 17

2.3 Proper Operation
The described components may only be installed and operated as described
in this manual. Commissioning, maintenance, inspection and operation are
only to be performed by trained personnel.
HEIDENHAIN contouring controls and their accessories are designed for
integration in milling, drilling and boring machines, and machining centers.
2.4 Trained Personnel
Trained personnel in the sense of this manual means persons who are familiar
with the installation, mounting, commissioning, and operation of the
HEIDENHAIN components. Furthermore, electrical engineering work on the
system may be carried out only by trained electrical engineering technicians or
persons trained specifically for the respective application.
Basically, persons who perform work on HEIDENHAIN components must
meet the following requirements:
They must have been trained or instructed in the standards of safety
They must have appropriate safety equipment (clothing, measuring
They should be skilled in first-aid practice.
engineering.
systems).
July 2011 2.4 Trained Personnel 17
Page 18
2.5 General Information
Danger
Danger
Please note the following during initial operation of your new machines
with the new HSCI hardware generation of the iTNC 530:
With the introduction of this hardware, the new functional safety (FS) is
available for the first time, featuring the following properties:
Safety category 3 (Performance Level d) in accordance with EN ISO
SIL 2 as per DIN EN 61508
Operating modes as per EN 12417
Integrated SPLC for adaptation to the machine
The enhancements regarding functional safety to the NC software are
fundamental new developments by HEIDENHAIN. This means that the
necessary software tests have been performed only partially, and that the
complete system does not yet have sufficient functional tests. This means
that special care must be taken when working with the affected new
machines, since faulty operation of the integrated safety functions of the
software cannot be ruled out.
Please inform your colleagues and employees using these machines of
these possible dangers. No persons should be within the traverse range of
the axes.
13849-1:
December 2008
Only the iTNC 530 HSCI control with NC software 606 42x may currently
be used for applications with functional safety. Other controls (e.g. the
TNC 6xx NCK-based controls) and NC software versions do not yet
support the use of functional safety!
However, NC software 606 42x has not yet been generally approved for
applications that use the integrated functional safety (FS) of the control.
Separate approval by HEIDENHAIN is required for the use of integrated
functional safety (FS) according to EN ISO 13849-1!
Every machine tool operator is exposed to certain risks.
Although protective devices (safeguards) can prevent access to dangerous
points, the operator must also be able to work with the machine without this
protection (e.g. if the guard door is open).
Several guidelines and regulations to minimize these risks have been
developed in recent years.
18 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Page 19

Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC obligates you as a machine-tool
manufacturer to perform detailed risk assessments in order to prove operator
safety during the various operating phases of the machine. The combination
of hazard analysis and risk evaluation leads to the determination of how much
risks must be reduced by design measures or control methods in order to
achieve an appropriate level of safety.
In accordance with EN 12417, the electronic controls of universal machines,
milling machines, lathes and machining centers must fulfill the requirements
of EN 13849-1 category 3 (previously EN 954-1) for their safety-related parts.
In particular this means that the control must be designed such that an
individual fault does not lead to loss of the safety function, and that any
individual fault is detectable if this is possible in an acceptable manner.
According to EN ISO 12100-1/2 (Safety of Machinery), it is important for safe
operation of the machine that the safety measures permit simple and
continuous use of the machine and that they do not impair its correct and
intended operation. If this is not the case, then this can lead to the safety
measures being circumvented in order to attain the simplest possible
operation of the machine.
The HEIDENHAIN safety strategy integrated in the iTNC 530 HSCI complies
with Category 3 as per EN 13849-1 and SIL 2 as per IEC 61508, features
safety-related operating modes in accordance with EN 12417, and assures
extensive operator protection.
The basis of the HEIDENHAIN safety strategy is the dual-channel processor
structure, which consists of the main computer (MC) and one or more CC
drive controller modules (CC = control computing unit).
All monitoring mechanisms are designed redundantly in the control systems.
Safety-related system data is subject to a mutual cyclic data comparison, see
page 4–46.
Safety-related errors always lead to safe stopping of all drives through defined
stop reactions.
Defined safety reactions are triggered and safe operating statuses are
achieved via safety-related inputs and outputs (in two channels) which have an
influence on the process in all operating modes.
July 2011 2.5 General Information 19
Page 20

Additional
Note
Note
Note
information
Documentation
This manual is a supplement to the Technical Manual of your control, and
describes the functions of the functional safety (FS) and the SPLC from
HEIDENHAIN. Therefore, please also refer to the following documentation:
• Technical Manual of your control
• "Inverter Systems and Motors" Technical Manual
• Online help of the PLCdesignNT development environment for (S)PLC
programming
Documentation for NC software 606 42x-01
For the documentation of the new iTNC 530 HSCI hardware generation,
please refer to the iTNC 530 HSCI Technical Manual.
Update Information No. 25 loses its validity as soon as the iTNC 530 HSCI
Technical Manual for NC software 606 42x becomes available.
You can download manuals, other documentation and PC software tools for
machine manufacturers from the HEIDENHAIN FileBase.
Specifics and constraints
The first software versions for functional safety of the iTNC 530 HSCI do not
include the full range of features necessary to provide functional safety for
all machine models. Please see page 4–88. Your contact person at
HEIDENHAIN will be glad to answer any questions concerning the iTNC 530
HSCI with functional safety.
Before planning a machine with functional safety, please inform yourself of
whether the current scope of functional safety features suffices for your
machine design.
In practice, and in the sense of this document, a HEIDENHAIN control system
for a machine tool consists of:
a HEIDENHAIN NC control with integrated safety and HSCI, an MC main
computer and CC controller units
peripheral units such as screen, keyboard, machine operating panel and
handwheel
the SPL or PL assemblies with their I/O modules for connecting safety and
standard inputs and outputs
synchronous and asynchronous feed and spindle motors
position and speed encoders
supply modules and inverters
20 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Page 21

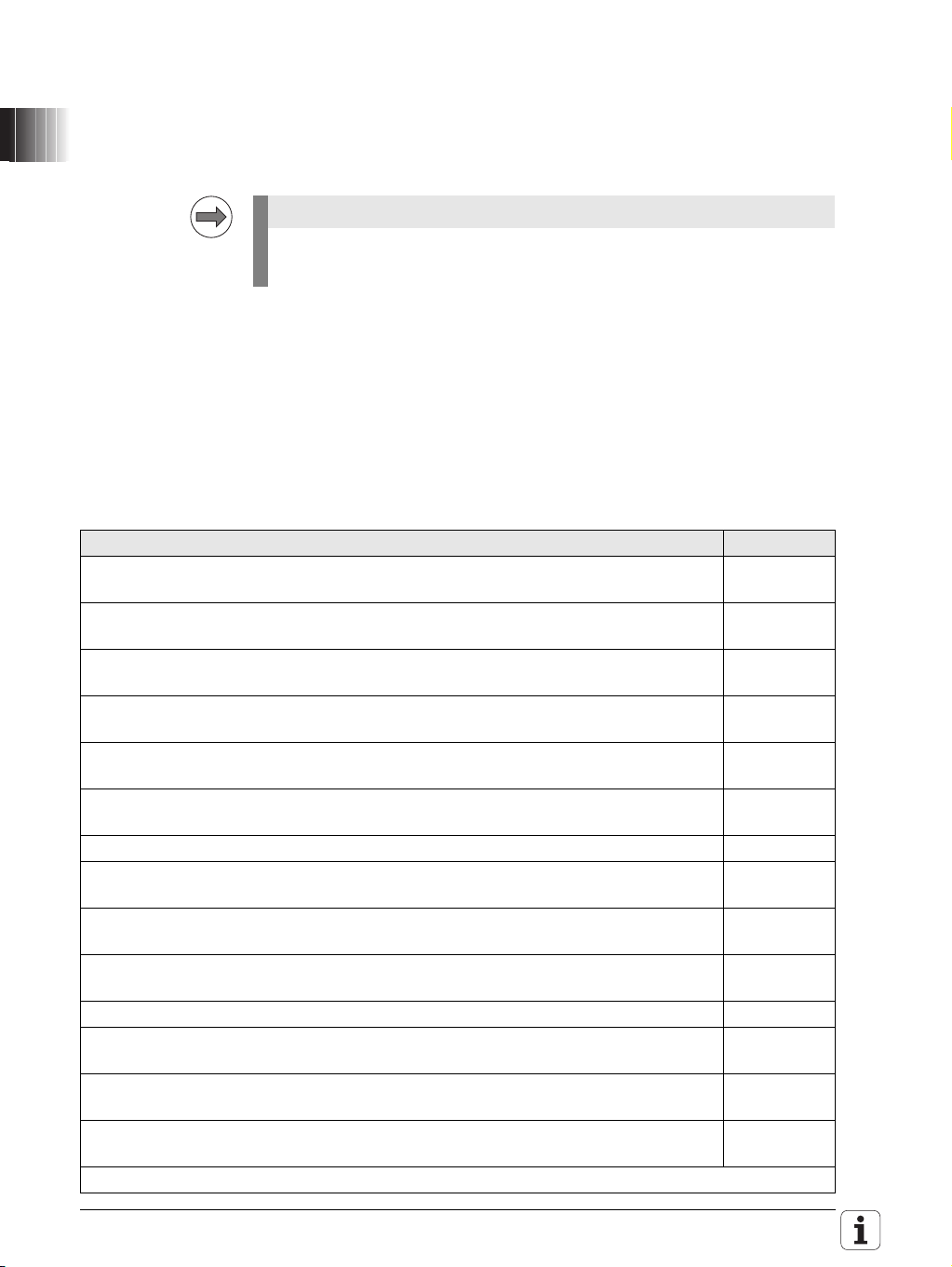
A prerequisite for the functional safety of HEIDENHAIN controls is the
USB
HR xxx FS
MB 620 FS
TE 6xx
PL 62xx FS
MC 6xxx
HDL
HSCI
BF 2xx
Cabinet
Panel
PSL
Inverter
CC 6110
X79
(X112)
UVW
POWER MODULE
READY
RESET
UVW
Permissive Buttons,
Key Switches
Emergency Stop,
Door Contacts,
Relais
connection of the actual control components via the common HSCI
connection (HSCI = HEIDENHAIN Serial Controller Interface).
Figure 3.1: Possible setup of an HSCI system
July 2011 2.5 General Information 21
Page 22

HEIDENHAIN control components for setting up a system with functional
safety:
Series Component of the control system
MC 6xxx MC main computer with HSCI interface for the
HEIDENHAIN NC control
CC 6xxx CC controller units with HSCI interface and
support for a variable number of control loops
PLB 6xxx FS Functional safety (FS) version of a bus module,
serves as carrier for several PLD-H xx-xx-xx (FS)
I/O modules. Designated SPL in this document.
PLD-H xx-xx-xx FS Functional safety (FS) version of an I/O module.
Designated SPLD in this document.
MB 6xx FS Functional safety (FS) version of a machine
operating panel. Designated SMOP in this
document.
TE 6xx Keyboard unit (ASCII keyboard, keys for
supporting the operator) without safety-relevant
tasks.
TE 6xx FS Functional safety (FS) version of a keyboard unit
with an integrated MB 6xx FS machine operating
panel. The MB is designated SMOP in this
document.
HR xxx FS Functional safety (FS) version of an HR
handwheel.
BF xxx Screen with HDL connection.
Position and speed
encoders
UM 1xxD, UVR 1x0D,
UV 130D, UR 2xxD,
UE 2xxD and UE 1xx
SIEMENSSIMODRIVE 611
HEIDENHAIN encoders with analog, EnDat 2.1
and EnDat 2.2 interface.
HEIDENHAIN power modules (UM), supply
modules (UV), regenerative supply modules
(UVR), inverter units (UE) and regenerative
inverters (UR).
The use of modules from Siemens'
SIMODRIVE 611 power module product family or
other non-HEIDENHAIN inverters has not been
approved for the integrated functional safety!
22 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Page 23

The HEIDENHAIN safety strategy enables you to implement the protection
Note
objectives defined in Directive 2006/42/EC easily and enjoy economic benefits
at the same time.
The following items may no longer be required:
Safety contactor combinations for emergency stop and guard door control
Time delay relays and auxiliary relays
Limit switches
Wiring effort
2.6 Overview of FS Components
One of the priorities of software release 606 42x-01 is the support of the new
digital real-time bus system HSCI (HEIDENHAIN Serial Controller Interface)
from HEIDENHAIN. HSCI combines the communication between axis system
and automation into one bus system between control components. Along
with simplifying the connection technology, HSCI is also the basis for safe,
dual-channel, digital communication, which is the technical prerequisite for
future integrated safety functions, referred to as "functional safety." The
official release of HSCI with integrated functional safety will be announced in
a separate Update Information once the FS system has been certified.
The following tables give an overview of the HSCI, FS and inverter
components of the iTNC 530 HSCI. The individual HEIDENHAIN components
are described in the iTNC 530 HSCI Technical Manual and the Inverters and
Motors Technical Manual.
In systems with functional safety, certain hardware components assume
safety-relevant tasks. Approval for these components must be granted for
each variant individually by HEIDENHAIN. In the following tables you will find
the basic ID number and variant for those hardware components that have
safety-relevant tasks.
The following lists, consisting of hardware components and their variants,
contain all hardware components that may be used in systems with
functional safety.
In HSCI systems with integrated functional safety (FS) you may use only
devices or variants that have been certified for use in such systems.
Please take the following lists into account when configuring your machine
and in case servicing is required. The right-most table column contains the
approved ID numbers of these components.
July 2011 2.6 Overview of FS Components 23
Page 24
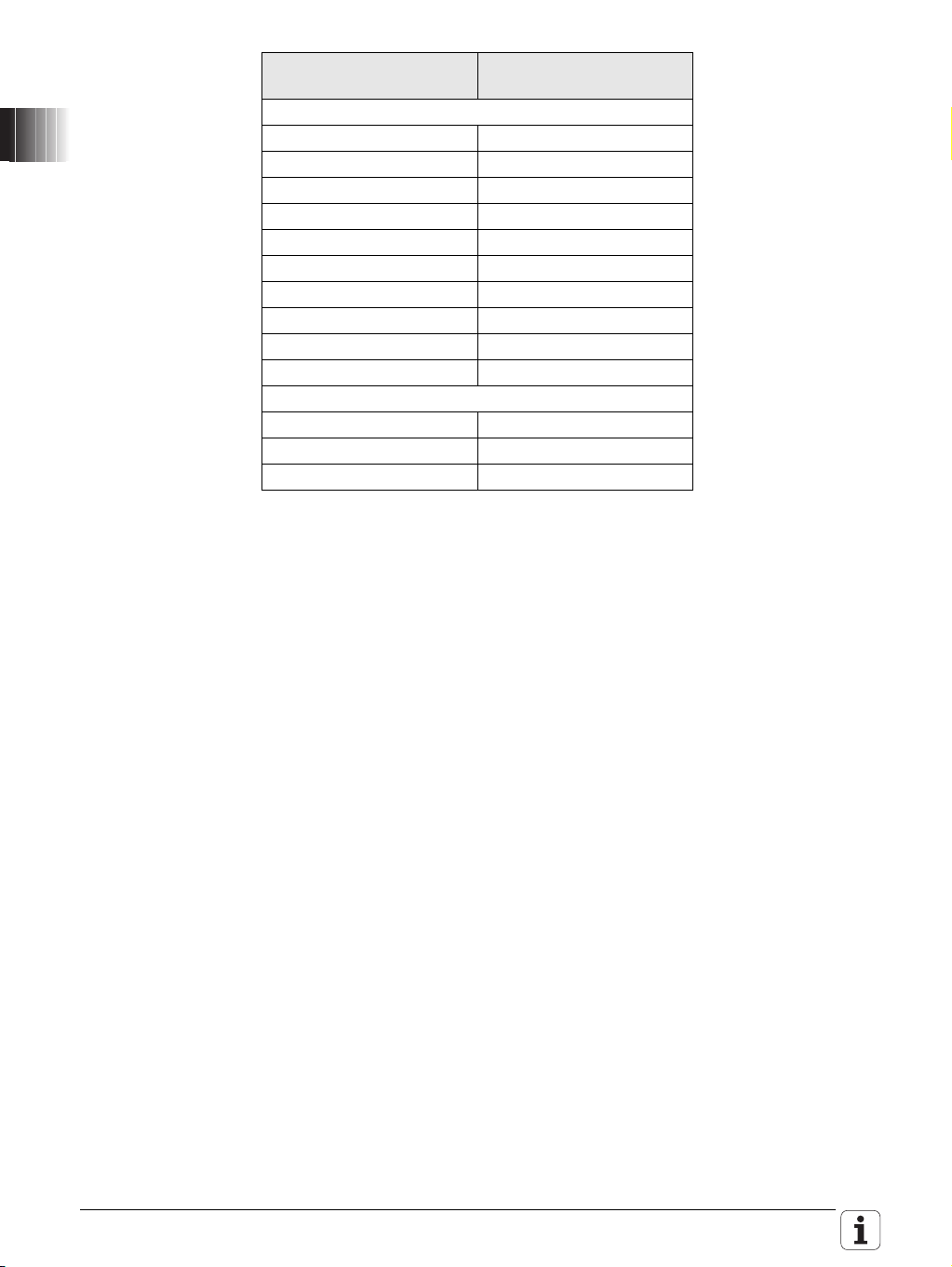
2.6.1 List of approved control components
Note
In systems with functional safety, certain hardware components assume
safety-relevant tasks. Approval for these components must be granted for
each variant individually by HEIDENHAIN. In the following tables you will find
the basic ID number and variant for those hardware components that have
safety-relevant tasks.
Systems with FS may consist of only those safety-relevant components for
which the variant is listed in the table below (e.g. xxx xxx-03).
Components indicated in this list with -xx do not assume any safety-relevant
task in the sense of functional safety (FS). You can use any variant of these
components.
Components indicated in this list with "Not yet approved for FS" are not
approved for use in systems with functional safety.
The list will be expanded or revised correspondingly when new components
are approved for use in systems with functional safety (FS). Should a
component you wish to use not be listed, please ask your contact person at
HEIDENHAIN if the component may be used.
Hardware component ID
MC 6241 Main computer 1.8 GHz with HDR, electrical cabinet version,
without Profibus
MC 6241 Main computer 1.8 GHz with HDR, electrical cabinet version,
with Profibus
MC 6222 Main computer with 15-inch TFT display, 1.8 GHz with SSDR,
operating-panel version, without Profibus
MC 6222 Main computer with 15-inch TFT display, 1.8 GHz with SSDR,
operating-panel version, with Profibus
MC 6341 Main computer with 15-inch TFT display, 2.2 GHz dual core with
HDR, electrical-cabinet version
MC 6341 Main computer with 15-inch TFT display, 2.2 GHz dual core with
HDR, electrical-cabinet version, with Profibus
HDR iTNC Hard disk for MC 6x41, 80 GB, NC software 606 420-01
HDR iTNC Hard disk for MC 6x41 (export version), 80 GB,
NC software 606 421-01
SSDR iTNC Solid State Disk for MC 6222, 32 GB,
NC software 606 420-01
SSDR iTNC Solid State Disk for MC 6222 (export version), 32 GB,
NC software 606 421-01
SIK iTNC SIK for MC 62xx, single-processor version, incl. SW option 2
SIK iTNC SIK for MC 62xx, single-processor version, incl. SW option 2
(export version)
SIK iTNC SIK for MC 63xx, single-processor version, incl. SW option 2
SIK iTNC SIK for MC 63xx, single-processor version, incl. SW option 2
(export version)
573 398-03
653 220-03
634 109-02
634 113-02
Not yet approved for FS
Not yet approved for FS
682 272-01
682 272-51
736 591-01
736 591-51
586 084-xx
586 084-xx
Not yet approved for FS
Not yet approved for FS
24 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Page 25

