Page 1

Item
Oxix
Quick Guide for Oxix
Calibration
Name:
Version: 04-2012 KJ
FW 846003-001
Release date: 12/07 2011
S/N at release date: 97060
New Calibration Menu..................................................................................................................... 2
Zero Point Calibration ..................................................................................................................... 3
Span Calibration ............................................................................................................................. 4
Salinity Correction Factor................................................................................................................ 5
Restore Factory Calibration ............................................................................................................ 6
Guide to Oxygen-free Solution for Checking Oxix D.O. Sensor Zero Point ..................................... 7
Method........................................................................................................................................ 7
Notes .......................................................................................................................................... 7
How it works................................................................................................................................ 7
Materials ..................................................................................................................................... 7
Safety Precautions...................................................................................................................... 7
EN 5.4 Oxix Quick guide for calibration 1204.doc
1/7
Page 2
Item
Oxix
Quick Guide for Oxix
Calibration
Name:
Version: 04-2012 KJ
FW 846003-001
Release date: 12/07 2011
S/N at release date: 97060
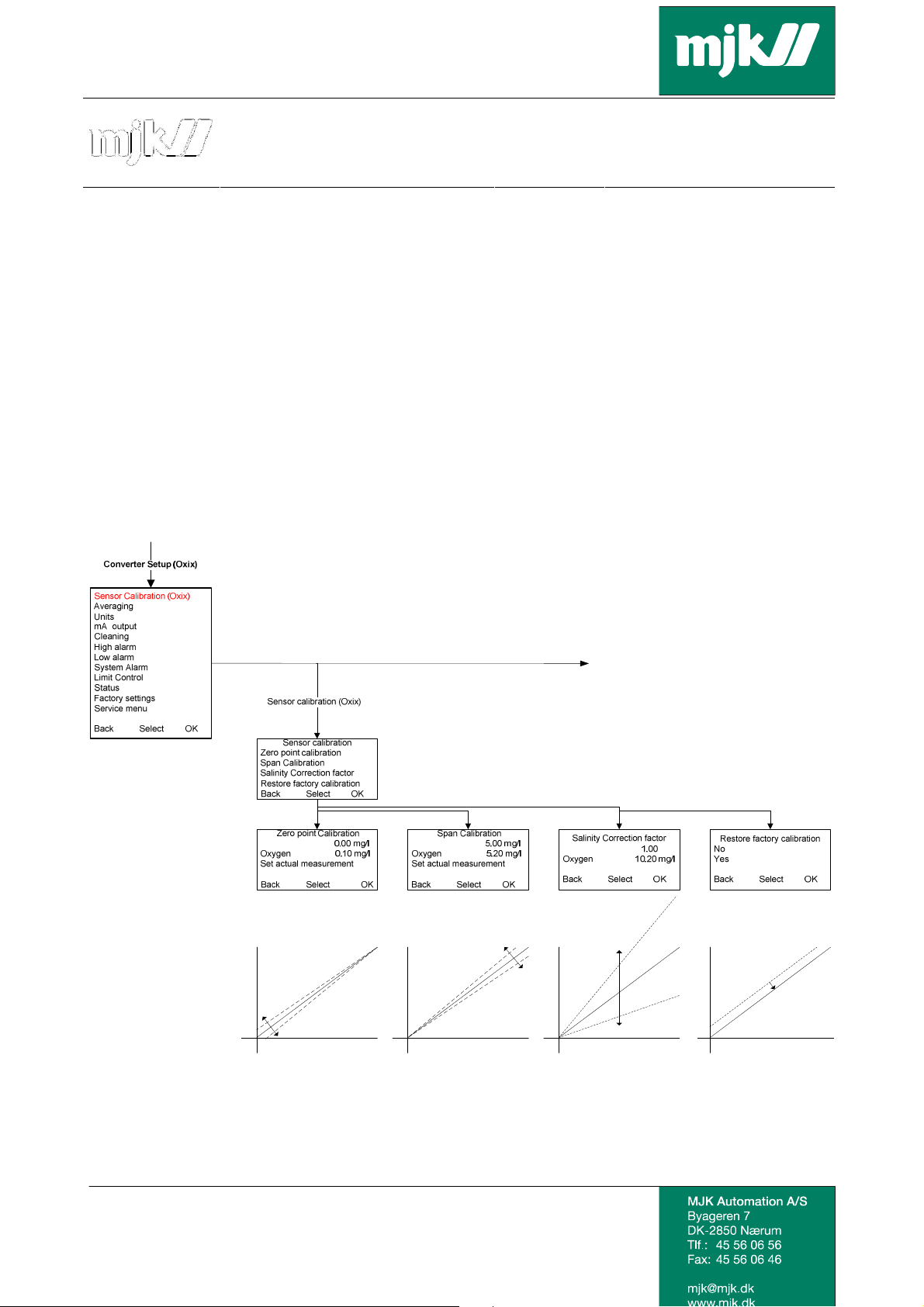
New Calibration Menu
Valid from firmware version 846003-001, a new calibration menu and method have been
introduced in the Oxix converter.
