Page 1

Table of Contents
Index
SUPERSCRIPT 1800
NETWORK USER’S GUIDE
July, 1999
808-878291-011A
Page 2

Proprietary Notice and Liability Disclaimer
The information disclosed in this document, including all
designs and related materials, is the valuable property of
NEC Technologies and/or its licensors, as appropriate
reserve all patent, copyright and other proprietary rights to
this document, including all design, manufacturing,
reproduction, use and sales rights thereto, except to the
extent said rights are expressly granted to others.
The NEC Technologies product(s) discussed in this document
are warranted in accordance with the terms of the Limited
Warranty Statement accompanying each product. However,
actual performance of each such product is dependent upon
factors such as system configuration, customer data and
operator control. Since implementation by customers of each
product may vary, the suitability of specific product
configurations and applications must be determined by the
customer and is not warranted by NEC Technologies.
To allow for design and specification improvements, the
information in this document is subject to change at any time
without notice. Reproduction of this document or portions
thereof without prior approval of NEC Technologies is
prohibited.
© NEC Technologies, Inc., 1999
Microsoft, Windows, Windows 95, Windows 98,
Windows NT, Windows NT Server, Windows for
Workgroups, and MS-DOS are registered trademarks of
Microsoft Corporation.
PostScript
NetWare
®
is a trademark of Adobe Systems Incorporated.
®
and Novell
®
are trademarks of Novell
Incorporated.
All other product, service, brand, or trade names used in this
publication are the trademarks or registered trademarks of
their respective companies or organizations. NEC disclaims
any responsibility for specifying which marks are owned by
which companies or organizations.
Copyright 1999
NEC Technologies, Inc.
1250 N. Arlington Heights Rd.
Itasca, IL 60143
All Rights Reserved.
Copyright 1999
NEC Corporation
7-1 Shiba 5-Chome, Minato-Ku
Tokyo 108-01, Japan
All Rights Reserved.
ii SuperScript 1800 — Network User’s Guide
Page 3

To move to a subject, click on a subject heading.
CONTENTS
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION
About this Guide 1
Network Printing 1
Print Clients 1
Print Jobs 2
Printer Drivers 2
Printer Port 2
Network Operating Systems 2
Network Topologies 2
Network Interface Card 2
Networking Features 2
Network Printer Manager 2
SuperScript 1800 Web Pages 2
Operator Panel Commands 3
NIC Flash Memory 3
CHAPTER 2: NETWORK TOPOLOGIES
Overview 5
Network Interface and Cabling 5
Types of Network Topologies 5
Peer-to-Peer Topology 5
Printer Server Topology 6
Printer Sharing Topology 7
What Next 7
CHAPTER 3: CONNECTING THE PRINTER
Overview 9
Where to Start 9
Installing the NIC 10
Accessing the Printer Controller Board 10
NIC Installation 11
Connecting the Printer 11
Configuring the NIC 12
SuperScript 1800 Web Pages 12
Using the Printer’s Operator Panel 12
Configuring the IP Address 12
Configuring the Printer for IPX 13
Configuring the Printer for UNIX Clients 14
Configuring the Printer for AppleTalk 14
Using the Network Printer Manager 15
Printing a Network Configuration Page 16
What Next 16
CHAPTER 4: PEER-TO-PEER TOPOPLOGY
Introduction 17
Basic Requirements 17
Configuring a Windows Client 17
Windows 95 and 98 Computers 17
Windows NT 4.0 Computers 19
Configuring a Macintosh Client 20
Requirements 20
The LaserWriter Printer Driver 20
AppleScript 20
Configuration Procedure 20
Configuring a UNIX Client 21
Configuration Procedures 21
CHAPTER 5: PRINTER SERVER TOPOLOGY
Introduction 23
NetWare Networks 23
Using NPM to Configure NetWare 23
Configuring an NDS Queue 24
Configuring a Bindery Queue 25
Configuring NetWare 3.12 27
Configuring NetWare 4.x and 5.x 28
Using the NetWare Printer Console 28
Using the NetWare Administrator 28
Configuring a Windows 3.1x Client 31
Configuring a Windows 95 or 98 Client 32
Configuring a Windows NT 4.0 Client 33
Configuring a Macintosh Client 34
Software Requirements 34
Printer Hardware Requirements 34
Installing the Software 34
iii
Page 4

Configuring a UNIX Client 34
Configuration Procedures 34
Windows NT Server Networks 35
Configuring Windows NT Server 35
Configuring a Windows 3.1x Client 38
Configuring a Windows 95 or 98 Client 39
Configuring a Windows NT 4.0 Client 40
Configuring a Macintosh Client 41
Software Requirements 41
Printer Hardware Requirements 41
Installing the Software 41
Configuring a UNIX Client 42
Configuration Procedures 42
APPENDIX A:
OPERATOR PANEL COMMANDS
Introduction 43
Network Menu Tree 43
NIC Configuration Commands 43
APPENDIX B:
NETWORK PRINTER MANAGER
Introduction 47
Installation 47
Starting NPM 47
Procedures 47
Main Window 48
Printers Menu 48
View Menu 48
Settings Menu 48
Maintenance Menu 48
Help Menu 48
Network Interface Window 48
General Tab 48
TCP/IP Tab 49
NetWare Tab 49
AppleTalk Tab 50
SNMP Tab 50
Printer Properties Window 51
Model Details 51
Printer Menu 51
Config Menu 52
Job Menu 52
PCL Menu 53
I/O Menu 53
PS Menu 54
Alerts Window 54
General Tab 54
Printer Status Window 55
Protocol Statistics Window 55
TCP/IP Tab 55
Upgrading the Firmware 55
APPENDIX C:
SUPERSCRIPT 1800 WEB PAGES
Introduction 57
Installation 57
How to View the Web Pages 57
Home Page 57
Admin Pages 58
General Information 58
General Configuration 58
TCP\IP Configuration 59
NetWare Configuration 59
AppleTalk Configuration 60
SNMP Configurations 61
SNMP Trap Configuration 61
SNMP Community Configuration 61
Operator Panel Pages 62
Printing Page 62
Config Page 63
Job Page 64
PCL Page 65
PS Page 65
Change Password 66
Network Printer Details 66
iv SuperScript 1800 — Network User’s Guide
Page 5

Protocol Statistics 67
TCP\IP Statistics 67
IPX Statistics 67
AppleTalk Statistics 68
SNMP Statistics 68
DLC Statistics 69
APPENDIX D:
TROUBLESHOOTING
Introduction 71
Basic Troubleshooting 71
APPENDIX E:
UPGRADING THE NIC FIRMWARE
Introduction 73
Prerequisites 73
Upgrade Procedures 73
Index
v
Page 6

vi SuperScript 1800 — Network User’s Guide
Page 7

CHAPTER 1
INTRODUCTION
A
BOUT
This user guide describes how to connect and configure your
SuperScript 1800 printer as a network printer. For
information about using the printer, see the NEC SuperScript
1800 User’s Guide .
The chapters in this guide, and the sections they contain, are
presented in a logical way that guides you from start to
finish.
Chapter 1, “Introduction,” introduces you to network
printing and the features of the SuperScript 1800 printer.
Chapter 2, “Networking Topologies,” introduces you to three
methods (topologies) used for networking your printer. Once
you understand how they work, select which method fits
your needs and requirements, then continue with Chapter 3,
“Connecting the Printer.”
Chapter 3, “Connecting the Printer,” describes how to install
a network interface card (NIC), in case you purchased a
printer without a NIC, then describes how to connect the
printer to a network. The final section describes how to
configure the NIC so it can communicate with your network.
Chapter 4, “Peer-to-Peer Topology,” and Chapter 5, “Printer
Server Topology,” describe how to implement the topologies
described in Chapter 2.
Appendix A, “Operator Panel Commands,” is a reference
that describes the network menu items in the printer’s
Operator Panel and how to navigate through them.
Appendix B, “Network Printer Manager,” describes what the
NEC SuperScript 1800 Network Printer Manager (NPM) is
used for and provides a detailed reference of the controls in
it.
THIS
G
UIDE
Appendix C, “The SuperScript 1800 Web Pages,” describes
what the printer web pages are used for and provides a
detailed reference of the controls in them.
Appendix D, “Troubleshooting,” provides basic information
about troubleshooting minor problems.
Appendix E, “Upgrading the NIC Firmware,” describes how
to upgrade the firmware located on the NIC.
N
ETWORK
Network printing involves a network to interconnect print
clients and a printer. Each client can use the network for
connecting to the printer.
P
RINTING
Print Clients
A print client is any computer that uses the network to
connect to the printer. They create print jobs then send them
to the printer. Listed below are the types of print clients that
can send print jobs to the SuperScript 1800.
• Windows NT 4.0 computers
• Windows NT Server 4.0 computers
• Windows 98 computers
• Windows 95 computers
• Windows 3.1x computers
• Macintosh computers running Mac OS 7.1 or higher
• UNIX computers
1
Page 8

Print Jobs
A print job is computer code that contains print data and
commands for processing the data. A print client application,
such as a word processor, spreadsheet, or graphics program,
creates print jobs.
Printer Drivers
Printer drivers are software located on a print client that
enables an application to communicate with the printer.
Supplied with your printer are the following printer drivers.
• PCL6 Printer Driver
• PCL5e Printer Driver
• Windows PostScript Printer Driver
Any one of these drivers can be used to enable an application
to communicate with the printer.
Macintosh computers running Mac OS 7.1 or higher, use the
LaserWriter8 printer driver. Supplied with your printer is an
NEC SuperScript 1800 PPD that helps the LaserWriter8
driver communicate with the printer.
UNIX computers have a software utility called LPR which
sends plain text or PostScript data to the printer. LPR is part
of their operating systems.
Printer Port
A printer port is a software interface on a print client that
makes the connection between the printer driver and the
printer. Typically, a printer port must be created on the print
client then selected from inside the printer driver.
Network Operating Systems
Networks use an operating system for managing the
network. Depending on the method (topology) used to
connect your printer to the network, a network operating
system (NOS) may have to be configured to recognize the
printer and make it available to print clients.
The SuperScript 1800 can directly connect to an Ethernet
10Base-TX or 100Base-TX network that is running the
following NOSs.
• Microsoft Windows NT Server 4.0
• Novell NetWare 3.12, 4.x, or 5.x
• AppleTalk
• UNIX
Network Topologies
A network topology describes how equipment, such as
printers and computers, are interconnected with the network.
Chapter 2, “Networking Topologies,” describes three
topologies for networking the SuperScript 1800.
Network Interface Card
Printers, computers, and other equipment uses network
interface cards (NIC) for connecting to a network. The NIC is
usually installed inside the printer or computer, and a cable is
used to interconnect the NIC with a network.
ETWORKING
N
For detailed information about the printer’s features, see the
SuperScript 1800 User’s Guide .
EATURES
F
Network Printer Manager
The SuperScript 1800 Network Printer Manager (NPM) is a
tool for remotely managing the printer, its NIC, and to some
extent, the network operating system. For detailed
information about the NPM, see Appendix B, “The Network
Printer Manager,” on page 47.
SuperScript 1800 Web Pages
The SuperScript 1800 Web Pages are a web site for viewing
and administering the printer. The web pages contain many
of the same controls as the NPM. After the printer’s NIC has
been configured with an IP address, a web browser can be
used to navigate to the address to view the pages.
2 SuperScript 1800 — Network User’s Guide
For detailed information about the web pages, see
Appendix C, “SuperScript 1800 Web Pages,” on page 57.
Page 9

Operator Panel Commands
Located on the printer is the Operator Panel. It has menus for
configuring the NIC and for other printer settings. The
commands in the Operator Panel are also available in the
NPM and the SuperScript 1800 Web Pages.
For detailed information about network commands located
in the Operator Panel, see Appendix A, “Operator Panel
Commands,” on page 43.
NIC Flash Memory
The printer’s NIC contains memory devices that hold
firmware for processing network communications. The
firmware also contains the printer’s web pages.
If NEC Technologies releases a upgraded version of the
firmware, a computer running Windows 95 is used to
upgrade the NIC firmware.
For information about upgrading the firmware, see
Appendix E, “Upgrading the NIC Firmware,” on page 73.
INTRODUCTION N
ETWORKING
F
EATURES
Networking Features 3
Page 10

4 SuperScript 1800 — Network User’s Guide
Page 11

CHAPTER 2
NETWORK TOPOLOGIES
O
VERVIEW
A network topology describes how a network interconnects
computers with other equipment such as a printer. This
chapter describes three topologies that can be used as
solutions for networking your SuperScript 1800 printer.
Note:
a computer the can send a print job to the printer.
ETWORK
N
There are two characteristics that define an interface to your
network—the physical and electrical.
Physically, the interface to your network must be an RJ-45
socket. Electrically, the interface must be Ethernet 10Base-TX
or 100Base-TX.
A network cable is used to interconnect the printer with the
network interface. The cable must be a Category 3, 4, or 5
cable with RJ-45 plugs fastened to both ends. If connecting to
a 100 Megabit Ethernet network, use a shielded Category 5
cable.
A network cable is not supplied with the printer.
In this user’s guide, the term “print client” means
NTERFACE
I
RJ-45 Plug
The RJ-45 plug is fastened to both ends
of a Category 3, 4, or 5 network cable.
Use this type of cable to interconnect
the printer with the network interface.
AND
ABLING
C
T
YPES
Three networking topologies can be used for networking
your SuperScript 1800 printer.
• Peer-to-Peer Topology
• Printer Server Topology
• Printer Sharing Topology
This chapter describes each topology. The following chapters
describe how to configure the printer and your computers to
use each topology, except for the Printer Sharing Topology .
Please refer to your computer’s documentation for
instructions on how to configure your computer to share a
printer.
P
EER
The Peer-to-Peer topology is the simplest way to network
your printer. It involves print clients, a printer, and a network
to interconnect everything. The Network Operating System
(NOS) can be Windows NT Server 4.0 or Novell NetWare
3.12, 4.x, or 5.x.
In this scenario, print clients use the network to send print
jobs directly to the printer. There is no intermediary
computer that gets involved between the printer and the
print clients.
Each client must compete with other clients for printer
availability. If the printer is busy processing a print job, each
client must hold their jobs until the printer is ready to accept
them. To help alleviate congestion, the printer can be
upgraded with more memory to temporarily store multiple
jobs until they are printed. Shown on the next page is an
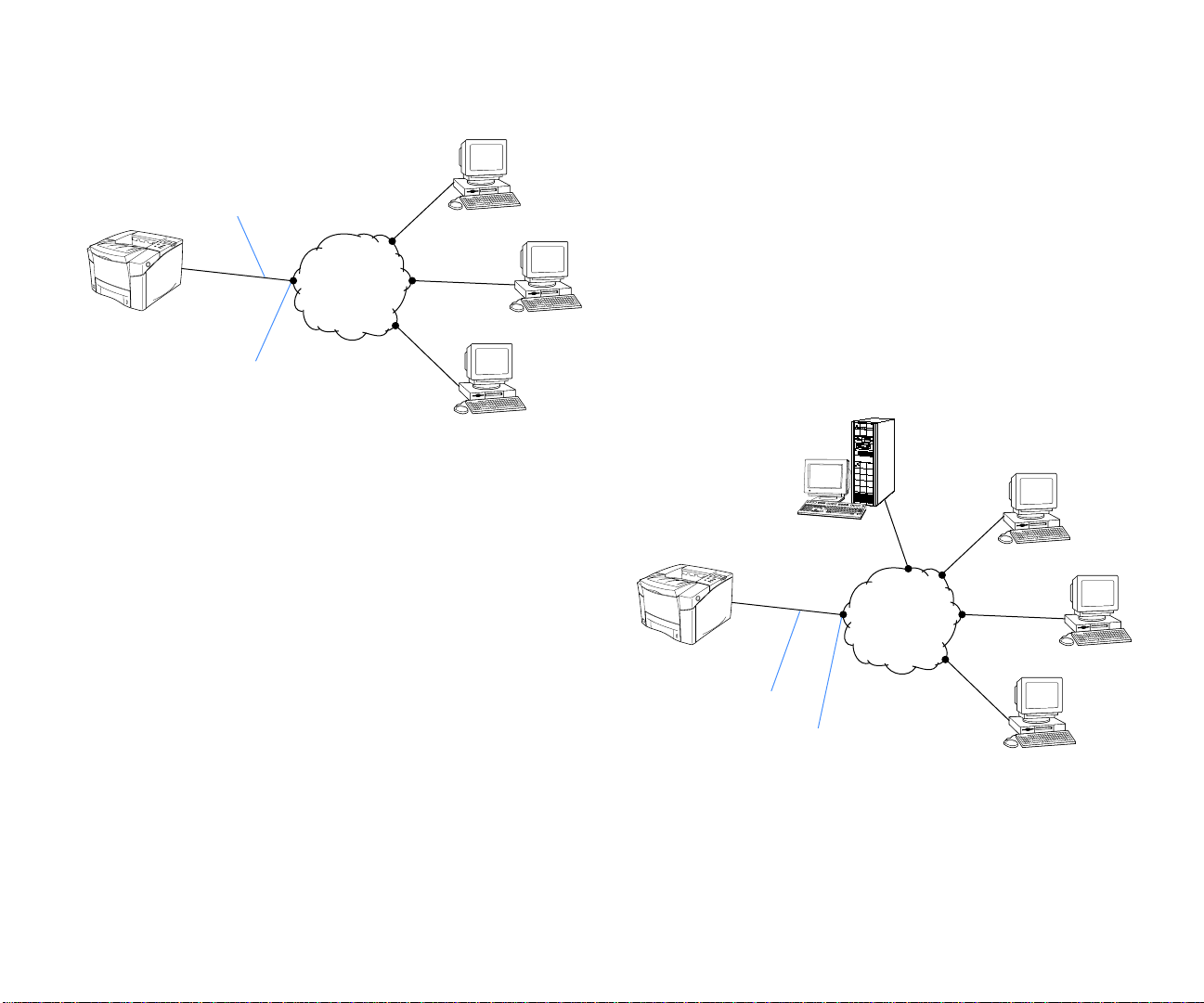
illustration of the Peer-to-Peer topology.
-
TO
OF
N
ETWORK
-P
EER
T
T
OPOLOGY
OPOLOGIES
5
Page 12
A
A
s
j
Peer-to-Peer Topology
n Ethernet LAN is used to interconnect the printer and print
clients. Print clients send print jobs directly to the printer, but
each must wait for printer availability.
printer in the sequence which they are received. This process
relieves a client from having to store the print job and allows
them to focus on other computing tasks. The server can also
be configured for controlling access to the printer and
recording all printing activity.
Shown below is a diagram of the printer server topology. The
cloud in the center of the diagram represents a LAN that
Network Cable
Print Client
interconnects the printer, the print clients, and the printer
server. The network can be a 10 or 100 megabit Ethernet LAN
that transports TCP/IP or IPX protocols.
Ethernet
Printer Server Topology
n Ethernet LAN is used to interconnect the printer, printer
erver, and print clients. Print clients send their print jobs to the
printer server where they are queued. The server then sends the
obs to the printer. The server also controls access to the printer.
Printer
Network Interface
Network
Print Client
Print Client
The cloud in the center of the diagram represents a Local
Area Network (LAN) that interconnects the printer and all
the print clients. The network can be a 10 or 100 megabit
The printer and each print client use their own network cable
Ethernet LAN that transports TCP/IP or IPX protocols.
Printer Server
Print Client
to connect to their own network interface.
For instructions about configuring a print client for this
scenario, read Chapter 4, “Peer-to-Peer Topology,” on page
17.
RINTER
P
ERVER
S
OPOLOGY
T
Printer
Network Cable
Ethernet
Network
Print Client
The printer server topology involves a computer, called a
printer server . All print clients send their print jobs to the
printer server. The printer server then sends the jobs to the
Network Interface
Print Client
printer. The NOS can be Windows NT Server or Novell
NetWare.
In this scenario, print clients use the network to send print
jobs directly to a computer that is configured as a printer
server . The server then sends the jobs to the printer.
The server uses a process called queueing, meaning it can
receive and store multiple print jobs. Jobs are sent to the
6 SuperScript 1800 — Network User’s Guide
Page 13
For information about configuring a print client for this
c
T
scenario, read Chapter 5, “Printer Server Topology,” on
page 23.
P
RINTER SHARING TOPOLOGY
Although this chapter provides a brief description of
Microsoft Printer Sharing, instructions for configuring your
computer to share a printer is not included in this User’s
Guide. Refer to your computer’s documentation for those
instructions.
The Printer Sharing topology involves a LAN that
interconnects the print clients. The printer is directly
connected to one print client using a parallel cable. The client
is then configured to share its printer. Clients that want to use
the printer must be configured so they can connect to the
printer.
If the sharing client receives a print job while it’s performing
other computing tasks, it may experience some slowdown.
The NOS can be Microsoft NT Server or Novell NetWare. The
LAN can be any type of network that can interconnect the
print clients.
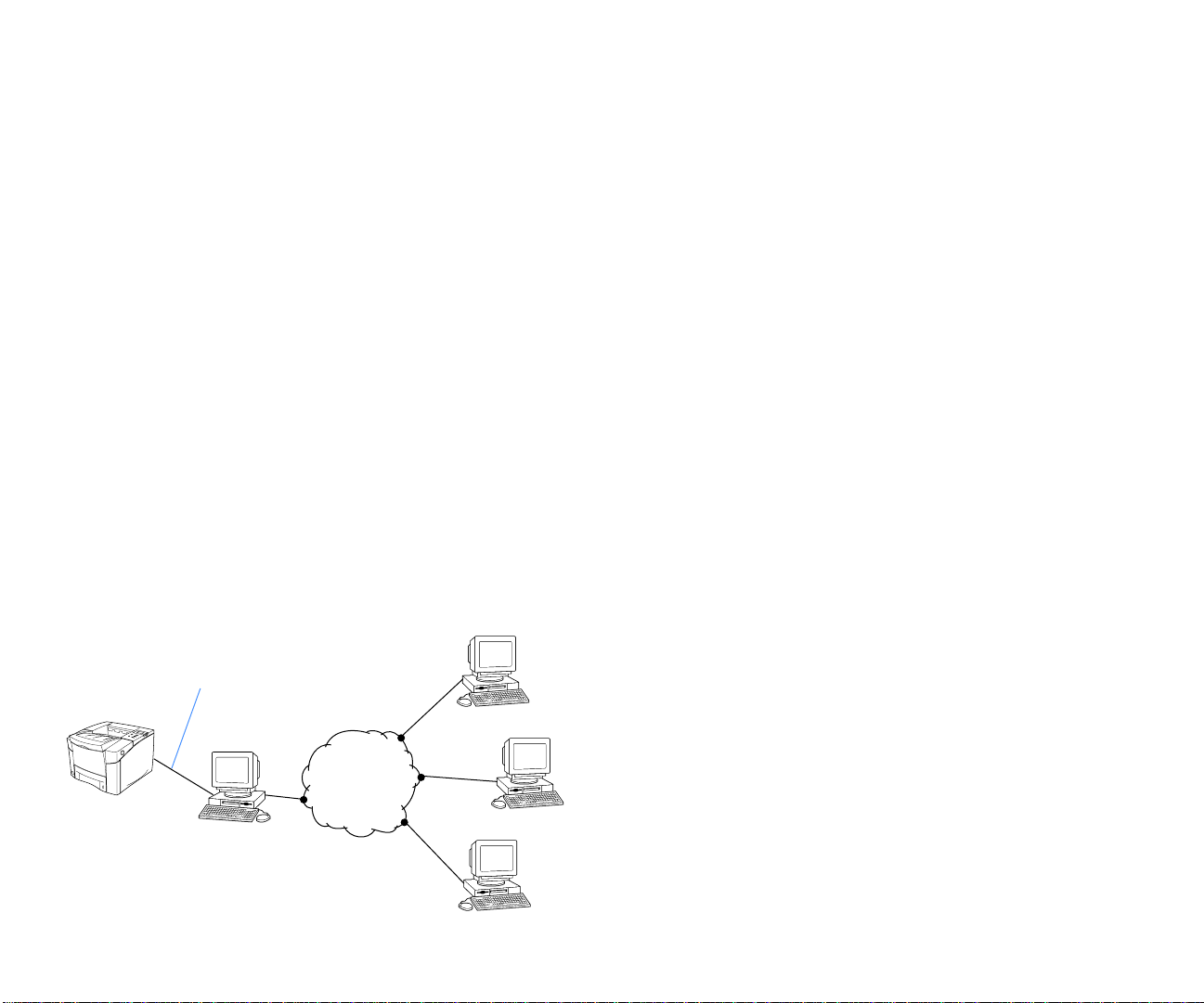
Printer Sharing Topology
In this scenario, a LAN is used to interconnect the print clients.
One print client is connected to the printer using a parallel
able, and is also configured to share it with other print clients.
he sharing client can control access to the printer.
W
HAT NEXT
After reading the previous sections about how the
SuperScript 1800 printer can be networked, select a topology
that best fits your needs and requirements, then read
Chapter 3, “Connecting the Printer,” on page 9.
If the Printer Sharing topology will be used, refer to your
computer’s documentation for instructions on how to share
the printer.
NETWORK TOPOLOGIES PRINTER SHARING TOPOLOGY
Printer
Parallel Cable
Print client sharing
its printer with other
print clients.
Print Client
Any type
of LAN
Print Client
Print Client
Printer Sharing Topology 7
Page 14

