Page 1
D-Link DGS-1224T
24-Port 10/100/1000Mbps
Gigabit Ethernet Switch + 2-Port mini GBIC
Web-Smart Switch
Manual
Second Edition
Building Networks for People
Page 2

Page 3

TABLE OF CONTENT
About This Guide................................................................................. 1
Purpose ............................................................................................ 1
Terms/Usage .................................................................................... 1
Introduction.......................................................................................... 3
Gigabit Ethernet Technology...........................................................3
Fast Ethernet Technology ................................................................ 4
Switching Technology ..................................................................... 5
VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network).............................................. 6
Features............................................................................................ 6
Unpacking and Installation .................................................................. 9
Unpacking........................................................................................ 9
Installation ....................................................................................... 9
Rack Mounting .............................................................................. 10
Connecting Network Cable............................................................ 11
AC Power....................................................................................... 11
Identifying External Components...................................................... 13
Front Panel..................................................................................... 13
Rear Panel...................................................................................... 14
Understanding LED Indicators ..........................................................15
Power and System LEDs ............................................................... 15
Ports 1~24 Status LEDs................................................................. 16
Option Ports mini-GBIC 1 & mini-GBIC 2 mini-GBIC Status LEDs
....................................................................................................... 16
Configuration ..................................................................................... 17
i
Page 4

Installing the Web Management Utility......................................... 17
Discovery List................................................................................ 18
Monitor List ................................................................................... 19
Device Setting................................................................................ 21
Toolbar........................................................................................... 22
Configuring the Switch .................................................................. 23
Login.............................................................................................. 24
Setup Menu .................................................................................... 25
Configuring Setup Setting.............................................................. 27
Port Settings............................................................................... 27
VLAN Settings (Virtual Local Area Network).......................... 29
Trunk Setting .............................................................................30
Mirror Setting............................................................................. 31
IEEE 802.1P QoS Setting ..........................................................33
Spanning Tree Setting................................................................ 33
SNMP Setting ............................................................................35
Jumbo Frame Setting .................................................................41
Device Status .............................................................................42
Statistic....................................................................................... 43
System Setting ...........................................................................44
Trap Setting................................................................................ 46
Set Password .............................................................................. 47
Backup Setting........................................................................... 48
Reset Setting ..............................................................................48
Logout............................................................................................ 49
ii
Page 5

Technical Specifications .................................................................... 37
iii
Page 6

Page 7
ABOUT THIS GUIDE
Congratulations on your purchase of the DGS-1224T 24-Port
10/100/1000Mbps Gigabit Ethernet+2-Port Mini GBIC Web Smart
Switch. This device integrates 1000Mbps Gigabit Ethernet, 100Mbps
Fast Ethernet and 10Mbps Ethernet network capabilities in a highly
flexible package.
Purpose
This guide discusses how to install and configure the DGS-1224T
Web Smart Switch.
Terms/Usage
In this guide, the term “Switch” (first letter upper case) refers to your
DGS-1224T Web Smart Switch, and “switch” (first letter lower case)
refers to other Ethernet switches.
1
Page 8

Page 9
INTRODUCTION
This chapter describes the features of the DGS-1224T and some
background information about Ethernet/Fast Ethernet/Gigabit Ethernet
switching technology.
Gigabit Ethernet Technology
Gigabit Ethernet is an extension of IEEE 802.3 Ethernet utilizing the
same packet structure, format, and support for CSMA/CD protocol,
full duplex, flow control, and management objects, but with a tenfold
increase in theoretical throughput over 100-Mbps Fast Ethernet and a
hundredfold increase over 10-Mbps Ethernet. Since it is compatible
with all 10-Mbps and 100-Mbps Ethernet environments, Gigabit
Ethernet provides a straightforward upgrade without wasting a
company’s existing investment in hardware, software, and trained
personnel.
The increased speed and extra bandwidth offered by Gigabit Ethernet
is essential to coping with the network bottlenecks that frequently
develop as computers and their busses get faster and more users use
applications that generate more traffic. Upgrading key components,
such as your backbone and servers to Gigabit Ethernet can greatly
improve network response times as well as significantly speed up the
traffic between your subnets.
Gigabit Ethernet enables fast optical fiber connections to support
video conferencing, complex imaging, and similar data-intensive
applications. Likewise, since data transfers occur 10 times faster than
Fast Ethernet, servers outfitted with Gigabit Ethernet NIC’s are able to
perform 10 times the number of operations in the same amount of time.
In addition, the phenomenal bandwidth delivered by Gigabit Ethernet
is the most cost-effective method to take advantage of today and
3
Page 10
tomorrow’s rapidly improving switching and routing internetworking
technologies. And with expected advances in the coming years in
silicon technology and digital signal processing that will enable
Gigabit Ethernet to eventually operate over unshielded twisted-pair
(UTP) cabling, outfitting your network with a powerful 1000-Mbpscapable backbone/server connection creates a flexible foundation for
the next generation of network technology products.
Fast Ethernet Technology
The growing importance of LANs and the increasing complexity of
desktop computing applications are fueling the need for high
performance networks. A number of high-speed LAN technologies
have been proposed to provide greater bandwidth and improve
client/server response times. Among them, 100BASE-T (Fast
Ethernet) provides a non-disruptive, smooth evolution from the
current 10BASE-T technology. The non-disruptive and smooth
evolution nature, and the dominating potential market base, virtually
guarantees cost-effective and high performance Fast Ethernet
solutions.
100Mbps Fast Ethernet is a standard specified by the IEEE 802.3
LAN committee. It is an extension of the 10Mbps Ethernet standard
with the ability to transmit and receive data at 100Mbps, while
maintaining the CSMA/CD Ethernet protocol. Since the 100Mbps
Fast Ethernet is compatible with all other 10Mbps Ethernet
environments, it provides a straightforward upgrade and takes
advantage of the existing investment in hardware, software, and
personnel training.
4
Page 11

Switching Technology
Another approach to pushing beyond the limits of Ethernet technology
is the development of switching technology. A switch bridges
Ethernet packets at the MAC address level of the Ethernet protocol
transmitting among connected Ethernet or Fast Ethernet LAN
segments.
Switching is a cost-effective way of increasing the total network
capacity available to users on a local area network. A switch increases
capacity and decreases network loading by dividing a local area
network into different segments, which don’t compete with each other
for network transmission capacity.
The switch acts as a high-speed selective bridge between the
individual segments. The switch, without interfering with any other
segments, automatically forwards traffic that needs to go from one
segment to another. By doing this the total network capacity is
multiplied, while still maintaining the same network cabling and
adapter cards.
Switching LAN technology is a marked improvement over the
previous generation of network bridges, which were characterized by
higher latencies. Routers have also been used to segment local area
networks, but the cost of a router, the setup and maintenance required
make routers relatively impractical. Today switches are an ideal
solution to most kinds of local area network congestion problems.
5
Page 12
VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network)
A VLAN is a group of end-stations that are not constrained by their
physical location and can communicate as if a common broadcast
domain, a LAN. The primary utility of using VLAN is to reduce
latency and need for routers, using faster switching instead. Other
VLAN utility includes:
Security, Security is increased with the reduction of opportunity in
eavesdropping on a broadcast network because data will be switched
to only those confidential users within the VLAN.
Cost Reduction, VLANs can be used to create multiple broadcast
domains, thus eliminating the need of expensive routers.
Port-based (or port-group) VLAN is the common method of
implementing a VLAN, and is the one supplied in the Switch.
Features
24×10/100/1000Mbps Auto-negotiation Gigabit Ethernet ports
All RJ45 ports support auto MDI/MDIX, so there is no need to
use cross-over cables or an up-link port
Half duplex transfer mode for connection speed 10Mbps and
100Mbps
Full duplex transfer mode for connection speed of 10Mbps,
100Mbps and 1000Mbsps
Gigabit Wire speed reception and transmission
Store-and-Forward switching scheme capability to support rate
adaptation and ensure data integrity
6
Page 13

