
FANUC I/O Unit-MODEL A
CONNECTION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
B-61813E/04
• No part of this manual may be reproduced in any form.
• All specifications and designs are subject to change without notice.
In this manual we have tried as much as possible to describe all the various matters.
However, we cannot describe all the matters which must not be done, or which cannot be
done, because there are so many possibilities.
Therefore, matters which are not especially described as possible in this manual should be
regarded as ”impossible”.
This manual contains the program names or device names of other companies, some of
which are registered trademarks of respective owners. However, these names are not
followed by or in the main body.
B-61813E/04 DEFINITION OF WARNING, CAUTION, AND NOTE
DEFINITION OF WARNING, CAUTION, AND NOTE
This manual includes safety precautions for protecting the user and
preventing damage to the machine. Precautions are classified into
Warning and Caution according to their bearing on safety. Also,
supplementary information is described as a Note. Read the Warning,
Caution, and Note thoroughly before attempting to use the machine.
WARNING
Applied when there is a danger of the user being
injured or when there is a damage of both the user
being injured and the equipment being damaged if
the approved procedure is not observed.
CAUTION
Applied when there is a danger of the equipment
being damaged, if the approved procedure is not
observed.
NOTE
The Note is used to indicate supplementary
information other than Warning and Caution.
- Read this manual carefully, and store it in a safe place.
s-1

B-61813E/04 PREFACE
PREFACE
Applicable models
This manual describe the following products:
Name of products Abbreviation
FANUC I/O Unit-MODEL A I/O Unit-A
Applicable CNCs
Name of products Abbreviation
FANUC Power Mate Power Mate
FANUC Series 0 (MODEL C) Series 0-C
FANUC Series 15 Series 15
FANUC Series 16 Series 16
FANUC Series 18 Series 18
FANUC Series 20 Series 20
FANUC Series 21 Series 21
FANUC SYSTEM F-MODEL D Mate F-D Mate
FANUC Power Mate i Power Mate i
FANUC Series 0i Series 0i
FANUC Series 15i Series 15i
FANUC Series 16i Series 16i
FANUC Series 18i Series 18i
FANUC Series 20i Series 20i
FANUC Series 21i Series 21i
FANUC Series 30i Series 30i
FANUC Series 31i Series 31i
FANUC Series 32i Series 32i
Other related models
Name of products Abbreviation
FANUC I/O Unit-MODEL B I/O Unit-B
Abbreviations of manufacturer names used herein
This manual uses the following abbreviations for manufacturers of
products such as connectors.
Manufacturer name Abbreviation
Daito Communication Apparatus Co., Ltd. Daito
Fujitsu Limited Fujitsu
HIROSE ELECTRIC CO., LTD. HIROSE ELECTRIC
HONDA TSUSHIN KOGYO CO., LTD. HONDA TSUSHIN
Molex Incorporated Molex
Nihon Weidmüller Co., Ltd. Weidmüller
SORIAU JAPAN SORIAU JAPAN
Tyco Electronics AMP K.K. Tyco Electronics
p-1


B-61813E/04 TABLE OF CONTENTS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
DEFINITION OF WARNING, CAUTION, AND NOTE .................................s-1
PREFACE....................................................................................................p-1
I. CONNECTION
1 FANUC I/O Link ...................................................................................... 3
1.1 CONFIGURATION......................................................................................... 4
1.2 ALLOCATION OF I/O POINTS...................................................................... 5
2 I/O Unit CONFIGURATION.....................................................................7
3 INSTALLATION ......................................................................................8
3.1 ENVIRONMENT FOR INSTALLATION .........................................................9
3.1.1 Environmental Conditions outside the Cabinet........................................................9
3.2 DESIGNING CONDITION FOR A CABINET ............................................... 10
3.3 OUTER DIMENSION OF I/O Unit................................................................ 11
3.4 MOUNTING AND DISMOUNTING MODULES............................................15
4 CONNECTION....................................................................................... 16
4.1 GENERAL CONNECTION DIAGRAM......................................................... 17
4.2 CONNECTING INPUT POWER SOURCE .................................................. 18
4.3 GROUNDING ..............................................................................................19
4.4 REQUIRED CURRENT ............................................................................... 20
4.5 INTERFACE MODULE (AIF01A, AIF01A2, AIF01B) ................................... 21
4.6 INTERFACE MODULE (AIF02C) CONNECTION........................................ 24
4.6.1 Overview ................................................................................................................24
4.6.2 Connection .............................................................................................................25
4.6.3 Setting with the DIP Switch ...................................................................................27
4.7 CONNECTING WITH I/O MODULES.......................................................... 28
5 DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULES .................................................. 30
5.1 LIST OF MODULES ....................................................................................31
5.2 CORRESPONDENCE BETWEEN I/O SIGNALS AND ADDRESSES IN A
MODULE .....................................................................................................34
5.2.1 Module with 16/32 Digital Inputs (DI) ..................................................................34
5.2.2 Module with 5/8/12/16/32 Digital Outputs (DO)...................................................34
5.2.3 AIO40A Module (Hybrid Module with 24 Input and 16 Output Points)...............35
5.3 SPECIFICATION FOR EACH MODULE ..................................................... 36
c-1

TABLE OF CONTENTS B-61813E/04
5.4 DETAILS OF I/O Unit CONNECTORS (HONDA TSUSHIN/HIROSE
ELECTRIC) AND TERMINAL BLOCK (WEIDMÜLLER).............................. 74
5.4.1 Modules Using the MR-50RMA Connector Manufactured by Honda Tsushin.....75
5.4.2 Modules Using the HIF3BB-50PA-2.54DS Connector Manufactured by
Hirose Electric........................................................................................................77
5.4.3 Modules Using the HIF4-40P-3.18DS Connector Manufactured by
Hirose Electric........................................................................................................79
5.4.4 Modules Using the Terminal Block BL3.5/24/90F Manufactured by
Weidmüller.............................................................................................................80
6 ANALOG INPUT MODULE................................................................... 81
6.1 12-BIT ANALOG INPUT MODULE (AAD04A)............................................. 82
6.1.1 Specifications .........................................................................................................82
6.1.2 Correspondence between Input Signals and Addresses in a Module .....................83
6.1.3 Connecting with Analog Input Module..................................................................85
6.2 16-BIT ANALOG INPUT MODULE (AAD04B)............................................. 86
6.2.1 Specifications .........................................................................................................86
6.2.2 Correspondence between Input Signals and Addresses in a Module .....................87
6.2.3 Connecting with Analog Input Module..................................................................89
7 ANALOG OUTPUT MODULE ............................................................... 90
7.1 12-BIT ANALOG OUTPUT MODULE (ADA02A)......................................... 91
7.1.1 Specification...........................................................................................................91
7.1.2 Correspondence between Output Signals and Addresses in a Module ..................92
7.1.3 Connection to Analog Output Module ...................................................................93
7.2 14-BIT ANALOG OUTPUT MODULE (ADA02B)......................................... 94
7.2.1 Specification...........................................................................................................94
7.2.2 Correspondence between Output Signals and Addresses in the Module ...............95
7.2.3 Connection between the Analog Output Module and Load ...................................96
8 HIGH-SPEED COUNTER MODULE .....................................................97
8.1 OUTLINE OF HIGH-SPEED COUNTER MODULE ..................................... 98
8.2 SPECIFICATIONS OF HIGH-SPEED COUNTER MODULE..................... 100
8.2.1 Pulse Counter .......................................................................................................100
8.2.2 Comparison Function ...........................................................................................100
8.2.3 Pulse Interface ......................................................................................................102
8.2.4 External Contact Input..........................................................................................105
8.2.5 External Contact Output.......................................................................................105
8.2.6 Marker Processing................................................................................................106
c-2

B-61813E/04 TABLE OF CONTENTS
8.2.7 LED indicators .....................................................................................................107
8.3 PMC INTERFACE .....................................................................................109
8.3.1 Mode A.................................................................................................................109
8.3.2 Mode B.................................................................................................................111
8.3.3 Details of PMC Interface Signals .........................................................................114
8.4 TOTAL CONNECTION OF HIGH-SPEED COUNTER MODULE.............. 117
8.4.1 Connection Diagram.............................................................................................117
8.4.2 Connector Signal List...........................................................................................117
8.4.2.1 C49 signal (for mode A).................................................................................. 118
8.4.2.2 C49 signal (for mode B) .................................................................................. 118
8.5 CONNECTION WITH PULSE GENERATOR ............................................119
8.5.1 Use of Phase A and B Pulses................................................................................119
8.5.2 Use of Positive/Negative Pulses...........................................................................120
8.6 CONNECTION WITH MACHINE (POWER MAGNETICS CABINET) .......121
8.6.1 Use in Mode A .....................................................................................................121
8.6.2 Use in Mode B......................................................................................................122
8.7 I/O SIGNALS CONVENTIONS .................................................................. 123
8.7.1 Solid State Relay Output Signals (OUT0 to OUT7) ............................................123
8.7.2 DC Input Signals (ME and CSP)..........................................................................124
8.7.3 +5-V Output from JA9 Connector........................................................................124
8.8 SUPPLEMENT ..........................................................................................125
8.8.1 Configuration of Mode A.....................................................................................125
8.8.2 Counter Presetting and Counting .........................................................................126
8.8.3 Setting Data ..........................................................................................................129
8.8.4 Reading Data ........................................................................................................130
8.9 EXAMPLE OF STARTING UP ACT01A ....................................................131
8.9.1 Mode A Startup Flowchart ...................................................................................131
8.9.2 Example of Mode A Ladder.................................................................................132
8.9.3 Mode B Startup Flowchart ...................................................................................136
8.9.4 Example of Mode B Ladder .................................................................................137
9 TEMPERATURE INPUT MODULE .....................................................144
9.1 OVERVIEW ............................................................................................... 145
9.2 TEMPERATURE INPUT MODULE SPECIFICATION ...............................146
9.3 PMC INTERFACE .....................................................................................147
9.3.1 PMC I/O Area ......................................................................................................147
9.3.2 Measurement Mode..............................................................................................148
9.3.3 Details of Output Signals (PMC → Temperature Module)..................................148
c-3

TABLE OF CONTENTS B-61813E/04
9.3.4 Details of Input Signals (Temperature Module → PMC) ....................................151
9.4 COMPLETE CONNECTION OF TEMPERATURE INPUT MODULE ........ 154
9.4.1 Temperature Input Module Connection Diagram ................................................154
9.4.2 Connector Signal Lists .........................................................................................155
9.4.3 Terminal Board Unit Connection Diagram ..........................................................156
9.5 TIMING CHARTS ......................................................................................157
9.6 MEASUREMENT EXAMPLES................................................................... 158
9.7 TERMINAL BOARD UNIT DIMENSIONS.................................................. 165
10 OPTICAL I/O Link ADAPTER.............................................................166
10.1 EXTERNAL DIMENSION OF OPTICAL I/O Link....................................... 167
10.2 WEIGHT OF OPTICAL I/O Link................................................................. 167
10.3 CONNECTION OF OPTICAL I/O Link....................................................... 168
10.4 POWER SOURCE OF OPTICAL I/O Link ADAPTER ...............................169
10.5 INSTALLATION CONDITIONS OF OPTICAL I/O Link ADAPTER ............169
10.6 CAUTIONS FOR USING OPTICAL I/O Link ADAPTERS ......................... 170
10.6.1 Configuring I/O Links Using Optical I/O Link Adapters ....................................170
10.6.2 When Using Series 16i/18i/21i-MODEL B as Master .........................................171
10.6.3 When Using Series 30i/31i/32i-MODEL B as Master .........................................172
10.7 OPTICAL FIBER CABLE ........................................................................... 174
10.7.1 External View of Optical Fiber Cable..................................................................174
10.7.2 Notice of Optical Fiber Cable Handling...............................................................175
10.7.3 Optical Fiber Cable Clamping Method ................................................................176
10.7.4 Relay Using an Optical Fiber Junction Adapter...................................................177
10.7.5 Maximum Transmission Distance by Optical Fiber Junction Cable....................179
11 I/O Link DUMMY UNIT........................................................................ 180
11.1 OVERVIEW ............................................................................................... 181
11.2 EXTERNAL DIMENSIONS ........................................................................ 181
11.3 LED INDICATORS..................................................................................... 182
11.4 WEIGHT ....................................................................................................182
11.5 POWER REQUIREMENTS ....................................................................... 182
11.6 INSTALLATION CONDITIONS.................................................................. 182
11.7 CONNECTION DIAGRAMS....................................................................... 183
11.7.1 When not Connecting FANUC I/O Link Dummy Units in Series.......................183
11.7.2 Connecting FANUC I/O Link Dummy Units in Series........................................184
11.7.3 Grounding.............................................................................................................184
11.7.4 K3X Cable............................................................................................................185
c-4

B-61813E/04 TABLE OF CONTENTS
12 TWO-CHANNEL I/O Link CONNECTOR ADAPTER .........................186
12.1 OVERVIEW ............................................................................................... 187
12.2 CONNECTION FOR USE OF TWO FANUC I/O Link CHANNELS ...........187
12.3 CONNECTING THE CNC WITH TWO-CHANNEL I/O Link CONNECTOR
ADAPTER.................................................................................................. 188
12.4 CABLING................................................................................................... 189
12.5 CONNECTING TWO-CHANNEL I/O Link CONNECTOR ADAPTER TO
I/O Units FOR THE FANUC I/O Link .........................................................189
12.6 CABLE LENGTH .......................................................................................190
12.7 INSTALLING TWO-CHANNEL I/O Link CONNECTOR ADAPTER........... 190
12.8 OUTSIDE DIMENSIONS OF TWO-CHANNEL I/O Link CONNECTOR
ADAPTER.................................................................................................. 191
12.9 MOUNTING TWO-CHANNEL I/O Link CONNECTOR ADAPTER ............192
13 THREE-CHANNEL I/O Link CONNECTOR ADAPTER .....................193
13.1 OVERVIEW ............................................................................................... 194
13.2 CONNECTION FOR USE OF FOUR FANUC I/O Link CHANNELS.......... 194
13.3 CONNECTING THE CNC WITH THREE-CHANNEL I/O Link
CONNECTOR ADAPTER.......................................................................... 195
13.4 CABLING................................................................................................... 195
13.5 ALLOCATING THREE-CHANNEL I/O Link CONNECTOR ADAPTER
SIGNALS ................................................................................................... 196
13.6 CONNECTING THREE-CHANNEL I/O Link CONNECTOR ADAPTER
SIGNAL TO EACH CHANNEL................................................................... 197
13.7 CONNECTING THREE-CHANNEL I/O Link CONNECTOR ADAPTER
TO TWO-CHANNEL I/O Link CONNECTOR ADAPTER........................... 199
13.8 CONNECTING THREE-CHANNEL I/O Link CONNECTOR ADAPTER
TO I/O Units FOR THE FANUC I/O Link ...................................................200
13.9 CABLE LENGTH .......................................................................................200
13.10 INSTALLING THREE-CHANNEL I/O Link CONNECTOR ADAPTER .......200
13.11 OUTSIDE DIMENSIONS OF THREE-CHANNEL I/O Link CONNECTOR
ADAPTER.................................................................................................. 201
13.12 MOUNTING THREE-CHANNEL I/O Link CONNECTOR ADAPTER......... 202
14 SAFETY FOR USING AC....................................................................203
14.1 ENVIRONMENT FOR INSTALLATION .....................................................204
14.1.1 Installation Category (Overvoltage Category) .....................................................204
14.1.2 Pollution Degree...................................................................................................204
c-5

TABLE OF CONTENTS B-61813E/04
II. MAINTENANCE
1 OVERVIEW .........................................................................................207
1.1 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION..................................................................... 208
1.2 I/O Unit-A CONFIGURATION.................................................................... 209
1.3 BLOCK DIAGRAM..................................................................................... 210
1.4 I/O Unit-MODEL A CONFORMING TO UL/C-UL ...................................... 211
1.5 LIST OF UNITS ......................................................................................... 212
1.5.1 Units Conforming to UL/C-UL Standard: Ordering Information
A03B-0819-Jxxx ..................................................................................................212
1.5.2 Other Units (not Conforming to UL/C-UL) .........................................................214
1.5.3 Early Units (Units not Conforming to UL/C-UL: Ordering Information
A03B-0807-Jxxx).................................................................................................214
2 INDICATION........................................................................................ 216
2.1 INTERFACE MODULE (AIF01A, AIF01A2) LED INDICATORS................ 217
2.2 INTERFACE MODULE (AIF01B) LED INDICATORS................................ 220
2.3 INTERFACE MODULE (AIF02C) LED INDICATORS................................ 221
2.3.1 PWR Indicator......................................................................................................221
2.3.2 LNK Indicators.....................................................................................................221
2.3.3 ER Indicators........................................................................................................221
2.3.4 LED Indicators .....................................................................................................221
2.3.5 M/S Indicator........................................................................................................222
2.3.6 No. Indicators .......................................................................................................223
2.4 LED INDICATORS ON THE INPUT/OUTPUT MODULES (HAVING 16
OR FEWER INPUT/OUTPUT POINTS) ....................................................223
3 FUSES................................................................................................. 224
4 REMOVING PC BOARDS...................................................................225
4.1 HOW TO REMOVE TERMINAL BOARD-TYPE I/O MODULE PC
BOARDS ................................................................................................... 226
4.2 HOW TO REMOVE INTERFACE AND CONNECTOR-TYPE I/O
MODULE PC BOARDS .............................................................................228
c-6