Hardware component ID
BF 250 15-inch TFT display with HDL connection
BF 260 19-inch TFT display with HDL connection
599 916-xx
617 978-xx
CC 6106 Controller unit for HSCI for max. 6 control loops
CC 6108 Controller unit for HSCI for max. 8 control loops
CC 6110 Controller unit for HSCI for max. 10 control loops
UEC 111 Controller unit with inverter and PLC, 4 control loops
UEC 112 Controller unit with inverter and PLC, 5 control loops
UEC 111 FS Controller unit with inverter and PLC, 4 control loops, functional
safety
UEC 112 FS Controller unit with inverter and PLC, 5 control loops, functional
safety
UMC 111 FS Controller unit with inverter and PLC for power supply via external
DC link, 4 control loops, functional safety
CMA-H 04-04-00 SPI expansion module for analog nominal-value outputs
PSL 130 Low-voltage power supply unit, 750 W, for +24 V NC and
+24 V PLC
PSL 135 Low-voltage power supply unit, 750 W, for +24 V NC, +24 V PLC
and +5 V NC
MS 110 Mounting case for multi-row configuration
MS 111 Mounting case for multi-row assembly, additional connection for
24 V supply to the fan
662 636-01
662 637-01
662 638-01
625 777-xx
625 779-xx
Not yet appro-
ved for FS
Not yet appro-
ved for FS
Not yet appro-
ved for FS
688 721-xx
575 047-xx
627 032-xx
658 132-xx
673 685-xx
TE 620 Keyboard unit without touchpad
TE 630 Keyboard unit with touchpad
TE 635Q FS TE with touchpad and integrated MB for HSCI connection,
functional safety
TE 645Q FS TE with touchpad and integrated MB for HSCI connection,
functional safety (19-inch)
MB 620 FS Machine operating panel for HSCI connection, functional safety
PLB 6001 FS HSCI adapter for OEM-specific machine operating panel,
functional safety
HR 410 FS Portable electronic handwheel with cable connection 337 159-11,
HR 520 FS Portable electronic handwheel with cable connection and display 670 304-01,
HR 550 FS Portable electronic handwheel with wireless transmission and
display
HRA 551 FS Handwheel adapter with integrated charger 731 928-01
July 2011 2.6 Overview of FS Components 25
625 806-xx
617 976-xx
662 255-01
685 394-01
660 090-01
Not yet appro-
ved for FS
578 114-03
670 305-01
598 515-02,
606 622-02
Page 26

Hardware component ID
HRA 550 FS Handwheel adapter with integrated charger 633 108-02
PLB 6104 PLB for HSCI, 4 slots 591 828-xx
PLB 6106 PLB for HSCI, 6 slots 630 058-xx
PLB 6108 PLB for HSCI, 8 slots 630 059-xx
PLB 6204 PLB for HSCI, 4 slots, with system module 591 832-xx
PLB 6206 PLB for HSCI, 6 slots, with system module 630 054-xx
PLB 6208 PLB for HSCI, 8 slots, with system module 630 055-xx
PLB 6104 FS PLB for HSCI, 4 slots, functional safety 590 479-03
PLB 6106 FS PLB for HSCI, 6 slots, functional safety 804 755-01
PLB 6108 FS PLB for HSCI, 8 slots, functional safety 804 756-01
PLB 6204 FS PLB for HSCI, 4 slots, with system module, functional safety 586 789-03
PLB 6206 FS PLB for HSCI, 6 slots, with system module, functional safety 622 721-03
PLB 6208 FS PLB for HSCI, 8 slots, with system module, functional safety 620 927-03
PLD-H 16-08-00 PL for PLB 6xxx: 16 digital inputs, 8 digital outputs 594 243-xx
PLD-H 08-16-00 PL for PLB 6xxx: 8 digital inputs, 16 digital outputs 650 891-xx
PLD-H 08-04-00 FS PL for PLB 6xxx FS: 8 digital inputs, 4 digital outputs, functional
safety
PLD-H 04-08-00 FS PL for PLB 6xxx FS: 4 digital inputs, 8 digital outputs, functional
safety
PLA-H 08-04-04 PL for PLB 6xxx, eight ±10 V inputs, four ±10 V analog outputs,
four PT 100 inputs
598 905-01,
598 905-02
727 219-02
675 572-xx
If other low-voltage power supply units are used for +24 V NC and +24 V PLC,
the output voltages must fulfill the requirements for Protective Extra Low
Voltage (PELV) with double basic insulation according to EN 50 178, also see
the iTNC 530 HSCI Technical Manual, chapter 3.8.
26 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Page 27

2.6.2 List of approved inverter components
Danger
In HSCI systems with integrated functional safety (FS) you may use only
inverters or power supply modules that have been approved for use in such
systems.
Please take this into account when configuring your machine and in case
servicing is required. Suitable devices are listed below in the right column of
the table.
Components indicated in this list with "Not yet approved for FS" are not yet
approved for use in systems with functional safety.
The list will be expanded or revised correspondingly when new components
are approved for use in systems with functional safety (FS). Should a
component you wish to use not be listed, please ask your contact person at
HEIDENHAIN if the component may be used.
Below you will find an overview of the devices that—according to ISO
13849— are permitted for use in systems with FS:
Hardware component Device ID for systems
Inverter modules
UM 117DW Not yet approved for FS
UM 116D Not yet approved for FS
UM 116DW Not yet approved for FS
UM 115D 671566-01
UM 114D 671288-01
UM 113D 730435-01
UM 112D 731984-01
UM 122D 667633-01
UM 121BD 667942-01
UM 111BD 671968-01
UM 121D 667838-01
UM 111D 667945-01
Power supply modules
UVR 120D 728252-01
UV 130D Not yet approved for FS
UVR 130D 728248-01
UVR 140D 728253-01
UVR 150D 728255-01
UVR 160D 728257-01
UVR 160DW 728258-01
UVR 170DW Not yet approved for FS
with integrated FS
July 2011 2.6 Overview of FS Components 27
Page 28
Hardware component Device ID for systems
with integrated FS
Non-regenerative compact inverters
UE 210D Not yet approved for FS
UE 211D Not yet approved for FS
UE 212D Not yet approved for FS
UE 230D Not yet approved for FS
UE 240D Not yet approved for FS
UE 241D Not yet approved for FS
UE 242D Not yet approved for FS
UE 110 Not yet approved for FS
UE 111 Not yet approved for FS
UE 112 Not yet approved for FS
Regenerative compact inverters
UR 242D Not yet approved for FS
UR 230D Not yet approved for FS
UR 240D Not yet approved for FS
28 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Page 29

2.6.3
Note
Differences between systems with and without functional safety (FS)
With the following HSCI control components, you must make a distinction
between those that are required in a system with functional safety and those
that can be used in a system without functional safety. Devices with FS are
listed below in the middle column:
Please refer to the lists of components approved for FS.
Device designation Device ID for systems
with integrated FS
Machine operating panels and keyboard units
In systems with FS you must use a machine operating panel for functional-
safety applications. In these operating panels, all keys have twin channels. A
movement can therefore be executed without additional permissive button/
key.
MB 620 (FS) 660 090-xx 617 973-xx
TE 635Q (FS) 662 255-xx 617 975-xx
TE 645Q(FS) 685 394-xx 682 104-xx
PLB basic modules
In FS systems, mixed use of PLB basic modules with and without FS is
possible. However, at least one PLB 62xx FS must be used in systems with
FS.
PLB 6104 (FS) 590 479-xx 591 828-xx
PLB 6106 (FS) 804 755-xx 630 058-xx
PLB 6108 (FS) 804 756-xx 630 059-xx
PLB 6204 (FS) 586 789-xx 591 832-xx
PLB 6206 (FS) 622 721-xx 630 054-xx
PLB 6208 (FS) 620 927-xx 630 055-xx
PLB 6001 (FS) Not yet available 668 792-xx
PLD-H I/O modules
In systems with FS, the mixed use of PLD-H modules with and without FS is
possible in PLB basic modules with FS. However, do not insert PLD-H modules
with FS in PLB basic modules without FS. Furthermore, the modules with FS
must always be inserted into the PLB with FS starting from the left.
PLD-H 16-08-00,
PLD-H 08-04-00FS
PLD-H 08-16-00,
PLD-H 04-08-00FS
Handwheels
In FS systems, handwheels with cross-circuit proof permissive buttons must be
used. Handwheels for which this has been implemented are identified with FS.
HR 410(FS) 337 159-xx,
HR 520 (FS) 670 304-xx,
598 905-xx 594 243
727 219-xx 650 891-xx
578 114-xx (with detent)
670 305-xx (with detent)
Device ID for systems
without integrated FS
296 469-xx,
535 220-xx (with detent)
670 302-xx,
670 303-xx (with detent)
July 2011 2.6 Overview of FS Components 29
Page 30

30 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Page 31

3 Directives and Standards
3.1 Applicable Directives
Compliance with the following directives is mandatory for the design of
machine tools:
Directives Applicable since
Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC December 29, 2009
EMC Directive 2004/108/EC July 20, 2007
Low Voltage Directive 2006/95/EC January 16, 2007
HEIDENHAIN controls with integrated safety strategy fulfill their share of the
requirements as specified in the above directives, thus enabling you as the
manufacturer to produce your machines in accordance with the machinery
directives.
HEIDENHAIN controls with integrated functional safety (FS), for which safetyrelevant specifications (suitability for certain PL or SIL levels) will be indicated
in the future, are not considered safety components in the sense of Machinery
Directive 2006/42/EC (article 2, letter c). Since these controls are also not
"partly completed machinery" (article 2, letter g), they do not fall under the
provisions of the Machinery Directive. For this reason we do not issue any EC
Declaration of Conformity nor a Declaration of Incorporation in the sense of
the Machinery Directive.
July 2011 3.1 Applicable Directives 31
Page 32

3.2 Basis for Testing
The safety functions described as well as the devices for controls with
functional safety (FS) are tested by TÜV Süd. The directives and standards
serving as the basis for testing are listed below:
European directives
Directives Applicable since
Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC December 29, 2009
EMC Directive 2004/108/EC July 20, 2007
Low Voltage Directive 2006/95/EC January 16, 2007
Functional safety
Safety standards Requirement Meaning / Designation
DIN EN 61508-1 to 4
(2001)
EN 954-1 (1996) Cat 3 Safety of Machinery – Safety-
DIN EN ISO 13849-1
(2008)
Due to the applications of the device or system, the following directives and
standards are also valid:
Safety standards Meaning / Designation
IEC 61800-5-2 (FDIS) (2006) Adjustable Speed Electrical Power
DIN EN 60204-1 (2007) Safety of Machinery – Electrical
SIL 2 Functional Safety of Electrical/
Electronic/Programmable
Electronic Safety-Related
Systems
Related Parts of Control
Systems
Cat 3 / PL d Safety of Machinery – Safety-
Related Parts of Control
Systems
Drive Systems – Part 5-2: Safety
Requirements – Functional
Equipment of Machines – Part 1:
General Requirements
32 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Page 33

Primary safety
Safety standards Meaning / Designation
DIN EN 50178 Electronic Equipment for Use in Power
Installations
Electromagnetic compatibility
Safety standards Meaning / Designation
DIN EN 61800-3 EMC product standard including
specific test methods for electrical
power drive systems
"EMC and functional safety for power drive systems with integrated safety
functions" principle for testing dated February 2007
July 2011 3.2 Basis for Testing 33
Page 34

Requirements of
IEC 61508 SIL 2
The goal is to control or avoid errors in the control, and to limit the probability
of dangerous failures to defined values. Safety integrated levels (SIL) have
been defined to measure the achieved level of safety-related performance.
The entire system, including all associated components, must achieve the
required safety integrated level. For systems with programmable electronics,
the SIL capability and the limited failure rate PFH (probability of dangerous
failure per hour) result from applying IEC 61508 during the development and
manufacture of these systems.
A safety integrated level corresponds to a defined range of probability for the
dangerous failure of safety functions. By achieving SIL 2, which the
HEIDENHAIN controls with functional safety do, the probability of failure of
the safety functions is between 10
-6
and 10-7 failures per hour.
Requirements
of EN 13849-1
Category 3,
Performance
Level d
Fulfillment of the
requirements
The EN 13849 standard (previously EN 954) is of special importance.
This standard groups the requirements for safety-related control components
into categories (B, 1, 2, 3, 4) and performance levels (a, b, c, d, e) in ascending
degrees of safety-related effectiveness.
Category B must always be fulfilled. It requires the following:
In accordance with the applicable standards, the design of safety-related parts
of machine controls and their safeguards must ensure that they can withstand
the influences to be expected.
To attain category 3, the occurrence of an individual fault must not result in the
loss of the safety function. The system must reliably detect individual faults.
The safety function must always remain in effect if an individual fault occurs.
The performance level determines the capability of the safety-related parts of
the control to perform a safety function. Performance Level d corresponds to
SIL 2 of IEC 61508 (see above), but is determined using a risk graph.
HEIDENHAIN controls with functional safety operate according to the
following principles in order to fulfill the requirements for category 3:
The control is structured in such a way that individual faults are detected, and
that an individual fault in the control does not result in loss of the safety
function.
Redundant structures, reciprocal data comparison and dynamic sampling of
safety-related signals are used for error detection.
The principles below are followed in order to fulfill the requirements of SIL 2:
In order to avoid faults in safety-related software, HEIDENHAIN adheres to
annexes A and B of IEC 61508-3.
Tables A.2 to A.15 and A.16 to A.19 of IEC 61508-2 are used to control random
faults and to avoid systematic faults.
34 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Page 35

