HP GbE2c User Manual

HP GbE2c Ethernet Blade Switch for c-Class BladeSystem
Command Reference Guide
Part number: 418118-003
Third edition: December 2006
Legal notices
© 2004, 2006 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Microsoft®, Windows®, and Windows NT® are U.S. registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. SunOS™ and Solaris™ are trademarks of Sun Microsystems, Inc. in the U.S. and other countries.
Cisco® is a registered trademark of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and certain other countries. Part number: 418118-003
Third edition: December 2006
2

Contents |
|
Command line interface |
|
Introduction ............................................................................................................................................. |
9 |
Additional references ............................................................................................................................... |
9 |
Connecting to the switch ........................................................................................................................... |
9 |
Establishing a console connection ......................................................................................................... |
9 |
Setting an IP address ......................................................................................................................... |
10 |
Establishing a Telnet connection.......................................................................................................... |
10 |
Establishing an SSH connection .......................................................................................................... |
10 |
Accessing the switch .............................................................................................................................. |
11 |
Idle timeout ........................................................................................................................................... |
12 |
Typographical conventions...................................................................................................................... |
13 |
Menu basics |
|
Introduction ........................................................................................................................................... |
14 |
Main Menu ........................................................................................................................................... |
14 |
Menu summary...................................................................................................................................... |
14 |
Global commands.................................................................................................................................. |
15 |
Command line history and editing............................................................................................................ |
16 |
Command line interface shortcuts............................................................................................................. |
17 |
Command stacking ........................................................................................................................... |
17 |
Command abbreviation ..................................................................................................................... |
17 |
Tab completion................................................................................................................................. |
17 |
First-time configuration |
|
Introduction ........................................................................................................................................... |
18 |
Configuring Simple Network Management Protocol support ................................................................... |
18 |
Setting passwords .................................................................................................................................. |
19 |
Changing the default administrator password ....................................................................................... |
19 |
Changing the default user password.................................................................................................... |
20 |
Changing the default operator password ............................................................................................. |
21 |
Information Menu |
|
Introduction ........................................................................................................................................... |
22 |
Menu overview...................................................................................................................................... |
22 |
System Information Menu ........................................................................................................................ |
23 |
SNMPv3 Information Menu ..................................................................................................................... |
23 |
SNMPv3 USM User Table information ...................................................................................................... |
24 |
SNMPv3 View Table information ............................................................................................................. |
25 |
SNMPv3 Access Table information........................................................................................................... |
25 |
SNMPv3 Group Table information ........................................................................................................... |
26 |
SNMPv3 Community Table information..................................................................................................... |
26 |
SNMPv3 Target Address Table information ............................................................................................... |
27 |
SNMPv3 Target Parameters Table information ........................................................................................... |
27 |
SNMPv3 Notify Table information............................................................................................................ |
28 |
SNMPv3 dump...................................................................................................................................... |
29 |
System information................................................................................................................................. |
30 |
Show last 100 syslog messages............................................................................................................... |
31 |
System user information .......................................................................................................................... |
31 |
Layer 2 information ................................................................................................................................ |
32 |
FDB information menu ............................................................................................................................ |
33 |
Show all FDB information................................................................................................................... |
34 |
Link Aggregation Control Protocol information ........................................................................................... |
34 |
LACP dump ........................................................................................................................................... |
35 |
802.1x information................................................................................................................................ |
36 |
Spanning Tree information ...................................................................................................................... |
37 |
|
Command line interface 3 |
Rapid Spanning Tree and Multiple Spanning Tree information |
..................................................................... 39 |
Common Internal Spanning Tree information ............................................................................................. |
41 |
Trunk group information.......................................................................................................................... |
42 |
VLAN information .................................................................................................................................. |
43 |
Layer 2 general information .................................................................................................................... |
43 |
Layer 3 information ................................................................................................................................ |
43 |
Route information................................................................................................................................... |
44 |
Show all IP Route information .................................................................................................................. |
45 |
ARP information..................................................................................................................................... |
46 |
Show all ARP entry information ........................................................................................................... |
46 |
ARP address list information ............................................................................................................... |
46 |
OSPF information................................................................................................................................... |
47 |
OSPF general information ....................................................................................................................... |
48 |
OSPF interface information...................................................................................................................... |
48 |
OSPF Database information menu............................................................................................................ |
48 |
OSPF route codes information ................................................................................................................. |
50 |
Routing Information Protocol information ................................................................................................... |
50 |
RIP Routes information ............................................................................................................................ |
50 |
RIP user configuration ............................................................................................................................. |
51 |
IP information ........................................................................................................................................ |
51 |
IGMP multicast group information ............................................................................................................ |
51 |
IGMP multicast router port information ...................................................................................................... |
52 |
VRRP information ................................................................................................................................... |
52 |
QoS information .................................................................................................................................... |
53 |
802.1p information................................................................................................................................ |
53 |
ACL information..................................................................................................................................... |
54 |
RMON Information Menu ....................................................................................................................... |
54 |
RMON history information ................................................................................................................. |
55 |
RMON alarm information .................................................................................................................. |
56 |
RMON event information ................................................................................................................... |
56 |
Link status information ............................................................................................................................ |
57 |
Port information ..................................................................................................................................... |
58 |
Logical Port to GEA Port mapping ............................................................................................................ |
59 |
Uplink Failure Detection information ......................................................................................................... |
59 |
Information dump................................................................................................................................... |
60 |
Statistics Menu |
|
Introduction ........................................................................................................................................... |
61 |
Menu information .................................................................................................................................. |
61 |
Port Statistics Menu ................................................................................................................................ |
62 |
802.1x statistics ............................................................................................................................... |
63 |
Bridging statistics .............................................................................................................................. |
64 |
Ethernet statistics ............................................................................................................................... |
65 |
Interface statistics .............................................................................................................................. |
67 |
Internet Protocol (IP) statistics .............................................................................................................. |
68 |
Link statistics..................................................................................................................................... |
68 |
Port RMON statistics.......................................................................................................................... |
69 |
Layer 2 statistics..................................................................................................................................... |
70 |
FDB statistics .................................................................................................................................... |
70 |
LACP statistics........................................................................................................................................ |
71 |
Layer 3 statistics..................................................................................................................................... |
71 |
GEA Layer 3 statistics menu ............................................................................................................... |
72 |
GEA Layer 3 statistics ........................................................................................................................ |
72 |
IP statistics........................................................................................................................................ |
72 |
Route statistics .................................................................................................................................. |
73 |
ARP statistics .................................................................................................................................... |
73 |
DNS statistics ................................................................................................................................... |
74 |
|
Command line interface 4 |
ICMP statistics .................................................................................................................................. |
74 |
TCP statistics..................................................................................................................................... |
75 |
UDP statistics .................................................................................................................................... |
76 |
IGMP Multicast Group statistics........................................................................................................... |
77 |
OSPF statistics menu.......................................................................................................................... |
77 |
OSPF global statistics ........................................................................................................................ |
78 |
VRRP statistics ................................................................................................................................... |
80 |
RIP statistics ...................................................................................................................................... |
81 |
Management Processor statistics .............................................................................................................. |
81 |
Packet statistics ................................................................................................................................. |
81 |
TCP statistics..................................................................................................................................... |
82 |
UDP statistics .................................................................................................................................... |
83 |
CPU statistics .................................................................................................................................... |
83 |
Access Control List (ACL) statistics menu ............................................................................................... |
83 |
ACL statistics .................................................................................................................................... |
83 |
SNMP statistics ................................................................................................................................. |
84 |
NTP statistics .................................................................................................................................... |
86 |
Uplink Failure Detection statistics......................................................................................................... |
87 |
Statistics dump.................................................................................................................................. |
87 |
Configuration Menu |
|
Introduction ........................................................................................................................................... |
88 |
Menu information .................................................................................................................................. |
88 |
Viewing, applying, reverting, and saving changes ..................................................................................... |
89 |
Viewing pending changes....................................................................................................................... |
89 |
Applying pending changes ..................................................................................................................... |
89 |
Reverting changes.................................................................................................................................. |
89 |
Saving the configuration ......................................................................................................................... |
