Page 1

ArmorPoint I/O
DeviceNet
Adapters
1738-ADN12, 1738-ADN18,
1738-ADN18P, 1738-ADNX
User Manual
Page 2
Important User Information
SHOCK HAZARD
Solid state equipment has operational characteristics differing from those of
electromechanical equipment. Safety Guidelines for the Application,
Installation and Maintenance of Solid State Controls (Publication SGI-1.1
available from your local Rockwell Automation sales office or online at
http://www.ab.com/manuals/gi) describes some important differ enc es
between solid state equipment and hard-wired electromechanical devices.
Because of this difference, and also because of the wide variety of uses for
solid state equipment, all persons responsible for applying this equipment
must satisfy themselves that each intended application of this equipment is
acceptable.
In no event will Rockwell Automation, Inc. be responsible or liable for
indirect or consequential damages resulting from the use or application of
this equipment.
The examples and diagrams in this manual are included solely for illustrative
purposes. Because of the many variables and requirements associated with
any particular installation, Rockwell Automation, Inc. cannot assume
responsibility or liability for actual use based on the examples and diagrams.
No patent liability is assumed by Rockwell Automation, Inc. with respect to
use of information, circuits, equipment, or software described in this manual.
Reproduction of the contents of this manual, in whole or in part, without
written permission of Rockwell Automation, Inc. is prohibited.
Throughout this manual, when necessary we use notes to make you aware of
safety considerations
.
WARNING
IMPORTANT
ATTENTION
BURN HAZARD
Identifies information about practices or circumstances
that can cause an explosion in a hazardous environment,
which may lead to personal injury or death, property
damage, or economic loss.
Identifies information that is critical for successful
application and understanding of the product.
Identifies information about practices or circumstances
that can lead to personal injury or death, property
damage, or economic loss. Attentions help you:
• identify a hazard
• avoid a hazard
• recognize the consequence
Labels may be located on or inside the equipment (e.g.,
drive or motor) to alert people that dangerous voltage may
be present.
Labels may be located on or inside the equipment (e.g.,
drive or motor) to alert people that surfaces may be
dangerous temperatures.
Page 3

Preface
Purpose of This Manual
This manual describes how to install, configure, and operate your
ArmorPoint I/O™ DeviceNet™ Adapters, catalog numbers
1738-ADN12, -ADN18, -ADN18P, and -ADNX.
See the following sections: Page:
Who Should Use This Manual P-2
What the Manual Contains P-2
Related Terms P-3
Related Products and Documentation P-5
Guidelines for Using Your Adapter P-6
Conventions Used in This Manual P-6
IMPORTANT
In this manual, we use ArmorPoint DeviceNet
adapters to refer to all the 1738 DeviceNet adapter
modules (1738-ADN12, -ADN18, -ADN18P, and
-ADNX). We use the specific catalog number (e.g.,
1738-ADNX) to refer to a specific module.
In the rest of this manual (except Chapter 4), we
refer to the ArmorPoint I/O DeviceNet adapters as
the adapters.
Who Should Use This Manual
In Chapter 4, we refer to the ArmorPoint I/O
DeviceNet adapter as the scanner because the
chapter describes how to configure the adapter on
the subnet.
You must be able to use RSNetWorx for DeviceNet™ software or a
similar configuration software to configure your adapter.
In this manual, we assume you know how to configure an ada pte r. If
you do not, refer to your software user manuals or online help before
attempting to use these adapters.
We also assume you are familiar with the ArmorPoint I/O product
line, including other fieldbus interfaces, I/O modules, and power
supplies. If you are not familiar with these components, you can read
some of the ArmorPoint I/O documents listed in the Related Products
and Documentation section.
1 Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 4
Preface 2
What the Manual Contains
This manual contains the following sections:
Chapter 1 - Install the ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapters
Description of how to install and wire the adapter
Chapter 3 - Use Auto Start Mode
Description of how to use the Auto
Start Mode on your adapter to quickly
get your system up and running
Chapter 2 - What Is the ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapter?
Overview of the adapter’s features and functionality
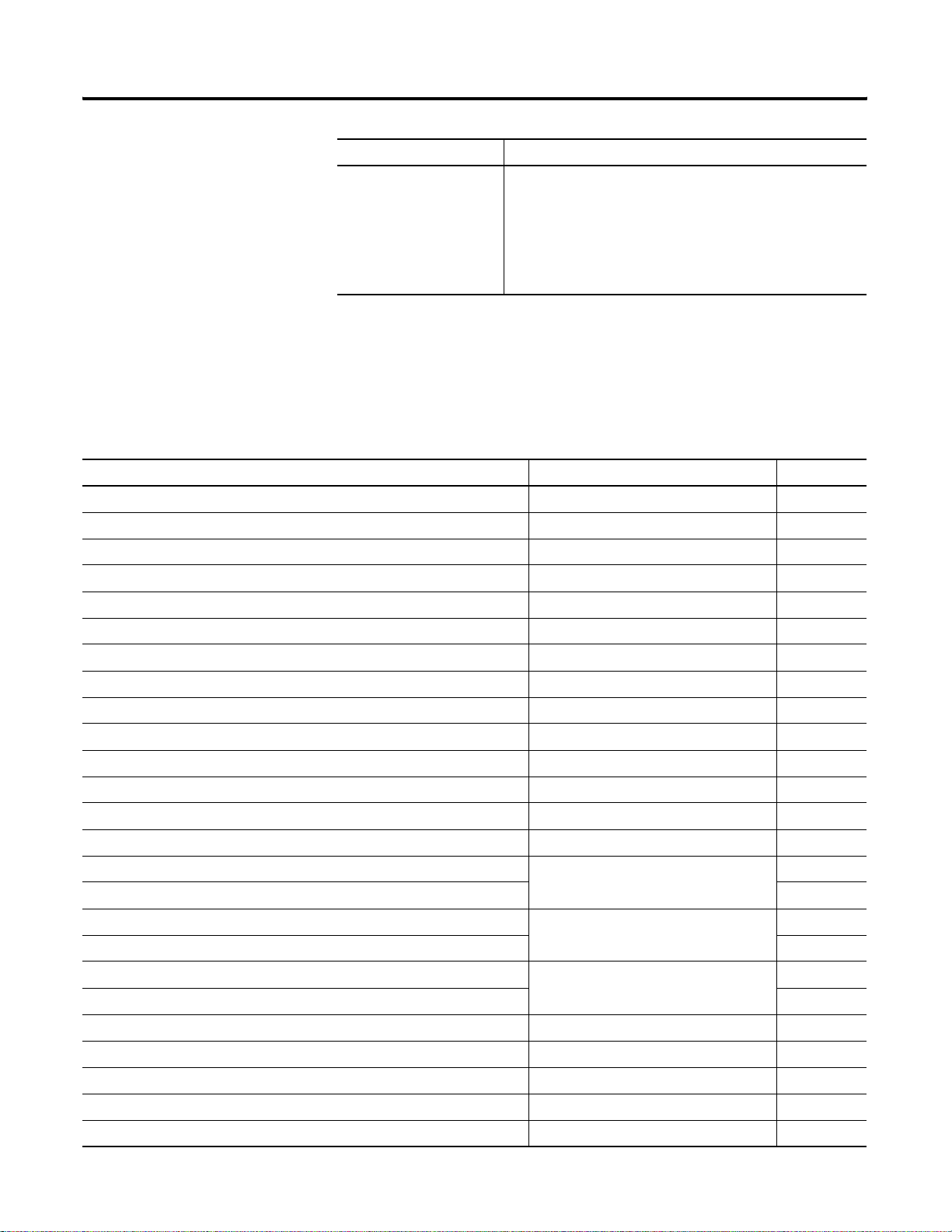
1738-ADN12
DeviceNet Out
DeviceNet In
Adapter
Status
DeviceNet
Status
PointBus
X1
Status
X10
PWR
Or
System
Power
R
Adapter
Power
Chapter 4 - Configure the
DeviceNet Scanner Subnet
Description of how to configure your
adapter on the subnet
Chapter 5 - Add the ArmorPoint
DeviceNet Adapter to the DeviceNet
Scanner’s Scanlist
Description of how to configure the
DeviceNet adapter and how to add it to the
scanlist
Appendix B - Quick Start
Learning how to use the 1738-ADN12
with a ControlLogix system on DeviceNet
Chapter 6 - Troubleshoot the
ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapter
Description of how to use the status
indicators and how to troubleshoot your
adapter
Appendix C - 1738-ADNX Rules and Guidelines
Rules and guidelines regarding how to use the
1738-ADNX
Appendix A - Specifications
Listing of the ArmorPoint adapters’
specifications
Appendix D - Default Data Maps
Listing of the default data maps for
1738 ArmorPoint I/O modules
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 5
Preface 3
Related Terms
This manual uses the following terms:
Term: Definition:
Adapter The adapter interfaces between DeviceNet devices and
ArmorPoint I/O modules. ArmorPoint I/O DeviceNet adapters
include the 1738-ADN12, -ADN18, -ADN18P, and -ADNX.
Auto Catalog Replace The ArmorPoint I/O DeviceNet adapter supports the swapping
of two identical modules connected to the adapter . That is, if a
1738-IB4M12 is in slot 3 and another 1738-IB4M12 is in slot 7,
the two modules can be removed from the ArmorPoint system
and the slot 3 module placed into slot 7, and vice-versa. When
Automatic Device Replacement (ADR) is active, the swapped
modules will be reconfigured to match the previous module in
their new slot. When ADR is not active, the configuration
parameters will not be modified, the swapped modules must
have identical configuration and values for their EDS file
parameters.
Auto Device Replacement
(ADR)
This refers to the ADR feature of a ControlLogix System on
DeviceNet. With ADR active, any device on the DeviceNet link
may be removed and replaced with an out-of-the-box
checkmark compliant DeviceNet device. The ADR feature will
result in downloading the values of the configuration
parameters of the EDS file of the removed device to the new
device.
Auto Start Mode A feature that lets the ArmorPoint I/O system get “up and
running” without the prerequisite to configure any of the EDS
parameters for the PointBus
Using Auto Start Mode will result in a scan list within the
adapter that stores the modules identity information.
Autobaud A feature in devices (e.g., ArmorPoint I/O modules) on the
DeviceNet network that causes them to listen to
communications on the network and set their own baudrate to
match the network rate.
Backplane The PointBus that consists of ArmorPoint I/O modules
connected to the ArmorPoint DeviceNet adapter.
Baudrate Rate of communications between devices on the DeviceNet
network. Backplane baudrate is used for the 1738-ADN12,
-ADN18, and -ADN18P. Subnet baudrate is used for the
1738-ADNX.
Change of State (COS) DeviceNet communications method in which the adapter
sends data based on detection of any changed value within
the input data. Data is independently received based on a
change of state from the sender . Data in both directions can be
acknowledged or unacknowledged depending on the run-time
configuration of the system.
Commissioning The period in time associated with post startup activities.
Commissioning implies that the system has been validated
and all configuration parameters are correct, all modules are
in good operating condition, and the adapter scanlist is
complete.
ControlFlash™ Utility software you can use to update the adapter’s firmware
with the most current boot and application code.
™ or ArmorPoint I/O modules.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 6
Preface 4
Term: Definition:
Cyclic DeviceNet communications method in which the adapter
sends data cyclically based on a configured time value. Data is
independently received cyclically from the sender . Data in both
directions can be acknowledged or unacknowledged
depending on the run time configuration of the system.
MACID Media Access Control Identifier (DeviceNet network address).
Master A DeviceNet network device (e.g., 1771-SDN) that initiates
communication with DeviceNet slave devices (e.g.,
ArmorPoint I/O modules) to retrieve data. The master only
receives unprompted data when the slave is enabled for COS
and there is a change in the device’s operating state.
Max Backplane MACID The 1738-ADNX has a unique attribute, Max(imum)
Backplane MACID. This value represents the highest node
address of a module residing on the backplane. This value
must be greater than or equal to the right most backplane
ArmorPoint I/O module, but must be less than that of any
non-backplane Subnet module.
Offline State of the adapter when it is not powered or maintaining
normal communication exchanges with other DeviceNet
devices.
Online State of the adapter when it is powered and maintaining
normal communication exchanges with other DeviceNet
devices.
PointBus The ArmorPoint I/O backplane PointBus maintains all
DeviceNet network protocol but also offers configuration
capabilities.
Polled DeviceNet communications method in which a module sends
data in response to received data.
Primary Network The primary DeviceNet network is defined as the DeviceNet
link that provides the direct connection between the
ArmorPoint DeviceNet adapter and a DeviceNet scanner.
RSNetWorx for DeviceNet Configuration software for the adapter and Subnet modules.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Scanlist The list of Subnet modules connected to the adapter. When
ADR is active, the scanlist stores the configured values of
each of the Subnet modules’ configurable parameters. When
ADR is not active, the scanlist stores only the module identity
information.
Scanner Operating state of the ArmorPoint DeviceNet adapter when it
retrieves I/O data from Subnet modules.
Slave A DeviceNet network device that cannot initiate
communication (except when configured with COS enabled)
but responds to a DeviceNet master device.
Strobe Adapter sends data in response to the strobe command. The
single bit allocated to the adapter in the strobe message is not
used. If the configured size of the input data (sent from the
adapter) is greater than 8 bytes, the strobe connection
establishment will fail. In this case, the input size must be
reconfigure to 8 bytes or less.
Page 7
Term: Definition:
Subnet 1738-ADNX only.
The Subnet DeviceNet network is defined as the DeviceNet
link that provides the expansion of the PointBus to let the
1738-ADNX use its lower connector to add an additional 500
meters and up to 63 nodes. These nodes will be bridged
through the 1738-ADNX up to the primary network. Note that
backplane modules are also part of the Subnet.
Preface 5
Related Products and
The following table lists related ArmorPoint I/O products and
documentation:
Documentation
Description Cat. No. Publication
ArmorPoint 24V dc Output Modules Installation Instructions 1738-OB2E, -OB2EP, -OB4E, -OV4E, -OB8E 1738-IN001
ArmorPoint 24V dc Input Modules Installation Instructions 1738-IB2, IB4, -IV4, -IB8, -IV8 1738-IN002
ArmorPoint 24V dc Analog Input Modules Installation Instructions 1738-IE2C, -IE2V 1738-IN003
ArmorPoint 24V dc Analog Output Modules Installation Instructions 1738-OE2C, -OE2V 1738-IN004
ArmorPoint RTD and Thermocouple Modules Installation Instructions 1738-IR2, -IT2I 1738-IN005
ArmorPoint AC Input Modules Installation Instructions 1738-IA2M12AC3, -IA2M12AC4 1738-IN006
ArmorPoint AC Output Module Installation Instructions 1738-OA2M12AC3 1738-IN007
ArmorPoint Relay Output Modules Installation Instructions 1738-OW4M12, -OW4M12AC 1738-IN008
ArmorPoint RS232 ASCII Module Installation Instructions 1738-232ASCM12 1738-IN009
ArmorPoint RS485 ASCII Module Installation Instructions 1738-485ASCM12 1738-IN010
ArmorPoint 24V dc VHSC Module Installation Instructions 1738-VHSC24M23 1738-IN011
ArmorPoint 5V dc Incremental Encoder Module Installation Instructions 1738-IJM23 1738-IN012
ArmorPoint SSI Module Installation Instructions 1738-SSIM23 1738-IN013
ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapters Installation Instructions 1738-ADN12, -ADN18, -ADN18P, -ADNX 1738-IN014
ArmorPoint PROFIBUS Adapter Installation Instructions
1738-APB
ArmorPoint PROFIBUS Adapter User Manual 1738-UM002
ArmorPoint ControlNet Adapter Installation Instructions
1738-ACNR
ArmorPoint ControlNet Adapter User Manual 1738-UM003
ArmorPoint EtherNet/IP Adapter Installation Instructions
1738-AENT
ArmorPoint EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual 1738-UM004
ArmorPoint Extension Units Installation Instructions 1738-EXT1, -EXT3 1738-IN018
ArmorPoint Field Potential Distributor Installation Instructions 1738-FPD 1738-IN019
ArmorPoint I/O 24V dc Expansion Power Supply Installation Instructions 1738-EP24DC 1738-IN020
DeviceNet Media Design & Installation Guide N/A DNET-UM072
Industrial Automation Wiring and Grounding Installation Instructions N/A 1770-4.1
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
1738-IN015
1738-IN016
1738-IN017
Page 8

Preface 6
If you need more information on these products, contact your local
Rockwell Automation/Allen-Bradley distributor, integrator or sales
office for assistance. For more information on the documentation,
refer to the Allen-Bradley Publication Index, publication SD499.
Guidelines for Using Your Adapter
Conventions Used In This Manual
Remember the following operational guidelines when using your
ArmorPoint DeviceNet adapter.
• Do not leave spaces in the I/O. Instea d, instal l all ArmorPoint
I/O modules adjacent to each other.
• Populate every position on the mounting base.
• ArmorPoint does not support removal and insertion under
power (RIUP). When an I/O module is removed, the IP67 seal is
broken and the backplane bus is interrupted.
• Use Allen-Bradley terminal markers to identify your ArmorPoint
I/O modules.
For more information on the Allen-Bradley terminal marking
kits, see the documents list on page
The following conventions are used thro ughout this manual:
• bullet lists (such as this one) provide information, not
procedural steps
• numbered lists provide sequential steps
• text written like this identifies screen, menu, toolbar names, field
names, buttons, and check boxes on screens
• a menu item in this format File>Save identifies the submenu item
after the caret (>) that is accessed from the main menu (name
before the caret)
• pictures of symbols and/or scre ens represent th e actual symbols
you see or the screens you use
Preface-5.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 9