3.3 Requirements on Safety Integrity
3.4 SIL and Target Failure Measures
A complete system from HEIDENHAIN, consisting of control, encoder and
drive, fulfills SIL 2. This corresponds to a PFH_total (probability of dangerous
failure per hour) of 10
Summary of the fulfilled safety categories and levels for the safety functions
described in this manual:
Complete system: SIL 2 and category 3
PFH_total: 10-7 to 10
Performance level: d
The safety functions and hardware components for functional safety (FS) are
certified by independent institutes. Upon request, your contact partner at
HEIDENHAIN can provide you with the safety-related characteristic values
needed for calculations as per EN ISO 13849-1.
-7
to 10-6.
-6
3.5 Storage and Operating Temperatures
The limit values for the individual HEIDENHAIN components are stated in the
iTNC 530 HSCI Technical Manual.
3.6 Limit Values for EM Noise Immunity
According to the current standards, safety related power drive systems with
integrated safety functions, abbreviated as PDS(SR), must have an increased
noise immunity to electromagnetic phenomena (electromagnetic compatibility
(EMC)). HEIDENHAIN complies with the limit values specified in the "EMC and
functional safety for power drive systems with integrated safety functions"
principle for testing dated February 2007. This specification is used when
testing and certifying the iTNC 530 HSCI with integrated safety.
3.7 Mission Time
An average life limit of 20 years is assumed for these controls.
July 2011 3.7 Mission Time 35
Page 36

36 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Page 37

4 Realization and Safety Functions
4.1 Glossary
A channel and
B channel
STL Statement list of the (S)PLC program
API Application programming interface
CC Controller computer:
Master CC Master controller computer:
All safety-related areas of the control (hardware and
software) have a dual-channel design. The two channels
are designated as the A channel and B channel.
Areas covered by the A channel are colored blue in this
document.
Areas covered by the B channel are colored red in this
document.
Interface between the (S)PLC program and the
respective safety-kernel software (SKERN MC, SKERN
CC) or the standard functions of the NC software.
Modular HSCI slaves, for servo drive control
CCs also assume safety-related tasks (see SPLC/
SKERN below). The MC determines the master CC on
the basis of the relative positions in the HSCI system.
The first CC in the HSCI system (nearest the MC)
becomes the master CC.
Modular HSCI slaves, for servo drive control
In a safety-related control system, the master CC alone
assumes the following special tasks in addition to the
usual tasks of every CC:
Represents the B channel of a safety-related control
system
Generates the output states of the SPLC of the
B channel (for the safety-related outputs on the SPL),
such as the outputs for controlling the brakes
Monitors the controlling of the motor holding brakes
of the B channel (via power module or SPLC) and the
disabling of power modules for all axes in the system
Supplies the B-channel data for cross comparison
Supplies the actual position values for the SPLC
July 2011 4.1 Glossary 37
Page 38

CC-CC
communication
FPGA Field programmable gate array:
HDL HEIDENHAIN display link:
HR Handrad HR (German) = Handwheel HW
HSCI HEIDENHAIN serial controller interface:
Special HSCI telegram for exchanging the following
data between two or more CCs:
States of the individual axes (at standstill or in motion)
Axis-group assignment
Actual position values of the axes
Status of brake control
Status of the axis-specific cutout ports of
the B channel
Information about fatal fault
Freely programmable logic circuit.
HDL is a data connection between the MC and the
screen/keyboard.
Handwheel for operating the machine.
HSCI is a field bus system that is based on Ethernet
hardware and has a line structure according to the
master-slave principle. There is one master in the
system; all other devices are slaves. All data transfers
are initiated by the master; however, direct
communication between the slaves is also possible.
IOC file Configuration file of the HSCI system:
Configuration of all participants in the HSCI system,
their sequence and configuration of the inputs and
outputs of the (S)PLC.
LIFT-OFF Function that lifts off the tool automatically from the
contour by a defined distance in the tool-axis direction
in order to protect the workpiece (e.g. in a power
failure).
MC Main computer:
Control hardware that also functions as a master for
HSCI.
PLC Programmable logic control:
The main task of the PLC program is the processing of
the input information from the PLs and the generation
of output states for the PLs (see page 4–42).
SKERN Safety-kernel software:
The software process of the safety-kernel software
(SKERN) runs in parallel to the SPLC. Basic safety
functions are permanently defined in the SKERN
software and cannot be changed (see page 4–45).
38 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Page 39

SMOP Safe machine operating panel:
The (safety-related) machine operating panel is an HSCI
slave to which safety-related keys for controlling a
machine tool are attached and to which further
(safety-related) inputs/outputs are connected (see page
6–152).
The safety-related data is transmitted from the SMOP
to the MC and CC over two channels via the HSCI
connection. The safety-related data is transferred from
there to the respective SPLC.
SPLC Safe programmable logic control:
The main task of the SPLC program is the processing of
the input information from the SPLs and the generation
of output states for the SPLs. This can be configured
flexibly using the SPLC program.
(see page 4–43)
SPL and PL (Safe) programmable logic unit:
A PL is an HSCI slave equipped with multiple I/O
modules. Each I/O module provides digital ((S)PLD) and/
or analog (PLA) inputs and/or outputs (I/Os). These I/Os
are read and controlled by the PLC and SPLC during
normal operation (see page 4–43).
An SPL is a dual-channel PL, which is equipped with
controllers for the A channel and the B channel. The
safety-related data is transmitted from the SPL to the
MC and CC over two channels via the HSCI connection.
The safety-related data is transferred from there to the
respective SPLC.
A safety-related control generally uses both SPLs and
single-channel PLs. Safety-functions require the use of
SPLs.
An (S)PL is structured as follows:
Bus module
All (S)PLs have a bus module. The bus module can
have only one controller (for the A channel), or two
controllers (for the A channel and the B channel) in the
case of a control with integrated safety.
System module
A system module has control-specific
I/Os and connections for touch probes. At least one
system module is present in every system.
I/O module – (S)PLD, PLx
One S(PL) has slots for four, six or eight I/O modules.
Both (safety-related) digital ((S)PLD) I/Os and, for
example, analog (PLA) I/Os can be inserted.
System PL
SPL with system module
July 2011 4.1 Glossary 39
Page 40

SPLD and PLD One SPL or PL has slots for four, six or eight digital I/O
modules.
A safety-related control generally uses both SPLDs and
single-channel PLDs. Safety-functions require the use
of SPLDs.
FS inputs,
FS outputs
(S)MP (Safety) machine parameters:
S status Safe status range of the HSCI telegram. The safe status
TM Tool magazine:
SSt Safety self-test:
WD Watchdog:
Safety-related dual-channel inputs/outputs. One FS
input/output consists of two physical terminals.
Parameters for adapting the control to the respective
machine tool (see page 5–95).
range contains bits for the status of watchdogs,
emergency stop and power-fail information, etc. of the
individual HSCI participants. The bits of the safe status
range provide the basic safety-related information of the
A channel (see page 4–75).
Tool magazine for the storage and management of
different tools.
Safety self-test (see page 7–157)
Counter for monitoring the status of other functions or
components.
40 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Page 41

4.2 Realization of the HEIDENHAIN Safety System
The dual-channel safety system of HEIDENHAIN controls is achieved by a
dual-channel control architecture. The two computers are located in the MC
main computer and CC controller unit components, where two independent
software processes run. These two processes realize two safety channels,
which capture and evaluate all safety-relevant signals in the two channels.
Faults are detected by mutual comparison of the states and data (cross
comparison) in the two channels. This way, the occurrence of just one fault in
the control does not lead to the safety functions being incapacitated.
The SPLC (safety-related PLC) and SKERN (safety-kernel software) software
processes are the basis of the two redundant channels. The two software
processes run on the MC (CPU) computer and the CC (DSP) controller unit
computer.
The dual-channel structure of the MC and CC is also used in the PL 6xxx FS
input/output systems and the MB 6xx FS machine operating panel. This
means that all safety-relevant signals (e.g. permissive buttons and keys, door
contacts, emergency stop button) are captured via two channels, and are
evaluated independently of each other by the MC and CC. The MC and CC use
separate channels to address the power modules, and to stop the drives in
case of a fault.
Furthermore, HEIDENHAIN controls with functional safety offer four safetyrelated operating modes as per the EN 12 417 standard (Machine Tools–
Safety–Machining Centers). The application-oriented operation offered by this
promises a high level of acceptance, and therefore safety.
4.3 Activation of Functional Safety (FS)
Functional safety is not a software option that must be enabled. If the control
identifies a PLB 62xxFS in the HSCI system during booting, functional safety
is activated. In this case, the following prerequisites must be fulfilled:
Functional safety versions of safety-related control components (e.g.
MB 620FS, HR 520FS)
Safety-related SPLC program
Configuration of safe machine parameters
Wiring of the machine for systems with functional safety
July 2011 4.3 Activation of Functional Safety (FS) 41
Page 42

4.4 (S)PLC Programs
MC 6xxx
CC 6xxx
B channel
A channel
DSP
CPU
HSCI Interface
Cross comparison
HSCI Interface
The main task of the (S)PLC program is the processing of the input information
from the (S)PLs and the generation of output states for the (S)PLs.
To do so, it edits the PLC memory via PLC commands with memory operands.
Logical states and signed bytes, words (16 bits) and doublewords (32 bits) are
saved in this memory.
Specific areas have different tasks:
Memory mapping the status of the inputs
Memory for timers and counters
Memory for internal states and calculations
Memory for the interface to the software of the MC and CC
Memory defining a map of the outputs to be set
This division of the memory is also called a memory map.
On a control with integrated safety, three different PLC programs with
separate memory maps are run simultaneously:
Standard PLC program on the hardware of the MC
SPLC program on the hardware of the MC
SPLC program on the hardware of each CC
42 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Figure 3.2: SKERN and SPLC
Page 43

4.5 SPLC
The safe PLC program (= SPLC program), the PL 6xxx FS (= SPL) input/output
modules and the MB 6xx FS (= SMOP) machine operating panel provide the
machine tool builder with a flexible configuration of the safety system. The
SPLC consists of the SPLC runtime system and the SPLC program. The SPLC
runtime system is part of the software supplied by HEIDENHAIN. It executes
the SPLC program that must be written by the machine tool builder. The
safety-related inputs and outputs as well as additional safety functions can be
programmed flexibly in the SPLC program. The SPLC is also responsible for
the import and processing of FS inputs, as well as for the output of FS outputs.
The SPLC software runs both on the MC (SPLC MC) and on every CC (SPLC
CC) completely independently. The SPLC MC is assigned to safety channel A,
and the SPLC CC to safety channel B. Every SPLC communicates with further
HSCI participants (e.g. SPL, SMOP) via HSCI. The evaluated data is then
transmitted to the respective SKERN (MC/CC). The SPLC requests the
execution of safety functions from the SKERN. However, the SKERN can
activate safety functions that provide an even higher degree of safety for the
operator.
The physical FS inputs (terminals on SPL or SMOP) of the A channel and the
B channel are first gated with AND; only the result of the AND operation is
then forwarded to the SPLC as input status. Consequently, the SPLCs of the
A channel and the B channel will receive the value 0 as input information if two
inputs have different states (e.g. A channel = 0, B channel = 1).
As with the standard PLC program, the PLCdesignNT PC software from
HEIDENHAIN is used to create the SPLC program. For requirements to be met
by the SPLC program, see page 184.
Tasks of the SPLC:
Flexible adaptation of the safety functions to the respective machine tool by
the machine tool builder
Import (reading in) of FS inputs
This includes, for example:
• External EMERGENCY STOP
• Axis-group-specific "Control Voltage ON" key
• Door contacts of the guard doors
• Permissive buttons and keys (on the handwheel, operating panel and
tool magazine)
• Keylock switches for the safety-related operating modes (SOM_1,
SOM_2, SOM_3, SOM_4)
• Test input for motor holding brake
• Feedback from chain of normally closed contacts
• Axis-direction keys
• Other keys with a Start function (NC start, spindle start, spindle jog)
• Keys with Stop function (NC stop, spindle stop)
Gating of FS inputs/outputs
July 2011 4.5 SPLC 43
Page 44

Realization of machine-specific safety functions
Realization of timer functions
Data transfer from the SPLC to the safety-kernel software (see also page 8–
193)
• Request for the safety-related operating mode (SOM_1, SOM_2,
SOM_3, SOM_4)
• Axis-group-specific request for monitoring the safely limited speed
(SLS) in the respectively active, safety-related operating mode
• Axis-specific and axis-group-specific activation of a permissible
movement after the evaluation of the inputs of axis-direction keys (of
SMOP, HW, TM)
• Axis-group-specific request for stop reactions (SS1, SS1F, SS2)
• Axis-group-specific state of the permissive buttons and keys
• Status of the chain of normally closed contacts
• Status of the "Control Voltage ON" (CVO) key
• Axis-group-specific drive enable (PDO = Permit Drive On)
• At least one machine operating key is pressed
• Status of the test input of the motor holding brakes
Controlling of outputs that are commanded by the safety-kernel software
(e.g. SBC safety function), or of safety-related outputs defined by the
machine tool builder.
The SPLC program of the master CC controls the SPLC outputs of the
B channel of each SPL; the SPLC program of the MC controls the SPLC
outputs of the A channel.
44 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Page 45

4.6 SKERN
The software process of the safety-kernel software (SKERN) and the SPLC run
in parallel on the MC and CC. Basic safety functions are permanently defined
in the SKERN software and cannot be changed by the machine tool builder.
The safety-kernel software receives status information and requests for safety
functions from the SPLC. The SKERN initiates safety functions and monitors
them. Furthermore, all dynamic tests are controlled by the safety-kernel
software.
The safety-kernel software is responsible for the realization of all basic safety
functions:
Initiation and monitoring of the stop reactions (SS0, SS1, SS1F, SS2)
Standstill monitoring in SOS state
Monitoring of the safely limited speeds (SLS) in the various safety-related
operating modes
Initiation of safe brake control (SBC)
Safely-limited position (SLP)
Nominal-actual value comparison of position values or speed values
Control of dynamic tests
Carrying out the cross comparison
Commanding the control of safety-related outputs of the SPLC (e.g. control
of motor holding brakes)
Transfer of axis-group states (STO, SOS, AUTO (AUTO = operation if the
guard doors are closed) or of the safety function in direct connection with
the operating mode: SLI_2 through SLI_4, SLS_2 through SLS_4) to the
SPLC
Transfer of the axis states (at standstill or in motion) to the SPLC
Transfer of the axis positions to the SPLC
Performing the safety self-test (SSt)
July 2011 4.6 SKERN 45
Page 46

4.7 Cross Comparison
Note
During the cross comparison, safety-related signals and operating states
(active safety functions) are exchanged between the MC and the CC, and
compared in both units. The cross comparison is performed by the SKERN of
the MC and the CC in a safety cycle (3 ms).
If one of the CCs or the MC detects a fault, an SS1 reaction is initiated.
The cross comparison contains the following data:
All output signals from the SPLC that are transferred to the safety-kernel
Status information of the safety-kernel software in the MC and CC.
Output signals from the SPL that are fed back to the safety-kernel software
Status information of the SPLC program on both the MC and CC
SS1F stop reactions requested by the SPLC runtime system
The gated and, where applicable, fed-through signals, which are the output
signals from the SPLC of the MC and CC to the respective SKERN, are
compared.
In the HEIDENHAIN system the SPLC output statuses mapped from the
physical inputs, and not the physical inputs themselves, are used for the cross
comparison during forced dynamic sampling. During forced dynamic sampling
the physical inputs are checked only for a short-circuit to +24 V. A real cross
comparison of the physical inputs is only performed during the safety self-test
to avoid problems with dual-channel keys that do not switch simultaneously.
software.
(outputs can be read back).
Each of the dual-channel hardware outputs has a feedback mechanism
on the I/O modules of the SPL, which can be used to read the status of the
output. This dual-channel information is sent from the SPL to the SPLCs via
the HSCI, and transferred to the safety-kernel software of the MC and CC.
The cross comparison is always active for all safety-related outputs.
(SPLC program is being executed).
A direct cross comparison of the physical input signals of the SPLC does
not take place.
46 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Page 47

4.8 Description of the Safety/Monitoring Functions
Danger
The risk analysis you have to carry out for the machine must state the
requirements to be fulfilled by the individual safety function.
Before using the control, you must check whether the safety functions
realized by HEIDENHAIN meet the requirements of your risk analysis.
All components (e.g. control hardware, control software, emergency stop
button, safety relays) that are involved in the individual safety functions must
meet the requirements for the safety function. The hardware of the individual
safety functions, including the wiring, must also be structured according to the
determined requirements.
4.8.1 Overview of the safety functions
In order to ensure operator protection, the control and drive system with
integrated HEIDENHAIN safety design provides a number of safety functions
you can request and initiate through the SPLC program, and parameterize
through SMPs. These safety functions to be complied with correspond to the
draft of the new DIN IEC 61800-5-2 standard.
Overview of definitions Brief description
Safe stop 0
(SS0)
Safe stop 1
(SS1)
Safe stop 1D
(SS1D)
Safe stop 1F
(SS1F)
The current to the drives is cut off. The
STO and SBC functions are initiated
immediately.
The drives are switched back on by
turning the machine off and on. The
stop reaction is carried out via two
channels.
The drives are stopped along the
emergency braking ramp. The STO
and SBC functions are initiated after
standstill.
The drives are switched back on via
Control Voltage ON. The stop reaction
is carried out via two channels.
Same as SS1, but axis-group-specific
switch-off with delay.
The drives are stopped along the
emergency braking ramp. The STO
and SBC functions are initiated after
standstill.
The drives are switched back on by
turning the machine off and on. The
stop reaction is carried out via two
channels.
July 2011 4.8 Description of the Safety/Monitoring Functions 47
Page 48

