Page 1

VOGEL-Spiralgehäusepumpen
Einbau-, Betriebs- und Wartungsanleitung
de
Baureihe: LSB
Originalbetriebsanleitung
VOGEL-Pompes à volute
fr
Série: LSB
VOGEL-Volute Casing Pumps
en
Model: LSB
Instructions de montage, de service et de maintenance
Traduction de la notice d’exploitation originale
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Instruction
Translation of the Original Operation Manual
Für künftige Verwendung aufbewahren !
de
Diese Betriebsanleitung vor dem Transport, dem Einbau, der Inbetriebnahme usw. genau beachten!
Conserver soigneusement ces instructions pour consultations ultérieures !
fr
Lire attentivement ces instructions de service avant le transport, le montage, la mise en service etc. !
Keep for further use !
en
Pay attention to this operating instruction before the delivery, installation, start-up a.s.o.!
Artikel Nr. 771076129 Rev. 02 01/2012
Page 2

EG-Konformitätserklärung
(nur gültig für komplette von Xylem Water Solutions Austria GmbH gelieferte
Aggregate)
(gemäß EG-Maschinenrichtlinie 2006/42/EG Anhang II A)
Hiermit erklärt der Hersteller:
Xylem Water Solutions Austria GmbH
Ernst Vogel-Strasse 2
2000 Stockerau
Austria
der Pumpenaggregate der Baureihe
LSB40-25-160, LSB40-25-200, LSB40-25-250, LSB50-32-160, LSB50-32-200, LSB50-32-250,
LSB50-32-315, LSB65-40-160, LSB65-40-200, LSB65-40-250, LSB65-40-315, LSB80-50-160,
LSB80-50-200, LSB80-50-250, LSB80-50-315, LSB100-65-160, LSB100-65-200, LSB100-65-250,
LSB100-65-315, LSB125-80-160, LSB125-80-200, LSB125-80-250, LSB125-80-315, LSB125100-200, LSB125-100-250, LSB125-100-315, LSB150-125-250, LSB150-125-315, LSB200-150250
Die gelieferten Aggregate entsprechen den einschlägigen Bestimmungen der EG-Maschinenrichtlinie
2006/42/EG.
Die mitgelieferten Drehstrommotore entsprechen den Bestimmungen der Richtlinie 2004/108/EG.
Die speziellen technischen Unterlagen nach Anhang VII A wurden erstellt.
Ich werde der zuständigen Behörde gegebenenfalls die vorgenannten speziellen technischen Unterlagen in
elektronischer Form auf Datenträgern übermitteln.
Die vorgenannten speziellen technischen Unterlagen können angefordert werden bei
Dipl.Ing. Gerhard Fasching
Abtlg. Research & Development
Xylem Water Solutions Austria GmbH
Ernst Vogel-Strasse 2
2000 Stockerau
Austria
Angewendete harmonisierte Normen, insbesondere
EN 809 :1998+A1:2009+AC:2010(D)
EN 953 :1997+A1:2009(D)
EN ISO 12100 :2010(D)
EN 60204-1 :2006/A1:2009 D
Bei einer nicht mit uns abgestimmten Veränderung des Aggregates verliert diese Erklärung ihre Gültigkeit,
ebenso wenn das Aggregat in Anlagen eingebaut wird, bei denen keine Konformitätserklärung
entsprechend Maschinenrichtlinie 2006/42/EG vorliegt.
Stockerau, 09.01.2012
................................................................................................
Dir. Peter Steinbach
Production manager
Page 3

Déclaration CE de conformité
(valable uniquement pour les agrégats complets, fournis par la société
Xylem Water Solutions Austria GmbH)
(en vertu de la Directive 2006/42/CE relatives aux machines, annexe II A)
Par la présente,
Xylem Water Solutions Austria GmbH
Ernst Vogel-Strasse 2
2000 Stockerau
Austria
fabricant de groupes de pompage de série type déclare :
LSB40-25-160, LSB40-25-200, LSB40-25-250, LSB50-32-160, LSB50-32-200, LSB50-32-250,
LSB50-32-315, LSB65-40-160, LSB65-40-200, LSB65-40-250, LSB65-40-315, LSB80-50-160,
LSB80-50-200, LSB80-50-250, LSB80-50-315, LSB100-65-160, LSB100-65-200, LSB100-65-250,
LSB100-65-315, LSB125-80-160, LSB125-80-200, LSB125-80-250, LSB125-80-315, LSB125100-200, LSB125-100-250, LSB125-100-315, LSB150-125-250, LSB150-125-315, LSB200-150250
Les groupes fournis répondent aux dispositions afférentes de la Directive 2006/42/CE relative aux
machines.
Les moteurs triphasés qui sont livrés avec ces groupes répondent aux dispositions afférentes de la
Directive 2004/108/CE relative à la basse tension.
Un dossier technique spécial a été établi en vertu de l’annexe VII A.
Je mettrai éventuellement le dossier technique susmentionné à la disposition des autorités compétentes et
ce, sous format électronique, sur un support de stockage de données.
Le dossier technique susmentionné peut être demandé à l’adresse suivante :
Dipl.Ing. Gerhard Fasching
Abtlg. Research & Development
Xylem Water Solutions Austria GmbH
Ernst Vogel-Strasse 2
2000 Stockerau
Austria
Normes harmonisées appliquées – principalement :
EN 809 :1998+A1:2009+AC:2010(D)
EN 953 :1997+A1:2009(D)
EN ISO 12100 :2010(D)
EN 60204-1 :2006/A1:2009 D
Si une modification qui n’a pas été approuvée de notre part est effectuée sur le groupe, la présente
déclaration n’est plus valable. Ceci est également le cas lorsque le groupe est incorporé dans des
machines pour lesquelles il n’existe aucune déclaration de conformité en vertu de la Directive 2006/42/CE
relative aux machines.
Stockerau, 09.01.2012
................................................................................................
Dir. Peter Steinbach
Production manager
Page 4

EC Declaration of Conformity
(valid only for Xylem Water Solutions Austria GmbH aggregate supplied in its
entirety)
(according to EC Directive on Machinery 2006/42/EC, Annex II A)
The manufacturer,
Xylem Water Solutions Austria GmbH
Ernst Vogel-Strasse 2
2000 Stockerau
Austria
of the pumps from the standard product line hereby declares:
LSB40-25-160, LSB40-25-200, LSB40-25-250, LSB50-32-160, LSB50-32-200, LSB50-32-250,
LSB50-32-315, LSB65-40-160, LSB65-40-200, LSB65-40-250, LSB65-40-315, LSB80-50-160,
LSB80-50-200, LSB80-50-250, LSB80-50-315, LSB100-65-160, LSB100-65-200, LSB100-65-250,
LSB100-65-315, LSB125-80-160, LSB125-80-200, LSB125-80-250, LSB125-80-315, LSB125100-200, LSB125-100-250, LSB125-100-315, LSB150-125-250, LSB150-125-315, LSB200-150250
The supplied aggregates meet the relevant regulations of the EC Directive on Machinery, 2006/42/EC
The three-phase electric motor supplied at the same time meets the relevant regulations of Directive
2004/108/EC.
Special technical documentation has been prepared, in accordance with Annex VII A.
If necessary, we can submit the above-listed special technical documentation, in electronic form on a data
storage medium, to the relevant authorities.
The above-listed special documentation can be requested at the following address:
Dipl. Ing. Gerhard Fasching
Abtlg. Research & Development
Xylem Water Solutions Austria GmbH
Ernst Vogel-Strasse 2
2000 Stockerau
Austria
Among others, the following harmonised standards have been applied:
EN 809 :1998+A1:2009+AC:2010(D)
EN 953 :1997+A1:2009(D)
EN ISO 12100 :2010(D)
EN 60204-1 :2006/A1:2009 D
A change to an aggregate which was not approved by us invalidates this declaration. This also applies in
the case that the aggregate is installed in equipment that does not have the declaration of conformity in
accordance with the Directive on Machinery, 2006/42/EC.
Stockerau, 09.01.2012
................................................................................................
Dir. Peter Steinbach
Production manager
Page 5

Einbau-, Betriebs- und Wartungsanleitung
INHALTSVERZEICHNIS
Leistungsschild der Pumpe......................................... 2
ATEX-Schild (nur für Pumpen entsprechend 94/9/EG)
....................................................................................2
1. Allgemeines ............................................................ 3
1.1 Gewährleistung ................................................. 3
2. Sicherheitshinweise ................................................ 3
2.1 Kennzeichnung von Hinweisen in der
Betriebsanleitung.....................................................3
2.2 Gefahren bei Nichtbeachtung der
Sicherheitshinweise................................................. 4
2.3 Sicherheitshinweise für den Betreiber / Bediener
................................................................................4
2.4 Sicherheitshinweise für Wartungs-, Inspektions-
und Montagearbeiten .............................................. 4
2.5 Eigenmächtiger Umbau und
Ersatzteilherstellung................................................4
2.6 Unzulässige Betriebsweisen ............................. 4
2.7 Explosionsschutz............................................... 5
2.8 Bestimmungsgemäße Verwendung.................. 6
3. Ausführungsbeschreibung ...................................... 6
3.1 Bauart................................................................ 6
3.1.1 Bezeichnungsschema .................................... 7
3.2 Wellenabdichtung.............................................. 7
3.3 Lagerung ........................................................... 7
3.4 Richtwerte für Schalldruckpegel........................ 7
3.5 Zulässige Stutzenkräfte und Momente an den
Pumpenstutzen ... ................................................... 7
3.6 Zulässige Drücke und Temperaturen................8
3.7 Kondenswasser................................................. 9
4. Transport, Handhabung, Zwischenlagerung........... 9
4.1 Transport, Handhabung .................................... 9
4.2 Zwischenlagerung / Konservierung...................9
5. Aufstellung / Einbau................................................9
5.1 Aufstellung des Aggregates .............................. 9
5.2 Anschluss der Rohrleitungen an die Pumpe... 10
5.3 Antrieb.............................................................10
5.4 Elektrischer Anschluss .................................... 11
5.5 Endkontrolle .................................................... 11
6. Inbetriebnahme, Betrieb, Außerbetriebnahme...... 11
6.1 Erstinbetriebnahme ......................................... 11
6.2 Antriebsmaschine einschalten. ....................... 11
6.3 Wiederinbetriebnahme .................................... 11
6.4 Grenzen des Betriebes.................................... 11
Baureihe LSB
6.5 Schmierung .....................................................12
6.6 Überwachung...................................................12
6.7 Außerbetriebnahme.........................................12
6.8 Zwischenlagerung / Längerer Stillstand...........12
7. Instandhaltung, Wartung .......................................13
7.1 Allgemeine Hinweise .......................................13
7.2 Gleitringdichtungen..........................................13
7.3 Motorlager........................................................13
7.4 Reinigung der Pumpe......................................13
8. Demontage der Pumpe und Reparatur.................13
8.1 Allgemeine Hinweise .......................................13
8.2 Allgemeines .....................................................14
8.3 Aus- und Einbau der Schutzgitter aus der
Antriebslaterne.......................................................14
8.4 Ausbau der Laufeinheit....................................14
8.5 Ausbau des Laufrades.....................................14
8.6 Ausbau der Wellenabdichtung.........................15
8.7 Ausbau der Steckwelle ....................................15
8.8 Instandsetzung ................................................15
8.9 Montage...........................................................15
9. Ersatzteilempfehlung, Reservepumpen ................16
9.1 Ersatzteile........................................................16
9.2 Reservepumpen ..............................................17
10. Störungen - Ursachen und Behebung.................18
11. Motorbetriebsanleitung........................................19
Montageanleitung Einzel-Gleitringdichtung ohne
Wellenschutzhülse (Ausführungscode S1..2)........... 21
Montageanleitung Einzel-Gleitringdichtung mit Quench
ohne Wellenschutzhülse (Ausführungscode S4..2).. 23
Schnittzeichnung Aggregat Ausführung S1..2, Laufrad
mit Rückenschaufeln................................................ 26
Schnittzeichnung Aggregat Ausführung S1..2, Laufrad
mit Entlastungsbohrungen........................................ 27
Schnittzeichnung Aggregat Ausführung S4..2, Laufrad
mit Rückenschaufeln................................................ 28
Schnittzeichnung Aggregat Ausführung S4..2, Laufrad
mit Entlastungsbohrungen........................................ 29
Anschlüsse............................................................... 30
Maßzeichnung.......................................................... 31
LSB 100-german Seite 1
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 6
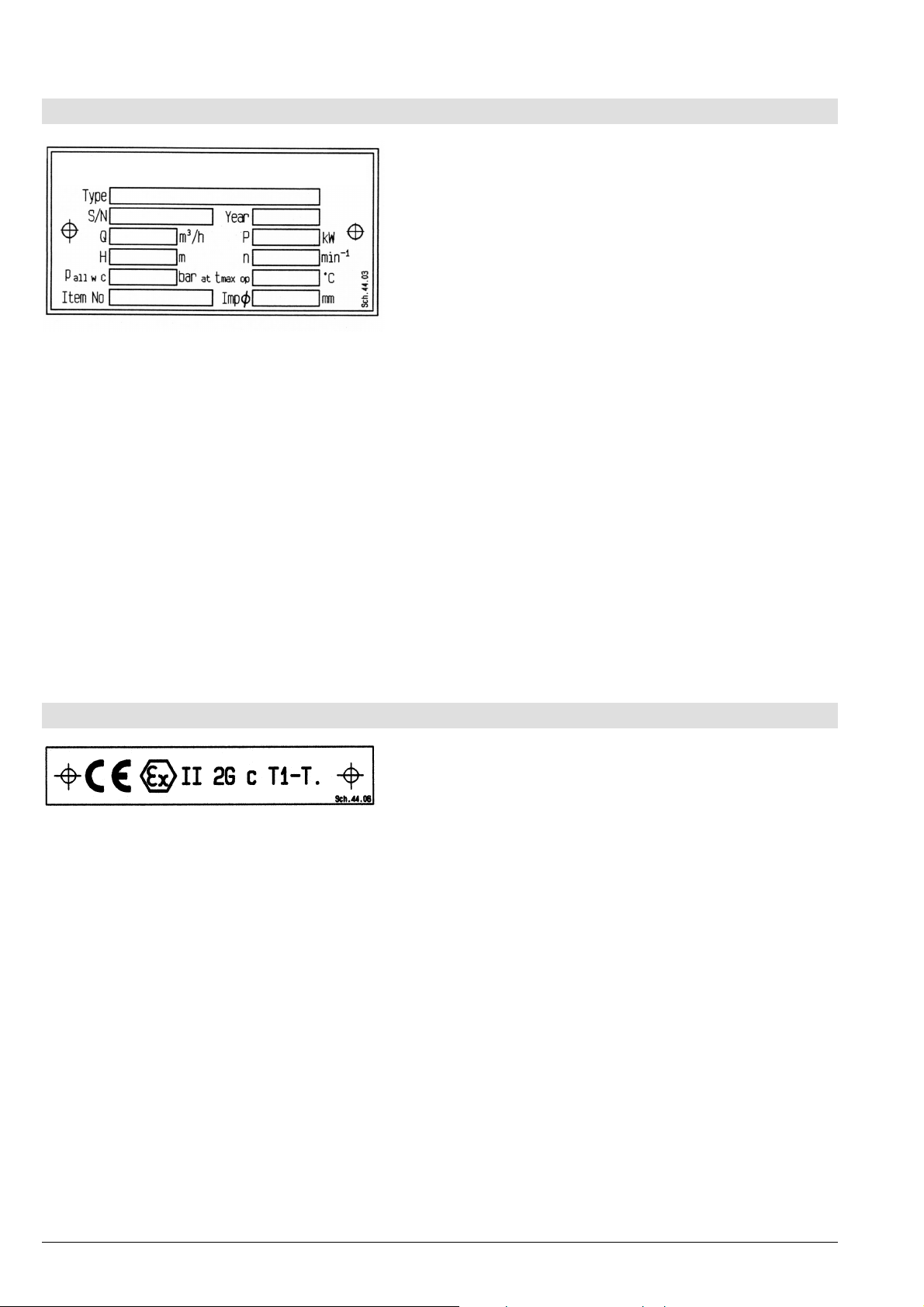
Einbau-, Betriebs- und Wartungsanleitung
Leistungsschild der Pumpe
Baureihe LSB
Type *) Typenbezeichnung der Pumpe
S/N *) Fabrikationsnummer
Year Baujahr
Q Förderstrom im Betriebspunkt
P Antriebsleistung im Betriebspunkt
H Förderhöhe (Energiehöhe) im Betriebspunkt
n Drehzahl
p
all w C
t
max op
Item No kundenspezifische Auftragsnummer
Imp∅ Außendurchmesser des Laufrades
Maximal zulässiger Gehäuse-Betriebsdruck
(=der höchste Austrittsdruck bei der festgelegten Arbeitstemperatur, bis zu dem das
Pumpengehäuse verwendet werden kann).
Maximal zulässige Arbeitstemperatur der
Förderflüssigkeit
*) Mit diesen Angaben sind für den Hersteller alle
Ausführungsdetails und Werkstoffe genau definiert.
Sie sind daher bei allen Rückfragen beim Hersteller
und bei der Bestellung von Ersatzteilen unbedingt
anzugeben.
ATEX-Schild (nur für Pumpen entsprechend 94/9/EG)
CE Kennzeichnung der Übereinstimmung mit der
Richtlinie 94/9/EG
Ex spezifische Kennzeichnug für den
Explosionsschutz
II Symbol für die Gerätegruppe
2G Symbol für die Gerätekategorie (2),
explosionsfähige Atmosphäre durch Gase,
Dämpfe oder Nebel (G)
c Symbol für die verwendete Zündschutzart
(konstruktive Sicherheit "c")
T1-T. Symbol zur Bezeichnung des theoretisch
verfügbaren Bereiches der Temperatur-
klassen - Angaben zur Temperaturklasse
siehe Kapitel 2.7.5; Angaben zur maximal
zulässigen Temperatur der Förderflüssigkeit
siehe Leistungsschild, Datenblatt und / oder
Auftragsbestätigung.
LSB 100-german Seite 2
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Die Konformität mit der Richtlinie 94/9/EG "Geräte und
Schutzsysteme zur bestimmungsgemäßen Verwendung in explosionsgefährdeten Bereichen" wird durch
die Ausstellung der EG-Konformitätserklärung und der
Anbringung des ATEX-Schild auf der Pumpe
(Antriebslaterne) erklärt. Das ATEX-Schild wird
zusätzlich zum Leistungsschild angebracht.
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 7

Einbau-, Betriebs- und Wartungsanleitung
Kenntnisse der Unfallverhütungsvorschriften
bzw. Qualifikation für diese Arbeiten aufweisen.
Liegen beim Personal nicht die entsprechenden
Bei Nichtbeachtung kann die Pumpe und deren
Explosionsgeschützte Betriebsmittel müssen für
Arbeiten in explosionsfähigen Atmosphären
1. Allgemeines
Baureihe LSB
Dieses Produkt entspricht den Anforderungen der
Maschinenrichtlinie 2006/42/EG.
Das Personal für Montage, Bedienung, Inspektion und Wartung muss die entsprechenden
Kenntnisse vor, so ist dieses zu unterweisen.
Die Betriebssicherheit der gelieferten Pumpe bzw. des
gelieferten Aggregates (= Pumpe mit Motor) ist nur
beim bestimmungsgemäßen Gebrauch entsprechend
dem beiliegenden Datenblatt und / oder der
Auftragsbestätigung bzw. Kapitel 6 "Inbetriebnahme,
Betrieb, Außerbetriebnahme" gewährleistet.
Der Betreiber ist für die Einhaltung der Instruktionen
und Sicherheitsvorkehrungen gemäß dieser
Betriebsanleitung verantwortlich.
Ein störungsfreier Betrieb der Pumpe bzw. des
Aggregates wird nur dann erreicht, wenn die Montage
und Wartung nach den im Maschinenbau und in der
Elektrotechnik gültigen Regeln sorgfältig durchgeführt
wird.
Sofern nicht alle Informationen in dieser Betriebsanleitung gefunden werden, ist rückzufragen.
Der Hersteller übernimmt für die Pumpe bzw. das
Aggregat keine Verantwortung, wenn diese Betriebsanleitung nicht beachtet wird.
Diese Betriebsanleitung ist für künftige Verwendung
sorgfältig aufzubewahren.
Bei Weitergabe dieser Pumpe oder dieses Aggregates
an Dritte ist diese Betriebsanleitung sowie die in der
Auftragsbestätigung genannten Betriebsbedingungen
und Einsatzgrenzen unbedingt vollständig mitzugeben.
Diese Betriebsanleitung berücksichtigt weder alle
Konstruktionseinzelheiten und Varianten noch alle
möglichen Zufälligkeiten und Ereignisse, die bei
Montage, Betrieb und Wartung auftreten können.
Das Urheberrecht an dieser Betriebsanleitung
verbleibt uns, sie ist nur dem Besitzer der Pumpe bzw.
des Aggregates zum persönlichen Gebrauch
anvertraut. Die Bedienungsanleitung enthält
Vorschriften technischer Art und Zeichnungen, die
weder vollständig noch teilweise vervielfältigt,
verbreitet oder zu Zwecken des Wettbewerbs
unbefugt verwendet oder an andere mitgeteilt werden
dürfen.
1.1 Gewährleistung
Gewährleistung gemäß unseren Lieferbedingungen
bzw. der Auftragsbestätigung.
Instandsetzungsarbeiten während der Garantiezeit
dürfen nur durch uns durchgeführt werden oder setzen
unsere schriftliche Zustimmung voraus. Andernfalls
geht der Garantieanspruch verloren.
Längerfristige Garantien beziehen sich grundsätzlich
nur auf die einwandfreie Verarbeitung und
Verwendung des spezifizierten Materials.
Ausgenommen von der Garantie ist natürliche
Abnutzung und Verschleiß, sowie sämtliche
Verschleißteile wie beispielsweise Laufräder, Wellenabdichtungen, Wellen, Wellenschutzhülsen, Lager,
Spalt- und Schleißringe, usw., weiters durch Transport
oder unsachgemäße Lagerung verursachte Schäden.
Voraussetzung für die Gewährleistung ist, dass die
Pumpe bzw. das Aggregat gemäß der am
Typenschild, im Datenblatt und / oder der
Auftragsbestätigung angeführten Betriebsbedingungen eingesetzt wird. Das gilt insbesondere für die
Beständigkeit der Materialien sowie einwandfreie
Funktion der Pumpe und Wellenabdichtung.
Sollten die tatsächlichen Betriebsbedingungen in
einem oder mehreren Punkten abweichen, so muss
die Eignung durch Rückfrage bei uns schriftlich
bestätigt werden.
2. Sicherheitshinweise
Diese Betriebsanleitung enthält grundlegende
Hinweise, die bei der Aufstellung, Inbetriebnahme
sowie während des Betriebes und bei der Wartung zu
beachten sind.
Daher ist diese Betriebsanleitung unbedingt vor
Montage und Inbetriebnahme vom zuständigen
Fachpersonal bzw. dem Betreiber der Anlage zu
lesen und muss ständig griffbereit am Einsatzort der
Pumpe bzw. des Aggregates zur Verfügung stehen.
Diese Betriebsanleitung berücksichtigt nicht die
allgemeinen Unfallverhütungsvorschriften sowie
ortsbezogene Sicherheits- und / oder Betriebsvorschriften. Für deren Einhaltung (auch durch
hinzugezogenes Montagepersonal) ist der
Betreiber verantwortlich.
Ebenso sind Vorschriften und Sicherheitsvorkehrungen bezüglich der Handhabung und Entsorgung des
geförderten Mediums und / oder Hilfsmedien für
Spülung, Sperrung, Schmierung, usw., insbesondere
LSB 100-german Seite 3
Artikel Nr. 771076129
wenn diese explosiv, giftig, heiß, usw. sind, nicht Teil
dieser Betriebsanleitung.
Für die fachgerechte und vorschriftkonforme Handhabung ist ausschließlich der Betreiber verantwortlich.
2.1 Kennzeichnung von Hinweisen in der
Betriebsanleitung
Die in dieser Betriebsanleitung enthaltenen
Sicherheitshinweise sind mit Sicherheitszeichen nach
DIN 4844 besonders gekennzeichnet:
Sicherheitshinweis!
Funktion beeinträchtigt werden.
EU-Gemeinschaftszeichen!
gekennzeichnet sein.
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 8

Einbau-, Betriebs- und Wartungsanleitung
zeichneten Abschnitte dieser Betriebsanleitung
Allgemeines Gefahrensymbol!
Personen können gefährdet werden.
Warnung vor elektrischer Spannung!
Direkt auf der Pumpe bzw. dem Aggregat angebrachte
Sicherheitshinweise müssen unbedingt beachtet und
in vollständig lesbarem Zustand gehalten werden.
In gleicher Weise, wie diese PumpenBetriebsanleitung sind auch alle eventuell beiliegenden Betriebsanleitungen von Zubehör (z.B. für
Motor) zu beachten und verfügbar zu halten.
2.2 Gefahren bei Nichtbeachtung der
Sicherheitshinweise
Die Nichtbeachtung der Sicherheitshinweise kann
zum Verlust jeglicher Schadensersatzansprüche
führen.
Nichtbeachtung kann folgende Gefährdung nach sich
ziehen :
Versagen wichtiger Funktionen der Maschine oder
Anlage.
Versagen von elektronischen Geräten und
Messinstrumenten durch Magnetfelder.
Gefährdung von Personen und deren
persönlichem Eigentum durch Magnetfelder.
Gefährdung von Personen durch elektrische,
mechanische und chemische Einwirkungen.
Gefährdungen der Umwelt durch Leckage von
gefährlichen Stoffen.
Beim Einsatz des Aggregates in explosionsgefährdeten Bereichen sind die mit Ex gekenn-
besonders zu beachten.
2.3 Sicherheitshinweise für den Betreiber
/ Bediener
In Abhängigkeit der Betriebsbedingungen sind
durch Verschleiß, Korrosion oder alterungsbedingt
die Lebensdauer und damit die spezifizierten Eigenschaften begrenzt. Der Betreiber hat dafür
Sorge zu tragen, dass durch regelmäßige Kontrolle und Wartung alle Teile rechtzeitig ersetzt
werden, die einen sicheren Betrieb nicht mehr
gewährleisten. Jede Beobachtung einer abnormalen Betriebsweise oder einer wahrnehmbaren
Beschädigung verbietet die weitere Benutzung.
Anlagen, bei denen der Ausfall oder das Versagen
zu Personen- oder Sachschäden führen kann,
sind mit Alarmeinrichtungen und / oder
Reserveaggregaten auszustatten und deren
Funktionstüchtigkeit in regelmäßigen Abständen
zu prüfen.
Besteht Verletzungsgefahr durch heiße oder kalte
Maschinenteile, müssen diese Teile bauseitig
gegen Berührung gesichert sein, bzw.
entsprechende Warnhinweise angebracht werden.
Berührungsschutz für sich bewegende Teile (z.B.
Laternenschutzblech) darf bei sich in Betrieb befindlichen Anlagen nicht entfernt werden.
LSB 100-german Seite 4
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Baureihe LSB
Bei Pumpen bzw. Aggregaten mit einem
Schallpegel über 85 dB(A) ist bei längerem
Aufenthalt in der unmittelbaren Umgebung ein
Gehörschutz zu verwenden.
Leckagen (z.B. der Wellenabdichtung) gefährli-
cher Fördergüter (z.B. explosiv, giftig, heiß)
müssen so abgeführt werden, dass keine Gefährdung für Personen und die Umwelt entsteht.
Gesetzliche Bestimmungen sind einzuhalten.
Gefährdungen durch elektrische Energie sind
auszuschließen (z.B. durch Beachten der örtlich
geltenden Vorschriften für elektrische Anlagen).
Bei Arbeiten an spannungsführenden Bauteilen
vorher Netzstecker ziehen bzw. Hauptschalter
ausschalten und Sicherung herausdrehen. Ein
Motorschutzschalter ist vorzusehen.
2.4 Sicherheitshinweise für Wartungs-,
Inspektions- und Montagearbeiten
Der Betreiber hat dafür zu sorgen, dass alle
Wartungs-, Inspektions- und Montagearbeiten von
autorisiertem und qualifiziertem Fachpersonal
ausgeführt werden, das sich durch eingehendes
Studium der Betriebsanleitung ausreichend
informiert hat.
Grundsätzlich sind Arbeiten an der Pumpe oder
am Aggregat nur im Stillstand und im drucklosen
Zustand durchzuführen. Alle Teile müssen Umgebungstemperatur angenommen haben. Sicherstellen, dass während der Arbeiten der Motor von
niemand in Betrieb gesetzt werden kann. Die in
der Betriebsanleitung beschriebene Vorgehensweise zum Stillsetzen der Anlage muss unbedingt
eingehalten werden. Pumpen oder Anlagen, die
gesundheitsgefährdende Medien fördern, müssen
vor dem Zerlegen dekontaminiert werden. Sicherheitsdatenblätter der jeweiligen Fördermedien beachten. Unmittelbar nach Abschluss der Arbeiten
müssen alle Sicherheits- und Schutzeinrichtungen
wieder angebracht bzw. in Funktion gebracht
werden.
2.5 Eigenmächtiger Umbau und
Ersatzteilherstellung
Umbau oder Veränderungen der Maschine sind nur
nach Absprache mit dem Hersteller zulässig.
Originalersatzteile und vom Hersteller autorisiertes
Zubehör dienen der Sicherheit.
Die Verwendung anderer Teile kann die Haftung für
die daraus entstehenden Folgen aufheben.
2.6 Unzulässige Betriebsweisen
Die Betriebssicherheit der gelieferten Maschine ist nur
bei bestimmungsgemäßer Verwendung entsprechend
der nachfolgenden Kapitel der Betriebsanleitung
gewährleistet.
Die im Datenblatt und / oder der Auftragsbestätigung
angegebenen Grenzwerte dürfen auf keinen Fall
überschritten werden.
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 9
Einbau-, Betriebs- und Wartungsanleitung
Beim Pumpenbetrieb muss das System der
berührte Innenraum der Pumpe ständig mit
Es kann somit keine explosionsfähige
Atmosphäre dort vorliegen und die Gefahr von
cherstellen, sind
Ebenso müssen alle Dichtungsräume und
Hilfssysteme der Wellenabdichtung sorgfältig
Die Kennzeichnung auf der Pumpe bezieht sich
. Für den Motor bzw. für
weitere Anbauten muss eine separate
Konformitätserklärung vorliegen sowie eine
Besteht auch während der Installationsphase
trolle keinesfalls durch kurzes Einschalten der
ungefüllten Pumpe erfolgen, um eine
m Falle der
Berührung drehender und stehender Teile zu
Es besteht die Gefahr, dass bereits nach kurzer
Zeit hohe Oberflächentemperaturen am
Pumpengehäuse durch rasches Aufheizen der
Ein rascher Druckanstieg im Innern der Pumpe
ng bis
Bei Pumpen mit Gleitringdichtungen können
grenzen überschritten werden. Trockenlauf
kann nicht nur bei nicht hinreichend gefülltem
n, sondern auch bei zu
Das Betreiben der Pumpe außerhalb des
zulässigen Betriebsbereichs kann ebenfalls
Im normalen Betriebszustand sind die höchsten
an der Oberfläche des
Beim Betreiben der Pumpe muss sichergestellt
werden, dass eine übermäßige Ablagerung von
bern), um ein Aufheizen der Pumpenoberfläche
Grenzwert der Temperatur
Die jeweils zulässige Arbeitstemperatur der
Pumpe ist dem Datenblatt und / oder der
Auftragsbestätigung bzw. dem Typenschild auf
2.7 Explosionsschutz
Beim Einsatz der Aggregate in explosionsgefährdeten
Bereichen sind zur Gewährleistung des Explosionsschutzes die Maßnahmen und Hinweise in Kapitel
2.7.1 bis 2.7.7 zwingend erforderlich.
2.7.1 Füllung des Aggregates
Saug- und Druckleitung und der flüssigkeits-
Förderflüssigkeit gefüllt sein.
Trockenlauf wird verhindert.
Kann der Betreiber dies nicht si
entsprechende Überwachungsmaßnahmen vorzusehen.
gefüllt sein.
2.7.2 Kennzeichnung
auf den Pumpenteil
Baureihe LSB
Flüssigkeit im Pumpeninneren entstehen.
birgt die Gefahr der Überbeanspruchu
zum Bersten.
Im Kapitel 6.4.1 sind die Mindestmengen angegeben.
Längere Betriebsphasen bei diesen Mengen und den
genannten Flüssigkeiten verursachen keine
zusätzliche Erhöhung der Oberflächentemperaturen
an der Pumpe.
Darüber hinaus sind die Hinweise in Kapitel 6 dieser
Betriebsanleitung zu beachten.
durch Trockenlauf die zulässigen Temperatur-
Dichtungsraum auftrete
hohen Gasanteilen im Medium.
einen Trockenlauf nach sich ziehen.
2.7.5 Temperaturgrenzen
entsprechende Kennzeichnung vorhanden sein.
Beispiel der Kennzeichnung auf dem Pumpenteil:
CE Ex II 2 G c T1-T.
Die Kennzeichnung gibt den theoretisch verfügbaren
Bereich der Temperaturklassen an. Die je nach
Pumpenausführung zulässigen Temperaturen
ergeben sich gemäß Kapitel 2.7.5. Das gleiche gilt für
den Antrieb.
Für ein Gesamtaggregat (Pumpe und Motor) mit
verschiedenen Temperaturklassen gilt die jeweils
niedrigste.
2.7.3 Drehrichtungskontrolle
Explosionsgefahr, darf die Drehrichtungskon-
unzulässige Temperaturerhöhung i
verhindern.
2.7.4 Betriebsweise der Pumpe
Die Pumpe darf nur mit voll geöffnetem saugseitigen
und leicht geöffnetem druckseitigem Absperrorgan
gestartet werden. Das Anfahren gegen eine
geschlossene Rückschlagarmatur ist jedoch möglich.
Unmittelbar nach dem Hochlauf ist das druckseitige
Absperrorgan auf den Betriebspunkt einzuregeln.
Siehe auch Kapitel 6.2.
Ein Betrieb mit geschlossenen Absperrorganen in
Saug- und / oder Druckleitung ist nicht erlaubt!
LSB 100-german Seite 5
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Temperaturen
Pumpengehäuses zu erwarten.
Die am Pumpengehäuse auftretende Oberflächentemperatur entspricht der Temperatur der zu
fördernden Flüssigkeit.
Im Bereich der Laterne und des Motors muss freier
Kontakt der Oberfläche zur Umgebung bestehen.
Staub verhindert wird (evtl. regelmäßiges Säu-
über die zulässige Temperatur zu vermeiden.
Der Betreiber der Anlage muss sicherstellen, dass
die festgelegte Arbeitstemperatur eingehalten
wird. Die maximal zulässige Temperatur der
Förderflüssigkeit am Pumpeneintritt ist abhängig
von der jeweils vorliegenden Temperaturklasse.
Die nachstehende Tabelle enthält unter Berücksichtigung der Temperaturklassen gemäß EN 13463-1 die
sich ergebenden theoretischen Grenzwerte der
Temperatur der Förderflüssigkeit.
Temperaturklasse gemäß
EN 13463-1
der Förderflüssigkeit
T4 (135°C) 135°C
T3 (200°C) 140°C
T2 (300°C) 140°C
T1 (450°C) 140°C
der Pumpe zu entnehmen.
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 10

Einbau-, Betriebs- und Wartungsanleitung
ieb
muss durch regelmäßige Inspektionsintervalle
sichergestellt werden, dass das Aggregat
sachgemäß gewartet und in technisch
und Regelgeräte,
Instrumentierungen und Zubehörteile müssen
den gültigen Sicherheitsanforderungen und
maßnahmen vorgesehen sein, damit Drehzahl,
Druck und Temperatur in der Pumpe und an der
Wellenabdichtung die im Datenblatt und / oder
der Auftragsbestätigung angegebenen
n.
Angegebene Zulaufdrücke (Systemdrücke)
und Druckleitung
so ausgeführt sein, dass möglichst geringe
Kräfte auf die Pumpe wirken. Ist dies nicht
gegebenen Werte auf keinen Fall überschritten
uch bei
Stillstand der Pumpe, also für alle in der Anlage
Das Fördermedium muss am Laufradeintritt
einen Mindestdruck NPSH aufweisen, damit
kavitationsfreies Arbeiten gesichert ist bzw. ein
der Pumpe verhindert wird. Diese
Wert (NPSHA) unter allen Betriebsbedingungen
Wert
2.7.6 Wartung
Für einen sicheren und zuverlässigen Betr
einwandfreiem Zustand gehalten wird.
Beispiel: Funktion der Wälzlager. Betriebsweise und
Einsatzbedingungen bestimmen wesentlich deren
tatsächlich erreichbare Lebensdauer.
Durch regelmäßige Kontrollen des Laufgeräusches
wird die Gefahr der Entstehung von Übertemperaturen
durch heißlaufende Lager verhindert. Siehe Kapitel 6.6
und 7.4.
Die Funktion der Wellenabdichtung ist durch
regelmäßige Überwachung sicherzustellen.
Werden Hilfssysteme (z.B. externe Spülung) installiert,
muss überprüft werden, ob
Überwachungseinrichtungen zur Sicherstellung der
Funktion notwendig sind.
2.7.7 Elektrische Schalt- und Regelgeräte,
Instrumentierung und Zubehörteile
Elektrische Schalt-
Explosionsschutzbestimmungen entsprechen.
2.8 Bestimmungsgemäße Verwendung
2.8.1 Drehzahl, Druck, Temperatur
Anlagenseitig müssen geeignete Sicherheits-
Grenzwerte mit Sicherheit nicht übersteige
dürfen auch nicht unterschritten werden.
Weiters sind Druckstöße, wie sie bei zu raschem
Abschalten der Anlage entstehen können, unbedingt
von der Pumpe fernzuhalten (z.B. durch druckseitiges
Rückschlagventil, Schwungscheibe, Windkessel).
Rasche Temperaturwechsel sind zu vermeiden. Sie
können einen Temperaturschock verursachen und zur
Zerstörung oder Beeinträchtigung der Funktion
einzelner Komponenten führen.
Baureihe LSB
2.8.2 Zulässige Stutzenkräfte und Momente
Grundsätzlich muss die Saug-
durchführbar, so dürfen die im Kapitel 3.5 an-
werden. Dies gilt sowohl im Betrieb als a
vorkommenden Drücke und Temperaturen.
2.8.3 NPSH
Abschnappen
Bedingung ist erfüllt, wenn der Anlagen-NPSH-
mit Sicherheit über dem Pumpen-NPSH(NPSHR) liegt.
Besonders bei Förderung von Flüssigkeit nahe dem
Siedepunkt ist auf den NPSH-Wert zu achten. Wenn
der Pumpen-NPSH-Wert unterschritten wird, kann
dies zu Materialschäden infolge Kavitation bis zu
Zerstörungen durch Überhitzen führen.
Der Pumpen-NPSH-Wert (NPSHR) ist bei jeder
Pumpentype in den Kennlinienblättern angegeben.
2.8.4 Sperrung, Spülung, Kühlung
Für geeignete Regulierungs- und
Überwachungsmöglichkeit einer eventuell
vorhandenen Sperrung oder Spülung ist zu sorgen.
Bei gefährlichen Fördermedien oder hohen
Temperaturen ist dafür Sorge zu tragen, dass bei
Ausfall des Sperr- oder Spülsystems die Pumpe außer
Betrieb gesetzt wird.
Sperr- und Spülsysteme müssen stets vor
Inbetriebnahme der Pumpe bereits in Betrieb sein.
Außerbetriebnahme erst bei Stillstand der Pumpe,
sofern dies durch die Art des Betriebes zulässig ist.
2.8.5 Rücklauf
In Anlagen, wo Pumpen in einem geschlossenen
System unter Druck (Gaspolster, Dampfdruck)
arbeiten, darf eine Entspannung des Gaspolsters auf
keinen Fall über die Pumpe erfolgen, da die
Rücklaufdrehzahl ein Vielfaches der Betriebsdrehzahl
sein kann und das Aggregat zerstört würde.
3. Ausführungsbeschreibung
3.1 Bauart
LSB-Pumpen sind einstufige Spiralgehäusepumpen
in Blockbauweise. Die hydraulische Auslegung
entspricht ISO 2858 / EN 22858, die technischen
Anforderungen ISO 5199 / EN 25199.
Die Motoren entsprechen DIN 42677-IM B5. Motor
und Pumpenwelle sind starr gekuppelt.
Die zulässigen Einsatzbedingungen und die Ausführungsdetails der gelieferten Pumpe sind im beiliegen-
LSB 100-german Seite 6
Artikel Nr. 771076129
den Datenblatt und / oder der Auftragsbestätigung
angegeben (siehe Bezeichnungsschema in Kapitel
3.2).
Einbaulage: LSB-Pumpen sind für Verwendung mit
horizontaler Welle, Druckstutzen oben, vorgesehen.
Davon abweichende Einbaulagen müssen zuvor vom
Hersteller freigeben werden.
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 11