I. CONNECTION


B-61813E/04 CONNECTION 1.FANUC I/O Link
1 FANUC I/O Link
I/O Link is a serial interface with a purpose to transfer I/O signals (bit
data) between CNC, cell controller, the I/O Unit-MODEL A, the Power
Mate and so on at high-speed.
- 3 -
1.FANUC I/O Link CONNECTION B-61813E/04
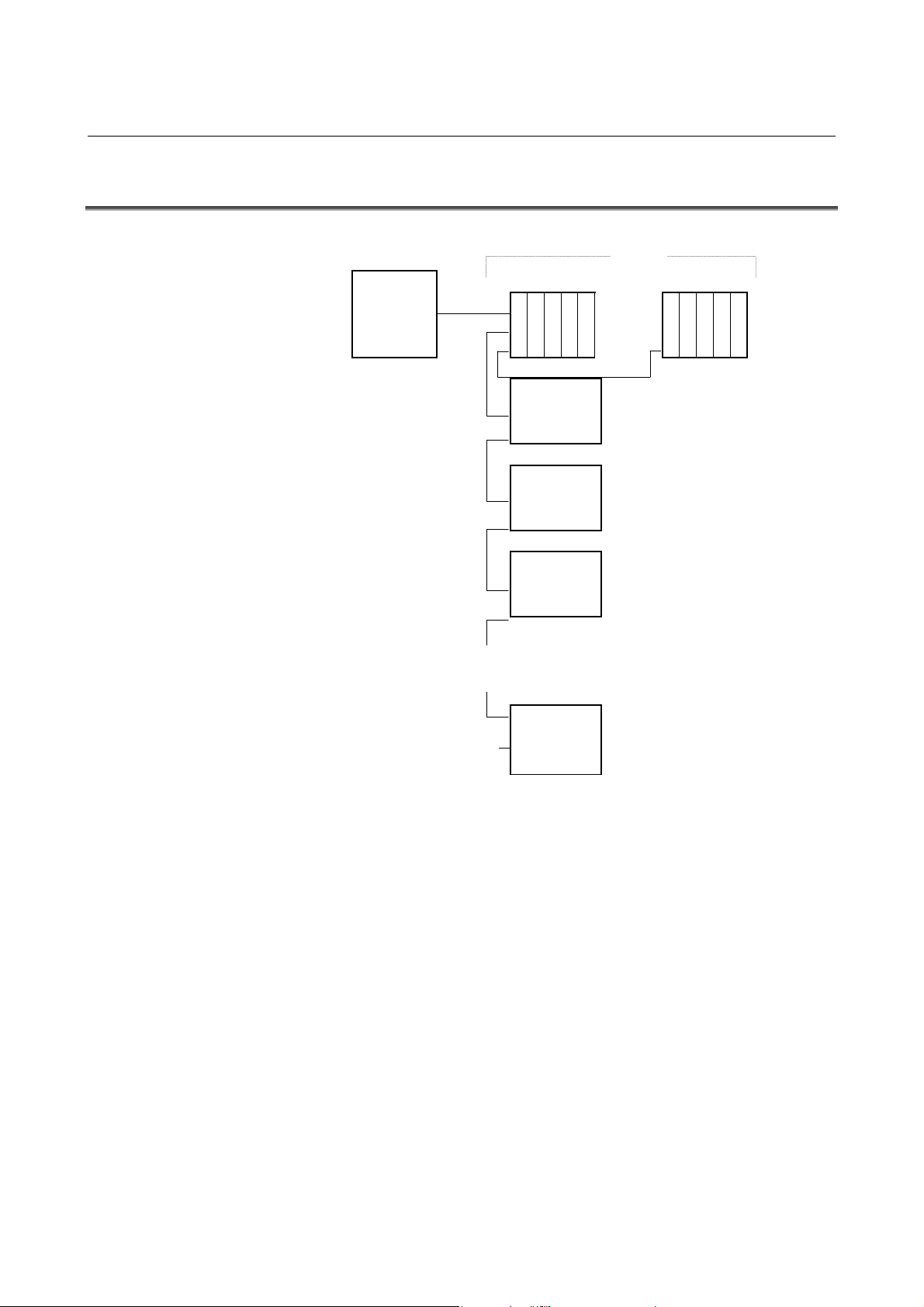
1.1 CONFIGURATION
CNC I/O Unit-A I/O Unit-A
Power Mate
Operator’s
panel
connection
unit
Power Mate
Series
0-C
: : :
: : :
: : :
Operator’s
panel
connection
unit
(1) The FANUC I/O Link is made up of one master and a number of
slaves.
Master: Series0-C, Series15/16/18/20/21,
Series15i/16i/18i/20i/21i/30i/31i/32i/0i,
Power Mate-D/H, Power Mate i-D/H, F-D Mate
Slave: I/O Unit-A, I/O Unit-B, Operator's panel connection unit,
Connector panel I/O module, Power Mate,
Series0-C, Servo unit β series (I/O Link option), and so on
(2) Up to 16 groups of slaves can be connected with a single I/O Link.
Number of slaves per one group is as follows.
I/O Unit-A..............................................Up to 2 units (i.e.2 bases)
I/O Unit-B................................................................ Up to 30 units
(Basic unit, basic and extension units).
Operator's panel I/O module ................................................ 1 unit
(1 basic module and extension modules (up to three)
Operator's panel connection unit, connector panel I/O module,
Power Mate, Series0-C, Servo unit β series (I/O Link option)
.............................................................................. 1 unit
(3) Any slave can be connected with any group. However, different
types of slaves cannot be connected with a single group.
Slave
Group
#0
Group
#1
Group
#2
Group
#3
Group
#15
- 4 -
B-61813E/04 CONNECTION 1.FANUC I/O Link
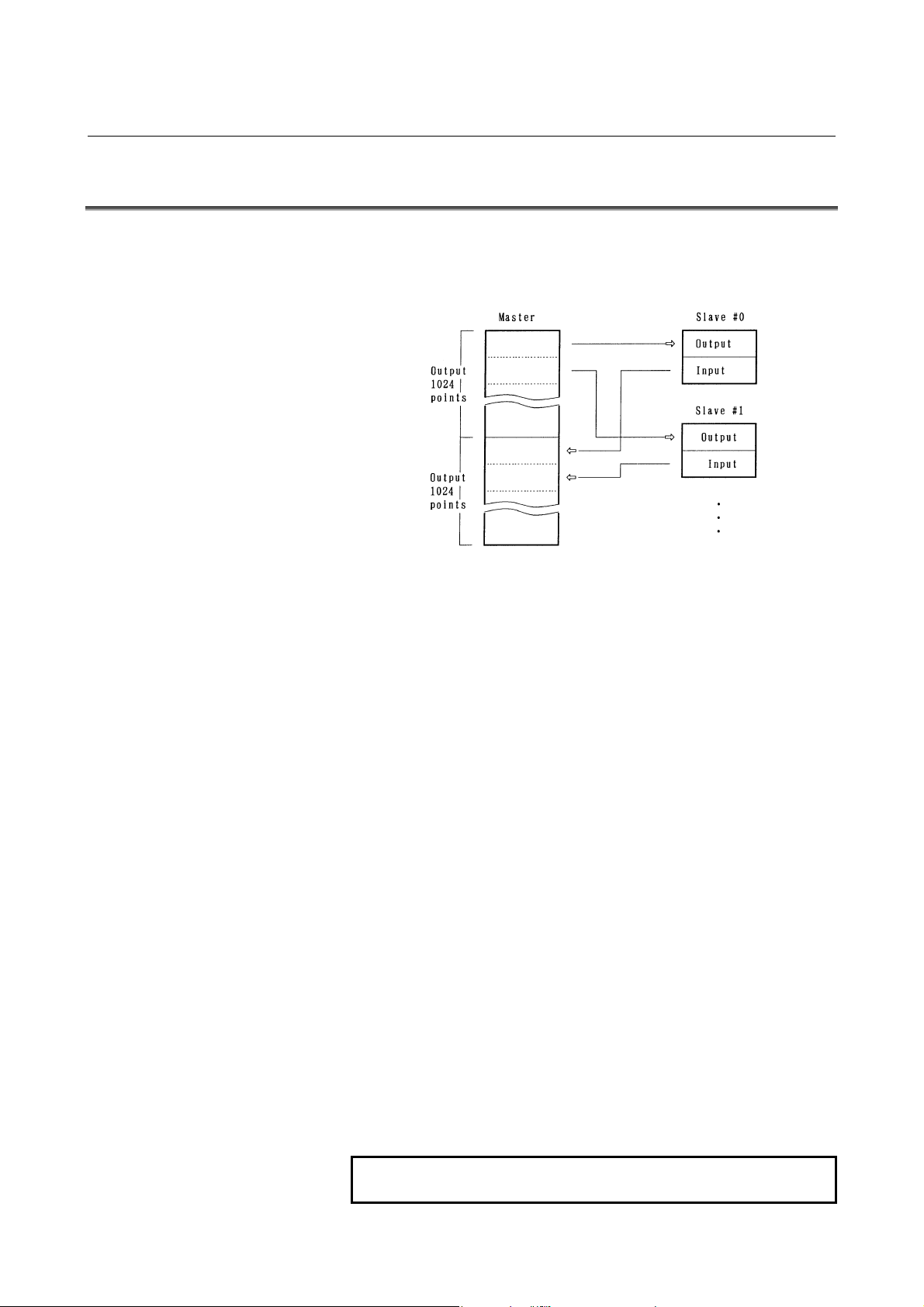
1.2 ALLOCATION OF I/O POINTS
I/O Link has 1024 input points per 1 channel and 1024 output points per
1 channel as viewed from the master.
I/O data is periodically transferred between the master and slaves by
allotting these I/O points to each slave.
Each slave can occupy as many I/O points as determined for it. For the
I/O Link, the total number of I/O points occupied by all slaves per
channel must meet:
Number of input points ≤ 1024
Number of output points ≤ 1024
Number of actual I/O points may differ from that of the occupied ones.
How to determine the number of I/O points to be allotted to each slave
and restrictions for allocation are shown in the followings.
(For the allocation method for I/O points, refer to the PMC
PROGRAMMING MANUAL.)
(1) Sum the numbers of the I/O points for all slaves connected with a
single I/O Link. The sum must satisfy the following restriction :
Number of input points ≤ 1024 (per one I/O Link)
Number of output points ≤ 1024 (per one I/O Link)
(2) Number of the occupied I/O points per one group must satisfy the
following restriction :
Number of input points ≤ 256 (per one group)
Number of output points ≤ 256 (per one group)
(3) Determine the number of I/O points for the I/O Unit-A using the
following.
[Output points]
Sum of the actual output Occupied output
points in a group points
0 to 32 ⇒ 32 points
40 to 64 ⇒ 64 points
72 to 128 ⇒ 128 points
136 to 256 ⇒ 256 points
NOTE
Count AOA05E as 8 points AOA12F as 16 points.
- 5 -
1.FANUC I/O Link CONNECTION B-61813E/04
[Input points]
Sum of the actual output Occupied output
points in a group points
0 to 32 ⇒ 32 points
40 to 64 ⇒ 64 points
72 to 128 ⇒ 128 points
136 to 256 ⇒ 256 points
However, as result of the calculation above, when the number of
input points is not larger than that of the output points in a single
group, the number of input points is assumed to be equal to that of
the output points.
Example 1 : When the following modules are used in the group
No. 0.
AOD32C 3 AID32A 5
AOA12F 2 AIA16G 3
[Output points]
32 × 3 + 16 × 2 = 128 ⇒ 128 points
[Input points]
32 × 5 + 16 × 3 = 208 ⇒ 256 points
Example 2: When the following modules are used in the group
No.2
AOD16C 7 AID16C 4
AOA05E 9 AIA16G 3
[Output points]
16 ×7 + 8 ×9 = 184 ⇒ 256 points
[Input points]
16 ×4 + 16×3 = 112 ⇒ 128 points
In this case, as the number of input points is not
larger than that of the output points, the number of
input points is assumed to be equal to that of the
output points, in other words, 256 points
.
- 6 -
B-61813E/04 CONNECTION 2.I/O Unit CONFIGURATION
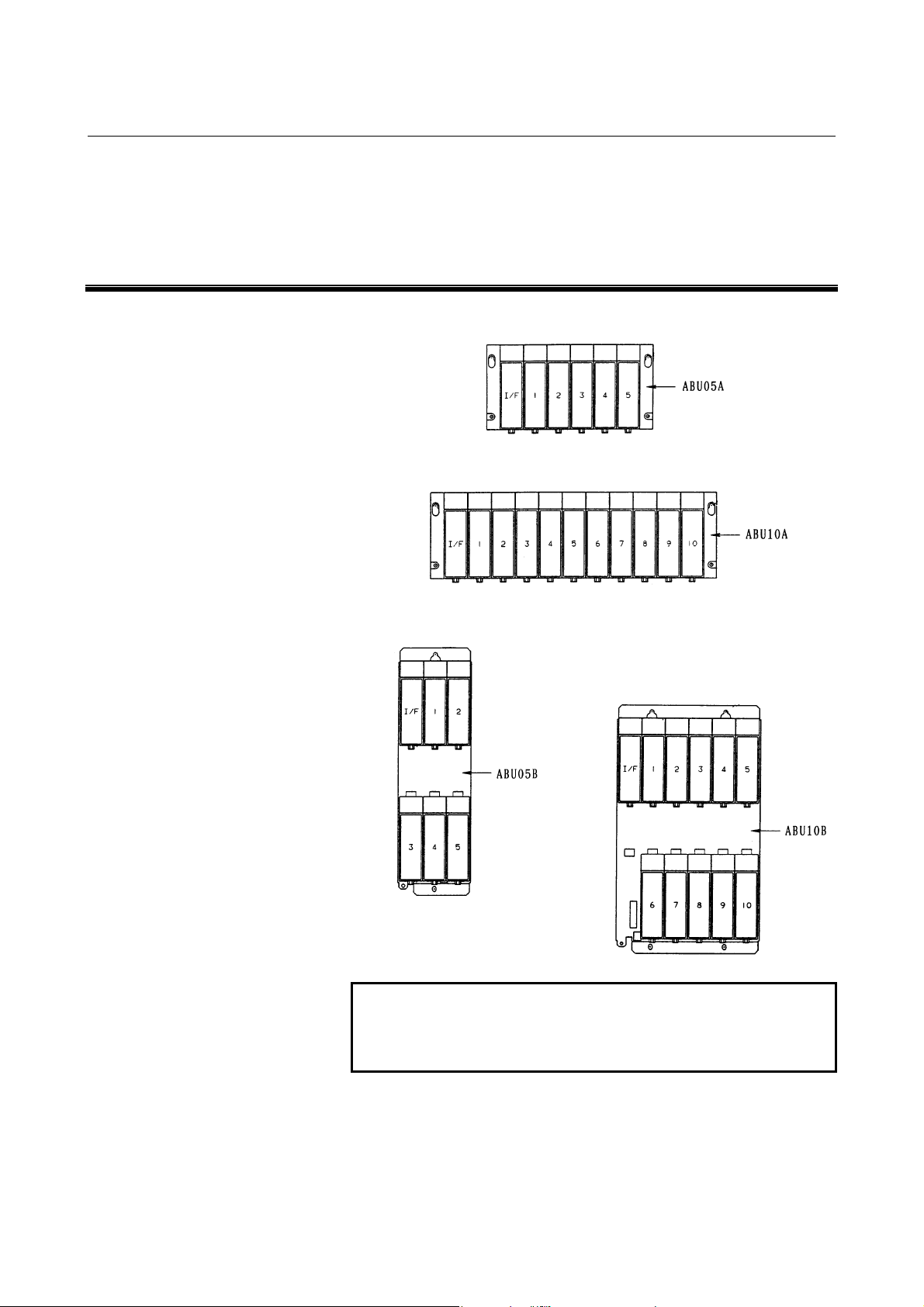
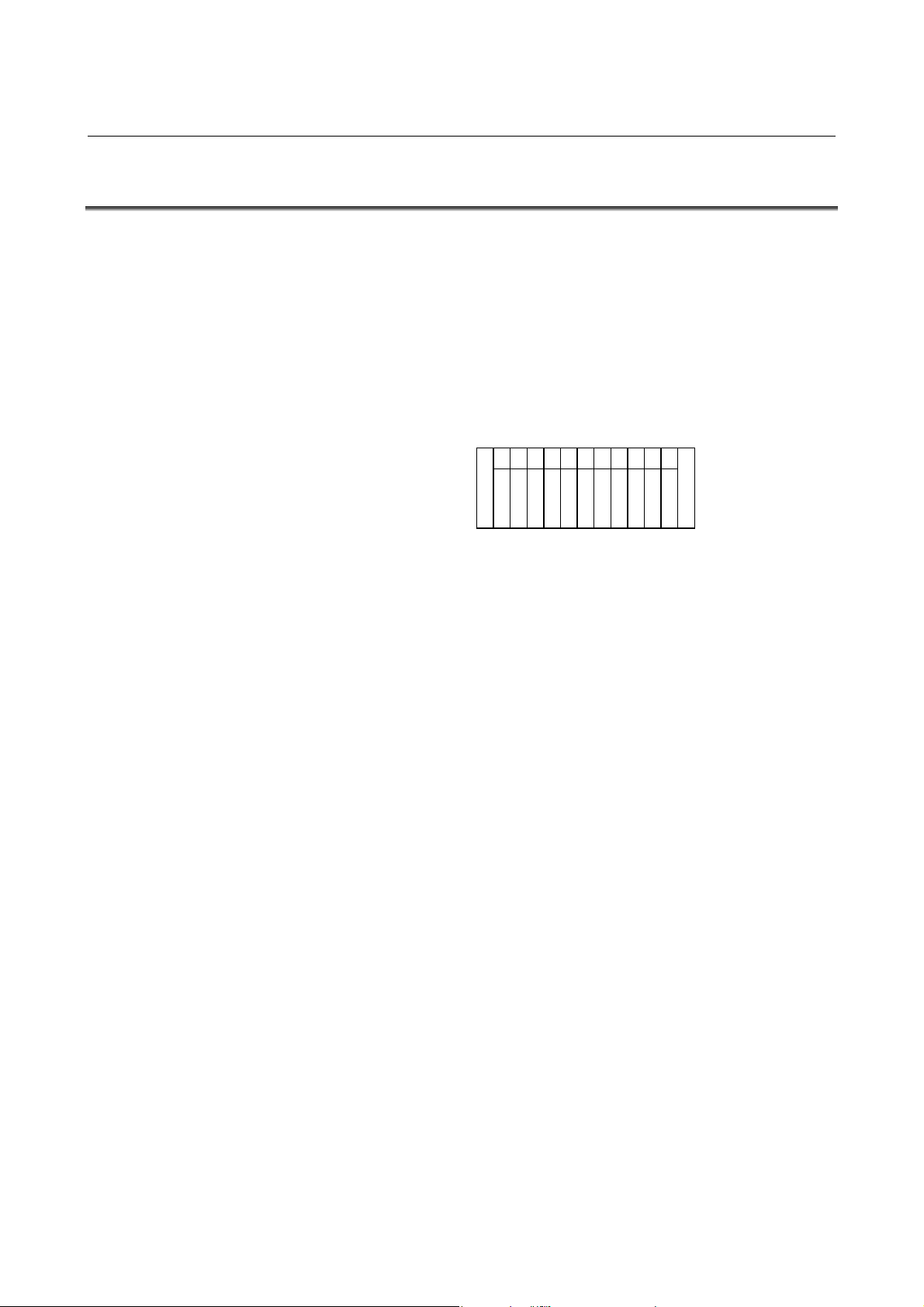
2 I/O Unit CONFIGURATION
5-slot horizontal base unit (ABU05A)
10-slot horizontal base unit (ABU10A)
5-slot vertical base unit (ABU05B)
10-slot vertical base unit (ABU10B)
NOTE
I/F : Interface module (AIF01A, AIF01A2,
AIF01B, or AIF02C)
1 to 10 : I/O modules
- 7 -