Overview of definitions Brief description
Safe stop 2
(SS2)
Safe torque off
(STO)
Safe operating stop
(SOS)
Safely limited speed
(SLS)
Safely limited position
(SLP)
Safe brake control
(SBC)
The axes and spindles are stopped
along the braking ramp. At standstill
the STO function is initiated for the
spindles, and the SOS function for the
axes. The stop reaction is carried out
via two channels.
The energy supply to the motor is
interrupted via two channels (by MC
and CC).
The drives remain under position
control and are monitored for
standstill via two channels (by MC and
CC).
The SS1 safety function is initiated if
defined speed limit values are
exceeded. Monitoring takes place via
two channels (by MC and CC).
The SS1 safety function is initiated if
an absolute position limit value is
exceeded. Monitoring takes place via
two channels (by MC and CC).
Dual-channel control of external motor
holding brakes (by MC and CC).
Safely limited increment
(SLI)
The function must be realized via the
SPLC program.
48 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Page 49

4.8.2 Overview of monitoring functions
Further monitoring functions are integrated in addition to the safety functions.
These monitoring functions can be programmed through SMPs to a certain
extent.
Overview of definitions Brief description
Nominal-actual value comparison
of position values
Nominal-actual value comparison
of speed values
Monitoring of the encoder
amplitudes
Monitoring of the encoder
frequency
Protection against unexpected
start-up
dv/dt monitoring of the axes/
spindle by the MC/CC
Dual-channel comparison (by MC and
CC) of the actual position values
(speed encoder, position encoder) to
the nominal position value.
Dual-channel comparison (by MC and
CC) of the actual speed values (speed
encoder, position encoder) to the
nominal speed value.
Dual-channel monitoring (by MC and
CC) of the signal amplitudes of the
encoders.
Dual-channel monitoring (by MC and
CC) of the input frequency of the
encoders.
If all axes or spindles of an axis group
do not move for more than 3 seconds
during SLS, an automatic axis-groupspecific transition to SOS or STO is
carried out.
During deceleration the axes and the
spindle are monitored via two
channels (by MC and CC) for a
decrease in speed.
Temperature monitoring Monitoring of the internal temperature
of HSCI components.
Monitoring of rotational speed of
fan
Monitoring of the supply voltages On each board, the supply voltages
July 2011 4.8 Description of the Safety/Monitoring Functions 49
Dual-channel monitoring (by MC and
CC) of the rotational speed of the
internal fans of HSCI components.
are monitored via two channels.
Page 50

4.8.3 Safe stop 0 (SS0)
Danger
CC: STO.B.x
BRK.B.x, BRK_REL.B.x
RDY.x off
MC: STO.A.x, STO.A.G, STOS.A.G
BRK_REL..A.x
Start of SS0 reaction
Spindle without brake coast to a stop
Spindle with holding brake
Axis only stopped
by holding brakes
Axis/Spindle: STO
Spindle
Axis
Breaking behavior upon SS0
An SS0 reaction is initiated in the event of a fault.
An SS0 reaction is initiated by the SKERN. The SPLC cannot request an SS0
reaction from the SKERN.
If an SS0 is initiated, the STO (see page 4–60) and SBC (see page 4–66) safety
functions are activated for the affected axis (axes) and spindle(s) via two
channels.
The switch-off of safe outputs must be realized through the SPLC program
(see page 8–197). The behavior of normal PLC outputs can be configured via
IOconfig.
Axes and spindles that do not have mechanical motor holding brakes
coast to a stop.
The measures to be taken against external force (e.g. sagging of hanging
axes) must be in accordance with Information Sheet No. 005 "Gravityloaded axes (vertical axes)" issued by the engineering technical
committee of the BGM (German Employer's Liability Association in the
metal industry).
After SS0, the drives can be restarted only by turning the main switch off
and back on (power supply voltage of the machine).
50 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Figure 3.3: Braking behavior upon stop 0
(For signal designations, see page 5–120)
Page 51

4.8.4 Safe stop 1 (SS1) – Fastest possible stopping
An SS1 reaction is initiated if a fault or an emergency stop occurs.
An emergency stop can be initiated internally by the SKERN itself, or can be
initiated depending on the safety-related inputs for emergency-stop buttons.
An SS1 reaction is initiated by the SKERN. The SPLC can request an axis-
group-specific SS1 reaction from the SKERN (for axis groups, see page 6–
136).
If an SS1 is initiated, the affected axis (axes) and spindle(s) are decelerated by
the respective CC as quickly as possible along the emergency braking ramp.
When the SS1 reaction starts, the monitoring timers with the time defined in
SMP525.x for the axes and in SMP526.x for the spindles are started. The
initiated deceleration process is additionally monitored via dv/dt monitoring
(see page 4–69).
The steepness of the emergency braking ramp (ramp for deceleration) is
defined in MP2590. The greater the value entered in MP2590, the steeper the
emergency braking ramp. The maximum value for MP2590 is limited by the
output power of the inverter. The minimum value is defined in MP1060. The
permissible acceleration of the axis during normal machining operation is
defined in MP1060. If the value in MP2590 is less than the value in MP1060,
the value from MP1060 will be used.
A special case is the value of 0 in MP2590, which results in deceleration at the
limit of current.
After the values for MP2590 and MP1060 have been defined, the collective
braking behavior of all axes must be checked by the machine tool builder by
initiating an emergency stop. It must be ensured that this does not lead to an
overload and, as a result, to the switch-off of the inverters. The maximum
permissible deceleration time of all axes must not be exceeded.
The switch-off of safe outputs must be realized through the SPLC program
(see page 8–197). The behavior of normal PLC outputs can be configured via
IOconfig.
July 2011 4.8 Description of the Safety/Monitoring Functions 51
Page 52

A distinction is made between the following cases for SS1 reactions:
Danger
MC: STO.A.G, STOS.A.G, STO.A.Sx RDY.x off
CC: BRK.B.x,
BRK_REL.B.x
CC: STO.B.x
CC: STO.A.Sx
Spindel: STO
MC: STO.A.x,
BRK_REL.A.x
Correct breaking behavior upon SS1
Start of SS1 reaction
Spindle
Axis
Spindle and axis
stopped along emergency
stop ramp by CC (SS1)
dv/dt monitoring active
Reaction time
of holding brake
MP2308 (200 ms)
Additionally stopped
by holding brakes
SMP525.x (Axis)
SMP526.x (Spindle)
Speed limits
Spindle n < 10 rpm
Axis F < 50 mm/min
Normal deceleration process
(timer monitoring and dv/dt monitoring do not respond):
If a standstill of the axes (feed rate < 50 mm/min) or spindles (speed < 10
rpm) within the time defined in SMP525.x or SMP526.x is detected by a CC,
this CC initiates the SBC safety function. After the time defined in MP2308
(default: 200 ms) has expired, this CC then initiates the STO safety function.
If the MC detects that the CC is in STO, the MC also initiates the STO and
SBC safety functions.
Faulty deceleration process (timer monitoring responds)
If the time set in SMP525.x or SMP526.x is exceeded in the timers on the
MC and CC during the deceleration process, the MC and CC initiate the SS0
safety function independently of each other.
Axes and spindles without mechanical motor holding brakes coast to a
stop if an SS0 is initiated.
The measures to be taken against external force (e.g. sagging of hanging
axes) must be in accordance with Information Sheet No. 005 "Gravityloaded axes (vertical axes)" issued by the engineering technical
committee of the BGM (German Employer's Liability Association in the
metal industry).
Faulty deceleration process (dv/dt monitoring responds)
The fault reaction is in accordance with the description of dv/dt monitoring
(see page 4–69).
After SS1, the restart of the drives is enabled by switching on the machine
control voltage (CVO) via the Control Voltage ON button (see page 4–81).
Figure 3.4: Braking behavior upon stop 1
52 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Page 53

SMP525.x
SMP526.x
MC: STO.A.G, STOS.A.G, STO.A.Sx
CC: STO.B.Sx
RDY.x off
MC: STO.A.x,
BRK_REL.A.x
CC: STO.B.x
BRK.B.x
BRK_REL.B.x
Braking behavior with wrong values in SMP525.x/SMP526.x
Start of SS1 reaction
Spindle
Axis
Spindle and axis
stopped along emergency
stop ramp by CC (SS1)
dv/dt monitoring active
Spindle coast to a stop
Axis stopped by
holding brakes
Figure 3.5: Braking behavior upon stop 1 with incorrect parameters
July 2011 4.8 Description of the Safety/Monitoring Functions 53
Page 54

4.8.5 Safe stop 1D (SS1D) – Delayed SS1
The SS1D stop reaction is a delayed SS1, in which, for example, the axis group
of the spindle is not decelerated until the axis groups of the NC axes have
been stopped.
The braking sequence of the axis groups for SS1D is defined in MP610.x.
The switch-off of safe outputs must be realized through the SPLC program
(see page 8–197). The behavior of normal PLC outputs can be configured via
IOconfig.
4.8.6 Safe stop 1F (SS1F) – Fastest possible stopping
An SS1F reaction is initiated in the event of a fatal fault.
An SS1F corresponds to an SS1 reaction, but it is initiated globally for all drives
of the machine tool. The switch-off of safe outputs must be realized through
the SPLC program (see page 8–197). The behavior of normal PLC outputs can
be configured via IOconfig.
After SS1F, the drives can be restarted only by turning the main switch off
and back on (power supply voltage of the machine)!
54 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Page 55

4.8.7 Safe stop 2 (SS2) – Controlled stopping
An SS2 reaction is initiated by the SKERN. The SPLC can request only
axis-group-specific SS2 reactions from the SKERN (see page 6–136 for axis
groups).
A distinction is made between the following cases for SS2 reactions:
Normal deceleration process
(timer monitoring and path monitoring do not respond):
An SS2 reaction is initiated by the SKERN or must be initiated by the SPLC
program upon:
Releasing an axis-direction key (axis-specific SS2 by the SKERN; the SPLC
program must set the attribute PP_AxFeedEnable = 0, see page 208)
Releasing the permissive button or key while the spindle is running (Figure
3.6) (axis-group-specific SS2 by the SKERN; permissive button/key
information is passed on by the SPLC program)
Releasing the permissive button or key during programmed movements in
the SOM_2 or SOM_3 operating mode (axis-specific SS2 by the SKERN; the
SPLC program must set the marker MG_Program_Running = 0, see page 205)
Pressing the NC stop key (SS2 reaction must be initiated through the SPLC
program)
Switching between safety-related SOM_x operating modes (SS2 reaction
must be initiated through the SPLC program)
Opening the guard door of an axis group during programmed movements
without pressing a permissive button or key (SS2 reaction must be initiated
through the SPLC program).
Selection of or switching to one of the following machine modes of
operation (SS2 reaction is initiated by the SKERN)
• Switching to the El. Handwheel mode of operation (El. Handwheel
mode of operation or activation of an HR 5xx handwheel)
• Switching to operation through machine operating panel
• Switching to the Reference run mode of operation
If an SS2 is initiated for the axes, the SKERN instructs the NC software to
decelerate the drives of the affected axis (axes) on the contour until standstill.
This ensures that the nominal contour is not departed from during the
deceleration process (workpiece protection). To do this, the axes are stopped
using interpolation.
When an SS2 reaction starts, the SKERN monitoring timers with the time
defined in SMP527.x for the axes are started, and path monitoring for the
permissible axis-specific path of traverse defined in SMP550.x is activated.
When the axes have come to a standstill (SKERN monitors for feed rate
< 50 mm/min), the safe operating stop (SOS) safety function is initiated for the
affected axes.
If the spindle is running at the same time, the SKERN initiates an SS1 for the
spindle of the working space after the axes have been brought to a standstill
through SS2. This must be realized in the SPLC program. On a machine with
multiple spindles, it is possible that a spindle can already be decelerated
before all axes have been stopped. This behavior can be achieved through a
suitable configuration of axis groups (see page 6–136).
July 2011 4.8 Description of the Safety/Monitoring Functions 55
Page 56

An SS2 reaction for the spindle must be initiated by the SPLC program upon:
Spindel: STO
MC: STOS.A.G, STO.A.Sx
CC: STO.B.Sx
RDY.x off
Start of SS2 reaction
SS1 for Spindle
Spindle and axis
stopped along emergency
stop ramp by CC (SS1)
dv/dt monitoring active
Decelerating on contour
Path monitoring active
Spindle
Axis
SMP527.x (Axis)
Axis: SOS
SMP526.x (Spindle)
Correct breaking behavior upon SS2
after releasing permissive buttons at turning spindle
Pressing the spindle stop key
Releasing the spindle jog key
If an SS2 is initiated for the spindle, the SKERN instructs the NC software to
decelerate the spindle of the axis group.
When an SS2 reaction starts, the SKERN monitoring timers with the time
defined in SMP528.x for the spindles are started.
When the spindles have come to a standstill (SKERN monitors for speed
< 10 rpm), the safe torque off (STO) safety function is initiated for the affected
spindles.
SMP549.x can be used to activate the same behavior for the spindles as for
the axes. The spindles will then also change to the SOS state as part of an SS2
reaction. This may be required for the configuration of lathes. However, the
change to SOS instead of STO is only possible if the SS2 reaction was
triggered by pressing the spindle stop key. If the SS2 reaction was triggered
by a different event, then the STO state is maintained at the end of a stop
reaction.
Faulty deceleration process (timer monitoring responds)
If the time defined in SMP527.x for the axes or the time defined in SMP528.x
for the spindles is exceeded in the SKERN timers during the deceleration
process, the SKERN initiates the SS1 safety function.
Faulty deceleration process (path monitoring responds)
If the axis-specific maximum permissible path defined in SMP550.x for the
SS2 reaction is exceeded, the SKERN initiates the SS1 safety function.
The machine control voltage (CVO) is not switched off at the end of an SS2
reaction! The drives can therefore be restarted directly.
Figure 3.6: Braking behavior upon stop 2 (releasing the permissive button or
key while the spindle is running)
56 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Page 57

Figure 3.7: Braking behavior upon stop 2 (pressing the spindle stop key)
RDY.x off
Spindle: STO
MC: STOS.A.G, STO.A.Sx
CC: STO.B.Sx
Correct breaking behavior upon SS2
after pressing spindle stop
Start of SS2 reaction
Spindle: braking at braking ramp
Spindle
SS2 reaction for spindle
SMP528.x (Spindle)
SMP527.x
RDY.x off
CC: STO.B.x
MC: STO.A.x,
BRK_REL.A.x
Decelerating on contour
Path monitoring active
Spindle and axis
stopped along emergency
stop ramp by CC (SS1)
dv/dt monitoring active
Spindle
Axis
Start of SS2 reaction
Spindle: STO
MC: STOS.A.G, STO.A.Sx
CC: STO.B.Sx
SMP525.x (Axis)
SMP526.x (Spindle)
*) see also braking behavior upon SS1
SS1*)
Axis
Spindle
Braking behavior with wrong value in SMP527.x for axis
Figure 3.8: Braking behavior upon stop 2 with incorrectly set parameters
July 2011 4.8 Description of the Safety/Monitoring Functions 57
Page 58

4.8.8 Summary of the stop reactions
MC CC
Stop 0
(SS0)
Stop 1
(SS1)
Immediate initiation of STO and
SBC:
Clearing of WD.A.STO, WD.A.SMC
and STO.A.P.x
Activation of motor holding brakes
Status of the signals:
–STO.A.G = 0
–STOS.A.G = 0
–STO.A.x = 0
–BRK_REL.A.x = 0
Restart: main switch Off/On
Stopping along the emergency
braking ramp:
"Drives Off" command for axes and
spindle to the CC.
Wait until all drives have been
switched off by the CC:
--> STO and activation of motor
holding brakes
For status of the signals, see above.
Restart: with Control Voltage ON
(CVO)
The deceleration process is
monitored by timers according to
SMP525.x/SMP526.x, and dv/dt
monitoring
Immediate initiation of STO and
SBC:
Clearing of STO.B.P.x
Activation of motor holding brakes;
error code to MC
Status of the signals:
–STO.B.x = 0
–BRK.B.x = 0
–BRK_REL.B.x = 0
Restart: main switch Off/On
Stopping along the emergency
braking ramp:
A command from the MC or
detection of the fault by the CC itself
leads to axis-specific electrical
deceleration along the emergency
braking ramp until standstill; then
axis-specific activation of the
mechanical brakes;
After 200 ms --> STO
For status of the signals, see above.
Restart: with Control Voltage ON
(CVO)
The deceleration process is
monitored by timers according to
SMP525.x/SMP526.x, and dv/dt
monitoring
(If the fault is detected by the CC
itself, an error message is sent to the
MC beforehand)
Stop 1F
(SS1F)
58 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Fault reaction:
Corresponds to stop 1 (SS1), but:
Restart: main switch Off/On
Fault reaction:
Corresponds to stop 1 (SS1), but:
Restart: main switch Off/On
Page 59

