Page 1

Service Manual
Fuller Heavy Duty Transmissions
TRSM0300
October 2007
RTO-11607L
RTO-11607L
RTO-11607LL
RTO-11607LL
RTOF-11607L
RTOF-11607LL
Page 2

For parts or service call us
Pro Gear & Transmission, Inc.
1 (877) 776-4600
(407) 872-1901
parts@eprogear.com
906 W. Gore St.
Orlando, FL 32805
Page 3

Page 4

TABLE OF CONTENTS
FOREWORD
MODEL DESIGNATIONS AND SPECIFICATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
LUBRICATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
OPERATION
(L) Models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
(LL) Models
POWER FLOW . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
TIMING . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
TORQUE RECOMMENDATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
TOOL REFERENCE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PRECAUTIONS
DISASSEMBLY . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
INSPECTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
REASSEMBLY . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
CHANGING INPUT SHAFT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
AIR SYSTEM
RANGE SHIFT AI R SYSTEM: ALL MODELS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DEEP REDUCTION AIR SYSTEM: (LL) Models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
AI R SYSTEM SCHEMATICS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DISASSEMBLY AND REASSEMBLY - SHIFTING CONTROLS
AIR SYSTEM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
GEAR SHIFT LEVER HOUSING ASSEMBLY . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SHIFT BAR HOUSING ASSEMBLY . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
REMOVAL - COMPANION FLANGE, AUXILIARY SECTION AND CLUTCH HOUSING
DISASSEMBLY - AUXILIARY SECTION (L) Models . . .
REASSEMBLY - AUXILIARY SECTION (L) Models . . . .
DISASSEMBLY - AUXILIARY SECTION (LL) Models . .
REASSEMBLY - AUXILIARY SECTION (LL) Models . . .
DISASSEMBLY - FRONT SECTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
REASSEMBLY - FRONT SECTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
INSTALLATION - COMPANION FLANGE, AUXILIARY SECTION
AND CLUTCH HOUSING . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
INSTALLATION - SHIFTING CONTROLS
SHIFT BAR HOUSING ASSEMBLY . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
GEAR SHIFT LEVER HOUSING ASSEMBLY . . . . . .
AIR SYSTEM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Page 5

FOREWORD
This manual is designed to provide detailed
information necessary to service and repair the Fuller
Transmissions listed on the cover.
As outlined in the Table of Contents, the manual is
divided into 3 main sections:
a. Technical information and reference
b. Removal, disassembly, reassembly and
installation
c. Options
The format of the manual is designed to be followed
in its entirety if complete disassembly and reassembly
of the transmission is necessary. But if only one
component of the transmission needs to be repaired,
refer to the Table of Contents for the page numbers
showing that component. For example, if you need to
work on the Shift Bar Housing, you will find
instructions for removal, disassembly and reassembly
on page 47. Instructions for installation are on page
¨
131. Service Manuals, Illustrated Parts Lists, Drivers
Instructions, Driver Training Programs and other
forms of product service information for these and
other Fuller Transmissions are available upon request.
A Technical Literature Order Form may be found in the
back of this manual*. You may also obtain Service
Bulletins, detailing
improvements, repair procedures and other servicerelated subjects by writing to the following address:
EATON CORPORATION
TRANSMISSION DIVISION
Technical Service Department
P.O. Box 4013
Kalamazoo, Michigan 49003
(616) 342-3000
information on product
Every effort has been made to ensure the
accuracy of all information in this brochure.
However, Eaton Transmission Division makes no
expressed or implied warranty or representation
based on the enclosed information.
omissions may be reported to Marketing
Communications, Eaton Transmission Division,
P.O. Box 4013, Kalamazoo, Ml 49003.
Any errors or
Page 6
MODEL DESIGNATIONS
AND SPECIFICATIONS
IMPORTANT: All Fuller Transmissions are identified
by model and serial number. This information is
stamped on the transmission identification tag and
affixed to the case.
DO NOT REMOVE OR DESTROY THE
TRANSMISSION IDENTIFICATION TAG.
Gear Ratios —
Model
RTO-11607L
RTO-11607LL
Deep Reduction
Rev.
—
18.53
LO-LO
_
23.18
Low Range High Range
LO 1st
14.87
14.87
8.79
8.79
2nd 3rd 4th
3.57
3.57
2.46
2.46
5.59
5.59
5th
1.57
1.57
6th 7th OD
1.00
1.00
.76
.76
Reverse
Low/High
11.89/3.33
11.89/3.33
Page 7

LUBRICATION
Proper
Lubrication . . .
the Key to long
transmission life
Proper lubrication procedures are the key to a
good all-around maintenance program. If the
oil is not doing its job, or if the oil level is
ignored, all the maintenance procedures in the
world are not going to keep the transmission
running or assure long transmission life.
so that the internal parts operate in a bath of
oil circulated by the motion of gears and shafts.
these procedures are closely followed:
Eaton
First 3,000 to 5,000 miles
(4827 to 8045 Km)
Every 10,000 miles
(16090 Km)
Every 250,000 miles
(402336 Km)
Every 100,000 miles (160,000 Km)
or every 3 years whichever occurs first fluid.
I
First 30 hours Factory fill Initial drain,
Every 40 hours Inspect fluid level Check for leaks
Every 500 hours Change transmission fluid where
I
Every 1,000 hours
I
I
First 3,000 to 5,000 miles Factory fill
(4827 to 8045 Km)
I
Every 10,000 miles
(16090 Km)
I
Every 50,000 miles
(80450 Km)
I
I
First 30 hours Change transmission lubricant on new units
Every 40 hours
Every 500 hours Change transmission Iubricant where
Every 1,000 hours Change transmission Iubricant
Change the oil filter when fluid or lubricant is changed.
®
Eaton
Fuller®Transmissions are designed
Thus, ail parts will be amply lubricated if
1. Maintain oil level. Inspect regularly.
2. Change oil regularly.
3. Use the correct grade and type of oil.
4. Buy from a reputable dealer.
Lubrication Change and Inspection
®
Roadranger®CD50 Transmission Fluid
HIGHWAY USE—Heavy Duty and Mid-Range
Factory fill
Inltlal drain
Check fluid level
Check for leaks
Heavy Duty Highway Change Interval
Change transmission
Mid-Range Highway Change Interval
Change transmission
OFF-HIGHWAY USE
severe dirt conditions exist.
Change transmission fluid
(Normal off-highway use),
Heavy Duty Engine Lubricant or
Mineral Gear Lubricant
HIGHWAY USE
Initial drain.
Inspect Iubricant level,
Check for leaks,
Change transmission
OFF-HIGHWAY USE
Inspect Iubricant level Check for leaks
severe dirt conditions exist.
(Normal off-highway use),
lubricant,
fluid,
Recommended Lubricants
Fahrenheit
(Celsius)
Ambient
Temperature
All
Above 10oF(-12oC.)
Above 10oF(-12oC.)
Below 10oF(-12oC.)
Above 10oF(-12oC.)
Below 10oF(-12oC.)
®
Grade
(SAE)
50
50
40
90
80W
Type
Eaton®Roadranger
CD50 Transmission
Fluid
Heavy Duty Engine 011
MI L-L-2104B C or D or
API-SF or API-CD
(Previous API designations 30
acceptable)
Mineral Gear 011 with rust
and oxidation Inhibitor
API-GL-1
The use of mild EP gear oil or multi-purpose gear oil is not recommended, but if
these gear oils are used, be sure to adhere to
the following limitations:
Do not use mild EP gear oil or multi-purpose gear oil when operating temperatures are
above 230°F (110
o
C). Many of these gear oils,
particularly 85W140, break down above 230°F
and coat seals, bearings and gears with deposits that may cause premature failures. If
these deposits are observed (especially a coating on seal areas causing oil leakage), change
to Eaton Roadranger CD50 transmission fluid,
heavy duty engine oil or mineral gear oil to
assure maximum component life and to maintain your warranty with Eaton. (Also see
“Operating Temperatures”.)
Additives and friction modifiers are not recom-
mended for use in Eaton Fuller transmissions.
Proper Oil Level
Make sure oil is level with filler opening. Because you can reach oil with your finger does
not mean oil is at proper level. One inch of oil
level is about one gallon of oil.
Draining Oil
Drain transmission while oil is warm. To drain
oil remove the drain plug at bottom of case.
Clean the drain plug before re-installing.
Refilling
Clean case around filler plug and remove plug
from side of case. Fill transmission to the
level of the filler opening. If transmission has
two filler openings, fill to level of both openings.
The exact amount of oil will depend on the
transmission inclination and model. Do not
over fill—this will cause oil to be forced out
of the transmission.
When adding oil, types and brands of oil
should not be mixed because of possible incompatibility.
4
, .
.
. . . .
Page 8