Up to 8K unicast addresses entities per device, self-learning, and
table aging
512KBytes packet buffer
Supports IEEE 802.3x flow control for full-duplex mode ports
Supports IEEE 802.1Q-based VLAN
Supports IEEE 802.1P-based QoS
Supports Port-trunking
Supports Port-mirroring
Supports Port-setting for Speed/Disable, Flow control and Port
priority
Support Jumbo-frame setting
Supports IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree protocol
Support Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
Supports MIB for:
RFC1213 MIB II.
Private MIB.
Easy configuration via WEB Browser
Easy setting via Web Management Utility
Standard 19” Rack-mount size
7
Page 14

Page 15

UNPACKING AND INSTALLATION
This chapter provides unpacking and installation information for the
Switch.
Unpacking
Open the shipping cartons of the Switch and carefully unpacks its
contents. The carton should contain the following items:
One DGS-1224T Web Smart Switch
One AC power cord, suitable for your area’s electrical power
connections
Four rubber feet to be used for shock cushioning
Screws and two mounting brackets
CD-Rom with Web Management Utility and User’s Guide
Quick Installation Guide
If any item is found missing or damaged, please contact your local
reseller for replacement.
Installation
The site where you install the hub stack may greatly affect its
performance. When installing, consider the following pointers:
Install the Switch in a fairly cool and dry place. See Technical
Specifications for the acceptable temperature and humidity operating
ranges.
Install the Switch in a site free from strong electromagnetic field
generators (such as motors), vibration, dust, and direct exposure to
sunlight.
9
Page 16
Leave at least 10cm of space at the front and rear of the hub for
ventilation.
Install the Switch on a sturdy, level surface that can support its weight,
or in an EIA standard-size equipment rack. For information on rack
installation, see the next section, Rack Mounting.
When installing the Switch on a level surface, attach the rubber feet to
the bottom of each device. The rubber feet cushion the hub and
protect the hub case from scratching.
Figure 1. Attach the adhesive rubber pads to the bottom
Rack Mounting
The switch can be mounted in an EIA standard-size, 19-inch rack,
which can be placed in a wiring closet with other equipment. Attach
the mounting brackets at the switch’s front panel (one on each side),
and secure them with the provided screws.
Figure 2. Combine the Switch with the provided screws
10
Page 17
Then, use screws provided with the equipment rack to mount each
switch in the rack.
Figure 3. Mount the Switch in the rack
Connecting Network Cable
The Switch supports 1000Mbps Gigabit Ethernet that runs in Autonegotiation mode and 10Mbps Ethernet or 100Mbps Fast Ethernet that
runs both in half and full duplex mode and 1000Mbps Gigabit
Ethernet runs in full duplex mode using four pair of Category 5 Cable.
These RJ-45 ports are Auto-MDI type port. The Switch can auto
transform to MDI-II or MDI-X type, so you can just make an easy
connection that without worrying if you are using a standard or
crossover RJ45 cable.
AC Power
The Switch used the AC power supply 100-240V AC, 50-60 Hz. The
power switch is located at the rear of the unit adjacent to the AC
power connector and the system fan. The switch’s power supply will
adjust to the local power source automatically and may be turned on
without having any or all LAN segment cables connected.
11
Page 18

Page 19

IDENTIFYING EXTERNAL COMPONENTS
This chapter describes the front panel, rear panel, and LED indicators
of the Switch.
Front Panel
The figure below shows the front panels of the Switch.
Figure 4. Front panel of 24-port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
LED Indicator:
Comprehensive LED indicators display the status of the switch and
the network (see the LED Indicators chapter below).
Gigabit Ethernet Ports (Port 1~24):
The Switch sixteen Gigabit twisted pair ports, supported auto negotiable
10/100/1000Mbps and auto MDI/MDIX crossover detection function, this
function gives true “plug and play” capability, just need to plug-in the
network cable to the hub directly and don’t care if the end node is NIC
(Network Interface Card) or switch and hub.
half-duplex mode for 10/100Mbps and full- duplex mode for
10/100/1000Mbps.
Mini GBIC Ports
The Switch is equipped with two mini-GBIC ports, supported optional
1000BASE-SX/LX mini-GBIC module.
Note: When the port was set to “Forced Mode”, the Auto
MDI/MDIX will be disabled.
These ports can operate in
13
Page 20
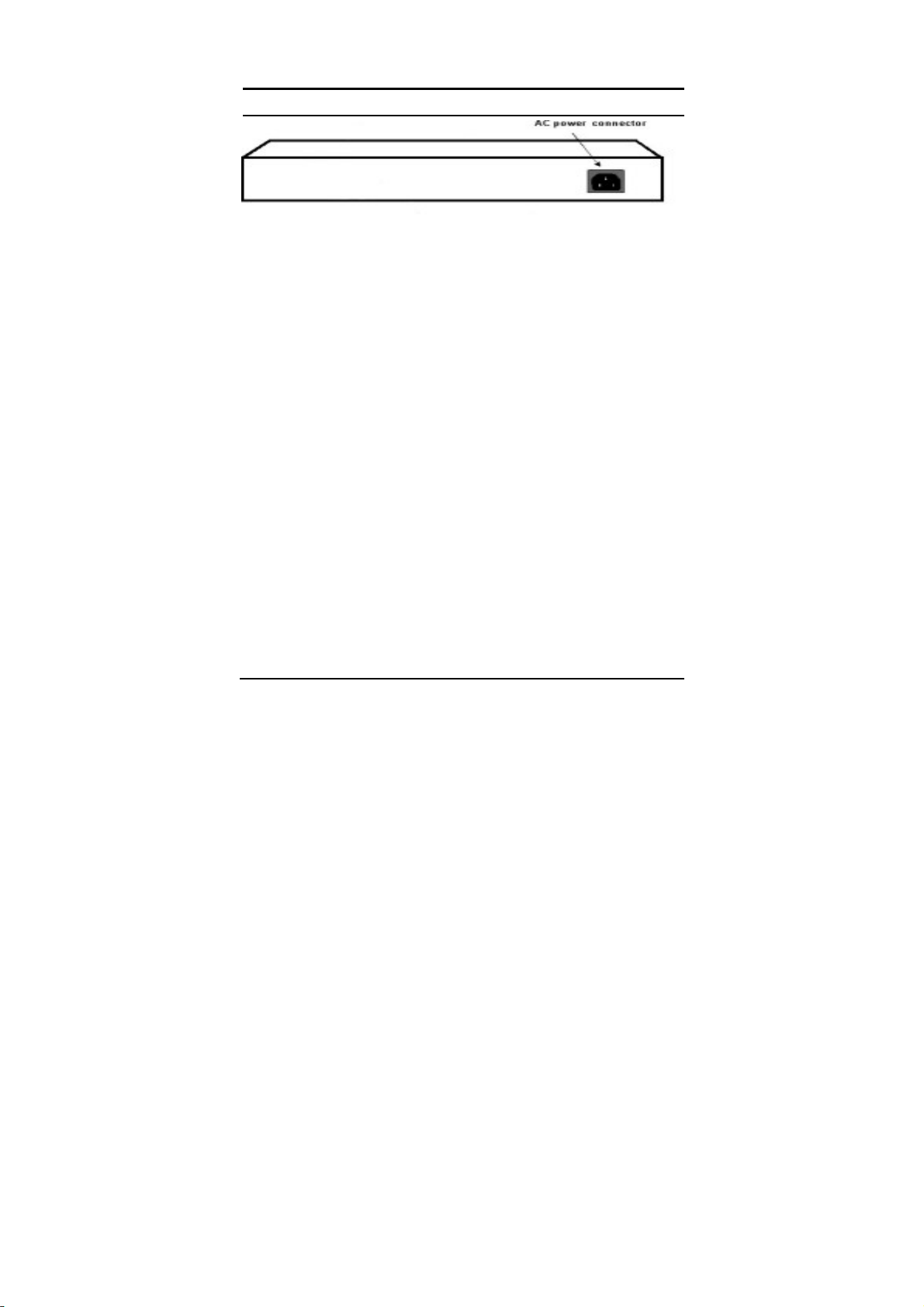
Rear Panel
b
●
Reset
utton
Figure 5. Rear panel of the Switch
AC Power Connector:
This is a three-pronged connector that supports the power cord. Plug
in the female connector of the provided power cord into this connector,
and the male into a power outlet. Supported input voltages range from
100-240V AC at 50-60Hz.
Reset:
The Reset button is to reset all the setting back to the factory default.
Note: Be sure that you recorded the setting of your device, else all
the setting will be erased when pressing the “Reset” button.
14
Page 21

