Siemens SLA24C01-D-3-P, SLA24C01-D-P, SLA24C01-S-3-P, SLA24C01-S-P, SLA24C02-D-3-P Datasheet
...
Standard EEPROM ICs
SLx 24C01/02/P
1/2 Kbit (128/256 × 8 bit) Serial CMOS-EEPROM with I2C Synchronous 2-Wire Bus and Page Protection Mode™
Data Sheet 1998-07-27
SLx 24C01/02/P |
|
|
Revision History: |
Current Version: 1998-07-27 |
|
|
|
|
Previous Version: |
06.97 |
|
|
|
|
Page |
Page |
Subjects (major changes since last revision) |
(in previous |
(in current |
|
Version) |
Version) |
|
|
|
|
3 |
3 |
Text was changed to “Typical programming time 5 ms for up to |
|
|
8 bytes”. |
|
|
|
5 |
5 |
WP = VCC protects the upper half entire memory. |
|
|
|
15 |
15 |
Figure 11: second command byte is a CSR and not CSW. |
|
|
|
4, 5 |
4, 5 |
CS0, CS1 and CS2 were replaced by n.c. |
|
|
|
5 |
– |
The paragraph “Chip Select (CS0, CS1, CS2)” was removed |
|
|
completely. |
|
|
|
11, 12 |
11, 12 |
The erase/write cycle is finished latest after 10 8 ms. |
|
|
|
21 |
21 |
The write or erase cycle is finished latest after 10 4 ms. |
|
|
|
19 |
24 |
“Capacitive load …” were added. |
|
|
|
25 |
25 |
Some timings were changed. |
|
|
|
25 |
25 |
The line “erase/write cycle” was removed. |
|
|
|
25 |
25 |
Chapter 8.4 “Erase and Write Characteristics” has been added. |
|
|
|
I2C Bus
Purchase of Siemens I2C components conveys the license under the Philips I2C patent to use the components in the I2C system provided the system conforms to the I2C specifications defined by Philips.
Edition 1998-07-27
Published by Siemens AG, Bereich Halbleiter, MarketingKommunikation, Balanstraße 73, 81541 München
© Siemens AG 1998.
All Rights Reserved.
Attention please!
As far as patents or other rights of third parties are concerned, liability is only assumed for components, not for applications, processes and circuits implemented within components or assemblies.
The information describes the type of component and shall not be considered as assured characteristics. Terms of delivery and rights to change design reserved.
For questions on technology, delivery and prices please contact the Semiconductor Group Offices in Germany or the Siemens Companies and Representatives worldwide (see address list).
Due to technical requirements components may contain dangerous substances. For information on the types in question please contact your nearest Siemens Office, Semiconductor Group.
Siemens AG is an approved CECC manufacturer.
Packing
Please use the recycling operators known to you. We can also help you – get in touch with your nearest sales office. By agreement we will take packing material back, if it is sorted. You must bear the costs of transport.
For packing material that is returned to us unsorted or which we are not obliged to accept, we shall have to invoice you for any costs incurred.
Components used in life-support devices or systems must be expressly authorized for such purpose!
Critical components1 of the Semiconductor Group of Siemens AG, may only be used in life-support devices or systems2 with the express written approval of the Semiconductor Group of Siemens AG.
1A critical component is a component used in a life-support device or system whose failure can reasonably be expected to cause the failure of that life-support device or system, or to affect its safety or effectiveness of that device or system.
2Life support devices or systems are intended (a) to be implanted in the human body, or (b) to support and/or maintain and sustain human life. If they fail, it is reasonable to assume that the health of the user may be endangered.
