Page 1

GSK980T
Turning Machine CNC System
User Manual
Page 2

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
Ⅰ
INTRODUCTION······························································································································1
1.1 Introduction································································································································· 1
1.2 Type Signification························································································································ 1
1.3 Type Table ··································································································································· 1
II. Programming ······································································································································2
2.1 General······································································································································ 2
2.1.1 Axes Definition ·················································································································· 2
2.1.2 Reference Point (Machine Zero Point) ··············································································· 2
2.1.3 Coordinate value and direction and dimension··································································· 2
2.1.4 Unit and Range of coordinate····························································································· 3
2.1.5 Initial and Modal Status of the Command ·········································································· 3
2.1.6 The Start of a Program········································································································3
2.1.7 The End of a Program········································································································· 3
2.1.8 Program Configuration······································································································· 3
2.1.9 Program Configuration······································································································· 3
2.2 controlled Axis·························································································································· 5
2.2.1 Number of Controlled Axis ································································································ 5
2.2.2 Unit Setting ························································································································ 5
2.2.3 Maximum Strokes ·············································································································· 5
2.3 Preparatory Function (G Function)···························································································· 6
2.3.1 Positioning(G00) ················································································································ 7
2.3.2 Linear Interpolation (G01)·································································································· 7
2.3.3 Circular Interpolation (G02,G03) ······················································································· 8
2.3.4 Thread Cutting (G32) ······································································································· 11
2.3.5 Return to Reference Point Automatically (G28) ······························································· 14
2.3.6 Dwell(G04) ······················································································································ 14
2.3.7 Work Coordinate System Setting(G0) ··············································································14
2.3.8 Feed per Minute (G98) ····································································································· 15
2.3.9 Feed per Revolution(G99) ································································································ 15
2.3.10 Constant Surface Speed Control(G96, G97)··································································· 17
2.3.11 Canned Cycle(G90, G92 G94)························································································ 20
2.3.12 Multiple Repetitive Cycle (G70~G75) ··········································································· 25
2.3.13 Notes on Multiple Repetitive Cutting Cycle (G70~G75)················································ 34
2.4 Spindle Function(S Function)·································································································· 34
2.4.1 Spindle Speed Command·································································································· 34
2.5 Tool Function·························································································································· 35
2.5.1 Procedures of tool Change································································································ 35
2.5.2 Tool selection (Change) Related Parameters ···································································· 36
2.6 Auxiliary Function(M function) ······························································································ 36
2.6.1 Description of M F unction ······························································································ 37
2.6.2 M function Related Data··································································································· 37
2.7 Program Configuration············································································································ 39
2.7.1 Program···························································································································· 39
2.7.2 Program Number ·············································································································· 41
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
Page 3

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
2.7.3 Sequence Number and Block···························································································· 42
2.7.4 Word and Address ············································································································ 42
2.7.5 Basic Addresses and Ranges of Command Values···························································· 43
2.7.6 End of Program ················································································································ 43
2.8 Coordinate Values and Dimensions························································································· 43
2.8.1 Absolute Commands and Incremental Commands ··························································· 43
2.8.2 Decimal Point Programming ···························································································· 45
2.8.3 Diameter Designation and Radius Designation ································································45
2.9 Tool Offset ······························································································································ 46
2.9.1 Geometry Tool Offset ······································································································· 46
2.9.2 T Code for Tool offset ······································································································ 46
2.9.3 Tool Offset Value Input by Moving the Tool To a Fixed Point ········································· 47
2.9.4 Direct Input of Tool Offset by Trial Cutting ·····································································47
2.10 Automatic Acceleration and Deceleration ············································································· 49
2.10.1 Speed Control In the Corner Between Blocks ···································································50
2.11 The Macro Program to User ·································································································· 50
2.11.1 The Macro Command ········································································································ 51
2.11.2 The Macro Program Body ······························································································ 51
2.11.3 Operation and Transfer Dictate(G65) ··········································································· 52
2.11.4 The Note about the Macro Program Body ······································································ 54
2.11.5 Example for User··············································································································· 55
III. Operation·········································································································································56
3.1 Operation Panel······················································································································· 56
3.1.1 LCD/MDI Panel ··············································································································· 56
3.1.2 Screen Change Keys········································································································· 57
3.1.3 Explanation of Key Board ································································································ 57
3.1.4 Machine Operation Panel ································································································· 58
3.2 Manual Operation···················································································································· 59
3.2.1 Manual Reference Point Return························································································ 59
3.2.2 Manual start Point Return································································································· 59
3.2.3 Manual Continuous Feed·································································································· 60
3.2.4 Step Feed ·························································································································· 61
3.2.5 Manual Handle Feed (Optional function) ········································································· 62
3.2.6 Manual auxiliary operation······························································································· 62
3.3 Automatic Operation ··············································································································· 64
3.3.1 Automatic Operation mode ······························································································ 64
3.3.2 Starting Automatic Operation ··························································································· 65
3.3.3 Executing Automatic Operation ······················································································· 65
3.3.4 Stopping and Terminating Memory Operation ·································································65
3.4 TEST OPERATION················································································································ 67
3.4.1 All Axis Machine Lock ···································································································· 67
3.4.2 Auxiliary Function Lock ·································································································· 67
3.4.3 Feedrate Override ············································································································· 67
3.4.4 Rapid Traverse Override··································································································· 68
3.4.5 Dry Running····················································································································· 68
3.4.6 Restart After Feed Hold···································································································· 68
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
Page 4

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
3.4.7 Single Block ····················································································································· 68
3.5 Safety Operation······················································································································ 69
3.5.1 Emergency Operation ······································································································· 69
3.5.2 Overtravel························································································································· 70
3.6 Alarm ······································································································································ 70
3.7 Program Storage & Edit ······································································································· 70
3.7.1 Preparation for Part Program Storage & Edit Operation ················································ 70
3.7.2 Registering Program to Memory ······················································································ 70
3.7.3 Program Number Searching ····························································································· 71
3.7.4 Deleting Program ············································································································· 71
3.7.5 Deleting All Program········································································································ 71
3.7.6 Output a program ············································································································· 72
3.7.7 Output All Programs········································································································· 72
3.7.8 Sequence Number Search································································································· 72
3.7.9 Inserting, Amending and Deleting of word······································································· 73
3.7.10 Number of Registered Programs····················································································· 76
3.7.11 Capacity of System Memory ·························································································· 76
3.8 Display and Setting Data········································································································· 76
3.8.1 Offset Amount ·················································································································· 76
3.8.2 The setting of setting parameter························································································ 77
3.8.3 The Setting and Display of Custom Macro Variable························································· 79
3.8.4 Parameter ························································································································· 80
3.8.5 Diagnoses ························································································································· 82
3.9 Display ···································································································································· 82
3.9.1 Status display···················································································································· 82
3.9.2 Display of key in data······································································································· 83
3.9.3 Program Number, Sequence Number Display ·································································· 83
3.9.4 The Display of Program Memory Used.··········································································· 84
3.9.5 Display of Command Value ([PRG] key) ········································································· 84
3.9.6 Current position display ([POS] key) ··············································································· 85
3.9.7 Display of Run Time and Parts Count ·············································································· 86
3.9.8 Alarm Display([ALM] key)······························································································ 86
3.9.9 Adjusting Brightness of LCD ··························································································· 87
IV CONNECTION·································································································································88
4.1 SYSTEM CONNECTION DIAGRAM··················································································· 88
4.1.1 Layout diagram of interfaces···························································································· 88
4.1.2 Descriptions of Interfaces································································································· 88
4.1.3 Connection Diagram········································································································· 89
4.2 Detail of connection ················································································································ 89
4.2.1 From CNC to Axis Driver ································································································ 89
4.2.2 Description of Signal········································································································ 90
4.3 Connection between CNC and Axis Driver············································································· 92
4.4 Spindle Encoder ······················································································································ 93
4.5 RS232-C Serial Interface(Optional) ························································································ 93
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
Page 5