89 |
Reminders............................................................................................................................................. |
90 |
System configuration .............................................................................................................................. |
90 |
System host log configuration ............................................................................................................. |
91 |
Secure Shell Server configuration ........................................................................................................ |
92 |
RADIUS server configuration............................................................................................................... |
93 |
TACACS+ server configuration ........................................................................................................... |
94 |
NTP server configuration.................................................................................................................... |
96 |
System SNMP configuration ............................................................................................................... |
96 |
SNMPv3 configuration ...................................................................................................................... |
97 |
User Security Model configuration....................................................................................................... |
98 |
SNMPv3 View configuration .............................................................................................................. |
99 |
View-based Access Control Model configuration................................................................................. |
100 |
SNMPv3 Group configuration .......................................................................................................... |
100 |
SNMPv3 Community Table configuration ........................................................................................... |
101 |
SNMPv3 Target Address Table configuration...................................................................................... |
102 |
SNMPv3 Target Parameters Table configuration.................................................................................. |
102 |
SNMPv3 Notify Table configuration .................................................................................................. |
103 |
System Access configuration............................................................................................................. |
104 |
Management Networks configuration ................................................................................................ |
104 |
User Access Control configuration..................................................................................................... |
105 |
User ID configuration....................................................................................................................... |
105 |
HTTPS Access configuration.............................................................................................................. |
106 |
Port configuration................................................................................................................................. |
106 |
Temporarily disabling a port ............................................................................................................ |
108 |
Port link configuration...................................................................................................................... |
108 |
Port ACL/QoS configuration............................................................................................................. |
109 |
Layer 2 configuration ........................................................................................................................... |
109 |
802.1x configuration ........................................................................................................................... |
109 |
802.1x Global configuration................................................................................................................. |
110 |
|
Command line interface 5 |
802.1x Port configuration ..................................................................................................................... |
111 |
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol / Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol configuration............................................ |
112 |
Common Internal Spanning Tree configuration......................................................................................... |
113 |
CIST bridge configuration ..................................................................................................................... |
114 |
CIST port configuration ......................................................................................................................... |
114 |
Spanning Tree configuration.................................................................................................................. |
115 |
Bridge Spanning Tree configuration .................................................................................................. |
116 |
Spanning Tree port configuration ...................................................................................................... |
117 |
Forwarding Database configuration ....................................................................................................... |
118 |
Static FDB configuration................................................................................................................... |
118 |
Trunk configuration .............................................................................................................................. |
119 |
IP Trunk Hash configuration .............................................................................................................. |
120 |
Layer 2 IP Trunk Hash configuration .................................................................................................. |
120 |
Link Aggregation Control Protocol configuration.................................................................................. |
120 |
LACP Port configuration ................................................................................................................... |
121 |
VLAN configuration......................................................................................................................... |
121 |
Layer 3 configuration ........................................................................................................................... |
122 |
IP interface configuration ................................................................................................................. |
123 |
Default Gateway configuration ......................................................................................................... |
124 |
IP Static Route configuration .................................................................................................................. |
124 |
Address Resolution Protocol configuration ............................................................................................... |
125 |
IP Forwarding configuration .................................................................................................................. |
125 |
Network Filter configuration .................................................................................................................. |
125 |
Route Map configuration....................................................................................................................... |
126 |
IP Access List configuration.................................................................................................................... |
127 |
Autonomous System Path configuration ................................................................................................... |
127 |
Routing Information Protocol configuration .............................................................................................. |
128 |
RIP Interface configuration................................................................................................................ |
129 |
RIP Route Redistribution configuration ................................................................................................ |
130 |
Open Shortest Path First configuration .................................................................................................... |
130 |
OSFP Area Index configuration......................................................................................................... |
131 |
OSPF Summary Range configuration ................................................................................................. |
132 |
OSPF Interface configuration ............................................................................................................ |
133 |
OSPF Virtual Link configuration ......................................................................................................... |
134 |
OSPF Host Entry configuration .......................................................................................................... |
135 |
OSPF Route Redistribution configuration............................................................................................. |
135 |
OSPF MD5 Key configuration........................................................................................................... |
136 |
IGMP configuration .............................................................................................................................. |
136 |
IGMP snooping configuration ........................................................................................................... |
137 |
IGMP static multicast router configuration........................................................................................... |
138 |
IGMP filtering configuration.............................................................................................................. |
138 |
IGMP filter definition ....................................................................................................................... |
139 |
IGMP filtering port configuration ....................................................................................................... |
139 |
Domain Name System configuration.................................................................................................. |
140 |
Bootstrap Protocol Relay configuration .................................................................................................... |
140 |
Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol configuration..................................................................................... |
141 |
VRRP Virtual Router configuration ...................................................................................................... |
141 |
VRRP Virtual Router Priority Tracking configuration .............................................................................. |
143 |
VRRP Virtual Router Group configuration ............................................................................................ |
143 |
VRRP Virtual Router Group Priority Tracking configuration .................................................................... |
144 |
VRRP Interface configuration............................................................................................................. |
145 |
VRRP Tracking configuration............................................................................................................. |
145 |
Quality of Service configuration............................................................................................................. |
146 |
QoS 802.1p configuration............................................................................................................... |
146 |
Access Control configuration ................................................................................................................. |
146 |
Access Control List configuration............................................................................................................ |
147 |
ACL Ethernet Filter configuration ....................................................................................................... |
148 |
|
Command line interface 6 |
ACL IP Version 4 Filter configuration.................................................................................................. |
148 |
ACL TCP/UDP Filter configuration ..................................................................................................... |
149 |
ACL Meter configuration .................................................................................................................. |
150 |
ACL Re-mark configuration ............................................................................................................... |
150 |
ACL Re-mark In-Profile configuration .................................................................................................. |
151 |
ACL Re-mark In-Profile Update User Priority configuration ..................................................................... |
151 |
ACL Re-mark Out-of-Profile configuration ............................................................................................ |
151 |
ACL Packet Format configuration....................................................................................................... |
152 |
ACL Group configuration ................................................................................................................. |
152 |
Remote Monitoring configuration ........................................................................................................... |
152 |
RMON history configuration............................................................................................................. |
153 |
RMON event configuration .............................................................................................................. |
154 |
RMON alarm configuration.............................................................................................................. |
154 |
Port mirroring ...................................................................................................................................... |
155 |
Port-based port mirroring ................................................................................................................. |
156 |
Uplink Failure Detection configuration..................................................................................................... |
156 |
Failure Detection Pair configuration ................................................................................................... |
157 |
Link to Monitor configuration ............................................................................................................ |
157 |
Link to Disable configuration............................................................................................................. |
158 |
Dump ................................................................................................................................................. |
158 |
Saving the active switch configuration .................................................................................................... |
158 |
Restoring the active switch configuration ................................................................................................. |
159 |
Operations Menu |
|
Introduction ......................................................................................................................................... |
160 |
Menu information ................................................................................................................................ |
160 |
Operations-level port options ............................................................................................................ |
160 |
Operations-level port 802.1x options ................................................................................................ |
161 |
Operations-level VRRP options .......................................................................................................... |
161 |
Boot Options Menu |
|
Introduction ......................................................................................................................................... |
162 |
Menu information ................................................................................................................................ |
162 |
Updating the switch software image ....................................................................................................... |
162 |
Downloading new software to the switch ........................................................................................... |
162 |
Selecting a software image to run .......................................................................................................... |
163 |
Uploading a software image from the switch ........................................................................................... |
164 |
Selecting a configuration block.............................................................................................................. |
164 |
Resetting the switch .............................................................................................................................. |
165 |
Accessing the ISCLI .............................................................................................................................. |
165 |
Maintenance Menu |
|
Introduction ......................................................................................................................................... |
166 |
Menu information ................................................................................................................................ |
166 |
System maintenance options............................................................................................................. |
167 |
Forwarding Database options........................................................................................................... |
167 |
Debugging options.......................................................................................................................... |
168 |
ARP cache options .......................................................................................................................... |
168 |
IP Route Manipulation options........................................................................................................... |
169 |
IGMP Multicast Group options.......................................................................................................... |
169 |
IGMP Snooping options................................................................................................................... |
170 |
IGMP Mrouter options ..................................................................................................................... |
170 |
Uuencode flash dump...................................................................................................................... |
171 |
FTP/TFTP system dump put ............................................................................................................... |
171 |
Clearing dump information............................................................................................................... |
171 |
Panic command .............................................................................................................................. |
172 |
Unscheduled system dumps ................................................................................................................... |
172 |
Index |
|
|
Command line interface 7 |
Command line interface 8