Install the ArmorPoint
DeviceNet Adapters
What Is the ArmorPoint
DeviceNet Adapter?
Table Of Contents
Chapter 1
Mount the Adapter and I/O Base. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
Set the Node Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
Wire the DeviceNet Adapters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
1738-ADN12 and 1738-ADNX. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
1738-ADN18 and 1738-ADN18P . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
1738 ArmorPoint DeviceNet Auxiliary Power . . . . . . . . 1-4
Chapter Summary and What’s Next . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
Chapter 2
Use the Adapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
Set Subnet/Backplane Baudrate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
Set Subnet/Backplane I/O Module Addresses . . . . . . . . 2-3
Configure the Subnet I/O. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
Configure the Primary DeviceNet Network . . . . . . . . . . 2-4
Remove and Reinsert Modules on the Backplane . . . . . 2-5
Understand the DeviceNet Network and Subnet. . . . . . . . . 2-6
DeviceNet Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-6
Backplane/Subnet Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-7
Adapter Features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-8
Communicate Through the Adapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-18
Map the Data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-18
Overview of the Communication Process . . . . . . . . . . . 2-19
Image Table Mapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-20
Communicate With I/O Modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-23
Use Diagnostic Tables. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-24
Chapter Summary and What’s Next . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-26
Chapter 3
Use Auto Start Mode
i Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Why Use Auto Start Mode? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
What Does Auto Start Mode Do?. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
How Is I/O Data Mapped Using Auto Start Mode?. . . . . 3-3
Requirement To Using Auto Start Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-4
Install the I/O Module. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-4
Remove the Module From the Mounting Base. . . . . . . . 3-5
Use RSNetWorx for DeviceNet. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-5
Begin Auto Start Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-7
Use Custom Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-9
Chapter Summary and What’s Next . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-10
Page 10

ii
Configure the DeviceNet
Scanner Subnet
Add the ArmorPoint DeviceNet
Adapter to the DeviceNet
Scanner’s Scanlist
Troubleshoot the ArmorPoint
DeviceNet Adapter
Chapter 4
Configuration Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
Add the Scanner To Your Network. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-2
Add I/O Modules To Your Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
Set the Scanner’s Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
Go On Line . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-8
Chapter Summary and What’s Next . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-8
Chapter 5
Configuration Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-1
Add the Adapter to Your Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-2
Set the Adapter’s Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3
Go On Line . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-6
Chapter Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-6
Chapter 6
Use the Status Indicators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-1
Guidelines for Using Your Adapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-3
Chapter Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-3
Specifications
Quick Start For the 1738-ADNX
Rules and Guidelines For
the 1738-ADNX
Appendix A
Appendix B
What’s In This Appendix? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-1
Assumptions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-1
Review of the 1738-ADNX Rules and the MACID Parameter B-9
Review of Auto Start Mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-11
Browse the Subnet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-15
Inputs and Outputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-19
Navigate Between Networks. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-24
Appendix C
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 11

Default Data Maps
iii
Appendix D
1738-IA2 Input Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . D-2
1738-IB2 Sink Input Module. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . D-2
1738-IB4 Sink Input Module. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . D-2
1738-IB8 Sink Input Module. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . D-3
1738-IV4 Source Input Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . D-3
1738-IV8 Source Input Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . D-3
1738-OA2 Output Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . D-4
1738-OB2E Electronically Protected Output Module . . . D-4
1738-OB2EP Protected Output Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . D-4
1738-OB4E Electronically Protected Output Module . . . D-5
1738-OB8E Electronically Protected Output Module . . . D-5
1738-OV4E Protected Sink Output Module . . . . . . . . . . D-6
1738-OW4 Relay Sink/Source Output Module . . . . . . . . D-6
1738-IE2C Analog Current Input Module. . . . . . . . . . . . D-7
1738-IE2V Analog Input Module. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . D-8
1738-OE2C Analog Current Output Module. . . . . . . . . . D-9
1738-OE2V Analog Output Module. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . D-9
1738-IJ Encoder/Counter Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . D-10
1738-IR2 RTD Input Module. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . D-10
1738-IT2I Isolated Thermocouple Input Module . . . . . D-11
1738-VHSC 24V dc High Speed Counter Module . . . . . D-12
1738-SSI Synchronous Serial Interface Absolute
Encoder Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . D-12
1738-232ASC ASCII Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . D-13
1738-485ASC ASCII Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . D-13
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 12

iv
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 13
Chapter
1.9 in.
2.0 in.
0.87 in.
2.0 in.
0.87 in.
2.0 in.
Drilling Dimension Drawing
1
Install the ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapters
This chapter describes how to install and wire your adapter.
See the following sections: Page:
Mount the Adapter and I/O Base 1-1
Set the Node Address 1-2
Wire the DeviceNet Adapters 1-3
Chapter Summary and What’s Next 1-4
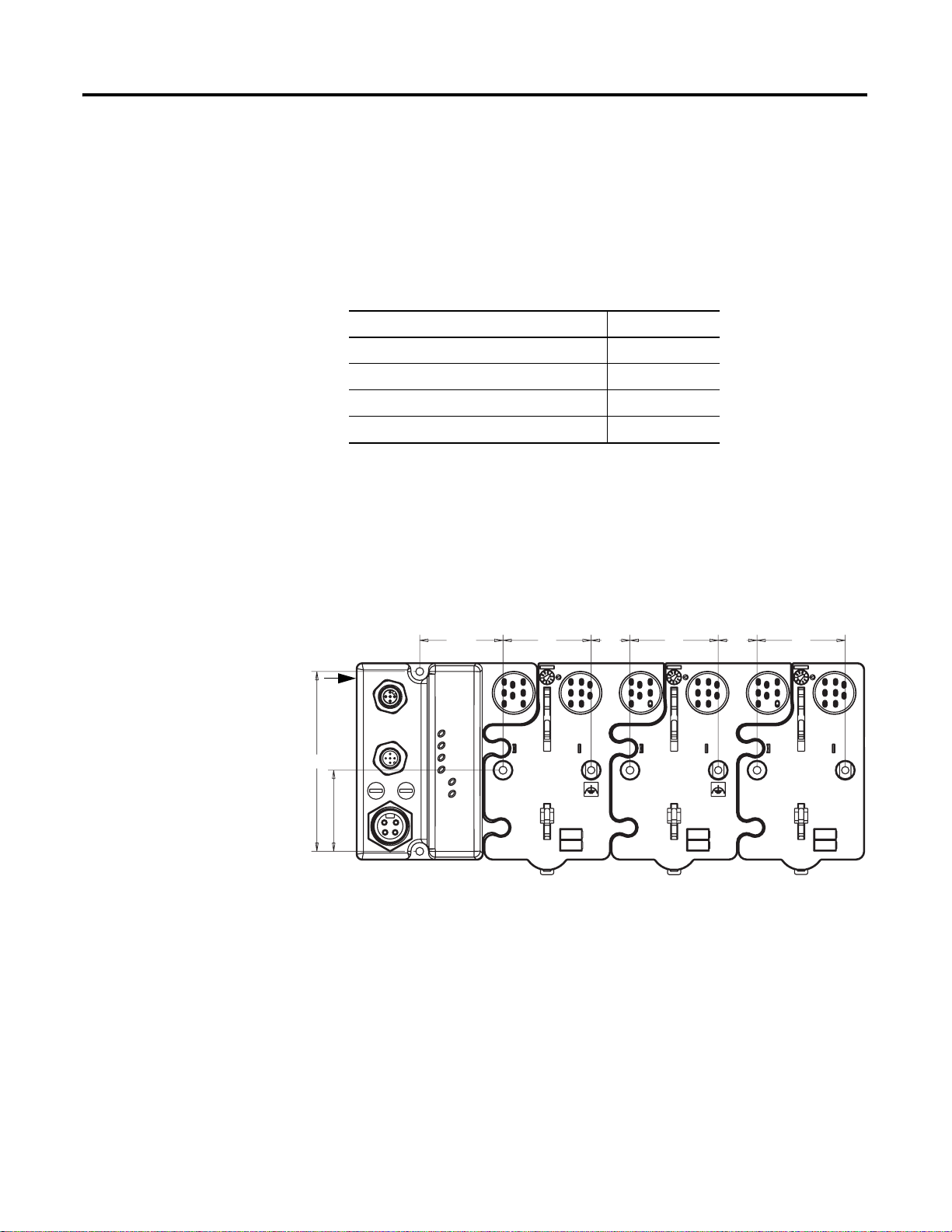
Mount the Adapter and I/O Base
Adapter
4.02 in.
102 mm
To mount the ArmorPoint adapter on a wall or panel, use the screw
holes provided in the adapter.
A mounting illustration for the ArmorPoint adapter with I/O bases is
shown below.
47.2 mm
1.81 in.
46 mm
50 mm
22 mm
50 mm
22 mm
Install the mounting base as follows:
1. Lay out the required points as shown in the drilling dimension
drawing.
50 mm
43769
2. Drill the necessary holes for #8 (M4) machine or self-tapping
screws.
3. Mount the adapter and I/O bases using #8 (M4) screws.
4. Ground the system using the ground lug connection in the I/O
base. (The ground lug connection is also a mounting hole.)
1 Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 14
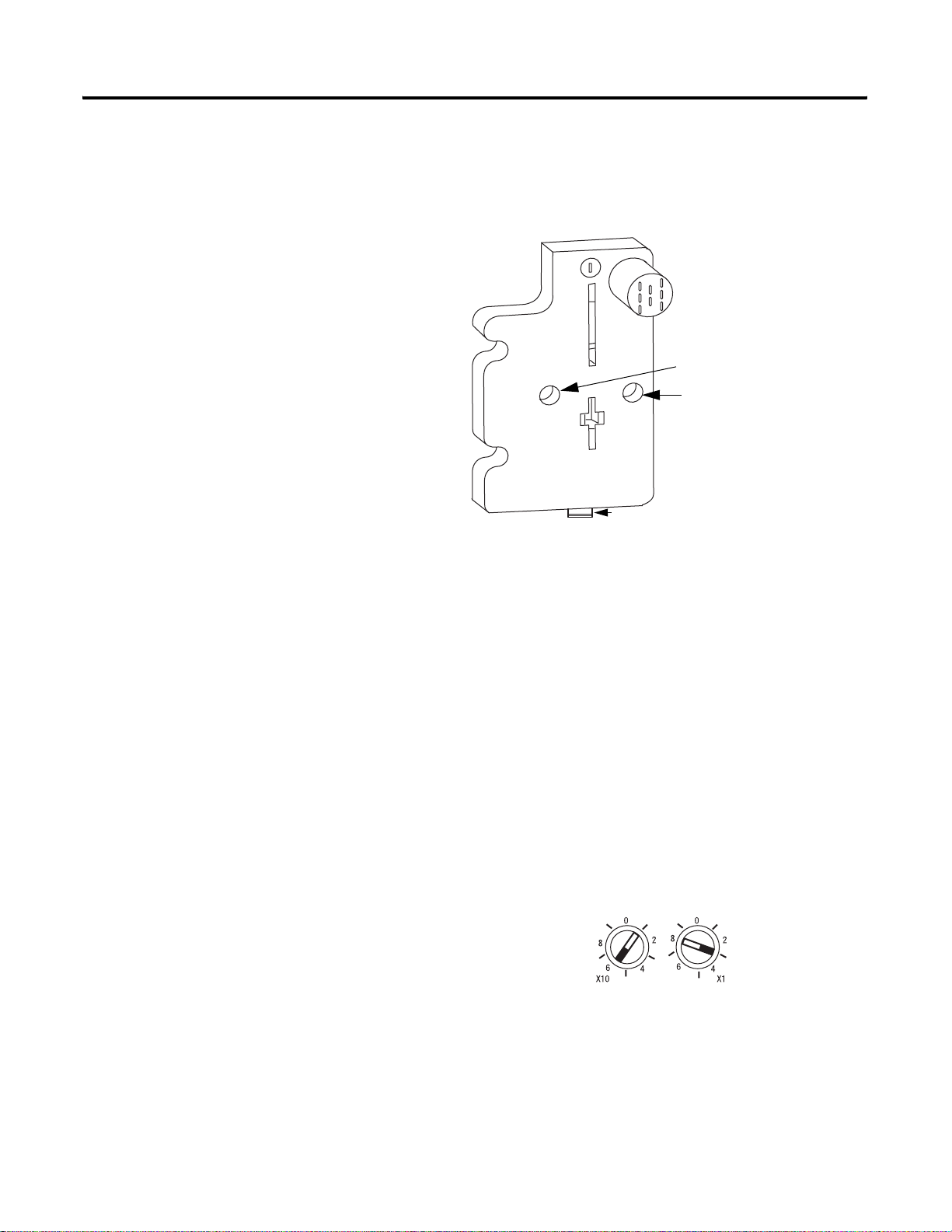
1-2 Install the ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapters
5. Mount the terminating base that was shipped with the adapter as
the last base in the backplane instead of the base that was
shipped with the I/O module.
Terminating base
Mounting hole
Ground connection
Set the Node Address
Latching mechanism holes
43787
Valid node addresses are 00 through 63.
Set the node address using either the rotary switches, RSNetWorx for
DeviceNet, DeviceNetManager, or another software configuration
tool. Setting the switches at any number from 64 through 99 lets the
software have address control.
Each module is shipped with the switches set for node address 63.
Remove the caps on the front of the module to access the switches
(refer to the X10 and X1 on the front of the module). The two
switches are:
• X10 (most significant digit) - left side of module
• X1 (least significant digit) - right side of module
This example shows the
node address set at 63.
31433-M
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
To reset the node addre ss, use a sma ll blade screwdriv er to rotate the
switches. Line up the small notch on the switch with the number
setting you wish to use and then cycle power.
Page 15
Install the ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapters 1-3
M
The rotary switches are read periodically. If the switches have been
changed since the last time they were read and th ey no longer match
the on line address, a minor fault will occur, which is indicated by a
flashing red Adapter Status LED. Settings of 64 through 99 cause the
module to use the last valid node address stored internally
. For
example, the last setting internal ly was 40. If a change is made to 68,
and then you power up, the address will default to 40.
The module is equipped with AutoBaud detect. AutoBaud lets the
module read the settings already in use on your DeviceNet network
and automatically adjusts to follow those settings.
Wire the DeviceNet Adapters
Following are wiring instructions for the ArmorPoint DeviceNet
adapters.
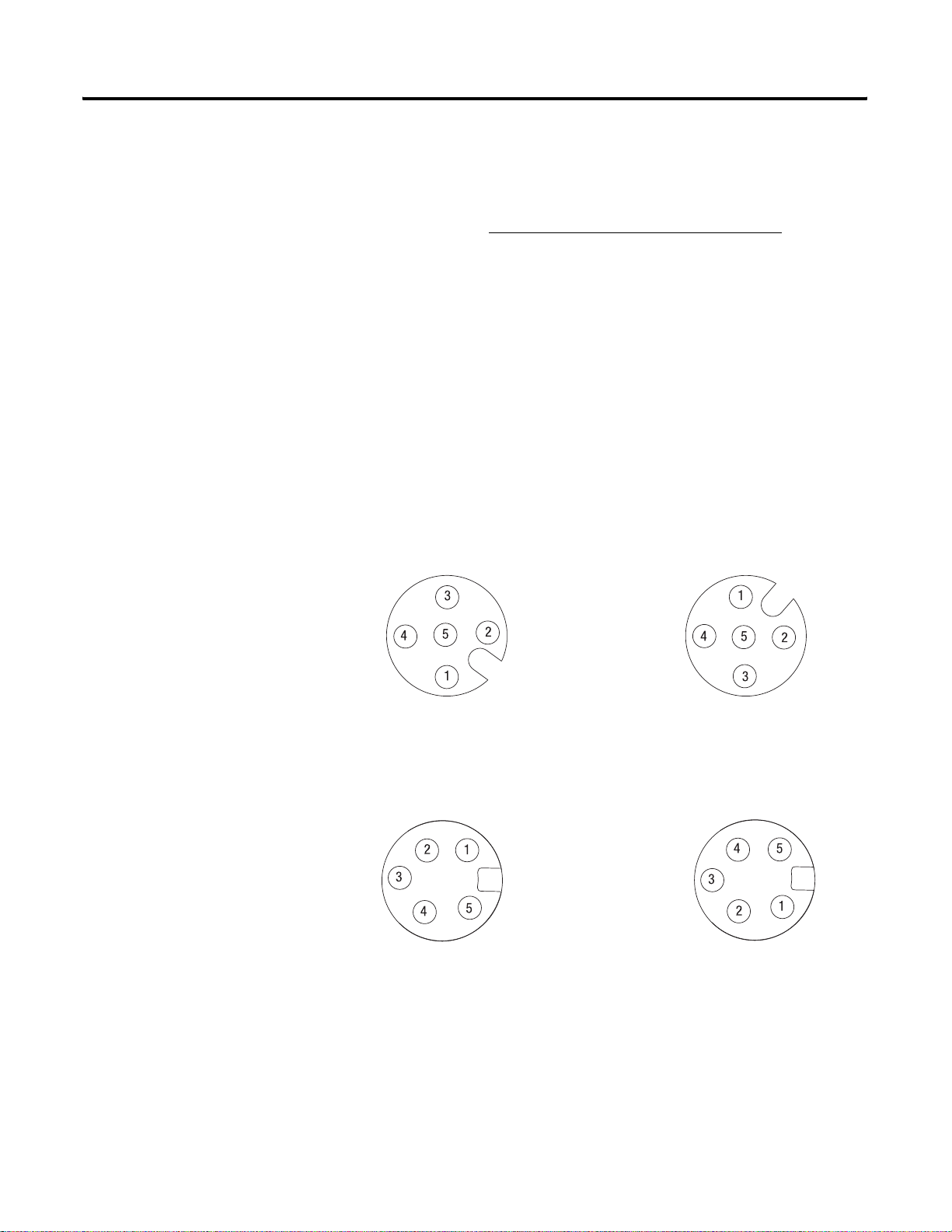
1738-ADN12 and 1738-ADNX
ale In Connector Female Out Connector (1738-ADN12)
(Subnet Out - 1738-ADNX only)
(view into connector)
Pin 1 - Drain
Pin 2 - +V
Pin 3 - -V
Pin 4 - CAN_High
43763
Pin 5 - CAN_Low
43764
1738-ADN18 and 1738-ADN18P
Male In Connector Female Out Connector
(1738-ADN18P only)
43746
(view into connector)
Pin 1 - Drain
Pin 2 - +V
Pin 3 - -V
Pin 4 - CAN_High
Pin 5 - CAN_Low
43749
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 16
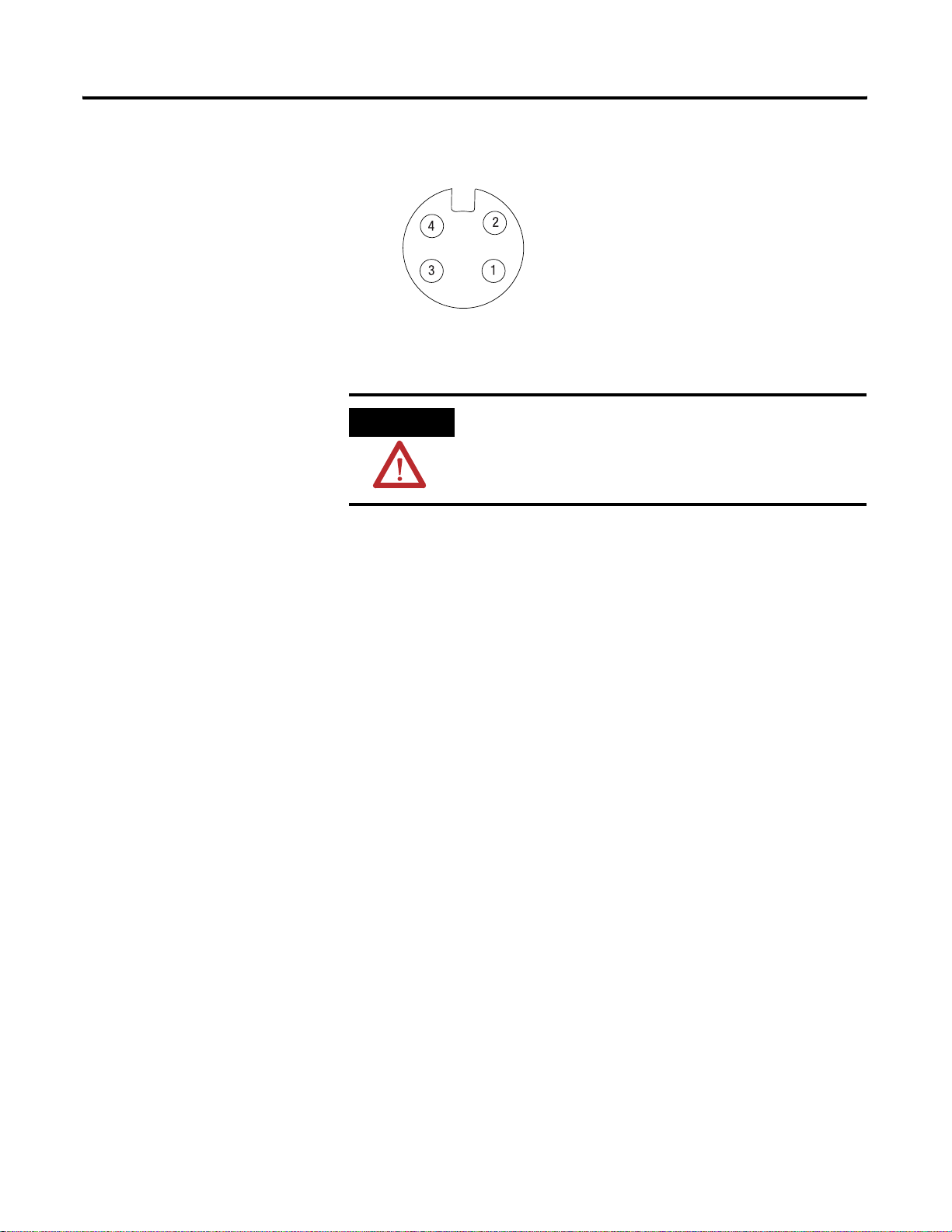
1-4 Install the ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapters
1738 ArmorPoint DeviceNet Auxiliary Power
Male In Connector
(view into connector)
Pin 1 - User Power +
Pin 2 - Adapter Power +
Adapter/Subnet + (1738-ADNX only)
Pin 3 - Adapter Power -
43587
Pin 4 - User Power -
Adapter/Subnet - (1738-ADNX only)
Chapter Summary and What’s Next
ATTENTION
Make sure all connectors and caps are securely
tightened to properly seal the connections against
leaks and maintain IP67 requirements.
In this chapter , you learned how to install and wire your DeviceNet
adapter. Move to chapter 2 to learn about the ArmorPoint DeviceNet
adapters.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 17