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
4-6 Spindle Analogue Control Interface(Optional) ······································································· 94
4-7 Handwheel ······························································································································ 94
4.8 Connection of power supply···································································································· 95
4.9 In put/output Interface············································································································· 96
4.9.1 Connecting Diagram········································································································· 96
4.9.2 Input Signals····················································································································· 96
4.9.3 Signal Description ············································································································ 97
4.9.4 Output Signal ················································································································· 100
4.9.5 Diagnose Address Table of Input and Output Signal ······················································ 101
V Adjustment of Machine ····················································································································102
5.1 Preparation before Power On ································································································ 102
5.2 Adjustment of Machine ········································································································· 102
5.2.1 Emergency Stop Button·································································································· 102
5.2.2 Adjustment of Drive Axis······························································································· 102
5.2.3 Toolpost Adjustment······································································································· 104
5.2.4 Spindle Adjustment ········································································································ 104
5.2.5 Single step/ Handle Feed ································································································ 104
5.2.6 Others Adjustment·········································································································· 104
5.3 Standard Parameter Setting and the Storage of Parameter, Diagnosis and Program ·············· 105
Appendix Ⅰ Parameter ·····················································································································106
Appendix II Diagnosis·························································································································114
Appendix III Alarm Code List·············································································································119
Appendix IV Binary to Decimal Conversion Table·············································································122
Appendix V Installation dimension·········································································································I
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
Page 6
GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
Ⅰ INTRODUCTION
1.1 Introduction
GSK980T is a well-pervading machine numerical-controlled system produced by my factory. As
a upgrading production of the economical CNC,GSK980T has following characteristic:
△ Adopting 16-bit CPU,CPLD and hardware interpolation to realize high-speed and um
level control
△ Adopting 4-layer PCB and having high integration, reasonable technology and high
reliability
△ Having Chinese display with LCD and friendly interface, convenient operation
△ Being able to adjusting accelerating or decelerating speed, matching step- motor or servo
motor
△ Being able to adjust the ratio of electronic gear and having convenient application
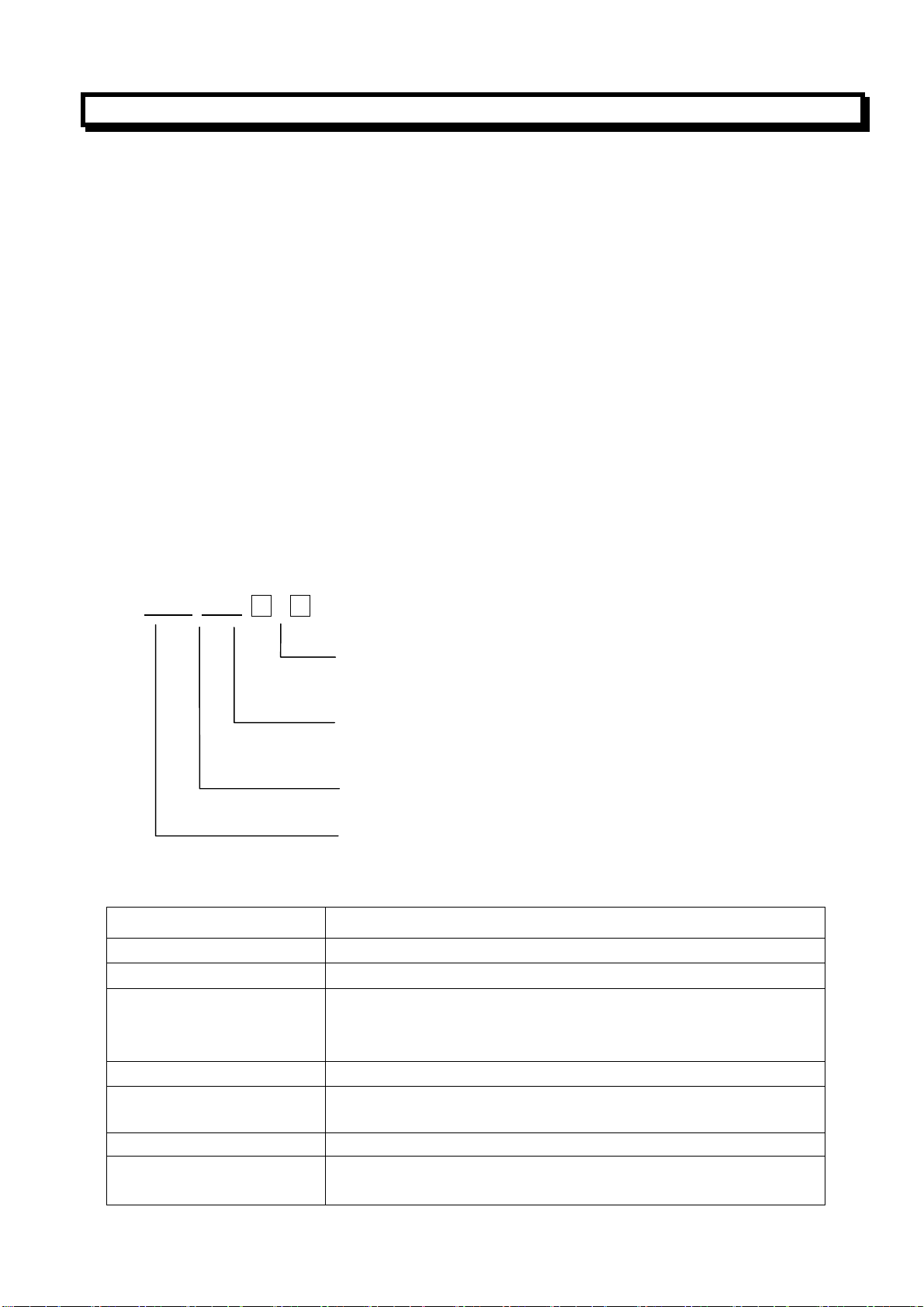
1.2 Type Signification
GSK 980T — 。
Assembly form: none:small panel(420×260mm)
L: big panel(420×320mm)
B: boxed assembly
Sort symbol :none: surface operation panel
A: alloy-solid operation panel
1.3 Type Table
Order type specification
GSK980T
GSK980T-L
GSK980T-B
GSK980TA
GSK980TA-L
GSK980TA-B
GSK980T-DF3A □□□
□
420×260mm surface operation panel
420×320mm surface operation panel
GSK980T-L boxed assembly,line goes out from the hole
of box bottom(line going out from the top of box must be
specified)
420×260mm alloy-solid operation panel
GSK980TA being assembled with the additional panel of
AP01,the size is 420×320mm
GSK980TA-L boxed assembly
Being assembled with DF3A with line going out from the
bottom of box(from the bottom of box)
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
Machine CNC of 980T series
Production symbol of GSK
1
Page 7
GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
GSK980T-DF3A □□□
□-B
GSK980T-DY3 □□□□
-B
GSK980T-DY3□□□□
Note :“□□□□”is 4-bit digit. the first 2-bit means the specification of driver in X axis, the
second 2-bit means the specification of driver in Z axis.
assembled in that axis.
Being assembled with DF3A with line going out from back
(from aerial socket in the back of box)
Being assembled with DY3 with line going out from back(from
aerial socket in the back of box)
Being assembled with DY3 with line going out from the bottom
of box(from the bottom of box)
“00” means no driver being
II. Programming
2.1 General
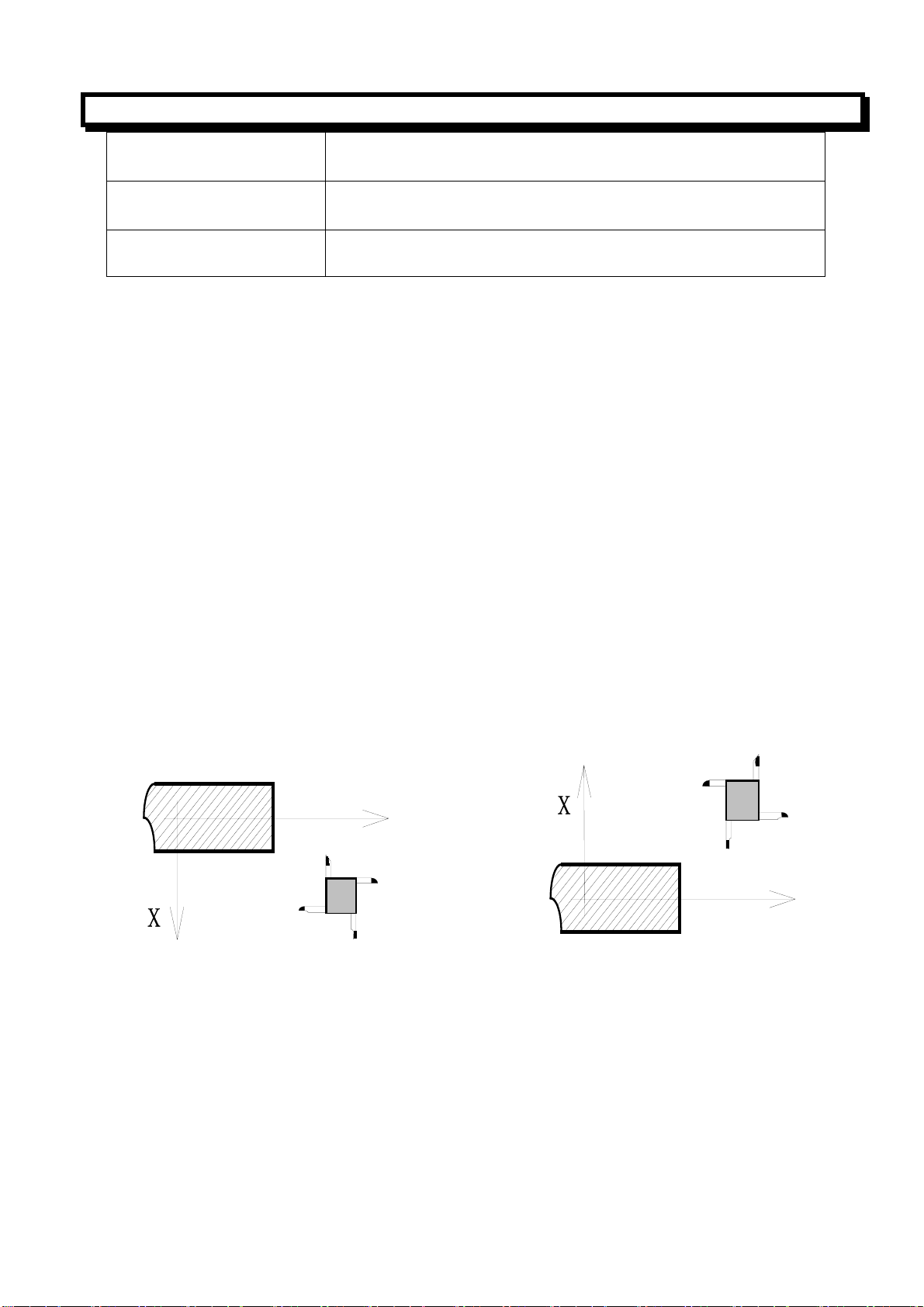
2.1.1 Axes Definition
In this CNC system, the main two axis of motion of the lathe machine is referred to as X and Z axis in
a right hand coordinate system. Since the spindle of the lathe is horizontal, the Z axis is horizontal as
well, the cross axis is denoted by X.A positive motion in both X and Z direction moves the tool away
from the workpiece.
The figure below shows the coordinate system of front toolpost lathe system and rear toolpost lathe
system. In the front toolpost system, a positive command moves the Z axis from left to right and the X
axis from back to front. In this CNC system we use front toolpost system for introducing the
programming.
Front toolpost system Rear toolpost system
Z
X
X
2.1.2 Reference Point (Machine Zero Point)
Reference point is a fixed position on a machine tool which the tool can easily be moved. Usually, the
reference point is set at the max. travel position of each axis at positive direction. Don’t use the
reference point return function (such as G28).if the reference point is not available on the
corresponding machine tool.
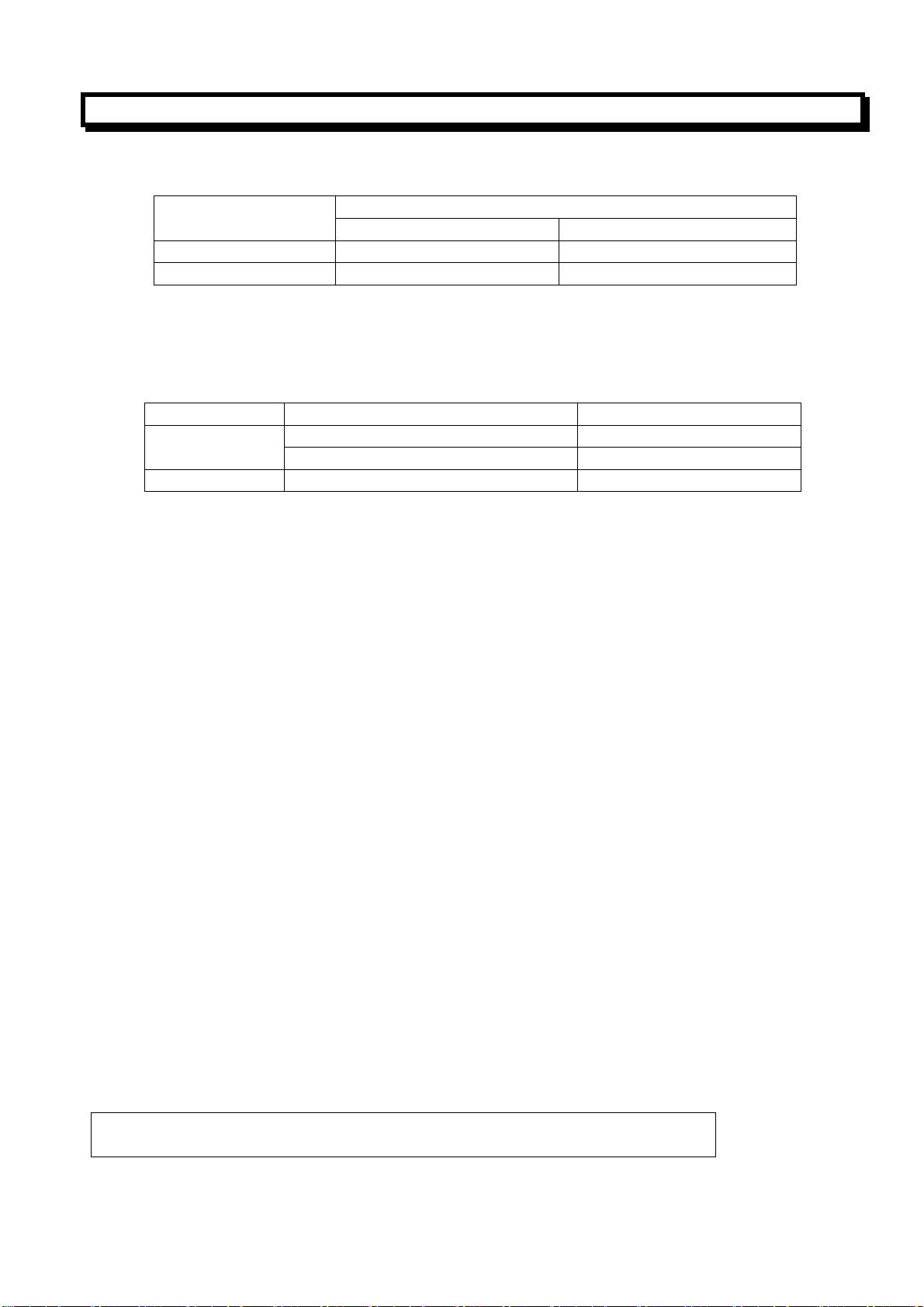
2.1.3 Coordinate value and direction and dimension
In this system, there are two ways to command the travels of the tool, the absolute command and
incremental command, the using of the absolute command and the incremental command depending
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
2
Z
Page 8
GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
on the address used. Absolute and incremental commands can be used together in one block. The
format of the address is as follows:
X axis X U
Z axis Z W
Address
Absolute command Incremental command
2.1.4 Unit and Range of coordinate
The least input of this system is 0.001mm and the maximum input is ±9999.99.
Axis Least input unit Least motion increment
0.001mm(Diameter program) 0.0005mm X axis
0.001mm(Radius program) 0.001mm
Z axis 0.001mm 0.001mm
2.1.5 Initial and Modal Status of the Command
Initial status is the status of the control before it is programmed. Modal status means after the
command is specified; it is effective until another command in the same group is specified .
2.1.6 The Start of a Program
At the beginning of program executing, the tool tips of the first programmed tool(standard tool)should
be the start point of the programmed workpiece coordinate system. Usually, the first programmed tool
is used as a standard tool which its offset compensation value is (0,0).
2.1.7 The End of a Program
Command code M30 is specified in the last block of a program to end the executing of a program.
Before ending the executing of grogram by M30, the tool must be programmed to return to the start
point of the workpiece coordinate system, and the corresponding tool offset compensation must be
cancelled.
2.1.8 Program Configuration
The definition of the work coordinate system is depending on the start point of the tool in the
corresponding work program by specifying a value after G50 is a floating coordinate, if G50 is not
commanded the current absolute coordinate value is treated as the start point of the program.
After a workpiece coordinate system is set, a point on the tool, such as the tool tip, is at specified
coordinate.
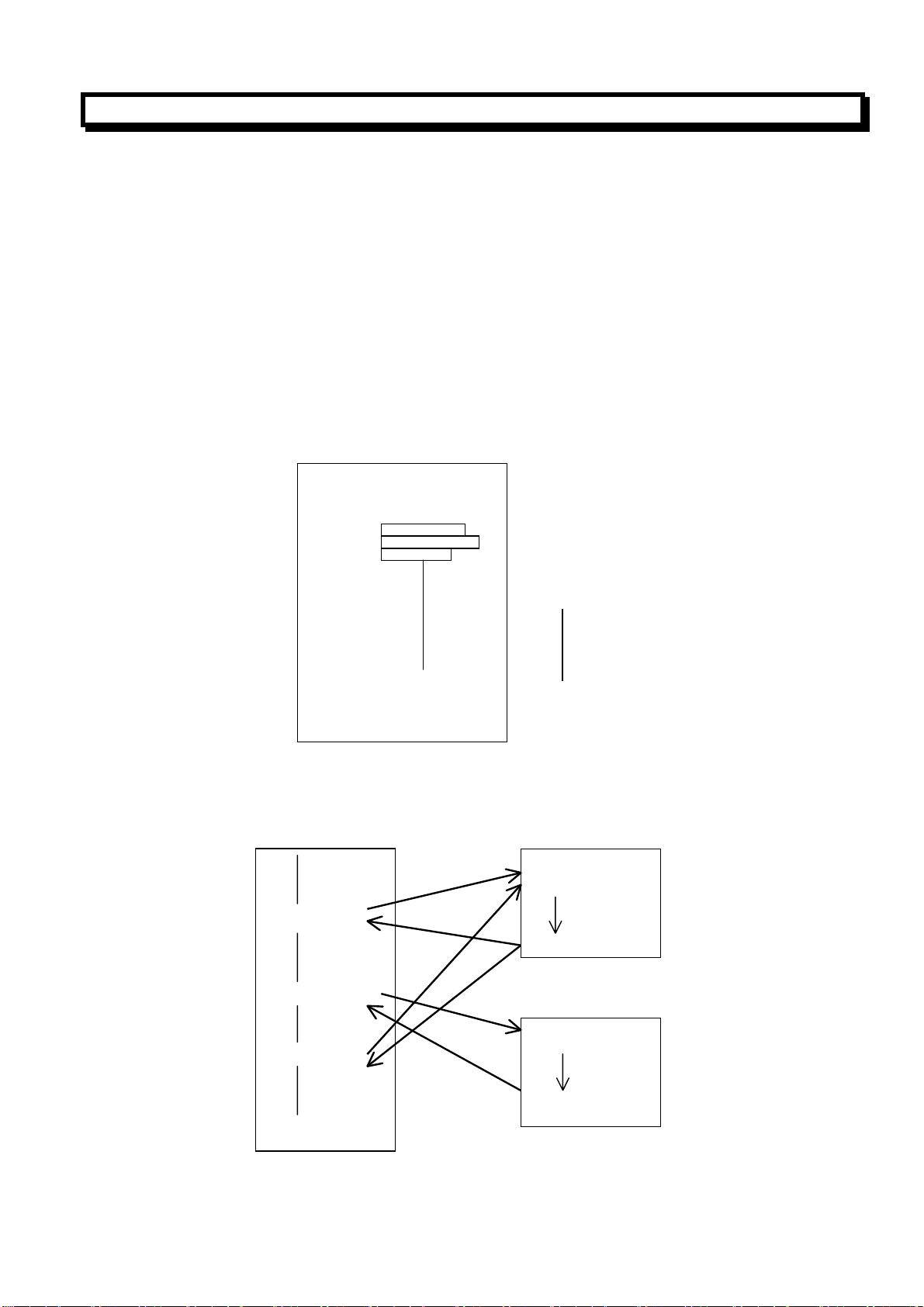
2.1.9 Program Configuration
(1) Bock
The configuration of one block of program in this system is designated as follows:
N O O O O G O O X O O .O Z O O . O M O O S O O T O O O
CR
N: Sequence Number
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
3
Page 9
GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
p
p
G: Preparatory Function
X,Z: Dimension word
M: Miscellaneous function
S: spindle function
T: Tool function
CR: End of block
Each block of a program contains a sequence number for discriminating the executed sequence of
each block the beginning of the block , and an end of bock code CR for indicating the end of the
block..
(2)Program
Normally, a program number is specified at the beginning of the program, and a program end code
M30 is specified at the end of the program.
CR:
00000:
M30CR
Program number
Block
Block
Block
End of program
(3) Main Program and Subprogram
M98p1001
M98P1002
M98p1001
Subprogram #1
01001;
M99
Subprogram #2
01002;
M99
Program for
attern #1
Program for
attern #2
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
4
Page 10
GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
When machining of the same pattern appears at many sections of a workpiece program, a program for
this pattern is created first, this is called the subprogram, on the other hand, the original program is
called the main program. When a subprogram execution command is executed during the executing of
the main program, commands of the subprogram are executed. When the executing of the subprogram
is finished, the sequence returns to the main program.
2.2 controlled Axis
2.2.1 Number of Controlled Axis
Number of Controlled Axis 2 Axis (X, Z)
Number of Simultaneously control axis 2 Axis (X, Z)
2.2.2 Unit Setting
Input /Output The least input unit The least Command unit
X:0.001mm (Diameter designation)
Metric input /output
When radius Program is designated, the movement on X axis is program in Radius.
Refer to the Operation manual issued by the machine builder for detail.
X:0.001mm (Radius designation )
Z:0.001 mm
Z:0.001 mm
X:0.0005mm
Z:0.001mm
X:0.001mm
Z:0.001mm
2.2.3 Maximum Strokes
Maximum Stroke = The least setting unit × 9999999
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
5
Page 11
GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
2.3 Preparatory Function (G Function)
A two-digit number following address G determines the meaning of the command for the concerned
block. G codes are divided into the following two types:
Type Meaning
One-shot G code The G code is effective only in the block in which it is specified
Modal G code The G code is effective until another G code in the same group is specified
(Example) G01 and G00 are modal G code in the same group
G01X_;
Z_; G01 is effective
G00Z_ ; G00 is effective
G Code List
G Code Group Function
G00
*G01
G02
G03
G28
G32 01 Thread cutting
G50 00 Coordination system setting
G65 00 Macro command
G70 Finishing cutting cycle
G71 Outer diameter coarse cutting cycle
G72 End face peck drilling cycle
G73 Pattern repeating
G74 End face peck drilling cycle
G75
G90 Outer diameter/internal diameter slot cutting cycle
G92 Thread cutting cycle
G94
G96 Constant surface speed control enable
G97
*G98 Feed per minute
G99
Note1: G codes marked with*are initial G codes when turning on power.
Note2: The G codes of 2:00 are one-shot G codes.
Note3: when a G code which is not listed in this G codes list or a G code
without a corresponding option function is specified, alarm (No.010) is
displayed.
Note4: G codes of different groups can be specified in the same block
of the program. If G codes of the same groups are specified in the same
block, the last specified one is effective.
Note5: The maximum spindle speed can be specified by G50 under the constant
line speed control.
Note6: G codes are displayed by each group number.
01
00
00
00
01
02
03
Positioning (Rapid traverse)
Linear interpolation (Cutting feed)
Circular interpolation CW
Circular interpolation CCW
Dwell, exactly stop G04
Return to reference point (Machine zero point)
Outer diameter/internal diameter slot cutting cycle
End face cutting cycle
Constant surface speed control disable
Feed per revolution
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
6
Page 12
GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
N
Note7: The clock wise or counterclockwise of G02,G03 commands are defined
by the direction of the coordination system.
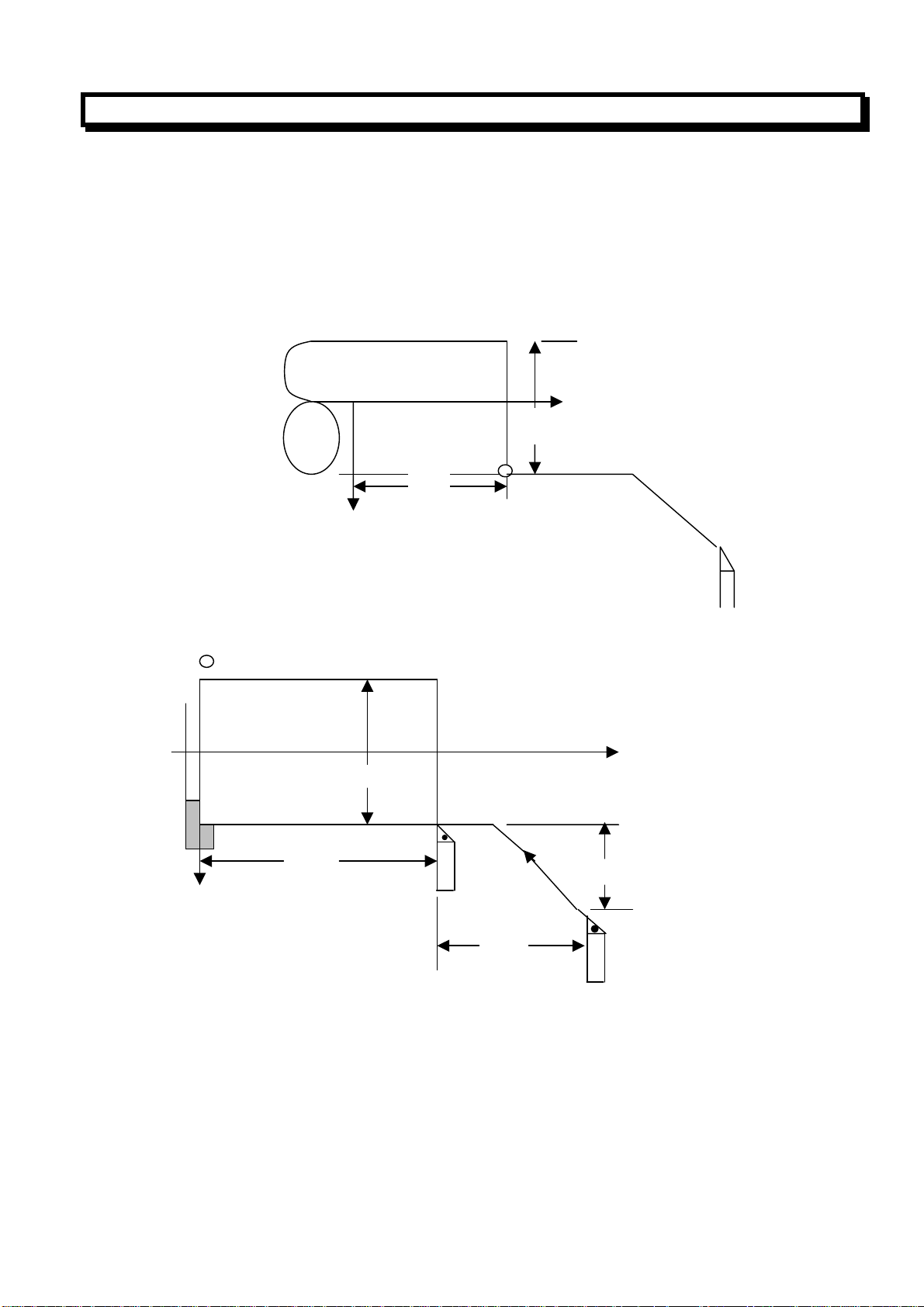
2.3.1 Positioning(G00)
The G00 command moves the tool to the specified position at a rapid traverse rate.
Format:G00X((U)__Z(W)__;
The tool is positioned with the rapid traverse rate for each axis separately.
(Example)
Note: the Rapid traverse speed of the G00 command is set by the machine builder
(ParameterNo.022~023),
The rapid traverse feed rate for each axis of G00 command depends on the machine builder’s setting
(Parameter No.022~023),it is controlled by Rapid traverse feed rate override switch on the operation
panel. (F0,25%,50%,100%),rapid traverse can not be specified by F code.
56.0
X
φ40.0
X
on linear interpolation positioning
X (Diameter programming)
36.0
Z
Z
G00 U-60.0 W-36.0;
G00 X40.0 Z56.0;or
