MV electrical network management
Easergy range
T200 P
MV substation control unit
User’s manual

Easergy T200 P Contents
T200 P ................................................................................................................................................................... 1
1 GENERAL DESCRIPTION......................................................................................................................... 3
1.1 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION ........................................................................................................................... 3
1.2 DESCRIPTION OF EQUIPMENT ........................................................................................................................ 5
1.3 T200 P BLOCK DIAGRAM .............................................................................................................................. 6
2 CONNECTION TO THE T200 .................................................................................................................... 8
2.1 STEP 1 - INSTALLING JAVA RUNTIME ENVIRONMENT 5.0 ................................................................................. 9
2.2 STEP 2 - INSTALLING THE USB DRIVER ....................................................................................................... 10
2.3 STEP 3 – CREATION OF THE PSTN OR GSM REMOTE NETWORK CONNECTION .............................................. 11
2.4 STEP 4 – STARTING CONNECTION WITH THE T200 ....................................................................................... 12
2.5 OVERVIEW OF THE EMBEDDED WEB SERVER OF THE T200 ........................................................................... 16
3 T200 SETTINGS ....................................................................................................................................... 22
3.1 COMMENT AREA : ....................................................................................................................................... 23
3.2 CONFIGURATION OF SYNCHRONIZATION BY GPS ......................................................................................... 24
3.3 CONFIGURATION OF SNTP SERVICE ........................................................................................................... 27
3.4 CONFIGURATION OF ETHERNET INTERFACES ............................................................................................... 28
3.5 SAVE/RESTORE CONFIGURATION PARAMETERS ........................................................................................... 29
3.6 DUMMY CONTROL OPTION .......................................................................................................................... 30
3.7 PARAMETERS FOR COMMUNICATION WITH THE SUPERVISOR ......................................................................... 31
3.8 SWITCH CONTROL PARAMETERS ................................................................................................................. 47
3.9 PARAMETERS OF THE VARIOUS OPTIONS ..................................................................................................... 50
3.10 AUTOMATION PARAMETERS .................................................................................................................... 52
3.11 PARAMETERS OF THE FAULT DETECTION MODULE .................................................................................... 55
3.12 CUSTOMIZATION OF T200 VARIABLES ..................................................................................................... 60
3.13 CUSTOMIZATION OF T200 CLASSES ........................................................................................................ 73
3.14 TESTS AT COMMISSIONING ..................................................................................................................... 74
4 OPERATION ............................................................................................................................................ 75
4.1 OPERATING MODE ...................................................................................................................................... 75
4.2 TESTING OF INDICATOR LAMPS AND FAULT DETECTION ................................................................................. 76
5 MAINTENANCE ....................................................................................................................................... 77
5.1 DIAGNOSTICS VIA THE FRONT PANEL INDICATOR LAMPS AND LOGS ................................................................ 78
5.2 POWER SUPPLIES ...................................................................................................................................... 81
5.3 CARD REPLACEMENT .................................................................................................................................. 82
6 APPENDIX A – CONFIGURABLE PARAMETERS ................................................................................ 83
7 APPENDIX B - GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS ................................................................................... 92
2
NT00113-EN-05
Overview General description
1 General description
1.1 Functional description
Easergy T200 P is designed to be installed with overhead switches remote controlled
by the MV network. It contains all the functions required to monitor and control one or
two MV/LV switchgear devices.
Management of MV switch opening/closing electric control unit
The control is triggered by actuation from the control station, by local operator control,
or by internal automatic controls.
Measurement acquisition and processing
The T200 P can incorporate the following measurements and processing functions:
For each channel:
Current measurement on each phase;
Calculation of the average load current;
Homopolar current measurement;
Single-phase or three-phase voltage measurement;
Measurement of the phase deviation between the upstream/downstream voltages
for management of opening points;
Calculation of active and RMS power (option);
Calculation of active energy (option);
Calculation of the power factor (option);
Frequency measurement.
Monitoring, for the purposes of remote indication and/or local display,
of MV substation and Easergy T200 P information:
Open/closed position of MV switch;
“Locked” state of MV switch;
Phase-to-phase or phase-to-earth fault current detection;
Voltage present;
Automatic control ON/OFF position;
Door open;
Local/remote operating mode;
Immediate alternating supply voltage failure;
Time-delayed alternating supply voltage failure;
Charger fault;
Battery fault;
External 12 V power supply failure;
Motorization supply voltage failure.
Logs
Time-stamped chronological logging of events and measurements.
This information can be transmitted to the control centre and archived in logs for
consultation and local downloading (in file form), by connection of a microcomputer.
Predefined automations
SEC (Sectionalizer): Automatic control for opening the MV switch following
detection of a number of fault currents in the source substation reset cycle.
ATS (Automatic Transfer of Source): Automatic source changeover upon voltage
loss detected on one of the channels.
VT (Voltage Time): The detection of voltage loss (switch closed) causes channel
opening and then reclosing when the voltage returns.
Backup power supply
For all the control unit components, the transmission equipment and the switch
motorization with a battery life of several hours in the event of an AC supply outage.
Local communication or communication with the remote control centre
One or two communication ports (option) are available for remote communication
with the control centre to manage two transmission channels. These ports can be
used redundantly (normal/backup), for repeater or maintenance applications. The
ports use either modems integrated in the COM card or external equipment
managed by the rack serial link.
A choice of modem for each port allowing any type of mounting:
Radio (600/1200 baud FSK or 1200/2400 FFSK);
PSTN isolated at 8 kV (300 to 14400 bits/s -V32 bis);
GSM / GPRS (quad-band version 900/1800/850/1900 MHz), SIM card accessible
on the front panel
GSM / 3G - UMTS & HSPA+ (3,75G), EDGE, GRPS & GSM. Quad-band modem
in GSM (900/1800/850/1900 MHz) and five band in 3G (800/850/AWS/1900/2100
MHz), SIM card accessible on the front panel
LL isolated at 8 kV (1200 baud FSK);
RS232 or RS485 isolated at 2 kV (19200 baud).
Note: In an RS232 link, port 1 is replaced by the RS232 port integral with the COM
card and accessible via the RJ45 connector on the right of the rack.
NT00113-EN-05
3

Overview General description
A catalogue of communication protocols for communication with the control centre,
changing constantly:
♦ IEC 870-5-101
♦ IEC 870-5-104
♦ DNP3, DNP3 / IP
♦ Modbus, Modbus / IP
♦ Other proprietary protocols (PID1, PUR2.2, PUR2.4, EDP, etc.).
An Ethernet communication port is available for communication with the control
centre or for access from the local PC for consultation/configuration (Modbus IP
protocol, IEC 870-5-104, DNP3 IP). This port is accessible on the front of the COM
card.
A USB communication port is available for communication with the local PC for
consultation/configuration. This port is accessible on the front of the COM card.
Communication with local equipment (option)
A Modbus RS485 communication port (2 wires - isolated at 2 kV) is available (on
option) for dialogue with equipment communicating with the T200 (e.g. Sepam, etc.).
Time synchronization of the equipment
Time setting for event dating can be performed:
by the laptop PC for consultation/configuration of the T200 (manually or
automatically via the PC time);
by the control centre (if the protocol permits);
by GPS sync (option). The minimum precision of time setting is in this case
approximately 50 ms;
by SNTP sync (option) from an Ethernet network. The precision of time setting is
in this case approximately one second.
IEC 61131-3 programmable logic controller
On option, the T200 can include an IEC 61131-3 embedded virtual programmable logic
controller.
A development platform (the RTU Control software supplied in appendix on the
Easergy CD) makes it possible to design, simulate and test on a target programs
written in the following PLC languages:
• SFC – Sequential Function Chart
• FBD – Function Block Diagram
• LD – Ladder Diagram
• ST – Structured Text
• Il – Instruction List
These PLC programs allow specific customized applications or additional functions to
be implemented on the T200 by combining or actuating existing T200 variables or
virtual variables to be created specifically for the PLC application.
Inter-equipment communication
The IEC 61131-3 programmable automatic control option also includes an interequipment communication function, allowing Modbus exchange, via a TCP/IP link,
between T200 devices connected to the same MV circuit. This communication allows
exchange of a data table between these T200 devices, in order to contribute, for
example (without any other PLC than the T200's), to an automatic control function
allowing detection and clearing of a current fault on an MV circuit.
(For more details regarding these three functions, refer to the specific "RTU Control &
Formulae" manual – ref. NT00320-xx).
Calculation formulae
The calculation formulae are a standard feature of the T200.
They can be used in the T200 to create new customized functions or applications not
requiring writing of a program in PLC language.
The functions that can be used in the formulae are:
- Mathematical functions;
- Statistical functions;
- Logical functions;
- Time/date functions;
- etc.
These formulae make it possible, more easily than with a PLC program, to create logic
equations based on combinations of variables. The types of variables that can be
used are the same as for PLC programs (existing T200 variables or virtual variables
created specifically). This inter-equipment communication is typically used in
applications of the self-healing network type.
4
NT00113-EN-05
Overview General description
1.2 Description of equipment
The enclosure
The equipment is housed in a 316L stainless steel enclosure ensuring:
Resistance to mechanical stresses;
Resistance to environmental stresses;
Compliance with EMC standards.
The enclosure is fitted with a key locking system.
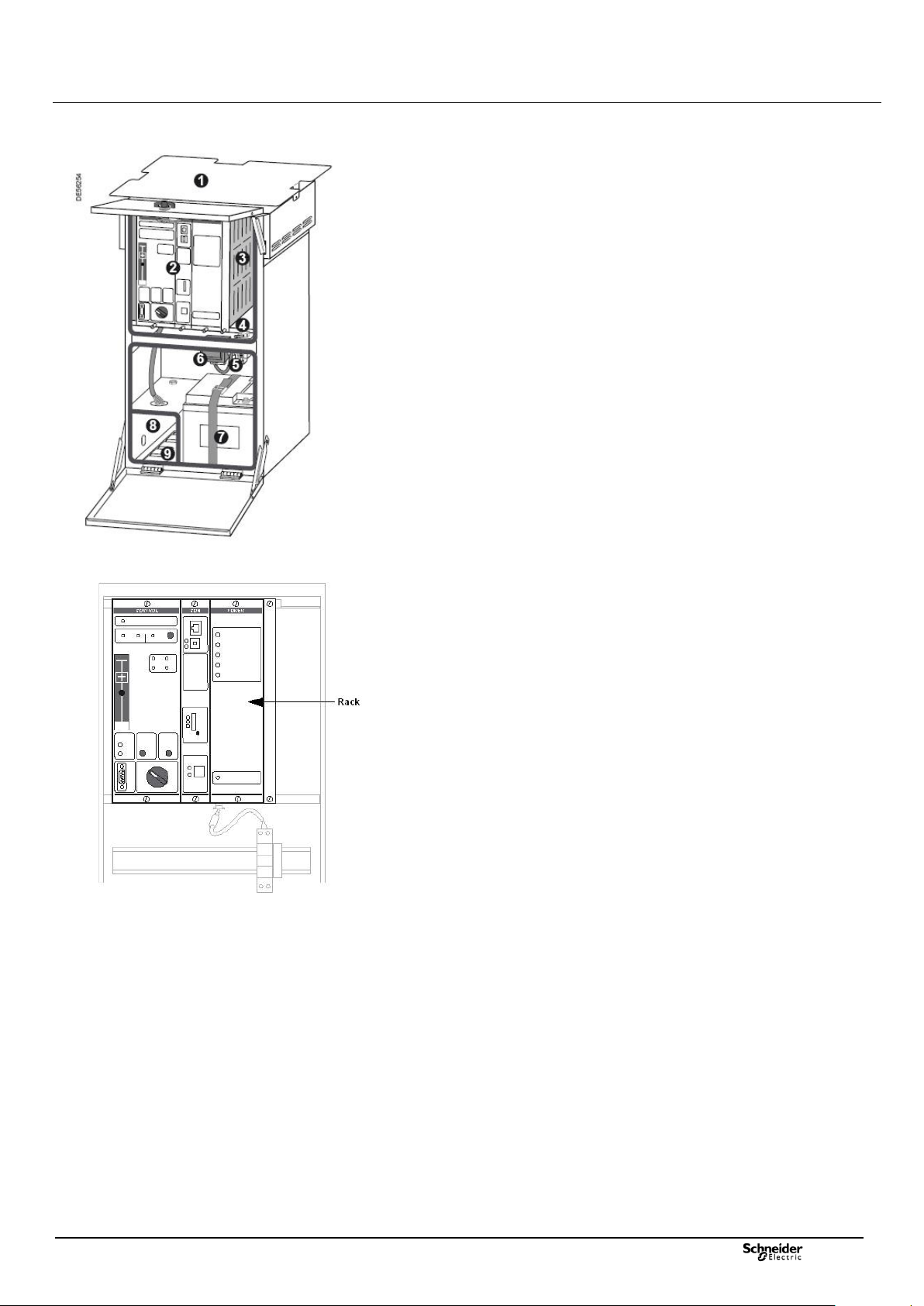
Its main constituent parts are:
1) A sun screen to restrict the influence of high external temperatures
2) A 6-unit rack containing all the electronic modules
3) Transmission equipment (radio, external modem, etc.)
4) A door switch
5) A lever type fuse holder for the AC power supply
6) A transformer for voltage measurement acquisition
7) A battery providing a backup power supply when the enclosure is no longer powered
by the AC supply
8) A “connection” part for connection to the motorization units and the toroid sensors
9) An anti-intrusion guard plate under the enclosure providing protection against any
malevolent attempt at disconnection of the “connection” part cords.
The rack
The rack contains three functional modules:
The Control module (marked CONTROL)
The control module controls the overall operation of the T200 P and the exchange of
information with the Power Supply and Communication modules.
This module implements several functions:
Interfacing with and monitoring and control of the MV switchgear;
Automatic control management;
Detection of fault currents on the MV line;
Detection of voltage loss;
Calculation of power (P, S, Q), energy, power factor, frequency;
Local operation.
The Communication module (marked COM)
The communication card serves as an interface between the cards of the “control
module”, the local equipment communicating via Modbus and the control centre.
It centralizes, processes and archives information and transmits it in accordance with
the communication protocol adopted.
The Power Supply module (marked POWER)
It supplies power to the enclosure, the battery charger and the associated selfmonitoring equipment.
NT00113-EN-05
5
Overview General description
2A
1A
PC
supply
2A
Voltage
transformer
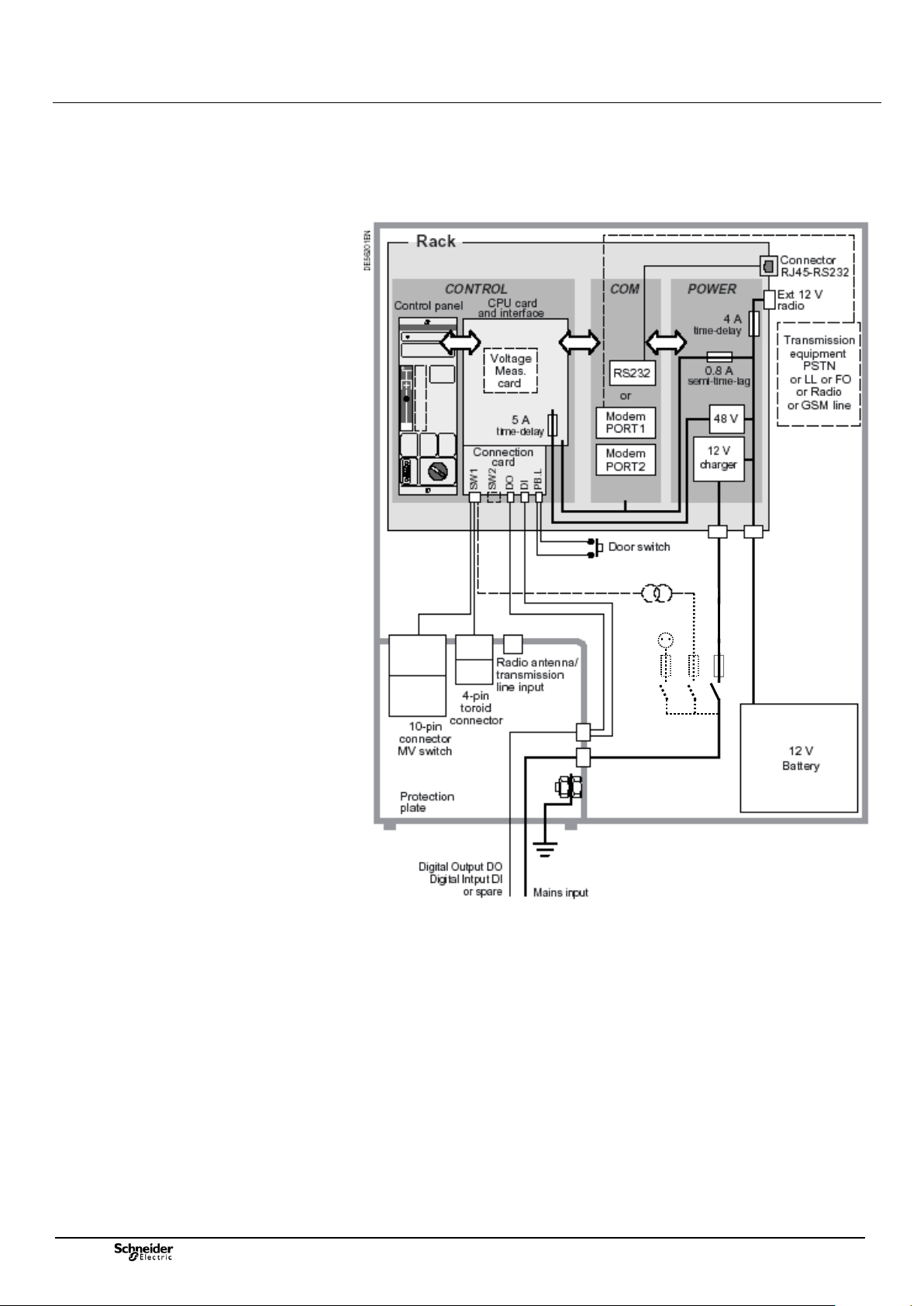
1.3 T200 P block diagram
Note: The various modules are connected via a “rack backplane card” not shown in this
diagram.
6
NT00113-EN-05

Installation Installing the enclosure
Refer to the T200P installation manual supplied with the equipment to obtain
information concerning installation of the T200P enclosure: "NT00030-FR-EN-ES-
xx".
NT00113-EN-05
7

Connection to the T200 Initialization of connection
Type B connector Type A connector
USB cable
“Cross-over” or “straight-through” Ethernet cable
depending on type of link access
2 Connection to the T200
Easergy T200 I must be configured from a configuration PC. This is
performed from the COM card (single access). It allows configuration of:
The parameters of the CPU card (date, fault detection, etc.).
The parameters of the Communication card (com. parameters, alarms,
etc.).
The system parameters (variable management, class management,
etc.).
Equipment required for T200 connection
For testing-maintenance configuration, the T200 requires:
A microcomputer operating under Windows 2000 or XP or Seven and
including Internet Explorer (version 5.5 or 6.0, 7, 8 or 9).
An USB port on this PC to perform connection with the T200.
An Ethernet port (RJ45) is available on the COM card for remote access to
the T200 from an Ethernet network.
This port can also be used for direct connection of the T200 with the PC.
The Ethernet cable required for Ethernet network-T200 connection or PCEthernet network connection is of the “straight-through” type.
The Ethernet cable required for PC-T200 connection is of the “cross-over”
type.
The USB cable required for PC-T200 connection is of the USB-A type at one
end and USB-B at the other.
A CD-ROM is supplied to the user for:
Installation of the USB driver for connection with the T200.
Installation of Java Runtime Environment 5.0 needed for port trace
operation (Supervisor-T200 frame analysis).
NB: TCP/IP ports 1168, 1169 and 1170 must be accessible on the PC
for trace operation. Contact the network administrator if it is necessary to
alter the PC or network configuration to deactivate the firewall on these ports.
Configuration of the T200 is performed directly from Internet Explorer.
No other additional software is needed to access the T200 testingmaintenance configuration operations (apart from Java Runtime 1.5).
Principle of the T200 embedded server
The T200 includes an embedded server which is initialized automatically as
soon as connection is established with the T200.
The data displayed by the T200 through this embedded server appears in the
form of HTML pages.
Various pages and sub-pages can be accessed by the user depending on
the rights available to him. The HTML pages displaying the information
managed by the T200 are refreshed in real time so as to update the latest
states.
Access and connection are secured by a Login and password. Several levels
of access to the HTML pages can be configured, provided one have the
required rights.
From the embedded server, it is possible to:
Configure the fault detector, communications and automatic control
parameters or system parameters (management of variables, classes,
rights, etc.);
View the states managed by the T200 (TSS, TSD, routine faults,
telemeasurements, etc.);
Save or load the T200 parameter configuration from files already
backed up on the PC;
Send remote control orders to the T200;
Transfer diagnostic logs in the form of Excel-compatible files;
Load a new software version of the T200 application.
The embedded server can be accessed both by the USB port and by the
Ethernet port. There is no difference in operation according to the type of port
used.
Initialization of connection to the T200
The T200 incorporates by default IP addresses necessary for local
connection from a PC. It is important to know these addresses in advance in
order to start a connection (these addresses are indicated on the Com card):
USB port: default address on the T200 = 212.1.1.10
Ethernet port: default address on the T200 = 172.16.0.5
Note: The USB address cannot be modified by the user. The Ethernet
address, on the other hand, can be modified (if the rights so permit) so as to
correspond to the local area network, which does not necessarily use the
same network addresses and masks.
For the T200 link via Ethernet, steps 2 and 3 are not necessary. In that case,
go directly to step 4.
8
NT00113-EN-05
Connection to the T200 Initialization of connection
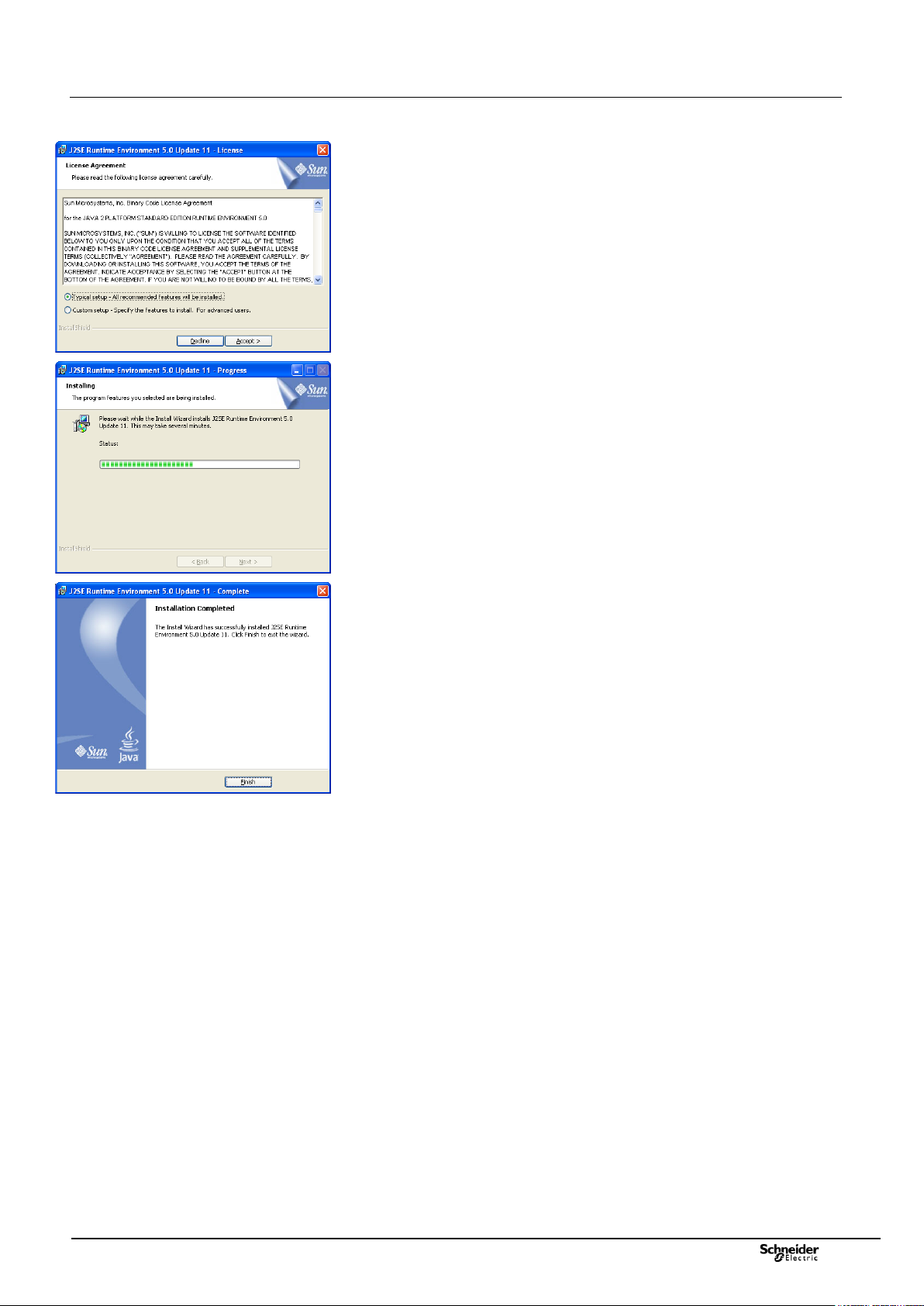
2.1 Step 1 - Installing Java Runtime
Environment 5.0
Insert the CD-ROM supplied with the T200 into the PC drive, then
double-click on the “jre-1_5_0_11-windows-i586-p-s.exe” installation file
on the CD-ROM (in folder : "D:\Tools\Java").
Software installation begins; click on the “Standard installation…" option
and then on “Accept”.
If new screen including Google options installation, deselect the two
proposed options "Google Toolbar" and "Google Desktop", then click on
"Next".
Wait until installation is completed, then click on “Terminate”.
NT00113-EN-05
9

Connection to the T200 Initialization of connection
2.2 Step 2 - Installing the USB driver
Carry out the following operations to install the USB driver:
Insert the Easergy CD-Rom supplied with the unit.
Insert the Easergy CD-ROM supplied with the equipment into the PC
drive.
A "Gamme Easergy / Easergy range – Vx.xx" window should
automatically appear on screen. If this is not the case, double-click on
the "Autorun.hta" file located in the CD root directory.
Click on the "Easergy series 3" link.
In the "Equipements Easergy series 3 / Easergy series 3 Equipment"
window which appears on screen, click on the "USB Driver" link.
Choose the setup language, then click on "ok".
Click on "Next" to start the "InstallShield Wizard" module.
Choose the installation directory (the directory proposed by default can
be kept), then click on "Next".
Then click on "Install" to start installation.
A driver setup window appears on screen; click on "Next".
Installation of the Easergy USB driver starts automatically.
At the end of installation, when the window showing that the driver has
been correctly installed appears on screen, click on the "Finish" button.
The Easergy USB driver is installed.
An "Easergy USB connection" start-up shortcut is also created
automatically on the PC desktop (see step 4).
Important note: Unlike the previous USB driver, this driver is installed for all
the USB ports of the PC. This driver needs therefore be installed only once,
irrespective of the USB port used. If a different USB port is used for a future
connection, Windows will automatically detect and install the Easergy USB
driver for this other USB port.
Note: Step 2 is therefore necessary only for the first connection to equipment
with the PC. For a future connection, go directly to step 4.
10
NT00113-EN-05

Connection to the T200 Initialization of connection
2.3 Step 3 – Creation of the PSTN or
GSM remote network connection
This step is to be taken into account only if the T200 includes a GSM or
PSTN (telephone) internal modem installed on the COM card.
This connection may possibly operate with an external PSTN or GSM
modem, but that depends on the modem used.
Note: It is not necessary to create this type of connection for the GPRS/3G
link.
With Windows 2000
Click on the Windows “Start” button.
Click on “Settings”.
Click on “Network connection and remote access”.
Click on “Establish a new connection”.
Click on "Connection to a private network".
From the list of peripherals displayed, select that corresponding to the
modem to be used for connection, by checking it.
Enter the phone number of the T200 to be contacted (this number may
be changed later, at each connection attempt).
Select the option “For all users”.
Give a name to the telephone connection to the T200 (e.g. “T200
remote connection”).
When the connection window is displayed on screen, there is no need to
give a user name and login password, and if necessary change the
phone number of the T200 to be contacted.
Click on the “Dial” option.
The PSTN or GSM remote network connection between the PC and the
T200 is initialized between the two devices, then a modem connection
status icon is inserted in the Windows toolbar.
With Windows XP
Click on the Windows “Start” button.
Click on “Control Panel”.
Click on “Network connections”.
Click on “Create a new connection”.
Select the option “Connect to the network at my workplace”.
Select the option “Dial-up connection”.
From the list of peripherals displayed, select that corresponding to the
modem to be used for telephone connection to the T200, by checking it.
Give a name to the telephone connection created (e.g. “T200 remote
connection”).
Enter the phone number of the T200 to be contacted (this number may
be changed later, at each connection attempt).
Select the option “Do not use my smart card”.
Select the option “All users”.
Check the option “Add a shortcut to this connection to my desktop”, then
on “Terminate”.
When the connection window is displayed on screen, there is no need to
give a user name and login password, and if necessary change the
phone number of the T200 to be contacted.
Click on the option “Dial number”.
The PSTN or GSM remote network connection between the PC and the
T200 is initialized between the two devices, then a modem connection
status icon is inserted in the Windows toolbar.
Note: Step 3 is no longer necessary after the first connection performed with
the T200. In that case, go directly to step 4.
NT00113-EN-05
11
Connection to the T200 Initialization of connection
2.4 Step 4 – Starting connection with
the T200
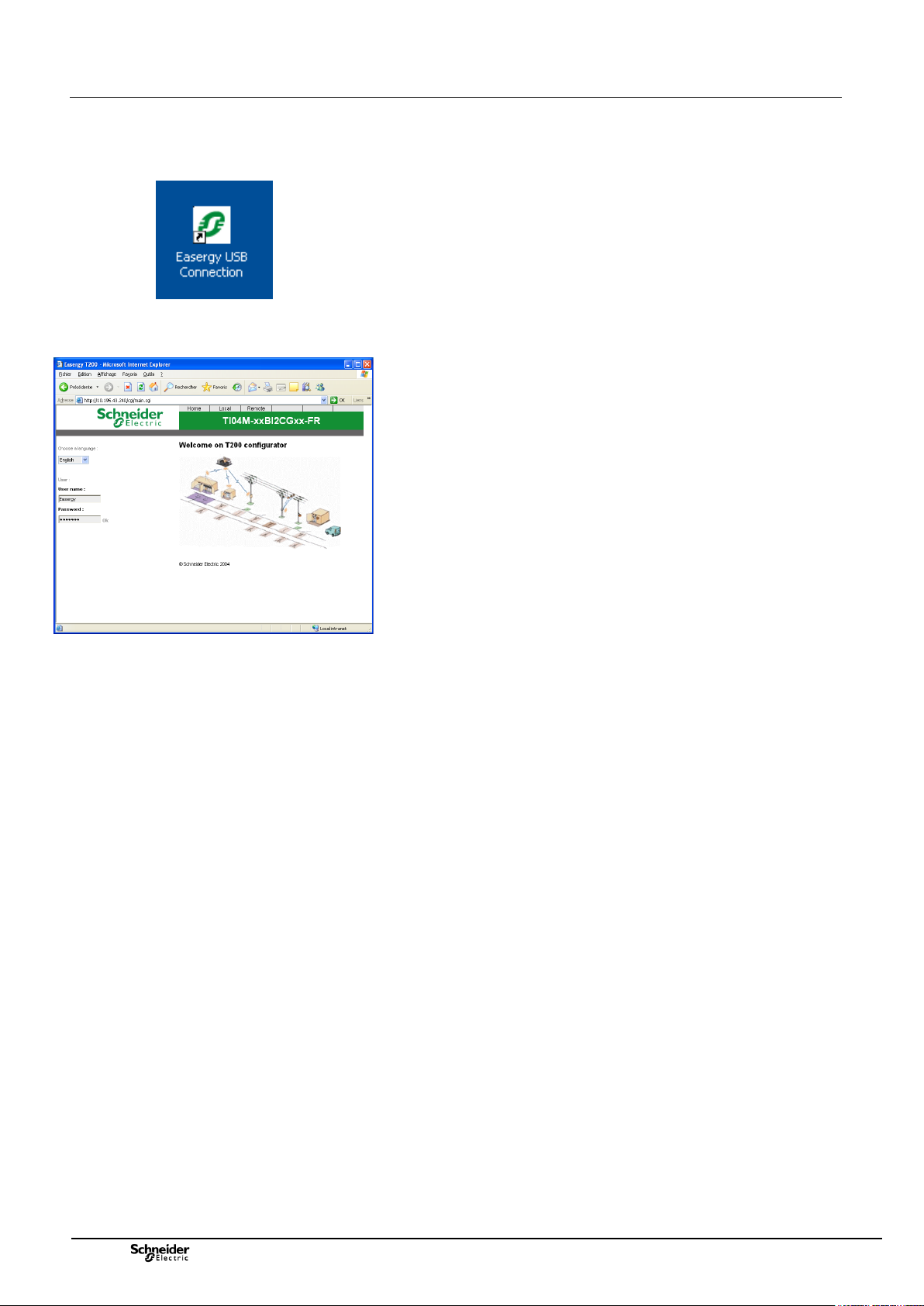
2.4.1 Local access via the USB port of the T200
The T200 being powered up without a “Fault” indicator lamp lit on the
COM card, connect the USB on one the USB port of the computer and
to the COM card of the unit.
Click on the "Easergy USB connection" shortcut already installed on the
desktop of the PC to start the USB connection.
Define the language to be used.
After few seconds, Internet explorer starts automatically and is
connected to the default USB IP address "212.1.1.10".
The connection to the unit is established automatically and the home
page of the Web server appears on screen.
Enter a “User name” and a “Password”, then click on “Ok”.
Access to the HTML pages is activated according to the rights related to
this user.
IMPORTANT NOTE: After powering up or a Reset of the T200, it is important
to wait for completion of initialization of the COM card before connecting the
USB cable, otherwise the connection is likely not to work.
When the T200 is powered up, the red “Fault” indicator lamp should flash for
approximately 10 s and then stay lit steadily for 3 s before going out.
Only then is connection of the USB cable possible.
Note: contrary to the old USB driver, to stop the USB connection, you just
have to disconnect the USB cable. Windows will stop automatically the
current USB connection.
12
NT00113-EN-05
Connection to the T200 Initialization of connection
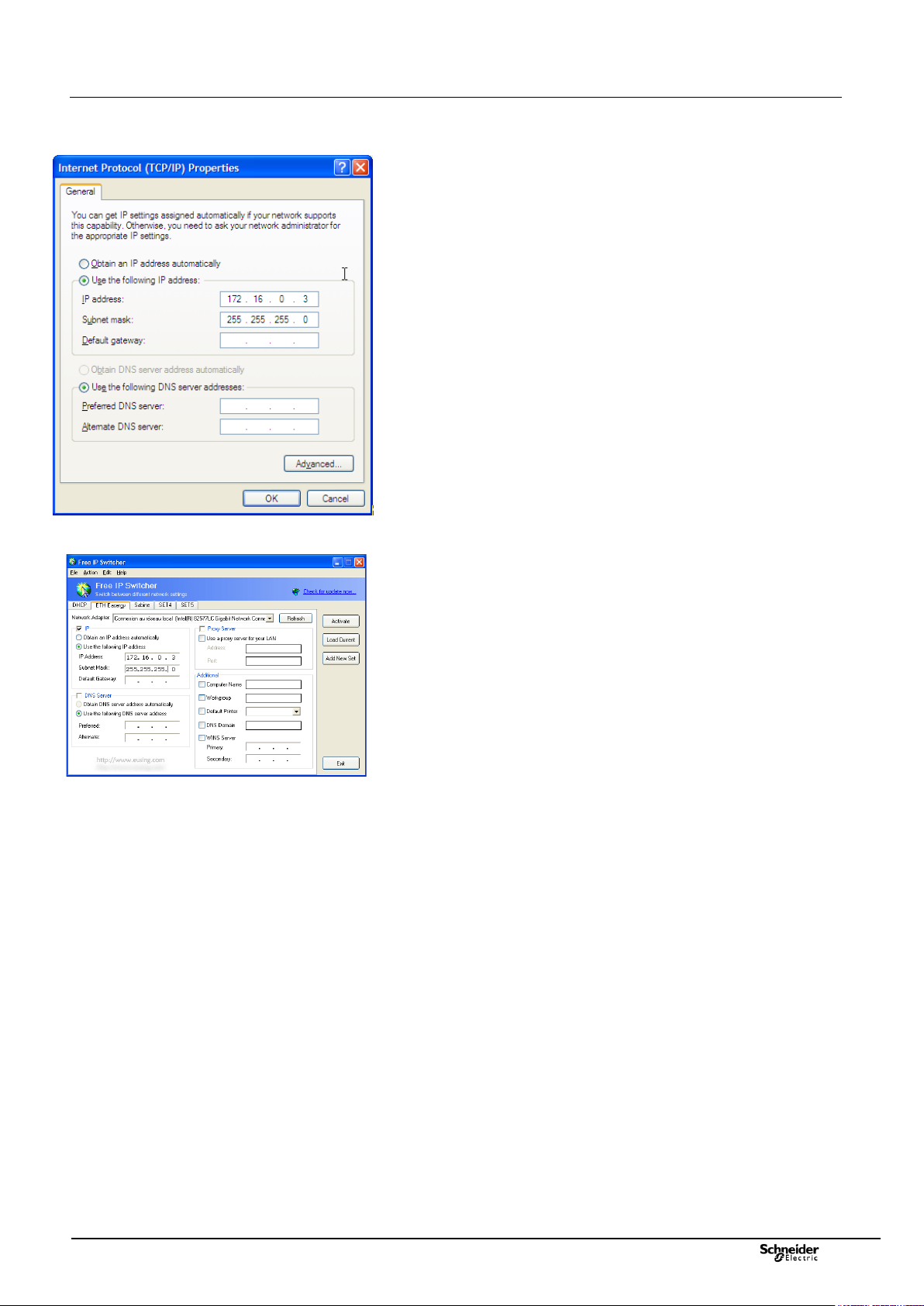
2.4.2 Local access via Ethernet port of T200
In the Windows Control Panel, click with the right mouse button on
"Connection to local area network" to be found in the "Network
Connections" directory.
Click on the "Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)" item, then on the "Properties"
button.
Then check the "Use the following IP address" option and then manually
enter the following items:
IP address = "172.16.0.3"
Subnet mask = " 255.255.255.0".
Click on the "Ok" button to accept the settings.
Start Internet Explorer.
Enter the IP address (172.16.0.5) in the “Address” field, then click on
“Ok”.
The home page of the embedded server appears on screen.
Define the language to be used.
Enter a “User name” and a “Password”, then click on “Ok”.
Access to the HTML pages is activated according to the rights related to
this user.
IMPORTANT NOTE: Once connection with the T200 is completed, you
should restore the original IP address configuration settings of the PC.
Note: there are useful utilities that can change automatically the TCP/IP
address of the PC. We recommend the software "Free IP Switcher" that can
be downloaded as a freeware on internet.
NT00113-EN-05
13