8 SuperScript 1800 — Network User’s Guide
Page 15

CHAPTER 3
CONNECTING THE
PRINTER
O
VERVIEW
In order for your printer to connect and communicate with a
Local Area Network (LAN), your printer must contain a
Network Interface Card (NIC). A network cable is then used
to interconnect the printer with your LAN.
The SuperScript 1800 can be ordered with or without an
installed NIC. If your printer did not come with a NIC, one
can be ordered from NEC. Ask for the 10/100Base-TX Network
Interface Kit, Order Number 1802. The kit can be ordered
across the internet from NEC’s web site at www.nec.com.
This chapter describes how to install the 10/100Base-TX
Network Interface Kit, how to connect the printer to your LAN,
and how to setup the NIC so the printer can communicate
with your network.
Where to Start
If a NIC is not installed in your printer, begin at the next
section, “Installing the NIC.” If your printer already has a
NIC installed, begin at “Connecting the Printer” on page 11
for instructions about physically connecting the printer to
your network.
9
Page 16
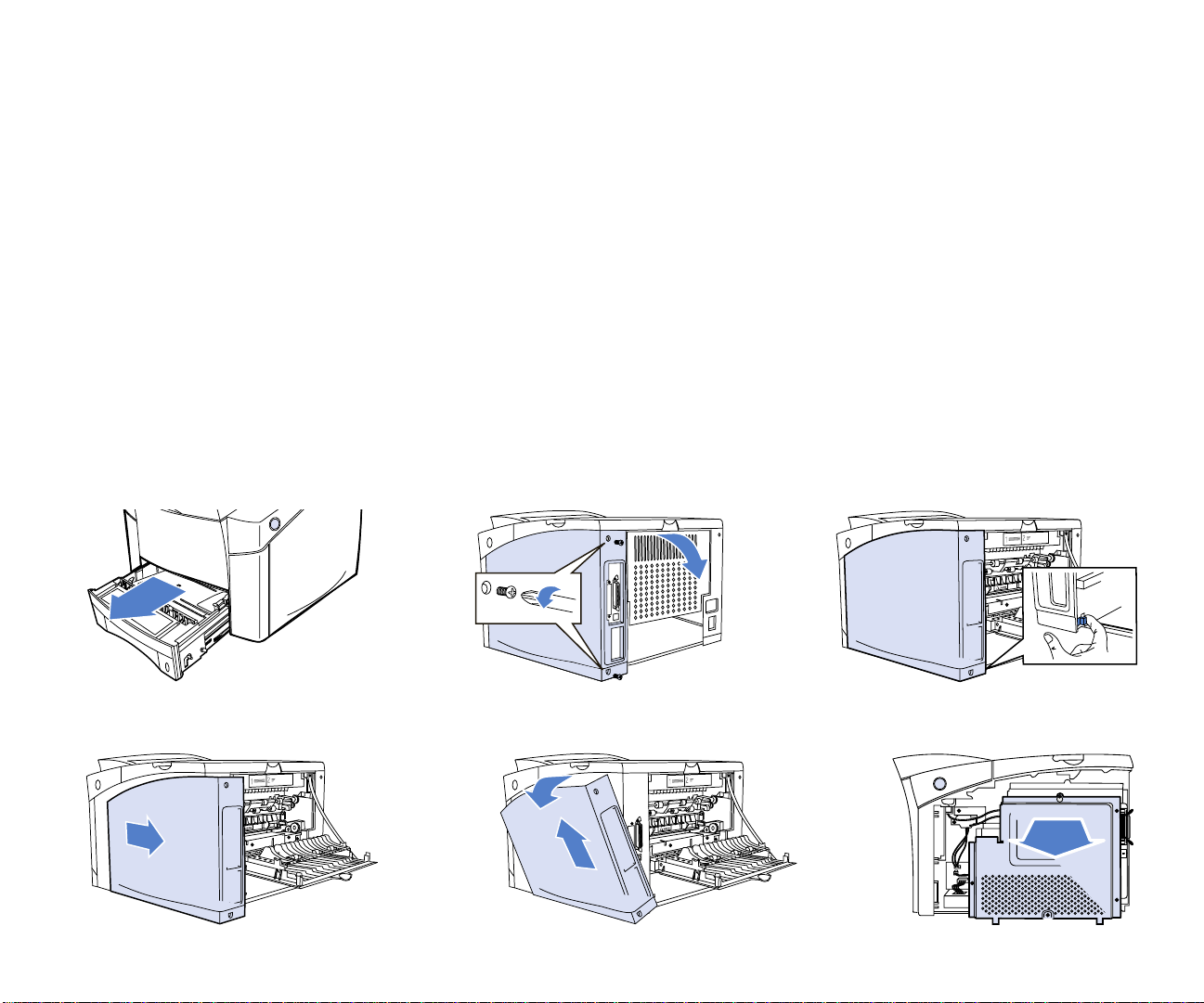
I
NSTALLING THE
Installing the NIC involves first accessing the printer
Controller Board.
NIC
Accessing the Printer Controller Board
The printer Controller Board manages and controls all
printer functions. It is also the place where the NIC is
installed.
To access the Controller Board:
1. Turn off the printer.
2. Pull out the 500-sheet Cassette tray (A).
3. Disconnect all cables from printer.
4. Position the printer so the right side of the printer can be
worked on.
5. Remove screws from the side cover then open
back cover (B).
Accessing the Printer Controller Board
6. Pull tab to release the side cover (C).
7. Slide side cover towards the back of the printer (D).
8. Rotate the side cover away from printer (assure wiresnaps on the parallel port are not in the way), then lift the
side cover away (E).
9. Loosen top screw of controller board cover, remove
remaining 4 screws, then remove the metal cover (F).
When finished with Step 9, continue at “NIC Installation” on
page 11.
A
DE
10 SuperScript 1800 — Network User’s Guide
BC
F
Page 17
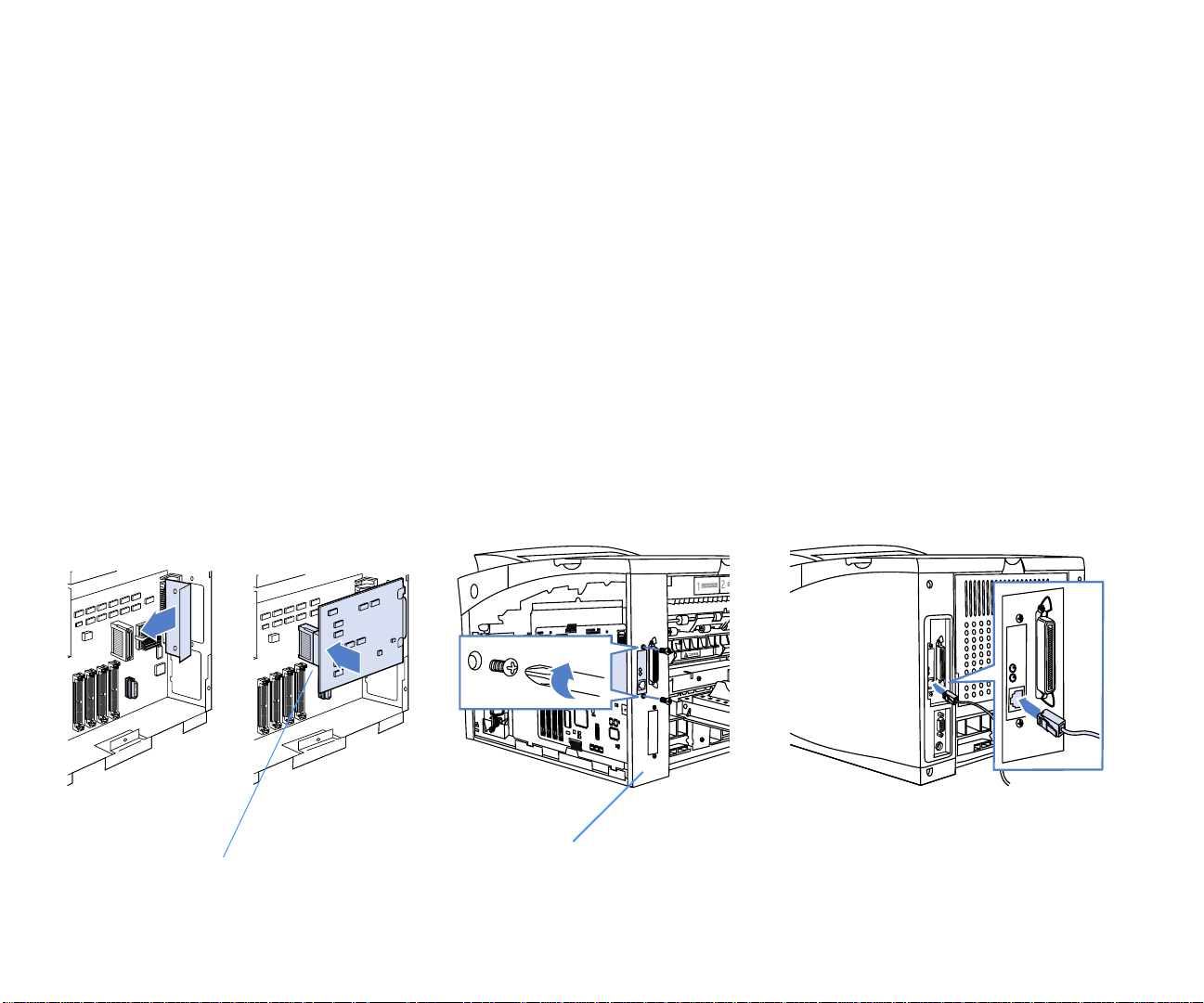
NIC Installation
A
To install the Network Interface Card:
1. Access the printer Controller Board as described
on page 10.
2. On the back of the printer, remove the two screws from
the metal back plate (located on Interface Panel), then
remove plate (A).
3. Located on the controller board is a NIC socket. Insert the
NIC into the socket (B).
4. Use the screws, removed in Step 2, to fasten the card (C).
5. Use the procedure in Step 1 as guide to replace printer
side-panel, 500-sheet Cassette, and printer cables.
After the NIC has been installed, follow the instructions
described in the next section to connect the printer to your
network.
Installing the Network Interface Card
C
ONNECTING THE PRINTER
After the NIC is installed, the printer can be physically
connected to your network.
You’ll need a Category 3, 4 or, 5 network cable to make the
interconnection. This cable is not supplied with your printer,
but can be purchased from your local computer hardware
store. Use a Category 5 shielded cable if connecting to a
100MB network
To physically connect the printer to your network:
1. Insert one end of the network cable into the socket
located on the NIC (D).
2. Insert the other end of the cable into the socket that
connects to your network.
After the printer is physically connected to your network,
follow the instructions in the next section to configure the
NIC.
CONNECTING THE PRINTER CONNECTING THE PRINTER
B
Connect to
socket on
controller board
C
Interface Panel
D
Connecting the Printer 11
Page 18

C
ONFIGURING THE
After the NIC is installed and the printer is physically
connected to your network, the NIC must be configured.
The NIC can be configured by using the printer’s Operator
Panel, or by using the NEC SuperScript 1800 Network Printer
Manager (NPM). It can also be configured by the SuperScript
1800 Web Pages.
Use the Operator Panel for configuring the most basic
parameters of the NIC, such as turning on TCP\IP, DHCP,
AppleTalk, and NetWare protocol stacks, and for configuring
an IP address. This method is suited for connecting to a small
or simple network.
The NPM is a tool that must run on a computer running
Windows 95 or 98. It has more controls for configuring the
NIC than the Operator Panel. Your network may be large and
have many printers connected to it. In this case, the NPM can
be used for performing all the tasks that can be done at the
Operator Panel, and also for assigning a printer name so that
it can be easily identified on a network by users. For
information about installing the NPM, see Appendix B on
page 47.
NIC
SuperScript 1800 Web Pages
Located in the printer are web pages that can be used for
configuring the printer and viewing printer operational
status. These pages can only be viewed after the printer has
been assigned an IP address through the Operator Panel or
NPM. The pages then can be viewed through any popular
web browser by navigating to the printer’s IP address.
If you plan on configuring the NIC through the printer’s
Operator Panel, afterwards, you can use the web pages to
assign a name to the printer, so it can be easily identified by
network users. IPX and AppleTalk protocol stacks may also
be turned on by using these pages.
For more information about the SuperScript 1800 Web Pages,
see Appendix C on page 57.
Using the Printer’s Operator Panel
Note: Appendix A, on page 43, provides detailed
information about navigating the Operator Panel network
menus.
Configuring the IP Address
The printer can be configured to use a static or dynamically
assigned IP address.
The static assignment can be done by directly entering in an
address, or by requesting one from a BOOTP or RARP server.
Subnet mask and gateway (router) addresses can also be
entered.
For dynamic assignment, the printer can be configured to
accept an address from a DHCP server.
To configure TCP\IP addressing:
1. From the printer’s Operator Panel, press GO until
OFFLINE appears in the Operator Panel display.
2. Press MENU until NETWORK MENU appears.
3. Press ITEM until CFG NET appears.
4. Press VALUE until YES appears.
5. Press SELECT.
6. Press ITEM until TCP\IP appears.
7. Press VALUE until YES appears.
8. Press SELECT.
9. Press ITEM until CFG TCP appears.
10. Press VALUE until YES appears.
11. Press SELECT.
12. Press ITEM until DHCP appears.
13. Do one of the following.
• If you plan on having a DHCP server dynamically
assign an IP address to the printer, press VALUE
until YES appears.
a. Then press SELECT.
b. Press GO to exit.
• If you plan on using a static IP address, press VALUE
until NO appears, then continue with the next step.
3. Press SELECT.
12 SuperScript 1800 — Network User’s Guide
Page 19