Chapter
2
What Is the ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapter?
This chapter describes the ArmorPoint I/O DeviceNet adapter,
including descriptions of the adapter’s features and functionality.
See the following sections: Page:
Use the Adapter 2-2
Understand the DeviceNet Network and Subnet 2-6
Adapter Features 2-8
Communicate Through the Adapter 2-18
Communicate With I/O Modules 2-23
Use Diagnostic Tables 2-24
Chapter Summary and What’s Next 2-26
1 Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - Februa ry 2005
Page 18
2-2 What Is the ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapter?
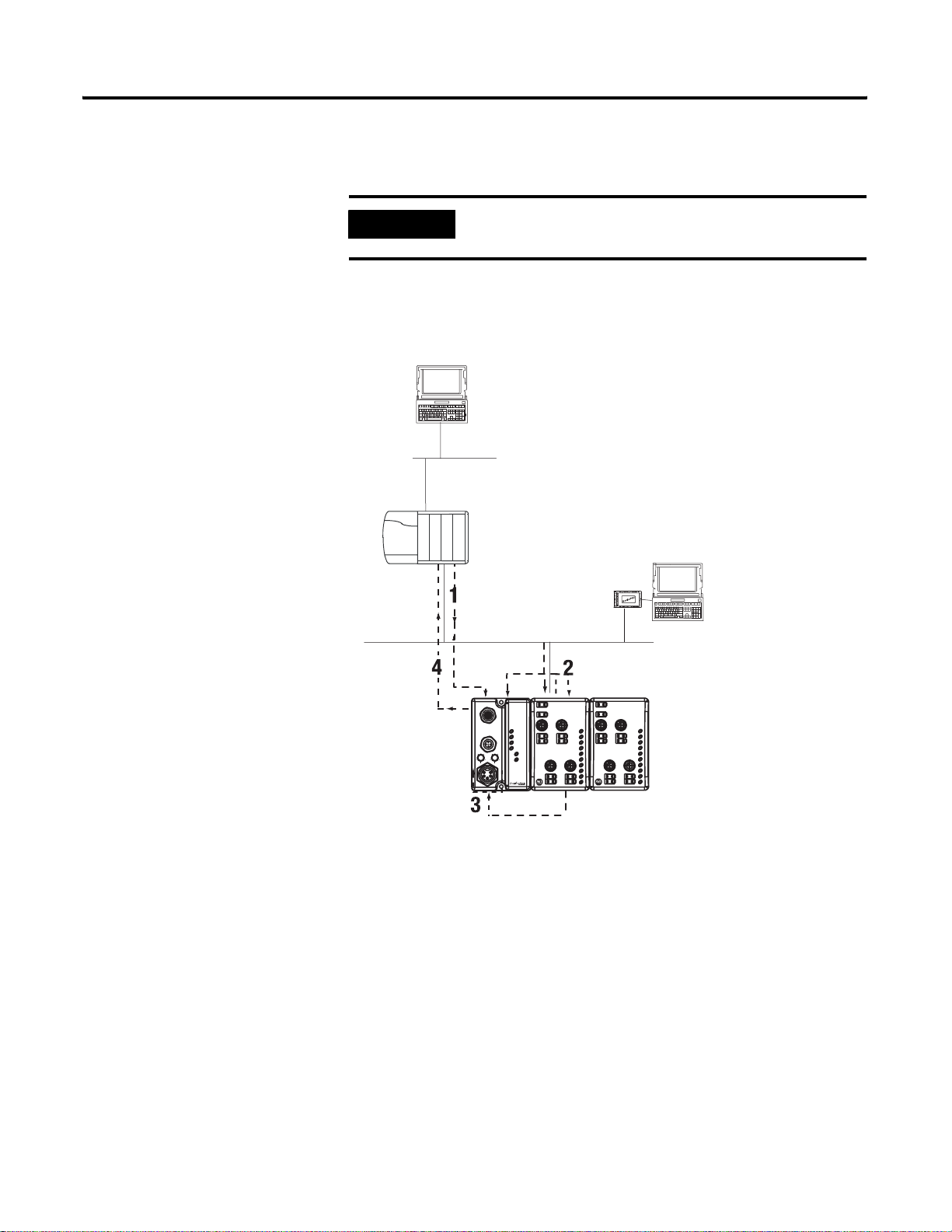
Use the Adapter
The adapter resides on the primary DeviceNet network and the
Subnet simultaneously.
The adapter interfaces between DeviceNet devices and ArmorPoint
I/O modules. The graphic below shows the adapter on the DeviceNet
network and PointBus.
ControlLogix chassis
IMPORTANT
The PointBus maintains all DeviceNet network
protocol but also offers configuration capab ilities.
computer with PLC
programming software
ControlNet network
1784-PCD
PCMCIA card
computer with
RSNetWorx for
DeviceNet software
DeviceNet network
See page 2-19 for an
explanation of the number
sequence.
ArmorPoint I/O modules
1738-ADN12 adapter
Subnet (1738-ADNX only)
DeviceNet Out
DeviceNet In
8
x10
PWR
1738-IB8M12
1738-ADN12
0
0
2
2
8
6
6
4
4
x1
Adapter
Status
DeviceNet
Status
PointBus
Status
System
Power
Adapter
Power
24V dc In
02
13
46
57
MOD
NET
02
13
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
1738-OB8EM12
24V dc Out
MOD
NET
0
1
43852
2
3
4
6
4
5
7
5
6
7
After you have installed your adapter into a ArmorPoint I/O system,
you must perform the following tasks:
1. Set Subnet/Backplane Baudrate
2. Set Subnet/Backplane I/O Module Addresses
3. Configure the Subnet I/O
4. Configure the Primary Device Net Network
The steps mentioned above are explained briefly here and then in
greater detail throughout this manual. Y ou must complete the steps for
the adapter to work with DeviceNet masters (e.g., 1756-DNB) on the
primary network and Subnet modules.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 19

What Is the ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapter? 2-3
1. Set Subnet/Backplane Baudrate
The adapter and Subnet/Backplane modules must use the same
baudrate to communicate with each other. Use one or both of the
following to set a Subnet/Backplane baudrate.
• Enable or disable the Backplane Autobaud feature for
ArmorPoint I/O modules. ArmorPoint I/O modules have
Autobaud enabled as the default- See page
• Set the adapter baudrate for the Subnet. The default for the
1738-ADN12, -ADN18, and -ADN18P is 1Mbaud. The default for
the 1738-ADNX is 125Kbaud - See page
You set the backplane baudrate for the 1738-ADN12, -ADN18,
and -ADN18P. You set the Subnet baudrate for the 1738-ADNX.
2-12.
2-9.
2. Set Subnet/Backplane I/O Module Addresses
Once the adapter and ArmorPoint I/O modules are communicating at
the same rate on the backplane, you must make sure all modules use
a valid MACID.
Set the Auto Address feature for ArmorPoint I/O modules - See
page 2-13.
For the 1738-ADNX, a DeviceNet configuration tool, such as
RSNetW orx for DeviceNet, may be required to set the node addre ss. (if
node address switches are not present on the Subnet device).
3. Configure the Subnet I/O
In the first two steps, you set a consistent communication rate and
made sure each module uses valid addresse s for communication. Next
you must configure the PointBus (e.g., set scan list).
You can configure the PointBus using one of two methods:
• Auto Start Mode (ASM) or
• Manually
For more information on configuring the PointBus, see Chapter 3 for
ASM or see Chapter 4 for manual configuration.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - Februa ry 2005
Page 20

2-4 What Is the ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapter?
4. Configure the Primary DeviceNet Network
Finally, you must configure the adapter for communication with a
master (e.g., 1756-DNB).
For more information on configuring the Devic eNet network, see
Chapter 5, Add the ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapter to the DeviceNet
Scanner’s Scanlist.
You must understand all of the adapter’s features to effectively use it
in your ArmorPoint I/O system. Keep these four steps in mind as you
read this manual:
1. Set Subnet/Backplane Baudrate
2. Set Subnet/Backplane I/O Module Addresses
3. Configure the Subnet I/O
4. Configure the Primary Device Net Network
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 21

What Is the ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapter? 2-5
Remove and Reinsert Modules on the Backplane
Removal and Insertion Under Power (RIUP) is not recommended in a
ArmorPoint System because of the following reasons.
• Removing a module breaks the IP 67 seal.
• Removing a module breaks the backp lan e bu s. Mod ule s to the
right of the removed module will be ‘lost’ to the adapter. Also,
the terminating resistor will be removed, causing system
uncertainty.
• Inserting a module under power may cause the adjacent module
to reset due to the addition of a large capacitive load on the
power bus.
IMPORTANT
If the module is removed wh ile it is under power, all
the modules to the right of the removed module will
disconnect from the PointBus and field power until
the module is reinstalled.
If you must remove and reinsert modules, we recommend the
following:
• Do not move I/O modules to different locations on the
mounting base after they have been installed and configured.
• If adjacent modules (i.e., 2 or more) are remo ved from the
backplane, replace all of them before attempting to operate the
ArmorPoint I/O system. Input data will hold last state until all
previously removed modules are replaced.
– If adjacent modules are removed and all but one is returned,
the adapter cannot verify the location of the returned
modules. For example, if modules are removed from node s 3
and 4 and only the module from node 4 is returned, the
adapter cannot verify the location. In this case, the adapter
alerts you via a flashing red PointBus status LED that it cannot
verify the presence of modules in the affected locations. I/O
data will not be exchanged with this node until both modules
have been reinserted.
– If modules of different types are removed and returned to
the wrong locations, the adapter identifies the returned
modules and alerts you (via RSNetWorx for DeviceNet) that
the error has occurred and must be corrected.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - Februa ry 2005
Page 22
2-6 What Is the ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapter?
– If modules of the same type are removed and returned to the
wrong locations, the adapter identifies the returned modules,
updates their MACIDs, and continues operation.
IMPORTANT
IMPORTANT
The removal and return scenario ex ists whether the
system is under power or not. If the system is under
power, the scenario arises immediately. If the system
is not under power, the scenario arises in the next
power cycle.
Also, the example above shows removal of two
adjacent modules. The scenario described exists
anytime 2 or more adjacent modules are removed
and all are not returned.
Care must be taken when replacing backplane I/O
modules. Each I/O module stores its configuration
parameters in internal non-volatile memory. You
must either enable ADR for all modules or manually
configure each module in a non-manufacturing
environment when the module is being replaced or
placed on the network for the first time. Failure to do
so could result in inadvertent control attributed to
different configuration settings.
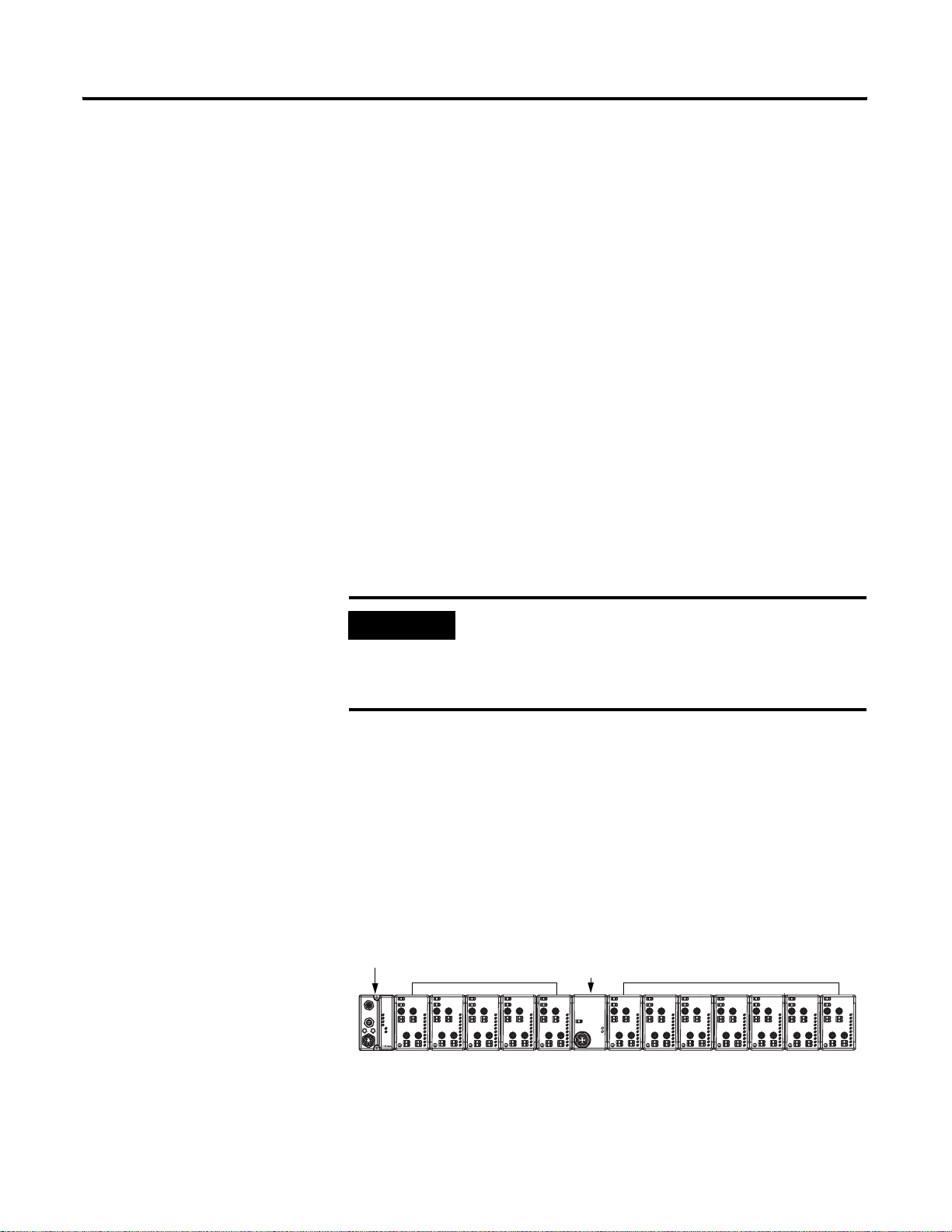
Understand the DeviceNet Network and Subnet
DeviceNet Network
Your adapter serves as a slave to DeviceNet masters. The adapter
receives data from and returns data to the master through the
following I/O connections:
• Change of State (COS)
• Cyclic
• Polled
• Strobe
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 23
What Is the ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapter? 2-7
1
Backplane/Subnet Network
On the Backplane/Subnet, your adapter acts as a scanner and is the
master of the Subnet modules. The adapter performs the following
functions:
• Exchanges I/O data with devices on the Backplane/Subnet
• Collects I/O data from the Backplane/Subnet and sends it to
devices on the DeviceNet network (e.g., scanners or controllers)
• Supplies power to the backplane I/O modules (See Appendix A
for power supply rules regarding I/O modules power
requirements.)
Data Collection
The adapter collects I/O data from up to 63 modules via the
Backplane/Subnet. The I/O modules appear on the primary
DeviceNet network as a single node, though, and require only one
DeviceNet node address.
IMPORTANT
If Automatic Device Replacement (ADR) is enabled
on the adapter, you can only connect up to 62
modules via the Subnet.
For more information on ADR, see page 2-15.
Module Power
The adapter supplies 5V logic power to ArmorPoint I/O modules by
converting 24V dc field power to PointBus 5V power.
You can connect up to 63 I/O modules to each adapter and you can
power the backplane I/O modules from the adapter (with a maximum
of 10A of field power). You may use the integrated, isolated 24V dc
expansion power unit (1738-EP24DC) to power additional I/O
modules, as shown below.
738-ADN12 adapter
1738-OB8EM12
1738-IB8M12
1738-ADN12
24V dc In
02
System
Power
Adapter
Power
13
46
57
02
13
MOD
NET
0
1
2
4
3
4
5
5
6
7
DeviceNet Out
Adapter
Status
DeviceNet In
DeviceNet
Status
PointBus
Status
0
0
2
2
8
8
6
6
4
4
x1
x10
PWR
24V dc Out
02
MOD
13
NET
0
1
2
46
3
6
4
5
7
57
6
7
ArmorPoint I/O
modules
1738-OB8EM12
1738-IB8M12
24V dc Out
24V dc In
02
MOD
13
MOD
NET
NET
0
1
2
4
3
6
4
5
7
5
6
7
1738-EP24DC
expansion power unit
1738-IB8M12
24V dc Power Supply
24V dc In
02
MOD
13
NET
0
0
1
1
2
2
46
3
3
4
4
5
5
57
6
6
7
7
ArmorPoint I/O
modules
1738-OB8EM12
1738-EP24DC
24V dc Out
02
MOD
13
NET
0
1
SYSTEM
2
POWER
FIELD
3
4
6
POWER
P
A
O
U
W
X
E
R
4
5
7
5
6
7
02
13
46
57
1738-OB8EM12
1738-IB8M12
24V dc Out
24V dc In
MOD
NET
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
02
13
4
5
02
MOD
13
NET
0
1
2
3
6
4
5
7
6
7
1738-IB8M12
24V dc In
46
57
MOD
NET
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
1738-OB8EM12
02
13
4
5
24V dc Out
02
MOD
13
NET
0
1
2
3
6
4
5
7
6
7
24V dc In
46
57
24V dc Out
02
MOD
13
MOD
NET
NET
0
0
1
1
2
2
3
4
3
6
4
4
5
5
7
5
6
6
7
7
1738-OB8EM12
1738-IB8M12
43851
For more information on the 1738-EP24DC expansion power unit, see
the ArmorPoint I/O 24V dc Expansion Power Supply Installation
Instructions, publication 1738-IN020.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - Februa ry 2005
Page 24

