Feature and Technical Overview
BlackBerry Enterprise Server for Novell GroupWise
Version: 4.1 | Service Pack: 6

SWDT305802-456826-0820070122-001

Contents
1 New in this release............................................................................................................................................................. 3
2 BlackBerry Enterprise Server architecture.................................................................................................................... 9
Architecture: BlackBerry Enterprise Server............................................................................................................................. 9
Architecture: BlackBerry Enterprise Server remote components........................................................................................ 13
3 BlackBerry Enterprise Server components and features............................................................................................ 17
BlackBerry messaging and collaboration services................................................................................................................. 17
BlackBerry Messaging Agent................................................................................................................................................ 17
BlackBerry Collaboration Service......................................................................................................................................... 19
BlackBerry Synchronization Service..................................................................................................................................... 22
BlackBerry Attachment Service............................................................................................................................................. 23
BlackBerry MDS........................................................................................................................................................................... 24
BlackBerry Applications......................................................................................................................................................... 25
Types of BlackBerry Applications.......................................................................................................................................... 26
BlackBerry MDS Connection Service................................................................................................................................... 27
BlackBerry MDS Integration Service.................................................................................................................................... 28
BlackBerry device management................................................................................................................................................ 30
Wireless implementation of BlackBerry devices................................................................................................................. 30
Centralized maintenance of BlackBerry devices................................................................................................................ 30
Controlling third-party applications on BlackBerry devices............................................................................................ 31
BlackBerry Enterprise Solution security................................................................................................................................... 31
Master encryption keys.......................................................................................................................................................... 32
Standard message encryption............................................................................................................................................... 32
Options for encrypting stored data...................................................................................................................................... 33
Controlling BlackBerry device access to the BlackBerry Enterprise Server................................................................... 35
Management of BlackBerry device security over the wireless network using IT administration commands........... 36
BlackBerry Policy Service........................................................................................................................................................... 36
BlackBerry Configuration Panel................................................................................................................................................ 38
4 BlackBerry Enterprise Server process flows.................................................................................................................. 39
Messaging process flows............................................................................................................................................................ 39
Process flow: Connecting to a messaging server............................................................................................................... 39
Process flow: Sending a message to a BlackBerry device................................................................................................. 39

Process flow: Sending a message from a BlackBerry device............................................................................................ 40
Process flow: Searching an organization's address book from a BlackBerry device.................................................... 41
Instant messaging process flows.............................................................................................................................................. 42
Process flow: Starting an instant messaging session using the BlackBerry Client for use with Microsoft Office
Live Communications Server 2005 (Windows Messenger)............................................................................................... 42
Process flow: Starting an instant messaging session using the BlackBerry Client for use with Microsoft Office
Live Communications Server 2005 (Microsoft Office Communicator)........................................................................... 43
Process flow: Starting an instant messaging session using the BlackBerry Client for use with Microsoft Office
Communications Server 2007............................................................................................................................................... 45
Process flow: Starting an instant messaging session using the BlackBerry Client for IBM Lotus Sametime........... 46
Process flow: Starting an instant messaging session using the BlackBerry Client for Novell GroupWise Messenger
.................................................................................................................................................................................................... 48
Process flow: Sending a file to a contact using the BlackBerry Client for IBM Lotus Sametime................................ 49
Message attachment process flows.......................................................................................................................................... 50
Process flow: Viewing a message attachment.................................................................................................................... 50
Process flow: Viewing an attachment through a link........................................................................................................ 52
Organizer data process flows.................................................................................................................................................... 52
Process flow: Synchronizing organizer data for the first time on a BlackBerry device................................................ 53
Process flow: Synchronizing subsequent changes to organizer data............................................................................. 54
Mobile data process flows.......................................................................................................................................................... 55
Process flow: Requesting BlackBerry Browser content on a BlackBerry device............................................................ 55
Process flow: Requesting BlackBerry Browser content while access control is turned on for the BlackBerry MDS
Connection Service................................................................................................................................................................. 56
Process flow: Requesting BlackBerry Browser content with two-factor authentication turned on........................... 57
Process flow: Pushing application content to a BlackBerry device................................................................................. 58
Process flow: Requesting BlackBerry MDS Runtime Applications from a BlackBerry device..................................... 59
BlackBerry device management process flows....................................................................................................................... 60
Process flow: Activating the BlackBerry device over the wireless network................................................................... 60
Process flow: Resending an IT policy to the BlackBerry device manually...................................................................... 61
Process flow: Authenticating the data on a BlackBerry device without connecting to the BlackBerry Infrastructure
.................................................................................................................................................................................................... 61
Process flow: Sending an application to a BlackBerry device over the wireless network............................................ 61
5 Glossary................................................................................................................................................................................ 63
6 Legal notice.......................................................................................................................................................................... 67

Feature and Technical Overview
New in this release
New in this release
Feature Description
Rich-content email messages BlackBerry® Enterprise Server version 4.1 SP6 supports HTML and rich-content
email messages for BlackBerry devices that are running BlackBerry® Device
Software version 4.5 or later. By default, this feature is turned on.
If users reply to messages or forward messages using their BlackBerry devices,
messages in HTML format or rich-content format appear in plain-text format.
The BlackBerry Enterprise Server and its components support HTML email
messages in a Japanese environment when the following options are selected in
the regional and language settings of the computer: Install files for complex
script and right-to-left languages, and Install files for East Asian languages.
View meeting invitee availability Users can view the availability of meeting invitees on BlackBerry devices that
are running BlackBerry Device Software version 4.5 or later. You can turn off this
feature using the BlackBerry Manager.
Remote search for email messages Users can search for email messages that are located on the messaging server
using BlackBerry devices that are running BlackBerry Device Software version
4.5 or later. You can turn off this feature using the BlackBerry Manager.
By default, the remote search feature can only retrieve messages that contain
the full search term that the user types.
Download native attachment formats Users can download message attachments in any native format on BlackBerry
devices that are running BlackBerry Device Software version 4.5 or later. Users
can open and make changes to native file formats using an appropriate thirdparty application on their BlackBerry devices. Depending on the file format, users
might be able to open a file using the media application on their BlackBerry
devices.
1
Attachment support for .amr file
format
You can specify the maximum file size of attachments that users can download
to their BlackBerry devices.
The BlackBerry Attachment Service now supports the .amr audio file format.
3

Feature and Technical Overview
Feature Description
Separate messages list on BlackBerry
devices for messages received from
BlackBerry Enterprise Server instances
You can add a separate messages list to users’ BlackBerry devices that contains
messages received from BlackBerry Enterprise Server instances only. This feature
is turned off by default. For more information about how to turn on this feature,
visit www.blackberry.com/support to see article KB15003.
Monitor wireless application push
failures
Apply application control policies to
BlackBerry MDS Runtime Applications
The new Software Config Status tab in the BlackBerry Manager allows you to
view any issues with the wireless delivery of applications.
You can now apply application control policies to BlackBerry MDS Runtime
Applications that are running on the BlackBerry® MDS Runtime version 4.5 or
later.
The “Allow External Access” property in BlackBerry MDS Integration Service
device policies does not apply to BlackBerry devices running BlackBerry MDS
Runtime version 4.5 or later. To apply this property, you must apply an application
control policy to a BlackBerry MDS Runtime Application. For more information,
see the BlackBerry Enterprise Server Administration Guide.
Unconditional message encryption for
the BlackBerry MDS Integration
All messages exchanged between BlackBerry devices and the BlackBerry MDS
Integration Service are now encrypted by default.
Service
Support for Microsoft® SQL Server®
2005 (64-bit)
Enhanced control of lost and stolen
BlackBerry devices
The BlackBerry Enterprise Server now supports the Microsoft SQL Server 2005
(64-bit) database management system.
You can specify a delay (in hours) when using the Erase Data And Disable
Handheld IT administration command over the wireless network. This change
applies to BlackBerry Device Software version 4.5 or later.
New in this release
Specify algorithms that BlackBerry
devices consider weak
4
The remote password reset cryptographic protocol is designed to allow you to
set the BlackBerry device password remotely, even if content protection is
enabled on the BlackBerry device. This change applies to BlackBerry Device
Software version 4.3 or later.
You can use the Weak Digest Algorithms IT policy rule to specify algorithms that
BlackBerry devices consider weak. This IT policy rule can be applied to BlackBerry
devices running BlackBerry Device Software version 4.3 or later.

Feature and Technical Overview
Feature Description
The BlackBerry Enterprise Server uses the list of weak digest algorithms when
verifying that the certificate chains for the certificates that BlackBerry devices
use with the SSL protocol over connections to external web servers are strong
enough.
BlackBerry devices use the list of weak digest algorithms when verifying that the
digital signatures on messages that BlackBerry devices receive are not generated
using a weak hash digest. BlackBerry devices use the list of weak digest
algorithms when verifying that the certificate chains for the certificates used to
sign messages that BlackBerry devices receive do not contain hashes generated
using a weak digest.
Digitally sign BlackBerry MDS
Runtime Applications
Developers can digitally sign BlackBerry MDS Runtime Applications that they
create using BlackBerry® MDS Studio, before publishing these applications to
the BlackBerry MDS Application Repository.
BlackBerry devices support using a private key with a corresponding certificate
in X.509 syntax to digitally sign BlackBerry MDS Runtime Applications. The
BlackBerry MDS Integration Service verifies the digital signature on the
BlackBerry MDS Runtime Application code before sending the application to
BlackBerry devices over the wireless network. When the BlackBerry device
receives the BlackBerry MDS Runtime Application, it displays the certificate
subject details as the code signer identity, and prompts the BlackBerry device
user to accept or reject the application.
Apply an encoding scheme to
BlackBerry data using transcoder
application code
You can apply an encoding scheme to BlackBerry data using transcoder
application code.
Third-party application developers can create encoding schemes that encrypt,
convert, or otherwise change the format of BlackBerry device data.
New in this release
Firewall Whitelist Addresses IT policy
rule
This feature applies to BlackBerry devices running BlackBerry Device Software
version 4.5 or later.
You can use the Firewall Whitelist Addresses IT policy rule to specify the list of
email addresses that the BlackBerry device firewall allows. The BlackBerry device
receives messages from these email addresses even if the user blocks all
incoming messages on the device. This IT policy rule can be applied to BlackBerry
devices running BlackBerry Device Software version 4.2.3 or later.
5

Feature and Technical Overview
Feature Description
Changes to the BlackBerry
Configuration Database schema
BlackBerry Enterprise Server version 4.1 SP6 contains changes to the BlackBerry
Configuration Database schema. The changes occur in the upgrade file that is
named UpgradeV20080410.sql.
Support for Microsoft® Office
Communications Server 2007
The BlackBerry Collaboration Service supports Microsoft Office Communications
Server 2007. BlackBerry Enterprise Server version 4.1 SP6 supports a new
collaboration client for use with this instant messaging server: the BlackBerry®
Client for use with Microsoft® Office Communications Server 2007.
Support for IBM® Lotus® Sametime®
The BlackBerry Collaboration Service supports IBM Lotus Sametime version 8.0.
version 8.0
New names for the BlackBerry
collaboration clients
The collaboration client that was previously named BlackBerry® Instant
Messaging for Microsoft® Office Live Communications Server 2005 is now
named the BlackBerry® Client for use with Microsoft® Office Live
Communications Server 2005.
The collaboration client that was previously named BlackBerry® Instant
Messaging for IBM® Lotus® Sametime® is now named the BlackBerry® Client
for IBM® Lotus® Sametime®.
New in this release
The collaboration client that was previously named BlackBerry® Instant
Messaging for Novell® GroupWise® Messenger is now named the BlackBerry®
Client for Novell® GroupWise® Messenger.
Connecting the BlackBerry
Collaboration Service to a remote
BlackBerry Attachment Service to
support file transfer for the BlackBerry
Client for IBM Lotus Sametime
Users can use the BlackBerry Client for IBM Lotus Sametime to send files to the
contacts in their contact lists. To optimize files for viewing on BlackBerry devices,
the BlackBerry Collaboration Service must be able to connect to the BlackBerry
Attachment Service.
If you have not installed the on the same computer as the BlackBerry
Collaboration Service, you must connect the BlackBerry Collaboration Service to
the remote BlackBerry Attachment Service.
For more information, see the BlackBerry Enterprise Server Installation Guide.
Control RIM value-added applications You can use new and existing IT policy rules to control RIM value-added
applications. For more information about new IT policy rules, see the Policy
Reference Guide.
6

Feature and Technical Overview
Feature Description
New naming conventions for the
BlackBerry® Mobile Data System and
related software
The component of the BlackBerry Enterprise Server that was previously named
the BlackBerry MDS Services is now named the BlackBerry MDS Integration
Service. The term BlackBerry MDS Services now refers collectively to the
BlackBerry MDS Integration Service and the BlackBerry MDS Connection
Service.
BlackBerry® MDS Studio Applications are now named BlackBerry® MDS
Runtime Applications. Java® applications that are developed for and used on
BlackBerry devices are now named BlackBerry Java Applications. Browser
applications that are developed for and used on BlackBerry devices are now
named BlackBerry® Browser Applications. The term BlackBerry Applications
refers collectively to BlackBerry MDS Runtime Applications, BlackBerry Java
Applications, and BlackBerry Browser Applications.
The BlackBerry Manager UI and the BlackBerry Enterprise Server documentation
reflect these new naming conventions.
New in this release
7


Feature and Technical Overview
BlackBerry Enterprise Server architecture
BlackBerry Enterprise Server architecture
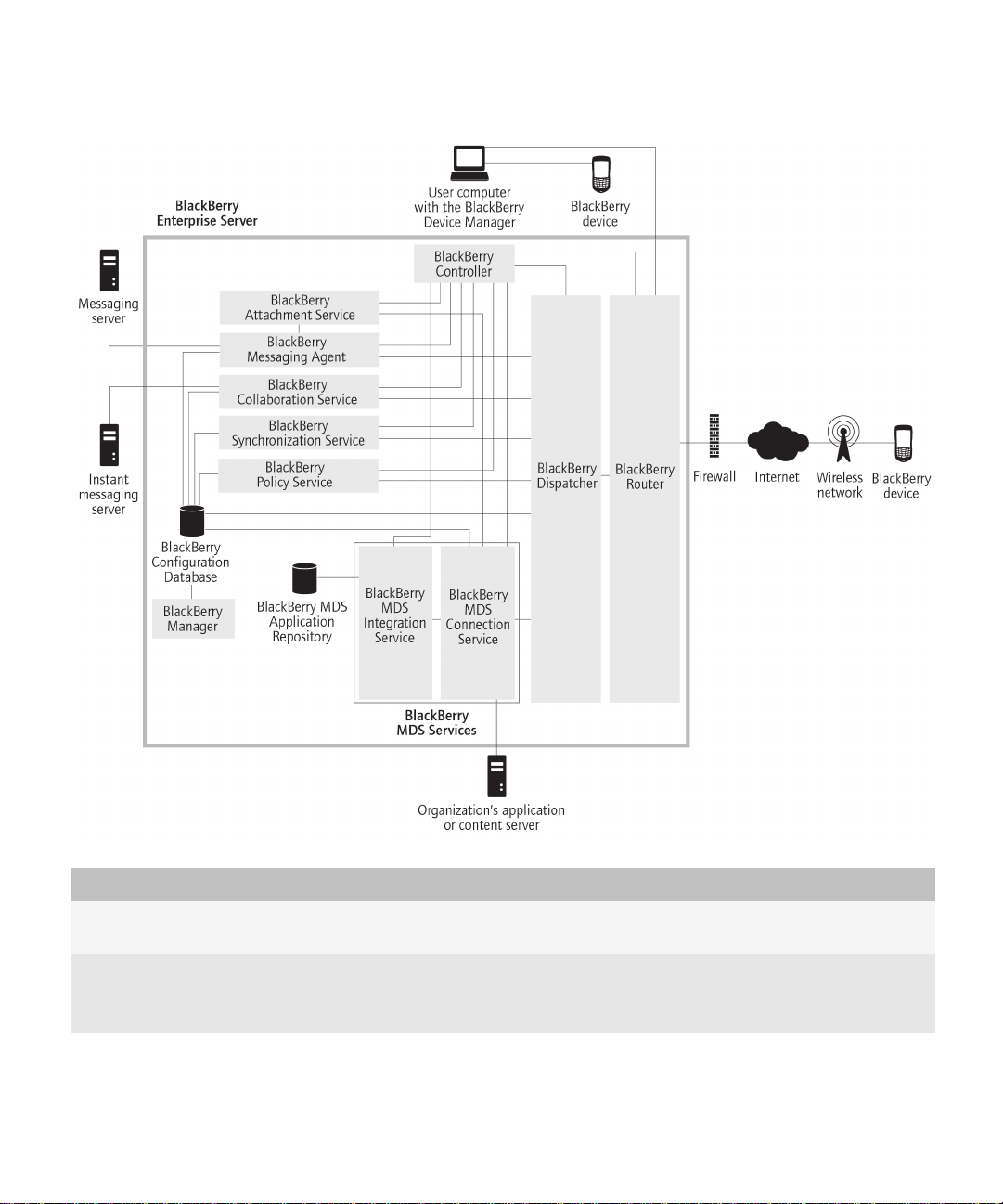
Architecture: BlackBerry Enterprise Server
The BlackBerry® Enterprise Server consists of various components that are designed to perform the following actions:
• provide productivity tools and data from an organization's applications to its BlackBerry device users
• monitor other BlackBerry Enterprise Server components
• process, route, compress, and encrypt data
• communicate with the wireless network
2
9
Feature and Technical Overview
Architecture: BlackBerry Enterprise Server
Component Description
BlackBerry Attachment Service The BlackBerry Attachment Service converts supported message attachments
into a format that users can view on their BlackBerry devices.
BlackBerry Collaboration Service The BlackBerry Collaboration Service provides a connection between your
organization's instant messaging server and the collaboration client on
BlackBerry devices.
10