Connection to the T200 Initialization of connection
2.4.3 Remote access via a local Ethernet
network (LAN) or a GPRS or 3G network
With the T200 powered up, connect the PC and the T200 to the local
Ethernet network (LAN) using appropriate cables (straight Ethernet
cables).
Start Internet Explorer.
Enter the IP address of the T200 corresponding to the Ethernet or
GPRS/3G access in the “Address” field, then click on “Ok”.
The home page of the embedded server appears on screen.
Define the language to be used.
Enter a “User name” and a “Password”, then click on “Ok”.
Access to the HTML pages is then activated according to the rights
related to this user.
Note: Generally the default IP address of the T200 cannot be used on the
Ethernet ,3G or GPRS network employed, and it must therefore be replaced,
in the T200's specific IP address configuration page, with an address
acceptable for the network (see section on IP address configuration). In that
case, the only way to access the T200's IP address configuration page is to
use the USB local connection.
Note 2: Unlike Ethernet access, the connection speed on a GPRS or 3G link
is relatively slow (max. theoretical connection speed for GPRS = 50Kbis/s,
3G = 2Mbits/s).
Accordingly, so that the display of data on screen may be slowed as little as
possible, following a GPRS or 3G connection the T200 automatically displays
the pages of the Web server in simplified mode (Web server configuration in
"Remote" mode).
However, it is possible to return to a standard display by clicking on "Local"
configuration, at the top of the Web server home page.
14
NT00113-EN-05

Connection to the T200 Initialization of connection
2.4.4 Remote access via telephone or GSM link
This access operates only when the T200 includes a GSM or PSTN (telephone)
internal modem installed on the COM card.
When an external modem is used, it is possible that this access may operate, but
that depends on the modem used.
Start the GSM-PSTN remote network connection created previously (=> step
3).
Click on “Dial number” to start remote network connection.
Once connection is established, start Internet Explorer.
In the address field of Internet Explorer, enter one of the following IP
addresses, depending on the port No. on which the RTC or GSM modem is
installed on the T200:
- For port 1: 212.1.0.1
- For port 2: 212.1.0.3
The home page of the embedded server then appears on screen.
Define the language to be used.
Enter a “User name” and a “Password”, then click on “Ok”.
Access to the HTML pages is activated according to the rights related to this
user.
Note: Unlike a standard USB or Ethernet access, the connection speed on a
telephone or GSM link is rather slow (9600 baud).
Accordingly, so that the display of data on screen may be slowed as little as
possible, following a PSTN or GSM connection the T200 automatically displays the
pages of the Web server in simplified mode (Web server configuration in "Remote"
mode).
However, it is possible to return to a standard display by clicking on "Local"
configuration, at the top of the Web server home page.
NT00113-EN-05
15
Connection to the T200 Overview of the Web server
Home Page
Monitoring Page
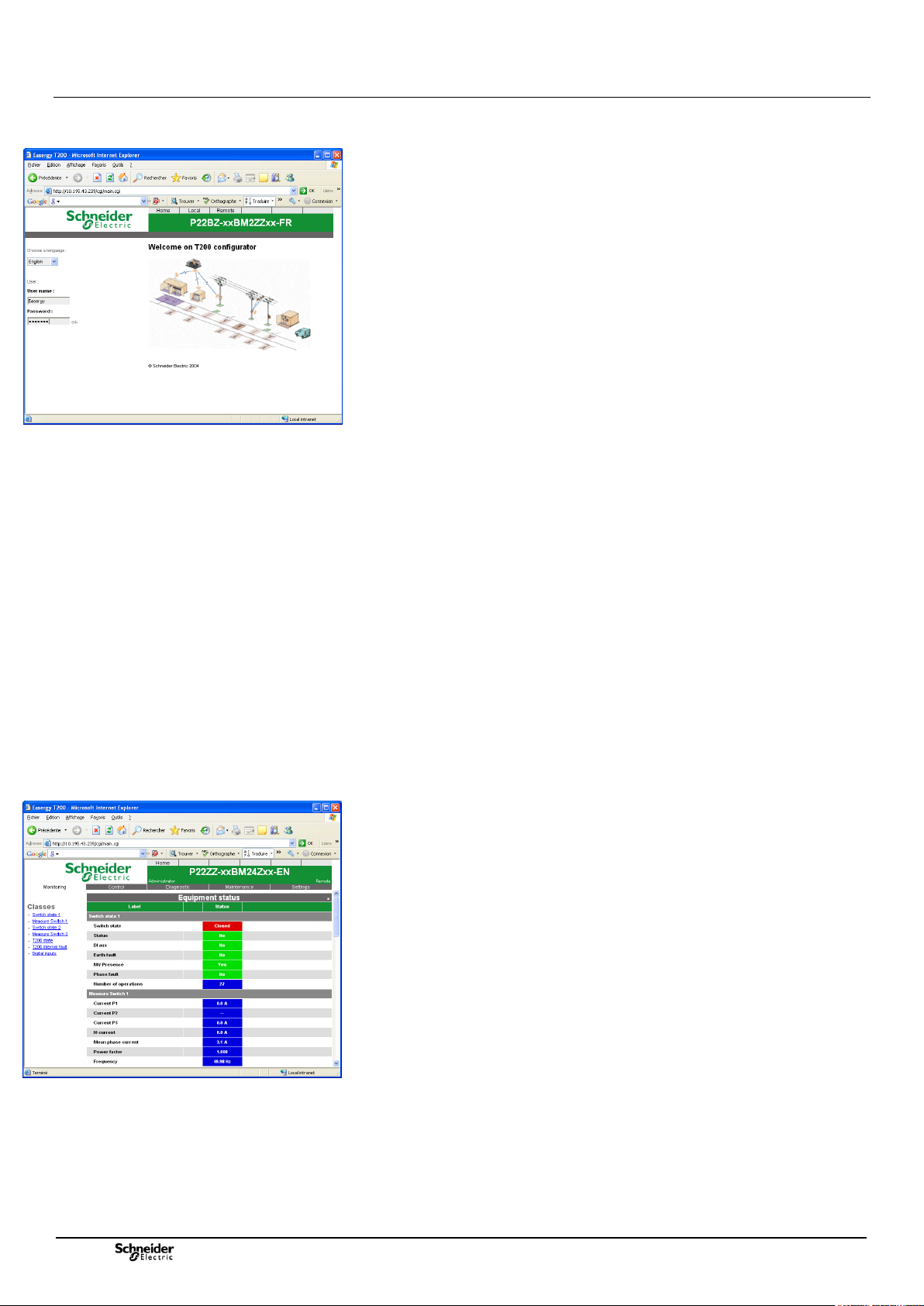
2.5 Overview of the embedded Web server of the T200
Once access to the embedded server has been identified by user name and password,
all the HTML pages can be consulted by simply clicking on the tabs or the associated
drop-down lists when they are available:
Details of the settings for each page are given in Appendix A.
Home Page:
This page is displayed at connection to the T200. It enables definition of the
language to be used for displaying the pages. It also allows definition of user access
rights by user name and password.
The users and passwords that can be accessed depend on the configuration defined
in the Maintenance page and the Users sub-menu.
By default, the “Easergy” user and “Easergy” password allow access as
“Administrator” to the embedded server.
Note: To protect your information, it is necessary to choose and use strong
passwords. Therefore, we recommend:
• Systematically change the default passwords as soon as possible the first time
you connect to the product.
• Renew your passwords with a reasonable frequency.
• Do not store passwords in a file on a computer station that is particularly
exposed to risk.
• Configure the software, including your web browser, so that it does not
"remember" the chosen passwords.
We recommend a simple rule: passwords should be at least 8 characters long and of
different types (upper case, lower case, numbers, special characters).
A click on the "Remote" option at the top of the page makes it possible to log on to
the T200 Web server with a simplified display of information (without images or
logos) so as to optimize data transfer times. This mode is used automatically for slow
remote network connections (PSTN or GSM at 9.6 Kbits/s).
A click on the "Local" button at the top of the page makes it possible to log on to the
T200 Web server with a normal display (all logos and images are transferred and
displayed). This mode is used automatically for high-speed local area connections:
USB (115.2 Kbits/s) or Ethernet (100 Mbits/s).
Monitoring Page:
This page can be used to consult the T200 states:
TSS: State of digital inputs, T200 internal faults, voltage presences, current faults,
etc.
TSD: open or closed state of switch, automatic control, digital outputs
TM: measurements of currents, voltages, frequency, etc.
Counters: number of operations or energy.
Note: Some displayed data is calculated and deduced by the T200:
Active, reactive, apparent power.
Phase difference between channels (deduced from the phase 1 voltages of each
channel).
Power factor or Cos φ.
Active power.
Neutral and average current (neutral current deduced in the case of a type A
arrangement - 3 phase toroids).
Phase-to-phase or phase-to-ground voltage (3-wire arrangement: phase-to-phase
voltages measured and phase-to-ground voltages deduced. 4-wire arrangement:
phase-to-ground voltages measured and phase-to-phase voltages deduced).
The page is displayed by class (e.g. State of channels, System, Automatic Control,
etc.).
Each class covers a category of information so as to facilitate viewing on screen.
The states of the indications or measurements are refreshed every 3 seconds
automatically.
The presentation, quantity of data displayed and content of this page may vary from
one application to another.
16
NT00113-EN-05

Connection to the T200 Overview of the Web server
Control Page
Drop-down list – Diagnostic page
Event log - Diagnostic page
Control Page
This page allows local control orders to be sent from the PC to:
The switches (change of position by CO/CF);
The operation and energy counters (counter initialization);
The automatic controls (switching ON/OFF);
The digital outputs (forced setting open or closed);
The fault detector (fault memory resetting).
The T200 must be in "Remote" mode to be able to send control orders.
The control orders on the TSDs make it possible to go to the state complementing
that displayed by the T200.
The control orders on the counters enable them to be initialized at a value predefined
by the user.
For safety reasons, each control order must be confirmed by the user.
The state of a control order in progress is displayed in orange (default colour).
The state of the control order is refreshed on screen automatically as soon as it is
completed.
Note: The colours of the states displayed can be modified by configuration.
Diagnostic Pages:
These pages allow consultation of the logs recorded in real time by the T200. The
event time stamping is 1 ms.
Each log allows consultation of the history of states occurring on the T200 with a
description of the states.
All the information present in the logs is time-and-date stamped by the T200's
internal clock.
The logs are as follows:
• Alarm log: (storage capacity: 2000)
Alarms can be generated and transmitted spontaneously to the control centre
after an information change of state, provided that this state has been configured
as alarmed.
A box associated with each alarm is checked when the control centre has
acknowledged this alarm.
Note: Information configured as alarmed automatically implies the generation of
an associated event (in the event log or measures log depending on type).
• Event log: (storage capacity: 10000)
Every change of state generates an event, provided that the use of events for this
state has been configured.
• System log: (storage capacity: 6000)
The equipment also incorporates a function for recording additional information to
facilitate operation and maintenance.
- Storage of transmission events (to determine the origin of a recurring
communication fault);
- Indication of transmission errors (CRC error, collisions, PSTN line out of order,
switchover to redundancy, etc.);
- Indication of system events (T200 start-up, T200 reset, change of
configuration, etc.).
• Measures log: (storage capacity: 30000)
The measurements managed by the T200 (phase current or mains voltage) can
be saved in a log, provided that their use has been configured.
The measurements can be recorded in several ways:
- Periodically (sampled or averaged value with configurable period);
- Upon exceeding a threshold (configurable high or low threshold);
- Upon variation or “dead band” (configurable variation %);
- Upon periodic recording of Min. and Max. values (configurable values and
period).
For all the logs, when the storage capacity is reached, the most recent event
occurring erases the oldest event on the list.
NT00113-EN-05
17
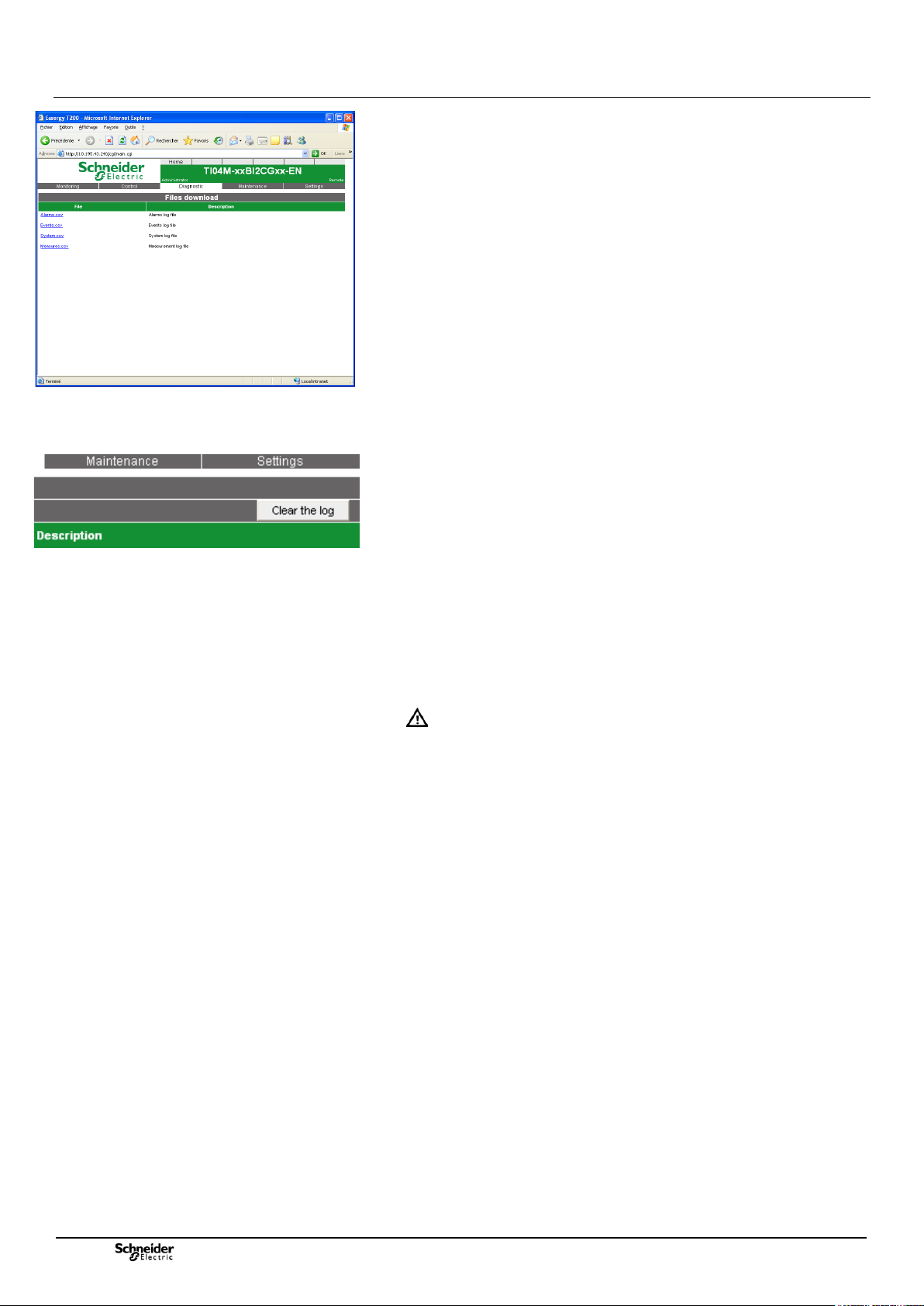
Connection to the T200 Overview of the Web server
Files download – Diagnostic page
• A Files download sub-menu allows these logs to be saved to the PC in the form of
Excel-compatible files (*.csv files).
These files can be consulted or transferred, to enable the establishment of statistics
or reviews.
A "Clear the log" button in each log can be used to empty their content, i.e. to erase
all the information saved previously.
Principle of saving to logs:
To increase the life of the flash memory, saving to the logs is performed every 5
min.
Accordingly, when a reset is performed on the T200, it is possible that the most
recent events that have occurred since the last backup may not be saved in the
logs. The only exception is when imminent cut-out occurs on the enclosure. In that
case, even if the time elapsed is less than 5 min., the T200 saves the events to the
logs before cutting off the power supply.
ATTENTION : After a change of configuration, it is important to wait for
about fifteen seconds (the time needed for the equipment to store the
parameters in memory) before performing a reset on the equipment.
Otherwise, the equipment is likely to lose its configuration permanently.
18
NT00113-EN-05
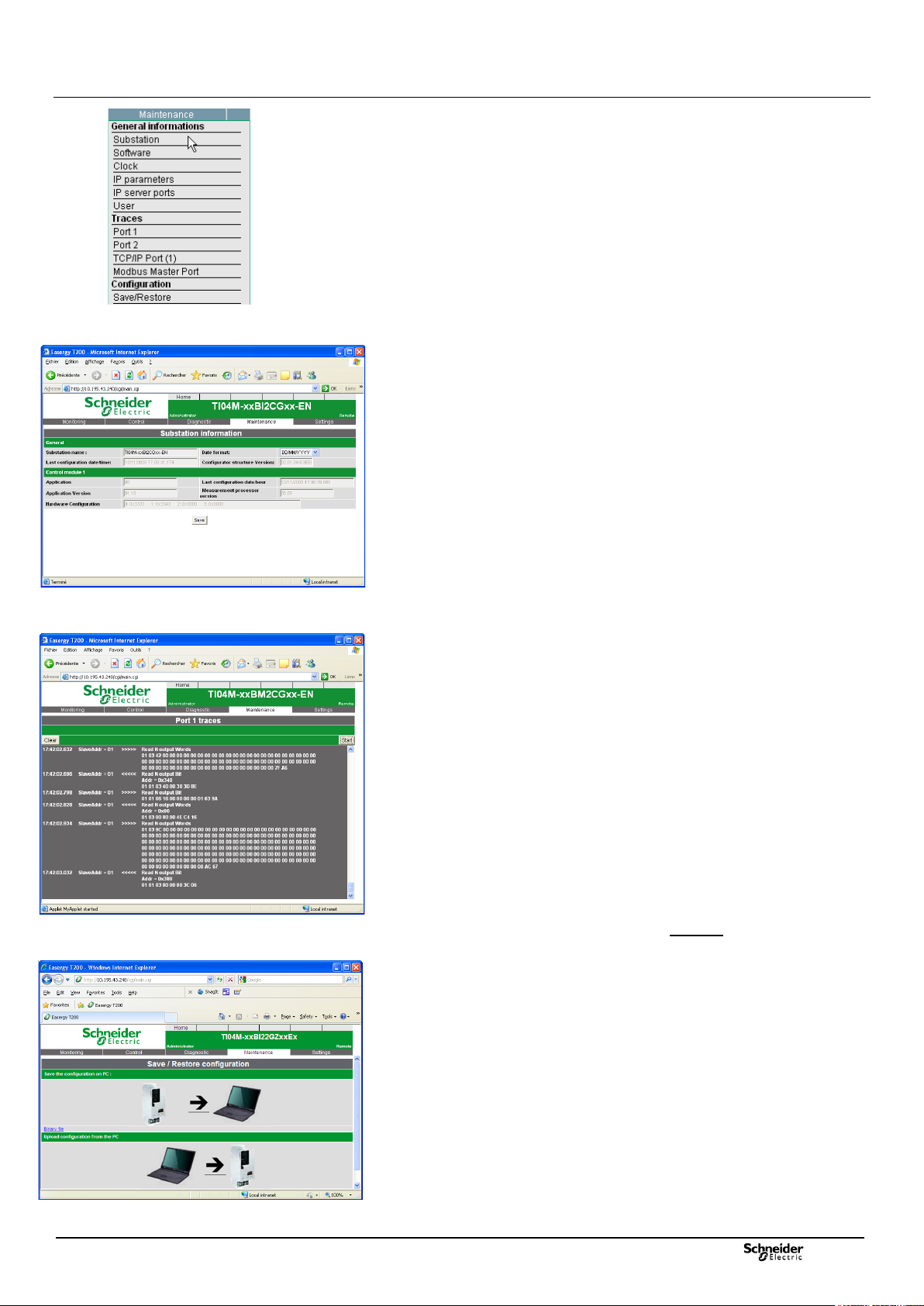
Connection to the T200 Overview of the Web server
Drop-down list – Maintenance page
Substation information – Maintenance page
Port trace – Maintenance page
Saving/backup – Maintenance page
Maintenance Pages:
Several pages can facilitate maintenance of the T200, by giving information or
allowing configuration of the T200 application:
1. General information: Specific sub-pages provide information concerning the
T200 application, namely:
- Substation page: information concerning the current application (version No.
of the application and fault detector, date and time of last configuration, name
of substation, etc.).
- Software page: information concerning the software used by the T200
(version, date and time of compilation, size and CRC32).
The T200 is capable of storing two different software versions in memory. It
is possible to switch from one software version to another simply by selection
(if two versions are available).
It is also possible to load a new software version from a file available on the
PC or from a floppy disk or CD-ROM.
ATTENTION : The loading process manages only the file format with .zip
extension. The software must therefore not be unzipped before loading it on
the T200 (file with .mem extension not managed).
Note: When loading a software on the T200, one in fact loads the protocol
used for remote transmission but also all the equipment operating options,
including some that are managed and displayed by the Web server if
configured and/or detected physically on the COM card, namely:
- The Modbus master function
- The function of synchronization by GPS
- The digital input counting function.
- Clock page: Allows the T200 date and time to be configured manually or
automatically from the time on the PC.
A click on the "Update" button causes the manual change of date and time to
be accepted.
A click on the "Synchronization" button allows the PC date and time to be
taken into account automatically for configuration on the T200.
Comment: This configuration is possible only if synchronization by SNTP
server or by GPS module is not installed in the T200.
- IP parameters page: Allows consultation or where applicable configuration
of the Ethernet and USB interface parameters (IP addresses, sub-network
masks, etc.).
When a GPRS or 3G modem is installed on the COM card, this page also
allows consultation of the IP addresses assigned automatically by the
GPRS/3G server.
NB: It is dangerous to modify the Ethernet IP parameters, with a risk of no
longer being able to access the T200. Call on competent authorities to
modify these parameters.
- IP server ports page: allows redefinition of the port numbers used by the
T200 for COM card access, in the event that the transmission network does
not accept the default numbers (e.g. restriction on certain GPRS/3G
operators).
By default, the following port Nos. are configured on the T200:
HTTP server port = 80
Telnet server port = 23
Port 1,2 and TCP/IP trace server port = 1168, 1169 and 1170
TCP/IP port trace server port = 1170
This page is optional depending on the embedded software in the T200 (e.g.
present page for software including GPRS transmission).
NB: If the HTTP port number is changed in this page, to be able to log
on to the T200 Web server again, it is essential to add the port number
at the end of the T200's IP address preceded by a colon
(e.g. 10.207.154.239:1500 for a T200 access on port 1500).
- User page: Allows creation, modification or deletion of users and
management of rights (login, password, access rights).
2. Port 1 & 2 & TCP/IP & Modbus Master traces: The "Port 1, 2 and TCP/IP
traces" pages allow viewing, for each available port, of communication
exchanges between the control centre and the T200.
The "Modbus Master trace" page allows viewing of exchanges between the
T200 and the Modbus slaves of the substation (see additional manual
NT00121-xx).
This trace is displayed on screen in decoded form to facilitate reading of the
frame's content:
Column 1: frame time-and-date stamping (in
hour:minute:second.thousandth of second format).
Column 2: direction of dialogue, RTU -> PC or PC -> RTU, with
associated address Nos of the PC and RTU.
Column 3: hexadecimal frame + brief description of the content of the
frame.
NT00113-EN-05
19

Connection to the T200 Overview of the Web server
Drop-down list – Settings page
Protocol parameters – Settings page
Control and automation – Settings page
Measurements and fault detection – Settings page
3. Configuration:
- Save/Restore page: Allows all the current T200 configuration parameters to
be saved to a file.
It is also possible to load from a file available on your PC or from a floppy disk
or CD-ROM the T200 configuration parameters coming from a preceding
backup or coming from another substation.
This file can be used to configure one or more other substations in the same
way without being obliged to reconfigure all the parameters one by one.
Note: During loading from a file, the data integrity is verified automatically so as
to ensure the compatibility of application versions.
Settings Pages
Configuration of the T200 is performed from pages grouped together in several
different categories:
1. Communication: Several pages allow you to configure the specific
communication parameters of the T200:
- Operation Mode page: For each communication port available on the T200,
it is possible to determine:
The protocol available;
The type of transmission medium to be used (Radio, PSTN, GSM, etc.);
The way in which the ports will be managed according to one of the
available modes:
Not used
Normal
Balanced – Normal/Backup
Main – Normal/Backup
Backup – Normal/Backup
Store & forward
- Protocol + TCP/IP Protocol pages: These pages are used to configure the
parameters specific to the protocol used:
Max. number of send operations
Collision avoidance system;
Configuration of link addresses;
Frame size;
etc.
Note: Each type of protocol has its specific configuration page. For more
details, refer to the specific user manual for the protocol installed on the
T200.
- Ports 1 & 2 transmission page: This page is used to configure the
parameters of the communication port (modem):
Baud rate (e.g. 19200 baud);
Parity, stop bit, etc.;
Time-out management (e.g. RTS-CTS, CTS-message, etc.);
etc.
Note: The parameters displayed in this page depend on the type of
transmission medium configured in the Operating modes page.
- Modbus Master Port and Slave Configuration page:
These 2 menus can be used to configure communication with Modbus
slaves. The parameters setup for communication with Modbus slaves is
covered by additional documentation (NT00121-xx).
2. Control Module No. x: Some parameters of the T200 are managed for each
Control module of the T200.
Two pages allow this configuration:
- Control and Automation page: This page can be used to configure the
parameters related to electrical control of the switch and automation
management:
Type of switch (Standard, PM6, CI2 or other);
Change-of-position waiting time;
Type of automatic control;
Etc.
- Measurements/Fault Detector Page: This page allows configuration of all
the T200 analogue information, namely:
Mains frequency;
Current and voltage measurement parameters;
Fault detection parameters;
Etc.
20
NT00113-EN-05

Connection to the T200 Overview of the Web server
Variable Configuration – Settings page
Classes Configuration – Settings page
Example of variables associated to a class
Excerpted from the page: "Monitoring"
3. Variable management: All the information managed by the T200 must be
configured separately to define its operation and how it will be managed by the
embedded server:
- Variable configuration page: The complete list of information (variables)
managed by the T200 is displayed in this page, under various categories.
Depending on the type of variable, the configuration page and the
parameters displayed may be different. There is a specific type of page for:
Digital control orders (e.g. TCD)
Double indications (e.g. TSD)
Single indications (e.g. TSS)
Analogue measurements (e.g. TM).
Counter (e.g. CNT).
The parameters to be configured for each variable are (for example):
Variable name
Type of access (operator session, administrator session, etc.);
Assignment class;
Logical, remote and internal addresses;
Measurement, event and alarm management;
Type of recording for measurements (periodic, upon exceeding
high or low threshold, upon % variation or indication of min. and
max. values per period);
etc.
Note: The parameters to be configured depend on the type of page
displayed.
- Classes Configuration page: The variables created can be grouped
together by classes, so as to facilitate the management and display of
variables. Each variable can be assigned to one of these classes by
configuration. This page can be used to create, modify or delete the
classes managed by the embedded server and determine those that will
be visible in the Monitoring page.
- Modbus master communication and Slaves configuration pages:
consult the user's manual NT00121-xx.
- Embedded PLC and Formulas and Peer to Peer pages: consult the
user's manual NT00320-xx.
NT00113-EN-05
21