1/2 Kbit (128/256 × 8 bit) Serial CMOS |
SLx 24C01/02/P |
EEPROMs, I2C Synchronous 2-Wire Bus, |
|
Page Protection Mode™ |
|
Features
•Data EEPROM internally organized as 128/256 bytes and 16/32 pages × 8 bytes
•Page protection mode, flexible page-by-page hardware write protection
–Additional protection EEPROM of 16/32 bits, 1 bit per data page
–Protection setting for each data page by writing its protection bit
–Protection management without switching WP pin
•Low power CMOS
•VCC = 2.7 to 5.5 V operation
•Two wire serial interface bus, I2C-Bus compatible
•Filtered inputs for noise suppression with Schmitt trigger
•Clock frequency up to 400 kHz
P-DIP-8-4
P-DSO-8-3
•High programming flexibility
–Internal programming voltage
–Self timed programming cycle including erase
–Byte-write and page-write programming, between 1 and 8 bytes
–Typical programming time 5 ms for up to 8 bytes
•High reliability
–Endurance 106 cycles1)
–Data retention 40 years1)
–ESD protection 4000 V on all pins
•8 pin DIP/DSO packages
•Available for extended temperature ranges
– Industrial: |
− 40 °C to + 85 °C |
– Automotive: − 40 °C to + 125 °C
1)Values are temperature dependent, for further information please refer to your Siemens Sales office.
Semiconductor Group |
3 |
1998-07-27 |

SLx 24C01/02/P
Ordering Information
Type |
Ordering Code |
Package |
Temperature |
Voltage |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SLA 24C01-D/P |
Q67100-H3547 |
P-DIP-8-4 |
– 40 °C … + 85 °C |
4.5 |
V...5.5 V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SLA 24C01-S/P |
Q67100-H3495 |
P-DSO-8-3 |
– 40 °C … + 85 °C |
4.5 |
V...5.5 V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SLA 24C01-D-3/P |
Q67100-H3546 |
P-DIP-8-4 |
– 40 °C … + 85 °C |
2.7 |
V...5.5 V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SLA 24C01-S-3/P |
Q67100-H3494 |
P-DSO-8-3 |
– 40 °C … + 85 °C |
2.7 |
V...5.5 V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
SLE 24C01-D/P |
Q67100-H3545 |
P-DIP-8-4 |
– 40°C … + 125 °C |
4.5 V...5.5 V |
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
SLE 24C01-S/P |
Q67100-H3493 |
P-DSO-8-3 |
– 40°C … + 125 °C |
4.5 V...5.5 V |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SLA 24C02-D/P |
Q67100-H3542 |
P-DIP-8-4 |
– 40 °C … + 85 °C |
4.5 |
V...5.5 V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SLA 24C02-S/P |
Q67100-H3537 |
P-DSO-8-3 |
– 40 °C … + 85 °C |
4.5 |
V...5.5 V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SLA 24C02-D-3/P |
Q67100-H3541 |
P-DIP-8-4 |
– 40 °C … + 85 °C |
2.7 |
V...5.5 V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SLA 24C02-S-3/P |
Q67100-H3536 |
P-DSO-8-3 |
– 40 °C … + 85 °C |
2.7 |
V...5.5 |
V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SLE 24C02-D/P |
Q67100-H3540 |
P-DIP-8-4 |
– 40°C … + 125 °C |
4.5 V...5.5 |
V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SLE 24C02-S/P |
Q67100-H3535 |
P-DSO-8-3 |
– 40°C … + 125 °C |
4.5 V...5.5 |
V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other types are available on request
–Temperature range (– 55 °C … + 150 °C)
–Package (die, wafer delivery)
1 Pin Configuration
P-DIP-8-4
N.C. |
|
|
1 |
|
8 |
|
|
VCC |
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||
N.C. |
|
|
2 |
7 |
|
|
WP |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|||||
N.C. |
|
|
3 |
6 |
|
|
SCL |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|||||
VSS |
|
|
4 |
5 |
|
|
SDA |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P-DSO-8-3
N.C. |
|
|
1 |
8 |
|
|
VCC |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
||||
N.C. |
|
2 |
7 |
|
|
WP |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|||||
N.C. |
|
3 |
6 |
|
|
SCL |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|||||
VSS |
|
4 |
5 |
|
|
SDA |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
IEP02514 |
|
||
IEP02515
Figure 1
Pin Configuration (top view)
Semiconductor Group |
4 |
1998-07-27 |

SLx 24C01/02/P
Pin Definitions and Functions
Table 1
Pin No. |
Symbol |
Function |
|
|
|
1, 2, 3 |
N.C. |
Not connected |
|
|
|
4 |
VSS |
Ground |
5 |
SDA |
Serial bidirectional data bus |
|
|
|
6 |
SCL |
Serial clock input |
|
|
|
7 |
WP |
Write protection input |
|
|
|
8 |
VCC |
Supply voltage |
Pin Description
Serial Clock (SCL)
The SCL input is used to clock data into the device on the rising edge and to clock data out of the device on the falling edge.