Feature and Technical Overview
Architecture: BlackBerry Enterprise Server
Component Description
BlackBerry Configuration Database The BlackBerry Configuration Database is a relational database that contains
configuration data that BlackBerry Enterprise Server components use. The
BlackBerry Configuration Database includes the following data:
• details about the connection from the BlackBerry Enterprise Server to the
wireless network
• user list
• address mappings between PINs and email addresses for BlackBerry MDS
Connection Service push features
• read-only copy of each master encryption key
BlackBerry Controller The BlackBerry Controller monitors the BlackBerry Enterprise Server
components and restarts them if they stop responding.
BlackBerry Dispatcher The BlackBerry Dispatcher compresses and encrypts all of the data that is sent
to and from BlackBerry devices. It sends the data through the BlackBerry Router,
to and from the wireless network.
BlackBerry Manager The BlackBerry Manager connects to the BlackBerry Configuration Database.
You can use the BlackBerry Manager to manage the BlackBerry Domain,
including user accounts and device administration. The BlackBerry Domain
consists of a single BlackBerry Configuration Database and all the BlackBerry
Enterprise Server instances that use it.
BlackBerry MDS Connection Service The BlackBerry MDS Connection Service enables users to access web content,
the Internet, or your organization's intranet, and also enables applications on
BlackBerry devices to connect to your organization's application or content
servers for application data and updates.
BlackBerry MDS Integration Service The BlackBerry MDS Integration Service provides application-level integration
for BlackBerry® MDS Runtime Applications on BlackBerry devices. You can use
the BlackBerry MDS Integration Service to install BlackBerry MDS Runtime
Applications that are stored in the BlackBerry MDS Application Repository on
BlackBerry devices. You can also use it to manage, update, and remove
BlackBerry MDS Runtime Applications.
BlackBerry MDS Application
Repository
The BlackBerry MDS Application Repository stores BlackBerry MDS Runtime
Applications that your organization's developers can create and publish using
the BlackBerry® MDS Studio or the BlackBerry® Plug-in for Microsoft® Visual
11

Feature and Technical Overview
Architecture: BlackBerry Enterprise Server
Component Description
Studio® developer tools. You can use the BlackBerry Manager to manage the
BlackBerry MDS Runtime Applications that are stored in the BlackBerry MDS
Application Repository.
BlackBerry Messaging Agent The BlackBerry Messaging Agent connects to your organization's messaging
server to provide messaging services, calendar management, address lookups,
attachment viewing, attachment downloading, and encryption key generation.
The BlackBerry Messaging Agent also acts as a gateway for the BlackBerry
Synchronization Service to access organizer data on the messaging server. The
BlackBerry Messaging Agent synchronizes configuration data between the
BlackBerry Configuration Database and the message store databases.
BlackBerry Policy Service The BlackBerry Policy Service performs administration services over the wireless
network. It sends IT policies and IT administration commands and provisions
service books. IT policies and IT administration commands define BlackBerry
device security, settings for synchronizing data over the wireless network, and
other configuration settings on BlackBerry devices. The BlackBerry Policy Service
also sends service books to configure feature and component settings on
BlackBerry devices.
BlackBerry Router The BlackBerry Router connects to the wireless network to send data to and from
BlackBerry devices. It also sends data within your organization's network to
BlackBerry devices that are connected to computers with the BlackBerry® Device
Manager.
BlackBerry Synchronization Service The BlackBerry Synchronization Service synchronizes organizer data between
BlackBerry devices and the messaging server over the wireless network.
organization's application or content
server
The organization's application or content server provides push applications and
intranet content for the BlackBerry MDS Services.
instant messaging server The instant messaging server stores instant messaging accounts.
messaging server The messaging server stores email accounts.
user's computer with the BlackBerry
Device Manager
The user's computer with the BlackBerry Device Manager enables users to
connect their BlackBerry devices to their computers using a serial or USB
connection. The BlackBerry Enterprise Server and BlackBerry devices use this
connection to send data between them.
12
Feature and Technical Overview
Architecture: BlackBerry Enterprise Server remote components
Component Description
Data traffic from BlackBerry devices bypasses the wireless network while
BlackBerry devices are connected to users' computers. The BlackBerry Device
Manager connects to the BlackBerry Router, which sends data directly to
BlackBerry devices.
Users can install the BlackBerry Device Manager separately from the
BlackBerry® Desktop Manager or with it as part of the full BlackBerry® Desktop
Software installation. The BlackBerry Device Manager is an optional component,
but it is required to support a bypass connection to the BlackBerry Router.
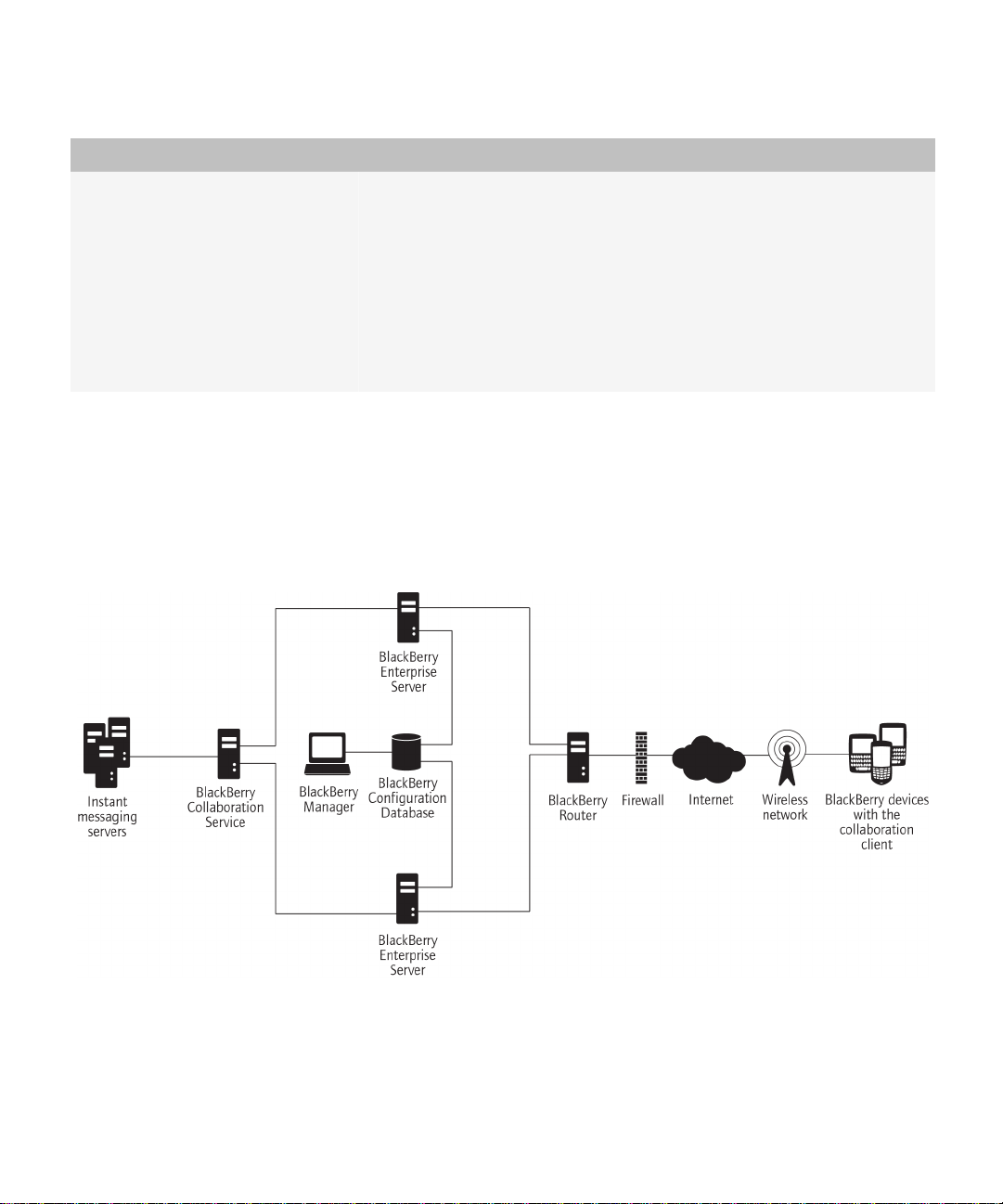
Architecture: BlackBerry Enterprise Server remote components
You can install all BlackBerry® Enterprise Server components on one computer, or you can install certain components on
separate computers. Different components impact system resources differently. You can choose to install only one remote
component on each computer in your organization's environment.
Sample architecture with a remote BlackBerry Collaboration Service
13
Feature and Technical Overview
Architecture: BlackBerry Enterprise Server remote components
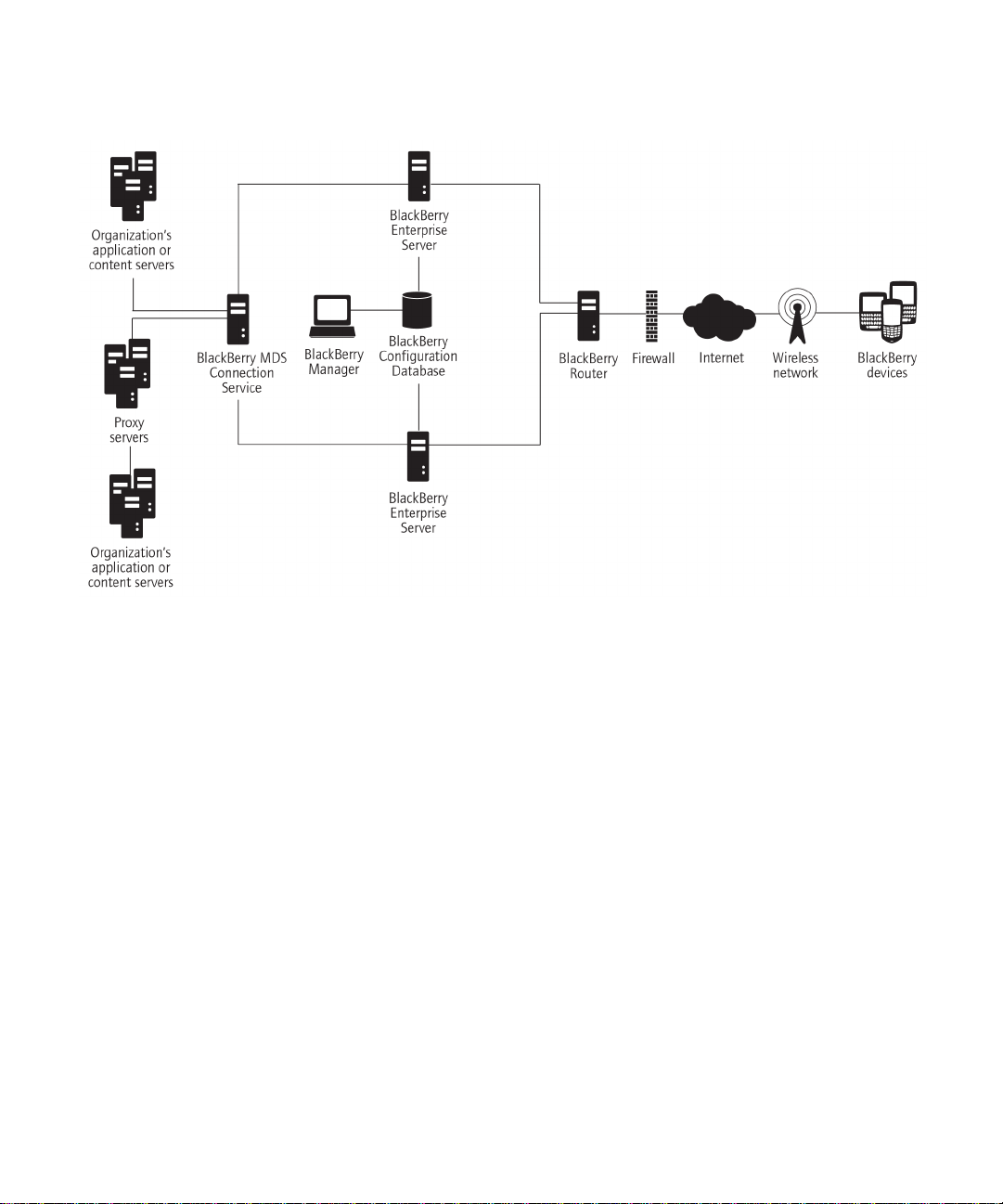
Sample architecture with a remote BlackBerry MDS Connection Service
14
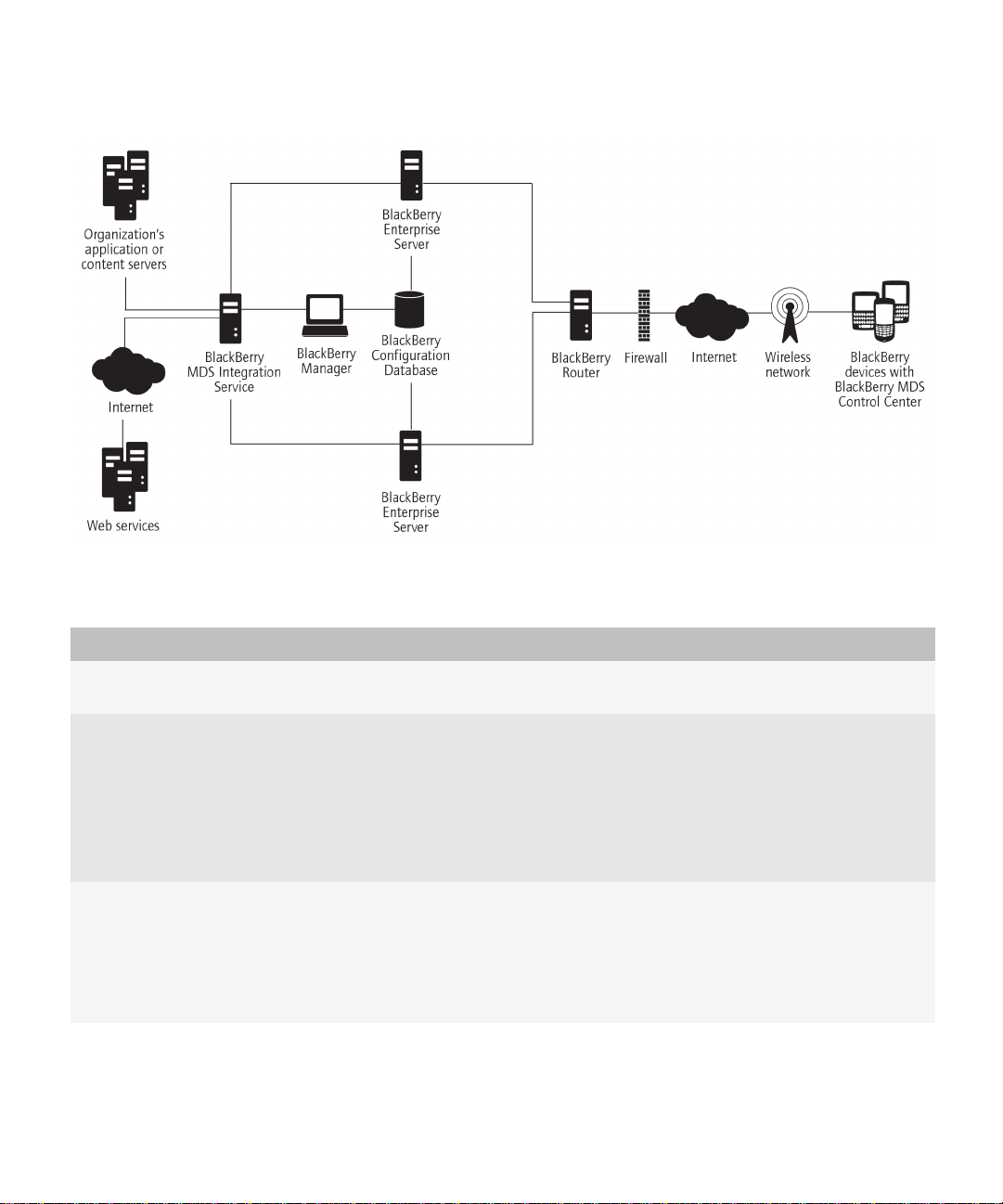
Feature and Technical Overview
Architecture: BlackBerry Enterprise Server remote components
Sample architecture with a remote BlackBerry MDS Integration Service
Component Description
BlackBerry Manager A remote BlackBerry Manager enables you to manage the BlackBerry Domain
from their computers.
BlackBerry Attachment Service A remote BlackBerry Attachment Service can support multiple BlackBerry
Enterprise Server instances.
The BlackBerry Attachment Service can use increased system resources when it
processes concurrent conversion requests. You can install the BlackBerry
Attachment Service on a remote computer to increase the number of concurrent
conversions without impacting message delivery.
BlackBerry Collaboration Service A remote BlackBerry Collaboration Service can support multiple BlackBerry
Enterprise Server instances.
The BlackBerry Collaboration Service uses a persistent socket connection for
each instant messaging session. You can install the BlackBerry Collaboration
Service on a remote computer to maximize the number of available sockets.
15