3.INSTALLATION CONNECTION B-61813E/04
3 INSTALLATION
- 8 -
B-61813E/04 CONNECTION 3.INSTALLATION
3.1 ENVIRONMENT FOR INSTALLATION
3.1.1 Environmental Conditions outside the Cabinet
The peripheral units and the control unit have been designed on the
assumption that they are housed in closed cabinets. In this manual
"cabinet" refers to the following:
• Cabinet manufactured by the machine tool builder for housing the
control unit or peripheral units;
• Operation pendant, manufactured by the machine tool builder, for
housing the LCD/MDI unit or operator's panel.
• Equivalent to the above.
The environmental conditions when installing these cabinets shall
conform to the following table. Section 3.2 describes the installation
and design conditions of a cabinet satisfying these conditions.
Ambient
temperature
of the cabinet
Humidity
Vibration
Meters above
sea level
Environment
NOTE
If the CNC is installed 1000 m or higher above sea level,
the allowable upper ambient temperature of the CNC in
the cabinet is changed as follows.
Assume that the allowable upper ambient temperature
of the CNC in the cabinet installed 1000 m or higher
above sea level decreases by 1.0°C for every 100 m rise
in altitude.
Example)
55°C - 1750/100 × 1.0°C = 47.5°C
Therefore, the allowable ambient temperature range is
from 0°C to 47.5°C.
Operating
Storage, Transport
Temperature change
Normal
Short period
(less than 1 month)
Operating
Non-operating
Operating
Non-operating
75%RH or less, no condensation
95%RH or less, no condensation
Normal machine shop environment
(The environment must be considered if the
cabinets are in a location where the density
of dust, coolant, organic solvent, and/or
corrosive gas is relatively high.)
0°C to 45°C
-20°C to 60°C
0.3°C/minute or less
0.5G or less
1.0G or less
Up to 1000 m
Up to 12000 m
(Note)
The upper allowable ambient temperature of the CNC
in the cabinet installed 1750 m above sea level is:
- 9 -
3.INSTALLATION CONNECTION B-61813E/04
3.2 DESIGNING CONDITION FOR A CABINET
When designing a cabinet to contain the I/O Unit-A, take the same care
as taken for the cabinet containing the CNC control unit and other units.
For details, refer to the CNC CONNECTION MANUAL.
In addition, when mounting the I/O Unit, conform to the followings in
view of maintenance, environmental durability, noise resistance and the
like.
(1) In order to ventilate inside the module well, mount the I/O Unit in
the direction shown in the figure below.
Upside
Downside
(2) Separate each I/O Unit at least 100 mm vertically from the other
units so as to ensure effective ventilation and make it easy to
attach/detach wires and modules.
(3) Do not put equipments which generate a large amount of heat
under the I/O Unit.
(4) Low-level signals are transferred through the signal cables K1X
and K2X. (For these cables, see the general connection diagram.)
Lay out these cables apart from the wires for AC power source and
the I/O wires of the I/O module by 100 mm or more.
(5) Make sure that there is no protruding portion such as a screw on
the mounting surface of the I/O Unit.
(6) Heat values of I/O Unit are listed in Table 3.3
- 10 -
B-61813E/04 CONNECTION 3.INSTALLATION
)
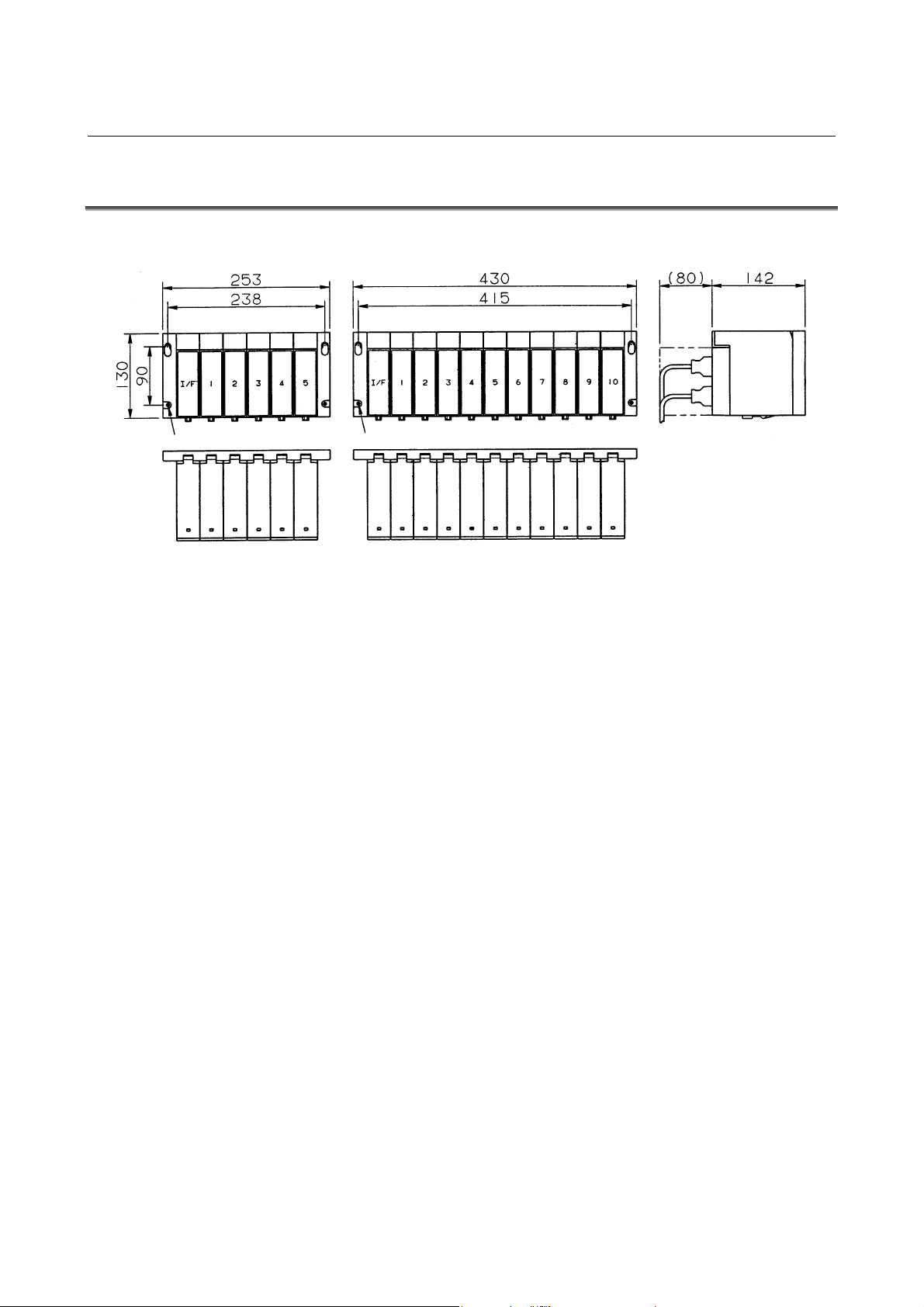
3.3 OUTER DIMENSION OF I/O Unit
Horizontal base units (ABU05A and ABU10A)
Hole for an M4 screw (4 places) Hole for an M4 screw (4 places
- 11 -
3.INSTALLATION CONNECTION B-61813E/04
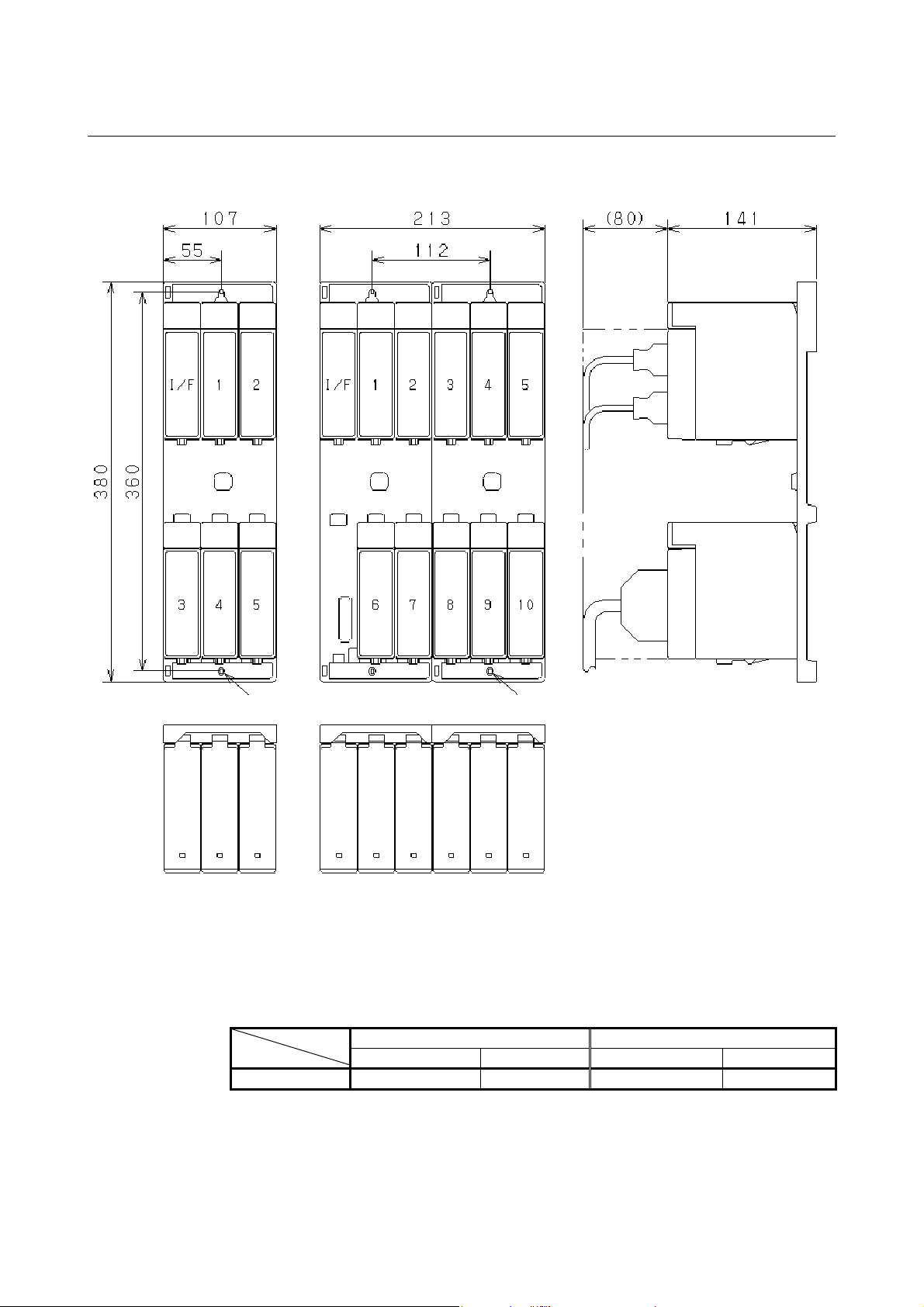
Vertical base units (ABU05B and ABU10B)
Hole for an M4 screw (2 places) Hole for an M4 screw (4 places)
* The ABU05B and ABU10B units that were shipped early on are
housed in a metal case.
The distances between mounting holes for the metal case and their
size are the same as for the plastic case used for the current units.
However, the width of the metal case differs from that of the
plastic case as listed below.
Width
Plastic case Metal case Plastic case Metal case
107mm 110mm 213mm 217mm
ABU05B ABU10B
- 12 -
B-61813E/04 CONNECTION 3.INSTALLATION
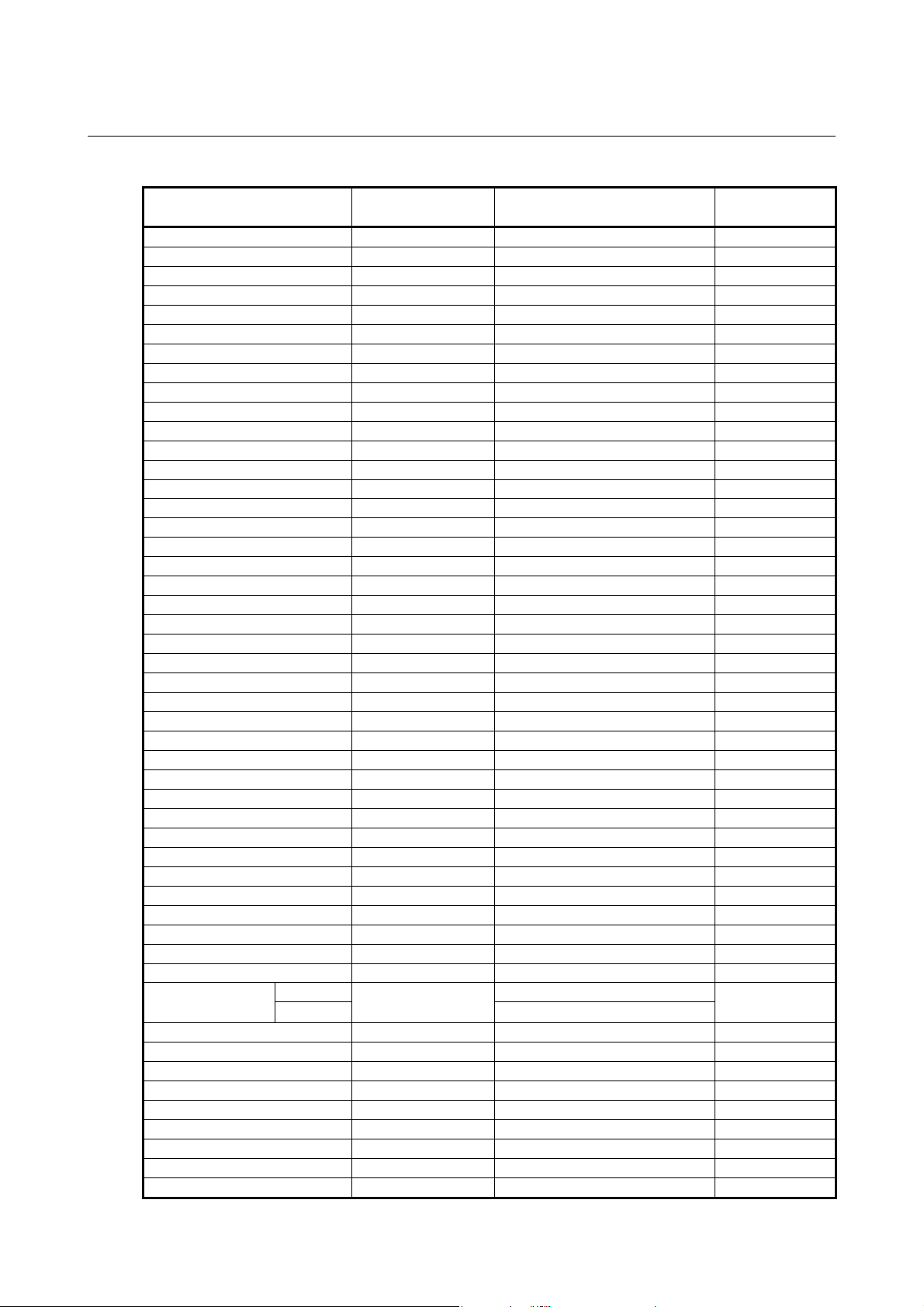
Table 3.3 Heat value and weight of each module
Module name
ABU10A - - 600
ABU10B - - 740
ABU05A - - 350
ABU05B - - 380
AIF01A 1.2 - 300
AIF01A2 1.2 - 300
AIF01B 1.2 - 270
AIF02C 1.2 - 300
Basic heat value
(W)
*1 AID32A1 1.2 0.23 250
*2 AID32B1 1.2 0.23 250
AID32H1 1.2 0.23 250
AID16C 0.1 0.21 300
AID16K 0.1 0.21 300
AID16D 0.1 0.21 300
AID16L 0.1 0.21 300
*3 AID32E1 0.1 0.23 220
AID32E2 0.1 0.23 220
*4 AID32F1 0.1 0.23 220
AID32F2 0.1 0.23 220
AIA16G 0.1 0.21 300
*5 AOD32A1 0.3 - 220
AOD08C 0.1 0.04+0.4×IL2 380
AOD08D 0.1 0.04+0.6×IL2 380
AOD08DP 0.1 0.04+0.1×IL2 310
AOD16C 0.1 0.04+1.4×IL2 300
AOD16D 0.1 0.04+1.4×IL2 320
AOD16D2 0.1 0.04+0.1×IL2 320
AOD16D3 0.1 0.04+0.1×IL2 320
AOD16DP 0.1 0.04+1.8×IL2 310
*6 AOD32C1 0.1 0.01+0.8×IL2 220
AOD32C2 0.1 0.01+0.8×IL2 220
*7 AOD32D1 0.1 0.01+0.8×IL2 200
AOD32D2 0.1 0.01+0.8×IL2 200
AOA05E 0.1 0.13+1.5×IL 370
AOA08E 0.1 0.13+1.5×IL 370
AOA12F 0.1 0.11+1.5×IL 320
AOR08G 0.1 0.3+0.1×IL2 300
AOR16G 0.1 0.3+0.1×IL2 350
AOR16H2 0.1 0.3+0.1×IL2 250
AIO40A
Input 0.23
Output
0.2
AAD04A 3.1 - 350
AAD04B 3.1 - 370
ADA02A 3.1 - 350
ADA02B 3.1 - 350
ACT01A 4.1 - 220
ATI04A 4.0 - 260
ATI04B 4.0 - 260
ATB01A - - 100
ATB01B - - 120
Heat value per one I/O point
(W)
0.01+1.3×IL
Weight (g)
350
- 13 -
3.INSTALLATION CONNECTION B-61813E/04
Module name
Optical I/O Link adapter - - 100
I/O Link dummy unit - - 120
Basic heat value
(W)
• Total ‘Heat value per 1 I/O point’ for simultaneous ON points plus
‘Basic heat value’ is the heat value of the module.
• IL : Load current of output
• *1 to *7 : "AxD32x" produced to the old specification is
equivalent to "AxD32x1" (with additional "1" at the
end) produced to the current specification.
(Example: Old specification AID32E → AID32E1)
Heat value per one I/O point
(W)
Weight (g)
- 14 -
B-61813E/04 CONNECTION 3.INSTALLATION
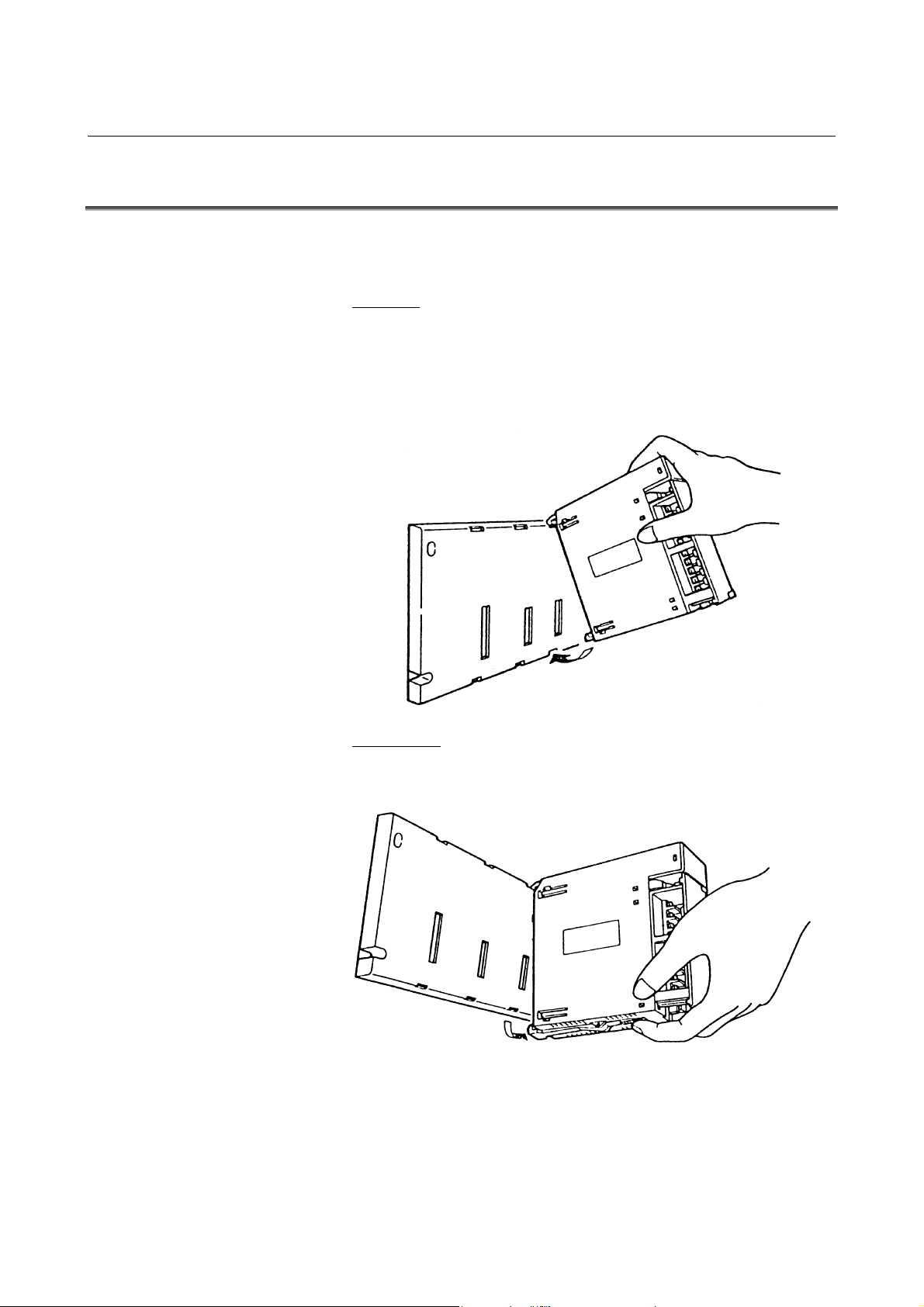
3.4 MOUNTING AND DISMOUNTING MODULES
Interface modules and various types of I/O modules can be mounted to
and dismounted from the base unit easily as shown below.
Mounting
Hang the hook at the top of the module on the groove in the upper
side of the base unit, and make the connector of the module
engage with that of the base unit. Push the module in the lower
groove of the base unit till the stopper in the lower side of the
module stops.
Dismounting
Release the stopper by pushing the lever at the bottom of the
module, and then push the module upwards.
- 15 -