MC CC
Stop 2
(SS2)
Deceleration along the contour:
Instruction to the NC software: Stop
the axes and spindles along the
braking ramp;
In addition, SS2 is reported to the
PLC. The PLC then issues an NC stop
or spindle stop.
Upon standstill:
--> SOS for axes, STO for spindles
(depending on SMP549.x)
Restart: direct restart possible
Deceleration process is monitored by
the timers according to SMP527.x/
SMP528.x, and path monitoring
according to SMP550.x
The switch-off of dual-channel safety-related FS outputs due to a stop reaction
must be realized through the SPLC program (see page 8–188).
Stopping with delay:
Sets monitoring timers with time
defined in SMP527.x
Upon standstill of axes or spindles:
--> SOS for axes, STO for spindles
(depending on SMP549.x)
Restart: direct restart possible
Deceleration process is monitored by
the timers according to SMP527.x/
SMP528.x, and path monitoring
according to SMP550.x
July 2011 4.8 Description of the Safety/Monitoring Functions 59
Page 60

4.8.9 Safe torque off (STO)
Note
The STO function provides protection against unexpected start-up of the
drives and against faulty reactions of axes and spindles (e.g. unexpected
increase in speed or unexpected direction of traverse).
In STO, the power supply to the motor is safely interrupted via two channels
(CC and MC). The drive cannot generate a torque, and is therefore unable to
execute any hazardous movements.
The safety function is realized in the HEIDENHAIN safety design by safely
disabling the pulses (PWM signals) for the power switches via two channels.
The PWM signals to the power output stages of the axes and spindles are
switched off immediately by the CC (–STO.B.x) and MC (–STO.A.x) (for signal
designations, see page 5–120). On the MC, the global signals –STO.A.G and –
STOS.A.G are also switched off.
If wired, the MC switches off the safety relays in the power supply units or
compact inverters (–STO.A.G, –STOS.A.G). This wiring was safety-relevant for
inverters of the old generation; when inverters of the new generation (new ID
numbers) are used, however, this wiring is not obligatory. However, control
systems with FS absolutely require the use of inverters and power supply
units that are approved for use in systems with functional safety (FS). The
wiring of the safety relays in the compact inverters or power supply units via
STO.A.G and STOS.A.G is then optional.
There is the additional possibility of using the main contactor to cut off power
to the drive system. However, this possibility is not safety-relevant for the
HEIDENHAIN safety design.
Standstill monitoring is not active in the STO safety function. The only
exception is the following function:
Test of the cut-out channels
If the STO function is active only in the CC, the MC monitors the standstill
position. Conversely, the CC monitors the standstill position if the STO
function is active only in the MC.
The safe torque off (STO) safety function must automatically switch off the
machine control voltage (CVO) via –STO.A.G. Therefore, the –STO.A.G
signal must be connected to the latch circuit of the machine control voltage
via a relay contact.
Please refer to the basic circuit diagram from HEIDENHAIN. The line voltage
of the machine is not switched off.
60 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Page 61

Danger
When the STO function is activated, the motor cannot generate a torque
anymore. This can result in a hazardous movement, such as may occur
with:
Axes and spindles without mechanical motor holding brakes (coasting to
a stop)
Vertical and inclined axes without weight compensation
Direct drives with low friction and self-retention
External force on the drive axes
The measures to be taken against external force (e.g. sagging of hanging
axes) must be in accordance with Information Sheet No. 005 "Gravityloaded axes (vertical axes)" issued by the engineering technical
committee of the BGM (German Employer's Liability Association in the
metal industry).
It is your duty as a machine tool builder to carry out a risk analysis and use
it as a basis to minimize the risks by taking suitable measures.
July 2011 4.8 Description of the Safety/Monitoring Functions 61
Page 62

4.8.10 Safe operating stop (SOS)
The SOS function provides protection against unexpected start-up of the
drives.
In SOS, all feedback control functions (speed, position, etc.) are maintained.
While the SOS function is active, control measures prevent the drive from
performing hazardous movements resulting from faults.
After the SOS function has been deactivated, e.g. by closing a guard or by a
start command, the machining motion of the drive can be restarted at the point
of interruption.
When the SOS safety function is active, dual-channel standstill monitoring is
performed by the MC and the CC.
Standstill is considered to be achieved if the spindle speed / axis feed rate falls
below the following limit values:
Spindle speed < 10 rpm
Axis feed rate < 50 mm/min
If these limit values for spindle speed and axis feed rate are exceeded when
the SOS function is active, the SS1 safety function is initiated.
If, however, the maximum permissible path defined in SMP545.x (limit value
for standstill monitoring in [mm] or [°]) is exceeded while adhering to the limit
values for the spindle speed and axis feed rate in SOS, the SS0 safety function
is initiated.
In the safety-related SOM_1 operating mode, the SOS safety function
becomes active when the guard door is opened.
Also, the nominal-actual value comparison of position values or speed values
is performed via two channels if the SOS safety function is active.
In control systems without FS, the axes of an axis group were disconnected
from power when the "axis group enabling (X150/X151 or MP4132) signal was
reset (= 0). This was the only possibility of preventing any further axis
motions. In systems with FS, you can ensure that the axes of an axis group
are at a standstill without disconnecting the axes from power. You can monitor
the axes for SOS instead—this is sufficient to ensure that they are at a
standstill.
62 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Page 63

4.8.11 Safely limited speed (SLS)
Attention
The safely-limited speed safety function is active in all operating modes
(except SOM_1) when the guard door is open. SLS monitors whether the
drives exceed the specified speed limit values.
In the HEIDENHAIN safety design, the speed limit values are monitored via
two channels by the MC and the CC, and a safe stop is initiated via SS1 if these
values are exceeded.
The speed limit values for the axes and spindle are defined in
EN 12417:2007 for the various safety-related operating modes, and are
stored in safe machine parameters in the HEIDENHAIN controls.
The monitoring for SLS is always axis-specific. During interpolating
movements (movements in which more than one axis is involved) the
resulting contour speed of the tool center point or tool can assume higher
values than the defined axis-specific limit values.
The machine tool builder must enter the axis-specific speed limit values
for SLS of the various safety-related operating modes in the SMPs such
that the permissible speed limit values of the standard are not exceeded
even when interpolating movements are executed. The resulting contour
speed of the tool center point must not exceed the permissible speed
limit values of the standard.
If the safely-limited speed (SLS) safety function is activated when the speeds
are already above the speed limit values (e.g. by opening the guard doors), SS1
will be initiated immediately. Pressing the F LIMITED soft key enables you to
open the guard doors without initiating an SS1 reaction.
If you press the F_LIMITED soft key, the maximum permissible speed of the
axes and of the spindle is limited to the defined safely-limited speed. The
limitation depends on the safe SOM_x operating mode selected by keylock
switch. The speed of axes and spindles is reduced to the limit values for
"safely limited speeds." If SOM_1 is active, the axes and spindles are brought
to a stop, because only then will you be allowed to open the guard doors in
SOM_1.
July 2011 4.8 Description of the Safety/Monitoring Functions 63
Page 64

4.8.12 Safely limited position (SLP)
Attention
The safely-limited position safety function replaces the conventional hardware
limit switches and is active in all operating modes.
Control measures ensure that an SS1 reaction is initiated if a defined absolute
position limit value (SMP650.x and SMP670.x) is exceeded. This is done by a
dual-channel comparison of the actual position to the position limit value. The
associated limit values are stored in safe machine parameters.
The technologically maximum possible overtravel of the axes must be
taken into account when setting the absolute position limit values.
The positive and negative absolute position limit values should be
selected such that during traverse to these positions the standard
software limit switches are reached first.
The first time the SLP safety function is initiated, the operator has the
possibility of returning the axes to the permissible area after switching the
machine back on.
If he uses this possibility and moves the axes in the wrong direction, the drives
will be stopped via SS1. Then the drives cannot be moved until the limit values
have been changed in the safe machine parameters.
The absolute position of the machine axes must be captured via two channels
in order to ensure the safely-limited position (SLP) function:
Axis reference run
After switching on the control, the absolute position is determined by
means of the "Traversing the reference marks" function.
For example, for position encoders with distance-coded reference marks
you must traverse two reference marks in order to determine the absolute
value of the position, and for absolute encoders with EnDat interface the
position value is read out when the control is switched on.
In the "Traversing the reference mark" machine mode of operation, only one
axis can be moved at any one time. If the control is in the Reference Run
mode, and more than one NC axis or auxiliary axis whose associated axis
groups are not in the AUTO or SOM_1 monitoring states are moving, then
the SKERN initiates an SS2 for all axis groups that are not in AUTO or
SOM_1.
If the guard door is open, an automated reference run can only be executed
by means of NC start and the permissive button or key.
If the guard door is closed, the reference run can be executed both by
means of NC start and directly by means of the axis-direction keys.
As long as the axes have not been homed, it is not possible to traverse the
axes in another machine mode of operation (such as Manual Operation or
El. Handwheel).
The absolute positions determined in this manner are compared to the last
axis positions stored in the control. If a difference between the two values
is found, the axes must be checked. If an axis that has not been checked is
not in the "Traversing the reference marks" mode of operation, the axis can
be moved only if the guard door is closed (independent of the active mode
of operation).
64 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Page 65

Axis check
Attention
Checking the axes is also required when the machine is commissioned or,
for example, after an encoder has been replaced. In addition, the axes must
be checked if an SMP, or an MP with an indirect influence on the safety
functions (e.g. MP960.x) has been changed. This is done by comparing the
actual value display to the actual position of the machine axes. The end user
is prompted to move the machine axes via soft key to a reference position
defined by you. After checking the markings applied to the machine table
and at fixed points, the end user must press the dual-channel permissive
key (PB) of the machine operating panel to confirm that the reference
position has actually been reached (end user's confirmation).
If the guard door is open, the axes can only be checked automatedly by
means of NC start.
If the guard door is closed, the axes can be moved to the test position both
by means of NC start and by means of the axis-direction keys. SOM_2,
SOM_3 or SOM_4 must be active for checking the axis. In SOM_1 the axes
cannot be checked.
As a machine tool builder, you must establish the assignment of the position
of the limit switches to the reference marks. In order to be able to verify this
assignment, a marking for every axis must be applied to the machine table
and the machine base at a clearly visible location. The marking corresponds
to a certain reference position and must be entered in SMP646.x.
The assignment of the axis position to the position of the limit switches
is ensured only if the axes have been checked, i.e. the limit switches at
the end of the traverse range (absolute position limit values) become
effective only for checked axes.
The safe operation of a machine requires that all axes have the "checked"
status. The axis display must not show any axis marked by the warning
symbol for "unchecked axis"!
Axes must be checked only by trained personnel.
The positions of the axes are saved before the machine is shut down and are
used as start positions after the machine is switched back on.
After the reference marks have been traversed or the absolute value has been
read out, the SKERN compares the position determined in this manner to the
respective position saved (in the MC and CC). If the deviation exceeds the
value saved in machine parameter SMP642.x because, for example, an axis
was moved manually while the control was inactive, the confirmation is
requested again, as during commissioning. The "Check axis positions" prompt
appears. After approaching the test position, the SKERN compares the
currently determined position to the reference position in SMP646.x. The
"Check axes" state cannot be left as long as the positions determined by the
SKERN MC and SKERN CC deviate from the reference position in SMP646.x
by more than the value in SMP642.x.
July 2011 4.8 Description of the Safety/Monitoring Functions 65
Page 66

The machine parameters for defining the safe limit switches (SMP650.x,
Note
SMP670.x) are referenced to the machine datum. The machine datum is
defined by the non-safe machine parameter MP960.x. Any changes made to
MP960.x are assumed by functional safety after the control has been
rebooted, and therefore affect the safe position limit values, which are shifted
according to the changes made to MP960.x. If major changes are made to the
value in MP960.x, this might lead to the position limit values being shifted to
such that the safety of the machine is affected. In order to prevent the user
from accidentally changing this value, a confirmation is requested, as during
commissioning. If the user notices that the change might affect the safety of
the machine, MP960.x must be reset to its original value. The actual value of
the axis must match the actual position.
4.8.13 Safe brake control (SBC)
In the SBC safety function, axis-specific dual channel control of the existing
motor holding brakes is carried out by the MC and CC. The SBC safety function
is requested by the respective SKERN and must then be executed by the
SPLC.
The existing mechanical motor holding brakes of axes and spindles are
activated via two channels:
After the request from the SKERN MC, the SPLC MC activates the brakes
axis-specifically via the safety-related outputs –BRK_REL.A.x of the SPL and
connected safety relays.
After the request from the SKERN CC, the SPLC CC activates the brakes
axis-specifically via the safety-related outputs –BRK_REL.B.x of the SPL and
connected safety relays (if present), or
The SKERN CC activates the brakes via –BRK.B.x if a corresponding inverter
interface is present.
See page 7–164 for the brake control block diagram.
In addition, all brakes are controlled collectively by the MC via the –STO.A.G
signal.
Hanging axes must be controlled axis-specifically. Do not combine them
into a group of axes whose brakes are controlled collectively rather than
individually.
The dual-channel controllability of the motor holding brakes is checked in the
safety self-test. In addition, the holding torque of the brakes is tested.
The operation and testing of motor-holding brakes must be in accordance with
Information Sheet No. 005 "Gravity-loaded axes (vertical axes)" issued by the
engineering technical committee (BGM (German Employer's Liability
Association in the metal industry)).
66 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Page 67

4.8.14 Safely limited increment (SLI)
Danger
With the current NC software version, the SLI safety function needs to be
realized by the machine manufacturer via the SPLC program. However, the
safety function does not monitor the increment itself, but rather the conditions
for maintaining the movement. The increment is monitored by the normal NC
software; there is no dual-channel monitoring by the SKERN for maintaining
the increment.
The increment function is activated with the INCREMENT OFF/ON soft key.
This opens an input window in which the user can enter the current increment.
When an axis-direction key is pressed, the NC software moves the axis by the
defined increment.
The SPLC program is to monitor the conditions for whether the axis
movement may exceed the defined increment. The axis-direction key must
remain pressed for maintaining the movement. While the axis-direction key is
pressed, the axis is moved once by the defined increment and is then stopped
automatically. If you want to move the axis by the increment again, you must
release the axis-direction key and press it again. In addition, it might be
necessary to press the permissive button or key, for example. The conditions
to be monitored for maintaining the axis movement must be defined by the
machine manufacturer. All necessary conditions must be monitored by the
SPLC program. As soon as one of the conditions is no longer fulfilled (e.g.
releasing the axis direction key), the SPLC program must initiate an SS2
reaction. Depending on the keylock switch, the respective SLS (safely limited
speed) must be active during the increment function.
4.8.15 Nominal-actual value comparison
Depending on the active safety-related operating mode and the type of axis,
position values or speed values are used in the nominal-actual value
comparison:
NC axes,
auxiliary
axes
Spindles No nominal-
You must ensure that no continuous actual-to-nominal value transfer takes
place through W1044 or PLC module 9145, since this would make fault
detection through the nominal-actual value comparisons impossible.
STO active SOM_1 active
(guard door is
closed)
No nominalactual value
comparison
actual value
comparison
Comparison
with speed
values
Comparison
with speed
values
SOM_2, SOM_3,
SOM_4 active
(guard door is
open)
Comparison with
position values
Comparison with
speed values
July 2011 4.8 Description of the Safety/Monitoring Functions 67
Page 68

4.8.16 Nominal-actual value comparison of position values
The nominal-actual value comparison of position values is active for all
position-looped axes in all operating modes. This monitoring function is active
only when the guard doors are open; however, no additional delay times for
permissible deviations are active.
The maximum permissible deviation between the actual and nominal value
can be set in SMP641.x. If the axes are intentionally operated with following
error, this does not need to be taken into account in the parameterization of
SMP641.x. The following error is automatically considered in position-value
monitoring.
If the maximum permissible deviation is exceeded, an SS1 reaction is initiated.
The SKERN CC monitors the motor encoder (rotary encoder), and the SKERN
MC monitors the position encoder (if present) or a specifically generated
position value of the motor encoder.
4.8.17 Nominal-actual value comparison of speed values
The nominal-actual value comparison of speed values is always active for the
speed-controlled axes, regardless of the selected safety-related operating
mode or the status of the guard doors. This monitoring function is a plausibility
check between the nominal value of the controller and the actual value of the
encoder. This monitoring function is to ensure that, for example, a failure or
confusion of encoders is detected.
The maximum permissible deviation between the actual and nominal value
can be defined in SMP630.x for the axes, and in SMP631.x for the spindle. In
SMP632.x or SMP633.x, you additionally define a time window within which
the limit values are allowed to be exceeded. The actual speed value must be
within the defined tolerance at least once within the time period defined in
SMP632.x or SMP633.x. If it is, the time set in SMP632 or SMP633.x,
respectively, restarts. If the actual value does not reach the permissible limit
values within the time window, an SS1 reaction is initiated.
The monitoring for the deviation defined in SMP630.x is always active, but in
SMP632.x and SMP633.x a time window is defined within which the actual
speed value must be at least once within the tolerance defined for the nominal
value. If this, for example, happens already after 0.5 seconds, the time in
SMP632.x already restarts after 0.5 seconds.
The SKERN CC monitors the motor encoder (rotary encoder), and the SKERN
MC monitors the position encoder (if present) or a specifically generated
position value of the motor encoder.
68 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Page 69