2-8 What Is the ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapter?
Adapter Features
Your adapter uses the following features on both the DeviceNet
network and the PointBus:
• Self-Test
• Field Upgradable Firmware
• Fully Configurable Software
• Connections
• Baudrates
Self-Test
When power is applied to the adapter, the adapter performs a
self-test. The adapter tests various internal and programmatic
memories and checks the status indicators (LEDs).
Field Upgradable Firmware
You can update the adapter’s firmware with the ControlFlash Utility
software. This feature lets you always use the most current firm ware.
Fully Software Configurable
The adapter is fully software configurable using RSNetWorx for
DeviceNet. You must configure the adapter to be used with a
DeviceNet master (e.g., 1756-DNB) and separately to be used with
Subnet devices.
For more information on how to configure your adapter to use with a
DeviceNet master, see Chapter 5, Add the ArmorPoint DeviceNet
Adapter to the DeviceNet Scanner’s Scanlist.
For more information on how to configure your adapter to use with
Subnet modules, see Chapter 4, Configure the DeviceNet Scanner
Subnet.
Connections
Y o ur adapter supports the following connections on both the primary
DeviceNet network and Subnet:
• I/O connections:
– Polled
– Strobe
– Cyclic
– COS
• Explicit connections
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 25

What Is the ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapter? 2-9
You can use I/O mapping to determine the data contained in each
connection.
The adapter supports Master/Slave connection types on the DeviceNet
network. On the Subnet, the adapter functions as a scanner device,
exchanging data with I/O modules.
Baudrates
Choose baudrates for the adapter in the RSNetWorx for DeviceNet
software. The adapter supports these rates:
• 125Kbaud
• 250Kbaud
• 500Kbaud
• Autobaud - The adapter detects the primary DeviceNet network
baudrate and automatically sets its own baudrate to match
the network.
• For the 1738-ADN12, -ADN18, and -ADN18P, the Po intBus can
be configured to operate at 1Mbaud (1000Kbaud).
• For the 1738-ADNX, the Subnet can be configured to operate at
125K, 250K, and 500K baud only.
Auto Start Mode
Auto Start Mode lets you easily get your adapter installed and
operating. In this mode, the adapter’s configurable features operate as
they were most recently configured. For example, if Autobaud on
DeviceNet was enabled in the adapter’s last configuration, it will be
enabled when Auto Start Mode is used.
For a more detailed explanation of how to use Auto Start Mode, see
Chapter 3.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - Februa ry 2005
Page 26

2-10 What Is the ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapter?
Auto Catalog Replace
Auto Catalog Replace corrects errors that might occur when backplane
modules of the same type are removed and replaced in the wrong
location. If modules of the same ty pe are removed and returned to th e
wrong locations, the adapter identifies the returned modules, updates
their MAC IDs, and continues operation.
IMPORTANT
If modules of different types are removed and
returned to the wrong locations, the adapter
identifies the returned modules and alerts you (via
RSNetWorx for DeviceNet, the Node Status Table,
and the Faulted Node Table) that the error has
occurred and must be corrected.
Backplane (1738-ADN12, -ADN18, -ADN18P)/Subnet (1738-ADNX) Baudrate
EDS parameter Backplane Baudrate is accessible from the primary
DeviceNet and sets a specific baudrate for all backplane I/O modules.
Set this parameter in RSNetWorx for DeviceNet to one of the
following baudrates:
• 125 Kbaud
• 250 Kbaud
• 500 Kbaud
• 1 Mbaud (available for all the ArmorPoint DeviceNet adapters
except the 1738-ADNX)
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
When you download this parameter , the adapter sends a command to
reset all present I/O modules on the backplane to the new baudrate.
If additional modules are connected to the adapter, you must
download the Backplane/Subnet Baudrate to make sure the new
modules use the same rate as the others.
Page 27

What Is the ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapter? 2-11
The baudrate may not take effect until power is recycled or the I/O
modules are reset.
IMPORTANT
Changes to the Backplane/Subnet Baudrate
parameter only take effect if they are downloaded on
an individual basis. (For example, if you change the
Backplane/Subnet Baudrate and download the
changes with additional changes to other features,
the Backplane/Subnet Baudrate remains at the
previous setting.)
Also, this parameter should be set to ‘Do Nothing’
when you download all parameters or when
Automatic Device Replacement is enabled for
the adapter.
If you want to set an I/O module to use a specific
baudrate (i.e., 125, 250, 500), you must first disable
Backplane Autobaud for that module.
Backplane/Subnet Baudrate performs the following functions:
• Sets the adapter’s Subnet baudrate
• Sends a message to all connected backplane I/O modules. If an
I/O module is set to autobaud, it receives the message but
ignores the new baudrate.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - Februa ry 2005
Page 28
2-12 What Is the ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapter?
Backplane Autobaud
The adapter itself never autobauds on the Subnet. Backplane
Autobaud automatically enables or disables Autobaud for all I/O
modules currently attached to the backplane. The adapter does not set
a specific rate though (as with Backplane Baudrate).
If you enable Backplane Autobaud in the adapter or the EDS
parameter access that you set from the primary DeviceNet, the adapter
only enables the Autobaud in all backplane I/O modules. When the
modules listen to communications on the DeviceNet network, they
detect the rate of communication and auto matically set their own
baudrates to match the network rate.
The module does not automatically detect the backplane baudrate
until power is cycled or the module is reset.
TIP
Autobaud, when enabled, is useful if you swap
ArmorPoint I/O modules between networks that are
operating at different baudrates.
Enable Backplane Baudrate in RSNetWorx for DeviceNet.
IMPORTANT
Changes to the Backplane Autobaud parameter only
take effect if they are downloaded on an individual
basis. (For example, if you enable the Backplane
Autobaud setting and download the change with
additional changes to other features, the Backplane
Baudrate remains disabled.)
This parameter should be set to ‘Do Nothing’ when
you download all parameters or when Automatic
Device Replacement is enabled for the adapter.
If you want to set an I/O module to use a specific
baudrate (i.e., 125, 250, 500), you must first disable
Autobaud for that module.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 29
What Is the ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapter? 2-13
Auto Address
The EDS parameter Auto Address is available from the primary
DeviceNet and lets the user sequentially order the node ad dresses of
backplane I/O modules. This parameter is not a mode but occurs on a
single occurrence only. The node address sele cte d is assigned to the
module closest to the adapter. The next closest module is assi gned the
next numerically higher value. The numbering pattern continues for
all connected backplane I/O modules.
Enable this parameter in the RSNetWorx for DeviceNet software.
IMPORTANT
Changes to the Auto Address parameter only take
effect if they are downloaded on an individual basis.
(For example, if you enable the Auto Address and
download the changes with additional changes to
other features, the node addresses of the I/O
modules remains disabled.)
This parameter should be set to ‘Do Nothing’ when
you download all parameters or when Automatic
Device Replacement is enabled for the adapter.
Physical List Acquire Status
The adapter maintains a physical list that indicates the order of the
node addresses of all ArmorPoint I/O modules present on the
backplane. Physical List Acquire Status shows the status of this
physical list acquire process.
The adapter requires that each backplane I/O module has a MACID
greater than that of its neighbor to its immediate left. The list is
created when power is applied to the adapter and each time a module
is inserted on the backplane.
The valid values are:
• Idle
• Busy
• Auto Start Mode
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - Februa ry 2005
Page 30

2-14 What Is the ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapter?
Cycling Node Status
Using the Cycling Node Status parameter, you can easily determine
the status of any ArmorPoint I/O modules with which the adapter is
experiencing problems. A corresponding text string appears, including
the MAC ID, and a description of the status code reported in the Node
Status Table. For more information on the Node Status Table,
see page 2-24.
For the connection sizes mentioned below, the I/O connection sizes
on DeviceNet are dependent on the scanlist configuration on the
backplane.
Poll/COS Connection Consume Size
Poll/COS Connection Consume Size shows the size (number of data
bytes) consumed by the poll/COS (Instance 2) I/O connection on the
primary DeviceNet.
Poll Connection Produce Size
Poll Connection Produce Size shows the size (number of data bytes)
produced by the polled (Instance 2) I/O connection on the primary
DeviceNet.
COS/Cyclic Connection Produce Size
COS Produce Size shows the size (number of data bytes) prod uced by
the Change of State I/O connection on the primary DeviceNet.
Strobe Connection Produce Size
The Strobe Produce Size shows the size (number of data bytes)
produced by the Strobe I/O connection on the primary DeviceNet.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 31

What Is the ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapter? 2-15
Cycling I/O Mapping
Cycling I/O Mapping is an EDS parameter accessible from the primary
DeviceNet that shows you how data is mapped in the adapter’s
scanlist. The data, as shown below, is listed in order o f active modules
in the scanlist.
The data format is NN OBBB:b-BBB:b,IDBBB:b-BBB:b, where:
• NN = node number
• O or I = data type (output or input)
• BBB = byte number
• b = bit number
• D = DeviceNet connection (C [COS/cyclic], S [strobe], or P [poll])
IMPORTANT
If an I/O module’s data has multiple mappings, you
must use RSNetWorx for DeviceNet to browse to the
backplane to view the mappings.
Automatic Device Replacement
With Automatic Device Replacement (ADR), the adapter automatically
configures a new replacement module.
IMPORTANT
The replacement module must match the original
module (i.e., same vendor I.D., device type, product
code, major and minor revision) for ADR to work.
The parameters that must match are those selected in
the electronic keying portion of the scanlist. You
determine the level of electronic keying.
The backplane configuration parameters (e.g., Auto
Address) should be set to ‘Do Nothing’.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - Februa ry 2005
Page 32

2-16 What Is the ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapter?
The adapter is capable of holding approximately 64K of configuration
data for ArmorPoint I/O modules connected to it. The adapter sends
configuration data to an I/O module each time connections are
created with that module (i.e., power cycle or module insertion to
backplane).
You can exchange an old module for a new one if the following
conditions are met:
• ADR is enabled in the adapter.
• The new module matches the old one (i.e., electronic keying).
• The new module is inserted in the proper location (only for
modules using the backplane).
For modules that do not use the backplane, you can exchange an old
module for a new one if the following conditions are met:
• The MACID equals 63.
• The new module matches the electronic keying of the old
module.
• Only one missing module matches th e electronic keying of the
old module.
If the conditions listed above are met, the new module’s MACID is
changed to the appropriate value, if necessary, and the configuration
information is subsequently downloaded to the module.
Physical Ordering
When power is applied, or when an I/O module is inserted, the
adapter detects the backplane I/O modules’ order, based on MACID.
With Physical Ordering, the adapter detects if any ArmorPoint I/O
modules connected to it are out of order. If this condition is detected,
the adapter changes the MACIDs of any new modules.
IMPORTANT
The adapter’s MACID is always 0 on Subnet. The MACIDs of each
attached backplane I/O module must be sequentially ordered (i.e.,
each module’s MACID is greater than the left adjacent module).
If any backplane I/O modules are missing when
power is applied, none of the backplane modules
enter run mode.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 33

What Is the ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapter? 2-17
Interscan Delay (ISD)
Interscan Delay is the time delay between consecutive I/O scans of
polled devices. The default setting is 10ms. The ISD=4ms for Auto
Start Mode. You can change this parameter in the Module window of
the scanner in the RSNetWorx for DeviceNet software.
The scanner uses this period of time to perform non-time-critical
communications on the DeviceNet network, such as communicating
with RSNetWorx for DeviceNet software. Setting this parameter to a
very low value increases the latency for non-time-critical scanner
operations, including the time required to respond to RSLinx software
and configuration functions. Setting this parameter to a very large
value reduces the freshness of the I/O data being collected by the
scanner and is not advisable.
Foreground to Background Poll Ratio
Foreground to Background Poll Ratio is the ratio of foreground to
background polls. You can set this parameter in the Module window
of the scanner in RSNetWorx for DeviceNet software.
Devices can be polled on every I/O scan (foreground) or they can be
polled less frequently (background). Whether a particular device will
be polled in the foreground or in the background i s determined by its
Poll Rate parameter on the Edit I/O Parameters dialog box, which is
accessed from the Scanlist property page.
The poll ratio sets the frequency of poll I/O messages to a device in
relation to the number of I/O scans. For example, if the poll ratio is
set to 5, the scanner will poll the selected devices once every six I/O
scans. We recommend that you use a poll ratio of 1.
Expected Packet Rate
Expected Packet Rate is the rate at which the packets will be expected
to be received by the scanner. You set this parameter in the Module
window (from the Advanced button) of the scanner in RSNetWorx for
DeviceNet software.
IMPORTANT
We recommend that you do not change the
Expected Packet Rate unless you are instructed to do
so by a Rockwell Automation technical support
representative.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - Februa ry 2005
Page 34

2-18 What Is the ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapter?
Transmit Retries
Transmit Retries are the maximum number of times that the scanner
will attempt to send an I/O message to a device before it times out
and generates an error message. Y ou set this parameter in the Module
window (from the Advanced button) of the scanner in RSNetWorx for
DeviceNet software.
Communicate Through the Adapter
IMPORTANT
As described previously in this manual, the adapter resides on the
DeviceNet network and the PointBus simultaneously. The adapter’s
functions are as follows:
• DeviceNet – adapter serves as a slave device that exchanges I/O
data with another DeviceNet scanner device (e.g., 1771-SDN) via
DeviceNet messages
• PointBus – adapter serves as master for up to 63 I/O modules,
using DeviceNet messages to consume from or produce data to
each module
IMPORTANT
W e recommend that you do not change the Transmit
Retries unless you are instructed to do so by a
Rockwell Automation technical support
representative.
.
If Automatic Device Replacement (ADR) is enabled
on the adapter, you can only connect up to 62
modules via the PointBus.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
For more information on ADR, see page 2-15.
Map the Data
Your adapter must store data temporarily before transferring it
between devices. You must map data to your adapter’s memory
before transferring it.
For a detailed description of the mapping process, see page 2-20.
Page 35