(Diameter programming)
30.0
2.3.2 Linear Interpolation (G01)
G01X (U) __Z (W) __F__;
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
7
Page 13
GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
This command specified a linear interpolation movement. Absolute or incremental dimension depends
on the address X, Z/U, W .The feedrate is specified by address F, and is effective until a new value is
specified .The feedrate need not be specified every time.
(Example)
φ40.0
20.0
Start Point
End point
46.0
φ20.0
G00 U20.0 W-26.0;
G01 X40.0 Z20.0;or
Diameter Programming
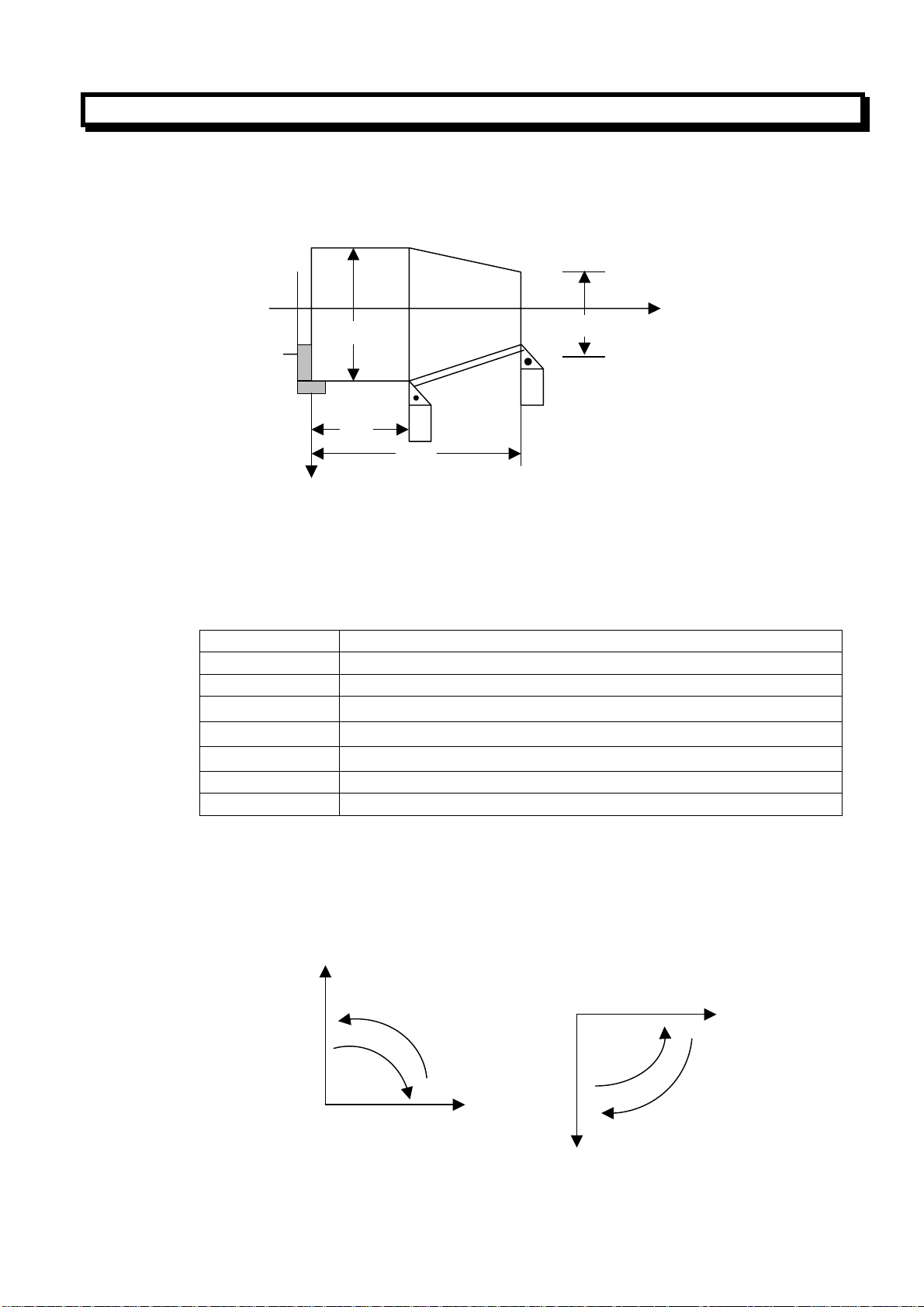
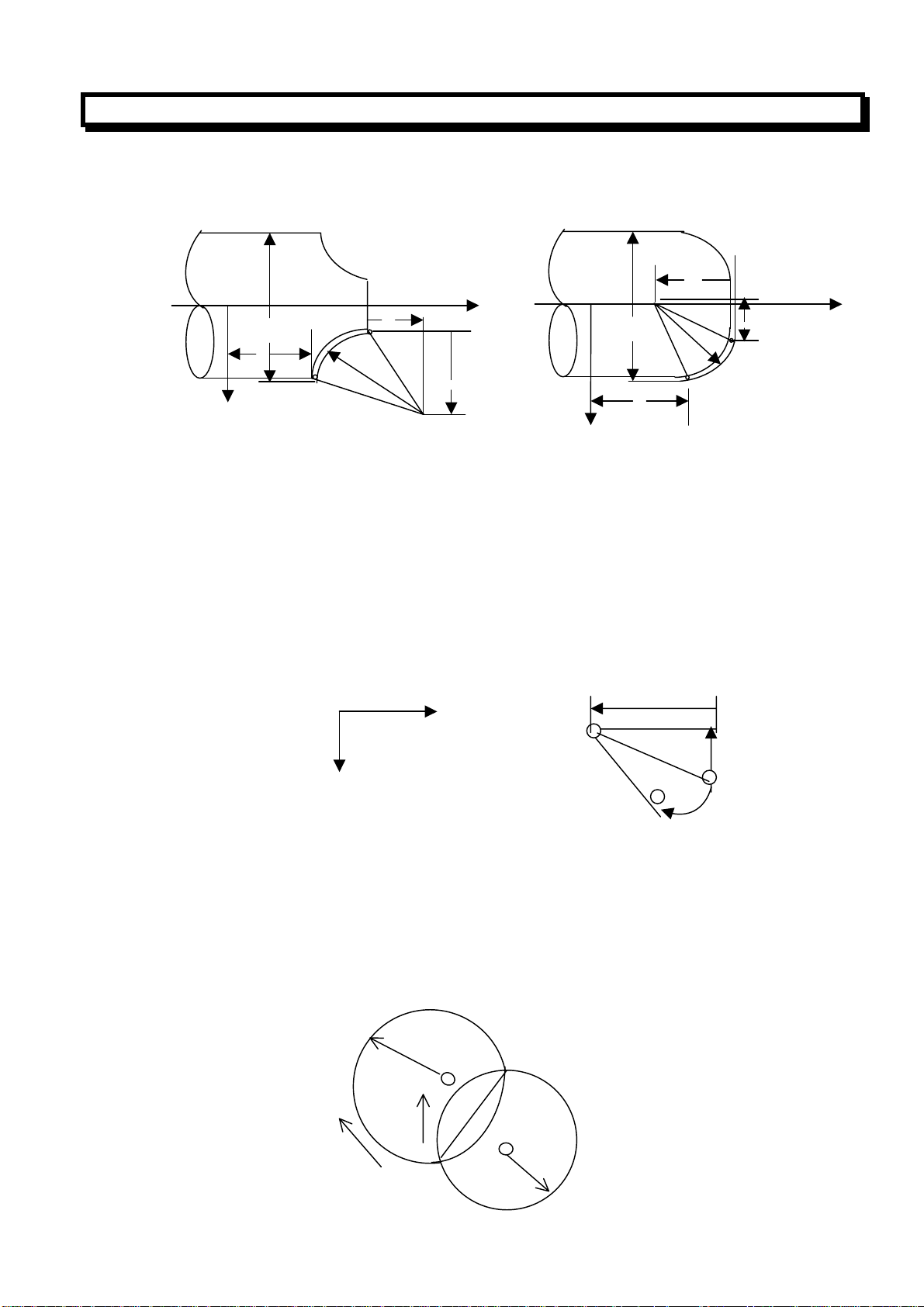
2.3.3 Circular Interpolation (G02,G03)
The command below can move the tool along a circular arc on the specified plane.
G02 X__Z__ R_F
G03 X__Z__ I_K_F
Command Description
G02 Clockwise direction(CW)
G03 Counterclockwise direction(CCW)
X、Z
U、Z
I、K
R Radius of arc (radius value)
F Feedrate along the arc
“Clockwise” and “Counterclockwise” on the Z-X plane of the Cartesian coordinate system are
defined when the Z-X plane is views from the positive to negative direction of the Y-axis, as
illustrated in the figure below:
The end point of the arc in the work coordinate system
Distance from the start point to the end point
Distance from the start point to the center of an arc
X
G03
G02
G02
Z
X
Cartesian coordinate system
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
8
G03
Z
Page 14
GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
X
Z
X
(Diameter programming)
(absolute value)
G02 X..Z..R..F..;
Or
G02 X..Z..I..K..F..;
K
R
Center of arc
Z
I
Center
of arc
K
X
R
Z
X
(Diameter Programming)
(absolute value)
G03 X..Z..R..F..;
or
G03 X..Z..I..k..F..;
Z
I
The end point of the arc is specified by address X, Z or U, W. Address U and W specify the distance
from the start point to the end point. The arc center is specified by address I and K for the X and Z
axis. However, the value following K or I is a vector component in which the arc is seem from the
start point, and is specified as an incremental value. As show below:
Z
Center
K
X
Start point
End point (X, Z)
I, K must be signed according to the direction. The arc center also can be specified by address R. As
show below:
G02 X_Z_R_F_;
G03 X_Z_R_F_;
In this case, two types of arcs are considered (One arc is less than 180°, the other is more than 180°),
as show in below figure. An arc exceeding 180° can not be commanded.
R=50
End point
1
2
R=50
Start point
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
9
Page 15
GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
(Example)
Absolute and increment programming:
G02 X50.0 Z30.0 125.0 F30;or
G02 U20.0 W-20.0 125.0 F30;or
G02 X50.0 Z30.0 R25.0 F30;or
G02 U20.0 W-20.0 R25. F30;
The federate in circular interpolation is specified by address F, and the federate is controlled to be the
feed rate along the arc (the tangential feedrate of the arc).
Note1:10, K0 can be omitted.
Note2: When X and Z are omitted simultaneously, the end point is the same as the start point,
and the center is specified with I and K, a 360° arc is specified
G02 I_;(Full circle)
When R is used ,an arc of 0° is specified:
G02 R_; (The tool does not move)
Note3: The error between the specified feedrate and the actual tool feedrate is ±2%. The
feedrate is measured along the arc after the tool nose compensation is applied.
Note4: If I, K and R addresses are specified simultaneously, the arc is specified by address R
and the I and K address are ignored.
Note5: When I and K are used, the difference in the radius values at the start point and the end
point of the arc dose not cause an alarm…
φ50.0
x
30.0
50.0
10.0
15.0
Z
R25.0
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
10
Page 16
GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
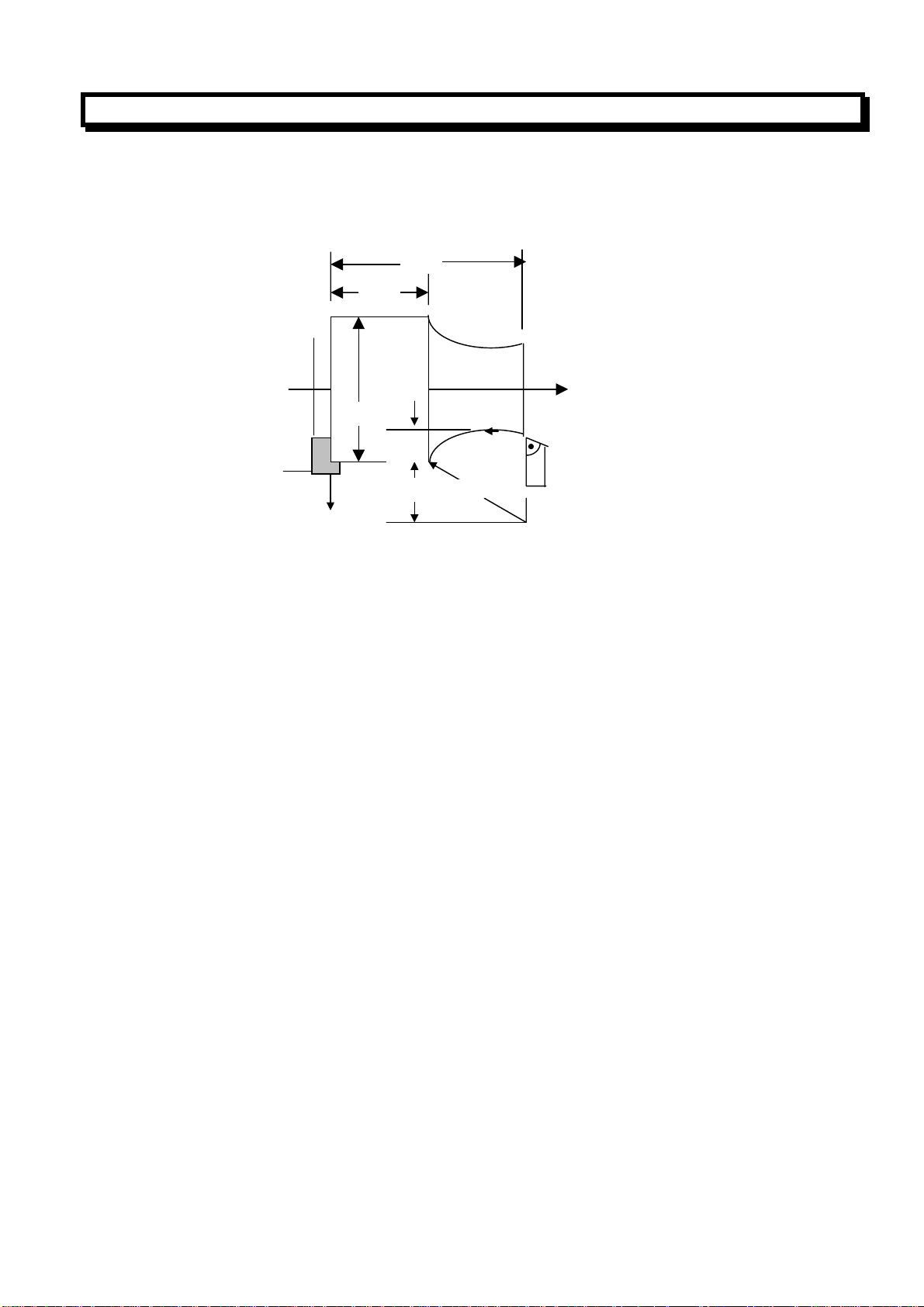
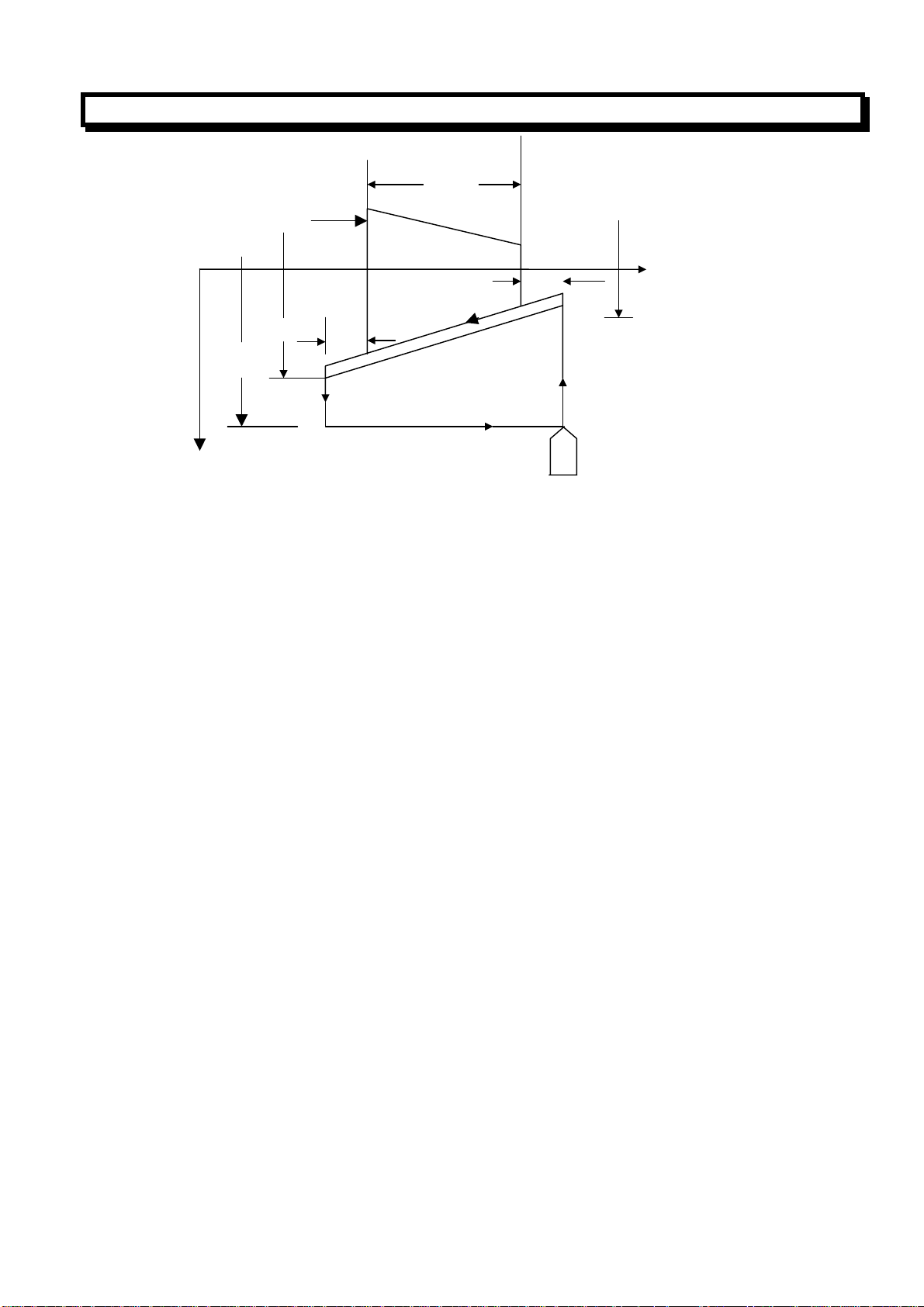
2.3.4 Thread Cutting (G32)
Equal lead straight thread, tapered screws and scroll threads can be cut by using Command G32.
Metric thread can be cut by using the below command (the lead of the thread is specified by F
address):
G32 X (U) _Z(W) _F_;(Metric thread)
F address specify the lead in long axis ranged from 0.001 to 500.000mm
Inch thread can be cut by using the below command(the teeth number is specified by I address):
G32 X (U) _Z(W) _I_;(Inch thread)
I address specified the teeth number per inch in long axis ranged from 0.060 to 254000.000 teeth/inch.
(Example)
G32 X__Z__F__;
X
Z
δ
X axis End point
In general, the thread cutting need to repeat along the same path in rough cutting through finish cuts
for a thread. Since the thread cutting starts when a I-revolution signal is output from the spindle
position encoder, thread cutting is started at a fixed point and the tool path on the workpiece is
unchanged for repeated threading cutting. The spindle speed must remain constant from rough cutting
through finish cutting. if not, thread lead error will occur.
L
L
L
Z axis
δ
Start point
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
11
Page 17
GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
LZ
Z
X
LX
α
Tapered thread
If
α≤45°
If
α>45°
the lead is LZ
the lead is LX
The lead always is specified in radius.
The lead can not be cut correctly due to reason of deceleration and acceleration in the beginning and
ending of the threading cutting, To cut a correct lead, the programmed length of the thread must be
longer than the actual length of the thread.
Example: thread cutting
70mm
Z
δ2
δ
1
X
Lead of thread: 4mm
δ1=3mm
δ2=1.5 mm
Depth of cutting in X-axis direction: 1MM(cut twice)
(Metric input, diameter programming)
G00 U-62.0;
G32 W_74.5 F4.0;
G00 U62.0;
W74.5
U-64.0;(Cut 1MM more in second cut )
G32 W-74.5 F4.0;
G00 U64.0
W74.5;
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
12
30mm
Page 18
GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
30mm
40mm
φ14.0
φ43.0
φ50.0
δ1
δ2
Z
X
Lead of thread :In Z axis direction:3.5mm
δ1=2mm
δ2=1mm
Depth of cutting in X axis direction:1MM(cut twice)
Using the above mentioned data to program:
(Metric Input, diameter programming)
G00 X12.0 Z72.0;
G32 X41.0 Z29.0 F3.5;
G00 X50.0 Z72.0;
X10.0; (1MM more in second cut)
G32 X39.0 Z29.0
G00 X50.0 Z72.0:
Note1: When the previous block also was a thread cutting block, the cutting will start immediately
without detecting the 1-revolution signal.
G32 Z__F__;
Z__; (1-revolution signal is not detected before the executing of this block)
G32__; (this block also is thread cutting block)
Z__F__;(1-revolution signal is also not detected)
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
13
Page 19
GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
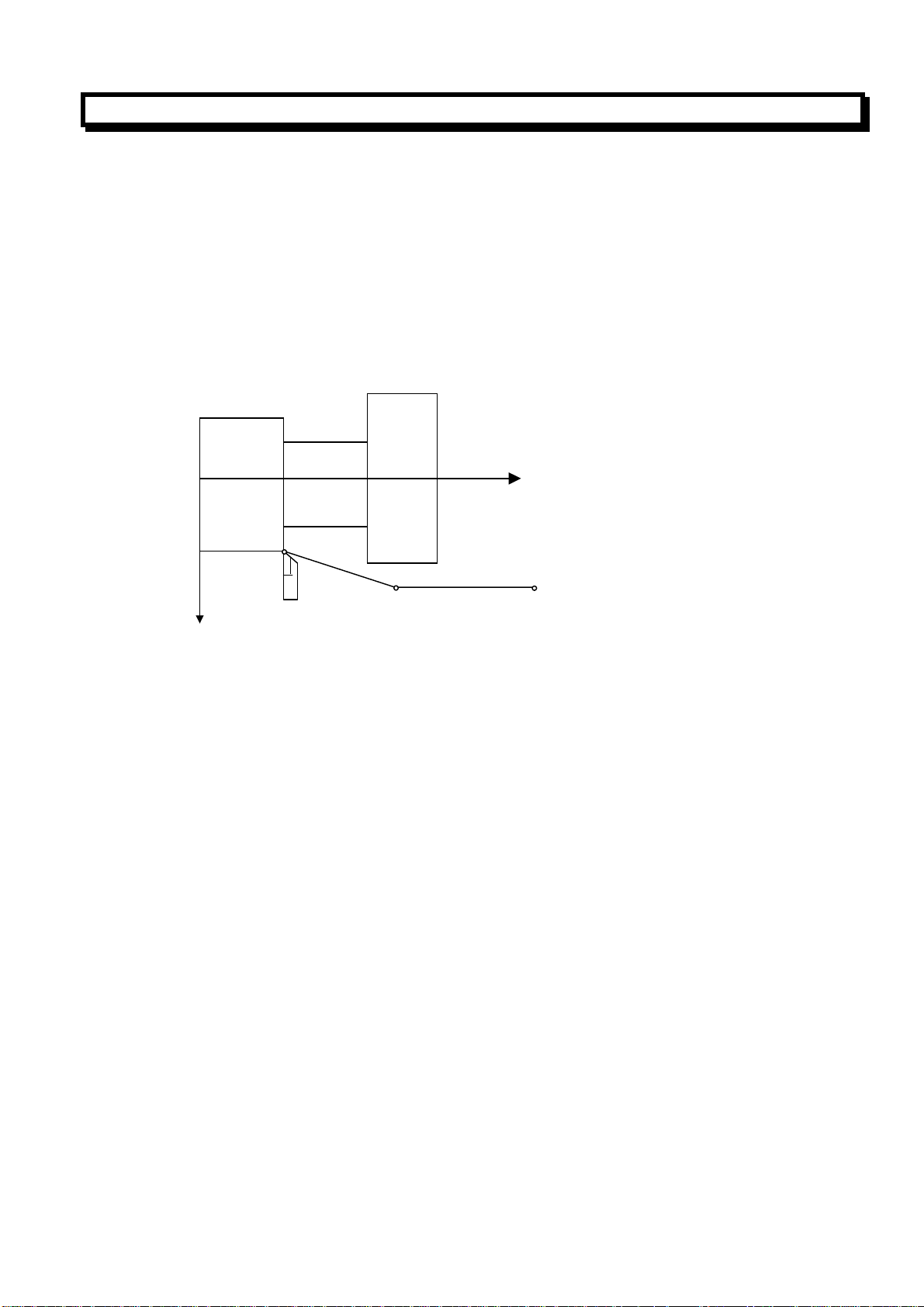
2.3.5 Return to Reference Point Automatically (G28)
G28 X (U)__Z(W)__;
This command can make the tools return to reference point automatically via an intermediate position,
the intermediate position is specified by addresses X(U)__Z(W).
(1)Positioning from the present position to the intermediate position of the designated axis at rapid
traverse rate(point A→point B).
(2)Return to reference point from the intermediate position at rapid traverse rate(point B→point R).
(3)If the machine lock is turn off, when the tool has returned to the reference point, the reference point
return completion led goes on.
Note1: If returning to the reference point manually has never been done after power on ,the motion of
returning to the reference point automatically from the intermediate point in G28 is same as that in
manual way. The direction of intermediate point is specified by parameter No.006(ZMX,ZMZ).
Note2:If the start point of machining program is same as the reference point ,doing G28 can return to
the start point of machining program.
Note3:If the start point of machining program is not same as the reference point ,returning to the start
point of machining program can be realized by rapid positioning command or operation of returning
to the start point, not by G28.
G28 X40 Z50
Present
Point A
X
Z
Reference point R
Intermediate point
B (40, 50)
2.3.6 Dwell(G04)
By specifying a dwell, the execution of the next block is delayed by the specified time.
Format:
G04 P__; or G04 X__; or G04 U__;
The unit of the delay time is second. Command value of the dwell time is from 0.001 to
99999.999second. If addresses P, X is omitted, this command can specified an exact stop.
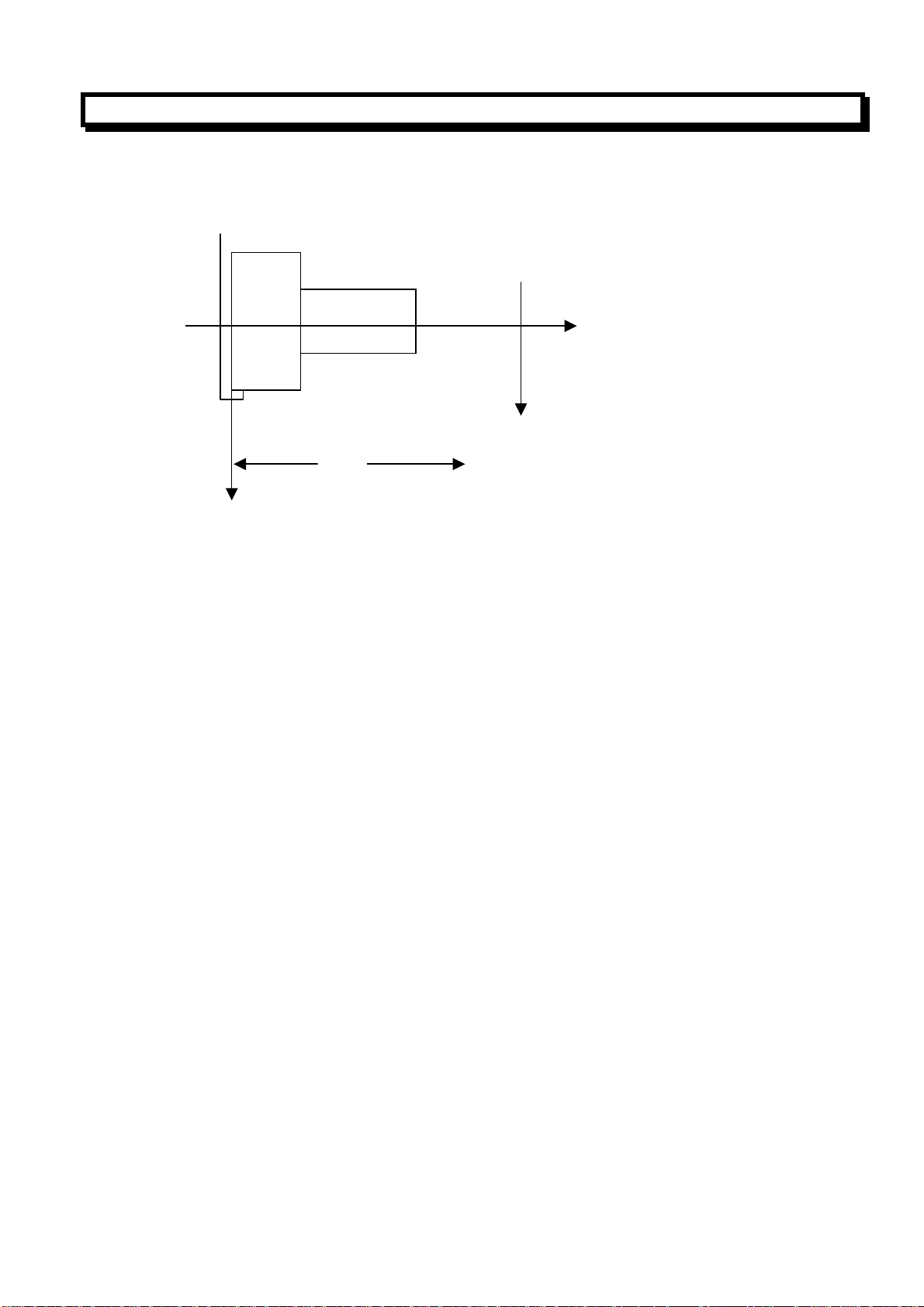
2.3.7 Work Coordinate System Setting(G0)
A work coordinate system can be set using the following the blow command:
G50 X(x) Z(z);
Use this command to set a coordinate system ,this coordinate system is referred as a workpiece
coordinate system, so a point on the tool, such as the tool tip ,is specified as coordinate value(x, z).
Once a workpiece coordinate system has been set, the absolute position of following blocks is
specified according to this coordinate system
When diameter programming, X address is specified by diameter value. When radius programming, X
address is specified by radius value.
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
14
Page 20
GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
(Example) Coordinate system setting with diameter designation
G50 X100.0 Z150.0;
100.00mm
Z
150.00mm
Start point = reference point
X
As illustrated in above figure, the reference point on the turret is superposition with the start point,
and the coordinate system is set by G50 at the start of the program. Thus, when an absolute command
is carried out, The start point will move to the position commanded. In order to move the tool tip to
the position commanded, the difference between the reference and the tool tip is compensated by the
too offset.
Note: If the coordinate system setting is carried out by G50, a coordinate system in which the position prior to
the effecting of the offset becomes the designated position, is set.
2.3.8 Feed per Minute (G98)
G98 specify the feed per minute, a number follows F specify the amount of feed of the cutting tool per
minute.
G98 is a modal code. Once a G98 is specified, it is available until a G99 (feed per revolution )is
specified.
2.3.9 Feed per Revolution(G99)
G99 specified the feed per spindle revolution. A number follows F specified the amount of feed the
cutting tool per spindle revolution.
G99 is also a modal code, once a G99 is specified; it is available until a G98 is specified.
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
15
Page 21
GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
Table 2.3.9 Feed Per Minute and Feed Per Revolution
Feed per minute Feed per revolution
Address F F
Command
code
Command
ranges
Limitation value
Override
The limitation takes place at a certain specified speed for both feed per
minute and feed per revolution. This clamping value is set by the machine
tool builder. (Override is applied to implement clamping of speed)
An override from 0~150%(10%per step)can be applied to both feed per
minute mode and feed per revolution mode
G98 G99
1~8000mm/min
(F1~F8000)
0.01~500.00mm/rev
(F1~F50000)
Note: when using feed per revolution mode, if it necessary to affix a position encoder to the spindle.
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
16
Page 22
GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
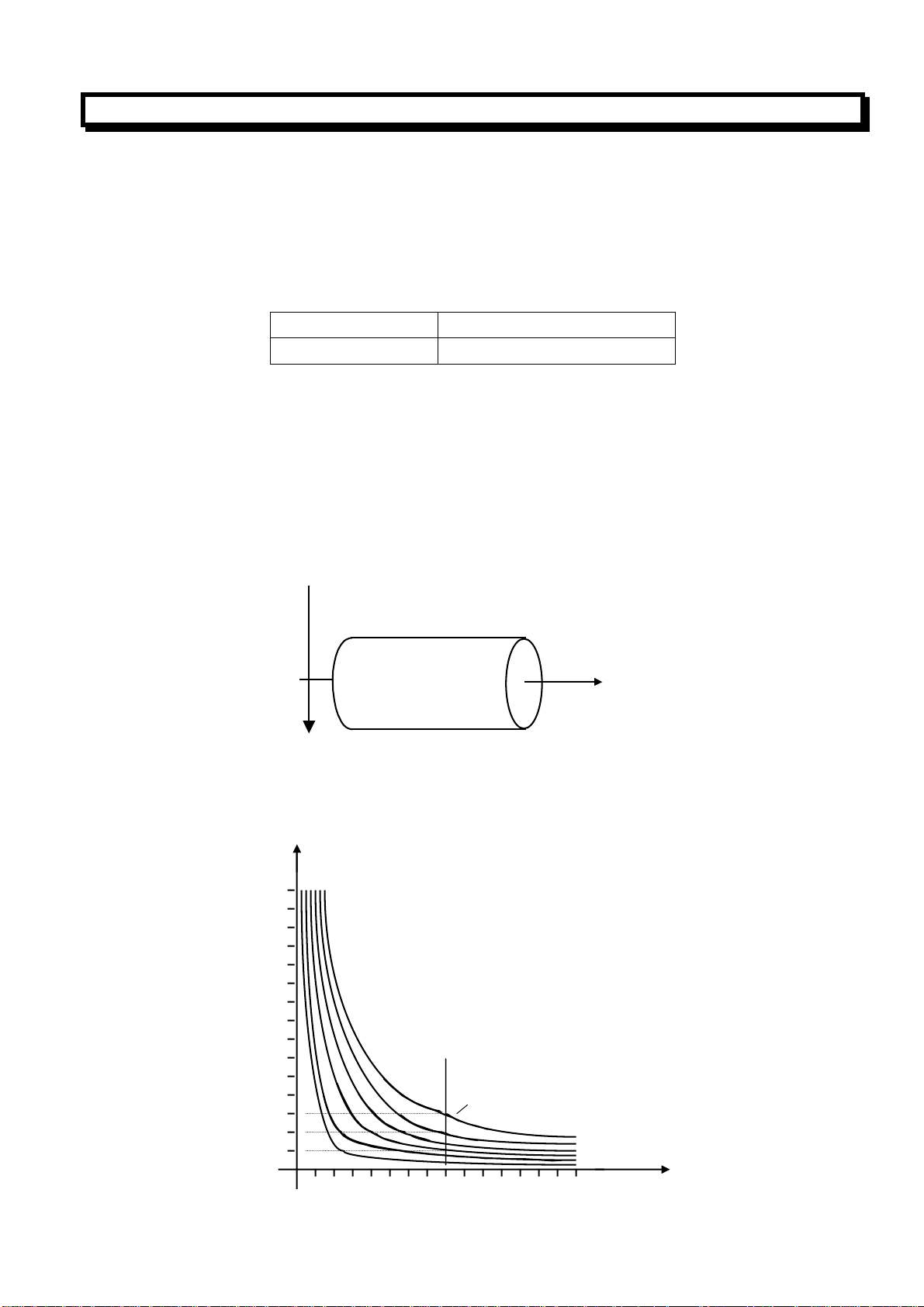
2.3.10 Constant Surface Speed Control(G96, G97)
When the surface speed is set by a value after address S, and the spindle speed is calculated according
to the relative position between the tool and the workpiece to keep the surface speed always the
specified value, so-called constant surface speed control. Voltage is fed to the spindle control section
so that the spindle rotates to produce the correct surface speed.
The units of the surface speed is as follows:
Input unit Surface speed unit
Metric system m/min
The units of the surface speed depend on the setting of the machine tool builder.
The Constant surface speed control is specified by the follow command:
G96 S__;
The surface speed is set after address S.
The constant speed control can be canceled by the following command:
G97 S__;
The spindle speed is set after address S.
It is necessary to apply the constant speed control on Z axis.
Z
X
Spindle speed (rpm)
(n)
3000
2800
2600
2400
2200
2000
1800
1600
1400
1200
1000
800
600
400
200
0
5
20
40 60 80
0
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
As show in the figure, the spindle
speed (rpm) coincides with the surface4
speed (m/min) at approx.
160mm(radius).
S
为
6
0
4
0
0
3
0
0
2
0
1
0
0
0
0
100
120140 160
m
0
min
180
200220 240260280300
17
单位(mm)
Page 23
GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
(1)Spindle Speed Override
An override for the specified surface speed or the spindle speed can be specified in
50,60,70,80,90,100,110,120%
(2)Maximum Spindle Speed Limitation
The value follows G50 S specify the maximum spindle speed for constant surface speed control in
rpm:
G50 S__;
When the spindle speed in constant surface speed control reaches the value specified in the above
command, the spindle speed is clamped at this maximum value.
(3)Constant Surface Speed Control for Rapid Traverse(G00)
For a Block in which G00is specified, the constant surface speed control is made by calculating the
surface speed based on the position at the end point of the rapid traverse block instead of calculating
the surface speed to a transient change of the tool position, Because at rapid traverse condition,
cutting is not executed.
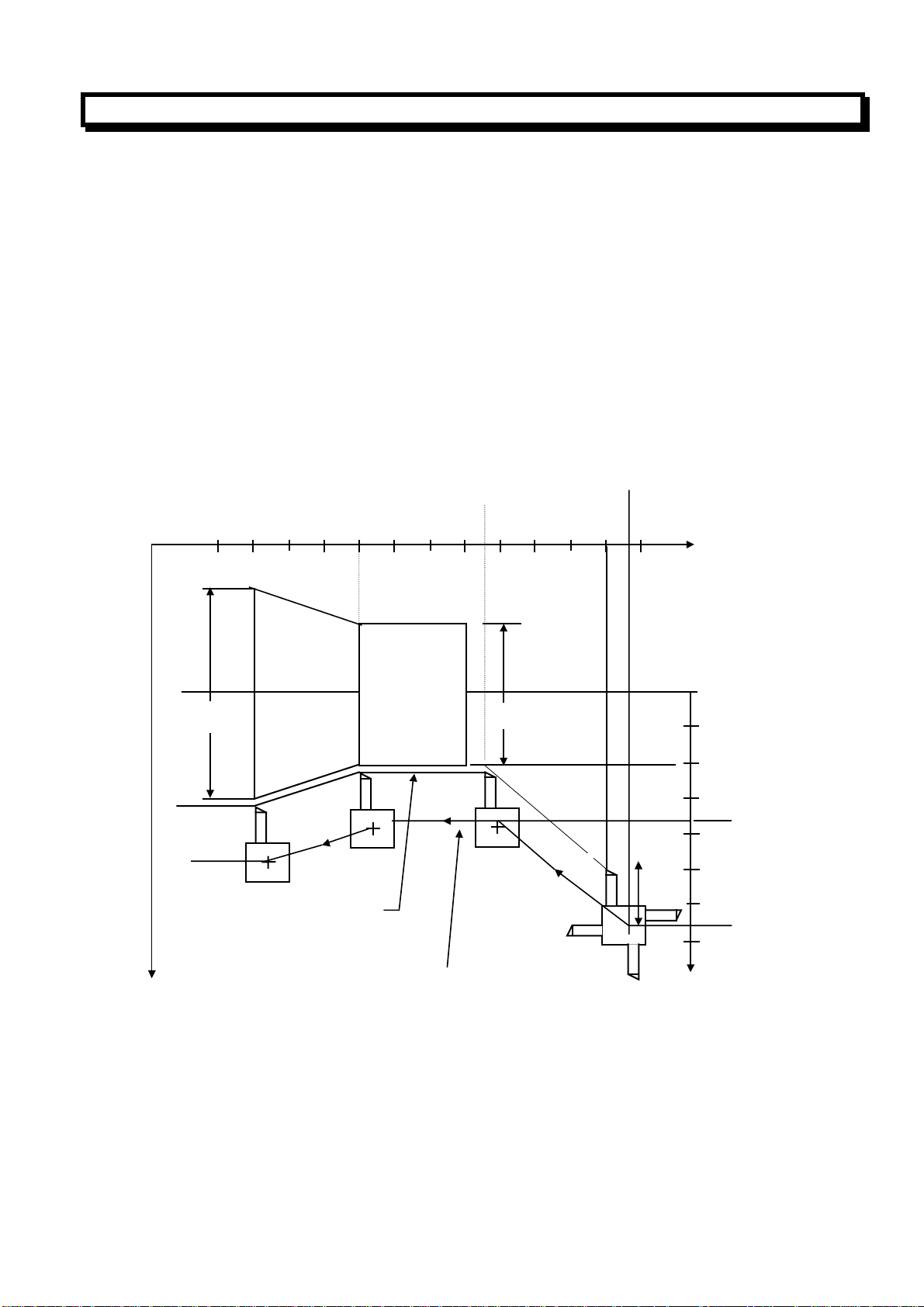
(Example:)
1050
300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000 1100 1200 1300 1400 1500
600
X
Φ
N1
Programmed path
Path after compensation
N15
N14
Φ
400
3
N11
2
1
Z
100
200
300
375
400
500
4
Radius value
1
600
700
675
(Diameter programming)
N8 G00 X1000.Z1400.;
N9 T0303;
N11 X400.Z1050.;
N12 G50 S3000; (Designation of Maximum spindle speed)
N13 G96 S200; (Surface speed 200m/,in)
N14 G01 Z700. F1000;
N15 X600. Z400.;
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
18
Page 24