Einbau-, Betriebs- und Wartungsanleitung
r Standardausführung verwendete
Gleitringdichtung ist nicht beständig gegen
Nähere Angaben über Gleitringdichtungen
sowie den damit verbundenen Unfallgefahren
in
3.1.1 Bezeichnungsschema
Auf Grund der Bezeichnung laut Datenblatt und / oder
der Auftragsbestätigung können alle Informationen
betreffend der gelieferten Pumpe in dieser Einbau-,
Betriebs- und Wartungsanleitung nachgelesen
werden, z.B.:
LSB 100 - 65 - 250 S1 V L 2 - 132
(0) (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) (7) (8)
Position (0) - Baureihenbezeichnung
LSB - ISO Blockpumpe
Position (1) - Saugstutzen in mm
Position (2) - Druckstutzen in mm
Position (3) - Laufradnenndurchmesser in mm
Position (4) - Wellenabdichtung
S1 - Einfach-Gleitringdichtung nach DIN
24960 l1k / EN 12756 Form U
S4 - Einfach-Gleitringdichtung nach DIN
24960 l1k / EN 12756 Form U
mit Quench (Drosselbuchse)
Position (5) - Material Laufrad
N = Grauguss (0.6025)
L = Sphäroguss (0.7043)
V = legierter Stahlguss (1.4408)
W = Duplex (1.4517)
Position (6) - Material Pumpengehäuse (gleiche
Codierung wie für Laufrad, Grauguss nicht verfügbar)
Position (7) - Steckwelle
2 - ohne Wellenschutzhülse (Duplex 1.4462
std)
Position (8) - IEC Motorbaugröße
3.2 Wellenabdichtung
Pumpen der Bauart LSB sind ausschließlich mit
Einfach-Gleitringdichtungen mit Einbaumaßen nach
EN 12756 (DIN 24960), Ausführung "K", Form "U"
abgedichtet.
Es stehen zwei Wellenabdichtungsvarianten zur
Verfügung. Auf dem Datenblatt und / oder der
Auftragsbestätigung ist die Art der Wellenabdichtung
angegeben. Eine Anleitung zu Montage und Betrieb
von Gleitringdichtungen ist auf der jeweiligen
"Montageanleitung der Wellenabdichtung" enthalten.
Die Nenngröße (d1) der Gleitringdichtung entnehmen
Sie der nachstehenden Tabelle.
40-25-160 33
40-25-200 33
40-25-250 43
50-32-160 33
50-32-200 33
50-32-250 43
50-32-315 43
65-40-160 33
65-40-200 33
65-40-250 43
65-40-315 43
80-50-160 33
80-50-200 33
80-50-250 43
80-50-315 43
LSB 100-german Seite 7
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Type
Nenngröße
d1 der Glrd.
Type
100-65-160 43
100-65-200 43
100-65-250 43
100-65-315 53
125-80-160 43
125-80-200 43
125-80-250 43
125-80-315 53
125-100-200 43
125-100-250 53
125-100-315 53
150-125-250 53
150-125-315 53
200-150-250 53
Nenngröße
d1 der Glrd.
Baureihe LSB
Die in de
Mineralöle.
finden Sie im Kapitel 6.6 sowie in Kapitel 7.2.
3.3 Lagerung
Die Lagerung erfolgt in den Wälzlagern des Motors.
Die Lager sind auf Lebensdauer fettgeschmiert und
somit wartungsfrei.
3.4 Richtwerte für Schalldruckpegel
Nennleist
ungsbed
arf P
N
kW
0,55 50,5 49,5 49,0 58,0 52,0 51,5
0,75 52,0 51,0 50,5 59,0 54,0 53,0
1,1 54,0 53,0 52,5 60,0 55,5 54,5
1,5 55,5 55,0 54,5 63,5 57,0 56,0
2,2 58,0 57,0 56,5 64,5 59,0 58,5
3,0 59,5 58,5 58,0 68,5 61,0 62,0
4,0 61,0 60,0 59,5 69,0 63,0 63,0
5,5 63,0 62,0 61,5 70,0 65,0 65,0
7,5 64,5 63,5 63,0 70,5 67,0 67,0
11,0 66,5 65,5 65,0 72,0 69,0 68,5
15,0 68,0 67,0 66,5 72,5 70,0 70,5
18,5 69,0 68,5 68,0 73,0 70,5 74,0
22,0 70,5 69,5 69,0 74,5 71,0 74,0
30,0 72,0 71,0 - 75,0 72,0 37,0 73,0 - - 76,0 - -
2950
min-1
Schalldruckpegel LpA gemessen in 1 m Abstand vom
Pumpenumriss nach DIN 45635, Teil 1 und 24. Raumund Fundamenteinflüsse sind nicht berücksichtigt. Die
Toleranz für diese Werte beträgt ±3 dB(A).
Zuschlag bei 60 Hz-Betrieb:
Pumpe allein: −
Pumpe mit Motor: +4 dB(A)
Schalldruckpegel LpA in dB(A)
Pumpe alleine Pumpe + Motor
1450
min-1
975
min-1
2950
min-1
1450
min-1
975
min-1
3.5 Zulässige Stutzenkräfte und Momente
an den Pumpenstutzen ...
... in Anlehnung an die Europump-Empfehlung für
Pumpen nach ISO 5199.
Die Angaben für Kräfte und Momente gelten nur für
statische Rohrleitungslasten.
Alle Werte für Kräfte und Momente sind auf die
Standardwerkstoffe EN-GJS400-18LT und 1.4408
bezogen.
Bild 1
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 12
Einbau-, Betriebs- und Wartungsanleitung
Baureihe LSB
∅DN
40-25-160 40 700 620 560 1100 730 500 590 1070 25 420 400 480 730 500 340 400 730
40-25-200 40 700 620 560 1100 730 500 590 1070 25 420 400 480 730 500 340 400 730
40-25-250 40 700 620 560 1100 730 500 590 1070 25 420 400 480 730 500 340 400 730
50-32-160 50 920 840 760 1450 780 560 650 1150 32 500 480 590 930 620 420 480 900
50-32-200 50 920 840 760 1450 780 560 650 1150 32 500 480 590 930 620 420 480 900
50-32-250 50 920 840 760 1450 780 560 650 1150 32 500 480 590 930 620 420 480 900
50-32-315 50 920 840 760 1450 780 560 650 1150 32 500 480 590 930 620 420 480 900
65-40-160 65 1180 1040 950 1850 840 620 670 1230 40 620 560 700 1100 730 500 590 1060
65-40-200 65 1180 1040 950 1850 840 620 670 1230 40 620 560 700 1100 730 500 590 1060
65-40-250 65 1180 1040 950 1850 840 620 670 1230 40 620 560 700 1100 730 500 590 1060
65-40-315 65 1180 1040 950 1850 840 620 670 1230 40 620 560 700 1100 730 500 590 1060
80-50-160 80 1400 1260 1150 2200 900 650 730 1320 50 840 760 920 1450 780 560 650 1150
80-50-200 80 1400 1260 1150 2200 900 650 730 1320 50 840 760 920 1450 780 560 650 1150
80-50-250 80 1400 1260 1150 2200 900 650 730 1320 50 840 760 920 1450 780 560 650 1150
80-50-315 80 1400 1260 1150 2200 900 650 730 1320 50 840 760 920 1450 780 560 650 1150
100-65-160 100 1880 1680 1520 2950 980 700 810 1450 65 1040 950 1180 1850 840 620 670 1230
100-65-200 100 1880 1680 1520 2950 980 700 810 1450 65 1040 950 1180 1850 840 620 670 1230
100-65-250 100 1880 1680 1520 2950 980 700 810 1450 65 1040 950 1180 1850 840 620 670 1230
100-65-315 100 1880 1680 1520 2950 980 700 810 1450 65 1040 950 1180 1850 840 620 670 1230
125-80-160 125 2210 2000 1800 3480 1180 840 1070 1710 80 1260 1150 1400 2200 900 650 730 1320
125-80-200 125 2210 2000 1800 3480 1180 840 1070 1710 80 1260 1150 1400 2200 900 650 730 1320
125-80-250 125 2210 2000 1800 3480 1180 840 1070 1710 80 1260 1150 1400 2200 900 650 730 1320
125-80-315 125 2210 2000 1800 3480 1180 840 1070 1710 80 1260 1150 1400 2200 900 650 730 1320
125-100-200 125 2210 2000 1800 3480 1180 840 1070 1710 100 1680 1520 1880 2950 980 700 810 1450
125-100-250 125 2210 2000 1800 3480 1180 840 1070 1710 100 1680 1520 1880 2950 980 700 810 1450
125-100-315 125 2210 2000 1800 3480 1180 840 1070 1710 100 1680 1520 1880 2950 980 700 810 1450
150-125-250 150 2800 2520 2270 4400 1400 980 1150 2050 125 2000 1800 2210 3480 1180 840 1070 1710
150-125-315 150 2800 2520 2270 4400 1400 980 1150 2050 125 2000 1800 2210 3480 1180 840 1070 1710
200-150-250 200 3750 3360 3030 5850 1820 1290 1490 2700 150 2520 2270 2800 4400 1400 980 1150 2050
Kräfte in N Momente in Nm Kräfte in N Momente in Nm Baugrößen
Fx Fy Fz
Saugstutzen Druckstutzen
Mx My Mz
∑F
∑M
∅DN
Fx Fy Fz
∑F
Mx My Mz
∑M
3.6 Zulässige Drücke und Temperaturen
Grundsätzlich gelten die im Datenblatt und / oder der
Auftragsbestätigung sowie am Leistungsschild
angegebenen Werte bezüglich Drücke und
Temperatur. Eine Über- oder Unterschreitung dieser
Werte ist unzulässig. Sind im Datenblatt und / oder der
Auftragsbestätigung keine Drücke und / oder
Für alle Pumpentypen, außer:
50-32-315 - 65-40-315 - 80-50-315 - 100-65-315 125-80-315 - 125-100-315
Temperatur festgelegt, so gelten die folgenden
Grenzen für Zulaufdruck und Raumtemperatur:
Zulaufdruck (Systemdruck) = Druck am
Pumpeneintritt: max. 5 bar
Raumtemperatur max. 40°C.
Bei Einsatz der Pumpen auch einschlägige Gesetze
und Vorschriften beachten (z.B. DIN 4747 oder DIN
4752, Abschnitt 4.5).
Nur für:
50-32-315 - 65-40-315 - 80-50-315 - 100-65-315 125-80-315 - 125-100-315
Kurve Gehäusewerkstoff Beschreibung
A 1.4408 Austenitischer Stahl
B 1.4517 Duplex Stahl
EN-GJS-400-18-LT
C
(0.7043)
Sphäroguß
LSB 100-german Seite 8
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Die angegebenen Druck- und Temperaturgrenzen
gelten für Standard-Gleitringdichtungen.
Einsatzgrenzen für andere Werkstoffe auf Anfrage.
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 13
Einbau-, Betriebs- und Wartungsanleitung
Entsorgen Sie die Verpackungsteile den
alten,
achten. Solange die Pumpe / das Aggregat
nicht am endgültigen Aufstellungsort befestigt
ist, muss es gegen Umkippen und Abrutschen
Die Anschlagseile dürfen nicht an den Ringösen
artung und Instandhaltung ist genügend
pletten Pumpenaggregates. Der Lüfter des
nen. Daher ist mindestens 10 cm Abstand des
3.7 Kondenswasser
Bei Motoren, die starken Temperaturschwankungen
oder extremen klimatischen Verhältnissen ausgesetzt
sind, empfehlen wir die Verwendung eines Motors mit
Stillstandsheizung um eine Kondenswasserbildung im
Motorinneren zu verhindern. Während des
Motorbetriebes darf die Stillstandsheizung nicht
eingeschaltet sein.
4. Transport, Handhabung, Zwischenlagerung
4.1 Transport, Handhabung
Überprüfen Sie die Pumpe / das Aggregat gleich
bei Anlieferung bzw. Eingang der Sendung auf
Vollständigkeit oder Schäden.
Der Transport der Pumpe / des Aggregates muss
fachgerecht und schonend durchgeführt werden.
Harte Stöße unbedingt vermeiden.
Die bei Auslieferung vom Werk vorgegebene
Transportlage beibehalten. Beachten Sie auch die
auf der Verpackung angebrachten Hinweise.
Saug- und Druckseite der Pumpe müssen
während Transport und Aufbewahrung mit
Stopfen verschlossen bleiben.
Baureihe LSB
örtlichen Vorschriften entsprechend.
Hebehilfen (z.B. Stapler, Kran, Kranvorrichtung,
Flaschenzüge, Anschlagseile, usw.) müssen
ausreichend dimensioniert sein und dürfen nur
von dazu befugten Personen bedient werden.
Das Anheben der Pumpe / des Aggregates darf
nur an stabilen Aufhängungspunkten wie
Gehäuse, Stutzen, Rahmen erfolgen. Bild 2 zeigt
die richtige Handhabung bei Krantransport.
Nicht unter schwebenden Lasten aufh
allgemeine Unfallverhütungsvorschriften be-
gesichert sein.
des Motors oder an Wellen befestigt werden.
Ein Herausrutschen der Pumpe / des Aggregates aus der Transportaufhängung kann Personen- und Sachschäden verursachen.
5. Aufstellung / Einbau
Bild 2
4.2 Zwischenlagerung / Konservierung
Pumpen oder Aggregate, die vor der Inbetriebnahme
längere Zeit zwischengelagert werden (max. 6 Monate), vor Feuchtigkeit, Vibrationen und Schmutz schützen (z.B. durch Einschlagen in Ölpapier oder Kunststofffolie). Die Aufbewahrung hat grundsätzlich an
einem von äußeren Einflüssen geschützten Ort, z.B.
unter trockenem Dach, zu erfolgen. Während dieser
Zeit müssen Saug- und Druckstutzen sowie alle anderen Zu- und Ablaufstutzen immer mit Blindflanschen
oder Blindstopfen verschlossen werden.
Bei längeren Zwischenlagerungszeiten können Konservierungsmaßnahmen an bearbeiteten Bauteiloberflächen und eine Verpackung mit Feuchtigkeitsschutz
notwendig werden!
5.1 Aufstellung des Aggregates
Die Pumpen müssen auf einem festen Unterbau festgeschraubt werden (z.B. Betonfundament, Stahlplatte,
Stahlträger, etc.). Der Unterbau muß allen während
des Betriebes entstehenden Belastungen standhalten.
Die Bauwerkgestaltung muss gemäss den
Abmessungen der Maßzeichnung vorbereitet sein. Die
Betonfundamente sollen eine ausreichende
Betonfestigkeit nach DIN 1045 oder gleichwertiger
Norm (min. BN 15) haben, um eine sichere,
funktionsgerechte Aufstellung zu ermöglichen.
Das Betonfundament muss abgebunden haben, bevor
das Aggregat aufgesetzt wird. Seine Oberfläche muss
LSB 100-german Seite 9
Artikel Nr. 771076129
waagrecht und eben sein. Die Lage und Größe der
Pumpenfüße und der Fundamentschrauben
entnehmen Sie der Maßzeichnung.
Als Fundamentschrauben können Spreizanker,
Klebeanker oder mit dem Fundament vergossene
Fundamentanker (Steinschrauben) verwendet werden.
Für W
Raum vorzusehen, besonders für das Auswechseln des Antriebsmotors oder des kom-
Motors muss genügend Kühlluft ansaugen kön-
Ansauggitters zu einer Wand, etc. erforderlich.
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 14
Einbau-, Betriebs- und Wartungsanleitung
rlagen ist für jeden Anwendungsfall
verschieden und soll daher von einem
Die Pumpe darf auf keinen Fall als Festpunkt
für die Rohrleitung verwendet werden. Die
sigen Rohrleitungskräfte dürfen nicht
Diese Anschlüsse sind funktionsentscheidend
Bei Verwendung in Zone 1 und 2 ist ein Motor
Die Pumpe ist beim Aufsetzen auf das Fundament
mit Hilfe einer Wasserwaage (am Druckstutzen)
auszurichten. Die zulässige Lageabweichung beträgt 0,2 mm/m. Unterlagsbleche müssen in unmittelbarer Nähe der Fundamentanker eingesetzt
werden und alle plan aufliegen.
Werden von benachbarten Anlagenbauteilen
Schwingungen auf das Pumpenfundament
übertragen, muss dieses durch entsprechende
schwingungsdämpfende Unterlagen abgeschirmt
werden (Schwingungen von außen können die
Lagerung beeinträchtigen).
Soll die Übertragung von Schwingungen auf be-
nachbarte Anlagenbauteile vermieden werden, ist
das Fundament auf entsprechende schwingungsdämpfende Unterlagen zu gründen.
Die Dimensionierung dieser schwingungsisolierenden Unte
erfahrenen Fachmann durchgeführt werden.
5.2 Anschluss der Rohrleitungen an die
Pumpe
zuläs
überschritten werden, siehe Kapitel 3.5.
5.2.1 Saug- und Druckleitung
Die Rohrleitungen müssen so bemessen und
ausgeführt sein, dass eine einwandfreie
Anströmung der Pumpe gewährleistet ist und
daher die Funktion der Pumpe nicht beeinträchtigt
wird. Besonderes Augenmerk ist auf die
Luftdichtheit von Saugleitungen und Einhaltung
der NPSH-Werte zu legen. Bei Saugbetrieb die
Saugleitung im horizontalen Teil zur Pumpe leicht
steigend verlegen, so dass keine Luftsäcke
entstehen. Bei Zulaufbetrieb die Zulaufleitung
leicht fallend zur Pumpe verlegen. Keine
Armaturen oder Krümmer unmittelbar vor dem
Pumpeneintritt vorsehen.
Bei Förderung aus unter Vakuum stehenden
Behältern ist die Anordnung einer
Vakuumausgleichsleitung vorteilhaft. Die
Rohrleitung soll eine Mindestnennweite von 25
mm aufweisen und muss über dem höchsten im
Behälter zulässigen Flüssigkeitsstand münden.
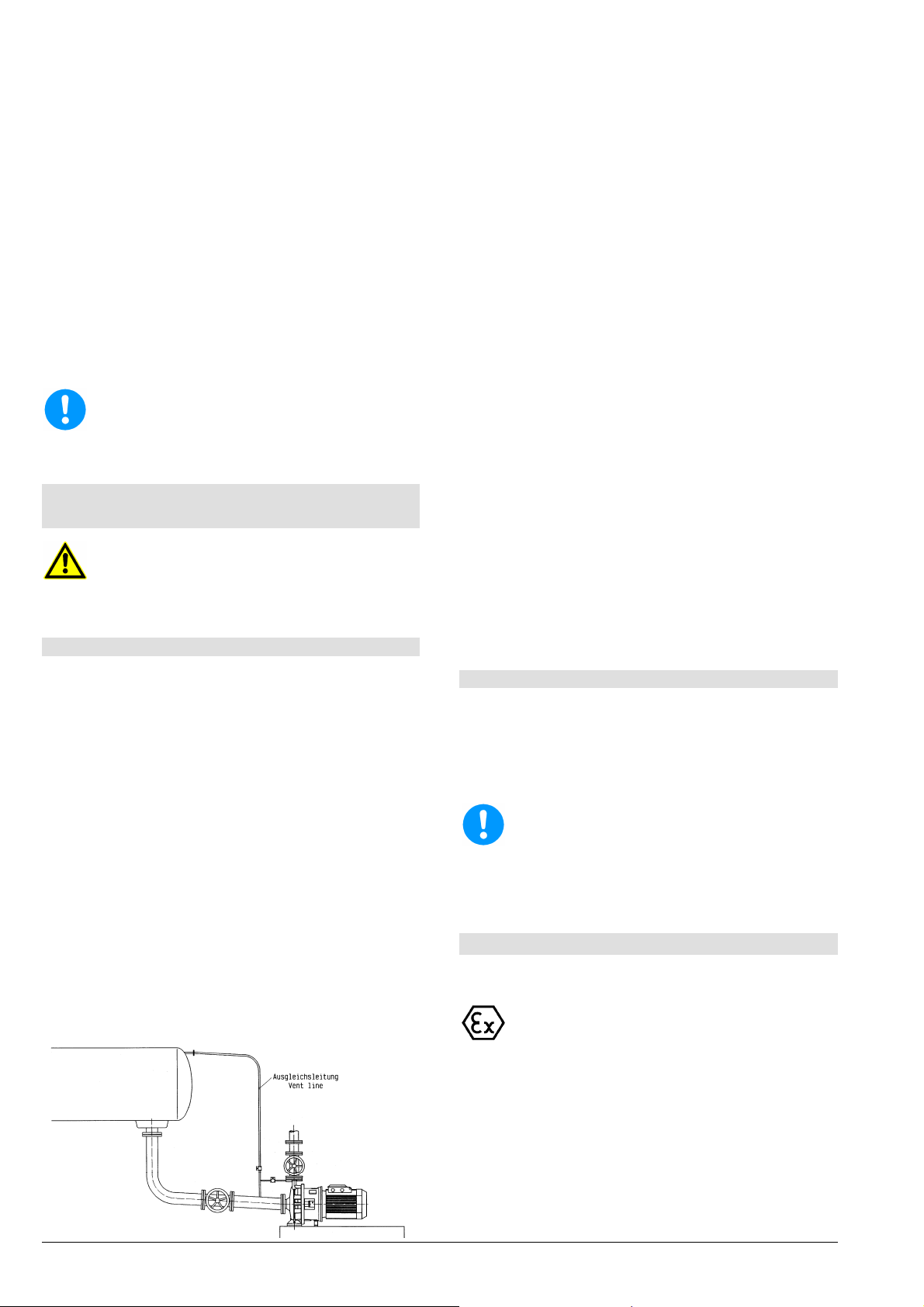
Eine zusätzliche absperrbare Rohrleitung (Bild 3) -
Pumpendruckstutzen-Ausgleichsleitung - erleichtert das Entlüften der Pumpe vor dem Anfahren.
Bild 3
LSB 100-german Seite 10
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Baureihe LSB
Achten Sie bei der Leitungsführung auf die
Zugängigkeit zur Pumpe bezüglich Wartung,
Montage, Demontage und Entleerung.
"Zulässige Stutzenkräfte und Momente an den
Pumpenstutzen ..." (Kapitel 3.7) beachten.
Wenn in den Rohrleitungen Kompensatoren
verwendet werden, so sind diese so abzufangen,
dass die Pumpe nicht durch den Druck in der
Rohrleitung unzulässig hoch belastet wird.
Vor Anschluss an die Pumpe:
Schutzabdeckungen der Pumpenstutzen
entfernen.
Vor Inbetriebnahme muss das Rohrsystem,
installierte Armaturen und Apparate von
Schweißperlen, Zunder usw. gereinigt werden.
Anlagen, die in direktem oder indirektem
Zusammenhang mit Trinkwassersystemen
stehen, sind vor Einbau und Inbetriebnahme von
eventuellen Verunreinigungen sicher zu befreien.
Zum Schutz der Wellenabdichtung (insbesondere
Gleitringdichtungen) vor Fremdkörpern empfohlen
im Anfahrbetrieb: Sieb 800 Mikron in Saug- /
Zulaufleitung.
Wird das Rohrsystem mit eingebauter Pumpe
abgedrückt, dann: maximal zulässigen
Gehäuseenddruck der Pumpe bzw. der
Wellenabdichtung beachten, siehe Datenblatt und
/ oder der Auftragsbestätigung.
Bei Entleerung der Rohrleitung nach Druckprobe
Pumpe entsprechend konservieren (sonst
Festrosten und Probleme bei Inbetriebnahme).
5.2.2 Zusatzanschlüsse
Eventuell erforderliche Sperr- oder Spülleitungen sind
zu installieren. Dem Datenblatt und / oder der
Auftragsbestätigung entnehmen Sie, welche
Leitungen, Drücke und Mengen notwendig sind. Lage
und Größe der Anschlüsse an die Pumpe siehe
Anhang "Anschlüsse".
und daher unerlässlich!
Eine Leitung zum Abführen eventueller Leckage der
Wellenabdichtung wird empfohlen. Anschluss siehe
Anhang "Anschlüsse".
5.3 Antrieb
Die Betriebsanleitung des Motorherstellers ist zu
beachten.
mit gültiger Atex-Zulassung zu verwenden.
Wenn im Zuge der Reparatur ein neuer Motor
verwendet wird, dann ist folgendes zu beachten:
Der Motor muß den in Blatt 1220.1A608D
genannten Anforderungen entsprechen (bei
Bedarf beim Hersteller anfordern).
Motorstummel und Motorflansch des neuen
Motors gut säubern (Lackreste entfernen).
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 15

Einbau-, Betriebs- und Wartungsanleitung
nen
befugten Elektrofachmann erfolgen. Die in der
men sind zu beachten. Die Vorschriften der
In explosionsgefährdeten Bereichen ist für die
14
Eine Überprüfung der Drehrichtung darf nur bei
uf
Die Anlage darf nur von Personal in Betrieb
en örtlichen
Sicherheitsbestimmungen und mit dieser
Betriebsanleitung (insbesondere mit den darin
enthaltenen Sicherheitsvorschriften und
Der Betrieb mit geschlossenem Absperrorgan
t nicht
Bei Anfahren gegen fehlenden Gegendruck ist
zustellen (Schieber nur wenig öffnen). Nach
Erreichen des vollen Gegendruckes Schieber
Erreicht die Pumpe nicht die vorgesehene
höhe oder treten atypische Geräusche
oder Schwingungen auf: Pumpe wieder außer
Betrieb setzen (siehe Kapitel 6.7) und Ursache
Besondere Vorsicht vor Berührung heißer
Maschinenteile und im ungeschützten Bereich
der Wellenabdichtung. Automatisch gesteuerte
Anlagen können sich jederzeit und
überraschend einschalten. Anlagenseitig
Die Einsatzgrenzen der Pumpe / des
Aggregates bezüglich Druck, Temperatur,
Leistung und Drehzahl sind im Datenblatt und /
oder der Auftragsbestätigung angegeben und
5.4 Elektrischer Anschluss
Der Elektroanschluss darf nur durch ei
Motorherstellers vorzunehmen. Ein Motorschutzschalter ist vorzusehen.
Baureihe LSB
Elektrotechnik gültigen Regeln und Vorschriften, insbesondere hinsichtlich Schutzmaßnah-
örtlichen nationalen Energieversorgungsunternehmen sind ebenso einzuhalten.
Vor Beginn der Arbeiten die Angaben auf dem
Motorleistungsschild auf Übereinstimmung mit dem
örtlichen Stromnetz überprüfen. Das Anklemmen der
Stromzuführungskabel des gekuppelten Antriebsmotors ist entsprechend dem Schaltplan des
elektrische Installation zusätzlich IEC 60079zu beachten.
gefüllter Pumpe erfolgen. Jeder Trockenla
führt zu Zerstörungen an der Pumpe.
5.5 Endkontrolle
Das Aggregat muss sich an der Steckwelle von Hand
leicht durchdrehen lassen.
6. Inbetriebnahme, Betrieb, Außerbetriebnahme
Betriebspunkt einstellen. Die am Typenschild bzw.
genommen werden, das mit d
Sicherheitshinweisen) vertraut ist.
6.1 Erstinbetriebnahme
Vor dem Einschalten der Pumpe muss sichergestellt
sein, dass nachstehende Punkte geprüft und
durchgeführt wurden:
Vor der Erstinbetriebnahme sind keine Schmier-
maßnahmen notwendig.
Pumpe und Saugleitung müssen bei
Inbetriebnahme vollständig mit Flüssigkeit gefüllt
sein.
Aggregat noch einmal von Hand aus durchdrehen
und leichten, gleichmäßigen Gang prüfen.
Kontrollieren, ob Laternenschutzbleche montiert
sind und alle Sicherheitseinrichtungen betriebsbereit sind.
Eventuell vorhandene Sperr- oder Spülleitungen
einschalten. Mengen und Drücke siehe Datenblatt
und / oder der Auftragsbestätigung.
Schieber in Saug- bzw. Zulaufleitung öffnen.
Druckseitigen Schieber auf ca. 25% der
Auslegungs-Fördermenge einstellen. Bei Pumpen
mit Druckstutzen-Nennweite kleiner DN 200 kann
der Schieber beim Anfahren auch geschlossen
bleiben.
Sicherstellen, dass das Aggregat vorschriftgerecht
elektrisch mit allen Schutzeinrichtungen angeschlossen ist.
Kurz Ein- und Ausschalten und dabei
Drehrichtung kontrollieren. Sie muss dem
Drehrichtungspfeil auf der Antriebslaterne
entsprechen.
6.2 Antriebsmaschine einschalten.
Sofort (max. 10 Sekunden bei 50 Hz bzw. max. 7
Sekunden bei 60 Hz Stromversorgung) nach dem
Hochlauf auf die Betriebsdrehzahl druckseitigen
Schieber öffnen und damit den gewünschten
LSB 100-german Seite 11
Artikel Nr. 771076129
im Datenblatt und / oder der Auftragsbestätigung
angegebenen Förderdaten müssen eingehalten
werden. Jede Änderung ist nur nach Rücksprache
mit dem Hersteller zulässig!
in der Saug- und / oder Druckleitung is
zulässig.
dieser durch druckseitiges Drosseln her-
öffnen.
Förder
suchen (siehe Kapitel 10).
6.3 Wiederinbetriebnahme
Bei jeder Wiederinbetriebnahme ist grundsätzlich wie
bei der Erstinbetriebnahme vorzugehen. Die Kontrolle
von Drehrichtung und Leichtgängigkeit des
Aggregates kann jedoch entfallen.
Eine automatische Wiederinbetriebnahme darf nur
dann erfolgen, wenn sichergestellt ist, dass die Pumpe
bei Stillstand mit Flüssigkeit gefüllt bleibt.
entsprechende Warnschilder anbringen.
6.4 Grenzen des Betriebes
unbedingt einzuhalten!
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 16

Einbau-, Betriebs- und Wartungsanleitung
Beim Fördern von Flüssigkeiten mit abrasiven
Bestandteilen ist ein erhöhter Verschleiß an
Hydraulik und Wellenabdichtung zu erwarten.
en gegenüber den
In explosionsgefährdeten Betrieben ist es
und
Wartungsarbeiten verlängern die Lebensdauer
Die auf dem Typenschild der Antriebsmaschine
angegebene Leistung darf nicht überschritten
werden.
Plötzlich auftretende Temperaturänderungen
(Temperaturschocks) sind zu vermeiden.
Pumpe und Antriebsmaschine sollen gleichmäßig
und erschütterungsfrei laufen, mindestens
wöchentlich kontrollieren.
6.4.1 Förderstrom min. / max.
Sofern in den Kennlinien oder Datenblättern keine
anderen Angaben gemacht sind, gilt:
Q
= 0,1 x Q
min
Q
= 0,3 x Q
min
Q
= 1,2 x Q
max
Q
= Förderstrom im Wirkungsgradoptimum
BEP
*) unter der Voraussetzung NPSH
für Kurzzeitbetrieb
BEP
für Dauerbetrieb
BEP
für Dauerbetrieb *)
BEP
Anlage
> (NPSH
Pumpe
+ 0,5 m)
6.4.2 Abrasive Medien
Die Inspektionsintervalle soll
üblichen Zeiten reduziert werden.
6.4.3 Zulässige Schalthäufigkeit
Die zulässige Schalthäufigkeit der Pumpe darf nicht
überschritten werden, siehe Diagramm 6.
100,0
10,0
max. zulässige Anläufe pro Stunde
1,0
1 10 100 1000
Motorleistung [kW]
Diagramm 6
Bei Elektromotoren ist die zulässige Schalthäufigkeit
der Betriebs- und Wartungsanleitung des
Motorlieferanten zu entnehmen.
Bei von einander abweichenden Werten ist die
kleinere Schalthäufigkeit zulässig.
6.5 Schmierung
Der Pumpenteil hat keine Lager und muss somit nicht
geschmiert werden.
Für die möglicherweise erforderliche Schmierung der
Motorlager bitte die Empfehlung in der Betriebs- und
Wartungsanleitung des Motorlieferanten beachten.
LSB 100-german Seite 12
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Baureihe LSB
6.6 Überwachung
sinnvoll, die Lagertemperatur und die Pumpenschwingungen zu überwachen.
Regelmäßig durchgeführte Überwachungs-
Ihrer Pumpe oder Anlage.
Pumpe mindestens wöchentlich auf Dichtheit
kontrollieren.
Die Regulierungs- und Überwachungsmöglich-
keiten eventuell vorhandener Sperr- oder
Spülsysteme sind wöchentlich auf ihre Funktion zu
überprüfen. Der Kühlwasseraustritt soll handwarm
sein.
Pumpen, die funktionsbedingt einem chemischen
Angriff bzw. abrasiven Verschleiß ausgesetzt sind,
müssen periodisch auf chemischen oder abrasiven Abtrag inspiziert werden. Die Erstinspektion
ist nach einem halben Jahr durchzuführen. Alle
weiteren Inspektionsintervalle sind auf Grund des
jeweiligen Zustandes der Pumpe festzulegen.
6.7 Außerbetriebnahme
Schieber in der Druckleitung unmittelbar (max. 10
Sekunden) vor Abschaltung des Motors schließen.
Nicht erforderlich, wenn druckbelastete Rückschlagklappe vorhanden ist.
Antriebsmaschine abschalten. Auf ruhigen Auslauf
achten.
Schieber auf der Saugseite schließen.
Hilfskreisläufe schließen.
Bei Frostgefahr Pumpe und Leitungen vollständig
entleeren.
Bleibt die Pumpe auch im Stillstand unter Druck
und Temperatur: Alle vorhandenen Sperr- und
Spülsysteme eingeschaltet lassen.
Sperrung der Wellenabdichtung muss
eingeschaltet bleiben, wenn Gefahr des
Lufteinsaugens besteht (bei Zulauf aus
Vakuumanlagen oder bei Parallelbetrieb mit
gemeinsamer Saugleitung).
6.8 Zwischenlagerung / Längerer
Stillstand
6.8.1 Zwischenlagerung neuer Pumpen
Wenn die Inbetriebnahme längere Zeit nach der Lieferung erfolgen soll, empfehlen wir zur Zwischenlagerung der Pumpe die folgenden Maßnahmen:
Pumpe an einem trockenen Ort lagern.
Durchdrehen der Pumpe von Hand einmal
monatlich.
6.8.2 Maßnahmen für längere Außerbetriebnahme
Pumpe bleibt eingebaut mit Betriebsbereitschaft:
In regelmäßigen Abständen sind Probeläufe von
einer Dauer von mindestens 5 Minuten durchzuführen. Die Zeitspanne zwischen den Probeläufen
hängt von der Anlage ab, sollte jedoch mindestens
1x pro Woche durchgeführt werden.
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 17
Einbau-, Betriebs- und Wartungsanleitung
Arbeiten an der Pumpe oder Anlage sind nur im
Stillstand durchzuführen. Beachten Sie
Instandhaltungsarbeiten und Wartung darf nur
hrenem Personal, das
mit dem Inhalt dieser Betriebsanleitung vertraut
Personal des Herstellers
Vor dem Öffnen der Pumpe unbedingt Kapitel 2
Die Pumpe darf nicht mit unter Druck
(z.B. Hochdruckreiniger)
Reparaturen an der Pumpe oder Anlage dürfen
nur von autorisiertem Fachpersonal oder durch
llers durchgeführt
Bei Ausbau der Pumpe unbedingt Kapitel 2
rdern, müssen dekontaminiert werden.
Beim Ablassen des Fördermediums ist darauf
zu achten, dass keine Gefährdungen für
Personen und Umwelt entsteht. Gesetzliche
Bestimmungen sind einzuhalten, ansonsten
Offene Flamme (Lötlampe, etc.) beim Zerlegen
nur dann als Hilfe verwenden, wenn dadurch
oder Explosionsgefahr oder die
schädlicher Dämpfe
Ersatzteile verwenden. Auf
richtigen Werkstoff und passende Ausführung
6.8.3 Längerer Stillstand
Inbetriebnahme ist als Erstinbetriebnahme zu
verstehen (siehe Kapitel 6).
a) Gefüllte Pumpen
Reservepumpen 1x wöchentlich kurz ein- und
sofort wieder ausschalten. Eventuell alternativ als
Hauptpumpe betreiben.
Steht die Reservepumpe unter Druck und
Temperatur: alle vorhandenen Sperr- und
Spülsysteme eingeschaltet lassen.
Nach 5 Jahren Motorlager erneuern.
7. Instandhaltung, Wartung
Baureihe LSB
b) Leerstehende Pumpen
Mindestens 1x wöchentlich von Hand aus
durchdrehen (nicht einschalten wegen
Trockenlauf).
Nach 5 Jahren Motorlager erneuern.
7.1 Allgemeine Hinweise
unbedingt Kapitel 2.
von geschultem und erfa
ist oder vom Servicedurchgeführt werden.
7.2 Gleitringdichtungen
und Kapitel 8 beachten.
Tritt bei der Gleitringdichtung tropfenweise
Fördermedium aus, so ist diese beschädigt und muss
ersetzt werden.
Austausch der Gleitringdichtung laut beigelegter
"Montageanleitung für Wellenabdichtung".
8. Demontage der Pumpe und Reparatur
7.3 Motorlager
Nach durchschnittlich 5 Jahren ist das Fett in den
Motorlagern so gealtert, dass ein Austausch der Lager
empfehlenswert ist. Jedoch sind die Lager nach
spätestens 25000 Betriebsstunden zu ersetzen bzw.
entsprechend der Wartungsanleitung des Motorlieferanten, wenn dieser eine kürzere Wartungsdauer
empfiehlt.
7.4 Reinigung der Pumpe
Äußerliche Verschmutzung an der Pumpe
beeinträchtigt die Wärmeabführung. Daher ist in
regelmäßigen Abständen (je nach
Verschmutzungsgrad) die Pumpe mit Wasser zu
reinigen.
stehendem Wasser
gereinigt werden - Wassereintritt in Lager.
8.1 Allgemeine Hinweise
Fachpersonal des Herste
werden.
sowie Kapitel 4.1 beachten.
Für Montagen und Reparaturen stehen auf
Anforderung geschulte Kundendienst-Monteure zur
Verfügung.
Pumpen, die gesundheitsgefährdende Flüssigkeiten fö
besteht Lebensgefahr!
LSB 100-german Seite 13
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Vor Beginn der Demontage muss das Aggregat so
gesichert werden, dass es nicht eingeschaltet
werden kann.
Das Pumpengehäuse muss drucklos und entleert
sein.
Alle Absperrorgane in der Saug-, Zulauf- und
Druckleitung müssen geschlossen sein.
Alle Teile müssen Umgebungstemperatur
angenommen haben.
Ausgebaute Pumpe, Baugruppen oder Einzelteile gegen Umkippen oder Wegrollen sichern.
keine BrandGefahr der Entwicklung
entsteht.
Nur Original-
achten.
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 18
Einbau-, Betriebs- und Wartungsanleitung
hrt werden oder es dürfen
nur nicht funkenbildende Werkzeuge verwendet
so weit anheben, als zum
Einschieben des Schutzgitters in das Fenster
unbedingt notwendig ist. Wenn das Schutzgitter
Schutzgitter noch einmal ausbauen, etwas
Schraubendreher oder Montiereisen nur im
eich von Laufradschaufeln ansetzen, damit
8.2 Allgemeines
Arbeiten, die eine Schlagbeanspruchung erfordern, dürfen nur außerhalb der explosiven Atmosphäre durchgefü
werden.
Demontage und Montage grundsätzlich nach der
zugehörigen Schnittzeichnung durchführen.
Es ist nur handelsübliches Werkzeug erforderlich.
Vor dem Zerlegen prüfen, ob die erforderlichen
Ersatzteile bereit liegen.
Die Pumpe immer nur so weit zerlegen, als dies für
den Austausch des zu reparierenden Teils erforderlich
ist.
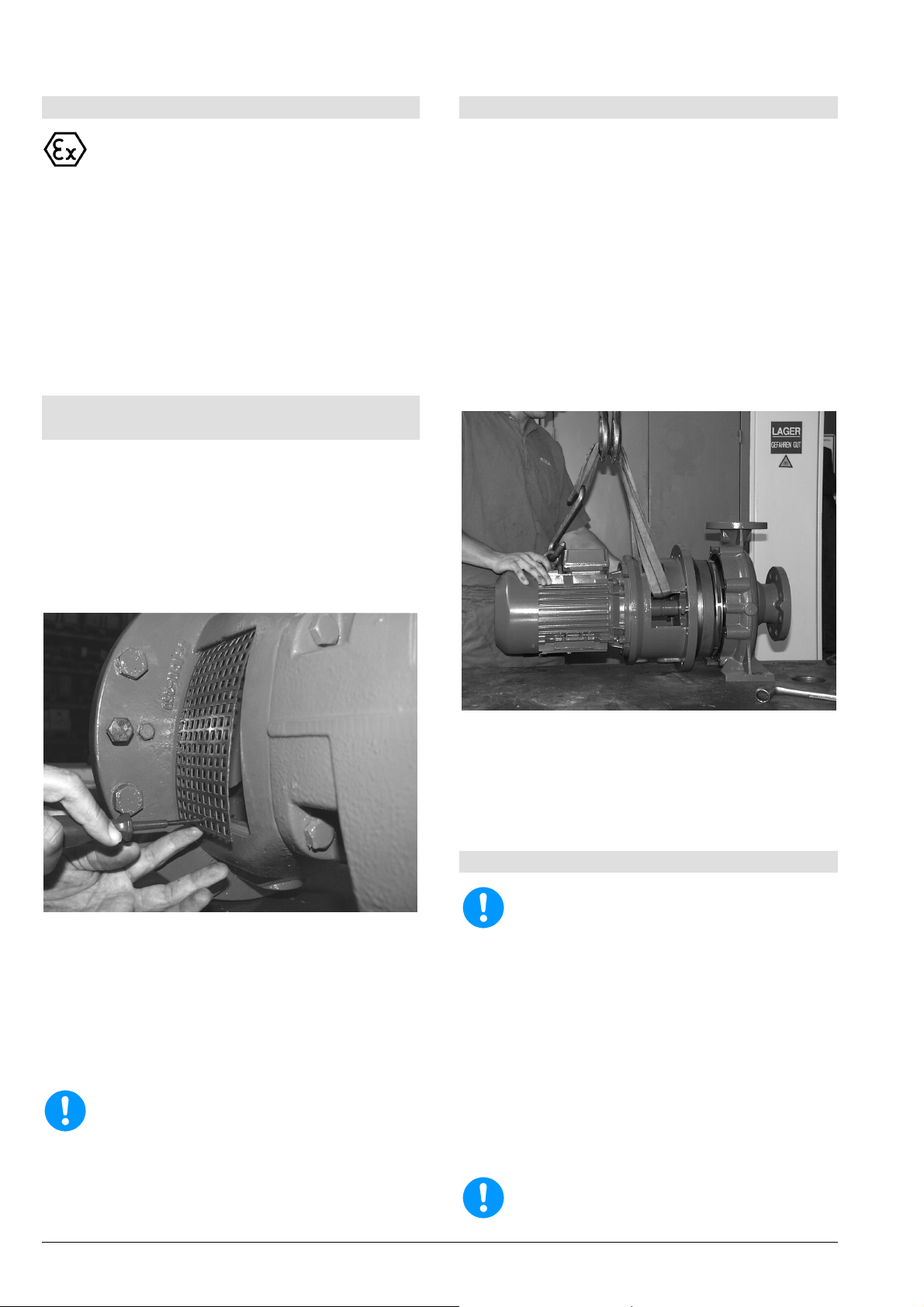
8.3 Aus- und Einbau der Schutzgitter aus
der Antriebslaterne
Die Schutzgitter (680) sind in die Fenster der
Antriebslaterne (681) geklemmt.
Zum Ausbau einen Schraubendreher ca. 4 cm durch
die unterste Lochreihe des Schutzgitters stecken.
Dann den Griff des Schraubendrehers soweit nach
oben ziehen, bis die Unterkante des Schutzgitters
etwas vom Fenster abhebt. Nun kann der
Schraubendreher samt Schutzgitter aus dem Fenster
herausgezogen werden (siehe Bild 8).
Baureihe LSB
8.4 Ausbau der Laufeinheit
Unter Laufeinheit versteht man alle Pumpenteile mit
Ausnahme des Spiralgehäuses (102V). Da die
Pumpen in Blockbauweise konstruiert sind, kann das
Spiralgehäuse (102V) auf dem Fundament und in der
Rohrleitung verbleiben, sofern nicht das
Spiralgehäuse selbst repariert werden soll.
Spiralgehäuse (102V) über Entleerungsstopfen
(912.11) entleeren.
Verschraubung etwaiger Sperr- oder
Spülwasserleitungen lösen.
Stützfuß (183) Verschraubung am Fundament
lösen (nicht bei allen Baugrößen vorhanden).
Laufeinheit an Hebezeug hängen, so dass beim
Ausbau die Laufeinheit weder nach unten sackt,
noch nach oben im Spiralgehäuse drückt.
Befestigungsbeispiel siehe Bild 9.
Bild 8
Beim Einbau zuerst Schraubendreher ca. 4 cm durch
die unterste Lochreihe des Schutzgitters stecken.
Dann den oberen Teil des Schutzgitters in den oberen
Rand der Fensteröffnung stecken. Nun den Griff des
Schraubendrehers so weit nach oben ziehen, bis die
Durchbiegung des Schutzgitters ausreicht, um dieses
bis zum Anschlag in das Fenster der Antriebslaterne
hinein zu schieben.
Schraubendreher nur
nach dem Einbau zu wenig im Fenster klemmt:
flacher drücken und wieder einbauen.
LSB 100-german Seite 14
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Bild 9
Gehäuseverschraubung (Kopfschrauben 901.11)
komplett abschrauben.
Laufeinheit axial aus dem Spiralgehäuse ziehen.
Dabei können die Abdrückschrauben (901.42)
verwendet werden.
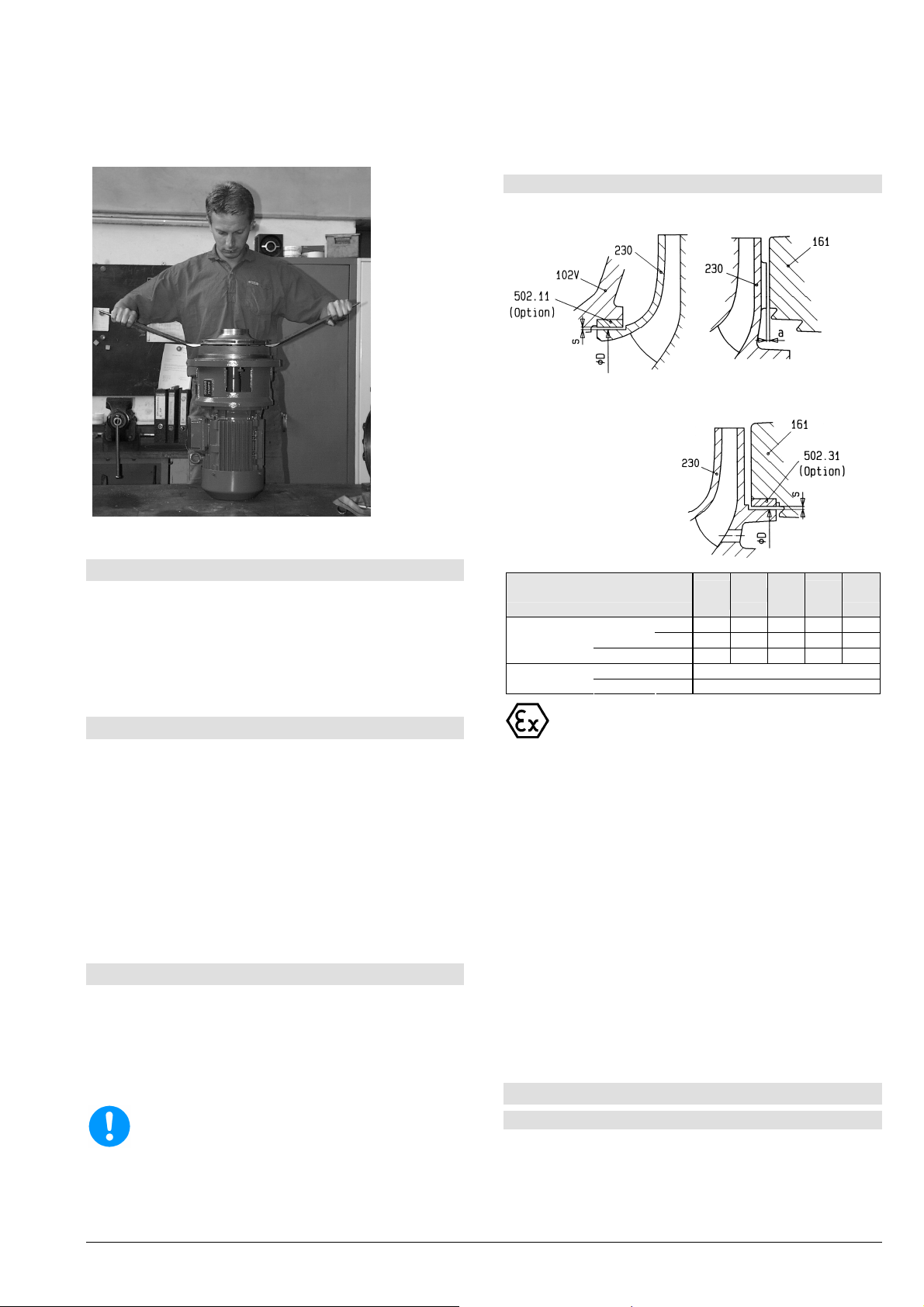
8.5 Ausbau des Laufrades
Beigelegte "Montageanleitung zu Wellenabdichtung" beachten.
Hat das Laufrad Rückenschaufeln, so
kontrollieren Sie vor dem weiteren Zerlegen die
axiale Spaltweite "a" zwischen Laufrad (230) und
Gehäusedeckel (161). Beurteilung der
gemessenen Spaltweite siehe Kapitel 8.8.1.
Laufradmutter (922) durch kurzen gefühlvollen
Schlag auf den Schraubenschlüssel lösen
(Rechtsgewinde). Eventuell mit einem Dorn in der
Querbohrung der Steckwelle (im Klemmbereich)
gegenhalten.
Laufrad (230) abziehen mit Hilfe zweier
Schraubendreher oder Montiereisen (Bild 10).
Passfeder (940.31) herausnehmen.
Ber
die Strömungskanäle nicht deformiert werden.
Ausgabe 01/2010
Revision 02
Page 19
Einbau-, Betriebs- und Wartungsanleitung
dichtungen sind nur zur einmaligen Verwendung
ützt" erreicht oder
überschritten, müssen die betroffenen Teile
Ein weiteres Zerlegen sowie der Zusammenbau
der Laufeinheit erfolgt leichter in vertikaler
Aufstellung. Kippgefahr beachten!
Bild 10
8.6 Ausbau der Wellenabdichtung
Vor der Demontage des Gehäusedeckels
"Montageanleitung zu Wellenabdichtung"
beachten.
Sechskantmutter (902.32) lösen (nicht bei allen
Pumpengrößen vorhanden) und Gehäusedeckel
(161) aus Lagerträgerlaterne (344) nehmen.
8.7 Ausbau der Steckwelle
Verschraubung (920.41) lösen und Motor samt
Steckwelle (210) aus der Antriebslaterne (341)
herausziehen.
Radiale Steckwellenverschraubung (904.41 und
904.42) lösen (Gewindestifte) und Steckwelle
(210) von der Motorwelle abziehen. Eventuell zur
Unterstützung (losbrechen) einen kräftigen
Schraubendreher in die Querbohrung der
Steckwelle einführen, damit gegen die Stirnfläche
der Motorwelle drücken und so die beiden Wellen
gegeneinander verschieben.
8.8 Instandsetzung
Nach dem Zerlegen sind alle Teile sorgfältig zu
reinigen und auf Verschleiß zu prüfen. Abgenützte
oder beschädigte Teile sind gegen Neuteile
(Ersatzteile) auszutauschen.
Es sind grundsätzlich neue Dichtelemente zu
verwenden.
Alle PTFE-Dichtelemente und Graphit-
geeignet.
In den meisten Fällen ist es zweckmäßig, falls
beschädigt absolut notwendig, die Wellenabdichtung
zu erneuern.
LSB 100-german Seite 15
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Baureihe LSB
Ablagerungen am Laufrad (230), im Spiralgehäuse
(102V) oder am Gehäusedeckel (161) sind zu
entfernen.
8.8.1 Dichtspalte beim Laufrad
Saugseite des Laufrades
Rückenschaufeln des
Laufrades
Antriebseite des Laufrades
Nur bei Pumpengröße
100-65-315
125-80-315
125-100-315
150-125-315
Nenndurchmesser D (mm)
Radialer Spalt
s (mm)
a (mm)
neu
abgenützt 0,78 0,85 0,90 1,05 1,15
neu 0,8 - 1,2 Axialer Spalt
abgenützt max. 1,7
60
68
min. 0,15 0,17 0,20 0,22 0,25
max. 0,19 0,22 0,24 0,27 0,30
85
100
120
135
155
175
220
Sind die Werte für "abgen
ersetzt werden.
Bei Spiralgehäusen (102V) mit Spaltring (502.11) bzw.
bei Gehäusedeckeln (161) mit Spaltring (502.31) gibt
es zur Wiederherstellung des korrekten Spaltes
folgende Möglichkeiten:
a) Laufrad (230) und Spaltring erneuern. Damit sind
die Originalmaße wiederhergestellt.
b) Spaltringe mit entsprechendem Innendurchmesser
anfertigen und so wieder die Original-Spaltweite
erreichen. Bitte nehmen Sie Kontakt mit dem
Hersteller auf.
Bei Spiralgehäusen (102V) bzw. Gehäusedeckeln
(161) ohne Spaltring kann im Reparaturfall auch
nachträglich ein Spaltring eingesetzt werden. Dazu ist
aber eine Nacharbeit (Nachdrehen) im Spiralgehäuse
bzw. im Gehäusedeckel erforderlich. Bitte nehmen Sie
Kontakt mit dem Hersteller auf.
8.9 Montage
8.9.1 Allgemeines
Die Montage wird in umgekehrter Reihenfolge
vorgenommen wie die Demontage, wobei zusätzlich
folgendes zu beachten ist:
Auf größte Reinlichkeit ist bei der Montage zu
achten.
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 20
Einbau-, Betriebs- und Wartungsanleitung
r dann verwenden, wenn
sichergestellt ist, dass es zwischen
Fördermedium und Gleitmittel zu keinen
Geschmiertes
Vor Inbetriebnahme unbedingt wieder alle
Hilfsleitungen und Sicherheitseinrichtungen
montieren bzw. anschließen und in Betrieb
Enge Schiebesitze, z.B. zwischen Steckwelle
(210) und Motorwelle oder Laufrad (230) und
Welle (210) sowie Gewinde eventuell mit
geeignetem Gleitmittel (z.B. Molykote / NeverSeeze) bestreichen, damit die Montage und auch
die nächste Demontage erleichtert wird.
Gleitmittel jedoch nu
Baureihe LSB
Späne aus dem Gewindeloch entfernen (z.B. mit
Druckluft), Gewindestifte (904.41 und 904.42)
einschrauben und sichern (z.B. mit Omnifit 100 M
oder Loctite).
Korrekten Rundlauf der Steckwelle gegenüber
dem Motorflansch mittels Meßuhr kontrollieren
(siehe Bild 11.). Der Zeigerausschlag der Meßuhr
darf max. 0,1 mm betragen.
gefährlichen Reaktionen kommen kann.
Schrauben sind mit folgenden Drehmomenten
anzuziehen:
Verschraubung Größe
Gehäuseschrauben
Alle übrigen Schrauben
M12 35 50
M16 105 150
M20 210 305
M10 35 50
M12 60 90
M16 150 220
Anziehdrehmoment in Nm
Gewinde
Trockenes
Gewinde
Keine übertriebene Gewalt anwenden.
Montage der Steckwelle siehe Kapitel 8.9.2.
Montage der Gleitringdichtung siehe separate
Beschreibung "Montageanleitung der
Wellenabdichtung" und Kapitel 8.5.
Bei Laufrädern mit Rückenschaufeln nach der
Montage des Laufrades (230) und nach
Festziehen der Laufradmutter (922) korrekten
Axialspalt zwischen Rückenschaufeln und
Gehäusedeckel (161) kontrollieren. Siehe Kapitel
8.8.1.
Nach dem Zusammenbau der Laufeinheit und
auch nach dem Einbau in das Spiralgehäuse
Welle drehen und damit Leichtgängigkeit der
Pumpe kontrollieren. Die Wellenabdichtungen
verursachen etwas Drehwiderstand, es darf aber
keine Berührung zwischen Metallteilen bemerkbar
sein.
setzen.
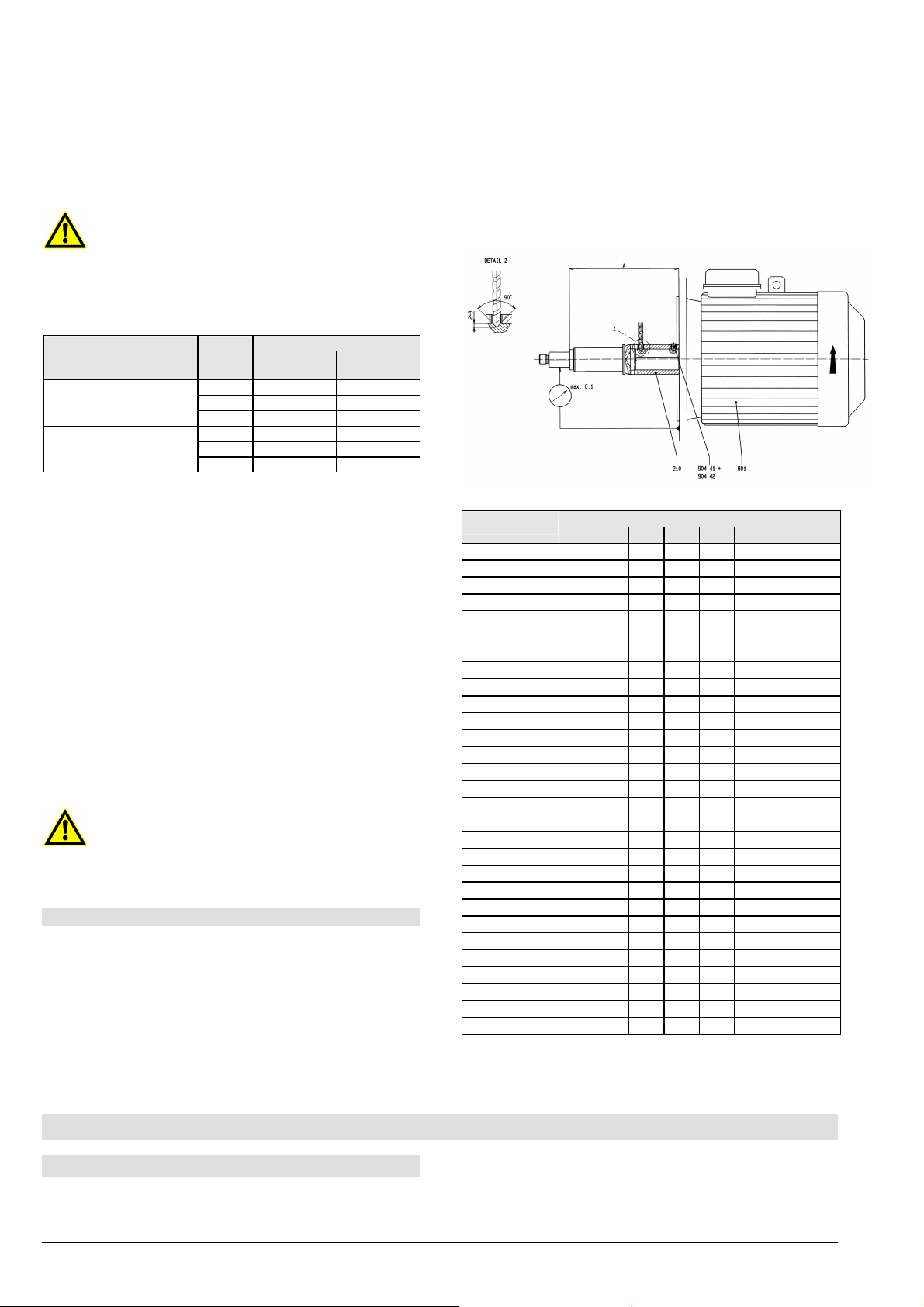
8.9.2 Montage der Steckwelle
Paßfeder in den Motorstummel einlegen.
Motorwellenstummel mit Gleitmittel bestreichen
(siehe Punkt 8.9.1.).
Steckwelle so weit auf die Motorwelle
aufschieben, bis das Maß A erreicht ist (siehe Bild
11 und Tabelle).
Motorwelle durch die radialen Steckwellen-
bohrungen ca. 2-3 mm tief mit einem Spiralbohrer
mit 90° Spitze ansenken (siehe Bild 11).
Type
40-25-160 157 157 197 197 197 232 - 40-25-200 157 157 197 197 197 232 - 40-25-250 162 162 202 202 202 237 237 237
50-32-160 157 157 197 197 197 232 - 50-32-200 157 157 197 197 197 232 - 50-32-250 162 162 202 202 202 237 237 237
50-32-315 - - 202 202 197 237 237 237
65-40-160 157 157 197 197 197 232 - 65-40-200 157 157 197 197 197 232 232 65-40-250 162 162 202 202 202 237 237 237
65-40-315 - - 202 202 197 237 237 237
80-50-160 157 157 197 197 197 232 232 80-50-200 157 157 197 197 202 232 232 232
80-50-250 - 162 202 202 202 237 237 237
80-50-315 - - 202 202 202 237 237 237
100-65-160 162 162 202 202 202 237 237 237
100-65-200 - 162 202 202 202 237 237 237
100-65-250 - 162 202 202 206 237 237 237
100-65-315 - - 206 206 202 241 241 241
125-80-160 - 162 202 202 202 237 237 237
125-80-200 - 162 202 202 202 237 237 237
125-80-250 - - 202 202 202 237 237 237
125-80-315 - - - 206 206 241 241 241
125-100-200 - - 202 202 202 237 237 237
125-100-250 - - 216 216 216 251 251 251
125-100-315 - - - - 206 241 241 241
150-125-250 - - - - 216 251 251 251
150-125-315 - - - - - 241 241 241
200-150-250 - - - - - 251 251 251
80 90 100 112 132 160 180 200
Bild 11
Maß A bei Motor-Baugröße
9. Ersatzteilempfehlung, Reservepumpen
9.1 Ersatzteile
Die Ersatzteile sind für die Bedingungen eines
zweijährigen Dauerbetriebes auszuwählen. Falls keine
LSB 100-german Seite 16
Artikel Nr. 771076129
anderen Richtlinien zu beachten sind, werden die in
unten angeführter Liste angegebenen Stückzahlen für
Ersatzteile empfohlen (nach DIN 24296).
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 21