What Is the ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapter? 2-19
K
K
K
Overview of the Communication Process
In a typical configuration, the adapter acts as an interface between a
DeviceNet scanner (e.g., 1756-DNB) and ArmorPoint I/ O mo dules.
The following example graphic shows information transferred from a
1756-DNB to ArmorPoint I/O modules.
IMPORTANT
Although information is exchanged between the
Logix5555 and 1756-DNB, this diagram (nor this
chapter) is not designed to explain such an
exchange.
Four data transfers are shown in the diagram, including:
1. Scanner to adapter
2. Adapter to I/O modules
3. I/O modules to adapter
4. Adapter to scanner
Key Points About Scanner to Adapter Transfer (Step 1 )
1. Scanner initiates transfer
2. Scanner uses DeviceNet I/O messaging to write data to adapter.
Data may contain:
• device output data
• configuration data
ey Points About Adapter to Output Module Transfer (Step 2)
1. Adapter initiates transfer
2. Adapter produces data for I/O module to consume.
Data may contain:
• device output data
• configuration data
ey Points About Input Module to Adapter Transfer (Step 3)
Adapter consumes data I/O module has produced.
Data may contain:
• device input data
• status data
ey Points About Adapter to Scanner Transfer (Step 4)
SDN consumes I/O data produced by adapter.
1738-ADN adapter
Data may contain:
• device input data
• status data
computer with PLC
programming software
ControlNet network
Logix5555 controller
The Logix5555 controller sits in the backp lane.
The 1756-DNB contained in the controller
communicates with the ArmorPoint adapter.
1784-PCD
PCMCIA card
DeviceNet network
DeviceNet Out
DeviceNet In
8
PWR
1738-IB8M12
1738-ADN12
0
0
2
2
8
6
6
4
4
x1
x10
Adapter
Status
DeviceNet
Status
PointBus
Status
System
Power
Adapter
Power
24V dc In
02
13
46
57
MOD
NET
02
13
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
1738-OB8EM12
24V dc Out
MOD
NET
0
1
2
3
4
6
4
5
7
5
6
7
ArmorPoint I/O modules
computer with
RSNetWorx for
DeviceNet software
The computers and PCMCIA card
shown in the diagram are required
to configure the processor,
adapter, and I/O modules.
Although the PCMCIA card is used
in this example, you can use other
communications cards, such as
PCID and KFD cards.
42409
Because the adapter simultaneously resides on the DeviceNet network
and on PointBus, it serves as a slave to the processor (i.e., steps 1 and
4) and a master to the I/O modules (i.e., steps 2 and 3).
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - Februa ry 2005
Page 36

2-20 What Is the ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapter?
The four data transfers are not necessarily sequential. Transfers 2 and
3 typically occur more frequently than transfers 1 and 4.
Image Table Mapping
Your adapter receives data from:
• master devices (e.g., scanners) - output data is then passed to
ArmorPoint I/O modules
• input modules - input data is passed to the scanner
The adapter must map the data it receives to its internal memory
before passing it to the appropriate device. The I/O map for a module
is divided into:
• read bytes - input and status bytes
• write bytes - output and configuration bytes
The data is mapped by 3 buffers for input data (each representing an
I/O connection on the primary DeviceNet) and 1 buffer for output
data (representing data sent for Poll or COS connections on the
primary DeviceNet).
The number of read bytes or write bytes can be 2 or more. The length
of each I/O module's read bytes and write bytes vary in size
depending on module complexity. Each I/O module suppo rts at least
1 input byte or 1 output byte. Status and configuration are optional,
depending on the module.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 37

What Is the ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapter? 2-21
The following graphic shows how the adapter maps information.
DeviceNet
Scanner
DeviceNet
ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapter
DeviceNet Poll Buffer
DeviceNet Strobe Buffer
DeviceNet COS/CYC Buffer
Subnet Modules
INPUT DATA
248 bytes
+ 2 bytes status
6 + 2 bytes
248 bytes
+ 2 bytes status
I/O MAPPING
OUTPUT DATA
Poll OR COS (inst 2)
248 + 2 bytes
Subnet
DeviceNet
42406
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - Februa ry 2005
Page 38

2-22 What Is the ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapter?
Byte 0
See the I/O Status Word Bit Definitions table for definitions of the first
2 bytes of each I/O message produced by the adapter on DeviceNet.
I/O Status Word Bit Definitions
Bit Operating Mode Operating Mode Description
0 0 = Run mode
1 = Idle mode
1 1 = Device failure (at least one
device failed)
2 1 = Communication failure
3 1 = Duplicate node
address failure
4 Reserved
5 Reserved
6 Reserved
Run - The adapter maps output data to
each module on PointBus.
Idle - Output data with zero length is
sent to I/O modules.
Device Failure - One or more of the
devices in the scanlist has failed to
communicate with the adapter.
Communications Failure - The
adapter has entered the BUSOFF state
on the Subnet. Another Subnet device
is configured with the wrong baud rate.
Byte 1
7 Reserved
0 Reserved
1 Reserved
2 Reserved
3 Reserved
4 Reserved
5 Reserved
6 Reserved
7 Reserved
Duplicate Node Address Failure There is another node with the same
address (0) as the scanner on the
Subnet and the adapter has failed its
Dup_MAC_ID test.
The first 2 bytes of output data on the DeviceNet network that are sent
to the adapter are reserved as a command word. No bits have
been defined.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 39

What Is the ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapter? 2-23
Communicate With I/O Modules
The adapter module supports multiple communication choices. These
choices all use the default I/O structure previously described. The
adapter’s master (e.g., 1756-DNB) makes the actual communication
choice. The choices are:
• Polled – Adapter sends data in response to received data.
• Strobe – Adapter sends data in response to the strobe command.
The single bit allocated to the adapter in the strobe message is
not used. If the configured size of the input data (sent from the
adapter) is greater than 8 bytes, the strobe connection
establishment will fail. In this case, the input size must be
reconfigured to 8 bytes or less (only 6 bytes are I/O data
because the first 2 bytes are the status word).
• Change of State – Adapter sends data based on detection of any
changed value within the input data. Data is independently
received based on change of state from the sender. Data in both
directions can be acknowledged or unacknowledged depending
on the run time configuration of the system.
• Cyclic – Adapter sends data cyclically based on a configured
time value. Data is independently received cyclically from the
sender. Data in both directions can be acknowledged or
unacknowledged depending on the run time con f iguration of
the system.
The adapter uses these messages to solicit data from or deliver data to
each device. Data received from the devices (i.e., input data) is
organized by the adapter and retransmitted to the master. Data
received from the master (i.e., output data) is organized in the adapter
and sent on to the I/O modules.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - Februa ry 2005
Page 40

2-24 What Is the ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapter?
Use Diagnostic Tables
The adapter maintains three diagnostic tables to manage the flow of
data between a processor and a network’s devices. You can access the
table over DeviceNet through the Scan Config Object (Class Code
0x90), Instance 1, via the following read-only attributes:
• Faulted Node Table (Attribute 0xA) - In this 8-byte table, each
bit represents a node on the backplane. For example, bit 0 in
byte 0 represents MACID 0 (the adapter), while bit 0 in byte 1
represents MACID 8 and so on. If a bit is set, a correspondin g
non-zero status value can be read from the Node State Table
described below.
• Idle Node Table (Attribute 0xB) - In this 8-byte table, each bit
also represents a node on the backplane, as with the Faulted
Node Table. If a bit is set in the Idle Node Table, the
corresponding node is in the scanlist and currently in idle mode.
• Node Status Table (Attribute 0xC) - This 64 byte table contains a
status code for each possible MACID on the backplane.
Non-zero values are accompanied with the respective bit in the
Faulted Node Table being set.
See the table Node Status T able Numeric Code Defi nitions for an
explanation of the text messages associated with the Node Status
Table.
Node Status Table Numeric Code Definitions
Numeric Code: Text Message: Definition: Take this action:
70 DupMAC Failure Adapter failed Duplicate Node
Address check.
71 Scanner Cfg Error Illegal data in the scan list table. Reconfigure the scan list table and
72 Comm Failure Slave device stopped communicating. Inspect the I/O modules and
73 Wrong Device Type Device’s identity information does not
match electronic key in scan list
table entry.
74 Port Overrun Error Data overrun on port detected. Modify your configuration and check for
75 Network Failure Communication has ceased on
the backplane.
76 No Msg for Scanner No direct network traffic for
scanner detected.
An I/O module has a MACID of zero.
Change the module’s address.
remove any illegal data.
verify connections.
Verify that the correct device is at this
node number.
Make sure that the device matches the
desired electronic key (vendor, product
code, product type).
invalid data.
Check network communication traffic.
Inspect the I/O modules and
verify connections.
No action. The scanner hears other
network communication.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 41

What Is the ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapter? 2-25
Node Status Table Numeric Code Definitions
Numeric Code: Text Message: Definition: Take this action:
77 Wrong Data Size Data size expected by the device does
not match scan list entry.
78 No Such Device Slave device in scan list table does
not exist.
Reconfigure your module for correct
transmit and receive data sizes.
Add the device to the network, or
delete scan list entry for that device.
79 Transmit Failure Adapter has failed to transmit
a message.
Make sure that other modules exist on
the backplane.
80 In Idle Mode Adapter is in IDLE mode. No action necessary.
If you want the adapter to run, put it in
RUN mode.
82 Fragmentation Error Error detected in sequence of
fragmented I/O messages
from device.
Check scan list table entry for slave
device to make sure that input and
output data lengths are correct.
Check slave device configuration.
83 Slave Init Error Slave device is returning error
Check accuracy of scan list table entry.
responses when scanner attempts to
communicate with it.
Check slave device configuration. Slave
device might be in another master’s
scan list.
Reboot slave device.
84 Not Yet Initialized Adapter is initializing the
No action.
DeviceNet channel.
85 Rcv Buffer Overflow Data size is larger than 255 bytes. Configure the device for a smaller data
size.
86 Device Went Idle Device is producing zero length data
(idle state) while channel is in
Check device configuration and slave
node status.
Run Mode.
89 ADR Failed Failure occurred when downloading
ADR data to the I/O module.
91 Port Bus Off Bus-off condition detected on
communications port.
Reconfigure the ADR download data for
the I/O module.
Check DeviceNet connections and
physical media integrity.
Scanner is detecting communications
errors.
92 Port Power Off N o network power detected on
communications port.
Check system for failed slave devices or
other possible sources of network
interference.
Provide network power.
Make sure that scanner drop cable is
providing network power to adapter
communications port.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - Februa ry 2005
Page 42

2-26 What Is the ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapter?
A user program can monitor the Device Failure Bit in the I/O
message(s) received from the adapter. When it has determined the bit
set, you can read the Faulted Node Table and Node Status Table,
using the Explicit Message Program Control Feature of the scanner
device, to determine the module experiencing problems and the
nature of those problems.
Chapter Summary and What’s Next
In this chapter you learned about the ArmorPoint DeviceNet adapters.
Move to Chapter 3 to learn about using Auto Start Mode.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 43

Chapter
Use Auto Start Mode
This chapter describes how to use the Auto Start Mode with your
ArmorPoint I/O DeviceNet adapters.
See the following sections: Page:
Why Use Auto Start Mode? 3-2
Install the I/O Module 3-4
Use RSNetWorx for DeviceNet 3-5
Begin Auto Start Mode 3-7
Use Custom Configuration 3-9
Chapter Summary and What’s Next 3-10
3
1. Install the I/O Module
DeviceNet Out
DeviceNet In
X10
PWR
X1
R
1738-ADN12
Adapter
Status
DeviceNet
Status
PointBus
Status
System
Power
Adapter
Power
Add and Commission
Non-Backplane I/O
Modules to the Subnet
43785
This chapter assumes you already have an ArmorPoint system
mounted. There are five simple steps to the Auto Start Mode:
2. Wire the DeviceNet Adapters 3. Install the I/O Module
1738-OB8EM12/A
24V dc Out
2
0
MOD
3
1
NET
0
1
2
3
6
4
43763
5. Use RSNetWorx
5. Begin Auto Start Mode4. 1738-ADNX Only
4
5
7
5
6
7
43771
for DeviceNet
1 Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 44

3-2 Use Auto Start Mode
Why Use Auto Start Mode?
Auto Start Mode offers you a quick and easy method of getting your
ArmorPoint I/O system ‘up and running’. If your ArmorPoint I/O
application can use default configuration, you should use Auto Start
Mode to easily begin operations.
Once your adapter is:
• installed
• connected to the system’s I/O modules
• online (in RSNetWorx for DeviceNet)
you only need to choose the Auto Start Mode option in the adapter’s
Parameters window in the RSNetW orx for DeviceNet software and the
adapter begins working with a default configuration.
IMPORTANT
Although Auto Start Mode allows your adapter to
operate with a default configuration, you can write a
custom configuration after operation has begun.
For more information on how to write custom
configuration for your adapter on DeviceNet, see
Chapter 5, Add the ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapter to
the DeviceNet Scanner’s Scanlist.
What Does Auto Start Mode Do?
When using Auto Start Mode, the adapter:
1. Sets all modules on the backplane to Auto Baud
2. Reads the Subnet module’s identity information
3. Sets backplane modules’ addresses sequentially
4. Generates a scanlist for the Subnet
5. Maps I/O data, based on byte, word, double-word, or fixed
boundaries
When this sequence of events is completed, the ArmorPoint I/O
modules connected to the adapter are ready to accept connections
from a scanner.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 45

Use Auto Start Mode 3-3
How Is I/O Data Mapped Using Auto Start Mode?
In Auto Start Mode, you can map I/O data in the adapter’s memory i n
one of the following ways:
• Byte Boundaries
• Word Boundaries
• Double Word Boundaries
• Fixed Boundaries
Byte Boundaries
Each node’s I/O data is mapped in the adapter’s memory at the next
available byte. This option works best in applications that use
Allen-Bradley PLCs and SLCs.
Word Boundaries
Each node’s I/O data is mapped in the adapter’s memory at the next
available word. This option works best in applications that use
Allen-Bradley PLCs and SLCs.
Double Word Boundaries
Each node’s I/O data is mapped in the adapter’s memory at the next
available double word. This option works best in applications that use
Allen-Bradley Logix products.
Fixed Boundaries
The map to the fixed location is based on the node add ress. Mapping
size ranges from 1 to 32 and is set using an EDS parameter. The
mapping for a node with address 1 begins on byte 2. The formula for
mapping is: 2+((N-1)(mapsize)), where N = node address.
Keep the following in mind when using fixed boundaries:
• You specify fixed map size using EDS parameters
• Data is mapped after status/channel words in I/O image,
beginning with byte 2
• No data area is reserved for MACID 0 (the adapter)
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 46

3-4 Use Auto Start Mode
Requirement To Using Auto Start Mode
Your ArmorPoint DeviceNet adapter must be free of I/O co nnections
on DeviceNet when you use Auto Start Mode. If you attempt to use
Auto Start Mode after another scanner device has established I/O
connections with the adapter, your attempt to use Auto Start Mode
will be rejected. When the adapter is configuring itself in Auto Start
Mode, no other device can establish I/O connections to the adapter.
Install the I/O Module
To install the module:
1. Using a bladed screwdriver, rotate the keyswitch on the
mounting base clockwise until the correct number for the I/O
module aligns with the notch in the base. (See the individual
ArmorPoint I/O module installation instructions for this
number.)
2. Position the module vertically above the mounting base. The
module will bridge two bases.
Module will bridge two bases.
1738-OB8EM12/A
24V dc Out
0
1
2
MOD
3
NET
0
1
2
3
6
4
5
4
5
7
6
7
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
43771
3. Push the module down until it engages the latching mechanism.
You will hear a clicking sound when the module is properly
engaged.
The locking mechanism will lock the module to the base.
Page 47

Use Auto Start Mode 3-5
Remove the Module From the Mounting Base
To remove the module from the mounting base:
1. Put a flat blade screwdriver into the slot of the orange latching
mechanism.
2. Push the screwdriver toward the I/O module to disengage the
latch.
The module will lift up off the base.
3. Pull the module off of the base.
For more information on installing and wiring the multiple ArmorPoint
I/O modules, see the installation instructions for each catalog number.
Use RSNetWorx for DeviceNet
You must use the RSNetWorx for DeviceNet software to configure
your adapter.
If you are using a 1738-ADNX adapter, make sure that you properly
configure non-backplane modules for baudrate and MACID.
Follow the steps below to use Auto Start Mode.
1. Go online in the software.
IMPORTANT
A.Click on the Network
pull-down menu.
B.Choose Online.
2. Once you are online, browse for the primary network (e.g., You
can use Single Pass Browse).
Auto Start Mode is only available when RSNetWorx
for DeviceNet is online.
A.Click on the Network
pull-down menu.
B.Choose a Browse type.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 48

3-6 Use Auto Start Mode
3. Click OK to synchronize your offline and online configuration.
The adapter appears on the screen.
4. Double click on the adapter icon.
Double click on
this icon.
You can either:
• Upload configuration from the device to update the software
• Download configuration from the software to the device
5. Click Yes to upload configuration from the device.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 49