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
N16 Z....;
The CNC use the programmed coordinate value on the X axis to calculate the surface speed. When
offset compensation is valid, this is not the value calculated according to the X axis coordinate after
offset. At the end point N15 in example above is not the turret center, but the tool nose, that is to say
at 600dia, the surface speed is 200m/min. If X axis coordinate value is negative, the CNC uses the
absolute value.
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
19
Page 25
GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
2.3.11 Canned Cycle(G90, G92 G94)
For repetitive machining peculiar to turning, such as the metal removal in rough cutting, the cutting of
the same path is made repetitively, by using these cycles. The said cutting specified in a range of three
to several dozen blocks can be specified in one block. In addition, only the values to be changed need
to be specified for repetition, the program using this cycle is very simple and useful.
The drawings in the examples below are for diameter programming. In radius programming,
change U/2 or X/2 to U or X respectively.
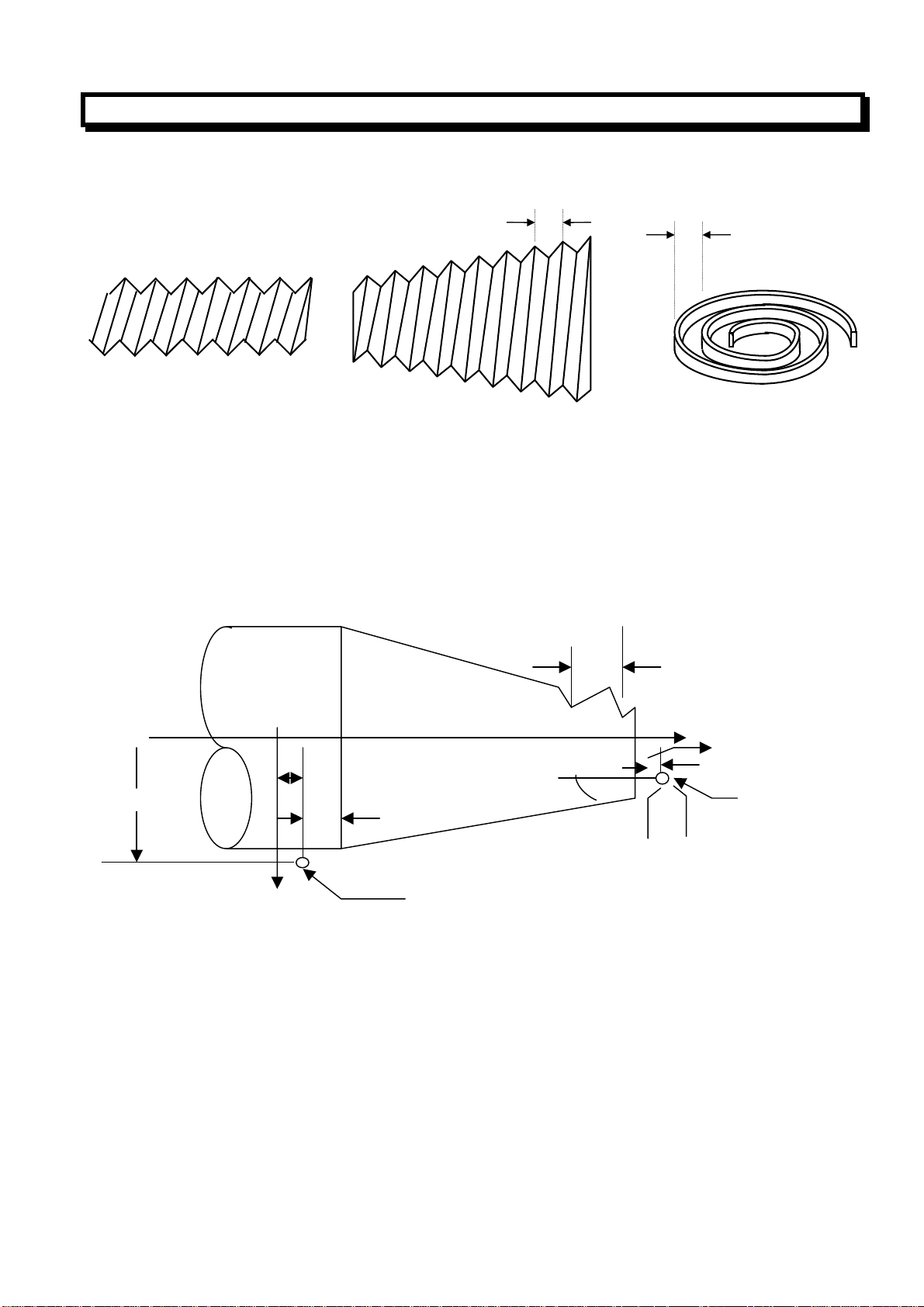
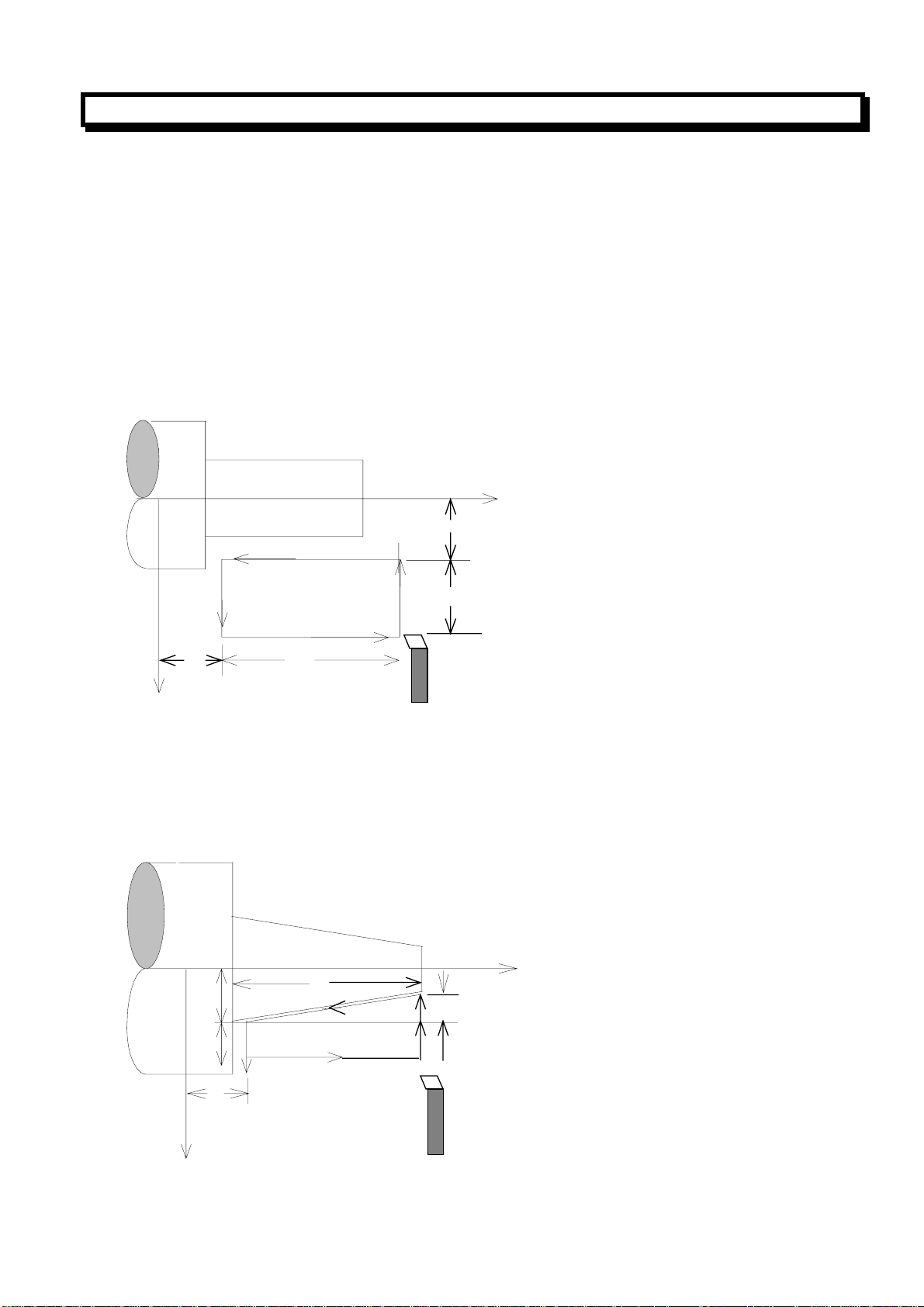
(1)Outer Diameter/Internal Diameter Cutting Cycle(G90)
(a)Cylinder cutting cycle
G90 X (U)__Z(W)__F__;
Z axis
X/2
2(F)
Xaxis
Z
3(F)
4(R)
W
1(R)
U/2
F:Cutting feed
R:Rapid traverse
Tool
In incremental programming, the signs of the numbers following address U and W depend on the
direction of paths1 and 2, in the cycle of above figure, the signs of U and W are negative. In single
block mode, Operation of 1,2,3,4 are performed by pressing the cycle start key.
(b)Taper cutting cycle
G90 X (U)__Z(W)__R__F__;
Z axis
X/2
2(F)
W
R
U/2
X axis
Z
3(F)
1(R)
4(R)
F:Cutting feed
R:Rapid traverse
Tool
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
20
Page 26
GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
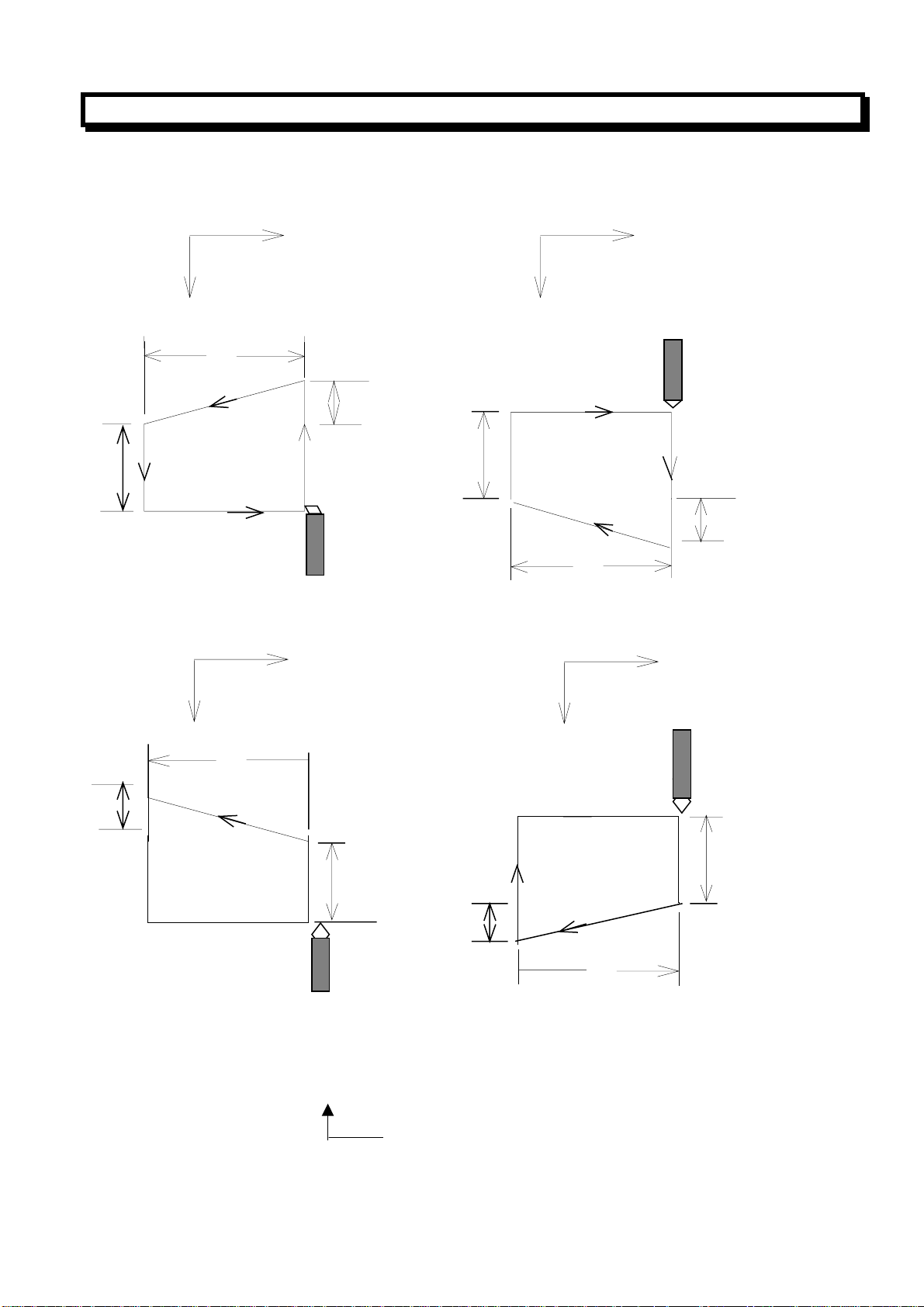
In incremental programming, the relation between the signs of the numbers following the address U、
W、R, and the tool paths are as follows:
1) U <, W<0, R<0 2) U >0, W<0, R>0
Z
Z
U/2
3(F)
X
W
R
2(F)
U/2
1(R)
4(R)
X
4(R)
3(F)
2(F)
W
U<0, W<0, R>0 4) U>0, W<0, R<0
But ︱R︱≤︱U/2︱ But ︱R︱≤︱U/2︱
X
W
Z
X
1(R)
R
Z
R
2(F)
3(F)
1(R)
4(R)
U/2
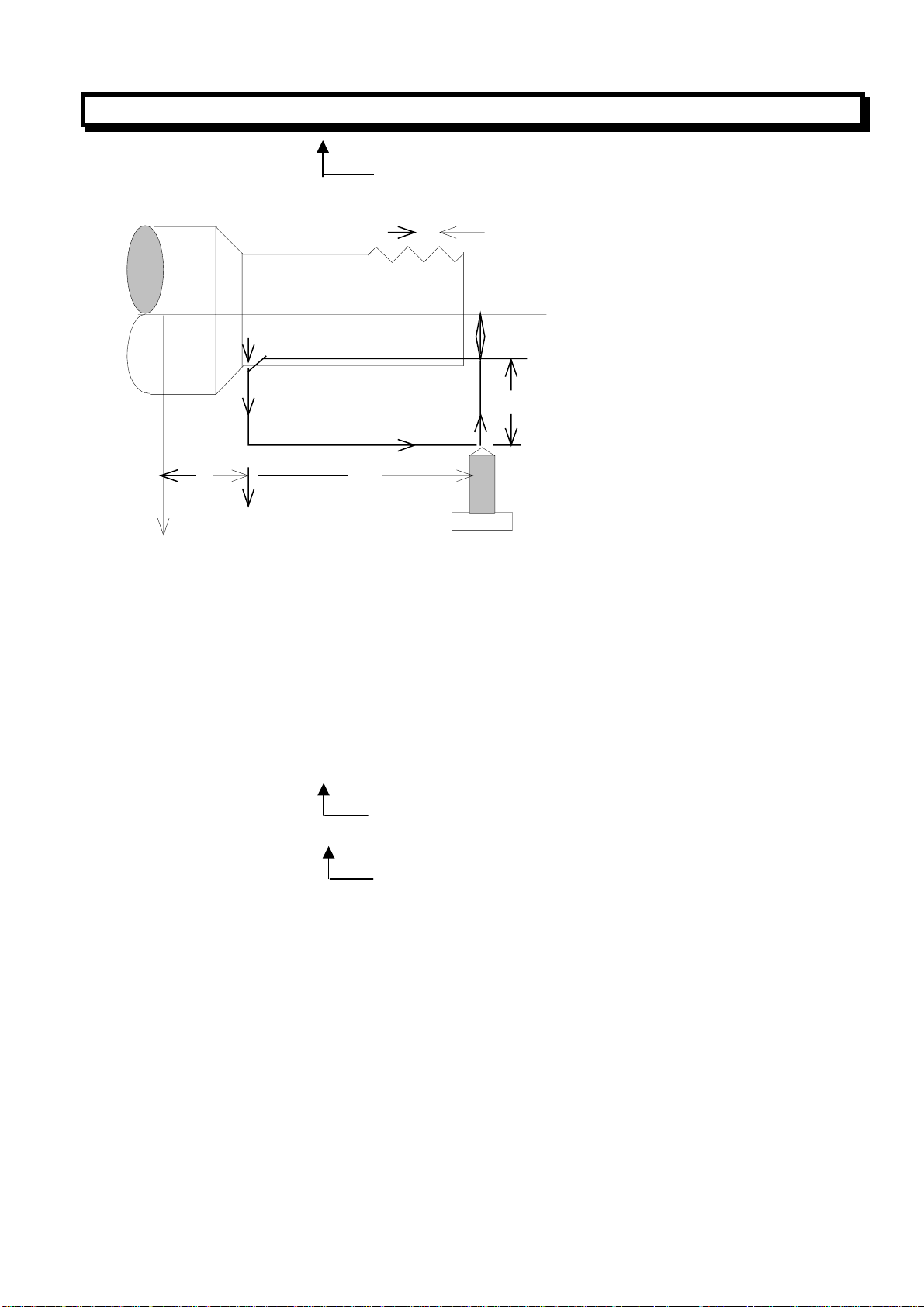
(2) Thread Cutting Cycle (G92)
(a) Straight thread cutting
G92X (U)__Z(W)__F__; (Metric thread)
G92X (U)__Z(W)__I__; (Inch thread)
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
R
Pitch specified (L)
21
3(F)
2(F)
4(R)
W
1(R)
U/2
Page 27
GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
Note: Address I for inch thread is not a modal command.
Pitch specified (Number of teeth/inch)
L
Z axis
F:Cutting feel
R:Rapid traverse
X axis
Z
Width of chanferring
2(F)
3(R)
4(R)
W
1(R)
X/2
U/2
Tool
In incremental programming, the signs of values of U and W commands depend on the direction of
paths 1 and 2. It is to say, if the direction of path 1 is negative along X axis, the value of U is negative.
The command of the lead of thread and the limitation of spindle is same with command G32. In single
block mode, single block is effective for operation1,2,3,4.
The length of the chamfering is set by parameter No.019THDCH. The width of the chamfering is set
by parameter No.THDCH*1/10*L (lead of thread)
Note 1:As mentioned in Note of G32.And, When the FEED HOLD key is pressed during the
execution of the thread cutting block, the feed would not stop until path 3 is finished.
(b)Taper Thread Cutting Cycle:
G92 X (U)__Z (W)__R__F__;
lead specified (L)
G92 X (U)__ Z (W)__R__I__;
lead specified (number of teeth/inch)
Note: Address I for inch thread is not a modal command.
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
22
Page 28
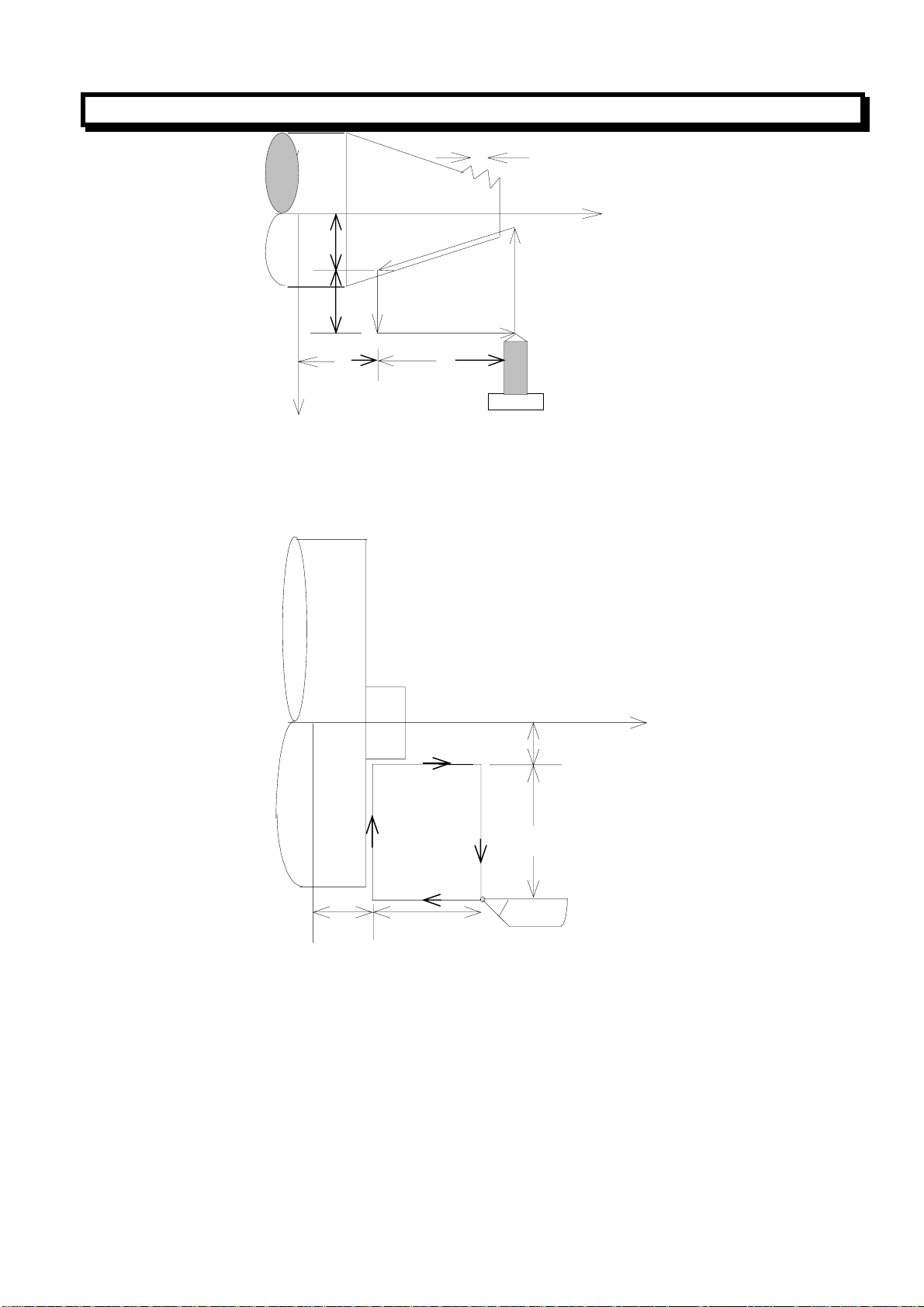
GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
X/2
U/2
X axis
3(R)
Z
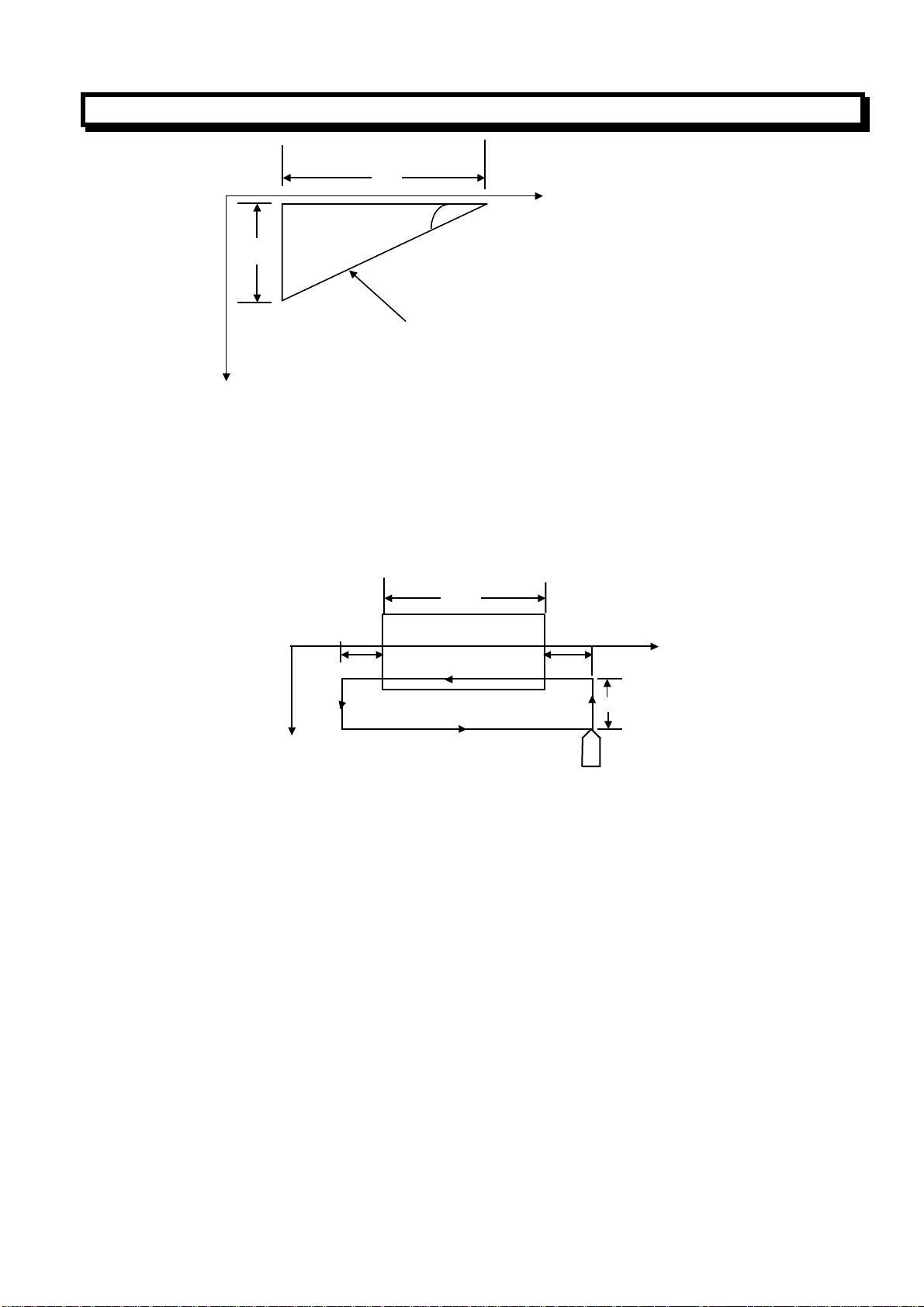
(3) End Face Cutting Cycle(G94)
(a)End Face Cutting Cycle
G94 X (U)__ Z(W)__F__;
2(F)
4(R)
W
L
Z axis
1(R)
F:Cutting feed
R:Rapid traverse
Tool
o
X axis
3(F)
2(F)
4(R)
1(R)
W
X/2
U/2
F:Cutting feed
R:Rapid traverse
Tool
Zaxis
In incremental programming, the signs of the value following address U and W depend on the
direction of paths 1 and 2. That is, if the path 1 is negative along Z axis, the sign of the value of W is
negative.
In single running mode, press Cycle start Key to perform the operation 1,2,3 and 4.
(b)Taper Face Cutting Cycle
G94 X (U)__Z (W)__R__F__;
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
23
Page 29
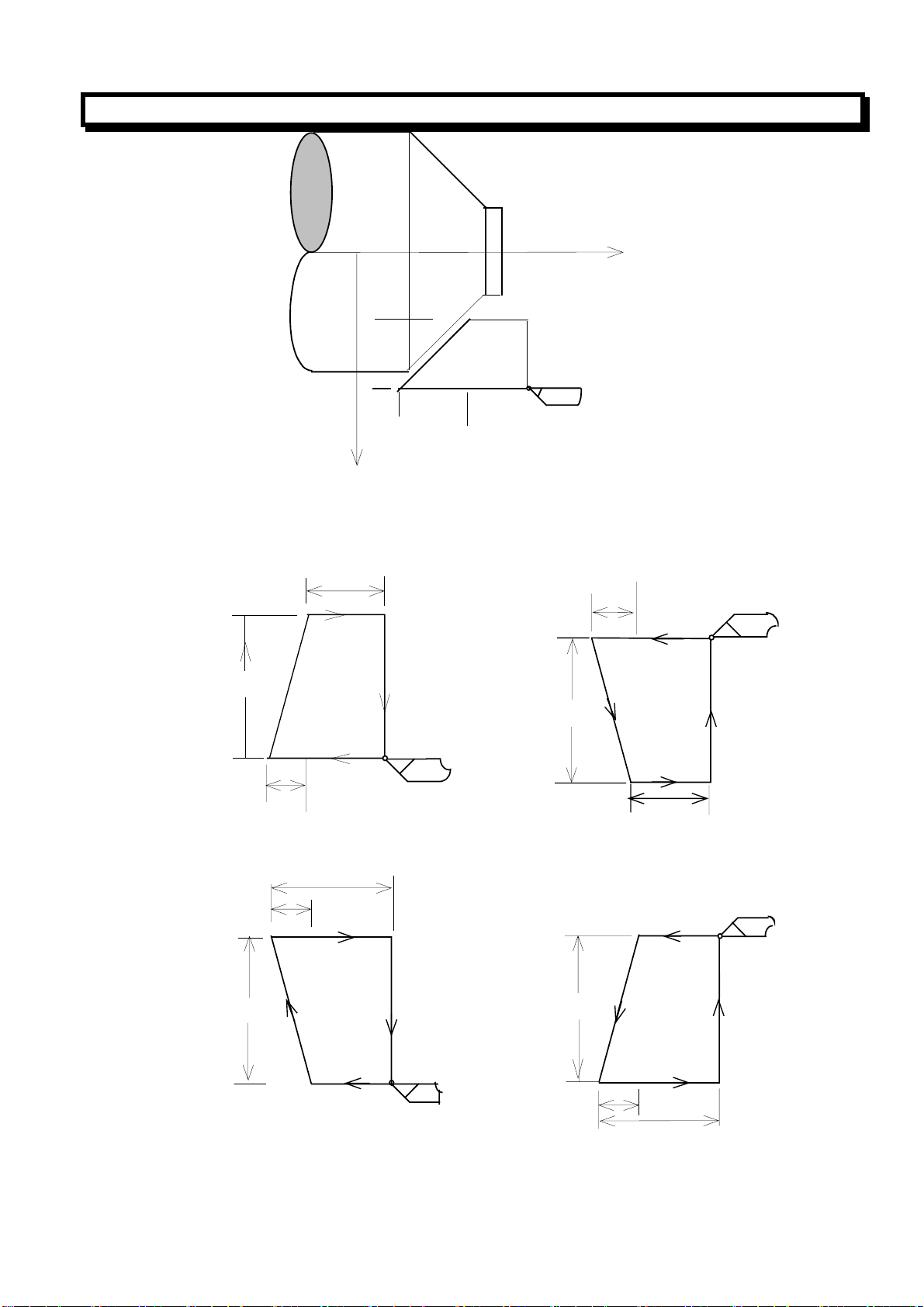
GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
Z axis
X/2
3(F)
U/2
2(F)
1(R)
4(R)
R
Z
X axis
W
F:Cutting feed
R:Rapid traverse
In incremental programming, the relationship between the signs of the values of U, W and R and the
tool paths is as follows:
1) U<0, W<0, R<0 2)U>0, W<0, R<0
U/2
R
2(F)
W
3(F)
4(R)
U/2
1(R)
3)U<0, W<0, R>0(︱R︱≤︱W︱) 4)U>0, W<0, R>0(︱R︱≤︱W︱)
R
2(F)
1(R)
3(F)
W
4(R)
W
R
1(R)
4(R)
2(F)
3(F)
W
U/2
2(F)
3(F)
1(R)
4(R)
U/2
R
Note 1: The data value of X (U), Z (W) and R of during canned cycle are modal as same as
G90,G92 and G94, if X (U), Z (W) or R is not newly commanded, the previously commanded
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
24
Page 30