4.CONNECTION CONNECTION B-61813E/04
4 CONNECTION
- 16 -
B-61813E/04 CONNECTION 4.CONNECTION
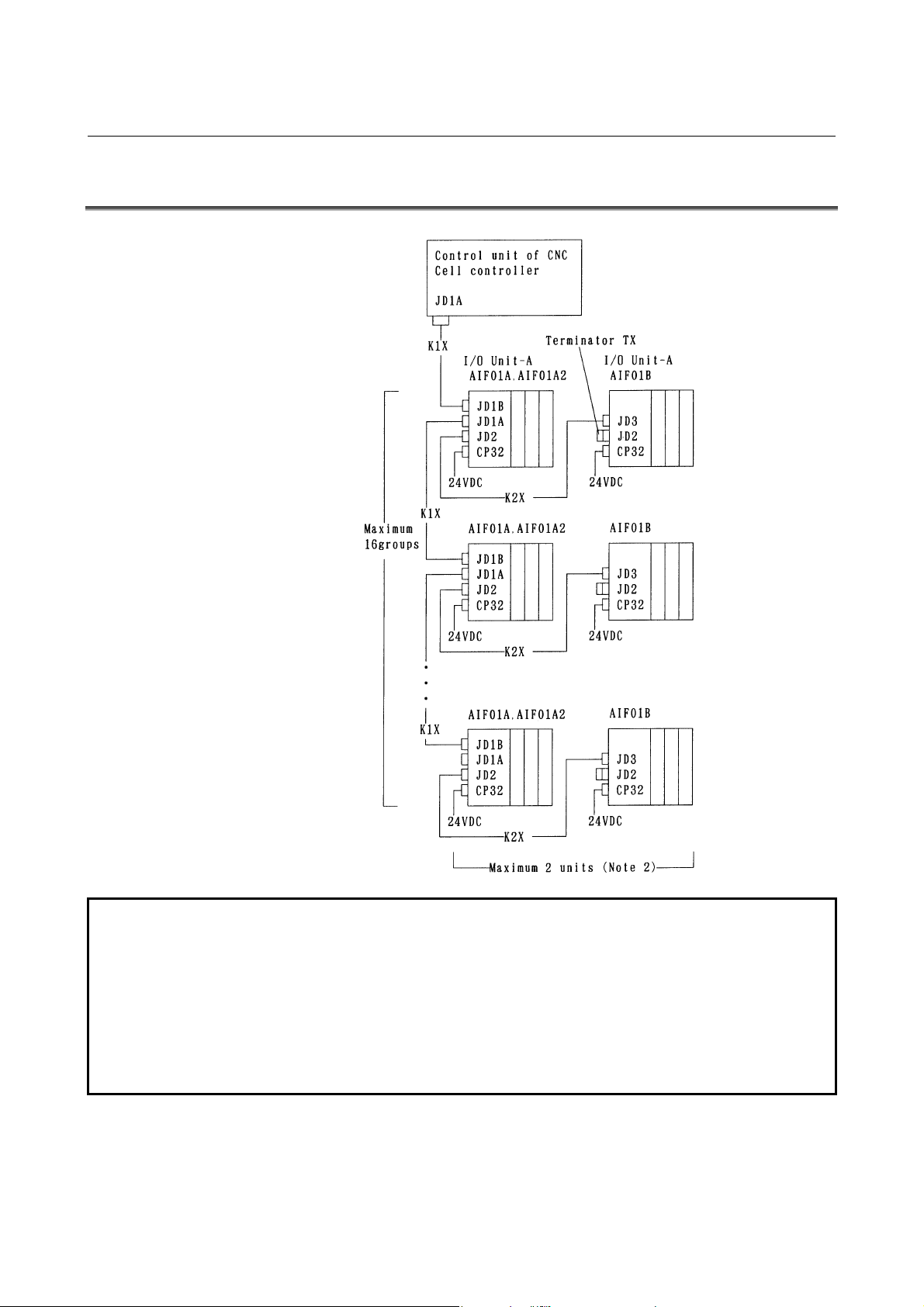
4.1 GENERAL CONNECTION DIAGRAM
NOTE
1 Number of I/O Units and connecting method are restricted depending on the
allocation of the I/O points. Refer to the section 1.2,"Allocation of I/O points."
2 If the master unit is the F-D Mate, one group can consist of up to four I/O Units.
3 Cable K1X can be an optical fiber cable by using the optical I/O link adapter.
See chapter 10.
4 Terminator TX is required for connector JD2 of the AIF01B that is the last unit to be
connected in the group. If no AIF01B is in use, no terminator has to be attached to the
JD2 connector of the AIF01A or AIF01A2.
- 17 -
4.CONNECTION CONNECTION B-61813E/04
4.2 CONNECTING INPUT POWER SOURCE
Connect the following power source with the connector CP32 or CP1 of
the interface module (AIF01A, AIF01A2, AIF01B, or AIF02C).
• Voltage: 24VDC ±10%
• Current: Determine from Table 4.4
AIF01A / AIF01B / AIF02C
CP32
1 +24V
2 GND
3
AIF01A2
CP1
1 +24V
2 GND
3
NOTE
Turn ON the power for the I/O Unit just when or
before the power for the CNC or the cell controller is
turned ON. When the CNC or cell controller power is
turned OFF, make sure to turn the power to the I/O
Unit OFF as well. If the power is not turned on and off
according to the above procedure, an error occurs in
the CNC or the controller, or the I/O Unit is not
normally connected to the power.
Power for the master device
Power for the I/O Unit
t ≥ 500 ms (Turn ON of the power for I/O Unit can be late 500 ms or less.)
SORIAU JAPAN (manufactured by former Nippon
Burndy) Tri-pole connector (Brown)
Housing : SMS3PNS-5 A63L-0001-0202#3LN
Contact : RC16M-SCT3 A63L-0001-0226
24VDC
Tyco Electronics
Housing : 1-178288-3
Contact : 1-175218-5
Housing and contact set
A02B-0120-K324
24VDC
- 18 -

B-61813E/04 CONNECTION 4.CONNECTION
4.3 GROUNDING
Connect the grounding terminal of the base unit (ABU05A, ABU05B,
ABU10A, or ABU10B) to ground.
(1) Horizontal type base unit
Use a wire of 2 mm
(2) Vertical type base unit
(a) For metal case (early shipment)
Grounding terminal
(M3 screw terminal)
M4 hole for grounding
NOTE
Connect the grounding terminal to the grounding hole
portion.
(b) For plastic case
(2) When the cable K1X (See overall connection figure in section 4.1)
runs between different cabinets, make sure to connect the cabinets
with a wire more than 5.5 mm
Grounding terminal
(M3 screw terminal)
2
or more for grounding.
2
.
- 19 -

4.CONNECTION CONNECTION B-61813E/04
4.4 REQUIRED CURRENT
Table 4.4 Required current of each module
Module name
AIF01A 50
AIF01A2 50
AIF01B 50
AIF02C 50
AID32A1 20+0.5×n 30+7.5×n
AID32B1 20+0.5×n 30+7.5×n
AID32H1 20+0.5×n 30+7.5×n
AID16C 5
AID16K 5
AID16D 5
AID16L 5
AID32E1 5
AID32E2 5
AID32F1 5
AID32F2 5
AIA16G 5+1.5×n
AOD32A1 14
AOD08C 5+2×n
AOD08D 5+2×n
AOD08DP 5+2×n
AOD16C 5+2×n
AOD16D 5+2×n
AOD16D2 5+2×n
AOD16D3 5+2×n
AOD16DP 5+2×n
AOD32C1 5+0.5×n
AOD32C2 5+0.5×n
AOD32D1 5+0.5×n
AOD32D2 5+0.5×n
AOA05E 5+5.5×n
AOA08E 5+5.5×n
AOA12F 5+4.5×n
AOR08G 5 10×n
AOR16G 5 10×n
AOR16H2 5 10×n
AIO40A
AAD04A 5 130
AAD04B 5 130
ADA02A 6 120
ADA02B 6 130
ACT01A 170+0.3×α
ATI04A 62.5 100
ATI04B 62.5 100
Input 20+0.5×n 30+7.5×n
Output 5+0.5×n
n: Number of the input and output points (for each module)
which turn ON simultaneously
α: +5-V current (mA) output to the outside
• Add the sums of the columns A and B for the modules to be used.
The sum is the required current.(Unit: mA)
• For each base unit, keep the sum of column A and the sum of
column B to within 500 mA and 1,500 mA, respectively.
Required current (mA) of+24V
A B
- 20 -