UNDERSTANDING LED INDICATORS
The front panel LEDs provides instant status feedback, and, helps
monitor and troubleshoot when needed.
Figure 6. LED indicators of the Switch
Power and System LEDs
POWER: Power Indicator
On : When the Power LED lights on, the Switch is receiving power.
Off : When the Power turns off or the power cord has improper connection.
CPU: Management Indicator
Blinking : When the CPU is working, the System LED is blinking.
On/Off : The CPU is not working.
15
Page 22

Ports 1~24 Status LEDs
Link/ACT: Link/Activity
On : When the Link/ACT LED lights on, the respective port is
Blinking : When the Link/ACT LED is blinking, the port is transmitting or
Off : No link.
successfully connected to an Ethernet network.
receiving data on the Ethernet network.
100/1000Mbps
Green : When the 1000Mbps LED lights Green, the respective port is
Amber : When the 100Mbps LED lights Amber, the respective port is
Off : When the respective port is connected to a 10Mbps Ethernet
connected to a 1000Mbps Gigabit Ethernet network.
connected to a 100Mbps Fast Ethernet network.
Option Ports mini-GBIC 1 & mini-GBIC 2 mini-GBIC
Status LEDs
Link/ACT: Link/Activity
On : When the mini-GBIC module is installed and connected to a
Blinking : When the LED is blinking, the mini-GBIC module is
Off : No link.
network, the Link/ACT LED lights on.
receiving data on a network.
1000Mbps
On :
Off :
When the 1000Mbps LED lights on, the respective port is
connected to a 1000Mbps Gigabit Ethernet network.
When the respective port is disconnected to the network
16
Page 23

CONFIGURATION
Through the Web Browser you can configure the Switch such as
VLAN, Trunking, QoS… etc.
With the attached Web Management Utility, you can easily discover
all the Web Management Switch, assign the IP Address, changing the
password and upgrading the new firmware.
Installing the Web Management Utility
The following gives instructions guiding you through the installations
of the Web Management utility.
1. Insert the Utility CD in the CD-Rom Drive.
2. From the Start menu on the Windows desktop, choose Run.
3. In the Run dialog box, type D:\Web Management
Utility\setup.exe (D:\ depends where your CD-Rom drive is
located) and click OK.
4. Follow the on-screen instructions to install the utility.
5. Upon completion, go to Program Files ->
web_management_utility and execute the Web Management
utility. (
Figure 7)
17
Page 24

Figure 7. Web Management Utility
The Web Management Utility was divided into four parts, Discovery
List, Monitor List, Device Setting and Toolbar function, for details
instruction, follow the below section.
Discovery List
This is the list where you can discover all the Web management
devices in the entire network.
By pressing the “Discovery” button, you can list all the Web
Management devices in the discovery list.
Double click or press the “Add to monitor list” button to select a
device from the Discovery List to the Monitor List.
18
Page 25

System word definitions in the Discovery List:
z MAC Address: Shows the device MAC Address.
z IP Address: Shows the current IP address of the device.
z Protocol version: Shows the version of the Utility protocol.
z Product Name: Shows the device product name.
z System Name: Shows the appointed device system name.
z Location: Shows where the device is located.
z Trap IP: Shows the IP where the Trap to be sent.
z Subnet Mask: Shows the Subnet Mask set of the device.
z Gateway: Shows the Gateway set of the device.
Monitor List
All the Web Smart Device in the Monitor List can be monitored; you
can also receive the trap and show the status of the device.
System word definitions in the Monitor List:
z S: Shows the system symbol of the Web-Smart device,
represent for device system is not alive.
z IP Address: Shows the current IP address of the device.
z MAC Address: Shows the device MAC Address.
z Protocol version: Shows the version of the Utility protocol.
z Product Name: Shows the device product name.
z System Name: Shows the appointed device system name.
z Location: Shows where the device is located.
z Trap IP: Shows the IP where the Trap to be sent.
z Subnet Mask: Shows the Subnet Mask set of the device.
z Gateway: Shows the Gateway set of the device.
19
Page 26

View Trap: The Trap function can receive the events that happen
from the Web Management Switch in the Monitor List.
There is a light indicator behind the “View Trap” button, when the
light indicates in green, it means that there is no trap transmitted, and
else when it indicates in red, it means that there is new trap
transmitted, this is to remind us to view the trap. (
Figure 8. View trap
Figure 8)
When the “View Trap” button is clicked, a Trap Information window
will pop out, it will show the trap information including the Symbol,
Time, Device IP and the Event occurred. (
Figure 9)
The symbol “
” represents the trap signal arise, this symbol will
disappear after you review and click on the event record.
Figure 9. Trap information
Note: In order to receive Trap information, switch has to be configured with
Trap IP and Trap Events in Web browser, which are available in the Trap
Setting Menu (see Page 46 for detail).
Add Item: To add a device to the Monitor List manually, enter the IP
Address of the device that you want to monitor.
Delete Item: To delete the device in the Monitor List.
20
Page 27

Device Setting
You can set the device by using the function key in the Device Setting
Dialog box.
Configuration Setting: In this Configuration Setting, you can set the
IP Address, Subnet Mask, Gateway, Set Trap to (Trap IP Address),
System name and Location.
Select the device in the Discovery list or Monitor List and press this
button, then the Configuration Setting window will pop out as
after filling up the data that you want to change, you must fill up the
password and press the “Set” to process the data changed immediately.
Figure 10. Configuration Setting
Password Change: You can use this Password Change when you
need to change the password, fill in the password needed in the dialog
box and press “Set” button to proceed the password change
immediately.
Figure 10,
Figure 11. Password Change
21
Page 28

Firmware Upgrade: When the device has a new function, there will
be a new firmware to update the device, use this function to update.
Figure 12. Firmware Upgrade
Web Access: Double click the device in the Monitor List or select a
device in the Monitor List and press this “Web Access” button to
access the device in Web browser.
Toolbar
The toolbar in the Web Management Utility have four main tabs, File,
View, Options and Help.
In the “File TAB”, there are Monitor Save, Monitor Save As, Monitor
Load and Exit.
Monitor Save: To record the setting of the Monitor List to the
default, when you open the Web Management Utility next time, it
will auto load the default recorded setting.
Monitor Save As: To record the setting of the Monitor List in
appointed filename and file path.
Monitor Load: To manually load the setting file of the Monitor List.
Exit: To exit the Web Management Utility.
22
Page 29