Command line interface
Introduction
The HP GbE2c switch is ready to perform basic switching functions right out of the box. Some of the more advanced features, however, require some administrative configuration before they can be used effectively. This guide provides a command reference for the HP GbE2c Ethernet Blade Switch and the HP GbE2c Layer 2/3 Ethernet Blade Switch.
The extensive switching software included in the switch provides a variety of options for accessing and configuring the switch:
•Built-in, text-based command line interfaces (AOS CLI and ISCLI) for access via a local terminal or remote Telnet/Secure Shell (SSH) session
•Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) support for access through network management software such as HP Systems Insight Manager
•A browser-based management interface for interactive network access through the Web browser
The command line interface provides a direct method for collecting switch information and performing switch configuration. Using a basic terminal, you can view information and statistics about the switch, and perform any necessary configuration.
This chapter explains how to access the AOS CLI to the switch.
Additional references
Additional information about installing and configuring the switch is available in the following guides, which are available at http://www.hp.com/go/bladesystem/documentation.
•HP GbE2c Ethernet Blade Switch for c-Class BladeSystem User Guide
•HP GbE2c Ethernet Blade Switch for c-Class BladeSystem ISCLI Reference Guide
•HP GbE2c Ethernet Blade Switch for c-Class BladeSystem Application Guide
•HP GbE2c Ethernet Blade Switch for c-Class BladeSystem Browser-based Interface Reference Guide
•HP GbE2c Ethernet Blade Switch for c-Class BladeSystem Quick Setup Instructions
Connecting to the switch
You can access the command line interface in one of the following ways:
•Using a console connection via the console port
•Using a Telnet connection over the network
•Using a Secure Shell (SSH) connection to securely log in over a network
Establishing a console connection
To establish a console connection with the switch, you need:
•A null modem cable with a female DB-9 connector (See the HP GbE2c Ethernet Blade Switch for c-Class BladeSystem User Guide for more information.)
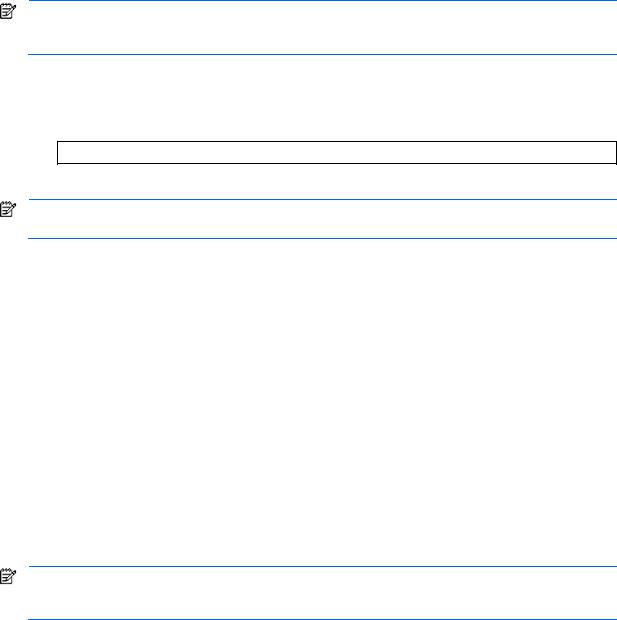
•An ASCII terminal or a computer running terminal emulation software set to the parameters shown in the table below
Table 1 Console configuration parameters
Parameter |
Value |
|
|
Baud Rate |
9600 |
|
|
Data Bits |
8 |
|
|
Parity |
None |
|
|
Stop Bits |
1 |
|
|
Flow Control |
None |
|
|
Command line interface 9

To establish a console connection with the switch:
1.Connect the terminal to the console port using the null modem cable.
2.Power on the terminal.
3.Press the Enter key a few times on the terminal to establish the connection.
4.You will be required to enter a password for access to the switch. (For more information, see the “Setting passwords” section in the “First-time configuration” chapter.)
Setting an IP address
To access the switch via a Telnet or an SSH connection, you need to have an Internet Protocol (IP) address set for the switch. The switch can get its IP address in one of the following ways:
•Management port access:
•Using a Dynamic Host Control Protocol (DHCP) server—When the /cfg/sys/dhcp command is enabled, the management interface (interface 256) requests its IP address from a DHCP server. The default value for the /cfg/sys/dhcp command is enabled.
•Configuring manually—If the network does not support DHCP, you must configure the management interface (interface 256) with an IP address. If you want to access the switch from a remote network, you also must configure the management gateway (gateway 4).
•Uplink port access:
•Using a Bootstrap Protocol (BOOTP) server—By default, the management interface is set up to request its IP address from a BOOTP server. If you have a BOOTP server on the network, add the Media Access Control (MAC) address of the switch to the BOOTP configuration file located on the BOOTP server. The MAC address can be found in the System Information menu (See the “System information” section in the “Information Menu” chapter.) If you are using a DHCP server that also does BOOTP, you do not have to configure the MAC address.
•Configuring manually—If the network does not support BOOTP, you must configure the management port with an IP address.
Establishing a Telnet connection
A Telnet connection offers the convenience of accessing the switch from any workstation connected to the network. Telnet provides the same options for user, operator, and administrator access as those available through the console port. By default, Telnet is enabled on the switch. The switch supports four concurrent Telnet connections.
Once the IP parameters are configured, you can access the CLI using a Telnet connection. To establish a Telnet connection with the switch, run the Telnet program on the workstation and enter the telnet command, followed by the switch IP address:
telnet <GbE2c Ethernet Blade Switch IP address>
You will then be prompted to enter a password. The password entered determines the access level: administrator, operator, or user. See the “Accessing the switch” section later in this chapter for description of default passwords.
Establishing an SSH connection
Although a remote network administrator can manage the configuration of a switch via Telnet, this method does not provide a secure connection. The Secure Shell (SSH) protocol enables you to securely log into the switch over the network.
As a secure alternative to using Telnet to manage switch configuration, SSH ensures that all data sent over the network is encrypted and secure. In order to use SSH, you must first configure it on the switch. See the “Secure Shell Server configuration” section in the “Configuration Menu” chapter for information on how to configure SSH.
The switch can perform only one session of key/cipher generation at a time. Therefore, an SSH/Secure Copy (SCP) client will not be able to log in if the switch is performing key generation at that time or if another client has just logged in before this client. Similarly, the system will fail to perform the key generation if an SSH/SCP client is logging in at that time.
Command line interface 10
The supported SSH encryption and authentication methods are listed below.
•Server Host Authentication—Client RSA authenticates the switch in the beginning of every connection
•Key Exchange—RSA
•Encryption:
•AES256-CBC
•AES192-CBC
•AES128-CBC
•3DES-CBC
•3DES
•ARCFOUR
•User Authentication—Local password authentication; Remote Authentication Dial-in User Service (RADIUS) The following SSH clients are supported:
•SSH 3.0.1 for Linux (freeware)
•SecureCRT® 4.1.8 (VanDyke Technologies, Inc.)
•OpenSSH_3.9 for Linux (FC 3)
•FedoraCore 3 for SCP commands
•PuTTY Release 0.58 (Simon Tatham) for Windows
NOTE: The switch implementation of SSH is based on versions 1.5 and 2.0, and supports SSH clients from version 1.0 through version 2.0. SSH clients of other versions are not supported. You may configure the client software to use protocol SSH version 1 or version 2.
By default, SSH service is not enabled on the switch. Once the IP parameters are configured, you can access the command line interface to enable SSH.
To establish an SSH connection with the switch, run the SSH program on the workstation by issuing the ssh command, followed by the user account name and the switch IP address:
>> # ssh <user>@<GbE2c Ethernet Blade Switch IP address>
You will then be prompted to enter your password.
NOTE: The first time you run SSH from the workstation, a warning message might appear. At the prompt, enter yes to continue.
Accessing the switch
To enable better switch management and user accountability, the switch provides different levels or classes of user access. Levels of access to the CLI and Web management functions and screens increase as needed to perform various switch management tasks. The three levels of access are:
•User—User interaction with the switch is completely passive; nothing can be changed on the switch. Users may display information that has no security or privacy implications, such as switch statistics and current operational state information.
•Operator—Operators can only effect temporary changes on the switch. These changes will be lost when the switch is rebooted/reset. Operators have access to the switch management features used for daily switch operations. Because any changes an operator makes are undone by a reset of the switch, operators cannot severely impact switch operation, but do have access to the Maintenance menu.
•Administrator—Only administrators can make permanent changes to the switch configuration, changes that are persistent across a reboot/reset of the switch. Administrators can access switch functions to configure and troubleshoot problems on the switch. Because administrators can also make temporary (operator-level) changes as well, they must be aware of the interactions between temporary and permanent changes.
Access to switch functions is controlled through the use of unique usernames and passwords. Once you are connected to the switch via the local console, Telnet, or SSH, you are prompted to enter a password. The password entered determines the access level. The default user names/password for each access level is listed in the following table.
NOTE: It is recommended that you change default switch passwords after initial configuration and as regularly as required under your network security policies. For more information, see the “Setting passwords” section in the “First-time configuration” chapter.
Command line interface 11