Use Auto Start Mode 3-7
Begin Auto Start Mode
After you upload the configuration from the device to the software,
begin Auto Start Mode (ASM).
1. Double click on the adapter icon to open the adapter properties
window.
2. Click on the Parameters tab.
3. Click on the right side of the Auto Start Mode line so that a
menu appears.
A.Click on the
Parameters window.
B.Use the Auto Start
Mode pull-down menu
to choose a mapping
option. The options are
described on page 3-3.
4. Download the Auto Start Mode value. Make sure you only
download this single value, as shown below.
A.Choose Single Value.
After 30-40 seconds, the adapter be gins operations and uses the
configuration most recently applied. During the Auto Start Mode
process, the Physical List Ac qui re Status field displays the words:
Auto Start Mode, but after the download is complete the field
displays the word Idle.
• Check for solid red indicators on all modules
• Verify that all non-backplane modules have the proper baudrate
(or have autobaud enabled)
B.Download the value.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 50

3-8 Use Auto Start Mode
• Check that MACIDs are set to proper values
• Check scanlist
– browse to Subnet and view scanlist, or look at mapping text
– Make sure the scanlist was saved (if not, investigate why?)
– If you are using the 1738-ADNX adapter, check the
Max(imum) Backplane MACID parameter. It should equal the
number of modules residing on the backplane.
After ASM has completed (that is, Physical List Acquire Sta tus
field is Idle), verify that the operation was successful and that
each I/O module was added to the adapter’s scanlist. The
PointBus Status LED should be solid green. This indicates only
that the adapter is able to establish I/O connections with each
module in its scanlist, not that each module on the Subnet was
successfully added to its scanlist.
To verify the presence of each module in the adapter’s scanlist,
perform one of the following checks:
• Each I/O module’s NET LED should be solid green. If the
device has neither LED, use one of the following methods.
– By browsing to the Subne t and uploading the adapter’s
scanlist using RSNetW orx for DeviceNet and verifying that the
device is found in the scanlist.
– By repeatedly uploading the EDS parameter Cycling I/O
Mapping to verify that a mapping for the concerned module
exists. See page
2-15 for more information about this
parameter.
If one of the following is observed, it is likely that one of the
Subnet modules has been addressed incorrectly or is
configured to communicate at the wrong baud rate.
• The adapter’s PointBus Status LED is solid or blinking red
• An I/O module’s NET LED is solid red
• It appears that the adapter has not saved a scanlist
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 51

Use Auto Start Mode 3-9
Use the following procedures to attempt to remedy a problem:
• Verify tha t each non- backplane module’s address and
baudrate have been set correctly.
• Verify that each backplane module is configured to autobaud.
The adapter’s EDS parameter Set Backplane Autobaud can be
used to set each module’s autobaud parameter. It is necessary
to cycle a module’s power before the autobaud parameter
change takes effect. In rare situations, it may be nece ssary to
download the parameter and cycle power several times
before each backplane module’s autobaud parameter has
been changed.
Note that if the adapter is configured to autobaud on the
primary DeviceNet network, network traffic on the primary
network is required before the backplane modules will attempt
to communicate. For this reason, it is sometimes helpful to have
RSLinx continuously browsing the primary network while
attempting the ASM process and verification.
Use Custom Configuration
When it is believed that each non-backplane module is co rrectly
configured and that each backplane module is able to
communicate on the Subnet, the ASM process can be attempted
again.
After successfully configuring your adapter with the Auto Start Mode
feature, the adapter must still be added to the primary DeviceNet
network scanner’s scanlist. See Chapter 5 for more information.
The Auto Start Mode is recommended to quickly and easily get your
ArmorPoint I/O system ‘up and running’. But this mode does not
prevent you from changing the adapter’s default configuration after
system operation has begun.
For more information on how to write custom configuration for your
adapter on DeviceNet, see Chapter 4, Configure the DeviceNet
Scanner Subnet and Chapter 5, Add the ArmorPoint DeviceNet
Adapter to the DeviceNet Scanner’s Scanlist.
IMPORTANT
The adapter’s ADR configuration for the Subnet
modules is reset when you run Auto Start Mode.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 52

3-10 Use Auto Start Mode
Chapter Summary and What’s Next
Auto Start Mode was discussed in this chapter. Move on to Chapter 4,
Configure the DeviceNet Scanner Subnet or to Chapter 5, Add the
ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapter to the DeviceNet Scanner’s Scanlist.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 53

Chapter
4
Configure the DeviceNet Scanner Subnet
This chapter describes how to custom configure your scanner for use
with ArmorPoint I/O modules.
See the following sections: Page:
Configuration Overview 4-1
Add the Scanner To Your Network 4-2
Add I/O Modules To Your Network 4-3
Set the Scanner’s Parameters 4-3
Go On Line 4-8
Chapter Summary and What’s Next 4-8
Configuration Overview
Your adapter works on two networks simultaneously and must be
configured for each separately. This chapter explains con figuration of
the scanner for use with ArmorPoint I/O modules.
For information on how to configure the adapter for use on the
DeviceNet Network see Chapter 5, Adding the DeviceNet adapters to
the DeviceNet Scanner’s Scanlist.
You must use the RSNetWorx for DeviceNet software to configure
your scanner. You can configure the scanner while it is:
• on line
• off line
This chapter shows configuration in the offline mode. Configuration
screens appear the same in both modes. Note that some screen
options are unavailable in offline mode. The only difference is that if
you make changes off line, you must take the scanner on line before
the configuration changes take effect.
IMPORTANT
1 Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Throughout most of this manual, we refer to the
ArmorPoint I/O DeviceNet adapter as the adapter.
The adapter also communicates with Subnet
modules as a scanner. In this chapter only, the
adapter is referred to as a scanner.
Page 54

4-2 Configure the DeviceNet Scanner Subnet
You must follow these steps during configuration:
1. Add the scanner to your network
2. Add I/O modules to your network
3. Set the scanner’s parameters
4. Go on line
Add the Scanner To Your Network
Follow these steps:
1. Start RSNetWorx for DeviceNet.
2. Add the scanner as shown below.
1. Expand the list of
communication adapters.
2. Select the 1738-ADN12
ArmorPoint Scanner.
IMPORTANT
3
The scanner appears
on the network.
The scanner must always exist on the Subnet at
Node 00.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 55

1. Expand the Category to display
the list of I/O modules.
Configure the DeviceNet Scanner Subnet 4-3
Add I/O Modules To Your Network
After you add the scanner, you must add the modules connected to
the scanner on the Subnet. In the offline mode, I/O modules must be
added individually. Follow these steps:
1. Add modules as shown below.
NOTE: Make sure you check under all the
categories that I/O modules reside (i.e.,
General Purpose Discrete I/O,
Rockwell Automation miscellaneous,
and Specialty I/O).
2. Double-click the I/O module you
want to add to the network.
TIP: You can also click and drag the
module name onto the network.
We used the 1738-IB4M12,
-OB4EM12, and -IE2CM12
I/O modules in this example.
Your netwo rk screen should
reflect the I/O modules on
your network.
Set the Scanner’s Parameters
After adding the scanner to the network, you must configure it for use
with I/O modules.
IMPORTANT
This chapter shows configuration in the of f li ne
mode. Changes set in this mode do not take effect
until the scanner goes on line. For more information
on how to go on line, see page 4-8.
1. Right-click on the scanner.
2. Click on Properties... to
configure your scanner.
1. Configure the scanner as shown below.
TIP: You can also double
click on the scanner to
view the Properties
window.
A window will open with a series of tabs along the top. Each tab
opens to a window that provides options to write configuration for
your scanner. These wind ows are sh own on the following pages.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 56

4-4 Configure the DeviceNet Scanner Subnet
e
s
General window
Type the scanner’s name here.
Type a description here (optional).
The scanner’s address must = 0.
This window also shows the
scanner’s device identity. These
fields are read-only.
Device Bridging window
Use Associate File to
associate this configuration
file with the configuration file
that configures the same 1738
ArmorPoint DeviceNet
scanner (called adapter on the
primary network) for
communication with a master
device on the primary
DeviceNet network.
For more information on the
need to maintain two
configuration files in the same
adapter and the simultaneous
presence of the adapter on
two networks (i.e., DeviceNet
as a slave and PointBus as a
master), see page 4-1.
Click OK to accept the parameters.
IMPORTANT: Configuration changes mad
in offline mode do not take
effect until the scanner goe
on line. For more
information on how the
scanner goes on line, see
page 4-8.
Use Clear Association to remove
previously established configuration
file associations that no longer apply
to your scanner.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 57

Module window
Set the Interscan Delay here.
Set the Foreground to Background
Poll Ratio here.
Configure the DeviceNet Scanner Subnet 4-5
Click here to reset the Interscan Delay
and Foreground to Background Poll
Ratio back to the module default values.
Click Advanced to change the
advanced module settings, as shown in
the following window.
Advanced window accessed from
Module window
We recommend you DO NOT change module
settings unless advised to do so by a Rockwell
Automation support representa tive.
Scanlist window
Add and remove I/O modules to and
from the scanlist on this screen.
To set any of the parameters on this
screen (e.g., Node Active) for a
specific module, first add the module
to the scanlist and then highlight the
module to make specific changes.
Click Automap on Add so a
checkmark appears to automap I/O
data when adding modules.
Click Edit I/O Parameters to edit
the module’s I/O parameters, as
shown below.
Set the Expected Packet Rate here.
Set the number of Transmit Retries here.
Click OK to accept new
settings.
Add modules to or remove
modules from the scanlist.
Choose Electronic Key
parameters for each module.
Edit I/O Parameters window
accessed from Scanlist window
Click OK when finished.
Click on the appropriate I/O data
transmission method (e.g., Polled) and
make other appropriate I/O parameter
changes on this screen.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 58

4-6 Configure the DeviceNet Scanner Subnet
t
Input window
Use this pull-down menu to
choose a Memory type.
The memory type
corresponds to an I/O
connections on DeviceNet.
Advanced Mapping window
accessed from Input window
Set Map From parameters here.
Click Apply Mapping to apply
changes and leave the screen open.
Click Close when finished.
Set Map To
parameters here.
Highlight a module and click Unmap to
unmap it.
Click Advanced to edit the advanced
mapping parameters, as shown below.
Click Options to edit the automap
options, as shown below.
Set the starting byte for I/O mapping.
Automap Options window
accessed from Input window
Choose a
Data
Alignmen
and click
OK.
Output window
Use this pull-down menu to
choose a memory type. This
corresponds to I/O on the
primary DeviceNet.
Set the starting byte for I/O
mapping here.
The bytes mapped last will
determine sizes on the
primary DeviceNet.
Highlight a module and click Unmap to
unmap it.
Click Advanced to edit the advanced
mapping parameters.
Click Options to edit the automap
options.
Note that the Advanced Mapping
and Options windows are the same
for output modules as those sh own for
input modules. See above for an
explanation of these windows.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 59

ADR window
Use this screen to choose
Automatic Device
Replacement options.
Configure the DeviceNet Scanner Subnet 4-7
Following are the remaining configuration windows.
You must have loaded each
device into RSNetWorx for
DeviceNet before you can
Load Device Config using
this button.
Summary window
IMPORTANT: You cannot change any
configuration parameters on this
screen. It is for information purposes
only. These buttons do not apply for
this window but are here to maintain
consistency among the windows.
This completes the configuration options. Your scanner must go on
line for configuration changes to take effect.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 60

4-8 Configure the DeviceNet Scanner Subnet
1. Click on Network.
2. Click on Online.
Go On Line
After you set configuration parameters, your scanner must go on line
to accept the configuration changes. Follow these steps:
1. Use the Network pulldown to go on line.
The software prompts you to save your configuration changes.
Click Yes.
Select the DeviceNet network
subnetwork.
This selection accesses the PointBus
to configure the adapter on the
DeviceNet network.
2. Choose your scanner’s network and apply the changes, as
shown below.
Click OK to apply the data
to your scanner.
Chapter Summary and What’s Next
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
In this chapter, you learned how to configure the scanner. Move to
Chapter 5 to learn how to add the ArmorPoint DeviceNet adapter to
the DeviceNet scanner’s scanlist.
Page 61

Chapter
5
Add the ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapter to the DeviceNet Scanner’s Scanlist
This chapter describes how to custom configure your adapter for use
with DeviceNet devices.
See the following sections: Page:
Configuration Overview 5-1
Add the Adapter to Your Network 5-2
Set the Adapter’s Parameters 5-3
Go On Line 5-6
Chapter Summary 5-6
Configuration Overview
Your adapter works on two networks simultaneously and must be
configured for each separately, which means that you will have two
separate RSNetWor x for DeviceNet software files.
This chapter explains configuration of the adapter for use on the
primary DeviceNet network. For information on how to configure the
adapter for use on the Subnet, see Chapter 4, Configure the DeviceNet
Scanner Subnet.
You must use the RSNetWorx for DeviceNet software to configure
your adapter. You can configure the adapter while it is:
• on line
• off line
This chapter shows configuration in the offline mode. Configuration
screens appear the same in both modes. Note that some screen
options are unavailable in offline mode. The only difference is that if
you make changes off line, you must take the adapter on line before
the configuration changes take effect.
1 Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 62

5-2 Add the ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapter to the DeviceNet Scanner’ s Scanlist
You must follow these steps during configuration:
1. Add the adapter to your network
2. Set the adapter’s parameters
3. Add the DeviceNet adapter’s scanlist (see the Quick Start,
Appendix B)
4. Go on line
Add the Adapter to Your Network
Follow these steps:
1. Start the RSNetWorx for DeviceNet software.
1. Expand the list of
communication adapters.
2. To add the adapter, you can
double click on the adapter
or click and drag the adapter
name onto the network.
2. Add the adapter as shown below.
3
The adapter appears
on the network.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 63

Add the ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapter to the DeviceNet Scanner’s Scanlist 5-3
Set the Adapter’s Parameters
After adding the adapter to the network, you must configure it for use
with master DeviceNet devices.
1. Right-click on the adapter.
2. Click on Properties to
configure your adapter.
IMPORTANT
This chapter shows configuration in the offline
mode. Changes set in this mode do not take effect
immediately. For configuration changes to take
place, you must:
• go on line with your adapter
• download the new configuration to your adapter
For more information on how to go on line, see
page 5-6.
1. Configure the adapter as shown below.
TIP: You can also double click on the adap ter
to view the Properties menus.
General window
Type the adapter’s name here.
Ty pe a description here (optional).
Select the desired address. This
address corresponds to the address
switch on the adapter.
This screen shows the adapter’s
device identity. These f ie lds are
read-only.
You see a window with a series of tabs. Each tab opens to a window
that provides options to write configuration for your adapter. The tabs
are shown on the following pages.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 64

5-4 Add the ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapter to the DeviceNet Scanner’ s Scanlist
Device Bridging window
Use Associate File to
associate this configuration
file with the configuration file
that configures the same
ArmorPoint DeviceNet
scanner for communication
with ArmorPoint I/O modules.
For more information on the
need to maintain two
configuration files in the same
adapter and the simultaneous
presence of the adapter on
two networks (i.e., DeviceNet
as a slave and Subnet as a
master), see page 5-1.
Use Clear Association to remove
previously established configuration
file associations that no longer apply
to your adapter.
Parameters window
Restore all parameter
default values.
For a description of a
specific parameter, highlight
the parameter below and
click here.
Any parameter with a lock shown before it cannot
be changed.
The values correspond to the I/O connection sizes
from the I/O Data window. They can be uploaded
from an adapter with a downloaded scanlist.
The following screens show how to change the
other parameters.
AutoAddress
Enable or disable autoaddress.
Auto Start Mode
IMPORTANT: The following
configuration parameters:
• Auto Start Mode
• Set Backplane Baudrate
• Set Backplane Autobaud
• AutoAddress Backplane
Modules
should only be used when on line and
should be set to Do Nothing when
Download All Parameters is selected
or when saving to a scanner’s ADR data.
Note:
The parameters Max Backplane
MACID and Fixed Map Size are found
only in the 1738-ADNX Parameters
window.
Backplane Baudrate
Set the backplane baudrate.
Backplane Autobaud
Configure backplane modules to autobaud.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
AutoAddress Backplane Modules
Choose the autoaddress.
Page 65

I/O Data window
Add the ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapter to the DeviceNet Scanner’s Scanlist 5-5
The following screens show the remaining configuration windows.
Connection sizes appear only when the Subnet
network file has been associated in the Device
Bridging window.
These values correspond to the 4 parameters
(Poll/COS Connection Consume Size, Poll
Connection Produce Size, COS Connection
Produce Size, Strobe Connection Produce
Size) found in the device’s Parameters
window.
EDS File window
Click here to view the EDS
file. An example of the
EDS file is shown below.
The window below shows an example EDS file.
This completes the configuration options. Your adapter must go on
line for the configuration to take effect.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 66

5-6 Add the ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapter to the DeviceNet Scanner’ s Scanlist
Go On Line
Follow these steps for the adapter to go on line:
1. Use the Network pulldown.
1. Click on Network.
2. Click on Online.
The software prompts you to save your configuration changes.
Click Yes.
Select the DeviceNet network.
This selection accesses the PointBus
to configure the adapter on the
DeviceNet network.
2. Choose your adapter’s network as shown below.
Click OK to apply the data
to your adapter.
To learn how to add the ArmorPoint DeviceNet adapter to the
scanner’s scanlist, refer to the Quick Start section, Appendix B.
Chapter Summary
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
In this chapter, you learned how to configure the adapter.
Page 67

Chapter
6
Use the Status Indicators
Troubleshoot the ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapter
This chapter describes how to troubleshoot your adapter.
See the following sections: See page:
Use the Status Indicators 6-1
Guidelines for Using Your Adapter 6-3
Chapter Summary 6-3
You can use the status indicators to troubleshoot your adapter. The
following graphic shows the adapter’s status indicators.
1738-ADN12
DeviceNet Out
DeviceNet In
X10
PWR
X1
R
Use the table below to troubleshoot your adapter
Indication Indication Probable Cause
Adapter Status Off No power applied to device.
Green Device is operating normally.
Flashing Red Recoverable fault.
1738-ADN12
Adapter
Status
DeviceNet
Status
PointBus
Status
System
Power
Adapter
Power
Adapter Status Indicator
DeviceNet Status Indicator
PointBus Status Indicator
System Power Indicator
Adapter Power Indicator
43785
Red Unrecoverable fault - may require device replacement.
Flashing Red/Green Device is in self-test.
1 Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 68