A factory calibration of both zero point and span has been made at delivery; these calibrations can
be done independently of each other. It is not usually necessary to calibrate. We recommend
checking the zero position every 6 to 12 months.
The calibration is saved in the converter and you will need to conduct a new calibration if the
sensor is moved to another converter.
We recommend conducting a factory reset of the sensor before conducting a new calibration, since
you avoid that any errors in an existing calibration affect the new calibration.
We have also added a menu with the possibility of adjusting salinity levels in the measurement.
EN 5.4 Oxix Quick guide for calibration 1204.doc
2/7
Page 3
Item
Oxix
Quick Guide for Oxix
Calibration
Zero Point Calibration
Name:
Version: 04-2012 KJ
FW 846003-001
Release date: 12/07 2011
S/N at release date: 97060
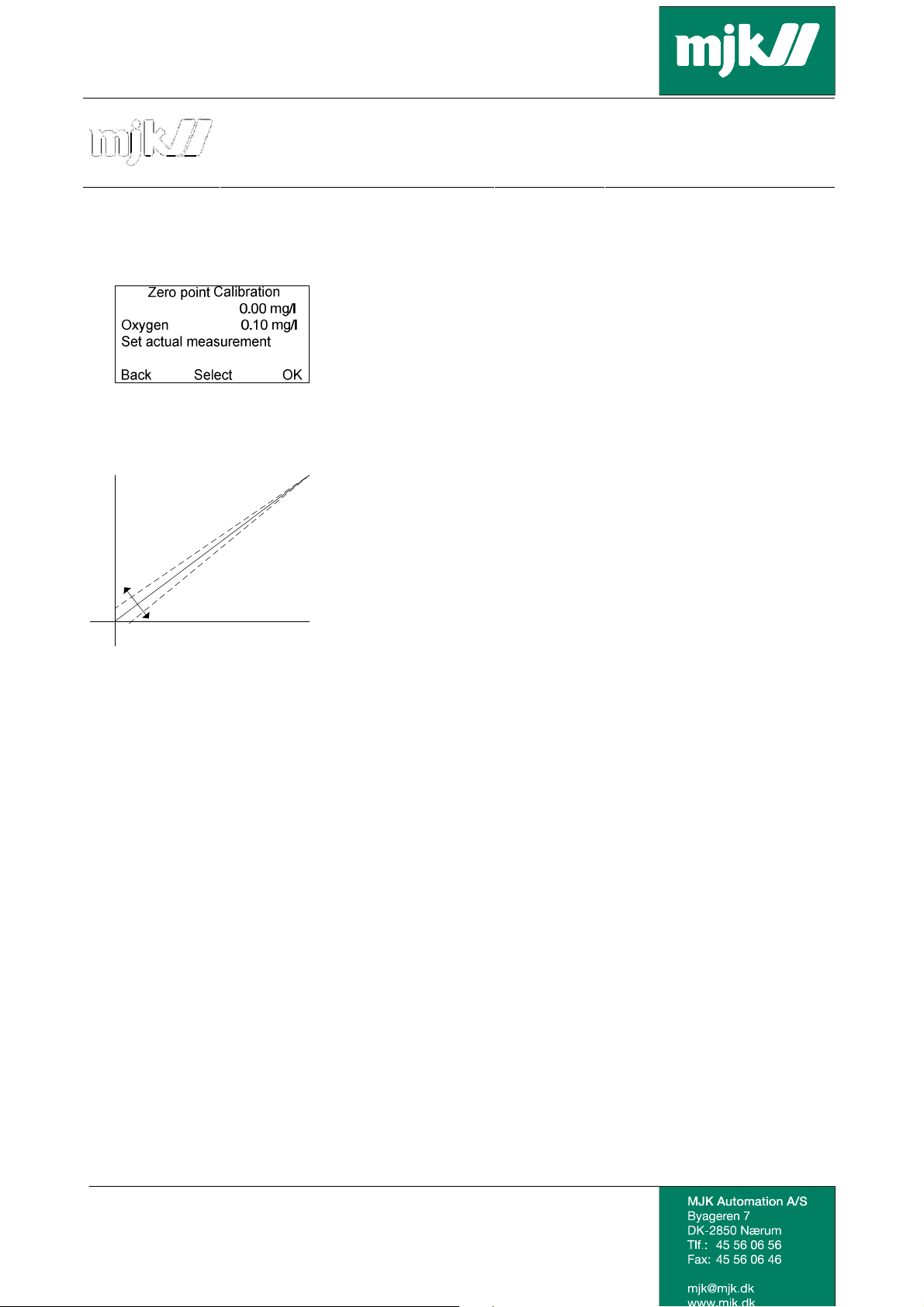
A zero point check or calibration is conducted as follows:
• The sensor is set for a zero point solution. The current measurement is shown in line 2
(0.10mg/l in this example).