B-61813E/04 CONNECTION 4.CONNECTION
A
4.5 INTERFACE MODULE (AIF01A, AIF01A2, AIF01B)
Details of the cables K1X, K2X and the terminator shown in the general
connection diagram are as follows.
(1) Cable K1X
CNC, Cell controller
or
IF01A, AIF01A2
JD1A
0V
11
SIN
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
0V
0V
0V
0V
0V
*SIN
SOUT
*SOUT
JD1A JD1B
10
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Connector HONDA TSUSHIN
PCR-E20FS
AIF01A, AIF01A2
JD1B
SIN
*SIN
SOUT
*SOUT
14
11
12
13
15
16
17
18
19
20
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
0V
0V
0V
0V
0V
0V
SIN (1)
*SIN (2)
SOUT (3)
*SOUT (4)
0V (11)
0V (12)
0V (13)
0V (14)
0V (15)
0V (16)
(3) SOUT
(4) *SOUT
(1) SIN
(2) *SIN
(11) 0V
(12) 0V
(13) 0V
(14) 0V
(15) 0V
(16) 0V
(a) Make sure to use twisted pair wires for signal SIN and *SIN,
and signals SOUT and *SOUT.
(i) Recommended cable material: A66L-0001-0284#10P
(twisted pair/shielded)
(ii) Shielding wires should be connected with the grounding
plate of the cabinet at the JD1A side using a cable clamp.
(Refer to the CONNECTION MANUAL for the CNC
and the cell controller.)
(iii) Maximum cable length: 10 m (15 m if used to connect
I/O devices within the same cabinet)
(iv) Make sure not to connect to the connector spare pins.
(v) In the following cases, make sure to use an optical I/O
link adapter and an optical fiber cable.(See Chapter 10)
• When the cable is more than 10 meters long.
• When the cable runs between different cabinets
and there is no appropriate ground wire between
the cabinets.
• When there is concern that the cable is influenced
by strong noise.
- 21 -

4.CONNECTION CONNECTION B-61813E/04
(vi) When an optical I/O link adapter is used: Cable to be
used between the interface module (AIF01A) and the
optical I/O link adapter is dissimilar to this cable. (See
Chapter 10.)
(2) Cable K2X
AIF01A, AIF01A2, or
AIF01B
• Connect the signals with a same name.
• Make sure to use twisted pair wires for the following signals:
S1 and * S1, S2 and *S2, S3 and *S3
S4 and * S4, S5 and *S5, S6 and *S6
• Do not connect the pins No.10, No.19 and No.20 as they are
used internally.
• Recommended cable material: A66L-0001-0284#10P
(twisted pair/shielded)
• Maximum cable length: 2m
AIF01B
- 22 -

B-61813E/04 CONNECTION 4.CONNECTION
(3) Terminator TX
Ordering information : A03B-0807-K806
Short-circuit
• If no AIF01B is in use, the TX terminator does not have to be
attached to the JD2 connector of the AIF01A or AIF01A2.
• If at least one AIF01B is in use, attach the terminator to the
JD2 connector of the last AIF01B in the same group.
• Short-circuit the TRM1s, the TRM2s and the TRM3s one
another respectively in a manner that a TRM1 is with another
TRM1 and so on.
- 23 -

4.CONNECTION CONNECTION B-61813E/04
A
A
4.6 INTERFACE MODULE (AIF02C) CONNECTION
4.6.1 Overview
One interface module (AIF02C) can control communication with both
I/O Unit-A and Unit-B, when it is connected to the FANUC I/O Link.
The following examples show a configuration in which two
conventional separate interface modules, I/O Unit-A and I/O Unit-B,
are used and a configuration in which the AIF02C is used.
(1) Configuration example in which separate interface modules
CNC cell controller
are used
(Note 2)
To the next group
CNC cell controller
To the next group
IF01A
IF01A2
(Note 2)
DI/DO unit
DI/DO unit
Group #0
Base expansion
Group #1
DI/DO unit
DI/DO unit
DI/DO unit
(2) Configuration example in which AIF02C is used
Group #0
(NOTE 1)
Group #1
Base expansion
DI/DO unit DI/DO unit
DI/DO unit
- 24 -

B-61813E/04 CONNECTION 4.CONNECTION
In this way, using the AIF02C eliminates the necessity for the interface
unit (BIF04A1) for I/O Unit-B, which has conventionally been used
separately; this configuration is suitable for a small I/O Unit-B system.
Note the following points.
NOTE
1 The AIF02C cannot be used for base expansion.
2 The BIF04A1 can branch to a maximum of eight
communication lines.
The AIF02C can branch only to a maximum of two
distributed link cables.
4.6.2 Connection
(1) Connection diagram
[a] Configuration with two distributed link cables (note the
(From group n-1)
setting of the terminating resistor.)
Groups n
and n+1
Distributed link
DI/DO unit DI/DO unit
DI/DO unit
(To group n+2)
DI/DO unit DI/DO unit
NOTE
*1 Set the terminating resistor DIP switch to ON.
*2 Set the terminating resistor DIP switch to OFF.
[b] Connection with one distributed link cable (note the setting
of the terminating resistor.)
(From group n-1)
Groups n
and n+1
Distributed link
DI/DO unit
DI/DO unit
DI/DO unit
DI/DO unit
(To group n+2)
NOTE
*1 Set the terminating resistor DIP switch to ON.
*2 Set the terminating resistor DIP switch to OFF.
- 25 -

4.CONNECTION CONNECTION B-61813E/04
(2) Connection with the I/O Link
The AIF02C occupies two groups on the I/O Link.
When groups #n and #n+1 are used, for example, the
smaller-numbered group, #n, is assigned to the I/O Unit-A, and the
larger-numbered group, #n+1, is assigned to the I/O Unit-B.
[a] Connection of the I/O link cable
Connect the I/O link cable from the previous group to JD1B.
Connect JD1A to the I/O link cable leading to the next group.
Use the K1X I/O link signal cable, the same I/O link signal
cable type as that for the AIF01A.
[b] Number of occupied I/O points on the I/O link
The nominal number of occupied I/O points may differ from
the actual number of I/O points.
For the details of the number of I/O points occupied by the I/O
Unit-B, refer to Section 4.3.1, "Number of points occupied on the
interface unit I/O link," of the FANUC I/O Unit-B MODEL
Connection Manual (B-62163E).
(3) Connection with the distributed link (I/O Unit-B)
[a] Number of distributed communication lines
"T1" can connect to two communication lines (twisted-pair
wires).
So, it is possible to branch to up to two lines.
To branch to more lines, you should use the I/O Unit-B
interface unit (BIF04A1), which enables branching to up to
eight communication lines.
[b] Terminal board "T1," used for connection with the
distributed link cable
The distributed link cable is connected to "T1."
AIF02C
T1
1S+
2S-
3FG
<1> Use twisted-pair wires as the distributed link cable.
<2> The distributed link cable is polarity-sensitive. Match
the signal polarity of the AIF02C with that of the basic
unit.
<3> The terminal board has M3 screws with a terminal
cover.
Refer to Section 4.4, "Connecting a Distributed Link," and Section
4.6.2.2, "Connecting the communications cable," of the FANUC I/O
Unit-MODEL B Connection Manual (B-62163E) for details.
- 26 -

B-61813E/04 CONNECTION 4.CONNECTION
4.6.3 Setting with the DIP Switch
In the AIF02C, distributed link settings can be made with the DIP
switch on the back of the module.
The settings and corresponding signals are shown below.
1
2
3
4 EDSP
5 Q
6 H
7 URDY
8 R
(1) EDSP (error display method selection)
Normally, set EDSP to the ON position.
(2) Q and H (communication speed setting)
Normally, set both Q and H to the OFF positions.
(3) URDY (setting of the power on/off information for the unit)
Normally, set URDY to the OFF position.
(4) R (terminating resistor setting)
The ON position means that a terminating resistor must be
installed. The OFF position means that no terminating resistor
need be installed.
When only one communication cable is connected to the AIF02C,
terminate it and the basic unit at the end of the communication
cable with a resistor.
When two communication cables are connected to the AIF02C,
terminate the basic unit connected to the end of each
communication cable with a resistor. Do not connect a terminating
resistor to the AIF02C. (Refer to Section 4.6.2, "Connection.")
Refer to Section 5.1.1, "DIP switch setting," of the FANUC I/O
Unit-MODEL B CONNECTION MANUAL (B-62163E).
Unused
- 27 -

4.CONNECTION CONNECTION B-61813E/04
play
4.7 CONNECTING WITH I/O MODULES
From the point of view of an external connecting method, there are two
types of I/O modules such as one with a terminal block and one with a
connector.
Terminal block manufactured by
Weidmüller (used in the AOD16D3)
Input/output
LED
A 0 . . . 7
B 0 . . . 7
dis
Specification of the terminal
block on the module
BL3.5//24/90F
The following three different connectors can be used on the
connector-type module.
Specification of the connector on the
module
Manufactured by HONDA TSUSHIN
MR-50RMA
Manufactured by HIROSE ELECTRIC
HIF3BB-50PA-2.54DS
Manufactured by HIROSE ELECTRIC
HIF4-40P-3.18DS
Module name
AID32A1
AID32B1
AID32H1
AID32E1
AID32F1
AOD32A1
AOD32C1
AOD32D1
AIO40A
AID32E2
AID32F2
AOD32C2
AOD32D2
AOR16H2
AOD16D2
- 28 -

B-61813E/04 CONNECTION 4.CONNECTION
(1) Connect with each module following the connection diagrams of
Sections 4.2 and 5.3.
(2) The terminal block is a removable type.
[Dismounting the terminal block]
<1> Open the cover of the terminal
block.
<2> Push up the latch at the top of the
terminal block.
<3> Drag out the tab at the top of the
terminal block and pull it out.
The terminal block will be
removed from the module.
[Mounting the terminal block]
<1> Insert the protruding portion at
the bottom of the terminal block
in the groove of the module
side.
<2> Push the terminal block using
the engaging point of the protruding portion and the groove
as an axis and mount it in the module firmly.
<3> Open the cover of the terminal block and check to make
sure the latch at the top of the terminal block is firmly set.
(3) Cautionary points when wiring terminal block type
2
• Wiring material : AWG22 to 18 (0.3 to 0.75 mm
)
A wire as this as possible is recommended.
• Crimp style terminal : M3.5
Crimp style terminal with no
insulation sleeve and a short distance
"A", as illustrated in the drawing
below, is recommended.
DAIDO SOLDERLESS TERMINAL 1.25-S3.5
NICHIFU 1.25-3.5S etc.
• Mark tube : Use a short mark tube as possible and cover
crimped part with the mark tube.
• Recommended tightening torque : 1 to 1.4 N⋅m
(4) Wiring to the terminal block manufactured by Weidmüller
2
• Wire with a cross section of 0.08 to 1.5 mm
(VDE)/AWG28
to AWG14 (UL/CSA)
• Recommended tightening torque: 0.8 N⋅m
• Size conformable when a ferrule (rod terminal) is used: 0.5 to
1.5 mm
2
Peeling length: 6 mm
- 29 -

5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULESCONNECTION B-61813E/04
5 DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULES
- 30 -

B-61813E/04 CONNECTION5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULES
5.1 LIST OF MODULES
(1) Digital input modules
Input
type
Non-
insulation
type DC
input
Insulation
type DC
input
AC input AIA16G
Module
name
AID32A1 24VDC
AID32B1 24VDC
AID32H1 24VDC
AID16C 24VDC
AID16K 24VDC
AID16D 24VDC
AID16L 24VDC
AID32E1 24VDC
AID32E2 24VDC
AID32F1 24VDC
AID32F2 24VDC
Rated
voltage
100 to
120VAC
Rated
current
7.5mA
7.5mA
7.5mA
7.5mA
7.5mA
7.5mA
7.5mA
7.5mA
7.5mA
7.5mA
7.5mA
10.5mA
(120VAC)
Polarity
*1
Both Maximum 20msec 32 Connector A Not provided
Both Maximum 2msec 32 Connector A Not provided
Both
NEG Maximum 20msec 16 Terminal block Provided
NEG Maximum 2msec 16 Terminal block Provided
POS Maximum 20msec 16 Terminal block Provided
POS Maximum 2msec 16 Terminal block Provided
Both Maximum 20msec 32 Connector A Not provided
Both Maximum 20msec 32 Connector B Not provided
Both Maximum 2msec 32 Connector A Not provided
Both Maximum 2msec 32 Connector B Not provided
-
Response time Points
Maximum 2msec
Maximum 20msec
ON: Maximum 35msec
OFF: Maximum 45msec
8
24
16 Terminal block Provided
NEG circuit example
POS circuit example
External
connection
*2
Connector A Not provided
LED display
Input pin
Current
+
-
Common pin
Input module
Common pin
+
-
Current
Input pin
Input module
NOTE
1 Polarity
NEGative : (Current source type, source type, or Nch)
Regard to be ON when input is at Low level.
POSitive : (Current sink type, sink type, or Pch)
Regard to be ON when input is High level.
2 Connectors (Section 5.4 shows a connector signal arrangement diagram as viewed
from the front of the module.)
Connector A : HONDA TSUSHIN MR-50RMA connector
It is recommended that the MR-50LW (housing) and MR50-FH
(soldering-type connector) or MRP-50F01 (crimp connector) +
MRP-F112 (contact) be used on the cable.
Connector B : HIROSE ELECTRIC HIF3BB-50PA-2.54DS
It is recommended that the HIF3BB-50D-2.54R (press-mount
connector) be used on the cable.
3 For the details of the specifications for each module, refer to the section 5.3.
- 31 -

5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULESCONNECTION B-61813E/04
(2) Digital output modules
External
connection
*2
Terminal block
B
LED
display
Not
provided
Provided Fuse
Not
provided
Not
provided
Not
provided
Not
provided
Output
protection
Not provided
Output
protection
device
Output
protection
device
Not provided
Not provided
Not provided
Not provided
Output type Module name
Non-insulation
type DC output
Insulation type
DC output
AC output
RELAY output
AOD32A1 5 to 24VDC 0.3A NEG 32 8 Connector A
AOD08C 2A NEG 8 8 Terminal block Provided Fuse
AOD08D 2A POS 8 8 Terminal block Provided Fuse
AOD08DP 2A POS 8 8 Terminal block Provided
AOD16C 0.5A NEG 16 8 Terminal block Provided Not provided
AOD16D 0.5A POS 16 8 Terminal block Provided Not provided
AOD16D2 2A POS 16 4 Connector C Provided Not provided
AOD16D3 2A POS 16 4
AOD16DP 0.3A POS 16 8 Terminal block Provided
AOD32C1 0.3A NEG 32 8 Connector A
AOD32C2 0.3A NEG 32 8 Connector B
AOD32D1 0.3A POS 32 8 Connector A
AOD32D2
AOA05E
AOA08E
AOA12F
AOR08G 4A - 8 1 Terminal block Provided Not provided
AOR16G
AOR16H2 30VDC 2A - 16 4 Connector B Provided Not provided
Rated
voltage
12 to 4VDC
100 to
240VAC
100 to
120VAC
Maximum
250VAC /
30VDC
Maximum
current
0.3A POS 32 8 Connector B
2A - 5 1 Terminal block Provided Fuse
1A - 8 4 Terminal block Provided Fuse
0.5A - 12 6 Terminal block Provided Fuse
2A - 16 4 Terminal block Provided Not provided
Polarity
*1
Points
Points/
common
(3) Digital input/output hybrid module
Input/output
type
Non-insulation
type DC input
Non-insulation
type DC output
Module name
AIO40A
Rated
voltage
24VDC
24VDC
Specification
Current rating:
7.5 mA
Response
time: 20 ms
(maximum)
Maximum
current:
0.2 A/point and
2A for common
Polarity
Points
*1
Both 24 24
NEG 16 16
Points/
common
External
connection
*2
Connector A
(shared by input
and output signals)
LED
display
Not
provided
Output
protection
Not provided
- 32 -