Serial Data (SDA)
SDA is a bidirectional pin used to transfer addresses, data or control information into the device or to transfer data out of the device. The output is open drain, performing a wired AND function with any number of other open drain or open collector devices. The SDA bus requires a pull-up resistor to VCC.
Write Protection (WP)
WP switched to VSS allows normal read/write operations.
WP switched to VCC protects the entire EEPROM against changes (hardware write protection).
Additionally write protection is managed by a protection bit associated to each page. (refer to chapter 7 Page Protection ModeTM)
Semiconductor Group |
5 |
1998-07-27 |
SLx 24C01/02/P
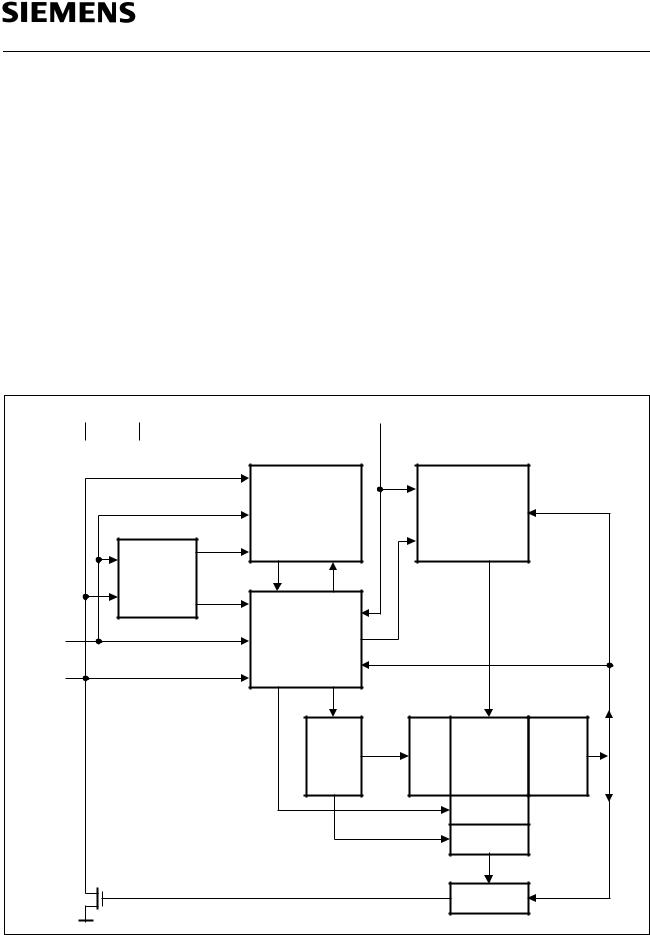
2 Description
The SLx 24C01/02/P device is a serial electrically erasable and programmable read only memory (EEPROM), organized as 128/256 × 8 bit. The data memory is divided into 16/ 32 pages. The 8 bytes of a page can be programmed simultaneously. Each page may be protected individually against changes by its associated protection bit.
The device conforms to the specification of the 2-wire serial I2C-Bus. Low voltage design permits operation down to 2.7 V with low active and standby currents.