Commissioning T200 settings
3 T200 settings
This chapter aims to provide the user with all the information needed to be able to
perform configuration of the T200 data.
Certain complex functions of the T200, in particular, require some detailed
explanations (fault detection, automatic control, etc.) for a better understanding of
how to configure the T200.
The functions discussed in this chapter are as follows:
Comment area
Configuration of synchronization by GPS
Configuration of SNTP service
Configuration of Ethernet interfaces
Backup/Restoral of configuration parameters
Configuration of communication with the Supervisor
Configuration of switch controls
Configuration of the various options
Automatic control configuration
Configuration of the fault detection module
T200 variable configuration
Class configuration
22
NT00113-EN-05
Commissioning GPS synchronization setting
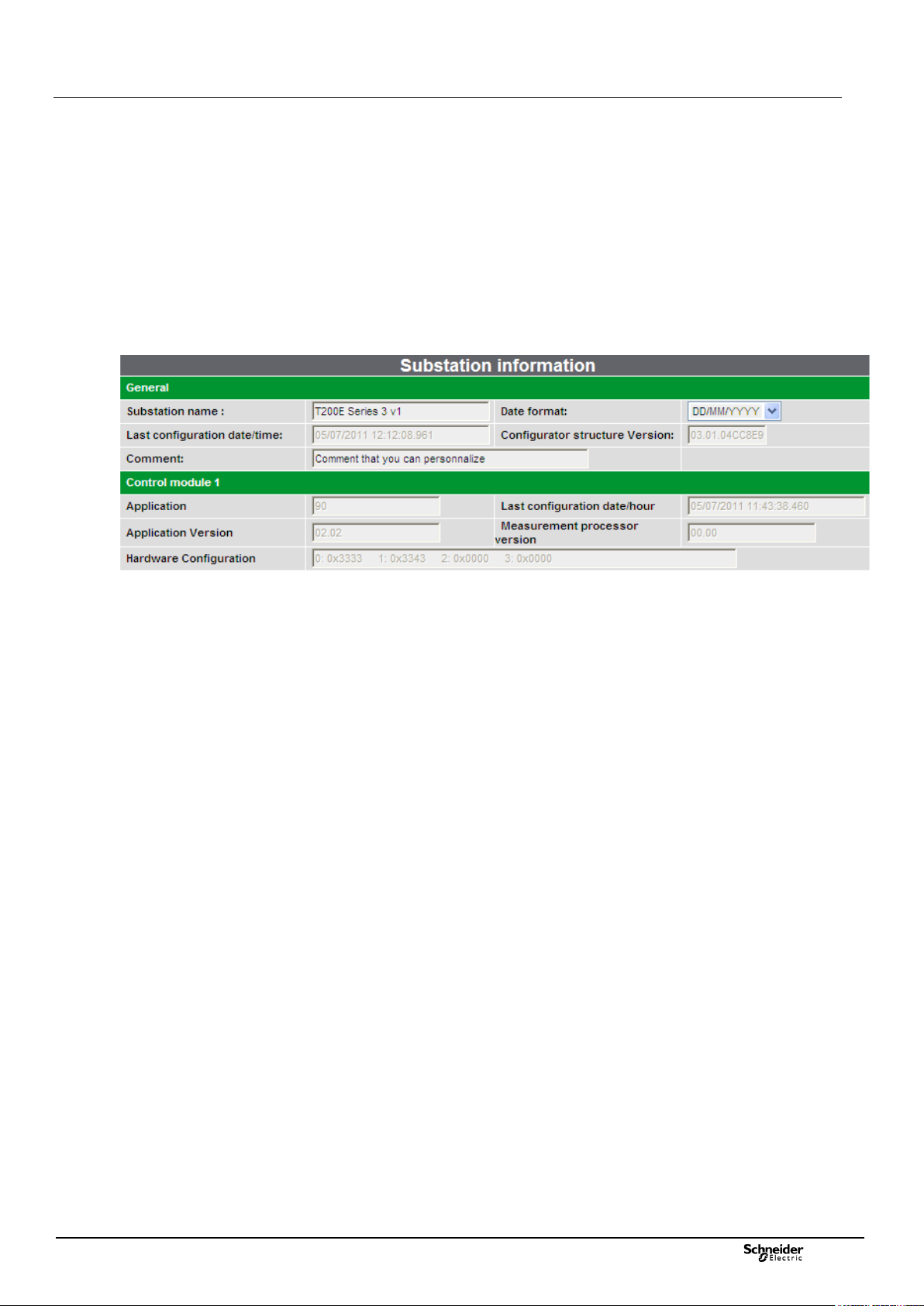
3.1 Comment area :
Access: "Maintenance/Substation" page.
The user can fill in an additional free 50-character comments area,
in the "Maintenance/Substation" page of the T200's embedded
Web server.
No special processing is performed on these comments. It is
simply a text to give the user explanations on the equipment or the
associated MV/LV substation.
NT00113-EN-05
23
Commissioning GPS synchronization setting
T200
MV/LV substation
Metal plate support
GPS antenna
Installation of the GPS antenna
Example of events generated by the GPS function in
the "System" log
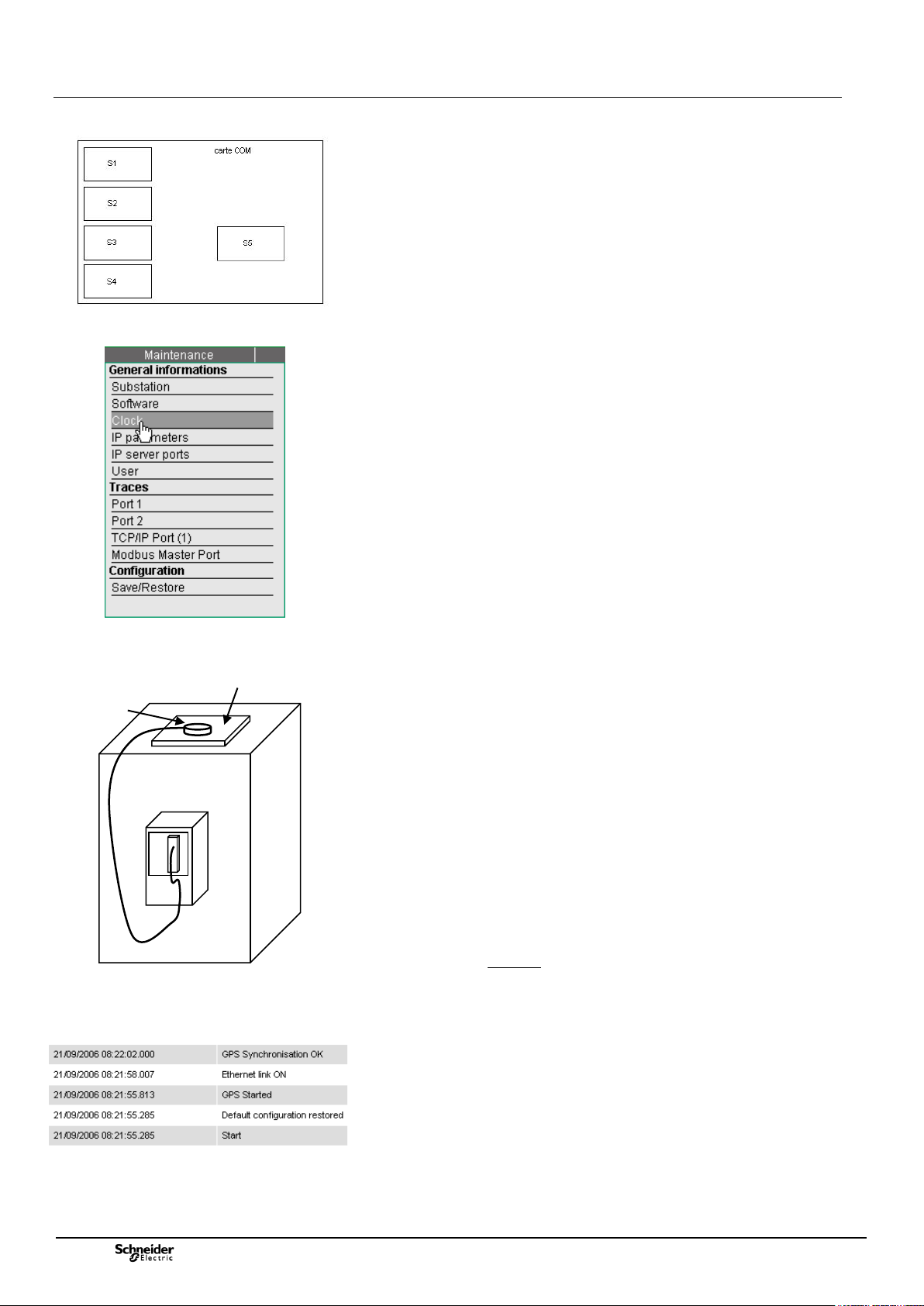
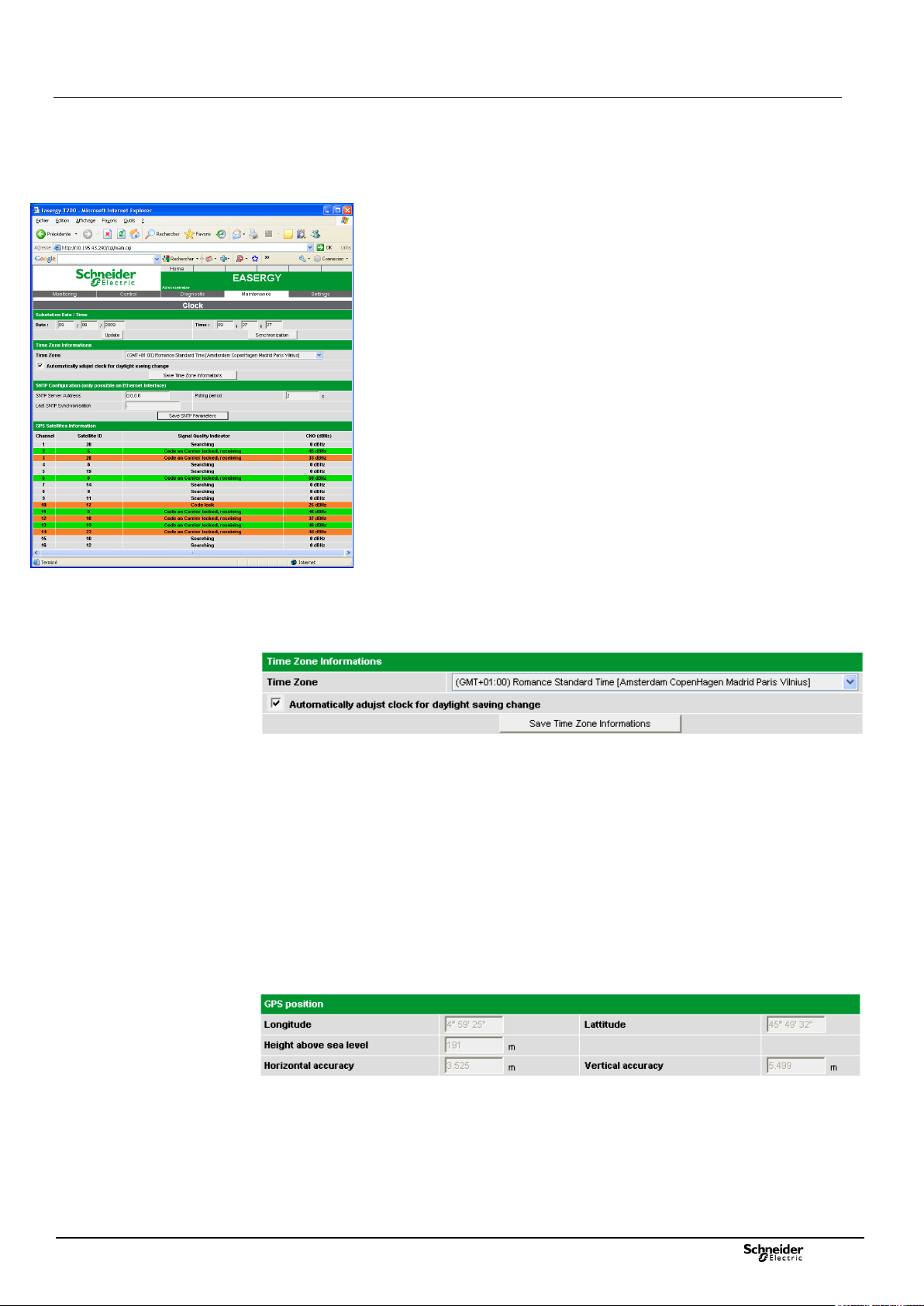
3.2 Configuration of synchronization by GPS
Access: "Maintenance/Clock" page.
In standard configuration, the T200's time can be set manually by the user or by
synchronization from a PC connected to the T200.
On option, the T200 can also be synchronized via a GPS module.
This module allows the equipment to time stamp events precisely, without internal
clock time drift.
The supply for this kit includes a GPS card, installed in factory on the COM card of
the T200 (slot S5) and a GPS antenna with a cable 5m long.
On option, an antenna extension cable 10m long is available.
Operating principle
The T200 is synchronized every second automatically from the GPS network,
provided that the satellite signal reception levels are adequate.
The T200 can receive information from at most 14 satellites at the same time.
The larger the number of satellites, the more precise will be the measurements
based on the GPS signals.
Upon initialization of the COM card, the minimum time for satisfactory reception of
the GPS satellite signals ranges between 5 min. and 15 min. (it depends on the
quality of the signals received).
The average precision of time setting is approximately 1 ms (discrimination between
two events: 10 ms).
Events specific to the GPS function are generated by the COM card (in the
"System" log) so as to provide information concerning the operating status of the
GPS module:
- "GPS started"
- "GPS synchronization OK"
- "GPS synchronization lost"
Comment: When the GPS option is present, it takes priority over SNTP time
synchronization or manual time synchronization.
Antenna mounting:
On request for this option, the T200 is supplied with a GPS signal acquisition card.
This card is installed in factory on slot "S5" of the COM card.
Note: The synchronization by GPS option can be installed only on a "full" type COM
card.
For the GPS option to operate, it is necessary to install the GPS antenna outside
the enclosure, on a horizontal metal mounting (the antenna being magnetized), in a
location where the GPS signals may not be disturbed by nearby obstacles that
could act as a screen (wall, building, etc.).
The GPS sensor should be installed so as to have a free field around it, so as to
receive the satellite signals correctly. (e.g. roof of the substation where the T200 is
located: see drawing opposite).
The GPS antenna can withstand a temperature range of: -40°C / +85°C.
24
NT00113-EN-05
Commissioning GPS synchronization setting
Information relating to the GPS function:
When the GPS card is installed on the COM card, the T200 automatically tries to
connect to the GPS network.
When the GPS signals are detected at a sufficient level, the "Clock synchronized by
GPS" display appears in the Maintenance/Clock page of the embedded Web server
of the T200 and the configuration/monitoring parameters related to this option are
displayed (see image below).
When the GPS signals are detected at a sufficient level, it is then no longer possible
to configure the PC time and date manually. The GPS card automatically takes
control of time setting for the device and also overrides time setting by SNTP (if the
latter is present).
For correct operation, the GPS option requires configuration of the following
parameters:
Information concerning the time zone:
The time provided by the GPS satellites is GMT universal time.
It is therefore necessary to configure the time zone corresponding to the country in
which the T200 is located so that the time on the T200 matches the local time in the
country. To do so, perform the following configuration:
- Time zone: In the proposed drop-down list choose the zone corresponding to
the local time zone (closest city having the same time zone).
- Adjust the clock for automatic observation of summer time: Check the
box "Adjust clock for automatic summer time adjustment" if the T200 is to
perform automatic time setting of the clock for changes related to the transition
to summer time and winter time.
- Save Time Zone information: Click on this button to accept changes in the
configuration.
GPS position:
This section gives information concerning the information delivered by the GPS
satellites, namely:
- Longitude and latitude
- Height above sea level
- Precision of horizontal measurement (longitude and latitude)
- Precision of vertical measurement (altitude)
Comment: The GPS position data appear in the page only when time
synchronization is performed with the satellites.
NT00113-EN-05
25
Commissioning GPS synchronization setting
GPS satellite data:
This section gives information concerning the quantity and quality of the GPS
signals received from the satellites:
- Channels 1 to 14: The T200 assigns a channel number for each satellite
detected.
- Satellite identification: GPS identification No. of the satellite detected.
- Signal status: Provides knowledge of the connection status of the satellites. 6
statuses can be displayed:
Not connected: displayed in grey colour
Search in progress: displayed in grey colour
Signal detected, but unusable: displayed in red colour
Signal captured: displayed in green colour if signal quality ≥ 45, otherwise in
orange colour
Signal and carrier wave captured: displayed in green colour if signal quality
≥ 45, otherwise in orange colour
Signal and carrier wave captured, reception: displayed in green colour if
signal quality ≥ 45, otherwise in orange colour
Comment: The colour of display of each line makes it possible to know the state of
the GPS connection:
Grey colour: no connection or connection in progress
Orange colour: connection performed but not finalized or with mediocre
reception level but sufficient for synchronization.
Green colour: Connection performed with very good reception level.
Red colour: Reception level too weak, no connection possible.
- Signal quality: Value displayed in dBHz allowing assessment of the quality of the
signal level received for each satellite.
Level ≥ 45 dBHz: Very good reception level
Functioning of GPS synchronization:
At least two satellites in reception are required (with reception level ≥ 45 dB) for
time synchronization and position locating (longitude and latitude) to be operational
on the T200.
The larger the number of satellites, the more precise will be the measurements
based on the GPS signals.
26
NT00113-EN-05

Commissioning Ethernet interface setting
3.3 Configuration of SNTP service
Access: "Maintenance/Clock" page.
The T200 incorporates an SNTP client. It allows the time on the internal clock of the T200
to be set automatically from a network synchronization server, when T200 is connected to
this network.
Comment: When the SNTP option is configured, it overrides manual synchronization of
the T200 time and date. It is then no longer possible to configure the PC time and date
manually.
Operating principle
The T200 includes the capability for defining 2 different SNTP servers, one main server
and one auxiliary server, each being on different networks.
When the "Polling period" time delay configured has expired, the T200 sends a request to
the main SNTP server.
If the T200 receives a synchronization from the main SNTP server, the time on the latter is
set and the synchronization cycle is completed.
If the T200 obtains no response from the main SNTP server after the end of delay "Max.
server response time" has elapsed, the T200 attempts a new connection again.
If the "Number of reconnection attempts" is reached, the T200 tries to become
synchronized with the auxiliary SNTP server.
The cycle ends once the T200U has been synchronized with the second server or when it
reaches the "Number of reconnection attempts".
Configuration parameters:
• SNTP server and auxiliary SNTP server: IP address of the main and auxiliary
SNTP servers.
Note: When the address is set to "0.0.0.0", the synchronization by SNTP function is
deactivated on the server.
• Synchronization period: Allows the time synchronization period to be defined via
the SNTP server. Configurable from 1 to 300 seconds.
• Number of reconnection attempts: Upon failure of synchronization with the server,
max. number of attempts to be made.
• Last SNTP synchronization: Indication of the time and date of the last SNTP
synchronization performed (consultation exclusively).
• SNTP server gateway and auxiliary SNTP gateway: Address of the gateway for
access to the main and auxiliary SNTP servers.
• Max. server response time: Maximum time waiting for the reply from the SNTP
server before making a further attempt at synchronization.
• Period of validity of the clock: Time after which the T200 must be resynchronized
with the SNTP server.
NT00113-EN-05
27
Commissioning SNTP service setting
T200
Supervisor 1
Supervisor 2
ADSL
GPRS
1 Ethernet interface
2 virtual IP address
10.x.x.x
10.a.a.a
10.y.y.y
10.b.b.b
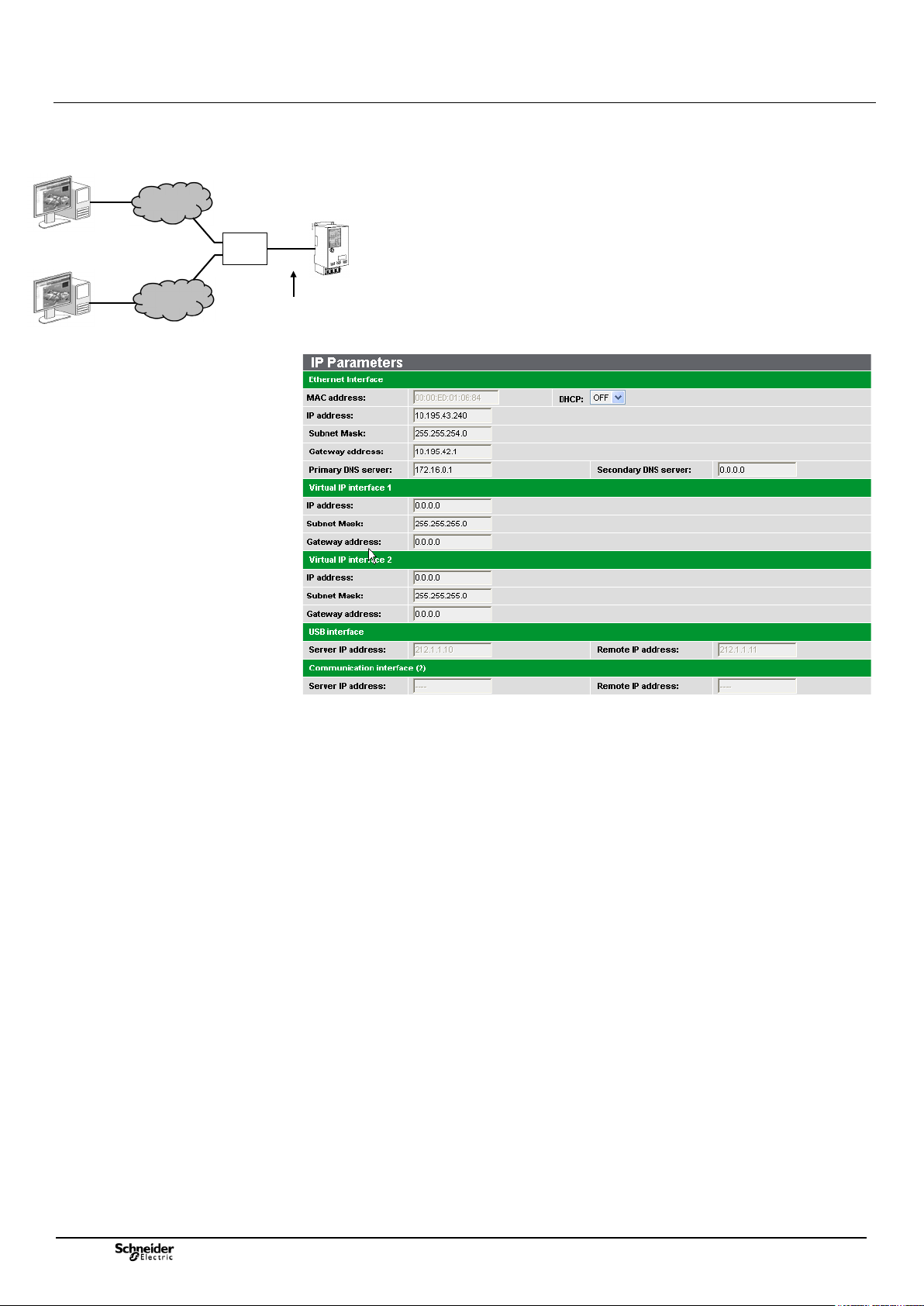
3.4 Configuration of Ethernet interfaces
Access: "Maintenance/IP Parameters" page.
This page can be used to configure the Ethernet connection parameters of the T200.
The T200 can include three IP addresses specific to the device, to allow simultaneous
connection from several TCPI/IP network access points including specific address (e.g.
Router
several Supervisors who wants to access T200 from different TCP/IP network – see
example).
The three IP addresses use the same network physical interface (single Ethernet port on
the COM card). For this reason, the two additional IP addresses added to that included as
standard in the "Ethernet Interface" part are called virtual Ethernet interfaces 1 and 2.
Note : The GPRS or 3G port is not is not affected by these virtual addresses.
Interface Ethernet :
• MAC address: Unique identification address for each T200, set in factory.
(Consultation exclusively)
• DHCP: Defines whether the router of the Ethernet local area network can allocate a
new IP address to the T200 automatically upon a new connection. It is recommended
not to activate this function or else you could no longer be able to log on to the T200
if the modified address is not known.
• IP address: Base IP address of the T200 (as standard: 172.16.0.5).
• Sub-network mask: The mask defines the possibility of configuration of the IP
address on the Ethernet network. For each IP address field, (0) means authorization
of 255 values and (255) means fixed value for this field.
(As standard: 255.255.255.0)
• Gateway addresses: IP address of the server's Ethernet gateway. The gateway
centralizes all the network IP accesses (as standard: 172.16.0.1).
• Primary DNS server: IP address of the primary DNS server (Domain Name Server).
The DNS enables the IP addresses to be associated with the website names (as
standard: 172.16.0.1).
• Secondary DNS server: IP address of the secondary DNS server (Domain Name
Server). Backup DNS server (as standard: 0.0.0.0).
Ethernet virtual interface 1 and 2:
• IP address: IP address for the virtual interface. If set to "0.0.0.0", the virtual interface
is deactivated.
• Sub-network mask: Sub-network mask of the virtual interface (same functioning as
the Ethernet interface).
• Gateway addresses: IP address of the Ethernet gateway of the virtual interface
(same functioning as the Ethernet interface).
USB interface:
• Server IP address: IP address of the T200's embedded Web server for USB access.
Unmodifiable (as standard: 212.1.1.10).
• Client IP address: IP address assigned to the PC connected via USB to the
embedded Web server. Unmodifiable. (As standard: 212.1.1.11).
28
NT00113-EN-05
Commissioning Ethernet interface setting
Backup/Restore page
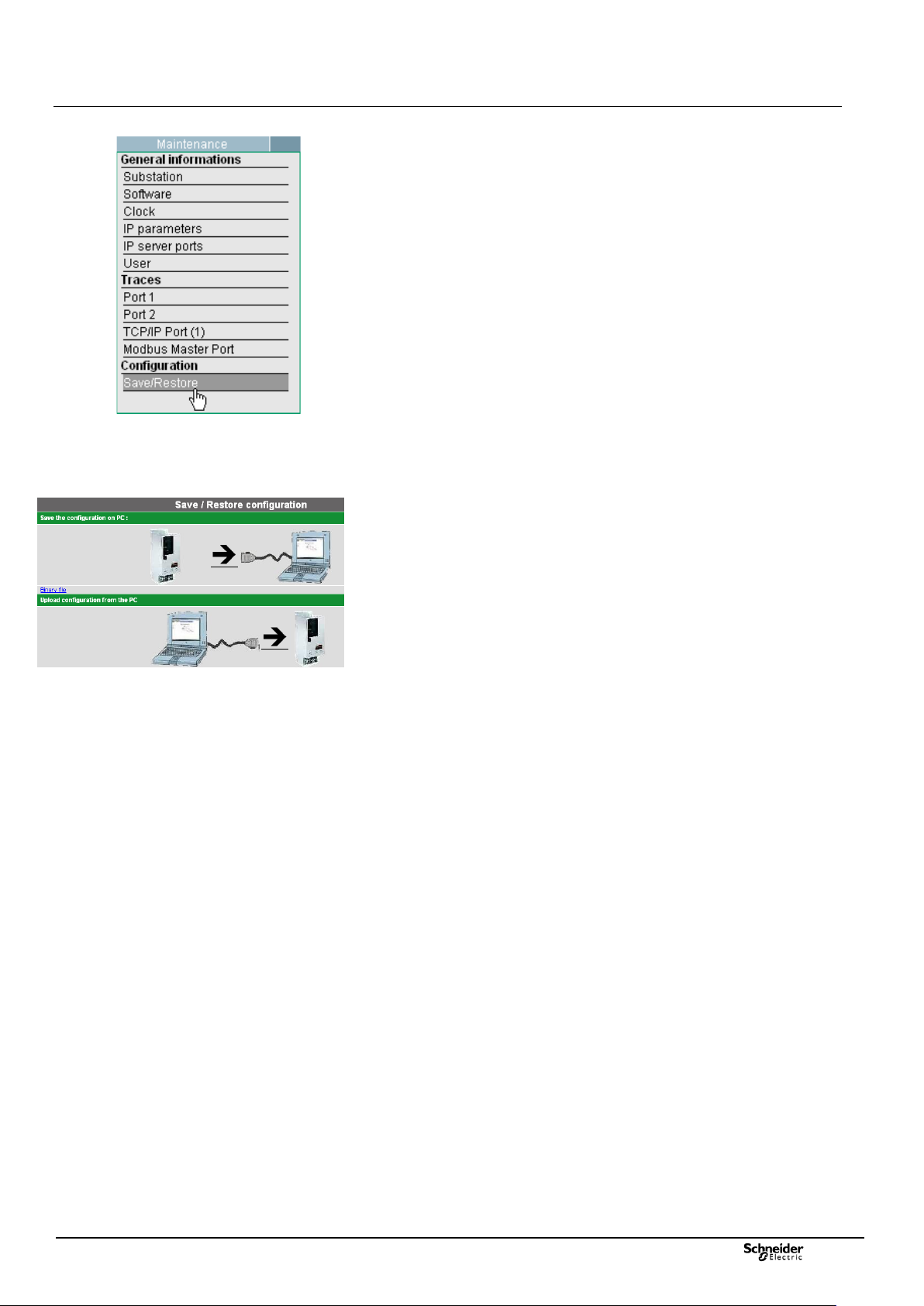
3.5 Save/Restore configuration parameters
Access: "Maintenance/Save-Restore" page.
The T200 can save in file form all the configurable parameters of the equipment
(except the parameters of the "IP parameters" page which remain specific to each
equipment item).
This file can then be used for downloading to other equipment of the same type,
thus enabling the T200 to be configured automatically without needing to redo the
entire configuration manually, which would be rather onerous.
However, the parameters specific to each T200 must then be personalized (e.g.
protocol address, fault detection thresholds, etc.).
The "Maintenance/Backup-Restoral" page provides access to backup/restoral
resources.
Saving the configuration on PC:
This section describes saving of the T200 configuration in file form (T200 PC
direction).
There are two possible backup file formats:
- Zipped text file: Click once on the arrow (T200 PC) and the T200 automatically
creates a compressed text file (file with *.zip extension) containing the T200
parameters.
- Binary file: Click once on the "Binary file" link and the T200 automatically creates
a binary file (file without extension) containing the T200 parameters.
Note: There is in theory no need to use the binary format for backup, except if you
want to generate a backup compatible with an old software version of the T200 (see
chapter below: "Backup file compatibility").
Downloading the configuration from the PC:
This section describes downloading to the T200 the parameters contained in a
backup file (PC -> T200 direction).
In this mode there is only a single button for downloading.
The T200 automatically detects the type of file downloaded and manages the
reading of information accordingly.
It is possible to download three types of files:
Text file (extension: *.txt)
Binary file (without extension)
Compressed text file (*.zip extension).
Backup file compatibility:
In the first T200 software versions (versions below V2.50 or V3.50), backup and
restoral was possible only in a single type of file format (binary file).
To be able to load these old backup files on a recent T200, it is essential that the
T200 include a V2.5x or V3.5x version. A V4.0x or upper version will not allow this
type of file to be loaded for reasons of incompatibility.
You should therefore proceed in two stages to load a configuration file coming from
an old software version on a T200 containing a recent software version of the V4.xx
or upper type:
1. Load the old configuration file on equipment incorporating an equivalent
software version (e.g. V2.5x for V2.yx versions and V3.5x for V3.yx versions,
with y is lower than 5).
2. Save the configuration in file form (choice of format: without extension or *.zip).
3. Load software version V4.xx or upper on this equipment.
4. Load the configuration file saved previously.
5. Save the configuration.
6. The file obtained will then be compatible with recent software (V4.xx or upper,
V2.5x or V3.5x).
Note: The file obtained will no longer be compatible with the old software
(versions below V2.50 or V3.50). If the software version has not been updated
on all the T200's, it is therefore wise to keep both types of backup (old and
new).
NT00113-EN-05
29
Commissioning Communication configuration
Display of the position of the fictitious "Dummy
Control" device in the "Monitoring" page of the Web
server.
3.6 Dummy Control option
Access: "Monitoring" page.
This option allows remote simulation, from the Supervisor, of an opening or closing
remote control action on the T200.
The aim is to verify protocol exchanges between the T200 and the Supervisor by
sending a double telecontrol, but without risk of really actuating a switch, because
the command is executed only on a fictitious device installed on the COM card
("Dummy Control" module).
This option requires addition of the "Dummy Control" module on the COM card on
the port 1 slot used for transmission to the Supervisor.
No specific parameters setup is necessary to use this option. The COM card
automatically detects the presence of this module on port 1.
Configuration of the T200 must nevertheless be provided for to use the Dummy
Control option. This option can be activated (on port 1 of the COM card) by the
"OFF line" configuration (available on the Easergy CD supplied with the T200 folder
"Tools\OFF-Line Configurator"), by generating a configuration file and loading it on
the T200.
Note: When the "Dummy Control" module is installed on port 1, it is no longer
possible to communicate on this port except in RS232 mode, and this only from the
DB9 port on the right-hand side of the rack..
30
NT00113-EN-05