6-2 Troubleshoot the ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapter
Indication Indication Probable Cause
DeviceNet Status Off Device is not on line:
Flashing Green Device is on line but has no connections in the established state.
Green Device is on line and has connections in the established state.
Flashing Red One or more I/O connection in timed-out state.
Red Critical link failure - failed communication device. Device
PointBus Status Off Device is not on line:
Flashing Green Device is on line but has no connections in the established state.
Green Device is on line and has connections in the established state.
Flashing Red One or more I/O connection in timed-out state.
- Device attempting to AutoBaud
- Device has not completed dup_MAC_ID test
- Device not powered - check module status indicator.
detected error that prevents it from communicating on the
network. (Possible duplicate MACID or baud rate mismatch).
- Device has not completed dup_MAC_ID test
- Device not powered - check module status indicator.
Red Critical link failure - failed communication device. Device
detected error that prevents it from communicating on the
network. (Possible duplicate MACID or baud rate mismatch).
Flashing Red/Green Communication faulted device - the device has detected a
network access error and is in communication faulted state.
Device has received and accepted an Identify Communication
Faulted Request - long protocol message.
PointBus Status
(1738-ADNX only)
Off No power applied to device.
Device not on line
Device has not completed dup_MAC_ID test.
Green Subnet on line and has connections in the established state.
Flashing Red Recoverable fault:
- No scanlist configured
- Problem with module in scanlist (missing, mismatch, etc.).
Red Unrecoverable fault may require device replacement
(Possible duplicate MACID or baud rate mismatch.)
System Power Off Not active - Field power is off or dc-dc-converter problem.
Green System power on - dc-dc converter active (5V).
Adapter Power Off Not active - Field power is off.
Green Power on, 24V present.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 69

Troubleshoot the ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapter 6-3
Guidelines for Using Your Adapter
Remember the following operational guidelines when using your
ArmorPoint DeviceNet adapter.
• Do not leave spaces in the I/O. Instead, install all ArmorPoint
I/O modules adjacent to each other.
• Populate every position on the mounting base.
• Do not add new I/O modules to the end of the ArmorPoint I/O
system while the system is under power.
• Use labels with the I/O mo dules.
• Do not move I/O modules to different locations on the
mounting base after they have been installed and configured.
• If adjacent modules (i.e., 2 or more) are removed, replace all of
them to operate the ArmorPoint I/O system. Input data will hold
last state until all previously removed module s are replaced.
• Use Allen-Bradley marker cards to identify your ArmorPoint I/O
modules. The cards are easily ordered from your Rockwell
Automation representative under the Bulletin 1492 number.
Chapter Summary
• Properly terminate the 1738-ADNX Subnet at the end s of the
Subnet trunk line.
• Correctly set the Max Backplane MACID (1738-ADNX only).
In this chapter you learned how to troubleshoot your adapter.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 70

6-4 Troubleshoot the ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapter
Notes:
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 71

Appendix
A
Specifications
Following are specifications for the 1738 ArmorPoint DeviceNet
adapters.
ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapters - 1738-ADN12, -ADN18, -ADN18P, and -ADNX
Expansion I/O Capacity • DeviceNet adapter backplane current output = 1.0 A maximum. See the following list for
backplane current consumption for each ArmorPoint I/O catalog number and the current
consumption for each of the ArmorPoint modules connected to the ArmorPoint
DeviceNet adapter. Verify that it is below 1.0 A.
• Backplane current can be extended beyond 1.0 A with a 1738-EP24DC Backplane
Extension Power Supply. The 1738-EP24DC can supply up to an additional 1.3 A of
backplane current.
• Multiple 1738-EP24DC modules can be used to reach the maximum of 63 modules.
Cat. No. PointBus Current Requirements
1738-IB2M12 75mA
1738-IB4xxx 75mA
1738-IB8xxx 75mA
1738-IV4xxx 75mA
1738-IV8xxx 75mA
1738-OB2EM12 75mA
1738-OB2EPM12 75mA
1738-OB4Exxx 75mA
1738-OB8Exxx 75mA
1738-OV4EM12 75mA
1738-OW4xxx 90mA
1738-IE2CM12 75mA
1738-OE2CM12 75mA
1738-IE2VM12 75mA
1738-OE2VM12 75mA
1738-IA2xxx 75mA
1738-OA2xxx 75mA
1738-IJM23 160mA
1738-SSIM23 110mA
1738-IR2M12 220mA
1738-IT2IM12 175mA
1738-VHSC24M23 180mA
1738-232ASCM12 75mA
1738-485ASCM12 75mA
DeviceNet Communication Rate
DeviceNet Cable
125K bit/s (500m maximum)
250K bit/s (250m maximum)
500K bit/s (100m maximum)
Refer to publication M115-CA001 for more information
1 Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - Februa ry 2005
Page 72

A-2 Specifications
ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapters - 1738-ADN12, -ADN18, -ADN18P, and -ADNX
DeviceNet Power Specifications
Power Supply
Note: In order to comply with CE Low Voltage Directives (LVD), you must use either a NEC Class
2, a Safety Extra Low Voltage (SELV) or a Protected Extra Low Voltage (PELV) power supply to
power this adapter. A SELV supply cannot exceed 30V rms, 42.4V peak or 60V dc under normal
conditions and under single fault conditions. A PELV supply has the same rating and is
connected to protected earth.
Input Voltage Rating 24V dc nominal
DeviceNet Input Voltage Range 11-25V dc DeviceNet specification
Input Overvoltage Protection Reverse polarity protected
DeviceNet Power Requirements 24V dc (+4% = 25V dc) @ 30 mA maximum
Power Supply Specifications
Power Supply
Note: In order to comply with CE Low Voltage Directives (LVD), you must use either a NEC Class
2, a Safety Extra Low Voltage (SELV) or a Protected Extra Low Voltage (PELV) power supply to
power this adapter. A SELV supply cannot exceed 30V rms, 42.4V peak or 60V dc under normal
conditions and under single fault conditions. A PELV supply has the same rating and is
connected to protected earth.
Input Voltage Rating 24V dc
10-28.8V dc range
Input Overvoltage Protection Reverse polarity protected
Inrush Current 6 A maximum for 10 ms
PointBus Output Current 1 A maximum @ 5V dc +
5% (4.75-5.25)
Field Side Power Requirements, Maximum 24V dc (+20% = 28.8V dc) @ 400 mA
Interruption
Output voltage will stay within specifications when input drops out for 10 ms at 10V with
maximum load
General Specifications
LED Indicators
1 green/red Adapter status
1 green/red DeviceNet status
1 green/red PointBus status
1 green System Power (PointBus 5V power)
1 green Adapter Power (24V from field supply)
Power Consumption, Maximum 8.1 W @ 28.8V dc
Power Dissipation, Maximum 2.8 W @ 28.8V dc
Thermal Dissipation, Maximum 9.5 BTU/hr. @ 28.8V dc
Isolation Voltage
(continuous-voltage withstand rating)
Field Power Bus
Nominal Voltage
Supply Voltage
Supply Current
50V rms
Tested at 1250V ac rms for 60 s
24V dc
10-28.8V dc range
10 A maximum
Dimensions Inches) (Millimeters) 4.41 H x 2.83 W x 2.56 D (112 H x 72 W x 65 D)
Operating Temperature IEC 60068-2-1 (Test Ad, Operating Cold),
IEC 60068-2-2 (Test Bd, Operating Dry Heat),
IEC 60068-2-14 (Test Nb, Operating Thermal Shock):
20 to 60°C (68 to 140°F)
Storage Temperature IEC 60068-2-1 (Test Ab, Un-packaged Non-operating Cold),
IEC 60068-2-2 (Test Bb, Un-packaged Non-operating Dry Heat),
-40 to 85°C (-40 to 185°F)
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 73

Specifications A-3
ArmorPoint DeviceNet Adapters - 1738-ADN12, -ADN18, -ADN18P, and -ADNX
General Specifications (continued)
Relative Humidity IEC 60068-2-30 (Test Db, Un-packaged Non-operating Damp Heat):
5-95% non-condensing
Shock IEC60068-2-27 (Test Ea, Unpackaged Shock):
Operating 30 g
Non-operating 50 g
Vibration IEC60068-2-6 (Test Fc, Operating):
5 g @ 10-500 Hz
ESD Immunity IEC 61000-4-2:
6 kV contact discharges
8 kV air discharges
Radiated RF Immunity IEC 61000-4-3:
10V/m with 1 kHz sine-wave 80%AM from 30 MHz to 2000 MHz
10V/m with 200 Hz 50% Pulse 100%AM at 900 Mhz
10V/m with 200 Hz 50% Pulse 100%AM at 1890 Mhz
EFT/B Immunity IEC 61000-4-4:
±4 kV at 5 kHz on power ports
±3 kV at 5 kHz on signal ports
Surge Transient Immunity IEC 61000-4-5:
±1 kV line-line(DM) and ±2 kV line-earth(CM) on power ports
±2 kV line-earth(CM) on shielded ports
Conducted RF Immunity IEC 61000-4-6:
10Vrms with 1 kHz sine-wave 80%AM from 150 kHz to 80 MHz
Emissions CSPR 11:
Group 1, Class A
Enclosure Type Rating Meets IP65/66/67 (when marked)
Mounting Base Screw Torque #8 screw, 7.5 in. lbs. in Aluminum, 16 in. lbs. in Steel
Wiring Category
1
1 - on power ports
1 - on communications ports
Weight Imperial (Metric) 0.80 lb. (0.36 kg)
Certifications:
2
(when product is marked)
c-UL-us UL Listed Industrial Control Equipment, certified for US and Canada
2
CE
European Union 89/336/EEC EMC Directive, compliant with:
EN 61000-6-4; Industrial Emissions
EN 50082-2; Industrial Immunity
EN 61326; Meas./Control/Lab., Industrial Requirements
EN 61000-6-2; Industrial Immunity
C-Tick Australian Radiocommunications Act,
compliant with: AS/NZS CISPR 11; Industrial Emissions
ODVA ODVA conformance tested to DeviceNet specifications
1. Use this Conductor Category information for planning conductor routing. Refer to Publication 1770-4.1, Industrial Automation
Wiring and Grounding Guidelines.
2. See the Product Certification link at www.ab.com for Declarations of Conformity, Certificates, and other certification details.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - Februa ry 2005
Page 74

A-4 Specifications
Notes:
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 75

Quick Start For the 1738-ADNX
Appendix
B
What’s In This Appendix?
In this Quick Start, you will learn how to use the 1738-ADNX with a
ControlLogix system on DeviceNet. You will also use one of the
1738-ADNX’s features (Auto Start Mode) in an exercise to
automatically configure devices on its Subnet
When you complete this quick start you will be familiar with:
• The 1738-ADNX as an adapter on the ControlLogix primary
DeviceNet network and as a scanner on the DeviceNet
expansion Subnet
• Configuring the 1738-ADNX with ArmorPoint I/O on its Subnet
• Using and applying the correct termination of the 1738-ADNX’s
Subnet
• Using the 1738-A DNX to expand the length of a DeviceNet
system
• Using the 1738-A DNX to implement a second baudrate for
Subnet devices
For rules and guidelines regarding how to use the 1738-ADNX,
see Appendix C of this manual.
.
Assumptions
1 Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
A ControlLogix DeviceNet system already exists to which you ar e
going to add new devices without modifying the existing system’s
architecture. Y ou are going to expand the length of the system beyond
its maximum specification and add new devices that can operate at a
different baudrate than the existing system.
The existing system attributes include:
• ControlLogix processor in a Logix chassis of 4 or more slots.
• 1756-ENBT (EtherNet/IP) in the Logix chassis.
• Configuration to 125 Kb aud with thin trunk (max distance is
100 m (328 ft.) (ControlLogix chassis may be connected on any
DeviceNet network.)
• ControlLogix processor with a 1756-DNB (DeviceNet) in slot 3
(slot 3 was picked for this example. This can be any slot.)
Page 76

B-2 Quick Start For the 1738-ADNX
The new Subnet system attributes include:
• Most field devices are more than 100 m from the ControlLogix
Processor
• Previously installed and documented at 500 Kbaud
• 1738-ADNX with discrete inputs and outputs for several field
devices
• The ability to be replicated several times in the future without
changing documentation. (i.e., devices will be replicated with
same attributes, node addresses, etc.)
The existing devices will be wired to ArmorPoint I/O.
NetLinx will let you configure everything from your PC, using the
1756-ENBT module and a 1756-DNB. You will be able to connect
from your computer over Ethernet to the ControlLogix backplane and
configure both the primary (remember the 1 73 8- ADNX will be a new
node on this network) and Subnet network (the 1738-ADNX will be
node 0 on this network).
When you have completed this exercise you will be able to browse
through the 1738-ADNX to see its backplane, using only the
RSNetWorx for DeviceNet software package.
1. Open RSNetWorx for DeviceNet by double clicking the icon on
your desktop.
2. From the RSNetWorx for DeviceNet main menu select File>New.
3. Select DeviceNet configuration.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 77

Quick Start For the 1738-ADNX B-3
4. Click OK.
Now that you have created a new DeviceNet project, go on line
by clicking the Online icon on the toolbar.
5. A list of the available drivers in RSLinx appears. Drill down from
Ethernet into your ControlLogix project through the backplane
to your 1756-DNB in slot 3. Select channel A, as shown below.
Your system may not be
configured as illustrated.
You must pick an Ethernet
driver that is configured
with the address of your
ControlLogix 1756-ENBT
bridge module.
6. Click OK to accept the path configuration.
7. Click OK to the prompt.
The sticker on the front of
your 1756-ENBT module
identifies the IP address
configured for your
module.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 78

B-4 Quick Start For the 1738-ADNX
RSNetWorx will go on line. A screen similar to the one below
will appear:
Your system may not look like the above system. (You may have more nodes.) It is only
important to verify that you have the 1756-DNB at node 0 and the 1738-ADNX at note 16.
8. After the browse is complete, from the RSNetWorx for
DeviceNet main menu select File>Save As.
9. Type in MainNetworkADNX as the filename (use this exact
name to avoid confusion later).
10. Click Save.
On the main network, the 1738-ADNX acts as an adapter.
• The rotary switches on the front of the 1738-ADNX should be set
to node 16.
• Verify your browse reported the 1738-ADNX at node 16.
• Later you will browse deeper to see the Subnet. (Note that on
the Subnet, the 1738-ADNX acts as a scanner and is always at
node 0 on that network.)
11. Download a blank scanlist to the 1756-DNB.
a. Y ou do not want the existing program in our Logix processors
to interfere with clearing the scanlist. T o en sure that this does
not occur, use the key switch to put
all the processors in
program mode then back to remote program (turn the keys
right then back to the middle position).
b. Double click the 1756-DNB to bring up its properties page.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 79

Quick Start For the 1738-ADNX B-5
c. Select the Scanlist tab and when prompted click Download.
12. When the download is complete, add the 1738-ADNX to the
scanlist by selecting the 1738-ADNX (node 16) and clic king the
single right arrow.
A warning window opens that says that the 1738-ADNX does
not contain any I/O data.
At this point, RSNetWorx for DeviceNet does not know how
many bytes of data are being inputted and outputted to the
Subnet so it cannot fill in the values for you.
13. Press OK to close the warning window.
14. To verify that there are no data for input and outputs, click the
1738-ADNX in the Scanlist window.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 80

B-6 Quick Start For the 1738-ADNX
X
15. Click Edit I/O Parameters.
Click the 1738-ADN
in the Scanlist and
then click Edit I/O
Parameters to
verify input and
output bytes.
16. Verify that nothing is filled in for input and output sizes (both
are zero). If you knew how much data was being produced and
consumed on the Subnet, you could fill these fields in manually.
Because it is easier to let RSNetWorx for DeviceNet fill in these
values for us, click Cancel to close this window.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 81

Quick Start For the 1738-ADNX B-7
Click the
ill
r
17. Remove the 1738-ADNX from the scanlist for now by clicking
the double arrows.
double left
arrow to
remove the
1738-ADNX
from the
Scanlist. Then
verify that the
Scanlist is
empty. Y ou w
return here
later after
RSNetWorx fo
DeviceNet
knows more
about the
devices on the
Subnet.
18. Click OK. When prompted if you want to download changes to
the device, click Yes.
At this point you have a choice:
• You could start another instance of RSNetWorx for DeviceNet
and configure the Subnet. You would then see the
1738-ADNX at node 0 on the Subnet and add the ArmorPoint
I/O to its scanlist. You would then map the data to the exact
location you want it. For example, if ladder logic was already
written, you could map it to an address.
• If you have not written your ladder logic yet and you are not
particular about the mapping, you could use the auto start
feature of the 1738-ADNX to map all the devices
automatically from the primary network. After the mapping is
complete, look at the Subnet to verify that eve rything worked
as expected.
19. Verify that the subnetwork taps are electronically isolated and
have their own terminating resistors at each end.
IMPORTANT
The Subnet must always be properly terminated. In
this example, there is a terminating resistor at each
end of the Subnet trunk.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 82