LUBRICATION
Operating Temperatures
—With Eaton
®
Roadranger
®
CD50 Transmission Fluid
Heavy Duty Engine Oil
and Mineral Oil
The transmission should not be operated consistently at temperatures above 250
However, intermittent operating temperatures
o
to 300
F (149oC) will not harm the transmission. Operating temperatures above 250
increase the lubricant’s rate of oxidation and
shorten its effective life. When the average
operating temperature is above 250
transmission may require more frequent oil
changes or external cooling.
The following conditions in any combina-
tion can cause operating temperatures of over
o
F: (1) operating consistently at slow
250
speeds, (2) high ambient temperatures, (3) restricted air flow around transmission, (4) exhaust system too close to transmission, (5)
high horsepower, overdrive operation.
External oil coolers are available to reduce
operating temperatures when the above conditions are encountered.
o
F (120oC).
o
F
o
F, the
Proper Lubrication Levels
as Related to Transmission
Installation Angles
If the transmission operating angle is more
than 12 degrees, improper lubrication can occur. The operating angle is the transmission
mounting angle in the chassis plus the percent of upgrade (expressed in degrees).
The chart below illustrates the safe percent
of upgrade on which the transmission can be
used with various chassis mounting angles.
For example: if you have a 4 degree transmission mounting angle, then 8 degrees (or 14
percent of grade) is equal to the limit of 12
degrees. If you have a O degree mounting
angle, the transmission can be operated on a
12 degree (21 percent) grade.
Anytime the transmission operating angle of
12 degrees is exceeded for an extended
period of time the transmission should be
equipped with an oil pump or cooler kit to
insure proper lubrication.
Note on the chart the effect low oil levels
can have on safe operating angles. Allowing
the oil level to fall 1/2” below the filler plug
hole reduces the degree of grade by approximately 3 degrees (5.5 percent).
Proper Lubrication Levels are Essential!
Transmission Oil Coolers are:
Recommended
— With engines of 350 H.P. and above
with overdrive transmissions
Required
— With engines 399 H.P. and above with
overdrive transmissions and GCW’S
over 90,000 lbs.
— With engines 399 H.P. and above and
1400 Lbs.-Ft. or greater torque
— With engines 450 H.P. and above
With EP or Multipurpose Gear Oil
—
Mild EP gear oil and multipurpose gear oil are
not recommended when lubricant operating
temperatures are above 230°F (110). In addition, transmission oil coolers are not recom-
mended with these gear oils since the oil
cooler materials may be attacked by these
gear oils. The lower temperature limit and oil
cooler restriction with these gear oils generally limit their success to milder applications.
Transmission Mounting Angle
Dotted line showing “2 Quarts Low” is for
reference only. Not recommended.
Page 9
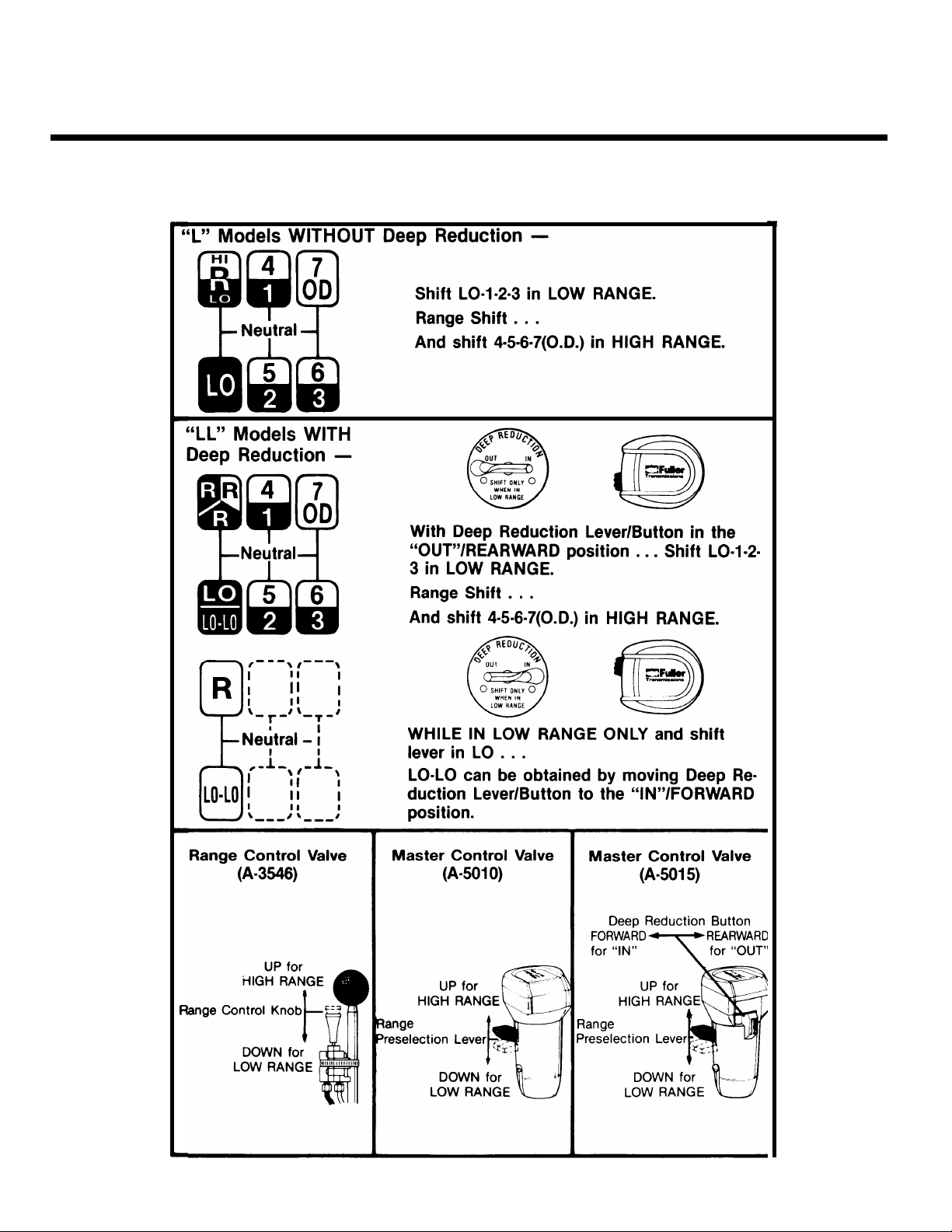
OPERATION
Shift Lever Patterns and
Shifting Controls
Page 10
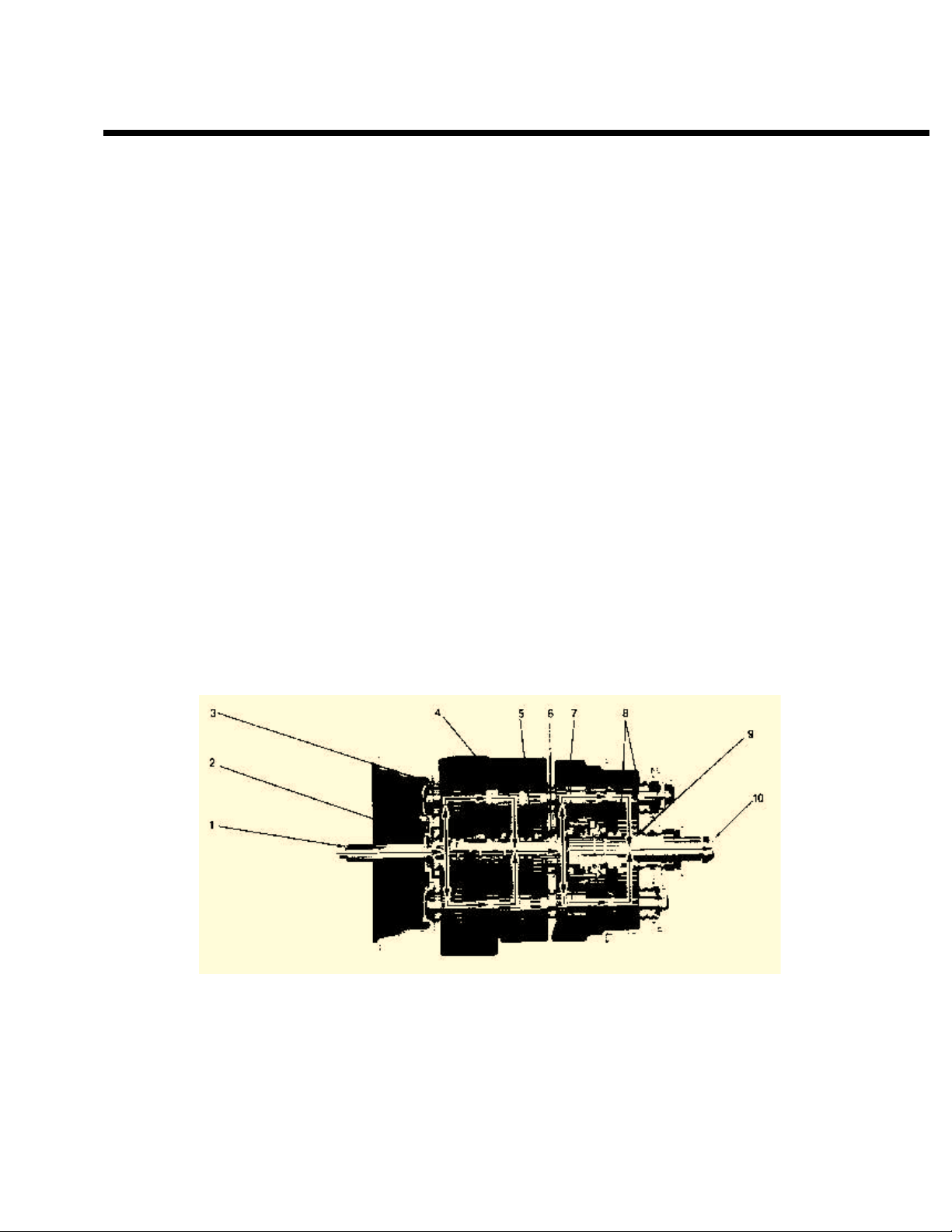
POWER FLOW
The transmission must efficiently transfer the engine's power, in terms of torque, to the vehicle's rear wheels.
Knowledge of what takes place in the transmission during torque transfer is essential when trouble-shooting and
making repairs as they become necessary.
Front Section Power Flow:
(Both Models)
1.
Power (torque) from the vehicle's engine is
transferred to the transmission's input shaft.
2.
Splines of input shaft engage internal splines in
hub of main drive gear.
Torque is split between the two countershaft drive
3.
gears.
4.
Torque is delivered along both countershaft to
mating countershaft gears of "engaged" mainshaft
gear. The cross section view shown below
illustrates LO/LO gear engagement.
5.
Internal clutching teeth in hub of engaged
mainshaft gear transfers torque to mainshaft
through sliding clutch.
6.
Mainshaft transfers torque directly to auxiliary
drive gear.
Auxiliary Section Power Flow:
(RTO-11607LL LO/LO)
7.
The auxiliary drive gear splits torque between the
two auxiliary countershaft drive gears.
Torque is delivered along both auxiliary
8.
countershaft to the mating "engaged" deep
reduction gear on output shaft.
Torque is transferred to output shaft through
9.
sliding clutch.
10.
Output shaft delivers torque to driveline as LO/LO.
DEEP REDUCTION POWER FLOW
Figure 1
Page 11

POWER FLOW
Auxiliary Section Power Flow:
LOW RANGE (All Models)
7.8.The auxiliary drive gear splits torque between the
two auxiliary countershaft drive gears.
Torque is delivered along both countershaft to
"engaged" low range gear on range mainshaft or
output shaft.
Torque is transferred to range mainshaft or output
9.
shaft through sliding clutch.
10.
Torque is delivered to driveline as LOW RANGE.
LOW RANGE POWER FLOW
(RTO-11607L Model Shown)
Auxiliary Section Power Flow:
HIGH RANGE (All Models)
7. The auxiliary drive gear transfers torque directly to
the range mainshaft or output shaft through
"engaged" sliding clutch.
Figure 2.
8. Torque is delivered through range mainshaft
and/or output shaft to driveline as HIGH RANGE
4th.
7
HIGH RANGE POWER FLOW
(RTO-11607L Model Shown)
Figure 3.
Page 12

TIMING
All Fuller twin countershaft transmissions are “timed”
at assembly.
It is important that proper timing
procedures are followed when reassembling the
transmission. Timing assures that the countershaft
gears will contact the mating mainshaft gears at the
same time, allowing mainshaft gears to center on the
mainshaft and equally divide the load.
Timing is a simple procedure of marking the
appropriate teeth of a gear set prior to installation and
placing them in proper mesh while in the transmission.
In the front section, it is necessary to ime only he drive
gear set. And depending on the model, only the low
range or deep reduction gear set is timed in the
auxiliary section.
A. Marking countershaft drive gear teeth.
1. Prior to placing each countershaft assembly into
case, clearly mark on each drive gear the gear
tooth which is directly over the keyway in gear.
(See illustration A.) This tooth is stamped with
an “O” to aid identification.
Meshing marked countershaft gear teeth with
C.
marked drive gear teeth. (After installing drive gear
and mainshaft assemblies, the countershaft
bearings are installed to complete countershaft
installation.)
1. When installing bearings on the left
countershaft, mesh the marked countershaft
gear tooth between two marked teeth on the
drive gear. Repeat the procedure when installing
the right countershaft bearings. (See Illustration
c.)
A. TOOTH ON COUNTERSHAFT
DIRECTLY OVER KEYWAY
MARKED FOR TIMING
B. Marking drive gear teeth.
1. Mark any two adjacent teeth on the drive gear.
2. Mark the two adjacent teeth on the drive gear
which are directly opposite the first set marked.
There should be an equal number of teeth
between the markings on each side of gear. (See
Illustration B.)
B. DRIVE GEAR TEETH
CORRECTLY MARKED
FOR TIMING
C. COUNTERSHAFT GEAR TEETH
MESHED WITH DRIVE GEAR TEETH
FOR CORRECT TIMING
Timing auxiliary section.
D.
(In the auxiliary section, the low speed gear set is
marked for timing instead of the drive gear set. )
Mark any two adjacent teeth on the large
1.
mainshaft low speed gear, then mark the two
adjacent teeth directly opposite—the same
procedure as used when marking the front
section drive gear.
2.
On each auxiliary countershaft assembly, mark
the tooth on the small low speed gear which is
stamped with an “O. ”
3.
Install the low speed gear and tailshaft assembly
in auxiliary housing.
4.
Partially install outer races of countershaft rear
bearings in case bores.
5.
Place the auxiliary countershaft assemblies into
position, meshing
marked tooth on each
countershaft gear between marked teeth on low
speed gear.
Countershafts will be partially
seated in rear bearing.
6.
Fully install rear bearings to complete auxiliary
countershaft installation.
Page 13

TORQUE RECOMMENDATIONS
Correct torque application is extremely important to assure long transmission life and dependable performance.
Over-tightening or under-tightening can result in a loose installation and, in many instances, eventually cause damage
to transmission gears, shafts, and/or bearings. Use a torque wrench whenever possible to attain recommended lbs./ft.
ratings. Do not torque capscrews dry.
FRONT SECTION: ALL MODELS
Page 14