Einbau-, Betriebs- und Wartungsanleitung
Zur Sicherung einer optimalen Verfügbarkeit
r, insbesondere bei Ausführungen
aus Sonderwerkstoffen und Gleitringdichtung,
auf Grund der längeren Beschaffungszeiten
Ersatzteile in trockenen Räumen und vor
Für Pumpen in Anlagen, deren Ausfall
Menschenleben gefährden bzw. hohe
hen können,
ist unbedingt eine ausreichende Anzahl von
Reservepumpen in der Anlage betriebsbereit zu
bereitschaft ist durch
stellen, siehe Kapitel
Reservepumpen entsprechend Kapitel 6.8
empfehlen wi
entsprechende Ersatzteile zu bevorraten.
Anzahl der Pumpen
Ersatzteile Stückzahl der Ersatzteile
Laufrad 1 1 1 2 2 2 20%
Spaltring 2 2 2 3 3 4 50%
Welle mit Passfedern
und Muttern
Dichtungen für
Pumpengehäuse Sätze
sonstige Dichtungen
Sätze
Gleitringdichtung Satz 1 1 2 2 2 3 25%
(einschließlich Reservepumpen)
2 3 4 5 6/7 8/9 10/+
1 1 1 2 2 2 20%
4 6 8 8 9 12 150%
4 6 8 8 9 10 100%
Ersatzteilbestellung
Bei Ersatzteilbestellung bitten wir Sie um folgende
Angaben:
Type:
S/N (Auftrags Nr.)
Teilebezeichnungen
Schnittzeichnung
______________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________
_______________________________________________
____________________________________________________
Alle Angaben finden Sie auf dem Datenblatt und / oder
der Auftragsbestätigung und der dazugehörigen
Schnittzeichnung.
Schmutz geschützt aufbewahren!
9.2 Reservepumpen
Sachschäden oder Kosten verursac
halten. Die Betriebslaufende Kontrolle sicherzu
6.8.
aufbewahren!
Baureihe LSB
LSB 100-german Seite 17
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 22
Einbau-, Betriebs- und Wartungsanleitung
Drehzahl der Antriebsmaschine mit vorgeschriebener
Drehzahl der Antriebsmaschine mit vorgeschriebener
größeres Laufrad verwenden (verfügbare Antriebsleistung
Pumpe und / oder Rohrleitung nicht völlig mit Flüssigkeit
/ Saugleitung verringern (Verlauf und
Zwei Phasen der Stromzuführung vertauschen (vom
an den bei Bestellung angegebenen Systemdruck /
10. Störungen - Ursachen und Behebung
Baureihe LSB
Die angeführten Hinweise auf Ursachen und
Behebung von Störungen sollen zur Erkennung des
Problems dienen. Für Störungen, die der Betreiber
nicht selbst beseitigen kann oder will, steht der
Kundendienst des Herstellers zur Verfügung. Bei
Reparaturen und Änderungen an der Pumpe durch
Förderstrom zu gering
Förderstrom hört nach einiger Zeit auf
Förderhöhe zu gering
Förderhöhe zu hoch
Antriebsmaschine überlastet
Unruhiger Lauf der Pumpe
Zu hohe Temperatur in der Pumpe
Zu hohe Temperatur an der
■
Gegendruck zu hoch Anlage auf Verunreinigungen überprüfen, Schieber geöffnet
■ ■
■ ■
■ ■
■ ■
■ ■
■ ■ ■
■ ■
■ ■ ■
■ ■ ■
■ ■ ■
■ ■
■ ■
■ ■ ■
■ ■
Drehzahl zu hoch Drehzahl verringern
Drehzahl zu klein Drehzahl erhöhen (verfügbare Antriebsleistung beachten)
■ ■
■ ■
Laufraddurchmesser zu groß kleineres Laufrad verwenden
Laufraddurchmesser zu klein
■ ■
Pumpe oder Saug- / Zulaufleitung verstopft reinigen
Luftsack in Rohrleitung entlüften
■ ■
Luft wird angesaugt Flüssigkeitsspiegel erhöhen
Ansaugen von Luft durch die Wellenabdichtung Sperrleitung reinigen
Drehrichtung falsch
■
Dichte und / oder Viskosität des Fördermediums zu hoch Rückfrage erforderlich
■
■ ■
■
Elektrische Anspeisung nicht korrekt (2-Phasenlauf) Spannung aller Phasen kontrollieren
■
■
Wellendichtung
■
Förderstrom zu klein Mindestfördermenge vergrößern (Schieber öffnen, Bypass)
■
Saughöhe zu groß / NPSH der Anlage zu klein Flüssigkeitsspiegel erhöhen
Anlagenbedingte Schwingungen Rückfrage erforderlich
■
■
■ Riefen und Rauigkeit an Welle Teil erneuern
■
■ Ablagerungen an Gleitringdichtung reinigen
■ ■ ■
■
■
Ursache
Zu hohe Temperatur an der Lagerung
Undichtheit an der Pumpe
Zu starke Leckage der Wellendichtung
Gegendruck zu gering, Förderstrom zu groß druckseitigen Schieber drosseln
Förderstrom zu groß Fördermenge verringern (Schieber drosseln)
gefüllt
Verschleiß der Innenteile abgenützte Teile erneuern
■
Unwucht des Laufrades Verstopfungen / Ablagerungen beseitigen
Rohrleitungskräfte zu hoch (Aggregat verspannt) ändern (Rohrleitungen abfangen, Kompensatoren, etc.)
■
Dichtung unzureichend Schrauben nachziehen
Lager schadhaft erneuern
Entlastungseinrichtung ungenügend Entlastungsbohrungen im Laufrad reinigen
den Betreiber sind besonders die Auslegungsdaten
auf dem Datenblatt und / oder der Auftragsbestätigung
sowie Kapitel 2 dieser Betriebsanleitung zu beachten.
Gegebenenfalls ist das schriftliche Einverständnis des
Herstellers einzuholen.
Behebung
Widerstände in der Druckleitung vermindern (Filter reinigen, ...)
größeres Laufrad verwenden (Antriebsleistung beachten)
Pumpendrehzahl (Leistungsschild) vergleichen
Bei Drehzahlregelung (Frequenzumformer) SollwertEinstellung kontrollieren
Pumpendrehzahl (Leistungsschild) vergleichen
Bei Drehzahlregelung (Frequenzumformer) SollwertEinstellung kontrollieren
beachten)
füllen
entlüften
Leitungsführung verbessern
Vordruck erhöhen
Widerstände der ZulaufNennweite ändern, Absperrorgane öffnen, Siebe reinigen)
Vakuumdichtheit der Saugleitung prüfen und herstellen
Sperrdruck erhöhen
Wellenabdichtung erneuern
Elektrofachmann durchzuführen)
gegebenenfalls Gleitringdichtung erneuern
eventuell Fremdspülung oder Quench vorsehen
ev. Laufrad erneuern; Welle auf Rundlauf prüfen
Fundamentplatte / Rahmen korrekt montiert / vergossen?
Kabelanschlüsse bzw. Sicherungen prüfen
Dichtung erneuern
abgenützte Teile ersetzen (Laufrad, Spaltringe)
Zulaufdruck angleichen
LSB 100-german Seite 18
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 23
Einbau-, Betriebs- und Wartungsanleitung
Anweisungen sind genau zu
befolgen, um die Sicherheit bei der Installation,
beim Betrieb und bei der Wartung des Motors
Personen, die mit diesen
Aufgaben befaßt sind, sind auf die vorliegende
Anleitung hinzuweisen. Die Nichtbefolgung der
hierin enthaltenen Anweisungen kann den
f dem
Leistungsschild angegebene Spannung den
Die Erdung vor allen anderen Anschlüssen
Es empfiehlt sich der Einbau eines
chutzschalters (30
zusätzlicher Schutz gegen
ebensgefährliche Stromstöße im Falle einer
Der Betrieb der Pumpe vor dem Anfüllen mit
bestimmen und Motor
11. Motorbetriebsanleitung
Baureihe LSB
Die nachstehenden
zu gewährleisten. Alle
Verlust der Gewährleistung zur Folge haben.
Stromanschluss
Vergewissern Sie sich, dass die au
Werten Ihres Speisenetzes entspricht.
vornehmen.
hochsensiblen Fehlerstrom-S
mA) als
l
fehlerhaften Erdung.
Den Netzanschluss mit einem allpoligen Schalter oder
einer anderen Vorrichtung, die die allpolige
Netzausschaltung sichert (also alle Speiseleitungen
unterbricht) und einen Abstand der Öffnungskontakte
von mindestens 3 mm aufweist, vornehmen.
Die Abdeckung des Klemmenbretts abnehmen, indem
man die Befestigungsschrauben aufschraubt. Die
Verbindungen wie auf der Rückseite der
Klemmenbrettabdeckung angegeben bzw. in
Abbildung 3 - 4.
Die Wechselstromausführung hat einen eingebauten
Überlastschutz, während die Drehstromausführung
kundenseitig gesichert werden muss. Verwenden Sie
dazu einen magnetothermischen Motorschutzschalter
oder einen Anlasser komplett mit Fernschalter,
Thermorelais und vorgelagerter Schmelzsicherung.
Das Überstromrelais ist auf dem Nennstrom des
Motors entsprechend dem Leistungsschild
einzustellen.
Das Thermorelais kann auf einen leicht niedrigeren
Wert als den der Volllast eingestellt werden, wenn die
Motorpumpe sicher nicht voll ausgelastet wird;
hingegen darf der Thermoschutz nicht auf einen
höheren Wert als den Nennstrom eingestellt werden.
Kontrolle der Drehrichtung bei Elektropumpen mit
Drehstrommotoren
Die Kontrolle der Drehrichtung kann vor dem Anfüllen
der Pumpe mit der zu pumpenden Flüssigkeit
erfolgen, vorausgesetzt, dass man die Pumpe nur
kurz drehen lässt.
der Flüssigkeit ist nicht zulässig.
Kontinuierlicher Trockenlauf beschädigt die
Gleitringdichtung.
Ist die Drehrichtung nicht entgegen dem Uhrzeigersinn
(von der Seite des Saugstutzens gesehen), so sind
zwei Speisedrähte umzustecken.
LSB 100-german Seite 19
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Störungssuche
Störung Mögliche Ursache Abhilfe
1. Die Pumpe startet
nicht
2. Überlastschutz
spricht an:
- zufällig
- systematisch
A) Spannungsabfall
im Netz
B) Sicherungen
durchgebrannt
B1 Ungeeignete
Sicherungen
(Ansprechstrom zu
niedrig)
B2 Motor oder
Speisekabel
beschädigt
C) Überlastschutz hat
eingegriffen
A) Momentaner
Ausfall einer Phase
C) Falsche
Einstellung des
Motorschutzschalters
D) Zu hohe
Fördermenge
E) Die Dichte oder
Viskosität der
Flüssigkeit
übersteigen die
Grenzwerte
A) Stromversorgung
sicherstellen
B1 Geeignete
Sicherungen
einbauen
B2 Motor reparieren
oder Kabel
austauschen
C) Überlastschutz
rückstellen (bei
erneutem Ausfall
siehe Punkt 2)
C) Auf den
Nennstrom des
Leistungsschildes
einstellen
D) Druckventil
schließen, bis die
Fördermenge dem
Arbeitsbereich der
Pumpe entspricht
E) Effektiv
erforderliche
Motorleistung
entsprechend
ersetzen
Ausgabe 01/2010
Revision 02
Page 24
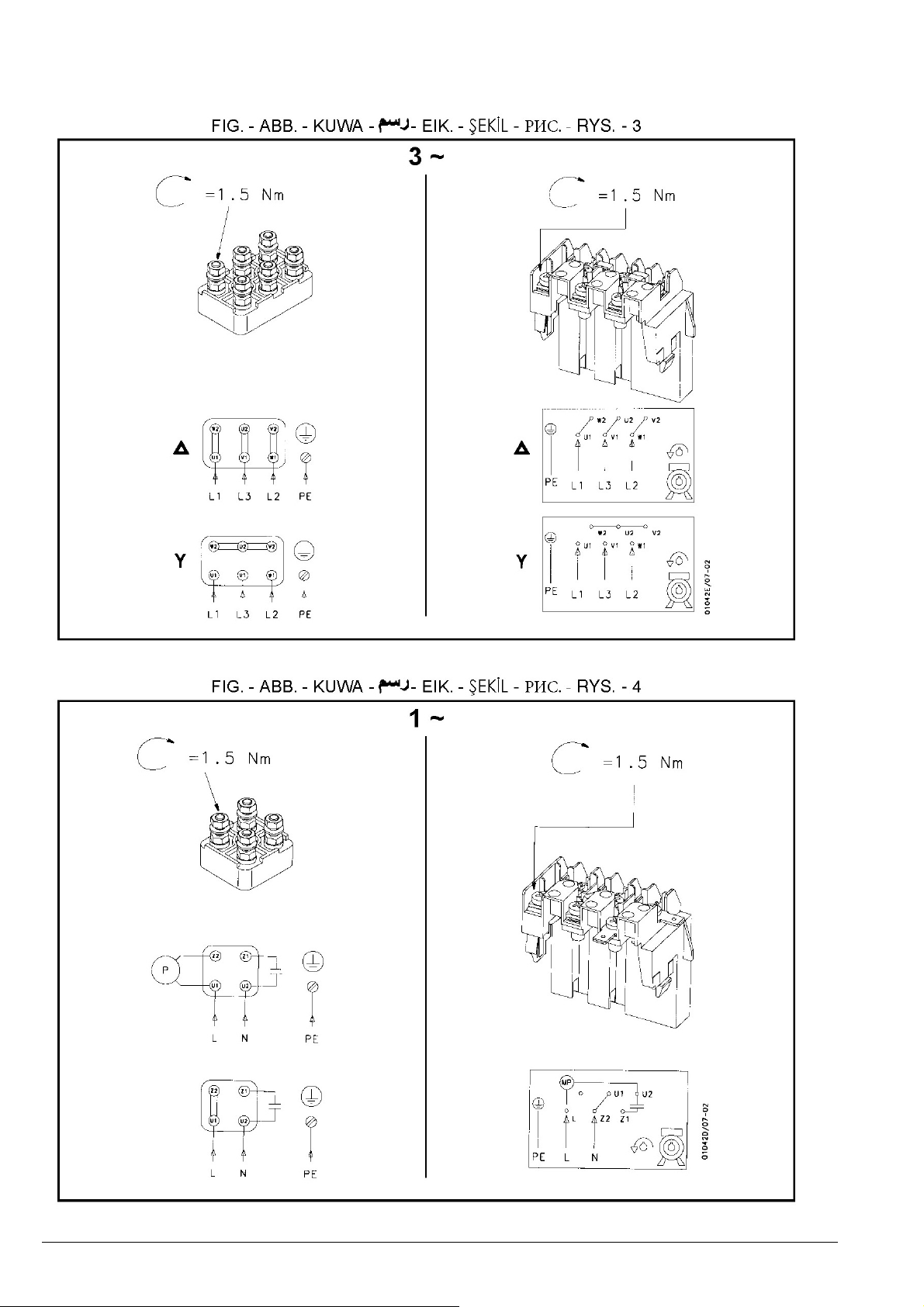
Einbau-, Betriebs- und Wartungsanleitung
Baureihe LSB
LSB 100-german Seite 20
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 25
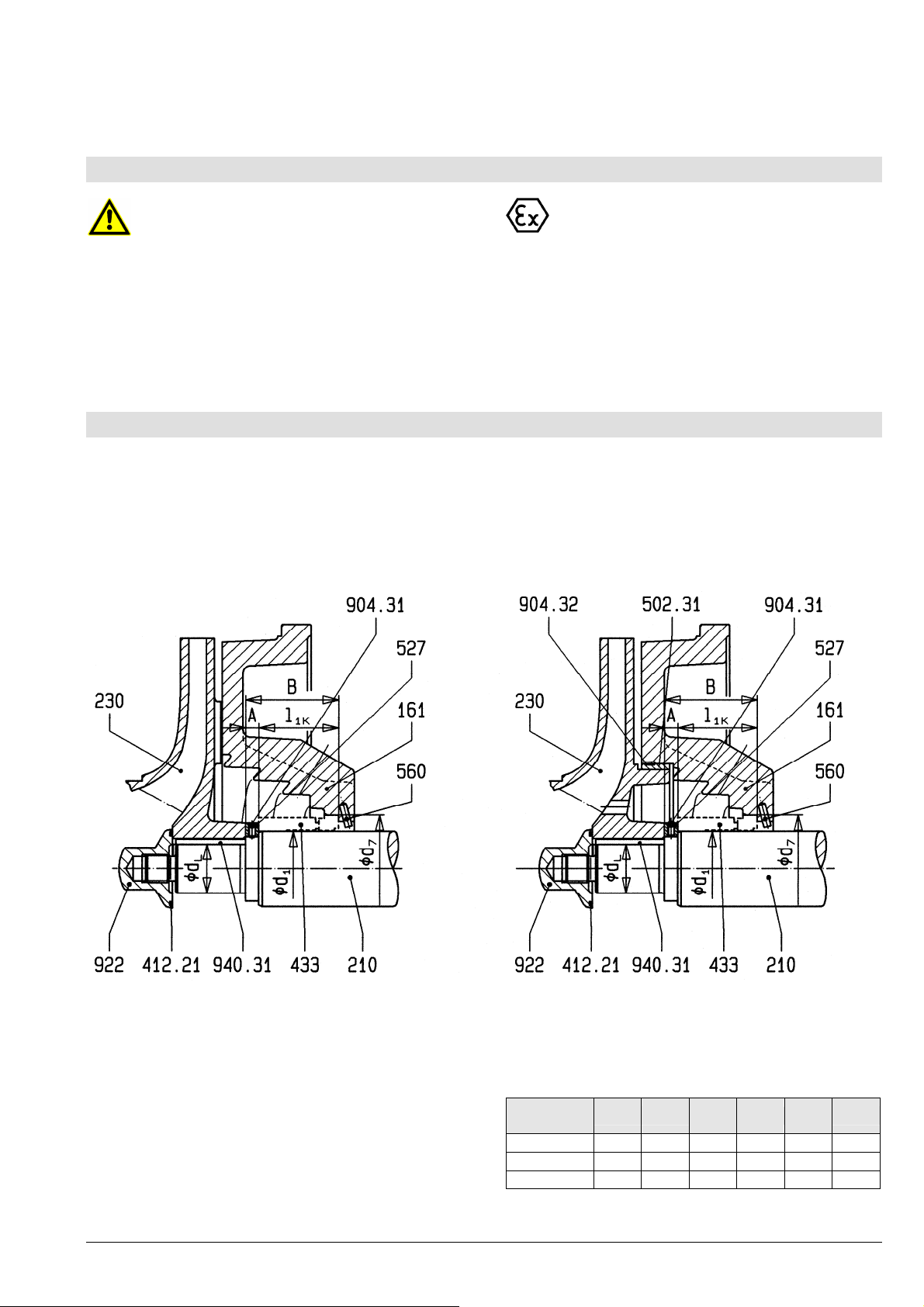
Einbau-, Betriebs- und Wartungsanleitung
und Ausbau, der
Bedienung, Inbetriebnahme und Instandhaltung
chtung beschäftigt ist, muss
neben dieser Montageanleitung auch die
und Wartungsanleitung der
jeweiligen Pumpe und besonders Kapitel 8.1
"Allgemeine Hinweise" und Kapitel 8.2
"Allgemeines" gelesen und verstanden haben
Für Pumpen die komform der Richtlinie 94/9/EG
(Atex95) für explosionsgefährdete Umgebung
ausgeführt sind, ist unbedingt die
Zusatzbetriebsanleitung zum Explosionsschutz
Baureihe LSB
Montageanleitung Einzel-Gleitringdichtung ohne Wellenschutzhülse (Ausführungscode S1..2)
1. Sicherheitshinweise
Jede Person, die mit dem Ein-
der Wellenabdi
Einbau-, Betriebs-
und diese unbedingt beachten!
2. Ausführungsbeschreibung
Diese Wellenabdichtung ist eine EinzelGleitringdichtung mit Einbaumaßen nach EN 12756
(DIN 24960) Ausführung "K". API Plan 02 / ISO Plan
00.
Durch den patentierten Zyklon-Dichtungsraum ist
keine zusätzliche Spülung des Gleitringdichtungsraumes erforderlich.
der Gleitringdichtung zu beachten.
Die folgenden Angaben sind, so weit sie den inneren
Aufbau der Gleitringdichtung betreffen, nur allgemein
gültig. Etwaige Besonderheiten entnehmen Sie dem
Typenblatt der Gleitringdichtung oder der Anleitung
des Gleitringdichtungherstellers.
Angaben über Werkstoffe und Einsatzbereich der
verwendeten Gleitringdichtungen entnehmen Sie dem
Datenblatt in der Betriebsanleitung bzw. der
Auftragsbestätigung.
Teilbezeichnungen:
161 Gehäusedeckel
210 Welle
230 Laufrad
412.21 O-Ring
433 Gleitringdichtung
502.31*) Spaltring
524 Wellenschutzhülse
527 a) Stellring
560 b) Stift
904.31 a) Gewindestift
904.32*) Gewindestift
922 Laufradmutter
940.31 Passfeder
LSB 100-german Seite 21
Artikel Nr. 771076129
*) optional
a) nicht bei allen Gleitringdichtungs-Bauarten
b) nur bei Gleitringdichtungen mit PTFE-O-
Ringen
Technische Änderungen vorbehalten!
Nenngröße
der Glrd.
∅d1 ∅d
l
7
1K
A B
∅d
L
33 33 48 42,5 7,5 50 19
43 43 61 45 7,5 52,5 28
53 53 73 47,5 10 57,5 38
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 26
Einbau-, Betriebs- und Wartungsanleitung
dichtungen, die bereits längere Zeit im Einsatz
waren, birgt die Gefahr von Undichtheiten an
der Gleitfläche nach dem Wiedereinbau. Es
r Ersatz der Gleitringdichtung
durch eine neue empfohlen. Die ausgebaute
Gleitringdichtung kann vom Hersteller überholt
Es dürfen nur Gleitringdichtungen eingebaut
werden, bei denen eine schriftliche
Bescheinigung der Konformität gemäß der
Bei Änderung der Gleitringdichtungstype
leitringdichtungsherstellers müssen
temperatur des Fördermediums und der
Auf größte Sauberkeit achten! Besonders die
Gleitflächen müssen sauber, trocken und
oder Gleitmittel auf die Gleitflächen der
Mineralische Fette oder Öle nur dann
ist, dass die
Elastomere der Gleitringdichtung ölbeständig
Nur Gleitmittel verwenden, von denen
sichergestellt ist, dass es zwischen ihnen und
dem Fördermedium zu keiner gefährlichen
lle erforderlichen Teile bereit, damit
die Montage zügig vor sich geht. Die Gleitmittel
wirken nur kurze Zeit, so dass danach die
Verschiebbarkeit und damit die automatische
scharfe
Kanten. Falls erforderlich Montagehülsen
Gleitringdichtungen mit Faltenbälgen bei
Montage so schieben, dass der Balg
zusammengedrückt und nicht gestreckt wird
3. Ausbau der Gleitringdichtung
Baureihe LSB
Verwenden Sie dazu die zugehörige Schnittzeichnung und das beiliegende Typenblatt der
Gleitringdichtung.
Ausbau und Zerlegen der Pumpe entsprechend
der Einbau-, Betriebs- und Wartungsanleitung bis
inklusive Kapitel 8.6.
Stellring (527) (sofern vorhanden) und rotierenden
Teil der Gleitringdichtung (433) von der Welle
(210) abziehen. Dem beiliegenden Typenblatt der
Gleitringdichtung ist zu entnehmen, ob vorher
Klemmschrauben an der Gleitringdichtung zu
lösen sind.
4. Einbau der Gleitringdichtung
Verwenden Sie dazu die zugehörige Schnittzeichnung und das beiliegende Typenblatt der
Gleitringdichtung.
Richtlinie 94/9/EG vorliegt.
bzw.des G
die Angaben der maximalen Betriebs-
Temperaturklasse erneut überprüft werden.
unbeschädigt bleiben. Auch keine Schmier-
Stationären Teil der Gleitringdichtung (433) aus
dem Gehäusedeckel (161) ziehen.
Aufnahmebohrung (∅d7) im Gehäusedeckel (161)
und die Oberfläche der Welle (210) reinigen.
Die Wiederverwendung von Gleitring-
wird daher de
werden und als Ersatz-Gleitringdichtung dienen.
Auf satte axiale Anlage der stationären Einheit im
Gehäusedeckel achten. Die Gleitfläche muss
genau senkrecht zur Welle stehen.
Falls ein Fixierstift (560) vorhanden ist, darauf
achten, dass dieser in die Nut der
Gleitringdichtung eingreift, ohne dass er die
Gleitringdichtung berührt.
Rotierende Einheit der Gleitringdichtung auf die
Welle (210) aufschieben.
Laufradseitige Anlagefläche der Gleitringdichtung
genau mit Wellenbund abschließen lassen (Maß
l1K). Für Gleitringdichtungen ohne eigene
Klemmschrauben dient der Stellring (527) als
Anschlag.
Gleitringdichtung auftragen.
Falls bei der Ersatzgleitringdichtung Gleitmittel
beigepackt ist, dann dieses verwenden.
verwenden, wenn völlig sicher
sind. Kein Silicon verwenden.
Reaktion kommen kann.
Stellen Sie a
Einstellung der Elastomere verloren geht.
Schieben Sie die Elastomere nie über
verwenden.
Stationären Teil der Gleitringdichtung gleichmäßig
in den Gehäusedeckel (161) drücken. Dazu
eventuell einen Stempel mit weicher Oberfläche
verwenden. Ungleiche Belastung bedeutet
Bruchgefahr für die Gleitfläche.
Gleitfläche nicht beschädigen!
LSB 100-german Seite 22
Artikel Nr. 771076129
(Reißgefahr!).
Weiterer Zusammenbau und Einbau der Pumpe
entsprechend Kapitel 8 der Einbau-, Betriebs- und
Wartungsanleitung.
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 27
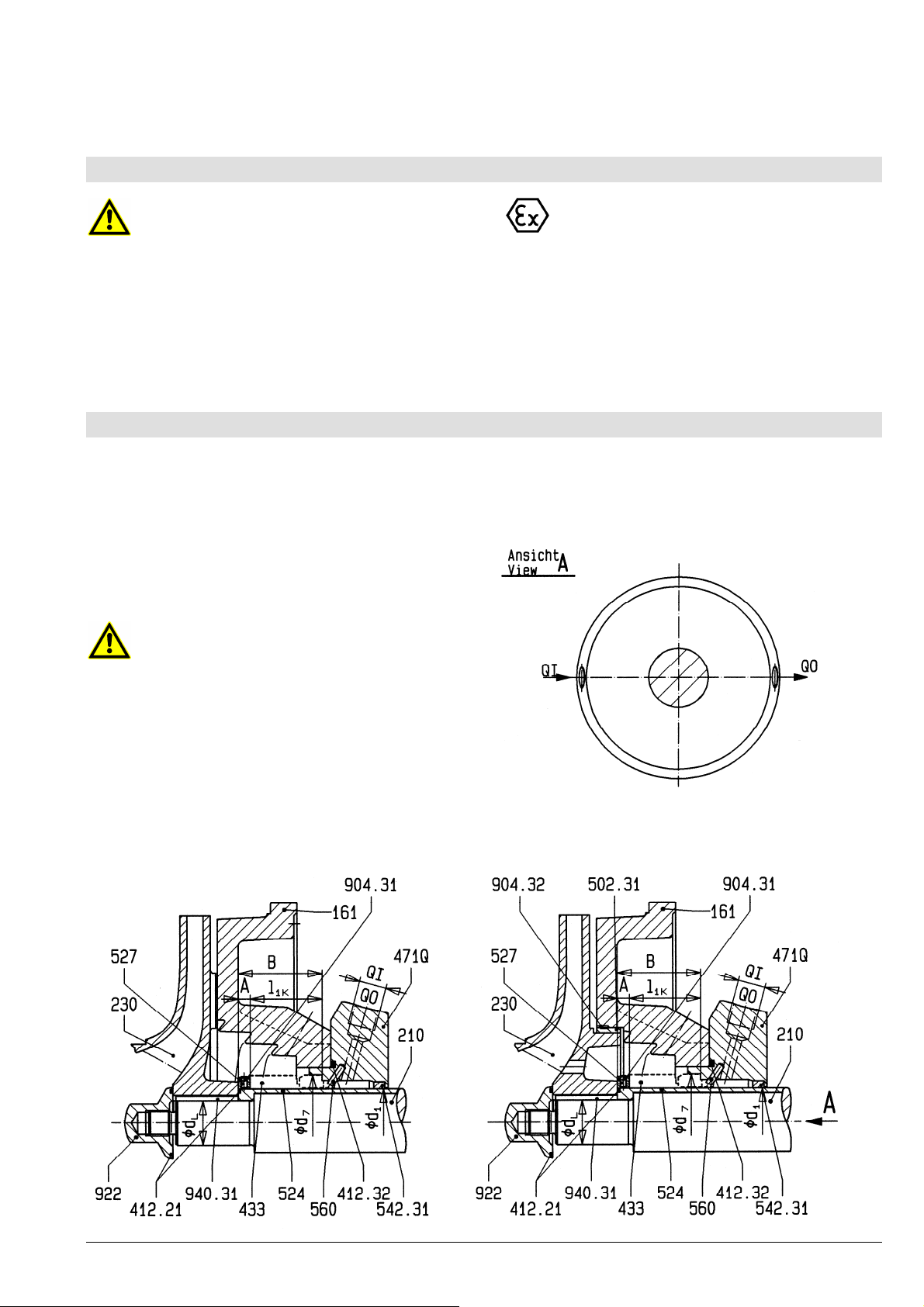
Einbau-, Betriebs- und Wartungsanleitung
r
Bedienung, Inbetriebnahme und Instandhaltung
der Wellenabdichtung beschäftigt ist, muss
neben dieser Montageanleitung auch die
und Wartungsanleitung der
jeweiligen Pumpe und besonders Kapitel 8.1
"Allgemeine Hinweise" und Kapitel 8.2
Allgemeines" gelesen und verstanden haben
Für Pumpen die komform der Richtlinie 94/9/EG
(Atex95) für explosionsgefährdete Umgebung
ausgeführt sind, ist unbedingt die
Zusatzbetriebsanleitung zum Explosionsschutz
Die Quenchflüssigkeit muß so ausgewählt
ihr und dem
Fördermedium zu keinen gefährlichen
flüssigkeit kann durch das Fördermedium
kontaminiert werden, daher ist durch den
Baureihe LSB
Montageanleitung Einzel-Gleitringdichtung mit Quench ohne Wellenschutzhülse (Ausführungscode S4..2)
1. Sicherheitshinweise
Jede Person, die mit dem Ein- und Ausbau, de
Einbau-, Betriebs-
"
und diese unbedingt beachten!
2. Ausführungsbeschreibung
Diese Wellenabdichtung ist eine EinzelGleitringdichtung mit Einbaumaßen nach EN 12756
(DIN 24960) Ausführung "K", Form "U". API Plan 62 /
ISO Plan 09. Die Beständigkeit der Werkstoffe im
Gleitringdichtungsraum (speziell die der Elastomere)
gegenüber der Quenchflüssigkeit ist zu beachten.
Der Quenchraum muß drucklos von Quenchflüssigkeit durchströmt werden. Anschluß siehe
folgende Schnittzeichnung.
werden, daß es zwischen
Reaktionen kommen kann. Die Quench-
der Gleitringdichtung zu beachten.
Die folgenden Angaben sind, so weit sie den inneren
Aufbau der Gleitringdichtung betreffen, nur allgemein
gültig. Etwaige Besonderheiten entnehmen Sie dem
Typenblatt der Gleitringdichtung oder der Anleitung
des Gleitringdichtungsherstellers.
Datenblatt in der Betriebsanleitung bzw. der
Auftragsbestätigung.
Betreiber gegebenenfalls auf eine entsprechende Entsorgung zu achten.
Durch den patentierten Zyklon-Dichtungsraum ist
keine zusätzliche Spülung des Gleitringdichtungsraumes erforderlich.
Angaben über Werkstoffe und Einsatzbereich der
verwendeten Gleitringdichtungen entnehmen Sie dem
QI ... Quench Eintritt (471Q)
Q0 ... Quench Austritt (471Q)
LSB 100-german Seite 23
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 28
Einbau-, Betriebs- und Wartungsanleitung
18
18
18
längere Zeit im Einsatz
waren, birgt die Gefahr von Undichtheiten an
der Gleitfläche nach dem Wiedereinbau. Es
wird daher der Ersatz der Gleitringdichtung
durch eine neue empfohlen. Die ausgebaute
Gleitringdichtung kann vom Hersteller überholt
Es dürfen nur Gleitringdichtungen eingebaut
tliche
Bescheinigung der Konformität gemäß der
Bei Änderung der Gleitringdichtungstype
bzw.des Gleitringdichtungsherstellers müssen
temperatur des Fördermediums und der
Auf größte Sauberkeit achten! Besonders die
Gleitflächen müssen sauber, trocken und
oder Gleitmittel auf die Gleitflächen der
Mineralische Fette oder Öle nur dann
verwenden, wenn völlig sicher ist, dass die
Elastomere der Gleitringdichtung ölbeständig
Nur Gleitmittel verwenden, von denen
ichergestellt ist, dass es zwischen ihnen und
dem Fördermedium zu keiner gefährlichen
Stellen Sie alle erforderlichen Teile bereit, damit
die Montage zügig vor sich geht. Die Gleitmittel
wirken nur kurze Zeit, so dass danach die
erschiebbarkeit und damit die automatische
Schieben Sie die Elastomere nie über scharfe
Kanten. Falls erforderlich Montagehülsen
Teilbezeichnungen:
161 Gehäusedeckel
210 Welle
230 Laufrad
412.21 O-Ring
412.32 O-Ring
433 Gleitringdichtung
471Q Quenchdeckel
502.31*) Spaltring
527 a) Stellring
542.31 Drosselbuchse
560 b) Stift
904.31 a) Gewindestift
904.32*) Gewindestift
923 Laufradmutter
940.31 Passfeder
3. Ausbau der Gleitringdichtung
*) optional
a) nicht bei allen Gleitringdichtungs-Bauarten
b) nur bei Gleitringdichtungen mit PTFE-O-Ringen
Technische Änderungen vorbehalten!
Nenngröße
der Glrd.
∅d1 ∅d
l
1K
7
33 33 48 42,5 7,5 50 19
43 43 61 45 7,5 52,5 28
53 53 73 47,5 10 57,5 38
Baureihe LSB
A B
∅d
QI, Q0
L
1/4-
3/8-
3/8-
NPT
NPT
NPT
Verwenden Sie dazu die zugehörige Schnittzeichnung und das beiliegende Typenblatt der
Gleitringdichtung.
Ausbau und Zerlegen der Pumpe entsprechend
der Einbau-, Betriebs- und Wartungsanleitung bis
inklusive Kapitel 8.6.
Stellring (527) (sofern vorhanden) und den
rotierenden Teil der Gleitringdichtung (433) von
der Welle (210) abziehen.
Dem beiliegenden Typenblatt der Gleitring-
dichtung ist zu entnehmen, ob vorher
Klemmschrauben an der Gleitringdichtung zu
lösen sind.
Gehäusedeckel (161) samt Quenchdeckel (471Q)
ausbauen. Sechskantschrauben (901.42) als
Abdrückhilfe verwenden.
4. Einbau der Gleitringdichtung
Verwenden Sie dazu die zugehörige Schnittzeichnung und das beiliegende Typenblatt der
Gleitringdichtung.
werden, bei denen eine schrif
Richtlinie 94/9/EG vorliegt.
die Angaben der maximalen Betriebs-
Stationären Teil der Gleitringdichtung (433) und
die Drosselbuchse (542.31) aus dem
Quenchdeckel (471Q) herausziehen.
Aufnahmebohrung (∅d7) im Quenchdeckel (471Q)
und die Oberfläche der Welle (210) reinigen.
.
Die Wiederverwendung von Gleitringdichtungen, die bereits
werden und als Ersatz-Gleitringdichtung dienen.
sind. Kein Silicon verwenden.
s
Reaktion kommen kann.
Temperaturklasse erneut überprüft werden.
unbeschädigt bleiben. Auch keine Schmier-
Gleitringdichtung auftragen.
Falls bei der Ersatzgleitringdichtung Gleitmittel
beigepackt ist, dann dieses verwenden.
LSB 100-german Seite 24
Artikel Nr. 771076129
V
Einstellung der Elastomere verloren geht.
verwenden.
Drosselbuchse (542.31) in den Quenchdeckel
(471Q) vorsichtig hineindrücken.
Stationären Teil der Gleitringdichtung gleichmäßig
in den Quenchdeckel (471Q) drücken. Dazu
eventuell einen Stempel mit weicher Oberfläche
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 29