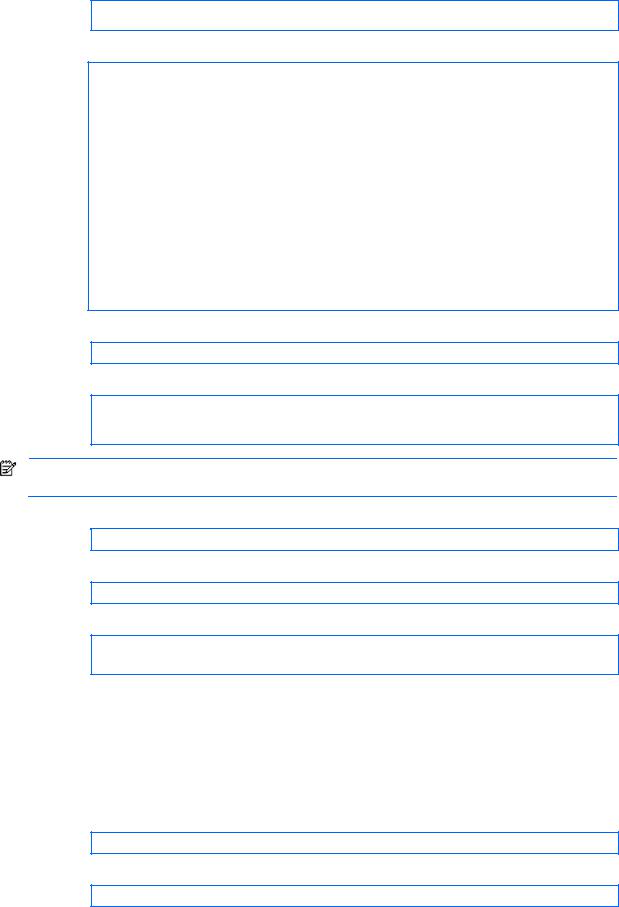
Table 2 User access levels
User account |
Description and tasks performed |
|
|
|
|
User |
The user has no direct responsibility for switch management. He or she can view all |
|
|
switch status information and statistics, but cannot make any configuration changes to the |
|
|
switch. The user account is enabled by default, and the default password is user. |
|
|
|
|
Oper |
The operator manages all functions of the switch. The operator can reset ports or the |
|
|
entire switch. By default, the operator account is disabled and has no password. |
|
|
|
|
Admin |
The super user administrator has complete access to all menus, information, and |
|
|
configuration commands on the switch, including the ability to change both the user and |
|
|
administrator passwords. The admin account is enabled by default, and the default |
|
|
password is admin. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTE: With the exception of the admin user, setting the password to an empty value can disable access to each user level.
Once you enter the administrator password and it is verified, you are given complete access to the switch.
After logging in, the Main Menu of the CLI is displayed. See the “Menu basics” chapter for a summary of the Main Menu options.
[Main Menu] |
|
info |
- Information Menu |
stats |
- Statistics Menu |
cfg |
- Configuration Menu |
oper |
- Operations Command Menu |
boot |
- Boot Options Menu |
maint |
- Maintenance Menu |
diff |
- Show pending config changes [global command] |
apply |
- Apply pending config changes [global command] |
save |
- Save updated config to FLASH [global command] |
revert |
- Revert pending or applied changes [global command] |
exit |
- Exit [global command, always available] |
>> Main# |
|
|
|
Idle timeout
By default, the switch will disconnect the console, Telnet, or SSH session after five minutes of inactivity. This function is controlled by the idle timeout parameter, which can be set from 1 to 60 minutes. For information on changing this parameter, see the “System configuration” section in the “Configuration Menu” chapter.
Command line interface 12

Typographical conventions
The following table describes the typographic styles used in this guide:
Table 3 Typographic conventions
Typeface or symbol |
Meaning |
Example |
|
|
|
AaBbCc123 |
This type depicts onscreen computer output and |
Main# |
|
prompts. |
|
|
|
|
AaBbCc123 |
This type displays in command examples and shows |
Main# sys |
|
text that must be typed in exactly as shown. |
|
|
|
|
<AaBbCc123> |
This italicized type displays in command examples |
To establish a Telnet session, enter: |
|
as a parameter placeholder. Replace the indicated |
host# telnet <IP address> |
|
text with the appropriate real name or value when |
Read the user guide thoroughly. |
|
using the command. Do not type the brackets. |
|
|
This also shows guide titles, special terms, or words |
|
|
to be emphasized. |
|
|
|
|
[ ] |
Command items shown inside brackets are optional |
host# ls [-a] |
|
and can be used or excluded as the situation |
|
|
demands. Do not type the brackets. |
|
|
|
|
Command line interface 13