TORQUE RECOMMENDATIONS
Cut 7191A
Page 15

TOOL REFERENCE
Some repair procedures pictured in this manual show
the use of specialized tools. Their actual use is from a tool supplier or made from dimensions as
recommended as they make transmission repair
easier, faster, and prevent costly damage to critical Prints are available upon request by writing.
parts.
But for the most part, ordinary mechanic’s tools such
as socket wrenches, screwdrivers, etc., and other
standard shop items such as a press, mauls and soft
bars are all that is needed to successfully disassemble
and reassemble any Fuller
PAGE
®
Transmission.
TOOL
57 Auxiliary Section Hanger Bracket
46
100
Tension Spring Driver
Snap Ring Pliers Tool Supplier
The specialized tools listed below can be obtained
required by the individual user. Detailed Fuller@ Tool
Eaton Corporation
Transmission Division
Technical Service Dept.
P.O. Box 4013
Kalamazoo, Michigan 49003
HOW OBTAINED
Made from Fuller
Print T-22823
Made from Fuller
®
Print T-11938
101
Impact Puller (1/2-13 Threaded End)
9 4 Bearing Drivers (Flanged-End)
87
Quill Snap Ring Installer
127 Torque Wrench, 1000 Lbs./Ft. Capacity
98
‘Dimensions necessary to determine specific tool number required.
Input Shaft Nut Installer
Tool Supplier
Made from Fuller
Series T-10842*
Made from Fuller
Print T-22917-F
Tool Supplier
Made from Fuller
Print T-22553-A
®
Print
®
®
Page 16

PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE
CHECK CHART
Page 17

PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE
PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE CHECK CHART
CHECKS WITHOUT PARTIAL
DISASSEMBLY OF CHASSIS OR CAB
1.
Air System and Connections
a. Check for leaks, worn air lines, loose
connections and capscrews. See AIR
SYSTEM.
2.
Clutch Housing Mounting
a. Check all capscrews in bolt circle of clutch
housing for looseness.
3.
Clutch Release Bearing (Not Shown)
a. Remove hand hole cover and check radial and
axial clearance in release bearing.
b. Check relative position of thrust surface of
release bearing with thrust sleeve on pushtype clutches.
4.
Clutch Pedal Shaft and Bores
a. Pry upward on shafts to check wear.
b. If excessive movement is found, remove
clutch release mechanism and check
bushings in bores and wear on shafts.
Lubricant
5.
a. Change at specified service intervals.
b. Use only the types and grades as
recommended. See LUBRICATION.
6.
Filler and Drain Plugs
a. Remove filler plugs and check level of
lubricant at specified intervals. Tighten filler
and drain plugs securely.
7.
Capscrews and Gaskets
a. Check all capscrews, especially those on
PTO covers and rear bearing covers for
looseness which would cause oil leakage. See
TORQUE RECOMMENDATIONS.
b. Check PTO opening and rear bearing covers
for oil leakage due to faulty gasket.
8.
Gear Shift Lever
a. Check for looseness and free play in housing.
If lever is loose in housing, proceed with
Check No. 9.
9. Gear Shift Lever Housing Assembly
a. Remove air lines at slave valve and remove the
gear shift lever housing assembly from
transmission.
b. Check tension spring and washer for set and
wear.
c. Check the gear shift lever spade pin and slot
for wear.
d. Check bottom end of gear shift lever for wear
and check slot of yokes and blocks in shift bar
housing for wear at contact points with shift
lever.
CHECKS WITH DRIVE LINE DROPPED
10. Universal Joint Companion
Flange or Yoke Nut
a. Check for tightness. Tighten to
recommended torque.
11. Output Shaft (Not Shown)
a. Pry upward against output shaft to check
radial clearance in mainshaft rear bearing.
CHECKS WITH UNIVERSAL JOINT
COMPANION FLANGE OR YOKE REMOVED
NOTE: If necessary, use a solvent and shop rag to
clean sealing surface of companion flange or
yoke. DO NOT USE A CROCUS CLOTH,
EMERY PAPER OR OTHER ABRASIVE
MATERIALS THAT WILL MAR SURFACE
FINISH.
12. Splines on Output Shaft
a. Check for wear from movement and chucking
action of the universal joint companion flange
or yoke.
13. Mainshaft Rear Bearing Cover
a. Check oil seal for wear.
Page 18

PRECAUTIONS
Disassembly
It is assumed in the detailed assembly instructions that the lubricant has been drained from transmission, the
necessary linkage and air lines were disconnected, and the transmission has been removed from vehicle chassis.
Removal of the gear shift lever housing assembly (or remote control assembly) is included in the detailed instructions
(Disassembly and Reassembly–Shifting Controls); however, this assembly MUST be detached from shift bar housing
before transmission can be removed.
FOLLOW CLOSELY EACH PROCEDURE IN THE DETAILED INSTRUCTIONS, MAKING USE OF THE TEXT,
ILLUSTRATIONS AND PHOTOGRAPHS PROVIDED.
BEARINGS
1.
reusable bearings as removed and protectively wrap
until ready for use. Remove bearings planned to be
reused with pullers designed for this purpose.
ASSEMBLIES - When disassembling the various
2.
assemblies, such as the mainshaft, countershaft,
and shift bar housing, lay all parts on a clean bench
in the same sequence as removed. This procedure
will simplify reassembly and reduce the possibility
of losing parts.
3.
SNAP RINGS - Remove snap rings with pliers
designed for this purpose. Snap rings removed in
this manner can be reused.
INPUT SHAFT - The input shaft can be removed
4.
from transmission without removing the
- Carefully wash and relubricate all
countershaft,
Special procedures are required and provided in this
manual.
5.
CLEANLINESS - Provide a clean place to work. It is
important that no dirt or foreign material enters the
unit during repairs.
damage bearings. It is always good practice to clean
the outside of the unit before starting the planned
disassembly.
WHEN USING TOOLS TO MOVE PARTS - Always
6.
apply force to shafts, housings, etc, with restraint.
Movement of some parts is restricted. Never apply
force to the part being driven after it stops solidly.
The use of soft hammers, bars and mauls for all
disassembly work is recommended.
mainshaft, or main drive gear.
Dirt is an abrasive and can
Inspection
Before reassembling the transmission, check each part carefully for abnormal or excessive wear and damage to
determine reuse or replacement. When replacement is necessary, use only genuine Fuller
performance and extended life from your unit.
Since the cost of a new part is generally a small fraction of the total cost of downtime and labor, avoid reusing a
questionable part which could lead to additional repairs and expense soon after initial reassembly. To aid in
determining the reuse or replacement of any transmission part, consideration should also be given to the unit’s
history, mileage, application, etc.
Recommended inspection procedures are provided in the following check list.
A. BEARINGS B. GEARS
Wash all bearings in clean solvent. Check balls,
1.
rollers and raceways for pitting, discoloration,
and spalled areas. Replace bearings that are
pitted, discolored, or spalled.
Lubricate bearings that are not pitted,
2.
discolored, or spalled and check for axial and
radial clearances.
Replace bearings with excessive clearances.
3.
Check bearing fits. Bearing inner races should
be tight to shaft; outer races slightly tight to
slightly loose in case bore. If bearing spins
freely in bore, however, the case should be
replaced.
Check gear teeth for frosting and pitting.
1.
Frosting of gear tooth faces present no threat
of transmission failure. Often in continued
operation of the unit, frosted gears will “heal”
and not progress to the pitting stage. In most
cases, gears with light to moderate pitted teeth
have considerable gear life remaining and can
be reused. But gears with advanced stage
pitting should be replaced.
Check for gears
2.
abnormally worn, tapered, or reduced in length
from clashing in shifting. Replace gears found
in any of these conditions.
®
parts to assure continued
with clutching teeth
Page 19

PRECAUTIONS
Inspection (Cont.)
3. Check axial clearance of gears. Where
excessive clearance is found, check gear snap
ring, washer, spacer, and gear hub for
excessive wear. Maintain .005” to .012” axial
clearance between mainshaft gears.
C.
SPLINES
1. Check splines on all shafts for abnormal wear.
If sliding clutch gears, companion flange, or
clutch hub have worn into the sides of the
splines, replace the specific shaft affected.
D. TOLERANCE/LIMIT WASHERS
1. Check surfaces of all limit washers. Washers
scored or reduced in thickness should be
replaced.
E. REVERSE IDLER GEAR ASSEMBLIES
1. Check for excessive wear from action of roller
bearings.
F. GRAY IRON PARTS
1. Check all gray iron parts for cracks and breaks.
Replace or repair parts found to be damaged.
Heavy castings may be welded or brazed
provided the cracks do not extend into bearing
bores or bolting surfaces. When welding,
however, never place the ground so as to allow
current to pass through the transmission.
G. CLUTCH RELEASE PARTS
1. Check clutch release parts. Replace yokes
worn at cam surfaces and bearing carrier worn
at contact pads.
2. Check pedal shafts. Replace those worn at
bearing surfaces.
H. SHIFT BAR HOUSING ASSEMBLY
1.
Check for wear on shift yokes and blocks at
pads and lever slot. Replace excessively worn
parts.
2.
Check yokes for correct alignment. Replace
sprung yokes.
3.
Check Iockscrews in yokes and blocks.
Tighten and rewire those found loose.
4.
If housing has been disassembled, check
neutral notches of shift bars for wear from
interlock balls.
I.
GEAR SHIFT LEVER HOUSING
ASSEMBLY
1. Check spring tension on shift lever. Replace
tension spring and washer if lever moves too
freely.
2 If housing is disassembled, check spade pin
and corresponding slot in lever for wear.
Replace both parts if excessively worn.
BEARING COVERS
J.
1. Check covers for wear from thrust to adjacent
bearing. Replace covers damaged from thrust
of bearing outer race.
2. Check bores of covers for wear. Replace those
worn oversize.
K.
OIL RETURN THREADS
AND SEALS
1. Check oil return threads in front bearing cover.
If sealing action of threads has been destroyed
by contact with input shaft, replace bearing
cover.
2. Check oil seal in mainshaft rear bearing cover.
If sealing action of lip has been destroyed,
replace seal.
L.
SLIDING CLUTCHES
1. Check all shift yokes and yoke slots in sliding
clutches for extreme wear or discoloration
from heat.
2. Check engaging teeth of sliding clutches for
partial engagement pattern.
M.
SYNCHRONIZER ASSEMBLY
1.
Check synchronizer for burrs, uneven and
excessive wear at contact surface, and metal
particles.
Check blocker pins for excessive wear or
2.
looseness.
Check synchronizer contact surfaces on the
3.
auxiliary drive and low range gears for
excessive wear.
N. O-RINGS
1. Check all O-rings for cracks or distortion.
Replace if worn.
Page 20

PRECAUTIONS
Reassembly
Make sure that interiors of case and housings are clean. It is important that dirt and other foreign materials be kept out
of the transmission during reassembly. Dirt is an abrasive and can damage polished surfaces of bearings and washers.
Use certain precautions, as listed below, during reassembly.
1. GASKETS - Use new gaskets throughout the
transmission as it is being rebuilt. Make sure all
gaskets are installed. An omission of any gasket can
result in oil leakage or misalignment of bearing
covers.
2. CAPSCREWS - To prevent oil leakage, use Loctite
242 thread sealant on all capscrews. For torque
ratings, see TORQUE RECOMMENDATIONS.
3. O-RINGS - Lubricate all O-rings with silicon
lubricant.
4. ASSEMBLY - Refer to the illustrations provided in
the detailed disassembly instructions as a guide to
reassembly.
5. INITIAL LUBRICATION - Coat all limit washers and
splines of shafts with Lubriplate during reassembly
to prevent
AXIAL CLEARANCES - Maintain original axial
6.
clearances of .005” to .012” for mainshaft gears.
scoring and galling of such parts.
BEARINGS - Use of flanged-end bearing drivers is
7.
recommended for the installation of bearings. These
special drivers apply equal force to both bearing
races, preventing damage to balls/rollers and races
while maintaining correct bearing alignment with
bore and shaft. Avoid using a tubular or sleeve-type
driver, whenever possible, as force is applied to only
one of the bearing races. See TOOL REFERENCE.
8.
—
UNIVERSAL JOINT COMPANION FLANGE OR
YOKE - Pull the companion flange or yoke tightly
into place with the output shaft nut, using 450-500
foot-pounds of torque. Make sure the speedometer
drive gear or a replacement spacer of the same width
has been installed. Failure to pull the companion
flange or yoke tightly into place will permit the
output shaft to move axially with resultant damage
to the rear bearing.
IMPORTANT: REFER TO THE APPROPRIATE ILLUSTRATED PARTS LIST
(SPECIFIED BY MODEL SERIES) TO ENSURE THAT PROPER PARTS
ARE USED DURING REASSEMBLY OF THE TRANSMISSION.
Page 21