B-61813E/04 CONNECTION5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULES
NEG circuit example
Common pin
POS circuit example
Output pin
Output module
+24V
Load
Current
0V
Current
+
-
Output pin
Output module
+24V
+
Load
0V
Common pin
NOTE
1 Polarity
NEGative : (Current sink type) Output is at Low level when ON.
POSitive : (Current source type) Output is at High level when ON.
2 Connector and terminal block B
(Section 5.4 shows a connector signal arrangement diagram as viewed from the front
of the module.)
Connector A : HONDA TSUSHIN MR-50RMA connector
It is recommended that the MR-50LW (housing) and MR50-FH
(soldering-type connector) or MRP-50F01 (crimp connector) +
MRP-F112 (contact) be used on the cable.
Connector B : HIROSE ELECTRIC HIF3BB-50PA-2.54DS
It is recommended that the HIF3BB-50D-2.54R (press-mount
connector) be used on the cable.
Connector C : HIROSE ELECTRIC HIF4-40P-3.18DS
It is recommended that the HIF4-40D-3.18R (press-mount
connector) be used on the cable.
Terminal block B : Weidmüller BL3.5/24/90F
The terminal block for the cable comes with the module.
3 For the details of the specifications for each module, refer to the section 5.3.
4 The maximum current of the DC output module includes the permissible rush current.
-
- 33 -

5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULESCONNECTION B-61813E/04
5.2 CORRESPONDENCE BETWEEN I/O SIGNALS AND
ADDRESSES IN A MODULE
The term "address in a module" refers to an address allocated within
each DI/DO module and relative to the start address (Xm, Yn) of the
module.
5.2.1 Module with 16/32 Digital Inputs (DI)
Input bits
Address in the
module
Xm A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Xm+1 B7 B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0
Xm+2 C7 C6 C5 C4 C3 C2 C1 C0
Xm+3 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
5.2.2 Module with 5/8/12/16/32 Digital Outputs (DO)
Address in the
module
Yn A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Yn+1 B7 B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0
Yn+2 C7 C6 C5 C4 C3 C2 C1 C0
Yn+3 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
When a contact connected to an input of an input module is closed, the
corresponding input signal becomes "1".
Output bits
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
When the output signal from an output module is "1", the corresponding
output contact (or transistor) is closed.
DI module of
16 points
DI module of
32 points
DO module of 5
and 8 points
DO module of 12
and 16 points
DO module of
32 points
- 34 -

B-61813E/04 CONNECTION5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULES
5.2.3 AIO40A Module (Hybrid Module with 24 Input and 16 Output
Points)
The allotment of this module requires 4 input and 2 output bytes.
Input byte 4 (Xm + 3) is invalid.
Input section
Address in the
module
Xm A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Xm+1 B7 B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0
Xm+2 C7 C6 C5 C4 C3 C2 C1 C0
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Input bits
Xm+3
Output section
Address in the
module
Yn D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Yn+1 E7 E6 E5 E4 E3 E2 E1 E0
- - - - - - - -
Output bits
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
- 35 -

5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULESCONNECTION B-61813E/04
5.3 SPECIFICATION FOR EACH MODULE
Specifications for the module are shown in the following pages.
(1) Input module AID32A1
(2) Input module AID32B1
(3) Input module AID32H1
(4) Input module AID16C
(5) Input module AID16K
(6) Input module AID16D
(7) Input module AID16L
(8) Input module AID32E1
(9) Input module AID32E2
(10) Input module AID32F1
(11) Input module AID32F2
(12) Input module AIA16G
(13) Output module AOD32A1
(14) Output module AOD08C
(15) Output module AOD08D
(16) Output module AOD08DP
(17) Output module AOD16C
(18) Output module AOD16D
(19) Output module AOD16D2
(20) Output module AOD16D3
(21) Output module AOD16DP
(22) Output module AOD32C1
(23) Output module AOD32C2
(24) Output module AOD32D1
(25) Output module AOD32D2
(26) Output module AOA05E
(27) Output module AOA08E
(28) Output module AOA12F
(29) Output module AOR08G
(30) Output module AOR16G
(31) Output module AOR16H2
(32) Input/output module AIO40A
- 36 -

B-61813E/04 CONNECTION5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULES
(1) Input module AID32A1 (Non-insulation type)
Item Specifications
Points/module 32 points
Points/common 16 points/common
Sink/source current Both directions
Input voltage 24VDC +10%, −20%
Input current 7.5mA (average)
ON voltage, current Min. 18VDC, min. 6mA
OFF voltage, current Max. 6VDC, max. 1.5mA
OFF→ON Max.20ms Response time
ON→OFF Max.20ms
Input display Not provided
External connection Connector (HONDA TSUSHIN MR-50RMA)
Terminal connection and
circuitry
+24V or GND can be selected for input common as above fig.
This is the value from input to output in the module. The actual value is
determined by adding it to the scanning time depending on each
system.
NOTE
1 Make sure to connect all common (CMA, CMC) pins.
2 This module outputs +24 V on pins 13, 17, 04, and 08.
- 37 -

5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULESCONNECTION B-61813E/04
(2) Input module AID32B1 (Non-insulation type)
Item Specifications
Points/module 32 points
Points/common 16 points/common
Sink/source current Both directions
Input voltage 24VDC +10%, −20%
Input current 7.5mA (average)
ON voltage, current Min. 18VDC, min. 6mA
OFF voltage, current Max. 6VDC, max. 1.5mA
OFF→ON Max.2ms Response time
ON→OFF Max.2ms
Input display Not provided
External connection Connector (HONDA TSUSHIN MR-50RMA)
Terminal connection and
circuitry
+24V or GND can be selected for input common as above fig.
This is the value from input to output in the module. The actual value is
determined by adding it to the scanning time depending on each
system.
NOTE
1 Make sure to connect all common (CMA, CMC) pins.
2 This module outputs +24 V on pins 13, 17, 04, and 08.
- 38 -

B-61813E/04 CONNECTION5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULES
(3) Input module AID32H1
Item Specifications
Points/module 32 points
Points/common 16 points/common
Sink/source current Both directions
Input voltage 24VDC +10%, −20%
Input current 7.5mA (average)
ON voltage, current Min. 18VDC, min. 6mA
OFF voltage, current Max. 6VDC, max. 1.5mA
Response time
Input display Not provided
External connection Connector (HONDA TSUSHIN MR-50RMA)
Terminal connection and
circuitry
OFF→ON Max.2ms (A0 to A7)
Max.20ms (B0 to D7)
ON→OFF Max.2ms (A0 to A7)
Max.20ms (B0 to D7)
+24V or GND can be selected for input common as above fig.
NOTE
1 Make sure to connect all common (CMA, CMC) pins.
2 This module outputs +24 V on pins 13, 17, 04, and 08.
This is the value from input to output in the module. The actual
value is determined by adding it to the scanning time depending
on each system.
- 39 -

5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULESCONNECTION B-61813E/04
(4) Input module AID16C
Item Specifications
Points/module 16 points
Points/common 16 points/common
Sink/source current Source current type
Input voltage 24VDC +10%, −20%
Input current 7.5mA (average)
ON voltage, current Min. 15VDC, min. 4mA
OFF voltage, current Max. 5VDC, max. 1.5mA
OFF→ON Max.20ms Response time
ON→OFF Max.20ms
Input display LED display
External connection Terminal block connector (20 terminals, M3.5 screw terminal)
Terminal connection and
circuitry
This is the value from input to output in the module. The actual value is
determined by adding it to the scanning time depending on each
system.
(Note)
NOTE
Pins 18 and 19 are for factory use only.
Do not connect any wire to them
- 40 -

B-61813E/04 CONNECTION5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULES
(5) Input module AID16K
Item Specifications
Points/module 16 points
Points/common 16 points/common
Sink/source current Source current type
Input voltage 24VDC +10%, −20%
Input current 7.5mA (average)
ON voltage, current Min. 15VDC, min. 4mA
OFF voltage, current Max. 5VDC, max. 1.5mA
OFF→ON Max.2ms Response time
ON→OFF Max.2ms
Input display LED display
External connection Terminal block connector (20 terminals, M3.5 screw terminal)
Terminal connection and
circuitry
This is the value from input to output in the module. The actual value is
determined by adding it to the scanning time depending on each system.
(Note)
NOTE
Pins 18 and 19 are for factory use only.
Do not connect any wire to them
- 41 -

5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULESCONNECTION B-61813E/04
(6) Input module AID16D
Item Specifications
Points/module 16 points
Points/common 16 points/common
Sink/source current Sink current type
Input voltage 24VDC +10%, −20%
Input current 7.5mA (average)
ON voltage, current Min. 15VDC, min. 4mA
OFF voltage, current Max. 5VDC, max. 1.5mA
OFF→ON Max.20ms Response time
ON→OFF Max.20ms
Input display LED display
External connection Terminal block connector (20 terminals, M3.5 screw terminal)
Terminal connection and
circuitry
This is the value from input to output in the module. The actual value is
determined by adding it to the scanning time depending on each system.
(Note)
NOTE
Pins 18 and 19 are for factory use only.
Do not connect any wire to them
- 42 -

B-61813E/04 CONNECTION5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULES
(7) Input module AID16L
Item Specifications
Points/module 16 points
Points/common 16 points/common
Sink/source current Sink current type
Input voltage 24VDC +10%, −20%
Input current 7.5mA (average)
ON voltage, current Min. 15VDC, min. 4mA
OFF voltage, current Max. 5VDC, max. 1.5mA
OFF→ON Max.2ms Response time
ON→OFF Max.2ms
Input display LED display
External connection Terminal block connector (20 terminals, M3.5 screw terminal)
Terminal connection and
circuitry
This is the value from input to output in the module. The actual value is
determined by adding it to the scanning time depending on each system.
(Note)
NOTE
Pins 18 and 19 are for factory use only.
Do not connect any wire to them
- 43 -

5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULESCONNECTION B-61813E/04
(8) Input module AID32E1
Item Specifications
Points/module 32 points
Points/common 8 points/common
Sink/source current Both directions
Input voltage 24VDC +10%, −20%
Input current 7.5mA (average)
ON voltage, current Min. 15VDC, min. 4.5mA
OFF voltage, current Max. 6VDC, max. 2mA
OFF→ON Max.20ms Response time
ON→OFF Max.20ms
Input display Not provided
External connection Connector (HONDA TSUSHIN MR-50RMA)
Terminal connection and
circuitry
This is the value from input to output in the module. The actual value is
determined by adding it to the scanning time depending on each system.
- 44 -

B-61813E/04 CONNECTION5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULES
(9) Input module AID32E2
Item Specifications
Points/module 32 points
Points/common 8 points/common
Sink/source current Both directions
Input voltage 24VDC +10%, −20%
Input current 7.5mA (average)
ON voltage, current Min. 15VDC, min. 4.5mA
OFF voltage, current Max. 6VDC, max. 2mA
OFF→ON Max.20ms Response time
ON→OFF Max.20ms
Input display Not provided
External connection Connector (HIROSE ELECTRIC HIF3BB-50PA-2.54DS in accordance with MIL
standard)
Terminal connection and
circuitry
This is the value from input to output in the module. The actual value is
determined by adding it to the scanning time depending on each system.
- 45 -

5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULESCONNECTION B-61813E/04
(10) Input module AID32F1
Item Specifications
Points/module 32 points
Points/common 8 points/common
Sink/source current Both directions
Input voltage 24VDC +10%, −20%
Input current 7.5mA (average)
ON voltage, current Min. 15VDC, min. 4.5mA
OFF voltage, current Max. 6VDC, max. 2mA
OFF→ON Max.2ms Response time
ON→OFF Max.2ms
Input display Not provided
External connection Connector (HONDA TSUSHIN MR-50RMA)
Terminal connection and
circuitry
This is the value from input to output in the module. The actual value is
determined by adding it to the scanning time depending on each system.
- 46 -

B-61813E/04 CONNECTION5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULES
(11) Input module AID32F2
Item Specifications
Points/module 32 points
Points/common 8 points/common
Sink/source current Both directions
Input voltage 24VDC +10%, −20%
Input current 7.5mA (average)
ON voltage, current Min. 15VDC, min. 4.5mA
OFF voltage, current Max. 6VDC, max. 2mA
OFF→ON Max.2ms Response time
ON→OFF Max.2ms
Input display Not provided
External connection Connector (HIROSE ELECTRIC HIF3BB-50PA-2.54DS in accordance with MIL
standard)
Terminal connection and
circuitry
This is the value from input to output in the module. The actual value is
determined by adding it to the scanning time depending on each system.
- 47 -

5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULESCONNECTION B-61813E/04
(12) Input module AIA16G
Item Specifications
Points/module 16 points
Points/common 16 points/common
Sink/source current 100 to 115VAC ±15%
Input voltage 132Vrms, 50/60 Hz
Input current 10.55mArms (120VAC, 50Hz)
ON voltage, current Min. 74Vrms, min. 6mArms
OFF voltage, current Max. 20Vrms, max. 2.2mArms
OFF→ON Max.35ms Response time
ON→OFF Max.45ms
Input display LED display
External connection Terminal block connector (20 terminals, M3.5 screw terminal)
Common 16 points/common
Terminal connection and
circuitry
This is the value from input to output in the module. The actual value is
determined by adding it to the scanning time depending on each system.
- 48 -

B-61813E/04 CONNECTION5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULES
(13) Output module AOD32A1 (Non-insulation type)
Item Specifications
Points/module 32 points
Points/common 8 points/common
Sink/source current Sink current type
Rated load voltage 5 to 24VDC +20%, −15%
Maximum load current 0.3A (however 2A/common)
Maximum voltage drop when ON 0.24V (load current ×0.8Ω)
Maximum leak current when OFF 0.1mA
OFF→ON Max.1ms Response time
ON→OFF Max.1ms
Input display Not provided
External connection Connector (HONDA TSUSHIN MR-50RMA)
Terminal connection and circuitry
NOTE
For the common (CMA, CMB, CMC, CMD) , make
sure to use both of them.
- 49 -

5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULESCONNECTION B-61813E/04
(14) Output module AOD08C
Item Specifications
Points/module 8 points
Points/common 8 points/common
Sink/source current Sink current type
Rated load voltage 12 to 24VDC +20%, −15%
Maximum load current 2A (however 4A/fuse)
Maximum voltage drop when ON 0.8V (load current ×0.4Ω)
Maximum leak current when OFF 0.1mA
OFF→ON Max.2ms Response time
ON→OFF Max.2ms
Input display LED display
External connection Terminal block connector (20 terminals, M3.5 screw terminal)
Fuse 5A, 1 piece for each output A0-A3 and A4-A7.
Terminal connection and circuitry
This is the value from input to output in the module. The actual value is
determined by adding it to the scanning time depending on each system.
- 50 -

B-61813E/04 CONNECTION5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULES
(15) Output module AOD08D
Item Specifications
Points/module 8 points
Points/common 8 points/common
Sink/source current Source current type
Rated load voltage 12 to 24VDC +20%, −15%
Maximum load current 2A (however 4A/fuse)
Limit of load Refer to load derating curve (Fig. 5.3(a))
Maximum voltage drop when ON 1.2V (load current ×0.6Ω)
Maximum leak current when OFF 0.1mA
OFF→ON Max.2ms Response
Time
Output display LED display
External connection Terminal block connector (20 terminals, M3.5 screw terminal)
Fuse 5A, 1 piece for each output A0-A3 and A4-A7.
Terminal connection and circuitry
ON→OFF Max.2ms
This is the value from input to output in the module. The actual value is
determined by adding it to the scanning time depending on each system.
- 51 -

5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULESCONNECTION B-61813E/04
(16) Output module AOD08DP
Item Specifications
Points/module 8 points
Points/common 8 points/common
Sink/source current Source current type
Rated load voltage 12 to 24VDC +20%, −15%
Maximum load current 2A (however 8A/common)
Output current limit
Maximum voltage drop when ON 0.18V (load current ×0.09Ω)
Maximum leak current when OFF 0.1mA
OFF→ON Max.2ms Response
Time
Output display LED display
External connection Terminal block connector (20 terminals, M3.5 screw terminal)
Terminal connection and circuitry
ON→OFF Max.2ms
2.8A (Min.)
Output
circuit
This is the value from input to output in the module. The actual value is
determined by adding it to the scanning time depending on each system.
Load
Internal
circuit
- 52 -

B-61813E/04 CONNECTION5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULES
t
• AOD08DP output protection
The internal circuit of this output module can detect a load
overcurrent and driver temperature. To be specific, if the load
current increases abnormally, for example, because of a
wiring ground fault, the internal limiter of the driver
suppresses the output current. If this condition lasts long, the
driver can get abnormally hot, thus causing the protection
circuit to turn off the output. After the output is turned off
and the driver temperature becomes lower, the protection
function is automatically reset to turn on the output; this
OFF/ON operations are repeated.
When the overheat protection circuit works to turn off the
output, the LED "F" on the front of the module lights red.
If the protection circuit turns off the output, the output
module can detect which DO has encountered the
abnormality, using a DI. This function can be allocated to
any DI address (1 byte). If an abnormality is detected, the DI
bit corresponding to the DO of interest switches between "1"
and "0". The DI bit stays "1" for at least 10 ms.
If the protection function worked, turn off the power for both
the DO and system, and remove the cause of the overload.
The following timing chart shows how the output and DI
behave when the output protection function works.
DO
DI(Xm)
Outpu
DI
10msec or more
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
The DI bit having the same bit number as the DO (A0 to A7)
bit where an abnormality was detected becomes "1".
NOTE
An overcurrent prolonged, for example, because of
a wiring ground fault may lead to the break-down of
a module. To avoid this failure, build a sequence
program that can turn off the DO corresponding to
the bit number of the DI bit which has been set to "1"
because of a failure detected on the driver.
Bit number
- 53 -