Einbau-, Betriebs- und Wartungsanleitung
Gleitringdichtungen mit Faltenbälgen bei
Montage so schieben, dass der Balg
zusammengedrückt und nicht gestreckt wird
schutzhülse und Welle nur dann verwenden,
wenn sichergestellt ist, dass es zwischen
Fördermedium und Gleitmittel zu keinen
Vor dem Einschalten der Pumpe unbedingt das
Spülsystem für den Quench wieder anschließen
verwenden. Ungleiche Belastung bedeutet
Bruchgefahr für die Gleitfläche.
Gleitfläche nicht beschädigen!
Auf satte axiale Anlage der stationären Einheit im
Quenchdeckel achten. Die Gleitfläche muss
genau senkrecht zur Welle stehen.
Falls ein Fixierstift (560) vorhanden ist, darauf
achten, dass dieser in die Nut der
Gleitringdichtung eingreift, ohne dass er die
Gleitringdichtung berührt.
Gehäusedeckel (161) vorsichtig einsetzen, bis er
axial in der Lagerträgerlaterne (344) anliegt.
Rotierende Einheit der Gleitringdichtung auf die
Welle (210) aufschieben.
Laufradseitige Anlagefläche der Gleitringdichtung
genau auf Maß A einstellen. Für Gleitringdichtung
ohne eigene Klemmschrauben dient der Stellring
(527) als Anschlag.
Baureihe LSB
(Reißgefahr!).
Gleitmittel (Molykote, etc.) zwischen Wellen-
gefährlichen Reaktionen kommen kann.
Weiterer Zusammenbau und Einbau der Pumpe
entsprechend Kapitel 8 der Einbau-, Betriebs- und
Wartungsanleitung.
und in Betrieb nehmen.
LSB 100-german Seite 25
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 30
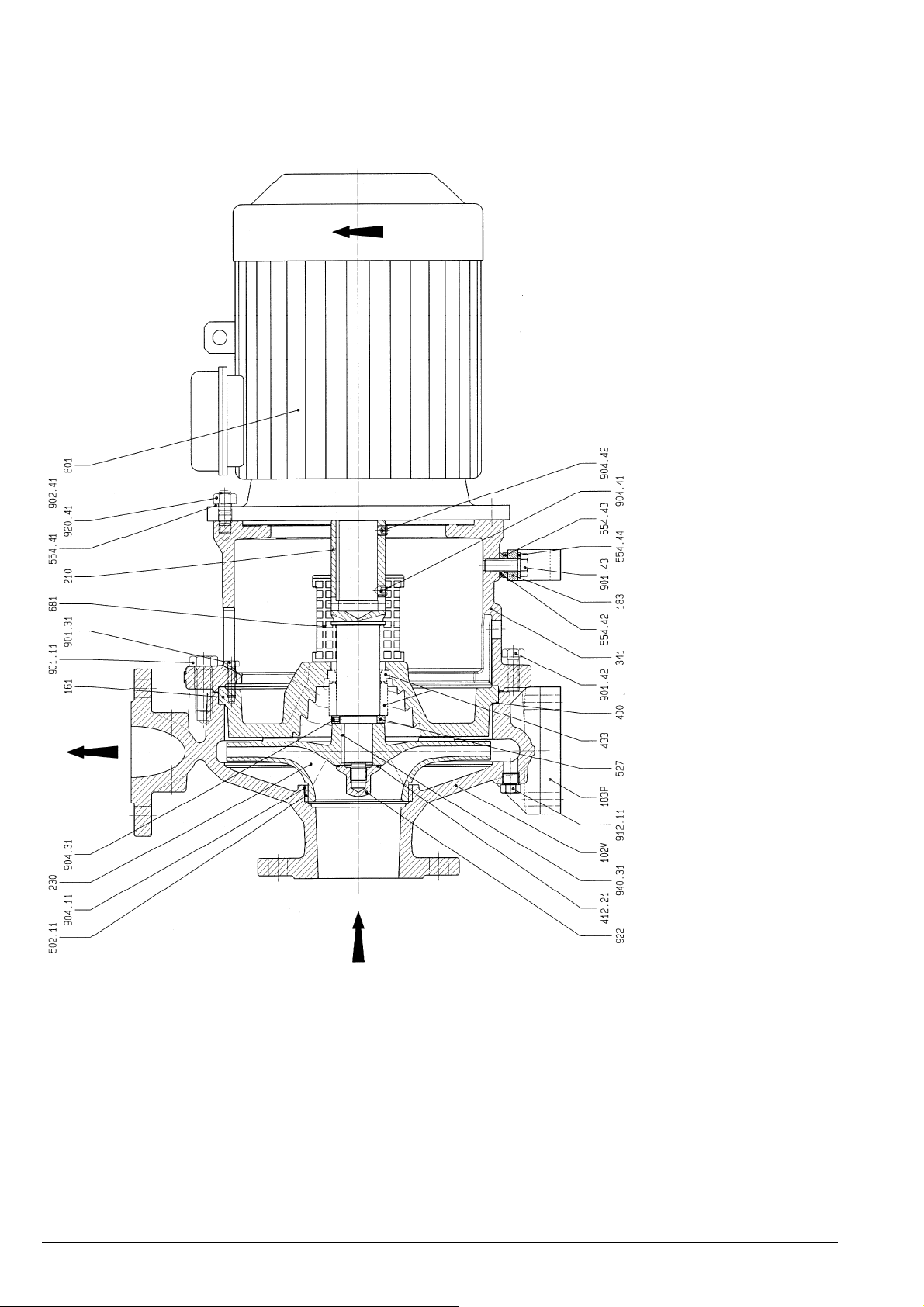
Einbau-, Betriebs- und Wartungsanleitung
Type:
Teilebezeic
h
nung
Spiralgehäuse Gehäusedeckel Stützfuss Pumpenunterlage Steckwelle Laufrad Antriebslaterne Flachdichtung O
-
Ring
Gleitringdichtung Spaltring Stellring Unterlegscheibe Kugelscheibe Kegelpfanne Unterlegscheibe Schutzblech Flanschmotor Sechskantschra
u
be
Sechskan
tschra
u
be
Sechskantschra
u
be
Sechskantschra
u
be
Stiftschraube Gewindestift Gewindestift Gewindestift Gewindestift Entleerungsstopfen Sechskantmutter Laufradmutter Passfeder
Nr.
102 V 161 183 ***) 183P **) 210 230 341 400 412.21 433 502.11 *) 527 **) 554.41 554.42 ***) 554.43 ***) 554.44 ***) 681 801 901.11 901.31 **) 901.42 901.43 ***) 902.41 904.11 *) 904.31 **) 904.41 904.42 912.11 920.41 922 940.31
Baureihe LSB
Ausführung: S1...2 Einzel-GLRD, nicht entlastet (DIN 24960, l1k / EN 12756, Ausf. K, Form U), Laufrad mit
Rückenschaufeln
Die Wellenabdichtung Ihrer Pumpe finden Sie auf dem Datenblatt / der Auftragsbestätigung. Siehe auch Kapitel
3.1.1 Bezeichnungsschema.
125-100-200 125-100-250 150-125-250 200-150-250
80-50-315 100-65-160 100-65-200 100-65-250 125-80-160 125-80-200 125-80-250
65-40-160 65-40-200 65-40-250 65-40-315 80-50-160 80-50-200 80-50-250
40-25-160 40-25-200 40-25-250 50-32-160 50-32-200 50-32-250 50-32-315
Gültig für
LSB 100-german Seite 26
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Technische Änderungen vorbehalten!
Nicht maßstäblich!
*) ... optional
**) ... nicht bei allen Ausführungen
***) ... nur bei IEC-Motorbaugröße:
160MA, 160M, 160L, 180M, 180L,
200L, 200LA
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 31

Einbau-, Betriebs- und Wartungsanleitung
Type:
Teilebezeic
h
nung
Spiralgehäuse Gehäusedeckel Stützfuss Pumpenunterlage Stec
kwelle
Laufrad Antriebslaterne Flachdichtung O
-
Ring
Gleitringdichtung Spaltring Spaltring Stellring Unterlegscheibe Kugelscheibe Kegelpfanne Unterlegscheibe Schutzblech Flanschmotor Sechskantschra
u
be
Sechskantschra
u
be
Sechskantschra
u
be
Sechskantschra
u
be
St
iftschraube
Gewindestift Gewindesift Gewindestift Gewindestift Gewindestift Entleerungsstopfen Sechskantmutter Laufradmutter Passfeder
Nr.
102 V 161 183 ***) 183P **) 210 230 341 400 412.21 433 502.11 *) 502.31 *) 527 **) 554.41 554.42 ***) 554.43 ***) 554.44 ***) 681 801 901.11 901.31 **) 901.42 901.43 ***) 902.41 904.11 *) 904.32 *) 904.31 **) 904.41 904.42 912.11 920.41 9
22
940.31
Baureihe LSB
Ausführung: S1...2 Einzel-GLRD, nicht entlastet (DIN 24960, l1k / EN 12756, Ausf. K, Form U), Laufrad mit
Entlastungsbohrungen
Die Wellenabdichtung Ihrer Pumpe finden Sie auf dem Datenblatt / der Auftragsbestätigung. Siehe auch Kapitel
3.1.1 Bezeichnungsschema.
150-125-315 125-100-315 125-80-315 100-65-315 Gültig für
Technische Änderungen vorbehalten!
Nicht maßstäblich!
LSB 100-german Seite 27
Artikel Nr. 771076129
*) ... optional
**) ... nicht bei allen Ausführungen
***) ... nur bei IEC-Motorbaugröße:
160MA, 160M, 160L, 180M, 180L,
200L, 200LA
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 32

Einbau-, Betriebs- und Wartungsanleitung
Type:
Teilebezeic
h
nung
Spiralgehäuse Gehäusedeckel Stützfuss Pumpenunterlage Steckwelle Laufrad Antriebslaterne Flach
dichtung
O
-
Ring
O
-
Ring
Gleitringdichtung Quenchdeckel Spaltring Stellring Drosselbuchse Unterlegscheibe Kugelscheibe Kegelpfanne Unterlegscheibe Schutzblech Flanschmotor Sechskantschra
u
be
Sechskantschra
u
be
Sechskantschra
u
be
Sechskantschra
u
be
Stiftschraube Stiftschraube Gewindestift Gewindestift Gewindestift Gewindestift Entleerungsstopfen Sechskantmutter Sechskantmutter Laufradmutter Passfeder
Nr.
102 V 161 183 ***) 183P **) 210 230 341 400 412.21 412.32 433 471Q 502.11 *) 527 **) 542.31 554.41 554.42 ***) 554.43 ***) 554.44 ***) 681 801 901.11 901.31 **) 901.42 901.43 ***) 902.31 902.41 904.11 *) 904.31 **) 904.41 904.42 912
.11
920.31 920.41 922 940.31
Baureihe LSB
Ausführung: S4...2 Einzel-GLRD, nicht entlastet (DIN 24960, l1k / EN 12756, Ausf. K, Form U), mit Quench,
Laufrad mit Rückenschaufeln
Die Wellenabdichtung Ihrer Pumpe finden Sie auf dem Datenblatt / der Auftragsbestätigung. Siehe auch Kapitel
3.1.1 Bezeichnungsschema.
125-100-200 125-100-250 150-125-250 200-150-250
80-50-315 100-65-160 100-65-200 100-65-250 125-80-160 125-80-200 125-80-250
65-40-160 65-40-200 65-40-250 65-40-315 80-50-160 80-50-200 80-50-250
40-25-160 40-25-200 40-25-250 50-32-160 50-32-200 50-32-250 50-32-315
Gültig für
LSB 100-german Seite 28
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Technische Änderungen vorbehalten!
Nicht maßstäblich!
*) ... optional
**) ... nicht bei allen Ausführungen
***) ... nur bei IEC-Motorbaugröße:
160MA, 160M, 160L, 180M, 180L,
200L, 200LA
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 33

Einbau-, Betriebs- und Wartungsanleitung
Type:
Teilebezeic
h
nung
Spiralgehäuse Gehäusedeckel Stützfuss Pumpe
nunterlage
Steckwelle Laufrad Antriebslaterne Flachdichtung O
-
Ring
O
-
Ring
Gleitringdichtung Quenchdeckel Spaltring Spaltring Stellring Drosselbuchse Unterlegscheibe Kugelscheibe Kegelpfanne Unterlegscheibe Schutzblech Flanschmotor Sechskantschra
u
be
Sechska
ntschra
u
be
Sechskantschra
u
be
Sechskantschra
u
be
Stiftschraube Stiftschraube Gewindestift Gewindestift Gewindestift Gewindestift Gewindestift Entleerungsstopfen Sechskantmutter Sechskantmutter Laufradmutter Passfeder
Nr.
102 V 161 183 ***) 183P **) 210 230 341 400 412.21 412.32 433 471Q 502.11 *) 502.31 *) 527 **) 542.31 554.41 554.42 ***) 554.43 ***) 554.44 ***) 681 801 901.1
1
901.31 **) 901.42 901.43 ***) 902.31 902.41 904.11 *) 904.31 **) 904.32 **) 904.41 904.42 912.11 920.31 920.41 922 940.31
Baureihe LSB
Ausführung: S4...2 Einzel-GLRD, nicht entlastet (DIN 24960, l1k / EN 12756, Ausf. K, Form U), mit Quench,
Laufrad mit Entlastungsbohrungen
Die Wellenabdichtung Ihrer Pumpe finden Sie auf dem Datenblatt / der Auftragsbestätigung. Siehe auch Kapitel
3.1.1 Bezeichnungsschema.
150-125-315 125-100-315 125-80-315 100-65-315 Gültig für
Technische Änderungen vorbehalten!
Nicht maßstäblich!
LSB 100-german Seite 29
Artikel Nr. 771076129
*) ... optional
**) ... nicht bei allen Ausführungen
***) ... nur bei IEC-Motorbaugröße:
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
160MA, 160M, 160L, 180M, 180L,
200L, 200LA
Page 34

Einbau-, Betriebs- und Wartungsanleitung
Anschlüsse
Baureihe LSB
Code Anzahl Anschlüsse
Lagerträger
24 32, 42, 48
PM1 *) 1 Druckmessung 1/4-18 NPT
PM2 *) 1 Druckmessung 1/4-18 NPT
D 1 Entleerung (Gehäuse)
3/8-18 NPT
DL 1 Entleerung (Laterne) G 1/2
QI **) 1 Quench-Eintritt 1/4-18 NPT 3/8-18 NPT
QO **) 1 Quench-Austritt 1/4-18 NPT 3/8-18 NPT
*) ... optional, bei Ausführung S2..1 und S4..2 möglich
**) ... nur bei Ausführung S4..2
Technische Änderungen vorbehalten!
Nicht maßstäblich!
LSB 100-german Seite 30
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 35

Einbau-, Betriebs- und Wartungsanleitung
Baureihe LSB
Maßzeichnung - Die Bezeichnung Ihrer Pumpe finden Sie auf dem Datenblatt / der Auftragsbestätigung. Siehe
auch Kapitel 3.1.1 Bezeichnungsschema.
Pumpe DN
DN
S
a b g2 h1 h2 m1 m2 n1 n2 p1 p2 s1 s2 x
D
LSB 40-25-160 .... - ... 40 25 80 50 10 132 160 100 70 240 190 15 30 14 13,5 100
LSB 40-25-200 .... - ... 40 25 80 50 10 160 180 100 70 240 190 15 30 14 13,5 100
LSB 40-25-250 .... - ... 40 25 100 65 10 180 225 125 95 320 250 15 30 14 13,5 100
LSB 50-32-160 .... - ... 50 32 80 50 10 132 160 100 70 240 190 15 30 14 13,5 100
LSB 50-32-200 .... - ... 50 32 80 50 10 160 180 100 70 240 190 15 30 14 13,5 100
LSB 50-32-250 .... - ... 50 32 100 65 10 180 225 125 95 320 250 15 30 14 13,5 100
LSB 50-32-315 .... - ... 50 32 125 65 10 200 250 125 95 345 280 15 30 14 13,5 100
LSB 65-40-160 .... - ... 65 40 80 50 10 132 160 100 70 240 190 15 30 14 13,5 100
LSB 65-40-200 .... - ... 65 40 100 50 10 160 180 100 70 265 212 15 30 14 13,5 100
LSB 65-40-250 .... - ... 65 40 100 65 10 180 225 125 95 320 250 15 30 14 13,5 100
LSB 65-40-315 .... - ... 65 40 125 65 10 200 250 125 95 345 280 15 30 14 13,5 100
LSB 80-50-160 .... - ... 80 50 100 50 10 160 180 100 70 265 212 15 30 14 13,5 100
LSB 80-50-200 .... - ... 80 50 100 50 10 160 200 100 70 265 212 15 30 14 13,5 100
LSB 80-50-250 .... - ... 80 50 125 65 10 180 225 125 95 320 250 15 30 14 13,5 100
LSB 80-50-315 .... - ... 80 50 125 65 10 225 280 125 95 345 280 15 30 14 13,5 100
LSB 100-65-160 .... - ... 100 65 100 65 10 160 200 125 95 280 212 15 30 14 13,5 100
LSB 100-65-200 .... - ... 100 65 100 65 10 180 225 125 95 320 250 15 30 14 13,5 140
LSB 100-65-250 .... - ... 100 65 125 80 10 200 250 160 120 360 280 15 30 18 13,5 140
LSB 100-65-315 .... - ... 100 65 128 80 10 225 280 160 120 400 315 15 30 18 13,5 140
LSB 125-80-160 .... - ... 125 80 125 65 10 180 225 125 95 320 250 15 30 14 13,5 140
LSB 125-80-200 .... - ... 125 80 125 65 10 180 250 125 95 345 280 15 30 14 13,5 140
LSB 125-80-250 .... - ... 125 80 125 80 10 225 280 160 120 400 315 15 30 18 13,5 140
LSB 125-80-315 .... - ... 125 80 125 80 10 250 315 160 120 400 315 15 30 18 13,5 140
LSB 125-100-200 .... - ... 125 100 125 80 10 200 280 160 120 360 280 15 30 18 13,5 140
LSB 125-100-250 .... - ... 125 100 140 80 10 225 280 160 120 400 315 15 30 18 13,5 140
LSB 125-100-315 .... - ... 125 100 140 80 10 250 315 160 120 400 315 15 30 18 13,5 140
LSB 150-125-250 .... - ... 150 125 140 80 10 250 355 160 120 400 315 15 30 18 13,5 140
LSB 150-125-315 .... - ... 150 125 140 100 10 280 355 200 150 500 400 15 30 22 13,5 140
LSB 200-150-250 .... - ... 200 150 160 100 10 280 375 200 150 500 400 15 30 22 13,5 180
LSB 100-german Seite 31
Artikel Nr. 771076129
H kann je nach Motorerzeuger variieren
G ... Gewicht für Pumpe ohne Motor in kg
Toleranzen entsprechend DIN EN 735
Maße in mm
Technische Änderungen vorbehalten!
Nicht maßstäblich!
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 36

Einbau-, Betriebs- und Wartungsanleitung
Baureihe LSB
Pumpe Bmax g1 ~H h U n4 n5 w ~G
LSB 40-25-160 .... - 80 119 15 408 176 - - - - 31
LSB 40-25-160 .... - 90 119 15 457 176 - - - - 31
LSB 40-25-160 .... - 100 144 15 530 216 - - - - 37
LSB 40-25-160 .... - 112 144 15 539 216 - - - - 37
LSB 40-25-160 .... - 132 150 35 666 216 20 - - - 37
LSB 40-25-160 .... - 160 175 60 771 251 45 210 180 206 43
LSB 40-25-200 .... - 80 119 15 408 176 - - - - 39
LSB 40-25-200 .... - 90 119 15 457 176 - - - - 39
LSB 40-25-200 .... - 100 144 15 530 216 - - - - 45
LSB 40-25-200 .... - 112 144 15 539 216 - - - - 45
LSB 40-25-200 .... - 132 150 15 666 216 - - - - 45
LSB 40-25-200 .... - 160 175 60 815 251 45 210 180 206 54
LSB 40-25-250 .... - 80 171 15 421 189 - - - - 60
LSB 40-25-250 .... - 90 171 15 470 189 - - - - 60
LSB 40-25-250 .... - 100 171 15 543 229 - - - - 65
LSB 40-25-250 .... - 112 171 15 552 229 - - - - 65
LSB 40-25-250 .... - 132 171 15 679 229 - - - - 65
LSB 40-25-250 .... - 160 175 15 828 264 - 210 180 219 75
LSB 40-25-250 .... - 180 180 20 859 264 5 210 180 219 75
LSB 40-25-250 .... - 200 225 65 964 264 50 280 250 219 75
LSB 50-32-160 .... - 80 119 15 408 176 - - - - 31
LSB 50-32-160 .... - 90 119 15 457 176 - - - - 31
LSB 50-32-160 .... - 100 144 15 530 216 - - - - 37
LSB 50-32-160 .... - 112 144 15 539 216 - - - - 37
LSB 50-32-160 .... - 132 150 35 666 216 20 - - - 37
LSB 50-32-160 .... - 160 175 60 771 251 45 210 180 206 43
LSB 50-32-200 .... - 80 119 15 408 176 - - - - 39
LSB 50-32-200 .... - 90 119 15 457 176 - - - - 39
LSB 50-32-200 .... - 100 144 15 530 216 - - - - 45
LSB 50-32-200 .... - 112 144 15 539 216 - - - - 45
LSB 50-32-200 .... - 132 150 15 666 216 - - - - 45
LSB 50-32-200 .... - 160 175 60 815 251 45 210 180 206 54
LSB 50-32-250 .... - 80 171 15 421 189 - - - - 60
LSB 50-32-250 .... - 90 171 15 470 189 - - - - 60
LSB 50-32-250 .... - 100 171 15 543 229 - - - - 65
LSB 50-32-250 .... - 112 171 15 552 229 - - - - 65
LSB 50-32-250 .... - 132 171 15 679 229 - - - - 65
LSB 50-32-250 .... - 160 175 15 828 264 - 210 180 219 75
LSB 50-32-250 .... - 180 180 20 859 264 5 210 180 219 75
LSB 50-32-250 .... - 200 225 65 964 264 50 280 250 219 75
LSB 50-32-315 .... - 100 201 15 543 229 - - - - 102
LSB 50-32-315 .... - 112 201 15 552 229 - - - - 102
LSB 50-32-315 .... - 132 201 15 679 229 - - - - 102
LSB 50-32-315 .... - 160 201 15 828 264 - 210 180 219 112
LSB 50-32-315 .... - 180 201 15 859 264 - 210 180 219 112
LSB 50-32-315 .... - 200 225 65 964 264 50 280 250 219 112
LSB 65-40-160 .... - 80 124 15 408 176 - - - - 32
LSB 65-40-160 .... - 90 124 15 457 176 - - - - 32
LSB 65-40-160 .... - 100 144 15 530 216 - - - - 39
LSB 65-40-160 .... - 112 144 15 539 216 - - - - 39
LSB 65-40-160 .... - 132 150 35 666 216 20 - - - 39
LSB 65-40-160 .... - 160 175 60 815 251 45 210 180 206 44
LSB 65-40-200 .... - 80 139 15 408 176 - - - - 44
LSB 65-40-200 .... - 90 139 15 457 176 - - - - 44
LSB 65-40-200 .... - 100 144 15 530 216 - - - - 50
LSB 65-40-200 .... - 112 144 15 539 216 - - - - 50
LSB 65-40-200 .... - 132 150 15 666 216 - - - - 50
LSB 65-40-200 .... - 160 175 35 815 251 20 210 180 206 60
LSB 65-40-200 .... - 180 180 60 846 251 45 210 180 206 60
LSB 65-40-250 .... - 80 171 15 421 189 - - - - 62
LSB 65-40-250 .... - 90 171 15 470 189 - - - - 62
LSB 65-40-250 .... - 100 171 15 543 229 - - - - 68
LSB 65-40-250 .... - 112 171 15 552 229 - - - - 68
LSB 65-40-250 .... - 132 171 15 679 229 - - - - 68
LSB 65-40-250 .... - 160 175 15 828 264 - 210 180 219 77
LSB 65-40-250 .... - 180 180 20 859 264 5 210 180 219 77
LSB 65-40-250 .... - 200 225 65 964 264 50 280 250 219 77
LSB 100-german Seite 32
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 37

Einbau-, Betriebs- und Wartungsanleitung
Baureihe LSB
Pumpe Bmax g1 ~H h U n4 n5 w ~G
LSB 65-40-315 .... - 100 201 15 543 229 - - - - 102
LSB 65-40-315 .... - 112 201 15 552 229 - - - - 102
LSB 65-40-315 .... - 132 201 15 679 229 - - - - 102
LSB 65-40-315 .... - 160 201 15 828 264 - 210 180 219 112
LSB 65-40-315 .... - 180 201 15 859 264 - 210 180 219 112
LSB 65-40-315 .... - 200 225 65 964 264 50 280 250 219 112
LSB 80-50-160 .... - 80 141 15 408 176 - - - - 36
LSB 80-50-160 .... - 90 141 15 457 176 - - - - 36
LSB 80-50-160 .... - 100 144 15 530 216 - - - - 43
LSB 80-50-160 .... - 112 144 15 539 216 - - - - 43
LSB 80-50-160 .... - 132 150 15 666 216 - - - - 43
LSB 80-50-160 .... - 160 175 35 815 251 20 210 180 206 49
LSB 80-50-160 .... - 180 180 60 846 251 45 210 180 206 49
LSB 80-50-200 .... - 80 157 15 408 176 - - - - 45
LSB 80-50-200 .... - 90 157 15 457 176 - - - - 45
LSB 80-50-200 .... - 100 157 15 530 216 - - - - 51
LSB 80-50-200 .... - 112 157 15 539 216 - - - - 51
LSB 80-50-200 .... - 132 157 15 666 216 - - - - 51
LSB 80-50-200 .... - 160 175 35 815 251 20 210 180 206 60
LSB 80-50-200 .... - 180 180 60 846 251 45 210 180 206 60
LSB 80-50-200 .... - 200 225 85 951 251 70 280 250 206 60
LSB 80-50-250 .... - 90 181 15 470 189 - - - - 69
LSB 80-50-250 .... - 100 181 15 543 229 - - - - 75
LSB 80-50-250 .... - 112 181 15 552 229 - - - - 75
LSB 80-50-250 .... - 132 181 15 679 229 - - - - 75
LSB 80-50-250 .... - 160 181 15 828 264 - 210 180 219 84
LSB 80-50-250 .... - 180 181 20 859 264 5 210 180 219 84
LSB 80-50-250 .... - 200 225 65 964 264 50 280 250 219 84
LSB 80-50-315 .... - 100 212 15 543 229 - - - - 108
LSB 80-50-315 .... - 112 212 15 552 229 - - - - 108
LSB 80-50-315 .... - 132 212 15 679 229 - - - - 108
LSB 80-50-315 .... - 160 212 15 828 264 - 210 180 219 118
LSB 80-50-315 .... - 180 212 15 859 264 - 210 180 219 118
LSB 80-50-315 .... - 200 225 40 964 264 25 280 250 219 118
LSB 100-65-160 .... - 80 164 15 421 189 - - - - 49
LSB 100-65-160 .... - 90 164 15 470 189 - - - - 49
LSB 100-65-160 .... - 100 164 15 543 229 - - - - 55
LSB 100-65-160 .... - 112 164 15 552 229 - - - - 55
LSB 100-65-160 .... - 132 164 15 679 229 - - - - 55
LSB 100-65-160 .... - 160 175 40 828 264 25 210 180 219 64
LSB 100-65-160 .... - 180 180 40 859 264 25 210 180 219 64
LSB 100-65-160 .... - 200 225 85 964 264 70 280 250 219 64
LSB 100-65-200 .... - 90 173 15 470 189 - - - - 53
LSB 100-65-200 .... - 100 173 15 543 229 - - - - 58
LSB 100-65-200 .... - 112 173 15 552 229 - - - - 58
LSB 100-65-200 .... - 132 173 15 679 229 - - - - 58
LSB 100-65-200 .... - 160 175 15 828 264 - 210 180 219 68
LSB 100-65-200 .... - 180 180 20 859 264 5 210 180 219 68
LSB 100-65-200 .... - 200 225 65 964 264 50 280 250 219 68
LSB 100-65-250 .... - 90 193 18 470 189 - - - - 74
LSB 100-65-250 .... - 100 193 18 543 229 - - - - 80
LSB 100-65-250 .... - 112 193 18 552 229 - - - - 80
LSB 100-65-250 .... - 132 193 18 679 229 - - - - 80
LSB 100-65-250 .... - 160 193 18 828 264 - 210 180 219 89
LSB 100-65-250 .... - 180 193 18 859 264 - 210 180 219 89
LSB 100-65-250 .... - 200 225 48 964 264 30 280 250 219 89
LSB 100-65-315 .... - 100 221 18 555 241 - - - - 115
LSB 100-65-315 .... - 112 221 18 564 241 - - - - 115
LSB 100-65-315 .... - 132 221 18 691 241 - - - - 115
LSB 100-65-315 .... - 160 221 18 840 276 - 210 180 231 125
LSB 100-65-315 .... - 180 221 18 871 276 - 210 180 231 125
LSB 100-65-315 .... - 200 225 18 976 276 - 210 180 231 125
LSB 125-80-160 .... - 90 188 15 470 189 - - - - 56
LSB 125-80-160 .... - 100 188 15 543 229 - - - - 62
LSB 125-80-160 .... - 112 188 15 552 229 - - - - 62
LSB 125-80-160 .... - 132 188 15 679 229 - - - - 62
LSB 125-80-160 .... - 160 188 15 828 264 - 210 180 219 71
LSB 100-german Seite 33
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 38

Einbau-, Betriebs- und Wartungsanleitung
Baureihe LSB
Pumpe Bmax g1 ~H h U n4 n5 w ~G
LSB 125-80-160 .... - 180 188 20 859 264 5 210 180 219 71
LSB 125-80-160 .... - 200 225 65 964 264 50 280 250 219 71
LSB 125-80-200 .... - 90 202 15 470 189 - - - - 63
LSB 125-80-200 .... - 100 202 15 543 229 - - - - 69
LSB 125-80-200 .... - 112 202 15 552 229 - - - - 69
LSB 125-80-200 .... - 132 202 15 679 229 - - - - 69
LSB 125-80-200 .... - 160 202 15 828 264 - 210 180 219 78
LSB 125-80-200 .... - 180 202 20 859 264 5 210 180 219 78
LSB 125-80-200 .... - 200 225 65 964 264 50 280 250 219 78
LSB 125-80-250 .... - 100 229 18 543 229 - - - - 91
LSB 125-80-250 .... - 112 229 18 552 229 - - - - 91
LSB 125-80-250 .... - 132 229 18 679 229 - - - - 91
LSB 125-80-250 .... - 160 229 18 828 264 - 210 180 219 100
LSB 125-80-250 .... - 180 229 18 859 264 - 210 180 219 100
LSB 125-80-250 .... - 200 229 23 964 264 5 280 250 219 100
LSB 125-80-315 .... - 112 240 18 564 241 - - - - 129
LSB 125-80-315 .... - 132 240 18 691 241 - - - - 129
LSB 125-80-315 .... - 160 240 18 840 276 - 280 250 231 139
LSB 125-80-315 .... - 180 240 18 871 276 - 280 250 231 139
LSB 125-80-315 .... - 200 240 18 976 276 - 280 250 231 139
LSB 125-100-200 .... - 100 217 18 543 229 - - - - 90
LSB 125-100-200 .... - 112 217 18 552 229 - - - - 90
LSB 125-100-200 .... - 132 217 18 679 229 - - - - 90
LSB 125-100-200 .... - 160 217 23 828 264 5 210 180 219 99
LSB 125-100-200 .... - 180 217 23 859 264 5 210 180 219 99
LSB 125-100-200 .... - 200 225 48 964 264 30 280 250 219 99
LSB 125-100-250 .... - 100 227 18 565 251 - - - - 100
LSB 125-100-250 .... - 112 227 18 574 251 - - - - 100
LSB 125-100-250 .... - 132 227 18 701 251 - - - - 100
LSB 125-100-250 .... - 160 227 18 850 286 - 220 180 241 109
LSB 125-100-250 .... - 180 227 18 881 286 - 220 180 241 109
LSB 125-100-250 .... - 200 227 23 986 286 5 280 250 241 109
LSB 125-100-315 .... - 132 257 18 691 241 - - - - 139
LSB 125-100-315 .... - 160 257 18 840 276 - 280 250 231 150
LSB 125-100-315 .... - 180 257 18 871 276 - 280 250 231 150
LSB 125-100-315 .... - 200 257 18 976 276 - 280 250 231 150
LSB 150-125-250 .... - 132 249 18 701 251 - - - - 114
LSB 150-125-250 .... - 160 249 18 850 286 - 280 250 241 123
LSB 150-125-250 .... - 180 249 18 881 286 - 280 250 241 123
LSB 150-125-250 .... - 200 249 18 986 286 - 280 250 241 123
LSB 150-125-315 .... - 160 263 20 840 276 - 280 250 231 149
LSB 150-125-315 .... - 180 263 20 871 276 - 280 250 231 149
LSB 150-125-315 .... - 200 263 20 976 276 - 280 250 231 149
LSB 200-150-250 .... - 160 293 20 850 286 - 280 250 241 163
LSB 200-150-250 .... - 180 293 20 881 286 - 280 250 241 163
LSB 200-150-250 .... - 200 293 20 986 286 - 280 250 241 163
Flanschabmessungen DNS, DND*)
ISO PN16 ISO PN25 ANSI Class 150RF
DN C d D K L DN C d D K L NPS C d D K L
25 16 65 115 85 4x14 - - - - - - 1 16 51 115 79,5 4x16
32 18 78 140 100 4x19 32 20 78 140 100 4x19 1 1/2 18 73 140 98,5 4x16
40 19 88 150 110 4x19 40 19 88 150 110 4x19 1 1/2 19 73 150 98,5 4x16
50 20 102 165 125 4x19 50 20 102 165 125 4x19 2 20 92 165 120,5 4x19
65 20 122 185 145 4x19 65 22 122 185 145 8x19 2 1/2 20 105 185 139,5 4x19
80 20 128 200 160 8x19 80 24 138 200 160 8x19 3 20 128 200 152,5 4x19
100 24 157 230 180 8x19 100 24 162 235 190 8x22 4 24 157 230 190,5 8x19
125 24 186 255 210 8x19 125 26 186 270 220 8x22 5 24 186 255 216 8x22
150 25,5 216 285 240 8x22 - - - - - - 6 25,5 216 285 241,5 8x22
200 29 270 345 295 12x22 - - - - - - 8 29 270 345 298,5 12x22
*) ... Die Flanschgrößen sowie den Nenndruck finden Sie auf dem Datenblatt / der Auftragsbestätigung. Siehe auch
Kapitel 3.1.1 Bezeichnungsschema.
LSB 100-german Seite 34
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 39

Instructions de montage, de service et de maintenance
SOMMAIRE
Plaque signalétique de la pompe.............................. 36
Plaque ATEX (exclusivement pour les pompes
conformes à 94/9/CE)...............................................36
1. Généralités............................................................ 37
1.1 Garantie........................................................... 37
2. Règles de sécurité ................................................ 37
2.1 Identification des consignes dans les
instructions de service........................................... 37
2.2 Dangers en cas d’inobservation des consignes
de sécurité............................................................. 38
2.3 Consignes de sécurité destinées à l’exploitant /
l’opérateur ............................................................. 38
2.4 Consignes de sécurité pour les travaux de
maintenance, d’inspection et de montage............. 38
2.5 Modifications arbitraires et fabrication de pièces
détachées.............................................................. 38
2.6 Modes de fonctionnement inadmissibles ........ 39
2.7 Protection contre les explosions ..................... 39
2.8 Utilisation selon les réglementations............... 40
3. Description de l’exécution.....................................41
3.1 Pompes ........................................................... 41
3.1.1 Schéma de spécifications ............................ 41
3.2 Garniture d’arbre ............................................. 41
3.3 Logement ........................................................ 41
3.4 Valeurs indicatives pour le N.P.A....................41
3.5 Forces et moments admissibles au niveau des
tubulures................................................................ 42
3.6 Pressions et températures admissibles .......... 42
3.7 Eau de condensation....................................... 43
4. Transport, manutention, stockage ........................ 43
4.1 Transport, manutention ................................... 43
4.2 Stockage / conservation..................................43
5. Mise en place, montage........................................ 44
5.1 Installation du groupe......................................44
5.2 Raccordement des conduites à la pompe.......44
5.3 Entraînement................................................... 45
5.4 Raccordement électrique ................................ 45
5.5 Contrôle final ................................................... 45
6. Mise en service, exploitation, mise hors service... 45
6.1 Première mise en service................................ 45
6.2 Brancher la machine d’entraînement. ............. 46
6.3 Remise en service........................................... 46
6.4 Limites de l’exploitation ................................... 46
6.5 Lubrification .....................................................47
6.6 Contrôle ...........................................................47
6.7 Mise hors service.............................................47
6.8 Stockage / arrêt prolongé ................................47
7. Entretien, maintenance .........................................48
7.1 Consignes générales.......................................48
7.2 Garnitures mécaniques ...................................48
7.3 Paliers du moteur ............................................48
7.4 Nettoyage de la pompe....................................48
8. Démontage de la pompe et réparation..................48
8.1 Consignes générales.......................................48
8.2 Généralités ......................................................48
8.3 Démontage et montage des grilles de protection
de la lanterne d’entraînement................................48
8.4 Démontage de l’unité de marche.....................49
8.5 Démontage de la roue mobile .........................49
8.6 Démontage de la garniture d’arbre..................50
8.7 Démontage de l’arbre d’emboîtement .............50
8.8 Remise en état ................................................50
8.9 Montage...........................................................50
9. Recommandations pour les pièces détachées,
pompes de réserve ...................................................52
9.1 Pièces détachées ............................................52
9.2 Pompes de réserve .........................................52
10. Dysfonctionnements - origine et réparation ........52
11. Mode d’emploi pour les moteurs .........................54
Garniture mécanique simple sans chemise de
protection d’arbre (code d’exécution S1..2).............. 56
Garniture mécanique simple avec quench sans
chemise de protection d’arbre (Code d’exécution
S4..2)………………………………………………….... 58
Schéma de coupe Exécution S1..2, roue mobile avec
ailettes dorsales........................................................ 61
Schéma de coupe Exécution S1..2, roue mobile avec
forages de déversement........................................... 62
Schéma de coupe Exécution S4..2, roue mobile avec
ailettes dorsales........................................................ 63
Schéma de coupe Exécution S4..2, roue mobile avec
forages de déversement........................................... 64
Raccordements........................................................ 65
Plan coté................................................................... 66
Série LSB
LSB 100-france Page 35
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 40
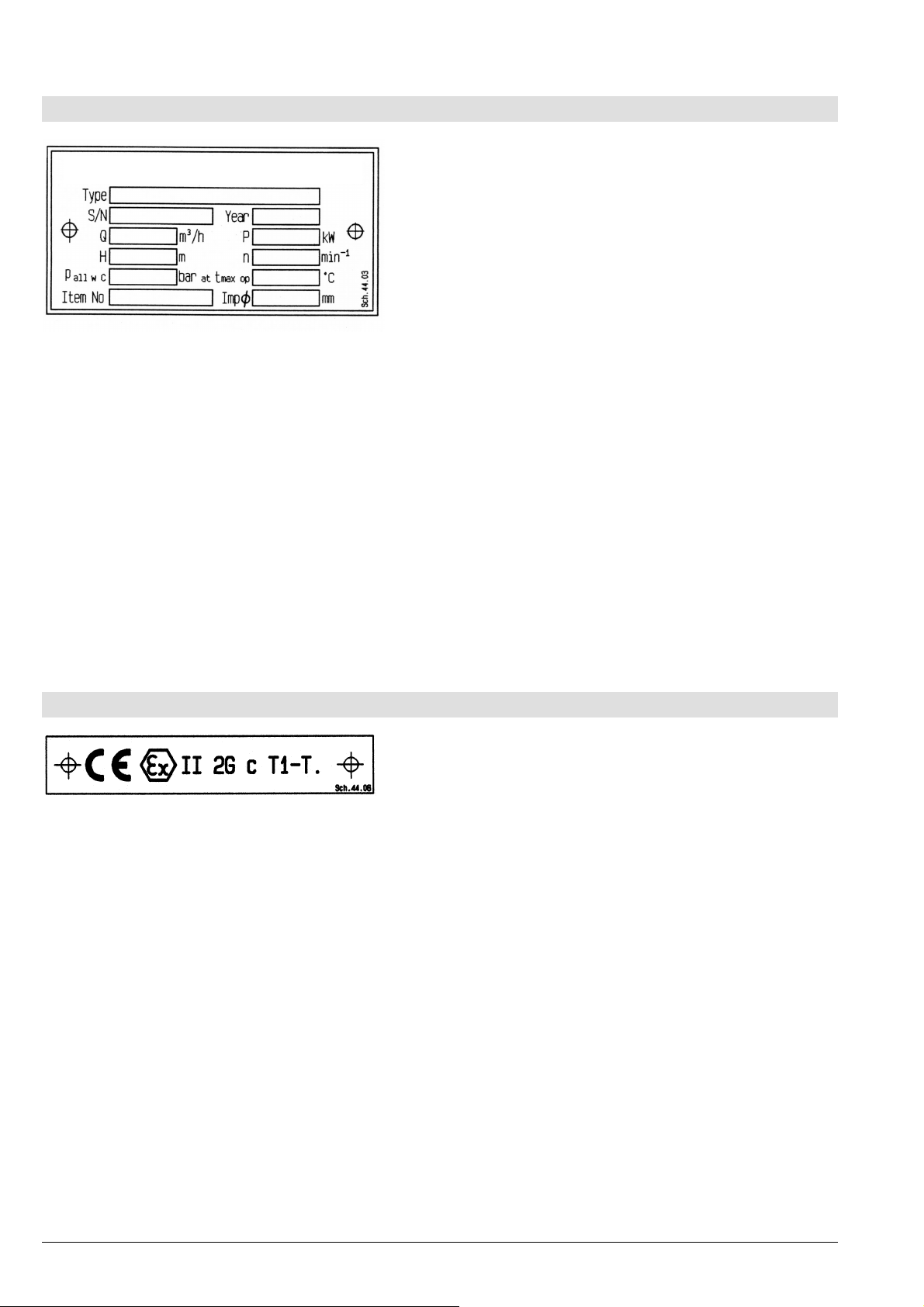
Instructions de montage, de service et de maintenance
Plaque signalétique de la pompe
Série LSB
Type *) Code de série de la pompe
S/N *) Code de fabrication
Year Année de construction
Q Débit au point de fonctionnement dynamique
P Puissance d’entraînement au point de
fonctionnement dynamique
H Hauteur manométrique (hauteur d’énergie) au
point de fonctionnement dynamique
n Vitesse de rotation
p
all w C
t
max op
Item Nr Numéro de commande spécifique au client
Imp∅ diamètre extérieur de la roue mobile
Pression de service maximale admissible dans le
corps (= la pression de sortie maximale pour la
température de service définie avec laquelle le
corps de la pompe peut être utilisé).
Température de service maximale admissible du
liquide de refoulement
*) Avec ces indications, tous les détails d’exécution et
matériaux sont exactement définis par le fabricant. Ils
devront donc être stipulés en cas de demande de
précisions supplémentaires et pour toute commande
de pièces détachées auprès du fabricant.
Plaque ATEX (exclusivement pour les pompes conformes à 94/9/CE)
CE Certification de conformité avec la directive
94/9/CE
Ex Certification spécifique pour la protection contre
l’explosion
II Symbole pour le groupe d’appareils
2G Symbole pour la catégorie d’appareils (2),
atmosphère explosible par gaz, vapeurs ou
brouillards (G)
c Symbole pour la protection «e» utilisée (sécurité
constructive "c")
T1-T. Symbole servant à indiquer le domaine
théoriquement disponible des classes de
température – Indications en matière de classe de
température, voir chapitre 2.7.5 ; Indications en
matière de température maximale admissible du
liquide de refoulement, voir plaque signalétique,
fiche technique et / ou confirmation de commande.
LSB 100-france Page 36
Artikel Nr. 771076129
La conformité avec la directive 94/9/CE "Appareils et
systèmes de protection destinés à être utilisés selon
les prescriptions en atmosphères explosibles" est
confirmée par l’établissement de la déclaration de
conformité CE et la fixation de la plaque ATEX sur la
pompe (lanterne d’entraînement). La plaque ATEX est
apposée en sus de la plaque signalétique.
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 41

Instructions de montage, de service et de maintenance
Les personnes chargées du montage, de
l’exploitation, de l’inspection et l’entretien
quises
des règles de prévention d’accidents et des
qualifications nécessaires pour ces travaux. Le
personnel doit suivre une formation si ces
Une inobservation peut porter préjudice à la
1. Généralités
Série LSB
Ce produit est conforme aux règles de sécurité de la
directive machines 2006/42/CE.
doivent disposer des connaissances re
connaissances ne sont pas acquises.
La sécurité de fonctionnement de la pompe ou du
groupe (= pompe et moteur) livré n’est assurée qu’en
cas d’utilisation conforme à sa destination stipulée sur
la fiche technique jointe et / ou dans la confirmation de
commande tout comme dans le chapitre 6 "Mise en
service, exploitation, mise hors service".
L’exploitant est responsable du respect des
instructions et des consignes de sécurité contenues
dans la présente notice.
Le montage et l’entretien effectués avec soin et selon
les règles applicables en construction de machines et
en électrotechnique sont la condition préalable d’un
bon fonctionnement de la pompe.
S’adresser au fabricant pour tout renseignement non
contenu dans cette notice.
En cas d’inobservation de ces instructions d’emploi, le
fabricant s’exonère de sa responsable pour la pompe
ou le groupe.
Conserver soigneusement ces instructions d’emploi
pour consultations ultérieures.
La cession de la pompe ou du groupe à un tiers ne
peut se faire qu’accompagnée de l’intégralité des
instructions, des conditions d’utilisation et limites
d’exploitation stipulées dans la confirmation de
commande.
Ces instructions d’emploi ne tiennent compte ni des
détails de construction ou des versions, ni des cas
fortuits ou d’événements pouvant se produire lors du
montage, de l’exploitation ou de l’entretien.
Nous conservons les droits d’auteur sur ces
instructions d’emploi que nous confions au propriétaire
de la pompe ou du groupe à des fins d’utilisation
personnelle. Ces instructions d’emploi contiennent des
indications techniques et des schémas dont la
reproduction partielle ou intégrale, leur diffusion ou
leur utilisation dans des buts concurrentiels ainsi que
leur divulgation sont interdites.
1.1 Garantie
Garantie selon nos conditions de vente ou la
confirmation de la commande.
Nous nous réservons le droit d’effectuer ou de
soumettre à notre accord écrit préalable les
interventions pendant le délai de garantie. Toute autre
intervention met un terme à la garantie.
En principe, les garanties à long terme sont limitées à
la bonne exécution et l’utilisation de matériaux
spécifiés. Sont exclus de la garantie l’usure et la
dégradation naturelles, ainsi que la totalité des pièces
d’usure, comme par exemple les roues mobiles, les
dispositifs d’étanchéité des arbres, les arbres, les
manchons de protection des arbres, les paliers, les
bagues à fente et les bagues d’usure etc. ainsi que les
dommages dus au transport ou à un stockage
incorrect.
L’utilisation de la pompe ou du groupe dans les
conditions indiquées sur la plaque signalétique, la
fiche technique et / ou la confirmation de commande,
est la condition préalable pour la garantie. Cette règle
s’applique notamment à la résistance des matériaux,
au bon fonctionnement de la pompe et de la garniture
d’arbre.
Le fonctionnement dans des conditions d’utilisation
réelles différentes par rapport à celles stipulées, est
soumis à la délivrance d’un certificat d’aptitude écrit
par nos soins.
2. Règles de sécurité
Il faut veiller au respect des consignes importantes
contenues dans ces instructions d’emploi concernant
le montage, l’installation, le fonctionnement et
l’entretien.
Aussi le personnel technique ou l’exploitant doit-il
prendre connaissance de la présente notice avant le
montage et la mise en service et la conserver
facilement accessible sur le site d’exploitation de la
pompe ou du groupe.
La présente notice ne contient ni les règles
générales sur la prévention des accidents ni la
réglementation locale en matière de sécurité et /
ou d’exploitation. Le respect de ces règles
(également par le personnel de montage extérieur)
est à la charge de l’exploitant.
Ne sont pas non plus inclues dans ces instructions de
service les réglementations et mesures de sécurité en
matière de manutention et d’évacuation du liquide de
LSB 100-france Page 37
Artikel Nr. 771076129
refoulement ou de tout autre liquide auxiliaire servant
à la vidange, à l’arrêt, à la lubrification etc.,
particulièrement lorsque ceux-ci sont explosifs,
toxiques, brûlants etc.
La responsabilité de manutention adéquate selon les
prescriptions est à la charge exclusive de l’exploitant.
2.1 Identification des consignes dans les
instructions de service
Les symboles de sécurité selon DIN 4844 distinguent
les consignes de sécurité contenues dans la présente
notice :
Consigne de sécurité !
pompe et à ses fonctions.
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 42