Feature and Technical Overview
Architecture: BlackBerry Enterprise Server remote components
Component Description
You can install only one type of BlackBerry Collaboration Service (for example,
IBM® Lotus® Sametime®), and users can use only one type of enterprise instant
messaging application on their BlackBerry devices.
BlackBerry MDS Connection Service A remote BlackBerry MDS Connection Service can support multiple BlackBerry
Enterprise Server instances.
The BlackBerry MDS Connection Service can use increased system resources
when it processes content requests. You can install the BlackBerry MDS
Connection Service on a remote computer to minimize the impact on message
and data delivery.
BlackBerry MDS Integration Service A remote instance of the BlackBerry MDS Integration Service can support
multiple BlackBerry Enterprise Server instances and one BlackBerry MDS
Application Repository.
The BlackBerry MDS Integration Service can use increased system resources
when processing content requests. You can install a BlackBerry MDS Integration
Service on a remote computer to minimize the impact on message delivery.
BlackBerry MDS Application
Repository
A remote BlackBerry MDS Application Repository can support one instance of
the BlackBerry MDS Integration Service. You must install the BlackBerry MDS
Application Repository on the same database server as the BlackBerry
Configuration Database.
BlackBerry Router A remote BlackBerry Router can support multiple BlackBerry Enterprise Server
instances.
The BlackBerry Router does not use many system resources, but it is a critical
connection point for the BlackBerry® Enterprise Solution. You can install multiple
standby instances of the BlackBerry Router as failover locations in the event that
the active BlackBerry Router is unavailable.
BlackBerry Configuration Database A remote BlackBerry Configuration Database can support multiple BlackBerry
Enterprise Server instances, which creates a BlackBerry Domain.
16

Feature and Technical Overview
BlackBerry Enterprise Server components and features
BlackBerry Enterprise Server components and features
3
BlackBerry messaging and collaboration services
The BlackBerry® messaging and collaboration services provide a wireless extension of an organization's messaging
environment. These services include the BlackBerry Messaging Agent, the BlackBerry Collaboration Service, the BlackBerry
Synchronization Service, and the BlackBerry Attachment Service.
BlackBerry Messaging Agent
The BlackBerry® Messaging Agent connects to an organization's messaging server and provides messaging services, calendar
management, address lookups, attachment viewing, attachment downloading, and encryption key generation. The
BlackBerry Messaging Agent also acts as a gateway for the BlackBerry Synchronization Service to access organizer data on
the messaging server. The BlackBerry Messaging Agent synchronizes configuration data between the BlackBerry
Configuration Database and the message store databases.
The BlackBerry Messaging Agent integrates with existing email accounts in your organization. The BlackBerry Messaging
Agent redirects messages from users’ email applications to their BlackBerry devices automatically. If users configure identical
signatures on their BlackBerry devices and in their email accounts, recipients cannot distinguish between the messages sent
from BlackBerry devices and those sent from email applications.
When users move or delete messages or mark messages as read or unread on their BlackBerry devices or in their email
applications, the BlackBerry Messaging Agent reconciles these changes over the wireless network between their BlackBerry
devices and the email applications. By default, both BlackBerry devices and the BlackBerry® Enterprise Server reconcile
email messages over the wireless network.
Wireless messaging features
BlackBerry® device users can use many of the same messaging features that are available in the email applications on their
computers.
Feature Description
email reconciliation The BlackBerry® Enterprise Server reconciles the status of messages between
users' BlackBerry devices and their email applications. If users delete, archive,
or move messages to personal folders in their email applications, the messages
are deleted from the message list on the users' BlackBerry devices. If users mark
messages as read or unread in their email applications, the messages appear
with the same status on their BlackBerry devices.
17

Feature and Technical Overview
BlackBerry messaging and collaboration services
Feature Description
Administrators can turn off wireless email reconciliation.
email message filters Users and BlackBerry Enterprise Server administrators can create and change
email message filters. Email message filters determine the actions that the
BlackBerry Enterprise Server takes if incoming messages match specific criteria:
forward, forward with priority, or do not forward to BlackBerry devices. For
example, users can create email message filters to forward messages from
specific senders to their BlackBerry devices with high priority.
message forwarding Users can turn off message forwarding to their BlackBerry devices, for example,
if they are outside of a wireless coverage area. Administrators can also turn off
message forwarding to users' BlackBerry devices.
signature Users can add a signature to all of the messages that they send from their
BlackBerry devices. Administrators can add a signature and disclaimers to all of
the messages that the members of a user group send or a specific user sends.
contact lookup Users can search for a contact’s first name, last name, or both in their
organization's directory. The BlackBerry Enterprise Server returns results for up
to 20 of the closest matches.
contact list updates When users select contacts from the contact lookup results, they can add the
contacts to the contact lists on their BlackBerry devices.
custom fields in the contact list If your organization maintains custom fields in users’ personal contact lists, you
can map these fields to corresponding fields that appear in the contact list on
BlackBerry devices. Users can use these custom fields to search for contacts on
their BlackBerry devices.
downloading attachments Users with BlackBerry® Device Software version 4.5 or later can download
attachments in any native format to their BlackBerry devices. Users can open
and make changes to native file formats using an appropriate third-party
application on their BlackBerry devices. Depending on the file format, users
might be able to open files using the media application on their BlackBerry
devices.
To manage network resources in your organization's environment, you can
change the maximum file size of attachments that users can download to their
BlackBerry devices.
18

Feature and Technical Overview
BlackBerry messaging and collaboration services
Feature Description
save sent messages Users can configure their BlackBerry devices to save copies of messages that
they send from their BlackBerry devices in the sent items folder in their email
applications.
BlackBerry Collaboration Service
The BlackBerry® Collaboration Service provides a connection between an organization's instant messaging server and the
collaboration client on BlackBerry devices. The BlackBerry Collaboration Service integrates with existing instant messaging
applications. The BlackBerry® Enterprise Server supports the following collaboration clients:
• BlackBerry® Client for use with Microsoft® Office Live Communications Server 2005
• BlackBerry® Client for use with Microsoft® Office Communications Server 2007
• BlackBerry® Client for IBM® Lotus® Sametime®
• BlackBerry® Client for Novell® GroupWise® Messenger
The BlackBerry Collaboration Service sends messages between the organization's instant messaging server, the BlackBerry
Enterprise Server, and BlackBerry devices using public APIs, protocols that are defined by IBM, Microsoft, and Novell, and a
Research In Motion proprietary protocol.
Instant messaging features
Using the collaboration clients on their BlackBerry® devices, users can use many of the same features that are available in
the instant messaging applications on their computers.
Feature Description
session management You can specify the number of simultaneous instant messaging sessions that the
BlackBerry Collaboration Service supports. You can also specify a timeout
threshold, after which the BlackBerry Collaboration Service ends inactive
sessions automatically and permits new sessions to start.
You can control whether users of certain versions of the BlackBerry® Client for
IBM® Lotus® Sametime® or the BlackBerry® Client for Novell® GroupWise®
Messenger can see an icon on their BlackBerry devices when contacts in their
contact lists are using the same collaboration clients. By default, the icon
appears.
conversations with multiple contacts Users can start and manage conversations with multiple instant messaging
contacts on their BlackBerry devices.
19

Feature and Technical Overview
BlackBerry messaging and collaboration services
Feature Description
availability status Users can change their availability status while they are logged in to their
collaboration clients. For example, users can set their availability status to away
or busy.
presence updates Using the latest version of the collaboration clients, users can set their
availability status to display as away if they do not use their BlackBerry devices
for a specified period of time.
presence level Using the latest version of the BlackBerry® Client for use with Microsoft® Office
Communications Server 2007, users can set the presence level of contacts in
their contact lists. Each presence level consists of rules that determine how a
contact can interact with a user through the instant messaging application. For
example, users can assign the Personal presence level to their contacts.
contact pictures Using the latest version of the collaboration clients, users can add pictures to
the contacts in their contact lists. The pictures that users add using the
collaboration clients on their BlackBerry devices are not synchronized with the
instant messaging applications on users' computers.
synchronized contact lists The instant messaging contact lists on users' BlackBerry devices are
synchronized with the contact lists in their organization's instant messaging
application.
contact alerts Users can request alerts when specific contacts become available.
file transfer Using the latest version of the BlackBerry Client for IBM Lotus Sametime, users
can send files to contacts in their contact lists. Recipients can view supported
file formats on their BlackBerry devices.
link instant messaging contacts to the
BlackBerry contact list
Using the latest version of the collaboration clients, users can link instant
messaging contacts to existing contact list entries on their BlackBerry devices,
or they can create new contact list entries for instant messaging contacts and
populate them with information from their organization's messaging server.
send email messages from contact list Using the latest version of the collaboration clients on their BlackBerry devices,
users can send email messages to contacts directly from their contact lists.
call contacts Using the latest version of the collaboration clients on their BlackBerry devices,
users can call instant messaging contacts directly from their contact lists. After
a user starts an instant messaging conversation with a contact, the user can
20

Feature and Technical Overview
BlackBerry messaging and collaboration services
Feature Description
make a call to that contact from the conversation window. Phone numbers for
contacts are retrieved from the messaging server or from the BlackBerry contact
list if the user is linked to an existing contact list entry.
email conversation history Using the latest version of the collaboration clients, users who are participating
in an instant messaging conversation can send the history of the conversation
as an email message to the participants of the conversation and to additional
contacts from their BlackBerry contact lists.
embedded links Users can click phone numbers in instant messages to make calls and they can
click links in instant messages to view web pages.
public groups Using the latest version of the BlackBerry Client for IBM Lotus Sametime, users
can add public groups to their instant messaging contact lists.
location information Using the latest version of the BlackBerry Client for IBM Lotus Sametime or the
BlackBerry Client for use with Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007,
users can set their current location to display in their contact information. For
example, users can set their current location to "In the office." This feature is not
available if your organization's environment uses IBM Lotus Sametime version
6.5.1.
announcements Using the latest version of the BlackBerry Client for IBM Lotus Sametime or the
BlackBerry Client for Novell GroupWise Messenger, users can send
announcements to groups or multiple contacts in their contact lists.
send messages to users who have not
been added to a contact list
Using the latest version of the BlackBerry Client for IBM Lotus Sametime, the
BlackBerry® Client for use with Microsoft® Office Live Communications Server
2005, or the BlackBerry Client for use with Microsoft Office Communications
Server 2007, users can send instant messages to contacts they have not added
to their contact lists.
dormant mode The collaboration clients enter dormant mode automatically after five minutes
of inactivity. In dormant mode, the applications do not receive presence updates
for contacts. Dormant mode is designed to reduce wireless network traffic in an
organization's messaging environment. The collaboration clients turn off
dormant mode when users open or use the applications, or receive conference
requests, alerts, or messages from contacts.
21

Feature and Technical Overview
BlackBerry messaging and collaboration services
BlackBerry Synchronization Service
The BlackBerry® Synchronization Service synchronizes organizer data such as tasks, memos, and contacts over the wireless
network so that the entries on BlackBerry devices are consistent with the entries in the email applications. With wireless
data synchronization and wireless email reconciliation, users do not have to connect their BlackBerry devices to the
BlackBerry® Desktop Software to synchronize organizer data and reconcile messages.
The BlackBerry Synchronization Service automatically backs up user settings and data over the wireless network from
BlackBerry devices to the BlackBerry Configuration Database. You can restore these settings and data to BlackBerry devices
when they activate over the wireless network. By default, the BlackBerry® Enterprise Server automatically backs up the
settings and data over the wireless network.
Synchronization features
You can change the settings for synchronization features to manage the user experience and the use of system resources
in your organization's environment.
Feature Description
initial synchronization When the BlackBerry® Enterprise Server sends service books to BlackBerry
devices to turn on wireless data synchronization, an initial data synchronization
process starts. This process synchronizes the data for calendar items and
messages between users' BlackBerry devices and the email applications on their
computers. It also resolves conflicting or duplicate entries to prevent data loss.
synchronization settings You can configure settings for wireless data synchronization that apply to
specific users, to user groups, or to all users on all BlackBerry Enterprise Server
instances. You can define which organizer data items the BlackBerry
Synchronization Service synchronizes, how data conflicts are resolved, and
whether changes are synchronized in both directions or in one direction only
between BlackBerry devices and email applications. You can use IT policies to
configure the settings for wireless data synchronization.
support for different types of user
access
The BlackBerry Enterprise Server requires access to the organizer application
databases for all users. You can define the location of the database replicas in
each user’s profile, set up roaming user profiles, or use web access templates in
your organization's messaging environment.
22

Feature and Technical Overview
BlackBerry Attachment Service
The BlackBerry® Attachment Service converts supported message attachments into a format that users can view on their
BlackBerry devices. The BlackBerry Attachment Service processes attachments and converts them into a binary format that
retains most of the layout, appearance, and navigation of the original attachments. You do not have to install the applications
that are associated with the attachment formats on BlackBerry devices. The attachment viewer installs automatically with
the BlackBerry® Device Software.
The BlackBerry Attachment Service receives attachments that are embedded in messages from the messaging server, through
the BlackBerry Messaging Agent. The BlackBerry Attachment Service also receives attachments that are accessed through
links in the BlackBerry® Browser.
The BlackBerry Attachment Service enables users to play supported audio attachments on supported BlackBerry devices
that are running BlackBerry Device Software version 4.2 or later. The BlackBerry Attachment Service can convert .wav files
into an audio format that a BlackBerry device series supports (for example, .mp3 files on BlackBerry® 8700 Series devices).
Attachment file formats supported by the BlackBerry Attachment Service
Format Extension
Adobe® Acrobat® versions 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, and 1.4 .pdf
ASCII text .txt
audio .amr, .mp3, .wav
Corel® WordPerfect® versions 6.0, 7.0, 8.0, 9.0 (2000), and
10.0
HTML .htm, .html
images .bmp, .gif, .jpeg, .jpg, .png, .tif, .tiff, .wmf
Microsoft® Excel® versions 97, 2000, 2003, 2007, and XP .xls, .xlsx
Microsoft® PowerPoint® versions 97, 2000, 2003, 2007,
and XP
Microsoft® Word versions 97, 2000, 2003, 2007, and XP .doc, .dot, .docx
RTF .rtf
ZIP archives .zip
.wpd
.pps, .ppt, .pptx
23

Feature and Technical Overview
BlackBerry MDS
BlackBerry MDS
The BlackBerry® Mobile Data System is a flexible framework for application development that you can use for adding and
managing applications in your environment. As a component of the BlackBerry® Enterprise Server, the BlackBerry MDS
offers security, wireless connectivity, and manageability options, while also supporting several preferred development
methods for creating and delivering wireless applications to BlackBerry devices. To simplify the integration of wireless
applications with existing applications and systems, the BlackBerry MDS uses standards-based methods and protocols.
Component Description
BlackBerry MDS Services You can use the BlackBerry MDS Services to send, maintain, and manage wireless
applications on BlackBerry devices. The BlackBerry MDS Services are designed
to provide wireless connectivity between applications on BlackBerry devices and
your organization's existing applications. The BlackBerry MDS Services include
the following components:
• BlackBerry MDS Integration Service: The BlackBerry MDS Integration
Service enables BlackBerry® MDS Runtime Applications to interact with
back-end systems using web services or direct database connections. You
can install the BlackBerry MDS Integration Service when you install the
BlackBerry Enterprise Server.
• BlackBerry MDS Connection Service: The BlackBerry MDS Connection
Service processes requests for web content from the BlackBerry® Browser
or from BlackBerry Java® Applications. The BlackBerry MDS Connection
Service also manages TCP/IP and HTTP-based connections between
BlackBerry Applications and the applications residing on your
organization’s application servers, web servers, or databases that are
located behind your organization's firewall.
BlackBerry MDS development tools Developers in your organization can use development tools to create the
following types of wireless applications for BlackBerry devices: BlackBerry
Browser Applications, BlackBerry Java Applications, and BlackBerry MDS
Runtime Applications.
For more information about BlackBerry development tools, visit
www.blackberry.com/developers.
BlackBerry MDS device software BlackBerry devices use BlackBerry MDS device software to run BlackBerry
Applications:
24

Feature and Technical Overview
BlackBerry MDS
Component Description
• BlackBerry® MDS Runtime: used to run BlackBerry MDS Runtime
Applications
• BlackBerry APIs and Java ME: used to run BlackBerry Java Applications;
standard on BlackBerry devices
• BlackBerry Browser: used to run BlackBerry Browser Applications; standard
on BlackBerry devices
To download the BlackBerry MDS Runtime, visit www.blackberry.com.
For more information about the BlackBerry MDS and the types of BlackBerry Applications, visit www.blackberry.com/
developers to see the BlackBerry Mobile Data System Technical Overview.
BlackBerry Applications
BlackBerry® devices support BlackBerry® Browser Applications, BlackBerry Java® Applications, and BlackBerry® MDS
Runtime Applications.
BlackBerry Browser Applications are simplified, web-based applications that users access using the BlackBerry Browser. For
example, a developer can create a BlackBerry Browser Application that your organization can use to collect data input from
BlackBerry device users.
BlackBerry Java Applications can range from simple applications, such as a game on BlackBerry devices, to complex
applications with an advanced user interface and various options for data management, storage, and network communication.
BlackBerry Java Applications can use a client-only architecture, meaning that they do not send data to or receive data from
a content server, or they can use a client/server application model, sending data to and receiving data from a content server.
For example, a developer can create a BlackBerry Java Application so that users can send data to and receive data from a
central sales database.
BlackBerry MDS Runtime Applications are lightweight, rich-client applications that are created using BlackBerry® MDS
Studio or the for Microsoft® Visual Studio®. BlackBerry MDS Runtime Applications communicate with an organization's
systems through the BlackBerry MDS Integration Service, a component of the BlackBerry® Enterprise Server. BlackBerry
MDS Runtime Applications can range from simple to complex, but they are typically forms-based applications that you can
use to access web services or databases that are located inside your organization's firewall. Web services or a database
contain the data and operations that developers can use to create BlackBerry MDS Runtime Applications, and they also
process the data that they receive from BlackBerry MDS Runtime Applications. For example, a developer can create a
BlackBerry MDS Runtime Application so that users can look up data from a directory in your organization.
Using BlackBerry MDS Studio version 2.0 or later or the BlackBerry Plug-in for Microsoft Visual Studio version 1.1 or later,
application developers in your organization can design BlackBerry MDS Runtime Applications that standard BlackBerry
Applications (for example, the address book) and custom BlackBerry Java Applications can invoke.
25