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
e
data is still effective.
In the example below, a canned cycle can be repeated only by specifying the new movement
commands for X axis, but the Z axis movement need not be re-commanded.
However, these data are cleared if a one-shot G code expect G04 or a G code, which is not in the same
group with G90, G92 and G94, is command.
(Example):
O
66
Z axis
1
6
1
2
8
4
X axis
The following program can perform the cycle in the above figure:
N030 G90 U-8.0 W-66.0 F4000;
N031 U-16.0;
N032 U-24.0;
N033 U-32.0;
2.3.12 Multiple Repetitive Cycle (G70~G75)
This optional canned cycle function is used to make the programming easy. For example, the data for
the finish workpiece shape can be used as the data for rough cutting automatically.
(1)Multiple Repetitive Cycle for Outer Diameter (G71)
As in the figure below, a finished shape of A to A’ to B is given by a program, the specified area is
removed by depth of cut △D, and the finish cutting allowance of △ U/2, and △W is left.
Program commanded
path
△W
Aˊ
△U/2
Cutting feed
Rapid travers
E
B
A
45
△D
C
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
25
Page 31

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
p
Format:
G71 U(ΔD) R(E) F(F) S(S) T(T);
G71 P(NS) Q(NF) U(ΔU)W(ΔW) ;
N(NS) ......
........
· F
· S
· T
The move commands of finished shape from A to A’ to B are
specified in the blocks from N (NS) to N (NF).
Sequence number must be s
ecified for each
N(NF) ......
△D: Cutting depth without sign. The cutting direction depends on the direction of AA’ (Radius
designation). This designation is modal and remains unchanged until the other value is
designated. This value also can be specified by the parameter No. 051, and the value of this
parameter can also be changed by the program command.
E: Escaping amount. It is a modal designation that remains unchanged until other value is designated.
This value also can be specified by parameter No. 052, and the value of parameter can also be
changed by program command.
NS: The sequence number of the first block of the program for finished shape.
NF: The sequence number of the last block of the program for finished shape.
△U: Distance and direction of finish cutting allowance in X direction (Diameter/Radius designation)
△W: Distance and direction of finish cutting allowance in Z direction.
F, S, T: Any F, S and T function specified in blocks N (NS) to N (NF) in the G71 cycle is ignored,
only the F, S, and T function in the G71 Command Block is effective.
F,S,T: During the cycle of G71,the function of F/S/T is noneffective
The following four cutting patterns of G 71 are considered. All these cutting cycle are made paralleled
to Z axis and the signs of △ U and △ W are as follows:
B
U(+)..W(+)
A
A
U(+)..W(-)
B
Z
A'
X
B
U(-)..W(+)
A'
A
A'
A'
U(-)..W(-)
A
Linear or
circular
interpolation
B
The tool path between A and A’ is specified in the block with sequence number NS including G00 or
G01, and in this block, a move command in the Z axis is not allowed. The tool path between A’ and B
must be steadily increasing or decreasing pattern in both X and Z axis.
Note1: subprogram can not be called in the blocks with sequence number from NS to NF.
Note2: Between sequence NS and NF, more than five blocks are not permitted.
(2)Stock Removal in Facing (G72)
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
26
Page 32