4. Press ITEM until CFG ADDRS appears.
5. Do one of the following.
• If you plan on having a BOOTP or RARP server
assign an IP address to the printer, press VALUE
until NO appears.
a. Then press SELECT.
b. Press ITEM until BOOTP or RARP appears.
c. Press VALUE until YES appears.
d. Press SELECT.
e. Press GO to exit.
f. Restart the printer.
• If you want to enter an IP address, press VALUE
until YES appears.
a. Then press SELECT.
b. Press ITEM until IP BYTE1 appears.
c. Press VALUE until YES appears.
d. Press SELECT.
e. Press VALUE until the first octet of the IP
address appears.
f. Press Select.
g. Repeat Steps “B” through “F” for IP BYTE2,
IP BYTE3, and IP BYTE4.
h. If you want to configure a subnet mask and/or
gateway (router) address, press ITEM to move to
the SM BYTE and GW BYTE menus, then use the
same procedures as described above.
i. Press GO to exit.
Configuring the Printer for IPX
If the printer will be communicating through a NetWare
network, use this procedure for turning on IPX and selecting
the type of Ethernet framing used by the network. The
printer can be configured to determination the framing
automatically, or set to use a specific type.
To configure IPX protocols:
1. From the printer’s Operator Panel, press GO until
OFFLINE appears on the Operator Panel display.
2. Press MENU until NETWORK MENU appears.
3. Press ITEM until CFG NET appears.
4. Press VALUE until YES appears.
5. Press SELECT.
6. Press ITEM until NetWare appears.
7. Press VALUE until YES appears.
8. Press SELECT.
9. Press ITEM until CFG NWAR appears.
10. Press VALUE until YES appears.
11. Press SELECT.
12. Press ITEM until AUTO appears.
13. Do one of the following.
• If you want the printer to automatically determine
the type of Ethernet framing used by your network,
press VALUE until ON appears. Using this method
may slow down the processing of print jobs.
a. Then press Select.
b. Press GO to exit.
• If you know what type of Ethernet framing is used
by your network, press VALUE until OFF appears.
Using this method may speed up the processing of
print jobs.
a. Then press SELECT.
b. Press ITEM until your frame type appears.
Framing for Ethernet 802.2, 802.3, II, or SNAP
can be selected.
c. Press VALUE until YES appears.
d. Press GO to exit.
CONNECTING THE PRINTER CONFIGURING THE NIC
Configuring the NIC 13
Page 20

Configuring the Printer for UNIX Clients
Use this procedure if computers running UNIX will be
sending print jobs to the printer.
To configure as a UNIX printer:
1. From the printer’s Operator Panel, press GO until
OFFLINE appears on the Operator Panel display.
2. Press MENU until NETWORK MENU appears.
3. Press ITEM until CFG NET appears.
4. Press VALUE until YES appears.
5. Press SELECT.
6. Press ITEM until LPD appears.
7. Press VALUE until YES appears.
8. Press SELECT.
9. Press GO to exit.
Configuring the Printer for AppleTalk
Use this procedure if Macintosh computers will be sending
print jobs to the printer.
Note: Since Macintosh computers send their print jobs
in the PostScript language, the SuperScript 1800
upgraded with the PostScript Level 2 Upgrade Kit
No. 1802). For more information, see Chapter 8, “Printer
Options,” of the SuperScript 1800 User’s Guide. If calling
from North America, you can dial 1-800-632-4650.
must
(Order
be
To configure the printer for AppleTalk:
1. From the printer’s Operator Panel, press GO until
OFFLINE appears on the Operator Panel display.
2. Press MENU until NETWORK MENU appears.
3. Press ITEM until CFG NET appears.
4. Press VALUE until YES appears.
5. Press SELECT.
6. Press ITEM until APL TALK appears.
7. Press VALUE until YES appears.
8. Press SELECT.
9. Press GO to exit.
After this procedure is completed you should use the
SuperScript 1800 Web Pages to assign an AppleTalk name to
the printer. This will make it easier for Macintosh users to
identify the printer.
The web pages can be viewed by using any popular web
browser to navigate to the printer’s IP address.
14 SuperScript 1800 — Network User’s Guide
Page 21

Using the Network Printer Manager
The SuperScript 1800 Network Printer Manager (NPM) is an
administrative tool that can also be used for configuring the
NIC.
The NPM must be installed on a computer running
Windows 95, 98, or NT 4.0 and which is connected to the
network. For more information about NPM, see Appendix B,
on page 47.
To configure the NIC using the Network Printer Manager:
1. Click the Windows Start button, point to Programs, then
NEC SuperScript 1800, and click NEC SuperScript 1800
Network Printer Manager to start the NEC SuperScript
1800 Network Printer Manager.
Once NPM starts, it will begin searching the network for
the printer. Every SuperScript 1800 printer found will be
listed in the NPM main window.
2. Select the printer that must have it’s NIC setup.
The printer can be identified from the Printer Name
column by its NIC serial number, NECnnnnnnnnnnnn,
where nnnnnnnnnnn is the MAC address of the card.
The MAC Address for the NIC can be determined by
printing a Network Configuration page. For instructions
about printing that page, see “Printing a Network
Configuration Page” on page 16.
3. From the Settings menu, select Network Interface to
open the Network Interface properties window.
4. Click the General tab to bring it to the front.
5. In the Printer Name text box, type in a name for the
printer.
6. In the Printer Description text box, type in a description
for the printer; for example, its location.
7. Click the TCP/IP tab to bring it to the front.
8. Assure the TCP/IP check box is selected.
9. From the IP Address Assignment Method drop-down
list, select the method used by the Network Operating
System (NOS) for assigning IP addresses to computers
and printers connected to the network.
Item Description
Static Select this item if you want to manually enter a
permanent IP address for the printer.
BOOTP Select this item if you want the NIC to broadcast
a request to a BOOTP server for an IP address.
The printer must be restarted after the NIC is
configured.
RARP Select this item if you want a the NIC to
broadcast a request to a RARP server for an IP
address. The printer must be restarted after the
NIC is configured.
DHCP Select this item if you want a DHCP server to
assign an IP address to the printer that may
automatically be changed by the server. One
cause for address change is if the printer is
restarted.
10. If the STATIC method was selected, in the IP Address
text boxes, type in the IP address for the printer.
• In the Subnet Mask text boxes, type in the subnet
mask.
• In the Default Gateway text boxes, type in the
gateway (router) IP address.
11. If print jobs will be received from NetWare clients, click
the NetWare tab to bring it to the front.
• Select the Enable NetWare check box.
• From the IPX Frame type options, select how the
printer must determine the type of Ethernet frames it
is receiving. If you do not know, select Auto.
CONNECTING THE PRINTER CONFIGURING THE NIC
Configuring the NIC 15
Page 22

12. If print jobs will be received from Macintosh clients, click
the AppleTalk tab to bring it to the front.
Note: Since Macintosh computers send their print jobs
in the PostScript language, the SuperScript 1800
upgraded with the PostScript Level 2 Upgrade Kit
No. 1802). For more information, see Chapter 8, “Printer
Options,” of the SuperScript 1800 User’s Guide. If calling
from North America, you can dial 1-800-632-4650.
• Select the AppleTalk Enabled check box.
• In the AppleTalk Printer Name text box, type in a
name for the printer. Macintosh users will see this
name in their Chooser window.
• From the Current Zone drop-down list, select which
AppleTalk zone the printer is located in.
13. Click OK to save the configuration.
14. From the Printers menu, select Exit to close NPM.
15. If BOOTP or RARP was selected as the IP address
assignment method in an earlier step, restart the printer.
must
(Order
be
P
RINTING A NETWORK
ONFIGURATION PAGE
C
To verify the NIC configuration, print a network
configuration page then inspect the values shown by the
page for accuracy.
Note: The network configuration information is also
available from the SuperScript 1800 Web Pages. To view
the pages, use any popular web browser to navigate to
the printer’s IP address. Netscape Navigator 4.x and
higher, Microsoft Internet Explorer 4.x and higher, or any
equivalent browser can be used.
To print a network configuration page:
1. From the printer Operator Panel, press the GO button
until OFFLINE appears in the Operator Panel Display.
2. Press Menu until NETWORK MENU appears.
3. Press Item until PRINT NET CFG appears.
4. Press Select to print the page.
W
HAT NEXT
After the NIC has been configured, continue at Chapter 4,
“Peer-to-Peer Topology,” or Chapter 5, “Printer Server
Topology,” depending on what type of topology you want to
create.
16 SuperScript 1800 — Network User’s Guide
Page 23
CHAPTER 4
A
PEER-TO-PEER
TOPOPLOGY
B
I
NTRODUCTION
The Peer-to-Peer topology is the simplest way to network
your printer. It involves print clients, a printer, and a network
to interconnect everything. The network operating system
(NOS) can be Windows NT Server 4.0 or Novell NetWare
3.12, 4.x, or 5.x.
In this scenario, print clients use the network to send print
jobs directly to the printer. There is no intermediary
computer that gets involved between the printer and the
print clients.
For more information about this type of topology, see “Peerto-Peer Topology” on page 5.
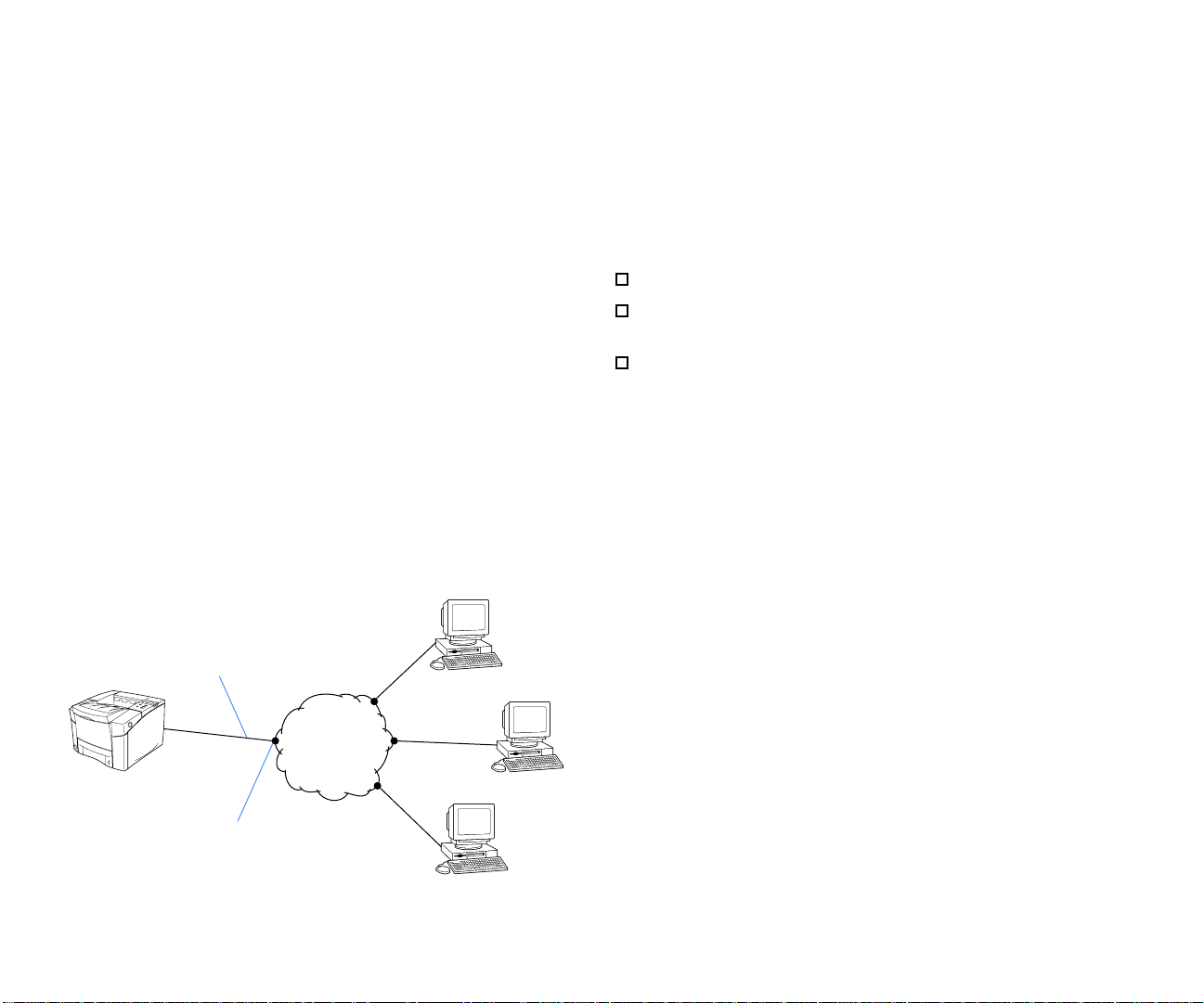
Peer-to-Peer Topology
n Ethernet LAN is used to interconnect the printer and print
clients. Print clients send print jobs directly to the printer, but
each must wait for printer availability.
Network Cable
Ethernet
Network
Printer
Network Interface
Print Client
Print Client
ASIC REQUIREMENTS
Before you configure a computer to communicate with the
printer, the following prerequisites must be met.
The NIC must be installed in the printer (see Page 10).
The printer must be physically connected to a network
(see Page 11).
The NIC must be configured (see Page 12).
C
ONFIGURING A
There are four types of networked Windows computers that
can be configured for sending print jobs to the SuperScript
1800 printer.
• Computers running Windows 95
• Computers running Windows 98
• Computers running Windows NT 4.0
Computers running Windows 3.1x cannot be configured as
print client in the peer-to-peer topology, but they can be a
client in the printer server topology.
W
INDOWS CLIENT
Windows 95 and 98 Computers
Configuring a Windows 95 or 98 computer so it can
communicate with the printer involves installing a printer
driver, then configuring a printer port.
When selecting a driver during the installation process, NEC
recommends using the PCL6 driver because of it’s advanced
features. Use the PCL5e driver for legacy applications. A
Windows Postscript driver may also be installed.
Print Client
17
Page 24

Note: To use the Windows PostScript printer driver, the
NEC PostScript Level 2 Upgrade Kit (Order No. 1802) must
be installed in the printer. See Chapter 8, “Printer
Options,” of the SuperScript 1800 User’s Guide for more
information.
To install a printer driver:
1. Insert the SuperScript 1800 Solutions CD into your
computer.
Note: If the NEC SuperScript 1800 Solutions CD
Installer appears on the monitor shortly after the disk is
inserted, go to Step 4, if not, go to Step 2.
2. From the desktop, double-click My Computer to open
the My Computer window.
3. Double-click the NEC SS1800 icon to start the installer.
As an alternative, right mouse button click on NEC
SS1800 then select Open or Autoplay to start the
installer. If neither one of these methods work, doubleclick Setup.exe which is located on the CD.
4. When the Welcome dialog box appears, click Next to
begin the installation.
5. When the Select Components dialog box appears, do the
following.
• Select the printer driver(s) you want to install.
Note: If selecting the Windows PostScript printer
driver (NEC 1800 PS Printer Driver), the NEC
PostScript Level 2 Upgrade Kit (Order No. 1802) must
be installed in the printer. See Chapter 8, “Printer
Options,” of the SuperScript 1800 User’s Guide for
more information.
Later, when the Add Printer Wizard appears, click the
Have Disk button then navigate the
Solutions CD
PostScript installation file. Depending on your
operating system, navigate to one of the following
directories
• \Ss1800\Win95\Ps
• \Ss1800\Win98\Ps
to the appropriate directory to get the
.
SuperScript 1800
• Select the SuperScript 1800 Network Printer
Manager.
• Select the [optional] Online User’s Guide.
• Select the [optional] On-line Network User’s Guide
if this computer will be used to administrate the
printer.
• Do not select SuperScript 1800 Status Monitor; this
component does not work across a network.
6. When the Setup dialog box appears, do the following.
• Select Print Client if this computer will be used to
send print jobs to the printer.
• Select Print and Administrative Client if this
computer will be used to send print jobs and
administer the printer. The Network Printer
Manager will be installed.
7. Follow the instructions that appear on your monitor to
complete the installation.
8. Restart your computer after the driver is installed.
The printer port can now be created.
To create a printer port:
1. From the Windows Start button, point to Settings then
select Printers to open the Printers window.
2. Select the printer driver that was installed.
3. From the File menu, select Properties to open the driver
properties window.
4. Click the Details tab to bring it to the front.
5. Click Add Port to open the Add Ports dialog box.
6. Select the Network radio button.
7. From the Ports list, select the NEC Network Printer Port.
8. Click OK to return to the driver properties window.
9. Click OK to accept the configured port.
18 SuperScript 1800 — Network User’s Guide
Page 25

Windows NT 4.0 Computers
Configuring a Windows NT 4.0 computer so it can
communicate with the printer involves installing a printer
driver, then configuring a printer port.
To install a printer driver:
1. Insert the SuperScript 1800 Solutions CD into your
computer.
Note: If the NEC SuperScript 1800 Solutions CD
Installer appears on the monitor shortly after the disk is
inserted, go to Step 4, if not, go to Step 2.
2. From the desktop, double-click My Computer to open
the My Computer window.
3. Double-click the NEC SS1800 icon to start the installer.
As an alternative, right mouse button click on NEC
SS1800 then select Open or Autoplay to start the
installer. If neither one of these methods work, doubleclick Setup.exe which is located on the CD.
4. When the Welcome dialog box appears, click Next to
begin the installation.
5. When the Select Components dialog box appears, do the
following.
• Select the printer driver(s) you want to install.
Note: If selecting the Windows PostScript printer
driver (NEC 1800 PS Printer Driver), the NEC
PostScript Level 2 Upgrade Kit (Order No. 1802) must
be installed in the printer. See Chapter 8, “Printer
Options,” of the SuperScript 1800 User’s Guide for
more information.
Later, when the Add Printer Wizard appears, click the
Have Disk button then navigate the
Solutions CD
PostScript installation file. Depending on your
operating system, navigate to one of the following
directories
• \Ss1800\Winnt\Ps
to the appropriate directory to get the
.
SuperScript 1800
• Select the SuperScript 1800 Network Printer
Manager.
• The Online User’s Guide and On-line Network
User’s Guide are optional.
• Do not select SuperScript 1800 Status Monitor. This
component does not work across a network.
6. When the Setup dialog box appears, do the following.
• Select Print Client if this computer will be used to
send print jobs to the printer.
• Select Print and Administrative Client if this
computer will be used to send print jobs and
administer the printer. The Network Printer
Manager will be installed.
7. Follow the instructions that appear on your monitor to
complete the installation.
8. Restart your computer after the driver is installed.
The printer port can now be configured.
To configure a printer port:
1. From the Windows NT Start button, point to Settings
then select Printers to open the Printers window.
2. Select the printer driver that was installed.
3. From the File menu, select Properties to open the driver
properties window.
4. Click the Ports tab to bring it to the front.
5. Click Add Port to open the Add Ports dialog box.
6. From the Available Ports list, select NEC Network
Printer Port.
7. Click New Port to open the Select Printer dialog box.
8. Navigate to the Printer Name Lists.
9. Select the printer.
10. Click OK to return to the Printer Ports dialog box.
11. Click OK to return to the Add Port dialog box.
12. Click OK to return to the driver properties window.
13. Click OK to accept the configured port.
PEER-TO-PEER TOPOPLOGY CONFIGURING A WINDOWS CLIENT
Configuring a Windows Client 19
Page 26