CHANGING INPUT SHAFT
Special Procedure For Changing Input Shaft
NOTE: In some cases in field repair it may be
necessary to replace only the input shaft due to
clutch wear on the splines.
In these instances, the input shaft can be
removed without disassembling the
transmission other than removing the shifting
bar housing. Removal of the clutch housing is
optional. Following is the detailed procedure.
A. INPUT SHAFT REMOVAL
1.
Remove the gear shift lever housing assembly (or
remote control assembly) from shift bar housing, if
necessary, and the shift bar housing assembly
from transmission case.
2. Remove the front bearing cover and gasket.
Page 22
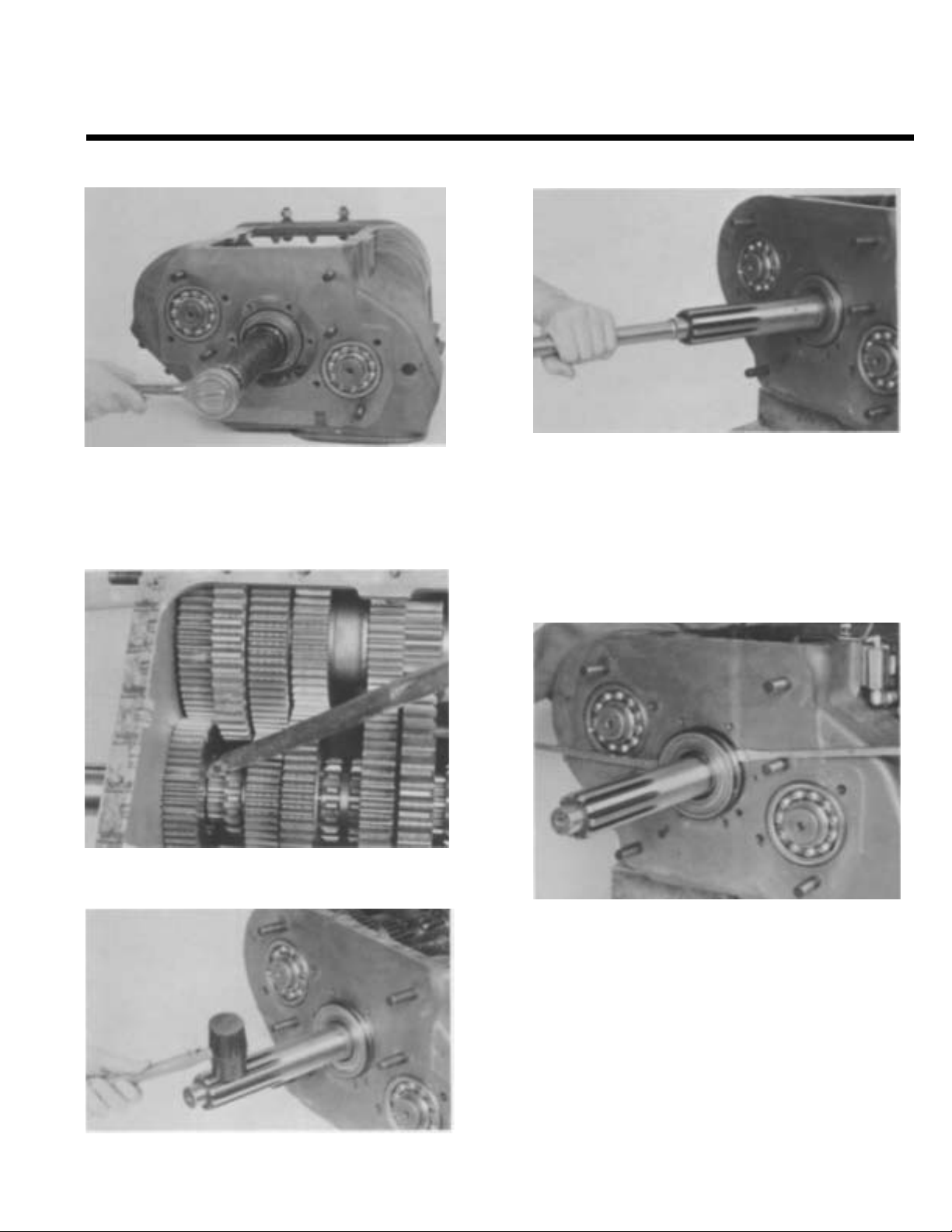
CHANGING INPUT SHAFT
Remove the drive gear bearing nut (left hand
3.
threads).
Suggestion: For removal of nut ONLY, engage two
mainshaft sliding clutches into gear to prevent the
input from rotating.
6.
Drive the input shaft back through the bearing and
into the case as far as possible. Drive the shaft
forward again to free the input shaft bearing from
the bore in the case.
NOTE: If this procedure does not free the bearing from
its bore, repeat steps 4 through 6.
4. Drive the input shaft as far forward as possible.
5. Tap the input shaft down to cock the input shaft
bearing in its bore.
7.
Pry the bearing from the input shaft with two large
screwdrivers.
Remove the spacer from the input shaft.
8.
Page 23

CHANGING INPUT SHAFT
9.
From the front of transmission, remove the snap
ring from I.D. of main drive gear using two small
screwdrivers. If mainshaft was previously locked in
two gears, it may become necessary to place
sliding clutches in the neutral position to rotate
input shaft and mainshaft for removal of snap ring.
Pull the input shaft forward from the splines of the
10.
drive gear.
4. Install spacer on input shaft.
B.
INPUT SHAFT INSTALLATION
1.
If necessary, install bushing in pocket of input
shaft.
Install new input shaft into splines of main drive
2.
gear just far enough to expose snap ring groove in
I.D. of drive gear.
Install snap ring in groove of drive gear.
3.
Move the clutch gear forward to contact end of
5.
input shaft in hub of drive gear. Block between rear
of sliding clutch and front of the overdrive gear.
When installing bearing this will hold input shaft in
position to seat the bearing properly.
Page 24

CHANGING INPUT SHAFT
6. Using a flanged-end driver, install the drive gear
bearing on shaft and into case bore. When applying
force to driver, use caution so as not to damage
bearing shield.
7. Remove the blocking from the mainshaft.
8.9.Apply Fuller¨adhesive sealant #71204 or equiva-
lent to the cleaned threads of input shaft and nut,
using caution so as not to contaminate bearing
with sealant.
Engage two mainshaft sliding clutches into gear to
prevent the mainshaft from rotating and install the
new drive gear bearing nut, left-hand threads, on
input shaft. Tighten nut with 250-300 Lbs./ Ft. of
torque. DO NOT REUSE OLD NUT.
Suggestion: To avoid damaging the O.D. of nut,
use the tool specifically designed for this purpose.
See TOOL REFERENCE.
10. With a punch and maul, peen the nut into the two
milled slots of input shaft, using caution so as not
to distort O.D. of nut.
To facilitate proper reinstallation of the shift bar
11.
housing assembly on case, make sure mainshaft
sliding clutches are placed in the neutral position.
12.
Reinstall the shift bar housing assembly, the front
bearing cover and all other parts and assemblies
previously removed, making sure to replace the
gaskets used.
NOTE: The above instructions are for changing the
input shaft only. To change the drive gear,
complete disassembly of the front section is
required.
Page 25