Instructions de montage, de service et de maintenance
moyens d’exploitation antidéflagrants
doivent être identifiés pour les travaux en
Avertissement contre les risques
En cas d’exploitation du groupe dans des
ibles, les sections de ces
instructions de service portant le symbole Ex
Symbole communautaire CE !
Les
La protection contre les contacts accidentels des
atmosphères explosibles.
Symbole général de danger !
Risques de dommages corporels.
d’électrocution !
Il est indispensable de suivre les consignes de
sécurité figurant directement sur la pompe ou le
groupe et elles doivent rester entièrement lisibles.
Tout comme pour les instructions de service de la
pompe, toutes les instructions de service
d’accessoires (moteur par exemple)
éventuellement jointes doivent être respectées et
rester accessibles.
Pour les pompe ou groupes ayant un niveau
L’écoulement des fuites (p.ex. de la garniture
Prévenir les risques électriques (notamment par le
2.2 Dangers en cas d’inobservation des
consignes de sécurité
L’inobservation des consignes de sécurité peut
mettre un terme à toute prétention à des
dommages et intérêts.
L’inobservation peut provoquer les risques suivants :
Défaillance de fonctions importantes de la pompe
ou de l’installation.
Défaillance des appareils électroniques et des
instruments de mesure à cause de champs
magnétiques.
Risques de dommages corporels et de biens
personnels à cause de champs magnétiques.
Risques de dommages corporels par
électrocution, action mécanique et chimique.
Risques de détérioration de l’environnement par
fuite de substances dangereuses.
atmosphères explos
doivent être particulièrement respectées.
2.4 Consignes de sécurité pour les
travaux de maintenance, d’inspection et
de montage
L’exploitant doit veiller à ce que les travaux
En principe, les interventions au niveau de la
2.3 Consignes de sécurité destinées à
l’exploitant / l’opérateur
Les conditions d’utilisation entraînant l’usure, la
corrosion et le vieillissement limitent la durée de
vie et donc les caractéristiques spécifiées. Le
contrôle et l’entretien continus sont à la charge de
l’exploitant qui doit assurer le remplacement en
temps voulu de toute pièce compromettant le bon
fonctionnement. Tout dysfonctionnement ou
endommagement perceptible interdit l’utilisation.
Si les pannes ou défaillances d’une installation
risquent de provoquer des dommages corporels
ou matériels, prévoir un système d’alarme et / ou
des doublons dont la sécurité de fonctionnement
est à vérifier à intervalles réguliers.
Toutes les parties brûlantes ou froides de
l’installation susceptibles de provoquer des
blessures doivent être isolées au niveau de
LSB 100-france Page 38
Artikel Nr. 771076129
2.5 Modifications arbitraires et fabrication
de pièces détachées
Toute modification ou transformation de la machine
n’est autorisée qu’après avoir consulté le fabricant.
Les pièces détachées d’origine et les accessoires
autorisés par le fabricant contribuent à la sécurité.
L’utilisation d’autres pièces peut mettre un terme à la
responsabilité pour les dommages qui pourraient en
résulter.
l’exécution contre tout contact ou apposer des
consignes d’avertissement conformes.
parties mobiles (p.ex. protection de
l’accouplement) ne peut être retirée pendant
l’exploitation de l’installation.
sonore supérieur à 85 dB(A), il est impératif de
porter une protection acoustique en cas de séjour
prolongé à proximité immédiate.
d’arbre) de fluides dangereux (p.ex. explosifs,
toxiques ou chauds) doit s’effectuer sans
provoquer de risques corporels ou pollutions.
Observer la réglementation en vigueur.
respect des règles locales applicables aux
installations électriques). Avant toute intervention
sur des pièces conductrices, couper l’alimentation
en débranchant la prise ou actionner le disjoncteur
principal et retirer les fusibles. Prévoir un
disjoncteur-protecteur.
d’entretien, d’inspection et de montage soient
réalisés par un personnel spécialisé autorisé et
qualifié qui aura soigneusement pris
connaissance, au préalable, de ces instructions de
service.
pompe ou du groupe ne s’effectuent qu’à l’arrêt et
hors pression. Toutes les pièces doivent être à
température ambiante. S’assurer que personne ne
peut remettre la pompe en marche pendant les
interventions. Il est indispensable de suivre la
procédure de mise à l’arrêt de l’installation décrite
dans les instructions de service. Avant le
démontage, décontaminer les pompes ou
installations véhiculant des fluides dangereux pour
la santé. Consulter les fiches techniques
respectives pour chaque liquide de refoulement.
Remettre en place et en service tous les
dispositifs de sécurité dès la fin des interventions.
Série LSB
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 43

Instructions de montage, de service et de maintenance
Durant l’exploitation de la pompe, les conduites
d'aspiration et de refoulement ainsi que
l’intérieur de la pompe en contact avec le liquide
quide de
On évitera ainsi toute atmosphère explosible et
Si l’exploitant n’est pas en mesure de garantir
de telles conditions, prévoir des mesures de
res
d’étanchéité et les systèmes auxiliaires de la
garniture d’arbre doivent être soigneusement
L’identification au niveau de la pompe fait
référence à la partie de la pompe. Pour le
el, une
déclaration de conformité particulière et une
S’il y a risque d’explosion durant la phase
d’installation, le contrôle du sens de rotation ne
doit jamais se faire par une brève mise en
marche de la pompe non remplie afin d’éviter
inadmissible en
cas de contact de parties rotatives et
De hautes températures risquent de se
manifester au niveau de la surface du corps de
la pompe par réchauffement rapide du liquide à
ne augmentation rapide de la pression à
l’intérieur de la pompe peut provoquer un risque
c garnitures mécaniques
peuvent dépasser les limites admissibles de
température par marche à sec. Une marche à
sec peut se produire, non seulement en cas de
zone d’étanchéité insuffisamment remplie, mais
aussi en présence de proportions trop élevées
Une exploitation de la pompe en dehors du
domaine d’exploitation admissible peut
En exploitation normale, les plus hautes
températures se manifestent au niveau de la
Durant l’exploitation de la pompe, veiller à éviter
tout dépôt excessif de poussière
(éventuellement par nettoyage régulier) afin
d’éviter un échauffement de la surface de la
pompe qui dépasserait la température
2.6 Modes de fonctionnement
inadmissibles
La sécurité d’exploitation de la pompe livrée ne peut
être garantie que s’il en est fait une utilisation
conforme à sa destination décrite dans les chapitres
suivants de ces instructions de service.
Ne dépasser en aucun cas les valeurs limite stipulées
dans la fiche technique et / ou dans la confirmation de
commande.
2.7 Protection contre les explosions
En cas d’exploitation du groupe en atmosphères
explosibles, respecter impérativement les mesures et
consignes des chapitres 2.7.1 à 2.7.7 afin de garantir
la protection contre toute explosion.
2.7.1 Remplissage du groupe
doivent être constamment remplis de li
refoulement.
tout risque de marche à sec.
contrôle adéquates.
De la même manière, toutes les chamb
2.7.4 Mode de fonctionnement de la pompe
La pompe ne peut être démarrée qu’avec un organe
d’arrêt entièrement ouvert du côté d’aspiration et
légèrement ouvert du côté de refoulement. Un
démarrage contre une garniture d’arrêt fermée est
cependant possible. Immédiatement après
l'accélération, l’organe d’arrêt du côté de refoulement
doit être ajusté au point de fonctionnement
dynamique.
Voir également chapitre 6.2.
Une exploitation avec un organe d’arrêt fermé
dans la conduite d’aspiration et / ou de
refoulement est interdite !
Les quantités minimales sont indiquées dans le
chapitre 6.4.1. De longues phases d’exploitation avec
de telles quantités et avec les liquides stipulés ne
provoquent aucune augmentation supplémentaire des
températures en surface au niveau de la pompe.
Par ailleurs, il est impératif de respecter les consignes
du chapitre 6 de ces instructions de service.
Série LSB
l’intérieur de la pompe.
U
de surcharge pouvant aller jusqu’à l’explosion.
Les pompes ave
remplis.
2.7.2 Identification
moteur et tout autre élément additionn
identification adéquate doivent être établies.
Exemple d’identification sur la partie de la pompe :
CE Ex II 2 G c T1-T.
L’identification indique la plage théoriquement
disponible des classes de température. Les
températures admissibles en fonction du type de
pompes sont déterminées dans le chapitre 2.7.5. Il en
va de même pour l’entraînement.
Pour un groupe complet (pompe et moteur) avec
différentes classes de température, c’est la plus faible
qui prévaut.
2.7.3 Contrôle du sens de rotation
une élévation de température
stationnaires.
LSB 100-france Page 39
Artikel Nr. 771076129
de gaz dans le liquide.
également provoquer une marche à sec.
2.7.5 Limites de température
surface du corps de la pompe.
La température de surface qui se manifeste au niveau
du corps de la pompe correspond à la température du
liquide à véhiculer.
Au niveau de la lanterne et du moteur, éviter
impérativement tout contact de la surface avec
l’environnement.
admissible.
L’exploitant de l’installation doit s’assurer que la
température de service définie est bien respectée.
La température maximale admissible du liquide de
refoulement au niveau de l’entrée de la pompe
dépend de la classe de température réelle.
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 44

Instructions de montage, de service et de maintenance
La température admissible de la pompe est
stipulée sur la fiche technique et / ou dans la
confirmation de commande et sur la plaque
Afin de garantir une exploitation sûre et fiable,
veiller régulièrement à ce que le groupe soit
entretenu convenablement et maintenu dans un
Les appareils de distribution et de réglage
électriques, l’installation d’instruments et
rmes
aux normes de sécurité et aux réglementations
en vigueur en matière de protection contre les
L’installation doit être munie de dispositifs de
sécurité adéquats garantissant avec certitude le
respect des valeurs limite de vitesse, de
pression et de température à l’intérieur de la
pompe et au niveau de la garniture d’arbre,
conformément à la fiche technique et / ou à la
es pressions
d’entrée stipulées (pressions du système) ne
doivent pas non plus être en deçà de la valeur
En principe, les conduites d’aspiration et de
refoulement doivent exécutées de telle sorte
qu’elles n’opèrent que de faibles forces sur la
s valeurs
stipulées dans le chapitre 3.5 ne doivent en
aucun cas être dépassées. Cela vaut aussi bien
dire pour toutes les pressions et températures
ssurer un bon fonctionnement sans
cavitation et d’éviter les arrêts brusques, le
fluide véhiculé doit présenter une pression
minimale NPSH à l’entrée de la roue. Ces
conditions sont réunies, si la valeur NPSH de
de
dessus de la valeur NPSH de la pompe
En prenant en compte les classes de température
conformes à EN 13463-1, le tableau ci-après contient
les valeurs limite théoriques de la température du
liquide de refoulement qui en résultent.
Classe de température
conforme à EN 13463-1
Valeur limite de la
température du liquide de
refoulement
T4 (135°C) 135°C
T3 (200°C) 140°C
T2 (300°C) 140°C
T1 (450°C) 140°C
En outre, protéger impérativement la pompe (p.ex. par
une vanne d’arrêt du côté de refoulement, un disque
volant, un réservoir d’air) contre les coups de bélier
qui risquent de se produire en cas de démarrage trop
rapide de l’installation. Eviter les changements
brusques de température. Ils peuvent provoquer un
choc thermique provoquant la destruction ou
l’endommagement de la fonctionnalité de certains
éléments.
2.8.2 Forces et moments admissibles au niveau
des tubulures
Série LSB
signalétique de la pompe.
2.7.6 Maintenance
état technique irréprochable.
Exemple : fonctionnalité des roulements. Le mode de
fonctionnement et les conditions d’exploitation
influencent grandement sur la durée de vie réellement
escomptable.
Un contrôle régulier du bruit de marche permet
d’éviter le risque d’apparition de températures
supérieures à la normale à cause de paliers
surchauffés. Voir les chapitres 6.6 et 7.4.
Le fonctionnement de la garniture d’arbre est garanti
par un contrôle régulier.
En cas d’installation de systèmes auxiliaires (p.ex.
écurage externe), s’assurer de la nécessité de
dispositifs de contrôle garantissant le bon
fonctionnement.
2.7.7 Appareils de distribution et réglage
électriques, installation d’instruments et
d’éléments accessoires
d’éléments accessoires doivent être confo
explosions.
2.8 Utilisation selon les réglementations
2.8.1 Vitesse de rotation, pression, température
confirmation de commande. L
minimale.
LSB 100-france Page 40
Artikel Nr. 771076129
pompe. Dans le cas contraire, le
pour la pompe en exploitation qu’à l’arrêt, c’estàprésentes dans l’installation.
2.8.3 NPSH
Afin d’a
l’installation (NPSHA) se situe avec certitu
dans toutes les conditions d’utilisation au-
(NPSHR).
Respecter tout particulièrement la valeur NPSH en
cas de refoulement de liquides proches du point
d'ébullition. Des valeurs NPSH trop basses risquent
de provoquer des dégâts matériels dus à la cavitation,
voire la destruction par surchauffement.
Les courbes caractéristiques précisent la NPSHR pour
chaque type de pompe.
2.8.4 Arrêt, écurage, refroidissement
Prévoir des options de régulation et de contrôle pour
les éventuels arrêts ou écurages en place.
En cas de liquides dangereux ou de températures
élevées, veiller à ce que la pompe soit mise hors
service en cas de défaillance du système d’arrêt, ou
d’écurage.
Les systèmes d’arrêt et d’écurage doivent toujours
être mis en marche avant la mise en service de la
pompe. Mise hors service après arrêt de la pompe
dans la mesure où le type d’exploitation le permet.
2.8.5 Reflux
Pour les installations où les pompes travaillent en
système fermé sous pression (coussin de gaz,
pression à vapeur), la détente du coussin de gaz par
la pompe est inadmissible car la vitesse de reflux peut
représenter un multiple de la vitesse de service, ce qui
pourrait détruire le groupe.
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 45

Instructions de montage, de service et de maintenance
La garniture mécanique utilisée dans l’exécution
Pour plus d’informations concernant les
garnitures mécaniques et les risques d’accident
qui y sont liés, consulter le chapitre 6.6 et le
3. Description de l’exécution
Série LSB
3.1 Pompes
Pompes LSB sont des pompes à volute à un étage
de processus. Conception hydraulique et cotes de
raccordement conformes à ISO 2858 / EN 22858,
exigences techniques à ISO 5199 / EN 25199.
Les moteurs sont conformes à DIN 42677-IM B5. Le
moteur et l’arbre de la pompe sont accouplés
rigidement.
Les conditions d’exploitation admissibles et les détails
d’exécution de la pompe livrée sont stipulés sur la
fiche technique jointe et / ou dans la confirmation de
commande (voir schéma de spécifications dans le
chapitre 3.2).
Position de montage : Les pompes LSB sont
prévues pour une utilisation avec un arbre horizontal
et des tubulures de refoulement sur le haut. Toute
position de montage qui différerait est soumise à
l'accord préalable du fabricant
.
3.1.1 Schéma de spécifications
Grâce à l’identification figurant sur la fiche technique
et / ou dans la confirmation de commande, toutes les
informations concernant la pompe livrée peuvent être
consultées dans ces instructions de montage, de
service et de maintenance, comme par exemple :
LSB 100 - 65 - 250 S1 V L 2 - 132
(0) (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) (7) (8)
Position (0) - Identification de la série
LSB - Pompe bloc ISO
Position (1) - Tubulures d’aspiration en mm
Position (2) - Tubulures de refoulement en mm
Position (3) - Diamètre nominal de la roue mobile en
mm
Position (4) - Garniture d’arbre
S1 - Garniture mécanique simple conforme à
DIN 24960 l1k / EN 12756 forme U
S1 - Garniture mécanique simple conforme à
DIN 24960 l1k / EN 12756 forme U
Position (5) - Matériel roue mobile
N = Fonte grise (0.6025)
L = Fonte à graphite sphéroïdal (0.7043)
V = Acier moulé allié (1.4408)
W = Duplex (1.4517)
Position (6) - Matériel corps de pompe (même
codification que pour la roue mobile, fonte grise non
disponible)
Position (7) - Arbre d’emboîtement
Position (8) - IEC taille du moteur
avec quench (douille de laminage)
2 - sans chemise de protection d’arbre
(Duplex 1.4462)
3.2 Garniture d’arbre
Les pompes de la série LSB sont exclusivement
étanchéifiées par des garnitures mécaniques simples
aux mesures d'installation conformes à EN 12756
(DIN 24960), exécution "K", forme "U".
Il existe deux types de garniture d’arbre. Le type de
garniture d’arbre est stipulé sur la fiche technique et /
ou dans la confirmation de commande. Un mode
d’emploi concernant le montage et l’exploitation de
garnitures mécaniques figure dans les "Consignes de
montage de la garniture d’arbre" respectives.
La taille nominale (d
stipulée dans le tableau suivant.
40-25-160 33
40-25-200 33
40-25-250 43
50-32-160 33
50-32-200 33
50-32-250 43
50-32-315 43
65-40-160 33
65-40-200 33
65-40-250 43
65-40-315 43
80-50-160 33
80-50-200 33
80-50-250 43
80-50-315 43
Type
) de la garniture mécanique est
1
Taille
d1 de la
garniture
mécanique
Type
100-65-160 43
100-65-200 43
100-65-250 43
100-65-315 53
125-80-160 43
125-80-200 43
125-80-250 43
125-80-315 53
125-100-200 43
125-100-250 53
125-100-315 53
150-125-250 53
150-125-315 53
200-150-250 53
Taille
d1 de la
garniture
mécanique
standard ne résiste pas aux huiles minérales.
chapitre 7.2.
3.3 Logement
Le logement s’effectue dans les paliers à roulements
du moteur. Les paliers sont lubrifiés à la graisse à vie
et ne requièrent donc aucune maintenance.
3.4 Valeurs indicatives pour le N.P.A.
Consommation
en puissance
nominale P
en kW
N
0,55 50,5 49,5 49,0 58,0 52,0 51,5
0,75 52,0 51,0 50,5 59,0 54,0 53,0
1,1 54,0 53,0 52,5 60,0 55,5 54,5
1,5 55,5 55,0 54,5 63,5 57,0 56,0
2,2 58,0 57,0 56,5 64,5 59,0 58,5
3,0 59,5 58,5 58,0 68,5 61,0 62,0
4,0 61,0 60,0 59,5 69,0 63,0 63,0
5,5 63,0 62,0 61,5 70,0 65,0 65,0
7,5 64,5 63,5 63,0 70,5 67,0 67,0
11,0 66,5 65,5 65,0 72,0 69,0 68,5
15,0 68,0 67,0 66,5 72,5 70,0 70,5
18,5 69,0 68,5 68,0 73,0 70,5 74,0
22,0 70,5 69,5 69,0 74,5 71,0 74,0
30,0 72,0 71,0 - 75,0 72,0 37,0 73,0 - - 76,0 - -
Niveau de pression acoustique LpA en dB(A)
pompe seule
2950
-1
min
1450
min-1
975
min-1
pompe + moteur
2950
min-1
1450
min-1
975
min-1
LSB 100-france Page 41
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 46

Instructions de montage, de service et de maintenance
Série LSB
N.P.A. L
de la pompe selon DIN 45635, Partie 1 et 24.
L’influence de la pièce et du socle n’a pas été prise en
mesuré à une distance d’1 m du périmètre
pA
Toutes les valeurs pour les forces et les moments se
rapportent aux matériaux standard EN-GJS400-18LT
et 1.4408.
compte. La tolérance pour ces valeurs est de ±3
dB(A).
Cœfficient de majoration pour une exploitation à 60
Hz :
Pompe seule : −
Pompe avec moteur : +4 dB(A)
3.5 Forces et moments admissibles au
niveau des tubulures
… en s’appuyant sur la recommandation
européenne pour les pompes conformes à ISO
5199.
Illustr. 1
Les données en matière de forces et de moments ne
s’appliquent qu’aux charges statiques des conduites.
Taille de
construction
40-25-160 40 700 620 560 1100 730 500 590 1070 25 420 400 480 730 500 340 400 730
40-25-200 40 700 620 560 1100 730 500 590 1070 25 420 400 480 730 500 340 400 730
40-25-250 40 700 620 560 1100 730 500 590 1070 25 420 400 480 730 500 340 400 730
50-32-160 50 920 840 760 1450 780 560 650 1150 32 500 480 590 930 620 420 480 900
50-32-200 50 920 840 760 1450 780 560 650 1150 32 500 480 590 930 620 420 480 900
50-32-250 50 920 840 760 1450 780 560 650 1150 32 500 480 590 930 620 420 480 900
50-32-315 50 920 840 760 1450 780 560 650 1150 32 500 480 590 930 620 420 480 900
65-40-160 65 1180 1040 950 1850 840 620 670 1230 40 620 560 700 1100 730 500 590 1060
65-40-200 65 1180 1040 950 1850 840 620 670 1230 40 620 560 700 1100 730 500 590 1060
65-40-250 65 1180 1040 950 1850 840 620 670 1230 40 620 560 700 1100 730 500 590 1060
65-40-315 65 1180 1040 950 1850 840 620 670 1230 40 620 560 700 1100 730 500 590 1060
80-50-160 80 1400 1260 1150 2200 900 650 730 1320 50 840 760 920 1450 780 560 650 1150
80-50-200 80 1400 1260 1150 2200 900 650 730 1320 50 840 760 920 1450 780 560 650 1150
80-50-250 80 1400 1260 1150 2200 900 650 730 1320 50 840 760 920 1450 780 560 650 1150
80-50-315 80 1400 1260 1150 2200 900 650 730 1320 50 840 760 920 1450 780 560 650 1150
100-65-160 100 1880 1680 1520 2950 980 700 810 1450 65 1040 950 1180 1850 840 620 670 1230
100-65-200 100 1880 1680 1520 2950 980 700 810 1450 65 1040 950 1180 1850 840 620 670 1230
100-65-250 100 1880 1680 1520 2950 980 700 810 1450 65 1040 950 1180 1850 840 620 670 1230
100-65-315 100 1880 1680 1520 2950 980 700 810 1450 65 1040 950 1180 1850 840 620 670 1230
125-80-160 125 2210 2000 1800 3480 1180 840 1070 1710 80 1260 1150 1400 2200 900 650 730 1320
125-80-200 125 2210 2000 1800 3480 1180 840 1070 1710 80 1260 1150 1400 2200 900 650 730 1320
125-80-250 125 2210 2000 1800 3480 1180 840 1070 1710 80 1260 1150 1400 2200 900 650 730 1320
125-80-315 125 2210 2000 1800 3480 1180 840 1070 1710 80 1260 1150 1400 2200 900 650 730 1320
125-100-200 125 2210 2000 1800 3480 1180 840 1070 1710 100 1680 1520 1880 2950 980 700 810 1450
125-100-250 125 2210 2000 1800 3480 1180 840 1070 1710 100 1680 1520 1880 2950 980 700 810 1450
125-100-315 125 2210 2000 1800 3480 1180 840 1070 1710 100 1680 1520 1880 2950 980 700 810 1450
150-125-250 150 2800 2520 2270 4400 1400 980 1150 2050 125 2000 1800 2210 3480 1180 840 1070 1710
150-125-315 150 2800 2520 2270 4400 1400 980 1150 2050 125 2000 1800 2210 3480 1180 840 1070 1710
200-150-250 200 3750 3360 3030 5850 1820 1290 1490 2700 150 2520 2270 2800 4400 1400 980 1150 2050
∅DN
Fx Fy Fz
Tubulures d’aspiration
Forces en N
∑F
Moments en Nm
Mx My Mz
∑M
∅DN
Tubulures de refoulement
Forces en N
Fx Fy Fz
∑F
Moments en Nm
Mx My Mz
∑M
3.6 Pressions et températures
admissibles
En principe, les valeurs de pressions et températures
stipulées sur la fiche technique et / ou dans la
confirmation de commande ainsi que sur la plaque
signalétique doivent être respectées. Des valeurs audelà ou en deçà de ces valeurs de référence sont
inadmissibles. Si aucune pression et / ou température
n’est stipulée sur la fiche technique et / ou dans la
confirmation de commande, respecter les limites de
pression d’arrivée et de température ambiante
suivantes :
LSB 100-france Page 42
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Pression d’arrivée (pression du système) =
Pression à l’entrée de la pompe : max. 5 bar
Température ambiante max. 40°C.
Lors de l’exploitation de la pompe, respecter
également les réglementations et prescriptions légales
en la matière (p.ex. DIN 4747 ou DIN 4752, section
4.5).
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 47

Instructions de montage, de service et de maintenance
Le recyclage des emballages s’effectue
Ne pas rester sous la charge pendante et
observer les règles générales de prévention
accidents. Avant la fixation sur son site de
fonctionnement définitif, il faut protéger la
pompe ou le groupe contre le basculement ou
Ne pas fixer les filins d’élingue aux œillets
de la pompe / du groupe hors
de sa suspension de transport peut provoquer
Pour tous les types de pompes, sauf :
50-32-315 - 65-40-315 - 80-50-315 - 100-65-315 - 125-80315 - 125-100-315
Seulement pour :
50-32-315 - 65-40-315 - 80-50-315 - 100-65-315 - 125-80315 - 125-100-315
Série LSB
Courbe Matériau du corps Description
A 1.4408 Acier austénitique
B 1.4517 Acier duplex
C
EN-GJS-400-18-LT
(0.7043)
Fonte à graphite sphéroïdal
Les limites de pression et de température stipulées
s’appliquent aux garnitures mécaniques standard.
Sur demande, les limites d’exploitation pour d’autres
matériaux peuvent être communiquées.
4. Transport, manutention, stockage
4.1 Transport, manutention
Dès la réception de la pompe / du groupe, vérifier
que la livraison est complète et contrôler l’absence
d’endommagements.
Le transport de la pompe / du groupe doit
s’effectuer avec précautions et selon les règles.
Eviter les chocs brutaux.
Maintenir la position de transport imposée à la
sortie d’usine. Respecter également les consignes
figurant sur l’emballage.
Le côté d’aspiration et le côté de refoulement de la
pompe doivent rester fermés par un bouchon
durant le transport et le stockage.
3.7 Eau de condensation
Pour les moteurs soumis à de fortes variations de
température ou à des conditions climatiques
extrêmes, l’utilisation d’un moteur à chauffage anticondensation est recommandée pour empêcher la
formation d’eau condensée à l’intérieur du moteur. Le
chauffage anti-condensation ne doit pas être branché
pendant l'exploitation du moteur.
annulaires du moteur ou aux arbres.
Tout glissement
des dommages corporels et matériels.
Illustr. 2
conformément à la réglementation en vigueur.
Les auxiliaires de levage (p.ex. chariot élévateur,
grue, système de grue, palan, filin d’élingue etc.)
doivent avoir les dimensions suffisantes et ne
doivent être exploités que par le personnel
autorisé.
Pour le levage, fixer la pompe / le groupe à des
attaches solides, telles que corps, brides ou
cadre. Le bon choix des attaches pour le transport
par grue figure sur l’illustration 2.
d’
le glissement.
LSB 100-france Page 43
Artikel Nr. 771076129
4.2 Stockage / conservation
Les pompes et groupes qui sont stockés pendant une
période prolongée avant leur mise en service (6 mois
max.) doivent être protégés contre l’humidité, les
vibrations et les impuretés (en les enveloppant dans
du papier huilé ou dans des feuilles en matière
plastique). En principe, ils doivent être conservés dans
un lieu à l’abri de toute influence extérieure, p.ex. sous
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 48

Instructions de montage, de service et de maintenance
Prévoir un espace suffisant pour l’entretien et la
iculièrement pour remplacer
le moteur d’entraînement ou l’intégralité du
groupe. Le ventilateur du moteur doit pouvoir
aspirer une quantité suffisante d’air de
refroidissement. Prévoir donc au moins 10 cm
Le dimensionnement de ces selles d’appui
atoires varie selon les utilisations et doit
donc être réalisé par un spécialiste
La pompe ne doit en aucun cas servir de point
de fixation pour la conduite. Les forces
conduites ne doivent
un toit sec. Pendant tout ce temps, les tubulures
d’aspiration et de refoulement tout comme les autres
buses d’admission et d’écoulement doivent toujours
rester fermées par des brides ou des bouchons
d’obturation.
En cas de période de stockage prolongée, des
mesures de conservation peuvent s’avérer
nécessaires au niveau de la surface façonnée de
certains éléments ainsi qu’un emballage protégeant
contre l’humidité!
5. Mise en place, montage
Série LSB
5.1 Installation du groupe
Les pompes doivent être solidement boulonnées à un
soubassement ferme (p.ex. socle en béton, plaque
d’acier, poutres en acier etc.). Le soubassement doit
pouvoir résister à toutes les sollicitations éventuelles
durant l’exploitation. La configuration de la
construction doit être préparée en fonction des
dimensions du dessin à l’échelle. Les socles en béton
doivent avoir une solidité suffisante conforme à DIN
1045 ou à toute autre norme équivalente (min. BN 15)
afin de permettre une mise en place sûre garantissant
une parfaite fonctionnalité.
Laisser prendre le socle en béton avant l’installation
du groupe. Sa surface doit être horizontale et plane.
Pour l’emplacement des béquilles de la pompe et des
boulons du socle de base, consulter le dessin à
l’échelle.
Il est possible d’utiliser comme boulons de socle des
ancres à expansion, des boulons d’ancrage à coller ou
des points d’ancrage scellés avec le socle (tiges
filetées à scellement à queue de carpe).
maintenance, part
d’écart entre la grille d'aspiration et le mur etc.
Ajuster la pompe à l’aide d’un niveau à bulle d’air
(au niveau de la tubulure de refoulement) lors de
sa mise en place sur le socle. L’écart de
positionnement admissible est de 0,2 mm/m. Les
plaques de calage doivent être posées à proximité
immédiate des points d’ancrage et être couchées
de manière plane.
S’il y a transmission de vibrations sur le socle de
la pompe à partir d’éléments d’installation placés à
proximité, il devra être protégé à l’aide de selles
d’appui antivibratoires adéquates (les vibrations
extérieures pouvant endommager le logement).
Afin d’éviter la transmission de vibrations sur des
éléments situés à proximité, le socle doit être
assis sur une selle d’appui antivibratoire
adéquate.
antivibr
expérimenté.
LSB 100-france Page 44
Artikel Nr. 771076129
5.2 Raccordement des conduites à la
pompe
admissibles au niveau des
pas être dépassées. Voir chapitre 3.5.
5.2.1 Conduite d’aspiration et de refoulement
La présentation et le dimensionnement des
conduites doivent pouvoir garantir une parfaite
arrivée à la pompe pour éviter de porter préjudice
au fonctionnement de la pompe. Accorder une
attention toute particulière à l’imperméabilité à l’air
des conduites d’aspiration et au respect des
valeurs NPSH. En mode d’aspiration, disposer la
conduite d’aspiration dans la partie horizontale de
la pompe en position légèrement ascendante afin
d’éviter la formation de poches d’air. En mode
d’arrivée, disposer la conduite d’arrivée en
position légèrement descendante vers la pompe.
Ne prévoir aucune robinetterie ou raccord à
proximité immédiate de l’entrée de la pompe.
En cas de refoulement à partir de réservoirs sous
vide, la mise en place d’une conduite
compensatrice de vide offre un avantage certain.
La conduite doit présenter une section nominale
de passage minimale de 25 mm et déboucher audessus de la plus haute hauteur admissible de
liquide dans le réservoir.
Une conduite supplémentaire obturable (illustr. 3)
- conduite compensatrice de refoulement de la
pompe - facilite le désaérage de la pompe avant le
démarrage.
Illustr. 3
Veiller au niveau du tracé de la conduite à garantir
l’accessibilité à la pompe pour l’entretien, le
montage, le démontage et la vidange.
"Forces et moments admissibles au niveau des
tubulures de la pompe ..." Voir chapitre 3.7.
Si des compensateurs sont utilisés dans les
conduites, ils doivent être arrêtés de manière à ce
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 49

Instructions de montage, de service et de maintenance
Ces raccordements sont vitaux pour le bon
En cas d’utilisation en zone 1 et 2, utiliser un
Le raccordement électrique ne peut être
effectué que par un spécialiste autorisé.
Respecter les règles et dispositions en vigueur
trotechnique, en particulier au niveau
des mesures de sécurité. Respecter également
les dispositions nationales applicables au
niveau local des compagnies d’alimentation en
Dans les atmosphères explosibles, respecter
14 pour l’installation
Un contrôle du sens de rotation ne peut se faire
que si la pompe est remplie. Toute marche à
niveau
La mise en service de l’installation est réservée
personnes maîtrisant les règles de sécurité
locales et les instructions de service présentes
(notamment leurs consignes et règles de
que la pompe ne soit pas sollicitée de manière
inadmissible par la pression dans la conduite.
Avant le raccordement à la pompe : Retirer les
chapeaux de protection des tubulures de la
pompe.
Avant la mise en service, nettoyer impérativement
Si un nouveau moteur est utilisé au cours des
réparations, respecter les points suivants :
Le moteur doit être conforme aux exigences
le système de conduites, les robinetteries
installées et les appareils en essuyant les gouttes
de sueur, en éliminant le mâchefer etc. Les
Bien nettoyer moignons et les brides du nouveau
installations directement ou indirectement en
contact avec des systèmes d’eau potable doivent
être libérées de toute impureté éventuelle avant
leur installation et leur mise en service.
5.4 Raccordement électrique
Pour la protection de la garniture d'arbre
(particulièrement des garnitures mécaniques)
contre les impuretés au moment du démarrage,
nous recommandons : filtre 800 microns dans la
conduite d’aspiration / de refoulement.
Si le système de conduites est soumis à pression
par une pompe incorporée : respecter la pression
maximale admissible à la sortie du corps de la
pompe ou de la garniture d’arbre. Voir fiche
technique et / ou confirmation de commande.
En cas de vidange de la conduite après épreuve
de pression, conserver la pompe de manière
adéquate (sinon fixation par la rouille et problèmes
au moment de la mise en service).
5.2.2 Raccordements supplémentaires
Avant d’entamer les travaux, vérifier la compatibilité
entre les données stipulées sur la plaque signalétique
du moteur et le réseau électrique local. Effectuer la
connexion à la borne des câbles d’alimentation
électrique du moteur d’entraînement accouplé
conformément au plan de couplage du fabricant du
moteur. Prévoir un disjoncteur-protecteur.
Installer les conduites d’arrêt et d’écurage
éventuellement nécessaires. Les conduites, les
pressions et les quantités nécessaires sont stipulées
sur la fiche technique et / ou dans la confirmation de
commande. Pour le positionnement et la taille des
raccordements à la pompe, voir l’annexe
“Raccordements“.
fonctionnement et donc indispensables !
Une conduite pour évacuer d’éventuelles fuites de la
garniture d’arbre est recommandée. Pour le
raccordement, voir l’annexe "Raccordements".
5.3 Entraînement
Respecter les consignes d’exploitation du
fabricant du moteur.
5.5 Contrôle final
Le groupe doit pouvoir pivoter facilement au niveau de
l’arbre d’emboîtement à l’aide de la main.
Série LSB
moteur avec une certification ATEX valable.
stipulées dans la fiche 1220.1A608D (en cas de
besoin, la demander auprès du fabricant).
moteur (éliminer les restes de peinture).
en élec
énergie.
par ailleurs IEC 60079électrique.
sec entraîne de graves dommages au
de la pompe.
6. Mise en service, exploitation, mise hors service
aux
sécurité).
6.1 Première mise en service
Avant de brancher la pompe, vérifier que les points
suivants ont été respectés et appliqués :
Aucune mesure de lubrification n’est nécessaire
avant la première mise en service.
LSB 100-france Page 45
Artikel Nr. 771076129
La pompe et la conduite d’aspiration doivent être
complètement remplies de liquide lors de la mise
en service.
Faire pivoter une nouvelle fois avec la main le
groupe et vérifier qu’il tourne facilement et
uniformément.
Vérifier que la tôle de protection de la lanterne est
montée et que tous les dispositifs de sécurité sont
prêts à l’exploitation.
Brancher les conduites d'arrêt et d’épurage
éventuellement en place. Pour les quantités et
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 50

Instructions de montage, de service et de maintenance
loitation avec un organe d’arrêt fermé
dans la conduite d’aspiration et / ou de
pression défaillante, la créer par étranglement
au niveau de la conduite de refoulement
anne que légèrement). Dès que la
pression est entièrement atteinte, ouvrir
Si la pompe n’atteint pas la hauteur
manométrique prévue ou si des bruits et
vibrations atypiques se manifestent : arrêter la
ercher les
Faire preuve d’une précaution particulière avant
de toucher les éléments chauds de la machine
et au niveau non protégé de la garniture d’arbre.
llations à commande automatique
peuvent à tout moment se remettre en marche.
Apposer les panneaux d’avertissement
Les limites d’exploitation de la pompe / du
empérature,
de puissance et de vitesse de rotation sont
stipulées sur la fiche technique et / ou dans la
confirmation de commande et elles doivent être
Ne pas oublier que le refoulement de liquides
contenant des éléments abrasifs entraîne une
jeure au niveau de l’hydraulique et du
joint d’arbre. Les intervalles d’inspection doivent
être réduits en conséquence par rapport aux
pressions, se référer à la fiche technique et / ou à
la confirmation de commande.
Ouvrir la vanne de la conduite d’aspiration ou
d’arrivée.
Régler la vanne du côté de refoulement à 25%
env. de la cylindrée de référence. Pour les
pompes ayant une section nominale de passage
au niveau des tubulures de refoulement, inférieure
à DN 200, la vanne peut aussi rester fermée au
moment du démarrage.
6.4 Limites de l’exploitation
Vérifier que le groupe est bien raccordé
électriquement à tous les dispositifs de protection
selon les consignes.
Mettre la pompe brièvement en marche et l’arrêter
pour contrôler le sens de rotation. Il doit être
conforme à la flèche du sens de rotation figurant
sur la lanterne d’entraînement.
La puissance stipulée sur la plaque signalétique
6.2 Brancher la machine d’entraînement.
Immédiatement (max. 10 secondes pour une
alimentation électrique de 50 Hz et max. 7
secondes pour une alimentation de 60 Hz) après
accélération à la vitesse de régime, ouvrir la
vanne au niveau de la conduite de refoulement et
régler ainsi le point de fonctionnement dynamique
souhaité. Respecter impérativement les valeurs
de refoulement stipulées sur la plaque
signalétique, sur la fiche technique et / ou dans la
confirmation de commande. Toute modification
doit être soumise au préalable à l’avis du
fabricant!
Toute exp
refoulement est interdite !
En cas de démarrage contre une contre-
(n’ouvrir la v
contrela vanne.
Eviter toute modification brutale de température
La pompe et la machine d’entraînement doivent
6.4.1 Débit min. / max.
Dans la mesure où aucune autre donnée ne figure
dans les courbes caractéristiques ou sur les fiches
techniques, les données à appliquer sont :
Q
min
Q
min
Q
max
Q
BEP
*) à condition que NPSH
6.4.2 Liquides abrasifs
Série LSB
Les insta
adéquats sur l’installation.
groupe en matière de pression, de t
respectées impérativement !
de la machine d’entraînement ne doit pas être
dépassée.
(choc thermique).
fonctionner uniformément et sans aucune
vibration et être contrôlées au moins une fois par
semaine.
= 0,1 x Q
= 0,3 x Q
= 1,2 x Q
= débit à rendement optimum
pour une courte exploitation
BEP
en exploitation continue
BEP
en exploitation continue )*
BEP
installation
> (NPSH
pompe
+ 0,5 m)
usure ma
pompe (voir chapitre 6.7) et en ch
causes (voir chapitre 10).
6.3 Remise en service
En principe, la remise en service s’effectue comme la
première mise en service. Mais le contrôle du sens de
rotation et du libre fonctionnement du groupe n’est pas
utile.
Une remise en service automatique ne peut se faire
qu’après avoir vérifié que la pompe reste remplie de
liquide à l’arrêt.
LSB 100-france Page 46
Artikel Nr. 771076129
intervalles normaux.
6.4.3 Fréquence d’enclenchement admissible
La fréquence d’enclenchement admissible de la
pompe ne doit pas être dépassée. Voir diagramme 6.
100,0
10,0
max. zulässige Anläufe pro Stunde
1,0
fréquence max. d´enclenchements adm./h
1 10 100 1000
Diagramme 6
puissance d´entrainement [kW]
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 51

Instructions de montage, de service et de maintenance
Dans les atmosphères explosibles, il est
recommandé de contrôler la température des
Afin de prolonger la durée de vie de la pompe
ou installation, effectuer régulièrement les
Pour les moteurs électriques, voir la fréquence
d’enclenchement admissible stipulée dans les
instructions de service et de maintenance du
fournisseur du moteur.
En cas de valeurs divergentes, adopter la plus petite
fréquence d’enclenchement.
6.8 Stockage / arrêt prolongé
6.8.1 Stockage de nouvelles pompes
Si la mise en service n’a lieu que longtemps après la
livraison, il est recommandé de prendre les mesures
de stockage suivantes pour la pompe :
Stocker la pompe dans un endroit sec.
Faire pivoter la pompe à la main une fois par
6.5 Lubrification
L’élément de pompe ne possédant aucun palier, toute
lubrification est superflue.
Pour ce qui de la lubrification éventuellement
nécessaire des paliers du moteur, consulter les
recommandations stipulées dans les instructions de
service et de maintenance fournies par le fournisseur
du moteur.
6.8.2 Mesures en cas d’arrêt prolongé
La pompe reste montée en état de service :
Effectuer à intervalles réguliers des courses
6.6 Contrôle
paliers et les vibrations de la pompe.
travaux de contrôle et d’entretien.
Contrôler l’étanchéité de la pompe au moins une
fois par semaine.
Vérifier chaque semaine le bon fonctionnement
des options de régulation et de contrôle
d’éventuels système d’arrêt et d’épurage en place.
L’eau de refroidissement doit être tiède à la sortie.
Les pompes qui, par leur destination, sont
exposées à une attaque chimique ou à une usure
abrasive doivent être inspectées périodiquement
afin de déceler toute altération chimique ou
abrasive. La première inspection doit se faire six
mois après la première mise en service. Tout
autre intervalle d’inspection est à définir en
fonction de l’état de la pompe.
6.7 Mise hors service
Fermer la vanne d’arrêt de la conduite de
refoulement immédiatement (max. 10 secondes)
avant d’arrêter le moteur. Opération inutile si
l’installation est équipée d’un clapet de retenue
sous charge.
Mettre à l’arrêt la machine d’entraînement. Veiller
l’absence de perturbations lors du ralentissement.
Fermer la vanne du côté d’aspiration.
Fermer les circuits auxiliaires.
En cas de risque de gel, vider intégralement la
pompe et les conduites.
Si la pompe reste sous pression et température
même à l’arrêt : Ne pas débrancher les systèmes
d’arrêt et d’épurage en place.
Le blocage de la garniture d’arbre doit rester
branché quand il y a risque d’aspiration d’air (en
cas d’arrivée à partir d’installations sous vide ou
d’exploitation parallèle avec une conduite
d’aspiration commune).
LSB 100-france Page 47
Artikel Nr. 771076129
6.8.3 Immobilisation prolongée
Pour la remise en service, procéder comme pour la
première mise en service (voir chapitre 6).
a) Pompes remplies
Brancher brièvement les pompes de réserve et les
Si la pompe de réserve est sous pression et
Remplacer les paliers du moteur au bout de 5
b) Pompes vides
La faire pivoter à la main au moins 1x par
Remplacer les paliers du moteur au bout de 5
Série LSB
mois.
d’essai d’au moins 5 minutes. Les intervalles entre
les courses d’essai dépendent de l’installation.
Néanmoins, effectuer une course d‘essai au
moins une fois par semaine.
redébrancher aussitôt 1 x par semaine.
Eventuellement et alternativement les mettre en
service comme pompe principale.
température : Ne pas débrancher les systèmes
d’arrêt et d’épurage en place.
ans.
semaine (ne pas la brancher pour éviter toute
marche à sec).
ans.
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 52

Instructions de montage, de service et de maintenance
Les interventions au niveau de la pompe ou de
l’installation ne sont effectuées qu’à l’arrêt.
nce sont
effectués exclusivement par des personnes
expérimentées, disposant de la formation
requise et maîtrisant le contenu des instructions
de service présentes ou par le personnel S.A.V
vement les chapitres 2 et 8
Ne pas nettoyer la pompe avec de l’eau sous
Les réparations au niveau de la pompe ou de
l’installation ne peuvent être effectuées que par
un personnel spécialisé ou autorisé par le
nt le chapitre 2 ainsi que le
Les pompes qui véhiculent des liquides pouvant
écontaminées.
L’écoulement du liquide de refoulement doit
exclure tout danger pour les personnes et
l’environnement. Respecter les réglementations
légales. Dans le cas contraire, il y a danger
urer que les pompes, groupes ou
éléments démontés ne puissent pas basculer
Ne faire usage d’une flamme nue (lampe à
souder etc.) pour démonter que s’il n’y a aucun
risque d’explosion ou d’émanation de vapeurs
pièces détachées d’origine.
Veiller à utiliser l’exécution et le matériau
Les interventions qui requièrent une contrainte
dynamique ne peuvent être effectuées qu’en
dehors d’atmosphères explosibles ou
ils ne produisant pas
7. Entretien, maintenance
Série LSB
7.1 Consignes générales
Respecter impérativement le chapitre 2.
Les travaux d’entretien et de maintena
du fabricant.
7.2 Garnitures mécaniques
Consulter impérati
avant d'ouvrir la pompe.
Si du liquide de refoulement s’écoule au goutte à
goutte au niveau de la garniture mécanique, cela
signifie qu’elle est endommagée et qu’elle doit être
remplacée.
Remplacer la garniture mécanique conformément aux
"Consignes de montage de la garniture d’arbre ".
8. Démontage de la pompe et réparation
7.3 Paliers du moteur
Après 5 ans en moyenne, la graisse est tellement
usée dans les paliers du moteur qu’il est recommandé
de remplacer les paliers. Néanmoins, les paliers
doivent être remplacés au plus tard après 25000
heures de service ou en fonction des instructions de
maintenance du fournisseur du moteur si celui-ci
recommande des intervalles de maintenance plus
courts.
7.4 Nettoyage de la pompe
Un encrassement extérieur au niveau de la
pompe nuit à l’évacuation de la chaleur. Nettoyer
à intervalles réguliers (en fonction du degré
d’encrassement) la pompe à l’eau.
pression (p.ex. nettoyeur haute pression) risque d’infiltration d’eau au niveau du palier.
8.1 Consignes générales
fabricant.
Lire impérativeme
chapitre 4.1 avant de démonter la pompe.
Sur demande, des monteurs expérimentés du S.A.V.
sont disponibles pour le montage et les réparations.
nuire à la santé doivent être d
mortel !
Avant de procéder au démontage, s’assurer que
le groupe ne puisse être remis en service.
Le corps de la pompe doit être sans pression et
vide.
Tous les organes d’arrêt des conduites
d’aspiration, d’arrivée et de refoulement doivent
être fermés.
Toutes les pièces doivent être à température
ambiante.
S’ass
ou rouler.
LSB 100-france Page 48
Artikel Nr. 771076129
nocives.
N’utiliser que des
adéquats.
8.2 Généralités
uniquement avec des out
d’étincelles.
En principe, le démontage et le montage s’effectuent
conformément au plan-coupe adéquat.
Seuls les outils courants dans le commerce sont
indispensables.
Avant le démontage, s’assurer de bien avoir toutes les
pièces détachées nécessaires.
N’effectuer que le démontage strictement nécessaire
au remplacement de la pièce à réparer.
8.3 Démontage et montage des grilles de
protection de la lanterne d’entraînement
Les grilles de protection (680) sont encastrées dans
les fenêtres de la lanterne d’entraînement (681).
Pour le démontage, introduire de 4 cm. un tournevis à
travers la rangée de trous la plus inférieure de la grille
de protection. Puis tirer le manche du tournevis vers le
haut jusqu’à ce que le bord inférieur de la grille se
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 53