C
ONFIGURING A
M
ACINTOSH CLIENT
Requirements
Before you configure a Macintosh computer to communicate
with the printer, the following requirements must be met.
• The computer must already be connected to the network
and able to communicate with it.
• The operating system must be Mac OS 7.1 or higher.
• The standard Macintosh LaserWriter8 printer driver must
be installed.
• AppleScript must be running on the computer.
• Since Macintosh computers send their print jobs to
printers in the PostScript language, the SuperScript 1800
must be upgraded with the PostScript Level 2 Upgrade Kit
(Order No. 1802).
See Chapter 8, “Printer Options,” of the SuperScript 1800
User’s Guide for more information about this upgrade.
The LaserWriter Printer Driver
The LaserWriter8 printer driver is standard to the Mac OS 7.1
and higher. Check the Macintosh Chooser to assure that it is
installed. If it isn’t, use the Mac OS help system for
information about installing it.
AppleScript
AppleScript is a standard program to the Mac OS 7.1 and
higher. It must be running before the configuration procedure
can begin.
To check and/or start AppleScript:
1. From the Apple menu, point to Control Panels then
select Extensions Manager to open the Extensions
Manager window.
2. Double-click on Extensions to view its contents.
3. Assure that AppleScript and AppleScriptLib are
selected.
If they are not selected, select them, then click Restart to
restart your computer.
Configuration Procedure
Configuring a Macintosh computer involves installing the
NEC SuperScript 1800 PPD and selecting the printer from the
network.
To configure a Macintosh computer:
1. Insert the SuperScript 1800 Solutions CD into your
Macintosh and the SS1800 window will appear.
2. Double-click the SuperScript 1800 Installer icon to begin
installing the PPD. Follow the instructions presented on
the monitor.
3. From the Apple menu, select Chooser to open the
Chooser window.
4. From the bottom left pane of the Chooser window assure
that the correct AppleTalk Zone is selected.
5. From the top left pane of the Chooser window, select
LaserWriter8 and printers will appear in the right pane
of the window.
6. Select the printer from the right-hand pane.
The name of the printer depends on whether or not the
printer was assigned a name as described in
“Configuring the NIC” on page 12.
If a name was assigned, it will appear in this pane. If a
name was not assigned, the Media Access Control (MAC)
address for the printer’s network interface card (NIC)
will be seen.
The MAC address can be identified as
NEC0000nnnnnnnn where nnnnnnnn is a serial number.
7. Click Create to setup the printer. When created, the NEC
SuperScript 1800 icon will appear on the desktop.
8. Close the Chooser window.
20 SuperScript 1800 — Network User’s Guide
Page 27

C
ONFIGURING A
Configuring a UNIX computer involves configuring the host
table, then adding access to the printer. Before doing the
procedures, the following requirements must be met.
• The computer must be running Sun Solaris OS 2.51 or
higher.
• The computer must be running X-Windows.
UNIX C
LIENT
Configuration Procedures
To configure the Host Table:
1. Login into the computer as root.
2. Move to a shell command prompt.
3. Type vi /etc/hosts then press ENTER to display the Host
Table (also known as the look-up table).
4. At the bottom of the table, add the IP address and a host
name for the printer.
5. Press esc to exit edit mode.
6. Type :wq! then press ENTER to save the changes and exit
the editor.
After the host table has been configured, add access to the
printer.
To add access to the printer:
1. From a shell prompt, type admintool & then press
ENTER to start Admintool.
2. From the Browse menu, select Printers to list all the
printers connected to the network.
3. From the Edit menu, point to Add, then select Access to
printer to open the Add Access to Printer dialog box.
4. In the Printer Name text box, type in a name for the
printer.
5. In the Printer Server text box, type in a server name for
the printer.
Use the host name that was assigned to the printer. The
host name was assigned in the Host Table.
6. In the Description text box, type in a description of the
printer; for example, its location.
7. If you want this printer to be the default printer, select
the Default Printer check box.
8. Click Apply to return to the Admintool main window.
Your UNIX computer is now ready to send print jobs to the
printer.
To print a file, move to a command prompt, then enter the
following command, where filename is the name of the file
you want to print.
/usr/ucb/lpr filename
Users can edit their startup file by including the path to the
lpr program so that they do not have to always type /usr/ucb
when they want to print.
PEER-TO-PEER TOPOPLOGY CONFIGURING A UNIX CLIENT
Configuring a UNIX Client 21
Page 28

22 SuperScript 1800 — Network User’s Guide
Page 29

CHAPTER 5
PRINTER SERVER
TOPOLOGY
Note: Before performing any procedures in this chapter,
the printer must be connected and configured as
described by Chapter 2, “Connecting the Printer” on
page 9.
I
NTRODUCTION
The printer server topology involves a computer, called a
printer server. All print clients send their print jobs to the
printer server. The printer server then sends the jobs to the
printer. The network operating system (NOS) can be
Windows NT Server or Novell NetWare. For more
information about this type of topology, see “Printer Server
Topology” on page 6. An outline of this chapter is shown
below.
NetWare Networks:
• Using NPM to Configure NetWare
• Configuring NetWare 3.12
• Configuring NetWare 4.x and 5.x
• Configuring a Windows 3.1x Client
• Configuring a Windows 95 or 98 Client
• Configuring a Window NT 4.0 Client
• Configuring a Macintosh Client
• Configuring a UNIX Client
Windows NT Server Networks:
• Configuring Windows NT Server
• Configuring a Windows 3.1x Client
• Configuring a Windows 95 or 98 Client
• Configuring a Window NT 4.0 Client
• Configuring a Macintosh Client
• Configuring a UNIX Client
NETW
Setting up a NetWare printer server topology involves
creating a print queues and servers, then configuring each
print client.
Queues on NetWare servers can be created with the NEC
SuperScript 1800 Network Printer Manager, NetWare Printer
Console, or the NetWare Administrator.
The Network Printer Manager (NPM) is supplied with your
printer as a program that can run on a Windows 95, 98, or
NT 4.0 computer. For instructions about installing NPM, see
Appendix B, on page 47.
The NetWare Printer Console is a component of
NetWare 3.12, 4.x, and 5.x. The NetWare Administrator is a
component of NetWare versions 4.x and 5.x.
If you plan on using NPM, begin at “Using NPM to
Configure NetWare” on page 23, then use the remaining
subsections to configure each print client.
If you plan on using one of the NetWare tools to configure the
NOS, determine which version of NetWare your network is
using, then begin at one of the following sections.
• “Configuring NetWare 3.12” on page 27.
• “Configuring NetWare 4.x and 5.x” on page 28.
ARE NETWORKS
Using NPM to Configure NetWare
NetWare has two kinds of directory systems for managing
their networks. One is the Bindery, and the other is the
NetWare Directory System (NDS). The NPM has a procedure
for both systems.
23
Page 30
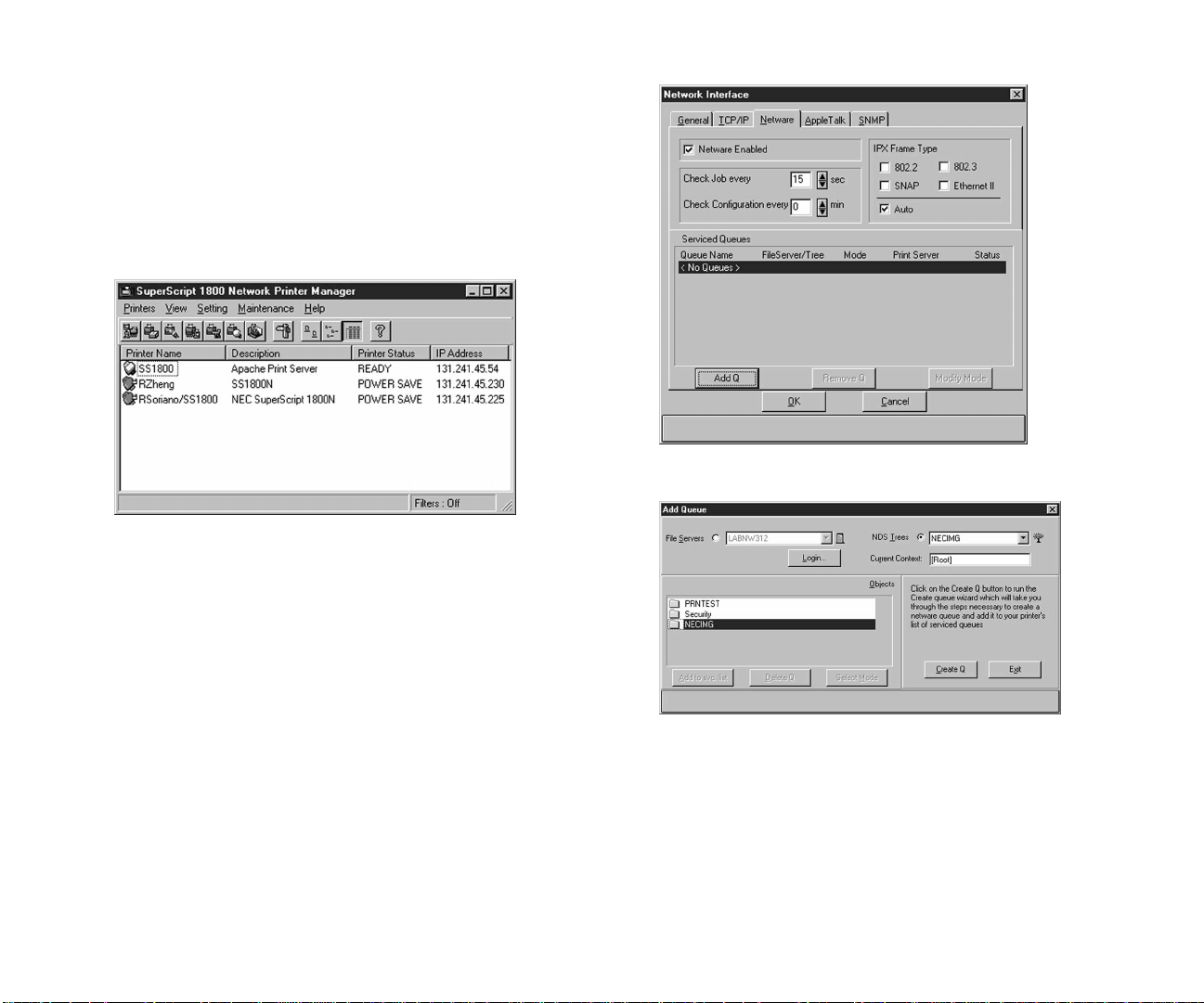
Configuring an NDS Queue
To configure an NDS Queue:
1. Move to the computer having the NPM.
2. Click the Windows Start button, point to Programs, then
NEC SuperScript 1800, and click NEC SuperScript 1800
Network Printer Manager to start the NEC SuperScript
1800 Network Printer Manager.
Once NPM starts, it will begin searching the network for
the printer. Every SuperScript 1800 printer that is found
will be listed in the NPM main window.
3. Double-click on your new printer to open the Network
Interface window.
4. Click the NetWare tab to bring it to the front.
5. Click Add Q to open the Add Queue dialog box.
24 SuperScript 1800 — Network User’s Guide
6. From the Objects list, navigate to where you want to
create a print queue.
Page 31
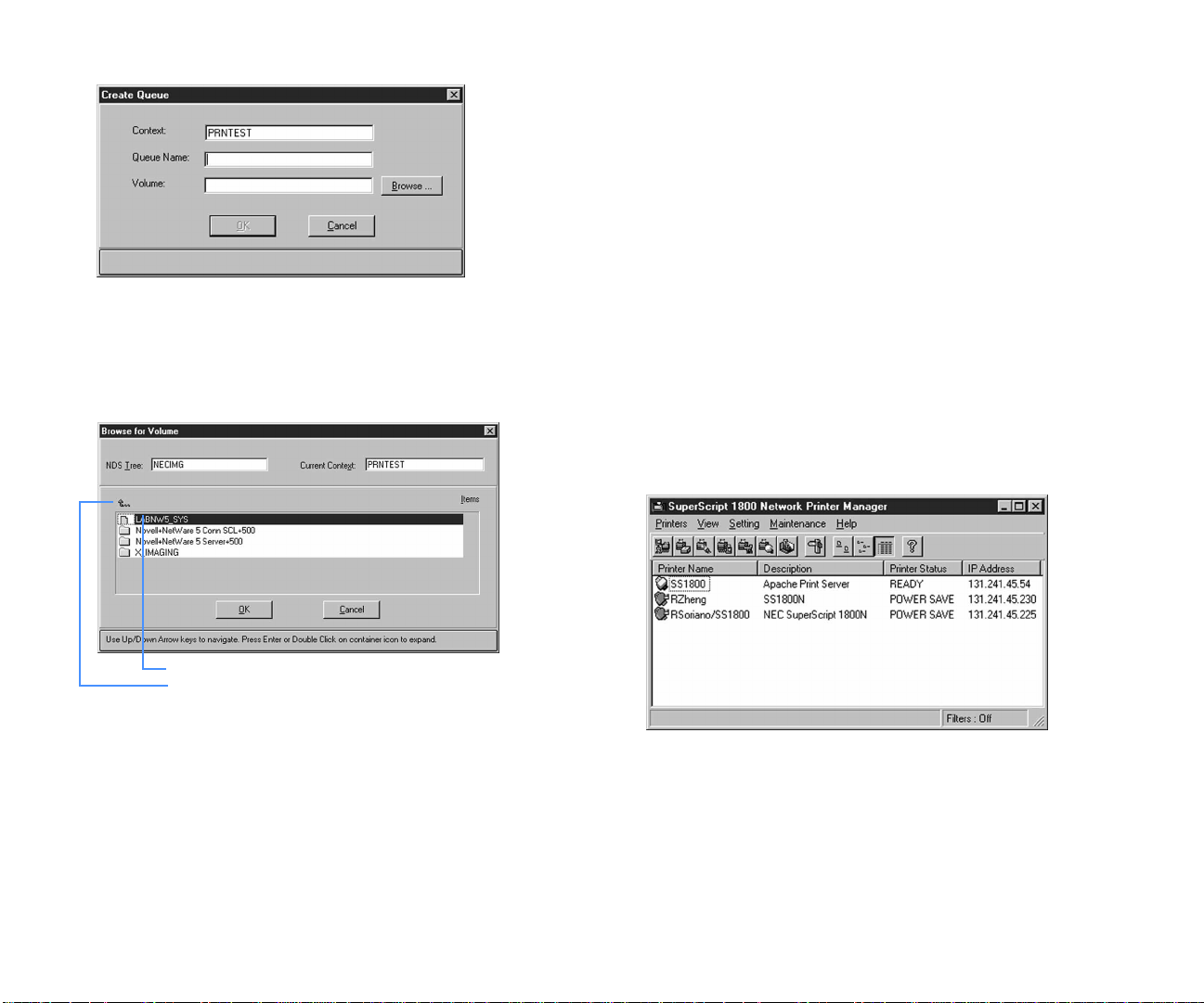
7. Click Create Queue to open the Create Queue dialog box.
8. In the Queue Name text box, type in a name for the new
queue.
9. Click Browse to open the Browse for Volume dialog box.
10. From the Items list, navigate to the location of the
volume you want to use.
Now you can configure the individual Windows, Macintosh,
and UNIX print clients. See the following sections for
instructions.
• “Configuring a Windows 3.1x Client” on page 31.
• “Configuring a Windows 95 or 98 Client” on page 32.
• “Configuring a Windows NT 4.0 Client” on page 33.
• “Configuring a Macintosh Client” on page 34.
• “Configuring a UNIX Client” on page 34
Configuring a Bindery Queue
To configure a Bindery Queue:
1. Move to the computer having the NPM.
2. Click the Windows Start button, point to Programs, then
NEC SuperScript 1800, and click NEC SuperScript 1800
Network Printer Manager to start the NEC SuperScript
1800 Network Printer Manager.
Once NPM starts, it will begin searching the network for
the printer. Every SuperScript 1800 printer that is found
will be listed in the NPM main window.
PRINTER SERVER TOPOLOGY NETWARE NETWORKS
Double-click on an item to navigate downwards.
Click here to navigate upwards.
11. Select the volume.
12. Click OK to return to the Create Queue dialog box.
13. Click OK and wait for a message box to appear.
14. When asked to add this queue to the print server’s list of
service queues, click Yes to return to the Network Interface
dialog box.
15. Click OK to accept the configuration.
3. Double-click on your new printer to open the Network
Interface window.
NetWare Networks 25
Page 32

4. Click the NetWare tab to bring it to the front.
5. Click Add Q to open the Add Queue dialog box.
7. From the Create Queue dialog box, type in a name for
your new print queue.
8. Click OK to open the Print Server Mode dialog box.
9. Select Pserver.
6. Select an existing queue, or click Create Q to open the
Create Queue dialog box.
If selecting an existing queue, go to Step 10, otherwise,
continue with the next step.
26 SuperScript 1800 — Network User’s Guide
10. Click OK and wait for a message box to appear.
11. When asked to add this queue to the print server’s list of
service queues, click Yes to return to the Network Interface
dialog box.
12. Click OK to accept the configuration.
Now you can configure the individual Windows, Macintosh,
and UNIX print clients. See the following sections for
instructions.
• “Configuring a Windows 3.1x Client” on page 31.
• “Configuring a Windows 95 or 98 Client” on page 32.
• “Configuring a Windows NT 4.0 Client” on page 33.
• “Configuring a Macintosh Client” on page 34.
• “Configuring a UNIX Client” on page 34
Page 33

Configuring NetWare 3.12
Use the NetWare Print Console to create a print queue then
assign a queue server.
To create a print queue then assign it to a queue server:
1. Obtain the MAC address for your printer’s network
interface card (NIC) by printing a NIC Configuration
Page. For instructions about this, see “Printing a
Network Configuration Page” on page 16.
In the LAN Interface Details section of the NIC
configuration page, the MAC address is identified by the
Physical Address.
2. From any client computer, log onto the network with
administrator privileges.
3. Start pconsole.exe.
This program can be found at the following path.
F:\Public\Pconsole.exe
4. From the Available Options list, select Change Current
File Server to display all the file servers attached to the
network.
Note: If the server you want is not seen, press Insert to
open the Other File Servers list, then make your selection
from there.
7. Select Print Queue Information to display the Print
Queues list.
8. Press Insert to display the New Print Queue Name dialog
box.
PRINTER SERVER TOPOLOGY NETWARE NETWORKS
5. Select the file server where the print queue must be
created.
6. Press esc to return to the Available Options list.
9. Type in a name for your print queue, then press Enter.
10. From the Print Queues list, select your new print queue.
11. Press Enter to display the Print Queue Information list.
12. Select Queue Servers, then press Enter to display the
Queue Server list.
13. Press Insert to display the Queue Server Candidates list.
NetWare Networks 27
Page 34