AIR SYSTEM
RTO-11607L
Page 26

AIR SYSTEM
RTO-11607LL
Page 27

AIR SYSTEM
RANGE SHIFT AIR SYSTEM - ALL MODELS
Operation
The Range Shift Air System consists of the air
filter/regulator, slave valve, a Range Control Valve or
Master Control Valve, range cylinder, fittings and
connecting air lines. See Air System Schematics.
CONSTANT AIR from the air filter/regulator is
supplied to the “S” or Supply Port of slave valve and
passed through to the INLET or “S” Port of control
valve.
WHILE IN LOW RANGE, the control valve is OPEN
and AIR is returned to slave valve at the "P” or End Port.
This signals the valve to supply AIR in Iine between the
Low Range or
Range Port of range cylinder housing. AIR received at
this port moves the range piston to the rear and causes
the auxiliary low range gear to become engaged.
WHILE IN HIGH RANGE, the control valve is
CLOSED and NO AIR is returned to the slave valve.
This signals the slave valve to supply AIR in line
between the High Range or “H” Port of valve and the
High Range Port of range cylinder cover. AIR received
at this port moves the range piston forward to engage
the auxiliary drive gear with sliding clutch and bypass
the low range gear set.
Range shifts can be made ONLY when the gear shift
lever is in, or passing through, neutral. Thus, the range
desired can be PRESELECTED while the shift lever is
in a gear position. As the lever is moved through
neutral, the actuating plunger in the shift bar housing
releases the slave valve piston, allowing it to move to
the selected range position.
“L” Port of slave valve and the Low
Troubleshooting
If the transmission fails to make a range shift or shifts
too slowly, the fault may be in the Range Shift Air
System or actuating components of the shift bar
housing assembly.
To locate the trouble, the following checks should be
made with normal vehicle air pressure applied to the
system, but with the engine off.
CAUTION: NEVER WORK UNDER A VEHICLE
WHILE ENGINE IS RUNNING as personal injury MAY
result from the sudden and unintended movement of
vehicle under power.
1. INCORRECT AIR LINE HOOK-UPS
(See Air System Schematics)
With the gear shift Iever in neutral, move the control
that provides range selection UP and DOWN.
A. If
the air lines are crossed between control
valve and slave valve, there will be CONSTANT
AIR flowing from the exhaust port of control
valve WHILE IN HIGH RANGE.
B. If the air lines are crossed between the slave
valve and range cylinder, the transmission
gearing will not correspond with the range
selection. A LOW RANGE selection will result
in a HIGH RANGE engagement and vice versa.
AIR LEAKS
2.
With the gear shift lever in neutral, coat all air lines
and fittings with soapy water and check for leaks,
moving the control that provides range selection
UP and DOWN.
If there is a steady leak from the exhaust port of
A.
control valve, O-rings and/or related parts of
the control valve are defective.
If there is a steady leak from breather of slave
B.
valve: an O-ring in valve is defective, or there is
a leak past O-rings of range cylinder piston.
If transmission fails to shift into LOW RANGE
C.
or is slow to make the range shift and the case
is pressurized,
section.
Tighten all loose connections and replace
D.
defective O-rings and parts.
3.
AIR FILTER/REGULATOR
(See illustration, Page 26.)
With the gear shift lever in neutral, check the
breather of air filter/regulator assembly. There
should be NO AIR leaking from this port. The
complete assembly should be replaced if a steady
leak is found.
Cut off the vehicle air supply to the air
filter/regulator assembly, disconnect the air line at
fitting in Supply OUTLET and install an air gauge in
opened port. Bring the vehicle air pressure to
normal. Regulated air pressure should be 57.5 to
62.5 PSI.
DO NOT ADJUST SCREW AT BOTTOM OF
REGULATOR TO OBTAIN CORRECT
READINGS.
PREADJUSTED within the correct operating
limits. Any deviation from these limits, especially
with regulators that have been in operation for
some time, is likely to be caused by dirt or worn
parts. if replacement or cleaning of the filter
element does nothing to correct the air pressure
readings, replace the complete assembly, as the air
regulator is nonserviceable.
CONTROL VALVE (See Pages 27 and 28.)
4.
With the gear shift lever in neutral, select HIGH
RANGE and disconnect the 1/8” O.D. airline at the
OUTLET or “P” Port of control valve.
A. When LOW RANGE is selected, a steady blast
of air will flow from opened port. Select HIGH
RANGE to shut off air flow. This indicates the
control valve is operating properly. Reconnect
air line.
see Check Note 7 of this
The air regulator has been
Page 28
AIR SYSTEM
B. If control valve does not operate properly,
check for restrictions and air leaks. Leaks
indicate defective or worn O-rings.
5. HIGH RANGE OPERATION
With the gear shift lever in neutral, select LOW
RANGE and disconnect the 1/4” I.D. air line at the
port of range cylinder cover. Make sure this line
leads from the High Range or “H” Port of slave
valve.
A.
When HIGH RANGE is selected, a steady blast
of air should flow from disconnected line.
Select LOW RANGE to shut off air flow.
Move the shift lever to a gear position and
B.
select HIGH RANGE. There should be NO AIR
flowing from disconnected line. Return the
gear shift lever to the neutral position. There
should now be a steady flow of air from
disconnected line. Select LOW RANGE to shut
off air flow and reconnect air line.
If the air system does not operate accordingly,
C.
the slave valve or actuating components of the
shift bar housing assembly are defective.
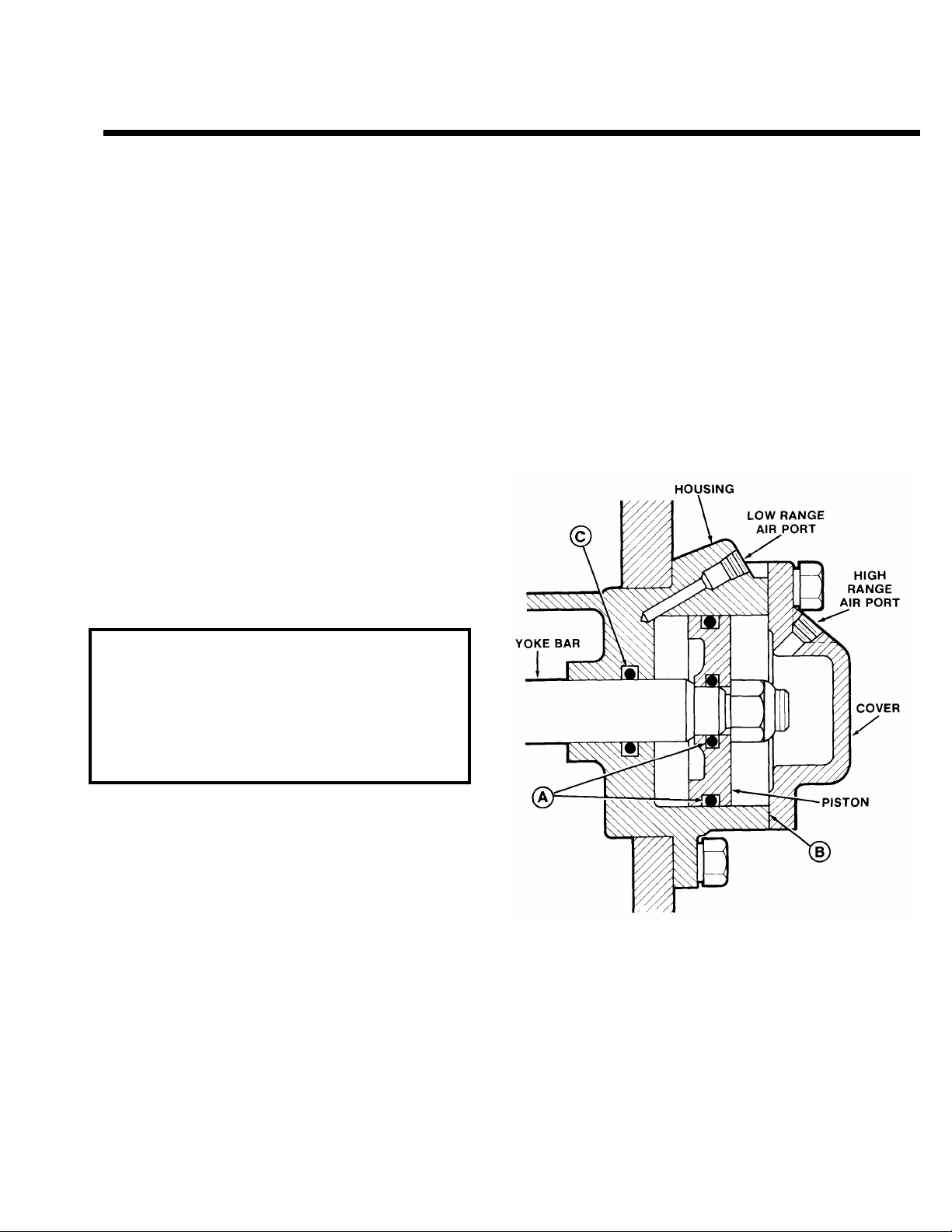
7. RANGE CYLINDER (Refer to the following
illustration.)
If any of the seals in the range cylinder assembly
are defective, the range shift will be affected.
Leak at either O-ring A results in complete
A.
failure to make a range shift; steady flow of air
from breather of slave valve in both ranges.
Leak at gasket B results in a steady flow of air to
B.
atmosphere while in HIGH RANGE.
Leak at O-ring C results in a slow shift to LOW
C.
RANGE; pressurizing of transmission case.
IMPORTANT: RANGE PRESELECTION
The plunger pin, located in case bore between the
slave valve and actuating plunger of shift bar
housing, prevents the slave valve from operating
while the shift lever is in a gear position. When the
lever
is moved to or through the neutral position,
the pin is released and the slave valve becomes
operational.
6. LOW RANGE OPERATION
With the gear shift lever in neutral, select HIGH
RANGE and disconnect the 1/4” I.D. air Iine at the
fitting on range cylinder housing. Make sure this
line leads from the Low Range or “L” Port of slave
valve.
When LOW RANGE is selected, a steady blast
A.
of air should flow from disconnected line.
Select HIGH RANGE to shut off air flow.
B.
Move the shift lever to a gear position and
select LOW RANGE. There should be NO AIR
flowing from disconnected line. Return the
gear shift lever to the neutral posiTion. There
should now be a steady flow of air from
disconnected line. Select HIGH RANGE to
shut off air flow and reconnect air line.
If the air system does not operate accordingly,
c.
the slave valve or actuating components of the
shift bar housing assembly are defective.
RANGE CYLINDER ASSEMBLY
ALL MODELS
Page 29

AIR SYSTEM
AIR FILTER/REGULATOR ASSEMBLY
The air filter contains a replaceable filter element which can be removed by turning out the end cap. This element
should be cleaned at each oil change, or more often under high humidity conditions. Replace if necessary.
SLAVE VALVES
PISTON-TYPE
POPPET-TYPE
Refer to the drawing for disassembly and reassembly of the piston-type slave valve assembly. Should the poppet-type
slave valve assembly prove to be defective, replace the complete assembly, as it is non-serviceable. The actuating
components used with these valve assemblies are non-interchangeable. Failure to use the correct plunger pin, spring
and alignment sleeve during installation on the transmission will cause hard shifting in Low Range gears.
Page 30

AIR SYSTEM
RANGE CONTROL VALVE
NOTE: This valve provides range
selection ONLY. When
equipped on LL Models, the
dash-mounted Deep Reduction
Valve is required to provide
deep reduction selections.
Removal and Disassembly Reassembly and Installation
Refer to the drawing for proper reassembly. Use a
Disconnect the air lines and loosen clamp securing
1.
the valve to gear shift lever. Remove valve.
Remove the four screws to separate the front and
2.
rear housings and remove the slide and two sets of
position springs and balls.
3.
Remove the seal, insert valve O-ring and spring from
rear housing.
4.
If necessary, remove the two felt seals. Punch out
the roll pin to remove the control knob from slide.
1.
VERY SMALL amount of silicone lubricant on the Orings to avoid clogging ports. A small amount of
grease on the position springs and balls will help to
hold them in place during reassembly.
Install the air lines with their sheathing and O-rings
2.
on the gear shift lever.
Secure the valve on gear shift lever with mounting
3.
clamp. The control knob should face to the front and
be approximately 6“ below the centerline of ball
grip.
Attach the air lines.
4.
Page 31

AIR SYSTEM
MASTER CONTROL VALVE A-5010
NOTE:
Cut 6146
This valve provides range selection ONLY.
When equipped on 15-Speed Models, the
dash-mounted Deep Reduction Valve is
required to provide deep reduction selections.
Removal and Disassembly Reassembly and Installation
Refer to the drawing for proper reassembly. Use a
Remove two screws holding bottom cover to valve
1.
and slide cover down gear shift lever to expose air
line fittings. Disconnect air lines.
2.
Loosen jam nut and turn control valve from gear shift
lever.
Pry medallion from recess in top cover.
3.
4.
Turn out the two screws to remove the top cover
from valve housing.
Turn out the two screws in side of valve housing to
5.
separate the housing.
Remove the Range Preelection Lever from left
6.
housing and the position balls and guide from lever.
7.
If necessary, remove spring and O-ring from bores
in left housing.
If necessary, remove springs, O-ring and sleeve
8.
from bores in right housing.
1.
VERY SMALL amount of silicone Iubricant on the Orings to avoid clogging ports. A small amount of
grease on the position springs and balls will help to
hold them in place during reassembly.
Reinstall control valve on gear shift lever and tighten
2.
jam nut.
3.
Attach air lines and reinstall bottom cover.
Page 32

AIR SYSTEM
DEEP REDUCTION AIR SYSTEM: LOW-LOW MODELS ONLY
Operation
In addition to the various components of the Range
Shift Air System, the Deep Reduction Air System
utilizes a reduction cylinder and a separate dashmounted Deep Reduction Valve OR the Master Control
Valve A-5015.
CONSTANT AIR from the air filter/regulator
assembly is supplied to the reduction cylinder at the
port on right side of cylinder cover. See Air System
Schematics.
With the Deep Reduction lever in the ’’OUT” position,
the valve is OPENED and AIR is supplied to the Center
Port of cylinder cover, moving the reduction piston
forward to disengage deep reduction gearing. With the
lever moved to the “IN” position, the valve is CLOSED
and NO AIR is supplied to the Center Port. CONSTANT
AIR from the air filter/regulator assembly moves the
reduction piston
gearing.
Lever to “OUT”
(Valve OPENED)
For models equipped with the Master Control Valve
A-5015, AIR is supplied to the built-in deep reduction
valve ONLY WHILE IN LOW RANGE from tee fitting at
the Low Range or “L” Port of slave valve. The insert
valve (see Page 33) MUST be installed in cylinder cover
to provide the proper air flow needed to move the
reduction piston in the cylinder. See schematic
provided on Page 31.
NOTE: The insert valve is NOT USED in the reduction
cylinder cover of models equipped with the
Deep Reduction Valve.
With the Deep Reduction Button in the
REARWARD position, the “SP” Port of control
valve is CLOSED and NO AIR is supplied to the
Center Port of cylinder cover.
rearward to engage reduction
Lever to “IN”
(Valve CLOSED)
Button REARWARD
(“SP” Port CLOSED)
WHILE IN LOW RANGE, the button can be moved
FORWARD to operate in DEEP REDUCTION. The
“SP” Port of valve is OPENED when deep reduction
selection is made, supplying AIR to the Center Port of
cylinder cover.
Button FORWARD
(“SP” Port OPENED)
NOTE:
WHILE IN HIGH RANGE, the mechanical
interlock of Master Control Valve prevents
movement of Deep Reduction Button to the
FORWARD position.
Troubleshooting
If the transmission fails to shift oR shifts too slowly to or
from DEEP REDUCTION, the fault may be in the Deep
Reduction Air System or related cOmponents of the
Range Shift Air System.
To Iocate the trouble, the following checks should be
made with normal vehicle air pressure supplied to the
system, but with the engine off. See CAUTION, Page
24.
NOTE: It is assumed that correct PSI readings were
obtained from the air filter/regulator and all air
lines have been checked for leaks.
For Models Equipped with
the Deep Reduction Valve . . .
1.
Air Supply (See Air System Schematics.)
With the gear shift lever in neutral, loosen the
connection at the INLET (End Port) or Deep
Reduction Valve until it can be determined that
CONSTANT AIR is supplied to valve. Reconnect
air line.
If there is NO AIR, check for a restriction in line
between the Deep Reduction Valve and slave valve,
making sure this line is connected to tee fitting at
the Supply or “S” Port of slave valve.
Page 33