Commissioning Communication configuration
Excerpted from the page: "Settings/Operating mode"
3.7 Parameters for communication with the supervisor
The COM card of the T200 is designed to detect automatically the type of modem
that is installed on the communication ports used for transmission to the SCADA
system (ports 1 and 2).
The configuration software automatically proposes a choice of media on these ports
which will correspond to the type of modem installed.
The parameters present in the configuration pages for ports 1 and 2 take into
account the type of medium that has been selected, because each type of medium
has specific configuration parameters.
The configuration page for protocol parameters may take also into account certain
parameters related to the type of medium selected.
Comment: The protocol parameters related to the type of medium will be described
in this chapter. The other parameters related to the protocol will not be described in
detail, however. For more information concerning the latter, refer to the User's
Manual for the protocol.
3.7.1 "Operating Mode" page
Access: "Settings/Operating Mode" menu
Objective of this page: Activate the transmission ports and select the type of modem
to be used and how it will be managed (up to two communication ports available).
The parameters for this page can be consulted and/or modified depending on the user profile.
Configuration for each port used (Port 1 or Port 2):
Mode: Allows choice (or merely gives an indication depending on the protocol)
of the transmission mode used for dialogue with the SCADA system.
Depending on the protocol used, there is a choice between one of the two
modes mentioned below. Some protocols are fixed from the transmission
mode viewpoint and do not allow this choice.
In that case, the T200 proposes merely an indication, with no possibility of
modification:
- Master/Slave: communicates exclusively in the Scada -> T200 direction.
No remote alarm function used in this mode.
Depending on the protocol, the exact title displayed may be:
"Unbalanced" (e.g. IEC protocol);
"Master/Slave" (e.g. PUR protocol);
"No report by exception" (e.g. Modbus protocol);
"No unsolicited response" (DNP3 protocol).
- Master/Master: communicates in both directions, Scada -> T200 and
T200 -> Scada.
The remote alarm function will be used in this mode if one of the modes
mentioned below corresponding to the Master/Master mode is configured.
On the other hand, the remote alarm function will not be used if the
Master/Slave mode mentioned above is configured.
Depending on the protocol, the exact title displayed may be:
"Balanced " (e.g. IEC protocol);
"Master/Master" (e.g. PUR protocol);
"Report by exception" (e.g. Modbus protocol);
"Unsolicited response" (e.g. DNP3 protocol).
Comment: The "Report by exception" mode is not really a Master/Master
mode. It is in fact a Master/Slave mode with the possibility of alarm sending
to the SCADA system by means of the "Report by exception" function,
which from the functional viewpoint resembles a Master/Master mode.
NT00113-EN-05
31

Commissioning Communication configuration
From the page: "Settings/Operating mode"
Link: Allows definition of the way in which the ports will be managed according
to one of the following modes:
Off: No transmission over this channel.
Normal: Main transmission channel to the SCADA system. Two
"Normal" channels with the same protocol but with different
characteristics (e.g. type of transmission) can be used if there are two
remote control systems (main and maintenance). The T200 cannot
manage simultaneous remote controls coming from the two systems.
Balanced – Normal/Standby: Two channels are necessary in this
mode. The operation of the channels is symmetric. In the event of a
fault on the channel in service, switchover to the other channel takes
place automatically.
Main – Normal/ Standby: Requires another channel as " Standby –
Normal/Standby". Same operation as "Balanced" but with priority use
of the main channel.
Standby – Normal/ Standby: Requires another channel as "Main –
Normal/Standby". Same operation as "Balanced" but with use of the
backup channel if failure of the Main channel. A configurable option
can be used to define a priority return to the main channel if the latter
becomes available again.
Store & Forward: Function used only in radio mode. In addition to the
normal channel function of transmission to the SCADA system, this
channel is also used for relaying to an auxiliary T200 located within
reach of transmission and which is not accessible by any other means.
Test: (in radio mode only). Allows a fixed frequency to be generated on
the radio network to allow antenna installation adjustment operations or
level measurements on fields received on another T200 within reach of
the first.
For further information on the "Normal/Standby" and "Store & Forward"
modes, see the corresponding chapters.
Note: Depending on the protocol, all the operating modes of the ports
mentioned above are not necessarily available.
Medium: Allows definition of the type of transmission medium to be used for
the link to the SCADA system, for each port. The choice proposed below
depends on the type of modem detected on the COM card port, namely:
RS232 modem not isolated installed on the port:
♦ Direct RS232 (internal interface)
♦ Radio (external with modem)
♦ PSTN (external modem, Hayes command)
♦ GSM (external modem, Hayes command)
♦ PSTN (UMPC and external modem)
RS232/RS485 modem isolated 2,5 KV installed on the port :
♦ Direct RS232 (internal interface)
♦ Radio (external with modem)
♦ PSTN (external modem, Hayes command)
♦ GSM (external modem, Hayes command)
♦ PSTN (UMPC and external modem)
♦ Direct RS485 (internal interface)
Radio modem installed on the port:
♦ 1200/2400 baud FFSK radio (internal modem)
♦ 600/1200 baud FSK radio (internal modem)
♦ 600/1200 baud LL radio (internal modem)
GSM/GPRS modem installed on the port:
♦ GSM (internal modem)
♦ GPRS (internal modem)
GSM/3G modem installed on the port:
♦ GSM (internal modem)
♦ 3G (internal modem)
PSTN modem installed on the port:
♦ PSTN (internal modem)
etc.
Configure the port according to the type of transmission medium wanted
based on the proposed choice.
Important note: A medium not configured or incorrectly configured
generates a fault on the COM card (red fault indicator lamp lit on the front
of the card).
32
NT00113-EN-05

Commissioning Communication configuration
Excerpted from the page: "Configuration/Operating
modes"
3.7.1.1 Configuration of Normal/Standby mode
The Normal/Standby mode allows the two communication ports to the Supervisor to
be used in communication redundancy management.
When the "Normal/Standby" mode is configured as link type on ports 1 and 2, the
"Quality of transmission parameters" section becomes accessible in the "Operating
modes" page and the corresponding parameters can be configured.
This mode requires the use of two communication channels (ports 1 and 2) to
operate.
Two operating modes are possible:
- Balanced mode: No criterion of priority of one channel over the other in this
mode. So long as communication functions on the channel in service, it stays on
that channel. Upon detecting loss of communication on the channel in service, it is
switched over to the other channel. Both channels must be declared as "Balanced".
- Main/Backup mode: In this mode, priority is given to one of the two
communication channels (channel declared as "main"). So long as communication
functions satisfactorily on this channel, it stays on this channel in priority. The
channel declared as "Backup" is used only in the event of operating failure on the
main channel. Return to the main channel can be enabled or inhibited by
configuration ("Authorize return to main channel" parameter). In this case, a time
delay must be set to define when to perform return to the main channel ("time delay
before return" parameter).
Reception quality criteria:
The T200 uses the transmission quality criteria to define the conditions of channel
changeover.
Two communication criteria quality for the T200 are configurable.
They concern the quality of transmission ("TxQuality") and the quality of reception
("RxQuality"). The value to be entered is indicated as a % of sent and received
frames which are correct.
Two separate cases must be considered:
- Master/Master mode (mode with alarms):
When the T200 has to take the initiative of sending frames to transmit an alarm, it
may decide to change transmission channel if the quality of the transmission
connection is not satisfactory. In that case, the T200 evaluates the quality of
transmission according to the quality of the response obtained following a request
upon alarm sent to the Supervisor.
A configurable parameter ("NbSrcv") define the number of repeats to be performed
in the event of poor quality of response by the Supervisor after sending an alarm.
The T200 uses this criterion to consider that the connection is poor and that it is
necessary to change over to the other channel.
- Master/Slave mode (mode without alarm):
In this mode, the T200 is Slave. It cannot take the initiative of changing transmission
channel. It must therefore inform the Supervisor that the connection is poor and that
it is necessary to change over to the backup channel.
To do so, the T200 will stop communicating if it considers that the connection is not
good on the channel in service. The supervisor must therefore be capable of
detecting the communication cutoff and take the initiative of changing over to the
other channel.
In this mode, the T200 cannot estimate the quality of the connection in
transmission. It is only the reception criteria that are taken into account.
Diagnostic:
For each port, the T200 gives information concerning the number of valid frames
sent and received and a quality percentage relative to the number of frames
handled.
NT00113-EN-05
33

Commissioning Communication configuration
Repeater T200
Distant T200
Supervisor
Obstacle
Excerpted from the page: "Configuration/Operating
modes"
3.7.1.2 Configuration of Store & Forward mode
The Store & Forward (or repeater) mode is used only in radio communication.
The Store & Forward function allows a T200 to serve as a radio relay for another
distant T200 which cannot be accessed directly by the Supervisor due to access
problems. The Distant T200 must be within transmission range of the first T200
acting as relay (Repeater T200).
Upon detecting a message which is not addressed to it, the Repeater T200 resends
it over the same channel so as to reroute it toward the T200 for which the message
is destined.
Three types of T200 can be managed in the "Store & Forward" mode:
- Standard T200: This is a conventional T200. It can communicate directly with the
control centre without going the through Repeater T200. This T200 must be
configured with "Normal" link type.
- Repeater T200: This will act as relay for other T200s which cannot communicate
directly with the Supervisor. This T200 must be configured with "Store & Forward"
link type.
- Distant T200: This is a distant T200 which cannot communicate directly with the
Supervisor and which will use the Repeater T200 as communication gateway to be
able to communicate with the Supervisor.
This T200 must be configured with "Normal" link type.
Specifications
The Repeater T200 uses the same port (and hence the same radio) to
communicate with the Supervisor and with the Distant T200s.
The Repeater T200 can manage only 10 Distant T200s at most.
These Distant T200s must be declared by configuration in the Repeater T200.
When the "Store & Forward" mode is configured on the Repeater T200, an
additional "Store & Forward Parameters" section is displayed in the "Operating
mode" page.
This part can be used to configure for each distant T200:
Scada end link address: This is the address that will have to be defined at the
Supervisor end to access the Distant T200. This address must be configured
identically in the Repeater T200. This address is used only for the SupervisorRepeater T200 connection.
Distant T200 end link address: This is the address that will have to be
configured on the Distant T200 and also identically in the Repeater T200. This
address is used only for the Repeater T200-Distant T200 connection.
The Repeater T200 has its specific link address so that the latter may be used as
a mere Standard T200 in addition to the Repeater function.
34
NT00113-EN-05

Commissioning Communication configuration
Repeater T200
Distant T200
Supervisor
Address A
Address B
Address B
Address A
Substitution principe of adresses link :
In blue
Supervisor for accessing Distant T200 (e.g. : address A)
In red
Repeater for accessing Distant T200 (e.g. : address A)
Operation
When the Supervisor wants to communicate with one of the Distant T200s, the
latter sends a protocol frame containing the link address of the Distant T200 to be
accessed.
The Repeater T200 receives this frame and sees that the address was not destined
for it but that it corresponds to the address of one of the Distant T200s defined in its
list of 10 Distant terminals.
The Repeater T200 sends back a frame to the corresponding Distant T200,
replacing the link address with that which has been defined for it in its list for this
Distant T200.
The Distant T200 receives the frame and replies to the request with a frame
containing the link address that is specific to it.
color : message including address used by the
color : : message including address used by the
The Repeater T200 receives the reply and sends a frame back to the Supervisor
according to the same principle of replacement of the link address between that
used by the Distant T200 and that used by the Supervisor.
Note: When a Master/Master type link is used, the Distant T200 can initiate
communication to send an alarm. The transmission principle remains the same.
Constraints of the Store & Forward function
1°) Due to rerouting of frames from one end or the other of the Repeater, the
transmission times are longer than for direct access on a Normal T200. For this
reason, the reply waiting times will have to be increased on the Distant T200s.
2°) The Repeater function of the T200 uses only a single transmission port. Radio
traffic over this channel is therefore fairly substantial due to the numerous
messages to be re-transmitted at the Distant T200 end and the Supervisor end.
Message collisions and repetitions must therefore be expected on the radio traffic.
3°) The handling of messages received by the Repeater T200 is treated as a whole.
The Repeater T200 will end retransmission of the message to be handled to the
Supervisor and the Distant T200 before being able to receive and handle other
messages. This constraint may result in repetition phenomena on devices other
than the Repeater T200.
4°) It should be borne in mind that if a Repeater T200 can no longer transmit for
whatsoever reason, all the Distant T200s will be affected by this noncommunication.
5°) The quality of the radio link largely depends on the efficiency of the collision
avoidance function. This function gives good results if the information giving the
busy state of the wireless network is reliable. Now, because the Distant T200s can
pick up frames sent by other T200s, the occupancy state of the wireless network
may be not as efficient as normally. The functioning of the Repeater system may be
degraded for this reason.
NT00113-EN-05
35

Commissioning Communication configuration
3.7.2 "Protocol" page
Access: "Settings/Protocol (+TCP/IP (1))" page.
The parameters of this page depend entirely on the type of protocol used.
Detailed explanations concerning this page will therefore not be given in this
manual.
Refer to the protocol User Manual for details concerning configuration of the
parameters of this page.
Note that certain parameters of this page depend on the type of modems installed
on the ports.
For example, the "Collision Avoidance Parameters" section (see image below) is
displayed in this page only when a Radio or PSTN modem (internal or external) is
configured on the COM card.
36
NT00113-EN-05

Commissioning Communication configuration
DSR
CD
Received frame
DTR
or
Send Cd
RTS
CTS Sent frame
Squelch
3.7.3 "Port 1 (or 2): Transmission" page
Access: "Settings/Port X: Transmission" page
The parameters display for this page depends on the type of modem installed on
the port of the COM card (port 1 or port 2) and on the transmission medium chosen
in the "Settings/Operating Mode" page.
Configuration procedure:
The T200 is factory-delivered with a default configuration corresponding to the type
of modem installed on the COM card (internal modem) or on the sliding plate of the
enclosure (external modem).
The user should then (if need be) adjust the parameters of this page (in particular
the modem management signals and associated time delays) depending on what is
required for the modems used or possibly the transmission network.
Concerning the adjustment of transmission delays, in theory one starts by
configuring high values for all the delays, checking first that dialogue is established
between the T200 and the Supervisor.
One starts by gradually reducing the first time delay in order to determine the
operating limit of the modem relative to the adjusted signal.
Then, this delay is increased by several tens of milliseconds to retain a safety
margin.
The procedure is then started again with the other delays.
This method allows T200-Supervisor transmission times to be optimized.
In case of doubt concerning the configuration, it is preferable to leave the default
values.
Modem management signals:
Before going into detail concerning the parameters to be configured, the function of
each modem management signal should be explained.
The following timing diagram shows the management signals involved during
communication between the T200 modem and the interface or the external radio, or
even directly with the control centre.
DSR (Data Send Ready):
This signal can be supplied to the T200 to indicate that the Control Centre (or the
modem) is capable of transmitting (or simply that it is energized).
This signal is used only in the case of an RS232 link (not used in radio mode).
CD (Carrier Detect):
This signal, when it exists, is used to confirm receipt of the received frame. It can
also be used to learn the transmission network occupancy.
DTR (Data Terminal Ready):
When the Control Centre uses DSR, DTR is used to indicate that the T200 is ready
for transmission (equivalent of DSR but in the other direction).
In radio mode with internal modem: This signal is used by the T200 to actuate radio
terminal transition to sending when it requires different commands for transition to
sending and carrier sending.
In radio mode with external modem: This signal is generally not used (with some
exceptions) because RTS is used as the sole command to cause rising of the send
command and cause rising of the carrier.
NT00113-EN-05
37

Commissioning Communication configuration
RTS (Request To Send):
This signal actuates sending of the modem carrier
CTS (Clear To Send):
After the T200 has performed the Request To Send, the sender sometimes takes a
certain time to rise in power before being able to send the messages submitted to it.
This is especially true for radio equipment. Accordingly, when the equipment is
ready to send, it indicates this to the T200 by causing the CTS signal to rise.
Squelch: This signal is used only in radio mode to indicate to the T200 the
occupancy state of the radio network.
Definition of modem management signals and time delays:
The T200 allows the user to configure, if necessary, use or not of the modem
management signals and the various associated time delays.
We give below the list of configurable options concerning these modem
management signals. Configuration is performed in the pages for ports 1 and 2 of
the T200 Web server:
• Delay before response: After receiving a message, this is the waiting time
before sending the message (response). This delay serves to avoid any
overlapping of signals between the message received and the message sent.
This delay is often used with a radio medium or with certain modems which
require a time lag to turn around, i.e. a minimum time to go from receive mode
to send mode.
♦ DTR management: If this option is selected, the DTR signal will be managed
during transmission exchanges with the modem.
• DTR - RTS delay (if RTS used):
♦ RTS management: If this option is selected, the RTS signal will be managed
during transmission exchanges with the modem.
♦ CTS management If this option is selected, the CTS signal will be managed
during transmission exchanges with the modem.
♦ RTS - CTS delay (if CTS used): This is the maximum time during which the
T200 waits for the CTS after the RTS has been activated. If, after this delay,
CTS has not become active, the T200 discontinues sending the frame.
• RTS (or CTS) delay - Message (if RTS or CTS used): This is the time
between transition to the active state of RTS (or CTS if this signal is used) and
the start of message sending. Typically this time lag is used to wait for a stable
carrier period established by the modem.
If necessary, when CTS is not available, the time for installation of the carrier
to solve the problem posed by the non-availability of this signal can be added
to this delay. Likewise, if the DTR and RTS commands are common, the time
for rise in power of the sender can be added.
38
NT00113-EN-05

Commissioning Communication configuration
Note: Example of delay to be configured on the T200, depending on the type
of radio:
- Motorola CM 340 or GM340 radio: RTS-Message delay = 150 ms
- TAIT 811x radio: RTS-Message delay = 100 ms
- MDS4710 radio: RTS-Message delay = 50 ms
♦ Message - RTS delay (if RTS used): This is the minimum time to be waited,
after sending a message, before causing RTS and DTR (or Send command) to
fall again. This delay prevents the end of the message from being truncated by
the premature fall of modem sending.
Note: Example of delay to be configured on the T200, depending on the type
of radio:
- Motorola CM 340 or GM340 radio: Message - RTS delay = 100 ms
- TAIT 811x radio: Message - RTS delay = 80 ms
- MDS4710 radio: Message - RTS delay = 50 ms
♦ DSR management If this option is selected, the DSR signal will be managed
during transmission exchanges with the modem.
♦ CD management: If this option is selected, the CD signal will be managed
during transmission exchanges with the modem.
General parameters (common to the various transmission
media):
As a general rule, certain configurable parameters of the ports 1 and 2 pages are
common to numerous types of modems. We shall describe in detail here the
meaning of these parameters and how to configure them.
♦ Baud rate: This is the speed of transmission between the T200 and the
modem. When an external modem is used, the configured speed is not
necessarily the speed that will be used for the link to the Supervisor, because
the external modem can use a different speed to that used for the RS232-T200
link.
The choice of available speeds differs depending on the type of modem
installed on the ports. Here are a few examples:
FFSK radio: 1200 or 2400 baud
External radio or internal RS232: 200 to 38400 baud
Internal GSM: 600 to 9600 baud
etc.
♦ Parity: This is the frame character parity for transmission to the Supervisor.
Some modems do not manage parity. In such cases, the T200 will have to be
configured with the "No parity" option. To be defined therefore according to the
type of modem used. Of course, the Control Centre must also be able to be
configured in this mode.
Note that when the parity is no longer used, transmission security is diminished
and a disturbed frame may be considered correct. (See protocol manual for
more details concerning this function).
There are four possible configurations: no parity, space, even or odd.
Note: Parity is not used in PSTN, GSM, GPRS, 3G and FFSK radio links.
♦ Number of stop bits: This is the number of stop bits used to define the end of
a frame during transmission.
There are two possible configurations: one or two stop bits.
• Frame error on idle line: The T200 is capable of detecting a gap greater than
1 bit between 2 characters of a frame.
With certain protocols, any frame having this feature can be rejected. This
allows secure transmission.
This frame rejection will be activated if this option is set to "Yes".
This configuration implies that the Supervisor and the modems involved in the
transmission circuit ensure that there are no gaps. While this is sometimes true
with regard to the Supervisor, it is not completely true for many modems (case
of packet transmission). In this specific case, "No" should be set. However,
transmission security must then be ensured by other means (see User Manual
of the protocol used for more information).
Note: This parameter is used only on a radio or LL link.
• Frame error on noisy outgoing cable: Some transmission networks could
constantly generate noise just at the start of frame. In that case this option
should be set to "No", to avoid systematically rejecting all the received frames
which could be considered incorrect. However, the incorrect character
generated by the noise located in the frame header will be eliminated when
reading the frame, because this character will not correspond to what is
expected by the protocol.
Note that, in most cases, this noise does not exist. In such cases, the option
should be set to "Yes".
Note: This parameter is used only on a radio or LL link.
NT00113-EN-05
39

Commissioning Communication configuration
Parameters specific to each transmission medium:
In this chapter we shall describe in detail the configuration parameters specific to
each modem (the other parameters having been described in detail in the preceding
chapter):
PSTN and GSM medium (internal or external modem):
♦ Dialing type: Choice of the type of dialling to be used for the telephone
call to the Supervisor during an alarm sequence.
There are two possible choices: pulse (decimal) and multifrequency (MF).
40
Note: Configuration available in PSTN but not in GSM.
♦ Modem Init: The Modem Init sequence is necessary to configure the
modem for operation linked to the T200 application.
The default Init sequence corresponds to the AT commands necessary
for an internal modem (modem installed on the COM card). For an
external modem, the Modem Init sequence is not defined in the
configuration supplied. It is up to the user to define it according to the
brand and model used (refer to the modem manual).
Note: Configuration available in PSTN but not in GSM.
NB: The Modem Init sequence is sent to the modem only after
initialization of the T200 COM card (following a reset or power up of the
T200). After changing the Init sequence, you must remember to
reinitialize the COM card for it to be taken into account by the modem.
Default Init sequence: &F0%S0=12S0=1&K0%C0E0&W0&Y0.
If in doubt, do not change this default Init sequence, because the T200Supervisor link is likely to no longer operate correctly.
♦ Caller communication delay: Maximum delay for connection between
the T200 and the Supervisor following a call by the T200 before release
of the PSTN line by the T200.
♦ Called communication delay: Maximum delay for connection between
the T200 and the Supervisor following a call by the Supervisor before
release of the PSTN line by the T200.
♦ Host tel number (main): Main phone number that the T200 uses to call
the Supervisor during an alarm sequence.
The T200 will try to call three times on this "normal" number before
switching to the "Backup" number.
♦ The codes accepted for telephone numbers are:
0 to 9 (for the call number);
P (for Pulse = decimal dialling setting);
T (for Tone = MF dialling setting);
W (for Wait);
space bar (for space);
+ (equivalent to "00" for international dialling).
Example of config.: "P 00W0674948960" or "P +W0674948960"
Note: A space must be inserted between the "T" or "P" and the call
number.
♦ Host telephone number (Standby): Secondary phone number that the
T200 uses to call the Supervisor during an alarm sequence. This phone
number is used only if the main number does not reply (i.e. after three
unsuccessful attempts).
The T200 will also try to call three times on this second number before
finally stopping calling, unless another alarm occurs, which will have the
consequence of reinitiating the alarm calls from the "Normal" number).
Same comment as for the "Normal" number concerning the codes to be
used for the call number.
NT00113-EN-05

Commissioning Communication configuration
Yellow status
indicator of
connection to the
GSM network
08:48:34.474 MODEM - Power up
08:48:35.986 MODEM - Command mode
08:48:36.994 MODEM - Tx : ATE0
08:48:39.518 MODEM - Tx : AT&S0
08:48:42.045 MODEM - Tx : AT
08:48:43.071 MODEM - Rx : OK
08:48:44.079 MODEM - Tx : AT+CPIN?
08:48:45.120 MODEM - Rx : +CPIN: SIM PIN
08:48:45.120 MODEM - Tx : AT+CPIN=****
08:48:47.230 MODEM - Rx : OK
08:48:47.230 MODEM - Tx : AT+CLCK="SC",0,****
08:48:49.770 MODEM - Tx : AT+CREG?
08:48:50.807 MODEM - Rx : +CREG: 0,1
08:48:50.807 MODEM - Tx : AT+CSCA=0689004000
08:48:54.818 MODEM - Tx : AT+CMCF=1
08:48:57.347 MODEM - Tx : AT+CSAS
08:48:59.875 MODEM - Tx : AT+CMEE=0
08:49:02.403 MODEM - Tx : AT&C1
08:49:04.929 MODEM - Tx : AT&D2
08:49:07.455 MODEM - Tx : AT+IPR=0
08:49:09.983 MODEM - Tx : ATS0=1
08:49:12.509 MODEM - Tx : AT+WIND=0
08:49:15.039 MODEM - Tx : AT+CICB=0
08:49:17.567 MODEM - Tx : AT+CBST=7,0,1
08:49:20.101 MODEM - Tx : AT&W
08:49:20.101 MODEM - Modem GSM initialized
Example of port trace during an attempt to connect
to the GSM network (Modem Init)
11:38:37.093 SlaveAddr = 03 <<<<< Reading N output words
Addr = 0x34
03 03 00 34 00 03 45 E7
11:38:37.113 SlaveAddr = 03 >>>>> Reading N output words
03 03 06 A9 AA AA A9 55 00
F6 9C
11:38:37.357 SlaveAddr = 04 <<<<< Reading N output words
Addr = 0x0
04 03 00 00 00 01 84 5F
11:38:37.593 SlaveAddr = 04 <<<<< Reading N output words
Addr = 0xf
04 03 00 0F 00 21 B5 84
Example of exchange frames during connection
established with the Supervisor (in Modbus
protocol)
Indications on the front panel of the GSM modem
for the COM card
NT00113-EN-05
GSM medium (internal or external modem):
♦ PIN Number: Configuration of the SIM card PIN code on four figures.
NB: After three validations of the page configuration or three modem
initializations with an incorrect PIN code, the SIM card is blocked. The
only solution in this case is to call the operator who will be able to unblock
it.
The first time that the T200 initializes the GSM modem, the latter asks the
modem if it needs the PIN code.
If the modem replies in the negative, the T200 will not manage the PIN
code and the latter will not need to be entered by the user.
On the other hand, if the modem replies that it needs the PIN code, the
T200 will manage this parameter and the PIN code must therefore be
configured.
Once the PIN code has been initialized a first time, the T200 asks the
modem to deactivate use of the PIN code.
The latter will therefore no longer be used by either the T200 or the GSM
modem.
♦ SMS service centre tel number: This is the number of the service centre
of the GSM operator which centralizes and stores all the SMS messages
sent to reroute them to the end user.
Contact the operator to know this number. It is also possible to find out
this number from a GSM telephone using the same operator as that used
by the SIM card of the T200, because the number can be looked up in the
telephone's configuration parameters.
Finally, it is also possible to find out this number in the port trace following
connection of the modem to the GSM network. The number is displayed
on the line including the "AT+CSCA" command (see enclosed example:
number=0689004000).
♦ SMS user tel number: SMS number that the T200 uses in the event of
an alarm sequence to send the text message to the user who is on
standby duty.
Same comment as for the "Normal" telephone number concerning the
codes to be used for the telephone number.
GSM modem connection status:
To check the connection status of the GSM modem, there are several
possibilities:
By flashing of the indicator lamp on the front of the GSM modem:
- The indicator lamp is lit steadily: the modem is not connected to
the GSM network.
- The indicator lamp flashes slowly (every 2.5 seconds): the
modem is connected to the network but there is no remote link.
- The indicator lamp flashes rapidly (every second): the modem is
connected to the network and a remote link is established.
By consulting the AT commands for modem initialization in the port
trace corresponding to the GSM modem: To the "AT+CREG"
command requested by the T200, the modem should reply "+CREG:
0.1" when the modem is connected to the network or "+CREG: 0.2"
if it is not (see example opposite).
Moreover, when the remote link is established between the T200
and the Supervisor, the port trace also displays protocol frame
exchanges between the T200 and the Supervisor.
41

Commissioning Communication configuration
42
15:59:28.157 MODEM - Tx : AT+WIND=0
15:59:30.683 MODEM - Tx : AT+CICB=0
15:59:33.210 MODEM - Tx : AT+CBST=7,0,1
15:59:35.741 MODEM - Tx : AT&W
15:59:48.333 MODEM - Modem GSM initialised
16:00:18.546 MODEM - Asking for level reception
16:00:19.581 MODEM - Rx : 20
16:00:19.590 MODEM - Rx : OK
16:00:39.732 MODEM - Asking for level reception
16:00:40.766 MODEM - Rx : 20
16:00:40.774 MODEM - Rx : OK
16:01:00.916 MODEM - Asking for level reception
16:01:01.950 MODEM - Rx : 23
16:01:01.957 MODEM - Rx : OK
The SMS messages sent contain the following information:
• Identification of the substation:
- equipment type (F200)
- slave address in Modbus, link address in IEC, etc.
- name of substation (configurable)
• Identification of the variable:
- variable name (configurable)
- variable state (configurable text associated with state 0 or
1 for digital, value + unity for analogue)
- change of state time
• Example of SMS message:
F200 125, Salvagny substation. Digital input 1: Deactivated
25/10 17:35:45
Level of GSM reception :
It is possible to know the level of GSM signal received by the modem of
T200.
This function is very useful to know if the T200 can correctly received
frames from the Supervisor or to adjust the installation of the antenna on
the support to optimize the reception.
To know the level of GSM signal received, you just have to consult the
port trace corresponding to GSM modem.
Once the modem is initialized, the T200 display automatically on screen
the level of GSM signal reception.
Remark : When the T200 detect a frame form the Supervisor, the display
of protocol frames gets priority from the GSM level indication.
Possible values for GSM signal :
- Reception GSM not detectable : level = 99
- Reception GSM not sufficient : level = 0 à 10
- Reception GSM correctly detected : level = 11 à 31
FSK or FFSK radio medium (internal or external modem):
♦ Caller communication delay: Maximum delay for connection between
the T200 and the Supervisor following a call by the T200 before release
of the radio link by the T200.
♦ Called communication delay: Maximum delay for connection between
the T200 and the Supervisor following a call by the Supervisor before
release of the radio link by the T200.
FSK LL 600/1200 baud medium (internal modem):
♦ Line type: Configuration of the type of LL line installed between the T200
and the Supervisor.
There are two possible configurations: two-wire or four-wire.
NT00113-EN-05

Commissioning Communication configuration
RS485 medium (internal modem):
♦ Polarization: Activates line polarization at the T200 end. The RS485 line
should be polarized at one termination, generally at the Master end.
♦ End-of-line resistance: Activates the load résistance at the T200 end.
The RS485 line should be loaded at both its terminations.
♦ Line type: Choice of type of transmission used: 2-wire or 4-wire.
GPRS or 3G medium (internal modem):
GPRS/3G operating conditions on T200:
For GPRS or 3G communication between the T200 and the Supervisor to be
able to operate, certain essential conditions must be obtained from the network
operator:
- The T200 must have a fixed IP address assigned by the operator:
The GPRS or 3G connection will not be able to operate if the T200 has a
dynamic IP address, because at the Supervisor end it will not be possible to
know the new IP addresses assigned to the T200 by the operator following a
reassignment. As a result, it will not be possible to initialize protocol
communication from the Supervisor.
Likewise, it will not be possible either to log on to the embedded Web server of
the T200 remotely from an Ethernet access if the IP address of the T200 is not
known.
The only way to know the IP address of the T200 in this case is to log on
locally (on site) to the embedded Web server of the T200 via an USB access,
which is hardly possible because that would imply going to the site for each
enclosure each time an IP address is reassigned.
As soon as the T200 is connected to the GPRS or 3G network, the IP address
assigned to the T200 is displayed in the "Server IP address" field that can be
consulted in the "Maintenance/IP server ports" page (see image below). It is
this address that must be used at the Supervisor end to connect to the T200
via Ethernet or via the protocol.
Comment: When connection to the GPRS or 3G network is not established,
dashes ("-") are displayed in place of the IP addresses.
- The IP ports used by the T200 must be opened by the operator:
A number of ports are used for the T200 application. The list of ports
used can be consulted in the "Maintenance - IP server ports" page of
the T200 Web server (see image below). All the ports mentioned in
this page must be opened at the GPRS/3G operator level for the
functions associated with these ports to be able to operate. If this is
not the case, it is always possible to select different port numbers in
this page to match port numbers available at the operator end.
Example: "HTTP server" port N°80 is not open for the operator
"Orange". A port number greater than 1024 should be configured on
the T200 to have an open port from this operator.
NT00113-EN-05
43