Instructions de montage, de service et de maintenance
Ne tirer le tournevis vers le haut que dans la
proportion absolument nécessaire à
l’encastrement de la grille de protection dans la
ction, après
encastrement, est encore un peu trop lâche
Redémonter la grille de protection, l’aplatir un
Lire les "consignes de montage de la garniture
pneu
qu’au niveau des ailettes de la roue mobile afin
soulève légèrement de la fenêtre. Retirer à présent le
tournevis avec toute la grille de protection de la
fenêtre (voir illustr. 8).
Série LSB
démontage, elle ne fléchisse pas vers le bas ou
qu’elle n’exerce aucune pression par le haut sur la
volute. Exemple de fixation voir illustr. 9.
Illustr. 8
Pour le démontage, introduire de 4 cm. un tournevis à
travers la rangée de trous la plus inférieure de la grille
de protection. Puis placer la partie supérieure de la
grille de protection au niveau du bord supérieur de
l’ouverture de la fenêtre. Tirer à présent le manche du
tournevis vers le haut jusqu’à ce que la flexion de la
grille de protection soit suffisante pour la pousser
jusqu’à la butée dans la fenêtre de la lanterne
d’entraînement.
fenêtre. Si la grille de prote
dans la fenêtre :
peu et la réencastrer.
8.4 Démontage de l’unité de marche
L’unité de marche comprend tous les éléments de la
pompe à l’exception de la volute (102V). Les pompes
étant construites en processus, la volute (102V) peut
rester sur le socle de base et dans la conduite dans la
mesure où ce n’est pas la volute qu’il faut réparer.
Vider la volute (102V) par le biais du bouchon de
vidange (912.11).
Desserrer les raccords à vis d’éventuelles
conduites d’arrêt ou à eau d’épurage.
Desserrer le raccord à vis de la béquille (183) au
niveau du socle de base (il n’existe pas sur toutes
les séries).
Accrocher l’unité de marche au dispositif de
levage de telle manière qu’au moment du
Illustr. 9
Dévisser complètement le raccord à vis du corps
(boulon à tête 901.11).
Tirer axialement l’unité de marche hors de la
volute. Il est possible d’utiliser les vis de
dégagement (901.42).
8.5 Démontage de la roue mobile
d’arbre" jointes.
Si la roue mobile a des ailettes dorsales, vérifier
avant de poursuivre le démontage le jeu axial "a"
entre la roue mobile (230) et le couvercle de corps
(161). Pour estimer le jeu mesuré, voir le chapitre
8.8.1.
Desserrer l’écrou de la roue mobile (922) en
frappant légèrement et brièvement sur le tournevis
(filetage à droite). Maintenir éventuellement à
l’aide d’un poinçon dans le forage transversal de
l’arbre d’emboîtement (au niveau des brides).
Retirer la roue mobile (230) à l’aide de deux
tournevis ou de démonte-pneu (Illustr. 10). Retirer
la clavette (940.31).
N’appliquer les tournevis ou démonte-
de ne pas déformer les canaux de circulation.
Tout autre démontage ou l’assemblage de l’unité
de marche est plus facile en position verticale.
Attention au risque de basculement !
LSB 100-france Page 49
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 54

Instructions de montage, de service et de maintenance
t les
garnitures en graphite ne peuvent être utilisés
Si les valeurs "d’état usé" sont atteintes ou
dépassées, les pièces concernées doivent être
Tout dépôt au niveau de la roue mobile (230), de la
volute (102V) ou du couvercle de corps (161) est à
éliminer.
8.8.1 Interstice étanche au niveau de la roue
mobile
Côté d’aspiration de la
roue mobile
Illustr. 10
8.6 Démontage de la garniture d’arbre
Lire “Consignes de montage de la garniture
d’arbre“ avant de procéder au démontage du
couvercle de corps.
Desserrer l’écrou à six pans (902.32) (qui n’est
pas sur toutes les pompes) et retirer le couvercle
de corps (161) de la lanterne du corps de palier
(344).
Côté d’entraînement de la roue mobile
Uniquement pour les tailles de pompe
100-65-315
125-80-315
125-100-315
150-125-315
Diamètre nominal D (mm)
8.7 Démontage de l’arbre d’emboîtement
Desserrer le raccord à vis (920.41) et retirer le
moteur avec l’arbre d’emboîtement (210) de la
lanterne d’entraînement (341).
Desserrer le raccord à vis radial de l’arbre
d’emboîtement (904.41 et 904.42 - vis sans tête)
et l’arbre d’emboîtement (210) de l’arbre du
moteur. Introduire éventuellement comme
auxiliaire (pour décoller) un tournevis résistant
dans le forage transversal de l’arbre
d’emboîtement, faire pression sur la surface
extérieure du moteur et pousser ainsi les deux
arbres l’un par rapport à l’autre.
8.8 Remise en état
Nettoyer soigneusement toutes les pièces après le
démontage et vérifier qu’elles ne sont pas usées.
Remplacer les pièces usées ou endommagées par de
nouvelles (pièces détachées).
En principe, utiliser de nouveaux éléments
d’étanchéité.
Tous les éléments d’étanchéité en PTFE e
qu’une seule fois.
Dans la plupart des cas, il est opportun, voire
indispensable, en cas de détérioration, de remplacer
la garniture d’arbre.
Interstice
radial
s (mm)
a (mm)
Pour les volutes (102V) avec une bague à fente
(502.11) ou les couvercles de corps (161) avec une
bague à fente (502.31), les possibilités suivantes
permettant de rétablir l’interstice correct peuvent être
appliquées :
c) Remplacer la roue mobile (230) et la bague à fente.
Les dimensions d’origine sont alors rétablies.
d) Fabriquer des bagues à fente d’un diamètre interne
adéquat et rétablir ainsi la largeur d’interstice d’origine.
Se mettre en contact avec le fabricant.
Pour les volutes (102V) ou les couvercles de corps
(161) qui n’en possèdent pas, il est possible, au cours
d’une réparation de les pourvoir d’une bague à fente.
Pour ce faire, un travail ultérieur (retorsion) dans la
volute ou le couvercle de corps est nécessaire. Se
mettre en contact avec le fabricant.
8.9 Montage
8.9.1 Généralités
Le montage se fait dans l’ordre inverse du démontage.
Les points suivants doivent cependant être respectés :
Ailettes dorsales de la
roue mobile
60
neuf
usé
neuf
usé
min. 0,15 0,17 0,20 0,22 0,25
max. 0,19 0,22 0,24 0,27 0,30
0,78 0,85 0,90 1,05 1,15
0,8 - 1,2 Interstice axial
max. 1,7
68
85
impérativement changées.
Série LSB
100
155
120
135
175
220
LSB 100-france Page 50
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 55

Instructions de montage, de service et de maintenance
Avant d’utiliser un lubrifiant, s’assurer qu’il n’y a
de réaction grave entre le liquide
Avant la mise en service, remonter ou raccorder
impérativement toutes les conduites auxiliaires
Veiller à ce que le montage se fasse dans la plus
grande propreté.
Enduire éventuellement les ajustements étroits
entre l’arbre d’emboîtement (210) et l’arbre du
moteur ou la roue mobile (230) et l’arbre (210)
ainsi que les filetages d’un lubrifiant adéquat
(p.ex. Molykote / Never-Seeze) afin que ce
montage et le prochain démontage soient plus
faciles.
aucun risque
de refoulement et ce lubrifiant.
Serrer les vis avec les couples de rotation
suivants :
Raccord à vis
Vis du corps
Toutes les autres vis
taille
M12
M16 105 150
M20 210 305
M10 35 50
M12 60 90
M16 150 220
Moment de torsion en Nm
Filetage
lubrifié
35 50
Filetage sec
Ne pas faire usage d’une force démesurée.
Pour le montage de l’arbre d’emboîtement, voir
chapitre 8.9.2.
Pour le montage de la garniture d’arbre, se référer
à la description à part "Consignes de montage de
la garniture d’arbre" et au chapitre 8.5.
Pour les roues mobiles à ailettes dorsales, vérifier
l’interstice axial correct entre les ailettes dorsales
et le couvercle de corps (161) après avoir monté
la roue mobile (230) et avoir serré fortement
l’écrou de la roue mobile (922). Voir chapitre
8.8.1.
Après avoir assemblé l’unité de marche et l’avoir
incorporée à la volute, faire pivoter l’arbre pour
vérifier que la pompe fonctionne librement. Les
garnitures d’arbre provoquent une certaine
résistance à la rotation. Néanmoins, aucun
frottement ne doit être perceptible entre les parties
métalliques.
et dispositifs de sécurité et remettre en marche.
8.9.2 Montage de l’arbre d’emboîtement
Insérer la clavette sur le moignon du moteur.
Enduire de lubrifiant le moignon de l’arbre du
moteur (voir point 8.9.1.).
Pousser l’arbre d’emboîtement aussi loin que
possible sur l’arbre du moteur jusqu’à ce que la
cote A soit atteinte (voir illustr. 11 et tableau).
A l’aide d’un foret hélicoïdal avec une pointe de
90°, chanfreiner l’arbre du moteur à travers les
forages radiaux de l’arbre d’emboîtement d’une
profondeur de 2-3 mm env. (voir illustr. 11).
Retirer les particules du trou taraudé (p.ex. avec
de l’air comprimé), serrer les vis sans tête (904.41
et 904.42) et consolider (p.ex. avec Omnifit 100 M
ou Loctite).
LSB 100-france Page 51
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Vérifier la rotation de l’arbre d’emboîtement par
40-25-160 157 157 197 197 197 232 - -
40-25-200 157 157 197 197 197 232 - -
40-25-250 162 162 202 202 202 237 237 237
50-32-160 157 157 197 197 197 232 - -
50-32-200 157 157 197 197 197 232 - -
50-32-250 162 162 202 202 202 237 237 237
50-32-315 - - 202 202 197 237 237 237
65-40-160 157 157 197 197 197 232 - -
65-40-200 157 157 197 197 197 232 232 -
65-40-250 162 162 202 202 202 237 237 237
65-40-315 - - 202 202 197 237 237 237
80-50-160 157 157 197 197 197 232 232 -
80-50-200 157 157 197 197 202 232 232 232
80-50-250 - 162 202 202 202 237 237 237
80-50-315 - - 202 202 202 237 237 237
100-65-160 162 162 202 202 202 237 237 237
100-65-200 - 162 202 202 202 237 237 237
100-65-250 - 162 202 202 206 237 237 237
100-65-315 - - 206 206 202 241 241 241
125-80-160 - 162 202 202 202 237 237 237
125-80-200 - 162 202 202 202 237 237 237
125-80-250 - - 202 202 202 237 237 237
125-80-315 - - - 206 206 241 241 241
125-100-200 - - 202 202 202 237 237 237
125-100-250 - - 216 216 216 251 251 251
125-100-315 - - - - 206 241 241 241
150-125-250 - - - - 216 251 251 251
150-125-315 - - - - - 241 241 241
200-150-250 - - - - - 251 251 251
Série LSB
rapport à la bride de moteur à l’aide d’un
comparateur à cadran (voir illustr. 11.). La
déviation de l’aiguille du comparateur à cadran
doit être au plus de 0,1 mm.
Illustr. 11
Type
80 90 100 112 132 160 180 200
Cote A pour les tailles
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 56

Instructions de montage, de service et de maintenance
délais d’approvisionnement et
pour assurer une disponibilité optimale, nous
préconisons de stocker les pièces détachées
requises notamment pour les exécutions en
matériaux spéciaux et les garnitures
Arbre avec clavettes et
Autres joints
Conserver les pièces détachées dans un
e est susceptible de
provoquer des risques corporels ou des dégâts
matériels lourds, prévoir un nombre suffisant de
pompes de réserve. Et contrôler régulièrement
Conserver les pompes de réserve
Série LSB
9. Recommandations pour les pièces détachées, pompes de réserve
9.1 Pièces détachées
Sélectionner des pièces détachées susceptibles de
fonctionner en exploitation continue pendant deux
ans. Si aucune autre directive n’est à respecter, le
nombre d’unités pour les pièces détachées indiqué
dans la liste ci-après est recommandé (selon DIN
24296).
En raison des
Commande des pièces détachées :
Type :
S/N (N° de commande):
Désignation pièce:
Schéma de coupe:
Tous les renseignements figurent sur la fiche
technique et / ou dans la confirmation de commande
et les schémas (coupe) correspondants.
endroit sec et à l’abri de la poussière !
mécaniques.
Nombre de pompes
Pièces détachées
Roue mobile
Bague à fente
écrous
Joints du corps de
pompe jeux
Garniture mécanique
jeux 4 6 8 8 9 10 100%
jeu
(y compris pompes de réserve)
2 3 4 5 6/7 8/9 10/+
Nombre d’unités de pièces détachées
1 1 1 2 2 2 20%
2 2 2 3 3 4 50%
1 1 1 2 2 2 20%
4 6 8 8 9 12 150%
1 1 2 2 2 3 25%
9.2 Pompes de réserve
Si la défaillance d’une pomp
leur bon fonctionnement (voir chapitre 6.8.).
conformément aux consignes du chapitre 6.8 !
10. Dysfonctionnements - origine et réparation
_____________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________
__________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
Les remarques concernant l’origine et la réparation de
dysfonctionnements sont censées permettre un
diagnostic du mauvais fonctionnement. Le S.A.V. du
fabricant intervient en cas de pannes que l’exploitant
ne veut ou ne peut pas réparer lui-même. Pour les
réparations ou les modifications de la pompe
effectuées par l’exploitant, il faut observer notamment
les indications concernant la construction figurant sur
la fiche technique et / ou dans la confirmation de
commande ainsi que les stipulations du chapitre 2 de
ces instructions d’emploi. Le cas échéant, il faut
demander l’accord écrit du fabricant.
LSB 100-france Page 52
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 57

Instructions de montage, de service et de maintenance
Utiliser une roue mobile plus grande (vérifier la puissance
Comparer la vitesse de rotation de la machine d’entraînement
avec la vitesse de rotation prescrite pour la pompe (plaque
isseur de
nt
avec la vitesse de rotation prescrite pour la pompe (plaque
En cas de régulation de la vitesse (convertisseur de
Utiliser une roue mobile plus grande (vérifier la puissance
s résistances de la conduite d’arrivée / d’aspiration
(modifier le tracé et la section nominale de passage, ouvrir les
’amenée du courant (à effectuer
Remplacer éventuellement la roue mobile; vérifier que l’arbre
dapter à la pression du système / à la pression d’arrivée
Série LSB
Débit trop faible
Débit s’arrête après un certain temps
Hauteur manométrique trop faible
Hauteur manométrique trop élevée
Machine d’entraînement en surcharge
Marche perturbée de la pompe
Température trop élevée de la pompe
Température trop élevée au niveau de
la garniture d’arbre
Température trop élevée au niveau du
Contre-pression trop élevée Vérifier l’encrassement de l’installation, vanne ouverte
Vitesse de rotation trop grande Réduire la vitesse de rotation
Vitesse de rotation trop faible Augmenter la vitesse de rotation (vérifier la puissance
Diamètre de la roue mobile trop petit
Pompe ou conduite d’aspiration / d’arrivée bouchée Nettoyer
Poche d’air dans la conduite Désaérer
L’air est aspiré Augmenter le niveau du liquide
Aspiration d’air par la garniture d'arbre Nettoyer la conduite de barrage
Sens de rotation incorrect Permuter 2 phases du câble d
Débit trop faible Augmenter la quantité de refoulement (ouvrir la vanne, By-
Diamètre de la roue mobile trop grand Utiliser une roue mobile plus petite
Pompe et / ou conduite non remplies intégralement de
Hauteur d’aspiration trop importante / NPSH de
Densité et / ou viscosité du liquide véhiculé trop
Alimentation électrique incorrecte (propagation
Vibrations inhérentes à l’installation Demander des informations plus détaillées
logement
Contre-pression trop faible, débit trop grand Etrangler la vanne du côté de refoulement
Débit trop important Réduire la quantité de refoulement (étrangler la vanne)
Usure des pièces internes Remplacer les pièces usées
Palier défectueux Remplacer
Dispositif de décharge insuffisant Nettoyer les alésages de décharge au niveau de la roue mobile
Origine
Fuite au niveau de la pompe
Drainage trop important au niveau de
la garniture d’arbre
liquide
l’installation trop faible
élevée
Rainures et rugosité au niveau de l’arbre Remplacer la pièce
Dépôts au niveau de la garniture mécanique Nettoyer
Déséquilibrage de la roue mobile Eliminer l’engorgement / les dépôts
Forces des conduites trop importantes (groupe
gauchi)
diphasée)
Etoupage insuffisant Resserrer les vis
Réparation
Réduire les résistances dans la conduite de refoulement
(nettoyer le filtre, ...)
d’entraînement)
signalétique)
En cas de régulation de la vitesse (convert
fréquences), contrôler le réglage de la valeur de consigne
d’entraînement admissible)
Comparer la vitesse de rotation de la machine d’entraîneme
signalétique)
fréquences), contrôler le réglage de la valeur de consigne
pass)
d’entraînement admissible)
Remplir
Désaérer
Améliorer le tracé de la conduite
Augmenter le niveau du liquide
Augmenter la pression d’entrée
Réduire le
organes d’arrêt, nettoyer le tamis)
Vérifier et rétablir l’étanchéité au vide de la conduite
d’aspiration
Augmenter la pression de barrage
Remplacer la garniture mécanique
par un électricien spécialisé)
Demander des informations plus détaillées
Le cas échéant, remplacer la garniture mécanique
Prévoir éventuellement un épurage externe ou un quench
tourne parfaitement
Modifier (arrêter les conduites, compensateurs, etc.)
Plaque de base / socle correctement montés / coulés ?
Contrôler la tension de toutes les phases
Vérifier les raccords de câbles et les fusibles
Remplacer les joints
Remplacer les pièces usées (roue mobile, bagues à fente)
A
stipulées au moment de la commande
LSB 100-france Page 53
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Ausgabe 01/2010
Revision 02
Page 58

Instructions de montage, de service et de maintenance
doivent être
impérativement respectées afin de garantir une
installation, une exploitation et une maintenance
du moteur en toute sécurité. Toute personne qui
se voit confier ces tâches doit connaître le
mode d’emploi présent. L’inobservation de ce
mploi peut exonérer le fabricant de sa
Vérifiez que la tension de secteur correspond à
La mise à terre doit être effectuée avant tout
lation d’un interrupteur différentiel à haute
supplémentaire contre les décharges
Aucun fonctionnement à sec n’est permis. La
peut
blement la garniture
B1 Les remplacer par
11. Mode d’emploi pour les moteurs
Série LSB
Les instructions suivantes
mode d’e
responsabilité.
Branchement électrique
celle de la plaque signalétique.
autre branchement. On recommande
l’instal
sensibilité (30 mA), comme protection
électriques mortelles en cas de mise à la terre
insuffisante.
Connecter la pompe par l’intermédiaire d’un
interrupteur omnipolaire ou de tout autre dispositif
assurant la déconnexion omnipolaire (qui interrompt
tous les fils d’alimentation) de la pompe par rapport au
secteur électrique: la distance entre les contacts ne
devra pas être inférieure à 3 mm.
Enlever le couvercle du bornier en dévissant les vis de
fixation. Effectuer les connexions suivant les
indications figurant sous le couvercle pour les versions
monophasées et comme à la fig. 3 - 4.
La série monophasée a une protection contre la
surcharge incorporée. La protection de la série
triphasée doit être effectuée par l’utilisateur par
l’intermédiaire d’un coupe-circuit magnétothermique
réglé selon le courant nominal de la plaquette au
moyen d’un disjoncteur rapide ou d’un démarreur avec
déclencheur, relais de protection et fusibles en amont.
Le relais de protection doit être étalonné suivant la
valeur nominale du courant du moteur, indiquée sur la
plaque.
On peut étalonner le relais suivant une valeur de
courant légèrement inférieure à celle de pleine charge,
lorsque la pompe est certainement sous-chargée,
mais on ne peut pas étalonner la protection
thermoampèremétrique à une valeur supérieure à
celle de pleine charge.
Contrôle du sens de rotation pour les moteurs
triphasés
Ce contrôle peut être effectué avant de remplir la
pompe avec le liquide à pomper, pourvu que la pompe
ne tourne que par brèves impulsions.
faire tourner à sec, de façon continue,
abîmer irrémédia
mécanique.
Si la pompe ne tourne pas dans le sens inverse aux
aiguilles d’une montre, inverser deux fils de
l’alimentation.
LSB 100-france Page 54
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Recherche des pannes
INCONVENIENT CAUSE PROBABLE REMEDES
1. L’électropompe ne
démarre pas
2. La protection
contre la surcharge
intervient:
- accidentellement
- systématiquement C) Réglage incorrect
A) Absence de
tension de secteur
B) Fusibles grillés:
B1 Inadéquats
(courant
d’intervention trop
bas)
B2 Le moteur ou le
câble d’alimentation
sont endommagés
C) Intervention de la
protection contre la
surcharge
A) Absence
momentanée d’une
phase
D) La pompe a un
débit supérieur au
débit indiqué sur la
plaque
E) Liquide dense et
visqueux
POSSIBLES
A) Fournir
alimentation
électrique
des fusibles
appropriés
B2 Réparer le moteur
ou remplacer le câble
C) Réarmer la
protection. Si elle
intervient de nouveau
voir Pannes 2)
C) Régler suivant le
courant de la plaque
D) Fermer la vanne
en refoulement
jusqu’à ce que la
valeur du débit
coïncide avec celle
de la plaque
E) Déterminer la
puissance effective
nécessaire et
remplacer le moteur
en conséquence
Ausgabe 01/2010
Revision 02
Page 59

Instructions de montage, de service et de maintenance
Série LSB
LSB 100-france Page 55
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 60

Instructions de montage, de service et de maintenance
Toute personne qui se voit confier le montage,
tation, la mise en service
et la remise en état de la garniture mécanique
doit, outre ces instructions de montage,
connaître également les instructions de
montage, de service et de maintenance de la
pompe en question et notamment avoir lu et
pitre 8.1 "Consignes générales"
et le chapitre 8.2 "Généralités" qu’il respectera
Pour les pompes à exécution conforme à la
directive 94/9/CE (Atex95) en matière
d’atmosphères explosibles, consulter
rvice
supplémentaires de la garniture mécanique
Série LSB
Garniture mécanique simple sans chemise de protection d’arbre (code
d’exécution S1..2)
1. Règles de sécurité
le démontage, l’exploi
impérativement les instructions de se
concernant la protection contres explosions.
compris le cha
impérativement !
Les données suivantes n’ont qu’une valeur générale
dans la mesure où elles concernent la structure
interne de la garniture mécanique. Consulter les
particularités éventuelles sur la fiche technique de la
garniture mécanique ou dans les instructions fournies
par le fabricant de la garniture mécanique.
2. Description de l’exécution
Cette garniture mécanique est une garniture
mécanique simple avec des cotes de montage
conformes à EN 12756 (DIN 24960) exécution "K".
API Plan 02 / ISO Plan 00.
La chambre d’étanchement à cyclone patentée rend
superflu tout autre épurage de la chambre de la
garniture mécanique.
Pour ce qui est des matériaux et du domaine
d’exploitation des garnitures mécaniques utilisées,
consulter la fiche technique figurant dans les
instructions de service ou dans la confirmation de
commande.
Désignation des pièces :
161 Couvercle de corps
210 Arbre
230 Roue mobile
412.21 Joint torique
433 Garniture mécanique
502.31*) Bague à fente
524 Chemise de protection d’arbre
527 a) Bague de butée
560 b) Goupille
904.31 a) Vis sans tête
904.32*) Vis sans tête
924 Ecrou de la roue mobile
940.31 Clavette
LSB 100-france Page 56
Artikel Nr. 771076129
*) optionnel
a) n’existe pas pour tous les types de garnitures
mécaniques
b) seulement pour les garnitures mécaniques
avec joints toriques en PTFE
Sous réserve de modifications techniques !
Taille
nominale
de la
∅d1 ∅d
l
1K
7
A B
∅d
L
garniture
mécanique
33 33 48 42,5 7,5 50 19
43 43 61 45 7,5 52,5 28
53 53 73 47,5 10 57,5 38
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 61

Instructions de montage, de service et de maintenance
Réutiliser des garnitures mécaniques qui ont
été longtemps en service peut entraîner des
risques de fuite au niveau de la surface de
glissement après le remontage. Il est donc
recommandé de remplacer la garniture
niture
démontée peut être révisée par le fabricant et
servir de garniture mécanique de
euvent être utilisées des garnitures
mécaniques faisant l’objet d’une confirmation
En cas de modification du type de garniture
mécanique ou de changement de fabricant,
es à la
température de service maximale du liquide de
Veiller à la plus grande propreté ! Les surfaces
de glissement doivent tout particulièrement
demeurer propres, sèches et en parfait état. Ne
n plus de lubrifiant les surfaces
N’utiliser des graisses minérales ou des huiles
l'élastomère de la garniture mécanique résiste à
Avant d’utiliser un lubrifiant, s’assurer qu’il n’y a
aucun risque de réaction grave entre le liquide
èces nécessaires pour
que le montage se fasse rapidement. Les
lubrifiants n’agissant que peu de temps, la
mobilité et le réglage automatique de
Ne jamais pousser l’élastomère sur des bords
les de montage si
Pousser les garnitures mécaniques à soufflets
de telle manière qu’ils soient comprimés et non
3. Démontage de la garniture mécanique
Série LSB
Pour ce faire, utiliser le plan-coupe adéquat et la fiche
technique jointe de la garniture mécanique.
Démonter la pompe conformément aux
instructions de montage, d’exploitation et de
maintenance jusqu’au chapitre 8.6 inclus.
Retirer la bague de butée (527) (si elle existe) et
l’élément rotatif de la garniture mécanique (433)
de l’arbre (210). Consulter la fiche technique jointe
de la garniture mécanique pour savoir si les vis
d’arrêt au niveau de la garniture mécanique
doivent être desserrées auparavant.
Retirer l’élément stationnaire de la garniture
mécanique (433) du couvercle de corps (161).
4. Montage de la garniture mécanique
Pour ce faire, utiliser le plan-coupe adéquat et la fiche
technique jointe de la garniture mécanique.
Seules p
écrite de conformité selon la directive 94/9/CE.
vérifier à nouveau les données relativ
refoulement et à la classe de température.
pas enduire no
de glissement de la garniture mécanique.
Utiliser le lubrifiant qui accompagne
éventuellement la garniture mécanique de
remplacement.
qu’après s’être vraiment assuré que
Nettoyer le perçage de positionnement (∅d7) dans
le couvercle de corps (161) et la surface de l’arbre
(210).
mécanique par une nouvelle. La gar
remplacement.
Veiller au joint à plat point axial de l’unité
stationnaire dans le couvercle de corps. La
surface de glissement doit être exactement à la
verticale de l’arbre.
S’il y a une goupille d’ajustage (560), veiller à ce
qu’elle s’engrène avec la rainure de la garniture
mécanique sans toucher celle-ci.
Enfiler l’unité rotative de la garniture mécanique
sur l’arbre (210).
Faire concorder exactement la surface d’appui de
la garniture mécanique du côté de la roue mobile
avec le collier de l’arbre (dimension l1K). Pour les
garnitures mécaniques sans propres vis d’arrêt, la
bague de butée (527) sert de butée.
étirés lors du montage (risque de déchirure !).
Pour tout autre assemblage et pour le montage de
la pompe, consulter les instructions de montage,
de service et de maintenance du chapitre 8.
l’huile. Ne jamais utiliser de silicone.
de refoulement et ce lubrifiant.
Préparer toutes les pi
l’élastomère s’estompent peu après.
effilés. Utiliser des douil
nécessaire.
Presser uniformément l’élément stationnaire de la
garniture mécanique dans le couvercle de corps
(161). Utiliser éventuellement un poinçon à
surface souple. Une sollicitation inégale peut
entraîner une rupture de la surface de glissement.
Ne pas endommager la surface de glissement !
LSB 100-france Page 57
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 62

Instructions de montage, de service et de maintenance
Toute personne qui se voit confier le montage,
le démontage, l’exploitation, la mise en service
et la remise en état de la garniture mécanique
doit, outre ces instructions de montage,
ement les instructions de
montage, de service et de maintenance de la
pompe en question et notamment avoir lu et
compris le chapitre 8.1 "Consignes générales"
et le chapitre 8.2 "Généralités" qu’il respectera
conforme à la
directive 94/9/CE (Atex95) en matière
d’atmosphères explosibles, consulter
impérativement les instructions de service
supplémentaires de la garniture mécanique
lectionné de telle
sorte qu'il n’y ait aucun risque de réaction grave
ci et le liquide de refoulement. Le
liquide quench peut être contaminé par le
liquide de refoulement. L'exploitant veillera alors
Série LSB
Garniture mécanique simple avec quench sans chemise de protection
d’arbre (Code d’exécution S4..2)
1. Règles de sécurité
Pour les pompes à exécution
connaître égal
concernant la protection contres explosions.
Les données suivantes n’ont qu’une valeur
générale dans la mesure où elles concernent la
impérativement !
structure interne de la garniture mécanique.
Consulter les particularités éventuelles sur la fiche
technique de la garniture mécanique ou dans les
instructions fournies par le fabricant de la
garniture mécanique.
2. Description de l’exécution
Cette garniture mécanique est une garniture
mécanique simple avec des cotes de montage
conformes à EN 12756 (DIN 24960) exécution "K",
forme "U". API Plan 62 / ISO Plan 09. Vérifier la
résistance des matériaux dans la chambre de la
garniture mécanique (notamment l’élastomère) par
rapport au liquide quench.
La chambre du quench doit être irriguée de liquide
quench sans pression. Pour le raccordement, voir le
plan-coupe ci-après.
Le liquide quench doit être sé
entre celui-
à ce qu’il soit recyclé de manière adéquate.
La chambre d’étanchement à cyclone patentée rend
superflu tout autre épurage de la chambre de la
garniture mécanique.
Pour ce qui est des matériaux et du domaine
d’exploitation des garnitures mécaniques utilisées,
consulter la fiche technique figurant dans les
instructions de service ou dans la confirmation de
commande.
QI ... Entrée quench (471Q)
Q0 ... Sortie quench (471Q)
LSB 100-france Page 58
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 63

Instructions de montage, de service et de maintenance
nitures mécaniques qui ont
été longtemps en service peut entraîner des
risques de fuite au niveau de la surface de
glissement après le remontage. Il est donc
recommandé de remplacer la garniture
mécanique par une nouvelle. La garniture
évisée par le fabricant et
servir de garniture mécanique de
rnitures
mécaniques faisant l’objet d’une confirmation
En cas de modification du type de garniture
mécanique ou de changement de fabricant,
vérifier à nouveau les données relatives à la
ce maximale du liquide de
Veiller à la plus grande propreté ! Les surfaces
de glissement doivent tout particulièrement
demeurer propres, sèches et en parfait état. Ne
faces
N’utiliser des graisses minérales ou des huiles
qu’après s’être vraiment assuré que
e mécanique résiste à
Avant d’utiliser un lubrifiant, s’assurer qu’il n’y a
aucun risque de réaction grave entre le liquide
Préparer toutes les pièces nécessaires pour
montage se fasse rapidement. Les
lubrifiants n’agissant que peu de temps, la
mobilité et le réglage automatique de
Ne jamais pousser l’élastomère sur des bords
effilés. Utiliser des douilles de montage si
18
18
18
Désignation des pièces :
161 Couvercle de corps
210 Arbre
230 Roue mobile
412.22 Joint torique
412.32 Joint torique
*) optionnel
a)
b) seulement pour les garnitures mécaniques
Sous réserve de modifications techniques !
434 Garniture mécanique
471Q Couvercle quench
502.31*) Bague à fente
527 a) Bague de butée
542.31 Douille de laminage
Taille
nominale de
la garniture
mécanique
560 b) Goupille
904.31 a) Vis sans tête
33 33 48 42,5 7,5 50 19
904.32*) Vis sans tête
925 Ecrou de la roue mobile
43 43 61 45 7,5 52,5 28
940.31 Clavette
53 53 73 47,5 10 57,5 38
3. Démontage de la garniture mécanique
avec joints toriques en PTFE
l
∅d
∅d
1
7
1K
A B
Série LSB
QI, Q0
∅d
L
1/4-
NPT
3/8-
NPT
3/8-
NPT
Pour ce faire, utiliser le plan-coupe adéquat et la fiche
technique jointe de la garniture mécanique.
Démonter la pompe conformément aux
instructions de montage, d’exploitation et de
maintenance jusqu’au chapitre 8.6 inclus.
Retirer la bague de butée (527) (si elle existe) et
l’élément rotatif de la garniture mécanique (433)
de l’arbre (210).
Consulter la fiche technique jointe de la garniture
mécanique pour savoir si les vis d’arrêt au niveau
de la garniture mécanique doivent être desserrées
auparavant.
Démonter le couvercle de corps (161) avec le
couvercle quench (471Q). Utiliser les écrous à six
pans (901.42) comme auxiliaire de dégagement.
4. Montage de la garniture mécanique
Pour ce faire, utiliser le plan-coupe adéquat et la fiche
technique jointe de la garniture mécanique.
Seules peuvent être utilisées des ga
écrite de conformité selon la directive 94/9/CE.
Retirer l’élément stationnaire de la garniture
mécanique (433) et la douille de laminage
(542.31) du couvercle quench (471Q).
Nettoyer le perçage de positionnement (∅d7) dans
le couvercle quench (471Q) et la surface de
l’arbre (210).
.
Réutiliser des gar
démontée peut être r
remplacement.
l'élastomère de la garnitur
l’huile. Ne jamais utiliser de silicone.
température de servi
refoulement et à la classe de température.
pas enduire non plus de lubrifiant les sur
de glissement de la garniture mécanique.
Utiliser le lubrifiant qui accompagne
éventuellement la garniture mécanique de
remplacement.
LSB 100-france Page 59
Artikel Nr. 771076129
de refoulement et ce lubrifiant.
que le
l’élastomère s’estompent peu après.
nécessaire.
Enfoncer prudemment la douille de laminage
(542.31) dans le couvercle quench (471Q).
Presser uniformément l’élément stationnaire de la
garniture mécanique dans le couvercle quench
(471Q). Utiliser éventuellement un poinçon à
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 64

Instructions de montage, de service et de maintenance
Pousser les garnitures mécaniques à soufflets
de telle manière qu’ils soient comprimés et non
N’utiliser un lubrifiant (Molykote etc.) entre la
de protection d’arbre et l’arbre
qu’après s’être assuré qu’il n’y a aucun risque
de réaction grave entre le liquide de
Avant de brancher la pompe, raccorder
impérativement le système d’épurage pour le
surface souple. Une sollicitation inégale peut
entraîner une rupture de la surface de glissement.
Ne pas endommager la surface de glissement !
Veiller au joint à plat point axial de l’unité
stationnaire dans le couvercle quench. La surface
de glissement doit être exactement à la verticale
de l’arbre.
S’il y a une goupille d’ajustage (560), veiller à ce
qu’elle s’engrène avec la rainure de la garniture
mécanique sans toucher celle-ci.
Positionner prudemment le couvercle de corps
(161) jusqu’à ce qu’il porte bien axialement dans
la lanterne du corps de palier (344).
Enfiler l’unité rotative de la garniture mécanique
sur l’arbre (210).
Régler exactement la surface d’appui de la
garniture mécanique du côté de la roue mobile à
la dimension A. Pour les garnitures mécaniques
Pour tout autre assemblage et pour le montage de
Série LSB
sans propres vis d’arrêt, la bague de butée (527)
sert de butée.
étirés lors du montage (risque de déchirure !).
chemise
refoulement et ce lubrifiant.
la pompe, consulter les instructions de montage,
de service et de maintenance du chapitre 8.
quench et mettre en service.
LSB 100-france Page 60
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 65

Instructions de montage, de service et de maintenance
Désignation des pièces
N°
102 V 161 183 ***) 183P **) 210 230 341 400 412.21 433 502.11 *) 527 **) 554.41 554.42 **
*)
554.43 ***) 554.44 ***) 681 801 901.11 901.31 **) 901.42 901.43 ***) 902.41 904.11 *) 904.31 **) 904.41 904.42 912.11 920.41 922 940.31
exécutions
Série LSB
Exécution : S1...2 Garniture mécanique simple, non équilibrée (DIN 24960, l
/ EN 12756, exéc. K, forme U),
1k
roue mobile avec ailettes dorsales
Pour connaître la garniture d’arbre de la pompe, consulter la fiche technique / la confirmation de commande. Voir
également le chapitre 3.1.1 Schéma de désignation.
125-100-200 125-100-250 150-125-250 200-150-250
80-50-315 100-65-160 100-65-200 100-65-250 125-80-160 125-80-200 125-80-250
65-40-160 65-40-200 65-40-250 65-40-315 80-50-160 80-50-200 80-50-250
40-25-160 40-25-200 40-25-250 50-32-160 50-32-200 50-32-250 50-32-315
Valable pour :
Volute
Couvercle de corps
Béquille
Appui de la pompe
Arbre d’emboîtement
Roue mobile
Lanterne d’entraînement
Joint plat
Joint torique
Ganiture mécanique
Bague à fente
Bague de butée
Rondelle
Rondelle sphérique
Rondelle à rotule concave
Rondelle
Tôle de protection
Moteur à bride
Vis à six pans
Vis à six pans
Vis à six pans
Vis à six pans
Goujon fileté
Vis sans tête
Vis sans tête
Vis sans tête
Vis sans tête
Bouchon de purge
Ecrou à six pans
Ecrou de la roue mobile
Clavette
*) ... optionnel
**) ... n’existe pas pour toutes les
***) ... uniquement pour les tailles de
moteurs IEC : 160MA, 160M, 160L, 180M,
180L, 200L, 200LA
Sous réserve de modifications techniques !
LSB 100-france Page 61
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Non à l’échelle !
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 66
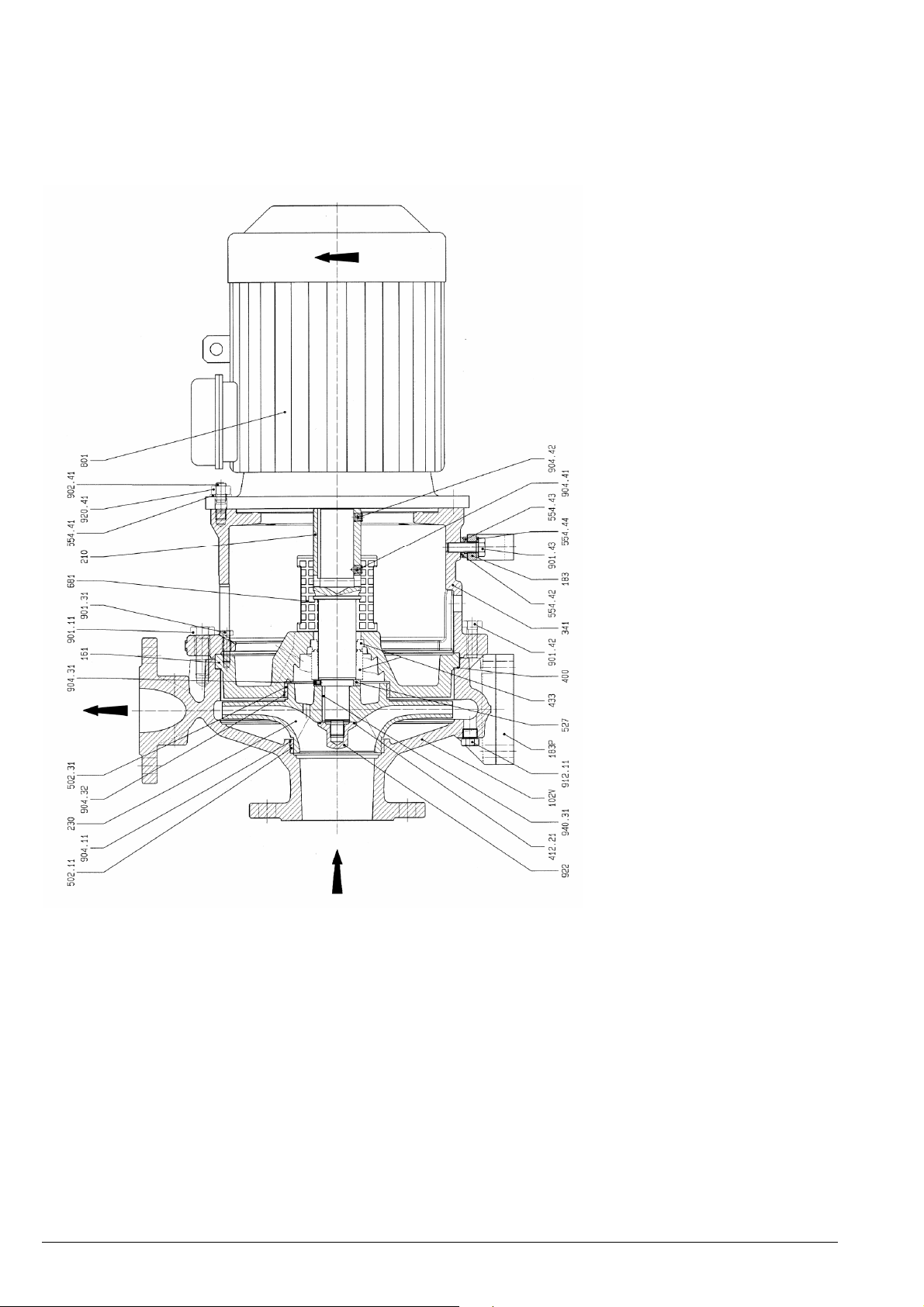
Instructions de montage, de service et de maintenance
Volute
102 V 161 183 ***) 183P **) 210 230 341 400 412.21 433 502.11 *) 502.31 *) 527 **) 554.41 554.42 ***) 554.43 ***) 554.44 ***) 681 801 901.11 901.31 **) 901.42 901.43 ***) 902.41 904.11 *) 904.32 *) 904.31 **) 904.41 904.42 912.11 920.41 922 940.31
Série LSB
Exécution : S1...2 Garniture mécanique simple, non équilibrée (DIN 24960, l
/ EN 12756, exéc. K, forme U),
1k
roue mobile avec forages de déversement
Pour connaître la garniture d’arbre de la pompe, consulter la fiche technique / la confirmation de commande. Voir
également le chapitre 3.1.1 Schéma de désignation.
150-125-315 125-100-315 125-80-315 100-65-315 Valable pour :
Désignation des pièces
Couvercle de corps
Béquille
Appui de la pompe
Arbre d’emboîtement
Roue mobile
Lanterne d’entraînement
Joint plat
Joint torique
Garniture mécanique
Bague à fente
Bague à fente
Bague de butée
Rondelle
Rondelle sphérique
N°
Sous réserve de modifications techniques !
LSB 100-france Page 62
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Rondelle à rotule concave
Rondelle
Tôle de protection
Moteur à bride
Vis à six pans
Vis à six pans
Vis à six pans
Vis à six pans
Goujon fileté
Vis sans tête
Vis sans tête
Vis sans tête
Vis sans tête
Vis sans tête
Bouchon de purge
Ecrou à six pans
Ecrou de la roue mobile
Clavette
*) ... optionnel
**) ... n’existe pas pour toutes les exécutions
***) …uniquement pour les tailles de moteurs
IEC : 160MA, 160M, 160L, 180M, 180L, 200L,
200LA
Non à l’échelle
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 67

Instructions de montage, de service et de maintenance
Volute
102 V
Série LSB
Exécution : S4...2 Garniture mécanique simple, non équilibrée (DIN 24960, l1k / EN 12756, exéc. K, forme U),
avec quench, roue mobile avec ailettes dorsales
Pour connaître la garniture d’arbre de la pompe, consulter la fiche technique / la confirmation de commande. Voir
également le chapitre 3.1.1 Schéma de désignation.
125-100-200 125-100-250 150-125-250 200-150-250
80-50-315 100-65-160 100-65-200 100-65-250 125-80-160 125-80-200 125-80-250
65-40-160 65-40-200 65-40-250 65-40-315 80-50-160 80-50-200 80-50-250
40-25-160 40-25-200 40-25-250 50-32-160 50-32-200 50-32-250 50-32-315
Valable pour:
Désignation des pièces
Couvercle de corps
Béquille
Appui de la pompe
Arbre d’entraînement
Roue mobile
Lanterne d’entraînement
Joint plat
Joint torique
Joint torique
Garniture mécanique
Couvercle quench
Bague à fente
Bague de butée
Douille de laminage
Rondelle
Rondelle sphérique
Rondelle à rotule concave
Rondelle
Tôle de protection
Moteur à bride
Vis à six pans
Vis à six pans
Vis à six pans
Vis à six pans
Goujon fileté
Goujon fileté
Vis sans tête
Vis sans tête
Vis sans tête
Vis sans tête
Bouchon de purge
Ecrou à six pans
Ecrou à six pans
Ecrou de la roue mobile
Clavette
N°
161
183 ***)
183P **)
210
230
341
400
412.21
412.32
433
471Q
502.11 *)
527 **)
542.31
554.41
554.42 ***)
554.43 ***)
554.44 ***)
681
801
901.11
901.31 **)
901.42
901.43 ***)
902.31
902.41
904.11 *)
904.31 **)
904.41
904.42
912.11
920.31
920.41
922
940.31
*) ... optionnel
**) ... n’existe pas pour toutes les exécutions
***) ... uniquement pour les tailles de moteurs
IEC : 160MA, 160M, 160L, 180M, 180L,
200L, 200LA
Sous réserve de modifications techniques !
LSB 100-france Page 63
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Non à l’échelle
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 68

Instructions de montage, de service et de maintenance
exécutions
Série LSB
Exécution : S4...2 Garniture mécanique simple, non équilibrée (DIN 24960, l1k / EN 12756, exéc. K, forme U),
avec quench, roue mobile avec forages de déversement
Pour connaître la garniture d’arbre de la pompe, consulter la fiche technique / la confirmation de commande. Voir
également le chapitre 3.1.1 Schéma de désignation.
150-125-315 125-100-315 125-80-315 100-65-315 Valable pour :
Désignation des pièces
Volute
Couvercle de corps
Béquille
Appui de la pompe
Arbre d’entraînement
Roue mobile
Lanterne d’entraînement
Joint plat
Joint torique
Joint torique
Garniture mécanique
Couvercle quench
Bague à fente
Bague À fente
Bague de butée
Douille de laminage
N°
102 V
161
183 ***)
183P **)
210
230
341
400
412.21
412.32
433
471Q
502.11 *)
502.31 *)
527 **)
542.31
Sous réserve de modifications techniques !
LSB 100-france Page 64
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Rondelle
Rondelle sphérique
554.41
554.42 ***)
Rondelle à rotule concave
Rondelle
Tôle de protection
Moteur à bride
554.43 ***)
554.44 ***)
681
801
Non à l’échelle
Vis à six pans
Vis à six pans
Vis à six pans
Vis À six pans
Goujon fileté
Goujon fileté
Vis sans tête
Vis sans tête
Vis sans tête
Vis sans tête
Vis sans tête
Bouchon de purge
Ecrou à six pans
Ecrou à six pans
Ecrou de la roue mobile
Clavette
901.11
901.31 **)
901.42
901.43 ***)
902.31
902.41
904.11 *)
904.31 **)
904.32 **)
904.41
904.42
912.11
920.31
920.41
922
940.31
*) ... optionnel
**) ... n’existe pas pour toutes les
***) ... uniquement pour les tailles de
moteurs IEC : 160MA, 160M, 160L, 180M,
180L, 200L, 200LA
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 69