14. The Queue Server Candidates list itemizes the MAC
address of each printer NIC on the network.
15. Select the address that identifies the SuperScript 1800.
16. Press Enter and the printer will appear in the Queue
Servers list.
Configuring NetWare 4.x and 5.x
For networks using NetWare 4.x or 5.x, the NetWare Printer
Console or NetWare Administrator can be used for setting up
a printer.
The NetWare Printer Console can be used to configure small
or simple networks. Use NetWare Administrator for large or
complex networks.
Using the NetWare Printer Console
The procedure for using the Printer Console is identical to the
one used for NetWare 3.12. See “Configuring NetWare 3.12”
on page 27 for instructions.
Using the NetWare Administrator
The NetWare Administrator is a program that must be run on
a Windows 95, 98, or NT 4.0 computer to create a print queue
and assign a queue server.
To create a print queue object then assign it to a queue server object:
1. Print the Network Configuration Page. Information on it
will be needed. For printing instructions, see “Printing a
Network Configuration Page” on page 16.
2. From a Windows 95, 98, or NT4.0 computer, log onto the
network with administrator privileges.
3. Start nwadmin.exe.
This program can be found at the following path.
F:\Public\Win32\Nwadmin32.exe
17. Exit the NetWare Printer Console.
Now you can configure the individual Windows, Macintosh,
and UNIX print clients. See the following sections for
instructions.
• “Configuring a Windows 3.1x Client” on page 31.
• “Configuring a Windows 95 or 98 Client” on page 32.
• “Configuring a Windows NT 4.0 Client” on page 33.
• “Configuring a Macintosh Client” on page 34.
• “Configuring a UNIX Client” on page 34
28 SuperScript 1800 — Network User’s Guide
4. Select or create an NDS Context (organizational unit and
Page 35

organization) where you want to create the new NDS
objects.
5. From the Object menu, select create to open the New
Object dialog box.
6. Select Printer then click OK to open the Create Printer
dialog box.
be obtained from the Network Configuration Page.
10. From the New Object dialog box, select Print Queue, then
click OK to open the Create Print Queue dialog box.
11. Select the Directory Service Queue radio button.
12. In the Print Queue Name text box, type in a name for the
new print queue object.
13. Next to the Print Queue Volume text box, click the Select
Object button to open the Select Object dialog box.
PRINTER SERVER TOPOLOGY NETWARE NETWORKS
7. In the Printer Name text box, type in a name for your
new printer object, then click Create.
8. From the New Object dialog box, select Printer Server,
then click OK to open the Create Print Server dialog box.
9. In the Print Server Name text box, type in a name for
your new print server object, then click Create.
Use the Printer Server Name that was assigned to the
printer when the printer’s NIC was setup. The name can
14. Select a Print Queue Volume then click OK.
15. From the Create Print Queue dialog box, click Create to
return to the Administrator main window.
16. Double-click the new printer object to open the Printer
window.
17. Click Assignments to begin assigning a print queue object
to the printer object.
18. Click Add to open the Select Object dialog box.
NetWare Networks 29
Page 36

19. Select the new print queue object.
20. Click OK to assign the queue to the printer object.
21. From the Printer window, click OK to return to the
Administrator main window.
22. Double-click on the new print server object to open the
Print Server window.
23. Click Assignments to begin assigning the printer object
to the printer server object.
24. Click Add to open the Select Object dialog box.
25. Select the new printer object.
26. Click OK to assign the printer to the printer server object.
27. From the Printer window, click OK to return to the
Administrator main window.
28. Double-click the new print queue object to open the Print
Queue window.
29. Click Assignments to view the assignment lists.
30. In the Authorized Print Servers list, assure that your
new print server object is listed.
31. In the Printers Servicing Print Queue list, assure that
your new printer object is listed.
Now you can configure the individual Windows, Macintosh,
and UNIX print clients that are connected to the network. See
the following sections for instructions.
• “Configuring a Windows 3.1x Client” on page 31
• “Configuring a Windows 95 or 98 Client” on page 32
• “Configuring a Windows NT 4.0 Client” on page 33
• “Configuring a Macintosh Client” on page 34
• “Configuring a UNIX Client” on page 34
30 SuperScript 1800 — Network User’s Guide
Page 37
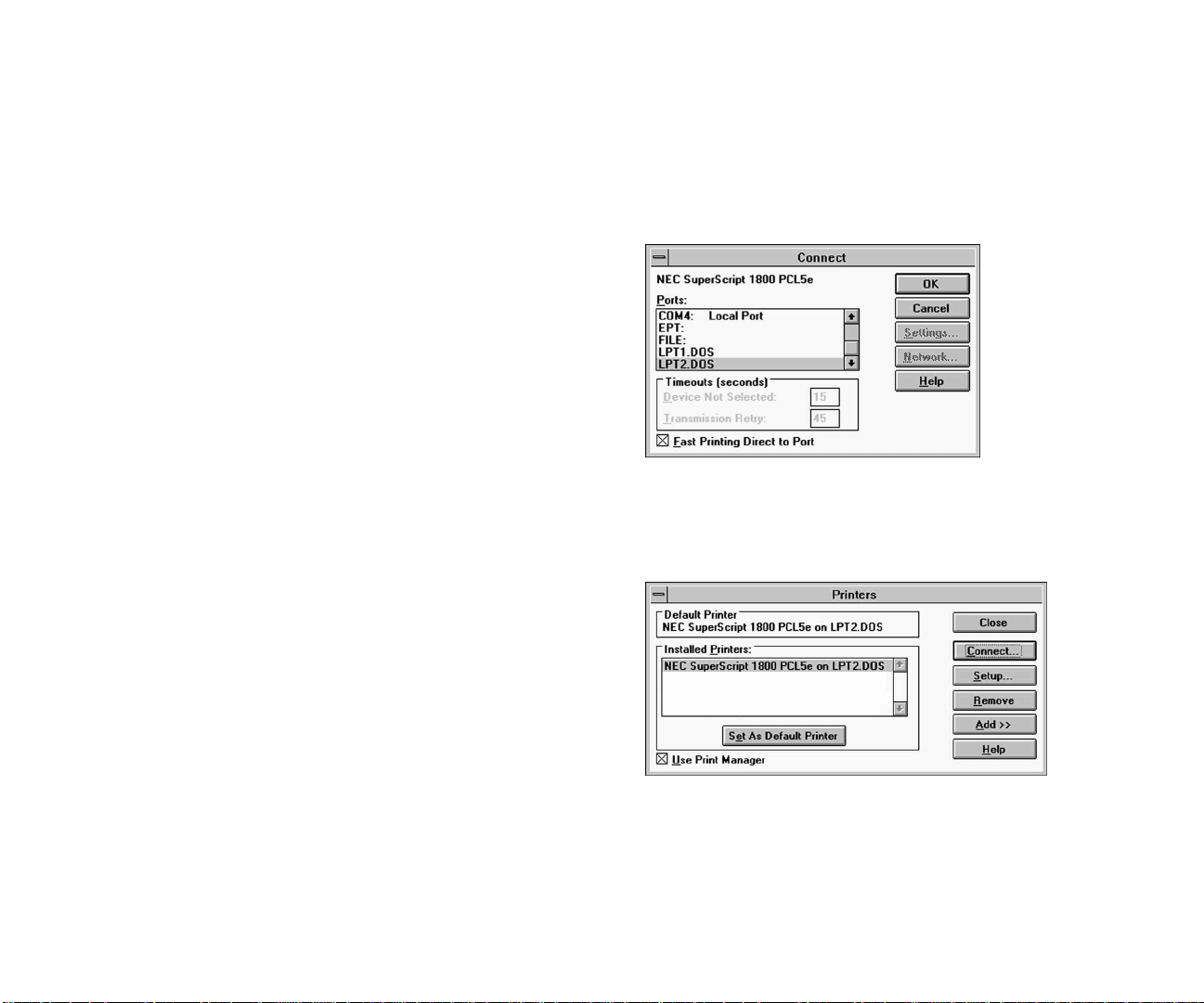
Configuring a Windows 3.1x Client
Computers running Windows 3.1x can be configured as a
NetWare print client after the NOS has been configured with
the NEC SuperScript 1800 Network Printer Manager,
NetWare Printer Console, or NetWare Administrator.
To configure a Windows 3.1x client, you must install a printer
driver then assign a printer port.
To install a printer driver:
1. Insert the SuperScript 1800 Solutions CD into the client
computer.
2. Open the Program Manager window.
3. From the File menu, select Run to open the Run dialog
box.
4. Click Browse to open the Browse dialog box.
5. From the Drives drop-down list, select your CD drive.
The directories and files located on the SuperScript 1800
Solutions CD will appear.
6. Select Setup.exe, then click OK to return to the Run
dialog box.
7. Click OK to begin installing the printer software.
When the Select Components dialog box appears, select
the Printer Driver check box then continue to follow the
instructions displayed on your monitor to finish the
install.
use 1 for port if using LPT1.DOS, use 2 if using
LPT2.DOS.
3. Save the changes to Startnet.bat, then exit the editor.
4. Restart the client to capture the print queue.
5. From the Program Manager window, double-click Printers
to open the Printers window.
6. From the Installed Printers list, select the printer.
7. Click Connect to open the Connect dialog box.
8. From the Ports list, select LPT1.DOS or LPT2.DOS.
9. Click OK to return to the Printers window.
The printer will be listed in Installed Printers list with
the new port.
PRINTER SERVER TOPOLOGY NETWARE NETWORKS
To assign a printer port:
1. From the client computer, use a text editor to open
Startnet.bat.
This file should be in the root directory of the client’s
hard drive.
2. After the login command line, add the capture command.
Login
Capture /Server=
sname
/Queue=
qname
/local=
port
Sname is the print server name, qname is the print queue
name, and port is the port number that will be created on
the client.
In a later step, the port will be selected as LPT1.DOS or
LPT2.DOS. So, depending on which port you plan to use,
10. Click Close to accept the port configuration.
NetWare Networks 31
Page 38

Configuring a Windows 95 or 98 Client
Computers running Windows 95 or 98 can be configured as a
NetWare print client after the NOS has been configured with
the NEC SuperScript 1800 Network Printer Manager,
NetWare Printer Console, or NetWare Administrator.
Configuring a computer running Windows 95 or 98 involves
installing a printer driver then creating a port.
To install a printer driver:
1. Insert the SuperScript 1800 Solutions CD into your
computer.
note: If the NEC SuperScript 1800 Solutions CD Installer
appears on the monitor shortly after the disk is inserted,
go to Step 4, if not, go to Step 2.
2. From the desktop, double-click My Computer to open
the My Computer window.
3. Double-click the NEC SS1800 icon to start the installer.
As an alternative, right mouse button click on NEC
SS1800 then select Open or Autoplay to start the
installer. If neither one of these methods work, doubleclick Setup.exe which is located on the CD.
4. When the Welcome dialog box appears, click Next to
begin the installation.
5. When the Select Components dialog box appears, do the
following.
• Select the printer driver(s) you want to install.
Note: If selecting the Windows PostScript printer
driver (NEC 1800 PS Printer Driver), the NEC
PostScript Level 2 Upgrade Kit (Order No. 1802) must
be installed in the printer. See Chapter 8, “Printer
Options,” of the SuperScript 1800 User’s Guide for
more information.
Later, when the Add Printer Wizard appears, click the
Have Disk button then navigate the
Solutions CD
PostScript installation file. Depending on your
operating system, navigate to one of the following
directories
• \Ss1800\Win95\Ps
• \Ss1800\Win98\Ps
to the appropriate directory to get the
.
SuperScript 1800
• Select the SuperScript 1800 Network Printer
Manager.
• The Online User’s Guide and On-line Network
User’s Guide are optional.
• Do not select SuperScript 1800 Status Monitor. This
component does not work across a network.
6. When the Setup dialog box appears, do the following.
• Select Print Client if this computer will be used to
send print jobs to the printer.
• Select Print and Administrative Client if this
computer will be used to send print jobs and
administer the printer. The Network Printer
Manager will be installed.
7. Follow the instructions that appear on your monitor to
complete the installation.
8. Restart your computer after the driver is installed.
The printer port can now be created.
To create a printer port:
1. From the Windows Start button, point to Settings then
select Printers to open the Printers window.
2. Select the printer driver that was installed.
3. From the File menu, select Properties to open the driver
properties window.
4. Click the Details tab to bring it to the front.
5. Click Add Port to open the Add Port dialog box.
6. Select the Network radio button.
7. Click Browse to open the Browse for Printer window.
8. Navigate to the print queue that was created earlier in this
chapter, then select it.
9. Click OK to return to the Add Port dialog box.
10. Click OK to return to the driver properties window.
11. Click OK to accept the configured port.
32 SuperScript 1800 — Network User’s Guide
Page 39

Configuring a Windows NT 4.0 Client
Computers running Windows NT 4.0 can be configured as a
NetWare print client after the NOS has been configured with
the NEC SuperScript 1800 Network Printer Manager,
NetWare Printer Console, or NetWare Administrator.
Configuring a computer running Windows NT involves
installing a printer driver, attaching a print queue to a port,
than verifying the attachment.
To install a printer driver:
1. Insert the SuperScript 1800 Solutions CD into your
computer.
note: If the NEC SuperScript 1800 Solutions CD Installer
appears on the monitor shortly after the disk is inserted,
go to Step 4, if not, go to Step 2.
2. From the desktop, double-click My Computer to open
the My Computer window.
3. Double-click the NEC SS1800 icon to start the installer.
As an alternative, right mouse button click on NEC
SS1800 then select Open or Autoplay to start the
installer. If neither one of these methods work, doubleclick Setup.exe which is located on the CD.
4. When the Welcome dialog box appears, click Next to
begin the installation.
5. When the Select Components dialog box appears, do the
following.
• Select the printer driver(s) you want to install.
Note: If selecting the Windows PostScript printer
driver (NEC 1800 PS Printer Driver), the NEC
PostScript Level 2 Upgrade Kit (Order No. 1802) must
be installed in the printer. See Chapter 8, “Printer
Options,” of the SuperScript 1800 User’s Guide for
more information.
Later, when the Add Printer Wizard appears, click the
Have Disk button then navigate the
Solutions CD
PostScript installation file. Depending on your
operating system, navigate to one of the following
directory
• \Ss1800\Winnt\Ps
to the appropriate directory to get the
.
SuperScript 1800
• Select the SuperScript 1800 Network Printer
Manager.
• The Online User’s Guide and On-line Network
User’s Guide are optional.
• Do not select SuperScript 1800 Status Monitor. This
component does not work across a network.
6. When the Setup dialog box appears, do the following.
• Select Print Client if this computer will be used to
send print jobs to the printer.
• Select Print and Administrative Client if this
computer will be used to send print jobs and
administer the printer. The Network Printer
Manager will be installed.
7. Follow the instructions that appear on your monitor to
complete the installation.
8. Restart your computer after the driver is installed.
A print queue can now be attached to a port.
To attach a print queue to a port:
1. Start Windows NT Explorer.
2. Navigate to the NetWare print server that was created
earlier in this chapter, then select the print queue.
3. From the File menu, select Capture Printer Port to open
the Capture Printer Port dialog box.
4. From the Device drop-down list, select a port.
5. Click Capture to attach the print queue to the port.
To assure the print queue is attached to a port:
1. From the Windows NT Start button, point to Settings
then select Printers to open the Printers window.
2. Select the printer driver that was installed.
3. From the File menu, select Properties to open the driver
properties window.
4. Click the Ports tab to bring it to the front.
5. Check the Ports list to determine if the new print queue is
attached to a port.
PRINTER SERVER TOPOLOGY NETWARE NETWORKS
NetWare Networks 33
Page 40

Configuring a Macintosh Client
Macintosh clients send print jobs over AppleTalk to a
NetWare print server. To the Macintosh client, the NetWare
print server looks like any other AppleTalk device in a zone.
Software Requirements
For Macintosh computers to connect to the printer, they must
meet three software requirements:
• The operating system must be Mac OS 7.1 or higher.
• The standard Macintosh LaserWriter8 printer driver must
be installed.
• The NEC SuperScript 1800 PPD must be installed.
Printer Hardware Requirements
Since Macintosh computers send their print jobs in the
PostScript language, the SuperScript 1800 must be upgraded
with the PostScript Level 2 Upgrade Kit (Order No. 1802).
Installing the Software
Software installation involves installing the LaserWriter
printer driver and SuperScript 1800 PPD.
I
NSTALLING THE LASERWRITER PRINTER DRIVER
The LaserWriter printer driver is standard to the Mac OS 7.1
and higher. Check the Macintosh Chooser to assure that it is
installed. If it isn’t, use the Mac OS help system for
information about installing it.
I
NSTALLING THE SUPERSCRIPT
The SuperScript 1800 PPD is installed from the SuperScript
1800 Solutions CD.
To install the SuperScript 1800 PPD:
1. Insert the SuperScript 1800 Solutions CD into your
Macintosh and the SS1800 window will appear.
2. Double-click the SuperScript 1800 Installer icon to begin
installing the PPD. Follow the instructions presented on
the monitor.
3. From the Apple menu, select Chooser to open the
Chooser window.
4. From the left pane of the Chooser window, select
LaserWriter8 and a name for the SuperScript 1800 printer
will appear in the right pane of the window.
1800 PPD
Note: If the printer’s NIC has been configured with an
AppleTalk Printer Name
60, that name will appear in the right pane. If a name was
not created, the MAC address for the printer’s NIC will
appear. The MAC address can be identified with the NEC
prefix, for example NEC000012345678.
, as described on Page 16 or Page
5. Click Create to setup the printer. When created, an icon
will appear on the desktop using the AppleTalk Printer
Name or MAC address as its label.
6. Close the Chooser window.
Configuring a UNIX Client
Configuring a UNIX computer involves two procedures:
configuring the host table, then adding access to the printer.
Before doing the procedures, the following requirements
must be met.
• The computer must be running Sun Solaris OS 2.51 or
higher.
• The computer must be running X-Windows.
Configuration Procedures
To configure the Host Table:
1. Login into the computer as root.
2. Move to a shell command prompt.
3. Type vi /etc/hosts then press ENTER to display the Host
Table (also known as the look-up table).
4. At the bottom of the table, add the IP address and a host
name for the printer.
5. Press esc to exit edit mode.
6. Type :wq! then press ENTER to save the changes and exit
the editor.
After the host table has been configured, add access to the
printer.
To add access to the printer:
1. From a shell prompt, type admintool & then press
ENTER to start Admintool.
2. From the Browse menu, select Printers to list all the
printers connected to the network.
3. From the Edit menu, point to Add, then select Access to
34 SuperScript 1800 — Network User’s Guide
Page 41