Commissioning Communication configuration
Configuration of GPRS or 3G parameters:
♦ Access Point Name (APN): Access Point Name. Name of the access point
for connection to the GPRS/3G network. This name is generally given by the
operator who provides access to the GPRS/3G network.
(e.g. "internet-entreprise" for the operator Orange).
♦ PIN number: Same as for GSM modem.
♦ Daily disconnect: One of the special features of GPRS/3G operation is that in
some cases of network unavailability, the T200 does not detect this link break.
The T200 will therefore remain connected continually to the network
(unavailable) even though the physical link is broken. The T200 can therefore
remain indefinitely in this mode and will no longer have a means of
reconnecting to the network, even if is available again, because to do so it
would have to be forced to disconnect from the network to then be able to
reconnect.
As a consequence, without a means of forcing automatic
disconnection/reconnection, the T200 will not by itself be able to restore
connection to the network.
The "Daily disconnection" option has therefore been provided to play this role
and thus allow T200 disconnection from the GPRS/3G network to be forced
automatically so as to reconnect it immediately afterward. This disconnection
can be programmed for a fixed time each day by means of the "Disconnection
time" setting.
This system works, but has the disadvantage that in the worst case scenario
the T200 may remain for at most 24 hours without any real connection to the
network (case of a brief network failure occurring just after the daily
disconnection time).
♦ Disconnect hour: Configuration of the selected daily disconnection time
according to the criteria described previously in "Daily disconnection".
This option should be entered only if the "Daily disconnection" option is used.
♦ PPP session timeout: Configuration of the delay maximum before
disconnection of T200 from GPRS/3G network, in case of no data transfer
detected by the T200.
♦ Specific ping IP address: The ping in theory makes it possible to verify and
measure the quality of the equipment's connection with another device
connected to the IP network.
This configurable parameter can determine to what IP address will be sent the
packet corresponding to the ping allowing this quality to be measured.
Configure, for example, a known Web server IP address or possibly that of the
supervisor, provided that the latter incorporate a known fixed IP address.
The configured address must correspond to a standard IP address format, i.e.
be in the form of four values of at most three digits separated by a dot (e.g.
192.168.2.101).
Operating principle of the regular ping test:
For the T200 application, the regular ping test is used chiefly as a means of
extending connection to the GPRS/3G network, when the Supervisor is no
longer capable of performing protocol communication with the T200 even
though the GPRS/3G network is still operational. Now, the T200 is designed to
monitor the IP data packet flow reaching it via the GPRS/3G network.
A 5 min. time delay (“PPP session timeout”) automatically disconnects the
T200 from the GPRS/3G network if no IP data flow reaches the T200.
Accordingly, if the T200 is disconnected from the network, the modem will be
reinitialized, thereby making the T200 unavailable for 1 min., the time needed
for reconnection of the modem to the GPRS/3G network.
44
NT00113-EN-05

Commissioning Communication configuration
TA
TA
TA
Problem on
GPRS network
T200 power up
1
0
Yes
No
Yes
No 1 0
GPRS network
availability
GPRS modem
reset
T200
connection to
the GPRS
Automatic ping
test
Supervisor
protocol
frames
TA
TB
TB
TB
TC
Test
ok
Test
ok
Test
failed
Supervisor
inoperative
T200 stays
connected
To avoid this drawback, the regular ping test is used to prevent disconnection
of the T200 when the problem is exclusively due to the Supervisor and not to a
network problem. In other words, if the T200 is still connected to the GPRS/3G
network, there is no reason to disconnect it because of a non-existent IP
protocol flow.
As soon as a ping address has been configured in this field, the T200 will try
every 4 minutes (“Ping time interval”) to send a ping to the specified IP
address. Accordingly, an IP data flow will return to the T200 and the latter will
not cut off the connection to the network.
If the result of the ping test is satisfactory, the T200 will remain connected to
the network, because it knows that it is available. The T200 will then do
nothing in particular except for the next ping test following the next 4 minutes
elapsed.
If the result of the ping test is unsatisfactory, after an extra minute the T200,
seeing no IP data flow for the last 5 min., will disconnect from the network
automatically (modem reset), and then try (after the end of modem
initialization) to reconnect to the network again.
If the network is still not available, the T200 will again request the modem to
reinitialize immediately, and this indefinitely until the next detection of the
network.
This phase of initialization and reconnection to the network requires
approximately 1 min. for the GPRS/3G modem (see enclosed diagram).
If the ping address is set to "0.0.0.0" (default value), the regular ping test is
deactivated.
Comment: The regular ping test method is preferable to the "Daily
disconnection" method because, for the regular ping test, network
disconnection lasts only 5 min. at most during a brief failure (case of network
disconnection just after the ping test).
Note: The regular (or manual) ping test sends to the specified IP address the
smallest possible number of data packets (equivalent to 0 byte), to avoid
causing the extra cost of an IP data flow transfer.
TA = Time for modem initialization + connection to the GPRS/3G network
(approximately 1 minute)
TB = Ping test period (4 minutes)
TC = Modem reset time (= 5 min.) if IP data flow non-existent on the T200
♦ Test Ping: Allows manually activation of the ping test. A click on this button
starts a manual ping test. This manual test is generally used to verify T200
connection to the GPRS/3G network immediately.
The T200 then displays the result of the test in a specific window (see
enclosed windows).
There are two possible results following this test: "Ping Ok" or "Ping failed"
NT00113-EN-05
45

Commissioning Communication configuration
08:48:34.474 MODEM - Power up
08:48:35.986 MODEM - Command mode
08:48:36.994 MODEM - Tx : ATE0
08:48:39.518 MODEM - Tx : AT&S0
08:48:42.045 MODEM - Tx : AT
08:48:43.071 MODEM - Rx : OK
08:48:44.079 MODEM - Tx : AT+CPIN?
08:48:45.120 MODEM - Rx : +CPIN: SIM PIN
08:48:45.120 MODEM - Tx : AT+CPIN=****
08:48:47.230 MODEM - Rx : OK
08:48:47.230 MODEM - Tx : AT+CLCK="SC",0,****
08:48:49.770 MODEM - Tx : AT+CREG?
08:48:50.807 MODEM - Rx : +CREG: 0,1
08:48:50.807 MODEM - Tx : AT+CSCA=0689004000
08:48:54.818 MODEM - Tx : AT+CMCF=1
08:48:57.347 MODEM - Tx : AT+CSAS
08:48:59.875 MODEM - Tx : AT+CMEE=0
08:49:02.403 MODEM - Tx : AT&C1
08:49:04.929 MODEM - Tx : AT&D2
08:49:07.455 MODEM - Tx : AT+IPR=0
08:49:09.983 MODEM - Tx : ATS0=1
08:49:12.509 MODEM - Tx : AT+WIND=0
08:49:15.039 MODEM - Tx : AT+CICB=0
08:49:17.567 MODEM - Tx : AT+CBST=7,0,1
08:49:20.101 MODEM - Tx : AT&W
08:49:32.706 MODEM - Tx : AT+CGCLASS?
08:49:33.720 MODEM - Rx : +CGCLASS: "B"
08:49:33.720 MODEM - Tx : AT+CGDCONT=1,"IP","internetcompany"
08:49:36.248 MODEM - Tx : AT+CGATT=1
08:49:38.769 MODEM - Tx : AT+CGREG?
08:49:39.784 MODEM - Rx : +CGREG: 0,1
08:49:39.784 MODEM - Tx : AT+CGACT=1,1
08:49:42.307 MODEM - Tx : ATD*99***1#
08:49:43.327 MODEM - Connection
08:49:44.335 MODEM - PPP link: UP -> ESTABLISH ()
08:49:44.350 MODEM - PPP link: OPEN -> AUTH ()
08:49:44.363 MODEM - PPP link: PAP: Local successfully
authenticated
08:49:44.363 MODEM - PPP link: SUCCESS -> NETWORK ()
08:49:44.363 MODEM - PPP link: IPCP UP -> NETWORK ()
08:49:44.400 MODEM - PPP link: IPCP CONFIGURED ->
NETWORK ()
08:49:44.401 MODEM - PPP link: connected,
local=90.95.65.78, dest=212.234.96.90
08:49:44.401 MODEM - GPRS modem initialized
Example of port trace in the event of a connection
to the GPRS network
♦ Ping time interval: Delay between two successive automatic “Test ping”.
♦ Ping attempts: Number of maximum attempts for the “Test ping” process in
case of no response from remote IP address.
♦ Ping time out: Maximum delay to wait for the response during the “Test ping”
to define “Ping error”.
♦ Authentication: When the GPRS/3G network requires authentication during
the connection phase, it is possible in such cases to activate this function by
checking the corresponding box.
The authorized encryption protocols are:
- PAP, CHAP, MSCHAP, MSCHAP V2
♦ Login: Configuration of the login used for authentication. Configure this field
only if the "Authentication" option has been checked.
♦ Password: Configuration of the password used for authentication. Configure
this field only if the "Authentication" option has been checked.
Note: To check that the modem is correctly connected to the GPRS/3G
network, it is possible to consult the trace of the port corresponding to the
GPRS/3G modem. The modem starts by initializing the GSM connection and
then the GPRS/3G connection. Accordingly, following the AT commands for
connection to the GSM network can be found the commands relating to
GPRS/3G connection. At the end of them, the trace should indicate "GPRS/3G
modem initialized" with also the indication of the IP addresses of the T200
assigned by the operator (
GPRS/3G gateway provider (
local=xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx) and the IP address of the
dest=xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx) (see example opposite).
Modem connection status:
Same comment as for the GSM modem.
Connection speeds in TCP/IP communication
Depending on the connection type, the T200/Scada link can be implemented
at different speeds. This is a maximum connection speed. They depend on
many factors such as the network's availability, the received signal level or the
location of the receiver:
• GPRS: max. bit rate = 19.2 Kbits/s (in practice)
• EDGE: max. bit rate = 64 Kbits/s (in theory)
• 3G: max. bit rate = 2 Mbits/s (in theory), 115 Kbits/s (in practice)
Automatic switchover of the 3G modem
The 3G modem has the feature that it can automatically switch over to EDGE
or GPRS mode if the 3G connection is momentarily unavailable, with the
possibility of returning to 3G mode automatically if connection is restored. This
provides a backup for the TCP/IP link.
Connection is therefore preserved in the event of a network problem, on
condition that the other EDGE or GRPS modes are available. Only the
transmission rate is affected by this automatic switchover from one network to
another.
46
NT00113-EN-05

Commissioning Configuration of switch controls
Active
Inactive
Closed position
Active
Inactive
Open position
Closed
Open
TSD
Non-complementarity
filtering time delay not
elapsed
Non-complementarity
filtering time delay
elapsed
Non-complementary switch positions
Undefined
Remote configuration:
The @ sign alongside each parameter of "Control &automation" page and
"Measurement and fault indicator" page allows to configure an external address.
This external address can be used by the SCADA, to configure or define remotely a
new value for the parameter associated, via the communication and the protocol. To
set the parameter, an analogue value can be written to this address.
3.8 Switch control parameters
Objective : Set processing of the switch control for each channel.
Access: "Settings/Control & Automation" page.
► Type of control:
There are four possible options: Standard, PM6, CI2, Other
Comment: The "CI2" and "Other" options are not managed at present.
The "PM6" option is managed but applies only to the T200 P.
The management of switch position control and monitoring signals is specific to
each type of switch.
The "Standard" option applies to the main cubicles used with a T200 I, in particular
Schneider cubicles of type SM6 or RM6.
Filtering principle for indication inputs related to remote
controls:
The interface between the T200 and the switch includes two electric signals for
motorization control (CO: Opening control / CF: closing control) and two signals for
the current switch position (O: open position / F: closed position).
The T200 systematically performs a consistency check on the positions read: it is in
theory impossible to have the "open" and "closed" signals simultaneously or neither
of the two signals at the same time, but this may occur following a system
malfunction. This complementary of the switch states is verified cyclically for
updating the states of the associated TSD variables.
In the case of non-complementary values, filtering is applied and the old TSD value
is kept during a configurable time delay (see No complementary filtered time
parameter). If the non-complementary persists after the time delay, this is probably
due to a fault relating to the signals delivered by the switch and the "undefined"
state is finally indicated in the TSD associated with the position.
NT00113-EN-05
47

Commissioning Configuration of switch controls
Phase
Event
Receipt of a switch order
End of order processing
CR end of order
End of degraded order
processing
CR external error or CR severe fault
CR end of order
Active
Inactive
Closing control
Active
Inactive
Opening control
TCD Switch state Order sending
CR: order in progress
TCD Switch state Order sending
CR: order in progress
Closed
Open
TSD
TSD Switch position - Open
CR: end of order
CR: external error
CR: end of order
Return position waiting time
T < Return position waiting time
Event recorded in event log
Legend :
Control unsuccessful
Control successful
Principle for switch position order processing:
The T200 internal control manager inhibits any order until the previous order has
been completed. The order processing status can be known by consulting the
events from the supervisor or in the local event log.
The events generated according to the order processing status are summarized in
the following table:
TCD xx - Switch state - Order
CR order in progress
3.8.1 "Standard" type control
This switch option is in theory not applicable for the T200 P. Applies only to the T200 I combined with a Merlin Gerin SM6 or RM6 type switch.
The principle of an order on the switch is to activate the switch control signal (24V
or 48V polarity depending on the model) for a determined time (Operating time
parameter).
With "Standard" control, the duration of the order is therefore fixed by this time
delay and does not depend on the time taken by the switch to change position.
The Open and Closed switch position inputs are read constantly throughout the
duration of the order with a consistency check so as to update the associated
position TSD variable (see Filtering principle for indication inputs related to remote
controls).
After the control relay has fallen, the order is considered as completed by the T200
when the switch indicates a position in conformity with the order (the TSD is
updated with the new status). The order is considered in error (e.g. external error) if
the position is not in conformity with the requested order or if undefined after a loss
of position filtering time delay (Return position waiting time).
48
NT00113-EN-05

Commissioning Configuration of switch controls
Active
Inactive
CO/CF control
TCD Switch state Order sending
CR: order in progress
TCD Switch state Order sending
CR: order in progress
Closed
Open
TSD
TSD Switch state - Open
CR: end of order
CR: external error
CR: end of order
Return position waiting time
T < Return position waiting time
Event stored in event log
Legend:
Control unsuccessful
Control successful
3.8.2 "PM6" type control
Reminder: The "PM6" configuration applies to the Merlin Gerin PM6 type switch.
With this type of switch, the principle is to apply the motor control signal until the
requested position is obtained. This control will be maintained only during a
configurable limited period (Return position waiting time parameter), and this in
the event that the position indicated by the TSD variable is not that which is
expected by the T200 (case of degraded control).
With this type of switch, the time for execution of the electrical order therefore
depends exclusively on the time taken by the switch to change position.
The Open and Closed switch statuses are read constantly with a consistency check
so as to update the associated position TSD variable (see Filtering principle for
indication inputs related to remote controls).
.
NT00113-EN-05
49

Commissioning Configuration of the various options
3.9 Parameters of the various options
Access: "Settings/Control & automation" page.
Some specific options allow operation of the T200 to be customized for the needs of
certain users.
One must be a system administrator to be able to modify these options.
The T200 is generally delivered without these specific options being activated
(factory settings).
The list of these configurable options is described in detail below:
BVE control (DOUT 1):
When this option is selected, digital output DOUT 1 is activated to cause
flashing of an external fault indication indicator lamp.
This output is activated as soon as the internal fault detector of the T200
detects and indicates the presence of a phase or earth fault.
DDEF test (DOUT 2):
When this option is selected, digital output DOUT 2 is activated whenever a
current exceeds the phase or earth fault detection threshold configured on the
T200.
The output goes low as soon as the fault returns below the threshold.
Double power supply management (DOUT 3):
When this option is selected, digital output DOUT 3 is used for the double
mains power supply management option if the latter is installed in the
enclosure.
This output can automatically actuate the power supply changeover relay in
the event of a power outage on the active channel.
T200 without COM card:
This option should be used when the T200 includes no COM card in the
equipment.
SF6 lack copying (channel1 on DI3, channel2 on
DI4) :
To be compatible with old versions of T200P (Series 1&2), the information
"SF6 lack" (connected on Harting switch connector - pin 9) is internally
associated to DI3 (channel 1) or to DI 4 (channel 2). So, when the "SF6 lack"
is detected, the DI3 (or DI4) is activated at the same time.
Note : If this option is checked, the DI 3 and DI 4 are not any more available
as digital inputs because they are already defined as “SF6 lack”.
50
NT00113-EN-05

Commissioning Configuration of the various options
Connector pin
Marking
Function
1 - 0V 2 CC
Closing control
3
OC
Opening control
4 O Open position
5 F Closed position
6 + + V 7 ST
Switch locked
8
HTA
MV voltage present
9 Not Connected
10 Not Connected
Connector pin
Marking
Function
1 - 0V 2 CC
Closing control
3
OC
Opening control
4 O Open position
5 F Closed position
6 + + V
7
ST F
Earthed Closed
position
8
ST O
Earthed Open
position
9 Not Connected
10 Not Connected
Connector pin
Marking
Function
1 - 0V 2 CC
Closing control
3
OC
Opening control
4 O Open position
5 F Closed position
6 + + V 7 B1
Free 1
8
B2
Free 2
9 Not Connected
10 Not Connected
Switch TSS management – "Standard" mode
Switch TSS management – "Earthing switch by
TSD" or "Specific 1" mode
Switch TSS management – "Free TSS" mode
8-bit measurement:
By default, on the T200 P series 3, the current (or voltage) measurements are
coded on 16 bits, whereas on the preceding series they were coded on 8 bits.
By selecting this option, however, it is possible to make the T200 compatible
with the old-generation T200s. This option is used especially when a
Supervisor already polls T200s of an old generation with measurements on 8
bits. Now, a given Supervisor can hardly read measurements in 2 different
formats.
Note: It is important to use the "OFF Line Configurator" to generate a
configuration file compatible with this option, because the option also implies a
change in configuration of the T200's internal variables.
Circuit breaker signalisation management :
There are several ways of acquiring status information coming from the switch
(pins 7, 8 and 9 of the 10-pin Harting connector for cubicle connection). The
option chosen affects the way in which the T200 processes this information.
There are several possible choices for this option:
Standard: This is the factory settings. The connections for the switch link
corresponding to this mode are shown opposite.
In this mode, the presence of the "Switch locked" signal inhibits the
execution of orders on the switch.
The "MV voltage present" signal is used by the ACO automatic control.
Earth breaker management by TSD: As standard, a single signal
coming from the switch is used to give the T200 the status of the earthing
switch (pin 7 of the 10-pin Harting connector).
By selecting this option, an additional input (pin 8) is used to manage the
earthing switch as a TSD and not a TSS.
The "Earthed Open Position" absent and "Earthed Closed Position"
present states inhibit the execution of orders on the switch.
The ACO automatic control cannot be used in this mode.
Free TSS: In this mode, pins 7 and 8 normally assigned to "Switch
locked" and "MV voltage present" can be used freely. They therefore
have no function predefined by the T200. They are merely DIs.
There is no inhibition of execution of orders on the switch whatever the
status of the free inputs.
The ACO automatic control cannot be used in this mode.
Specific mode 1: This mode is similar to the "Earthing switch
management by TSD" mode, with an additional special feature:
When the T200 is in local mode, all orders to the switch are inhibited. The
automatic controls can therefore no longer operate in Local mode.
The connection system is identical to the "Earthing switch management
by TSD" mode.
Note: Same comment as for the previous option concerning the
possibility of using the "OFF Line Configurator" to generate a
configuration file compatible with this option.
Position reading of sector circuit breaker :
Option only available when the AC supply protection is made by circuit
breaker instead of fuse holder. When this option is used, the T200
manage DI 5 to indicate when circuit breaker protection is open.
U measurements by capacitor divisor other than
RL27:
Case of voltage measurement done by capacitor divisor (RL27 type) but
without using the calibration process done by RL27.
Hit and Run function (availability to be confirmed)
This option makes it possible to add a time delay before execution of a
local control order sent via a switch. The operator can thus leave the
MV/LV substation before switchover of the switch (thus providing extra
safety). This time delay is configurable. During application of the time
delay, the indicator lamp showing the switch's position on the local
monitoring panel flashes slowly (once per sec.). By default, the time delay
is set to 15 seconds. It is configurable from 0 s to 15 s in increments of 1
s. Configure 0 s to deactivate the Hit & Run function.
NT00113-EN-05
51

Commissioning Automation configuration
Parameter
Description
Config. range
Automatic type
Choice of automatic control type.
None or Sectionalizer
BTA
Default counter
Time after which the automatic control
the source substation resetting cycle.
20000 to 240000 ms
Number of
Number of faults detected by the T200
automatic control.
1 to 4
Id
Current
Default counter clear time
Voltage
dip
Time
In
1st
fault
2nd
fault
3rd
fault
4th
fault
Example of configuration for sectionalizer automatic
control (Configuration/Control & Automation page)
3.10 Automation parameters
Access: "Settings/Control & Automation" page.
3.10.1 Sectionalizer automation control
The purpose of this automatic control is to order opening of the MV switch managed
by the T200 following the detection of a number of fault currents during
unsuccessful slow resetting cycles for the upstream circuit breaker. The
sectionalizer automatic control therefore converts the switch into a sectionalizing
switch.
For the automatic control to work, the T200 must be provided with the fault current
detection function.
For automatic control to operate on a channel, it must be selected for that channel
(Automatic type parameter).
It is possible to assign the presence of automatic control or not channel by channel.
All the channels of the T200 can be configured with this automatic control or not.
Automatic control can be enabled or disabled, in general on the T200 (TCD 9),
remotely from the Supervisor or locally via the CONTROL panel of the T200.
NB: It is not possible to change the type of automatic control on a channel
when the "automatic control Enabled/Disabled" TSD (TSD 9) is in ON position.
It is essential to return TSD9 to OFF position to be able to change type of
automatic control on one of the channels.
Likewise, it is not possible to send a remote control to the TSD 9 to place it in
ON position, if no automatic control is activated on one of the channels of the
corresponding CONTROL module.
Manual control of the switches remains possible in “Local” mode from the
CONTROL panel or in "remote" mode from the Supervisor, even if automatic control
is activated in ON position.
Operation:
In nominal operating conditions, the line is energized and the switch is closed.
The automatic control system sends an opening order to the switch if:
- the switch is closed;
- the counted number of fault currents is reached;
- the current fault has disappeared;
- the MV voltage is not present.
Important note: The "Rapid" fault can be counted as the first fault detected by the
T200 if the time to detect the "slow" fault configured on the T200 is less than the
actual time of presence of the first "rapid" fault or if the actual time of presence of
the rapid fault is the same as that for the slow fault (that depends on the network
configuration).
The enclosure must be powered from a low-voltage source generated by the
MV line on which the unit is installed.
Configuration parameters:
52
-> Choose Sectionalizer
or
Changeover switch or
clear time
system is reset if the conditions of
automatic control action are not met.
(in increments of 5000
ms)
This time begins after first fault
detection in the fault elimination cycle.
Must be greater than the total time of
authorized default
before actuating channel opening by
NT00113-EN-05

Commissioning Automation configuration
Parameter
Description
Config. range
Network ATS configuration
Automation type
Choice of automatic control type.
Voltage time
None or Sectionalizeur or
Voltage time
Permutation waiting
Waiting time for stability of voltage
the changeover cycle
100 ms to 200s (in
Time before returning
(T2)
Waiting time for stability of voltage
return to that channel
5s to 60s (in increments
Type
Choice of changeover type. (see
SW1 -> SW2 or
Auto-SW2
Network ATS - Semi-Auto mode
SW2 voltage
Vn
T1 RT
T1 RT
RT
RT
Network ATS - Auto-SW1 mode
SW1 voltage
Vn
O
T1 RT
RT RTT2 RT
0
Vn
0
C
SW1
O
C
SW2
O
RT = Switch response time
0
C
SW1
O
C
RT
SW2
RT = Switch response time
Example of configuration for Network ATS automatic
transfer system
(Configuration/Control & Automation page)
NT00113-EN-05
3.10.2 ATS automatic control (source changeover)
Automatic changeover control manages automatic changeover of voltage sources
of the MV secondary distribution network to ensure maximum availability of voltage,
in case of failure of one of the voltage sources.
Accordingly, upon disappearance of the voltage on one channel, changeover to the
other channel is performed automatically, depending on the options configured.
To activate "ATS" automatic transfer system on a channel, simply set the Type of
Automatic Control variable in the specific page of the embedded Web server
("Control and Automation" page):
Several operating modes can be selected (Operating mode parameter), namely:
SW1 SW2 or SW2 SW1 mode:
This option allows only one changeover to be enabled.
Automatic transfer system switches only from the priority channel to the backup
channel. Automatic transfer system then remains on that channel.
Semi-Auto SW1 SW2 mode:
In the event of a voltage loss on the active channel, automatic transfer system
switches to the other channel after a time delay T1.
In this mode, there is no concept of priority source. Changeover to one or other of
the channels takes place as soon as the changeover conditions are met.
Auto SW1 or Auto SW2 mode:
In this mode, one can define a concept of priority of one channel relative to the
other (channel 1 or 2). Automatic transfer system remains on the priority channel so
long as the voltage associated with that channel is present.
In the event of a voltage loss on the priority channel, automatic transfer system
switches to the other channel after a time delay T1. After the changeover, return to
the priority channel occurs if the voltage on that channel is present during a time
delay T2.
Changeover sequences:
In the event of voltage loss on the normal channel, changeover involves opening
the normal channel after time delay T1 and then closing the backup channel.
Configuration parameters :
-> Choose Network ATS [1/2] or
type
(T1)
on normal way
disappearance on the channel that
was operational before the start of
return on the normal channel before
details of operation above)
Changeover sequence:
Changeover takes place if the following conditions are met:
■ Automatic control enabled.
■ Position of channel 1 and 2 switches complementary: TSD variable SW1 closed
position and SW2 open position (or SW2 closed and SW1 open).
■ No fault current on the two channels
■ "MV earthing switch" absent on the two channels;
■ MV voltage absent on the enabled channel;
■ MV voltage present on the other channel.
Return to the main channel for the “AUTO” modes occurs if:
■ the priority channel is open;
■ the MV voltage on the priority channel is present during time delay T2.
Special feature of reset upon MV voltage return:
When a current fault is stored in memory on one of the two channels managed by
ATS automatic control, MV presence is necessary on both channels at the same
time to reset the memory of this fault.
This rule is valid even if only one of the two channels has been configured with
active reset upon MV voltage return.
ATS[1/2] Network or
increments with 100 ms)
with 1 s)
SW2 -> SW1 or
SW1 <-> SW2 or
Auto-SW1 or
53

Commissioning Automation configuration
Parameter
Description
Config. range
Automation type
Choice of automatic control type.
None or Sectionalizer
or Voltage Time
AC Off time
Waiting time before switch opening
0 to 32700 ms (in 100
By default: 200 ms
Closing time
Waiting time before switch reclosing
0 to 32700 ms (in 100
By default: 200 ms
Monitoring time
Time during which maintenance of the
reclosing of the switch
0 to 32700 ms (in 100
By default: 200 ms
Configuration of Voltage Time automatic control:
T0: Voltage failure timeout (0 to 327 s in 0.1 s
increments)
T1: Closing timeout (0 to 327 s in 0.1 s increments)
T2: Monitoring timeout (0 to 327 s in 0.1 s increments)
Example of configuration for Voltage Time automatic
control (Configuration/Control & Automation page)
3.10.3 Voltage time automatic control
Voltage Time automatic control is not supplied as a standard feature. It is
available on option (specific software version for EDP).
Voltage Time (VT) automatic control is used for certain switches without current
sensors not allowing the network to be reconfigured by means of Sectionalizer
automatic control.
This automatic control system works on the principle of opening all the switches on
the network in the event of a voltage loss (opening of upstream circuit breaker) and
gradually restoring the network power by closing the switches in succession, one
after the other.
If the closing of a switch causes line tripping, the switch is blocked in open position
and the cycle restarts to restore power in the healthy upstream part.
The circuit-breaker upstream protection should also be provided with the Voltage
Time automatic control function.
For this function, the following options are required on the T200 P:
Voltage measurement and monitoring.
Voltage Time automatic control enabled on the channel (by configuration).
Operation:
The line is energized and the switch is closed.
Mains voltage loss: switch opening following a timeout To (Voltage failure
timeout parameter).
Voltage return: switch closing following timeout T1 (Closing timeout parameter)
and monitoring of voltage maintenance during a timeout T2 (Monitoring timeout
parameter).
Voltage loss during timeout T2: switch opening and automatic control locking.
The automatic control function is reinitialized following locking by the “Reset
automation” push button on the local CONTROL panel.
Note : The delay "T1" must be different on each T200 so that the automation VT
can work properly (the lower value on the T200 nearest the circuit breaker).
The VT function can be activated or deactivated from the local control panel or by a
telecontrol order. The switches can be controlled manually in “Local” mode.
Configuration parameters:
-> Choose Voltage Time
following mains voltage loss
following mains voltage return
mains voltage is monitored following
or Changeover switch
ms increments)
ms increments)
ms increments)
54
NT00113-EN-05

Commissioning Fault detector configuration
Parameter
Description
Config. range
Network
frequency
MV network frequency
50 Hz or 60 Hz
(by default 50 Hz)
Voltage input
Type of sensors used for measurement
Set in factory on PM6
Parameter
Description
Config. range
Voltage
Value of the transformer
voltage measurement
Primary: 100 to 36000
(by default: 230 / 230)
Voltage sensor
Choice of type of voltage sensor
U21 or U21_U32 or
(by default: U21)
Nominal
voltage
MV network voltage rating value.
20 to 36000 V
(by default: 230 V)
Threshold AC
Minimum percentage of the voltage
- Yes" TSS
70% to 120%
Threshold AC
Maximum percentage of the voltage
- No" TSS
5% to 95%
Acknowledge
ON
Power-on filtering time to define
100 to 80000 ms
By default: 100 ms
Acknowledge
OFF
Power-off filtering time to define
100 to 80000 ms
By default: 100 ms
MV network parameters
Voltage measurement parameters
3.11 Parameters of the fault detection module
Access: "Measurements/fault detector configuration" page.
The Measurements/fault detector page allows setting of the parameters relating to
measurements and fault detection, namely:
Type of mains frequency.
Voltage and current measurement parameters.
Fault detection thresholds and time delays.
3.11.1 Configuration of network characteristics
Allows definition of the MV network characteristics
Configuration parameters:
Comment: The grey shaded parameters in the table are set in factory and can be
modified only by the manufacturer.
3.11.2 Configuration of voltage measurements
To perform voltage measurement, the T200 needs to know certain parameters
relating to the characteristics of the MV network and the type of transformer used
for measurement:
PT transformation ratio.
Type of arrangement for the voltage tap (star or delta).
Network voltage rating value.
Voltage absent and present detection thresholds and time for taking into
account.
Residual voltage (phase-to-phase voltage imbalance).
Comment: The "Voltage present threshold" and "Voltage absent threshold"
parameters together with the "Time delay for taking into account voltage present
and voltage absent" parameters can generate the "MV voltage present" telesignal
(TSS73) delivered by the T200.
Configuration parameters:
transformer
configuration
supply ON
supply OFF
time AC supply
time AC supply
primary/secondary ratio used for
setup
rating to define "MV voltage present
rating to define "MV voltage present
"MV voltage present - Yes" TSS
"MV voltage present - No" TSS
Secondary: 100/√3 to 240 V
U21_U32_U13 or V1 or
V1_V2 or V1_V2_V3
(by default: 90%)
(by default: 80%)
(in 10 ms increments)
(in 10 ms increments)
NT00113-EN-05
55

Commissioning Fault detector configuration
Circuit breaker
protection side
T200 side
I phase threshold = 350
A
I phase threshold =
330 A
I0 threshold = 45 A
I0 threshold = 40 A
Delay, I max = 250 ms
Delay, I max = 225 ms
Delay, I0 = 250 ms
Delay, I0 = 225 ms
Parameter
Description
Config. range
Current input
Type of sensors used for measurement
Set in factory on PM6
Current
ratio
Value of the toroid primary/secondary
Primary: 50 to 2500
(by default: 500/1)
Current
configuration
Choice of type of toroid setup:
2 phase toroids + 1 homopolar
I1,I3,I0 or I1,I2, I3
Current measurement parameters
Example of fault detector configuration
3.11.3 Configuration of current measurements
There are two possible choices concerning the toroid setup on the overhead switch:
Three phase toroids (Configuration: I1, I2, I3)
Two phase toroids and one homopolar toroid (Configuration: I1, I3, I0)
The "I1 I3 I0" configuration is set by default.
The ratio of the toroid should also be entered when toroids having characteristics
different from those provided by the manufacturer are used.
The two values to be configured correspond to the Primary/Secondary ratio of the
toroids, in other words the transformation ratio of the toroids.
(e.g. "500/1" means a toroid transformation ratio equal to 500).
The default value "500/1" corresponds to the type of toroids supplied for a PM6
switch.
Configuration parameters:
transformer
transformer
Comment: The grey shaded parameters in the table are set in factory and can be
modified only by the manufacturer.
ratio used for current measurement
3 phase toroids or
3.11.4 Configuration of current fault detection:
General rule for configuration:
The thresholds Imax and I0 should be set on the T200 to correspond to those set on
the circuit breaker protection device upstream of the network.
In theory, the fault detection thresholds and time delays to be set on the T200
should be slightly less than those of the upstream circuit breaker protection device
so that the T200 may detect presence of the fault current before opening of the
circuit breaker.
Moreover, the current configured for the earth fault on the T200 should be greater
than the downstream capacitive current.
Secondary: 1 or 5
(by default: I1, I3, I0)
56
NT00113-EN-05