AIR SYSTEM
2. Deep Reduction
Schematics.)
With the gear shift lever in neutral, disconnect the
air line leads from OUTLET of Deep Reduction
Valve.
A.
WHILE IN LOW RANGE, move the Deep
Reduction Valve Lever to the “IN” position.
There should be NO AIR from disconnected
line.
B.
Move the valve lever to the “OUT” position.
There should now be CONSTANT AIR flowing
from disconnected line. Return the valve Iever
to the “IN” position to shut off air flow and
reconnect air line.
Valve (See Air System
3. Reduction Cylinder (Refer to the following
Illustration.)
If any of {he seals in the reduction cylinder
assembly are defective, the deep reduction shift
will be affected. The degree of air lost will govern
the degree of failure, from slow shiftIng to
complete shift failure.
Leak at O-ring A results in a slow shift to
A.
engage deep reduction gearing; pressurizing
of transmission case; deep reduction gearing
can be disengaged.
Leak at O-ring B results in slow shifting or
B.
complete failure to engage and disengage
deep reduction gearing; steady flow of air from
exhaust port of Deep Reduction Valve when
lever is in the “IN” position.
Leak at gasket C results in a slow shift to
C.
disengage deep reduction gearing; steady flow
of air to atmosphere.
REDUCTION CYLINDER ASSEMBLY
(Models equipped with Deep Reduction Valve ONLY.)
Page 34

AIR SYSTEM
For Models Equipped with
the Master Control Valve A-5015 . . .
1. Air Supply (See schematic below.)
With the gear shift lever in neutral, select LOW
RANGE and loosen the connection at the “H” Port
of control valve until it can be determined that AIR
is supplied to valve. Reconnect air line. If there is
NOTE: Arrows are provided in
this schematic to note
direction of air flow
through PRESSUR-
IZED LINES SHOWN
AS SHADED AREA
ONLY.
NO AIR, check for a restriction in the 1/8” O.D. air
line between the control valve and slave valve,
making sure this line is connected to tee fitting at
the Low Range or “L” Port of slave valve.
Page 35

AIR SYSTEM
2. Master Control Valve (See Page 34 and
schematic on preceding page.)
With the gear shift lever in neutral, disconnect the
1/8” O.D. air line at the Center Port of reduction
cylinder cover, making sure this line Ieads from the
“SP” Port of control valve.
WHILE IN LOW RANGE, move the Deep
A.
Reduction Button FORWARD. There should be
AIR flowing from disconnected line. Move the failure. Two indications of defective O-rings or
button REARWARD to shut off air flow and
reconnect air line.
If the preceding conditions did not exist, the
B.
control valve is defective, or there is a
restriction in the air lines.
Reduction Cylinder (Refer to the following
3.
illustration.)
If any of the seals in the reduction cylinder
assembly are defective, the deep reduction shift
will be affected. The degree of air lost will govern
the degree of failure, from slow shifting to
complete shift failure.
Leak at O-ring A results in a slow shift to
A.
engage deep reduction gearing; pressurizing
of transmission case; deep reduction gearing
can be disengaged.
B.
Leak at O-ring B results in slow shifting or
complete failure to engage and disengage
deep reduction gearing; steady flow of air from
exhaust port of control valve and/or cylinder
cover when Deep Reduction Button is in the
FORWARD position.
Leak at gasket C results in a slow shift to
C.
disengage deep reduction gearing; steady flow
of air to atmosphere.
4. Insert Valve (See next page.)
Any constant flow of air from exhaust port of
cylinder cover usually indicates a faulty insert
valve. Exhaust should occur ONLY BRIEFLY when
Deep Reduction Button is moved FORWARD
WHILE IN LOW RANGE.
A faulty insert valve, leaking at the O-rings of
valve O.D. or from inner seals, will result in shift
seals are:
A. CONSTANT AIR flowing from exhaust port of
cylinder cover.
B. CONSTANT AIR flowing from exhaust port ”E”
of control valve WHILE DEEP REDUCTION
BUTTON IS REARWARD (providing the
control valve is operating properly).
The three O-rings in position on valve O.D can be
replaced. However, if an inner seal is damaged, the
complete assembly MUST be replaced.
REDUCTION CYLINDER ASSEMBLY
(Models equipped with Master Control A-5015 ONLY.)
Page 36

AIR SYSTEM
Insert Valve: LL Models
Equipped with Master Control Valve A-5015
The insert valve is a self-contained 1-3/16” valve
assembly located in the reduction cylinder cover. It
CANNOT be disassembled except for the three ORINGS ON outer diameter. The O-rings provide a
stationary seal and do not move in cylinder.
CENTER PORT,
SIGNAL LINE FROM
CONTROL VALVE
"SP” PORT.
INSERT VALVE
RETAINING NUT
BOTTOM EXHAUST PORT
When installing the insert valve in bottom bore of
cover, apply Fuller #71206 silicone lubricant or its
equivalent to O-rings and cylinder walls. Install valve in
bore with flat surface to the inside. When installing the
special valve retaining nut, apply Fuller #71204
adhesive/sealant or its equivalent to threads and
tighten. See TORQUE RECOMMENDATIONS.
Travel of the small insert valve piston is only 3/16”.
As shown in the illustrations below, when NO AIR is
applied to the top side of valve piston, CONSTANT AIR
supplied from the regulator passes freely through the
insert valve and to the back side of cylinder piston,
moving the yoke bar forward to disengage deep
reduction gearing (LOW RANGE AND HIGH RANGE).
When AIR is supplied to the top side of valve piston
through signal line, the piston moves down to cutoff air
supplied to the back side of cylinder piston. This air is
exhausted out bottom port of cover when CONSTANT
AIR supplied from the regulator is directed to the front
side of cylinder piston, moving the yoke bar rearward
to engage deep reduction gearing (LO/LO).
LO/LO
AIR APPLIED THROUGH SIGNAL LINE
PUSHES INSERT
VALVE PISTON DOWN
LOW RANGE
TO BACK SIDE
OF PISTON,
YOKE BAR
FORWARD
Cut 7450A
AND
HIGH RANGE
NO AIR ON
SIGNAL LINE
CONSTANT
AIR
CONSTANT
AIR SEALED
OFF AT THIS
POINT
CONSTANT
AIR
AIR EXHAUST THROUGH BOTTOM
PORT FROM BACK SIDE OF PISTON
Page 37

AIR SYSTEM
MASTER CONTROL VALVE A-5015
NOTE:
This valve provides BOTH range and deep
reduction selection, replacing the need for
separate units (Range Control Valve A-3546 or
Master Control Valve A-5010 with dash-mounted
Deep Reduction Valve).
Removal and Disassembly Reassembly and Installation
Refer to the drawing for proper reassembly. Use a
1.
Remove two screws holding bottom cover to valve
and slide cover down gearshift lever to expose air
line fittings. Disconnect air lines.
2.
Loosen jam nut and turn control valve from gear shift
lever.
Pry medallion from recess in top cover.
3.
4.
Turn out the two screws to remove the top cover
from valve housing,
Remove the actuator button from valve housing and
5.
the spring retainer, springs, seal and detent parts
from actuator and/or valve housing.
Turn out the two screws in side of valve housing to
6.
separate the housing.
7.
Remove the Range Preelection Lever from left
housing and the position balls and guide from lever.
If necessary, remove springs, O-ring and retainer
8.
from bores in right housing.
1.
VERY SMALL amount of silicone lubricant on the O-
rings to avoid clogging ports. A small amount of
grease on the position springs and balls will help to
hold them in place during reassembly.
Reinstall control valve on gear shift lever and tighten
2.
jam nut.
Attach air lines and reinstall bottom cover.
3.
Page 38

7L: 8: 9: and 10 Speed (2-Speed Auxiliary)
Range—LO
A-3546 Range
Valve
Down
Outlet
PS
A-4688 Slave Valve
S
A-5010 Roadranger
Valve
OR
Down
P
OR
Slave Valve
Identification
A-4688 Valve
A-5000 Valve
19470 Valve
SP
19470 or A-5000
Slave Valve
HI
Air Filter/Regulator
Assembly
Air from
Vehicle
Source
HI
LO
Constant Air
S
Range Cylinder
Assembly
LO
Air to Housing
Port
No Air
P
LO
Schematic
For all questions
concerning
removal and
replacement,
refer to Eaton
Service and Parts
Literature.
HI
Page 39

7L: 8: 9: and 10 Speed (2-Speed Auxiliary)
Range—HI
A-3546 Range
Valve
Up
Outlet
PS
A-4688 Slave Valve 19470 or A-5000
S
A-5010 Roadranger
Valve
OR
Up
P
OR
SP
Slave Valve
Slave Valve
Identification
A-4688 Valve
A-5000 Valve
19470 Valve
HI
Schematic
For all questions
concerning
removal and
replacement,
refer to Eaton
Service and Parts
Literature.
Air Filter/Regulator
Assembly
Air from
Vehicle Source
HI
LO
Constant Air
S
Range Cylinder
Assembly
LO
P
LO
No Air
Air to Cover
Port
HI
Page 40

RT, RTO, & RTX XX607LL: XX608LL: and XX615 Models
Deep Reduction
A-3546 Range
Valve
Down
A-5010 Roadranger
Valve
OR
Down
Outlet
PS
SP
A-4688 Slave Valve 19470 or A-5000
Slave Valve
R
P
S
OR
Slave Valve
Identification
A-4688 Valve
A-5000 Valve
19470 Valve
R
HI
Schematic
For all questions
concerning
removal and
replacement,
refer to Eaton
Service and Parts
Literature.
Air Filter/Regulator
Assembly
Air from
Vehicle
Source
Deep Reduction Valve
E
D
OUT
Reduction
Cylinder
Assembly
Constant Air
HI
LO
E
R
P
E
SHIFT ONLY
WHEN IN LOW
RANGE
DO NOT
PRE-SELECT
S
P
LO
Range Cylinder Assembly
D
U
C
T
I
O
N
IN
In
LO
Air to
Housing
Port
No Air
R
No Air
HI
Page 41

RT, RTO, & RTX XX607LL: XX608LL: and XX615 Models
Range—LO
A-3546 Range
Valve
Down
A-5010 Roadranger
Valve
OR
Down
Outlet
PS
SP
A-4688 Slave Valve 19470 or A-5000
Slave Valve
R
P
S
OR
Slave Valve
Identification
A-4688 Valve
A-5000 Valve
19470 Valve
R
HI
Air Filter/Regulator
Assembly
Air from
Vehicle
Source
Deep Reduction Valve
Reduction
Cylinder
Assembly
Constant Air
HI
LO
OUT
E
E
D
PRE-SELECT
D
E
R
P
SHIFT ONLY
WHEN INLOW
RANGE
DO NOT
S
P
LO
Schematic
For all questions
concerning
removal and
Range Cylinder Assembly
U
C
T
I
O
N
IN
Out
LO
Air to
Housing
Port
R
No Air
HI
replacement,
refer to Eaton
Service and Parts
Literature.
Page 42

RT, RTO, & RTX XX607LL: XX608LL: and XX615 Models
Range—HI
A-3546 Range
Valve
Up
A-5010 Roadranger
Valve
OR
Up
Outlet
PS
SP
A-4688 Slave Valve 19470 or A-5000
Slave Valve
R
P
S
OR
Slave Valve
Identification
A-4688 Valve
A-5000 Valve
19470 Valve
R
HI
Schematic
For all questions
concerning
removal and
replacement,
refer to Eaton
Service and Parts
Literature.
Air Filter/Regulator
Assembly
Air from
Vehicle
Source
Deep Reduction Valve
Reduction
Cylinder
Assembly
Constant Air
D
OUT
HI
LO
R
P
E
E
SHIFT ONLY
WHEN INLOW
RANGE
DO NOT
PRE-SELECT
S
P
LO
Range Cylinder Assembly
D
U
E
C
T
I
O
N
IN
Out
No Air
LO
R
Air to
Cover
HI
Port
Page 43