Menu basics
Introduction
The AOS CLI is used for viewing switch information and statistics. In addition, the administrator can use the CLI for performing all levels of switch configuration.
To make the CLI easy to use, the various commands have been logically grouped into a series of menus and submenus. Each menu displays a list of commands and/or submenus that are available, along with a summary of what each command will do. Below each menu is a prompt where you can enter any command appropriate to the current menu.
This chapter describes the Main Menu commands, and provides a list of commands and shortcuts that commonly are available from all the menus within the CLI.
Main Menu
The Main Menu displays after a successful connection and login. The following table shows the Main Menu for the administrator login. Some features are not available under the user login.
[Main Menu] |
|
info |
- Information Menu |
stats |
- Statistics Menu |
cfg |
- Configuration Menu |
oper |
- Operations Command Menu |
boot |
- Boot Options Menu |
maint |
- Maintenance Menu |
diff |
- Show pending config changes [global command] |
apply |
- Apply pending config changes [global command] |
save |
- Save updated config to FLASH [global command] |
revert |
- Revert pending or applied changes [global command] |
exit |
- Exit [global command, always available] |
|
|
Menu summary
The Main Menu displays the following submenus:
•Information Menu
The Information Menu provides submenus for displaying information about the current status of the switch: from basic system settings to VLANs, and more.
•Statistics Menu
This menu provides submenus for displaying switch performance statistics. Included are port, IP, ICMP, TCP, UDP, SNMP, routing, ARP, and DNS.
•Configuration Menu
This menu is available only from an administrator login. It includes submenus for configuring every aspect of the switch. Changes to configuration are not active until explicitly applied. Changes can be saved to non-volatile memory (NVRAM).
•Operations Command Menu
Operations-level commands are used for making immediate and temporary changes to switch configuration. This menu is used for bringing ports temporarily in and out of service. This menu is available only from an administrator and operator login.
•Boot Options Menu
The Boot Options Menu is available only from an administrator login. This menu is used for upgrading switch software, selecting configuration blocks, and for resetting the switch when necessary. This menu is also used to set the switch back to factory settings.
•Maintenance Menu
This menu is used for debugging purposes, enabling you to generate a technical support dump of the critical state information in the switch, and to clear entries in the Forwarding Database and the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) and routing tables. This menu is available only from an administrator and operator login.
Menu basics 14

Global commands
Some basic commands are recognized throughout the menu hierarchy. These commands are useful for obtaining online Help, navigating through menus, and for applying and saving configuration changes.
For help on a specific command, type help. The following screen displays:
Global Commands: [can be issued from any menu] |
|
||
help |
up |
pwd |
|
lines |
verbose |
exit |
quit |
diff |
apply |
save |
revert |
ping |
traceroute |
telnet |
history |
pushd |
popd |
who |
|
The following are used to navigate the menu structure: |
|
||
. |
Print current menu |
|
|
.. Move up one menu level |
|
|
|
/ |
Top menu if first, or command separator |
|
|
!Execute command from history
The following table describes the global commands.
Table 4 Global commands
Command |
Action |
|
|
|
|
? command or help |
Provides usage information about a specific command on the current menu. When used |
|
|
|
without the command parameter, a summary of the global commands is displayed. |
|
|
|
. or |
Displays the current menu. |
|
|
|
|
.. or |
up |
Moves up one level in the menu structure. |
|
|
|
/ |
|
If placed at the beginning of a command, displays the Main Menu. Otherwise, this is used |
|
|
to separate multiple commands placed on the same line. |
|
|
|
lines |
Sets the number of lines (n) that display on the screen at one time. The default is 24 lines. |
|
|
|
When used without a value, the current setting is displayed. |
|
|
|
diff |
|
Shows any pending configuration changes that have not been applied. |
|
|
diff flash displays all pending configuration changes that have been applied but not |
|
|
saved to flash memory (NVRAM), as well as those that have not been applied. |
|
|
|
apply |
Applies pending configuration changes. |
|
|
|
|
save |
|
Saves the active configuration to backup, and saves the current configuration as active. |
|
|
save n saves the current configuration as active, without saving the active configuration |
|
|
to backup. |
|
|
|
revert |
Removes changes that have been made, but not applied. |
|
|
|
revert apply removes all changes that have not been saved. |
|
|
|
exit or quit |
Exits from the command line interface and logs out. |
|
|
|
|
ping |
|
Verifies station-to-station connectivity across the network. The format is: |
|
|
ping <host name> | <IP address> [ (number of tries)> [ |
|
|
msec delay ]] |
|
|
• IP address is the hostname or IP address of the device. |
|
|
• number of tries (optional) is the number of attempts (1-32). |
|
|
• msec delay (optional) is the number of milliseconds between attempts. |
|
|
|
traceroute |
Identifies the route used for station-to-station connectivity across the network. The format is: |
|
|
|
traceroute <host name> | <IP address> [<max-hops> [ msec |
|
|
delay ]] |
|
|
• IP address is the hostname or IP address of the target station. |
|
|
• max-hops (optional) is the maximum distance to trace (1-16 devices) |
|
|
• msec delay (optional) is the number of milliseconds to wait for the response. |
|
|
|
pwd |
|
Displays the command path used to reach the current menu. |
|
|
|
Menu basics 15

Table 4 Global commands
Command |
Action |
|
|
|
|
verbose n |
Sets the level of information displayed on the screen: |
|
|
• 0 |
= Quiet: Nothing displays except errors, not even prompts. |
|
• 1 |
= Normal: Prompts and requested output are shown, but no menus. |
|
• 2 |
= Verbose: Everything is shown. This is the default. |
|
• When used without a value, the current setting is displayed. |
|
|
|
|
telnet |
This command is used to Telnet out of the switch. The format is: |
|
|
telnet <hostname> | <IP address> [port] |
|
|
|
|
history |
Displays the history of the last ten commands. |
|
|
|
|
pushd |
Remembers the current location in the directory of menu commands. |
|
|
|
|
popd |
Returns to the last pushd location. |
|
|
|
|
who |
Displays users who are logged in. |
|
|
|
|
Command line history and editing
Using the command line interface, you can retrieve and modify previously entered commands with just a few keystrokes. The following options are available globally at the command line:
Table 5 Command line history and editing options
Option |
Description |
|
|
history |
Displays a numbered list of the last ten previously entered commands. |
|
|
!! |
Repeats the last entered command. |
|
|
!n |
Repeats the nth command shown on the history list. |
|
|
<Ctrl-p> or |
Recalls the previous command from the history list. This can be used multiple times to work |
Up arrow key |
backward through the last ten commands. The recalled command can be entered as is, or |
|
edited using the options below. |
|
|
<Ctrl-n> or |
Recalls the next command from the history list. This can be used multiple times to work forward |
Down arrow key |
through the last ten commands. The recalled command can be entered as is, or edited using the |
|
options below. |
|
|
<Ctrl-a> |
Moves the cursor to the beginning of the command line. |
|
|
<Ctrl-e> |
Moves cursor to the end of the command line. |
|
|
<Ctrl-b> or |
Moves the cursor back one position to the left. |
Left arrow key |
|
|
|
<Ctrl-f> or |
Moves the cursor forward one position to the right. |
Right arrow key |
|
|
|
<Backspace> or Delete Erases one character to the left of the cursor position. |
|
key |
|
|
|
<Ctrl-d> |
Deletes one character at the cursor position. |
|
|
<Ctrl-k> |
Erases all characters from the cursor position to the end of the command line. |
|
|
<Ctrl-l> |
Redisplays the current line. |
|
|
<Ctrl-u> |
Clears the entire line. |
|
|
Other keys |
Inserts new characters at the cursor position. |
|
|
. |
Prints the current level menu list. |
|
|
.. |
Moves to the previous directory level. |
|
|
Menu basics 16
Command line interface shortcuts
The following shortcuts allow you to enter commands quickly and easily.
Command stacking
As a shortcut, you can type multiple commands on a single line, separated by forward slashes (/). You can connect as many commands as required to access the menu option that you want.
For example, the keyboard shortcut to access the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Configuration Menu from the Main# prompt is:
Main# cfg/sys/ssnmp/name
Command abbreviation
Most commands can be abbreviated by entering the first characters that distinguish the command from the others in the same menu or submenu.
For example, the command shown above could also be entered as:
Main# c/sys/ssn/n
Tab completion
By entering the first letter of a command at any menu prompt and pressing the Tab key, the CLI will display all commands or options in that menu that begin with that letter. Entering additional letters will further refine the list of commands or options displayed.
If only one command fits the input text when the Tab key is pressed, that command will be supplied on the command line, waiting to be entered. If the Tab key is pressed without any input on the command line, the currently active menu displays.
Menu basics 17