In the “View TAB”, there are view log and clear log function, this
function will help you to show trap setting.
View Log: To show the event of the Web Management Utility and
the device.
Clear Log: to clear the log.
In the “Option TAB”, there are Refresh Time function, this function
helps you to refresh the time of monitoring the device. Choose 15 secs,
30 secs, 1 min, 2 min and 5 min to select the time of monitoring.
In the “Help TAB”, there is About function, it will show out the
version of the Web Management Utility.
Configuring the Switch
The DGS-1224T Web Smart Switch has a Web GUI interface for
smart switch configuration. The Switch can be configured through the
Web Browser. A network administrator can manage, control and
monitor the switch from the local LAN. This section indicates how to
configure the Switch to enable its smart functions including:
Port Setting (Speed/Disable, Duplex mode, Flow Control,
Priority)
Virtual LAN Group setting (VLAN)
Port Trunking
Port Mirroring
QoS
Jumbo frame
Spanning Tree
SNMP
System Setting
Device status and Statistic
23
Page 30

Login
Before you configure this device, note that when the Web Smart
Switch is configured through an Ethernet connection, make sure the
manager PC must be set on same the IP network. For example, when
the default network address of the default IP address of the Web Smart
Switch is 192.168.0.1, then the manager PC should be set at
192.168.0.x (where x is a number between 2 and 254), and the default
subnet mask is 255.255.255.0.
Open Internet Explorer 5.0 or above Web browser.
Enter IP address http://192.168.0.1
setting) to the address location.
Or through the Web Management Utility, you do not need to
remember the IP Address, select the device shown in the Monitor List
of the Web Management Utility to settle the device on the Web
Browser.
When the following dialog page appears, remain enter the default
password "admin" and press Login to enter the main configuration
window.
(the factory-default IP address
Figure 13.
Figure 14.
24
Page 31

After entering the password, the main page comes up, the screen will
display the device status.
Figure 15. Device Status
Setup Menu
When the main page appears, find the Setup menu in the left side of
the screen (
configure. There are fifteen options: Port Settings, VLAN Settings,
Trunk Setting, Mirror Setting, QoS Setting, Spanning Tree Setting,
SNMP Setting, Jumbo Frame Setting, Device Status, Statistic, System
Settings, Trap Setting, Password Setting, Backup Setting and Reset
Setting as shown in the Main Menu screen.
Figure 16). Click on the setup item that you want to
25
Page 32

Figure 16. Setup menu
26
Page 33

Configuring Setup Setting
Find that there are eight items, including Port Settings, VLAN Settings,
Trunk Settings, Mirror Settings, QoS Setting, Spanning Tree Setting,
SNMP Setting and Jumbo Frame Setting in Setup menu.
Port Settings
In Port Settings menu (Figure 17), this page will show each port’s status,
press the ID parameter to set each port’s Speed, Flow Control, QoS
priority and Link Status. When you need to renew the posted
information, press the “Refresh” button.
The Link Status in the screen will show the connection speed and
duplex mode; else this dialog box will show down when the port is
disconnected.
Figure 17. Port Setting
Note:
1. Be sure that you have to re-setting the Gigabit port
when transferring the media type (Fiber to Copper or
Copper to Fiber).
27
Page 34

The priority of Gigabit Fiber port is higher than Copper.
To change the port setting, click on the ID parameter to enter to the
selected port to configure its Speed/Disable and Flow control setting.
Figure 18.
Speed/Disable:
This setting has six modes—100M Full, 100M Half, 10M Full, 10M
Half, Auto and Disable—for speed or port disable selections.
Flow Control:
This setting determines whether or not the Switch will be handling
flow control. Set FlowCtrl to Enable for avoiding data transfer
overflow. Or it sets to Disable; there is either no flow control or other
hardware/software management.
When the port is set to forced mode, then the flow control will
automatically set to Disable.
Default Priority:
The Default Priority is specific the 802.1P QoS priority level to
related port, all of the received data packet will follow the Default
Priority level forwarding data packet to other port.
28
Page 35

VLAN Settings (Virtual Local Area Network)
VID Table Setting: select the VID group that you set.
When you select VID Table Setting, press “Add new VID” to create
new VID group, from port 01 ~ port 24, select Untag Port, Tag Port
or Not Member for each port. To save the VID group, press
“Apply” button. To remove the selected VID group, select the VID
group and press “Remove the VID” button. To modify the VID
group setting, select the VID group and change the setting, and
press “Apply” button to save the settings.
Figure 19. 802.1Q VID Table Setting
Port VID Setting:
When you select Port VLAN setting, fill in each port’s PVID value
between 1 and 4094.
29
Page 36

Figure 20. 802.1Q Port VID Setting
Trunk Setting
The Trunk function enables to cascade two or more devices with a
larger bandwidths.
There are three Trunk groups to be set; and there are default ports in
each member. Checked “Enable” to use the trunk function, select
the ports in each member to be trunk, and click “Apply” to activate
the selected trunk group.
30
Page 37

Figure 21. Trunk Settings
Be sure that the selected trunk setting port must connect to the
device with a same VLAN group.
Mirror Setting
Port Mirroring is a method of monitoring network traffic that forwards
a copy of each incoming and/or outgoing packet from one port of a
network switch to another port where the packet can be studied. It
enables the manager to keep close track of switch performance and
alter it if necessary.
Configuring the port mirroring by assigning a source port from which
to copy all packets and a sniffer port where those packets will be sent.
The selection of the sniffer mode is as follow:
TX (transmit) mode: this mode will duplicate the data transmit from
the source port and forward to the sniffer port.
RX (receive) mode: this mode will duplicate the data that send to the
source and forward to the sniffer port.
31
Page 38

Both (transmit and receive) mode: this mode will duplicate both the
data transmit from and data that send to the source port, then it will
forward to the sniffer port.
Figure 22. Mirror setting
32
Page 39

IEEE 802.1P QoS Setting
To set the Switch QoS base on IEEE 802.1p,
Figure 23. IEEE 802.1P-based QoS setting
Spanning Tree Setting
This Switch supports the 802.1d Spanning Tree Protocol.
Every segment will have a single path to the root bridge. All
bridges listen for BPDU packets. However, BPDU packets are sent
more frequently - with every Hello packet. BPDU packets are sent
even if a BPDU packet was not received. Therefore, each link
between bridges is sensitive to the status of the link. Ultimately this
difference results in faster detection of failed links, and thus faster
topology adjustment. A draw-back of 802.1d is this absence of
immediate feedback from adjacent bridges.
Figure 24. Spanning Tree Setting
33
Page 40

STP Function: To selecting enable or disable STP function on the
Switch.
Bridge Priority: This value between 0 and 65535 to specify the
priority for forwarding packets. The lower the value, the higher the
priority. The default is 32768.
Bridge Max Age: This value may be set to ensure that old
information does not endlessly circulate through redundant paths in
the network, preventing the effective propagation of the new
information. Set by the Root Bridge, this value will aid in
determining that the Switch has spanning tree configuration values
consistent with other devices on the bridged LAN. If the value ages
out and a BPDU has still not been received from the Root Bridge,
the Switch will start sending its own BPDU to all other switches for
permission to become the Root Bridge. If it turns out that your
switch has the lowest Bridge Identifier, it will become the Root
Bridge. The user may choose a time between 6 and 40 seconds. The
default value is 20.
Bridge Hello Time: The user may set the time interval between
transmission of configuration messages by the root device, thus
stating that the Switch is still functioning. A time between 1 and 10
seconds may be chosen, with a default setting of 2 seconds.
Bridge Forward Delay: The maximum amount of time (in seconds)
that the root device will wait before changing states. The user may
choose a time between 4 and 30 seconds. The default is 15 seconds.
Port Path Cost: This defines a metric that indicates the relative
cost of forwarding packets to specified port list. The value between
1 and 65535 to determine the cost. The lower the number, the
greater the probability the port will be chosen to forward packets.
The default value is 10.
34
Page 41