DISASSEMBLY AND REASSEMBLY
SHIFTING CONTROLS
RANGE SHIFT AIR SYSTEM
A. To Remove the Range Shift Control
Valve. (RTO-11607L)
NOTE: The example shown in this sequence uses an
A-5010 master control valve and a #19470 slave
valve. Disassembly is similar for units equipped
with different control and slave valve
combinations.
1. Slide the shroud off the master control and
disconnect the nylon air lines at the master control
valve.
2. Disconnect the two nylon air lines at slave valve on
transmission.
Page 44

DISASSEMBLY AND REASSEMBLY
SHIFTING CONTROLS
C. To Remove the Slave Valve
Assembly
Remove the master control valve, shroud and nylon
3.
air lines from the shift lever.
B.
To Remove the Air Regulator
and Filter Assembly
1. Disconnect and remove the air line between the
slave valve and air regulator.
2. Remove street ell and reducer from regulator if
necessary.
1. Remove the two air lines between the slave valve
and range cylinder.
2. Turn out the four capscrews and remove the slave
valve from the transmission. Remove the sleeve
from the slave valve.
3. Turn out capscrews and remove the air regulator
and filter assembly from transmission.
Page 45

DISASSEMBLY AND REASSEMBLY
SHIFTING CONTROLS
3. If necessary, remove fittings from slave valves.
4. Remove the actuating spring and pin from bore in
transmission.
Page 46

DISASSEMBLY AND REASSEMBLY
SHIFTING CONTROLS
RANGE SHIFT AIR SYSTEM
A. Remove the Range Shift Control
Valve (RTO-11607LL)
NOTE: The example shown in this sequence uses an
A-5015 Master Control Valve, a Deep
Reduction Cylinder and an A-4688 Slave Valve.
1. Remove retaining screws, slide the shroud off the
master control and disconnect the nylon air lines at
the master control valve.
2. Disconnect the three nylon air lines at the slave
valve.
Page 47

DISASSEMBLY AND REASSEMBLY
SHIFTING CONTROLS
B. To Remove Air Regulator
and Filter Assembly
3. Disconnect the nylon air line at the deep reduction
cylinder.
1. Remove the air line between the air regulator and
the deep reduction cylinder.
4.
Remove the master control valve, shroud and nylon
air lines from the shift lever.
2. Remove the air line running from the air regulator
to the slave valve at the regulator.
Page 48

DISASSEMBLY AND REASSEMBLY
SHIFTING CONTROLS
3. Turn out capscrews and remove the air regulator
and filter assembly from transmission.
C. To Remove the Slave Valve
2. Disconnect the two air lines running between the
slave valve and the range cylinder, at the range
cylinder.
1.
Remove the hose clamp holding the air lines to the
auxiliary.
Turn out the four capscrews and remove the slave
.
3
valve from the transmission.
Page 49

DISASSEMBLY AND REASSEMBLY
SHIFTING CONTROLS
4. Remove the hat type sleeve from the bore in the
slave valve.
5. Remove the actuating spring and pin from bore in
transmission.
Page 50

DISASSEMBLY AND REASSEMBLY
SHIFTING CONTROLS
GEAR SHIFT LEVER HOUSING
Page 51

DISASSEMBLY AND REASSEMBLY
SHIFTING CONTROLS
A. Removal and Disassembly
1. Turn out the capscrews, jar lightly to break the
gasket seal and remove the gear shift lever housing
from the shift bar housing.
B.
Reassembly and Installation
1.
Install the spade pin in the bore in the housing. If
previously removed,
groove.
Install the gear shift lever in the housing, fitting the
2.
slot in the lever ball over the spade pin.
Place the tension spring washer over the lever ball
3.
with the dished side up.
install the O-ring in the
2. Secure the housing in a vise and use a large
screwdriver to twist between the spring and side of
the housing, forcing the spring from under the
three lugs. Do one coil at a time. Remove the
spring.
3. Remove the washer and gear shift Iever.
4. Remove the spade pin from the bore in the housing.
If necessary, remove the O-ring from the housing.
4. Seat the tension spring under the lugs in the
housing, seating one coil at a time. Use of a spring
driving tool is recommended.
5. Make sure that the three tension springs and balls
are in the shift bar housing bores and install the
gear shift lever housing and gasket on the shift bar
housing.
Page 52

DISASSEMBLY AND REASSEMBLY
SHIFTING CONTROLS
SHIFT BAR HOUSING ASSEMBLY
A. Removal and Disassembly
Shift Bar Housing
1. Remove the capscrews from the shift bar housing.
2. Jar the housing to break the gasket seal, and Iift the
housing up and off.
Page 53

DISASSEMBLY AND REASSEMBLY
SHIFTING CONTROLS
3. Tilt the housing, and remove the three tension balls
and springs.
4. Place housing in a vice with plunger side up and cut
lock wire from all capscrews.
5. Remove the capscrews from all shift yokes and
blocks.
6. Slide the direct shift rail out of yokes and the
housing.
NOTE: Rails not being removed must be in the neutral
position.
Page 54

DISASSEMBLY AND REASSEMBLY
SHIFTING CONTROLS
7. Remove center rail, yoke and block, being careful
to remove the neutral interlock pin from the rail.
8. Remove air system interlock plunger.
9. Remove reverse rail and yoke.
10. Remove the two interlock balls from the front web.
Page 55

DISASSEMBLY AND REASSEMBLY
SHIFTING CONTROLS
11. Clamp the reverse yoke in a soft jawed vice and
remove the snap ring from the reverse yoke
plunger.
12. Remove the retainer, springs and plunger from the
bore.
Page 56

DISASSEMBLY AND REASSEMBLY
SHIFTING CONTROLS
SHIFT BAR HOUSING ASSEMBLY
A. To Reassemble Shift Bar Housing
1. Coat the reverse yoke plunger lightly with oil, and
install in bore.
2. Install the springs in the bore, with the smaller
diameter spring inside the larger.
3. Install the hat shaped retainer in the bore with the
crown to the outside.
4. Install the retaining snap ring.
5. Check the plunger for smooth operation by
pushing it down into the bore several times and
checking for free return.
Page 57

DISASSEMBLY AND REASSEMBLY
SHIFTING CONTROLS
6. Install the reverse rail through the reverse yoke,
with the neutral notches to the rear.
7. Line up the hole in the rail with the hole in the yoke
and install capscrew.
CAUTION: Do not torque capscrews beyond 45 ft.
lbs. or rails could be distorted.
8. Drop first interlock ball into web.
9. Install range plunger in bore.
Page 58

DISASSEMBLY AND REASSEMBLY
SHIFTING CONTROLS
10. Put reverse rail in neutral and start center rail
partially in, installing center block with tapped hole
toward the rear.
11. Install center yoke, and before pushing the rail
completely in, install the interlock pin.
12. The shorter capscrew with the beveled head must
be installed in the center block.
13. Drop the second ball in the web.
Page 59

DISASSEMBLY AND REASSEMBLY
SHIFTING CONTROLS
With the center and reverse rails in the neutral
14.
position, install the direct rail through the block
and yoke.
Install all capscrews and lockwire.
15.
16.
Check that the lockout feature is working by
putting one rail in gear and attempting to move the
other two rails out of the neutral position. They
should not move.
Page 60

REMOVAL - COMPANION FLANGE,
AUXILIARY SECTION AND
CLUTCH HOUSING
COMPANION FLANGE, AUXILIARY SECTION
AND CLUTCH HOUSING
A. To Remove the Universal Joint
Companion Flange or Yoke
Lock the transmission by engaging two gears with
1.
the mainshaft sliding clutches.
2. Use a large breaker bar to turn output shaft nut
from the output shaft
Page 61

REMOVAL - COMPANION FLANGE,
AUXILIARY SECTION AND
CLUTCH HOUSING
B. To Remove the Auxiliary Section
from Transmission
3. Pull the companion flange or yoke from splines of
output shaft.
4. Remove the speedometer drive gear or
replacement spacer from hub of flange/yoke or
from inside rear bearing cover remaining on output
shaft (inset). For some models, it is necessary to
remove the snap ring in groove of output shaft
PRIOR to removal of the speedometer gear or
spacer.
NOTE: Temporarily reinstall output shaft nut to
protect the threads during auxiliary removal.
1. Turn out the capscrews that attach the two
sections.
2. Insert three puller screws in the tapped holes of
housing flange.
3. Tighten puller screws evenly to move auxiliary
section to the rear and just far enough from front
section to break gasket seal.
Page 62

REMOVAL - COMPANION FLANGE,
AUXILIARY SECTION AND
CLUTCH HOUSING
Attach lifting eye to auxiliary and hook a hoist into
4.
position before sliding auxiliary section
completely off dowels.
5.
Remove the gasket from the front section.
3. Jar clutch housing with a rubber mallet to break
gasket seal and pull from transmission case.
Remove gasket.
Removal of Clutch Housing
C.
1.
For models so equipped, remove the clutch release
mechanism and/or clutch brake assembly. See
OPTIONS.
2.
Turn out the four capscrews and remove the six
nuts and lockwashers from studs securing the
clutch housing to transmission case.
Page 63

DISASSEMBLY - AUXILIARY SECTION
AUXILIARY SECTION (LOW)
A. To Remove The Auxiliary
Countershaft Assemblies
1. Remove countershaft bearing covers and the range
cylinder cover.
2. Remove the countershaft snap ring.
Page 64

DISASSEMBLY - AUXILIARY SECTION
Ñ
3. Remove the locknut holding the range piston in the
housing.
4. Cut the lockwire from the shift yoke capscrews.
5. Remove the capscrews from the shift yoke.
6. Slide the yoke bar back slightly to provide
clearance and lift out the shift yoke.
Page 65

DISASSEMBLY - AUXILIARY SECTION
Remove the piston from the yoke bar.
7.
Drive the countershaft assemblies out through the
9.
countershaft bearings using a soft bar and maul.
NOTE: Support the countershaft on the input side to
prevent them from dropping.
8. Pull the yoke bar out the input side of housing.
If necessary, secure the assembly in a vise and
10.
remove the bearing inner race from front of
countershaft with jaw pullers.
NOTE: The vise used should be equipped with brass
jaws or wood blocks to prevent damage to the
countershaft.
Page 66

DISASSEMBLY - AUXILIARY SECTION
REAR HOUSING ASSEMBLY
Cut 6544-10/80
B. To Remove the Synchronizer
Assembly, Mainshaft Assembly
and Range Shift Air Cylinder
1. Slide the synchronizer assembly off the mainshaft.
2. Drive the mainshaft assembly out using a soft bar
and maul.
NOTE: Support the gear while driving.
Page 67

DISASSEMBLY - AUXILIARY SECTION
3. Remove the rear bearing cover and the outer roller
bearing.
5. Remove the range cylinder housing.
4. Tap out bearing cups and spacer using a soft
punch.
6. Remove the O-Ring from the small bore in the
housing if it is damaged or needs replacement.
Page 68

DISASSEMBLY - AUXILIARY SECTION
7. Remove the countershaft bearings with a flat driver
and a maul.
Page 69

DISASSEMBLY - AUXILIARY SECTION
Cut 6552-9/80
C. Mainshaft Disassembly
I
1. Remove the bearing inner spacer from the
mainshaft.
2. Press the inner bearing from the mainshaft.
CAUTION: Support the mainshaft from below so it
does not drop and sustain damage during
the pressing operation.
Page 70

DISASSEMBLY - AUXILIARY SECTION
3. Remove the spline washer from the hub of low
speed gear.
Page 71

DISASSEMBLY - AUXILIARY SECTION
SYNCHRONIZER
ASSEMBLY
Cut 480-4179
D. Synchronizer Disassembly
1. Pull upward to remove the high range synchronizer
from pins.
2. Remove the sliding clutch from low range
synchronizer pins.
CAUTION: There are three springs which will be
released as the high range synchronizer is
removed from the pins. Cover the
assembly with a rag to prevent losing
springs.
Page 72

REASSEMBLY - AUXILIARY SECTION
AUXILIARY SECTION (LOW)
A. Mainshaft Reassembly
1. Mark two adjacent gear teeth, and two teeth 180¡
from the first two teeth for timing purposes.
IMPORTANT! There should be the same number of
teeth between the markings on each side of the gear.
3. Install low speed gear on mainshaft with clutching
teeth down.
2. Place the spline spacer in hub of low speed gear,
shoulder toward rear.
4. Install the spacer washer with chamfer side up.
Page 73