Feature and Technical Overview
BlackBerry MDS
For more information about customizing BlackBerry MDS Runtime Applications, visit www.blackberry.com/developers to
see the BlackBerry MDS Studio Developer Guide and the BlackBerry Plug-in for Microsoft Visual Studio Developer Guide.
Types of BlackBerry Applications
Type BlackBerry® Mobile Data System components used
BlackBerry® Browser Applications Developers create the applications using:
• standard web development tools
The BlackBerry® Enterprise Server communicates with the applications using:
• BlackBerry MDS Connection Service
BlackBerry devices run the applications using:
• BlackBerry Browser
BlackBerry Java® Applications Developers create the applications using:
• BlackBerry® Java® Development Environment
• standard Java application development tools
The BlackBerry Enterprise Server communicates with the applications using:
• BlackBerry MDS Connection Service
BlackBerry devices run the applications using:
• BlackBerry APIs and Java ME
BlackBerry MDS Runtime Applications Developers create the applications using:
• BlackBerry® MDS Studio
• BlackBerry® Plug-in for Microsoft® Visual Studio®
The BlackBerry Enterprise Server communicates with the applications using:
• BlackBerry MDS Integration Service
• BlackBerry MDS Connection Service
BlackBerry devices run the applications using:
• BlackBerry® MDS Runtime
For more information about the options for developing BlackBerry Applications, visit www.blackberry.com/developers to see
the BlackBerry Mobile Data System Technical Overview.
26

Feature and Technical Overview
BlackBerry MDS
BlackBerry MDS Connection Service
The BlackBerry® MDS Connection Service connects wireless applications on BlackBerry devices to the applications on an
organization’s application servers or web servers. After a wireless application is installed on a BlackBerry device, it can receive
data from push applications that are located on application servers or web servers. The application can also receive data by
sending a pull request from a BlackBerry device to applications that are located on application servers or web servers. The
BlackBerry MDS Connection Service processes push and pull requests and delivers data and updates to BlackBerry
Applications.
The BlackBerry MDS Connection Service also receives and responds to web requests from the BlackBerry® Browser and other
BlackBerry Applications, so that users can view Internet and intranet content on their BlackBerry devices. The BlackBerry
MDS Connection Service sends login requests and requests for instant messaging sessions from BlackBerry devices to the
BlackBerry Collaboration Service. If you stop the BlackBerry MDS Connection Service, you also stop the BlackBerry
Collaboration Service.
Feature Description
protocol connections You can define connections to the web servers on your organization’s intranet
or the Internet using standard Internet protocols such as HTTP, HTTPS, and TCP/
IP.
encrypted communications The BlackBerry MDS Connection Service encrypts content using the same
standard BlackBerry encryption that the BlackBerry Dispatcher uses to encrypt
messages and other data.
data conversion The BlackBerry MDS Connection Service converts data from application servers
and web servers into a format that BlackBerry Applications can interpret and
display.
data optimization The BlackBerry MDS Connection Service processes content for viewing in the
BlackBerry Browser. For example, the BlackBerry MDS Connection Service can
change the data format or remove extraneous data to reduce network traffic.
authentication methods You can configure authentication requirements that match your organization's
sign-on scheme using standard methods such as NTLM, Kerberos™, and LTPA.
You can also define a period of time after which the BlackBerry MDS Connection
Service requests user credentials and caches cookies.
You can use two-factor authentication to create VPN connections between
wireless applications on BlackBerry devices and your organization’s application
servers and web servers.
27

Feature and Technical Overview
BlackBerry MDS
Feature Description
integration with proxy servers You can provide access to specific content through your organization's proxy
servers using the following items:
• proxy exclusion list, which defines the organization-specific URLs that the
BlackBerry MDS Connection Service uses to connect directly to external
web services instead of routing the connections through the organization's
proxy server
• proxy auto-configuration (.pac) file
access control You can configure push initiators and push rules that define which server-side
push applications can send application data and updates to BlackBerry devices,
and which users can receive push requests. You can configure pull rules to specify
which web servers users can access using the BlackBerry Browser and other
applications on BlackBerry devices.
media content management You can control which media files users can receive and access using the
BlackBerry Browser and BlackBerry Applications. You can prevent users from
receiving certain media types (for example, video files), or you can prevent users
from receiving specific subtypes of media (for example, .mp3 files). You can also
configure size limits for media files that users can receive on their BlackBerry
devices.
BlackBerry MDS Integration Service
The BlackBerry® MDS Integration Service allows you to install, update, and manage BlackBerry® MDS Runtime Applications
on BlackBerry devices. The BlackBerry MDS Integration Service supports standard methods of integrating wireless
applications and enterprise applications, for example, by allowing BlackBerry MDS Runtime Applications to access and use
web services on an application server.
Your organization’s developers can create BlackBerry MDS Runtime Applications using the BlackBerry® MDS Studio or the
BlackBerry® Plug-in for Microsoft® Visual Studio®, and publish those applications to the BlackBerry MDS Application
Repository. Using the BlackBerry Manager, you can install, upgrade, and remove BlackBerry MDS Runtime Applications on
BlackBerry devices over the wireless network, and you can manage and quarantine different versions of BlackBerry MDS
Runtime Applications.
28

Feature and Technical Overview
Feature Description
installation options By default, users can search for and install the BlackBerry MDS Runtime
Applications that are stored in the BlackBerry MDS Application Repository, using
the BlackBerry MDS Control Center on their BlackBerry devices. You can prevent
users from searching for the applications. You can also make the installation,
upgrade, or removal of specific BlackBerry MDS Runtime Applications from
BlackBerry devices mandatory.
encrypted communication The BlackBerry MDS Integration Service encrypts all of the data that it sends to
and receives from BlackBerry devices.
troubleshooting tools The BlackBerry Manager displays a series of error messages when unexpected
behavior occurs, such as when an application cannot connect to a content server.
You can respond to possible issues by quarantining a BlackBerry MDS Runtime
Application on a single user’s BlackBerry device or in the BlackBerry MDS
Application Repository.
message monitoring BlackBerry MDS Runtime Applications can request data from an application
server or web server using a series of messages. Web servers return the requested
data using the same message format.
You can monitor the messages that BlackBerry MDS Runtime Applications send
to or recieve from the application servers or web servers that host application
content.
PKI-compliant application certificates The BlackBerry MDS Studio creates certificates and uses them to sign
applications that comply with the PKI X.509 standard.
You can use these certificates to encrypt the connections that the BlackBerry
MDS Integration Service establishes to sensitive content.
control over user access and
permissions
You can configure and assign BlackBerry MDS Integration Service device policies
to users and user groups to control how users discover and access BlackBerry
MDS Runtime Applications, and to define whether BlackBerry MDS Runtime
Applications can access data from other applications on BlackBerry devices.
performance management You can specify message queue limits for data that BlackBerry MDS Runtime
Applications send and receive.
29

Feature and Technical Overview
BlackBerry device management
BlackBerry device management
You can use the BlackBerry® Enterprise Server to control how you implement, maintain, and upgrade BlackBerry devices
across your organization.
Wireless implementation of BlackBerry devices
Administrators can activate users' BlackBerry® devices over the wireless network, instead of activating the BlackBerry devices
through a direct connection with the BlackBerry Manager computer, or instructing users to activate their BlackBerry devices
using the BlackBerry® Desktop Manager on their computers. During the wireless activation process, 200 of the user’s most
recent email messages are sent to the BlackBerry device, and on initial synchronization, populates the BlackBerry device
with the user’s organizer data.
You can use the wireless activation process, with message prepopulation and automatic wireless backup, to provide a user
who is away from the office with a replacement BlackBerry device that contains the same user settings and data as the user's
previous BlackBerry device. You can also use the wireless activation process to redistribute a BlackBerry device to a new
user.
Centralized maintenance of BlackBerry devices
You can use the BlackBerry® Manager to manage all BlackBerry devices in a BlackBerry Domain from a single location.
Feature Description
central software location You can store and install BlackBerry® Device Software and add the BlackBerry
Applications from a central location. From this location, you can update the
software version and deliver the software over the wireless network to all
BlackBerry devices in a BlackBerry Domain.
BlackBerry device configurations You can use software configurations to compare the BlackBerry Device Software
and wireless applications on a BlackBerry device with the BlackBerry Device
Software and wireless applications defined in the user’s software configuration.
The BlackBerry Manager reports this information so that you can identify
BlackBerry devices that are not running the most recent or preferred version of
the BlackBerry Device Software or wireless applications.
BlackBerry device reporting The BlackBerry device agent sends information to the BlackBerry Manager over
the wireless network. This enables you to keep a current statistical inventory of
the BlackBerry devices that are implemented in your organization.
30

Feature and Technical Overview
Feature Description
wireless application delivery You can use software configurations to send BlackBerry Java® Applications to
BlackBerry devices over the wireless network.
BlackBerry Enterprise Solution security
Controlling third-party applications on BlackBerry devices
Feature Description
control the installation and removal of
third-party applications
control the resources that third-party
applications can access
control the availability of BlackBerry®
MDS Runtime Applications
Allow users to download and install third-party applications on BlackBerry®
devices or prevent them from downloading applications. You can also remove
applications from BlackBerry devices over the wireless network.
Create application control policies or BlackBerry MDS Integration Service device
policies that specify the resources that third-party applications can access on
BlackBerry devices (for example, message, phone, and key store).
Create IT policies that specify the type of connections that third-party
applications on BlackBerry devices can establish (for example, opening network
connections inside the firewall).
Create BlackBerry MDS Integration Service device policies to control whether
users can search for BlackBerry MDS Runtime Applications in the BlackBerry
MDS Application Repository.
BlackBerry Enterprise Solution security
The BlackBerry® Enterprise Solution is designed to encrypt data in transit at all points between the BlackBerry device and
the BlackBerry® Enterprise Server to protect your organization from data loss or alteration. Only the BlackBerry Enterprise
Server and the BlackBerry device can access the data that they send between them. If events that threaten the wireless
security of your organization occur, third parties, including wireless service providers, cannot access your organization's
potentially sensitive information in a decrypted format.
The BlackBerry Enterprise Solution uses symmetric key cryptography to encrypt messages and user data that it sends over
the transport layer to provide the following criteria for the security of wired and wireless solutions.
Criteria Description
confidentiality The BlackBerry Enterprise Solution uses encryption to make sure that only the intended
message recipients can view the contents of the message.
31

Feature and Technical Overview
BlackBerry Enterprise Solution security
Criteria Description
integrity The BlackBerry Enterprise Solution protects each message that the BlackBerry device
sends with one or more message keys. To prevent third-party decryption or alteration
of the message data, the message keys are designed to consist of random data.
Only the BlackBerry Enterprise Server and the BlackBerry device know the value of
the master encryption key, recognize the format of the decrypted and decompressed
message, and automatically reject a message that is not encrypted with the correct
master encryption key.
authenticity The BlackBerry device authenticates itself to the BlackBerry Enterprise Server to prove
that it knows the master encryption key before the BlackBerry Enterprise Server can
send data to the BlackBerry device.
Master encryption keys
The BlackBerry® Enterprise Server and the BlackBerry device each store a copy of the unique master encryption key of the
BlackBerry device.
Only the BlackBerry Enterprise Server and the BlackBerry device know the value of the master encryption key. When you
activate a BlackBerry device over the wireless network, the BlackBerry Enterprise Server and the BlackBerry device use an
authenticated link to communicate the value of the master encryption key.
For a user to send and receive messages on the BlackBerry device, the BlackBerry Enterprise Server and the BlackBerry
device must store matching copies of the master encryption key of the BlackBerry device. If the stored keys do not match,
the following actions occur:
• the BlackBerry Enterprise Server and the BlackBerry device must delete messages that they receive from each other
because they cannot decrypt them
• the BlackBerry device requires the user to generate a new master encryption key
Standard message encryption
The BlackBerry® Enterprise Solution uses a symmetric key encryption algorithm to protect data in transit between the
BlackBerry device and BlackBerry® Enterprise Server. This standard BlackBerry encryption, which is designed to provide
strong security, protects data in transit to the BlackBerry Enterprise Server when the message data is outside the
organization's firewall.
Standard BlackBerry encryption is designed to encrypt messages that the BlackBerry device sends or that the BlackBerry
Enterprise Server forwards to the BlackBerry device
32

Feature and Technical Overview
BlackBerry Enterprise Solution security
• from the time the user sends an email message or PIN message from the BlackBerry device to when the BlackBerry
Enterprise Server receives the message
• from the time the BlackBerry Enterprise Server receives a message to when the user opens the decrypted message on
the BlackBerry device.
Before the BlackBerry device sends a message it compresses the message and then encrypts the message using the master
encryption key, which is unique to that BlackBerry device. The BlackBerry device does not use the master encryption key in
the compression process.
When the BlackBerry Enterprise Server receives the message from the BlackBerry device, the BlackBerry Dispatcher decrypts
the message using the master encryption key for the BlackBerry device, and then decompresses the message.
How the BlackBerry Enterprise Solution uses an AES encryption algorithm
The BlackBerry® Enterprise Solution uses an AES algorithm in CBC mode to create message keys and master encryption
keys that contain 256 bits of key data.
The way that the BlackBerry device implements AES is designed to protect user data and encryption keys on the BlackBerry
device from traditional attacks and side-channel attacks. Side-channel attacks can occur in the form of power analysis
readings or electromagnetic radiation emissions.
The BlackBerry device implements AES in a way that uses countermeasures (a masking operation, table splitting, and
applications of random masks) to hide the true operations taking place on the BlackBerry device. These countermeasures
are designed to help protect the cryptographic keys and plain-text data against potential side-channel attacks at all points
during the AES encryption and decryption operations so that the attacks do not reveal data that can expose the encryption
key.
Options for encrypting stored data
You can configure the BlackBerry® Enterprise Solution to encrypt the user data and the encryption keys on a locked BlackBerry
device.
Protection of user data on locked BlackBerry devices
When the content protection feature on the BlackBerry® device is turned on, the BlackBerry device is designed to protect
user data in the following ways:
• use 256-bit AES encryption to encrypt stored data
• use an ECC public key to encrypt data that the BlackBerry device receives
33

Feature and Technical Overview
BlackBerry Enterprise Solution security
User data that the BlackBerry device can encrypt when the content protection feature is turned on
Item Description
AutoText all text that automatically replaces the text that a BlackBerry® device user
types
BlackBerry® Browser
• content that web sites or third-party applications push to the BlackBerry
device
• web sites that the user saves on the BlackBerry device
• browser cache
calendar
• subject
• location
• meeting organizer
• meeting participants
• notes included in the appointment or meeting invitation
address book contacts all contact information except the contact title and category
For information about using the Force Include Address Book In Content
Protection IT policy rule to prevent users from turning off encryption for the
address book, see the Policy Reference Guide.
message list
• subject
• email addresses
• message body
• attachments
memo list
• title
• information included in the body of the note
Open Mobile Alliance™ DRM
applications
a key that identifies the BlackBerry device and a key that identifies the SIM
card (if available) that the BlackBerry device adds to DRM forward-locked
applications
RSA SecurID® library the contents of the .sdtid file seed that is stored in flash memory
tasks
• subject
• information included in the body of the task
34

Feature and Technical Overview
BlackBerry Enterprise Solution security
Protection of master encryption keys on locked BlackBerry devices
If you turn on the content protection of master encryption keys feature, the BlackBerry® device uses the grand master key
to encrypt the master encryption keys that are stored in flash memory and stores the decrypted grand master key in RAM.
When you, the user, or the password timeout locks the BlackBerry device, the BlackBerry device continues to receive data
and does not free the memory associated with the grand master key. When the BlackBerry device receives data that is
encrypted with a master encryption key while it is locked, it uses the decrypted grand master key to decrypt the required
master encryption key that is stored in flash memory and receive the data.
Controlling BlackBerry device access to the BlackBerry Enterprise Server
You can turn on the Enterprise Service Policy to control which BlackBerry® devices can connect to the BlackBerry® Enterprise
Server. After you turn on the Enterprise Service Policy, by default, the BlackBerry Enterprise Server prevents connections
from new BlackBerry devices that you associate with it; however, it allows connections from BlackBerry devices that are
already activated on the BlackBerry Enterprise Server. The Enterprise Service Policy also applies to devices with BlackBerry®
Connect™ software, devices with BlackBerry® Built-In™ software, and devices that are running the BlackBerry® Application
Suite.
You can use the Enterprise Service Policy to create allowed lists that control which BlackBerry devices users can activate on
a BlackBerry Enterprise Server, over the wireless network, or over a serial connection. BlackBerry devices that meet the
allowed list criteria can complete the activation process on that BlackBerry Enterprise Server.
You can define the following types of criteria:
• specific, allowed BlackBerry device PINs as a string
• allowed range of BlackBerry device PINs
You can also control access to the BlackBerry Enterprise Server based on specific manufacturers and models of BlackBerry
devices. The BlackBerry Manager includes lists of allowed manufacturers and models based on the properties of the
BlackBerry devices that are associated with the BlackBerry Enterprise Server. You can clear items in these lists to prevent
further connections by BlackBerry devices of a specific manufacturer or model.
You can allow a specific user to override the Enterprise Service Policy so that the user can still connect to the BlackBerry
Enterprise Server even if that user's BlackBerry device or BlackBerry enabled device meets criteria that you exclude from
the allowed list.
35