printer to open the Add Access to Printer dialog box.
4. In the Printer Name text box, type in a name for the
printer.
5. In the Printer Server text box, type in a server name for
the printer.
Use the host name that was assigned to the printer. The
host name was assigned in the Host Table.
6. In the Description text box, type in a description of the
printer; for example, its location.
7. If you want this printer to be the default printer, select
the Default Printer check box.
8. Click Apply to return to the Admintool main window.
Your UNIX computer is now ready to send print jobs to the
printer.
To print a file, move to a command prompt, then enter the
following command, where filename is the name of the file
you want to print.
/usr/ucb/lpr filename
Users can edit their start-up file by including the path to the
lpr program so that they do not have to always type /usr/ucb
when they want to print.
W
INDOWS
NT S
ERVER NETWORKS
To configure Windows NT Server as a print server:
Note: At the end of this procedure, you will be asked for
the install disks for each client operating system that will
be communicating with the server.
1. Obtain the IP address for your printer by printing a NIC
Configuration Page.
For instructions about this, see “Printing a Network
Configuration Page” on page 16.
2. Insert the NEC SuperScript 1800 Solutions CD into the
computer running Windows NT Server.
If the NEC SuperScript 1800 Installer begins, click Cancel
to exit it.
3. From the Windows NT Server Start button, point to
Settings then select Printers to open the Printers window.
4. Double-click Add Printers to start the Add Printers
Wizard.
5. When asked how this printer will be managed, select My
Computer.
PRINTER SERVER TOPOLOGY WINDOWS NT SERVER NETWORKS
Note: Before performing any procedures in this section,
the printer must be connected and configured as
described by Chapter 2, “Connecting the Printer” on
page 9.
To set up the printer server topology for a network using
Windows NT Server 4.0, configure Windows NT Server as a
print server, then configure the individual print clients.
Configuring Windows NT Server
Note: This procedure involves installing a PCL5e, PCL6,
or PostScript Level 2 printer driver onto the computer
running Windows NT Server. If the PostScript driver is
selected, the printer must have the PostScript Level 2
Upgrade Kit installed. For more information, see
Chapter 8, “Printer Options” of the
User’s Guide
.
SuperScript 1800
Windows NT Server Networks 35
Page 42
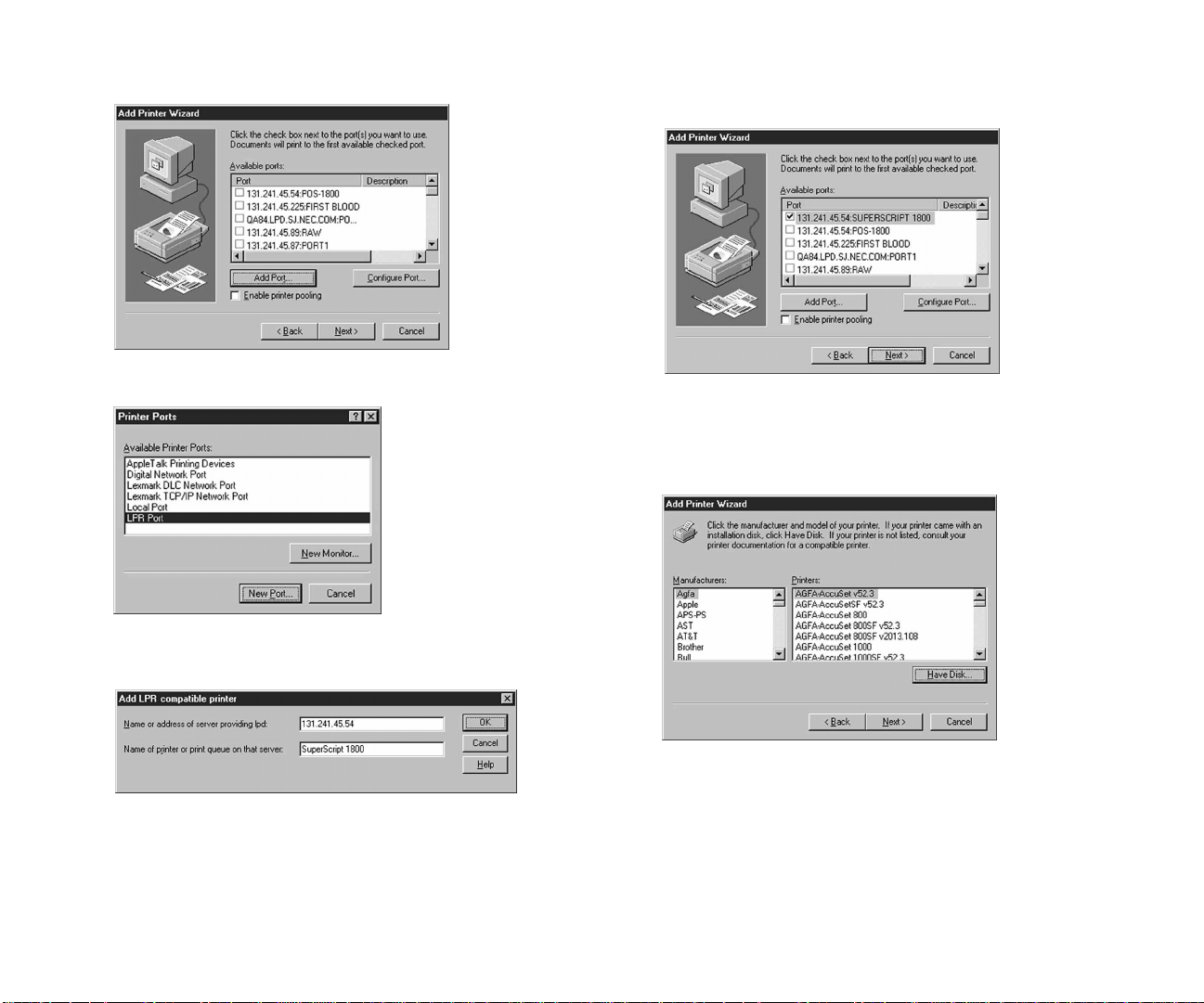
6. When asked which port do you want to use, click Add
Port to open the Printer Ports dialog box.
7. From the Available Printer Ports list, select LPR Port.
12. Click Close to return to the Add Printer Wizard.
13. The printer’s IP address and name will appear in the
Available Ports list.
14. Click Next to continue.
15. When asked if your printer came with an installation
disk, click Have Disk to open the Install From Disk dialog
box.
8. Click New Port to open the Add LPR Compatible Printer
dialog box.
9. In the Name or Address of Server Providing LPR text
box, type in the IP address for your printer.
10. In the Name of Printer text box, type in a name for your
printer.
11. Click OK to return to the Printer Ports dialog box.
36 SuperScript 1800 — Network User’s Guide
16. From the Copy Manufacturer’s Files From drop-down
list, select the disk drive containing the NEC SuperScript
1800 Solutions CD.
17. Click Browse to navigate to the NEC1800.INF file.
This file will install the printer driver software onto the
computer running Windows NT Server. A PCL6, PCL5e,
or PostScript Level 2 printer driver can be installed.
NEC recommends using the PCL6 driver because of its
Page 43

advanced features. Use the PCL5e driver for legacy
applications that cannot communicate with the PCL6
driver.
Note: If the PostScript driver is going to be installed, the
PostScript Level 2 Upgrade Kit must be installed in the
printer. For more information, see Chapter 8, “Printer
Options” of the
SuperScript 1800 User’s Guide
.
Listed below are the paths to each driver.
• PostScript driver: \\SS1800\WINNT\PS
• PCL6 driver: \\SS1800\WINNT\PCL6
• PCL5e driver: \\SS1800\WINNT\PCL5e
18. Select the INF file for the printer driver you want to
install.
19. Click Open to return to the Install From Disk dialog box.
20. Click OK to return to the Add Printer Wizard.
Your selected driver will appear in the Printers list.
22. When asked if you want this printer as the default
printer, select Ye s if you want to this computer to use the
printer for printing.
23. When asked if you want to share this printer with other
network users, select Shared.
PRINTER SERVER TOPOLOGY WINDOWS NT SERVER NETWORKS
21. Click Next to continue.
24. In the Share Name text box, type in a name for the
printer. This name will appear to other network users.
25. From the list, select the operating systems of all
computers that will be using this printer.
26. Click Next to finish the installation.
Note: You will be asked for the install disks for each
operating systems you selected.
Windows NT Server Networks 37
Page 44

Now you can configure the individual Windows, Macintosh,
and UNIX print clients that are connected to the network. See
the following sections for instructions.
• “Configuring a Windows 3.1x Client” on page 38.
• “Configuring a Windows 95 or 98 Client” on page 39.
• “Configuring a Windows NT 4.0 Client” on page 40.
• “Configuring a Macintosh Client” on page 41.
• “Configuring a UNIX Client” on page 42.
Configuring a Windows 3.1x Client
Computers running Windows 3.1x can be configured as a
Windows NT Server client after Windows NT Server has
been configured with the NEC SuperScript 1800 Network
Printer Manager or directly from NT Server itself.
To configure a Windows 3.1x client, you must install a printer
driver then create a printer port.
To install a printer driver:
1. Insert the SuperScript 1800 Solutions CD into the client
computer.
2. Open the Program Manager window.
3. From the File menu, select Run to open the Run dialog
box.
4. Click Browse to open the Browse dialog box.
5. From the Drives drop-down list, select your CD drive.
The directories and files located on the SuperScript 1800
Solutions CD will appear.
6. Select Setup.exe, then click OK to return to the Run
dialog box.
7. Click OK to begin installing the printer software.
When the Select Components dialog box appears, select
the Printer Driver check box then continue to follow the
instructions displayed on your monitor to finish the
install.
To create a printer port:
1. From the Program Manager window, double-click Main to
open the Main window.
2. From the Main window, double-click Control Panel to
open the Control Panel window.
3. From the Control Panel window, double-click Printers to
open the Printers window.
4. From the Installed Printers list, select the printer.
5. Click Connect to open the Connect dialog box.
6. From the Ports list, select LPT1, LPT2, or LPT3.
7. Click Network to open Connect Network Printer dialog
box.
38 SuperScript 1800 — Network User’s Guide
Page 45
8. From the Show Shared Printers on list, select the printer
server.
9. From the Shared Printers on list, select the printer.
10. Click OK to return to the Connect dialog box.
11. Click OK to return to the Printers window.
The new printer will appear in the Printers window.
12. Click Close to accept the port configuration.
Configuring a Windows 95 or 98 Client
Computers running Windows 95 or 98 can be configured as a
Windows NT Server client after Windows NT Server has
been configured with the NEC SuperScript 1800 Network
Printer Manager or directly from NT Server itself.
Configuring a computer running Windows 95 or 98 involves
installing a printer driver then creating a printer port.
To install a printer driver:
1. Insert the SuperScript 1800 Solutions CD into your
computer.
Note: If the NEC SuperScript 1800 Solutions CD
Installer appears on the monitor shortly after the disk is
inserted, go to Step 4, if not, go to Step 2.
2. From the desktop, double-click My Computer to open
the My Computer window.
3. Double-click the NEC SS1800 icon to start the installer.
As an alternative, right mouse button click on NEC
SS1800 then select Open or Autoplay to start the
installer. If neither one of these methods work, doubleclick Setup.exe which is located on the CD.
4. When the Welcome dialog box appears, click Next to
begin the installation.
5. When the Select Components dialog box appears, do the
following.
• Select the printer driver(s) you want to install.
Note: If selecting the Windows PostScript printer
driver (NEC 1800 PS Printer Driver), the NEC
PostScript Level 2 Upgrade Kit (Order No. 1802) must
be installed in the printer. See Chapter 8, “Printer
Options,” of the SuperScript 1800 User’s Guide for
more information.
Later, when the Add Printer Wizard appears, click the
Have Disk button then navigate the
Solutions CD
PostScript installation file. Depending on your
operating system, navigate to one of the following
directories
• \Ss1800\Win95\Ps
• \Ss1800\Win98\Ps
to the appropriate directory to get the
.
SuperScript 1800
• Select the SuperScript 1800 Network Printer
Manager.
• Select the [optional] Online User’s Guide.
• Select the [optional] On-line Network User’s Guide
if this computer will be used to administrate the
printer.
• Do not select SuperScript 1800 Status Monitor; this
component does not work across a network.
6. When the Setup dialog box appears, do the following.
• Select Print Client if this computer will be used to
send print jobs to the printer.
• Select Print and Administrative Client if this
computer will be used to send print jobs and
administer the printer. The Network Printer
Manager will be installed.
7. Follow the instructions that appear on your monitor to
complete the installation.
8. Restart your computer after the driver is installed.
The printer port can now be created.
PRINTER SERVER TOPOLOGY WINDOWS NT SERVER NETWORKS
Windows NT Server Networks 39
Page 46

To create a printer port:
1. From the Windows Start button, point to Settings then
select Printers to open the Printers window.
2. Select the printer driver that was installed.
3. From the File menu, select Properties to open the driver
properties window.
4. Click the Details tab to bring it to the front.
5. Click Add Port to open the Add Ports dialog box.
6. Select the Network radio button.
7. From the Ports list, select the NEC Network Printer Port.
8. Click OK to return to the driver properties window.
9. Click OK to accept the configured port.
Configuring a Windows NT 4.0 Client
Computers running Windows NT 4.0 can be configured as a
Windows NT Server client after Windows NT Server has
been configured with the NEC SuperScript 1800 Network
Printer Manager or directly from NT Server itself.
Configuring a computer running Windows NT involves
installing a printer driver then creating a printer port.
To install a printer driver:
1. Insert the SuperScript 1800 Solutions CD into your
computer.
note: If the NEC SuperScript 1800 Solutions CD Installer
appears on the monitor shortly after the disk is inserted,
go to Step 4, if not, go to Step 2.
2. From the desktop, double-click My Computer to open
the My Computer window.
3. Double-click the NEC SS1800 icon to start the installer.
As an alternative, right mouse button click on NEC
SS1800 then select Open or Autoplay to start the
installer. If neither one of these methods work, doubleclick Setup.exe which is located on the CD.
4. When the Welcome dialog box appears, click Next to
begin the installation.
5. When the Select Components dialog box appears, do the
following.
• Select the printer driver(s) you want to install.
Note: If selecting the Windows PostScript printer
driver (NEC 1800 PS Printer Driver), the NEC
PostScript Level 2 Upgrade Kit (Order No. 1802) must
be installed in the printer. See Chapter 8, “Printer
Options,” of the SuperScript 1800 User’s Guide for
more information.
Later, when the Add Printer Wizard appears, click the
Have Disk button then navigate the
Solutions CD
PostScript installation file. Depending on your
operating system, navigate to one of the following
directories
• \Ss1800\Winnt\Ps
to the appropriate directory to get the
.
SuperScript 1800
• Select the SuperScript 1800 Network Printer
Manager.
• The Online User’s Guide and On-line Network
User’s Guide are optional.
• Do not select SuperScript 1800 Status Monitor. This
component does not work across a network.
6. When the Setup dialog box appears, do the following.
• Select Print Client if this computer will be used to
send print jobs to the printer.
• Select Print and Administrative Client if this
computer will be used to send print jobs and
administer the printer. The Network Printer
Manager will be installed.
7. Follow the instructions that appear on your monitor to
complete the installation.
8. Restart your computer after the driver is installed.
The printer port can now be created.
40 SuperScript 1800 — Network User’s Guide
Page 47

To create a printer port:
1. From the Windows NT Start button, point to Settings
then select Printers to open the Printers window.
2. Select the printer driver that was installed.
3. From the File menu, select Properties to open the driver
properties window.
4. Click the Ports tab to bring it to the front.
5. Click Add Port to open the Add Port dialog box.
6. Select the Network radio button.
7. Click Browse to open the Open window.
8. Navigate to the printer, then select it.
9. Click OK to return to the Add Port dialog box.
10. Click OK to return to the driver properties window.
11. Click OK to accept the configured port.
Configuring a Macintosh Client
Macintosh clients send print jobs over AppleTalk to a
Windows NT print server. To the Macintosh client, the
Windows NT computer looks like any other AppleTalk
device in a zone.
Software Requirements
For Macintosh computers to connect to the printer, they must
meet three software requirements:
• The operating system must be Mac OS 7.1 or higher.
• The standard Macintosh LaserWriter8 printer driver must
be installed.
• The NEC SuperScript 1800 PPD must be installed.
Printer Hardware Requirements
Since Macintosh computers send their print jobs in the
PostScript language, the SuperScript 1800 must be upgraded
with the PostScript Level 2 Upgrade Kit (Order No. 1802).
Installing the Software
Software installation involves installing the LaserWriter
printer driver and SuperScript 1800 PPD.
I
NSTALLING THE LASERWRITER PRINTER DRIVER
The LaserWriter printer driver is standard to the Mac OS 7.1
and higher. Check the Macintosh Chooser to assure that it is
installed. If it isn’t, use the Mac OS help system for
information about installing it.
I
NSTALLING THE SUPERSCRIPT
1800 PPD
The SuperScript 1800 PPD is installed from the SuperScript
1800 Solutions CD.
To install the SuperScript 1800 PPD:
1. Insert the SuperScript 1800 Solutions CD into your
Macintosh and the SS1800 window will appear.
2. Double-click the SuperScript 1800 Installer icon to begin
installing the PPD. Follow the instructions presented on
the monitor.
3. From the Apple menu, select Chooser to open the
Chooser window.
4. From the left pane of the Chooser window, select
LaserWriter8 and a name for the SuperScript 1800 printer
will appear in the right pane of the window.
Note: If the printer’s NIC has been configured with an
AppleTalk Printer Name
60, that name will appear in the right pane. If a name was
not created, the MAC address for the printer’s NIC will
appear. The MAC address can be identified with the NEC
prefix, for example NEC000012345678.
, as described on Page 16 or Page
5. Click Create to setup the printer.
When created, an icon will appear on the desktop using
the AppleTalk Printer Name or MAC address as its label.
6. Close the Chooser window.
PRINTER SERVER TOPOLOGY WINDOWS NT SERVER NETWORKS
Windows NT Server Networks 41
Page 48

Configuring a UNIX Client
Configuring a UNIX computer involves two procedures:
configuring the host table, then adding access to the printer.
Before doing the procedures, the following requirements
must be met.
• The computer must be running Sun Solaris OS 2.51 or
higher.
• The computer must be running X-Windows.
Configuration Procedures
To configure the Host Table:
1. Login into the computer as root.
2. Move to a shell command prompt.
3. Type vi /etc/hosts then press ENTER to display the Host
Table (also known as the look-up table).
4. At the bottom of the table, add the IP address and a host
name for the printer.
5. Press esc to exit edit mode.
6. Type :wq! then press ENTER to save the changes and exit
the editor.
After the host table has been configured, add access to the
printer.
To add access to the printer:
1. From a shell prompt, type admintool & then press
ENTER to start Admintool.
2. From the Browse menu, select Printers to list all the
printers connected to the network.
3. From the Edit menu, point to Add, then select Access to
printer to open the Add Access to Printer dialog box.
4. In the Printer Name text box, type in a name for the
printer.
5. In the Printer Server text box, type in a server name for
the printer.
Use the host name that was assigned to the printer. The
host name was assigned in the Host Table.
6. In the Description text box, type in a description of the
printer; for example, its location.
7. If you want this printer to be the default printer, select
the Default Printer check box.
8. Click Apply to return to the Admintool main window.
Your UNIX computer is now ready to send print jobs to the
printer.
To print a file, move to a command prompt, then enter the
following command, where filename is the name of the file
you want to print.
/usr/ucb/lpr filename
Users can edit their start-up file by including the path to the
lpr program so that they do not have to always type /usr/ucb
when they want to print.
42 SuperScript 1800 — Network User’s Guide
Page 49

APPENDIX A
OPERATOR PANEL
COMMANDS
I
NTRODUCTION
Located on the SuperScript 1800 printer is the Operator Panel
that can be used for configuring the printer settings. Among
the setting that can be configured are the printer network
settings.
For instructions about using the Operator Panel, read
Chapter 5, “The Operator Panel,” in the SuperScript 1800
User’s Guide.
The printer network settings can also be configuring with the
SuperScript 1800 Network Printer Manager and SuperScript
1800 Web Pages. Both are described later in this user’s guide.
N
ETWORK
The Operator Panel has a network menu that contains all the
commands for configuring the printer network settings. The
flowchart at the end of Appendix A describes the path
through all the network commands. Use the flowchart to
help you navigate the commands.
NIC C
The following table lists and describes all the SuperScript
1800 network commands. The left column shows the
command as it is seen on the Operator Panel display. The
right-hand column describes the command.
M
ENU TREE
ONFIGURATION COMMANDS
Command Description
RESET NIC If set to YES, the network interface card can be
restarted.
CFG NET If set to YES, then you can navigate the network
commands.
TCP/IP If set to ON, the TCP/IP commands can be
navigated.
If set to NO, then the LPD, APL TALK and
NETWARE commands can be navigated.
CFG TCP If set to Ye s , the NIC addressing commands can
be navigated.
DHCP If set to YES, the NIC will accept dynamically
assigned IP addresses from a DHCP server.
CFG ADRS If set to YES, the IP address (IP BYTEn), subnet
mask address (SM BYTEn), and gateway address
(GW BYTEn) commands can be navigated.
If set to NO, the BOOTP and RARP commands
can be navigated.
BOOTP If set to YES, the NIC will broadcast a BOOTP
request for an IP address. The request will be
broadcasted when the printer is restarted.
If set to NO, the RARP command can be
navigated.
RARP If set to YES, the NIC will broadcast a RARP
request for an IP address. The request will be
broadcasted when the printer is restarted.
43
Page 50