4.8.18 Protection against unexpected start-up
Note
The SKERN monitors the rotational speed of all axis and spindle motors to
provide protection against unexpected start-up. If all motors of an axis group
are at a standstill for more than 3 seconds, the safety-kernel software of the
MC and the safety-kernel software of the CC initiate an axis-group-specific
SS2 independently of each other.
The "Protection against unexpected start-up" safety function is active in the
following machine modes of operation when the guard door is open:
Program Run, Full Sequence operating mode
Program Run, Single Block operating mode
Positioning with Manual Data Input (MDI) operating mode
Here are some instances in which the safety function triggers an SS2
reaction in the operating modes mentioned above:
If the override potentiometer is turned down after the start of an NC block
During long dwell times (e.g. programmed waiting times) > 3 seconds in
an NC block
Three seconds after the end or cancellation of an NC program, if the axes
or spindle remain at a standstill
To prevent this automatic transition from SLS to SOS/STO (such as during very
slow movements or for the tapping cycle, etc.), you have to press the
permissive key on the machine operating panel. If the guard door is closed,
there will be no transition to SOS/STO. This function only provides additional
protection when the guard door is open. The same applies to the handwheel
when the safety-related operating mode 4 (SOM_4) is active.
4.8.19 dv/dt monitoring of the braking processes
The dv/dt monitoring function performed by the SKERN ensures that there is
no further increase in the speed of axes and spindles after an SS1 or SS1F has
been initiated.
The dv/dt monitoring of axes verifies that the axes are not accelerated
anymore after the waiting time defined in SMP530.x has expired. If a fault
occurs, an axis-specific SS0 is initiated for the affected axis, and an SS1F for
all other axes and spindles.
The dv/dt monitoring function does not respond if an axis coasts to a stop, e.g.
after an SS0 reaction.
If the time defined in SMP525.x is exceeded during the deceleration process,
an SS0 reaction is initiated.
dv/dt monitoring of the spindle is being introduced as a new safety function in
service pack 05. The safety function monitors deceleration process of the
spindle during an SS1 reaction. The waiting time for dv/dt monitoring of the
spindle is permanently defined and cannot be configured via an SMP.
After an SS1 reaction has been initiated, the SKERN monitors the spindle
speed to ensure that it continually decreases. Should the monitoring
determine that the speed remains constant or even increases, an SS0 reaction
is initiated for the spindle. SS1F is initiated for all other axes.
July 2011 4.8 Description of the Safety/Monitoring Functions 69
Page 70

4.8.20 Response times, definitions, demand rates
The following data apply to stop reactions:
Response times
The data applies to all safety functions.
• Response time of the SKERN:
The corresponding stop reaction is initiated no later than two HSCI
cycles (2 * 3 ms) after the fault has occurred.
• Response time of the SPLC:
The corresponding stop reaction is initiated no later than 22 HSCI cycles
(22 * 3 ms = 2 * SPLC cycle + 2 * HSCI cycle; SPLC cycle = max.
30 ms, HSCI cycle = 3 ms) after the fault has occurred.
• Response time of the CC:
CC-CC communication
Data is transmitted between the CCs at an interval of 3 ms. If the CC
software detects a telegram to be faulty, a fault reaction is initiated
within 4 * 3 ms.
• The time until the axes come to a standstill after the stop reaction has
been initiated must be added to the response time of the control. The
times resulting from the corresponding MPs (e.g. acceleration) and the
behavior of the CC (deceleration at the limit of current) must be used for
this calculation.
• HEIDENHAIN specifies a target value of 150 ms within which the axes
must come to a standstill (finger protection).
Definitions and monitoring ranges
• Speed: SLS + 5 %
• Absolute position: > SMP650 and < SMP670
• Standstill of the axes: < 50 mm/min
• Standstill of the spindle: < 10 rpm
70 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Page 71

Worst-case
consideration of
response times
Time Reactions of HSCI participants Signal involved
Response times after initiation of emergency stop:
t = 0 Emergency stop initiated via
emergency stop button ES.SMOP
on SMOP
t = 200 µs Safe status bits of all HSCI
participants are set correspondingly
Reaction of MC
Safe/Fastest reaction:
t = 200 µs + 3 ms
t = 200 µs + 3 ms + reaction of CC "Normal" time until switch-off by
t = 200 µs + 3 ms + time from SMPs "Maximum" time until switch-off
The MC detects –ES.A = 0 and
initiates an emergency stop reaction
(SS1)
MC:
The MC is informed about the
switch-off of the CC through a
message from the CC and initiates
STO.A and SBC.
After the SS1F reaction has been
performed, the SKERN MC
demands that the SPLC program
activate the brakes and switch off
the FS outputs (the machine
manufacturer is responsible for the
implementation).
by MC:
The time of the monitoring timers
defined in SMP525.x for the SS1
reaction for axes, or in SMP526.x
for the SS1 reaction for spindles is
exceeded. The MC initiates STO.A
and SBC.
After the SS1F reaction has been
performed, the SKERN MC
requests the SPLC program to
activate the brakes and to switch off
the FS outputs (the machine
manufacturer is responsible for the
implementation).
–ES.A.SMOP = 0
–ES.B.SMOP = 0
–ES.A = 0
–ES.B = 0
–ES.A = 0
At standstill the MC
sets:
–STO.A.x = 0,
–BRK_REL.A.x = 0
At standstill the MC
sets:
–STO.A.x = 0,
–BRK_REL.A.x = 0
Reaction of CC
Fastest reaction:
t = 200 µs + 3 ms
July 2011 4.8 Description of the Safety/Monitoring Functions 71
The CC detects –ES.B = 0 in the
safe state and initiates an
emergency stop reaction (SS1).
Deceleration process along the
emergency braking ramp (MP2590).
–ES.B = 0
Page 72

Time Reactions of HSCI participants Signal involved
t = 200 µs + 3 ms + max. 100 ms
a
"Normal" time from the start of the
SS1 reaction by the CC to the
standstill of the axes
At standstill the CC
sets:
–BRK_REL.B.x = 0
t = 200 µs + 3 ms + max. 100 ms +
MP2308
After the standstill of the axes and
SBC, the CC initiates STO.B with a
delay (by the time in MP2308).
After the SS1F reaction has been
performed, the SKERN CC requests
the SPLC program to switch off the
FS outputs (the machine
manufacturer is responsible for the
implementation).
Safe reaction:
t = 600 µs + 6 ms
The CC receives an HSCI telegram
with information about –ES.B = 0
from the µC.B of the SMOP
t = 600 µs + 6 ms + 3 ms The CC detects –ES.B = 0 in the
telegram and initiates an
emergency stop reaction (SS1).
Deceleration process along the
emergency braking ramp (MP2590).
t = 600 µs + 6 ms + 3 ms +
max. 100 ms
a
"Normal" time from the start of the
SS1 reaction by the CC to the
standstill of the axes
t = 600 µs + 6 ms + 3 ms +
max. 100 ms + MP2308
After the standstill of the axes and
SBC, the CC initiates STO.B with a
delay (by the time in MP2308).
After the SS1F reaction has been
performed, the SKERN CC requests
the SPLC program to switch off the
FS outputs (the machine
manufacturer is responsible for the
implementation).
The CC sets:
–STO.B.x = 0
–ES.B = 0
–ES.B = 0
At standstill the CC
sets:
–BRK_REL.B.x = 0
The CC sets:
–STO.B.x = 0
t = 600 µs + 6 ms + time from SMPs "Maximum" time until switch-off
by CC:
The time of the monitoring timers
defined in SMP525.x for the SS1
reaction for axes, or in SMP526.x
The CC sets:
–STO.B.x = 0,
–BRK_REL.B.x = 0
for the SS1 reaction for spindles is
exceeded. The CC initiates STO.B
and SBC.
After the SS1F reaction has been
performed, the SKERN CC requests
the SPLC program to switch off the
FS outputs (the machine
manufacturer is responsible for the
implementation).
a. Time that is assumed by HEIDENHAIN to be the maximum deceleration time for feed axes.
2
An axis speed of 5 m/min and a braking acceleration of 1 m/s
were assumed.
72 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Page 73

Response times after opening the guard door
at speeds > SLS:
Time Reactions of HSCI participants Signal involved
t = 0 Activation of SD guard door contacts
at the SPL inputs
t = max. 22 ms Capturing the signals of the SPL
inputs of the µC.A and µC.B of the
SPL via PICs.
Safe reaction:
t = 22 ms + 6 ms
t = 22 ms + 6 ms + 2*SPLC cycle The SKERN of the MC receives
t = 22 ms + 6 ms + 2*SPLC cycle
+ 3 ms
t = 22 ms + 6 ms + 2*SPLC cycle
+ 3 ms + cut-out time of CC
The MC and the CC receive an HSCI
telegram with information about –
SD.A.x = 0 from the µC.A and –SD.B.x
= 0 from the µC.B of the SPL
Reaction of MC
information about the open guard
door because the SLS axis-group
status was set by the SPLC
The SKERN of the MC monitors for the
SLS safety function and detects that the
limit values have been exceeded:
Initiation of SS1 stop reaction
"Normal" time
The MC is informed about the switchoff of the CC through a message from
the CC and initiates STO.A and SBC.
After the SS1F reaction has been
performed, the SKERN MC requests
the SPLC program to activate the
brakes and to switch off the FS outputs
(the machine manufacturer is
responsible for the implementation).
until switch-off by MC:
–SD.A.x = 0
–SD.B.x = 0
–SD.A.x = 0
–SD.B.x = 0
–SD.A.x = 0
–SD.B.x = 0
At standstill the MC
sets:
–STO.A.x = 0,
–BRK_REL.A.x = 0
t = 22 ms + 6 ms + 2*SPLC cycle
+ 3 ms + time from SMPs
July 2011 4.8 Description of the Safety/Monitoring Functions 73
"Maximum" time
The time of the monitoring timers
defined in SMP525.x for the SS1
reaction for axes, or in SMP526.x for the
SS1 reaction for spindles is exceeded.
The MC initiates STO.A and SBC.
After the SS1F reaction has been
performed, the SKERN MC requests
the SPLC program to activate the
brakes and to switch off the FS outputs
(the machine manufacturer is
responsible for the implementation).
until switch-off by MC:
At standstill the MC
sets:
–STO.A.x = 0,
–BRK_REL.A.x = 0
Page 74

Time Reactions of HSCI participants Signal involved
Reaction of CC
t = 22 ms + 6 ms + 1*SPLC cycle The SKERN of the CC receives
information about the open guard
door because the SLS axis-group
status is set by the SPLC
t = 22 ms + 6 ms + 1*SPLC cycle
+ 3 ms
t = 22 ms + 6 ms + 1*SPLC cycle
+ 3 ms + max. 100 ms
t = 22 ms + 6 ms + 1*SPLC cycle
+ 3 ms + max. 100 ms
a
a
+
MP2308
t = 22 ms + 6 ms + 1*SPLC cycle
+ 3 ms + time from SMPs
The SKERN of the CC monitors for the
SLS safety function and detects that
the limit values have been exceeded:
Initiation of SS1 stop reaction.
Deceleration process along the
emergency braking ramp (MP2590).
"Normal" time from the start of the
SS1 reaction by the CC to the
standstill of the axes.
After the standstill of the axes and
SBC, the CC initiates STO.B with a
delay (by the time in MP2308).
After the SS1F reaction has been
performed, the SKERN CC requests
the SPLC program to switch off the
FS outputs (the machine
manufacturer is responsible for the
implementation).
"Maximum" time until switch-off by
CC:
The time of the monitoring timers
defined in SMP525.x for the SS1
reaction for axes, or in SMP526.x for
the SS1 reaction for spindles is
exceeded. The CC initiates STO.B and
SBC.
After the SS1F reaction has been
performed, the SKERN CC requests
the SPLC program to switch off the
FS outputs (the machine
manufacturer is responsible for the
implementation).
At standstill the CC
sets:
–BRK_REL.B.x = 0
At standstill the CC
sets:
–STO.B.x = 0
At standstill the CC
sets:
–STO.B.x = 0,
–BRK_REL.B.x = 0
a. Time that is assumed by HEIDENHAIN to be the maximum deceleration time for feed axes.
2
An axis speed of 5 m/min and a braking acceleration of 1 m/s
were assumed.
74 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Page 75

4.8.21 Safe status bits
The safe status bits are transmitted to every HSCI participant via the HSCI
telegram. The individual HSCI participants (MC, CC, SPL, SMOP) themselves
can set the safe status bits, evaluate the received bits and react to them. The
fault reactions defined for the individual safe status bits vary depending on the
type of HSCI participant, see page 4–78.
Safe status bit Signal Meaning
0 –ES.A Emergency stop channel A
The control has initiated the SS1 alarm
reaction.
1 –ES.B Emergency stop channel B
The control has initiated the SS1 alarm
reaction.
2 –ES.A.HW Emergency stop channel A, handwheel;
no function in controls without
functional safety.
The control has initiated the SS1 alarm
reaction.
3 –ES.B.HW Emergency stop channel B, handwheel;
no function in controls without
functional safety.
The control has initiated the SS1 alarm
reaction.
4 –STO.A.MC.WD Watchdog of MC software, switch-off
of inverters, A channel (with functional
safety: switch-off of FS outputs).
The control has initiated the SS1 alarm
reaction.
5 –STOS.A.MC Spindle is switched off by the MC,
A channel, STOS.A.G is initiated
(CC: switch-off of spindle); no function
in controls without functional safety.
6 –STO.B.CC.WD Watchdog of CC software, switch-off of
inverters, B channel
The control has initiated the SS1F alarm
reaction.
7 –SMC.A.WD "Fast" watchdog of MC software; alarm
on CC, which initiates the deceleration
of the axes.
The control has initiated the SS1 alarm
reaction.
8 –SPL.WD With FS: Multi-channel watchdog of
SPL firmware (A/B channel); serious
error of PL.
Without FS: Single-channel watchdog of
PL firmware.
The control has initiated the SS1F alarm
reaction.
July 2011 4.8 Description of the Safety/Monitoring Functions 75
Page 76

Safe status bit Signal Meaning
9 –SMOP.WD With FS: Multi-channel watchdog of
SMOP firmware (A/B channel); serious
error of MOP machine operating panel
(SS1F).
Without FS: Single-channel watchdog of
MOP firmware (machine operating
panel)
10 –PF.PS.AC Power supply of inverter too low
(parameterized LIFT OFF function in
some cases).
11 –PF.PS.DC DC-link voltage U
too low
Z
The control has initiated the SS1 alarm
reaction.
12 –PF.BOARD Fault in the supply voltage of the
respective module.
The control has initiated the SS1F alarm
reaction.
13 –N0 Internal safe status bit
The control has initiated the SS1 alarm
reaction.
14 –REQ.SS2 The control has initiated the SS2 alarm
reaction. Possible causes include:
Speed of MC fan or CC fan outside
the tolerance
Temperature of MC, CC, UEC, UMC,
PL or MB outside the tolerance
CC has detected an internal fault
15 – Reserved
76 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Page 77

The following additional status bits are available for an external PL:
Safe status bit Signal Meaning
16 –SPL.A.WD SPL watchdog, channel A
17 –SPL.B.WD Only in controls with functional safety
(FS): SPL watchdog, channel B
18 PGOOD.NC Voltage monitoring of NC reports a fault
19 PGOOD.PLC Voltage monitoring of PLC reports a
fault
20 –INT Internal interrupt
21..31 1 Reserved
The following additional status bits are available for an external MB machine
operating panel:
Safe status bit Signal Meaning
16 –SMOP.A.WD SMOP watchdog, channel A
17 –SMOP.B.WD Only in controls with functional safety:
SMOP watchdog, channel B
18 PGOOD.A Voltage monitoring of channel A reports
a fault
19 PGOOD.B Voltage monitoring of channel B reports
a fault
20 1 Reserved
21..31 1 Reserved
July 2011 4.8 Description of the Safety/Monitoring Functions 77
Page 78