Feature and Technical Overview
BlackBerry Policy Service
Management of BlackBerry device security over the wireless network using IT administration
commands
Goal Description
erase application data on a lost or stolen BlackBerry® device If a BlackBerry device is lost or stolen, you can send the Erase
data and disable BlackBerry device IT administration
command to delete all information and application data
from the BlackBerry device and make the BlackBerry device
unavailable.
lock a misplaced BlackBerry device If a BlackBerry device is misplaced but likely not stolen or
lost, you can send the Set password and lock the BlackBerry
device IT administration command to set a password and
lock the BlackBerry device. You can also send this IT
administration command if a user forgets the BlackBerry
device password.
label a BlackBerry device with owner information If a BlackBerry device is stolen or lost, you can send the Set
owner information IT administration command to make
owner information appear on the screen when the
BlackBerry device is locked. The owner information might
include contact information that the finder can use to return
the BlackBerry device to the owner.
BlackBerry Policy Service
The BlackBerry® Policy Service performs administration services over the wireless network. It sends IT policies and IT
administration commands and provisions service books.
The BlackBerry® Enterprise Server uses the BlackBerry Policy Service to send IT policies to BlackBerry devices. An IT policy
is made up of rules that define BlackBerry device security, settings for synchronizing data over the wireless network, and
other behaviors for the individual user accounts or groups of user accounts that you define. You can use the BlackBerry
Manager to configure IT policies.
36

Feature and Technical Overview
BlackBerry Policy Service
Feature Description
wireless delivery When you configure IT policies, all settings take effect when the BlackBerry
Policy Service delivers them to BlackBerry devices over the wireless network.
New IT policy rule settings write to the user configurations on BlackBerry
devices automatically.
To keep the IT policy rule settings current, the BlackBerry Enterprise Server
periodically sends the IT policies to BlackBerry devices over the wireless
network.
IT policy coverage When you install the BlackBerry Enterprise Server and add user accounts to it,
the BlackBerry Policy Service adds the user accounts to the default IT policy
automatically. Until BlackBerry devices accept the IT policy, the user accounts
are not active on the BlackBerry Enterprise Server.
You can assign a different IT policy to user accounts. User accounts must
always be assigned to one IT policy. If you delete all IT policies, the BlackBerry
Policy Service assigns user accounts to the default IT policy automatically.
IT policy assignment You can assign an IT policy to individual user accounts or groups of user
accounts.
resend options If the BlackBerry Enterprise Server cannot send an updated IT policy to a
BlackBerry device immediately—for example, if a user is outside of a wireless
coverage area—you can resend the IT policy manually or configure the period
of time after which the BlackBerry Policy Service resends the IT policy
automatically. The BlackBerry Enterprise Server continues to resend the IT
policy automatically until it sends the IT policy to a BlackBerry device
successfully.
security enforcement You can configure IT policies to override user-defined security settings on
BlackBerry devices.
You can configure IT polices that define security settings for BlackBerry
devices and the BlackBerry® Desktop Software. For example, you can configure
whether a BlackBerry device password is required, the length of time that a
password can exist before it is not valid, and the length and composition of a
password. You can also use IT policies to specify encryption key details.
37

Feature and Technical Overview
BlackBerry Configuration Panel
BlackBerry Configuration Panel
The BlackBerry® Configuration Panel displays data, such as BlackBerry Configuration Database settings, that the
BlackBerry® Enterprise Server setup application gathered during the installation process. You can use the BlackBerry
Configuration Panel to change configuration data after you install the BlackBerry Enterprise Server.
38

Feature and Technical Overview
BlackBerry Enterprise Server process flows
BlackBerry Enterprise Server process flows
4
Messaging process flows
Process flow: Connecting to a messaging server
1. A BlackBerry® Enterprise Server opens a connection that allows multiple logins to a Novell® GroupWise® server using
the trusted application key, and opens a connection to a user's post office.
The peek mode is set between the BlackBerry Enterprise Server and the Novell GroupWise server.
2. The Novell GroupWise connector creates a TCP/IP connection to the Novell GroupWise server using the Novell
GroupWise Object API. This connection remains open while the BlackBerry Enterprise Server is running.
3. The BlackBerry Enterprise Server starts processing transactions when all active users are connected.
You can add users to the BlackBerry Enterprise Server without restarting the Novell GroupWise server or the BlackBerry
Enterprise Server.
Process flow: Sending a message to a BlackBerry device
1. A new message arrives in a user’s Novell® GroupWise® mailbox.
2. The BlackBerry® Messaging Agent polls the user's mailbox and detects the message.
3. The BlackBerry Messaging Agent applies global filter rules to the messages in the user’s mailbox and filters the messages
that match the filter criteria.
If no global filter rules apply, the BlackBerry Messaging Agent applies user-defined filter rules to the messages in the
user’s mailbox.
4. The BlackBerry Messaging Agent sends the first 2 KB of the message to the BlackBerry Dispatcher.
5. The BlackBerry Dispatcher compresses the first 2 KB of the message, encrypts it with the master encryption key of the
BlackBerry device, and sends the encrypted data to the BlackBerry Router.
6. The BlackBerry Router sends the encrypted data to the wireless network over port 3101.
39

Feature and Technical Overview
Messaging process flows
7. The wireless network verifies that the PIN belongs to a valid BlackBerry device that is registered with the wireless
network, and sends the message data to the BlackBerry device.
8. The BlackBerry device sends a delivery confirmation to the BlackBerry Dispatcher. The BlackBerry Dispatcher sends
the delivery confirmation to the BlackBerry Messaging Agent.
If the BlackBerry Messaging Agent does not receive a delivery confirmation within four hours, it sends the message to
the wireless network again.
The delivery confirmation verifies that the wireless network delivered the message to the BlackBerry device, but it does
not verify that the user received or opened the message.
9. The BlackBerry device decrypts and decompresses the message so that the user can view it, and notifies the user that
the message has arrived.
Process flow: Sending a message from a BlackBerry device
This process flow applies to new messages, reconciled messages (messages that are moved, deleted, or marked as read or
unread), and wireless calendar entries.
1. A user sends a message from a BlackBerry® device.
The BlackBerry device assigns a RefId to the message. If the message is a meeting invitation or calendar entry, the
BlackBerry device appends the calendar information to the message.
2. The BlackBerry device compresses and encrypts the message, and sends the message to the wireless network over port
3101.
3. The wireless network sends the message to the BlackBerry® Enterprise Server.
The BlackBerry Enterprise Server accepts only encrypted messages from the BlackBerry device.
4. The BlackBerry Dispatcher uses the master encryption key of the BlackBerry device to decrypt and decompress the
message.
If the BlackBerry Dispatcher cannot decrypt the message using the master encryption key, the BlackBerry Enterprise
Server ignores the message and sends an error message to the BlackBerry device.
5. The BlackBerry Messaging Agent sends the message to the user’s email application.
6. The BlackBerry Messaging Agent sends a copy of the message to the Sent Items view in the user’s email application.
40

Feature and Technical Overview
7. The messaging server delivers the message to the recipients.
Process flow: Searching an organization's address book from a BlackBerry device
1. A user performs a contact lookup on a BlackBerry® device.
2. The BlackBerry device assigns a RefId to the search request, compresses and encrypts the request, and sends the request
to the BlackBerry® Enterprise Server over port 3101.
3. The BlackBerry Dispatcher decrypts and decompresses the request with the master encryption key of the BlackBerry
device, and sends the request to the BlackBerry Messaging Agent.
4. The BlackBerry Messaging Agent searches the Novell® GroupWise® address book that is synchronized in the BlackBerry
Configuration Database and retrieves the 20 closest matches to the contact lookup request.
The BlackBerry Messaging Agent sends the contact lookup results to the BlackBerry Dispatcher.
5. The BlackBerry Dispatcher encrypts the results with the master encryption key of the BlackBerry device, compresses
the encrypted data, and sends it to the BlackBerry Router for delivery to the BlackBerry device.
6. The BlackBerry Router sends the encrypted data to the wireless network over port 3101.
7. The wireless network verifies that the PIN belongs to a valid BlackBerry device that is registered with the wireless
network, and sends the encrypted data to the BlackBerry device.
8. The BlackBerry device sends a delivery confirmation to the BlackBerry Dispatcher, which sends it to the BlackBerry
Messaging Agent.
If the BlackBerry Enterprise Server does not receive a delivery confirmation within four hours, it resubmits the contact
lookup results to the wireless network.
9. The BlackBerry device decrypts and decompresses the contact lookup results with the master encryption key so that
the user can view them on the BlackBerry device or add them to the contact list on the BlackBerry device.
41

Feature and Technical Overview
Instant messaging process flows
Instant messaging process flows
Process flow: Starting an instant messaging session using the BlackBerry Client for use with
Microsoft Office Live Communications Server 2005 (Windows Messenger)
1. A user logs in to a collaboration client on a BlackBerry® device.
2. The BlackBerry device compresses and encrypts the user ID and password and sends them through the BlackBerry
Router to the BlackBerry Dispatcher over port 3101.
3. The BlackBerry Dispatcher sends the request to the BlackBerry Collaboration Service over port 3201. If the BlackBerry
Collaboration Service is located on a remote computer, the request remains encrypted using a Research In Motion
proprietary protocol.
4. The BlackBerry Collaboration Service checks the BlackBerry Configuration Database to find out if the maximum number
of instant messaging sessions has been reached, and performs one of the following actions:
• If the maximum number of sessions has been reached and a timeout limit is set, the BlackBerry Collaboration
Service logs out any instant messaging sessions on BlackBerry devices that are out of coverage, and any instant
messaging sessions that are no longer sending status messages to the BlackBerry Collaboration Service.
• If there are no idle sessions, the BlackBerry Collaboration Service sends a "Server Busy" status message to the
BlackBerry device and rejects the login request.
• If the maximum number of sessions is not set and the number of sessions equals the total number that the
Microsoft® Real-Time Communications API supports, the BlackBerry Collaboration Service sends a "Failed" status
message to the BlackBerry device and rejects the login request.
5. The BlackBerry Collaboration Service checks the BlackBerry Configuration Database to verify that the user has
permission to use the collaboration client, and places the request in the local queue for the BlackBerry Instant Messaging
Connector.
42

Feature and Technical Overview
Instant messaging process flows
6. On the computer that hosts the BlackBerry Collaboration Service, the MSMQ software version 3.0 or later sends the
request in XMPP format, encrypted with AES, to the BlackBerry Instant Messaging Connector.
The BlackBerry Collaboration Service opens the connection using TLS.
7. The BlackBerry Instant Messaging Connector creates an RTC client object for the session, which maintains an open TLS
connection between the collaboration client and the Microsoft® Office Live Communications Server for the duration
of the session.
The default transport protocol is TLS. If you changed the transport protocol to TCP, it requires more dedicated
connections for each session and supports fewer sessions.
8. The BlackBerry Instant Messaging Connector returns the acceptance to the local queue on the BlackBerry Collaboration
Service.
9. The BlackBerry Collaboration Service returns the acceptance, in encrypted and compressed format, through the
BlackBerry Dispatcher to the BlackBerry device, and creates a cache of the connectivity information to maintain the
new instant messaging session.
10. The collaboration client on the BlackBerry device starts the instant messaging session using the RTC connection object.
Process flow: Starting an instant messaging session using the BlackBerry Client for use with
Microsoft Office Live Communications Server 2005 (Microsoft Office Communicator)
1. A user logs in to a collaboration client on a BlackBerry® device.
2. The BlackBerry device compresses and encrypts the user ID and password, and sends them through the BlackBerry
Router to the BlackBerry Dispatcher over port 3101.
3. The BlackBerry Dispatcher sends the request to the BlackBerry Collaboration Service over port 3201. If the BlackBerry
Collaboration Service is located on a remote computer, the request remains encrypted using a Research In Motion
proprietary protocol.
43