First-time configuration
Introduction
This chapter describes how to perform first-time configuration and how to change system passwords. To begin first-time configuration of the switch, perform the following steps.
1.Connect to the switch console. After connecting, the login prompt displays.
GbE2c Ethernet Blade Switch for HP c-Class Blade System.
Copyright(C)2006 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
Password:
2.Enter admin as the default administrator password.
The system displays the Main Menu with administrator privileges.
[Main Menu] |
|
info |
- Information Menu |
stats |
- Statistics Menu |
cfg |
- Configuration Menu |
oper |
- Operations Command Menu |
boot |
- Boot Options Menu |
maint |
- Maintenance Menu |
diff |
- Show pending config changes [global command] |
apply |
- Apply pending config changes [global command] |
save |
- Save updated config to FLASH [global command] |
revert |
- Revert pending or applied changes [global command] |
exit |
- Exit [global command, always available] |
>> Main# |
|
|
|
3. From the Main Menu, enter the following command to access the Configuration Menu:
Main# /cfg
The Configuration Menu is displayed.
[Configuration Menu]
sys |
- System-wide Parameter Menu |
port |
- Port Menu |
l2 |
- Layer 2 Menu |
l3 |
- Layer 3 Menu |
qos |
- QOS Menu |
acl |
- Access Control List Menu |
rmon |
- RMON Menu |
pmirr |
- Port Mirroring Menu |
ufd |
- Uplink Failure Detection Menu |
dump |
- Dump current configuration to script file |
ptcfg |
- Backup current configuration to FTP/TFTP server |
gtcfg |
- Restore current configuration from FTP/TFTP server |
cur |
- Display current configuration |
Configuring Simple Network Management Protocol support
NOTE: SNMP support is enabled by default.
1.Use the following command to enable SNMP:
>># /cfg/sys/access/snmp disable|read only|read/write
2.Set SNMP read or write community string. By default, they are public and private respectively:
>># /cfg/sys/ssnmp/rcomm|wcomm
3.When prompted, enter the proper community string.
4.Apply and save configuration if you are not configuring the switch with Telnet support. Otherwise apply and save after the performing the “Optional Setup for Telnet Support” steps.
First-time configuration 18

>>System# apply
>>System# save
Setting passwords
HP recommends that you change all passwords after initial configuration and as regularly as required under the network security policies. See the “Accessing the switch” section in the “Command line interface” chapter for a description of the user access levels.
To change the user, operator, or administrator password, you must log in using the administrator password. Passwords cannot be modified from the user or operator command mode.
NOTE: If you forget your administrator password, call HP technical support for help using the password fix-up mode.
Changing the default administrator password
The administrator has complete access to all menus, information, and configuration commands, including the ability to change the user, operator, and administrator passwords.
The default password for the administrator account is admin. To change the default password:
1.Connect to the switch and log in using the admin password.
2.From the Main Menu, use the following command to access the Configuration Menu:
Main# /cfg
The Configuration Menu is displayed.
[Configuration Menu]
sys |
- System-wide Parameter Menu |
port |
- Port Menu |
l2 |
- Layer 2 Menu |
l3 |
- Layer 3 Menu |
qos |
- QOS Menu |
acl |
- Access Control List Menu |
rmon |
- RMON Menu |
pmirr |
- Port Mirroring Menu |
ufd |
- Uplink Failure Detection Menu |
dump |
- Dump current configuration to script file |
ptcfg |
- Backup current configuration to FTP/TFTP server |
gtcfg |
- Restore current configuration from FTP/TFTP server |
cur |
- Display current configuration |
First-time configuration 19
3.From the Configuration Menu, use the following command to select the System Menu:
>>Configuration# sys
The System Menu is displayed.
[System Menu] |
|
syslog |
- Syslog Menu |
sshd |
- SSH Server Menu |
radius |
- RADIUS Authentication Menu |
tacacs+ |
- TACACS+ Authentication Menu |
ntp |
- NTP Server Menu |
ssnmp |
- System SNMP Menu |
access |
- System Access Menu |
date |
- Set system date |
time |
- Set system time |
timezone |
- Set system timezone (daylight savings) |
idle |
- Set timeout for idle CLI sessions |
notice |
- Set login notice |
bannr |
- Set login banner |
hprompt |
- Enable/disable display hostname (sysName) in CLI prompt |
bootp |
- Enable/disable use of BOOTP |
dhcp |
- Enable/disable use of DHCP on Mgmt interface |
reminders - Enable/disable Reminders |
|
cur |
- Display current system-wide parameters |
4.Enter the following command to set the administrator password:
System# access/user/admpw
5.Enter the current administrator password at the prompt:
Changing ADMINISTRATOR password; validation required...
Enter current administrator password:
NOTE: If you forget your administrator password, call your technical support representative for help using the password fix-up mode.
6.Enter the new administrator password at the prompt:
Enter new administrator password:
7.Enter the new administrator password, again, at the prompt:
Re-enter new administrator password:
8.Apply and save the change by entering the following commands:
System# apply
System# save
Changing the default user password
The user login has limited control of the switch. Through a user account, you can view switch information and statistics, but you cannot make configuration changes.
The default password for the user account is user. This password cannot be changed from the user account. Only the administrator has the ability to change passwords, as shown in the following procedure.
1.Connect to the switch and log in using the admin password.
2.From the Main Menu, use the following command to access the Configuration Menu:
Main# cfg
3.From the Configuration Menu, use the following command to select the System Menu:
>>Configuration# sys
4.Enter the following command to set the user password:
First-time configuration 20

System# access/user/usrpw
5.Enter the current administrator password at the prompt.
Only the administrator can change the user password. Entering the administrator password confirms your authority.
Changing USER password; validation required...
Enter current administrator password:
6.Enter the new user password at the prompt:
Enter new user password:
7.Enter the new user password, again, at the prompt:
Re-enter new user password:
8.Apply and save the changes:
System# apply
System# save
Changing the default operator password
The operator manages all functions of the switch. The operator can reset ports or the entire switch. Operators can only effect temporary changes on the switch. These changes will be lost when the switch is rebooted/reset. Operators have access to the switch management features used for daily switch operations. Because any changes an operator makes are undone by a reset of the switch, operators cannot severely impact switch operation.
By default, the operator account is disabled and has no password. This password cannot be changed from the operator account. Only the administrator has the ability to change passwords, as shown in the following procedure.
1.Connect to the switch and log in using the admin password.
2.From the Main Menu, use the following command to access the Configuration Menu:
Main# cfg
3.From the Configuration Menu, use the following command to select the System Menu:
>>Configuration# sys
4.Enter the following command to set the operator password:
System# access/user/opw
5.Enter the current administrator password at the prompt.
Only the administrator can change the user password. Entering the administrator password confirms your authority.
Changing OPERATOR password; validation required...
Enter current administrator password:
6.Enter the new operator password at the prompt:
Enter new operator password:
7.Enter the new operator password, again, at the prompt:
Re-enter new operator password:
8.Apply and save the changes:
System# apply
System# save
First-time configuration 21