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
As show in the figure below, this cycle is the same as G71 except that the cutting is made by an
operation parallel to X axis.
△W
B
△U/2
Program command
path
45
E
Tool path
A
A'
C
Cutting feed
△D
Rapid traverse
G72 W (△D) R(E) F(F) S(S) T(T);
G72 P(NS)Q(NF)U(△U)W(△W);
The means of △D, E, NS, △U, △W, F, S, T are the same as those in G71.
Using G72, the following four cutting patterns are considered. All of these cutting cycles are made
paralleled to X axis.
The signs of △ U and △ W are as follows:
RR
U(+)..W(-)..
U (+)..W (+)..
Both linear and circular
interpolation is possible
A’
A’
A
A
A
A
A’
A’
The tool path between A and A’ is specified in the block with sequence number “NS” in which G00 or
G01 can be included, but in and in this block, a move command in the X axis can not be specified.
The tool path between A’ and B must be steadily increasing or decreasing pattern in both X and Z
axis.
Note1:The subprogram is not called in the block with the sequence number from NS to NF.
Note2: Between sequence NS and NF, more than five blocks are not permitted.
U (-)..W (+)..
R
U (-)..W (-)..
R
Z
X
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
27
Page 33

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
N
(3)Pattern Repetitive Cutting Cycle (G73)
Using cutting cycle permits cutting a fixed pattern repeatedly, with a pattern being displaced bit by
bit. By this cutting cycle, it is possible to efficiently cut work whose rough shape has already been
made by forging or casting method, etc.
B
A'
△W
A
△U/2
C
△U/2
△u/2 △i+
△W
△K+△W
D
The pattern commanded in the program should be as follows:
A to A’ to B.
G73 U(△I)W(△K)R(D) F(F) S(S) T(T);
G73 P(NS)Q(NF)U(△U)W(△W);
N (NS)………
· · · · · · · · · · · · · ·
·
The finish move command between A and B is
specified in the block from sequence number NS to
F
N (NF) · · · ·
△I: Distance and direction of relief in the X axis direction (Radius designation). This
designation is modal and is not changed until the other value is designated. This value also can
be specified by parameter No.053, and the parameter is changes by the program command.
△K: Distance and direction of relief in the Z axis direction (Radius designation). This
designation is modal and is not changed until the other value is designated. This value also can
be specified by parameter No.054, and the parameter is changes by the program command.
D: The number of division, which is the same as the repetitive count for rough cutting. This
designation is modal and is not changed until the other value is designated. This value also can
be set by parameter No.055, and the parameter is changed by the program command.
NS: The sequence number of the last block of the program of finish shape.
NF: The sequence number of the last block of the program of finish shape.
△U: The finish cutting allowance in X direction (Diameter/Radius designation).
△W: The finish cutting allowance in Z direction.
F, S, and T: Any F, S, and T function specified in the blocks between sequence number from NS to NF
are non effective, but the F, S and T function is effective in the G73 block.
Note1: △I, △K, or△U, △W is specified by address U and W respectively, the difference of
them is determined by the address of P and Q.
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
28
Page 34

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
Note 2:The cutting cycle is performed by G73 command with P and Q specification. The four
cutting patterns are considered. Take care of the sign of △U, △W, △I, △K. When the
cutting cycle is terminated, the tool returns to point A.
Note3: Between sequence NS and NF, more than five blocks are not permitted.
(4) Finish Cutting Cycle (G70)
After rough cutting by G71, G72 and G73, the finish cutting can be performed by the following
command:
G70 P (NS)Q(NF);
NS: The sequence number of the first block of the program of finish shape.
NF: The sequence number of the last block of the program of finish shape.
Note 1: F, S and T specified in the block G71, G72 and G73 are noneffective for the G70
block .but F, S and T specified in the blocks between sequence number from Ns to NF for finish
cutting are effective.
Note 2: When the cutting specified by G70 is terminated, the tool returns to the start point and
the next block is read.
Note3: The subprogram can not be called in the blocks with sequence number from NS to NF
between G70 and G73.
Note4:Between sequence NS and NF, more than five blocks are not permitted.
Example:
●Multiple repetitive cycle for outer diameter(G71):
80
10
20 30
d
e
c
100 60
30
b
a
40
2 10
X axis
0.2
End point`
Z axis
Diameter designation, metric input)
(
Start point
N010 G50 X200.0 Z220.0 ;(Workpiece coordinate system setting)
N020 M3 S300;(Spindle CW rotation, spindle speed: 300 rpm)
N030 M8;(Coolant on)
N040 T0101;(Rough cutting tool)
N050 G00 X160.0 Z180.0 ;(Positioning, come close to the workpiece)
N060 G71 U4.0 R1.0 F300 S200;(Cutting depth 8mm[diameter designation] for each cut,1mm
relief)
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
29
Page 35

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
N070 G71 P080 Q120 U0.2 W2.0;
N080 G00 X40.0 ;
( rough cutting a---d ,Finishing allowance in X
direction 0.2mm, Z direction 2mm)
N090 G01 Z140.0 F100 S800 ;(The federate and spindle speed in finish cutting of G70)
N100 X60.0 W-30.0 ;
N110 W-20.0 ;
N120 X100.0 W-10.0 ;
N130 G00 X200.0 Z220.0 (Rapid traverse to a safe point)
N140 T0202;(Tool No.2 and No.2 Offset)
N150 G00 Z175.0(Positioning at rapid traverse speed)
N160 G70 P80 Q120;(finish cutting a---d)
N170 G00 X200.0 Z220.0 M05 S0; (Return to start point, stop the spindle)
N180 M09;(Coolant off)
N190 T0100;(Standard tool, cancel tool offset)
N200 M30;(End of program)
●Multiple repetitive cycle(G70 G72)
70
190
20
a
15
20
2
b
c
d
Z
4
0
8
0
160
8
8
110
X
7
Start poinp
O0002;
N010 G50 X220.0 Z190.0 ; (Workpiece coordinate system setting)
N015 T0202; (Exchange the tool No.2 and do No.2 tool-compensation)
N017 M03 S200; (Spindle CW rotation and the speed is 200rpm)
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
30
Page 36

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
N020 G00 X176.0 Z132.0 ; (Rapid positioning and closing to workpiece)
N030 G72 W7.0 R1.0 F200; (Forward distance 7mm and backward distance 1mm)
N040 G72 P050 Q090 U4.0 W2.0 ; (Rough cutting a—d, Finishing allowance X4mm, Z2mm)
N050 G00 Z70.0 S500 ; (Rapid positioning)
N060 G01 X160.0 F120 ;
N070 X80.0 W20.0 ; (Cutting a—b)
N080 Z105.0 ; (Cutting b—c)
N090 X40.0Z125.0 ; (Cutting c—d)
N100 G0 X220.0 Z190.0; (Rapid traverse to stare point)
N105 T0303;
N107 G00 X176 Z132 ;
N110 G70 P050 Q090 ; (Finishing cutting a--d)
N120 G0 X220.0 Z190.0; (rapid traverse to start point)
N130 M5 S0; (Spindle stopping)
N140 T0200;
N150 M30; (End of program)
●Multiple repetitive cycle(G73)
40
180 160
X
10
40
R20
120
10
80
20
2
40
14
2
220
Z
14
110
130
16
起点
(Diameter designation, metric input)
N010 G50 X260.0 Z220.0 ;
N011 G99 G00 X220.0 Z160.0 M03;
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
31
16
Page 37

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
R
R
N012 G73 U14.0 W14.0 R0.003 F0.3 S280;(R0.003 means cycling 3 times)
N013 G73 P014 Q018 U4.0 W2.0 ;
N014 G00 X80.0 W-40.0 ;
N015 G01 W-20.0 F0.15 S0600 ;
N016 X120.0 W-10.0 ;
N017 W-20.0 S0400 ;
N018 G02 X160.0 W-20.0 R20.0 ;
N019 G0 X250.0 Z200.0 ;
N020 G70 P014 G018;
N021 G0 X260.0 Z220.0;
N022 M30;
(5) End Face Peck Drilling(G74)
The cutting path showed in the figure below is performed by the following command. Chip breaking
is possible in this cycle as shown below: If X(U) and P are omitted, operation only in the Z axis
direction, to be used for drilling.
Z
△K’
W
e
X
B
F F F F F
C
R R
△i’
U/2
△i
△d
△k△k△k
△k
A
0<△i’≤△i
0<△k’≤△k
G74 R(e) F(f);
G74X(U)Z(W)P(△i)Q(△k)R(△d);
e: Return amount along Z axis after a cutting of depth △K. This value also can be set by parameter
No.056 and the parameter is changed by the program command.
X: X component of point B.
U: The incremental amount from A to B.
Z: The Z component of point C.
W: The increment amount from A to C.
△i; Movement amount in X direction(without sign, diameter).
△k: Movement amount in Z direction (without sign)
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
32
Page 38

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
△d: Relief amount of the tool at the bottom of the cutting(diameter).Usually, the sign of △d is
plus(+). If address X(U) and △I are omitted, It need a sign to specified the relief direction.
F: Cutting federate.
Note 1: Both e and △d are specified by address R, the meaning of address R is determined by
the present of address X(U), that is, if (X(U) is specified, R represents △d.
Note 2: The cycle operation is performed by the G74 command with X(U) specification.
Note 3: Between sequence NS and NF, more than five blocks are not permitted.
(6)Outer Diameter and Inner Diameter Grooving Cycle(G75)
The following command can execute operation as show in the figure below. It is equivalent to G74
except Thai X is replaced by Z. Chip breaking is possible in this cycle, and grooving, cutting off in X
axis is possible.(In this case Z, W and Q are omitted).
G75 R(e) F(f);
G75X(U)Z(W)P(△I)Q(△k)R(△d);
Z
W
△d
X
F
F
F
F
F
R
R
R
R
U/2
e
B
F
C
△i
E: Return amount along X axis after a cutting of depth △I. This value also can be set by parameter
No.056 and the parameter is changed by the program command.
X: X component of point C.
U: The incremental amount from A to C.
Z: The Z component of point B.
W: The incremental amount from A to B.
△i: Movement amount in X direction(without sign, diameter)
△k: Movement amount in Z direction (without sign)
△d: Relief amount of the tool at the bottom of the cutting (diameter). Usually, the sign of △d is plus
(+). If address X(U) and △ I are omitted, It need a sign to specified the relief direction.
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
33
Page 39

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
F: Cutting federate.
Both G74 and G75 are used for grooving, cutting off and drilling. They can control the tool relief
automatically.
Note: Between sequence NS and NF, more than five blocks are not permitted.
2.3.13 Notes on Multiple Repetitive Cutting Cycle (G70~G75)
(1). In the where the multiple repetitive cutting cycle is command, the address P, Q.
X, Z, U, W, and R must be specified correctly for each block.
(2). In the block which is specified by the address P in G71, G72 and G73 commands, G00 or G01 of
01 group must be commanded, if it is not commanded, alarm No.065 is generated.
(3)G70,G71 and G72 can not be commanded in MDI mode. If on of them is commanded, alarm
No.67 is generated. G74 and G75 can be command in MDI mode.
(4) In the blocks in which G70,G71,G72 or G73 are commanded and in the blocks between the
sequence number specified by address P and Q, M98/M99 can not be commanded.
(5) in the blocks between the sequence number specified by address P and Q of G70, G71 G72,
G73,the following commands can not be specified:
★ One shot G code except for G04 (Dwell)
★ 01 group G code except G00, G01 G02 and G03
★ 06 group G code.
★ M98/M99
(6) While multiple repetitive cutting cycle(G70~G75) is being executed, it is permitted to stop the
cycle operation to perform manual operation. But when the cycle operation is restart the tool should
be returned to the position where the cycle operation is stop. It the cycle operation is added to the
absolute value. And operation following is not correct, the tool path is shifted by the movement
amount in manual operation.
(7) When G70,G71,G72,and G73 is being executed, the sequence number specified by address P and
Q should not be specified twice or more in the same program.
(8) In G70,G71,G72and G73 cutting cycle, the last block of the finishing shape blocks group specified
by address P and Q can not be chamfering or corner rounding, if is ,alarm No.69 is generated.
2.4 Spindle Function(S Function)
2.4.1 Spindle Speed Command
By specified a numerical value following address S, to transmitted code signal to the machine tool for
spindle speed control. Only one S code can be specified in one block.
Refer to the appropriate operator manual issued by the machine tool builder for detail such as the
number of digits of S code of how to use S code, etc…
When a movement command and a S command is specified in the same block, they are executed at
the sam4e time.
(1) S 2-digit
By specifying address S followed by 2-digit numerical value to control the speed of the spindle
(Parameter No.001BIT-0).
This system support 4 levels mechanical spindle speed gear change.(When the spindle analogue
control in not available). Refer to the operation manual issued by the machine tool builder for the
detail of the number of the levels of the spindle speed change and the relation between the S code and
the spindle speed.
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
34
Page 40

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
t
t
S1~S4
The execution time of S code is set by diagnosis No.081.
Setting value:0~255(128msec.~32.640msec.)
Setting time=Setting value ×128 m sec.
(2)S4-digit(Optional function)
The spindle speed can be specified directly by address S followed by a 4-digit value (unit:
rpm)(Parameter No.001BIT4=1), The unit for specifying the spindle speed may vary depending s the
machine tool builder.
2.5 Tool Function
By specifying a 2-digit numerical value following address T to select tools on the machine. One tool
code can be commanded in one block. When a movement command and a T code are specified in the
same block, they are executed simultaneously.
Refer to the manual issued by the machine tool builder for detail of the using of T code.
The value after the T code indicates the desired tool, the last two digits is used as the offset number
which indicating the compensation amount for tool offset.
T○○ ○○
Tool offset number
Tool selection
The number of the tools of the system can be set by the parameter No.084; the maximum value is 8.
2.5.1 Procedures of tool Change
Ta<#077,076*selec ti on num ber
positive rot at ion output ( TL+ 0 0 5。6)
rever se output signal(TL- 005。7)
lpost in-postiton( T4~T1 00.3~00.0)
lock up input signal(TCP 00.7)
Tb<#085
In above figure,#076,#077are time constant set by diagnosis correspondingly.
If Ta≥(#077,076) × current commanded tool number, system alarms: tool change overtime
If Tb≥#083, system alarms: Toolpost motor reverse rotation overtime.
When T code being executed, TL+ signal is output to rotate the toolpost ,and TL+ signal is cancelled
when tool in-position signal is received(input),TL- is output after a delay of time T1 to rotate the
toolpost in opposite direction while the control detected the signal*TCP. When signal *TCP is
detected, system delays a time set by diagnosis No.D085, and then cancels the output of signal TL-,
Tool changing is same with the tool number stored in Diagnosis No.075, Tool change is not performed,
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
35
T1=#082
T2=#083
Page 41

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
control go on to the executing of the next program directly.
If the TCP can not be detected in the time set by diagnoses No.083, system alarms and turns off the
signal TL-.
2.5.2 Tool selection (Change) Related Parameters
1. System parameter
Toolpost in-position signal(*T6~*T1), set by parameter No.P011 Bit 1 TSGN.
TSGN 0: Toolpost in-position signal logic “1”is valid(constant opened).
1: Toolpost in-position signal logic “0”is valid(constant closed)
Toolpost lock up signal(*TCP),set by parameter No.P011 Bit0 TCPS.
TCPS 0: Toolpost lock up signal logic“0”is valid(constant closed).
1: Toolpost lock up signal logic“1”is valid(constant opened)
Note: If the TCP signal is not provided with the toolpost controller, Set the Bit 0 TCPS of parameter No.011
to“0”,The control dose not detect the TCP signal during tool changing. By setting toolpost lock up time
constant D085 to control the toolpost reverse time directly.
2.Diagnosis
T1: Time delay from toolpost positive rotation signal is turned off to the toolpost reverse signal is
turned off.
Ttool selection number: Tool selection number.
Diagnosis No.084, Setting Value 0~8
T2: Time delay after the toolpost lock up signal is detected.]
Diagnosis No.085, Setting value 0~255 (0~4080 msec) Unit: 16 msec.
T—Tool number: The maximum time for tool changing(on time):
Diagnosis No.076(lower byte),No.77(upper byte).Setting value 0~65535
(0~1048s) Unit: 16 msec.
Tt: The maximum time of the tool change between the first tool to the last tool.
Diagnosis No.078(lower bite)No.079(upper byte), Setting value 0~65535
(0~1048 s) Unit: 16 msec.
Tlock up: The time limitation for toolpost lock up signal detecting.
Diagnosis No.083, Setting value 0~255(0~16320 msec.) Unit: 64 msec.
Tc: Current tool number:
Diagnosis No.075, the diagnosis is set by the system automatically,
Ta: When T code being executed, system calculates the maximum time it need for tool change
between the current tool position to the commanded tool position.
Ta=T-Tool number× Number difference of tool:
Example: The total tool number of machine is 6
(1) The current tool(position) number is 1, the commanded Tool(position) number is 5,and the number
difference of tool change is 4.
(2) The current tool number is 5, the commanded tool number is 2, and number difference of number is 3.
Tb: The time limitation for toolpost lock up signal detecting.
2.6 Auxiliary Function(M function)
When a movement command and a M code are specified in the same block, they are executed
simultaneously.
(Example)N1 G01 X50.0 Z-50.0 M05;(Spindle stop)
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
36
Page 42