Feature and Technical Overview
Instant messaging process flows
4. The BlackBerry Collaboration Service checks the BlackBerry Configuration Database to find out if the maximum number
of sessions has been reached, and performs one of the following actions:
• If the maximum number of sessions has been reached and a timeout limit is set, the BlackBerry Collaboration
Service logs out any instant messaging sessions on BlackBerry devices that are out of coverage, and any instant
messaging sessions that are no longer sending status messages to the BlackBerry Collaboration Service.
• If there are no idle sessions, the BlackBerry Collaboration Service sends a "Server Busy" status message to the
BlackBerry device and rejects the login request.
• If the maximum number of sessions is not set and the number of sessions equals the total number that the HTTP
persistent connection supports, the BlackBerry Collaboration Service sends a "Failed" status message to the
BlackBerry device and rejects the login request.
5. The BlackBerry Collaboration Service checks the BlackBerry Configuration Database to verify that the user has
permission to use the collaboration client, and tries to authenticate the user using Integrated Windows® Authentication;
if the authentication is not successful, the BlackBerry Collaboration Service tries a forms-based login process instead.
The BlackBerry Collaboration Service sends a login request in JSON, a lightweight data-interchange format, to the
Microsoft® Office Communicator Web Access server.
The BlackBerry Collaboration Service opens the connection using HTTPS over port 443. The administrator can also
configure the connection to use HTTP, the transport protocol that the AJAX service uses, or a custom port number.
6. The Microsoft Office Communicator Web Access server formats the request using a Microsoft API and sends the request
to the Microsoft® Office Live Communications Server over an MTLS connection.
7. The Microsoft Office Live Communications Server accepts the request, processes the login information, and sends the
acceptance to the Microsoft Office Communicator Web Access server.
8. The Microsoft Office Communicator Web Access server sends the acceptance to the BlackBerry Collaboration Service.
9. The BlackBerry Collaboration Service sends the acceptance, in encrypted and compressed format, through the
BlackBerry Dispatcher to the BlackBerry device, and creates a cache of the connectivity information to maintain the
new instant messaging session.
10. The collaboration client on the BlackBerry device starts the session using an open GET request over the HTTPS persistent
connection.
The BlackBerry Collaboration Service receives server-initiated events from the Microsoft Office Communicator Web Access
server using an HTTP GET or HTTPS GET request, and sends these events to the collaboration client over this session. The
BlackBerry Collaboration Service sends events that the BlackBerry device initiates to the Microsoft Office Communicator
Web Access server using an HTTP POST or HTTPS POST request.
44
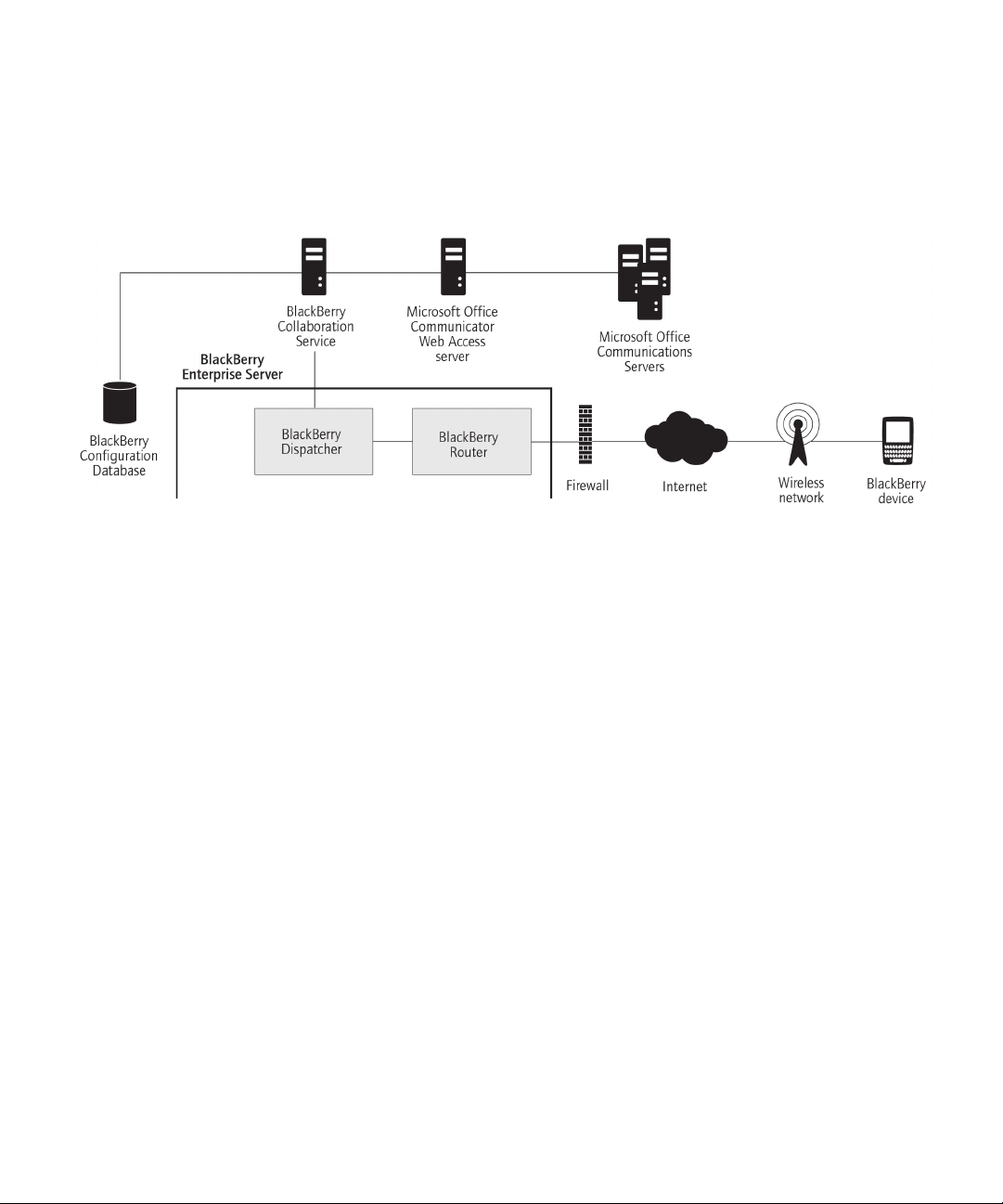
Feature and Technical Overview
Instant messaging process flows
Process flow: Starting an instant messaging session using the BlackBerry Client for use with
Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
1. A user logs in to a collaboration client on a BlackBerry® device.
2. The BlackBerry device compresses and encrypts the user ID and password, and sends them through the BlackBerry
Router to the BlackBerry Dispatcher over port 3101.
3. The BlackBerry Dispatcher sends the request to the BlackBerry Collaboration Service over port 3201. If the BlackBerry
Collaboration Service is located on a remote computer, the request remains encrypted using a Research In Motion
proprietary protocol.
4. The BlackBerry Collaboration Service checks the BlackBerry Configuration Database to find out if the maximum number
of sessions has been reached, and performs one of the following actions:
• If the maximum number of sessions has been reached and a timeout limit is set, the BlackBerry Collaboration
Service logs out any instant messaging sessions on BlackBerry devices that are out of coverage, and any instant
messaging sessions that are no longer sending status messages to the BlackBerry Collaboration Service.
• If there are no idle sessions, the BlackBerry Collaboration Service sends a "Server Busy" status message to the
BlackBerry device and rejects the login request.
• If the maximum number of sessions is not set and the number of sessions equals the total number that the HTTP
persistent connection supports, the BlackBerry Collaboration Service sends a "Failed" status message to the
BlackBerry device and rejects the login request.
5. The BlackBerry Collaboration Service checks the BlackBerry Configuration Database to verify that the user has
permission to use the collaboration client, and tries to authenticate the user using Integrated Windows® Authentication;
if the authentication is not successful, the BlackBerry Collaboration Service tries a forms-based login process instead.
The BlackBerry Collaboration Service sends a login request in XML format to the Microsoft® Office Communicator Web
Access Server.
45
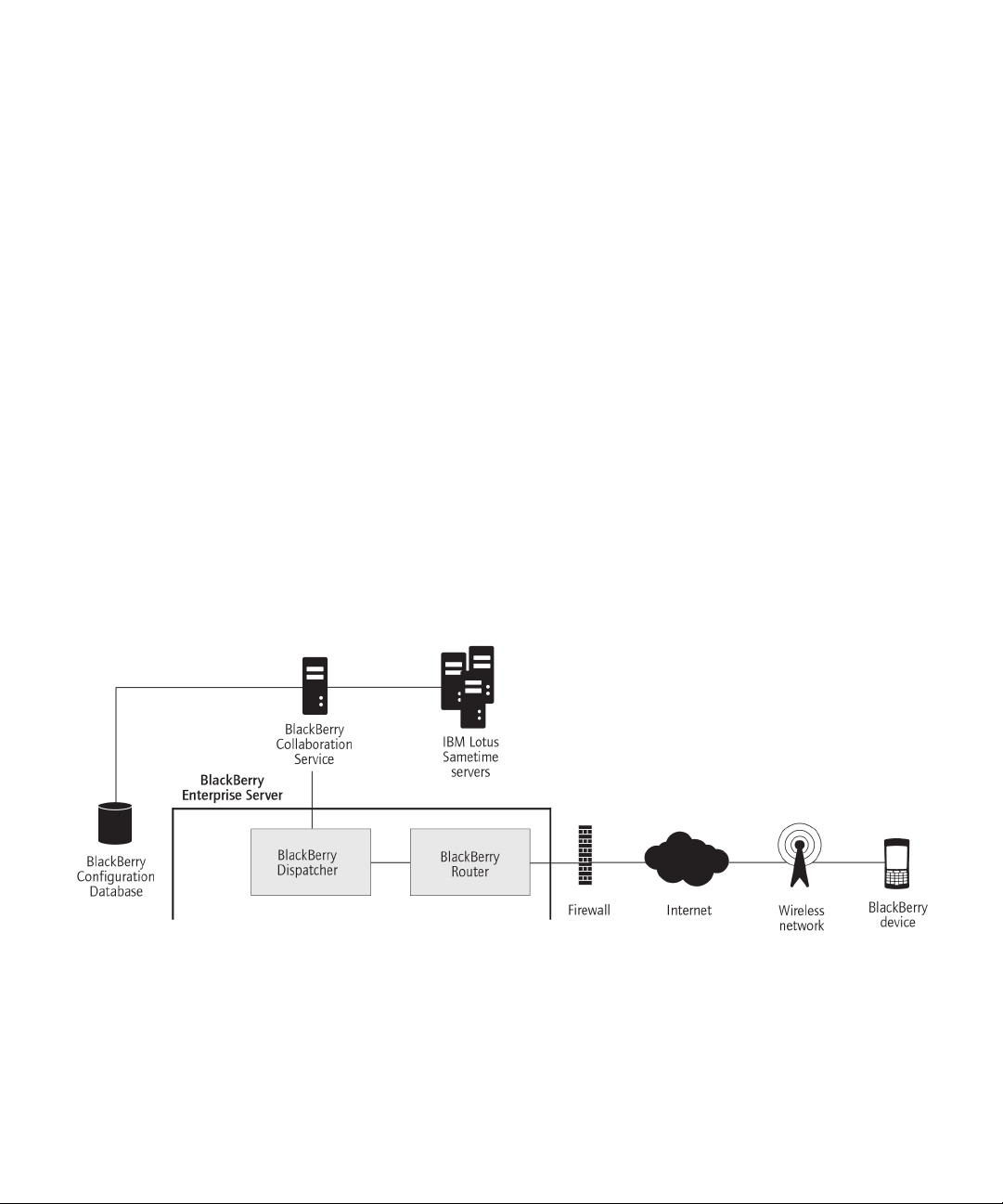
Feature and Technical Overview
Instant messaging process flows
The BlackBerry Collaboration Service opens the connection using HTTPS over port 443. The administrator can also
configure the connection to use HTTP, the transport protocol that the AJAX service uses, or a custom port number.
6. The Microsoft Office Communicator Web Access server formats the request using a Microsoft API and sends the request
to the Microsoft® Office Live Communications Server over an MTLS connection.
7. The Microsoft Office Live Communications Server accepts the request, processes the login information, and sends the
acceptance to the Microsoft Office Communicator Web Access server.
8. The Microsoft Office Communicator Web Access server sends the acceptance to the BlackBerry Collaboration Service.
9. The BlackBerry Collaboration Service sends the acceptance, in encrypted and compressed format, through the
BlackBerry Dispatcher to the BlackBerry device, and creates a cache of the connectivity information to maintain the
new instant messaging session.
10. The collaboration client on the BlackBerry device starts the session using an open GET request over the HTTPS persistent
connection.
The BlackBerry Collaboration Service receives server-initiated events from the Microsoft Office Communicator Web Access
server using an HTTP GET or HTTPS GET request, and sends these events to the collaboration client over this session. The
BlackBerry Collaboration Service sends events that the BlackBerry device initiates to the Microsoft Office Communicator
Web Access server using an HTTP POST or HTTPS POST request.
Process flow: Starting an instant messaging session using the BlackBerry Client for IBM Lotus
Sametime
1. A user logs in to a collaboration client on a BlackBerry® device.
2. The BlackBerry device compresses and encrypts the user ID and password, and sends them through the BlackBerry
Router to the BlackBerry Dispatcher over port 3101.
46

Feature and Technical Overview
Instant messaging process flows
3. The BlackBerry Dispatcher sends the request to the BlackBerry Collaboration Service over port 3201. If the BlackBerry
Collaboration Service is located on a remote computer, the request remains encrypted using a Research In Motion
proprietary protocol.
4. The BlackBerry Collaboration Service checks the BlackBerry Configuration Database to find out if the maximum number
of sessions has been reached, and performs one of the following actions:
• If the maximum number of sessions has been reached and a timeout limit is set, the BlackBerry Collaboration
Service logs out any instant messaging sessions on BlackBerry devices that are out of coverage, and any instant
messaging sessions that are no longer sending status messages to the BlackBerry Collaboration Service.
• If there are no idle sessions, the BlackBerry Configuration Database sends a "Server Busy" status message to the
BlackBerry device and rejects the login request.
• If the maximum number of sessions is not set and the number of sessions equals the total number that the IBM®
Lotus® Sametime® API supports, the BlackBerry Configuration Database sends a "Failed" status message to the
BlackBerry device and rejects the login request.
5. The BlackBerry Collaboration Service checks the BlackBerry Configuration Database to verify that the user has
permission to use the collaboration client, and connects to the IBM Lotus Sametime server. The BlackBerry Collaboration
Service starts an encrypted proxy connection over TCP/IP using the IBM Lotus Sametime API, reformats the request
from the RIM proprietary protocol format into one that the IBM Lotus Sametime API supports, and sends the request.
By default, the BlackBerry Collaboration Service starts the connection over port 1533 unless you specify a custom port
number.
6. The IBM Lotus Sametime server accepts the login request from the BlackBerry device, starts a dedicated TCP/IP
connection for the session, and starts listening for requests from the BlackBerry device for that session.
7. The BlackBerry Collaboration Service sends the acceptance, in encrypted and compressed format, through the
BlackBerry Dispatcher to the BlackBerry device, and creates a cache of the connectivity information to maintain the
new instant messaging session.
47
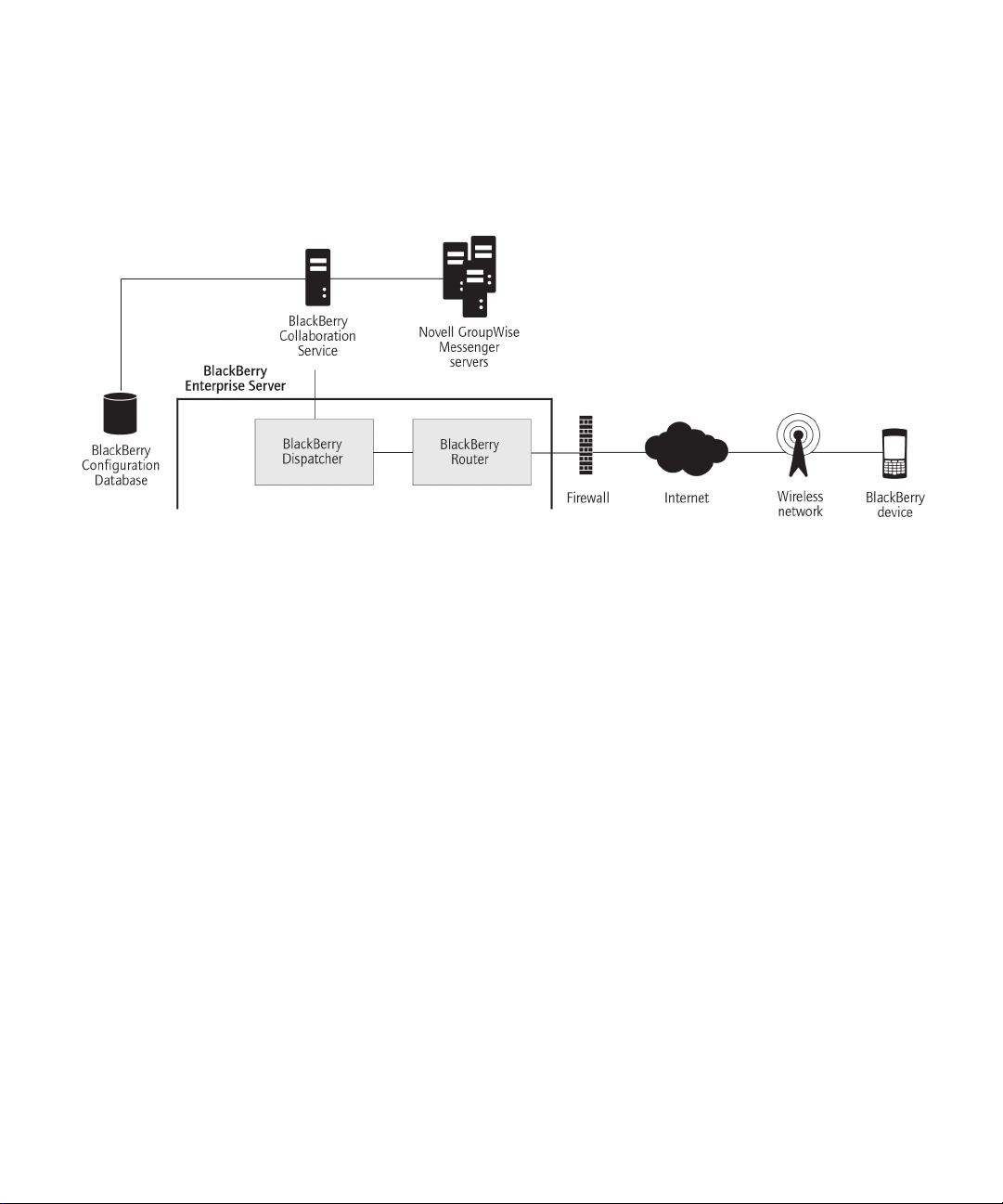
Feature and Technical Overview
Instant messaging process flows
Process flow: Starting an instant messaging session using the BlackBerry Client for Novell
GroupWise Messenger
1. A user logs in to a collaboration client on a BlackBerry® device.
2. The BlackBerry device compresses and encrypts the user ID and password and sends them through the BlackBerry
Router to the BlackBerry Dispatcher over port 3101.
3. The BlackBerry Dispatcher sends the request to the BlackBerry Collaboration Service over port 3201. If the BlackBerry
Collaboration Service is located on a remote computer, the request remains encrypted using a Research In Motion®
proprietary protocol.
4. The BlackBerry Collaboration Service checks the BlackBerry Configuration Database to find out if the maximum number
of sessions has been reached, and performs one of the following actions:
• If the maximum number of sessions has been reached and a timeout limit is set, the BlackBerry Collaboration
Service logs out any instant messaging sessions on BlackBerry devices that are out of coverage, and any instant
messaging sessions that are no longer sending status messages to the BlackBerry Collaboration Service.
• If there are no idle sessions, the BlackBerry Configuration Database sends a "Server Busy" status message to the
BlackBerry device and rejects the login request.
• If the maximum number of sessions is not set and the number of sessions equals the total number that the Novell®
GroupWise® protocol supports, the BlackBerry device sends a "Failed (300)" status message to the BlackBerry
device and rejects the login request.
5. The BlackBerry Collaboration Service checks the BlackBerry Configuration Database to verify that the user has
permission to use the collaboration client, and connects to the Novell® GroupWise® Messenger server.
The BlackBerry Collaboration Service starts an encrypted proxy (SSL) connection using the Novell GroupWise protocol
and sends the request. By default, the BlackBerry Collaboration Service opens this connection over port 8300, but it
can also open this connection over a custom port number.
48

Feature and Technical Overview
Instant messaging process flows
6. The Novell GroupWise Messenger server accepts the login request from the BlackBerry device, opens a dedicated SSL
connection for the session, and starts listening for requests from the BlackBerry device.
7. The BlackBerry Collaboration Service sends the acceptance, in encrypted and compressed format, through the
BlackBerry Dispatcher to the BlackBerry device, and creates a cache of the connectivity information to maintain the
new instant messaging session.
Process flow: Sending a file to a contact using the BlackBerry Client for IBM Lotus Sametime
1. A user opens a conversation with a contact, clicks Send File on the menu, and selects a file to send to the contact.
2. The BlackBerry® Client for IBM® Lotus® Sametime® creates an invitation request and sends it to the BlackBerry
Collaboration Service.
3. The BlackBerry Collaboration Service checks the size of the file to verify that it does not exceed the maximum file size
that is configured on the BlackBerry® Enterprise Server, associates the file extension and the conversation ID with the
invitation request, and sends the request to the IBM® Lotus® Sametime® server.
4. The IBM Lotus Sametime server checks the size of the file to verify that it does not exceed the maximum file size that
is configured on the IBM Lotus Sametime server (by default, 1 MB), associates the file with the conversation that is open
between the sender and the recipient, and sends the request to the BlackBerry Collaboration Service.
5. The BlackBerry Collaboration Service converts the request into an instant messaging invitation and sends it to the client
on the recipient's BlackBerry device.
6. In the conversation window on the recipient's client, the recipient receives a request to accept or decline the file. The
recipient can also select an option to optimize the file for viewing on the BlackBerry device.
The BlackBerry Collaboration Service can optimize files for viewing on the BlackBerry device only if it has access to the
BlackBerry Attachment Service in your organization's environment.
7. The recipient accepts the request.
If the recipient selected the optimize option, the file will be downloaded to the memory of the BlackBerry device. If the
recipient did not select the optimize option, the client prompts the recipient to save the file to a location in the file
system on the BlackBerry device.
49

Feature and Technical Overview
8. The recipient's client sends a content request packet to the BlackBerry Collaboration Service.
9. The BlackBerry Collaboration Service requests the file size from the IBM Lotus Sametime server, and sends data to the
IBM Lotus Sametime server to begin the file transfer process.
The media transfer state on the BlackBerry Collaboration Service is set to transfer.
10. The sender's client sends the data for the file in content message packets to the BlackBerry Collaboration Service.
11. The BlackBerry Collaboration Service checks the order of the content message packets and sends them to the recipient's
client using a BlackBerry instant messaging protocol.
12. The recipient's client receives the first content message packet, sends an acknowledgement message to the BlackBerry
Collaboration Service, and requests the next content message packet from the BlackBerry Collaboration Service. This
continues until the client receives all of the content message packets.
If the recipient selected the option to optimize the file for viewing, the BlackBerry Attachment Service converts the file
into a format that is optimized for viewing on the BlackBerry device.
13. When the BlackBerry Collaboration Service receives an acknowledgement message for the last content message packet
from the recipient's client, it changes its media transfer state to done and stops the file transfer process on the IBM
Lotus Sametime server.
14. In the conversation window, the client notifies the recipient that the file has been received.
The recipient can open the file from the conversation window or from the file system on the BlackBerry device. The
BlackBerry device uses the BlackBerry® Browser to render supported files. If the recipient selected the option to optimize
the file for viewing, the recipient can open and view supported files in the attachment viewer on the BlackBerry device.
The recipient can also save the optimized file to a location in the file system on the BlackBerry device.
Message attachment process flows
Message attachment process flows
Process flow: Viewing a message attachment
1. A user receives a message with an attachment on a BlackBerry® device.
2. The BlackBerry Messaging Agent verifies that the format of the attachment is valid for conversion.
50