REASSEMBLY - AUXILIARY SECTION
B. Mainshaft Installation
5. Heat the rear bearing in oil to 50oF and drop down
into position on mainshaft.
CAUTION: Use asbestos gloves when handling
heated bearings.
1. Install the outer bearing races and spacer into the
housing. Make certain the lip on the outer race
seats against the housing.
6. Install the inner race spacer above the bearing on
the mainshaft.
2. Position the mainshaft and gear assembly in the
housing.
3. Heat the outer bearing in oil to 250
bearing into position and hold in place until it cools
and seats on the shaft.
o
F. Slide the
Page 74

REASSEMBLY - AUXILIARY SECTION
If previously removed, install the oil seal in rear
4.
bearing cover, lip of seal to the rear. The spring in
the seal should be toward the inside of the
transmission.
C. Synchronizer Reassembly
5.
Locate the unshielded capscrew hole in the rear
bearing cover, and install the capscrew with the
brass washer (or brass washer and plastic sleeve,
depending on model) in this hole.
1. Place the larger low range synchronizer face down
on the bench with pins up. Install the sliding clutch
(recessed side up) down over the pins on the
synchronizer.
6. Bolt the cover into place using a new gasket.
o
NOTE: The cover may be rotated 180
speedometer opening location.
for proper
2. Install the three springs into their bores.
Page 75

REASSEMBLY - AUXILIARY SECTION
D. Synchronizer Installation
Position the
3.
the springs
synchronizer pins. Seat the ring by pushing down
and twisting counterclockwise to compress
springs.
high range synchronizer ring so that
contact the side of the low speed
1. Position the synchronizer in the low range
position, and slide the assembly onto the
mainshaft.
Page 76

REASSEMBLY - AUXILIARY SECTION
E. Countershaft Installation
1.2.Seat the bearings part way in the bores with a soft
mallet.
If previously removed, install the bearing inner race
on front of each countershaft.
4. Mesh the marked tooth on each countershaft with
the marked teeth on the mainshaft gear, and slide
the countershaft into position.
3. Locate gear tooth on both countershaft with "O"
stamp and mark for timing.
Drive the countershaft bearings into the housing
5
.
with a stepped driver and maul, until both bearings
are fully seated on the shoulder in housing.
Page 77

REASSEMBLY - AUXILIARY SECTION
6. With a soft bar and maul, drive the countershafts to
the rear to expose snap ring grooves in counter-
shaft.
NOTE: It will be necessary to temporarily install the
bearing covers to hold the countershaft
bearings in place during this operation.
8. Reinstall the rear bearing covers using new
gaskets.
7. Install the snap rings.
F. Range Cylinder Installation
1. Bolt the cylinder housing into place using a new
gasket.
NOTE: The air port should be located in the 10 o'clock
position.
Page 78

REASSEMBLY - AUXILIARY SECTION
2. If previously removed, lubricate the O-ring and
install in the small bore in the cylinder.
3. Position the shift yoke, and slide the yoke bar
through the shift yoke and into the cylinder body
from the input side.
5. Install O-rings on OD and ID of piston and apply a
light coat of silicone lubricant to the O-rings,
6. Install the piston in the housing with the stepped
face to the inside.
4. Install the yoke capscrews and lock with safety
wire.
7. Install a new locknut on the yoke bar to secure the
piston.
Page 79

REASSEMBLY - AUXILIARY SECTION
8. Install the cylinder cover using a new gasket.
NOTE: The air port opening should be located at the
11 o'clock position.
Page 80

DISASSEMBLY - AUXILIARY SECTION
AUXILIARY SECTION (LOW - LOW)
A. Countershaft Removal
1. Remove the countershaft bearing covers.
2. Remove the range cylinder cover.
Page 81

DISASSEMBLY - AUXILIARY SECTION
Remove the snap rings from the countershaft
3. Remove the locking nut from the range yoke shaft
and discard.
5.
bearings.
4. Remove the reduction cylinder cover.
6. Cut the lockwire and remove capscrews.
Page 82

DISASSEMBLY - AUXILIARY SECTION
7. Slide the yoke bar part way into the range cylinder
housing to allow clearance for the shift yoke to be
lifted out.
8. Remove piston from yoke bar, and slide yoke bar
out from gear side of housing.
9. Drive out countershaft using a soft-bar and maul.
CAUTION: Support the countershaft from the gear
side to prevent them from dropping.
10. If necessary, secure the assembly in a vise and
remove the bearing inner race from front of
countershaft with jaw pullers.
NOTE: The vise used should be equipped with brass
jaws or wood blocks to prevent damage to the
countershaft.
Page 83

DISASSEMBLY - AUXILIARY SECTION
B. Synchronizer and Low Range
Gear Removal
1. Slide the synchronizer from the mainshaft.
2. Remove the square key from the range mainshaft.
3. Turn the tolerance washer to line up the splines
and slide the low range gear off the mainshaft.
4. Remove spacer from inside low range gear.
Page 84

DISASSEMBLY - AUXILIARY SECTION
5. Slide the coupler off mainshaft.
6. Remove the snap ring from the mainshaft.
Page 85

DISASSEMBLY - AUXILIARY SECTION
C. Reduction and Range Cylinder Removal
1. Cut lockwire and remove capscrew from reduction
cylinder yoke.
2. Slide yoke and reduction clutch forward off
mainshaft.
Page 86

DISASSEMBLY - AUXILIARY SECTION
3. Remove the reduction cylinder body and yoke bar.
4. Remove the range cylinder body by removing
capscrews.
Page 87

DISASSEMBLY - AUXILIARY SECTION
D. Mainshaft Removal
1. Remove C-ring from end of quill,
2. Pry range mainshaft off output shaft quill with two
large screwdrivers.
NOTE: Bearing can be removed from range mainshaft
if replacement is necessary.
Page 88

DISASSEMBLY - AUXILIARY SECTION
3. Remove rear bearing cover.
4. Remove snap ring from output shaft.
5. Slide speedospacer (or gear, depending on model)
off output shaft.
6. Temporarily reinstall rear bearing cover.
7. Drive the output shaft out through the bearing with
a soft bar and maul.
8. Remove rear bearing cover.
Page 89

DISASSEMBLY - AUXILIARY SECTION
9. Remove the spacer and two outer races from bore.
CAUTION:
The bearing is a matched set. If one piece
of the bearing is damaged, the whole set
must be replaced.
10. Drive out the two countershaft bearings.
Page 90

DISASSEMBLY - AUXILIARY SECTION
E. Mainshaft Disassembly
Remove the washer from inside the deep reduction
3.
gear.
Press the inner bearing and deep reduction gear off
1.
the mainshaft.
2. Remove the spacer and oil retention ring from the
deep reduction gear.
Page 91

DISASSEMBLY - AUXILIARY SECTION
F. Reduction Cylinder Insert
Valve Disassembly
1. Remove the nut from the reduction cylinder cover.
2. Remove the insert valve from the cover.
3. Check the orifices in the valve for obstructions, and
check the O-rings for damage. Replace any
damaged or questionable O-rings.
Page 92

REASSEMBLY - AUXILIARY SECTION
AUXILIARY SECTION (LOW - LOW)
Cut 6590-1/81
.
A. Mainshaft Reassembly
1. Use a driver to install range mainshaft and bearing
on quill.
2. Use a "O" ring driver to install the C-ring on the
nose of the quill.
Page 93

REASSEMBLY - AUXILIARY SECTION
3. Mark two sets of gear teeth at a point 180 degrees
apart for timing purposes.
4. Turn the mainshaft assembly over in the vise, and
drop the externally splined washer down on the
shaft.
6. Install the rear spacer with the machined surface
riding on the machined surface of the gear.
5.
Install the reduction gear on the mainshaft with
conical clutching teeth facing down.
Page 94

REASSEMBLY - AUXILIARY SECTION
B. Main Shaft Installation
3. Heat the inner bearing in oil to 250oF and lower into
place.
CAUTION: Use asbestos gloves when handling
heated bearings.
1. Install the oil deflector in the rear housing bore with
the cupped surface facing up. Use a large bearing
driver to drive the deflector down until the top
surface of the deflector is 2" below the machined
surface of the output shaft bore.
NOTE: If available, use two bearing outer spacers
stacked on top of each other to drive the oil
deflector into the bore. The deflector will beat
the proper depth when the top of the top spacer
is flush with the machined surface of the output
shaft bore.
4. Install the bearing inner spacer on the shaft and
against the front bearing cone.
2. Install the rear housing over the output shaft,
allowing the housing to rest on the reduction gear.
Page 95

REASSEMBLY - AUXILIARY SECTION
5. Stack the two bearing cups and outer spacer in the
output shaft bore in the proper sequence. Make
sure that the front bearing cup taper matches the
taper direction of the front bearing cone.
6.7.Tap the two cups and outer spacer lightly and
evenly into the case bore until the Iip of the rear cup
seats against the machined surface. It will be
necessary to block under the rear housing slightly
to permit the output shaft assembly to move far
enough.
Heat and install the rear bearing cone on the shaft
and in the rear cup, taper facing down.
8. Put speedo spacer (or drive gear) into place on
shaft and install snap ring. Reposition housing in
vise.
9. Tap the end of the output drive shaft with a soft bar
and maul to make certain the mainshaft and
bearings are seated.
10. Install the rear bearing cover using a new gasket
and positioning the speedo drive gear bore at
either the 10 o'clock or 3 o'clock position.
NOTE: The capscrew with the brass washer must be
installed in the unshielded capscrew hole
using a new plastic collar.
Page 96

REASSEMBLY - AUXILIARY SECTION
C. Reduction Cylinder Assembly
1.
Replace inner O-ring on reduction cylinder and
external O-ring on reduction yoke bar. Lube both
O-rings with silicone lube and install yoke bar in
cylinder,
3.
Install the insert valve into the cover with the tip
pointing out.
2. Lube the O-rings on the insert valve with silicone
lubricant.
4. Reinstall the insert valve retaining nut.
Page 97

REASSEMBLY - AUXILIARY SECTION
D. Low Range Gear Installation
5. Line up air hole in reduction cylinder body with
hole in cover. Install a new gasket and match up the
holes.
6. Install the reduction cylinder using a new gasket.
Position the cylinder so the insert valve is at 6
oÕclock.
1. Slide the low-low clutch part way onto the
mainshaft, with the splined side toward the
reduction gear.
2. Mesh the shift yoke with the clutch and slide back
onto yoke bar.
Page 98

REASSEMBLY - AUXILIARY SECTION
3. Install yoke capscrew and lockwire into place. 6. Install low range gear on mainshaft with machined
surface facing machined surface on coupler.
4. Install snap ring on mainshaft.
5. Install coupler, with clutching teeth to rear.
7. Install the spacer-tolerance washer with beveled
teeth facing out, and mesh it inside the low range
gear.
NOTE: Splined washers with varying thicknesses are
available. Use the washer that provides the
tightest fit in the hub of the gear.
Page 99

REASSEMBLY - AUXILIARY SECTION
E. Countershaft Installation
If previously removed, install the bearing inner race
1.
on front of each countershaft.
8. Rotate the spacer-tolerance washer to line up the
square notch in the washer with the keyway in the
range mainshaft. Install the key in the keyway,
shoulder to rear.
9. If the synchronizer was disassembled, rebuild as
detailed in low range auxiliary section.
10. Slide the synchronizer into position on the
mainshaft.
2. Locate the stamped "O" on each countershaft gear.
Mark the gear tooth directly above the "O" for
timing purposes.
3. Install the countershaft bearings with a flanged
driver.
Page 100

REASSEMBLY - AUXILIARY SECTION
4. Mesh the marked tooth on each countershaft with
the marked teeth on the reduction gear.
5. Drive the countershaft bearings fully into place in
the housing.
7. When the snap ring grooves are fully exposed,
install the snap rings.
Temporarily install the countershaft bearing
6.
covers and use a soft bar and maul to drive the
countershaft back into the bearing.
8. Install the bearing covers with new gaskets.
 Loading...
Loading...