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
X
Execution of the move
command and spindle stop
command is started at the
same time
Z
2.6.1 Description of M F unction
When address M followed by a number is specified, a corresponding signal is transmitted to the
machine side, this signal is used for turning ON/OFF the control of the machine. Normally, only
Description:
M03: Spindle CW rotation.
M04: Spindle CCW rotation.
M05: Spindle stop .
M08: Coolant on.
M09: Coolant off (No signal output).
M32: Lubrication on .
M33: Lubrication off (No signal output0).
M10: Defined by user
The executing time of the other M code(not the pulse length) is set by diagnoses No.80.
Setting value:0~255(128msec.~32.640 msec)
Set time =Setting value×128msec.
The following M code indicate special meaning:
(1)M30: End of program
1)This indicates the end of the main program.
2)Automatic operation is stopped and the CNC unit is reset.
3) Control return to the start of the program.
4)1 is added to the workpiece counter.
(2) M00:Program stop .
Automatic operation is stop after a block containing M00 is executed. When the program is stopped,
all existing modal information remains unchanged as in single block operation. The automatic
operation can be restarted by actuating the CNC.
(3)M98/M99(Calling of subprogram/End of subprogram)
These codes are used to call subprogram, or the program ended with M99 indicates this program can
be executed repetitively, Refer to the subprogram control section for details.
2.6.2 M function Related Data
Diagnosis data No.072~090 are user data which can be set depends on the actual situation by binary
numerical value. Refer to the appendix Binary Number to Decimal Number Correspondence Table for
detail of the relation between binary number and decimal number.
Setting procedures: Set the program switch to off In MDI mode, move the cursor to the head position
of the diagnosis number to be changed, input the binary number with the data input keys and the press
“IN” key to set input.
The methods to move the cursor:
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
37
Page 43

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
1)Use the pages change keys or the cursor move keys:
2)Use the searching function: P→The diagnoses number→IN
No.076,077: The maximum time of tool change when the number difference of tool change is 1.
(T---tool position)
Unit:16 msec.
Setting range:0~65535
Setting value:[№077×256+№076]×16 msec
Setting range: 0~1048.560 s
No.078, 079: The upper limit of the time for rating the toolpost from the first position to the last
positions.
Unit: 16msec.
Setting range:0~65535
Setting value:[№079×256+№078]×16 msec
Setting range: 0~1048.560 s
No.080: The execution time of M code.
Unit: 128 msec.
Setting range:0~255
Setting value: (No.080+1)×128 msec
Setting range: 128~32.768 s
No.081: The execution time of S code.
Unit: 128 msec.
Setting range:0~255
Setting value: (No.081+1)×128 msec
Setting range: 128~32.768 s
No.082: Time change time T1 (The delay time required from the toolpost positive rotation signal end
to the tool post reverse rotation signal issue).
Unit: 16 msec.
Setting range:0~255
Setting value: (No.082+1)×16 msec
Setting range: 16~4.096 s
No.083: The delay time for checking the *TCP signal(the upper limit time for the toolpost reverse
rotation).
Unit: 64 msec.
Setting range:0~255
Setting value: (№.083+1)×64 msec
Setting range: 64~16.32 s
No.084: Maximum tool number selectable.
Setting range:1~6
No.085: When signal*TCP is detected, system delays a time set by diagnosis No.D085, and then
cancels the output of signal TL-, Tool changing is compete.
Unit:16 msec.
Setting range:0~255
Setting value: (No.083+1)×16 msec
Setting range:16~4.096 s
No.087,088: T2(Time from spindle command end to spindle brake issue)
Unit:16 msec.
Setting range:0~65535
Setting value: (No.088×256+No.087)×16 msec
Setting range:0~1048.560 s
No.089,090: T3(Spindle brake signal output time).
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
38
Page 44

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
Unit:16 msec.
Setting range:0~65535
Setting value: (No.090×256+No.089)×16 msec
Setting range:0~1048.560 s
2.7 Program Configuration
2.7.1 Program
A program consists of group of blocks, which contains addresses information necessary for machining.
One block is separated from another with and End of block code (For ISO code is LF, for EIA code is
CR).
(1) Main Program and Subprogram
(a) Subprogram
Program can be divided into two types, main program and subprogram. Normally, the CNC operates
according to the main program. When a calling subprogram command is encountered in the executing
of the main program, control is passed to the subprogram. When a return to main program command
is encountered in the subprogram, control is returned to the main program.
Main Program Subprogram
Command 1
Command 2
...
...
...
Subprogram
Calling command
Command n
...
...
...
Comman
Comman
...
...
...
Return to the
main program
The Memory of CNC can store up to 63 main program and subprograms(standard specification). A
main program can be selected to operate the CNC machine.
(b) Subprogram
If a fixed sequence appears repeatedly in a program, this sequence can be stored as a subprogram in
the memory to simplify the program. The main program can call a subprogram called .subprogram
can also call another subprogram.
When the main program calls a subprogram, it is regarded as a one-level subprogram call. Thus,
subprogram calls can be nested up to two levels in this CNC system as show below:
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
39
Page 45

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
prog
Main Programm
O0001;
...
...
...
M98P1000;
...
...
...
...
M30;
Subprogram
O1000;
...
...
...
M98P2000;
...
...
...
...
M99;
One –level nesting
Subprogram
O2000;
...
...
...
M98P3000;
...
...
...
...
M99;
Two-level nesting
When the macro function is effective, the subprogram nested up to four levels. A single call command
can repetitively call a subprogram up to 999 times.
1) Subprogram configuration
Format of a subprogram:
0□□□□; Subprogram number
……………………;
………………………..;
………………………
……
Subprogram
……
……
……………………….;
………….. .;
M99 ; Subprogram end
A subprogram starts with a program number which consists of address O following by a-digit number
and ends with M99 command. M99 can be specified in the same block with other command or
specified separately as one block.
(Example) X……M99;
Note 1: For compatibility with other device, N□□□□ can be used at the start of a program
instead of a subprogram number that follows O(:), the sequence number after N is registered as a
subprogram number.
2) Subprogram execution
A subprogram can be called by a main program or another subprogram, the format of the call
subprogram command is as below:
M98
Called Sub
Number of times the subprogram
is called repeatedly
ram Number
When the number of times is omitted, the subprogram is called just one time.
(Example) M98 P51002;
This command specifies call the subprogram Number 1002 five times repeatedly. The subprogram
calls command M98 P_can be specified in the same block with move command.
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
40
Page 46

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
(Example) X1000 M98 P1200;
In this case, the subprogram No.1200 will be called after an X movement.
(Example) Execution sequence of subprogram called from a main program:
Main Program
N0010 ......... ;
N0020 ......... ;
N0030 M98 P21010 ;
N0040 ......;
N0050 M98 P1010 ;
N0060 ..... ;
1
23
Subprogram
O1010 ;
N1020 ...... ;
N1030 ...... ;
N1040 ..... ;
N1050 ........ ;
N1060 ...... M99 ;
Same way as the main program calls a subprogram is used for a subprogram calls another
subprogram.
Note 1: If the subprogram number specified by address P can not be found, alarm number PS078 will be
output.
Note 2: When Command M98 P0000 is input by MDI mode, the subprogram will not called.
3) Special Usage
The following special method can be used in calling subprogram:
If address P is used to specify the sequence number, control doses not return to the block after the
calling block when the execution of a subprogram is finished, but returns to the block with the
sequence number specified by address P.
P code is not effective if the main program is operated in a mode other than the memory operation
mode.
This method takes much more time than the normal return method.
Main Program
Subprogram
N0010 ......... ;
N0020 ......... ;
N0030 ..... ;
N0040 M98 P1010 ;
N0050 ........ ;
N0060 ..... ;
N0070 ..... ;
O1010 ;
N1020 ...... ;
N1030 ...... ;
N1040 ..... ;
N1050 ........ ;
N1060 ...... ;
N1070 M99 P0070 ;
If Command M99 is executed during the execution of a main program, control returns to the start of
the main program.
2.7.2 Program Number
Many programs can be registered in the memory of this CNC system. In order to identify one program
from another, address O followed by a 4-digit number is specified at the beginning of each program
registered in the memory.
O □□□□
Program number (1~9999,leading zero can be omitted)
Address O
A program starts by a program number and ends by command M30 or M99.
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
41
Page 47

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
2.7.3 Sequence Number and Block
A program consists of several commands. One command unit is called a block. One block is separated
from another with an End of block code. Notation “;”or “;” is used as an End of block code in this
operation manual.
At the head of a block, a sequence number consisting of address N followed by a number not longer
than four digits can be specified.
Sequence number may be specified in a random order and any numbers can be skipped. Sequence can
be specified for all the block of a program or only for desired blocks of a program. For normal
machining procedures, the sequence number should be arranged blocks in ascending order. It is
convenient to specified sequence number for the blocks specifying important machining step (such as
tool change or machining proceeds to a mew surface with table indexing).
Note: Because 0 can not be as program number, 0 must not be used for a sequence number for the reason of
compatibility with program number.
2.7.4 Word and Address
Word is the basic of a block, a block consists of one or more words. A word consists of and address
followed by a number (the plus sign (+) or minus sign (-)may be prefixed to a number).
X 1000
Address Number
Word
One of the letters A to Z can be used as an address. An address defines the meaning of a number that
follows the address. The addresses and their meanings used in this system are as showed as the below
table:
Depending on the preparatory function, the same address may have deferent meanings.
Function Address Meaning
Program number O Program number
Sequence number N Sequence number
Preparatory function G Specified a movement mode (linear, arc etc )
X, Z, U, W Coordinate axis move command
Dimension words
R Radius of arc
I, K Coordinate of the center of arc
Feedrate F Feedrate
Spindle function S Spindle speed
Tool function T Tool number
Auxiliary function M ON/OFF control of the machine tool
Dwell P, U, X Dwell time
Program number P Subprogram number
Number of repetitions P Number of subprogram repetition
Parameter P, Q, R Specified the sequence number of the
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
42
Page 48

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
repeated section of a program
2.7.5 Basic Addresses and Ranges of Command Values
Basic addresses and the ranges of values specified for the addresses are as follows. All these values
are the limits of the CNC side, which are totally different from the limits of the machine tool side. For
Example, the CNC allow a tool to traverse up to about 10 meter along the X axis, but for a machine
tool, the actual stroke along the X axis may be limited to 2 meter.
Similarly, the CNC allow a cutting Feedrate up to 15000mm per minute, but the machine may not
allow cutting federate more than 4000mm per minute. When programming, the user should read the
operation manual issued by the machine tool builder carefully as well as this manual to be familiar
with the limits.
Table 2.7.5 Basic addresses and ranges of command values
Function Address Input in mm
Program number O 1~9999
Sequence number N 1~9999
Preparatory function G 0~99
Dimension word X,Z,U,W,I,K,A,R ±999.99mm
Feed per minute F 1~~~500.00mm/rev
Feed per revolution/lead of
thread
Spindle function S 0~9999
Tool function T 0~9932
Auxiliary function M 0~99
Dwell X,U,P 0~~~9999.999s
Designation of program number
or number of repetitions
Sequence number P,Q 1~9999
Note: Actually, feed per revolution and the lead of thread are calculated into feed per minute
depending on their relationship with spindle speed, and then restricted by the limit on feed per minute.
F 0~9999
P 1~9999
2.7.6 End of Program
By specifying one of the following codes at the end of a program to indicate the end of the program:
ELA ISO Meaning
M30 CR M30 LF End of main program and return to the start of the program
M99 CR M99 LF End of subprogram
If one of the program end codes is encountered during the executing of a program, the control will
stop the execution of the program and the reset state is set. When M30 CR or M30 LF is executed,
control return to the start of the program (automatic mode). When the subprogram end code is
executed, control will return to the program that calls this subprogram.
2.8 Coordinate Values and Dimensions
2.8.1 Absolute Commands and Incremental Commands
Command method for moving the tool can be indicated by absolute or incremental command. For
absolute command, control moves the tool to a point at a specified distance from Zero point of the
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
43
Page 49

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
A
workpiece coordinate system. Increment command moves the tool by specified the distance from the
previous tool position to the next tool position.
30.0
70.0
40.0
End point
100.0
Z
Start point
X
Commands specifying movement from start point to end point by Absolute or increment value:
Absolute value: X70.0 Z40.0; or
Increment value: U40.0 W-60.0;
Deference addresses are used by absolute and increment command:
Absolute Increment command Description
X U X axis
Z W Z axis
Example: X_ W_ ;
Absolute value (Z axis)
Incremental value (X axis)
Example:
50.0
Program
450.0
Z
Specifies movement from
A to B in the above figure
X400.0 Z50.0
Φ400.0
X
Command method Address
Absolute
command
Incremental
Command
Specifies the end point
coordinate value
Specifies the distance
from the start point to the
X(coordinate value on X axis )
Z(coordinate value on Z axis
U(coordinate value on X axis )
W(coordinate value on Z axis) U200.0 W-400.0;
Φ200.0
B
end point
Note1: Absolute dimension value and incremental dimension value can be used together in one block. In the
above example, the follows command can be specified: X400.0 W-400.0
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
44
Page 50

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
s
Note2: When both X and U or W and Z are used together in one block, the one specified later is effective.
2.8.2 Decimal Point Programming
Numerical values can be input with or without a decimal point.(Parameter No.013 Pod1)Decimal
point can be used for specifying a distance, time or speed, The using of a decimal point depend on the
limit of an address.
Z15.0 Z15mm
Z15 Z0.015MM (Parameter No.013 PODI=1)
F10.0 10mm/r, 10mm/min
F10 0.01MM/r 0.01MM/min(Parameter No,013 Podi=0)
F10 10MM/r 10MM/min (ParameterNo.013 PODI=1)
The following address can be specified with decimal point:
X, Z, U, W, R, A, K, I, F
2.8.3 Diameter Designation and Radius Designation
Since the cross section of the workpiece of lathe machine is usually circular, In CNC lathe control
system programming, the dimensions can be specified in diameter and radius.
D1,D2 ..... Diameter Programming
R1,R2 ..... Radius programming
Z axi
1
D
2
D
2
B
A
R
X axis
When the diameter dimension value is specified, it is called diameter designation. When the radius
dimension value is specified, if is called radius programming. Diameter or radius programming can be
specified by parameter(ParameterNo.001BIT2=1).
When using diameter designation, note the conditions listed in the below table:
Item Notes
Z axis command No relation with diameter and radius
X axis command Specified in diameter
Incremental command U
Coordinate system setting(G50) Specifies a coordinate value of X axis in diameter
Tool offset compensation value X
component
Cutting depth along X axis for command
G90,G92 G94
Radius designation in circular
interpolation(R, I, K )
Feedrate along X axis Change of radius/rev. Or change of radius/min
Display of position on X axis Display in diameter
Note 1: In the following explanations, if the type of programming (diameter or radius)is not specified, X axis
Command the movement path B→A, D2→D1 of
above figure in diameter
Parameter(NO.004, ORC) specifies diameter of
radius
Specified in radius value
Specified in radius value
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
45
Page 51

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
graduation indicates a diameter value in diameter programming and a radius value in radius programming.
Note 2: When a diameter value is specified for the tool offset value, it indicates that when the outer diameter
is cut by a new tool offset value changed by 10mm the otter diameter changed by a diameter value of 10mm.
Note 3: When using a radius value for the tool offset value, the tool length itself can be set.
2.9 Tool Offset
Actually, the amounting position of tool used in machining a workpiece is different from the position
of the standard tool used in programming. The different amount of distance between the standard tool
and the actual tool (usually between the tool noses)is regarded as the tool offset value. In this system,
tool offset is specified by T code; there is no G code to specify tool offset.
There is only one types of tool offset can be specified in this system. Geometry offset.
2.9.1 Geometry Tool Offset
Standard tool
The task of a CNC program is made the tool nose of a standard tool to move along a specified path, It
need all the tool to be mounted correctly to ensure the tool noses are at the same point as the standard
tool. Actually, there is difference between the tool noses of the mounted tool and the standard tool,
Geometry tool offset is used to compensate the difference when the tool actually used differs from the
standard tool used in programming.
Offset amount on X
axis
Offset amount on Z axis
Actual tool
2.9.2 T Code for Tool offset
Meaning of T code:
T ○○ ○○
A) Tool Selection
Tool selection is made by specified the T code corresponding to the tool number.
Refer to the operation manual issued by the machine tool builder for the relationship between the tool
selection number and the tool.
Tool offset number
Tool number
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
46
Page 52

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
B) Tool Offset Number
A tool offset number is used to select the tool offset value corresponding to the tool number that is
selected to begin the offset function. Tool offset value must be input by keyboard. There are two offset
amounts corresponding to one offset number, one X axis, one Z axis.
Offset number
01
02
03
…
…
…
When T code is specified and its offset number is not zero, the corresponding tool offset is effective.
A tool offset number of 00 means that the tool offset is cancelled.
Ranges of offset value: 0 to 999.999mm
Diameter or radius designation can be selected for offset amount on X axis by setting Parameter No.
004: ORC
On X axis On Z axis
0.040
0.060
0
.
.
.
Offset amount
0.020
0.030
0
.
.
.
2.9.3 Tool Offset Value Input by Moving the Tool To a Fixed Point
When setting the tool offset value, press the [IN] key when an address(U, V, W) but not a number has
been keyed in, the corresponding relative coordinate value is set as an offset value. This is used as
following procedures to set the tool offset values conveniently:
(1) Move the tool tip of a standard tool to the standard point manually.
(2)Reset the relative coordinate values U and W to 0.
(3)Select the tool offset number of the standard tool.
(4)Press [X] [O] [IN], and [Z] [O] [IN] to set the tool offset value of the standard tool to 0.
(5)Move the tool to set an offset value to the standard point.
(6)After selecting the tool offset number, the corresponding relative coordinate value will be set
as the desired offset value by pressing [U] or [X], and [W] or [Z] and then [IN].The different
between the standard tool and the actual tool is indicated accordingly.
(7)Repeat procedures(5) and (6), offset value of other tool can be calculated and set
automatically.
Note: this input method is effective or not, depends on the setting of NOFC of Parameter No.010.
2.9.4 Direct Input of Tool Offset by Trial Cutting
To set an offset value, use the following convenient method. Suppose that a work coordinate system
has been set according to a standard tool, move a actual tool to cut the surface A and B, input the
measured values, the deference between the actual tool to cut the surface A and B, input the measured
values, the deference between the actual tool and the standard tool will be calculated automatically
and used as the offset value:
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
47
Page 53

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
X
β
α
Z
Surface A
Surface B
(1)Setting the work coordinate system using a standard tool:
(a)Cut surfaces A in manual mode with the standard tool.
(b)Release the tool in X direction only, without moving Z axis and stop the spindle.
(c)Measure the distance βfrom the zero point of the workpiece coordinate system to surface A,
select MDI mode, Press[PRG], key in: G50 Z “β”,Input this value as the desired X axis work
coordinate value for current surface B, and set the address of this offset number(Standard tool offset
number+ 100)Z=“β”.
(d)Cut surface B in manual mode with the standard tool.
(e)Release the tool in Z direction only, without moving X axis and stop the spindle.
(f)Measure distance α, select MDI mode, Press[PRG], key in:G50 X“α”,Input this value as the
desired X axis work coordinate value for current surface B, and the address of this offset number
(Standard tool offset Number=100) X=“α”
(2) Offset value input of non-standard tool
(a)Cut surface A in manual mode with the this desired tool.
(b)Release the tool in X direction only, without moving Z axis and stop the spindle.
(c)Measure the distance“β”from the zero point of the workpiece coordinate system to surface A, and
the input this value as a measured value data for Z axis in the desire tool offset number, this address of
this offset number satisfies:
Address of offset number =the desired offset number+100
(d)Cut surface B in manual mode
(e)Release the tool in Z direction only, without moving X axis and stop the spindle.
(f)Measure the distance“α”,input this value to address X, this address=the desired tool offset
number+100.
Example: in order to set the offset value to the address corresponding to offset number 03, the measured
values“α”and “β”should be set to address 103.
If the coordinate value on surface B is 105.00,and the measured value is 104.00, the setting value of address
should be 104.0, and the offset value corresponding to offset number is set to 1.0 automatically.
(3)Repeat the procedures (2) to set the offset value of other tools.
Note1: Direct input of the tool offset value is effective when the parameter DOFS(parameter No.12) is 1.
Note 2: Distance“α”is always measured in terms of diameter.
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
48
Page 54

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
e
2.10 Automatic Acceleration and Deceleration
Acceleration/deceleration is automatically applied at the start/end of a tool movement to prevent a
mechanical shock, resulting in smooth start and stop of movement. Automatic
acceleration/deceleration is also applied when federate change, so the change of speed is also smooth.
Rapid traverse: Linear type acceleration/deceleration (Time constant is set by parameter common to
all axis ) (parameter No.029)
Jog feed: Exponential acceleration/deceleration(time constant is set by parameter common to all axis)
(parameter No.029)
Feedrate after interpolation
Acceleration/
deceleration
control
Feedrate after
acceleration/deceleration
Drive control
CNC
Command
Pulse distribution
(Interpolation
Feedrate
Rapid traverse
Acceleration/
deceleration
control
Feedrate after interpolation
Feedrate after
Acceleration/deceleration
Time
Motors
Drive control
T
R
Cutting feedrate Jog feedrate
T
C
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
T
R
T
:Acceleration/Deceleration time
C
Constant(Parameter No.029)
T
C
49
Tim
Time
Page 55