The device operates at 5.0 V ± 10% with a maximum clock frequency of 400 kHz and at 2.7 ... 4.5 V with a maximum clock frequency of 100 kHz. The device is available as 5 V type (VCC = 4.5 … 5.5 V) with two temperature ranges for industrial and automotive applications and as 3 V type (VCC = 2.7 … 5.5 V) for industrial applications. The EEPROMs are mounted in eight-pin DIP and DSO packages or are also supplied as chips.
V SS |
V CC |
WP |
|
|
|
|
Chip Address |
|
Programming |
|
|
|
|
|
Control |
|
|
|
Control |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Logic |
|
|
H.V. Pump |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Start/ |
|
|
|
|
|
Stop |
|
|
|
|
|
Logic |
|
|
|
|
|
Serial |
|
|
|
|
SCL |
Control |
|
|
|
|
|
Logic |
|
|
|
|
SDA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Address |
X |
|
EEPROM |
Page |
|
|
Prot. Bit |
|||
|
Logic |
DEC |
|||
|
|
EEPROM |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Page Logic |
|
|
|
|
|
Y DEC |
|
|
|
|
|
Dout/ACK |
|
|
|
|
|
|
IEB02531 |
Figure 2
Block Diagram
Semiconductor Group |
6 |
1998-07-27 |
SLx 24C01/02/P
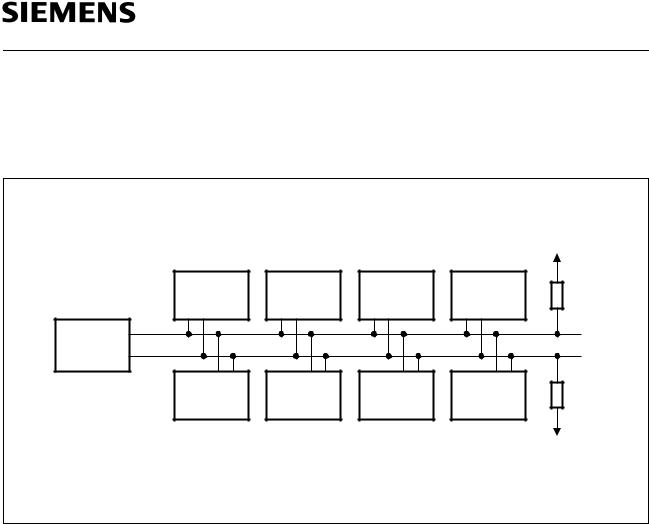
3 I2C-Bus Characteristics
The SLx 24C01/02/P devices support a master/slave bidirectional bus oriented protocol in which the EEPROM always takes the role of a slave.
|
|
|
|
VCC |
|
Slave 1 |
Slave 2 |
Slave 3 |
Slave 4 |
|
SCL |
|
|
|
Master |
SDA |
|
|
|
|
Slave 5 |
Slave 6 |
Slave 7 |
Slave 8 |
|
|
|
|
VCC |
|
|
|
|
IES02183 |
Figure 3
Bus Configuration
Master Device that initiates the transfer of data and provides the clock for both transmit and receive operations.
Slave Device addressed by the master, capable of receiving and transmitting data.
Transmitter The device with the SDA as output is defined as the transmitter. Due to the open drain characteristic of the SDA output the device applying a low level wins.
Receiver The device with the SDA as input is defined as the receiver.