Information Menu
Introduction
You can view configuration information for the switch in the user, operator, and administrator command modes. This chapter discusses how to use the CLI to display switch information.
Menu overview
Command: /info
[Information Menu]
sys |
- System Information Menu |
l2 |
- Layer 2 Information Menu |
l3 |
- Layer 3 Information Menu |
qos |
- QoS Menu |
acl |
- Show ACL information |
rmon |
- Show RMON information |
link |
- Show link status |
port |
- Show port information |
geaport |
- Show system port and gea port mapping |
ufd |
- Show Uplink Failure Detection information |
dump |
- Dump all information |
The following table describes the Information Menu options.
Table 6 Information Menu options
Command |
Usage |
|
|
|
|
sys |
Displays system information. |
|
|
|
|
l2 |
Displays the Layer 2 Information Menu. |
|
|
|
|
l3 |
Displays the Layer 3 Information Menu. |
|
|
|
|
qos |
Displays the Quality of Service (QoS) Information Menu. |
|
|
|
|
acl |
Displays the Access Control List Information Menu. |
|
|
|
|
rmon |
Displays the Remote Monitoring Information Menu. |
|
|
|
|
link |
Displays configuration information about each port, including: |
|
|
• |
Port number |
|
• Port speed (10 Mb/s, 100 Mb/s, 1000 Mb/s, or any) |
|
|
• Duplex mode (half, full, or any) |
|
|
• Flow control for transmit and receive (no, yes, or any) |
|
|
• Link status (up or down) |
|
|
|
|
port |
Displays port status information, including: |
|
|
• |
Port number |
|
• Whether the port uses VLAN tagging or not |
|
|
• Port VLAN ID (PVID) |
|
|
• |
Port name |
|
• |
VLAN membership |
|
|
|
geaport |
Displays GEA port mapping information, used by service personnel. |
|
|
|
|
ufd |
Displays Uplink Failure Detection information |
|
|
|
|
dump |
Dumps all switch information available from the Information Menu (10K or more, depending on |
|
|
your configuration). |
|
|
If you want to capture dump data to a file, set your communication software on your workstation to |
|
|
capture session data prior to issuing the dump commands. |
|
|
|
|
Information Menu 22
System Information Menu
Command: /info/sys
[System Menu] |
|
snmpv3 |
- SNMPv3 Information Menu |
general |
- Show general system information |
log |
- Show last 100 syslog messages |
user |
- Show current user status |
dump |
- Dump all system information |
|
|
The following table describes the System Information Menu options.
Table 7 System Information Menu options
Command |
Usage |
|
|
snmpv3 |
Displays the SNMP v3 Menu. |
|
|
general |
Displays system information, including: |
|
• System date and time |
|
• Switch model name and number |
|
• Switch name and location |
|
• Time of last boot |
|
• MAC address of the switch management processor |
|
• IP address of IP interface #1 |
|
• Hardware version and part number |
|
• Software image file and version number |
|
• Configuration name |
|
• Log-in banner, if one is configured |
|
|
log |
Displays 100 most recent syslog messages. |
|
|
user |
Displays the User Access Information Menu. |
|
|
dump |
Dumps all switch information available from the Information Menu (10K or more, depending on your |
|
configuration). |
|
|
SNMPv3 Information Menu
Command: /info/sys/snmpv3
[SNMPv3 Information Menu]
usm |
- Show usmUser table information |
view |
- Show vacmViewTreeFamily table information |
access |
- Show vacmAccess table information |
group |
- Show vacmSecurityToGroup table information |
comm |
- Show community table information |
taddr |
- Show targetAddr table information |
tparam |
- Show targetParams table information |
notify |
- Show notify table information |
dump |
- Show all SNMPv3 information |
SNMP version 3 (SNMPv3) is an extensible SNMP Framework that supplements the SNMPv2 Framework by supporting the following:
•a new SNMP message format
•security for messages
•access control
•remote configuration of SNMP parameters
For more details on the SNMPv3 architecture, see RFC2271 to RFC2276.
Information Menu 23

The following table describes the SNMPv3 Information Menu options.
Table 8 SNMPv3 Information Menu options
Command |
Usage |
|
|
usm |
Displays User Security Model (USM) table information. |
|
|
view |
Displays information about view name, subtrees, mask and type of view. |
|
|
access |
Displays View-based Access Control information. |
|
|
group |
Displays information about the group that includes the security model, user name, and |
|
group name. |
|
|
comm |
Displays information about the community table. |
|
|
taddr |
Displays the Target Address table. |
|
|
tparam |
Displays the Target parameters table. |
|
|
notify |
Displays the Notify table. |
|
|
dump |
Displays all the SNMPv3 information. |
|
|
SNMPv3 USM User Table information
Command: /info/sys/snmpv3/usm
usmUser Table: |
|
User Name |
Protocol |
-------------------------------- |
-------------------------------- |
adminmd5 |
HMAC_MD5, DES PRIVACY |
adminsha |
HMAC_SHA, DES PRIVACY |
v1v2only |
NO AUTH, NO PRIVACY |
|
|
The User-based Security Model (USM) in SNMPv3 provides security services such as authentication and privacy of messages. This security model makes use of a defined set of user identities displayed in the USM user table. The USM user table contains information like:
•the user name
•a security name in the form of a string whose format is independent of the Security Model
•an authentication protocol, which is an indication that the messages sent on behalf of the user can be authenticated
•the privacy protocol.
The following table describes the SNMPv3 User Table information.
Table 9 User Table parameters
Field |
Description |
|
|
User Name |
This is a string that represents the name of the user that you can use to access the switch. |
|
|
Protocol |
This indicates whether messages sent on behalf of this user are protected from disclosure using a |
|
privacy protocol. GbE2c software supports DES algorithm for privacy. The software also supports |
|
two authentication algorithms: MD5 and HMAC-SHA. |
|
|
Information Menu 24

SNMPv3 View Table information
Command: /info/sys/snmpv3/view
View Name |
Subtree |
Mask |
Type |
------------------ ---------------------------- |
------------- |
-------- |
|
iso |
1 |
|
included |
v1v2only |
1 |
|
included |
v1v2only |
1.3.6.1.6.3.15 |
|
excluded |
v1v2only |
1.3.6.1.6.3.16 |
|
excluded |
v1v2only |
1.3.6.1.6.3.18 |
|
excluded |
|
|
|
|
The user can control and restrict the access allowed to a group to only a subset of the management information in the management domain that the group can access within each context by specifying the group’s rights in terms of a particular MIB view for security reasons.
The following table describes the SNMPv3 View Table information.
Table 10 View Table parameters
Field |
Description |
|
|
View Name |
Displays the name of the view. |
|
|
Subtree |
Displays the MIB subtree as an OID string. A view subtree is the set of all MIB object instances |
|
which have a common Object Identifier prefix to their names. |
|
|
Mask |
Displays the bit mask. |
|
|
Type |
Displays whether a family of view subtrees is included or excluded from the MIB view. |
|
|
SNMPv3 Access Table information
Command: /info/sys/snmpv3/access
Group Name |
Model |
Level |
Match |
ReadV |
WriteV |
NotifyV |
---------- |
------- |
------------ |
------ |
--------- |
-------- |
------- |
v1v2grp |
snmpv1 |
noAuthNoPriv |
exact |
iso |
iso |
v1v2only |
admingrp |
usm |
authPriv |
exact |
iso |
iso |
iso |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The access control sub system provides authorization services.
The vacmAccessTable maps a group name, security information, a context, and a message type, which could be the read or write type of operation or notification into a MIB view.
The View-based Access Control Model defines a set of services that an application can use for checking access rights of a group. This group’s access rights are determined by a read-view, a write-view, and a notify-view. The read-view represents the set of object instances authorized for the group while reading the objects. The write-view represents the set of object instances authorized for the group when writing objects. The notify-view represents the set of object instances authorized for the group when sending a notification.
Information Menu 25

The following table describes the SNMPv3 Access Table information.
Table 11 Access Table parameters
Field |
Description |
|
|
Group Name |
Displays the name of group. |
|
|
Prefix |
Displays the prefix that is configured to match the values. |
|
|
Model |
Displays the security model used, for example, SNMPv1, or SNMPv2 or USM. |
|
|
Level |
Displays the minimum level of security required to gain rights of access. For example, |
|
noAuthNoPriv, authNoPriv, or auth-Priv. |
|
|
Match |
Displays the match for the contextName. The options are: exact and prefix. |
|
|
ReadV |
Displays the MIB view to which this entry authorizes the read access. |
|
|
WriteV |
Displays the MIB view to which this entry authorizes the write access. |
|
|
NotifyV |
Displays the Notify view to which this entry authorizes the notify access. |
|
|
SNMPv3 Group Table information
Command: /info/sys/snmpv3/group
Sec Model |
User Name |
Group Name |
---------- |
----------------------------- |
------------------------------- |
snmpv1 |
v1v2only |
v1v2grp |
usm |
adminmd5 |
admingrp |
usm |
adminsha |
admingrp |
|
|
|
A group is a combination of security model and security name that defines the access rights assigned to all the security names belonging to that group. The group is identified by a group name.
The following table describes the SNMPv3 Group Table information.
Table 12 Group Table parameters
Field |
Description |
|
|
Sec Model |
Displays the security model used, which is any one of: USM, SNMPv1, SNMPv2, and SNMPv3. |
|
|
User Name |
Displays the name for the group. |
|
|
Group Name |
Displays the access name of the group. |
|
|
SNMPv3 Community Table information
Command: /info/sys/snmpv3/comm
Index |
Name |
User Name |
Tag |
---------- |
---------- |
-------------------- |
---------- |
trap1 |
public |
v1v2only |
v1v2trap |
This command displays the community table information stored in the SNMP engine.
Information Menu 26