5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULESCONNECTION B-61813E/04
(17) Output module AOD16C
Item Specifications
Points/module 16 points
Points/common 8 points/common
Sink/source current Sink current type
Rated load voltage 12 to 24VDC +20%, −15%
Maximum load current 0.5A (however 2A/common)
Maximum voltage drop when ON 0.7V (load current ×1.4Ω)
Maximum leak current when OFF 0.1mA
OFF→ON Max.2ms Response time
ON→OFF Max.2ms
Output display LED display
External connection Terminal block connector (20 terminals, M3.5 screw terminal)
Terminal connection and circuitry
This is the value from input to output in the module. The actual value is
determined by adding it to the scanning time depending on each system.
- 54 -

B-61813E/04 CONNECTION5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULES
(18) Output module AOD16D
Item Specifications
Points/module 16 points
Points/common 8 points/common
Sink/source current Source current type
Rated load voltage 12 to 24VDC +20%, −15%
Maximum load current 0.5A (however 2A/common)
Maximum voltage drop when ON 0.7V (load current ×1.4Ω)
Maximum leak current when OFF 0.1mA
OFF→ON Max.2ms Response time
ON→OFF Max.2ms
Output display LED display
External connection Terminal block connector (20 terminals, M3.5 screw terminal)
Terminal connection and circuitry
This is the value from input to output in the module. The actual value is
determined by adding it to the scanning time depending on each system.
- 55 -

5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULESCONNECTION B-61813E/04
(19) Output module AOD16D2
Item Specifications
Points/module 16 points
Points/common 4 points/common
Sink/source current Source current type
Rated load voltage 12 to 24VDC +20%, −15%
Maximum load current 2A (4A/common)
Maximum voltage drop when ON 0.4V (load current ×0.2Ω)
Maximum leak current when OFF 0.1mA
OFF→ON Max.2ms Response time
ON→OFF Max.2ms
Output display LED display
External connection Connector (HIROSE ELECTRIC HIF4-40P-3.18DS)
Terminal connection and circuitry
This is the value from input to output in the module. The actual value is
determined by adding it to the scanning time depending on each system.
Load
Output circuit
Output terminal
Internal
circuit
- 56 -

B-61813E/04 CONNECTION5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULES
(20) Output module AOD16D3
Item Specifications
Points/module 16 points
Points/common 4 points/common
Sink/source current Source current type
Rated load voltage 12 to 24VDC +20%, −15%
Maximum load current 2A (4A/common)
Maximum voltage drop when ON 0.4V (load current ×0.2Ω)
Maximum leak current when OFF 0.1mA
OFF→ON Max.2ms Response time
ON→OFF Max.2ms
Output display LED display
External connection 24-pin terminal block (BL3.5/24/90F) manufactured by Weidmüler
Conformable wire (maximum): 1.5 mm
Note: The terminal block for the cable comes with this module.
Fuse One 5A fuse for each of output sets A0 to A3, A4 to A7, B0 to B3, and B4 to B7
MP50 (A60L-0001-0046#5.0) manufactured by Daito.
Ordering information for a 4-fuse set: A03B-0819-K104
Terminal connection and circuitry
This is the value from input to output in the module. The actual value is
determined by adding it to the scanning time depending on each system.
2
(VDE)/AWG 14 (UL/CSA)
Fuse
Fuse
Fuse
Load
Fuse
Output circuit
Output terminal
Internal
circuit
- 57 -

5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULESCONNECTION B-61813E/04
(21) Output module AOD16DP
Item Specifications
Points/module 16 points
Points/common 8 points/common
Sink/source current Source current type
Rated load voltage 12 to 24VDC +20%, −15%
Maximum load current 0.3A (2.4A/common)
0.5A (2A/common)
See the "Load reduction curve" shown in Fig. 5.3 (f).
Maximum voltage drop when ON 0.63V (load current ×1.25Ω)
Maximum leak current when OFF 40µA
OFF→ON Max.2ms Response time
ON→OFF Max.2ms
Output display LED display
External connection Connector (20 terminals, M3.5 screw terminal)
Terminal connection and circuitry
• Output protection
The internal circuit of this output module can detect a load overcurrent. To
be specific, if the load current increases abnormally, for example, because
of a cable ground fault or an internal DO driver is abnormally heated for
some reason, the protection circuit for the DO driver (4-point unit) works to
keep the output of the DO driver turned off until the cause is removed.
When the overheat protection function works, the LED "F" on the module
lights.
This is the value from input to output in the module. The actual value is
determined by adding it to the scanning time depending on each system.
Load
Output circuit
Output terminal
Internal
circuit
- 58 -

B-61813E/04 CONNECTION5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULES
(22) Output module AOD32C1
Item Specifications
Points/module 32 points
Points/common 8 points/common
Sink/source current Sink current type
Rated load voltage 12 to 24VDC +20%, −15%
Maximum load current 0.3A (however 2A/common)
Maximum voltage drop when ON 0.24V (load current ×0.8Ω)
Maximum leak current when OFF 0.1mA
OFF→ON Max.2ms Response time
ON→OFF Max.2ms
Output display Not provided
External connection Connector (HONDA TSUSHIN MR-50RMA)
Terminal connection and circuitry
NOTE
For the common (CMA, CMB, CMC, CMD), make
sure to use both of them.
- 59 -

5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULESCONNECTION B-61813E/04
(23) Output module AOD32C2
Item Specifications
Points/module 32 points
Points/common 8 points/common
Sink/source current Sink current type
Rated load voltage 12 to 24VDC +20%, −15%
Maximum load current 0.3A (however 2A/common)
Maximum voltage drop when ON 0.24V (load current ×0.8Ω)
Maximum leak current when OFF 0.1mA
OFF→ON Max.2ms Response time
ON→OFF Max.2ms
Output display Not provided
External connection Connector (HIROSE ELECTRIC HIF3BB-50PA-2.54DS in accordance with MIL
standard)
Terminal connection and circuitry
NOTE
For the common (CMA, CMB, CMC, CMD), make
sure to use both of them.
- 60 -

B-61813E/04 CONNECTION5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULES
(24) Output module AOD32D1
Item Specifications
Points/module 32 points
Points/common 8 points/common
Sink/source current Source current type
Rated load voltage 12 to 24VDC +20%, −15%
Maximum load current 0.3A (however 2A/common)
Maximum voltage drop when ON 0.24V (load current ×0.8Ω)
Maximum leak current when OFF 0.1mA
OFF→ON Max.2ms Response Time
ON→OFF Max.2ms
Output display Not provided
External connection Connector (HONDA TSUSHIN MR-50RMA)
Terminal connection and circuitry
Load
Output circuit
Internal
circuit
NOTE
For the common (CMA, CMB, CMC, CMD), make
sure to use both of them.
- 61 -

5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULESCONNECTION B-61813E/04
(25) Output module AOD32D2
Item Specifications
Points/module 32 points
Points/common 8 points/common
Sink/source current Source current type
Rated load voltage 12 to 24VDC +20%, −15%
Maximum load current 0.3A (however 2A/common)
Maximum voltage drop when ON 0.24V (load current ×0.8Ω)
Maximum leak current when OFF 0.1mA
OFF→ON Max.2ms Response time
ON→OFF Max.2ms
Output display Not provided
External connection Connector (HIROSE ELECTRIC HIF3BB-50PA-2.54DS in accordance with MIL
standard)
Terminal connection and circuitry
Load
Output circuit
Internal
circuit
NOTE
For the common (CMA, CMB, CMC, CMD), make
sure to use both of them.
- 62 -

B-61813E/04 CONNECTION5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULES
(26) Output module AOA05E
Item Specifications
Points/module 5 points
Points/common 1 points/common
Rated load voltage 100 to 230VAC ±15%, 47 to 63Hz
Maximum load current 2A/point (however 5A/module)
Maximum rush current 25A ( 1 period)
Limit of load Refer to load derating curve (Fig. 5.3 (b))
Maximum voltage drop when ON 1.5Vrms
Maximum leak current when OFF 3.0mA (115VAC), 6.0mA (230VAC)
OFF→ON Max.1ms Response time
ON→OFF Half of the load
frequency or less
Output display LED display
External connection Terminal block connector (20 terminals, M3.5 screw terminal)
Fuse 3.2A, 1 piece for each output A0 to A4
Terminal connection and circuitry
This is the value from input to output in the module. The actual value
is determined by adding it to the scanning time depending on each
system.
- 63 -

5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULESCONNECTION B-61813E/04
(27) Output module AOA08E
Item Specifications
Points/module 8 points
Points/common 4 points/common
Rated load voltage 100 to 230VAC ±15%, 47 to 63Hz
Maximum load current 1A/point (however 2A/common)
Maximum in rush current 10A (1 period)
Maximum voltage drop when ON 1.5Vrms
Maximum leak current when OFF 3.0mA (115VAC), 6.0mA (230VAC)
OFF→ON Max.1ms Response time
ON→OFF Half of the load
frequency or less
Output display LED display
External connection Terminal block connector (20 terminals, M3.5 screw terminal)
Fuse 3.2A, 1 piece for each output A0 to A3 and A4 to A7
Terminal connection and circuitry
Load
This is the value from input to output in the module. The actual value
is determined by adding it to the scanning time depending on each
system.
- 64 -

B-61813E/04 CONNECTION5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULES
(28) Output module AOA12F
Item Specifications
Points/module 12 points
Points/common 6 points/common
Rated load voltage 100 to 115VAC ±15%, 47 to 63Hz
Maximum load current 0.5A/point (however, 2A/common)
Maximum in rush current 5A (1 period)
Limit of load Refer to load derating curve (Fig. 5.3 (c))
Maximum voltage drop when ON 1.5Vrms
Maximum leak current when OFF 1.5mA (115VAC)
OFF→ON Max.1ms Response time
ON→OFF Half of the load
frequency or less
Output display LED display
External connection Terminal block connector (20 terminals, M3.5 screw terminal)
Fuse 3.2A, 1 piece for each output A0 to A5 and B0 to B5
Terminal connection and circuitry
This is the value from input to output in the module. The actual value
is determined by adding it to the scanning time depending on each
system.
- 65 -

5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULESCONNECTION B-61813E/04
(29) Output module AOR08G
Item Specifications
Points/module 8 points
Points/common 1 points/common
Maximum load 30VDC/250VAC, 4A (resistance load)
Minimum load 5VDC, 10mA
Limit of load Refer to load derating curve (Fig. 5.3 (d))
Maximum voltage drop when ON 1.5Vrms
Maximum leak current when OFF 1.5mA (115VAC)
OFF→ON Max.15ms Response time
ON→OFF Max.15ms
Output display LED display
External connection Terminal block connector (20 terminals, M3.5 screw terminal)
Mechanical Min. 20,000,000 times Relay life
Electrical Min. 100,000 times (resistance load)
Terminal connection and circuitry
V : Direct current power or alternating current power
This is the value from input to output in the module. The actual value is
determined by adding it to the scanning time depending on each system.
- 66 -

B-61813E/04 CONNECTION5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULES
(30) Output module AOR16G
Item Specifications
Points/module 16 points
Points/common 4 points/common
Maximum load 30VDC/250VAC, 2A (resistance load)
Minimum load 5VDC, 10mA
Maximum current 4A/common
Limit of load Refer to load derating curve (Fig. 5.3 (e))
OFF→ON Max.15ms Response time
ON→OFF Max.15ms
Output display LED display
External connection Terminal block connector (20 terminals, M3.5 screw terminal)
Mechanical Min. 20,000,000 times Relay life
Electrical Min. 100,000 times (resistance load)
Terminal connection and
circuitry
V : Direct current power or alternating current power
This is the value from input to output in the module. The actual value is
determined by adding it to the scanning time depending on each system.
Load
- 67 -

5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULESCONNECTION B-61813E/04
(31) Output module AOR16H2
Item Specifications
Points/module 16 points
Points/common 4 points/common
Maximum load 30VDC, 2A (resistance load)
Minimum load 5VDC, 10mA
Maximum current 4A/common
Limit of load Refer to load derating curve (Fig. 5.3 (e))
OFF→ON Max.15ms Response time
ON→OFF Max.15ms
Output display LED display
External connection Connector (HIROSE ELECTRIC HIF3BB-50PA-2.54DS in accordance with MIL
standard)
Mechanical Min. 20,000,000 times Relay life
Electrical Min. 100,000 times (resistance load)
Terminal connection and
circuitry
This is the value from input to output in the module. The actual value is
determined by adding it to the scanning time depending on each system.
- 68 -

B-61813E/04 CONNECTION5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULES
(32) Input/output module AIO40A
- Input specifications
Item Specifications
Points/module 24 points
Points/common 24 points/common
Sink/source current Both directions
Input voltage 24VDC +10%, −20%
Input current 7.5mA (average)
ON voltage, current Min. 18VDC, min. 6mA
OFF voltage, current Max. 6VDC, max. 1.5mA
OFF→ON Max.20ms Response time
ON→OFF Max.20ms
Input display Not provided
External connection Connector (HONDA TSUSHIN MR-50RMA, shared by output signals)
- Output specifications
Item Specifications
Points/module 16 points
Points/common 16 points/common
Sink/source current Sink current type
Rated load voltage 24VDC +20%, −15%
Maximum load current 0.2A (however 2A/common)
Maximum in rush current 0.2A
Limit of load • If the output current per point is 0.1 A or lower, all of the 16 points E0 to E7 and F0 to
F7 can be turned on at a time.
• If the output current per point is higher than 0.1 A but not higher than 0.2 A, do not
turn on more than 3 points at a time.
Maximum voltage drop when ON 1.5V
Maximum leak current when OFF 1.0mA (30VDC)
OFF→ON Max.1ms Response time
ON→OFF Max.1ms
Output display Not provided
External connection Connector (HONDA TSUSHIN MR-50RMA, shared by input signals)
This is the value from input to output in the module. The actual value is
determined by adding it to the scanning time depending on each system.
This is the value from input to output in the module. The actual value is
determined by adding it to the scanning time depending on each system.
- 69 -

5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULESCONNECTION B-61813E/04
•Input/output module
Terminal connection and
circuitry
Input section
Output section
To the automatic
polarity
discrimination
circuit
Internal
circuit
Output circuit Input circuit
Either 24 V or 0 V can be selected as an input common potential as shown above.
(Solid line: 24-V common. Dotted line: 0-V common.)
- 70 -

B-61813E/04 CONNECTION5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULES
Fig.5.3 (a) AOD08D Load reduction curve
NOTE
Ambient temperature means the temperature
surrounding the I/O Unit and not that surrounding the
cabinet containing the I/O Unit.
Fig.5.3 (b) AOA05E Load reduction curve
- 71 -

5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULESCONNECTION B-61813E/04
Fig.5.3 (c) AOA12F Load reduction curve
NOTE
Ambient temperature means the temperature
surrounding the I/O Unit and not that surrounding the
cabinet containing the I/O Unit.
Fig.5.3 (d) AOR08G Load reduction curve
- 72 -

B-61813E/04 CONNECTION5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULES
(
)
Fig.5.3 (e) AOR16G, AOR16H2 Load reduction curve
NOTE
Ambient temperature means the temperature
surrounding the I/O Unit and not that surrounding the
cabinet containing the I/O Unit.
Point
16
Simultaneous ON points
12
8
6
4
10 20 30 40 50 55
(°C)
0.5A /points (2A/common)
Fig.5.3 (f) AOD16DP Load reduction curve
0.3A /points
0.5A /points (1.5A/common)
Ambient temperature
0.5A /points
(1A/common)
- 73 -

5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULESCONNECTION B-61813E/04
5.4 DETAILS OF I/O Unit CONNECTORS (HONDA
TSUSHIN/HIROSE ELECTRIC) AND TERMINAL BLOCK
(WEIDMÜLLER)
Given below are the details (signal arrangement diagrams as viewed
from the front of the module) of the connector pins and AOD16D3
terminal block for the I/O Units (32-point input module, 32-point
output module, and 24-point input/16-point output hybrid module)
explained in Section 5.3.
- 74 -