Command Description
IP BYTE
SM BYTE
GW BYTE
LPD If set to YES, the NIC will accept print jobs from
APL TALK If set to YES, the NIC will accept print jobs from
NETWARE If set to YES, the NetWare commands can be
CFG NWAR If set to YES, the NetWare IPX/SPX protocols will
AUTO If set to YES, the NIC will read the header of each
EN_8023 Set to YES if your NetWare network is
EN_II Set to YES if your NetWare network is
EN_8022 Set to YES if your NetWare network is
n
Use this command for configuring a static IP
address for the NIC. The letter n indicates which
octet of the address is currently being viewed or
configured.
Use the ITEM button to navigate between octets.
Use the VALUE button to select a number for a
specific octet.
n
Use this command for configuring a subnet mask
for the IP address. The letter n indicates which
octet of the address currently being viewed or
configured.
Use the ITEM button to navigate between octets.
Use the VALUE button to select a number for a
specific octet.
n
Use this command for configuring a gateway IP
address. The letter n indicates which octet of the
address currently being viewed or configured.
Use the ITEM button to navigate between octets.
Use the VALUE button to select a number for a
specific octet.
UNIX computers running LPR software.
Macintosh computers.
navigated.
be accepted by the NIC.
Ethernet frame to determine which type of
framing is being sent to the printer from your
NetWare network.
Use Auto if you don’t know which framing is
being used, however, this will be at the expense
of slower processing time by the NIC.
communicating with Ethernet 802.3 framing.
communicating with Ethernet II framing.
communicating with Ethernet 802.2 framing.
Command Description
EN_SNAP Set to YES if your NetWare network is
UPDATE Set to YES if you are going to update the NIC
BOOT SVR Set to WINDOWS if upgrading the NIC firmware
SV-IP Bn Use this command for configuring an IP address
FACTORY
DEFAULT
PRINT
NET CFG
communicating with Ethernet SNAP framing.
firmware. See Appendix E, “Upgrading the NIC
Firmware,” on page 73 for more information.
from Windows 95 computer.
Set to UNIX if upgrading the NIC firmware from
UNIX computer.
for the computer that will be updating the NIC
firmware. The letter
address is currently being viewed or configured.
Use the ITEM button to navigate between octets.
Use the VALUE button to select a number for a
specific octet.
Set to YES if you want to configure the NIC using
the NIC default values.
This can be used as a method for cleaning up the
NIC. If the default values are applied, you must
still reconfigure the NIC so that it can
communicate with your network.
Set to YES if you want to print out a page that
describes the settings applied to the NIC.
n
indicates which octet of the
44 SuperScript 1800 — Network User’s Guide
Page 51

Network Menu Flowchart
READY
OFFLINE
NETWORK MENU
RESET NIC
no
CFG NET
APL TALK
NETWARE
off
off
no
yes
TCP/IP
LPD
on
CFG NWAR
no
yes
on
on
CFG TCP
yes
yes
BOOTP
AUTO
yes
DHCP
off
no
no
RARP
EN_8023
EN_II
EN_8022
EN_SNAP
no
CFG ADRS
NIC CONFIGURATION COMMANDS
yes
IP BYTE1
IP BYTE2
IP BYTE3
IP BYTE4
SM BYTE1
SM BYTE2
SM BYTE3
SM BYTE4
GW BYTE1
GW BYTE2
GW BYTE3
GW BYTE4
no
FACTORY DEFAULT
PRINT NET CFG
UPDATE
UNIX
yes
BOOT SVR
Windows
SV-IP B1
SV-IP B2
SV-IP B3
SV-IP B4
NIC Configuration Commands 45
Page 52

46 SuperScript 1800 — Network User’s Guide
Page 53

APPENDIX B
NETWORK PRINTER
MANAGER
I
NTRODUCTION
The SuperScript 1800 Network Printer Manager (NPM) is a
multi-purpose tool for administering networked SuperScript
1800 printers. Use the NPM for performing the following
administrative tasks.
• Viewing all SuperScript 1800 printers connected to the
network.
• Viewing the general settings for a specific printer.
• Viewing the network interface settings for a specific
printer.
• Creating NetWare queues and servers.
• Viewing protocol statistics for a specific printer.
• Viewing the job queue for a specific printer.
• Viewing the operational status of a specific printer.
• Creating alerts for monitoring specific printers.
• Upgrading the printer controller board firmware for a
specific printer.
• Adding ports to networked printers. These ports are
local to the computer running NPM, and can be selected
by printer drivers.
• Starting the Add Printer Wizard.
• Viewing a printer driver’s properties sheet.
• Printing test pages.
I
NSTALLATION
The NPM can be installed on a computer running
Windows 95 or 98 that is connected to the network.
To install NPM on a Windows computer connected to the
network as a NetWare client, follow the instructions
described by “Configuring a Windows 95 or 98 Client” on
page 32.
To install NPM on a Windows computer connected to the
network as a Windows NT Server 4.0 client, follow the
instructions described by “Configuring a Windows 95 or 98
Client” on page 39.
S
TARTING
To start the NPM:
• From the Windows Start button, point to Programs then
NEC SuperScript 1800, then select NEC SuperScript
1800 Printer Manager.
P
ROCEDURES
For instructions about creating queues for networks using
NetWare, see “Using NPM to Configure NetWare”
on page 23.
For instructions about using NPM to upgrade the firmware
for a printer’s controller board, see Appendix E, on page 73.
For detailed information about using NPM to perform other
tasks, see the Network Printer Manager Help.
To view Help:
1. Start the Network Printer Manager.
2. From the Help menu, select Contents to start the help
system.
NPM
47
Page 54

M
AIN
W
INDOW
When NPM is started, it begins to search the network for all
SuperScript 1800 printers that are connected to the local area
network. Once found, they are listed in the main window.
The name, description, status, and IP address for each printer
is displayed.
Printers Menu
Use the Printers menu for adding a printer port, starting the
Add Printer Wizard, viewing a printer driver, viewing a job
queue for a specific printer, and for exiting the NPM.
View Menu
Use the View menu for controlling how information is
displayed in the main window and for displaying the button
bar.
Settings Menu
Use the Settings menu for viewing the network interface
properties, the printer operator panel, and for creating alerts
for a specific printer.
Maintenance Menu
Use the Maintenance menu for viewing the operational
status, protocol statistics, and printing a test page for specific
printer. Printer firmware is upgraded from here.
Help Menu
Use the Help menu for starting the NPM help system, and for
determining which version of the NPM you’re running.
N
ETWORK INTERFACE
The Network Interface window can be opened from the
Settings menu. Use the Network Interface window for
viewing and configuring the NIC for a specific printer. It can
also be used for creating NetWare printer queues and servers.
W
INDOW
General Tab
Item Description
Printer Name Use this text box to name your printer. This
name will appear in the main window and
can be seen by users on the network.
Printer Description Use this text box for describing the printer,
for example, its location.
Enable Password Use this check box for controlling who can
make changes to the settings.
Set Password Opens a dialog box for creating a
password.
48 SuperScript 1800 — Network User’s Guide
Page 55

TCP/IP Tab NetWare Tab
NETWORK PRINTER MANAGER NETWORK INTERFACE WINDOW
Item Description
TCP/IP Enabled Use this check box to turn on the TCP/IP
protocol stack.
IP Address
Assignment
Method
TCP/IP Parameters Use these text boxes to enter a static IP
Use this drop-down list for selecting how
an address will be assigned to the printer.
Select Static if you want to manually enter
a permanent address. Select DHCP if you
want a DHCP server to assign an address;
however, if the printer is restarted, it may
be assigned a different address. Select
BOOTP or RARP if you want the NIC to
broadcast a request for an address from a
BOOTP or RARP server. The printer must
be restarted if BOOTP or RARP is
selected.
address. Enter a default gateway (router)
address if users from a different TCP/IP
network want to use the printer.
Item Description
NetWare Enabled Use this check box to turn on the IPX
protocol stack.
Check Job Every Use this spinner for selecting how much
time will pass until the NPM verifies the
network settings for a selected file server.
Check Configuration
Every
IPX Frame Type Use these options to select the type of
Serviced Queues This list displays all the print queues
Add Q Click to add a print new print queue.
Remove Q Click to remove a selected queue.
Modify Mode Click here to switch between NetWare
Use this spinner for selecting how much
time will pass until the NPM verifies the
network settings for a print queue.
Ethernet framing used by your IPX
network.
attached to specific printers.
Bindery and NetWare NDS modes.
Network Interface Window 49
Page 56

AppleTalk Tab SNMP Tab
Item Description
AppleTalk Enabled Use this check box to turn on the
AppleTalk protocol stack.
Last Error Occurred This text box displays the last error
message that occurred in the AppleTalk
stack.
AppleTalk Printer
Name
Timer Value for
Aging A-Router
Entry
Current Zone Use this drop-down list to select which
Wait Time Before
Retransmitting a
Tickle Packet
50 SuperScript 1800 — Network User’s Guide
Use this text box for naming the printer for
Macintosh users. They will be able to
identify the printer with this name.
Use this spinner for setting the amount of
seconds that must pass when the router
entry in the RTMP router table will die.
AppleTalk zone the printer is in.
Use this spinner for setting the amount of
time that must pass before the NIC
verifies the connection with a Macintosh
computer.
Item Description
Enable
Authentication Traps
IP Address Use these text boxes to enter the address
Community Name
(for address pairs)
Address Pair Use to move between IP address and
Community Name
(for r/w access)
Read Access Controls MIB reading privileges from a
Write Access Controls MIB writing privileges to a
Use this check box to turn on the SNMP
agent.
of the printer containing MIB variables that
you want to trap. This address must be
associated with a specific [trap]
community name.
Use this text box to identify a specific trap
community name. One or more printers
can be associated with this name.
[trap] Community Name pairs.
Use to move between trap community
names.
specific community.
specific community.
Page 57
P
RINTER PROPERTIES
W
INDOW
The Printer Properties window is started from the Setting
menu by selecting Operator Panel. Use this window for
adjusting the basic properties for a specific printer. For more
detailed explanation of each control, see Chapter 5, “The
Operator Panel,” in the SuperScript 1800 User’s Guide.
Model Details
Item Description
Printer Name This text box to identifies the printer
name.
Printer Model This text box for identifies the printer
model.
Software Version This text box identifies the version of the
printer Controller Board Firmware.
Printer Menu
Item Description
Paper Use to set the what size of paper is loaded
in the paper tray.
Tray 1 Size Controls the size of the paper tray.
Paper Source Controls which tray is supplying the paper.
Resolution Controls the printing resolution in dpi.
Copies Controls the number copies printed.
Left Margin Controls the width of the left margin in
inches.
Top Margin Controls the width of the top margin in
inches.
Duplex Switches between duplex and single sided
printing.
Auto Carriage Return Use for backward compatibility with older
PCL printer drivers.
NETWORK PRINTER MANAGER PRINTER PROPERTIES WINDOW
Printer Properties Window 51
Page 58

Config Menu Job Menu
Item Description
Personality Switches the printer between the PCL and
PostScript printer languages. Use Auto if
both types will be used.
Tray Lock Use to select which tray the printer should
not use when the original tray runs empty.
Power Save Use to select how much idle time must
pass before power save mode is entered.
Econo Mode Reduces the amount of toner used for
graphics in a print job.
Jam Recovery If set to Off, a jammed sheet will not be
reprinted.
Auto Continue If set to On, and the wrong paper size is
loaded, the printer will begin printing after
waiting 60 seconds.
Tray Switch If set to On, and a tray runs out of paper,
the printer will switch to a tray that
contains the same paper.
Low Toner If selected, printing will stop when toner is
low. Press GO to by-pass this control.
52 SuperScript 1800 — Network User’s Guide
Item Description
Paper Type Use to switch between paper weights.
Toner Density Controls how much toner is used in a print
job.
SET Turns on NEC’s Sharp Edge Technology
printing mode for text or photos.
Menu Clear Use to set all controls to their default
values.
Memory
Optimization
I/O Timeout Controls the time in seconds that should
Duplex Top Margin Controls the second page top margin.
Duplex Left Margin Controls the second page left margin.
Short Edge Binding Controls the margin added to the binding
Long Edge Binding Controls the margin added to the binding
If set to Yes, complex print jobs can be
printed more efficiently.
pass before printing the last page of a print
job that does not end with a command to
print the page.
edge of landscape print jobs.
edge of portrait print jobs.
Page 59

PCL Menu I/O Menu
NETWORK PRINTER MANAGER PRINTER PROPERTIES WINDOW
Item Description
Font Number Controls the default font for PCL printing.
Courier Controls which version of courier to use.
Symbol Set Controls the 8-bit code for symbols.
Lines Controls how many lines must be read
before the page begins printing.
Font Pitch Controls the default font size for
monospaced PCL fonts.
Font Height Controls the default font size for
proportional PCL fonts.
Yes Click to print the printer’s PCL font list.
Item Description
Baud Rate Controls the bit rate used when a print
client and the printer are communicating.
Available when a serial card is installed in
the printer.
Robust XON During serial mode, if set to On, the printer
will broadcast a message every second
saying it has room for storing a print job.
Printer Properties Window 53
Page 60
PS Menu
Item Description
Yes Click to print a list of which PostScript
fonts are installed in the printer.
A
LERTS
Use the Alerts window for monitoring specific printers and
their conditions. When a condition occurs with the printer, an
alert message box will appear (outside of NPM). Alert
messages can be recorded in a log file.
W
INDOW
6. From the Available Alerts list, select the alert you want
to monitor.
7. Click Add to move the alert to the Active Alerts list.
8. If you want to record the alerts, click Enable Logging of
Alerts, then click Browse to select a location to store the
alert log.
The contents of the log can be viewed from the View Log
tab.
9. Click OK.
When the Network Printer Manager (NPM) is made aware of
an alert, it will display an message outside the NPM.
Shown is the General tab of the Alerts window.
General Tab
To set an alert:
1. From the Settings menu, select Alerts to open the Alerts
window.
2. From the Printer Available list, select the printer you
want to monitor.
3. Click Add to move the printer to the Printer to Monitor
list.
4. Assure Enable Alerts is selected.
5. Click the Alerts tab to bring it to the front.
54 SuperScript 1800 — Network User’s Guide
Page 61

P
RINTER STATUS
The Printer Status window can be started from the
Maintenance menu by selecting Printer Status. Use it for
viewing the operational state of a specific printer. Shown
below is the Printer Status window.
W
INDOW
P
ROTOCOL STATISTICS
The Protocol Statistics window is started from the Settings
menu. Use it for viewing packet, framing, and error activity
at a specific printer’s NIC. Five tabs are used for presenting
information about the following types of network traffic.
• TCP/IP Traffic
• IPX Traffic
• AppleTalk Traffic
• SNMP Traffic
• DLC Traffic
Shown below is the Protocol Statistics window with the
TCP/IP tab at the front.
W
INDOW
TCP/IP Tab
NETWORK PRINTER MANAGER PRINTER STATUS WINDOW
U
PGRADING THE FIRMWARE
Upgrading the Controller Board firmware is described by
Appendix E, on page 47.
Printer Status Window 55
Page 62

56 SuperScript 1800 — Network User’s Guide
Page 63

APPENDIX C
SUPERSCRIPT 1800 WEB
PAGES
I
NTRODUCTION
The SuperScript 1800 Web Pages are a web site for viewing
and administering the printer. The web pages contain many
of the same controls as the NEC SuperScript 1800 Network
Printer Manager (NPM). The main difference is that NPM can
create NetWare printer and server queues.
Use the web pages for performing the following
administrative tasks.
• Printer operational status.
• Setting up the printer.
• Viewing instructions about using the printer.
• Viewing a printer’s settings.
• Viewing a printer’s network interface settings.
• Viewing a printer’s protocol statistics.
• Printing a NIC configuration page.
• Learning how to get printer supplies and accessories.
• Learning about NEC and NEC Technologies.
H
OW TO VIEW THE
After the printer is connected to your network, and assigned
an IP address, any popular web browser can be used to
navigate to its IP address. Netscape Navigator 4.x and higher,
Microsoft Internet Explorer 4.x and higher, or any equivalent
browser can be used.
H
OME PAGE
The printer’s home page is the starting point for navigating
to all the other printer web pages. The left side of the page
displays information about the operational status for a
specific printer.
WEB P
AGES
I
NSTALLATION
There is no installation required. The pages are located
directly on the printer’s Controller Board.
57
Page 64

A
DMIN PAGES
Use the network administration pages for viewing and
configuring the network settings for a specific printer.
From the Home page, click Network Administration to view
the General Information page. From there, Click Admin to
view the Admin menu items.
General Information
Use the General Information page for getting a general view of
the entire NIC configuration.
General Configuration
Use the General Configuration page for naming the printer and
creating password protection. From the Admin menu, click
General to view the General Configuration page.
Item Description
Printer Name This text box to identifies the printer
name.
Printer Description Use this text box to describe the printer,
for example, where it is located.
Enable Password
Protection
Password Click here to create a password.
Use this check box for turning on
password protection.
58 SuperScript 1800 — Network User’s Guide
Page 65

TCP\IP Configuration
Use the TCP\IP Configuration page for adjusting the network
addressing for the NIC. From the Admin menu, click
TCP\IP to view this page.
Item Description
TCP/IP Enabled Use this check box to turn on the TCP/IP
protocol stack.
IP Address
Assignment
Method
Use this drop-down list for selecting how
an address will be assigned to the printer.
Select Static if you want to manually enter
a permanent address. Select DHCP if you
want a DHCP server to assign an address;
however, if the printer is restarted, it may
be assigned a different address. Select
BOOTP or RARP if you want the NIC to
broadcast a request for an address from a
BOOTP or RARP server. The printer must
be restarted if BOOTP or RARP is
selected.
NetWare Configuration
Use the NetWare Configuration page for turning on and
adjusting the NetWare protocol stack. From the Admin
menu, click NetWare to view this page.
Item Description
NetWare Enabled Use this check box to turn on the IPX
protocol stack.
IPX Frame Type Use these options to select the type of
Ethernet framing used by your IPX
network.
ADMIN PAGES
Admin Pages 59
Page 66

AppleTalk Configuration
Use the AppleTalk Configuration page for turning on the
AppleTalk protocol stack and for giving the printer an
AppleTalk Printer Name. From the Admin menu, click
AppleTalk to view this page.
Item Description
AppleTalk Enabled Use this check box to turn on the
AppleTalk protocol stack.
Last Error Occurred This text box displays the last error
message that occurred in the AppleTalk
stack.
AppleTalk Printer
Name
Timer Value for
Aging A-Router
Entry
Current Zone Use this drop-down list to select which
PAP Use this spinner for setting the amount of
Use this text box for naming the printer for
Macintosh users. They will be able to
identify the printer with this name.
Use this spinner for setting the amount of
seconds that must pass when the router
entry in the RTMP router table will die.
AppleTalk zone the printer is in.
time that must pass before the NIC
verifies the connection with a Macintosh
computer.
60 SuperScript 1800 — Network User’s Guide
Page 67