Feature and Technical Overview
Message attachment process flows
If the format is not valid and the user’s BlackBerry device is Java® based, the Open Attachment menu item does not
appear on the user’s BlackBerry device.
3. The user clicks the Open Attachment menu item to view the attachment on the BlackBerry device.
4. The attachment viewer sends the request to the BlackBerry Messaging Agent, which connects to the BlackBerry
Attachment Service over port 1900.
5. The BlackBerry Attachment Service retrieves the attachment in binary format from the user’s message store using the
BlackBerry Messaging Agent link to the messaging server.
The BlackBerry Attachment Service distills the attachment and extracts the content, layout, appearance, and navigation
information from it.
6. The BlackBerry Attachment Service organizes, stores, and links the information in a proprietary DOM in a binary XML
style.
The BlackBerry Attachment Service formats the attachment for the BlackBerry device and converts it to UCS format.
The formatting is based on the request for content (for example, page and paragraph information, or search words) and
the available BlackBerry device information (for example, screen size, display, or available space).
7. The BlackBerry Attachment Service sends the UCS data to the BlackBerry Messaging Agent using a TCP/IP connection
over port 1900.
8. The BlackBerry Messaging Agent sends the converted attachment to the BlackBerry Dispatcher.
9. The BlackBerry Dispatcher compresses the first portion of the attachment, encrypts it with the master encryption key
of the BlackBerry device, and sends the first portion of the attachment to the BlackBerry Router.
10. The BlackBerry Router sends the first portion of the attachment to the wireless network over port 3101, which verifies
that the PIN belongs to a valid BlackBerry device that is registered with the wireless network.
11. The wireless network delivers the attachment to the BlackBerry device.
The BlackBerry device sends a delivery confirmation to the BlackBerry Dispatcher, which sends it to the BlackBerry
Messaging Agent. If the BlackBerry® Enterprise Server does not receive a delivery confirmation within 4 hours, it sends
the attachment data to the wireless network again.
12. The BlackBerry device uses its master encryption key to decrypt and decompress the attachment so that the user can
view it.
13. The user views the attachment on the BlackBerry device by selecting a section from the table of contents, or by viewing
the full attachment. The original formatting of the attachment, including indents, tables, fonts, and bullets, is reflected
on the BlackBerry device.
51

Feature and Technical Overview
Organizer data process flows
Process flow: Viewing an attachment through a link
1. A user clicks the Get Link menu item to view an attachment on a BlackBerry® device.
2. The BlackBerry device sends the request to the BlackBerry® Enterprise Server over port 3101.
3. The BlackBerry Dispatcher sends the request to the BlackBerry MDS Connection Service over port 3201.
4. The BlackBerry MDS Connection Service creates an HTTP session for the user and sends the request to the web server.
The BlackBerry MDS Connection Service retrieves the requested content and sends it to the BlackBerry Attachment
Service.
5. The BlackBerry Attachment Service extracts the content, layout, appearance, and navigation information from the
attachment, and organizes, stores, and links the information in a proprietary DOM in a binary XML style.
6. The BlackBerry Attachment Service formats the attachment for the BlackBerry device and converts it to UCS format.
The formatting is based on the request for content (for example, page and paragraph information, or search words) and
the available BlackBerry device information (for example, screen size, display, or available space).
7. The BlackBerry Attachment Service sends the converted attachment to the BlackBerry MDS Connection Service using
HTTP.
8. The BlackBerry MDS Connection Service sends the first 250 KB of content to the BlackBerry Dispatcher over port 3201.
9. The BlackBerry Dispatcher compresses the content, encrypts it with the master encryption key of the BlackBerry device,
and sends the content to the BlackBerry Router.
10. The BlackBerry Router sends the content to the BlackBerry device.
11. The BlackBerry device uses its master encryption key to decrypt and decompress the attachment so that the user can
view it.
12. The user views the attachment on the BlackBerry device using the browser plug-in for the attachment viewer.
The attachment viewer processes 3 KB at a time.
Organizer data process flows
52

Feature and Technical Overview
Organizer data process flows
Process flow: Synchronizing organizer data for the first time on a BlackBerry device
1. A user activates a new BlackBerry® device or upgrades an existing BlackBerry device and receives the service book for
the BlackBerry Synchronization Service.
2. The BlackBerry device requests the synchronization configuration information from the BlackBerry Synchronization
Service.
The configuration information indicates whether wireless data synchronization on the BlackBerry® Enterprise Server
is turned on, and which database can be synchronized. The configuration information also provides database
synchronization types and conflict resolution settings. All data that the BlackBerry device and the BlackBerry Enterprise
Server send between them is compressed and encrypted.
3. The BlackBerry Synchronization Service returns the configuration information and synchronizes the databases using
that information.
A synchronization agent on the BlackBerry device tracks which databases can be synchronized over the wireless network.
If data already exists on both the BlackBerry device and the BlackBerry Enterprise Server, the BlackBerry Synchronization
Service merges, adds, or updates the records during the synchronization process. If data exists on only the BlackBerry
device or the BlackBerry Enterprise Server, the BlackBerry Synchronization Service restores the data from that location.
The BlackBerry device and the BlackBerry Enterprise Server do not delete records during the initial synchronization
process.
After the BlackBerry Synchronization Service registers a database for wireless data synchronization, it can no longer
be synchronized or restored using the BlackBerry® Desktop Software.
The initial synchronization process is complete when the data on the BlackBerry device and the data on the BlackBerry
Enterprise Server are synchronized. Future changes on the BlackBerry device or the BlackBerry Enterprise Server are
synchronized over the wireless network.
53

Feature and Technical Overview
Organizer data process flows
If the user changes data on the BlackBerry device or in the organizer application on the user's computer during the initial
synchronization process, the BlackBerry Synchronization Service synchronizes the changes after the initial synchronization
successfully completes.
If the user connects the BlackBerry device to a computer that is running the BlackBerry® Device Manager, the initial
synchronization can occur over the connection to the BlackBerry Router instead of over the wireless network.
Process flow: Synchronizing subsequent changes to organizer data
1. A user saves a change to the organizer data or the BlackBerry® device settings (for example, a new AutoText entry) on
a BlackBerry device or in the organizer application on the user's computer.
2. Based on where the user made the change, the BlackBerry device or the BlackBerry® Enterprise Server adds the change
to a changelist and sends the changelist to the BlackBerry Synchronization Service.
The changelist includes target database and record information for the organizer application.
3. The BlackBerry Synchronization Service sends a change to organizer data over the wireless network, along with other
entries in the changelist for that user.
The BlackBerry Synchronization Service sends other changes, including BlackBerry device information, time zone
information, and backup and restore data, at the batch synchronization interval that is set on the BlackBerry Enterprise
Server. By default, the batch synchronization interval is 10 minutes.
To prevent synchronization errors, the BlackBerry Enterprise Server and the BlackBerry device can send only a single
changelist at a time for a user account.
4. The BlackBerry Synchronization Service writes a synchronization request entry to the SynchRequest table of the
BlackBerry Configuration Database, and sends the changed records to the BlackBerry Dispatcher.
5. The BlackBerry Dispatcher compresses the content, encrypts it with the master encryption key of the BlackBerry device,
and sends the content to the BlackBerry Router for delivery to the BlackBerry device.
54

Feature and Technical Overview
6. The BlackBerry device sends a delivery confirmation to the BlackBerry Synchronization Service for each record that it
receives.
7. The BlackBerry Synchronization Service receives delivery confirmations and deletes the corresponding synchronization
request entries from the SyncRequest table, and writes an entry to the SyncRecordState table for each delivery
confirmation.
Each organizer database record has a unique identifier that is mapped to a corresponding record on the BlackBerry
device.
Mobile data process flows
Mobile data process flows
Process flow: Requesting BlackBerry Browser content on a BlackBerry device
1. A user requests Internet or intranet content from the organization's content server using the BlackBerry® Browser on
a BlackBerry device.
2. The BlackBerry device sends the request to the BlackBerry® Enterprise Server over port 3101.
3. The BlackBerry Dispatcher sends the request to the BlackBerry MDS Connection Service over port 3200.
4. The BlackBerry MDS Connection Service creates an HTTP session for the user and retrieves the requested Internet or
intranet content from the content server.
The BlackBerry MDS Connection Service converts the content so that the user can view it on the BlackBerry device,
and sends the content to the BlackBerry Dispatcher over port 3200.
5. The BlackBerry Dispatcher compresses the content, encrypts it with the master encryption key of the BlackBerry device,
and sends it to the BlackBerry Router.
6. The BlackBerry Router sends the encrypted content to the wireless network over port 3101.
7. The wireless network verifies that the PIN belongs to a valid BlackBerry device that is registered with the wireless
network and sends the encrypted content to the BlackBerry device.
8. The BlackBerry device sends a delivery confirmation to the BlackBerry Router, and decrypts and decompresses the
content so that the user can view it in the BlackBerry Browser.
55

Feature and Technical Overview
Mobile data process flows
If the BlackBerry MDS Connection Service does not receive a delivery confirmation within the flow control timeout limit,
it sends a message to the wireless network to delete the pending content.
Process flow: Requesting BlackBerry Browser content while access control is turned on for the
BlackBerry MDS Connection Service
1. A user requests Internet or intranet content from the organization's content server using the BlackBerry® Browser on
a BlackBerry device.
2. The BlackBerry device sends the request to the BlackBerry® Enterprise Server over port 3101.
3. The BlackBerry Dispatcher sends the request to the BlackBerry MDS Connection Service over port 3200.
4. The BlackBerry MDS Connection Service checks the BlackBerry Configuration Database to verify whether pull
authorization is turned on, and whether the user has permission to pull content from the specified content server.
If the user does not have permission to pull content from the specified content server, the BlackBerry MDS Connection
Service rejects the request and sends an error message to the BlackBerry device.
5. The BlackBerry MDS Connection Service creates an HTTP session for the user and sends the user’s authentication
credentials to the content server. If the user authenticates successfully, the BlackBerry MDS Connection Service sends
the HTTP request to the content server. If the user does not authenticate successfully, the BlackBerry Browser displays
an "HTTP 403 Error" message, and prompts the user to type the correct credentials.
6. The BlackBerry MDS Connection Service retrieves the content from the content server, converts it so that the user can
view it on the BlackBerry device, and sends it to the BlackBerry Dispatcher over port 3200.
7. The BlackBerry Dispatcher compresses the content, encrypts it with the master encryption key of the BlackBerry device,
and sends it to the BlackBerry Router.
8. The BlackBerry Router sends the encrypted content to the wireless network over port 3101.
9. The wireless network verifies that the PIN belongs to a valid BlackBerry device that is registered with the wireless
network and sends the encrypted content to the BlackBerry device.
10. The BlackBerry device sends a delivery confirmation to the BlackBerry Router, and decrypts and decompresses the
content so that the user can view it in the BlackBerry Browser.
56

Feature and Technical Overview
Mobile data process flows
If the BlackBerry MDS Connection Service does not receive a delivery confirmation within the flow control timeout limit,
it sends a message to the wireless network to delete the pending content.
Process flow: Requesting BlackBerry Browser content with two-factor authentication turned on
1. A user requests Internet or intranet content from the organization's content server using the BlackBerry® Browser on
a BlackBerry device.
2. The BlackBerry device sends the request to the BlackBerry® Enterprise Server over port 3101.
3. The BlackBerry Dispatcher sends the request to the BlackBerry MDS Connection Service over port 3200.
4. The BlackBerry MDS Connection Service checks whether the user's BlackBerry device is running an authenticated
connection that can support the content request.
If the BlackBerry device is not running an authenticated connection, the BlackBerry MDS Connection Service redirects
the user to a login web page. If the user logs in successfully, using an RSA SecurID® user name and passcode, the
BlackBerry MDS Connection Service creates a connection to the content server. By default, the BlackBerry device caches
the user’s credentials for 24 hours of activity on the authenticated connection, or 60 minutes of inactivity.
5. The BlackBerry MDS Connection Service creates an HTTP session for the user and retrieves the Internet or intranet
content from the content server. The BlackBerry MDS Connection Service converts the content so that the user can
view it on the BlackBerry device, and sends the content to the BlackBerry Dispatcher over port 3200.
6. The BlackBerry Dispatcher compresses the content, encrypts it with the master encryption key of the BlackBerry device,
and sends it to the BlackBerry Router.
7. The BlackBerry Router sends the encrypted content to the wireless network over port 3101.
8. The wireless network verifies that the PIN belongs to a valid BlackBerry device that is registered with the wireless
network and sends the encrypted content to the BlackBerry device.
9. The BlackBerry device sends a delivery confirmation to the BlackBerry Router, and decrypts and decompresses the
content so that the user can view it in the BlackBerry Browser.
If the BlackBerry MDS Connection Service does not receive a delivery confirmation within the flow control timeout limit,
it sends a message to the wireless network to delete the pending content.
57

Feature and Technical Overview
Mobile data process flows
Process flow: Pushing application content to a BlackBerry device
1. A push application on an application server or content server behind the organization's firewall sends an HTTP POST
request to a central push server over the listen port for the content server. The default port number is 8080.
One or more instances of the BlackBerry® MDS Connection Service in a BlackBerry Domain can be defined as a central
push server. A push application specifies the BlackBerry® Enterprise Server host name and the connection port number
that the BlackBerry MDS Connection Service listens on.
2. The central push server checks the BlackBerry Configuration Database for the following information about the intended
recipients of the application content: the PINs that are associated with the users, whether the users' PINs are enabled
for the BlackBerry MDS Connection Service, and the active BlackBerry Enterprise Server instances that the users are
located on.
Users who do not appear in the BlackBerry Configuration Database, or whose accounts are pending deletion, cannot
receive the push content.
3. The central push server responds to the push application to acknowledge that it is processing the request, and sends
the push content to the active instances of the BlackBerry MDS Connection Service that are associated with the active
instances of the BlackBerry Enterprise Server.
4. The BlackBerry MDS Connection Service converts the content so that it can be viewed on the user's BlackBerry device,
and sends the content to the BlackBerry Dispatcher over port 3200.
5. The BlackBerry Dispatcher compresses the content, encrypts it with the master encryption key of the BlackBerry device,
and sends it to the BlackBerry Router.
6. The BlackBerry Router sends the encrypted content to the wireless network over port 3101, which verifies that the PIN
belongs to a valid BlackBerry device that is registered with the wireless network.
7. The wireless network sends the encrypted content to the BlackBerry device.
8. The BlackBerry device sends a delivery confirmation to the BlackBerry Router.
If the BlackBerry MDS Connection Service does not receive a delivery confirmation within the flow control timeout limit,
it sends a message to the wireless network to delete the pending content.
9. The BlackBerry device decrypts and decompresses the content.
58

Feature and Technical Overview
Mobile data process flows
The BlackBerry Application detects the incoming content by listening on a port number that the application developer
specified. For example, the BlackBerry® Browser listens for push application connections on port 7874. The application
displays the content on the BlackBerry device when the user runs the application.
Process flow: Requesting BlackBerry MDS Runtime Applications from a BlackBerry device
1. A user searches for available BlackBerry® MDS Runtime Applications using the BlackBerry MDS Control Center on a
BlackBerry device.
2. The BlackBerry device sends a request for a list of available applications to the BlackBerry® Enterprise Server over port
3101.
3. The BlackBerry Dispatcher sends the request to the BlackBerry MDS Connection Service over port 3200.
4. The BlackBerry MDS Connection Service sends the request to the BlackBerry MDS Integration Service.
5. The BlackBerry MDS Integration Service checks which BlackBerry MDS Runtime Applications are available in the
BlackBerry MDS Application Repository, compiles a list of applications that the user can discover from the BlackBerry
device, and sends the list to the BlackBerry MDS Connection Service.
6. The BlackBerry MDS Connection Service formats the list of applications so that it can be viewed on the BlackBerry
device and sends it to the BlackBerry Dispatcher over port 3200.
7. The BlackBerry Dispatcher compresses the list, encrypts it with the master encryption key of the BlackBerry device, and
sends it to the BlackBerry Router.
8. The BlackBerry Router sends the list to the BlackBerry device, which decrypts and decompresses the list.
9. In the BlackBerry MDS Control Center on the BlackBerry device, the user views the list of BlackBerry MDS Runtime
Applications that are available to download from the BlackBerry MDS Application Repository, and selects a BlackBerry
MDS Runtime Application to install on the BlackBerry device.
10. The BlackBerry device sends the request for the BlackBerry MDS Runtime Application to the BlackBerry Dispatcher
over port 3101.
11. The BlackBerry Dispatcher sends the request to the BlackBerry MDS Connection Service over port 3200.
59