Commissioning Fault detector configuration
Parameter
Description
Config. range
Imax threshold
Fault current detection threshold I max
10 to 800 A
By default: 500 A
I0 threshold
Homopolar fault current detection threshold
2 to 160 A
By default: 20 A
Imax fault
I max. fault filtering time. Any fault > Imax
loss)
40 to 800 ms
ms
I0 fault duration
I0 fault filtering time. Any fault > I0 threshold
20 to 800 ms
ms
Imax fault
"Rapid" fault filtering time. Any fault > Imax
as a "rapid" fault
Set in factory at
Voltage
If selected, the detector uses the image of
network voltage absent
Set in factory at
Validation time
Mains power-off filtering time to confirm the
fault
Set in factory at 3
Inrush time
Inrush function filtering time. Any fault
ignored by the T200 fault detector
Set in factory at 3
Inrush
If selected, can filter the faults resulting from
due to transformer magnetization)
Checked or not
Reset on
recovery
Reset (if selected) or not of the memory of
voltage return.
Checked or not
RAZ voltage
Time delay for filtering the presence of mains
0 to 70 s
By default: 3 s
Automatic FPI
Maximum time delay for indication of a current
automatically erased.
0 to 120 min. (in 5
By default: 2 h
Current measurement parameters
Configuration parameters:
duration
duration (fast
mode)
absence =
PWR card
voltage failure
threshold and of a duration exceeding this
time will be considered by the T200 as a
phase fault (if validated by voltage and current
and of a duration exceeding this time will be
considered by the T200 as an earth fault (if
validated by voltage and current loss)
threshold and of a duration exceeding this
time and less than the "Time for taking into
account Imax" will be indicated by the T200
enclosure mains voltage present instead of
using the voltage present/absent thresholds
delivered by the fault detector to define
presence of a phase or zero sequence current
appearing during this time configured
following a network voltage return will be
closing of the upstream circuit breaker (faults
(in 1 A
increments)
(in 1 A
increments)
(in 1 ms
increments)
By default: 200
(in 1 ms
increments)
By default: 200
50 ms
not selected
s
s
checked
voltage
return duration
reset
Comment: The grey shaded parameters in the table are set in factory and can be
modified only by the manufacturer.
fault detection indication upon network
voltage to reset the stored fault
fault. At the end of this delay, the fault is
checked
(in 1 s
increments)
min. increments)
Why a fault confirmation time?
In theory, in the event of a fault, any current exceeding the configured threshold
should be followed by opening of the circuit breaker, to avoid incorrect fault
indications.
When a current exceeds the threshold and the detection time, the algorithm of the
T200 fault detector waits until the circuit breaker opens (detection of voltage absent)
before actually indicating the fault. The maximum waiting time for circuit-breaker
opening is called the fault confirmation time
(Default value set in factory: 3 seconds).
Comment: If the circuit breaker opens 1 second after occurrence of the fault, the
T200 indicates the fault as soon as circuit-breaker opening is detected and not just
after the 3 seconds' wait. On the other hand, if voltage absent is detected only after
the 3 seconds, the fault is not indicated.
Why a reset time upon voltage return?
Once the fault has been indicated by the T200, it is stored in memory so long as the
mains voltage is absent, to be able to locate the fault on the network during general
interrogation of the T200 from the Supervisor. By default, this memory is cleared
upon mains voltage return (configurable parameter).
NT00113-EN-05
57

Commissioning Fault detector configuration
Why use the inrush?
In the event of circuit-breaker closing, the strong inrush currents corresponding to
the currents for magnetisation of the transformers and saturation of the toroids
downstream of the fault can trigger the fault detectors for the equipment on the MV
network.
Generally, this type of fault does not last very long and weakens rather quickly
(significant duration < 200 ms). They can therefore be filtered easily by using the
"Inrush" function, designed to ignore the presence of any fault during 3 seconds
after closing of the circuit breaker.
The disadvantage of this operating procedure is that if a real fault appears during
these 3 seconds, it will not be taken into account by the T200.
It is therefore not always advantageous to use the inrush function.
It in fact depends on the network characteristics, and in particular the time of
presence of the first "Rapid" fault during the upstream circuit-breaker reset cycle.
Several scenarios are therefore conceivable depending on this fault duration:
The inrush should be used in the following cases:
If there are tripping/resetting cycles (with presence of inrush currents).
If the time delay for the first "Rapid" fault of the circuit-breaker cycle is fairly
short, approximately 100 ms (rule also valid for the second "Normal" fault, but
generally the second fault lasts a longer time than the first one).
If the first "Rapid" fault needs to be detected.
There is no need to use the inrush in the following case (alternative solution if
possibility of configuration):
If there are tripping/resetting cycles (without presence of inrush currents).
If the time delay for the first "Rapid" fault of the circuit-breaker cycle is fairly
long, exceeding 200 ms (rule also valid for the second "Normal" fault, but
generally the second fault lasts a longer time than the first one).
If the first "Rapid" fault does not need to be detected.
Comment: The "Rapid" fault is not counted by the "Sectionalizer" automatic
control).
Alternative configuration solution without inrush with the T200:
No inrush (standard configuration)
Rapid Imax < 80 ms, Normal Imax > 200 ms
Alarm to SCADA system on the TSS (Imax, rapid)
Example of situation with Inrush not used and fault acknowledgment time set to 200
ms.
58
NT00113-EN-05

Commissioning Fault detector configuration
Active
Inactive
Active
Inactive
TSS17: Immediate AC supply OFF
Active
Inactive
Time-delayed undervoltage indication
TSS18: Delayed AC supply OFF
Configuration of power supply failure filtering time
(Settings/Measurement and fault indicator page)
3.11.5 Configuration of supply voltage monitoring
The T200 activates an "Immediate AC supply OFF" indication (TSS 17) as soon as
the enclosure's mains supply voltage is absent.
Another "Delayed AC supply OFF" indication (TSS18) is activated when TSS17 is
activated for a time exceeding a configurable period (see opposite).
TSS 18 therefore plays a role of power supply under voltage signal filtering. The
purpose of this filtering is not to send too many successive alarms to the Supervisor
whenever TSS17 changes state, following regular MV network failures (e.g. during
circuit-breaker reset cycles). It is therefore preferable to use the alarms on the
TSS18 rather than on the TSS17 in some cases.
Note: The alarms can be generated only if the remote alarm function is activated on
the equipment.
Power supply failure time delay parameter:
configurable from 0 to 21600 seconds
Note: The power supply failure signal is also used by the current fault detector in
particular for the automatic control functionality.
NT00113-EN-05
59

Commissioning Variable configuration
Variable
type
Use
Description
TCD
Double
Allows control of the switch associated
always associated with a TSD.
TSD
Double
Indication of the state of the switch or
undefined).
TSS
Single signalisation
Indication of binary state (presence,
by the T200 (DI, current faults, etc.).
TM
Telemeasurement
Analogue measurements performed by the
CNT
Counters
Operation or energy counter.
Settings/Variable configuration page
Different types of variable existing on T200P
Example of configuration with or without event and
alarm saving
3.12 Customization of T200 variables
Access: "Settings/Variable configuration" page.
3.12.1 Definition of variables
T200 is supplied as standard with all the variables necessary for operation of the
equipment. This configuration takes into account all the options installed on the
equipment (number of channels, type of modem, protocol, other options, etc.).
The user can, however, modify this configuration to adapt it to his needs, for
example to add options later or to modify the operation of certain functions (e.g.
fault detector thresholds, alarms, communication parameters, etc.).
The T200 Web server provides access to all the variables defined by default on the
T200.
The level of access to a variable (visible in read-only mode, accessible in write
mode, not visible) depends on how the variables have been configured.
The parameters for this page can be consulted and/or modified depending on the
user profile.
With the factory settings, you must be an administrator to be able to change the
level of access to a variable.
To consult the list of variables configured on the equipment, open the
"Settings/Variable configuration" page.
The variables present in this page are grouped by classes.
In each class, a number of variables of several different types are found ("type"
column).
Variable types:
The variables break down into several types presented in the table below.
telecommand
signalisation
In the standard version it is not possible add extra variables to those already
created as standard.
Note: However, when the "local Modbus network" option is present in the
equipment, it is possible to add variables corresponding to this option (see "local
Modbus network" User Manual for more information).
Variable addresses:
All the variables can be configured with an external address. This external address
allows the variable to be made accessible in read or write mode from the Supervisor
by means of the protocol used for transmission.
A variable which has no address configured (address = "-") will not be accessible
from the Supervisor.
The values of the addresses configured depend on the type of protocol used.
Note: Refer to the user manual for the protocol installed on the T200 for more
information concerning the addressing tables related to this protocol.
with a channel or enabling/disabling of
automatic control. This type of variable is
automatic control (open, closed or
absence) of certain information managed
T200 (current, voltage, etc.).
60
NT00113-EN-05

Commissioning Variable configuration
Event
TSS
TSD
TM
CNT
Comments
Change of state
Saving upon detecting any change of
state of the variable
Upon loss of closing
Saving upon detecting the loss of
without being open)
Regular saving
Saving of the variable's state at fixed
periods of time
High threshold
Saving upon exceeding a high
threshold
Low threshold
Saving upon exceeding a low
threshold
Dead band
Saving upon % variation of the
variable
Active maximum
Saving of the maximum value reached
over a given period
Active minimum
Saving of the minimum value reached
over a given period
Example of events configuration for a TM.
Configuration available in the Settings/Variable
configuration page and then by clicking on the variable
name TMx.
Saving variables
T200 included a number of logs allowing archiving of events of various types (event
log, alarm log, measurement log).
The logs can be accessed by the user via the embedded Web server ("Diagnostic"
page).
All the variables can be configured separately with or without being saved as a
measurement (if it is a measurement), event or alarm in these logs.
Note: The system log, for its part, does not take into account variable changes of
state but rather information concerning the internal operation of the equipment.
When a variable is configured to be saved in a log, a specific symbol appears in the
Variable configuration page on the same line as the variable:
= Saving to alarm log
= Saving to event log or to measurement log (if it is a measurement).
:
3.12.2 Events associated with variables
An event is generated by the T200 when a change of state occurs on a variable.
The T200 manages two types of event tables associated with these changes of
state:
The local event table: This is the event log that can be consulted locally
on the T200. The changes of state concerning variables can be recordable in
this log or not, the aim being to have a history of changes of variables. For the
recording of a change of state on a variable to be effective, the variable must
have been defined by configuration as an event ("event" (TM) or "activate
recording" (TSS, TSD) box checked in the variable configuration page).
The protocol event table: This is an event stack for protocol
communications. This stack will be read by the Supervisor during
communications between the T200 and the Supervisor. Contrary to local
events, it is not possible to configure a variable with or without saving in the
protocol event stack. This is because any change of state on a variable
automatically generates saving in this protocol event stack (except for TMs for
which one can choose to configure event saving in the stack or not).
Since protocol events are not configurable, we shall speak in the remainder of the
chapter only of configuration of the events associated with the local logs.
For each type of variable, it is possible to choose how to process the variable for its
associated saving (with alarm or not, criterion for saving in an internal log).
The following table summarizes how to save these events for each type of variable.
This table is valid for each type of internal log (except the system log).
Note: Configuration available in the Settings/Variable configuration page and then
by clicking on the name of a variable.
position of the closed state (although
NT00113-EN-05
61

Commissioning Variable configuration
Example of saving in internal logs
Settings available in the Settings/Variable configuration
page and then by clicking on the name of the variable.
Choice of alarm level
In the local logs, events are registered with a brief descriptive text corresponding to
the change of state of the variable and a date and time of occurrence saved by the
T200 for locating them in time.
3.12.3 Alarm reporting / Alarm acknowledgement
An alarm should be used for events which must be indicated rapidly to the
Supervisor, i.e. without waiting for interrogation by the Supervisor (e.g. if the
interrogation frequencies of the SCADA system are rather spaced out over time).
The alarms are therefore valid only for non-permanent type transmission (e.g.
PSTN, GSM, Radio), i.e. for types of transmission which require a deliberate
interrogation action by the Supervisor.
On a permanent connection (RS232, RS485, OF, GPRS/3G, LL), it is therefore not
necessary to use the remote alarm function because the retransmission of
information between the T200 and the Supervisor theoretically takes place fairly
regularly or even continuously (e.g. polling).
Note that the "Alarm configuration" section is displayed in the configuration page for
the variable only if the protocol is configured as Master/Master and if at least one of
the communication ports is of the non-permanent type.
Alarm levels in PSTN or GSM:
On a PSTN or GSM link, three configurable access levels associated with an alarm
allow definition of the various ways of processing calls during retransmission of an
alarm:
"sms" level: retransmission of the alarm by SMS to an operator on standby duty.
"scada" level: retransmission of the alarm by the protocol to the Supervisor.
"scada + sms" level: retransmission of the alarm by the protocol and by SMS.
Call sequences triggering an alarm on a non-permanent link:
On a non-permanent link, any change of state of a variable, if the latter has been
configured to trigger an alarm, give rise to the sending of frames to the Supervisor
to inform it of the change of state that has occurred. At the same time, the T200
saves the change of state information in the alarm log.
In PSTN or GSM, the T200 attempts to join the Supervisor three times on the main
telephone number, then if this fails makes three further attempts on the backup
telephone number. If the call still does not get through, the calls are stopped unless
a new alarm occurs, which reinitiates the call sequence from the normal number.
The call sequences take into account the time delays configured in the "Protocol"
page (refer to the Protocol manual for more details).
In radio mode, the T200 attempts to send a frame over the radio network to the
Supervisor to retransmit the change of state information. If the call does not get
through, the T200 attempts to call the Supervisor indefinitely without any restriction
regarding the number of attempts. The call sequences take into account the time
delays configured in the "Protocol" page. It is recommended not to configure
excessively short time delays so as not to mobilize the radio network constantly
(refer to the Protocol manual for more details).
In all cases, receipt of the event triggering an alarm by the SCADA system causes
acknowledgement of the alarm.
If the alarm information does not reach the Supervisor, no acknowledgement is
performed.
The acknowledgement of alarms by the SCADA system can be checked in the
"Alarm log" via the checked box opposite the alarm that has been acknowledged.
NB: This box is checked by the T200 only for alarm retransmissions on nonpermanent links. This is not managed for permanent links.
Note: The acknowledgement is internal to the T200 and is the subject of no
particular order from the Supervisor in the frame destined for the T200.
62
NT00113-EN-05

Commissioning Variable configuration
Parameter
Description
Variable
name:
Customization of the variable name.
Type:
Type of variable, double or single: "Double" by default for a TCD
(unmodifiable).
Access:
Defines the level of accessibility of this variable (administrator, operator,
used for access to the Web server.
Order:
The SCADA order can be reversed depending on the hardware configuration
of the digital outputs of the T200 (active on low level or on high level).
Class:
Allows a variable to be associated with a defined class. It is advisable to
so as to make reading in the pages of the Web server easier.
Logical
address:
Logical address assigned to this variable by the T200. This is in fact the
logical name of the variable (TCD+No.) (unmodifiable).
Internal
Internal address assigned to this variable by the T200. This is in fact a
and the COM card (unmodifiable).
Logical
input:
A TCD is always associated with a TSD. The T200 automatically assigns the
External
Address providing access to this variable in read/write mode from the
An address set to "-" is made inaccessible from the Supervisor.
3.12.4 Configuration of double command (TCD)
By clicking on the name of a TCD type variable in the Settings / Variable
configuration page, one can obtain access to its settings, namely:
Configuration of a TCD:
General parameters:
monitoring). The level of accessibility is defined with the login and password
group together those variables having an information link in the same class
address:
address of
associated
address:
Note: Refer to the manual for the protocol which is installed on the T200 for details
concerning the external address tables.
Modbus address for the internal bus link between the CONTROL module
TSD which is associated with this variable (in theory, should not be
modified).
Supervisor via the protocol. The address is specific to each protocol used
(Modbus, IEC, DNP3).
The basic T200 includes for each variable the configuration of the external
addresses corresponding to the installed protocol.
NT00113-EN-05
63

Commissioning Variable configuration
Parameter
Description
Variable
name:
Customization of the variable name.
Type:
Type of variable, double or single: "Single" by default for a TSS
(unmodifiable).
Logical
address:
Logical address assigned to this variable automatically by the T200. This is
in fact the logical name of the variable (TSS+No.) (unmodifiable).
Class:
Allows a variable to be associated with a defined class. It is advisable to
class so as to make reading in the pages of the Web server easier.
Access:
Defines the level of accessibility of this variable (administrator, operator,
used for access to the Web server.
Internal
Internal address assigned to this variable by the T200. This is in fact a
COM card (unmodifiable).
External
Address providing access to this variable in read/write mode from the
An address set to "-" is made inaccessible from the Supervisor.
Active status
Allows definition of a text and a colour to be displayed in the "Monitoring"
value 1).
Inactive
definition:
Allows definition of a text and a colour to be displayed in the "Monitoring"
value 0).
3.12.5 Configuration of single signalisation (TSS)
By clicking on the name of a TSS type variable in the Settings / Variable
configuration page, one can obtain access to its settings, namely:
Configuration of a TSS:
General parameters:
group together those variables having the same information link in the same
monitoring). The level of accessibility is defined with the login and password
address:
address:
definition:
status
Note: Refer to the manual for the protocol which is installed on the T200 for details
concerning the external address tables.
Modbus address for the internal link between the CONTROL module and the
Supervisor via the protocol. The address is specific to each protocol used
(Modbus, IEC, DNP3).
The basic T200 includes for each variable the configuration of the external
addresses corresponding to the installed protocol.
and "Control" pages to represent the active state of the variable (binary
and "Control" pages to represent the inactive state of the variable (binary
64
NT00113-EN-05

Commissioning Variable configuration
Parameter
Description
"Activate"
check box
Check this box to activate saving of the variable in the event log according
to the following configured criteria.
On active
Check this box to save a change of state in the active state of the variable
in the event log.
On inactive
Check this box to save a change of state in the inactive state of the
variable in the event log.
Parameter
Description
"Activate"
check box:
Check this box to activate saving of the variable in the alarm log according
to the following configured criteria.
On active:
Check this box to save a change of state in the active state of the variable
in the alarm log.
On inactive:
Check this box to save a change of state in the inactive state of the
variable in the alarm log.
Alarm level:
Three configurable levels corresponding to the various possibilities for
Alarm acknowledgement"
"Time-delayed
box:
Check this box if the alarm is to be retransmitted to the Supervisor only
Time-delayed
alarm:
Choice of the unit (hour, minute, second) and the waiting time before
retransmission of the alarm.
Record configuration:
By record is meant the saving of changes of state in the event log.
Alarm configuration:
By alarm is meant the saving of changes of state in the alarm log, but also:
- In PSTN or GSM mode: call sequence to the Supervisor then retransmission of
the alarm corresponding to the change of state.
- In radio mode: sending of a frame to the Supervisor to retransmit the alarm
corresponding to the change of state.
Comment: The alarms are not used on permanent links. The following
configuration should not be used for a permanent link:
alarm retransmission to the Supervisor (see section on "Alarm reporting /
alarm" check
after a configurable time delay.
TSS test:
The "TSS test" button at the bottom of the TSS configuration page allows the TSS
to be made active (fictitiously) for a few seconds (10 seconds).
That makes it possible, for example, to perform testing of state retransmission to the
Supervisor, although without being obliged actually to generate the change of state
for this TSS.
NT00113-EN-05
65

Commissioning Variable configuration
Parameter
Description
Type:
Type of variable, double or single: "Double" by default for a TSD
(unmodifiable).
Other status:
Allows definition of a text and a colour to be displayed in the "Monitoring"
and "Control" pages to represent the undefined state of the variable.
Parameter
Description
On status
change:
Check this box to save any change of state of the variable in the event log.
On leaving
close:
Check this box to save the loss of the switch closed state (loss of the active
state of the variable) in the event log.
Parameter
Description
On status
change:
Check this box to save any change of state of the variable in the alarm log.
On leaving
close:
Check this box to save the loss of the switch closed state (loss of the active
state of the variable) in the alarm log.
= Difference of configuration between a TSD and a TSS.
3.12.6 Configuration of double telesignals (TSD)
By clicking on the name of a TSD type variable in the Settings / Variable
configuration page, one can obtain access to its settings.
Note: The configuration is practically identical to that of a TSS. We have noted in
this section merely the differences between a TSD and a TSS:
Difference of configuration between a TSD and a TSS:
General parameters:
Record configuration:
Alarm configuration:
66
NT00113-EN-05
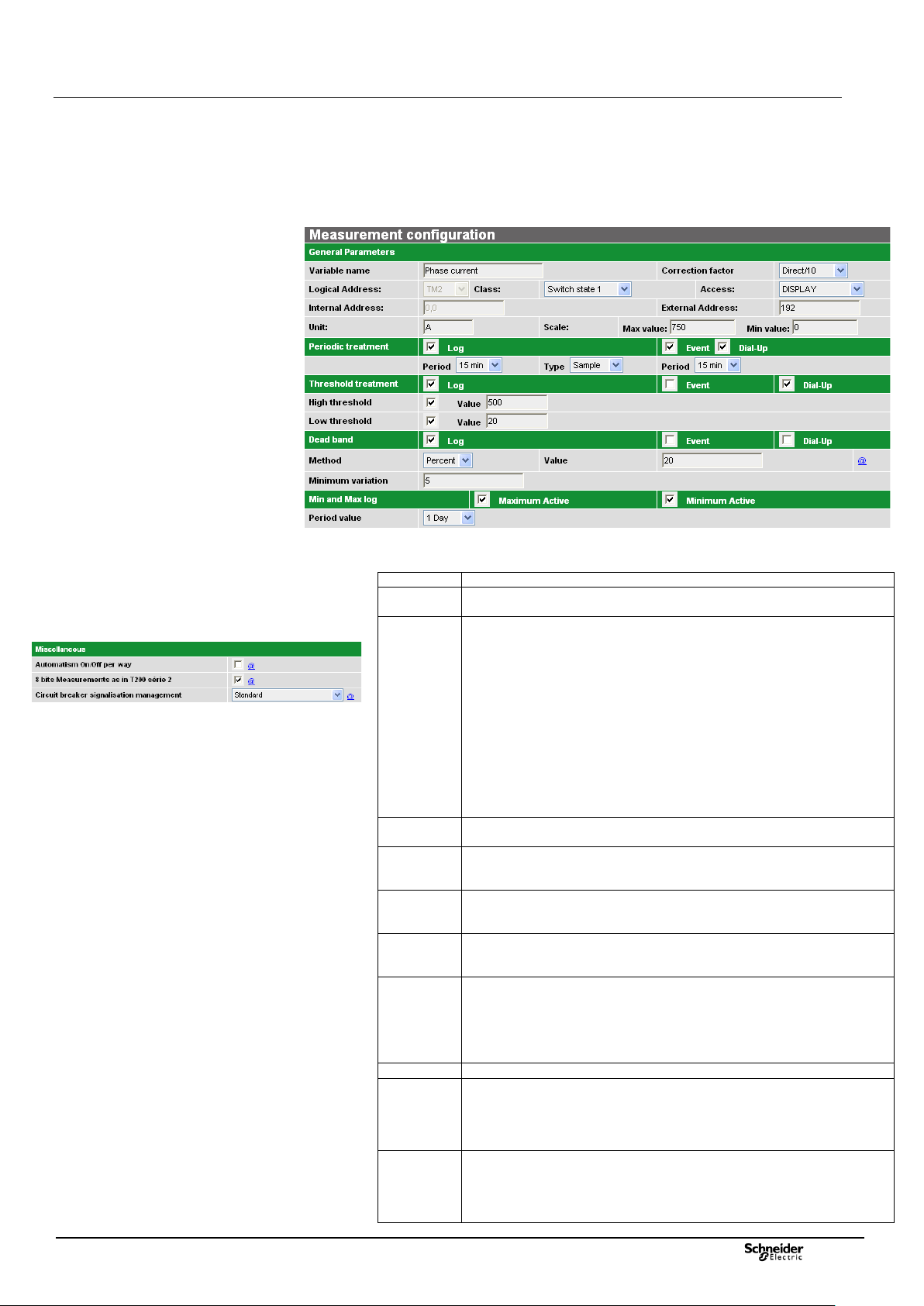
Commissioning Variable configuration
Parameter
Description
Variable
name:
Customization of the variable name.
Correction
Allows definition of a correction factor for display of the measurement in the
CONTROL module concerned by this TM.
Logical
address:
Logical address assigned to this variable by the T200. This is in fact the
logical name of the variable (TM+No.) (unmodifiable).
Class:
Allows a variable to be associated with a defined class. It is advisable to
so as to make reading in the pages of the Web server easier.
Access:
Defines the level of accessibility of this variable (administrator, operator,
used for access to the Web server.
Internal
Internal address assigned to this variable by the T200. This is in fact a
COM card (unmodifiable).
External
Address providing access to this variable in read/write mode from the
An address set to "-" is made inaccessible from the Supervisor.
Unit:
Unit to be associated with measurement for display in "Monitoring" page.
Max. scale
Should correspond to the maximum value that can be taken in practice by
NB: The value configured influences the precision of the measurement.
Min. scale
Should correspond to the minimum value that can be taken in practice by the
NB: The value configured influences the precision of the measurement.
"8-bit measurement" check box for compatibility of T200
series 2 or L500 type TMs
Excerpted from the page: "Settings/Automat. control"
3.12.7 Telemeasurement (TM) configuration
By clicking on the name of a TM type variable in the Settings / Variable
configuration page, one can obtain access to its settings, namely:
Configuration of a TM:
General parameters:
factor:
Monitoring page. The default factors to be configured for each TM of a T200
series 3 are as follows:
- Phase current: "Direct/10"
- Mains voltage: "Direct"
Note: This factor does not change the format of the measurement sent in
the protocol frame.
NB: For compatibility of measurements with the T200 series 1 and 2 or with
an L500 type supervisor, configure as follows:
- Phase current: "Direct
- Mains voltage: "Direct*100"
- Also check that the "8-bit measurement" box is checked in the
"Miscellaneous" section of the "Settings/Automatic control" page of the
address:
address:
NT00113-EN-05
value:
value:
group together those variables having an information link in the same class
monitoring). The level of accessibility is defined with the login and password
Modbus address for the internal link between the CONTROL module and the
Supervisor via the protocol. The address is specific to each protocol used
(Modbus, IEC, DNP3).
The basic T200 includes for each variable the configuration of the external
addresses corresponding to the installed protocol.
the measurement value. For "Raw" or "Normalized" type measurements, this
Max. value is used for calculation during measurement retransmission to the
SCADA system or for display in the Monitoring page. (see note 2 below).
measurement value. For "Raw" or "Normalized" type measurements, this
Min. value is used for calculation during measurement retransmission to the
SCADA system or for display in the Monitoring page. (see note 2 below).
67
Commissioning Variable configuration
Parameter
Description
"Log" check box:
Check this box to activate saving of the measurement in the
measurement log according to the criteria configured below.
Period:
Can be used to choose the period for saving of the measurement in the
measurement log.
Type:
Can be used to choose how to save the measurement:
- "Sampled": instantaneous measurement at each configured period
"Event" check
Check this box to activate saving of the measurement in the protocol
notes 1 and 2 below)
Period:
Can be used to choose the period for saving of the measurement in the
protocol stack and/or the alarm log
"Dial up" check
Check this box to activate saving of the measurement in the alarm log
criterion configured above.
Parameter
Description
"Log" check box:
Check this box to activate saving of the measurement in the
measurement log according to the criteria configured below.
High threshold:
Check the box to activate saving of the measurement upon exceeding
the high threshold.
High threshold
value
Configure the high threshold value which will cause processing of the
defined records.
Low threshold:
Check the box to activate saving of the measurement upon exceeding
the low threshold.
Low threshold
value
Configure the low threshold value which will cause processing of the
defined records.
"Dial up" check
Check this box to activate saving of the measurement in the alarm log
criteria configured above.
Note: Refer to the manual for the protocol which is installed on the T200 for details
concerning the external address tables.
Note 2: The T200 manages the transmission of measurements to the SCADA
system and measurement display in the "Monitoring" page according to two
formats:
Direct (or adjusted) value: corresponds to the real value in the reference unit
(does not take into account the configured "Min. and Max. scale" values).
Raw (or normalized) value: corresponds to a value calculated and scaled in
accordance with a formula taking into account the configured "Min. and Max.
scale" values. (see the protocol User Manual for details concerning
measurement calculation).
The choice of "Normalized" or "Adjusted" configuration is generally made in the
"Protocol" page.
Periodic treatment:
- "Averaged": mean of measurements over the configured period
box:
box:
Comment: The alarms are not used on permanent links. The "Call" check box
should not be used for a permanent link.
Note 1: The measurements cannot be saved in the internal event log.
Note 2: The Modbus protocol of the T200 does not enable measurements to be
saved in the protocol event stack. It is therefore no use checking the "Events" box
for this protocol.
The solution for retransmitting the measurements in Modbus protocol is:
- On a permanent link: They will be read during the next interrogations coming from
the Supervisor. There is therefore nothing special to do.
- On a non-permanent link: Check the "Call" box to retransmit it immediately (or
after the configured period), or wait for the next interrogation by the Supervisor.
event stack according to the period criteria configured below. (see
and sending of a frame to the Supervisor according to the period
Threshold treatment:
box:
Comment: The alarms are not used on permanent links. The "Call" check box
should not be used for a permanent link.
Note 1: Same as for previous section.
Note 2: Same as for previous section.
68
and sending of a frame to the Supervisor according to the threshold
NT00113-EN-05

Commissioning Variable configuration
Parameter
Description
"Log" check box:
Check this box to activate saving of the measurement in the
measurement log according to the % criterion configured below.
Method:
Fixed: A fixed change in the value of the variable results in an
associated processing operation.
Value:
Configure the minimum variation percentage or the minimum fixed
defined records.
Minimum change:
Whatever the method (fixed or percentage), a minimum change in the
alarm, etc.).
"Event" check
Check this box to activate saving of the measurement in the protocol
and 2 below)
"Dial up" check
Check this box to activate saving of the measurement in the alarm log
configured above.
Parameter
Description
"Maximum active"
check box:
Check this box to activate saving in the measurement log of the
maximum value reached in the period configured below.
"Minimum active"
check box:
Check this box to activate saving in the measurement log of the
minimum value reached in the period configured below.
Period value:
Can be used to configure the period for saving of the measurement in
the measurement log.
Dead band:
associated processing operation (saving, alarm).
Percentage: A change in percentage of the variable results in an
value of measurement variation which will cause processing of the
value of the TM is necessary for the variable to be processed (event,
box:
box:
Comment: The alarms are not used on permanent links. The "Call" check box
should not be used for a permanent link.
Note 1 and Nota 2 : Same as for previous section.
Note 3: On software V2.xx, the "Method" and "Minimum change" parameters are
not available. Processing is performed on a percentage and without a minimum
change.
event stack according to the % criterion configured above. (see notes 1
and sending of a frame to the Supervisor according to the % criterion
Min. and Max. recording:
NT00113-EN-05
69

Commissioning Variable configuration
Parameter
Description
Variable
name:
Customization of the variable name.
Correction
Allows definition of a correction factor for display of the counter in the
(default factor: "Direct")
Logical
address:
Logical address assigned to this variable by the T200. This is in fact the
logical name of the variable (CNT+No.) (unmodifiable).
Class:
Allows a variable to be associated with a defined class. It is advisable to
class so as to make reading in the pages of the Web server easier.
Access:
Defines the level of accessibility of this variable (administrator, operator,
password used for access to the Web server.
Internal
Internal address assigned to this variable by the T200. This is in fact a
the COM card (unmodifiable).
External
Address providing access to this variable in read/write mode from the
An address set to "-" is made inaccessible from the Supervisor.
Unit:
Unit to be associated with the counter for display in the "Monitoring" page.
(by default: with no unit)
Max. scale
Should correspond to the maximum value that can be taken in practice by
NB: The value configured influences the precision of the counter.
Min. scale
Should correspond to the minimum value that can be taken in practice by
NB: The value configured influences the precision of the counter.
TCD reset
address :
Address of the remote internal command to define the "Preset" value for
the counter.
3.12.8 Counter (CNT) configuration
By clicking on the name of a CNT type variable in the Configuration / Variable
configuration page, one can obtain access to its settings, namely:
Configuration of a CNT:
General parameters:
factor:
Monitoring page.
Note: This factor does not change the format of the counter sent in the
protocol frame.
group together those variables having an information link in the same
monitoring). The level of accessibility is defined with the login and
address:
address:
value:
value:
70
Modbus address for the internal link between the CONTROL module and
Supervisor via the protocol. The address is specific to each protocol used
(Modbus, IEC, DNP3).
The basic T200 includes for each variable the configuration of the external
addresses corresponding to the installed protocol.
the counter value. For "Raw" or "Normalized" type measurements, this
Max. value is used for scaling of the display in the monitoring page only.
(See note 2 below).
the counter value. For "Raw" or "Normalized" type measurements, this
Min. value is used for scaling of the display in the monitoring page only.
(See note 2 below).
NT00113-EN-05