SNMP Configurations
Use the SNMP Configuration page for turning on SNMP and
for configuring SNMP traps. Two pages are used for making
the configurations: the SNMP Trap Configuration page, and
the SNMP Community Configuration page. From the Admin
menu, click SNMP to view these pages.
SNMP Trap Configuration
Item Description
Community Name Use this text box to identify a specific trap
community name. One or more printers
can be associated with this name.
Read Access Controls MIB reading privileges from a
specific community.
Write Access Controls MIB writing privileges to a
specific community.
SNMP Community Configuration
Item Description
Enable
Authentication Traps
IP Address Use this text box to enter the address of
Community Name Use this text box to identify a specific trap
Use this check box to turn on the SNMP
agent.
the printer containing MIB variables that
you want to trap. This address must be
associated with a specific [trap]
community name.
community name. One or more printers
can be associated with this name.
ADMIN PAGES
Admin Pages 61
Page 68

O
PERATOR PANEL PAGES
Use the Operator Panel pages for adjusting the printer settings
that can be configured from the printer’s Operator Panel.
From the Admin menu, click Panel to view the Operator Panel
pages.
Printing Page
From the Operator Panel Menu Settings, click Printing to
view the Printing page.
Item Description
Paper Use to set the what size of paper is loaded
in the paper tray.
Tray 1 Size Controls the size of the paper tray.
Paper Source Controls which tray is supplying the paper.
Orientation Use to select landscape or portrait
printing.
Resolution Controls the printing resolution in dpi.
Copies Controls the number copies printed.
Left Margin Controls the width of the left margin in
inches.
Top Margin Controls the width of the top margin in
inches.
Duplex Switches between duplex and single sided
printing.
Auto Carriage Return Use for backward compatibility with older
PCL printer drivers.
62 SuperScript 1800 — Network User’s Guide
Page 69

Config Page
Use the Config page for adjusting the paper tray settings for
the printer. From the Operator Panel Menu Settings, click
Config to view the Config page.
Item Description
Personality Switches the printer between the PCL and
PostScript printer languages. Use Auto if
both types will be used.
Tray Lock Use to select which tray the printer should
not use when the original tray runs empty.
Power Save Use to select how much idle time must
pass before power save mode is entered.
Econo Mode Reduces the amount of toner used for
graphics in a print job.
Jam Recovery If set to Off, a jammed sheet will not be
reprinted.
Auto Continue If set to On, and the wrong paper size is
loaded, the printer will begin printing after
waiting 60 seconds.
Tray Switch If set to On, and a tray runs out of paper,
the printer will switch to a tray that
contains the same paper.
Low Toner If selected, printing will stop when toner is
low. Press GO to by-pass this control.
OPERATOR PANEL PAGES
Operator Panel Pages 63
Page 70

Job Page
Use the Job page for adjusting the paper type, toner, and
duplex settings. From the Operator Panel Menu Settings,
click Job to view the Job page.
Item Description
Paper Type Use to switch between paper weights.
Toner Density Controls how much toner is used in a print
job.
SET Turns on NEC’s Sharp Edge Technology
printing mode for text or photos.
Memory
Optimization
I/O Timeout Controls the time in seconds that should
Duplex Top Margin Controls the second page top margin.
Duplex Left Margin Controls the second page left margin.
Short Edge Binding Controls the margin added to the binding
Long Edge Binding Controls the margin added to the binding
If set to Yes, complex print jobs can be
printed more efficiently.
pass before printing the last page of a print
job that does not end with a command to
print the page.
edge of landscape print jobs.
edge of portrait print jobs.
64 SuperScript 1800 — Network User’s Guide
Page 71
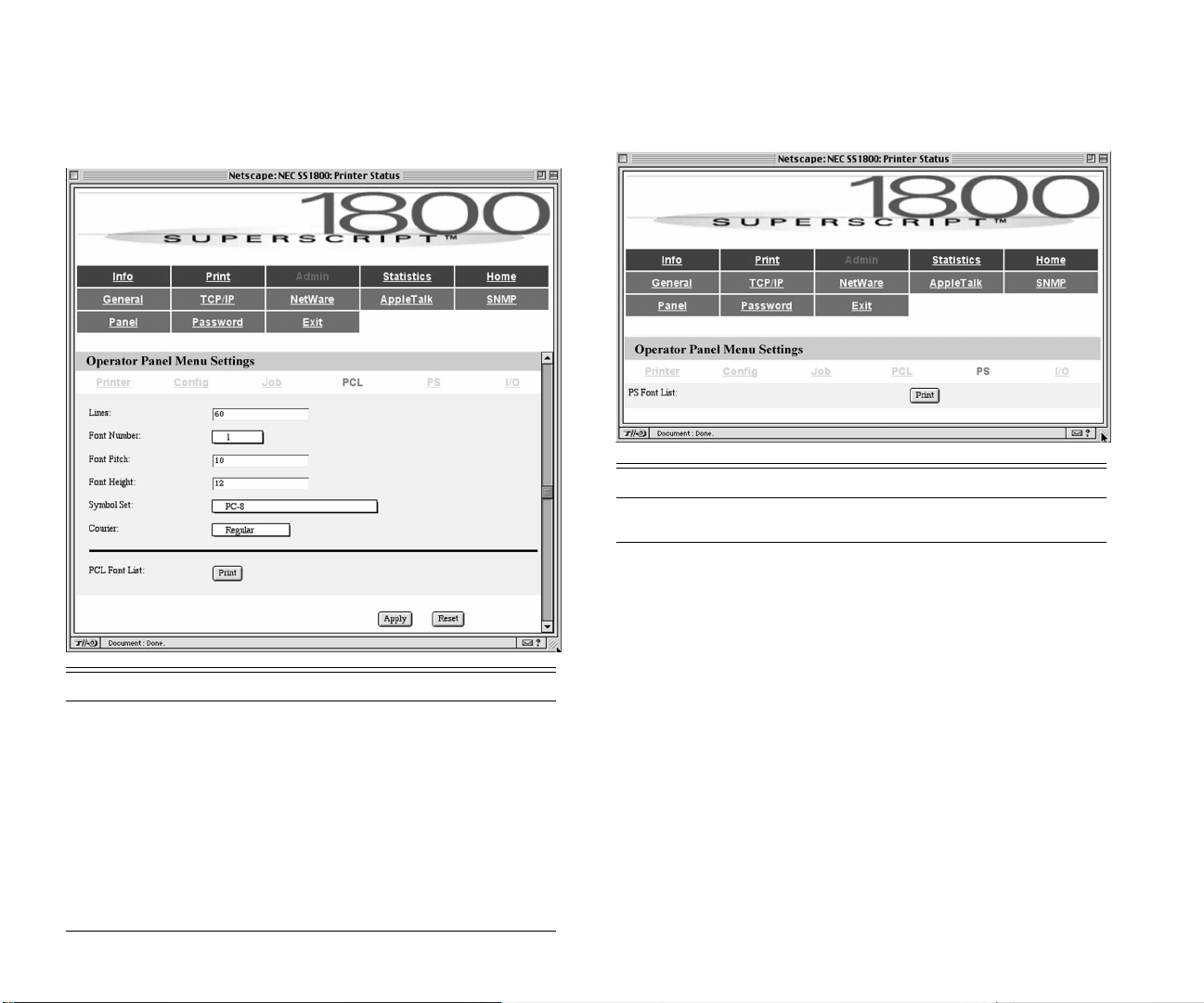
PCL Page
Use the PCL page for adjusting how the Printer Control
Language (PCL) fonts are used and for viewing which fonts
are stored in the printer. From the Operator Panel Menu
Settings, click PCL to view this page.
PS Page
Use the PS page for viewing the PostScript Level 2 fonts
stored in the printer. From the Operator Panel Menu
Settings, click PS to view this page.
Item Description
PS Font List Click to print a list of PostScript fonts
installed in the printer.
OPERATOR PANEL PAGES
Item Description
Font Number Controls the default font for PCL printing.
Courier Controls which version of courier to use.
Symbol Set Controls the 8-bit code for symbols.
Lines Controls how many lines must be read
before the page begins printing.
Font Pitch Controls the default font size for
monospaced PCL fonts.
Font Height Controls the default font size for
proportional PCL fonts.
PCL Font List Click to print the printer’s PCL font list.
Operator Panel Pages 65
Page 72

C
HANGE PASSWORD
Use the Change Password page for changing a password. From
the Admin menu, click Password to view this page
Item Description
New Password To begin to change an existing password,
type in a new password in here.
Confirm new
password
OK Click here to change the password.
As a confirmation, type in your new
password in here.
.
N
ETWORK PRINTER DETAILS
Use the Network Printer Details page to view the network
interface configuration of the NIC. From the Home page,
click Network Print Details to view this page
.
66 SuperScript 1800 — Network User’s Guide
Page 73

P
ROTOCOL STATISTICS
Use the Protocol Statistics pages for viewing a variety of
network traffic parameters at the printer’s NIC. From the
Main menu, click Statistics to view these pages.
TCP\IP Statistics
From the Protocol Statistics menu, click TCP\IP to view the
TCP\IP Statistics page.
IPX Statistics
From the Protocol Statistics menu, click IPX to view the IPX
Statistics page.
PROTOCOL STATISTICS
Protocol Statistics 67
Page 74

AppleTalk Statistics
From the Protocol Statistics menu, click AppleTalk to view
the AppleTalk Statistics page.
SNMP Statistics
From the Protocol Statistics menu, click SNMP to view the
SNMP Statistics page.
68 SuperScript 1800 — Network User’s Guide
Page 75

DLC Statistics
From the Protocol Statistics menu, click DLC to view the
DLC Statistics page.
PROTOCOL STATISTICS
Protocol Statistics 69
Page 76

70 SuperScript 1800 — Network User’s Guide
Page 77

APPENDIX D
TROUBLESHOOTING
I
NTRODUCTION
Use this Appendix as an aid for troubleshooting.
B
ASIC TROUBLESHOOTING
Symptom Possible Cause or Resolution
Green LED on NIC
remains illuminated
NIC not
communicating
SNMP
communication
failure
UNIX host cannot
print
Printer not detected
by Network Printer
Manager
Printer not visible in
Chooser
NIC is not operational.
Restart the printer.
Set NIC to default settings, restart printer,
then configure the NIC.
Assure the printer is on.
Perform ping test. If ping test passes,
community names may be limited by
permissions (see NetworK Printer
Manager).
Verify connection with ping test.
Verify printer’s name on the host’s lookup
table.
Use lpstat or lpadmin to verify the printer is
enabled.
Inspect the connection at NIC.
Inspect NetWare file server consoles for
error messages.
Assure the printer is on.
Click refresh.
Ping the NIC from the Macintosh computer
to verify the network connection.
If communication is through a router, verify
that the router supports AppleTalk.
Symptom Possible Cause or Resolution
Printer is not
receiving print jobs
from NetWare
clients
Printer does not
print jobs from
Win32 clients
Printer does not
appear in Network
Printer Manager
Printer drops
characters
Test page is not
printed
NIC flash upgrade
process failed
During Network
Printer Manager
installation,
“Unable to copy
sammon.dll”
message appears
Use Network Printer Manager to confirm
that the IPX configuration is correct and a
print queue is serviceable.
Use Pconsole or Nwadmin to inspect the
printer’s configuration.
Use Network Printer Manager to determine
if the printer is installed. Inspect NIC
settings.
Ping the NIC from the Macintosh computer
to verify the network connection.
If a client is sending PostScript print jobs,
assure the PostScript option is installed in
the printer.
Assure the PostScript SIMM is securely
installed.
Increase printer memory.
Restart the printer.
Repeat the upgrade process.
Assure a previous copy of Network Printer
Manager has been removed.
Assure the computer is restarted after
removal.
If problem continues, remove the
sammon.dll file. It is located at in the
\\windows\system directory. Then restart
the computer.
71
Page 78

Symptom Possible Cause or Resolution
“Unable to
configure printer
notifications”
message appears
while Network
Printer manager is
running.
“Unable to add the
Port List...” message
appears when using
the Network Printer
Manager to add a
printer port.
Assure the computer was restarted after
Network Printer Manager was installed.
Assure the computer was restarted after
Network Printer Manager was installed.
Assure the computer has the TCP\IP or
IPX\SPX network protocol stacks running.
72 SuperScript 1800 — Network User’s Guide
Page 79

APPENDIX E
UPGRADING THE NIC
FIRMWARE
I
NTRODUCTION
Located on the network interface card (NIC) are flash
memory devices for storing the NIC firmware. The firmware
contains instructions that are used by the NIC for
communicating with a network. If for some reason the
firmware must be upgraded, it can be easily done.
For information about NIC firmware upgrades, such as
whether you need one or not, and how to receive them, visit
NEC’s web site at www.nec.com.
P
REREQUISITES
Before the NIC firmware can be upgraded, the following
prerequisites must be met.
The NIC must be installed in the printer (see page 10).
The printer must be physically connected to a network
(see page 11).
The NIC must be configured (see page 12).
A Windows 95 computer must be used for performing
the upgrade.
The computer must be connected to the same network as
the printer. Meaning, communications between the
computer and the printer must not cross a network
router.
The computer must be configured to use TCP/IP. See
your Windows 95 User Guide or the Windows 95 Help
System for information about how to determine this.
The IP Address for the computer must be known.
The address can be determined by clicking the Windows
Start button, selecting Run, then typing winipcfg in the
Run dialog box.
The SuperScript 1800 Network Printer Manager must be
installed in the computer (see page 47).
A copy of the NIC firmware must be obtained from
NEC’s web site and stored on the computer.
U
PGRADE PROCEDURES
Two procedures are used for upgrading the NIC firmware.
The first one involves configuring the printer so that it is in
upgrade mode and entering the IP address for the
Windows 95 computer. The second procedure describes how
to use the computer to upgrade the firmware.
After both procedures are completed, the printer will
automatically reset itself so it can begin receiving print jobs.
To configure the printer:
1. From the printer Operator Panel, press the GO button
until OFFLINE appears in the Operator Panel display.
2. Press the Menu button until NETWORK MENU appears.
3. Press Item until CFG NET NO appears.
4. Press Value until CFG NET YES appears.
5. Press Select to set the value.
6. Press Item until UPDATE NO appears.
7. Press Value until UPDATE YES appears.
8. Press Select.
9. Press Item until BOOT SVR UNIX appears.
10. Press Value until BOOT SVR WINDOWS appears.
11. Press Select.
12. Press Item until SV-IP B1 appears.
13. Press Value until the first octet of the IP address for the
Windows 95 computer appears.
14. Press Select.
73
Page 80

15. Press Item until SV-IP B2 appears.
16. Press Value until the second octet appears.
17. Press Select.
18. Press Item until SV-IP B3 appears.
19. Press Value until the third octet appears.
20. Press Select.
21. Press Item until SV-IP B4 appears.
22. Press Value until the fourth octet appears.
23. Press Select.
24. Press GO until READY appears.
After configuring the printer, the firmware can then be
upgraded.
To upgrade the NIC firmware:
Note: Some of the following steps may appear to be
slow because of network traffic.
1. Move to the Windows 95 computer.
2. Click the Windows Start button, point to Programs, then
NEC SuperScript 1800, and click NEC SuperScript 1800
Network Printer Manager to start the NEC SuperScript
1800 Network Printer Manager.
Once the manager starts, it will begin searching the
network for the printer. Every SuperScript 1800 printer
that is found will be listed in the Network Printer
Manager.
3. Select the printer that must have it’s NIC firmware
upgraded.
4. From the Maintenance menu, select Upgrade Firmware
to open the Choose the Upgrade Firmware File dialog
box.
5. From the list, select the printer that must have it’s NIC
firmware upgraded.
6. Click Browse to open the Open dialog box.
7. Navigate to the location of the upgrade file then select it.
It will have an AIF filename extension.
8. Click Open to return to the Choose the Upgrade
Firmware File dialog box.
9. Click Start to begin upgrading the firmware.
10. When the upgrade is completed, click OK.
74 SuperScript 1800 — Network User’s Guide
Page 81

Index
To move to a subject, click on a subject heading.
A
Alerts, creating 54
AppleTalk
configuring from Network Printer
Manager 50
configuring from the printer 14
configuring from web pages 60
C
cable, network printer 5
configuration page, NIC 16, 58
F
flash memory, NIC 3
I
IP Address, configuring the printer’s
from Network Printer Manager 15
from the printer 12
from the web pages 59
IPX, turning on and configuring
from Network Printer Manager 15
from the printer 13
from the web pages 59
M
Macintosh client
Peer-to-Peer Topology, in a 20
Printer Server Topology, in a
as a NetWare client 34
as an NT Server client 41
N
naming the printer
from Network Printer Manager 48
from the web pages 58
NetWare, configuring
from Network Printer Manager 49
from web pages 59
Network Configuration Page 16
Network Interface Card
configuring 12
installing 10
ordering 9
what is a 2
Network Interface Window 48
Network Operating Systems 2
Network Printer Manager
using to configure NetWare 23
using to configure the NIC 15
what is 2
network printing, what is 1
Network Topologies
used by the printer 5
what are 2
NIC 2
NIC Flash Memory, what is 3
NOS 2
NPM 2
O
Operator Panel commands
from Network Printer Manager 51
from web pages 62
P
password protection 48, 58
passwords, changing 66
Pconsole.exe 27
Peer-to-Peer Topology
described 5
how to configure 17
Print Clients, what are 1
Print Job, what is a 2
Printer Drivers, defined 2
Printer Port
what is a 2
Windows 3.1x client 31, 38
Windows 95 & 98 clients 18, 32, 40
Windows NT 4.0 client 19, 33, 41
Printer Server Topology
described 6
NetWare
How to configure 23
Macintosh client 34
NPM, using 23
Nwadmin32.exe, using 28
Pconsole.exe, using 27
UNIX client 34
Windows 3.1x client 31
Windows 95 or 98 client 32
Windows NT 4.0 client 33
Windows NT Server
configuring the server 35
Macintosh client 41
UNIX client 42
Windows 3.1x client 38
Windows 95 or 98 clients 39
Windows NT 4.0 client 40
Printer Sharing Topology 7
Printer Status (web page) 57
Printer Status Window 55
Protocol Statistics
viewing from Network Printer
Manager 55
viewing from web pages 67
Q
queues, creating
with Network Printer Manager 23
with Nwadmin32.exe 28
with Pconsole.exe 27
S
SNMP traps, creating 50, 61
SuperScript 1800 Web Pages 2, 57
T
TCP/IP, configuring
from Network Printer Manager 49
from web pages 59
from the printer 12
75
Page 82

U
UNIX client
Peer-to-Peer Topology 21
Printer Server Topology
NetWare network, in a 34
NT Server network, in a 42
UNIX printer, creating a 14
W
Web Pages 2, 57
Windows 3.1x
Peer-to-Peer Topology 17
Printer Server Topology
NetWare client 31
NT Server client 38
Windows 95 and 98
Peer-to-Peer Topology 17
Printer Server Topology
NetWare client 32
NT Server client 39
Windows NT 4.0 Workstation
Peer-to-Peer Topology 19
Printer Server Topology
NetWare client 33
NT Server client 40
Windows NT Server, configuring 35
76 SuperScript 1800 — Network User’s Guide
 Loading...
Loading...