The following table describes the SNMPv3 Community Table information.
Table 13 Community Table parameters
Field |
Description |
|
|
Index |
Displays the unique index value of a row in this table. |
|
|
Name |
Displays the community string, which represents the configuration. |
|
|
User Name |
Displays the User Security Model (USM) user name. |
|
|
Tag |
Displays the community tag. This tag specifies a set of transport endpoints from which a command |
|
responder application accepts management requests and to which a command responder |
|
application sends an SNMP trap. |
|
|
SNMPv3 Target Address Table information
Command: /info/sys/snmpv3/taddr
Name |
Transport Addr |
Port |
Taglist |
Params |
---------- |
--------------- |
---- |
---------- |
--------------- |
trap1 |
47.81.25.66 |
162 |
v1v2trap |
v1v2param |
This command displays the SNMPv3 target address table information, which is stored in the SNMP engine. The following table describes the SNMPv3 Target Address Table information.
Table 14 Target Address Table parameters
Field |
Description |
|
|
Name |
Displays the locally arbitrary, but unique identifier associated with this snmpTargetAddrEntry. |
|
|
Transport Addr |
Displays the transport addresses. |
|
|
Port |
Displays the SNMP UDP port number. |
|
|
Taglist |
This column contains a list of tag values which are used to select target addresses for a |
|
particular SNMP message. |
|
|
Params |
The value of this object identifies an entry in the snmpTargetParamsTable. The identified entry |
|
contains SNMP parameters to be used when generating messages to be sent to this transport |
|
address. |
|
|
SNMPv3 Target Parameters Table information
Command: /info/sys/snmpv3/tparam
Name |
MP Model |
User Name |
Sec Model Sec Level |
|
------------------- |
-------- |
-------------------- --------- ----------- |
||
v1v2param |
snmpv2c |
v1v2only |
snmpv1 |
noAuthNoPriv |
|
|
|
|
|
Information Menu 27

The following table describes the SNMPv3 Target Parameters Table information.
Table 15 Target Parameters Table
Field |
Description |
|
|
Name |
Displays the locally arbitrary, but unique identifier associated with this snmpTargeParamsEntry. |
|
|
MP Model |
Displays the Message Processing Model used when generating SNMP messages using this |
|
entry. |
|
|
User Name |
Displays the securityName, which identifies the entry on whose behalf SNMP messages will be |
|
generated using this entry. |
|
|
Sec Model |
Displays the security model used when generating SNMP messages using this entry. The system |
|
may choose to return an inconsistentValue error if an attempt is made to set this variable to a |
|
value for a security model which the system does not support. |
|
|
Sec Level |
Displays the level of security used when generating SNMP messages using this entry. |
|
|
SNMPv3 Notify Table information
Command: /info/sys/snmpv3/notify
Name |
Tag |
-------------------- |
-------------------- |
v1v2trap |
v1v2trap |
The following table describes the SNMPv3 Notify Table information.
Table 16 |
SNMPv3 Notify Table |
|
|
Field |
Description |
|
|
Name |
The locally arbitrary, but unique identifier associated with this snmpNotifyEntry. |
|
|
Tag |
This represents a single tag value which is used to select entries in the |
|
snmpTargetAddrTable. Any entry in the snmpTargetAddrTable that contains a tag |
|
value equal to the value of this entry is selected. If this entry contains a value of zero length, no |
|
entries are selected. |
|
|
Information Menu 28

SNMPv3 dump
Command: /info/sys/snmpv3/dump
Engine ID = 80:00:07:50:03:00:0F:6A:F8:EF:00 |
|
|
|
|||
usmUser Table: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
User Name |
|
Protocol |
|
|
|
|
-------------------------------- |
|
-------------------------------- |
||||
admin |
|
NO AUTH, NO PRIVACY |
|
|
||
adminmd5 |
|
HMAC_MD5, DES PRIVACY |
|
|
||
adminsha |
|
HMAC_SHA, DES PRIVACY |
|
|
||
v1v2only |
|
NO AUTH, NO PRIVACY |
|
|
||
vacmAccess Table: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group Name Prefix Model |
Level |
Match |
ReadV |
WriteV |
NotifyV |
|
---------- ------ ------- ------------ |
------ |
------- |
-------- |
------ |
||
admin |
usm |
noAuthNoPriv |
exact |
org |
org |
org |
v1v2grp |
snmpv1 |
noAuthNoPriv |
exact |
org |
org |
v1v2only |
admingrp |
usm |
authPriv |
exact |
org |
org |
org |
vacmViewTreeFamily Table: |
|
|
|
View Name |
Subtree |
Mask |
Type |
-------------------- |
--------------- ------------ |
-------------- |
|
org |
1.3 |
|
included |
v1v2only |
1.3 |
|
included |
v1v2only |
1.3.6.1.6.3.15 |
|
excluded |
v1v2only |
1.3.6.1.6.3.16 |
|
excluded |
v1v2only |
1.3.6.1.6.3.18 |
|
excluded |
vacmSecurityToGroup Table: |
|
|
Sec Model |
User Name |
Group Name |
---------- |
------------------------------- |
----------------------- |
snmpv1 |
v1v2only |
v1v2grp |
usm |
admin |
admin |
usm |
adminsha |
admingrp |
snmpCommunity Table: |
|
|
|
Index |
Name |
User Name |
Tag |
---------- |
---------- -------------------- ---------- |
||
snmpNotify |
Table: |
|
|
Name |
|
Tag |
|
-------------------- |
|
-------------------- |
|
snmpTargetAddr Table: |
|
|
|
Name |
Transport |
Addr Port Taglist |
Params |
---------- |
--------------- ---- ---------- --------------- |
||
snmpTargetParams Table: |
|
||
Name |
|
MP Model User Name |
Sec Model Sec Level |
-------------------- |
|
-------- ------------------ --------- ------- |
|
Information Menu 29

System information
Command: /info/sys/gen
System Information at 6:56:22 Thu Jan 11, 2006
Time zone: America/US/Pacific
GbE2c Ethernet Blade Switch for HP c-Class Blade System sysName:
sysLocation: RackId: Default RUID
RackName: Default Rack Name
EnclosureSerialNumber: -none-
EnclosureName: Default Chassis Name
BayNumber: 1
Switch is up 0 days, 14 hours, 56 minutes and 22 seconds.
Last boot: 17:25:38 Mon Jan 8, 2006 (software reset)
MAC address: 00:10:00:01:00:01 |
IP (If 1) address: 10.14.4.16 |
|
Revision: |
|
|
Switch Serial No: |
|
|
Hardware |
Part No: |
Spare Part No: |
Software |
Version 2.0.0 (FLASH image2), active configuration. |
|
System information includes:
•System date and time
•Switch model name and number
•HP c-Class Rack name and location
•Time of last boot
•MAC address of the switch management processor
•IP address of the switch
•Software image file and version number
•Current configuration block (active, backup, or factory default)
•Login banner, if one is configured
Information Menu 30
 Loading...
Loading...