• Set the desired measuring value on the first line using the up and down arrow keys.
• Save the current measurement setup by pressing OK.
The value is saved in the converter and will correct the measurement value of the sensor.
See section Guide to Oxygen-free Solution for Checking Oxix D.O. Sensor Zero Point.
EN 5.4 Oxix Quick guide for calibration 1204.doc
3/7
Page 4

Item
Oxix
Quick Guide for Oxix
Calibration
Span Calibration
Span Calibration
5.00 mg/l
Oxygen 5.20 mg/l
Set actual measurement
Back Select OK
Name:
Version: 04-2012 KJ
FW 846003-001
Release date: 12/07 2011
S/N at release date: 97060
A span check or calibration is conducted as follows:
• The sensor is measuring. The current measurement is shown in line 2 (5.20 mg/l in this
example).
• Set the desired measuring value on the first line using the up and down arrow keys.
• Save the current measurement setup by pressing OK.
It is generally difficult to conduct a span calibration. Usually, a reference sensor is used to verify
the measurement. For non-oxygen solutions, a variation of 1 to 5% between two sensors can occur
(even when the sensors are placed right next to each other). Air bubbles on the optical window will
create measurement variations.
Theory on making oxygen saturated solution
An oxygen saturated solution can be made from demineralised water being oxygenated for a
minimum of 30 minutes with atmospheric air. This saturation can then be calculated into an oxygen
concentration.
The temperature of the solution is measured with decimal and the atmospheric pressure is
measured with mm Hg.
The ppm or mg/l value of the saturated solution at the given temperature can then be decided by
using a matrix.
EN 5.4 Oxix Quick guide for calibration 1204.doc
4/7
Page 5
Item
Oxix
Quick Guide for Oxix
Calibration
Salinity Correction Factor
Name:
Version: 04-2012 KJ
FW 846003-001
Release date: 12/07 2011
S/N at release date: 97060
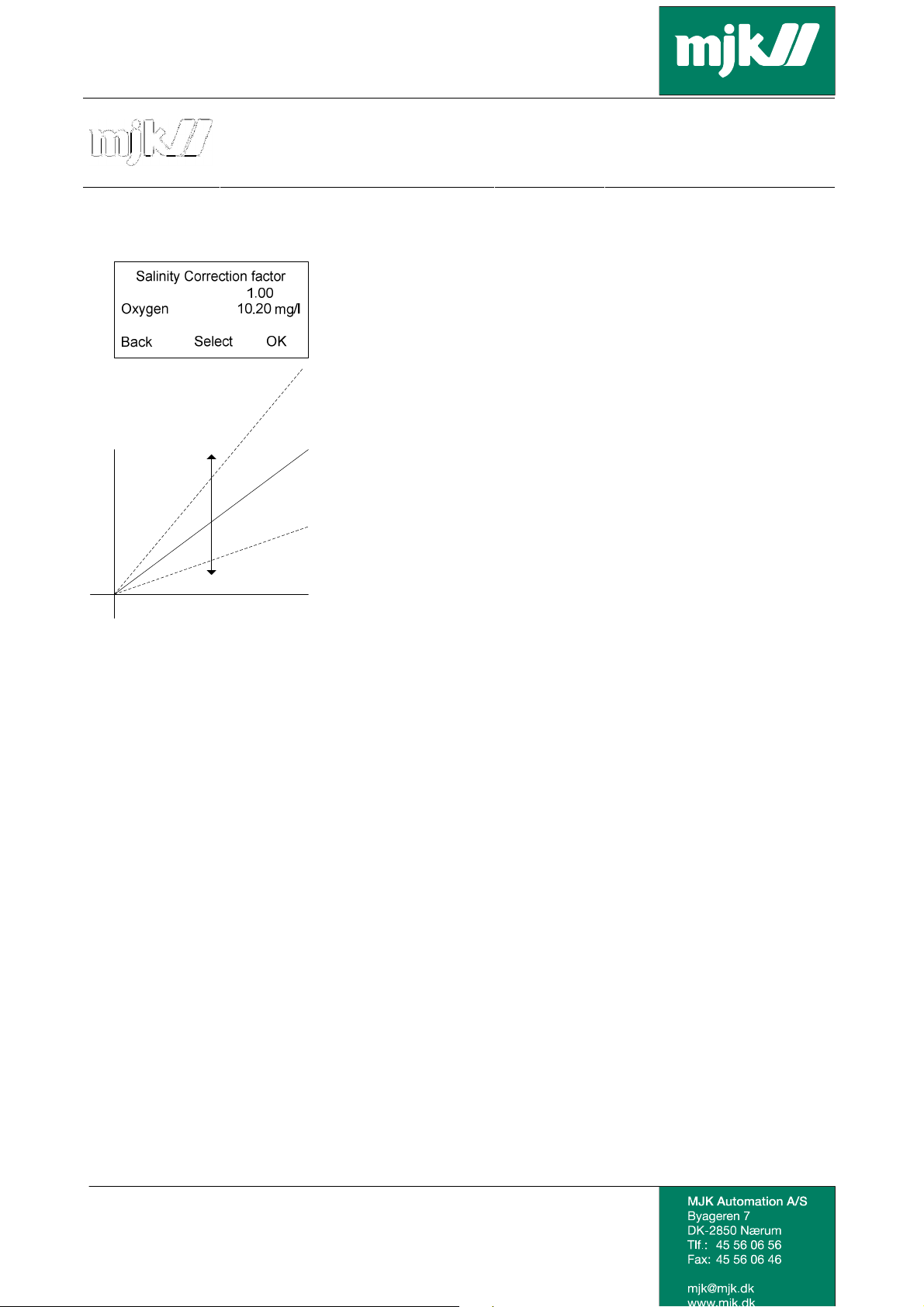
Oxix in salinity applications
A salinity correction factor is entered as follows:
• The sensor is measuring. The current measurement is shown in line 2 (10.20 mg/l in this
example).
• Set the desired salinity correction factor on the first line using the up and down arrow keys.
The interval is from 0.500 to 1.500.
• Save the current correction factor setup by pressing OK.
When measurement is done in the ppm or mg/litre units, a salinity correction is required (not when
measuring in % SAT!).
The correction factor for the current application is found in a matrix with factors for different salinity