B-61813E/04 CONNECTION5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULES
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
5.4.1 Modules Using the MR-50RMA Connector Manufactured by
Honda Tsushin
• AID32A1/AID32B1/AID32H1 (32-point DC input module)
33 D7 01 D6
34 D5 02 D3
35 D2 03 D0
36 CMC 04 +24V
37 C7 05 GND
38 C5 06 C3
39 C2 07 C0
40 CMC 08 +24V
41 CMC 09 GND
42 B7 10 B6
43 B5 11 B3
44 B2 12 B0
45 CM
46
47
48
49 CM
50 CM
7 14 GND
5 15 A3
2 16 A0
• AID32E1/AID32F1 (32-point DC input module)
33 D7 01 D6
34 D5 02 D3
35 D2 03 D0
36 CMD 04
37 C7 05
38 C5 06 C3
39 C2 07 C0
40 CMC 08
41 CMC 09
42 B7 10 B6
43 B5 11 B3
44 B2 12 B0
45 CMB 13
46
47
48
49 CM
50 CM
7 14
5 15 A3
2 16 A0
19 D4
20 D1
21 CMC
22 C6
23 C4
24 C1
25
26
27 B4
28 B1
29 CM
30
31
32
19 D4
20 D1
21 CMD
22 C6
23 C4
24 C1
25
26
27 B4
28 B1
29 CMB
30
31
32
6
4
1
6
4
1
13 +24V
17 +24V
18 GND
17
18
- 75 -

5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULESCONNECTION B-61813E/04
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
• AOD32A1/AOD32C1 (32-point DC output module)
33 D7 01 D6
34 D5 02 D3
35 D2 03 D0
36 CMD 04 +24V-D
37 C7 05
38 C5 06 C3
39 C2 07 C0
40 CMC 08 +24V-C
41 CMC 09
42 B7 10 B6
43 B5 11 B3
44 B2 12 B0
45 CMB 13 +24V-B
46
47
48
49 CM
50 CM
7 14
5 15 A3
2 16 A0
• AOD32D1 (32-point DC output module)
33 D7 01 D6
34 D5 02 D3
35 D2 03 D0
36 CMD 04
37 C7 05 0V-D
38 C5 06 C3
39 C2 07 C0
40 CMC 08
41 CMC 09 0V-C
42 B7 10 B6
43 B5 11 B3
44 B2 12 B0
45 CMB 13
46
47
48
49 CM
50 CM
7 14 0V-B
5 15 A3
2 16 A0
19 D4
20 D1
21 CMD
22 C6
23 C4
24 C1
25
26
27 B4
28 B1
29 CMB
30
31
32
19 D4
20 D1
21 CMD
22 C6
23 C4
24 C1
25
26
27 B4
28 B1
29 CMB
30
31
32
6
4
1
6
4
1
17 +24V-
18
17
18 0V-
- 76 -

B-61813E/04 CONNECTION5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULES
A
A
• AIO40A (24-point DC input/16-point DC output hybrid module)
33 B0 01 A0
34 B1 02 A1
35 B2 03 A2
36 B3 04 A3
37 B4 05 A4
38 B5 06 A5
39 B6 07 A6
40 B7 08 A7
41 +24V 09 +24V
42 F0 10 E0
43 F1 11 E1
44 F2 12 E2
45 F3 13 E3
46 F4 14 E4
47 F5 15 E5
48 F6 16 E6
49 F7 17 E7
50 0V 18 0V
19 C0
20 C1
21 C2
22 C3
23 C4
24 C5
25 C6
26 C7
27 CM
28 CM
29 CM
30 SP
31 0V
32 0V
5.4.2 Modules Using the HIF3BB-50PA-2.54DS Connector
Manufactured by Hirose Electric
• AID32E2/AID32F2 (32-point DC input module)
A01 B01
A02 D7 B02 D6
A03 D5 B03 D4
A04 D3 B04 D2
A05 D1 B05 D0
A06 CMD B06 CMD
A07 B07
A08 C7 B08 C6
A09 C5 B09 C4
A10 C3 B10 C2
A11 C1 B11 C0
A12 CMC B12 CMC
A13 B13
A14 B7 B14 B6
A15 B5 B15 B4
A16 B3 B16 B2
A17 B1 B17 B0
A18 CMB B18 CMB
A19 B19
A20 A7 B20 A6
A21 A5 B21 A4
A22 A3 B22 A2
A23 A1 B23 A0
A24 CMA B24 CMA
A25 B25
- 77 -

5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULESCONNECTION B-61813E/04
• AOD32C2 (32-point DC output module)
A01 B01 +24V-D
A02 D7 B02 D6
A03 D5 B03 D4
A04 D3 B04 D2
A05 D1 B05 D0
A06 CMD B06 CMD
A07 B07 +24V-C
A08 C7 B08 C6
A09 C5 B09 C4
A10 C3 B10 C2
A11 C1 B11 C0
A12 CMC B12 CMC
A13 B13 +24V-B
A14 B7 B14 B6
A15 B5 B15 B4
A16 B3 B16 B2
A17 B1 B17 B0
A18 CMB B18 CMB
A19 B19 +24V-A
A20 A7 B20 A6
A21 A5 B21 A4
A22 A3 B22 A2
A23 A1 B23 A0
A24 CMA B24 CMA
A25 B25
• AOD32D2 (32-point DC output module)
A01 0V-D B01
A02 D7 B02 D6
A03 D5 B03 D4
A04 D3 B04 D2
A05 D1 B05 D0
A06 CMD B06 CMD
A07 0V-C B07
A08 C7 B08 C6
A09 C5 B09 C4
A10 C3 B10 C2
A11 C1 B11 C0
A12 CMC B12 CMC
A13 0V-B B13
A14 B7 B14 B6
A15 B5 B15 B4
A16 B3 B16 B2
A17 B1 B17 B0
A18 CMB B18 CMB
A19 0V-A B19
A20 A7 B20 A6
A21 A5 B21 A4
A22 A3 B22 A2
A23 A1 B23 A0
A24 CMA B24 CMA
A25 B25
- 78 -

B-61813E/04 CONNECTION5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULES
• AOR16H2 (16-point relay output module)
A01 CMA B01 CMA
A02 CMA B02 CMA
A03 A0 B03 A0
A04 A1 B04 A1
A05 A2 B05 A2
A06 A3 B06 A3
A07 CMB B07 CMB
A08 CMB B08 CMB
A09 A4 B09 A4
A10 A5 B10 A5
A11 A6 B11 A6
A12 A7 B12 A7
A13 CMC B13 CMC
A14 CMC B14 CMC
A15 B0 B15 B0
A16 B1 B16 B1
A17 B2 B17 B2
A18 B3 B18 B3
A19 CMD B19 CMD
A20 CMD B20 CMD
A21 B4 B21 B4
A22 B5 B22 B5
A23 B6 B23 B6
A24 B7 B24 B7
A25 B25
5.4.3 Modules Using the HIF4-40P-3.18DS Connector Manufactured
by Hirose Electric
• AOD16D2 (16-point DC output module)
A01 A0 B01 0V-A
A02 A1 B02 0V-A
A03 A2 B03 CMA
A04 A3 B04 CMA
A05 CMA B05 CMA
A06 A4 B06 0V-B
A07 A5 B07 0V-B
A08 A6 B08 CMB
A09 A7 B09 CMB
A10 CMB B10 CMB
A11 CMC B11 CMC
A12 B0 B12 CMC
A13 B1 B13 CMC
A14 B2 B14 0V-C
A15 B3 B15 0V-C
A16 CMD B16 CMD
A17 B4 B17 CMD
A18 B5 B18 CMD
A19 B6 B19 0V-D
A20 B7 B20 0V-D
- 79 -

5.DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT MODULESCONNECTION B-61813E/04
5.4.4 Modules Using the Terminal Block BL3.5/24/90F Manufactured
by Weidmüller
• AOD16D3 (16-point DC output module)
01 CMA
02 A0
03 A1
04 A2
05 A3
06 0V-A
07 CMB
08 A4
09 A5
10 A6
11 A7
12 0V-B
13 CMC
14 B0
15 B1
16 B2
17 B3
18 0V-C
19 CMD
20 B4
21 B5
22 B6
23 B7
24 0V-D
- 80 -

B-61813E/04 CONNECTION 6.ANALOG INPUT MODULE
6 ANALOG INPUT MODULE
- 81 -

6.ANALOG INPUT MODULE CONNECTION B-61813E/04
6.1 12-BIT ANALOG INPUT MODULE (AAD04A)
6.1.1 Specifications
Item Specifications
Number of input
channel
Analog input • Voltage input
Digital output 12 bit binary (complementary representation of "2".)
Input/output
correspondence
Resolution 5mV or 20µA
Total precision Voltage input ±0.5%(For full scale)
Conversionary time Max.2ms
Maximum input
voltage/current
Isolation Photocoupler isolated (between the input signal and the
Output connecting Removable terminal block (20 terminals, M3.5 screw
Required input points 64 points
NOTE
Conversion time means that only in a module.
Actual response speed is determined by adding the
scanning time depending on each system to this
conversion time.
4 channel/module
-10VDC to+10VDC(input resistance 4.7MΩ)
• Current input
-20mADC to+20mADC(input resistance 250Ω)
Caution) Which method to use, voltage input or current
input, can be selected by connecting the
corresponding input to the terminal block.
Current input ±1%(For full scale)
±15V, ±30mA
base)
However, not isolated between input channels
terminal)
Analog input Digital output
+10V +2000
+5V or + 20mA +1000
0V or 0mA 0
-5V or -20mA -1000
-10V -2000
(Note)
- 82 -

B-61813E/04 CONNECTION 6.ANALOG INPUT MODULE
6.1.2 Correspondence between Input Signals and Addresses in a
Module
In the analog input module AAD04A, the 4-channel analog input
signals are cyclically A-D converted in order, and the converted digital
data are written in the following addresses. Therefore, in the PMC
program, it is possible at any time to know the values for the analog
input signals by referring to the following addresses.
Address
in module 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
0 D07-0 D06-0 D05-0 D04-0 D03-0 D02-0 D01-0 D00-0
Channel 0
1 X-0 X-0 X-0 X-0 D11-0 D10-0 D09-0 D08-0
2 D07-1 D06-1 D05-1 D04-1 D03-1 D02-1 D01-1 D00-1
Channel 1
3 X-1 X-1 X-1 X-1 D11-1 D10-1 D09-1 D08-1
4 D07-2 D06-2 D05-2 D04-2 D03-2 D02-2 D01-2 D00-2
Channel 2
5 X-2 X-2 X-2 X-2 D11-2 D10-2 D09-2 D08-2
6 D07-3 D06-3 D05-3 D04-3 D03-3 D02-3 D01-3 D00-3
Channel 3
7 X-3 X-3 X-3 X-3 D11-3 D10-3 D09-3 D08-3
D00-n and D11-n correspond to the weights of 2
Here, D11-n corresponds to the sign bit in the complementary
representation of "2."
In addition, in X-n is written the same value as that in D11-n.
NOTE
1 When addressing I/O modules, the beginning
address for this module should be assigned to an
even one. Moreover, when an A-D converted value is
referred to in a PMC program, make sure to read the
data in unit of a word (16 bits).
2 Note that on the PMC-N, -NA, and -QA (PMC for the
Series 15 and F-D Mate), the high-order one byte and
low-order one byte of a word (16 bits) are
interchanged with each other as described below.
Bits
0
and 211 respectively.
- 83 -

6.ANALOG INPUT MODULE CONNECTION B-61813E/04
Addresses for word-unit operation in the PMC-N, NA, and QA
Analog input module → PMC
Address in the
Channel 0 0 D07-0 to D00-0 X-0,D11-0 to D08-0
Channel 1 +2 D07-1 to D00-1 X-1,D11-1 to D08-1
Channel 2 +4 D07-2 to D00-2 X-2,D11-2 to D08-2
Channel 3 +6 D07-3 to D00-3 X-3,D11-3 to D08-3
module High-order byte Low-order byte
- 84 -

B-61813E/04 CONNECTION 6.ANALOG INPUT MODULE
Ω
6.1.3 Connecting with Analog Input Module
Voltage input (channel0)
Voltage
supply
Note
4-1
+
-
GND
Note
4-2
I0+
①
③
V0-
⑤
COM0
⑦
FG0
⑨
I1+
②
V1+
④
V1-
⑥
COM1
⑧
FG1
⑩
Analog input module (AAD04A)
250
Ω
processor
Multi
AD
converter
250
Current input (channel 2)
Current
supply
Note
+
-
GND
4-1
Note
4-2
Note 2
I2+
⑪
V2+
⑬
V2-
⑮
COM2
⑰
FG2
⑲
I3+
⑫
V3+
⑭
V3-
⑯
COM3
⑱
FG3
⑳
NOTE
1 Though the example above shows the connection of channels 0 and 2, it is just the
same with the channel 1 (I1+, V1+, V1-, COM1 and FG1) and the channel 3 (I3+, V3+,
V3-, COM3 and FG3).
2 Either voltage input or current input can be specified for each channel. When current
input is specified, make sure to short-circuit in + and Vn+ (n: 0 to 3).
3 Use shielded cables of twisted pair for connecting.
4 Fix a reference voltage by connecting the COMn (where n is 0, 1, 2, or 3) terminal of
this module to the common line (GND) of the voltage or current source to be used as
shown above (Note 4-1). If the voltage or current source has a terminal shared by the
external output (terminal OUT-) and ground (GND), the Vn- and COMn (where n is 0,
1, 2, or 3) of this module can be connected to each other as shown above (Note 4-2).
- 85 -

6.ANALOG INPUT MODULE CONNECTION B-61813E/04
6.2 16-BIT ANALOG INPUT MODULE (AAD04B)
6.2.1 Specifications
Item Specifications
Number of input channel 4 channel/module
Analog input • Voltage input
-10VDC to+10VDC(input resistance 4.7MΩ)
• Current input
-20mADC to+20mADC(input resistance 250Ω)
Caution) Which method to use, voltage input or
current input, can be selected by
connecting the corresponding input to the
terminal block.
Digital output 16 bit binary (complementary representation of "2".)
Input/output
correspondence
Resolution Voltage input: 0.3125mV
Total precision Voltage input: ±0.5%(For full scale)
Conversionary time Max.2ms
Maximum input
voltage/current
Isolation Photocoupler isolated (between the input signal and
Output connecting Removable terminal block(20 terminals, M3.5
Required input points 64 points
Name assigned to module “AD04A” or “/8”
NOTE
Conversion time means that only in a module.
Actual response speed is determined by adding the
scanning time depending on each system to this
conversion time.
Voltage input Current input
Current input: 1.25µA
Current input: ±1%(For full scale)
±15V, ±30mA
the base)
However, not isolated between input channels
screw terminal)
Analog input
+10V - +32000
+5V +20mA +16000
0 0 0
-5V -20mA -16000
-10V - -32000
(Note)
Digital
output
- 86 -

B-61813E/04 CONNECTION 6.ANALOG INPUT MODULE
6.2.2 Correspondence between Input Signals and Addresses in a
Module
In the analog input module AAD04B, the 4-channel analog input
signals are cyclically A-D converted in order, and the converted digital
data are written in the following addresses. Therefore, in the PMC
program, it is possible at any time to know the values for the analog
input signals by referring to the following addresses.
Address
in module 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
0 D07-0 D06-0 D05-0 D04-0 D03-0 D02-0 D01-0 D00-0
Channel 0
1 D15-0 D14-0 D13-0 D12-0 D11-0 D10-0 D09-0 D08-0
2 D07-1 D06-1 D05-1 D04-1 D03-1 D02-1 D01-1 D00-1
Channel 1
3 D15-1 D14-1 D13-1 D12-1 D11-1 D10-1 D09-1 D08-1
4 D07-2 D06-2 D05-2 D04-2 D03-2 D02-2 D01-2 D00-2
Channel 2
5 D15-2 D14-2 D13-2 D12-2 D11-2 D10-2 D09-2 D08-2
6 D07-3 D06-3 D05-3 D04-3 D03-3 D02-3 D01-3 D00-3
Channel 3
7 D15-3 D14-3 D13-3 D12-3 D11-3 D10-3 D09-3 D08-3
D00-n and D15-n correspond to the weights of 2
Here, D15-n corresponds to the sign bit in the complementary
representation of "2." (where n represents one of the channel numbers 0
to 3)
Bits
0
and 215 respectively.
- 87 -

6.ANALOG INPUT MODULE CONNECTION B-61813E/04
NOTE
1 When addressing I/O modules, the beginning
address for this module should be assigned to an
even one. Moreover, when an A-D converted value is
referred to in a PMC program, make sure to read the
data in unit of a word (16 bits).
2 This module has a very high resolution. When
A/D-converted values are input to a system for
reference by the PMC program, they may disperse
largely depending on the system. If this is the case,
the dispersion of input values can be suppressed by
obtaining their moving average in the PMC program
or lowering the resolution by masking the
lowest-order bit if possible.
3 Note that on the PMC-N, -NA, and -QA (PMC for the
Series 15 and F-D Mate), the high-order one byte and
low-order one byte of a word (16 bits) are
interchanged with each other as described below.
Addresses for word-unit operation in the PMC-N, NA, and QA
Analog input module → PMC
Address in the
Channel 0 0 D07-0 to D00-0 D15-0 to D08-0
module High-order byte Low-order byte
Channel 1 +2 D07-1 to D00-1 D15-1 to D08-1
Channel 2 +4 D07-2 to D00-2 ,D15-2 to D08-2
Channel 3 +6 D07-3 to D00-3 D15-3 to D08-3
- 88 -
 Loading...
Loading...