4.8.22 Fault reaction to safe status bits
Note
An entry consisting of "- - -" in the following table means that the dual-channel
outputs are not switched off based on the safe status bits. They are only
switched off automatically if the control crashes, if an internal fault of the
component occurs, or if there is a fault in the HSCI communication.
The SPLC program must switch off the FS outputs.
The SKERN demands via the interface signal NN_GenOutputEnable that the
SPLC program switch off the FS outputs in case of a fault, also see page 8–
188.
Name Evaluation and reaction
MC CC SPL SMOP
- - -
–REQ.SS2 SS2 SS2 - - -
–N0 - - -
d
SS1 - - -
e
e
–PF.BOARD SS1F SS1F Switch-off of FS outputs
–PF.PS.DC
–PF.PS.AC
a
a
–SMOP.WD SS1F SS1F
–SPL.WD SS1F SS1F
–SMC.A.WD SS1 SS1 - - -
–STO.B.CC.WD SS1F SS1F - - -
–STOS.A.MC - - -
b
- - -
SS1 - - -
LIFT-OFF LIFT-OFF - - -
f
f
- - -
Switch-off of FS
outputs
d
Detection
- - -
e
e
e
c
e
e
e
(test)
- - -
- - -
- - -
- - -
e
e
e
e
e
–STO.A.MC.WD SS1 SS1 - - -
–ES.B.HW SS1
f
–ES.A.HW SS1 SS1
–ES.B SS1f SS1
–ES.A SS1 SS1
SS1
f
f
f
f
c
Switch-off of FS
outputs
- - -
c
e
a. The evaluation of these signals and their reactions can be deactivated via a PLC module.
b. If –PF.PS.DC is active, the watchdogs of the MC are not retriggered anymore. The other
HSCI participants therefore detect the MC as being defective.
c. The FS outputs are switched off automatically only on the HSCI participant on which the
fault occurs (locally). Local fault detection by evaluating the internal fault bits (control crash,
internal fault of the component, fault in the HSCI communication).
78 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Page 79

d. The outputs are not switched off based on the safe status bits. They are only switched off
automatically if the control crashes, if an internal fault of the component occurs, or if there
is a fault in the HSCI communication.
e. No reaction
f. Fast reaction, not relevant for safety. The CC receives safety-relevant information via the
HSCI telegram.
July 2011 4.8 Description of the Safety/Monitoring Functions 79
Page 80

4.8.23 Behavior when a fault is detected
General
information
Stop reactions Stop reactions are defined and divided into categories in EN 60204-1. The stop
If an emergency stop or an error occurs, specific stop functions are used to
bring all drives to a safe standstill as quickly as possible.
Once a stop function has been initiated it is always run in its entirety, even if
the cause of its initiation is no longer applicable. This applies regardless of the
Control Voltage ON (CVO) status. The machine cannot be restarted until the
stop function and the associated braking reaction have been run in their
entirety.
However, a stop reaction that has been initiated can be replaced by a higherpriority stop.
The cause of SS0/SS1F/SS1/SS2 reactions is displayed on the screen.
The stop reaction with the highest priority is the SS0 reaction, followed by
SS1F and SS1. The SS2 stop reaction has the lowest priority. These stop
functions can be initiated by every monitoring channel (MC/CC).
reactions and all further safety functions are described in detail under Safety
Functions (see page 4–47). The table below shows the assignment of the
stop reactions to the categories.
EN 60204-1 HEIDENHAIN Priority
Category 0 Safe stop 0 (SS0) Highest priority
Category 1 Safe stop 1F (SS1F)
Safe stop 1 (SS1)
Safety function
states
Category 2 Safe stop 2 (SS2) Lowest priority
The safety functions are described in detail under Safety Functions (see page
4–47). The table below shows which safety function provides which safety
level to the end user.
For the initiation of safety functions by the SPLC and SKERN, it always applies
that the safety function providing the higher level of protection to the machine
operator is active.
Safety function Level
Safe torque off (STO) Highest safety
Safe operating stop (SOS)
Safely-limited speed (SLS) Lowest safety
80 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Page 81

Restarting the
Danger
Danger
drives after stop
reactions
After SS1F or SS0
(i.e. the STO safety function is active), the restart of the drives can only be
enabled by switching the main switch off and back on.
For safety reasons, switching the main switch back on leads to a new safety
self-test.
There is an increased risk when the machine is switched on (booting), and
especially when the drives are switched on. It must be ensured that there
are no persons in the immediate danger zone!
If an SS1 was initiated, the drives can be restarted by simply switching on the
machine control voltage, without actuating the main switch. All logic functions
of the machine are retained while the control voltage is switched off, and
continue to run unimpeded.
An unexpected restart by resetting the emergency stop button is not possible,
since the safe torque off (STO) operating status was initiated via two
channels.
For large machine tools whose work zone cannot be fully seen, the use of
an additional reset button in accordance with EN 954 or EN 13849 is
compulsory.
The reset button must be situated outside the danger zone in a safe position
from which there is good visibility for checking that no person is within the
danger zone. Switching the machine back on by using Control Voltage ON
(CVO) is not permissible until the reset button has been pressed. This
functionality must be realized in the SPLC program.
After an SS2 (SOS), a restart is possible without actuating the main switch and
without switching on the machine control voltage.
July 2011 4.8 Description of the Safety/Monitoring Functions 81
Page 82

4.8.24 Stop reactions depending on the fault situations
The following tables show which stop reactions, depending on the fault that
occurred, are triggered by the MC or the CC:
Safe stop 0 (SS0)
Active state: Fault situation: SS0 reaction
initiated by:
SOS Axis is moving at < 50 mm/min, but the path from SMP545
has been exceeded
SS1 Limit values for dv/dt monitoring according to SMP530.x
during the SS1 reaction have been exceeded (alarm code of
the CC: E240)
SS1 Limit value for timer monitoring according to SMP525 or
SMP526 during the SS1 reaction has been exceeded (alarm
code of the CC: E200)
MC, CC
(axis-specific)
MC, CC
(axis-specific)
MC, CC
(axis-specific)
82 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Page 83

Safe stop 1F (SS1F)
Active state: Fault situation: SS1F reaction
initiated by:
NM (normal
mode = normal
operation)
NM Error while checking the watchdog counters MC, CC
NM Internal safety-relevant software error MC
NM One of the device-specific monitored voltages exceeds the
NM Monitoring detects that the voltages exceed or fall below
NM Error during the "Axis checked" status comparison
NM Fatal system error occurred MC, CC
NM Active safe status bit:
NM Error while monitoring the CRC checksums (applies to all
Booting Different types of axes assigned to the same axis group MC, CC
NM dv/dt monitoring responds for an axis or spindle, and SS0
NM SSO has been requested for an axis group. As a result,
NM SS1F has been requested for an axis group. As a result,
NM Invalid axis-group state MC, CC
NM Invalid stop reaction requested MC, CC
NM Invalid safety function requested MC, CC
SOM_2,
SOM_3
SOM_4 Operating mode switched to SOM_2 or SOM_3 for an axis
NM Axis group without spindle requests SLI for a spindle
NM Spindle axis group requests SLI for axes MC, CC
NM Invalid SMP checksum MC, CC
Booting The motor shaft speed entered in or transferred for
Booting The rated speed for gear ranges entered in or transferred
STO SMP1054.x parameterized incorrectly (SMP = 0) CC
NM Watchdog WD.A.HSCI is reset MC, CC or SPL
SS0 reaction requested by the SPLC program MC, CC
MC, CC
defined limit values (signal –PF.BOARD)
MC, CC
the defined limit values
MC
between the MC and CC
MC, CC
–STO.B.CC.WD, –SPL.WD, –SMOP.WD and –PF.BOARD
MC, CC
CRC checksums)
MC, CC
is initiated for the respective axis. SS1F is initiated for all
other drives.
MC, CC
SS1F follows for all other axis groups.
MC, CC
SS1F also follows for all other axis groups.
Operating mode switched to SOM_4 for an axis group MC, CC
MC, CC
group
MC, CC
(= operating mode SOM_S requested)
CC
MP3210 is not between 0 and 100 [* 1000 rpm]
CC
for MP3510 is less than or equal to 0 rpm
July 2011 4.8 Description of the Safety/Monitoring Functions 83
Page 84

Safe stop 1 (SS1)
Active state: Fault situation: SS1 reaction
initiated by:
STO Test of the chain of normally-closed contacts before
retriggering the MC watchdogs, to see whether all contacts
are closed
NM Limit values for safely limited position (SLP) exceeded MC, CC
NM Limit values for safely limited increment (SLI) exceeded MC, CC
NM Limit values for amplitude monitoring exceeded MC, CC
NM Error reported by encoder-frequency monitoring MC, CC
SS2 Limit values for path (SMP550.x) or time (SMP527.x,
SMP528.x) exceeded during SS2 reaction
SOM_S When the guard door is open:
Limit value of < two revolutions (SLI) or speed of < 50 rpm
(SLS) exceeded
SOM_2,
SOM_3,
SOM_4
SOM_2,
SOM_3,
SOM_4
SOM_2,
SOM_3,
SOM_4
NM Emergency stop initiated via one of the emergency stop
NM Internal emergency stop initiated via the SKERN (e.g. by IPO,
NM Error during nominal-actual value monitoring with position or
NM Error while performing forced dynamic sampling MC, CC
SOS Limit values for the safe operating stop SOS exceeded:
NM Bit 0 of SMP560 is not set to enable SOM_4 when that
NM Error found during cross-comparison MC, CC
NM Active safe status bit:
SOM_1 Moving a safe axis with open guard door MC, CC
NM SS1 reaction initiated by the SPLC program MC, CC
When the guard door is open:
Speed of the axes exceeds the respective limit values for
SLS
When the guard door is open:
Spindle shaft speed exceeds the respective limit values for
SLS
SMPs for limit values for SLS parameterized incorrectly
(SMP = 0)
buttons
CC)
speed values
Axis movements > 50 mm/min or > 10 rpm
operating mode is switched to
–SMC.A.WD, –STO.A.MC.WD, –ES.A.x, –ES.B.x, –
PF.PS.DC and –N0 (–N0 and –PF.PS.DC only CC reaction)
MC
MC, CC
MC, CC
MC, CC
MC, CC
CC
MC, CC
MC, CC
MC, CC
MC, CC
MC, CC
MC, CC
84 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Page 85

Safe stop 2 (SS2)
Active state: SS2 reaction
initiated by:
NM The temperature exceeded or fell below the limit values MC, CC
NM The fan speed fell below the limit values MC, CC
SOM_2,
SOM_3,
SOM_4
SOM_2 Number of axes permitted to move in SOM_2 exceeded.
SOM_3,
SOM_4
NM Maximum time in SMP511 for performing the safety self-
SLS Protection against unexpected start-up becomes active
SOM_2,
SOM_3
SOM_2,
SOM_3,
SOM_4
SOM_2,
SOM_3,
SOM_4
SOM_2,
SOM_3,
SOM_4
SOM_2,
SOM_3,
SOM_4
NM Active safe status bit –REQ.SS2 MC, CC
NM Untested axis moved MC, CC
NM SS2 reaction initiated by the SPLC program MC, CC
No valid permissive button or key active for switching on the
spindle while NC program is running
Only one axis may be moved.
Number of axes permitted to be moved by the handwheel
(e.g. with axis-direction keys) exceeded. Only one axis may
be moved if SMP560 bit 9 = 0.
test (with open guard door) exceeded
(switches to SOS state)
No valid permissive button or key, or permissive button or
key released during movement
NC stop or spindle stop key is pressed, and the SPLC
program requests an SS2 reaction
Axis-direction key was released during movement MC, CC
Spindle jog key released while spindle was active MC, CC
Switch between machine operating modes (e.g. from El.
Handwheel to Manual Operation mode)
MC, CC
MC, CC
MC, CC
MC, CC
MC, CC
MC, CC
MC, CC
MC, CC
July 2011 4.8 Description of the Safety/Monitoring Functions 85
Page 86

Reaction upon
errors during the
safety self-test
(SSt)
Active state: Fault situation: Reaction upon
error:
STO Illegal start of the SSt by the PLC: Guard doors not closed MC, CC wait
STO Illegal start of the SSt by the PLC: Not all drives had been
switched off by the MC after the brake test before the SSt
(alarm code of the CC: C037)
STO Emergency-stop circuit not closed MC, CC wait
STO Request that the chain of normally-closed contacts is not
closed (alarm code of the CC: E001)
STO Request that the chain of normally-closed contacts is not
open (alarm code of the CC: E001)
STO The guard doors are not closed during the safety self-test MC, CC wait
STO CVO key active before such a request is placed. The
message "Switch off external dc voltage" is displayed.
STO CVO key is not pressed after "Switch on external dc
voltage" prompt
SOS During the SSt, SOS is active on the MC and CC, unless
you activate STO for test purposes. If SOS is active, then a
safe operating stop is watched for. However, only the path
is monitored, but not the speeds.
STO MC does not test the motor brake control although the
parameter setting requires it
STO Error during test of motor brake control SS1F initiated by
NM Limit values for the safe operating stop (SOS) exceeded
during test of motor brake control
STO No machine operating key may be pressed MC, CC wait
STO Error while switching on all spindle power modules via a
global signal. The power modules do not report readiness
within 10 seconds.
STO Error while switching on all axis power modules via a global
signal. The power modules do not report readiness within
10 seconds.
STO Error while switching off all spindle power modules via a
global signal STOS.AG. The power modules are still ready
although the time in SMP2172 has expired.
SS1F initiated by
CC
SS1F initiated by
MC, CC
SS1F initiated by
MC, CC
MC waits
MC, CC wait
SS0 initiated by
MC, CC
SS1F initiated by
CC
MC
MC requires that a
safe position be
moved to
SS1F initiated by
MC, CC
SS1F initiated by
MC, CC
SS1F initiated by
MC, CC
86 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Page 87

STO Error while switching off all axis power modules via a global
signal STO.AG. The power modules are still ready although
the time in SMP2172 has expired.
STO Error during axis-specific switch-on of the power modules.
The power modules do not report readiness within 10
seconds.
STO Error during axis-specific switch-off of the power modules
via STO.A.x and STO.B.x. The power modules are still
ready although the time in SMP2172 has expired.
STO Error while checking the internal watchdogs during the
self-test
SS1F initiated by
MC, CC
SS1F initiated by
MC, CC
SS1F initiated by
MC, CC
SS1F initiated by
MC, CC; MC aborts
SSt
July 2011 4.8 Description of the Safety/Monitoring Functions 87
Page 88

4.9 Special Features of Software Version 606 42x-01
Note
The first software versions for functional safety of the iTNC 530 HSCI do not
include the full range of features necessary to provide functional safety for all
machine models.
Before planning a machine with functional safety, please inform yourself of
whether the current scope of functional safety features suffices for your
machine design.
Your contact person at HEIDENHAIN will be glad to answer any questions
concerning the iTNC 530 HSCI with functional safety.
The current constraints and specifics are listed below:
Switching of safe machine parameters (SMPs)
For reasons of safety, safe machine parameters cannot be switched or
changed without entering the OEM password. The changes do not become
active until the OEM password has been entered. Also, if safe machine
parameters are changed, a partial acceptance test is required. This mechanism
in software version 606 42x-01 prevents you from switching between
different parameter sets of safe machine parameters. This mechanism has the
following consequences:
Exchanging axes while the PWM output remains the same is not possible
Interchangeable heads cannot be realized at present
It is possible, however, to create a parameter set for a maximum configuration
of the machine. Axes can then be activated or deactivated via MP10. This is
possible without the OEM password, but it requires rebooting the control and
checking the switched axis (axes) again. This means that the deactivation/
activation of optional axes or indexing fixtures is possible. Save the maximum
configuration in the safe machine parameters. Then use MP10 to switch the
axes.
Master-slave-torque and gantry modes
In software 606 42x-01, only the master axis can be configured as a safe axis.
The slave axis must be configured as a non-safe axis. As a result, all safety
functions for axis monitoring are active only for the master axis.
Switch-off
The master axis is switched off via two channels (by the SKERN MC and
SKERN CC). The slave axis is switched off once by the SKERN MC (STO.A.x
signal), and also through the standard functions of the NC software in the MC
and CC. The CC also uses the STO.B.x PWM interface signal.
Brake test
See "Brake test for synchronized axes" on page 7 – 168
Master-slave operation is nevertheless possible, depending on the machine
design. The machine tool builder is responsible for the implementation.
88 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Page 89