Port Path Priority: Select a value between 0 and 255 to specify the
priority for a specified port for forwarding packets. The lower the
value, the higher the priority. The default is 128.
SNMP Setting
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an OSI Layer 7
(Application Layer) designed specifically for managing and
monitoring network devices. SNMP enables network management
stations to read and modify the settings of gateways, routers, switches,
and other network devices. Use SNMP to configure system features
for proper operation, monitor performance and detect potential
problems in the Switch, switch group or network.
Managed devices that support SNMP include software (referred to as
an agent), which runs locally on the device. A defined set of variables
(managed objects) is maintained by the SNMP agent and used to
manage the device. These objects are defined in a Management
Information Base (MIB), which provides a standard presentation of
the information controlled by the on-board SNMP agent. SNMP
defines both the format of the MIB specifications and the protocol
used to access this information over the network.
The Switch supports the SNMP versions 1. In SNMP v.1, user
authentication is accomplished using 'community strings', which
function like passwords. The remote user SNMP application and the
Switch SNMP must use the same community string. SNMP packets
from any station that has not been authenticated are ignored (dropped).
The default community strings for the Switch used for SNMP v.1
management access are:
public - Allows authorized management stations to retrieve MIB
objects.
35
Page 42

private - Allows authorized management stations to retrieve and
modify MIB objects.
Traps
Traps are messages that alert network personnel of events that occur
on the Switch. The events can be as serious as a reboot (someone
accidentally turned OFF the Switch), or less serious like a port
status change. The Switch generates traps and sends them to the
trap recipient (or network manager). Typical traps include trap
messages for Device boot up, Authentication Failure, Port status
change and Abnormal transmit/receive data packet error.
MIBs
Management and counter information are stored by the Switch in the
Management Information Base (MIB). The Switch uses the standard
MIB-II Management Information Base module. Consequently, values
for MIB objects can be retrieved from any SNMP-based network
management software. In addition to the standard MIB-II, the Switch
also supports its own proprietary enterprise MIB as an extended
Management Information Base. The proprietary MIB may also be
retrieved by specifying the MIB Object Identifier. MIB values can be
either read-only or read-write.
Enabled / Disabled: To selecting enable or disable SNMP function
on the Switch.
36
Page 43

SNMP Community / Trap: To configure the SNMP Community or
SNMP Trap configuration.
Configure SNMP Community:
Figure 25. SNMP Community Setting
Add Group: To add a SNMP Community group, press “Add
Group” button, the Add SNMP Community configuration window
will pop out; fill in the community name and assign the community
enable read_only or read_write. Press “Apply” button to execute the
setting.
Figure 26. Add SNMP Community group
Delete Group: To delete previously defined SNMP Community
group, press “Delete Group” button, the Delete SNMP Community
37
Page 44

configuration window will pop out; checked the delete dialog box.
Press “Apply” to delete the selected SNMP Community Group.
Figure 27. Delete SNMP Community group
Modify Group: To modify previously defined SNMP Community
group, click on the ID parameter to enter to the selected SNMP
Community Group to configure its community name and
community enable. Press “Apply” to save change of the SNMP
Community Group.
Figure 28. Modify SNMP Community group
Configure SNMP Trap:
Figure 29. Configure SNMP Trap Setting
38
Page 45

Trap authentication fail: When checked the dialog box of the
Trap authentication fail, when fail to authentication, the Switch
will trap the authentication fail even to the SNMP host.
Add Trap: To create a recipient of SNMP traps generated by the
Switch’s SNMP agent, press “Add Trap” button, and the SNMP
Trap Set window will pop out; you can fill in the community name
and trap IP address of the remote management station that will
serve as the SNMP host for the Switch and checked the events
selection to enabled selected event traps.
Figure 30. Add SNMP Trap
Delete Trap: To delete previously defined SNMP Trap, press
“Delete Trap” button, the Delete SNMP Trap Delete configuration
window will pop out; checked the delete dialog box. Press “Apply”
to delete the selected SNMP Trap setting.
39
Page 46

Figure 31. Delete SNMP Trap
40
Page 47

Modify Trap: To modify previously defined SNMP Trap, click on
the ID parameter to enter to the selected SNMP Trap to configure
its community name, IP address and events. Press “Apply” to save
change of the SNMP Trap.
Figure 32. Modify SNMP Trap
Jumbo Frame Setting
To enable or disable the Jumbo Frame function on the Switch.
Figure 33. Jumbo frame setting
41
Page 48

Device Status
Click on the “Status” to present the device status on this screen, it will
show the System Status, Port Status, VLAN Status, Trunk Status and
Mirror Status.
Figure 34. Device Status
Press “Refresh” when you need to renew the posted information.
42
Page 49

Statistic
The Statistic Menu screen will show the status of each port packet
count.
Figure 35. Statistic
For Detail packet information, click on the ID parameter as Figure 36.
43
Page 50

Figure 36.
System Setting
The System Setting includes the System name, Location name, Login
Timeout, IP Address, Subnet Mask and Gateway. Through the Web
Management Utility, you can easily recognize the device by using the
System Name and the Location Name.
The Login Timeout is to set the idle time-out for security issue, when
there is no action in running the Web Smart Utility and the time is up,
you must re-login to Web Smart Utility before you set the Utility.
Fill up the IP Address, Subnet Mask and Gateway for the device.
44
Page 51

Figure 37. System Setting
45
Page 52

Trap Setting
The Trap Setting enables the device to monitor the Trap through the
Web Management Utility, set the Trap IP Address of the manager
where the trap to be sent.
Figure 38. Trap Setting
System Events: Monitoring the system’s trap.
Device Bootup: a trap when booting up the system.
Illegal Login: a trap when there is using a wrong password
login, and it will record from where the IP to be login.
Fiber Port Events: Monitoring the Fiber port status.
Link Up/Link Down: a trap when there is linking status
happens in fiber port.
Abnormal* Receive Error: a trap when there are receive data
error in fiber port.
Abnormal* Transmit Error: a trap when there are transmit
data error in fiber port.
Copper Port Events: Monitoring the Copper port status.
Link Up/Link Down: a trap when there is linking status
happens in copper port.
46
Page 53

Abnormal* Receive Error: a trap when there are receive data
error in copper port.
Abnormal* Transmit Error: a trap when there are transmit
data error in copprt port.
Abnormal*: 50 error packet count within 10 seconds.
Set Password
Password is the invaluable tool for the manager to secure Web
Management Switch, use this function to change the password.
If you forget the password, press the “Reset” button in the rear panel
of the Switch, the current setting includes VLAN, Port Setting… etc.
will be lost and the Switch will restore to the default setting.
Figure 39. Set Password
47
Page 54