B-8 Quick Start For the 1738-ADNX
se
)
To properly terminate the 1738-ADNX when using a Subnet,
refer to the illustration.
Terminator Resistor
Note that standard DeviceNet
terminator resistors are
shown in this illustration.
Refer to the On-Machine
Connectivity catalog,
publication no. M115-CA001,
Network Media section, for
other DeviceNet connection
options.
Drop
Terminator Resistor
Trunk
Main
Drop
Trunk
Subnet
DeviceNet In
Subnet Out
X10
PWR
Adapter
Terminator Resistor
• If you are not going to use the Subnet, you must still
terminate it!
• Note that the non-terminating base is shipped with the
1738-ADNX only. The terminating base is shipped with all the
other ArmorPoint DeviceNet adapters.
• Do not use carbon resistors. Metal film is recommended.
1738-ADNX With Subnet (1738-ADNX Subnet Drop Off Subnet Trun k
Terminator Resistor
1738-ADNX
Adapter
Status
DeviceNet
Status
PointBus
Status
System
Power
Adapter
Power
X1
I/O Base I/O Base non-terminating ba
43899
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Continue ONLY after you have verified that the taps are
terminated correctly.
20. Double click on the 1738-ADNX to open the properties window.
In the next step you will download the EDS defaults to the
1738-ADNX.
Page 83

Quick Start For the 1738-ADNX B-9
21. Select the Parameters tab and choose Download.
22. Verify that your window looks similar to the following window.
Review of the 1738-ADNX Rules and the MACID Parameter
To understand some of the MACID parameters, you should review
some of the rules for using the 1738-ADNX.
• The 1738-ADNX always has address 0 on the Subnet.
• All ArmorPoint I/O backplane module MACIDs must be
numerically less than those of non-backplane Subnet modules.
• Each backplane module’s MACID must be greater than that of its
left neighboring module.
• The 1738-ADNX has a unique attribute: Max(imum) Backplane
MACID. This value represents the highest node address of a
module residing on the backplane. This value must be greater
than or equal to the rightmost backplane ArmorPoint I/O
module, but must be less than that of any non-backplane Subnet
module. You select this value to allow for the future addition of
backplane modules. The attribute’s default value is 31,
representing the middle of the address range.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 84

B-10 Quick Start For the 1738-ADNX
• The 1738-ADNX will automatically maintain the MACIDs of the
backplane modules.
• Note that the assignment of the MACIDs of the non-backplane
subnet modules is manual and is not performed or retained by
the 1738-ADNX.
• The 1738-ADNX supports 125 kb, 250 kb, and 500 kb baudrates.
For this example, you are going to set the Subnet to 125 kb.
When using Auto Start Mode, the adapter:
• Sets all ArmorPoint I/O modules on the backplane to Autobaud.
• Reads all ArmorPoint I/O module IDs on the backplane.
• Sets the ArmorPoint I/O module addresses sequentially.
• Sets the Max Backplane MACID.
• Generates a scanlist for the backplane.
• Maps automatically I/O data, based on byte (I/O data is mapped
in the adapter’s memory at the next available byte), word (I/O
data is mapped at the next available word), double-word (I/O
data is mapped at the next available double word) or fixed (the
data is mapped to a fixed allocation size). You will choose one
of these four options from a pulldown menu later in this Quick
Start.
IMPORTANT
Your 1738-ADNX DeviceNet adapter must be free of
I/O connections when you use Auto Start Mode. If
another scanner device has established I/O
connections with the adapter (if it is mapped in
another scanner’s scanlist), the attempt to use Auto
Start Mode is rejected. Also, when the adapter is
configuring itself in Auto Start Mode, no other device
can establish I/O connections to the adapter.
When the adapter completes this sequence of events, the
ArmorPoint I/O modules connected to the adapter are ready to
accept connections from a scanner.
IMPORTANT
Although Auto Start Mode lets your adapter operate
with a default configuration, you can choose to
manually change the configuration after operation
has begun or you can write a custom configuration.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 85

Quick Start For the 1738-ADNX B-11
When Auto Start Mode is used, the adapter and connected I/O
modules go through the following sequence of events:
• Connections are established to I/O modules
• The adapter makes Change of State (COS) connections if the I/O
module supports COS, if not, the connection is Polled
• Data is mapped to the connections
The notes above explain parameter 1 – Max Backplane MACID. Next
you will review parameter 6, Auto Start Mode and parameter 7, Fixed
Map Size.
Review of Auto Start Mode
1. Select parameter 6, then click the help icon to display
information about Auto Start Mode.
A window describing Auto Start Mode opens.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 86

B-12 Quick Start For the 1738-ADNX
Right now, the 1738-ADNX is not in another scanner’s scanlist so
you can use the Auto Start Mode feature. By using Auto Start
Mode, the 1738-ADNX will map all the devices on the Su bnet
and automatically adjust the value for the following parameters:
• 1, Max Backplane MACID
• 9, Poll/COS Connection Consume Size
• 10, Poll Connection Produce Size
• 11, COS Connection Produce Size, and
• 12, Strobe Connection Produce Size.
2. Select the pulldown box next to the Auto Start Mode parameter.
Y ou can map the data using the four options discussed earlier. If
you choose to use the Map Data With Fixed Map Size option, the
map size is selected with parameter 7, Fixed Map Size.
3. For this example, choose Map Data To Word Boundaries as shown
below:
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 87

Quick Start For the 1738-ADNX B-13
Notice that parameters 9, 10, 11 and 12 are still at their default of
2 bytes. These values will be filled out for you when this action
is complete.
Download
parameters to
the device
Monitor
icon
4. Make sure All is selected and the Monitor value then click the
icon to download parameters to the device (this triggers the
Auto Start Mode).
5. Click the Monitor icon and notice:
• Parameter 6 has gone back to Do Nothing. The Auto Start has
begun and will not repeat unless you trigger it again later.
• Parameter 8, Phys List Acqu ire Status, indicates you are in Auto
Start Mode. Give the system at least a minute or two to
complete the configuration you requested then go to the next
step.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 88

B-14 Quick Start For the 1738-ADNX
d
6. Wait for parameter 8 to return to idle. Then click the Monitor
icon to end monitoring. Notice the following:
• Parameter 1 has been filled in for you. There are three
ArmorPoint I/O modules in the backplane, causing the
default to change from 31 to 3.
• Parameter 3: Verify the Backplane Baudrate is 125 Kbaud. If it is
not, you will need to find out why and make the necessary
corrections.
• Parameter 9, 10, 11, and 12 have been filled in for you.
Expand the
column to
view all the
text.
Consume size is
data that the
adapter will
consume from
the scanner.
These are the
outputs being
sent from the
scanner to the
ArmorPoint I/O
adapter.
Produce size is
data the
1738-ADNX
adapter will
produce for the
1756-DNB
scanner. This
will be discusse
in more detail
later in this
section.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Note that you do not need to view the Subnet to determine
where the data has been mapped. You can go back to monitor
mode and view parameter 14, Cycling I/O Mapping. The help for
this parameter states how to use the parameter to determine
mapping.
7. Press OK to close this window.
Page 89

Quick Start For the 1738-ADNX B-15
8. From the RSNetWorx for DeviceNet main menu, select
File>Save.
Browse the Subnet
IMPORTANT
Look at the Subnet at this point to make things more clear.
1. From the RSNetW orx for DeviceNet main menu, select File>New
and then select DeviceNet Configuration.
2. Click OK.
Now that you have a new DeviceNet project created.
3. Click the Online icon.
Last time you browsed to the 1756-DNB. This time you will
browse a little deeper.
You must save your work before moving on.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 90

B-16 Quick Start For the 1738-ADNX
Last time you browsed the main network
This time you will browse the Subnet
4. Drill down from Ethernet into your ControlLogix demo box
through the backplane to your 1756-DNB in slot 3, channel A,
1738-ADNX and select DeviceNet Subnet as shown below:
5. To go on line, click OK to accept the path configuration and then
OK to the prompt.
Wait for the browse to complete.
6. From the RSNetWorx for DeviceNet main menu, select
File>Save As.
7. Type in SubNetADNX as the filename.
8. Click Save.
IMPORTANT
You must save your work before continuing.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 91

Quick Start For the 1738-ADNX B-17
The nodes can be in any order. Verify:
o
9. Verify your screen appears as shown below.
• All four are there
• They have the correct node numbers
On the Subnet, the 1738-ADNX is a scanner and it is always at
node 0. It is OK for some or all of the node numbers on the
Subnet to be the same as devices on the primary network.
Because they are two different networks, duplicate node errors
will not occur. The 1738-ADNX will communicate back to the
1756-DNB scanner as a single entity (only taking up one node
number on the main network).
10. Double click on the 1738-ADNX to bring up its properties page.
11. Select the Scanlist tab and when prompted select Upload.
To view the configuration you just created, upload the scanlist
from the 1738-ADNX.
Make sure
you click
Upload! You
do not want t
download
over the
configuration
you just
created.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 92

B-18 Quick Start For the 1738-ADNX
• Verify your scanlist matches that shown below.
• Notice that all the ArmorPoint I/O modules have been added
to the scanlist, as you probably expected.
You are about to look at the input and output tabs. Based on
your selections earlier, all the data should be mapped to word
boundaries.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 93

Quick Start For the 1738-ADNX B-19
e
n
Inputs and Outputs
1. Select the Input tab. A single word is 16 bits. Notice that the
mapping is as expected.
• The first two bytes (1 byte = 8 bits) are reserved as read only.
• The first word is completely used, so the 1738-IB4M12 can map
to the beginning of the next word (byte 2, bit 0).
• There is a space between the 1738-IB4M12 and the
1738-OB4EM12 because the next word does not start until byte
4.
This field describes how th
data is transferred betwee
the I/O modules and the
adapter on the PointBus
Subnet.
The current memory
buffer selected is
COS/Cyclic. There are
also buffers for Polled
and Strobed. This is
how the data will be
transferred to the
scanner (1756-DNB in
this example).
Note the mapping in the
1738-ADNX Scanner is
shown in byte
increments. The
1756-DNB displays in
double words (4 bytes).
Use the scroll bar as
needed to see all of the
data.
The first 2 bytes are
reserved for status.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 94
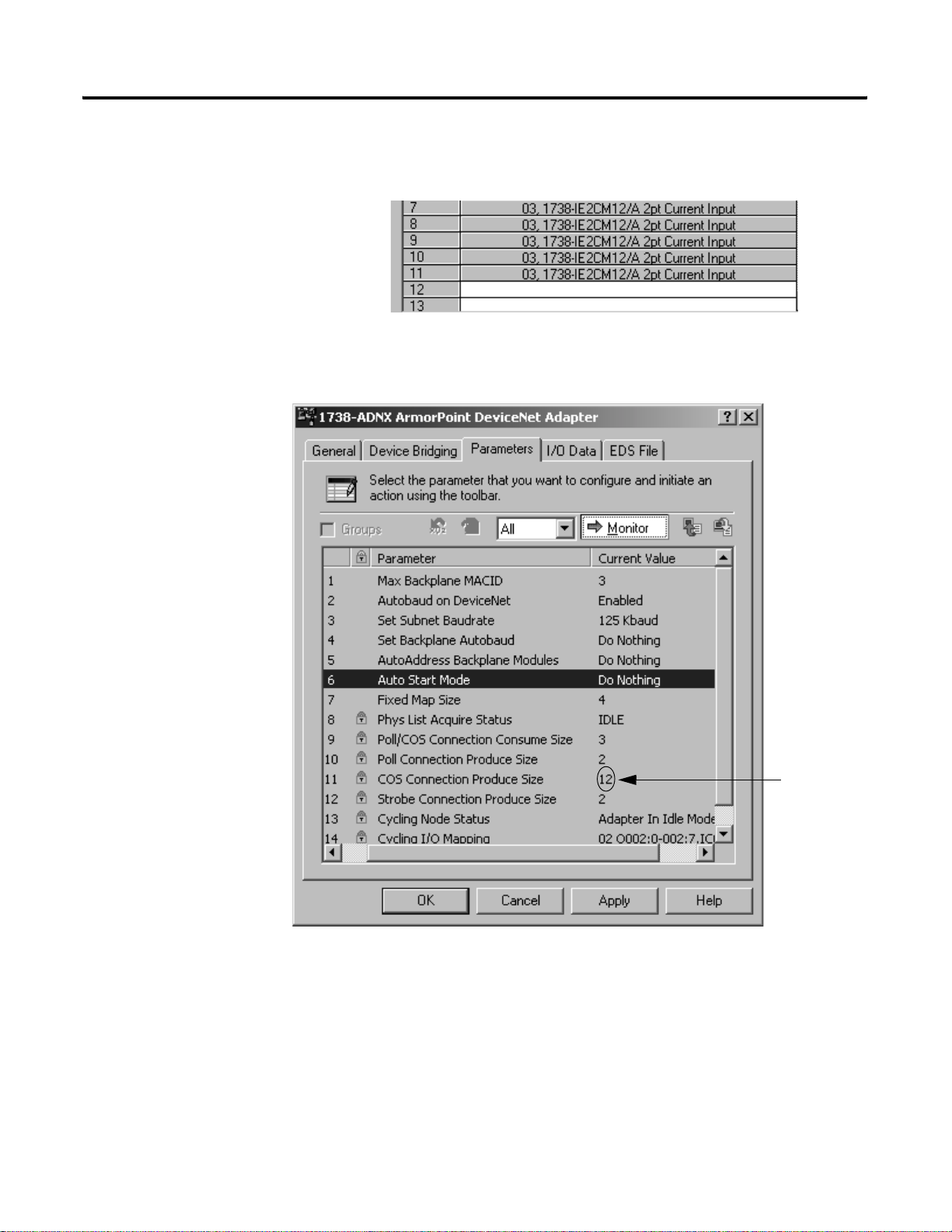
B-20 Quick Start For the 1738-ADNX
Earlier view of the parameters.
Scroll down and notice that bytes 0 throug h 11 = 12 bytes total
were enough for the input data.
This matches what you observed earlier on the main network:
The primary
network knew
you were
producing 12
bytes of data.
• The data mapped in the 1738-ADNX will be exchanged with the
1756-DNB scanner.
• There are thre e memory buffers that the 1738-ADNX uses for
input data to the scanner on Device Net. The buffers are
COS/cyclic, polled, and strobed. You can map data into any of
the three buffer areas on the adapter.
• Currently, all of the I/O modules are mapped to the COS/cyclic
buffer.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 95

Quick Start For the 1738-ADNX B-21
Earlier view of the parameters.
2. Select the pulldown listbox next to the Memory label in the
middle of the window to display the three memory buffer
choices.
3. Select each of the choices and view the mapping. You will see
that only the COS/cyclic buffer is b ein g used (There are 2 bytes
reserved for status in each buffer. These words are not for a
specific module.)
4. Set the Memory selection back to COS/cyclic.
Note that for the 1738-ADNX, each line in the mapping area
represents a byte of data. When you view the 1756-DNB, each
line will be 4 bytes of data (double word).
Now you are ready to take a look at the output side. Based on
the numbers you saw on the main network you expect to see 3
bytes (two of them are going to be reserved status words).
The primary
network knew
you were
consuming 3
bytes of data.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 96

B-22 Quick Start For the 1738-ADNX
You should still be looking at the subnet 1738-ADN X Input tab.
Now select the Output tab and verify you have the following:
• Notice that only the output module 1738-OB4EM12 appears.
These two say read
only, but since it is
an output tab, a
better description is
reserved for future
use.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
5. Expand the plus next to node 2.
• Several revisions ago (RSNetWorx for DeviceNet V3.21) the
ability to view I/O details from the Input and Output windows
was added into the software.
• From the Input and Output windows, you can view detailed I/O
information for each device in the scanlist of a DeviceNet
scanner.
• To view the I/O details for a particular device, click the plus sign
(+) located to the left of the device. If a plus sign is not
displayed, there are not any I/O details for that device.
• This feature is driven by each device’s EDS file.
Page 97

Quick Start For the 1738-ADNX B-23
Click OK and not Cancel to close the window.
6. Select Output V alue #1 and notice the exact location of that bit is
displayed. You can easily tell that Output Value #1 is in byte 2,
bit 1 (see the highlighted portion of byte 2). This information
will make it very easy to write your ladder logic late r.
You uploaded the scanlist and looked at the input and output
data. Now you are about to save this information to your hard
disk.
7. Click OK (not cancel) to close this window.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 98

B-24 Quick Start For the 1738-ADNX
8. From the RSNetWorx for DeviceNet main menu, select
File>Save.
IMPORTANT
You must save your work before moving on.
Now all the information is saved in the file SubnetADNX.dnt.
Navigate Between Networks
A nice feature of RSNetWorx for DeviceNet is the easy way it lets you
commission the Subnet. You can have two DeviceNet projects
because there are actually two DeviceNet networks. Another nice
feature of RSNetWorx for DeviceNet is the easy way it lets you
navigate between two related networks rather than having to keep
track of which network file goes with what.
RSNetWorx for DeviceNet provides an easy way to associate two
networks that will allow quick navigation between them. You will
look at that now.
1. Double click on the 1738-ADNX icon to pull up its properties
page.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 99

Quick Start For the 1738-ADNX B-25
2. Select the Device Bridging tab. The following window opens.
This window lets you define a file that is associated with this
one through the 1738-ADNX. Once you specify the associated
file, you will be able to jump to that file through a menu
selection from the 1738-ADNX. The file you nee d to associate in
this case is the MainNetworkADNX.dnt project file you created
earlier.
3. Click the Associate File button.
4. Make sure you are looking in the Networks folder in the path
shown below.
5. Select MainNetworkADNX.dnt then the Open button. The
MainNetworkADNX.dnt file will appear in the File box as shown
below.
6. Click OK to close the properties window.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
Page 100

B-26 Quick Start For the 1738-ADNX
7. From the RSNetWorx for DeviceNet main menu, select
File>Save. Now you can observe how you would switch
networks.
Switch Between Networks
1. Move the cursor over the 1738-ADNX in the network browse
window.
2. Press the right mouse button.
3. Click Associated Network from the menu.
If prompted to save your changes, you must select Yes (you will
probably not get this prompt if you saved earlier).
To get back to the main network, associate the SubnetADNX.dnt
project to MainNetworkADNX.dnt using the following steps:
4. Double click on the 1738-ADNX adapter at Node 16.
5. Click the Device Bridging tab.
Publication 1738-UM001A-EN-P - February 2005
 Loading...
Loading...