This absolutely requires that the master axis and the slave axis be firmly
Note
connected with each other via a mechanical connection. All movements of the
slave axis must always affect the master axis. Problems of the slave axis (such
as axis "runaway") can then be detected by the FS monitoring functions of the
master axis as long as the master axis is not in the STO state. No safe
monitoring functions are active while the STO safety function is active. In the
STO state, movements of the slave are detected by the normal NC software
(e.g. following-error monitoring of the master), and not by functional safety.
The machine tool builder's risk analysis of the master-slave axes must
ensure that the master axis and the slave axis are mechanically firmly
connected with each other, and that the motor holding brake of the master
axis suffices as motor holding brake for the synchronized axes.
The risk analysis of the synchronized master-slave axes must prove whether
this type of master-slave operation is sufficient for the safety design of the
machine.
C-axis operation
This version of the FS software does not yet support safe C-axis operation. It
is not possible to operate an axis and a spindle alternately with a common
drive.
Traverse ranges
Switching the traverse range with MP100.x does not affect functional safety.
Machine parameter MP100.x is used to operate axes alternately as NC or PLC
axes. The SKERN derives this axis status solely from the entry in MP100.0.
The indices of MP100.x can only be used to switch the standard functions of
the NC software. For the SKERN the configuration in MP100.0 remains
decisive. In software version 606 42x-01, the safety-related examination of the
axes is inextricably linked to MP100.0. Therefore, the safety-related
examination of an axis always remains the same. PLC axes are sometimes
subject to more stringent safety requirements (e.g. movement possible only
in connection with permissive button or key).
Safe traverse-range switchover with MP100.x is not possible if software
version 606 42x-01 is being used.
July 2011 4.9 Special Features of Software Version 606 42x-01 89
Page 90

Alternating table operation
Here, you must first remember the constraints regarding the ranges of
traverse. For alternating table operation, an axis (e.g. two rotary tables as
"A axis" and "a axis", respectively) must usually be operated alternately as NC
axis and PLC axis. This switchover is still possible for the NC software, but not
for the safety-related examination of the axis. Also, in functional safety, this
axis must be defined in a separate axis group. As a result, for example, the
axes X, Y, Z must be configured in an axis group for NC axes, and the two
rotary tables (A axes) must also each be defined in a separate axis group. This
results in three axis groups.
This leads to a problem if the axis group of the NC axes and one of the two
A-axis groups are to be interpolated and moved together. The problem is
caused by the "Protection against unexpected start-up" safety function.
The "Protection against unexpected start-up" function sets an axis group
consisting of axes to the SOS status, and an axis group consisting of spindles
to the STO status (as a result of an SS2 reaction, configurable via SMP549.x)
if the axes/spindles of this axis group are not moved for more than three
seconds. Once the axes of this axis group are in the STO state, this state
cannot be left automatically anymore.
The NC axes and the A axis are in two separate axis groups. In an NC program
it is not unusual that especially the A axis is at a standstill for more than three
seconds, and this results in the "Protection against unexpected start-up"
function becoming active. Later in NC program run, however, the A axis
should be moved again, which is then no longer possible. The same problem
occurs with an SS2 reaction (deceleration along the contour). In this case,
standstill monitoring may prevent you from moving up to the end of the
contour.
Version 606 42x-01 of the FS software does not support alternating table
operation if the different axis groups are to be interpolated and moved
together.
90 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Page 91

EnDat 2.2
Version 606 42x-01 of the FS software does not support EnDat 2.2 encoders.
This applies to all EnDat 2.2 encoders with or without functional safety (FS).
Non-HEIDENHAIN inverters
The use of modules from Siemens' SIMODRIVE 611 power module product
family or other non-HEIDENHAIN inverters has not been approved for the
integrated functional safety!
Spindles with gear ranges
Spindles with gear ranges and only one motor encoder (single-encoder
system) are not supported. Spindles with a gear ratio (one or more than one
gear range) can be used as safe spindles only if they have a motor encoder and
a position encoder. The position encoder must be mounted behind the
gearbox or the transmission so that it returns the actual speed of the spindle,
i.e. of the tool.
Variable gear ratio
Safe axes with a variable gear ratio in MP1054.x (distance per motor
revolution) cannot be operated with software version 606 42x-01. A variable
gear ratio is a formula in MP1054.x, which does not provide a constant factor
as the result.
July 2011 4.9 Special Features of Software Version 606 42x-01 91
Page 92

4.10 Requirements the Application Must Meet
The machine tool builder uses the basic circuit diagrams as a basis for wiring.
This is a non-binding proposal, and must be adapted by the customer to the
requirements of the machine that he uses. The machine tool builder is
autonomously responsible for adhering to the relevant standards and safety
regulations.
It is imperative that the following requirements be fulfilled:
The normally closed contacts of all relays with safety-relevant functions
must be wired to the chain of normally closed contacts. The chains of
normally closed contacts are checked when the control is switched on.
The brakes must be controlled via two channels. In the HEIDENHAIN design
this occurs by switching off the motor holding brakes via two channels.
The temporal demands placed on the safety functions must be checked on
the machine and documented.
A comprehensive test of all safety-relevant functions must be performed
before commissioning. The results of this functional test must be
documented.
The safety self-test, including the test of the motor brakes and motor brake
control, must be repeated within no more than 168 hours.
For each specific machine, a calculation of the safety characteristic numbers
is to be performed in accordance with ISO 13849-1 for all components used,
including external safety components.
When installing and operating HEIDENHAIN components, please refer to
the Technical Manual of the respective control as well as to the "Inverter
Systems and Motors" Technical Manual.
Encoders
The following encoder configurations can be used on HEIDENHAIN control
systems with functional safety in order to monitor safe axes:
Two-encoder systems (speed and position encoders) with analog encoder
signals (1 VPP, EnDat 2.1)
Single-encoder systems (speed encoder) with analog encoder signals
(1 V
, EnDat 2.1)
PP
Single-encoder systems (speed encoder) with certified EnDat 2.2
FS encoder (as soon as these are supported)
Two-encoder systems (speed and position encoders) with EnDat 2.2
encoders without certified encoder or with certified EnDat 2.2 FS encoder
(as soon as these are supported)
92 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Page 93

Danger
External devices used in safety functions of the control must meet the
following requirements:
Safety contactor combinations (SCC) or corresponding devices
Only devices that correspond to EN ISO 13849-1 Category 3,
Performance Level d or EN 61508 SIL 2 may be used as safety contactor
combinations (SCC) or corresponding devices (e.g. safety-relevant PLC).
Safety relays
Only devices that correspond to EN ISO 13849-1 Category 3,
Performance Level d and EN 61508 SIL 2 and have a positively-driven
normally closed relay contact may be used as safety relays.
Encoders
The control system with FS performs plausibility checks in order to
detect faults in encoders. However, the plausibility checks can detect
faults only if the drive moves. But, in the SOS safety function, the drive
is kept in its current position, and there is no movement. If the
connection between the drive and the encoder loosens at this point in
time, this fault cannot be detected by the control system.
For safe axes/spindles with a single-encoder system, this results in the
following requirement for the encoder used:
Use only encoders for which the loosening of the connection between
the drive and encoder at standstill is ruled out. The encoder manufacturer
must be able to exclude the "loosening of the mechanical coupling" fault
for the chosen encoder. The "mechanical coupling" characteristic value
provides information on the "loosening of the mechanical connection"
fault.
Dual-encoder systems and non-safe axes/spindles are not affected by
this requirement.
July 2011 4.10 Requirements the Application Must Meet 93
Page 94

4.11 Remaining Risks
Please keep the following in mind in addition to the information given in
chapter (2–14) 2:
If the machine is switched off via the main switch and wired as suggested
If an inverter is defective, in rare cases this can lead to the drives being no
in the basic circuit diagram, the main contactor of the UV(R) power supply
unit is switched off through the leading main-switch contact. This results in
the immediate switch-off of the PWM pulses to the inverters. The torque is
removed from the axes and spindles, and the available holding brakes of the
drives are activated at the same time. The delay times caused by the wiring
and the brake relays can lead to a a slight sagging of hanging axes until the
holding brakes engage.
This causes a problem only if the machine is switched off via the main
switch while the drives are in closed-loop control.
longer controlled. The torque is removed from the axes and spindles. The
delay times until the detection of the failure can lead to a a slight sagging of
hanging axes until the holding brakes engage.
This causes a problem only if the defect occurs while the drives are in
closed-loop control.
94 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Page 95

5 Safety-Related MPs and Signals
Danger
5.1 Safety-Related Machine Parameters (SMPs)
A machine parameter is safety-relevant if it has an effect on the safety-related
software, and therefore on the safety of the machine. SMPs are firmly linked
with the safety-related software. They are monitored via a checksum and can
be changed only after entering a separate code number and the OEM
password (see page 5–99).
The input values of the safe machine parameters are defined and entered
during commissioning of the machine.
The safe machine parameters are protected from unauthorized changes to
ensure that the safety of the machine is not endangered. For this purpose, a
machine parameter file (*.mpl) containing the machine parameters to be
protected is defined in the PLC:\OEM.SYS file using the MPLOCKFILE = ...
keyword. These parameters are specified in the same way as in a normal
machine parameter file, except that no values are assigned.
The MPLOCKFILE indicates the MPs that require the corresponding code
number in order to be edited. The machine tool builder can add any number of
MPs to the MPLOCKFILE in order to protect them from being changed by the
end user. MPs that have been added by the OEM can be edited without
entering the OEM password.
However, only the SMPs that have been defined as such by HEIDENHAIN are
used for generating the checksum for SMPs. This is an internal list of machine
parameters that cannot be edited by the machine tool builder. You will find a
list of these machine parameters on page 5–99 ff. If one of these MPs is
changed, the control reboots. The OEM password must be entered for the
new machine parameter value to go into effect. Then a partial acceptance test
must be performed.
The machine parameter file for SMPs, *.MPL ("MPLOCKFILE"), must be
activated in the OEM.SYS file.
The machine tool builder is autonomously responsible for any changes to
the *.MPL file ("MPLOCKFILE").
Changes can lead to the loss of safety!
After entering the code number 95148 or in the Machine parameter
programming mode of operation, you can only edit the machine parameters
that are not contained in the MPLOCKFILE file. Safety-related controls from
HEIDENHAIN contain the default entry MPLOCKFILE = PLC\mp\SGMP.MPL in the
OEM.SYS file. This MPLOCKFILE contains all machine parameters that are relevant
for the safety of the machine, and can have any desired name. The file
extension *.mpl is important, however. SMPs are indicated by color in the MP
editor.
July 2011 5.1 Safety-Related Machine Parameters (SMPs) 95
Page 96

The following code numbers and the OEM password control the access rights
Danger
to MPs and SMPs in the iTNC 530:
Entry of the code number 95148 or 984651 if no MPLOCKFILE is present
Reading and editing of all machine parameters. Since there is no
MPLOCKFILE, there are no SMPs. The code number 95148 or 984651 can be
changed using the token MPPASSWORD in the OEM.SYS file. After that, the
code number 95148 or 984651 only gives you read access to the MP file.
Entry of code number 95148 if MPLOCKFILE is present
Reading and editing of all machine parameters that are not listed in
MPLOCKFILE. The machine parameters of MPLOCKFILE can only be read, not
edited. This code number cannot be changed if MPLOCKFILE is present, and
is therefore always valid.
Entry of code number 984651 and MPPASSWORD if MPLOCKFILE is
present
Reading and editing of all machine parameters and safety-related machine
parameters (MPs in MPLOCKFILE). After the control has been rebooted, any
changes to the SMPs must be confirmed by entering the OEM password.
You can change this code number by means of the keyword MPPASSWORD =
in the OEM.SYS file to protect the machine parameters of MPLOCKFILE from
unauthorized changes. This renders 984651 invalid for the changing of MPs.
After that, the code number 984651 will only give you read access to the
machine parameters of MPLOCKFILE.
OEM password 5038167 and SGMPCHANGE
After SMPs have been edited and the control has been rebooted, the OEM
password must be entered to confirm the changes.
You must change this OEM password by means of the keyword SGMPCHANGE
= in the OEM.SYS file to protect the SMPs from unauthorized changes! This
will render 5038167 invalid.
The password 5038167 must be changed during commissioning of the
machine in order to protect the machine parameters of MPLOCKFILE and the
SMPs from unauthorized changes!
The message Safe machine parameters have been edited. Run a partial
acceptance test! can appear if an acceptance test of the machine parameters
has already been performed (i.e. a valid checksum is stored), but one or more
than one SMP was changed later on.
96 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Page 97

This message displays a list of the SMPs that have been changed. Use this list
Danger
to check whether the safe machine parameters contained are those safe
machine parameters you changed deliberately. For the changes to go into
effect, enter the OEM password.
Only the machine tool builder is permitted to load edited SMPs by entering
the OEM password that is known to him (e.g. for optimizing the MPs).
Changing any SMPs necessitates a partial acceptance test!
The end user cannot put the control fully into service after changing SMPs,
because he does not know the OEM password. If an incorrect password is
entered or password entry is canceled, the control returns to the Power
Interrupted state.
The following procedure is used to edit SMPs:
The (edited) SMP parameter set is transmitted to the SKERN. The SKERN
compares the checksum of the new SMP parameter set with the checksum
saved for the last valid SMP parameter set (= reference SMP parameter set).
If the checksum is the same, the control goes into normal operation.
If the checksum has changed, you are prompted by a dialog to perform a
partial or complete acceptance test. You must confirm this by entering the
OEM password and pressing the permissive key.
July 2011 5.1 Safety-Related Machine Parameters (SMPs) 97
Page 98

Then the SKERN checks for all SMPs whether an SMP has changed compared
Note
Danger
to its reference SMP parameter set. Each comparison is used to create a list
of SMPs that require a partial acceptance test to be performed. After the PLC
and the SPLC have been started, the SKERN prompts you to confirm for every
SMP in the list of edited SMPs that you will perform a partial acceptance test
for this SMP. To confirm the prompt, press the permissive key. After all SMPs
in the list have been confirmed, the new checksum of the edited SMPs is
loaded and saved in non-volatile memory.
You must perform the partial or complete acceptance test as prompted by
the control!
If an SMP has been edited and the OEM password is not available, the SMPs
can be corrected to the original value in the Programming and Editing mode
of operation by pressing the MOD soft key and then entering the code number
984651 or, if applicable, by using the password defined in OEM.SYS >
MPPASSWORD= .... There is also the possibility of using the code number to
reimport and reactivate an SMP set (from the manufacturer) matching the
checksum via the file system (with the PGM MGT soft key). Changes made to
machine parameters in the meantime by the end user, however, will be lost
during this process.
The (S)MP set defined by you during commissioning of the machine must be
supplied together with the machine when the machine is shipped.
Start-up of the control is successful only if the active SMPs match a checksum
saved in the control.
Operator protection must be the most important criterion in defining the
SMP values. Therefore, the parameterizable tolerances, limit values and
delay times must be determined during commissioning depending on the
requirements of the machine, and must be optimized regarding operator
protection.
After the acceptance test, you must remove all invalid (old) machine
parameter files from the hard disk (so as to avoid old data from being
confused with new data).
The current data that corresponds to the acceptance test must be saved.
98 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
Page 99

Safe machine
parameters
SMP (iTNC 530): SMP511
Description: Time until the safety self-test. A test of the
HEIDENHAIN control components must be
performed after no more than 168 hours.
Input: 1 to 10080 [min]
Default value: 10080 minutes = 168 hours
SMP (iTNC 530): SMP525.x
Description: Default time for stopping the axes along the
emergency braking ramp upon SS1 reaction (axisspecific)
Input: 0.000 to 10.000 [s]
Default value: 1 [s]
SMP (iTNC 530): SMP526.x
Description: Default time for stopping the spindles along the
emergency braking ramp upon SS1 reaction (axisspecific)
Input: 0.000 to 10.000 [s]
Default value: 1 [s]
SMP (iTNC 530): SMP527.x
Description: Default time for controlled stopping of the axes upon
SS2 reaction (axis-specific)
Input: 0.000 to 10.000 [s]
Default value: 1 [s]
SMP (iTNC 530): SMP528.x
Description: Default time for controlled stopping of the spindles
upon SS2 reaction (axis-specific)
Input: 0.000 to 10.000 [s]
Default value: 1 [s]
July 2011 5.1 Safety-Related Machine Parameters (SMPs) 99
Page 100

SMP (iTNC 530): SMP530.x
Attention
Description: Delay time for dv/dt monitoring
Input: 0.000 to 10.000 [s]
Default value: 0.030 [s]
SMP (iTNC 530): SMP535.x
Description: Run times of the max. 16 timers for the SPLC program
Input: 0.0 to 1 000 000.0 [s]
Default value: 0 [s]
SMP (iTNC 530): SMP540.x
Description: Limit value for the "safely limited speed" (SLS) of the
axes in safe operating mode 3 (SOM_3)
Input: 0 to 5000 [mm/min] or [°/min]
Default value: 2000 [mm/min] or [°/min]
SMP (iTNC 530): SMP541
Description: Limit value for the "safely limited speed" (SLS) of the
spindle in safe operating mode 3 (SOM_3); MP560=0
Input: 0 to 6000 [rpm]
Default value: 500 [rpm]
The speed limit values for the axes and spindle are defined in
EN 12417:2007 for the different safety-related operating modes.
100 HEIDENHAIN Technical Manual Functional Safety
 Loading...
Loading...