Backup Setting
The backup tools help you to backup the current setting of the Switch.
Once you need to backup the setting, press the “Backup” button to
save the setting.
To restore a current setting file to the device, you must specify the
backup file and press “Restore” button to proceed the setting of the
recorded file.
Figure 40. Backup Setting
Note: when restoring a recorded file, the current password will not be erased.
Reset Setting
The Factory Reset button helps you to reset the device back to the
default setting from the factory. Be aware that the entire configuration
will be reset, the IP address of the device will be set to default setting
192.168.0.1.
Figure 41. Reset Setting
48
Page 55

Logout
When press this function, the web configuration will go back to first
Login page.
Figure 42. Logout
49
Page 56

Page 57

TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
General
Standards IEEE 802.3 10BASE-T Ethernet
Protocol CSMA/CD
Data Transfer Rate Ethernet: 10Mbps (half duplex), 20Mbps (full-duplex)
Topology Star
Network Cables 10BASET: 2-pair UTP Cat. 3, 4, 5; up to 100m
Number of Ports 24 × 10/100/1000Mbps Auto-MDIX RJ-45 ports
IEEE 802.3u 100BASE-TX Fast Ethernet
IEEE 802.3ab 1000BASE-T Gigabit Ethernet
IEEE 802.3x Full Duplex Flow Control
IEEE 802.3z 1000BASE-SX/LX Gigabit Ethernet
Fast Ethernet: 100Mbps (half duplex), 200Mbps (full-duplex)
Gigabit Ethernet: 2000Mbps (full-duplex)
100BASE-TX: 2-pair UTP Cat. 5; up to 100m
1000BASE-T: 4-pair UTP Cat. 5; up to 100m
Fiber module: mini-GBIC Fiber module
2 × mini-GBIC fiber slot
Physical and Environmental
AC inputs 100-240V AC, 50/60 Hz internal universal power supply
Power Consumption 32 Watts (Max)
Temperature
Humidity Operating: 10% ~ 90%, Storage: 5% ~ 90%
Dimensions 440 x 210 x 44 mm (W x H x D)
EMI: FCC Class A, CE Mark Class A, VCCI Class A
Safety: CUL, LVD
Operating: 0° ~ 50° C, Storage: -10° ~ 70° C
37
Page 58

Transmits Method: Store-and-forward
Filtering Address Table: 8K entries per device
Packet
Filtering/Forwarding Rate:
MAC Address Learning: Automatic update
Transmits Method: Store-and-forward
RAM Buffer: 512K bytes per device
1000Mbps Gigabit Ethernet: 1,488,000/pps
Performance
38
Page 59

Subject to the terms and conditions set forth herein, D-Link Systems, Inc. (“D-Link”) provides this Limited Warranty:
• Only to the person or entity that originally purchased the product from D-Link or its authorized reseller or distributor, and
• Only for products purchased and delivered within the fifty states of the United States, the District of Columbia, U.S. Possessions or Protectorates, U.S.
Military Installations, or addresses with an APO or FPO.
Limited Warranty: D-Link warrants that the hardware portion of the D-Link product described below (“Hardware”) will be free from material defects in
workmanship and materials under normal use from the date of original retail purchase of the product, for the period set forth below (“Warranty Period”), except
as otherwise stated herein.
• Hardware (excluding power supplies and fans): Five (5) Years
• Power supplies and fans: One (1) Year
• Spare parts and spare kits: Ninety (90) days
The customer's sole and exclusive remedy and the entire liability of D-Link and its suppliers under this Limited Warranty will be, at D-Link’s option, to repair or
replace the defective Hardware during the Warranty Period at no charge to the original owner or to refund the actual purchase price paid. Any repair or
replacement will be rendered by D-Link at an Authorized D-Link Service Office. The replacement hardware need not be new or have an identical make, model
or part. D-Link may, at its option, replace the defective Hardware or any part thereof with any reconditioned product that D-Link reasonably determines is
substantially equivalent (or superior) in all material respects to the defective Hardware. Repaired or replacement hardware will be warranted for the remainder
of the original Warranty Period or ninety (90) days, whichever is longer, and is subject to the same limitations and exclusions. If a material defect is incapable
of correction, or if D-Link determines that it is not practical to repair or replace the defective Hardware, the actual price paid by the original purchaser for the
defective Hardware will be refunded by D-Link upon return to D-Link of the defective Hardware. All Hardware or part thereof that is replaced by D-Link, or for
which the purchase price is refunded, shall become the property of D-Link upon replacement or refund.
Limited Software Warranty: D-Link warrants that the software portion of the product (“Software”) will substantially conform to D-Link’s then current functional
specifications for the Software, as set forth in the applicable documentation, from the date of original retail purchase of the Software for a period of ninety (90)
days (“Software Warranty Period”), provided that the Software is properly installed on approved hardware and operated as contemplated in its documentation.
D-Link further warrants that, during the Software Warranty Period, the magnetic media on which D-Link delivers the Software will be free of physical defects.
The customer's sole and exclusive remedy and the entire liability of D-Link and its suppliers under this Limited Warranty will be, at D-Link’s option, to replace
the non-conforming Software (or defective media) with software that substantially conforms to D-Link’s functional specifications for the Software or to refund
the portion of the actual purchase price paid that is attributable to the Software. Except as otherwise agreed by D-Link in writing, the replacement Software is
provided only to the original licensee, and is subject to the terms and conditions of the license granted by D-Link for the Software. Replacement Software will
be warranted for the remainder of the original Warranty Period and is subject to the same limitations and exclusions. If a material non-conformance is
incapable of correction, or if D-Link determines in its sole discretion that it is not practical to replace the non-conforming Software, the price paid by the original
licensee for the non-conforming Software will be refunded by D-Link; provided that the non-conforming Software (and all copies thereof) is first returned to DLink. The license granted respecting any Software for which a refund is given automatically terminates.
Non-Applicability of Warranty: The Limited Warranty provided hereunder for Hardware and Software portions of D-Link's products will not be applied to and
does not cover any refurbished product and any product purchased through the inventory clearance or liquidation sale or other sales in which D-Link, the
sellers, or the liquidators expressly disclaim their warranty obligation pertaining to the product and in that case, the product is being sold "As-Is" without any
warranty whatsoever including, without limitation, the Limited Warranty as described herein, notwithstanding anything stated herein to the contrary.
Submitting A Claim: The customer shall return the product to the original purchase point based on its return policy. In case the return policy period has
expired and the product is within warranty, the customer shall submit a claim to D-Link as outlined below:
• The customer must submit with the product as part of the claim a written description of the Hardware defect or Software nonconformance in sufficient
detail to allow D-Link to confirm the same, along with proof of purchase of the product (such as a copy of the dated purchase invoice for the product) if the
product is not registered.
• The customer must obtain a Case ID Number from D-Link Technical Support at 1-877-453-5465, who will attempt to assist the customer in resolving any
suspected defects with the product. If the product is considered defective, the customer must obtain a Return Material Authorization (“RMA”) number by
completing the RMA form and entering the assigned Case ID Number at https://rma.dlink.com/
• After an RMA number is issued, the defective product must be packaged securely in the original or other suitable shipping package to ensure that it will
not be damaged in transit, and the RMA number must be prominently marked on the outside of the package. Do not include any manuals or accessories
in the shipping package. D-Link will only replace the defective portion of the product and will not ship back any accessories.
• The customer is responsible for all in-bound shipping charges to D-Link. No Cash on Delivery (“COD”) is allowed. Products sent COD will either be
rejected by D-Link or become the property of D-Link. Products shall be fully insured by the customer and shipped to D-Link Systems, Inc., 17595 Mt.
Herrmann, Fountain Valley, CA 92708. D-Link will not be held responsible for any packages that are lost in transit to D-Link. The repaired or replaced
packages will be shipped to the customer via UPS Ground or any common carrier selected by D-Link. Return shipping charges shall be prepaid by DLink if you use an address in the United States, otherwise we will ship the product to you freight collect. Expedited shipping is available upon request and
provided shipping charges are prepaid by the customer.
D-Link may reject or return any product that is not packaged and shipped in strict compliance with the foregoing requirements, or for which an RMA number is
not visible from the outside of the package. The product owner agrees to pay D-Link’s reasonable handling and return shipping charges for any product that is
not packaged and shipped in accordance with the foregoing requirements, or that is determined by D-Link not to be defective or non-conforming.
What Is Not Covered: The Limited Warranty provided herein by D-Link does not cover: Products that, in D-Link’s judgment, have been subjected to abuse,
accident, alteration, modification, tampering, negligence, misuse, faulty installation, lack of reasonable care, repair or service in any way that is not
contemplated in the documentation for the product, or if the model or serial number has been altered, tampered with, defaced or removed; Initial installation,
installation and removal of the product for repair, and shipping costs; Operational adjustments covered in the operating manual for the product, and normal
maintenance; Damage that occurs in shipment, due to act of God, failures due to power surge, and cosmetic damage; Any hardware, software, firmware or
other products or services provided by anyone other than D-Link; and Products that have been purchased from inventory clearance or liquidation sales or
other sales in which D-Link, the sellers, or the liquidators expressly disclaim their warranty obligation pertaining to the product. While necessary maintenance
or repairs on your Product can be performed by any company, we recommend that you use only an Authorized D-Link Service Office. Improper or incorrectly
performed maintenance or repair voids this Limited Warranty.
Disclaimer of Other Warranties: EXCEPT FOR THE LIMITED WARRANTY SPECIFIED HEREIN, THE PRODUCT IS PROVIDED “AS-IS” WITHOUT ANY
WARRANTY OF ANY KIND WHATSOEVER INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NON-INFRINGEMENT. IF ANY IMPLIED WARRANTY CANNOT BE DISCLAIMED IN ANY TERRITORY WHERE A
PRODUCT IS SOLD, THE DURATION OF SUCH IMPLIED WARRANTY SHALL BE LIMITED TO THE DURATION OF THE APPLICABLE WARRANTY
PERIOD SET FORTH ABOVE. EXCEPT AS EXPRESSLY COVERED UNDER THE LIMITED WARRANTY PROVIDED HEREIN, THE ENTIRE RISK AS TO
THE QUALITY, SELECTION AND PERFORMANCE OF THE PRODUCT IS WITH THE PURCHASER OF THE PRODUCT.
.
Page 60