Commissioning Variable configuration
Parameter
Description
Type of object
Selection of the variable type on which the counter is incremented
(Digital or Analogue)
Object
Name of the variable to which the counter is assigned
Counting method
Depending on the type of object, the methods displayed are as follows:
particular.
Pulse width
Pulse length (in ms) after which the T200 will consider a state as high.
Inhibition after
Period during which the T200 inhibits pulse detection after zero
rebounds in the event of a return to zero.
Integration period
Useful period of the measurement in the case of an integrating meter
(DI type variable) or mean (AI type variable)
Conversion factor
Used in the case of a pulse counter. Weight of the pulse sent. With
the conversion factor.
Active state
Field used only in the case of a time counter.
State of the variable (high or low) which activates the time counter.
Parameter
Description
"Recording"
check box:
Check this box to activate saving of the counter in the measurement log
according to the criterion configured below.
"Event" check
Check this box to activate saving of the counter in the protocol event
and 2 below)
Period:
Can be used to choose the period for saving of the counter in the
measurement log and in the protocol stack to the Supervisor.
Note: Refer to the manual for the protocol which is installed on the T200 for details
concerning the external address tables.
Note 2: The T200 manages measurement display in the "Monitoring" page
according to two formats:
Direct (or adjusted) value: corresponds to the real value in the reference unit
(does not take into account the configured "Min. and Max. scale" values).
Raw (or normalized) value: corresponds to a value calculated and scaled in
accordance with a formula taking into account the configured "Min. and Max.
scale" values. (See the protocol User Manual for details concerning the
calculation).
The choice of "Normalized" or "Adjusted" configuration is generally made in the
"Protocol" page.
It should be noted that, unlike the measurements, the Min. and Max. values
configured for the counters do not affect counter sending in the protocol frames to
the Supervisor.
Internal counting:
For a DI type variable:
Pulse counter: The counter is incremented at each switchover of the
variable to high state.
Time counter: The T200 calculates the period during which the
variable is in the high or low state. The display in the monitoring page is
in the form "day, hour, minute, second".
Integrating meter: Over a given range of time (integration period), the
T200 calculates the number of high states of the variable.
For example, the integrating meter makes it possible to obtain power
values from a power meter with pulse output.
For an AI/AO type variable:
Integrating meter: The meter is incremented each second by the
current value of the defined analogue variable.
For example, the T200 can poll power type analogue variables on the
Modbus Master port; the meter can then obtain the energy from the
power calculation.
“Mean” counter: The counter analyses an analogue variable and
displays the mean value of the variable over the configured integration
period. This function allows smoothing of analogue variables in
reset
Routine processing:
NT00113-EN-05
box:
Note 1: The counters cannot be saved in the internal event log.
Note 2: The Modbus protocol of the T200 does not enable counters to be saved in
the protocol event stack. It is therefore no use checking the "Events" box for this
protocol.
crossing by the variable. This filter makes it possible to avoid possible
each pulse sent, the counter value is incremented in accordance with
stack according to the period criterion configured below. (see notes 1
71

Commissioning Variable configuration
Parameter
Description
"Recording"
check box:
Check this box to activate saving of the counter in the measurement log
according to the value criterion configured below.
"Event" check
box:
Check this box to activate saving of the counter in the protocol event
stack according to the criterion configured below.
Value
Configure the minimum value which will cause processing of the
records defined above.
Parameter
Description
"Recording"
check box:
Check this box to activate saving of the counter in the measurement log
according to the % criterion configured below.
"Event" check
box:
Check this box to activate saving of the counter in the protocol event
stack according to the criterion configured below.
Value as %:
Configure the minimum counter variation percentage which will cause
processing of the records defined above.
checked
checked
checked
checked
(see note below)
(see note below)
The solution for retransmitting the counters in Modbus protocol is:
- On a permanent link: They will be read during the next interrogations coming from
the Supervisor. There is therefore nothing special to do.
Processing on threshold:
Note 1: Same as for previous section.
Note 2: Same as for previous section.
Dead band:
Note 1: Same as for previous section.
Note 2: Same as for previous section.
3.12.9 Summary of records in logs and stacks:
The following table summarizes the possibilities for recording in the various logs
and in the protocol event stack according to each type of variable:
Type Event log Alarm log Measurement
TSS If corresponding
check box
TSD If corresponding
check box
TM If "Dial up" check
CNT If "Log" check box
Note: For a TM or a CNT, several measurement processing operations can be
performed according to the type of transmission:
- "Event" box only checked: Saving of the TM or CNT in the protocol stack without
call sequence to the Supervisor (general case of the permanent link, except in
Modbus protocol).
- "Event" + "Dial up" boxes checked: Saving of the TM in the protocol stack and
call to the Supervisor (general case of the non-permanent link).
Not applicable with CNT.
- "Dial up" box only checked: Call to the Supervisor without saving of the TM in
the protocol stack (specific case of the non-permanent link in Modbus protocol).
Not applicable with CNT.
If corresponding
check box
If corresponding
check box
box checked
log
Always
Always
If "Log" check box
checked
checked
Protocol event
stack
If "Event" check box
checked
If "Log" check box
checked
72
NT00113-EN-05

Commissioning Class configuration
Class configuration page
Creation of a new class
Check boxes: "Deletion" and "Monitoring"
Example of variables associated to a class
Excerpted from the page: "Monitoring"
3.13 Customization of T200 classes
Access: "Settings/Classes configuration" page.
3.13.1 Definition of classes
A class allows the T200 variables to be grouped in various categories in the
monitoring and control pages of the Web server (e.g. "Monitoring" and "Control"
pages), so as to make the data display clearer.
Note: The variable configuration page also adopts the same organization of
variables by class.
3.13.2 Classes configuration
The factory configuration settings of the T200 include by default a number of
classes.
However, it is possible to modify this configuration to customize the display of the
variables in the pages.
The "Settings/Classes configuration" page can be used to create a new class, or
to modify or delete an existing class.
Creating a class:
To create a new class, simply enter its name in the empty "Class name" field and
click on the associated "Save" button.
Once the class has been created, it is then possible to configure a variable of the
T200 to be attached to that class (see chapter on "Customization of T200
variables").
Modifying a class:
Modification concerns only the change of class name or the possibility of making a
class visible or invisible in the pages of the Web server.
To modify the name of a class, simply change the title in the class entry field and
click on the associated "Save" button.
A specific check box can be used to define whether a class and the variables
associated with that class will be visible in the monitoring pages ("Monitoring" and
"Control" pages).
Selection of this check box and a click on the "Save" button makes the class visible
in the pages (and conversely for deselection).
Deleting a class:
A specific check box in the page can be used to delete an existing class.
Selection of this check box and a click on the "Delete" button permanently erases
the selected class.
Note: It is not possible to erase a class if variables are still attached to that class.
NT00113-EN-05
73

Commissioning Tests
See “Operation” for a more detailed description of
Easergy T200 P operation.
See “Operation” for a step-by-step description of the
various transmission stages indicated by the indicator
lamps on the front panel of the Communication module.
3.14 Tests at commissioning
During the tests, a microcomputer designed for configuration of the T200 can
remain connected to the Communication module. It can be used to monitor the
status of the equipment, time-stamped events and communications sent over the
internal Modbus link.
Commissioning sheet ref. NT00004 can be used.
“Local/Remote” switch set to “Local”
Check that the PC has taken the “local equipment” information into account.
Check that the MV cubicle switchgear is operating correctly, for example that
each channel can open and close and that the positions of the switches correspond
to the status of the indicator lamps.
Check “locked” information (earthing switch):
Check that the equipment has taken the “locked” inputs into account.
“Local/Remote” switch set to “Remote”
Check that the switch status is correctly displayed on the control station.
Check that the switch connecting cables are correctly marked and disconnect
them: a remote alarm is generated after a one-minute time-out.
Check that the HA10 switch connectors are fitted with polarizing pins.
If you have dummy devices, install them on the HA10 connectors to ensure that
neither the battery nor the MV cubicle is overloaded.
Telecontrol order check:
Check that each order processed by the remote control station is correctly
transmitted and executed by the equipment, for example that each channel can
open and close.
Check that the switch position information received at the remote control station
corresponds to the status of the indicator lamps.
“Digital inputs” check:
Check that the equipment has taken the “Digital inputs” into account and that the
indications have been forwarded to the remote control station.
Check the internal fault current detection function:
The “Test” pushbutton on the Control module activates the indications
corresponding to those channels for which the Current Measurement option is
installed.
Note: A current simulator supplied as an optional extra can be used for this check.
It performs a complete test of the acquisition system.
Disconnect the dummy devices and reconnect the switch connecting cables to their
HA10 connector (polarization).
Telecontrol order check:
Check that each order processed by the remote control station is correctly
transmitted and executed by the equipment, for example that each channel can
open and close.
Check that the switch position information received at the remote control station
corresponds to the status of the indicator lamps.
Check “locked” information (earthing switch):
Check that the equipment has taken the “Locked” inputs into account and that the
notifications have been forwarded to the remote control station.
“AC supply OFF” alarm check:
Open the AC supply fuse block. The remote alarm is generated immediately, or
after the configured time-out.
Measurement checking:
Check that the equipment takes into account the measurements performed
(currents, voltages, frequency, power, etc.) according to the options installed on the
T200 and retransmits them to the remote control station.
IMPORTANT NOTE: These tests can store time-stamped events.
Remember to erase them from the configuration PC.
74
NT00113-EN-05

Operation Control and monitoring
Port 2 (standard COM) or
auxiliary equipment port
(extended COM)
Port 1 (extended COM) sends
data (for modem other than
RS232)
Port 1 (extended COM)
receives data (for modem
other than RS232)
Port 2 (extended COM) sends
data
Port 2 (extended COM) receives
data
4 Operation
4.1 Operating mode
Easergy T200 P can be used locally via the Control module or remotely from a
remote control station, depending on the position of the “Local/Remote” switch.
An indicator lamp showing the status of the equipment is located at the top of the
control panel (front panel of the Control module).
A PC can be connected to the "COM" module to provide further information about
the status of Easergy T200 P and its operating history.
NT00113-EN-05
75

Operation Control and monitoring
4.1.1 Switch control
The switches can only be controlled via the Control module if:
The battery is connected
The “Local/Remote” switch is set to “Local”;
24 V/48 V voltage is present;
When an order is implemented, the switch moves to the complementary position:
If a switch is off, a switch-on order can be given.
If a switch is on, a switch-off order can be given.
4.1.2 Other orders
The Power supply module is used to reset the power supply:
It can reinstate the “Telecoms supply” when this output has been cut off due to
over consumption.
It can reinstate the supply to the equipment after it has been switched off due
to an excessive drop in the 12 V supply.
4.2 Testing of indicator lamps and fault
detection
On the Control module, a stored fault current is shown by a red indicator lamp
included in each channel block diagram.
A “Test” pushbutton is used to trigger simultaneous testing of all the control
panel indicator lamps and at the same time testing of fault detection acquisition
systems.
So long as the "Test" button is held down, all the CONTROL panel indicator
lamps remain lit. This allows indicator lamp operation to be checked.
When the "Test" button is released, all the indicators go out except the channel
indicator lamps which remain lit for 3 seconds.
A lit indicator lamp indicates that fault detection is functioning on the channel
(simulation of phase-to-phase and phase-to-earth current faults with fictitious
750 A current).
The “Reset” pushbutton is used to erase stored fault currents.
76
NT00113-EN-05

Maintenance Information display
Monitoring page
Event log
5 Maintenance
General
The equipment does not require regular maintenance.
The integrated battery test keeps users informed of the battery availability status.
Note: Replacement fuses are provided in the “accessories” bag attached inside the
basic enclosure.
The T200 has certain tools to perform maintenance or fault finding on the
equipment.
This requires a PC-compatible microcomputer with Internet Explorer (or an
equivalent software) installed. It is then possible to read the internal states of the
equipment and the events stored in memory by the T200 (see also section on
Commissioning).
The tools available for maintenance and fault finding are as follows:
Monitoring page
The screen on the left shows an example of a 1-channel Easergy T200 P, with
internal fault detector option, provided with a current acquisition card and a
transformer for voltage measurement.
This menu allows viewing of all the states and information managed by the T200:
The switch state: “Open”, “Closed” or “locked”;
Stored fault currents: “I Max.” and “I Max. transient” on each phase;
Current measurement on each phase, average current and neutral current;
Voltage measurement, phase-to-ground and phase-to-phase;
Power measurement, active, reactive and apparent;
Frequency and power factor measurement;
Operation and energy counter values;
The automatic control status, ON or OFF;
Equipment faults;
The operating mode: local or remote;
AC supply OFF, Delayed AC supply OFF;
The state of digital inputs 1 to 8;
The state of digital outputs 1 to 4.
Comment: The indications are refreshed every second.
Consulting the logs
The various logs available (events, alarms and system) make it possible to know
the history of everything that has occurred on the T200.
This can be useful to find the cause of a fault during fault finding.
All the events displayed in the logs are time stamped so as to know the date of
origin of a fault.
Given the large number of time-stamped events saved, it is possible to go back
sufficiently far in time to trace the cause of a problem.
When the maximum number is exceeded, the oldest event on the list is erased by
the most recent one.
The logs can be saved on PC in the form of Excel-compatible files so as to be
able to perform fault finding, reviews or statistics later.
The logs can be transferred by e-mail so as to be able to forward the report on a
problem to an accessory department or person or possibly to exchange an opinion
with the manufacturer of the T200.
Indicator lamp indications
The T200 provides a certain amount of information via the indicator lamps on the
front panel of the rack modules (see section on Operation – Control and
monitoring).
These indicator lamps provide information concerning the operating state of the
T200 and concerning the presence of any fault, where applicable.
Comment: A diagnostic through the state of the indicator lamps on the front panel
is not always adequate to find the cause of a fault. A lit indicator lamp indicates the
presence of a fault, but it is often necessary to consult the logs or the “Monitoring”
page to determine precisely the cause of a fault.
For more information, consult the diagnostic table below.
NT00113-EN-05
77

Maintenance Diagnostics via the front panel indicator
Symptoms
Possible causes
Solutions
Log*
Easergy T200: no
Communication module
The battery charger output
Check the charger and the battery. If necessary, replace the Power
Charger fault
No power supply to the
See “48 V LED extinguished” in the symptom column below
Motorization
Loss of battery capacity or
See "Battery fault LED lit" in the symptom column below
Battery fault
Accessory
supply failure
Connect the PC to the COM module and consult the logs.
Configuration
parameter error
The Control module software
is faulty
Press the key Reset on the Power Supply module.
If the LED does not go out after a few seconds, replace the CPU card.
Replace the gF type 2 A HRC fuse, 10 x 38 mm, in the lower
enclosure panel.
Power supply
failure
The output connector of the
disconnected
Power supply
No supply to the enclosure
Connect the AC supply.
Check the cause of the AC supply outage. If the AC supply remains
the Power Supply module and/or the battery.
Wait for the AC supply voltage to be reinstated (the enclosure is now
running on battery)
Power supply
failure
Check that AC supply is ON and that the charger is supplying 12 V.
charging for 24 hours, replace the battery.
Replace the 5 x 20 mm, 0.8 A semi time-lag fuse on the Power supply
module.
If the “AC supply OFF” LED is
to a long AC supply outage
Check the cause of the AC supply outage. If the AC supply remains
the Power Supply module and/or the battery.
Enclosure power supply cut
in the 12 V voltage
Power Supply module failure
Replace the Power Supply module.
lamps and logs
5.1 Diagnostics via the front panel indicator lamps and logs
The “Equipment
fault” LED on the
Control module
is lit.
(you are advised
to connect a PC to
the Control
module to
determine the
cause of the fault:
“Visualization"
page
The "AC supply
OFF" LED on the
front panel of the
Power Supply
module is lit AC
OFF
communication between the
Control module and the
voltage is too high or too low
switchgear
charge fault
No telecommunications power
supply (Radio or Modem)
Problem on the Control
module
AC supply fuse blown
mains fuse holder is
Enclosure power supply cut
off automatically due to
prolonged AC supply outage
Replace the Control module and/or the Communication module
Supply module and/or the battery
See “external 12 V LED extinguished” in the symptom column below
Configuration loss: Reconfigure the T200.
Other faults: perform resetting on the power supply card.
If the fault persists, replace the CPU card.
Put the connector back in place on the power supply card.
OFF, run another supply cycle by pressing the Reset button on the
Power Supply module. If the power supply does not restart, change
Modbus
communication
fault
power supply
failure
equipment power
loss or memory
fault or program
error or
failure
Temporary AC supply outage
The "Battery
fault" LED on the
front panel of the
Power Supply
module is lit
The "Rack 12 V"
LED on the front
panel of the
Power Supply
module is
extinguished
(*) The events can be consulted in one or more of the various available logs:
Event log;
Alarm log;
System log.
In these logs, the information appears in the form "TSSxx - Information (log column) - Fault".
Loss of battery capacity or
charge fault
Fuse blown
lit, the enclosure supply has
been cut off automatically due
off automatically due to a drop
To do this, disconnect the battery and measure the voltage on the
rack battery connector. If the voltage is null, replace the Power Supply
module. Otherwise, after reconnecting the battery, reset the Power
Supply module to trigger a battery test; if the problem recurs after
OFF, run another supply cycle by pressing the Reset button on the
Power Supply module. If the power supply does not restart, change
Check the charger and the battery. If necessary, replace the Power
Supply module and/or the battery.
Battery fault
78
NT00113-EN-05

Maintenance Diagnostics via the front panel indicator
Symptoms
Possible causes
Solutions
Log*
Replace the 5 x 20 mm, 0.4 A semi time-lag fuse on the Power Supply
module.
Accessory
failure
Consumption at the output >
1.3 A ± 0.3 A for 3 min
Check the transmission equipment and reinstate the supply by
pressing the Reset button on the Power supply module.
If the “AC supply OFF” LED is
to a long AC supply outage
Check the cause of the AC supply outage. If the AC supply remains
the Power Supply module and/or the battery.
Enclosure power supply cut
drop in the 12 V voltage
Accessory
failure
Replace the 5 x 20 mm, 5 A time-lag
enclosure.
Motorization
failure
If the “AC supply OFF” LED is
to a long AC supply outage
Check the cause of the AC supply outage. If the AC supply remains
the Power Supply module and/or the battery.
Motorization power supply cut
drop in the 48 V voltage
Check the charger and the battery. If necessary, replace the Power
Power supply cut off following
motorization 48 V)
Following the 48V cutoff, if the temperature of the charger drops in
the problem persists, replace the power supply card.
T200 CPU card failure
Replace the T200 CPU card.
Motorization
failure
The equipment is not
powered up
Replace the 5 x 20 mm, 0.8 A semi time-lag fuse on the Power supply
module.
Control module failure
Replace the Control module.
The card program is no
longer running
The equipment is not
powered up
Replace the 5 x 20 mm, 0.8 A semi time-lag fuse on the Power supply
module.
Connect the PC to the COM module. Refer to the system log to
module presumed to be defective.
Interface or
(x)
Stop the USB driver, disconnect the USB cable from the
replace the Communication module.
The Communication
flashes slowly
The Communication module
With the USB cable disconnected and the USB driver stopped, press
after a few seconds, replace the Communication module.
lamps and logs
The "external 12 V"
LED on the front
panel of the Power
Supply module is
extinguished
The "48 V" LED on
the front panel of
the Power Supply
module is
extinguished
Fuse blown
lit, the enclosure supply has
been cut off automatically due
off automatically due to a
Power Supply module failure Replace the Power Supply module.
Fuse blown
lit, the enclosure supply has
been cut off automatically due
off automatically due to a
overheating of the power
supply card charger (e.g.
excessive power
consumption on the
OFF, run another supply cycle by pressing the Reset button on the
Power Supply module. If the power supply does not restart, change
Check the charger and the battery. If necessary, replace the Power
Supply module and/or the battery.
fuse on the CPU card of the Control module in the left-hand part of the
OFF, run another supply cycle by pressing the Reset button on the
Power Supply module. If the power supply does not restart, change
Supply module and/or the battery.
less than one minute, the 48V power supply returns automatically. On
the other hand, if the temperature does not drop 1 minute after the 48V
cut-off, a manual reset should be performed on the power supply card
to restore the 48V power supply (thermal protection requiring action). If
equipment
power supply
equipment
power supply
power supply
Motorization
power supply
failure
Power Supply module failure Replace the Power Supply module.
All the Control
module indicator
lamps are
extinguished
The Communication
module "ON" LED is
extinguished
The Communication
module "Fault"
LED is lit
The Communication
module "Fault" LED
flashes rapidly
module "Fault" LED
Supply fuse blown
Supply fuse blown
Configuration problem on one
of the COM or CONTROL
modules or internal
connection fault between the
modules
The Communication module
software is faulty, or starting
with USB cable connected.
software is faulty
Power up the equipment.
Reset by pressing the Reset button on the Power Supply module.
Power up the equipment.
determine the error. Check the conformity of configuration of the COM
and/or CONTROL modules of the T200 (example of fault:
incompatibility of the configured modem with that installed on the COM
card or internal connection problem between one of the CONTROL
modules and the COM module). If the fault persists, replace the
Communication module, then press the Reset key on the Power
Supply module. If the LED does not go out after a few seconds,
the Reset key on the Power Supply module. If the LED does not go out
power supply
modem
initialization
error (x)
/ Control
Module error
RESET
NT00113-EN-05
79

Maintenance Diagnostics via the front panel indicator
Other diagnostics
Event
Possible causes
Solutions
Check:
the connection between Easergy T200 and the switches.
It is recommended to wait for about fifteen seconds before resetting the device
"Maintenance / Save-Restore" menu of the embedded Web server.
The loading process
managed)
lamps and logs
the connection of the battery (the command on switches cannot work if the
Operation orders not
executed
The switch order was not
executed
battery is not connected)
the position of the “Local/Remote” switch;
the validity of the order issued;
Loss of T200
configuration
Error during software
loading
Device reset performed
immediately after a change in
the device's configuration
manages only the file format
with .zip extension. The
software must therefore not
be unzipped before loading it
on the T200.
(file with .mem extension not
following a change in configuration parameters of the T200.
Use the "OFF line Configurator" configuration generation tool provided in
appendix (on the Easergy CD) to create a configuration file (text file) according to
the options used on the T200. Then load this file on the T200 via the
Start the loading operation again without unzipping the software
80
NT00113-EN-05

Maintenance Power supplies
IMPORTANT NOTE:
Use batteries having recent production
dates (less than three months' old).
Do not store more than six months
without recharging.
Do not throw the batteries away.
5.2 Power supplies
Powering down the equipment:
Switch off the AC supply outside the equipment or on the safety fuse block within the
enclosure.
Disconnect the supply to the battery circuit:
Unplug the battery connector under the rack.
All the LEDs on the front panels of the rack should now be extinguished.
The Easergy T200 P enclosure is now powered down.
Toroid safety precautions
The current transformers connector are IP2X. There is no particular risk to disconnect
toriod temporary (< 10 mn).
Shorting is required if switching off the current transformer is not temporary (> 10
minutes). No particular danger in shorting the CT with appropriate shorting plug. The
voltage incurred between open terminals is limited below 1000 Vac.
IMPORTANT NOTE: There is no need to alter the cables when connecting the
toroid and power supply cables to the cubicle. The cables must never be modified.
Battery maintenance:
Replacing the battery
Before carrying out any work on the battery, disconnect it from the equipment by
unplugging the connector from the base under the rack.
Remove the battery by sliding it outwards, raise the terminal covers and undo the two
terminal nuts, then disconnect the Faston lugs from the connecting cord.
To install a new battery, repeat this sequence in the reverse order.
Servicing and storing the batteries
Sealed lead batteries are used. The advantages of this type of battery include the fact that
there is no risk of explosion, no acid leakage and no servicing requirement.
However, this type of battery has its limitations:
Limited number or recharging cycles;
Average service life of 10 years, with ageing accelerated by temperatures outside
the recommended range;
Ageing during storage (do not store for more than six months without recharging, as
this type of battery does not withstand a total discharge);
Difficult to predict the end of battery service life.
The Power Supply module is designed to optimize the characteristics of the battery.
A battery fault alarm informs the remote control system of an imminent discharge.
Note: the battery is an important element for the unit because the command on switches
cannot operate without the battery connected and charged.
Replacing fuses
Replacement fuses are provided in the “accessories” bag attached inside the enclosure.
“AC supply” fuse
This fuse is located in the lower panel of the enclosure.
gG type HRC fuse of rating 2 A, 10 x 38 mm.
“Rack power supply” fuse
The fuse protecting the power supply to all the electronic modules is located on the Power
Supply module card.
Fuse: 5 x 20 mm, 0.8 A semi-time-lag.
“External 12 V supply” fuse
The fuse is located on the Power Supply card.
Fuse: 5 x 20 mm, 4 A time-lag.
“48 V supply” fuse
The fuse is located on the CPU card of the Control module.
This card is located in the left-hand part of the rack. It is accessible after removing the
control panel (front of the Control module).
Fuse: 5 x 20 mm, 5 A time-lag.
To replace the fuses:
a) Power down the enclosure.
b) Replace the defective fuse.
c) Power up the enclosure.
NT00113-EN-0
81

Maintenance Replacement of spare parts
5.3 Card replacement
Replacing the Power Supply module
a) Power down the enclosure (see the previous page) and disconnect the Battery
and Mains connectors on the underside of the card.
b) Release the two locking screws on the Power Supply module and remove it from
its slot.
c) Insert the new module, locking it in position.
d) Reconnect the Battery and Mains connectors to the underside of the card and
power up the enclosure.
Replacing the Communication module
a) Power down the enclosure (see the previous page).
b) Release the two locking screws and remove the Communication module from its
slot.
c) Insert the new module, locking it in position.
d) Power up the enclosure.
Replacing the control panel or the T200 CPU card
Purpose: to replace the control panel or the T200 CPU card or add/replace the
voltage measurement card..
a) Power down the enclosure (see the previous page).
b) Release the two locking screws on the front panel of the Control module.
c) Disconnect the ribbon cable from the rear of the front panel by separating the two
levers on each side of the connector base.
d) If necessary, remove the T200 CPU card from its slot after loosening its locking
screw (at the bottom left-hand, on the front of the card) and disconnecting all the
connectors from the Connection card (under the rack).
Installing the T200 CPU card
e) Push the new T200 CPU card firmly home and tighten its locking screw again (at
the bottom left-hand, on the front of the card).
f) Reconnect all the connectors to the Connection card (under the rack).
g) Attach the end of the 26-pin ribbon cable from the control panel to the connector
on the T200 CPU card.
h) Screw the control panel firmly into position.
i) Power up the enclosure.
Installing the voltage measurement card
e) Plug the measurement card into the T200 CPU card and secure it with the screw.
f) Install the T200 CPU card and the control panel (see above).
g) Power up the enclosure.
82
NT00113-EN-05

Appendix A Configurable parameters
User, Operator or Administrator
Pattern
: Accessible or modifiable only as Operator or Administrator
Pattern
: Accessible or modifiable only as Administrator
Pattern
: No access (read-only) or non-existent
Page: Home
Sub-page
Section
Parameter / button
Configuration
Comments
Home
Back to home page
Local/Remote
Local/Remote
Local: normal access. Remote: simplified access (images
and logos not loaded)
Choice of
Language
Français/
pagnõl/Deutsch
User
User name
No restriction
Confirmation by OK
Password
No restriction
Confirmation by OK
Page: Monitoring
Sub-page
Section
Parameter / button
Configuration
Comments
Classes
Channel x
Access to the corresponding class states
Channel x
measurements
Access to the corresponding class states
T200 information
Access to the corresponding class states
T200 internal faults
Access to the corresponding class states
Digital inputs
Access to the corresponding class states
Page: Control
Sub-page
Section
Parameter / button
Configuration
Comments
Channel x
Operation preset
Allows the operation counter value to be changed
Channel x
F-O control
Allows the switch status to be changed
Channel x
measurements
Active energy preset
Allows the active energy counter value to be changed
Channel x
measurements
Reactive energy preset
Allows the reactive energy counter value to be changed
T200
information
ON/OFF control
Allows the automatic control status to be changed
Digital inputs
F-O control
Allows the state of the digital outputs to be changed
Page: Diagnostic
Sub-page
Section
Parameter / button
Configuration
Comments
Alarm log
Clear log
The "Ack" box is checked when the SCADA system has
The "Clear log" button clears the log's content
Event log
Clear log
The "Clear log" button clears the log's content
System log
Clear log
The "Clear log" button clears the log's content
Measurement
log
Clear log
The "Clear log" button clears the log's content
File transfer
Alarms.csv
Transfers the alarms log in Excel file form
"Open" opens the file under Excel
Events.csv
Same as for the events log
System.csv
Same as for the system log
Measures.csv
Same as for the measurements log
6 Appendix A – Configurable parameters
Definition of access levels according to the patterns in each box in the table:
Pattern
: Accessible or modifiable as
range
language
English/Português/Es
range
range
83
range
acknowledged the alarm
"Save" saves the file to the PC
NT00113-EN-05
Appendix A Configurable parameters
Page: Maintenance
Sub-page
Section
Parameter / button
Configuration range
Comments
Terminal
General
Name of terminal
No restriction
At the user's choice
Date format
DD/MM/YYYY
YYYY/MM/DD
Defines the date format to be displayed in the logs
Date/time of last config.
Consultation exclusively
Configurator structure version
Consultation exclusively
Comment area
No restriction
At the user's choice
Control module
Application
Manufacturer information. Consultation exclusively
Date/time of last configuration
Manufacturer information. Consultation exclusively
Application version
Measurement processor version
Hardware configuration
Save Takes into account the change
Software
Software
All displayed parameters
Name of software, version, date and time of compilation, type of
Consultation exclusively
Software 1
Checked or not
Selection of software 1
Software 2
Checked or not
Selection of software 2
Download software
Allows the T200 software to be updated
Clock
Terminal
Date
Consistent date format
(year > 2000)
Time
Consistent time format
Update
Allows the T200 date and time to be updated manually
Synchronization
Allows the T200 date and time to be updated automatically by the PC
SNTP service
SNTP server
Consistent IP address
IP address of the main SNTP server.
synchronization by this SNTP server is deactivated.
Auxiliary SNTP server
Consistent IP address
Same as for the auxiliary SNTP server.
Polling period
1 to 300 s
As standard: 1 s. Allows the time synchronization period to be defined
via the SNTP server. Configurable from 1 to 120 seconds.
Number of reconnection attempts
0 to 9
As standard: 3. Upon failure of synchronization with the server, max.
number of attempts to be made.
Last SNTP synchronisation
Date and Time
Indication of the time and date of the last SNTP synchronization
performed (consultation exclusively).
SNTP server gateway
Consistent IP address
Address of the gateway for access to the main SNTP server.
Auxiliary SNTP server gateway
Consistent IP address
Address of the gateway for access to the auxiliary SNTP server.
Max. server response time
1 to 60 s
As standard: 2 s. Maximum time waiting for the reply from the SNTP
server before maki ng a further attempt at synchronization.
Clock validity period:
1 to 1440 min.
As standard: 35 min. Time after which the T200 must be
resynchronized with the SNTP server.
Update
Allows the T200 date and time to be updated manually.
Synchronization
Allows the T200 date and time to be updated automatically by the PC.
IP parameters
Ethernet
Mac address
Unique identification address for each T200, set in factory. Consultation
exclusively
DHCP
Active
Defines whether the server of the Ethernet local area network can
or not (inactive)
IP address
Consistent IP address
Ethernet IP address of the T200 (by default: 172.16.0.5)
Sub-network mask
Consistent mask
The mask enables (0) or inhibits (255) the choice of accessible IP
address values (by default: 255.255.255.0)
Gateway addresses
Consistent IP address
IP address of the server's Ethernet gateway. The gateway centralizes
all the network IP accesses (by default: 172.16.0.1)
Primary DNS server
Consistent IP address
IP address of the primary DNS server (Domain Name Server). The
names (by default: 172.16.0.1)
Secondary DNS server
Consistent IP address
IP address of the secondary DNS server (Domain Name Server).
Backup DNS server (by default: 0.0.0.0)
Virtual interface
IP address
Consistent IP address
Virtual Ethernet IP address 1 and 2 of the T200 (as standard: 0.0.0.0).
Sub-network mask
Consistent mask
The mask enables (0) or inhibits (255) the choice of usable IP address
values (as standard: 255.255.255.0).
Gateway addresses
Consistent IP address
IP address of the server's virtual Ethernet gateway. Operation identical
to the Ethernet Interface part.
USB interface
Server IP address
IP address allocated to the T200's embedded Web server for USB
access. Unmodifiable (by default: 212.1.1.10)
Client IP address
IP address allocated to the PC connected via USB to the embedded
Web server. Unmodifiable. (by default: 212.1.1.11)
Communication
Server IP address
IP address allocated to the T200's embedded Web server by the
GPRS/3G network operator. Unmodifiable.
Client IP address
IP address allocated by the GPRS/3G network operator to the client
Unmodifiable.
Save / Cancel
Allows changes to be saved/cancelled
IP server port
TCP services
HTTP server port
Valid port number
Port number for the HTTP server of the T200. (By default: 80). Any
10.207.154.240:1500 for access with a port No. = 1500)
Telnet server port
Valid port number
Port number for the Telnet server of the T200. (By default: 23)
Port 1 trace server port
Valid port number
Port number for the port 1 trace server of the T200. (By default: 1168)
Port 2 trace server port
Valid port number
Port number for the port 2 trace server of the T200. (By default: 1169)
TCP/IP port trace server port
Valid port number
Port number for the TCP/IP port trace server of the T200.
(By default: 1170)
Save Allows changes to be saved
MM/DD/YYYY
X
information
date/time
interface
Inactive
compression, size, CRC32.
Note: When the address is set to "0.0.0.0", the function of
allocate automatically on connection an IP address to the T200 (active)
84
1 and 2:
interface
DNS enables the IP addresses to be associated with the website
(Supervisor) which will log on to the T200 Web server.
change of port No. implies indication with the IP address (e.g.
NT00113-EN-05