Semiconductor Group |
7 |
1998-07-27 |
SLx 24C01/02/P
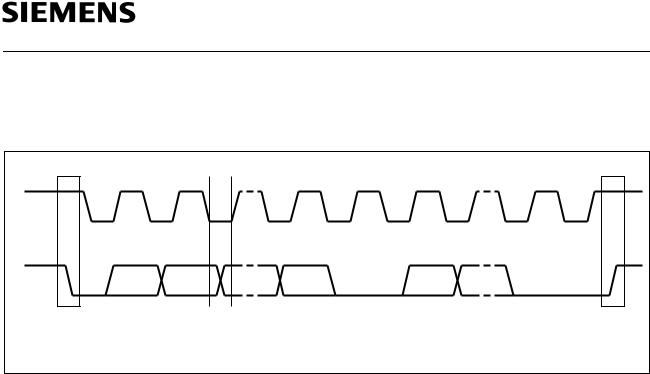
The conventions for the serial clock line and the bidirectional data line are shown in
figure 4. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
SCL |
1 |
2 |
8 |
9 |
1 |
9 |
SDA |
|
|
|
ACK |
|
ACK |
START Condition |
|
Data allowed |
|
Acknowledge |
|
STOP Condition |
|
|
to Change |
|
|
|
IED02128 |
Figure 4
I2C-Bus Timing Conventions for START Condition, STOP Condition, Data Validation and Transfer of Acknowledge ACK
Standby |
Mode in which the bus is not busy (no serial transmission, no |
|
programming): both clock (SCL) and data line (SDA) are in high |
|
state. The device enters the standby mode after a STOP condition |
|
or after a programming cycle. |
START Condition |
High to low transition of SDA when SCL is high, preceding all |
|
commands. |
STOP Condition |
Low to high transition of SDA when SCL is high, terminating all |
|
communications. A STOP condition initiates an EEPROM |
|
programming cycle. A STOP condition after reading a data byte |
|
from the EEPROM initiates the Standby mode. |
Acknowledge A successful reception of eight data bits is indicated by the receiver by pulling down the SDA line during the following clock cycle of SCL (ACK). The transmitter on the other hand has to release the SDA line after the transmission of eight data bits.
The EEPROM as the receiving device responds with an acknowledge, when addressed. The master, on the other side, acknowledges each data byte transmitted by the EEPROM and can at any time end a read operation by releasing the SDA line (no ACK) followed by a STOP condition.
Data Transfer Data must change only during low SCL state, data remains valid on the SDA bus during high SCL state. Nine clock pulses are required to transfer one data byte, the most significant bit (MSB) is transmitted first.
Semiconductor Group |
8 |
1998-07-27 |

SLx 24C01/02/P
4 Device Addressing and EEPROM Addressing
After a START condition, the master always transmits a Command Byte CSW or CSR. After the acknowledge of the EEPROM a Control Byte follows, its content and the transmitter depend on the previous Command Byte. The description of the Command and Control Bytes is shown in table 2.
Command Byte |
Selects operation: the least significant bit b0 is low for a write |
|
operation (Chip Select Write Command Byte CSW) or set high for a |
|
read operation (Chip Select Read Command Byte CSR). In both |
|
Command Bytes, the bit positions b3 to b1 are left undefined. |
Control Byte |
Following CSW (b0 = 0): contains the seven or eight lower bits of |
|
the EEPROM address (EEA) bit A6 or A7 to A0, or an additional |
|
command byte for the handling of the protection bit. |
|
Following CSR (b0 = 1): contains the data read out, transmitted by |
|
the EEPROM. The EEPROM data are read as long as the master |
|
pulls down SDA after each byte in order to acknowledge the |
|
transfer. The read operation is stopped by the master by releasing |
|
SDA (no acknowledge is applied) followed by a STOP condition. |
Table 2
Command and Control Byte for I2C-Bus Addressing of Chip and EEPROM
|
|
|
|
Definition |
|
|
|
Function |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
b7 |
b6 |
b5 |
|
b4 |
b3 |
|
b2 |
b1 |
b0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CSW |
1 |
0 |
1 |
|
0 |
x |
|
x |
x |
0 |
Chip Select for Write |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CSR |
1 |
0 |
1 |
|
0 |
x |
|
x |
x |
1 |
Chip Select for Read |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
EEA |
A7 |
A6 |
A5 |
|
A4 |
A3 |
|
A2 |
A1 |
A0 |
EEPROM address |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The device has an internal address counter which points to the current EEPROM address.
The address counter is incremented
–after a data byte to be written has been acknowledged, during entry of further data byte
–during a byte read, thus the address counter points to the following address after reading a data byte.
Semiconductor Group |
9 |
1998-07-27 |
 Loading...
Loading...