Limitation of Liability: TO THE MAXIMUM EXTENT PERMITTED BY LAW, D-LINK IS NOT LIABLE UNDER ANY CONTRACT, NEGLIGENCE, STRICT
LIABILITY OR OTHER LEGAL OR EQUITABLE THEORY FOR ANY LOSS OF USE OF THE PRODUCT, INCONVENIENCE OR DAMAGES OF ANY
CHARACTER, WHETHER DIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, DAMAGES FOR LOSS OF
GOODWILL, LOSS OF REVENUE OR PROFIT, WORK STOPPAGE, COMPUTER FAILURE OR MALFUNCTION, FAILURE OF OTHER EQUIPMENT OR
COMPUTER PROGRAMS TO WHICH D-LINK’S PRODUCT IS CONNECTED WITH, LOSS OF INFORMATION OR DATA CONTAINED IN, STORED ON,
OR INTEGRATED WITH ANY PRODUCT RETURNED TO D-LINK FOR WARRANTY SERVICE) RESULTING FROM THE USE OF THE PRODUCT,
RELATING TO WARRANTY SERVICE, OR ARISING OUT OF ANY BREACH OF THIS LIMITED WARRANTY, EVEN IF D-LINK HAS BEEN ADVISED OF
THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. THE SOLE REMEDY FOR A BREACH OF THE FOREGOING LIMITED WARRANTY IS REPAIR, REPLACEMENT
OR REFUND OF THE DEFECTIVE OR NON-CONFORMING PRODUCT. THE MAXIMUM LIABILITY OF D-LINK UNDER THIS WARRANTY IS LIMITED TO
THE PURCHASE PRICE OF THE PRODUCT COVERED BY THE WARRANTY. THE FOREGOING EXPRESS WRITTEN WARRANTIES AND REMEDIES
ARE EXCLUSIVE AND ARE IN LIEU OF ANY OTHER WARRANTIES OR REMEDIES, EXPRESS, IMPLIED OR STATUTORY.
Governing Law: This Limited Warranty shall be governed by the laws of the State of California. Some states do not allow exclusion or limitation of incidental
or consequential damages, or limitations on how long an implied warranty lasts, so the foregoing limitations and exclusions may not apply. This Limited
Warranty provides specific legal rights and you may also have other rights which vary from state to state.
Trademarks: D-Link is a registered trademark of D-Link Systems, Inc. Other trademarks or registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Copyright Statement: No part of this publication or documentation accompanying this product may be reproduced in any form or by any means or used to
make any derivative such as translation, transformation, or adaptation without permission from D-Link Corporation/D-Link Systems, Inc., as stipulated by the
United States Copyright Act of 1976 and any amendments thereto. Contents are subject to change without prior notice. Copyright 2004 by D-Link
Corporation/D-Link Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
CE Mark Warning: This is a Class A product. In a residential environment, this product may cause radio interference, in which case the user may be required
to take adequate measures.
FCC Statement: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These
limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a commercial installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate
radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communication. However,
there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. Operation of this equipment in a residential environment is likely to cause
harmful interference to radio or television reception. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be
determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
For detailed warranty information applicable to products purchased outside the United States, please contact the corresponding
local D-Link office.
Page 61

Product Registration
Register online your D-Link product at http://support.dlink.com/register/
Product registration is entirely voluntary and failure to complete or return this form will
not diminish your warranty rights.
Page 62