levels, where the salinity level is shown by electrical conductivity.
It is assumed that the salinity level in the application is stable, as the factor can only be entered
manually. Alternatively, Oxix can be used without correction factor and in itself correct the DO
measuring based on the measured conductivity by third-party equipment.
EN 5.4 Oxix Quick guide for calibration 1204.doc
5/7
Page 6

Item
Oxix
Quick Guide for Oxix
Calibration
Restore Factory Calibration
Restore factory calibration
No
Yes
Back Select OK
Name:
Version: 04-2012 KJ
FW 846003-001
Release date: 12/07 2011
S/N at release date: 97060
The sensor should be reset before calibrating zero point or span by using Reset Factory
Calibration.
This helps avoiding any errors in an existing calibration affecting the new calibration.
EN 5.4 Oxix Quick guide for calibration 1204.doc
6/7
Page 7

Item
Oxix
Quick Guide for Oxix
Calibration
Name:
Version: 04-2012 KJ
FW 846003-001
Release date: 12/07 2011
S/N at release date: 97060
Guide to Oxygen-free Solution for Checking Oxix D.O. Sensor
Zero Point
Method
• Clean Oxix® and its optical window thoroughly.
• Dissolve 3 tablespoons Na2SO3 in 4 litres of tap water in an open container (bucket).
• Stir for about 1 minute.
• Immerse the sensor and let it rest in the solution for at least 30 minutes. (Towards the
bottom with the window down; check that there are no air bubbles on the lens.
Notes
This solution actually contains a concentration of approximately 0.10 ppm dissolved oxygen.
In time, if the solution is left alone, stratification will occur so that the concentration will be higher
towards to the surface.
If you need a reference sample with a dissolved oxygen concentration close to zero (approx. 0.02
ppm), the reference sample must be made with demineralised water and the solution must rest for
12-24 hours before measuring it.
It is important that the sensor and the optical window are completely clean when zero-point or
calibration is conducted.
How it works
Na2SO3 (sodium sulphite) removes oxygen from the solution since Na2SO3 is oxidized by O2
(oxygen) into Na2SO4 (sodium sulphate) following the reaction:
2Na2SO3+O2 → 2 Na2SO
Materials
Bucket
Measuring jug
Tablespoon
Chemicals/Reagents
Sodium sulphite, Na2SO3, CAS-Nr. 7757-83-7 (Supplier VWR, Bie & Berntsen)
Tap water (alternatively, demineralised water)
Safety Precautions
Safety instructions for Na2SO3: None. There are no R- or S-phrases for the product.
4
EN 5.4 Oxix Quick guide for calibration 1204.doc
7/7
 Loading...
Loading...