Feature and Technical Overview
12. The BlackBerry MDS Connection Service sends the request to the BlackBerry MDS Integration Service.
13. The BlackBerry MDS Integration Service sends the BlackBerry MDS Runtime Application content from the BlackBerry
MDS Application Repository to the BlackBerry MDS Connection Service.
14. The BlackBerry MDS Connection Service converts the content so that it can be viewed on the BlackBerry device, and
sends the content to the BlackBerry Dispatcher over port 3200.
15. The BlackBerry Dispatcher compresses the content, encrypts it with the master encryption key of the BlackBerry device,
and sends it to the BlackBerry Router.
16. The BlackBerry Router delivers the content to the BlackBerry device, which decrypts and decompresses it.
17. The BlackBerry MDS Runtime Application installs on the BlackBerry device automatically.
18. The BlackBerry device sends an installation confirmation to the BlackBerry MDS Integration Service.
BlackBerry device management process flows
BlackBerry device management process flows
Process flow: Activating the BlackBerry device over the wireless network
The user receives or purchases a new BlackBerry® device.
1. The user contacts your organization's IT department to activate the BlackBerry device.
2. The administrator uses the BlackBerry Manager to create a temporary activation password for the user account and
communicates that password to the user. The password applies to the user account only.
3. To activate the BlackBerry device over the wireless network, the user opens the activation application on the BlackBerry
device and types the appropriate email address and the activation password.
4. The BlackBerry device sends an activation request message to the email account. The message contains information
about the BlackBerry device, such as routing information and the public keys for the BlackBerry device.
5. The BlackBerry® Enterprise Server sends the BlackBerry device an activation response that contains routing information
about the BlackBerry Enterprise Server and the public keys for the BlackBerry Enterprise Server.
6. The BlackBerry Enterprise Server and the BlackBerry device establish a master encryption key. The BlackBerry Enterprise
Server and the BlackBerry device confirm knowledge of the master encryption key to one another. If the confirmation
succeeds, the activation proceeds and further communication between the BlackBerry Enterprise Server and the
BlackBerry device is encrypted.
7. The BlackBerry Enterprise Server sends the IT policy to the BlackBerry device. If the BlackBerry device cannot accept
the IT policy, the activation does not complete.
8. The BlackBerry Enterprise Server sends the appropriate service books (for example, the messaging service book, wireless
calendar service book, browser service book, and other service books) to the BlackBerry device. The user can now send
messages from and receive messages on the BlackBerry device.
9. If the user is configured for wireless synchronization, and the BlackBerry device has wireless backup and wireless
calendar synchronization turned on, the BlackBerry Enterprise Server sends user data to the BlackBerry device.
60

Feature and Technical Overview
BlackBerry device management process flows
Process flow: Resending an IT policy to the BlackBerry device manually
1. In the BlackBerry® Manager, the administrator clicks a user account, and then clicks Resend IT Policy.
2. The BlackBerry Policy Service reads the current IT policy settings of the user account from the BlackBerry Configuration
Database to determine which IT policy to send to the BlackBerry device.
3. The BlackBerry Policy Service prepares to send the IT policy using the GME protocol by adding the unique identifier
and version of the BlackBerry® Enterprise Server.
4. The BlackBerry Policy Service adds the unique key that the BlackBerry Domain uses to sign IT policy data packets to
the IT policy data packet.
5. The BlackBerry Policy Service sends the IT policy data packet to the BlackBerry Dispatcher.
6. The BlackBerry Dispatcher encrypts the IT policy data packet with the master encryption key of the BlackBerry device,
compresses the content, and then sends it to the BlackBerry Router for delivery to the BlackBerry device.
7. The BlackBerry Router sends the encrypted IT policy data packet over port number 3101 to the wireless network. The
wireless network verifies that the PIN belongs to a valid BlackBerry device that is registered on the wireless network.
Process flow: Authenticating the data on a BlackBerry device without connecting to the
BlackBerry Infrastructure
1. A user connects a BlackBerry® device to a computer that the BlackBerry® Device Manager is running on.
2. The BlackBerry Router uses a unique authentication protocol to verify that the user is a valid BlackBerry device user.
This authentication sequence uses the authentication information for the BlackBerry® Enterprise Server and the
BlackBerry device that the SRP authentication sequence uses to validate the BlackBerry Enterprise Server before
allowing it to connect to the BlackBerry® Infrastructure. The BlackBerry Router cannot access the value of the master
encryption key on the BlackBerry device and the BlackBerry Enterprise Server.
3. The BlackBerry device and the BlackBerry Router use the BlackBerry Device Manager to send data to one another over
the physical connection, behind the firewall. All data that the BlackBerry device and the BlackBerry Enterprise Server
send to each other is compressed and encrypted. This data bypasses the wireless network.
The movement of wireless data over an SRP connection is restored when the user disconnects the BlackBerry device
from the computer or closes the BlackBerry Device Manager.
Process flow: Sending an application to a BlackBerry device over the wireless network
1. A BlackBerry® Enterprise Server administrator adds a BlackBerry Java® Application to a network drive, and adds the
BlackBerry Java Application to a user’s software configuration in the BlackBerry Manager. The administrator specifies
wireless delivery for the application.
2. The BlackBerry Policy Service sends the software configuration to the BlackBerry Dispatcher.
61

Feature and Technical Overview
BlackBerry device management process flows
3. The BlackBerry Dispatcher compresses the data, encrypts it with the master encryption key of the BlackBerry device,
and sends it to the BlackBerry Router.
4. The BlackBerry Router sends the data to the wireless network over port 3101.
5. The wireless network verifies that the user’s PIN belongs to a valid BlackBerry device that is registered with the wireless
network.
6. The BlackBerry device receives and applies the updated software configuration, and compares the applications in the
software configuration to the applications that are installed on the BlackBerry device.
If the applications do not match those that are defined in the software configuration (for example, an earlier version of
an application is installed on the BlackBerry device), the BlackBerry device requests the required updates from the
BlackBerry Policy Service.
7. The BlackBerry Policy Service receives the request and sends the applications to the BlackBerry Dispatcher.
8. The BlackBerry Dispatcher compresses the data, encrypts it with the master encryption key of the BlackBerry device,
and sends it to the BlackBerry Router.
9. The BlackBerry Router sends the application data to the wireless network over port 3101, which verifies that the PIN
belongs to a valid BlackBerry device that is registered with the wireless network.
10. The BlackBerry device decrypts and decompresses the application data, and installs the BlackBerry Java Application.
The BlackBerry Java Application appears on the home screen of the BlackBerry device, or it appears in the list of installed
applications on the BlackBerry device.
62

Feature and Technical Overview
Glossary
Glossary
AES
Advanced Encryption Standard
AJAX
Asynchronous JavaScript® and XML
API
application programming interface
ASCII
American Standard Code for Information Interchange
BlackBerry Domain
A BlackBerry Domain consists of the BlackBerry Configuration Database with its users and any BlackBerry® Enterprise
Server instances that connect to it.
BlackBerry MDS
BlackBerry® Mobile Data System
CBC
cipher block chaining
DOM
Document Object Model
5
DRM
Digital Rights Management
ECC
Elliptic Curve Cryptography
GME
The gateway message envelope (GME) protocol is a Research In Motion proprietary protocol that allows the transfer of
compressed and encrypted data between the wireless network and BlackBerry devices. The protocol defines a routing
layer that specifies the types of message contents allowed and the addressing information for the data. Gateways and
routing components use this information to identify the type and source of the BlackBerry device data, and the
appropriate destination service to route the data to.
HTTP
Hypertext Transfer Protocol
63

Feature and Technical Overview
HTTPS
Hypertext Transfer Protocol over Secure Sockets Layer
Java ME
Java® Platform, Micro Edition
JSON
JavaScript® Object Notation
LTPA
Lightweight Third-Party Authentication
messaging server
A messaging server sends and processes messages and provides collaboration services, such as updating and
communicating calendar and address book information.
MSMQ
Microsoft® Message Queuing
MTLS
Mutual Transport Layer Security
Glossary
NTLM
NT LAN Manager
PAC
proxy auto-configuration
PIN
personal identification number
PKI
Public Key Infrastructure
RTC
real-time communications
SIM
Subscriber Identity Module
SRP
Server Routing Protocol
SSL
Secure Sockets Layer
64

Feature and Technical Overview
TCP
Transmission Control Protocol
TCP/IP
Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) is a set of communication protocols that is used to transmit
data over networks, such as the Internet.
TLS
Transport Layer Security
UCS
Universal Content Stream
VPN
virtual private network
XML
Extensible Markup Language
XMPP
Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol
Glossary
65


Feature and Technical Overview
Legal notice
Legal notice
©2008 Research In Motion Limited. All rights reserved. BlackBerry®, RIM®, Research In Motion®, SureType® and related
trademarks, names, and logos are the property of Research In Motion Limited and are registered and/or used in the U.S.
and countries around the world.
Adobe and Acrobat are trademarks of Adobe Systems Incorporated. Corel and WordPerfect are trademarks of Corel
Corporation. IBM, Lotus, and Sametime are trademarks of International Business Machines Corporation. Kerberos is a
trademark of Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Microsoft, Excel, Outlook, PowerPoint, Visual Studio, and Windows are
trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. Novell and GroupWise are trademarks of Novell, Inc. Open Mobile Alliance is a
trademark of Open Mobile Alliance Ltd. RSA SecurID is a trademark of RSA Security. Java and JavaScript are trademarks of
Sun Microsystems, Inc. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
The BlackBerry smartphone and other devices and/or associated software are protected by copyright, international treaties,
and various patents, including one or more of the following U.S. patents: 6,278,442; 6,271,605; 6,219,694; 6,075,470;
6,073,318; D445,428; D433,460; D416,256. Other patents are registered or pending in the U.S. and in various countries
around the world. Visit www.rim.com/patents for a list of RIM (as hereinafter defined) patents.
This documentation including all documentation incorporated by reference herein such as documentation provided or made
available at www.blackberry.com/go/docs is provided or made accessible "AS IS" and "AS AVAILABLE" and without condition,
endorsement, guarantee, representation, or warranty of any kind by Research In Motion Limited and its affiliated companies
("RIM") and RIM assumes no responsibility for any typographical, technical, or other inaccuracies, errors, or omissions in this
documentation. In order to protect RIM proprietary and confidential information and/or trade secrets, this documentation
may describe some aspects of RIM technology in generalized terms. RIM reserves the right to periodically change information
that is contained in this documentation; however, RIM makes no commitment to provide any such changes, updates,
enhancements, or other additions to this documentation to you in a timely manner or at all.
6
This documentation might contain references to third-party sources of information, hardware or software, products or services
including components and content such as content protected by copyright and/or third-party web sites (collectively the
"Third Party Products and Services"). RIM does not control, and is not responsible for, any Third Party Products and Services
including, without limitation the content, accuracy, copyright compliance, compatibility, performance, trustworthiness,
legality, decency, links, or any other aspect of Third Party Products and Services. The inclusion of a reference to Third Party
Products and Services in this documentation does not imply endorsement by RIM of the Third Party Products and Services
or the third party in any way.
EXCEPT TO THE EXTENT SPECIFICALLY PROHIBITED BY APPLICABLE LAW IN YOUR JURISDICTION, ALL CONDITIONS,
ENDORSEMENTS, GUARANTEES, REPRESENTATIONS, OR WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED,
INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY CONDITIONS, ENDORSEMENTS, GUARANTEES, REPRESENTATIONS OR
WARRANTIES OF DURABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE OR USE, MERCHANTABILITY, MERCHANTABLE
QUALITY, NON-INFRINGEMENT, SATISFACTORY QUALITY, OR TITLE, OR ARISING FROM A STATUTE OR CUSTOM OR A
COURSE OF DEALING OR USAGE OF TRADE, OR RELATED TO THE DOCUMENTATION OR ITS USE, OR PERFORMANCE
OR NON-PERFORMANCE OF ANY SOFTWARE, HARDWARE, SERVICE, OR ANY THIRD PARTY PRODUCTS AND SERVICES
REFERENCED HEREIN, ARE HEREBY EXCLUDED. YOU MAY ALSO HAVE OTHER RIGHTS THAT VARY BY STATE OR
PROVINCE. SOME JURISDICTIONS MAY NOT ALLOW THE EXCLUSION OR LIMITATION OF IMPLIED WARRANTIES AND
67

Feature and Technical Overview
Legal notice
CONDITIONS. TO THE EXTENT PERMITTED BY LAW, ANY IMPLIED WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS RELATING TO THE
DOCUMENTATION TO THE EXTENT THEY CANNOT BE EXCLUDED AS SET OUT ABOVE, BUT CAN BE LIMITED, ARE HEREBY
LIMITED TO NINETY (90) DAYS FROM THE DATE YOU FIRST ACQUIRED THE DOCUMENTATION OR THE ITEM THAT IS
THE SUBJECT OF THE CLAIM.
TO THE MAXIMUM EXTENT PERMITTED BY APPLICABLE LAW IN YOUR JURISDICTION, IN NO EVENT SHALL RIM BE LIABLE
FOR ANY TYPE OF DAMAGES RELATED TO THIS DOCUMENTATION OR ITS USE, OR PERFORMANCE OR NONPERFORMANCE OF ANY SOFTWARE, HARDWARE, SERVICE, OR ANY THIRD PARTY PRODUCTS AND SERVICES
REFERENCED HEREIN INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION ANY OF THE FOLLOWING DAMAGES: DIRECT,
CONSEQUENTIAL, EXEMPLARY, INCIDENTAL, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, PUNITIVE, OR AGGRAVATED DAMAGES, DAMAGES
FOR LOSS OF PROFITS OR REVENUES, FAILURE TO REALIZE ANY EXPECTED SAVINGS, BUSINESS INTERRUPTION, LOSS
OF BUSINESS INFORMATION, LOSS OF BUSINESS OPPORTUNITY, OR CORRUPTION OR LOSS OF DATA, FAILURES TO
TRANSMIT OR RECEIVE ANY DATA, PROBLEMS ASSOCIATED WITH ANY APPLICATIONS USED IN CONJUNCTION WITH
RIM PRODUCTS OR SERVICES, DOWNTIME COSTS, LOSS OF THE USE OF RIM PRODUCTS OR SERVICES OR ANY PORTION
THEREOF OR OF ANY AIRTIME SERVICES, COST OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS, COSTS OF COVER, FACILITIES OR SERVICES,
COST OF CAPITAL, OR OTHER SIMILAR PECUNIARY LOSSES, WHETHER OR NOT SUCH DAMAGES WERE FORESEEN OR
UNFORESEEN, AND EVEN IF RIM HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
TO THE MAXIMUM EXTENT PERMITTED BY APPLICABLE LAW IN YOUR JURISDICTION, RIM SHALL HAVE NO OTHER
OBLIGATION, DUTY, OR LIABILITY WHATSOEVER IN CONTRACT, TORT, OR OTHERWISE TO YOU INCLUDING ANY
LIABILITY FOR NEGLIGENCE OR STRICT LIABILITY.
THE LIMITATIONS, EXCLUSIONS, AND DISCLAIMERS HEREIN SHALL APPLY: (A) IRRESPECTIVE OF THE NATURE OF THE
CAUSE OF ACTION, DEMAND, OR ACTION BY YOU INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO BREACH OF CONTRACT,
NEGLIGENCE, TORT, STRICT LIABILITY OR ANY OTHER LEGAL THEORY AND SHALL SURVIVE A FUNDAMENTAL BREACH
OR BREACHES OR THE FAILURE OF THE ESSENTIAL PURPOSE OF THIS AGREEMENT OR OF ANY REMEDY CONTAINED
HEREIN; AND (B) TO RIM AND ITS AFFILIATED COMPANIES, THEIR SUCCESSORS, ASSIGNS, AGENTS, SUPPLIERS
(INCLUDING AIRTIME SERVICE PROVIDERS), AUTHORIZED RIM DISTRIBUTORS (ALSO INCLUDING AIRTIME SERVICE
PROVIDERS) AND THEIR RESPECTIVE DIRECTORS, EMPLOYEES, AND INDEPENDENT CONTRACTORS.
IN ADDITION TO THE LIMITATIONS AND EXCLUSIONS SET OUT ABOVE, IN NO EVENT SHALL ANY DIRECTOR, EMPLOYEE,
AGENT, DISTRIBUTOR, SUPPLIER, INDEPENDENT CONTRACTOR OF RIM OR ANY AFFILIATES OF RIM HAVE ANY LIABILITY
ARISING FROM OR RELATED TO THE DOCUMENTATION.
Prior to subscribing for, installing, or using any Third Party Products and Services, it is your responsibility to ensure that your
airtime service provider has agreed to support all of their features. Installation or use of Third Party Products and Services
with RIM's products and services may require one or more patent, trademark, copyright, or other licenses in order to avoid
infringement or violation of third party rights. You are solely responsible for determining whether to use Third Party Products
and Services and if any third party licenses are required to do so. If required you are responsible for acquiring them. You
should not install or use Third Party Products and Services until all necessary licenses have been acquired. Any Third Party
Products and Services that are provided with RIM's products and services are provided as a convenience to you and are
provided "AS IS" with no express or implied conditions, endorsements, guarantees, representations, or warranties of any
kind by RIM and RIM assumes no liability whatsoever, in relation thereto. Your use of Third Party Products and Services shall
be governed by and subject to you agreeing to the terms of separate licenses and other agreements applicable thereto with
third parties, except to the extent expressly covered by a license or other agreement with RIM.
68

Feature and Technical Overview
Legal notice
The terms of use of any RIM product or service are set out in a separate license or other agreement with RIM applicable
thereto. NOTHING IN THIS DOCUMENTATION IS INTENDED TO SUPERSEDE ANY EXPRESS WRITTEN AGREEMENTS OR
WARRANTIES PROVIDED BY RIM FOR PORTIONS OF ANY RIM PRODUCT OR SERVICE OTHER THAN THIS
DOCUMENTATION.
Certain features outlined in this documentation require a minimum version of BlackBerry® Enterprise Server Software,
BlackBerry® Desktop Software, and/or BlackBerry® Device Software and may require additional development or Third Party
Products and Services for access to corporate applications.
This product includes software developed by the Apache Software Foundation (www.apache.org/) and/or licensed pursuant
to Apache License, Version 2.0 (www.apache.org/licenses/). For more information, see the NOTICE.txt file included with the
software. Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for
the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
Research In Motion Limited
295 Phillip Street
Waterloo, ON N2L 3W8
Canada
Research In Motion UK Limited
200 Bath Road
Slough, Berkshire SL1 3XE
United Kingdom
Published in Canada
69
 Loading...
Loading...