Appendix A Configurable parameters
Page: Maintenance
Sub-page
Section
Parameter / button
Configuration range
Comments
User
User name
No restriction
User name for the session
Password
No restriction
Password for the session
Type
Administrator
Operator
The Administrator has full access
The Operator has restricted access
Save Saves changes
Recycle bin
Check box to select a session to be deleted
Delete
Deletes an existing session if the corresponding box is checked
Port traces 1
TCP/IP
Trace options
Start / Stop
Start/Stop frame motion PC – T200
Erase
Erases the content of the trace
Backup /
Saves the
configuration
T200 -> PC arrow
Allows the configuration to be saved on the PC in file form
Loads the
configuration
PC -> T200 arrow
Enables the configuration to be loaded on the PC from a file
Operating
Communication
Port 1 or 2 mode
Depends on the
by exception
Definition of transmission mode to be used:
Port 1 link
Not used
- Channel not available
first.
Port 2 link
Same as Port 1
Same as Port 1
Port 1 medium
Direct RS232 (internal)
3G (internal)
- RS232 modem integral with COM card
- Internal 3G modem on COM card
Port 2 medium
Same as Port 1
Same as Port 1
Communication
TCP/IP port link
Not used
- Channel not available
mode.
Save Allows the configuration to be taken into account
and 2 and
Restoral
modes
General
communication
parameters
terminal
terminal
parameters on
physical ports
protocol:
- IEC: Unbalanced or
balanced mode
- DNP3: Unsolicited
response or No
unsolicited response
- Modbus: Report by
exception or No report
Normal
Balanced –
Normal/Backup
Main – Normal/Backup
Backup –
Normal/Backup
Store and Forward
Test
- Without alarms:
"Unbalanced" or "Master/Slave" or "No report by exception" or
"Unsolicited response".
- With alarms:
"Balanced" or "Master/Master" or "Report by exception".
- Main transmission channel. Two "normal" channels of different
characteristics can be used if there are two control PCs (main and
maintenance). The T200 cannot manage simultaneous TCDs coming
from the two systems.
- Two channels are necessary in this m ode. The operation of the
channels is balanced. In the event of a fault on the channel in service,
switchover to the other channel takes place automatically.
- Requires another channel as "Backup – Normal/Backup".
Same operation as "Balanced" but with the priority use of this channel.
- Requires another channel as "Main – Normal/Backup". Same
operation as "Balanced" but with use of this channel if failure of the
Main channel.
- Function used in radio mode. In addition to the normal channel
function of transmission to the SCADA system, this channel is also
used for relaying to an auxiliary T200 located within transmission range
and not accessible by any other means.
- (in radio mode only). Allows a fixed frequency to be generated on the
radio network for antenna installation adjustment operations or level
measurements on fields received on another T200 within range of the
parameters on
TCP/IP ports
Radio (external)
600/1200 FSK radio
(internal)
600/1200 FSK LL
(internal)
PSTN (external)
1200/2400 FFSK
(internal)
PSTN (internal)
GSM (external)
GSM (internal)
GPRS (internal)
Normal
- For external radio with integral modem
- FSK radio modem on COM card
- FSK radio modem on COM card
- For external PSTN modem accessible by Hayes command
- FFSK radio modem on COM card
- Internal PSTN modem on COM card
- For external GSM modem accessible by Hayes command
- Internal GSM modem on COM card
- Internal GPRS modem on COM card
- Channel used for transmission to the Supervisor via the Ethernet
interface on condition that the protocol supports this transmission
NT00113-EN-05
85

Appendix A Configurable parameters
Page: Settings
Sub-page
Section
Parameter / button
Configuration range
Comments
Protocol
Refer to the User Manual for the protocol used for more information.
TCP/IP protocol
Refer to the User Manual for the protocol used for more information.
Port 1 or 2
Direct RS232
Baud rate
200 to 38400 baud
Frame transmission rate (600, 1200 bds only with FSK radio, 1200 with LL,
1200 or 2400 bds with FFSK radio)
Parity
None or Space or Even or
Odd
Transmission parity
Stop bits
1 or 2
Stop bit in frame
Frame error on noisy
outgoing cable
Yes or no
The start of the frame can be filtered or not to avoid reading any noise
Frame error on line at
rest
Yes or no
Any holes in the frame can be filtered or not
Delay before response
0 to 10000 ms
In 10 ms increments. Upon reception, wait before sending the response to
avoid frame overlapping (by default:0 ms)
DTR management:
Checked or not
Data Terminal Ready. DTR is used by the T200 to indicate that it is ready
for transmission
DTR - RTS delay:
0 to 10000 ms
In 10 ms increments. Time delay to be complied with between rising of the
between the send order and carrier rise. (By default: 0 ms)
RTS management
Checked or not
Request To Send. If this option is selected, the RTS signal will be managed
during transmission exchanges with the modem.
CTS management
Checked or not
Clear To Send. The modem enables the CTS as soon as ready after RTS
enabling by the T200
RTS to CTS delay
10 to 10000 ms
In 10 ms increments. Time delay between receiving the RTS and sending
the CTS by the modem (by default: 20 ms).
RTS (or CTS) to
message delay:
0 to 1000 ms
In increments of 10 ms. Time delay between rise of RTS (or CTS if
managed) and sending the message.
Message to RTS delay
0 to 10000 ms
In 10 ms increments. Time delay between the end of the message and RTS
falling by the T200 (by default: 20 ms)
DTR management
Checked or not
Data Terminal Ready. The modem causes the DTR to rise after powering
up or when it is Clear To Send
CD management
Checked or not
Carrier Detect. The carrier can be used by the modem to detect reception of
a message.
LL
Type of line
2-wire or 4-wire
Choice of type of leased line used.
PSTN or GSM
Calling party call delay
1 to 600 s
Allows the call to be released when the T200 is called after the configured
time delay (by default: 30 s)
Called party call delay
1 to 600 s
Allows the call to be released when the SCADA system is called after the
configured time delay. (By default: 60 s)
Telephone No. (normal)
0 to 9, P, T or space
Main telephone No. to be used in case of alarm retransmission
Telephone No.
(backup)
0 to 9, P, T or space
Backup telephone No. to be used in case of alarm retransmission if main
No. cannot be reached.
Modem init. sequence
No restriction. Record
AT commands necessary to initialize the PSTN modem. With internal PSTN
&F0%S0=12S0=1&K0%C0E0&W0&Y0)
PSTN
Type of dialling
Pulse or voice frequency
Type of dialling used for alarm retransmission.
GSM
PIN code
0000 to 9999
PIN code of the GSM card.
SMS service centre No.
0 to 9, P, T or space
Telephone No. of the SMS service centre (gateway for SMS's)
User SMS No.
0 to 9, P, T or space
Telephone No. of the user for sending SMS's.
RS485
Polarization
Checked or not checked
Activates polarization of the T200 end line. The RS485 line should be
polarized at one termination only, generally on the Master side.
End-of-line resistance
Checked or not checked
Active the T200 end load resistance. The RS485 line should be loaded at
both its terminations.
Type of line
2-wire or 4-wire
Choice of type of transmission used: 2-wire or 4-wire.
GPRS or 3G
Access Point Name
(APN)
No restriction.
Name of GPRS/3G access point provided by the GPRS/3G network
operator.
PIN Number
0000 to 9999
PIN code of the GSM card.
Daily disconnect
Checked or not checked
Override setting of automatic disconnection/reconnection of the T200 to the
by itself autonomously.
Disconnection hour:
0 to 23
Configuration of the selected daily disconnection time according to the
criteria described in "Daily disconnection".
PPP session timeout
1 to 60 min
Configuration of the delay maximum before disconnection of T200 from
GPRS/3G network, in case of no data transfer detected by the T200
Specific Ping IP adress
Consistent
The ping makes it possible to verify and measure the quality of the
the packet corresponding to the ping allowing this quality to be measured.
Ping test
Button that can be used to set the ping test manually to verify T200
the test: "Ping Ok" or "Ping failed".
Ping time interval
1 to 360 min
Delay between two successive automatic “Test ping”
Ping attemps
0 to 10
Number of maximum attempts for the “Test ping” process in case of no
response from remote IP address.
Ping Timeout
1 to 360 s
Maximum delay to wait for the response during the “Test ping” to define
“Ping error”.
Authentication
Checked or not checked
When the GPRS/3G network requires authentication in the connection
Encryption protocols accepted: PAP, CHAP, MSCHAP, MSCHAP V2
Login
No restriction
Configuration of the login used for authentication. Confi gure this field only if
the "Authentication" option has been checked.
Password
No restriction
Configuration of the password used for authentication. Configure this field
only if the "Authentication" option has been checked.
Save Allows the configuration to be taken into account
Transmission
or RS485
or Radio
or PSTN
or GSM line
or LL
DTR and RTS signals. In external radio, this corresponds to the time delay
consistent AT commands
IP address, e.g.
192.168.2.169
mode, default AT commands not modifiable. (By default:
GPRS/3G network at a fixed time. In the event of loss of connection with the
network, this process allows the T200 to reconnect, because it cannot do so
equipment's connection with another device connected to the Ethernet
network. Enter the known IP address of another device capable of receiving
connection to the GPRS/3G network. The T200 then displays the result of
86
phase, activate this function by checking the box.
NT00113-EN-05

Appendix A Configurable parameters
Page: Settings
Sub-page
Section
Parameter / button
Configuration range
Comments
Control./
Controls
Type of control
Standard
Other
- Standard = Separate CO/CF controls
- Other = Specific cubicle connection (e.g. RL27)
Time delay pending
position return
1000 to 30000 ms
In 100 ms increments. Waiting time for change of switch position following
an order, before sending a telecontrol fault. (By default: 15000 ms)
Non-complementarity
filtering time delay
1000 to 30000 ms
In 100 ms increments. Waiting time for non-complementarity following a
loss of switch state before sending a position fault (by default: 10000 ms)
Execution time delay
50 to 15000 ms
In 50 ms increments. Switch motorization control relay rise time. Not used
(by default: 2200 ms)
Miscellaneous
BVE control (DOUT 1)
Checked or not checked
When this option is selected, digital output DOUT 1 is activated to cause
fault detector detects and indicates the presence of a phase or earth fault.
DDEF test (DOUT 2)
Checked or not checked
When this option is selected, digital output DOUT 2 is activated whenever a
the T200, then goes low as soon as the fault returns below the threshold.
Double power supply
Checked or not checked
When this option is selected, digital output DOUT 3 is used for the double
enclosure.
T200 without COM card
Checked or not checked
This option should be used when the T 200 includes no COM card in the
equipment.
SF6 lack copying
Checked or not checked
To be compatible with old versions of T200P (Series 1&2), the information
as digital inputs because they are already defined as “SF6 lack”.
8-bit measurements
Checked or not checked
By checking this option, the T200 measurements are made compatible with
the old-generation T200s coded on 8 bits (instead of 16 bits).
Circuit breaker
Several choices:
Choice of mode of acquisition of the position coming from the switch:
mode.
Position reading of
Checked or not checked
Option only available when the AC supply protection is made by circuit
DI 5 to indicate when circuit breaker protection is open.
U measurements by
than RL27
Checked or not checked
Case of voltage measurement done by capacitor divisor (RL27 type) but
Automation
Type of automation
None
Changeover switch
- No automatic control
- Power supply source changeover depending on the source available
Sectionalizer
Fault counter reset time
20000 to 240000 ms
In 5000 ms increments
automatic control reset (by default: 30000 ms)
No. of faults authorized
1 to 4
Number of faults to be taken into account before opening upon automatic
control action
ATS[1/2] Network
Changeover delay time
100 to 200000 ms
In 100 ms increments. Waiting time before changeover action if the
conditions are required (by default: 1000 ms)
Time before normal
channel return
5000 to 60000 ms
In 1000 ms increments. Waiting time before switchover to normal channel
upon channel voltage return. (By default: 10000 ms)
Operating mode
Auto SW2
Choice of changeover mode:
- Ditto with priority return to SW2 if available
Voltage Time
Voltage failure timeout
0 to 32700 ms
In 100 ms increments. Waiting time following voltage disappearance before
opening the channel. (By default: 200 ms)
Closing timeout
0 to 32700 ms
In 100 ms increments. Waiting time following voltage return before reclosing
the channel. (By default: 200 ms)
Monitoring timeout
0 to 32700 ms
In 100 ms increments. Time for monitoring non-disappearance of the
channel opens and automatic control is blocked. (By default: 200 ms)
Save Allows the configuration to be taken into account.
Autom.
Automatic control
No. x
(except PM6)
management (DOUT 3)
(channel 1 on DI3,
channel2 on DI4)
signalisation
management
PM6
CI2
- Standard
- Earth breaker
management by TSD
- Free TSS
- Specific mode 1
- PM6 = Single CO/CF control on CO
- CI2 = Control execution time at 100 ms
with a PM6
flashing of an external fault indicator lamp, whenever the T200's internal
current exceeds the phase or earth fault detection threshold configured on
mains power supply management option if the latter is installed in the
"SF6 lack" (connected on Harting switch connector - pin 9) is internally
associated to DI3 (channel 1) or to DI 4 (channel 2). So, when the "SF6
lack" is detected, the DI3 (or DI4) is activated at the same time.
Note : If this option is checked, the DI 3 and DI 4 are not any more available
- Standard (factory settings). A single TSS used in this "Locked switch"
mode (pin 7 of the 10-pin Harting connector). The presence of this TSS
inhibits execution of orders on the switch.
- Earth breaker management by TSD: An additional input (pin 8) allows the
earth switch to be managed as a TSD and not as a TSS.
- Free TSS: Pins 7 and 8 normally assigned to "Switch locked" and "MV
voltage present" can be used freely and used as mere DIs
- Specific mode 1: similar to the "Earth breaker management by TSD"
mode, with in addition the inhibition of orders when the T200 is in "Local"
Channel x
automatic control
automatic control
sector circuit breaker
capacitor divisor other
delay
Voltage Time
Sectionalizer
SW1->SW2
SW2->SW1
SW1<-> SW2
Auto SW1
breaker instead of fuse holder. When this option is used, the T200 manage
without using the calibration process done by RL27.
- Opening on voltage dip without fault detection
- Opening on voltage dip due to fault detected
Maximum waiting time to detect the number of faults configured before
- Switchover only from SW1 to SW2
- Switchover only from SW2 to SW1
- Switchover from SW1 to SW2 or vice versa
- Ditto with priority return to SW1 if available
voltage following voltage return. If this is the case during the timeout, the
NT00113-EN-05
87

Appendix A Configurable parameters
Page: Settings
Sub-page
Section
Parameter / button
Configuration range
Comments
Measurements/ faul t
MV network
characteristics
Mains frequency
50 or 60 Hz
Choice of mains frequency. (By default: 50 Hz).
Voltage
Transformer
primary ratio
100 to 36000
Primary transformation ratio of PT. (By default: 230).
Transformer secondary
100, 110, 115, 120
240/√3
Secondary transformation ratio of PT. (By default: 230).
Configuration of voltage
U21
V1_V2_V3
Choice of sensor mode for voltage measurement
Voltage rating
20 to 36000 V
Network voltage rating. (By default: 230 V)
Voltage present
threshold
70% to 120%
Minimum threshold for validation of voltage presence. (By default: 90%)
Voltage absent
threshold
5% to 95%
Maximum threshold for validation of voltage absent. (By default: 80%)
Residual voltage
5% to 95%
Min. phase-to-phase imbalance threshold for taking into account a voltage
fault. (By default: 30%).
Voltage present timeout
100 to 180000 ms
In 10 ms increments. Minimum voltage presence time for taking into
account voltage presence. (By default: 100 ms)
Voltage absent time-out
100 to 180000 ms
In 10 ms increments. Minimum voltage absence time for taking into account
voltage absence (By default: 100 ms)
Measurements /
Current
Transformer
primary ratio
50 to 2500
Primary transformation ratio of toroids. (By default: 500).
Transformer secondary
ratio
1 or 5
Secondary transformation ratio of toroids. (By default: 1).
Current sensors
I1,I2,I3 or I1,I3,I0
Type A arrangement (3 phases) or type B (2 phases + homopolar – type
PM6). (By default: I1,I3,I0).
Fault detection
I max. threshold
10 to 800 A
Phase fault detection threshold. (By default: 500 A)
I0 threshold
2 to 160 A
Earth fault detection threshold. (By default: 20 A)
Time delay for taking
into account Imax
40 to 800 ms
Time for taking into account Imax fault. (By default: 200 ms)
Time delay for taking
into account I0
40 to 800 ms
Time for taking into account I0 fault. (By default: 200 ms)
Inrush
Checked or not
Use of the Inrush function or not. (By default: not checked)
Reset upon voltage
return
Checked or not
If checked, fault detection storage resetting upon voltage return. (By default:
checked)
Time delay for resetting
upon voltage return
0 to 70 s
In 1s increments. Voltage presence time for resetting the fault storage
memory. (By default: 3 s)
Detector reset time
delay
1 to 12 h
Time to reset the fault stored in memory automatically, if still present. (By
default: 2 h)
Power supply
Time-delayed under
0 to 21600 s
In 15 min. increments. Time delay for filtering the power supply
extended mains power supply failure. (By default: 7200 s)
Save Allows the configuration to be taken into account
detector
measurement
configuration
ratio
100/√3, 110/√3, 115/√3,
120/√3
200, 220, 230, 240
200/√3, 220/√3, 230/√3,
fault detector
measurement
configuration
configuration
sensors
U21_U32
U21_U32_U13
V1
V1_V2
Depends on the type of arrangement (star or delta)
(by default: U21)
functions
voltage indication delay
undervoltage signal supplied by the power supply card. Allows indication of
88
NT00113-EN-05

Appendix A Configurable parameters
Page: Settings
Sub-page
Section
Parameter / button
Configuration range
Comments
Variable
General
Variable name
No restriction
Name given to variable.
Type
Single or double
TCD = double control only
Access
Administrator
Monitoring
Access right for this variable. The variable will be readable or modifiable
rights.
Order
Reverse or normal
The reverse choice reverses the order of the control bits for the TCD and
(By default: Normal )
Class
(Complete list of all
classes defined)
Allows a variable to be assigned to an existing class.
Logical address
TCD internal No. assigned automatically by the T200 (unmodifiable).
Internal address
Address for the COM-CPU internal Modbus link (unmodifiable).
Associated logical
address TS
TSD1 to TSD40 or none
No. of the TSD associated with the TCD used by the T200 for reading the
state.
External address
Format 'x' (e.g. 1) for all
- DNP3: 'x,x' (word, class)
External address used for retransmission of this TCD variable in the
Save Allows the configuration to be taken into account
Cancel
Enables return to the preceding configuration
Variable
Global
Variable name
No restriction
Name given to variable.
Type
Single or double
TSD = double information
TSS = single information
Logical address
TSD internal No. assigned automatically by the T200 (unmodi fiable).
Class
(Complete list of all
classes)
Allows a variable to be assigned to an existing class.
Access
Administrator
Monitoring
Access right for this variable. The variable will be readable or modifiable
rights.
Internal address
Address for the COM-CPU internal Modbus link (unmodifiable).
External address
Format 'x' (e.g. 2)
External address used by SCADA for this variable
State definition:
Active (1)
No restriction
Name displayed for an active state of the variable
State colour:
Active (1)
Black, blue, green or red
colour
Display colour for an active state of the variable
State definition:
Inactive (0)
No restriction
Name displayed for an inactive state of the variable
State colour:
Inactive (0)
Black, blue, green or red
colour
Display colour for an inactive state of the variable
Other state:
No restriction
Name displayed for an undefined state of the variable
State colour:
Undefined
Black, blue, green or red
colour
Display colour for an undefined state of the variable
(only with TSD and not with TSS)
Recording
Enable
Checked or not
Enabling of the record or not upon change of state of this variable in the
event log
Upon any change of
active (TSS)
Checked or not
Saving of the event upon any change of state of the variable (TSD) or upon
Upon loss of closing
(TSS)
Checked or not
Saving of the event upon disappearance of the closed state of the variable
Alarm
Enable
Checked or not
Enabling of the alarm or not upon change of state of this variable and
saving in the alarm log.
Upon any change of
active (TSS)
Checked or not
Activation of the alarm and saving of alarm upon any change of state of the
Upon loss of closing
(TSS)
Checked or not
Activation of the alarm and saving of alarm upon disappearance of the
(TSS).
Alarm level
Scada + sms
sms
Several possible actions in the event of a retransmission of alarm
Time-delayed alarm
Checked or not
Activates a time delay before sending the alarm.
Delay value
0 to 99
Number of hours, minutes or seconds for the delay before sending the
alarm to the SCADA
Hours or Minutes or
Seconds
Checked according to
choice
Choice of unit for the value of the alarm delay
Save Allows the configuration to be taken into account
Cancel
Enables return to the preceding configuration
configuration
Control configuration
configuration
Indications
configuration
parameters
parameters
Operator
protocols except:
- Modbus: 'x,x' (word, bit)
Operator
depending on the type of access configured and the associated access
the double telesignal (TSD) in the protocol frame to the Supervisor.
E.g.: TCD and TSD on normal: bit 1 = opening, bit 2 = closing
TCD and TSD on reverse: bit 1 = closing, bit 2 = opening
protocol link to the Supervisor.
depending on the type of access configured and the associated access
configuration
configuration
Undefined
state (TSD) or upon
(TSD) or upon inactive
state (TSD) or upon
(TSD) or upon inactive
Scada
(only with TSD and not with TSS)
appearance of the active state (TSS).
(TSD) or upon appearance of the inactive state (TSS).
variable (TSD) or upon appearance of the active state (TSS)
closed state of the variable (TSD) or upon appearance of the inactive state
depending on the defined level.
NT00113-EN-05
89
Appendix A Configurable parameters
Page: Settings
Sub-page
Section
Parameter / button
Configuration range
Comments
Variable
General parameters
Variable name
No restriction
Name given to variable.
Correction coefficient
Direct or raw or
Definition of a coefficient of multiplication to be applied to the measurement
voltage = direct*100
Logical address
TM internal No. assigned automatically by the T200 (unmodifiable).
Class
(Complete list of all
classes)
Allows a variable to be assigned to an existing class.
Access
Administrator
Monitoring
Access right for this variable. The variable will be readable or modifiable
rights.
Internal address
Address for the COM-CPU internal Modbus link (unmodifiable).
External address (SCADA)
Format 'x' (e.g. 2)
External address used by SCADA for this variable
Unit
No restriction
Unit for display of the variable
Max. value
Integer
Maximum value that can be taken in practice by the measurement value.
NB: The value configured influences the precision of the measurement.
Min. value
Integer
Minimum value that can be taken in practice by the measurement value.
NB: The value configured influences the precision of the measurement.
Regular processing
Recording
Checked or not
Enabling of regular saving of the measurement in the measurement log or
not.
Period
15 min., 30 min. or 1 h
Measurement recording period
Type
Averaged or sampled
Way of calculating the measurement for recording in the measurements log
Event
Checked or not
Enabling of regular saving of the measurement in the protocol event stack
or not.
Call
Checked or not
Enabling of regular sending of the al arm to SCADA and saving in the alarm
log or not.
Period
15 min., 30 min. or 1 h
Event or call saving period.
Processing on
Recording
Checked or not
Enabling of saving of the measurement in the measurements log or not
upon exceeding threshold
Event
Checked or not
Enabling of saving or not upon exceeding the measurement threshold in
the protocol event stack.
Call
Checked or not
Enabling of sending of the alarm to SCADA and saving in the alarm log or
not upon exceeding threshold.
High threshold
Checked or not
Enabling of high threshold or not
Low threshold
Checked or not
Enabling of low threshold or not
High threshold value
No restriction
Value for enabling exceeding of the high measurement threshold
Low threshold value
No restriction
Value for enabling exceeding of the low measurement threshold
Dead band
Recording
Checked or not
Enabling of recording of the measurement in the measurements log or not
through variation
Event
Checked or not
Enabling of regular saving or not upon variation of the measurement in the
protocol event stack.
Call
Checked or not
Enabling of sending of the alarm to SCADA and saving in the alarm log or
not following measurement variation.
Method
Fixed or percentage
Fixed: A fixed change in the value of the variable results in an associated
associated processing operation.
Value
0 to Max. scale value
Fixed value or % measurement variation for dead band processing
Minimum change
0 to Max. scale value
Minimum change in the measurement variation for the dead band to be
processed
Min. and Max.
Active maximum
Checked or not
Recording or not of the maximum measurement reached over the period
configured
Active minimum
Checked or not
Recording or not of the minimum measurement reached over the period
configured.
Period
1, 7 or 14 days
Calculation period for min. and max. value
Save Allows the configuration to be taken into account
Cancel
Enables return to the preceding configuration
configuration
Measurement
configuration
Direct/10 to direct/10000
or Direct*10 to
direct*10000
variable for its correct display in the monitoring page. Allows display in the
correct format relative to the real size
By default for T200 series 3: current = direct/10 and voltage = direct
By default for T200 series 1 or 2 or L500 compatibility: current = direct and
threshold
Operator
depending on the type of access configured and the associated access
processing operation (saving, alarm).
Percentage: A change in percentage of the variable results in an
recording
90
NT00113-EN-05

Appendix A Configurable parameters
Page: Settings
Sub-page
Section
Parameter / button
Configuration range
Comments
Variable
General parameters
Variable name
No restriction
Name given to variable.
Correction coefficient
Direct or raw or
Definition of a coefficient of multiplication to be applied to the counter
voltage = direct*100
Logical address
CNT internal No. assigned automatically by the T200 (unmodifiable).
Class
(Complete list of all
classes)
Allows a variable to be assigned to an existing class.
Access
Administrator
Monitoring
Access right for this variable. The variable will be readable or modifiable
rights.
Internal address
Address for the COM-CPU internal Modbus link (unmodifiable).
External address
(SCADA)
Format 'x' (e.g. 2)
External address used by SCADA for this variable
Unit
No restriction
Unit for display of the variable
Max. value
Integer
Maximum value that can be taken in practice by the counter value.
NB: The value configured influences the precision of the counter.
Min. value
Integer
Minimum value that can be taken in practice by the counter value.
NB: The value configured influences the precision of the counter.
TCD reset address
TCD 1 to 40
Address for the counter reset command.
Internal counting
Type of object
Digital or Analogue
Selection of the variable type on which the counter is incremented
Object
TSSxx or Dixx or TMxx or
AIxx
Name of the variable to which the counter is assigned
Counting method
Pulse counter
Depending on the type of object, the methods displayed are as follows:
- “Mean” counter.
Pulse width
0 to 2000 ms
In 10 ms increments. Pulse length (in ms) after which the T200 will consider
a state as high.
Inhibition after reset
0 to 2000 ms
In 10 ms increments. Period during which the T200 inhibits pulse detection
possible rebounds in the event of a return to zero.
Integration period
0 to 86400 s
Useful period of the measurement in the case of an integrating meter (DI
type variable) or m ean (AI type variable).
Conversion factor
0 to 10000
Used in the case of a pulse counter. Weight of the pulse sent. With each
conversion factor.
Active state
Low or High
Field used only in the case of a time counter.
State of the variable (high or low) which activates the time counter.
Regular processing
Recording
Checked or not
Enabling of regular recording of the counter in the measurement log or not.
Event
Checked or not
Enabling of regular saving of the counter in the protocol event stack or not.
Call
Checked or not
Enabling of regular sending of the alarm to SCADA and saving in the alarm
log or not.
Period
15 min., 30 min. or 1 h
Counter recording period.
Processing on
Recording
Checked or not
Enabling of recording of the counter in the measurements log or not upon
exceeding threshold
Event
Checked or not
Enabling of saving or not upon exceeding the counter threshold in the
protocol event stack.
Call
Checked or not
Enabling of sending of the alarm to SCADA and saving in the alarm log or
not upon exceeding threshold.
Value
No restriction
Value for enabling exceeding of the high counter threshold.
Dead band
Recording
Checked or not
Enabling of saving or not upon counter variation in the measurement log.
Event
Checked or not
Enabling of saving or not upon counter variation in the protocol event stack.
Call
Checked or not
Enabling of sending of the alarm to SCADA and saving in the alarm log or
not following counter variation.
Value as %
0 to 255
% variation of the counter for the dead band criterion.
Save Allows the configuration to be taken into account.
Cancel
Enables return to the preceding configuration.
Class
Recycle bin
Checked or not
Selection of class to be deleted or not
Monitoring
Checked or not
Selection or not of class display in the Monitoring page
Class name
No restriction
Class name to be displayed
Save Allows a modification or a creation to be recorded for each class
Delete
Allows a class that has been selected earlier to be deleted
configuration
Counters
Direct/10 to 10000 or
Direct*10 to 10000
variable for its correct display in the monitoring page. Allows display in the
correct format relative to the real size
By default for T200 series 3: current = direct/10 and voltage = direct
By default for T200 series 1 or 2 or L500 compatibility: current = direct and
Operator
- Time counter
- Integrating meter
depending on the type of access configured and the associated access
• For a DI type variable:
- Pulse counter.
- Time counter.
- Integrating meter.
• For an AI/AO type variable:
- Integrating meter.
after zero crossing by the variable. This filter makes it possible to avoid
pulse sent, the counter value is incremented in accordance with the
threshold
management
NT00113-EN-05
91

Appendix B General characteristics
Controllable switch
1 channel (2 channels on option)
Indication inputs
Open door + 8 free digital inputs
230 Vac - 50 Hz, 120 VA Protected by HRC fuse of 4 A rating, type gF
Permissible mains voltage: 90 V to 270 Vac (43 V and 57 V on option).
Charger
12V
7 A
12 Vdc (10.8 V to 14.8 V) 1 A continuous-duty, 7 A max.
Protection if consumption > 1.3 A for more than 3 min.
48 Vdc (44.8 V to 59 V) max. 6 A for 12 s and 15 A, 50 ms Protected by 5-A fuse.
fuse. Permanent consumption tolerated on 24 V for auxiliary equipment: 90 mA
Total discharge, periodic tests every 12 hours (10A duri ng 100 ms).
Two consecutive unsuccessful tests generate battery fault
Power reserve
at 20°C
Up to 16 h + 10 open/close cycles (in radio communications)
Service life
at 20°C
10 years
Insulation (50 Hz/1 min.): 10 kV
Impulse wave (1.2 / 50 µs): 5 kV
Insulation (50 Hz/1 min.): 2 kV
Impulse wave (1.2 / 50 µs): 5 kV
Level 4: 4 kV (mains and sensors),
2 kV (other circuits)
Electrostatic discharges
IEC 61 000-4-2
Level 3; 6 kV on contact 8KV in air
Radiated electromagnetic
field
Radio frequency on FSM
IEC 61 000-4-6
0.15 MHz to 80 MHz – 10 V rms
Damped oscillatory waves
IEC 61 000-4-12
2.5 kV common mode, 1 kV differential mode
Pulsed magnetic field
IEC 61 000-4-9
1000 A/m peak
Impulse waves
IEC 61 000-4-5
Coupling between line wires 1 kV, between wire and frame earth 2 kV
50 Hz magnetic fields
IEC 61 000-4-8
30 A/m continuous-duty and 300 A/m 1 to 3 s
Relative humidity
IEC 60 68-2-3
Less than 95% at 40°C
Salt spray test
IEC 60 68-2-11
336 h
Storage temperature
IEC 60 68-2-14
–40°C to +70°C
Vibrations
IEC 60 68-2-6
10 to 500 Hz; 1 g or 0.075 min. peak-to-peak
Dimensions
H x L x D
630 mm x 410 mm x 350 mm
Protection
IEC 60529
IP55
Measurements
(options)
Current measurement
and fault detection
Phase-to-phase fault
threshold
Precision (excluding
sensors)
Precision (excluding
sensors)
Energy
from -10°C to 55°C
Precision 2%
Power factor
from -10°C to 55°C
Precision 1.7%
Measurement of phase shift
measurements
General characteristics
Digitizing
12 bits
7 Appendix B - General characteristics
Capacity
Output loops Enclosure lighting + 3 digital outputs
Power supply
AC supply Characteristics
Rack power supply
Power supply
Battery
Characteristics
Dielectric
Electromagnetic
Telecommunications
Motorization
Type
Charging time
Capacity
Monitoring
AC supply input IEC 60 255-4
Toroid input IEC 60 255-4
Rapid transients IEC 61 000-4-4
12 Vdc (10.8 V to 14.8 V). Protected by a 0.8 A fuse
48 V (or 24 V on
option)
IEC 61 000-4-3 80 MHz - 1 GHz - 30 V/m
Permanent consumption tolerated on 48 V for auxiliary equipment: 90 mA
24 Vdc (21.6 V to 29,6 V) max. 12 A for 12 s and 15 A, 50 ms Protected by 10A
Sealed lead maintenance-free type
10 h to 24 h
12 Vdc - 38 Ah
Successful test if U Bat.> 11,2V, at the end of the test.
Climatic
Mechanical
Voltage measurements
Other measurements
Temperature
Enclosure material
Weight
–25°C to +55°C
316L stainless steel
40 kg
Configurable from 10 to 800 A in increments of 1 A
Earth fault threshold
Fault duration
Values returned
from -10°C to 55°C 1.6% from 20 to 800 A
Values returned
from -10°C to 55°C 1.2 % at 240Vac max (0.5 % at +20°C)
Power from -10°C to 55°C P, S, Q: precision 2.8%
Frequency
between two U
from -10°C to 55°C Expressed in degrees; precision ± 3°C
Configurable for 2 to 160 A in increments of 1 A
40 to 800 ms in increments of 1 ms
3I, Imean, Io
3 U and 3 V
Mean value over 10 periods; precision 0.1%
NT00113-EN-05
92

Easergy T200I Personal notes
93
NT00113-EN-05

Easergy T200I Personal notes
94
NT00113-EN-05

Easergy T200I Personal notes
NT00113-EN-05
95

Easergy T200I Personal notes
96
NT00113-EN-05

NT00113-EN-05 03/2021
Schneider Electric
35 rue Joseph Monier
92500 Rueil Malmaison
France
+33 (0)1 41 29 70 00
www.schneider-electric.com
As standards, specifications and designs change from
time to time, please ask for confirmation of the
information given in this publication.
© Schneider Electric. All Rights Reserved.
 Loading...
Loading...