Instructions de montage, de service et de maintenance
Raccordements
Série LSB
Code Nombre
Raccordements
PM1 *) 1 Mesurage de la pression
PM2 *) 1 Mesurage de la pression
Corps de palier
24 32, 42, 48
1/4-18 NPT
1/4-18 NPT
D 1 Vidange (corps) 3/8-18 NPT
DL 1 Vidange (lanterne) G 1/2
QI **) 1 Entrée quench
QO **) 1 Sortie quench
1/4-18
NPT
1/4-18
NPT
3/8-18 NPT
3/8-18 NPT
*) ... optionnel, possible pour les exécutions S2..1 et S4..2
**) ... exclusivement pour l’exécution S4..2
Sous réserve de modifications techniques !
Non à l’échelle !
LSB 100-france Page 65
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 70

Instructions de montage, de service et de maintenance
Série LSB
Plan coté - Pour connaître la désignation de la pompe, consulter la fiche technique / la confirmation de commande.
Voir également le chapitre 3.1.1 Schéma de désignation.
Pompe
DN
DN
S
a b g2 h1 h2 m1 m2 n1 n2 p1 p2 s1 s2 x
D
LSB 40-25-160 .... - ... 40 25 80 50 10 132 160 100 70 240 190 15 30 14 13,5 100
LSB 40-25-200 .... - ... 40 25 80 50 10 160 180 100 70 240 190 15 30 14 13,5 100
LSB 40-25-250 .... - ... 40 25 100 65 10 180 225 125 95 320 250 15 30 14 13,5 100
LSB 50-32-160 .... - ... 50 32 80 50 10 132 160 100 70 240 190 15 30 14 13,5 100
LSB 50-32-200 .... - ... 50 32 80 50 10 160 180 100 70 240 190 15 30 14 13,5 100
LSB 50-32-250 .... - ... 50 32 100 65 10 180 225 125 95 320 250 15 30 14 13,5 100
LSB 50-32-315 .... - ... 50 32 125 65 10 200 250 125 95 345 280 15 30 14 13,5 100
LSB 65-40-160 .... - ... 65 40 80 50 10 132 160 100 70 240 190 15 30 14 13,5 100
LSB 65-40-200 .... - ... 65 40 100 50 10 160 180 100 70 265 212 15 30 14 13,5 100
LSB 65-40-250 .... - ... 65 40 100 65 10 180 225 125 95 320 250 15 30 14 13,5 100
LSB 65-40-315 .... - ... 65 40 125 65 10 200 250 125 95 345 280 15 30 14 13,5 100
LSB 80-50-160 .... - ... 80 50 100 50 10 160 180 100 70 265 212 15 30 14 13,5 100
LSB 80-50-200 .... - ... 80 50 100 50 10 160 200 100 70 265 212 15 30 14 13,5 100
LSB 80-50-250 .... - ... 80 50 125 65 10 180 225 125 95 320 250 15 30 14 13,5 100
LSB 80-50-315 .... - ... 80 50 125 65 10 225 280 125 95 345 280 15 30 14 13,5 100
LSB 100-65-160 .... - ... 100 65 100 65 10 160 200 125 95 280 212 15 30 14 13,5 100
LSB 100-65-200 .... - ... 100 65 100 65 10 180 225 125 95 320 250 15 30 14 13,5 140
LSB 100-65-250 .... - ... 100 65 125 80 10 200 250 160 120 360 280 15 30 18 13,5 140
LSB 100-65-315 .... - ... 100 65 128 80 10 225 280 160 120 400 315 15 30 18 13,5 140
LSB 125-80-160 .... - ... 125 80 125 65 10 180 225 125 95 320 250 15 30 14 13,5 140
LSB 125-80-200 .... - ... 125 80 125 65 10 180 250 125 95 345 280 15 30 14 13,5 140
LSB 125-80-250 .... - ... 125 80 125 80 10 225 280 160 120 400 315 15 30 18 13,5 140
LSB 125-80-315 .... - ... 125 80 125 80 10 250 315 160 120 400 315 15 30 18 13,5 140
LSB 125-100-200 .... - ... 125 100 125 80 10 200 280 160 120 360 280 15 30 18 13,5 140
LSB 125-100-250 .... - ... 125 100 140 80 10 225 280 160 120 400 315 15 30 18 13,5 140
LSB 125-100-315 .... - ... 125 100 140 80 10 250 315 160 120 400 315 15 30 18 13,5 140
LSB 150-125-250 .... - ... 150 125 140 80 10 250 355 160 120 400 315 15 30 18 13,5 140
LSB 150-125-315 .... - ... 150 125 140 100 10 280 355 200 150 500 400 15 30 22 13,5 140
LSB 200-150-250 .... - ... 200 150 160 100 10 280 375 200 150 500 400 15 30 22 13,5 180
LSB 100-france Page 66
Artikel Nr. 771076129
H peut varier selon le fabricant du moteur
G ... Poids de la pompe sans moteur en kg
Tolérances conformes à DIN EN 735
Dimensions en mm
Sous réserve de modifications techniques !
Non à l’échelle !
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 71

Instructions de montage, de service et de maintenance
Série LSB
Pompe
LSB 40-25-160 .... - 80 119 15 408 176 - - - - 31
LSB 40-25-160 .... - 90 119 15 457 176 - - - - 31
LSB 40-25-160 .... - 100 144 15 530 216 - - - - 37
LSB 40-25-160 .... - 112 144 15 539 216 - - - - 37
LSB 40-25-160 .... - 132 150 35 666 216 20 - - - 37
LSB 40-25-160 .... - 160 175 60 771 251 45 210 180 206 43
LSB 40-25-200 .... - 80 119 15 408 176 - - - - 39
LSB 40-25-200 .... - 90 119 15 457 176 - - - - 39
LSB 40-25-200 .... - 100 144 15 530 216 - - - - 45
LSB 40-25-200 .... - 112 144 15 539 216 - - - - 45
LSB 40-25-200 .... - 132 150 15 666 216 - - - - 45
LSB 40-25-200 .... - 160 175 60 815 251 45 210 180 206 54
LSB 40-25-250 .... - 80 171 15 421 189 - - - - 60
LSB 40-25-250 .... - 90 171 15 470 189 - - - - 60
LSB 40-25-250 .... - 100 171 15 543 229 - - - - 65
LSB 40-25-250 .... - 112 171 15 552 229 - - - - 65
LSB 40-25-250 .... - 132 171 15 679 229 - - - - 65
LSB 40-25-250 .... - 160 175 15 828 264 - 210 180 219 75
LSB 40-25-250 .... - 180 180 20 859 264 5 210 180 219 75
LSB 40-25-250 .... - 200 225 65 964 264 50 280 250 219 75
LSB 50-32-160 .... - 80 119 15 408 176 - - - - 31
LSB 50-32-160 .... - 90 119 15 457 176 - - - - 31
LSB 50-32-160 .... - 100 144 15 530 216 - - - - 37
LSB 50-32-160 .... - 112 144 15 539 216 - - - - 37
LSB 50-32-160 .... - 132 150 35 666 216 20 - - - 37
LSB 50-32-160 .... - 160 175 60 771 251 45 210 180 206 43
LSB 50-32-200 .... - 80 119 15 408 176 - - - - 39
LSB 50-32-200 .... - 90 119 15 457 176 - - - - 39
LSB 50-32-200 .... - 100 144 15 530 216 - - - - 45
LSB 50-32-200 .... - 112 144 15 539 216 - - - - 45
LSB 50-32-200 .... - 132 150 15 666 216 - - - - 45
LSB 50-32-200 .... - 160 175 60 815 251 45 210 180 206 54
LSB 50-32-250 .... - 80 171 15 421 189 - - - - 60
LSB 50-32-250 .... - 90 171 15 470 189 - - - - 60
LSB 50-32-250 .... - 100 171 15 543 229 - - - - 65
LSB 50-32-250 .... - 112 171 15 552 229 - - - - 65
LSB 50-32-250 .... - 132 171 15 679 229 - - - - 65
LSB 50-32-250 .... - 160 175 15 828 264 - 210 180 219 75
LSB 50-32-250 .... - 180 180 20 859 264 5 210 180 219 75
LSB 50-32-250 .... - 200 225 65 964 264 50 280 250 219 75
LSB 50-32-315 .... - 100 201 15 543 229 - - - - 102
LSB 50-32-315 .... - 112 201 15 552 229 - - - - 102
LSB 50-32-315 .... - 132 201 15 679 229 - - - - 102
LSB 50-32-315 .... - 160 201 15 828 264 - 210 180 219 112
LSB 50-32-315 .... - 180 201 15 859 264 - 210 180 219 112
LSB 50-32-315 .... - 200 225 65 964 264 50 280 250 219 112
LSB 65-40-160 .... - 80 124 15 408 176 - - - - 32
LSB 65-40-160 .... - 90 124 15 457 176 - - - - 32
LSB 65-40-160 .... - 100 144 15 530 216 - - - - 39
LSB 65-40-160 .... - 112 144 15 539 216 - - - - 39
LSB 65-40-160 .... - 132 150 35 666 216 20 - - - 39
LSB 65-40-160 .... - 160 175 60 815 251 45 210 180 206 44
LSB 65-40-200 .... - 80 139 15 408 176 - - - - 44
LSB 65-40-200 .... - 90 139 15 457 176 - - - - 44
LSB 65-40-200 .... - 100 144 15 530 216 - - - - 50
LSB 65-40-200 .... - 112 144 15 539 216 - - - - 50
LSB 65-40-200 .... - 132 150 15 666 216 - - - - 50
LSB 65-40-200 .... - 160 175 35 815 251 20 210 180 206 60
LSB 65-40-200 .... - 180 180 60 846 251 45 210 180 206 60
LSB 65-40-250 .... - 80 171 15 421 189 - - - - 62
LSB 65-40-250 .... - 90 171 15 470 189 - - - - 62
LSB 65-40-250 .... - 100 171 15 543 229 - - - - 68
LSB 65-40-250 .... - 112 171 15 552 229 - - - - 68
LSB 65-40-250 .... - 132 171 15 679 229 - - - - 68
LSB 65-40-250 .... - 160 175 15 828 264 - 210 180 219 77
LSB 65-40-250 .... - 180 180 20 859 264 5 210 180 219 77
LSB 65-40-250 .... - 200 225 65 964 264 50 280 250 219 77
LSB 100-france Page 67
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Bmax
g1 ~H h U n4 n5 w ~G
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 72

Instructions de montage, de service et de maintenance
Série LSB
Pompe
LSB 65-40-315 .... - 100 201 15 543 229 - - - - 102
LSB 65-40-315 .... - 112 201 15 552 229 - - - - 102
LSB 65-40-315 .... - 132 201 15 679 229 - - - - 102
LSB 65-40-315 .... - 160 201 15 828 264 - 210 180 219 112
LSB 65-40-315 .... - 180 201 15 859 264 - 210 180 219 112
LSB 65-40-315 .... - 200 225 65 964 264 50 280 250 219 112
LSB 80-50-160 .... - 80 141 15 408 176 - - - - 36
LSB 80-50-160 .... - 90 141 15 457 176 - - - - 36
LSB 80-50-160 .... - 100 144 15 530 216 - - - - 43
LSB 80-50-160 .... - 112 144 15 539 216 - - - - 43
LSB 80-50-160 .... - 132 150 15 666 216 - - - - 43
LSB 80-50-160 .... - 160 175 35 815 251 20 210 180 206 49
LSB 80-50-160 .... - 180 180 60 846 251 45 210 180 206 49
LSB 80-50-200 .... - 80 157 15 408 176 - - - - 45
LSB 80-50-200 .... - 90 157 15 457 176 - - - - 45
LSB 80-50-200 .... - 100 157 15 530 216 - - - - 51
LSB 80-50-200 .... - 112 157 15 539 216 - - - - 51
LSB 80-50-200 .... - 132 157 15 666 216 - - - - 51
LSB 80-50-200 .... - 160 175 35 815 251 20 210 180 206 60
LSB 80-50-200 .... - 180 180 60 846 251 45 210 180 206 60
LSB 80-50-200 .... - 200 225 85 951 251 70 280 250 206 60
LSB 80-50-250 .... - 90 181 15 470 189 - - - - 69
LSB 80-50-250 .... - 100 181 15 543 229 - - - - 75
LSB 80-50-250 .... - 112 181 15 552 229 - - - - 75
LSB 80-50-250 .... - 132 181 15 679 229 - - - - 75
LSB 80-50-250 .... - 160 181 15 828 264 - 210 180 219 84
LSB 80-50-250 .... - 180 181 20 859 264 5 210 180 219 84
LSB 80-50-250 .... - 200 225 65 964 264 50 280 250 219 84
LSB 80-50-315 .... - 100 212 15 543 229 - - - - 108
LSB 80-50-315 .... - 112 212 15 552 229 - - - - 108
LSB 80-50-315 .... - 132 212 15 679 229 - - - - 108
LSB 80-50-315 .... - 160 212 15 828 264 - 210 180 219 118
LSB 80-50-315 .... - 180 212 15 859 264 - 210 180 219 118
LSB 80-50-315 .... - 200 225 40 964 264 25 280 250 219 118
LSB 100-65-160 .... - 80 164 15 421 189 - - - - 49
LSB 100-65-160 .... - 90 164 15 470 189 - - - - 49
LSB 100-65-160 .... - 100 164 15 543 229 - - - - 55
LSB 100-65-160 .... - 112 164 15 552 229 - - - - 55
LSB 100-65-160 .... - 132 164 15 679 229 - - - - 55
LSB 100-65-160 .... - 160 175 40 828 264 25 210 180 219 64
LSB 100-65-160 .... - 180 180 40 859 264 25 210 180 219 64
LSB 100-65-160 .... - 200 225 85 964 264 70 280 250 219 64
LSB 100-65-200 .... - 90 173 15 470 189 - - - - 53
LSB 100-65-200 .... - 100 173 15 543 229 - - - - 58
LSB 100-65-200 .... - 112 173 15 552 229 - - - - 58
LSB 100-65-200 .... - 132 173 15 679 229 - - - - 58
LSB 100-65-200 .... - 160 175 15 828 264 - 210 180 219 68
LSB 100-65-200 .... - 180 180 20 859 264 5 210 180 219 68
LSB 100-65-200 .... - 200 225 65 964 264 50 280 250 219 68
LSB 100-65-250 .... - 90 193 18 470 189 - - - - 74
LSB 100-65-250 .... - 100 193 18 543 229 - - - - 80
LSB 100-65-250 .... - 112 193 18 552 229 - - - - 80
LSB 100-65-250 .... - 132 193 18 679 229 - - - - 80
LSB 100-65-250 .... - 160 193 18 828 264 - 210 180 219 89
LSB 100-65-250 .... - 180 193 18 859 264 - 210 180 219 89
LSB 100-65-250 .... - 200 225 48 964 264 30 280 250 219 89
LSB 100-65-315 .... - 100 221 18 555 241 - - - - 115
LSB 100-65-315 .... - 112 221 18 564 241 - - - - 115
LSB 100-65-315 .... - 132 221 18 691 241 - - - - 115
LSB 100-65-315 .... - 160 221 18 840 276 - 210 180 231 125
LSB 100-65-315 .... - 180 221 18 871 276 - 210 180 231 125
LSB 100-65-315 .... - 200 225 18 976 276 - 210 180 231 125
LSB 125-80-160 .... - 90 188 15 470 189 - - - - 56
LSB 125-80-160 .... - 100 188 15 543 229 - - - - 62
LSB 125-80-160 .... - 112 188 15 552 229 - - - - 62
LSB 125-80-160 .... - 132 188 15 679 229 - - - - 62
LSB 125-80-160 .... - 160 188 15 828 264 - 210 180 219 71
LSB 100-france Page 68
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Bmax
g1 ~H h U n4 n5 w ~G
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 73

Instructions de montage, de service et de maintenance
Série LSB
Pompe
LSB 125-80-160 .... - 180 188 20 859 264 5 210 180 219 71
LSB 125-80-160 .... - 200 225 65 964 264 50 280 250 219 71
LSB 125-80-200 .... - 90 202 15 470 189 - - - - 63
LSB 125-80-200 .... - 100 202 15 543 229 - - - - 69
LSB 125-80-200 .... - 112 202 15 552 229 - - - - 69
LSB 125-80-200 .... - 132 202 15 679 229 - - - - 69
LSB 125-80-200 .... - 160 202 15 828 264 - 210 180 219 78
LSB 125-80-200 .... - 180 202 20 859 264 5 210 180 219 78
LSB 125-80-200 .... - 200 225 65 964 264 50 280 250 219 78
LSB 125-80-250 .... - 100 229 18 543 229 - - - - 91
LSB 125-80-250 .... - 112 229 18 552 229 - - - - 91
LSB 125-80-250 .... - 132 229 18 679 229 - - - - 91
LSB 125-80-250 .... - 160 229 18 828 264 - 210 180 219 100
LSB 125-80-250 .... - 180 229 18 859 264 - 210 180 219 100
LSB 125-80-250 .... - 200 229 23 964 264 5 280 250 219 100
LSB 125-80-315 .... - 112 240 18 564 241 - - - - 129
LSB 125-80-315 .... - 132 240 18 691 241 - - - - 129
LSB 125-80-315 .... - 160 240 18 840 276 - 280 250 231 139
LSB 125-80-315 .... - 180 240 18 871 276 - 280 250 231 139
LSB 125-80-315 .... - 200 240 18 976 276 - 280 250 231 139
LSB 125-100-200 .... - 100 217 18 543 229 - - - - 90
LSB 125-100-200 .... - 112 217 18 552 229 - - - - 90
LSB 125-100-200 .... - 132 217 18 679 229 - - - - 90
LSB 125-100-200 .... - 160 217 23 828 264 5 210 180 219 99
LSB 125-100-200 .... - 180 217 23 859 264 5 210 180 219 99
LSB 125-100-200 .... - 200 225 48 964 264 30 280 250 219 99
LSB 125-100-250 .... - 100 227 18 565 251 - - - - 100
LSB 125-100-250 .... - 112 227 18 574 251 - - - - 100
LSB 125-100-250 .... - 132 227 18 701 251 - - - - 100
LSB 125-100-250 .... - 160 227 18 850 286 - 220 180 241 109
LSB 125-100-250 .... - 180 227 18 881 286 - 220 180 241 109
LSB 125-100-250 .... - 200 227 23 986 286 5 280 250 241 109
LSB 125-100-315 .... - 132 257 18 691 241 - - - - 139
LSB 125-100-315 .... - 160 257 18 840 276 - 280 250 231 150
LSB 125-100-315 .... - 180 257 18 871 276 - 280 250 231 150
LSB 125-100-315 .... - 200 257 18 976 276 - 280 250 231 150
LSB 150-125-250 .... - 132 249 18 701 251 - - - - 114
LSB 150-125-250 .... - 160 249 18 850 286 - 280 250 241 123
LSB 150-125-250 .... - 180 249 18 881 286 - 280 250 241 123
LSB 150-125-250 .... - 200 249 18 986 286 - 280 250 241 123
LSB 150-125-315 .... - 160 263 20 840 276 - 280 250 231 149
LSB 150-125-315 .... - 180 263 20 871 276 - 280 250 231 149
LSB 150-125-315 .... - 200 263 20 976 276 - 280 250 231 149
LSB 200-150-250 .... - 160 293 20 850 286 - 280 250 241 163
LSB 200-150-250 .... - 180 293 20 881 286 - 280 250 241 163
LSB 200-150-250 .... - 200 293 20 986 286 - 280 250 241 163
ISO PN16
DN C d D K L DN C d D K L NPS C d D K L
25 16 65 115 85 4x14 - - - - - - 1 16 51 115 79,5 4x16
32 18 78 140 100 4x19 32 20 78 140 100 4x19 1 1/2 18 73 140 98,5 4x16
40 19 88 150 110 4x19 40 19 88 150 110 4x19 1 1/2 19 73 150 98,5 4x16
50 20 102 165 125 4x19 50 20 102 165 125 4x19 2 20 92 165 120,5 4x19
65 20 122 185 145 4x19 65 22 122 185 145 8x19 2 1/2 20 105 185 139,5 4x19
80 20 128 200 160 8x19 80 24 138 200 160 8x19 3 20 128 200 152,5 4x19
100 24 157 230 180 8x19 100 24 162 235 190 8x22 4 24 157 230 190,5 8x19
125 24 186 255 210 8x19 125 26 186 270 220 8x22 5 24 186 255 216 8x22
150 25,5 216 285 240 8x22 - - - - - - 6 25,5 216 285 241,5 8x22
200 29 270 345 295 12x22 - - - - - - 8 29 270 345 298,5 12x22
Bmax
g1 ~H h U n4 n5 w ~G
Dimensions des brides DNS, DND*)
ISO PN25 ANSI Class 150RF
*) ... Pour connaître la taille des brides et la pression nominale, consulter la fiche technique / la confirmation de
commande. Voir également le chapitre 3.1.1 Schéma de désignation.
LSB 100-france Page 69
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 74

Instructions de montage, de service et de maintenance
Série LSB
LSB 100-france Page 70
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 75

Installation, Operation and Maintenance Instruction
TABLE of CONTENTS
Pump Name Plate..................................................... 72
ATEX-Label (only for pumps in compliance with EC
directive 94/9/EG) ..................................................... 72
1. General ................................................................. 73
1.1 Guarantee ....................................................... 73
2. Safety Regulations................................................ 73
2.1 Marking of References in the Operating
Instructions............................................................73
2.2 Dangers of non-observance of the Safety
Instructions............................................................78
2.3 Safety Instructions for the Operator / Worker . 78
2.4 Safety Instructions for Maintenance, Inspections
and Mounting Work ............................................... 78
2.5 Unauthorized Alteration and Spare Parts
Production ............................................................. 78
2.6 Undue Operation.............................................78
2.7 Explosion Protection........................................ 78
2.8 Use acc. to Regulations .................................. 76
3. Description............................................................76
3.1 Design ............................................................. 76
3.2 Shaft Sealing...................................................77
3.3 Bearing............................................................77
3.4 Approximate Value for Sound Pressure Level 77
3.5 Permitted Nozzle Loads and Torques at the
Pump Nozzles ... ................................................... 77
3.6 Permitted pressures and temperatures........... 78
3.7 Condensate.....................................................79
4. Transport, Handling, Storage................................ 79
4.1 Transport, Handling......................................... 79
4.2 Storage / Conservation.................................... 79
5. Mounting / Installation...........................................79
5.1 Mounting of Pump / Unit.................................. 79
5.2 Connection of Pipings to the Pump.................80
5.3 Drive................................................................80
5.4 Electric Connection ......................................... 80
5.5 Final Control....................................................81
6. Start-up, Operation, Shut down ............................ 81
6.1 Initial start-up................................................... 81
6.2 Switch on drive................................................81
6.3 Restarting........................................................81
6.4 Limits of Operation .......................................... 81
Model LSB
6.5 Lubrication .......................................................82
6.6 Monitoring........................................................82
6.7 Shutting down..................................................82
6.8 Storage / longer periods of non-operation.......82
7. Servicing, Maintenance.........................................83
7.1 General remarks..............................................83
7.2 Mechanical seals .............................................83
7.3 Motor bearings.................................................83
7.4 Cleaning of pump ............................................83
8. Dismantling and repair of pump ............................83
8.1 General remarks..............................................83
8.2 General............................................................83
8.3 Removal and Installation of screen in the motor
lantern....................................................................83
8.4 Removal of the Back Pull Out Assembly.........84
8.5 Removal of Impeller.........................................84
8.6 Removal of Shaft Sealing ................................84
8.7 Removal of Stub Shaft.....................................84
8.8 Reconditioning.................................................85
8.9 Mounting..........................................................85
9. Spare parts, Spare pumps ....................................86
9.1 Spare parts ......................................................86
9.2 Stand-by pumps...............................................86
10. Faults - Causes and Solutions ............................87
11. Motor Operating Instructions...............................88
Installation Manual - Single mech. seal without shaft
sleeve (Design code S1..2) .......................................90
Installation Manual - Single mech. seal with quench
without shaft sleeve (Design code S4..2) ……….......92
Sectional drawing pump unit (Design code S1..2),
Impeller with back vanes...........................................95
Sectional drawing pump unit (Design code S1..2),
Impeller with balancing holes ....................................96
Sectional drawing pump unit (Design code S4..2),
Impeller with back vanes...........................................97
Sectional drawing pump unit (Design code S4..2),
Impeller with balancing holes ....................................98
Connections ..............................................................99
Dimensional drawing...............................................100
LSB 100-english page 71
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 76

Installation, Operation and Maintenance Instruction
Pump Name Plate
Model LSB
Type *) Type of pump
S/N *) Serial number
Year Year of construction
Q Rated capacity at the operating point
P Rated power at the operating point
H Head (Energy head) at the operating point
n Speed
p
all w C
t
max op
Item No Customer related order number
Imp∅ Outer diameter of the impeller
Max. permitted casing-operation-pressure
(=highest discharge pressure at the rated
operating temperature to which the pump
casing can be used).
Maximum permitted operating temperature of
pumped liquid
*) All details of design and materials are defined with
this information. They must be stated on all inquiries to
the manufacturer resp. orders of spare.
ATEX-Label (only for pumps in compliance with EC directive 94/9/EG)
CE Marking of compliance with the EC directive
94/9/EG
Ex specific marking for explosion protection
II Symbol for the appliance group
2G Symbol for the category (2), explosive
atmosphere due to gases, vapors or mist (G)
c Symbol for used ignition protection
(constructual safety "c")
T1-T. Symbol for classification of the theoretically
available range of the temperature classes data for temperature class refer to chapter
2.7.5; Data for maximum permitted
temperature of pumped liquid refer to pump
name plate, data sheet and / or order
confirmation.
LSB 100-english page 72
Artikel Nr. 771076129
The conformity with the EC directive 94/9/EG
"Appliances and Protection Systems for designated
use in areas endangered to explosion" is declared by
the issue of the EC-Declaration of Conformity and the
attachment of the ATEX-label at the pump (adapter).
The ATEX-label is attached additionally to the pump
name plate.
Ausgabe 01/2010
Revision 02
Page 77

Installation, Operation and Maintenance Instruction
ff employed on installation, operation,
inspection and maintenance must be able to
prove that they know about the relevant
dent prevention regulations and that they
are suitably qualified for this work. If the staff
, they
observance can impair the pump and its
plosive
1. General
Model LSB
This product corresponds with the requirements of the
Machine directive 2006/42/EG.
The sta
acci
does not have the relevant knowledge
should be provided with suitable instruction.
The operation safety of the delivered pump resp. unit
(= pump with motor) can only be guaranteed on
designated use according to the attached data sheet
and / or order confirmation resp. chapter 6 "Start-up,
Operation, Shut down".
The operator is responsible for following the
instructions and complying with the safety
requirements given in these Operating Instructions.
Smooth operation of the pump or pump unit can only
be achieved if installation and maintenance are carried
out carefully in accordance with the rules generally
applied in the field of engineering and electrical
engineering.
If not all the information can be found in these
Operating Instructions, please contact us.
The manufacturer takes no responsibility for the pump
or pump unit if the Operating Instructions are not
followed.
These Operating Instructions should be kept in a safe
place for future use.
If this pump or pump unit is handed on to any third
party, it is essential that these Operating Instructions
and the operating conditions and working limits given
in the Confirmation of Order are also passed on in full.
These Operating Instructions do not take into account
all design details and variants nor all the possible
chance occurrences and events which might happen
during installation, operation and maintenance.
We retain all copyright in these Operating Instructions;
they are intended only for personal use by the owner
of the pump or the pump unit. The Operating
Instructions contain technical instructions and
drawings which may not, as a whole or in part, be
reproduced, distributed or used in any unauthorised
way for competitive purposes or passed on to others.
1.1 Guarantee
The guarantee is given in accordance with our
Conditions of Delivery and / or the confirmation of
order.
Repair work during the guarantee period may only be
carried out by us, or subject to our written approval.
Otherwise the guarantee ceases to apply.
Longer-term guarantees basically only cover correct
handling and use of the specified material. The
guarantee shall not cover natural wear and tear and all
parts subject to wear, such as impellers, shaft
sealings, shafts, shaft sleeves, bearings, wear rings
etc. or damage caused by transport or improper
handling.
In order for the guarantee to apply, it is essential that
the pump or pump unit is used in accordance with the
operating conditions given on the name plate,
confirmation of order and in the data sheet. This
applies particularly for the endurance of the materials
and smooth running of the pump and shaft sealing.
If one or more aspects of the actual operating
conditions are different, we should be asked to
confirm in writing that the pump is suitable.
2. Safety Regulations
These Operating Instructions contain important
instructions which must be followed when the pump is
assembled and commissioned and during operating
and maintenance. For this reason, these Operating
Instructions must be read by the skilled staff
responsible and / or by the operator of the plant before
it is installed and commissioned, and they must be left
permanently available at the place where the pump or
pump unit is in use.
These Operating Instructions do not refer to the
General Regulations on Accident Prevention or
local safety and / or operating regulations. The
operator is responsible for complying with these
(if necessary by calling in additional installation
staff).
Equally, instructions and safety devices regarding
handling and disposal of the pumped media and/or
auxilliary media for flushing, lubrication a.s.o.,
especially if they are explosive, toxical, hot a.s.o., are
not part of this operating instruction.
LSB 100-english page 73
Artikel Nr. 771076129
For the competent and prescribed handling only the
operator is responsible.
2.1 Marking of References in the
Operating Instructions
The safety regulations contained in these Operating
Instructions are specially marked with safety signs
acc. to nach DIN 4844:
Safety reference!
Nonfunction.
EC-Ex Marking
Products intended for use in ex
atmospheres must be marked.
General Symbol for Danger!
Persons can be endangered.
Warning of electric voltage!
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 78

Installation, Operation and Maintenance Instruction
e unit in areas endangered
to explosion special attention must be paid to
During operation of the pump the system of the
pressure pipe and the pump itself
must permanently be filled with the pumped
Thus, no explosive atmosphere can develop
Safety instructions attached directly to the pump resp.
unit must be followed under any circumstances.
Further they must be kept in good readable condition.
In the same way, as these Operating Instructions
of the pump, all possibly attached Operating
Instructions of accessories (e.g. motor) must be
noticed and kept available.
2.2 Dangers of non-observance of the
Safety Instructions
Non-observance of the Safety Instructions can
lead to loss of any claim for damages.
Further, non-observance can lead to following risks:
Failure of important functions of the machine or
facility.
Failure of electronic appliances and measuring
instruments by magnetic fields.
Endangering of persons and their personal
property by magnetic fields.
Endangering of persons by electric, mechanic and
chemical influences.
Endangering of environment through leakage of
dangerous substances.
On application of th
sections marked with Ex.
2.3 Safety Instructions for the Operator /
Worker
Depending on the operating conditions, wear and
tear, corrosion or age will limit the working life of
the pump/pump unit, and its specified
characteristics. The operator must ensure that
regular inspection and maintenance are carried
out so that all parts are replaced in good time,
which would otherwise endanger the safe
operation of the system. If abnormal operation or
any damage are observed, the pump must cease
operation immediately.
If the breakdown or failure of any system or unit
could lead to people being hurt or property being
damaged, such system or unit must be provided
with alarm devices and/or spare modules, and
they should be tested regularly to ensure that they
function properly.
If there is any risk of injury from hot or cold
machine parts, these parts must be protected
against contact by the user, or suitable warning
signs must be affixed.
Contact protection on moving parts (e.g. coupling
guards) must not be removed from systems that
are in operation.
If the sound level of a pump or pump unit is above
85 dB(A) an ear protection has to be used when
staying near the pump for some time.
If dangerous media (e.g. explosive, toxic, hot) leak
out (e.g. from shaft seals), these must be directed
away so that there is no danger to people or the
environment. The provisions of the law must be
observed.
LSB 100-english page 74
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Measures should be taken to exclude any danger
from electricity (e.g. by complying with the local
regulations on electrical equipment). If work is
carried out on live electrical components, they
should be unplugged from the mains or the main
switch turned off and fuse unscrewed. A motor
protection switch is to be provided.
Model LSB
2.4 Safety Instructions for Maintenance,
Inspections and Mounting Work
The operator is responsible that any maintenance,
inspections and mounting work is made by
authorized competent personnel, which must be
informed by having read the Operating
Instructions.
Basically, all work on the pump or pump unit
should only be carried out when the pump is
stationary and not under pressure. All parts must
be allowed to return to ambient temperature.
Make sure that no-one can start the motor during
such work. It is essential that the procedure for
stopping the system described in the Operating
Instructions is observed. Pumps or pump systems
that carry media that are dangerous to health must
be decontaminated before being taken apart.
Safety Data Sheets for the various liquids handled.
Immediately after finishing work, all safety and
protective devices must be replaced or restarted.
2.5 Unauthorized Alteration and Spare
Parts Production
Alteration or changes of the machine are permitted
after agreement with the manufacturer.
Original spare parts and accessory authorized by the
manufacturer are serving the safety.
The use of other parts can lead to loss of liability for
therefrom resulting consequences.
2.6 Undue Operation
The operating safety of the delivered machine can
only be guaranteed by designated use acc. to the
following chapters of the Operating Instructions.
The limits stated in the data sheet and / or order
confirmation must not be exceeded under any
circumstances.
2.7 Explosion Protection
On application of units in areas endangered to
explosion measures and references in the chapters
2.7.1 to 2.7.6 must be observed, so that explosion
protection is guaranteed.
2.7.1 Filling of unit
suction and
liquid.
and the danger of dry-run is avoided.
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 79

Installation, Operation and Maintenance Instruction
If the operator can´t guarantee that, according
Equally all seal casings, auxiliary systems of the
shaft sealing, as well as heating and cooling
The marking of the pump refers to the pump
tions a
aration of Conformity, as well as a
If danger of explosion is also existing during
e rotation control must not be
up of the empty pump,
to avoid undue temperature increase in case of
There´s a danger, that high surface
res are developing at the pump
casing after relatively short time, through fast
ase inside the pump can
On pumps with mech. seals the permitted
run. Dry run not only can occur on insufficiently
sing, but also because of too much
Operation of the pump out of the permitted
Under normal operating conditions the highest
surface
of the pump casing and in the area of the
During operation of the pump it must be
red that an overabundant sedimentation of
dust is avoided (regular cleaning), to prevent
heating of pump surface over the permitted
The particular allowed operating temperature of
n the data sheet and / or the
order confirmation resp. the type plate at the
For a secure and reliable operation it must be
secured by regular inspections, that the unit is
maintained competently and is kept in good
monitoring measures must be provided.
2.7.5 Temperature limits
temperatures must be expected at the
Model LSB
systems must be filled carefully.
2.7.2 Marking
itself. For the motor resp. further addi
separate Decl
corresponding marking must be available.
Example of of marking at pump:
CE Ex II 2 G c T1-T.
The marking shows the theoretically applicable range
of temperature classes. The different temperatures,
permitted acc. to pump design, result as shown in
chapter 2.7.5. The same is valid for the drive.
For a whole unit (pump, motor) with different
temperature classes the lowest is valid.
2.7.3 Rotation Control
installation, th
carried out by short start-
contact of rotating and stationary parts.
2.7.4 Operation of pump
The pump must only be started up with fully opened
suction side and slightly opened pressure side valve.
The start-up against closed non-return valve, however,
is possible. Immediately after the start-up the
discharge side valve must be adjusted to the operating
point.
Refer to chapter 6.2, as well.
Operation with closed valve in suction and / or
discharge pipe is not permitted!
bearings.
The surface temperature occurring at pump casing
corresponds with the temperature of the pumped
liquid.
In the area of lantern and motor free contact of
surface to environment must be given for proper
cooling.
secu
temperature.
The operator of the plant must secure that the
defined operating temperature is observed. The
max. allowed temperature of the pumped liquid at
suction depends on the particular temperature
class.
The following table shows the theoretical temperature
limits of the pumped liquid in consideration of the
temperature classes acc. to EN 13463-1.
Temperature class acc.
EN 13463-1
Temperature class acc.
EN 13463-1
T4 (135°C) 135°C
T3 (200°C) 140°C
T2 (300°C) 140°C
T1 (450°C) 140°C
the pump is shown i
pump.
2.7.6 Maintenance
temperatu
heating of the liquid inside the pump.
Fast pressure incre
lead to overload and, thus, the pump can burst.
In chapter 6.4.1 the minimum flow is stated. Longer
operating phases with these flows and the named
liquids don´t cause additional increase of surface
temperature at the pump.
Furthermore the references in chapter 6 of these
operating Instructions must be taken into
consideration.
temperature limits can be exceeded due to dry-
filled seal ca
gas in the medium.
operating range can lead to dry-run, as well.
LSB 100-english page 75
Artikel Nr. 771076129
technical condition.
Example: Function of bearings. Operation and
application conditions are essentially responsible for
their achievable life cycle.
By regular control of the lubricant and the running
sound the danger of occurring over temperatures by
bearings running hot or defect bearing seals is
avoided. Refer to chapter 6.6 and 7.4.
The function of the shaft sealing must be secured by
regular control.
If auxiliary systems (e.g. external flushing, cooling,
heating) are installed, it must be checked, if monitoring
devices are necessary to secure the function.
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 80

Installation, Operation and Maintenance Instruction
Electric switches and control devices,
mentation and accessories must
correspond with the valid safety requirements
Suitable safety measures must be taken at the
plant to ensure that the speed, pressure and
temperature of the pump and the shaft sealing
eed the limit values given in the data
sheet and / or order confirmation. The given
admission pressures (system pressures) must
asically the suction and discharge piping must
be designed in such way, that as little forces as
possible are effective to the pump. If that is not
possible, the values shown in chapter 3.5 must
not be exceeded under any circumstances. This
e operation as well as for the
standstill of the pump and therefore for all
sible pressures and temperatures of the
The pumped liquid must have a min. pressure
NPSH at the impeller inlet, so that cavitation
p. a "break off" of the
pump flow is prevented. This condition is
value of the system
value of the pump
2.7.7 Electric switches and control device,
Instrumentation and accessories
2.8.3 NPSH
Model LSB
instru
and regulations for explosion protection.
2.8 Use acc. to Regulations
2.8.1 Speed, Pressure, Temperature
do not exc
also be sufficiently high.
Further, pressure shocks, as can occur on too fast
shut down of the facility, must be kept away from the
pump (e.g. by non-return valve at pressure side,
airtanks). Quick temperature changes must be
avoided. They could cause a temperature shock and
lead to damage or impair the function of single
components.
2.8.2 Permitted Nozzle Loads and Torques
B
is valid for th
pos
unit.
3. Description
free work is secured res
fulfilled, when NPSH(NPSHA) lies above NPSH(NPSHR) under all operating conditions.
Attentention must especially be piad to the NPSHvalue on pumping liquids near the vapour pressure. If
the NPSH-value of the pump remains under, this can
lead from damage of the material due to cavitation to
destruction by overheating.
The NPSH-value of the pump (NPSHR) is shown in
the curves of every pump type.
2.8.4 Sealing, Flushing, Cooling
Suitable provisions for the regulation and monitoring of
sealing, flushing or cooling are to be provided.
When handling dangerous liquids or if temperatures
are high, care should be taken to ensure that the
pump ceases operating if the sealing, flushing or
cooling system fails.
Sealing, flushing and cooling systems must always be
operational before the pump is started up. They
should not be taken out of operation until the pump
has stopped, provided that the nature of the operation
allows this at all.
2.8.5 Back Flow
In systems where pumps are operating in closed
circuits under pressure (gas cushions, steam
pressure), the pressure of the gas cushion must not
be reduced via the pump, since the back flow speed
may be much higher than the operating speed, which
would destroy the unit.
3.1 Design
LSB-pumps are single-stage volute casing pumps in
block design. Hydraulic design and dimensions comply
with ISO 2858/ EN 22858, the technical design
complies with ISO 5199/EN 25199.
The motors comply with DIN 42677-IM B5. Motor and
pump shaft are coupled rigidly.
The permitted application conditions and design
details of the delivered pump are shown in the
attached data sheet and / or the order confirmation
(see Design Coding System in chapter 3.2).
Installation position: LSB-pump are intended for use
with horizontal shaft, discharge up. Installation
positions deviating therefrom must be approved by the
manufacturer.
3.1.1 Design Coding System
Due to the coding on data sheet and / or order
confirmation all information regarding the delivered
pump can be found in this Installation, Operation and
Maintenance Instruction, e.g.:
LSB 100-english page 76
Artikel Nr. 771076129
LSB 100 - 65 - 250 S1 V L 2 - 132
(0) (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) (7) (8)
Position (0) - Name of Model
LSB - ISO block pump
Position (1) - Suction Nozzle in mm
Position (2) - Discharge Nozzle in mm
Position (3) - Nominal diameter of impeller in mm
Position (4) - Shaft sealing
S1 - Single-mech. seal acc. DIN 24960 l1k /
EN 12756 form U
S4 - Single-mech. seal acc. DIN 24960 l1k /
EN 12756 form U
with Quench (throttle bush)
Position (5) - Material Impeller
N = Cast Iron (0.6025)
L = Ductile Iron (0.7043)
V = Carbon Steel (1.4408)
W = Duplex (1.4517)
Position (6) - Material pump casing (same coding as
impeller, cast iron not available)
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 81

Installation, Operation and Maintenance Instruction
The mech. seal used in the standard design is
as well as
the dangers of accidents, connected to them
Position (7) - Stub shaft
2 - without shaft sleeve (Duplex 1.4462 std)
Position (8) - IEC Motor size
3.2 Shaft Sealing
Pumps of design LSB are exclusively sealed with
single mech. seals with installation dimensions acc. to
EN 12756 (DIN 24960), design "K", form "U".
Two shaft sealing variants are available. On the data
sheet and / or the order confirmation the kind of shaft
sealing is given. An instruction for the mounting and
operation of mech. seals is contained in the particular
"Mounting Instruction of Shaft Sealing".
For nominal size (d1) of the mech. seal refer to
following chart.
40-25-160 33
40-25-200 33
40-25-250 43
50-32-160 33
50-32-200 33
50-32-250 43
50-32-315 43
65-40-160 33
65-40-200 33
65-40-250 43
65-40-315 43
80-50-160 33
80-50-200 33
80-50-250 43
80-50-315 43
nom. size
Type
not resistant to mineral oils.
d1 of mech.
seal
Type
100-65-160 43
100-65-200 43
100-65-250 43
100-65-315 53
125-80-160 43
125-80-200 43
125-80-250 43
125-80-315 53
125-100-200 43
125-100-250 53
125-100-315 53
150-125-250 53
150-125-315 53
200-150-250 53
For further details about mech. seals,
nom. size
d1 of mech.
seal
Model LSB
3.4 Approximate Value for Sound
Pressure Level
Nominal
power
PN
in kW
0,55 50,5 49,5 49,0 58,0 52,0 51,5
0,75 52,0 51,0 50,5 59,0 54,0 53,0
1,1 54,0 53,0 52,5 60,0 55,5 54,5
1,5 55,5 55,0 54,5 63,5 57,0 56,0
2,2 58,0 57,0 56,5 64,5 59,0 58,5
3,0 59,5 58,5 58,0 68,5 61,0 62,0
4,0 61,0 60,0 59,5 69,0 63,0 63,0
5,5 63,0 62,0 61,5 70,0 65,0 65,0
7,5 64,5 63,5 63,0 70,5 67,0 67,0
11,0 66,5 65,5 65,0 72,0 69,0 68,5
15,0 68,0 67,0 66,5 72,5 70,0 70,5
18,5 69,0 68,5 68,0 73,0 70,5 74,0
22,0 70,5 69,5 69,0 74,5 71,0 74,0
30,0 72,0 71,0 - 75,0 72,0 37,0 73,0 - - 76,0 - -
2950
min-1
Sound pressure level LpA measured in 1 m distance
from pump surface acc. to DIN 45635, part 1 and 24.
Room and foundation influences are not considered.
The tolerance for these values is ±3 dB(A).
Addition with 60 Hz-operation:
Pump alone: −
Pump with motor: +4 dB(A)
Sound pressure level LpA in dB(A)
Pump alone Pump + Motor
1450
min-1
975
min-1
2950
min-1
1450
min-1
975
min-1
3.5 Permitted Nozzle Loads and Torques
at the Pump Nozzles ...
... following the Europump-Recommendation for
pump acc. to ISO 5199.
The data for forces and torques are only valid for static
piping loads.
All values for forces and torques refer to standard
materials EN-GJS400-18LT and 1.4408.
refer to chapter 6.6 and chapter 7.2.
3.3 Bearing
The shaft is guided by the ball bearings of the motor.
The bearings are grease lubricated for life and,
therefore maintenance-free.
LSB 100-english page 77
Artikel Nr. 771076129
pic 1
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 82

Installation, Operation and Maintenance Instruction
Model LSB
∅DN
40-25-160 40 700 620 560 1100 730 500 590 1070 25 420 400 480 730 500 340 400 730
40-25-200 40 700 620 560 1100 730 500 590 1070 25 420 400 480 730 500 340 400 730
40-25-250 40 700 620 560 1100 730 500 590 1070 25 420 400 480 730 500 340 400 730
50-32-160 50 920 840 760 1450 780 560 650 1150 32 500 480 590 930 620 420 480 900
50-32-200 50 920 840 760 1450 780 560 650 1150 32 500 480 590 930 620 420 480 900
50-32-250 50 920 840 760 1450 780 560 650 1150 32 500 480 590 930 620 420 480 900
50-32-315 50 920 840 760 1450 780 560 650 1150 32 500 480 590 930 620 420 480 900
65-40-160 65 1180 1040 950 1850 840 620 670 1230 40 620 560 700 1100 730 500 590 1060
65-40-200 65 1180 1040 950 1850 840 620 670 1230 40 620 560 700 1100 730 500 590 1060
65-40-250 65 1180 1040 950 1850 840 620 670 1230 40 620 560 700 1100 730 500 590 1060
65-40-315 65 1180 1040 950 1850 840 620 670 1230 40 620 560 700 1100 730 500 590 1060
80-50-160 80 1400 1260 1150 2200 900 650 730 1320 50 840 760 920 1450 780 560 650 1150
80-50-200 80 1400 1260 1150 2200 900 650 730 1320 50 840 760 920 1450 780 560 650 1150
80-50-250 80 1400 1260 1150 2200 900 650 730 1320 50 840 760 920 1450 780 560 650 1150
80-50-315 80 1400 1260 1150 2200 900 650 730 1320 50 840 760 920 1450 780 560 650 1150
100-65-160 100 1880 1680 1520 2950 980 700 810 1450 65 1040 950 1180 1850 840 620 670 1230
100-65-200 100 1880 1680 1520 2950 980 700 810 1450 65 1040 950 1180 1850 840 620 670 1230
100-65-250 100 1880 1680 1520 2950 980 700 810 1450 65 1040 950 1180 1850 840 620 670 1230
100-65-315 100 1880 1680 1520 2950 980 700 810 1450 65 1040 950 1180 1850 840 620 670 1230
125-80-160 125 2210 2000 1800 3480 1180 840 1070 1710 80 1260 1150 1400 2200 900 650 730 1320
125-80-200 125 2210 2000 1800 3480 1180 840 1070 1710 80 1260 1150 1400 2200 900 650 730 1320
125-80-250 125 2210 2000 1800 3480 1180 840 1070 1710 80 1260 1150 1400 2200 900 650 730 1320
125-80-315 125 2210 2000 1800 3480 1180 840 1070 1710 80 1260 1150 1400 2200 900 650 730 1320
125-100-200 125 2210 2000 1800 3480 1180 840 1070 1710 100 1680 1520 1880 2950 980 700 810 1450
125-100-250 125 2210 2000 1800 3480 1180 840 1070 1710 100 1680 1520 1880 2950 980 700 810 1450
125-100-315 125 2210 2000 1800 3480 1180 840 1070 1710 100 1680 1520 1880 2950 980 700 810 1450
150-125-250 150 2800 2520 2270 4400 1400 980 1150 2050 125 2000 1800 2210 3480 1180 840 1070 1710
150-125-315 150 2800 2520 2270 4400 1400 980 1150 2050 125 2000 1800 2210 3480 1180 840 1070 1710
200-150-250 200 3750 3360 3030 5850 1820 1290 1490 2700 150 2520 2270 2800 4400 1400 980 1150 2050
Forces in N Torques in Nm Forces in N Torques in Nm Sizes
Fx Fy Fz
Suction nozzle Discharge nozzle
Mx My Mz
∑F
∑M
∅DN
Fx Fy Fz
Mx My Mz
∑F
∑M
3.6 Permitted pressures and temperatures
Basically the values, regarding pressures and
temperatures, given in the data sheet and / or the
order confirmation, as well as on the name plate.
Exceeding or remaining under of these values are
undue. If there are no pressures and / or temperatures
mentioned in data sheet and / or order confirmation,
the following limits are valid for suction pressure and
room temperature:
For all pump types, except:
50-32-315 - 65-40-315 - 80-50-315 - 100-65-315 125-80-315 - 125-100-315
Suction pressure (System pressure) = Pressure at
pump suction: max. 5 bar
Ambient temperature max. 40°C.
On Application of pumps local laws and regulations
must be noticed, as well (e.g. DIN 4747 or DIN 4752,
section 4.5).
Only for:
50-32-315 - 65-40-315 - 80-50-315 - 100-65-315 125-80-315 - 125-100-315
Curve Casing material Description
A 1.4408 Austenitic Steel
B 1.4517 Duplex Steel
EN-GJS-400-18-LT
C
(0.7043)
Ductile Iron
LSB 100-english page 78
Artikel Nr. 771076129
The given pressure and temperature limits are valid
for standard mech. seals.
Application limits for other materials on request.
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 83