International Offices
o
U.S.A
17595 Mt. Herrmann Street
Fountain Valley, CA 92708
TEL: 1-800-326-1688
URL: www.dlink.com
Canada
2180 Winston Park Drive
Oakville, Ontario, L6H 5W1
Canada
TEL: 1-905-8295033
FAX: 1-905-8295223
URL: www.dlink.ca
Europe (U. K.)
th
Floor, Merit House
4
Edgware Road, Colindale
London NW9 5AB
U.K.
TEL: 44-20-8731-5555
FAX: 44-20-8731-5511
URL: www.dlink.co.uk
Germany
Schwalbacher Strasse 74
D-65760 Eschborn
Germany
TEL: 49-6196-77990
FAX: 49-6196-7799300
URL: www.dlink.de
France
No.2 all’ee de la Fresnerie
78330 Fontenay le Fleury
France
TEL: 33-1-30238688
FAX: 33-1-30238689
URL: www.dlink.fr
Netherlands
Weena 290
3012 NJ, Rotterdam
Netherlands
Tel: +31-10-282-1445
Fax: +31-10-282-1331
URL: www.dlink.nl
Belgium
Rue des Colonies 11
B-1000 Brussels
Belgium
Tel: +32(0)2 517 7111
Fax: +32(0)2 517 6500
URL: www.dlink.be
Italy
Via Nino Bonnet n. 6/b
20154 – Milano
Italy
TEL: 39-02-2900-0676
FAX: 39-02-2900-1723
URL: www.dlink.it
Sweden
P.O. Box 15036, S-167 15 Bromma
Sweden
TEL: 46-(0)8564-61900
FAX: 46-(0)8564-61901
URL: www.dlink.se
Denmark
Naverland 2, DK-2600
Glostrup, Copenhagen
Denmark
TEL: 45-43-969040
FAX: 45-43-424347
URL: www.dlink.dk
Norway
Karihaugveien 89
N-1086 Oslo
Norway
TEL: +47 99 300 100
FAX: +47 22 30 95 80
URL: www.dlink.no
Finland
Latokartanontie 7A
FIN-00700 HELSINKI
Finland
TEL: +358-10 309 8840
FAX: +358-10 309 8841
URL: www.dlink.fi
Spain
Avenida Diagonal, 593-95, 9th floor
08014 Barcelona
Spain
TEL: 34 93 4090770
FAX: 34 93 4910795
URL: www.dlink.es
Portugal
Rua Fernando Pahla
50 Edificio Simol
1900 Lisbon Portugal
TEL: +351 21 8688493
URL: www.dlink.es
Czech Republic
Vaclavske namesti 36, Praha 1
Czech Republic
TEL :+420 (603) 276 589
URL: www.dlink.cz
Switzerland
Glatt Tower, 2.OG CH-8301
Glattzentrum Postfach 2.OG
Switzerland
TEL : +41 (0) 1 832 11 00
FAX: +41 (0) 1 832 11 01
URL: www.dlink.ch
Greece
101, Panagoulis Str. 163-43
Helioupolis Athens, Greece
TEL : +30 210 9914 512
FAX: +30 210 9916902
URL: www.dlink.gr
Luxemburg
Rue des Colonies 11,
B-1000 Brussels,
Belgium
TEL: +32 (0)2 517 7111
FAX: +32 (0)2 517 6500
URL: www.dlink.be
Poland
Budynek Aurum ul. Walic-w 11
PL-00-851
Warszawa
Poland
TEL : +48 (0) 22 583 92 75
FAX: +48 (0) 22 583 92 76
URL: www.dlink.pl
Hungary
R-k-czi-t 70-72
HU-1074
Budapest
Hungary
TEL : +36 (0) 1 461 30 00
FAX: +36 (0) 1 461 30 09
URL: www.dlink.hu
Singapore
1 International Business Park
#03-12 The Synergy
Singapore 609917
TEL: 65-6774-6233
FAX: 65-6774-6322
URL: www.dlink-intl.com
Australia
1 Giffnock Avenue
North Ryde, NSW 2113
Australia
TEL: 61-2-8899-1800
FAX: 61-2-8899-1868
URL: www.dlink.com.au
India
D-Link House, Kurla Bandra Complex Road
Off CST Road, Santacruz (East)
Mumbai - 400098
India
TEL: 91-022-26526696/56902210
FAX: 91-022-26528914
URL: www.dlink.co.in
Middle East (Dubai)
P.O.Box: 500376
Office: 103, Building:3
Dubai Internet City
Dubai, United Arab Emirates
Tel: +971-4-3916480
Fax: +971-4-3908881
URL: www.dlink-me.com
Turkey
Ayazaga Maslak Yolu
Erdebil Cevahir Is Merkezi
5/A Ayazaga – Istanbul
Turkiye
TEL: +90 212 289 56 59
FAX: +90 212 289 76 06
URL: www.dlink.com.tr
Egypt
19 El-Shahed Helmy, El Masri
Al-Maza, Heliopolis
Cairo, Egypt
TEL:+202 414 4295
FAX:+202 415 6704
URL: www.dlink-me.com
Israel
11 Hamanofim Street
Ackerstein Towers, Regus Business Center
P.O.B 2148, Hertzelia-Pituach 46120
Israel
TEL: +972-9-9715700
FAX: +972-9-9715601
URL: www.dlink.co.il
LatinAmerica
Isidora Goyeechea 2934
Ofcina 702
Las Condes
Santiago – Chile
TEL: 56-2-232-3185
FAX: 56-2-232-0923
URL: www.dlink.cl
Brazil
Av das Nacoes Unidas
11857 – 14- andar - cj 141/142
Brooklin Novo
Sao Paulo - SP - Brazil
CEP 04578-000 (Zip Code)
TEL: (55 11) 21859300
FAX: (55 11) 21859322
URL: www.dlinkbrasil.com.br
South Africa
Einstein Park II
Block B
102-106 Witch-Hazel Avenue
Highveld Technopark
Centurion
Gauteng
Republic of South Africa
TEL: 27-12-665-2165
FAX: 27-12-665-2186
URL: www.d-link.co.za
Russia
Grafsky per., 14, floor 6
Moscow
129626 Russia
TEL: 7-095-744-0099
FAX: 7-095-744-0099 #350
URL: www.dlink.ru
China
No.202,C1 Building, Huitong Office Park, No. 71, Jiangu
Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing
100025, China.
TEL +86-10-58635800
FAX: +86-10-58635799
URL: www.dlink.com.cn
Taiwan
2F, No. 119, Pao-Chung Rd.
Hsin-Tien, Taipei
Tai wa n
TEL: 886-2-2910-2626
FAX: 886-2-2910-1515
URL: www.dlinktw.com.tw
Headquarters
2F, No. 233-2, Pao-Chiao Rd.
Hsin-Tien, Taipei
Tai wa n
TEL: 886-2-2916-1600
FAX: 886-2-2914-6299
URL: www.dlink.com.tw
Page 63

Registration Card
All Countries and Regions Excluding USA
Print, type or use block letters.
Your name: Mr./Ms_____________________________________________________________________________
Organization: ________________________________________________ Dept. ____________________________
Your title at organization: ________________________________________________________________________
Telephone: ______________ _________________________ Fax:___________________________ _____________
Organization's full address: ______________________________________________________________________
__________________________ ___________________________________________ _______________________
Country: _____________________________________________________________________________________
Date of purchase (Month/Day/Year): _______________________________________________________________
Product Model Product Serial No. * Product installed in type of
computer
Product was purchased from:
Reseller's name: ______________________________________________________________________________
Telephone: _______________________________________
Answers to the following questions help us to support your product:
1. Where and how will the product primarily be used?
Home Office Travel Company Business Home Business Personal Use
2. How many employees work at installation site?
1 employee 2-9 10-49 50-99 100-499 500-999 1000 or more
3. What network protocol(s) does your organization use ?
XNS/IPX TCP/IP DECnet Others_____________________________
4. What network operating system(s) does your organization use ?
D-Link LANsmart Novell NetWare NetWare Lite SCO Unix/Xenix PC NFS 3Com 3+Open Cisco Network
Banyan Vines DECnet Pathwork Windows NT Windows 98 Windows 2000/ME Windows XP
Others__________________________________________
5. What network management program does your organization use ?
D-View HP OpenView/Windows HP OpenView/Unix SunNet Manager Novell NMS
NetView 6000 Others________________________________________
6. What network medium/media does your organization use ?
Fiber-optics Thick coax Ethernet Thin coax Ethernet 10BASE-T UTP/STP
100BASE-TX 1000BASE-T Wireless 802.11b and 802.11g wireless 802.11a Others_________________
7. What applications are used on your network?
Desktop publishing Spreadsheet Word processing CAD/CAM
Database management Accounting Others_____________________
8. What category best describes your company?
Aerospace Engineering Education Finance Hospital Legal Insurance/Real Estate Manufacturing
Retail/Chain store/Wholesale Government Transportation/Utilities/Communication VAR
System house/company Other________________________________
9. Would you recommend your D-Link product to a friend?
Yes No Don't know yet
10.Your comments on this product?
__________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________
* Product installed in
computer serial No.
(* Applies to adapters only)
Page 64

 Loading...
Loading...