Installation, Operation and Maintenance Instruction
Dispose of all packing materials in accordance
Take note of the general regulations on
The pump / pump unit must be secured against
tipping over and slipping until it has been fixed
Sling ropes must not be fixed to ends of shafts
Slipping out of the pump / unit of the transport
lifting device can cause damages to persons
Sufficient space must be provided for
nance and repair work, especially for
replacing the drive motor or the complete pump
unit. The motor fan must be able to take in
enough cool air, and the intake grille must
t least 10 cm away from any wall,
3.7 Condensate
On motors which are subject to strong temperature
deviations or extreme climatic conditions, we
recommend the use of a motor with stand-by heating
4. Transport, Handling, Storage
4.1 Transport, Handling
Check the pump / pump unit immediately upon
delivery / receipt of despatch for damage or
missing parts.
The pump / pump unit must be transported
carefully and by competent personnel. Avoid
serious impacts.
Keep the pump / pump unit in the same position in
which it was supplied from the factory. Take note
of the instructions on the packaging.
The suction and discharge side of the pump must
be closed with plugs during transport and storage.
Model LSB
to avoid formation of condensate inside the motor.
The stand-by heating must not be switched on during
the operation of the motor.
with local regulations.
Lifting devices (e.g. fork-lift truck, crane, crane
device, pulleys, sling ropes, etc.) must be
sufficiently strong and must only be used by
authorized persons.
The pump / pump unit may only be lifted by solid
points such as the casing, flanges or frame.
Picture 2 shows the correct method of carrying by
crane.
Do not stand underneath suspended loads.
prevention of accidents.
in its final location.
or the ring loops of the motor.
and things.
5. Mounting / Installation
pic 2
4.2 Storage / Conservation
Pumps or units, which are stored over a longer period
before start-up (max. 6 months), must be protected
from moisture, vibrations and dirt (e.g. by wrapping in
oil paper or plastic). Pumps must basically be stored in
a place where they are protected from the weather,
e.g. under dry cover. During this time, all suction and
discharge branches and all other intakes and outlets
must be closed with dummy flanges or plugs.
For longer periods of storage conservation
measurements at machined surfaces and packing with
moisture protection can be necessary!
5.1 Mounting of Pump / Unit
The pumps must be bolted to a solid base (e.g.
concrete foundation, steel plate, steel bracket, etc.).
This base must withstand all loads occurring during
operation. The place, where the pump is mounted
must be prepared acc. to the dimensions of the
dimensional drawings. The concrete foundations
should have sufficient firmness acc. to DIN 1045 or
equal standard (min. BN 15), to ensure a secure,
functional mounting. The concrete foundation must
have set, before the unit is erected. Its surface must
be horizontal and even. For the position and size of
the pump feet and the foundation screws refer to the
dimensional drawing.
LSB 100-english page 79
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Concrete expansion bolts, epoxy capsule anchor bolts
or anchor bolts grouted with the foundation (stone
screws), can be used for.
mainte
therefore be a
etc.
When mounting the pump on the foundation it
must be adjusted at the discharge nozzle by
means of a spirit-level (at discharge nozzle). The
permitted deviation is 0,2 mm/m. Levelling shims
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 84

Installation, Operation and Maintenance Instruction
The size of these insulating pads will vary,
pending on circumstances, and should
fore be determined by an experienced
The pump must not be used as fixed point for
the piping. The permitted piping loads must not
These connections are essential for the
On application in zone 1 and 2 a motor with
Electrical connection work may only be carried
out by an authorised professional. The rules
electrical technology,
especially those concerned with safety
ures, must be observed. The regulations
of the national power supply companies
must be inserted next to the foundation anchors
and must lie plainly.
If vibrations are transmitted to the foundation from
adjoining components, it must be guarded through
adequate vibration damping paddings (vibrations
from outside can impair the bearing).
To prevent vibrations being transmitted to
adjoining components, the foundation should be
laid on a suitable insulating base.
de
there
specialist.
5.2 Connection of Pipings to the Pump
be exceeded, refer to chapter 3.5.
5.2.1 Suction and discharge pipe
The pipes must be of a size and design that liquid
can flow freely into the pump and that the pump
functions without problems. Particular attention is
to be paid to ensuring that suction pipes are
airtight and that the NPSH values are observed.
Under suction lift condition lay the suction pipe in
the horizontal section towards the pump so that it
is slightly inclined upwards so that no air traps
occur. Do not install fittings or elbows right before
the suction nozzle.
If the suction supply is under vacuum and
entrained gas may be present in the liquid, it is
recommended that a vent line (min. diameter 25
mm) be considered upstream of the pump suction
with return to the suction supply, above the max
liquid level.
An additional flushed piping - discharge branch-
vent line - makes it easier to de-aerate the pump
before start-up (pic 3).
pic 3
When laying the pipes, make sure that the pump
is accessible for maintenance, installation and
disassembly.
Notice "Permitted Forces on Flanges" (chapter
3.7).
If expansion joints are used in the pipes, they
have to be supported in such a way that the pump
is not loaded unduly high because of the pressure
in the pipes.
Model LSB
Before connecting up to pump: remove protective
coverings from suction and discharge branches.
Before starting up, the pipe system, fittings and
equipment must be cleaned to remove weld
spatter, scale etc. Any pollutants are to be
completely removed from pump units that are
directly or indirectly connected to drinking water
systems before being installed and taken into use.
To protect the shaft sealing (especially mechanical
seals) against foreign impurities, it is
recommended that a sieve, 800 micron, is
installed in the suction / intake pipe when the
motor is being started up.
If the pipe system is tested with the pump
installed, do not exceed the maximum permitted
casing pressure of the pump and/or shaft sealing
(see data sheet).
When emptying the pipe after the pressure test,
make sure that the pump is treated properly
(danger of rust and problems when starting up).
5.2.2 Additional connections
Any required sealing, flushing or cooling pipe
connections must be installed. Please consult the data
sheet to see which pipes, pressures and amounts are
necessary. The position and size of connections to the
pump are given in the appendix, "Connections".
function!
It is recommended that a pipeline is installed to take
off any leakage from the shaft seal. For connection,
see appendix, "Connections".
5.3 Drive
Note the Operating Instructions of the motor
manufacturer.
valid Atex-certification must be used.
If in the process of the repair a new motor is used , the
following has to be noticed:
The motor must comply with the requirements
stated in sheet 1220.1A608 (order from
manufacturer, on demand).
Clean motor end and motor flange of new motor
carefully (remove varnish).
5.4 Electric Connection
and regulations valid for
meas
operating in that area must also be observed.
Before starting work, check that the information on the
motor name plate is the same as the local mains
network. The power supply cable of the coupled drive
LSB 100-english page 80
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 85

Installation, Operation and Maintenance Instruction
14
must additionally be noticed for the electric
The direction of rotation must only be checked
when the pump is full. Dry running will cause
The plant may only be started up by people who
are familiar with the local safety regulations and
with these Operating Instructions (especially
ons and safety
Operation with closed valve in the suction and /
pressure must be produced through throttling at
If pump does not reach attended head or if
k for
Be particularly careful not to touch hot machine
parts and when working in the unprotected shaft
seal area. Remember that automatically
ystems may switch themselves on
Suitable warning signs
The operating limits of the pump / unit regarding
pressure, temperature, performance and speed
order
firmation and must be observed under any
motor must be connected up in accordance with the
wiring diagram produced by the motor manufacturer.
A protective motor switch must be provided.
In areas endangered to explosion IEC 60079-
installation.
damage to the pump.
6. Start-up, Operation, Shut down
with the safety regulati
instructions given here).
6.1 Initial start-up
Before starting up the pump, check, if the following
points were controlled and carried out:
There´s no need to lubricate the pump before
starting it up.
Pump and suction pipe must be filled completely
with liquid when starting up.
Turn pump unit once again by hand and check
that it moves smoothly and evenly.
Check that lantern guard sheets are mounted and
that all safety devices are operational.
Switch on any existing sealing or flushing pipings.
For quantities and pressures refer to data sheet
and / or order confirmation.
Open valve in suction /intake pipe.
Set discharge side valve to approx. 25% of rated
flow quantity. With pumps with a discharge branch
rated width less than 200, the valve can remain
closed when starting up.
Secure, that unit is electrically connected acc. to
all regulations and with all safety devices.
Check direction of rotation by switching on and off
briefly. It must be the same as the directional
arrow on the drive lantern.
6.2 Switch on drive
Immediately (max. 10 seconds on 50 Hz resp.
max. 7 seconds on 60 Hz currency feed) after
reaching normal operating speed open discharge
valve adjust the required operating point. The
pumping data shown at the type plate resp. in the
data sheet and / or the order confirmation must be
met. Every change is only permitted after talking
with the manufacturer!
or discharge piping is not permitted.
LSB 100-english page 81
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Model LSB
5.5 Final Control
It must be possible to turn the unit easily by hand at
the stub shaft.
On starting-up without back-pressure, the back-
the discharge side. After reaching full backpressure open valve.
atypical sounds or vibrations do occur:
Switch off pump (see chapter 6.7) and see
causes (see chapter 10).
6.3 Restarting
Basically, the same procedure should be followed as
for starting up for the first time. However, there is no
need to check the direction of rotation and the
accessibility of the pump unit.
The pump should only be automatically restarted if it
has been made sure that the pump has remained
filled whilst stand by.
controlled s
suddenly at any time.
should be affixed.
6.4 Limits of Operation
are shown in the data sheet and / or
con
circumstances!
Do not exceed the output given on the motor
name plate.
Avoid sudden changes in temperature
(temperature shocks).
The pump and motor should run evenly and
without vibrations; check at least once a week.
6.4.1 Flow min. / max.
If no other data are given in the curves or data sheets,
the following is valid:
Q
= 0,1 x Q
min
= 0,3 x Q
Q
min
Q
= 1,2 x Q
max
Q
= Flow in efficiency optimum
BEP
*) on condition that NPSH
for for short time operation
BEP
for continuous operation
BEP
for continuous operation *)
BEP
facility
> (NPSH
pump
+ 0,5 m)
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 86

Installation, Operation and Maintenance Instruction
On pumping liquids with abrasive components
ling
tion
hould be reduced compared to the usual
In areas endangered to explosion it is
mended to monitor the temperature of the
tend
6.4.2 Abrasive Media
an increased wear at hydraulic and shaft sea
must be expected. The intervals of inspec
s
times.
6.4.3 Permitted number of starts
The permitted number of starts of the pump must not
be exceeded, see diagram 6.
100,0
10,0
max. perm. starts/h
1,0
1 10 100 1000
Motor power [kW]
diagram 6
With electric motors, the permitted number of starts is
given in the attached motor operating instructions.
If two different figures are given, the lower figure is
valid.
6.5 Lubrication
The pump has no bearings and, therefore there´s no
need for lubrication.
For possibly required lubrication of the motor bearings
refer to the Operation and Maintenance Instructions of
the motor supplier.
6.6 Monitoring
recom
bearings and the vibrations of the pump.
Regular monitoring and maintenance will ex
the life of your pump or pump system.
Check pump for leaks at least once a week.
Check the regulating and monitoring devices of
any sealing or flushing systems once a week to
ensure that they function properly. Outgoing
cooling water should be handwarm.
Pumps which are exposed to corrosive chemicals
or to wear through abrasion must be inspected
periodically for corrosion or wear and tear. The
first inspection should be carried out after six
months. All further inspection intervals should be
determined on the basis of the state of the pump.
LSB 100-english page 82
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Model LSB
6.7 Shutting down
Close the valve in discharge pipe right before
(max. 10 seconds) switching off the motor. This is
not necessary if there is a spring-loaded check
valve.
Switch off motor (make sure it runs down quietly).
Close the valve on suction side.
Close auxiliary circuit.
On danger of freezing empty pump and pipes
completely.
If pump remains under pressure and temperature
when stationary: leave existing sealing and
flushing systems switched on.
The shaft sealing must remain sealed if there is a
risk of air being sucked in (in the event of supply
from vacuum systems or parallel operation with
shared suction pipe).
6.8 Storage / longer periods of nonoperation
6.8.1 Storage of new pumps
If the putting into operation shall happen a longer
period after the delivery, we recommend the following
measures for the storage of the pump:
Store pump at a dry place.
Rotate pump by hand at least once a month.
6.8.2 Measures for longer putting out of operation
Pump remains installed and in ready for operation:
Test runs of 5 min. duration must be made in
regular intervals. The span between the test runs
is depending on the plant. However, it should be
made once a week, at least.
6.8.3 Longer periods of non-operation
Start-up must be handled like initial start-up (see
chapter 6).
a) Filled pumps
Switch stand-by pumps on and immediately off
again once a week. Possibly use as main pump.
If the stand-by pump is under pressure and
temperature: leave all existing sealing and flushing
systems swiched on.
Replace motor bearings after 5 years.
b) Drained pumps
Turn shaft at least 1x week (do not switch on
because of dry running).
Replace motor bearings after 5 years.
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 87
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Instruction
Work should only be carried out on the pump or
You must
Maintenance and servicing work must only be
carried out by trained, experienced staff who
iar with the contents of these Operating
Instructions, or by the Manufacturer's own
Before opening the pump, it is essential that you
sed
Repair to the pump or pump system may only
be carried out by authorised skilled personnel or
If dangerous liquids are pumped the appropriate
disposal of the handled liquid is necessary
re the disassembly of the pump. Pay
fact, that even in drained pumps
there are remainders of the handled liquid. If
necessary the pump must be flushed or
decontaminated. Laws must be observed,
its or single
While disassembling the pump use of an open
flame (blowlamp, etc.) only, when there is no
danger of setting fire, cause an explosion or
Pay attention to
Works, which require shocks (hammer), must
only be performed outside the explosive
sparking tools must be
7. Servicing, Maintenance
Model LSB
7.1 General remarks
pump unit when it is not in operation.
observe chapter 2.
are famil
service staff.
7.2 Mechanical seals
note chapter 2 and chapter 8.
If the liquid being handled leaks out at the mechanical
seal, it is damaged and must be replaced.
Replacement of the mech. seal according to
accompanying "Mounting Instructions for Shaft
sealing".
8. Dismantling and repair of pump
8.1 General remarks
7.3 Motor bearings
After approx. 5 years the grease in the motor bearings
is so aged, that a replacement of the bearings is
recommended. However, the bearings must be
replaced after 25000 operating hours, at least, resp.
acc. to the Maintenance Instruction of the motor
supplier, if that recommends a shorter maintenance
period.
7.4 Cleaning of pump
Dirt on the outside of the pump has an adverse
effect on transmission of heat. The pump should
therefore be cleaned with water at regular
intervals (depending on the degree of dirt).
The pump must not be cleaned with pressuri
water - water will get into the bearings.
Use original spare parts only.
the right materials and the matching design.
by the manufacturer´s specialist staff.
When disassembling the pump pay attention to
chapter 2 and chapter 4.1.
For mounting and repair you can order specialized
personnel if you want.
befo
attention to the
otherwise danger to health is existing!
Before the disassembly the pump has to be
secured in such a way, that it can´t be started.
The pump casing must be drained and without
pressure.
All locking devices in the suction- and discharge-
pipe must be closed.
All parts must have taken on the temperature of
the environment.
Secure disassembled pumps, un
parts against tipping over or rolling off.
cause injurious vapours.
LSB 100-english page 83
Artikel Nr. 771076129
8.2 General
atmosphere or only nonused.
Carry out disassembly and mounting according to the
appropriate sectional drawing.
You will only need common tools.
Before disassembly check if required parts are ready.
Disassemble the pump only so far, as required for the
replacement of the repair part.
8.3 Removal and Installation of screen in
the motor lantern
The guard plates (680) are fixed in the windows of the
motor lantern (681).
For removing insert a screwdriver about 4 cm into the
last row with punches of the guard plate. Then pull up
the screwdriver until the lower edge of the guard plate
lifts off the window. Now you can remove the
screwdriver together with the guard plate from the
window (see picture 8).
On installation insert the screwdriver about 4 cm into
the last row with punches of the guard plate. Then put
the upper part of the guard plate into the upper edge
of the window. Now pull up the screw driver until the
guard plate is bent through so much, that it can be
inserted into the lower edge of the window of the
motor lantern.
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 88

Installation, Operation and Maintenance Instruction
s absolutely
necessary to insert the guard plate into the
window. If the guard plate doesn´t stick fast in
Dismantle guard plate once again, flatten it and
Notice attached "Mounting Instruction for Shaft
Be sure to locate pry bars under impeller vanes
Model LSB
Using the jack screws provided (901.42), separate
the Back Pull Out Assembly from the casing.
8.5 Removal of Impeller
pic 8
Pull up screw driver only so far as i
the window after installation:
install again.
8.4 Removal of the Back Pull Out
Assembly
The back pull out assembly consists of all pump parts
except the volute casing (102V). As the pumps are
constructed in block design, the volute casing (102V)
can remain on the foundation and in the piping, if it´s
not the volute casing itself, which must be repaired.
Drain volute casing (102V) via drain plug (912.11).
Loosen screws of existing sealing or flushing
pipings.
Loosen screws of support food (183) from the
foundation (not existing on all sizes).
Hang the Back Pull Out Assembly onto a lifting
device, so that it won´t sink down or press into the
volute casing during the dismounting. Example
see picture 9 for lifting recommendations.
Loosen hexagen head bolt (901.11) from the
casing.
LSB 100-english page 84
Artikel Nr. 771076129
pic 9
Sealing".
If the impeller has back vanes check the axial
clearance "a" between the impeller (230) and
casing cover (161) before you continue the
dismounting. Refer to sect. 8.8.1.
Loosen impeller nut with a sensitive hit on the
wrench (right-hand thread). If necessary back up
with a pry bar in the cross boring of the stud shaft
(in clamp area).
Draw off the impeller (230) with two screw drivers
or pry bars (picture 10). Remove key (940.31).
to prevent damage to the impeller.
For further dismounting, and for installation, the
Back Pull Out Assembly should be placed in a
vertical position. Prevent assembly from tipping!
pic 10
8.6 Removal of Shaft Sealing
Before you remove casing cover notice "Mounting
Instructions for Shaft Sealing".
Unfasten hexagonal nut (902.32) (not available on
all pump sizes) and take casing cover (161) out of
bearing bracket (344).
8.7 Removal of Stub Shaft
Loosen screws (920.41) and pull motor with stub
shaft (210) out of the motor lantern (341).
Loosen radial stub shaft screwing (904.41 and
904.42) (stud bolts) and deduct stub shaft (210)
from motor shaft. For support (break loose) you
can insert a solid screw driver into the cross
boring, press it against the front face of the motor
and move both shafts against each other.
Ausgabe 01/2010
Revision 02
Page 89

Installation, Operation and Maintenance Instruction
sealing elements and graphite
When the wear limits has been reached or
galling compound must be compatible with
Before starting the pump do not forget to install
8.8 Reconditioning
After disassembly all parts must be cleaned and
checked for wear carefully. Worn or damaged parts
must be replaced by new parts (spare parts).
It is recommended in most cases to replace mech.
seal, ball bearings and seals (flat seal, O-rings).
All PTFEsealings are intended for being used only once.
In most cases it make sense, if damaged absolutely
necessary, to renew the mech. seal and the bearings
Deposits on the impeller (230), in the volute casing
(102V) or on the casing cover must be removed.
8.8.1 Clearance at impeller
Suction side of impeller
Back vanes of impeller
Drive side of impeller
Only with pump size
100-65-315
125-80-315
125-100-315
150-125-315
Nominal diameter D (mm)
Radial
clearance
s (mm)
clearance
a (mm)
new
worn 0,78 0,85 0,90 1,05 1,15
new 0,8 - 1,2 Axial
worn max. 1,7
exceeded, the worn parts must be replaced.
min. 0,15 0,17 0,20 0,22 0,25
max. 0,19 0,22 0,24 0,27 0,30
60
68
85
100
120
135
155
175
220
For volute casings (102V) with a wear ring (502.11)
and cover casings (161) with a wear ring (502.31)
there are the following possibilities to restore the
correct clearance:
a) Renew impeller (230) and wear ring. Then the
original measures are restored.
b) A customized wear ring (bored to fit) can be
supplied to avoid replacement of the impeller.
Please contact factory for details.
When volute casing (102V) or casing cover (161)
without wear ring must be repaired, a wear ring can be
installed to renew pump performance. Remachining of
the volute casing and / or casing cover is required.
Please contact the factory for details and assistance.
LSB 100-english page 85
Artikel Nr. 771076129
8.9 Mounting
Model LSB
8.9.1 General
Re-assemble the pumps using the reverse order of
steps as completed for pump disassembly. However
the following observations should be considered:
Pay attention to the utmost cleanliness when
reassembling the pump.
For tight tolerances e.g. between stub shaft (210)
and motor shaft or impeller (230) and shaft (210),
as well as thread, use suitable anti-galling
compound (e.g. Molykote / Never-Seeze), so that
the next mounting and dismounting will be easier.
Antithe pumpage.
Screws should be tightened, with the following
torque:
Location
Casing Screws
All other scres
Screw
Size
M12 35 50
M16 105 150
M20 210 305
M10 35 50
M12 60 90
M16 150 220
Screw torque in Nm
Lubricated
threads
Dry threads
Do not use excessive force.
For mounting of stub shaft refer to chapter 8.9.2.
For mounting of mech. seal refer to separate
"Mounting Instruction of Shaft Sealing" and
chapter 8.5.
For impellers with back vanes the axial clearance
between the back vanes and the casing cover
(161) should be checked after mounting the
impeller (230) and tightening the impeller nut (922)
(see chapter 8.8.1).
After the mounting of the back pull out assembly,
and its assembly into the volute casing, turn the
shaft and control the free moving of the pump in
this way. The shaft sealings will cause slightly
resistance when turning, but there must not be
any contact between metal parts.
and connect all security devices.
8.9.2 Mounting of Stub Shaft
Insert key in the motor stump.
Put anti-galling compound onto the motor stump
(see point 8.9.1).
Push stub shaft up the motor shaft to measure A
(see pict. 11 and chart).
Drill countersink into motorshaft, appr. 2-3 mm
depth, through the radial bore in the motor shaft
(see pict. 11), by useing a twistdrill with 90° tip.
Remove cuttings out of the stud hole (e.g. with
compressed-air), screw in and make safe thread
pins (904.41 and 904.42) (e.g. with Omnifit 100 M
or Loctite).
Check smooth running of stub shaft opposite to
motor flange with a dial gauge. The pointer
deflection of the dial gauge must not exceed 0,1
mm.
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 90

Installation, Operation and Maintenance Instruction
To ensure optimum availability, we recommend
that suitable quantities of spare parts are held in
stock, especially if these are made from special
als,
by pumps are kept ready for use in plants where
failure of a pump could endanger human life or
cause damage to property or high costs.
Regular checks should be carried out to ensure
that such pumps are always ready for use (see
pic 11
Type
Measure A by motor size
80 90 100 112 132 160 180 200
Model LSB
40-25-160 157 157 197 197 197 232 - 40-25-200 157 157 197 197 197 232 - 40-25-250 162 162 202 202 202 237 237 237
50-32-160 157 157 197 197 197 232 - 50-32-200 157 157 197 197 197 232 - 50-32-250 162 162 202 202 202 237 237 237
50-32-315 - - 202 202 197 237 237 237
65-40-160 157 157 197 197 197 232 - 65-40-200 157 157 197 197 197 232 232 65-40-250 162 162 202 202 202 237 237 237
65-40-315 - - 202 202 197 237 237 237
80-50-160 157 157 197 197 197 232 232 80-50-200 157 157 197 197 202 232 232 232
80-50-250 - 162 202 202 202 237 237 237
80-50-315 - - 202 202 202 237 237 237
100-65-160 162 162 202 202 202 237 237 237
100-65-200 - 162 202 202 202 237 237 237
100-65-250 - 162 202 202 206 237 237 237
100-65-315 - - 206 206 202 241 241 241
125-80-160 - 162 202 202 202 237 237 237
125-80-200 - 162 202 202 202 237 237 237
125-80-250 - - 202 202 202 237 237 237
125-80-315 - - - 206 206 241 241 241
125-100-200 - - 202 202 202 237 237 237
125-100-250 - - 216 216 216 251 251 251
125-100-315 - - - - 206 241 241 241
150-125-250 - - - - 216 251 251 251
150-125-315 - - - - - 241 241 241
200-150-250 - - - - - 251 251 251
9. Spare parts, Spare pumps
9.1 Spare parts
Spare parts should be selected to last for two-years
continuous operation. If no other guidelines are
applicable, we recommend that you stock the number
of parts listed below (in accordance with VDMA
24296).
materials and in the case of mechanical se
because of the longer delivery times.
Number of pumps (incl. stand-by pumps)
Spare Parts Number of spare parts
Impeller 1 1 1 2 2 2 20%
Wear ring 2 2 2 3 3 4 50%
Shaft with keys and nuts 1 1 1 2 2 2 20%
Joints for pump casing
sets
other joints
sets
Mech. seal
sets
2 3 4 5 6/7 8/9 10/+
4 6 8 8 9 12 150%
4 6 8 8 9 10 100%
1 1 2 2 2 3 25%
Ordering spare parts
When ordering spare parts, please supply the
following information:
LSB 100-english page 86
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Type:
S/N (Order No.)
Part name
Sectional drawing
______________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________
All the information is given in the data sheet and the
relevant sectional drawing.
Store spare parts in dry and clean rooms.
9.2 Stand-by pumps
It is essential that a sufficient number of stand-
Point 6.8).
Store stand-by pumps according to point 6.8.
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 91

Installation, Operation and Maintenance Instruction
re given on
10. Faults - Causes and Solutions
Model LSB
The following notes on causes of faults and how to
repair them are intended as an aid to recognising the
problem. The manufacturer's Customer Service
Department is available to help repair faults that the
operator cannot or does not want to repair. If the
Discharge too low
Discharge stops after a time
Head too low
Head too high
Drive mechanism overloaded
Pump not running quietly
Temperature in pump too high
■
Back-pressure too high
■ ■
■ ■
■ ■
■ ■
■ ■
■ ■ ■
■ ■
■ ■ ■
■ ■ ■
■ ■ ■
■ ■
■ ■
■ ■ ■
■ ■
Speed too high reduce speed
Speed too low increase speed (check available motor power)
■ ■
■ ■
Impeller diameter too big use smaller impeller
Impeller diameter too small use larger impeller (check available motor power)
■ ■
Pump or suction/intake pipe blocked clean
Air pocket in pipeline vent
■ ■
Air being sucked in increase liquid level
Air being sucked in through shaft sealing clean sealing pipe
Direction of rotation is wrong swap over two phases of power supply (to be done by an
■
Density and/or viscosity of liquid handled is too high seek assistance
■
■ ■
■
Electricity supply not right (2-phase running) check voltage of all phases
■
■
Temperature in shaft sealing too high
■
Flow too little increase min. flow (open discharge valve, bypass)
■
Pump and/or pipes not completely filled with liquid fill
Suction height too big / NPSH of system too small
■
■
■
■ ■ ■
■
■
System-related vibrations (resonance) seek assistance
Cause
Temperature at the bearing too high
Pump leaking
Leakage rate at shaft sealing too high
Back-pressure too low, discharge too low throttle discharge valve
Flow too big reduce flow (throttle discharge valve)
Inner components suffering from wear replace worn parts
■
Lines and roughness at shaft replace parts
■
Deposits on mechanical seal
■
Impeller out of balance
Forces in pipeline too high (pump unit under strain) change (support pipes, use compensators, etc.)
■
Sealing insufficient tighten screws
Bearing damaged replace
Relief fittings insufficient
LSB 100-english page 87
Artikel Nr. 771076129
operator repairs or changes the pump, the design data
on the data sheet and chapter 2 of these Operating
Instructions should be particularly taken into account.
If necessary, the written agreement of the
manufacturer must be obtained.
Solution
check facility for pollution, open discharge valve
reduce resistance in discharge pipe (e.g. clean filter if
necessary)
use larger impeller (note available motor power)
compare speed of motor with specified pump speed (rating
plate)
when adjusting speed (frequency transformer) check reference
value setting
compare speed of motor with specified pump speed (rating
plate)
when adjusting speed (frequency transformer) check reference
value settings
vent
improve course of pipe
increase liquid level and admission pressure
reduce resistance in the intake/suction pipe (change course
and rated width, open shut-off valves, clean filters)
check if suction pipe is vacuum-tight
increase sealing pressure
replace shaft sealing
electrician)
clean
replace mechanical seal if necessary
if necessary provide additional rinsing or quench
remove blocks/deposits
replace impeller if broken or unevenly worn
check shafts to ensure that they are running true
is foundation plate/frame properly cast in place?
check cable connections and fuses
replace sealing
clean relief openings in impeller
replace worn parts (impeller, split rings)
adjust in line with the system pressure/intake pressu
ordering
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 92

Installation, Operation and Maintenance Instruction
The following instructions must be followed
exactly, to guarantee the safety at the
installation, at the operation and at the
intenance of the motor. All persons should
be directed to the present manual which are
performing these tasks. The neglect of the
instructions can cause the loss of the
Make sure that the rated voltage corresponds to
Ground the pump before making any other
We recommend that a high sensitivity
differential switch (30 mA) be installed as extra
protection against lethal electric shocks in the
The pump must not be run until it is filled with
Continuous dry running will damage the
delivery is higher than
E) Dense and viscous
11. Motor Operating Instructions
ma
guarantee.
Electrical connections
the supply voltage.
connection.
event of faulty grounding.
Connect the pump to the mains using a multiple-pole
switch or other device ensuring multiple-pole
disconnection (interruption of all the supply wires) from
the mains, with a contact separation of at least 3 mm.
Remove the terminal board cover by first removing the
screws.
Carry out the connections as indicated on the back of
the terminal board cover, and as shown in fig. 3 - 4.
The single-phase version has a built-in overload
protection; the three-phase version must be equipped
by the user with a magneto-thermal switch or
magnetic starter with overload and undervoltage
protection, a thermal relay and fuses installed
upstream.
The overload relay must be set to the motor current
rating. The thermal relay may be set to a current value
slightly lower than the full load value when the electric
pump is definitely underloaded, but the thermal
overload protection must not be set to current values
higher than the full load values.
Checking the rotation direction of electric pumps
with three-phase motors.
The direction of rotation may be checked before the
pump is filled with the liquid to be pumped, provided
it is run for very short starts only.
liquid.
mechanical seal beyond repair.
If the direction of rotation is not anti-clockwise when
facing the pump from the suction side interchange two
supply leads.
LSB 100-english page 88
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Model LSB
Fault finding chart
PROBLEM PROBABLE CAUSE POSSIBLE
1. The pump doesn’t
start
2. Overload
protection trips:
– accidentaly
– systematically
A) No electrical
power
B) Blown fuses:
B1 Because
inadeguate (blowing
current too low)
B2 Because the
motor or the supply
cable are damaged
C) Overload
protection previously
tripped
A) Momentary loss of
a phase
C) Incorrect setting
of the motor switch
D) The pump’s
the rated one
liquid
REMEDIES
A) Supply electrical
power
B1 Replace fuses
with adequate ones
B2 Repair the motor
or replace the cable
C)Reset the
protection (if it trips
again see problem 2)
C) Set to rated
current
D) Close the delivery
valve until the
capacity returns to
the rated value
E) Determine the
actual power
requirements and
replace the motor
accordingly
Ausgabe 01/2010
Revision 02
Page 93

Installation, Operation and Maintenance Instruction
Model LSB
LSB 100-english page 89
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 94

Installation, Operation and Maintenance Instruction
Every person, who is responsible for the
up and
maintenance of the shaft seal, must also have
read and understood the Installation, Operation
intenance Instruction of the particular
pump and especially chapter 8.1 "General
remarks" and chapter 8.2 "General", and follow
For pumps which are designed in conformity
with the Directive 94/9/EG (Atex95) for
environment endangered to explosion, the
additional Operating Instruction for explosion
Installation Manual - Single mech. seal without shaft sleeve
(Design code S1..2)
1. Safety Instructions
installation, removal, operation, start-
Model LSB
and Ma
the instructions under any circumstances!
2. Design Description
This shaft seal is a single mech. seal with installation
dimensions acc. to EN 12756 (DIN 24960) design "K".
API plan 02 / ISO plan 00.
Due to the patented Cyclon Seal Chamber no
additional flushing of the mech. seal chamber is
required.
protection of the mech. seal must be noticed.
The following descriptions are only valid commonly, as
far as they refer to the inner design of the mech. seal.
For possible particularities refer to the data sheet of
the mech. seal or instruction of the mech. sealmanufacturer.
For data of materials and application range of used
mech. seals refer to the data sheet in the operation
instruction resp. the order confirmation.
Index of parts:
161 Casing cover
210 Shaft
230 Impeller
412.21 O-ring
433 Mech. seal
502.31*) Wear ring
527 a) Fixing ring
560 b) Pin
904.31 a) Set screw
904.32*) Set screw
926 Impeller nut
940.31 Key
LSB 100-english page 90
Artikel Nr. 771076129
*) optional
a) not for all designs
b) only for mech. seals with PTFE-O-rings
This leaflet is subject to alteration!
Nominal
size of
∅d1 ∅d
l
1K
7
A B
∅d
L
mech. seal
33 33 48 42,5 7,5 50 19
43 43 61 45 7,5 52,5 28
53 53 73 47,5 10 57,5 38
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 95

Installation, Operation and Maintenance Instruction
The reuse of mech. seals, which have already
ing
at the seal faces after reinstallation. Therefore
al through a
new one is recommended. The dismounted
mechanical seal can be reconditioned by the
facturer and serve as a replacement
It is only allowed to install mech. seals, which
have a certificate of Conformity acc. the
On changing the mech. seal type resp. the
mech. seal manufacturer the data regarding
max. operating temperature of the pumped
emperature class must be
Pay attention to the utmost cleanness!
Especially the seal faces must be clean, dry and
damaged. Don´t apply lubrication on the seal
Use mineral grease or oil only, if you are
completely sure that the elastomers of the
Use only lubricants when you are sure that
there can´t occur any dangerous reactions
Make all required parts available, so that
assembly can be completed quickly. The
After that the axial movability and, thus, the
Don´t push elastomers over sharp edges. If
Push mech. seals with bellows in such a way,
that the bellow is compressed and not stretched
3. Removal of mech. seal
Model LSB
For that purpose use the appropriate sectional drawing
and the enclosed data sheet of the mech. seal.
Remove and disassemble the pump acc. to the
Installation, Operation and Maintenance
Instructions including chapter 8.6.
Remove fixing ring (527) (if existing) and rotating
part of the mech. seal (433) from shaft (210).
Refer to the enclosed data sheet of the mech.
seal, if set screws are to be loosened at the mech.
seal at first.
Remove stationary part of the mech. seal (433)
out of the casing cover (161).
4. Installation of a mech. seal
For that purpose use the sectional drawing and data
sheet of the mech. seal.
Directive 94/9/EG.
medium and t
checked again.
Clean drilling for stationary seal rng (∅d7) in the
casing cover (161) and surface of shaft (210).
been used for a longer time, can lead to leak
the replacement of the mech. se
manu
mech.seal.
Push the rotating unit of the mech. seal on the
shaft (210).
Complete the face on the impeller side of the
mech. seal exactly with the shaft (measure l1K).
For mech. seals without own set screws the fixing
ring (527) serves as a stop.
(danger of tearing apart!).
Further mounting and installation of the pump
referring to the repair instructions.
un
faces of the mech. seal.
If a lubricant is provided with the replacement
mech. seal, you should use this.
mech. seal are oil resistant. Use no silicone.
between the pumpage and the lubricant.
lubricants are only effective for a short time.
automatic adjustment of the elastomeres is lost.
necessary use mounting devices.
Press the stationary part of the mech. seal in the
casing cover (161). For this you can eventually
use a stamp with a soft surface. Unequal load can
lead to cracking of the seal face.
Don´t damage seal face!
Pay attention that the stationary ring is in solid
contact with the casing cover. The seal face must
be installed perpendicular to the shaft.
If a pin (560) is existing, be careful that it fits into
the slot of the mech. sealing, without touching the
mech. seal.
LSB 100-english page 91
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 96

Installation, Operation and Maintenance Instruction
Every person, who is responsible for the
up and
maintenance of the shaft seal, must also have
erstood the Installation, Operation
and Maintenance Instruction of the particular
pump and especially chapter 8.1 "General
remarks" and chapter 8.2 "General", and follow
y
with the Directive 94/9/EG (Atex95) for
environment endangered to explosion, the
additional Operating Instruction for explosion
The liquid of the quench must be selected in
such way that there can not occur any
rous reactions with the handled fluid. The
liquid of the quench can be contaminated due to
handled fluid, therefore the operator must
Model LSB
Installation Manual - Single mech. seal with quench without shaft sleeve
(Design code S4..2)
1. Safety Instructions
For pumps which are designed in conformit
installation, removal, operation, start-
read and und
protection of the mech. seal must be noticed.
The following descriptions are only valid commonly, as
the instructions under any circumstances!
far as they refer to the inner design of the mech. seal.
For possible particularities refer to the data sheet of
the mech. seal or instruction of the mech. sealmanufacturer.
2. Description
This shaft seal is a single mech. seal with installation
dimensions acc. EN 12756 (DIN 24960) design "K",
form "U". API plan 62 / ISO plan 09. The resistance of
the materials in the mech. seal chamber (especially of
elastomeres) against the quench liquid has to be
noticed.
The quench chamber must be flown through by the
quench liquid without pressure. For connection refer to
the following sectional drawing.
dange
the
care for an adequate disposal.
Because of the patented Cyclone Seal Chamber no
additional flushing of the seal chamber is necessary.
For description of materials and operational range of
the mech. seals supplied please refer to the data
sheet in the Operation Instruction resp. order
confirmation.
QI ... Quench suction (471Q)
Q0 ... Quench discharge (471Q)
LSB 100-english page 92
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 97

Installation, Operation and Maintenance Instruction
18
18
18
The reuse of mech. seals, which have already
ng
at the seal faces after reinstallation. Therefore
the replacement of the mech. seal through a
new one is recommended. The dismounted
mechanical seal can be reconditioned by the
facturer and serve as a replacement
It is only allowed to install mech. seals, which
have a certificate of Conformity acc. the
e resp. the
mech. seal manufacturer the data regarding
max. operating temperature of the pumped
medium and temperature class must be
Pay attention to the utmost cleanness!
Especially the seal faces must be clean, dry and
apply lubrication on the seal
Use mineral grease or oil only, if you are
completely sure that the elastomers of the
Use only lubricants when you are sure that
there can´t occur any dangerous reactions
Make all required parts available, so that
assembly can be completed quickly. The
ctive for a short time.
After that the axial movability and, thus, the
Don´t push elastomers over sharp edges. If
Index of parts:
161 Casing cover
210 Shaft
230 Impeller
412.23 O-ring
412.32 O-ring
435 Mech. seal
471Q Quench cover
502.31*) Wear ring
527 a) Fixing ring
542.31 Throttle bush
560 b) Pin
904.31 a) Grub screw
904.32*) Grub screw
927 Impeller nut
3. Removal of mech. seal
Model LSB
*) optional
a) not for all designs
b) only for mech. seals with PTFE-O-rings
Subject to techn. alterations!
Nominal
size of
∅d1 ∅d
l
7
1K
A B
∅d
mech. seal
33 33 48 42,5 7,5 50 19
43 43 61 45 7,5 52,5 28
53 53 73 47,5 10 57,5 38
QI, Q0
L
1/4-
3/8-
3/8-
NPT
NPT
NPT
For that purpose use the appropriate sectional
drawing and the enclosed data sheet of the mech.
seal.
Remove and disassemble the pump acc. to the
Installation, Operation and Maintenance
Instructions including chapter 8.6.
Remove fixing ring (527) (if existing) and rotating
part of the mech. seal (433) from shaft (210).
Refer to the enclosed data sheet of the mech.
seal, if set screws are to be loosened at the mech.
seal at first.
Remove casing cover (161) together with quench
cover (471Q). Use hexagonal screws (901.42) as
jack screws.
4. Installation of mech. seal
For that purpose use the appropriate sectional
drawing and the enclosed data sheet of the mech.
seal.
Directive 94/9/EG.
On changing the mech. seal typ
checked again.
undamaged. Don´t
faces of the mech. seal.
If a lubricant is provided with the replacement
mech. seal, you should use this.
mech. seal are oil resistant. Use no silicone.
between the pumpage and the lubricant.
Pull stationary part of the mech. seal (433) and
throttle bush (542.31) out of quench cover (471Q).
Clean drilling for stationary seal ring (∅d7) in the
quench cover (471Q) and surface of the shaft
(210).
.
been used for a longer time, can lead to leaki
manu
mech. seal.
lubricants are only effe
automatic adjustment of the elastomeres is lost.
necessary use mounting devices.
Put throttle bush (542.31) into quench cover
(471Q) carefully.
Press the stationary part of the mech. seal in the
quench cover (471Q). For this you can eventually
use a stamp with a soft surface. Unequal load can
lead to cracking of the seal face.
Don´t damage seal face!
Pay attention that the stationary ring is in solid
contact with the quench cover. The seal face must
be installed perpendicular to the shaft.
If a pin (560) is existing, be careful that it fits into
the slot of the mech. sealing, without touching the
mech. seal.
Insert casing cover (161) carefully, until it fits
axially in the bearing frame lantern (344).
Push the rotating unit of the mech. seal on the
shaft (210).
LSB 100-english page 93
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 98

Installation, Operation and Maintenance Instruction
Push mech. seals with bellows in such a way,
that the bellow is compressed and not stretched
friction device (Molykote, etc.) between
shaft sleeve and shaft only, if you are sure that
dangerous reactions between pumped liquid
Before starting the pump connect flushing
Adjust the face on the impeller side of the mech.
seal exactly on measure A. For mech. seals
without own set screws the fixing ring (527) serves
as a stop.
(danger of tearing apart!).
Model LSB
Use anti-
no
and anti-friction device can occur.
Further assembly and installation of pump acc.
chapter 8 of Installation, Operation and
Maintenance Instruction.
system for quench and put it into operation.
LSB 100-english page 94
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 99

Installation, Operation and Maintenance Instruction
Type:
Part name:
Volute casing
Casing cover Support foot Pump alignment Stub shaft Impeller Motor lanterne Gasket O
-
ring
Mech. seal Wear ring Fixing ring Washer Bev
elwasher
Bevelcup Washer Guard plate Flange motor
Hexagonal screw
Hexagonal screw Hexagonal screw Hexagonal screw
Stud
Grub screw Grub screw Grub screw Grub screw Drain plug Hexagonal nut
Impeller nut Key
No.
102 V 161 183 ***) 183P **) 210 230 341 400 412.21 433 502.11 *) 527 **) 554.41 554.42 ***) 554.43 ***) 554.44 ***) 681 801 901.11 901.31 **) 901.42 901.43 ***) 902.41 9
04.11 *)
904.31 **) 904.41 904.42 912.11 920.41 922 940.31
Model LSB
Design: S1...2 Single mech. seal, unbalanced (DIN 24960, l1k / EN 12756, design K, form U), Impeller with
back vanes
You find the shaft sealing of your pump on the data sheet / the order confirmation. Refer to chapter 3.1.1, Design
coding system, as well.
125-100-200 125-100-250 150-125-250 200-150-250
80-50-315 100-65-160 100-65-200 100-65-250 125-80-160 125-80-200 125-80-250
65-40-160 65-40-200 65-40-250 65-40-315 80-50-160 80-50-200 80-50-250
40-25-160 40-25-200 40-25-250 50-32-160 50-32-200 50-32-250 50-32-315
Valid for
*) ... optional
**) ... not for all designs
***) ... with IEC-Motor sizes: 160MA,
160M, 160L, 180M, 180L, 200L,
200LA, only
Subject to techn. alterations!
LSB 100-english page 95
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Not to scale!
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
Page 100

Installation, Operation and Maintenance Instruction
Part name
Volute casing Casing cover Support foot Pump alignment St
ub shaft
Impeller Motor lantern Gasket O
-
ring
Mech. seal
Wear ring Wear ring Fixing ring Washer Bevelwasher Bevelcup Washer Guard plate Flange motor Hexagonal screw Hexagonal screw Hexagonal screw Hexagonal screw Stud Grub screw Grub screw Grub screw Grub
screw
Grub screw Drain plug
Hexagonal nut
Impeller nut Key
No.
102 V 161 183 ***) 183P **) 210 230 341 400 412.21 433 502.11 *) 50
2.31 *)
527 **) 554.41 554.42 ***) 554.43 ***) 554.44 ***) 681 801 901.11 901.31 **) 901.42 901.43 ***) 902.41 904.11 *) 904.32 *) 904.31 **) 904.41 904.42 912.11 920.41 922 940.31
Model LSB
Design: S1...2 Single-mech. seal, unbalanced (DIN 24960, l1k / EN 12756, design K, form U), Impeller with
balancing holes
For the shaft sealing of your pump refer to data sheet / order confirmation. See chapter 3.1.1, design coding
system, as well.
150-125-315 125-100-315 125-80-315 100-65-315 Valid for type:
LSB 100-english page 96
Artikel Nr. 771076129
Subject to techn. alterations!
Not to scale!
*) ... optional
**) ... not for all designs
***) ... only with IEC-motor sizes:
160MA, 160M, 160L, 180M, 180L,
200L, 200LA
Revision 02
Ausgabe 01/2010
 Loading...
Loading...