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
N
2.10.1 Speed Control In the Corner Between Blocks
As automatic acceleration and deceleration being adopted after interpolation, arcs will appear in the
corner between blocks during cutting. a quasi-stopping command(G04)can be inserted to cancel
these arcs.
For example:there is one motion only in X axis in one block and another motion in Z axis in the other
block. During the deceleration in X axis, acceleration being done in Z axis, then the trace of tool is
below:
If a quasi-stopping command being inserted, the tool will move along the solid line above according
to command. Otherwise, larger the cutting speed is or larger the time-constant in acc&dec is, larger
the radian of the corner. In G02 or G03 command, the radius of actual tool trace is shorter than that
specified in block. In order to reduce the error, the time constant should be smaller to the best under
permission in machine system.
Note: The following disposal will be adopted in CNC between blocks
ext block
Before block
Insert a quasi-stopping command
X
The trace of program
The actual trace of tool
Z
Point positioning Cutting No move
Point positioning
Cutting
No move
×:The next block can be done after speed is zero commanded in before block.
○:The next block can be done immediately after finishing interpolation in before block.
× × ×
× ○ ×
× × ×
2.11 The Macro Program to User
Store some function realized by a set of dictate to memory as a subprogram and use a command to
stand for this function, which can be transferred in program. This set of dictate is called the macro
program body, sometime being called macro program. The corresponding command is called “macro
command to user”,sometime being called transferring command.
Macro command to user
Main program
The macro program body
A set of dictate to
realize some
function
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
50
Page 56

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
The programmer only need to remember the macro command, not the body of the macro program.
The greatest characteristic is using variable in the macro program body, which can be in operation and
evaluation.
2.11.1 The Macro Command
Format :M98 P□□□□;
Use the above command to call the macro program body specified by P.
Program number of the macro program body being called
2.11.2 The Macro Program Body
General CNC dictate and variable, operation ,transfer dictate are usable in the macro program body,
which being started with the program number following O and ended with M99.
(1) The using method of variable
Address in the macro program can be specified by variable. The variable value can be specified by
evaluation in main program or setting in keyboard, or by evaluation in calculating during doing macro
program body.
Several variable can be used, which is differentiated by variable number.
(a) expression of variable
symbol“#”is to express variable, the format is following:
#i(I=200,202,203,204……)
Eg.#205,#209,#1005
(b) citation of variable
variable can replace the value of address
If there is <address>#I or <address>-#I ,then the positive or negative value of variable is taken as
address value.
Eg.F#203…if #203=15,it’s same as F15.
Z-#210…if #210-250,it’s same as Z-250.
G#230…if #230=3,it’s same as G3.
When taking variable to replace variable number, not ##200, but #9200 is used, that is “9”behind #
meaning replacing variable number.
For example:
O8000;
G65 H01……;
G00 X#101……;
…
…
G65 H82…;
…
M99
Construction of macro program body
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
Program number
Operation dictate
CNC dictate using variable
Transferring dictate
Macro program ending
51
Page 57

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
If #200=205,#205=500
X#9200 is same as X500
X-#9200 is same as X-500
Note1:address O and N can’t cite variable.eg.O#200,N#220 is invalid in program
Note2: if exceeding the maxi value specified by address, the variable isn’t used. eg. if
#230=120,M#230 is invalid
Note3:display and setting of variable:variable can display in LCD or be set by keys.
(2) variable type
There is public variable and system public according to variable number, they have different usage
and characteristic
(a)public variable #200~#231
It is public in main program and every macro program. namely, #I in one macro program is same as in
others. so public variable #I as a operation result can be used in other macro program.
The usage of public variable isn’t specified in system can be used free
#200~#231 are all “0”when power on.
(b)system variable
It’s usage is fixed in system.
Port input signal #1000~#1015
System can know state of port input signal by reading the value of #1000~#1015.
Bit: 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
000
Variable number
Socket number
TCP X16 DECX X14 T04 T03 T02 T01
#1007
XS6:49
#1006
XS6:47
#1005
XS40:1
#1004
XS40:2
#1003
XS40:3
#1002
XS40:4
#1001
XS40:5
#1000
XS40:6
SP ST DECZ ESP
#1015
XS40:7
#1014
XS40:8
#1013
XS40:9
#1012
XS40:10
T08 T07 T06 T05
#1011
XS40:19
#1010
XS40:20
#1009
XS40:21
#1008
XS40:22
The value of 16-bit DI will be evaluated to #1000~#1015,#1032.
Output signal #1100~#1107
#1100~#1107 can be evaluated to change their before states
bit: 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
TL-
UO7
#1107
XS40:12
TL+
UO6
#1106
XS40:13
UO5 UO4 S04
UO3
#1105
XS39:10
#1104
XS39:9
#1103
XS39:8
S03
UO2
#1102
XS39:14
S02
UO1
#1101
XS39:1
S01
UO0
#1100
XS39:5
The 8-bit DO can be evaluated “1”or“0”by #1100~#1107.
2.11.3 Operation and Transfer Dictate(G65)
usual format:
G65 Hm P#i Q#k;
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
52
Page 58

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
m:01~99 means the function of operation or transfer.
#i:variable to store operation result.
#j:variable1 in operation. it can be constant, which be expressed directly without #.
#k:variable2 in operation. it can be constant
meaning:#i=#j○#k
Operation symbol specified by Hm
eg.P#200 Q#201 R#202……#200=#201○#202;
P#200 Q#201 R15……#200=-#201○15;
P#200 Q-100 R#202……#200=-100○#202;
Note1:variable doesn’t include decimal.
Eg.#100=10
X#100……0.01mm
Note2:code H specified by G65 doesn’t effect selected offset
G code H code function specification
G65 H01 evaluation #i=#j
G65 H02 addition #i=#j+#k
G65 H03 subtraction #i=#j-#k
G65 H80 unconditional transfer transfer to N
G65 H81 conditional transfer1 If #I=#j,goto N
G65 H82 conditional transfer2
G65 H83 conditional transfer3
G65 H84 conditional transfer4
G65 H85 conditional transfer5
G65 H86 conditional transfer6
If #I≠#j,goto N
If #I>#j,goto N
If #I<#j,goto N
If #I≥#j,goto N
If #I≤#j,goto N
G65 H99 producing P/S alarm Produce No.500+N P/S alarm
(1) operation dictate
(a) evaluation, #i=#j
G65 H01 P#I Q#J
Eg.G65 H01 P#201 Q1005;(#201=1005)
G65 H01 P#201 Q#210;(#201=#210)
G65 H01 P#201 Q-#202;(#201=-#202)
(b) addition, #i=#j+#k
G65 H02 P#I Q#J r#K
Eg.G65 H02 P#201 Q#202 R15;(#201=#202+15)
(c) subtraction, #i=#j-#k
G65 H03 P#I Q#J r#K
Eg. G65 H03 P#201 Q#202 R#203;(#201=#202-#203)
Note1:specify(P)~(S)by degree unit is 1‰degree.
Note2:when Q,R aren’t specified in operation, their value is “0”.
Note3:decimal is omitted in operation.
(2) transfer dictate
(a) unconditional transfer
G65 H80 Pn; n:sequence number
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
53
Page 59

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
Eg.G65 H80 P120; (transfer to N120 block)
(b) conditional transfer1 #j.EQ.#k(=)
G65 H81 Pn Q#J R#K; n:sequence number
Eg.G65 H81 P1000 Q#201 R#202;
When #201=#202,transfer to N1000 block, when #201≠#202,run sequently.
(c) conditional transfer2 #j.NE.#k(≠)
G65 H82 Pn Q#J R#K; n:sequence number
Eg.G65 H82 P1000 Q#201 R#202;
When #201≠#202,transfer to N1000 block, when #201=#202,run sequently.
(d) conditional transfer3 #j.GT.#k(>)
G65 H83 Pn Q#J R#K; n:sequence number
Eg.G65 H83 P1000 Q#201 R#202;
When #201>#202,transfer to N1000 block,when #201≤#202,run sequently.
(e) conditional transfer4 #j.LT.#k(<)
G65 H84 Pn Q#J R#K; n:sequence number
Eg.G65 H84 P1000 Q#201 R#202;
When #201<#202,transfer to N1000 block,when #201≥#202,run sequently.
(f) conditional transfer5 #j.GE.#k(≥)
G65 H85 Pn Q#J R#K; n:sequence number
Eg.G65 H85 P1000 Q#201 R#202;
When #201≥#202,transfer to N1000 block,when #201<#202,run sequently.
(g) conditional transfer6 #j.LE.#k(≤)
G65 H86 Pn Q#J R#K; n:sequence number
Eg.G65 H86 P1000 Q#201 R#202;
When #201≤#202,transfer to N1000 block,when #201>#202,run sequently.
(h) produce P/S alarm
G65 H99 Pi; i:alarm number+500
Eg.G65 H99 P15;
Produce P/S alarm No.515.
Note1:when the transfer address is positive, searching direction is sequent first ,then restrorse. when
negative, searching direction is retrorse first ,then sequent.
Note2:sequence number can be specified by variable also.
G65 H81 P#200 Q#201 R#202
When condition is satisfied, transfer to the block specified by #200
2.11.4 The Note about the Macro Program Body
(1) the method of using key
press # after G,X,Z,U,W,R,I,K,F,H,M,S,T,P,Q to input #
(2) operation and transfer dictate can be commanded in MDI mode
expect G65,other address only can be input, not be displayed.
(3) H,P,Q, R must be written behind G65 in operation and transfer, only O and N can be written
before G65.
H02 G65 P#200 Q#201 R#202; error
N100 G65 H01 P#201 Q10; right
(4) single block
usually, program doesn’t stop in doing operation or transfer when program switch is ON. but, single
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
54
Page 60

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
block can stop according to parameter(No.013 SBKM),which is used in debugging.
(5) variable range is -232~+232-1,while right display range is -9999999~+9999999,******* will
displayed when exceeding this range.
(6) subprogram nesting is 4 layers
(7) variable only is integer, decimal in operation result will be omitted.
(8) Doing time of operation and transfer is different conditionally. the average time is 10ms.
2.11.5 Example for User
eg. user dictate M61(feed automatically)
main program
O0001:
N10 G50 X100 Z100;(define coordinate system)
N20 G00 U50 F100;(fast traverse)
N30 G01 U0.8;(feed)
N40 M61;(call subprogram No.O9061)
N50 G0 X100 Z100;(finish feed and clear point)
N60 M99;(repeat doing)
subprogram(M61)
O9061:
N10 G65 H01 P#1104 Q1;(U04=1 output feed signal)
G65 H82 P20 Q#1004 R1;(if X14=1,sequently do.if X14=0,do N20 block)
G65 H01 P#1100 Q0;(cancel feed signal,U04=0)
M99 P50;(transfer N50 block)
N20 M99 P30;(transfer N30 block)
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
55
Page 61

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
3.1 Operation Panel
3.1.1 LCD/MDI Panel
LCD/MDI panel of GSK980T
III. Operation
980T
MST
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
56
Page 62

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
3.1.2 Screen Change Keys
Screen change keys are used to switch display screen, For GSK980T, there are seven types of display
screen can be selected: Position, Program, and Tool offset, Alarm, Setting, Parameter and Diagnosis.
Explanation of screens:
[POS]:Current position display, there are total four pages corresponding to absolute coordinate display,
relative coordinate display, Overall, Position/program. They can be selected by page change keys.
[PRG];Program display and edit, there are total three pages: MDI/MODAL, PRG, Content/Program
memory used.
[OFT]:Display and setting compensation data and micro variable including:[Offset],[Macro variable].
[PAR]:Parameter display and setting.
[DGN]:Display of diagnosis data.
[ALM]:Display of alarm messages.
[SET]:Display and setting parameter, parameter ON/OFF and Program ON/OFF.
3.1.3 Explanation of Key Board
Number Name Description
1
2 Output key(OUT) Starts the file output from RS232 interface
3 Address/numeric keys Input letter, numeric, and other characters
4
5
6
7
8
9
Reset Key(∥)
Input key(IN) Confirm the input of parameter, offset value, etc, Start
Cancel (CAN) Cancel the character of symbol input to the key input
Cursor move keys There are four kings cursor move keys:
Page change keys There are two kinds of page change keys:
Edit keys(INS, DEL, ALT) For editing program including Insertion, deletion and
CHC key Display mode change key for the meaning of Bit
Reset CNC and cancel alarm
the input of file from RS232 interface; confirm the
input of command from MDI mode.
buffer. Then content of the key input buffer is
displayed by the LCD screen.
For example: when the key input buffer is displayed
as:
N001
And the cancel key(CAN)is pressed, N0001 is
canceled.
↓: moves the cursor in a downward direction.
↓: Depress the cursor move key, the cursor moves
continuously
W\L: Used to set the ON/OFF of the parameter switch
and the display bit of the bit parameter and bit
diagnosis.
↓: Changeover the page on the LCD screen in the
forward direction;
↓: Changeover the page on the LCD screen in the
reverse direction.
amend.
parameter and bit diagnosis.
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
57
Page 63

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
3.1.4 Machine Operation Panel
Buttons and switches on the operation panel are listed at the below table:
Description of button and switches
Name Function
Cycle start button
Feed hold button The tool decelerates and the stops.
Mode select button Select operation mode
Rapid traverse button By pressing this button, the tool is fed rapidly.
Feed direction select push
button
Start point return button
Rapid traverse override Select the amount of rapid traverse override.
Step/handle feed amount During step mode, select the moving amount per step.
Emergency stop . By pressing this button, the machine is stop emergently
Machine lock Machine lock.
Feedrate override Select the amount of override for automatic operation
Manual continuous federate Select the feed rate of manual continuous feed.
Handle feed axis selection Select the axis moved by the manual handle
Step/handle feed amount
Spindle start
Spindle override
Coolant on
Lubrication on
Manual tool change
Start the automatic operation cycle. The indicator indicating
automatic operation is on during the automatic operation.
Select the movement direction for manual continuous feed
and step feed.
When this switch is in the ON positron, start point return
mode is selected.
During manual handle feed, select the multiplier of the
moving amount per step.
Manual spindle forward rotation, reverse rotation, spindle
jog, spindle stop
Spindle override selecting(analogue spindle speed control
signal)
Coolant pump start (refer to the operation manual issued by
machine tool builder for detail)
Lubrication on (refer to the operation manual issued by
machine tool builder for detail)
Manual change of tools (refer to the Operation Manual
issued by machine tool builder for detail
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
58
Page 64

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
3.2 Manual Operation
3.2.1 Manual Reference Point Return
(1) Push the Reference point return key to select the reference point return operation mode. “Mach
ZRN” will be displayed at the right bottom of the LCD screen.
(2) Depress the feed direction key until the reference point of the selected axis is reached.
The tool moves along the selected axis to the decelerated point at the rapid traverse rate, the moves to
the reference point at the speed FL(Parameter No.032). A rapid traverse override is effective during
rapid traverse motion. FL speed is set by parameter No.032.(When reference point return mode Bis
selected)
(3) When the reference point is reached, the reference point return completion LED lights.
Reference point return completion LED
3.2.2 Manual start Point Return
(1)Push the start point return key to select the start point return operation mode,[程序回零]
will be displayed at the right bottom of the LCD screen.
(2)Select the axis.
The tool moves along the selected axis to the start point and stops, then the address of the
position[X], [Z], [U], [W] is flickering. After the start point return is complete, the tool-offset
compensation will be canceled automatically.
Start point return completion LED
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
59
Page 65

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
3.2.3 Manual Continuous Feed
(1) Push the Manual operation key to select the MDI mode. “MDI” will be displayed at the right
bottom of the LCD screen.
(2) Select the axis to be moved.
The selected axis moves along the selected direction.
(3) Select the JOG federate.
Feedrate
override(percentage)
0 0
10 2.0
20 3.2
30 5.0
40 7.9
50 12.6
60 20
70 32
80 50
90 79
100 126
110 200
120 320
Metric input Mm/min
Feedrate
130 500
140 790
150 1260
Note: The federate in the above table is about3%
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
60
Page 66

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
(4) Rapid Traverse
Once press the Rapid traverse key, the status of this key switch between ON and OFF, when the
switch is ON, the Rapid traverse LED on the operation is lit, the tool is fed rapidly.
PAPID TRAVERSE RAPIDTRAVERSELED
It is possible to move the axis in the selected direction at rapid traverse while this key is switched ON.
Note 1: The rapid traverse federate and the time constant, Acceleration/Deceleration mode are the same with
G00.
Note 2: IF the Zero point return operation does not executed after power on or the release of the emergency
stop, IF the Rapid traverse LED is on, the manual federate is jog feed rate or raid traverse federate
depending on the setting of parameter No.012(ISOT).
3.2.4 Step Feed
(1) Press the Step feed mode key to select the step feed/Handle mode, “HANDLE”is displayed at the
right bottom of the LCD screen (When handle feed function is not available).
(2) Select the desired amount of movement: Press the step feed amount select key to select the desired
step feed amount. The corresponding value is displayed at the left bottom of the LCD screen. This
function is available only for the machine without manual pulse generator.
Step feed amount
Input system 0.001 0.01 0.1 1
Metric input(mm) 0.001 0.01 0.1 1
(3) Select the axis
When the key is press once, the axis moves by the amount specified in the selected direction.
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
61
Page 67

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
3.2.5 Manual Handle Feed (Optional function)
Rotating the manual pulse generator can minutely move the tool.
(1) Press the HANKLE key to select the manual handle feed mode, “HANDLE” is displayed at the
right bottom of the LCD screen.
(2) Select the axis along which the tool is moved by pressing a handle feed axis selection key. The
address[U]or [W] corresponding to the selected axis is flickering.
Handle feed axis selection key
Note: These keys are available only in handle feed mode.
(3) Rotating the Handle
Manual Pulse generator
CW: +direction
CCW: -direction
(4)Select the magnification for the distance the tool is to be moved by pressing a handle feed
magnification key (These keys are used as the step feed amount keys in step feed mode)
Handle feed magnification key (step feed amount key)
Input system
Metric input (mm) 0.001 0.01 0.1 1
0.001 0.01 0.1 1
Movement amount per graduation
3.2.6 Manual auxiliary operation
(1) Tool Post indexing
In Manual/Handle feed /Step feed mode, Depress this key, the tool post indexes to the next
position(Refer to the Operation Manual issued by the machine tool builder for detail information).
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
62
Page 68

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
(2) Coolant ON and OFF
In Manual/Handle feed/Step feed mode, Once press this key, the coolant is switch between
ON and OFF.
(3) Lubrication ON and OFF
In Manual/Handle feed/Step feed mode, press this key to switch the lubrication status
between ON and OFF.
(4) Spindle Forward
(5) Spindle Reverse
(6) Spindle Stop
Indicator of the Key: in any operation mode, the indicator is lit if the spindle is stop.
(7) Spindle speed override(When spindle analogue control function is available)
In Manual or handle feed or step feed mode, press this key, spindle rotates forward.
In Manual or handle feed or step feed mode, press this key, spindle rotates reverse.
In Manual or handle feed or step feed mode, press this key, spindle rotates forward.
Increase: Once press the increase key, the spindle speed override is increased step by step from the
current override in following sequence:
50%→60%→70%→80%→90%→100%→110%→120%→ 120% · ·
Decrease: Once press the decrease key, the spindle speed override is decreased step by step from the
current override in the following sequence:
120%→110%→100%→90%→80%→70%→60%→50%→ 50%→· · ·
(8) LED indicator on the operation panel
Reference point return completion LED.
It is when at the completion of reference point return. When the tool leave the reference point the
LED is OFF.
MST
Rapid traverse Single block
Machine lock Auxiliary lock
Note: The spindle reverse/forward rotation, coolant on, and manual tool change buttons are effective
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
63
Try running
Page 69

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
only in manual operation mode.
3.3 Automatic Operation
3.3.1 Automatic Operation mode
(1) Memory operation
(a)Programs should be Stored in the memory in advance.
(b)Select a program from the registered programs.
(c)Press the automatic operation mode selecting button.
(d)Press the cycle start button on the machine operation panel.
Automatic operation mode selection button Cycle start button
The automatic operation starts when the cycle start button is pressed.
(2) MDI operation
Function for operation one block of program entered from the LCD/MDI panel.
Example: X10.5 Z200.5
(a)Select the MDI mode by pressing the MDI mode selection button.
(b)Press[PRG]key
(c)Press page change key to display a screen.
Program O2000 N0100
(MODAL)
X
Z
U
W
R
F
M
S
T
P
Q
Address
MDI
F 200
G01 M
G97 S
T
G69
G99
G21
SACT 0000
S 0000 T0200
(d)Key in X10.5;
(e)Press[IN]key, the data, X10.5, is input and displayed. If you find an error in the keyed-in number
before press the IN key, press the [CAN] key and then key in the correct number again. If an error in
found after the [IN]key is pressed, key in the data again from the beginning.
(f)Key in Z200.5
(g)Press [IN] key, the data, Z200.5, is input and displayed.
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
64
Page 70

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
Program O2000 N0100
(MODAL)
X 10.500
Z 200.500
U
W
R
F
M
S
T
P
Q
Address
MDI
F 200
G01 M
G97 S
T
G69
G99
G21
SACT 0000
S000 T0200
(h)Press Cycle start button.
Before pressing the cycle start button, canceling Z200.5, the following method is used:
(a)Press [Z] key and the [CAN]key and [IN]key in this order.
(b)Press the cycle button
3.3.2 Starting Automatic Operation
(1) Memory Operation
(2) Select the desired execution program.
(3) Press the cycle start button on the operation panel.
3.3.3 Executing Automatic Operation
After automatic operation mode is started, the following are executed:
(1) One block command is read from the specified program.
(2) The block command is decoded to be the executable data.
(3) The command executed is started.
(4) The command in the next block is read.
(5) The command is decoded to allow immediate execution, this process is also named buffering.
(6) After the preceding block is executed, execution of the next block can be started immediately. This
is because the buffering has been executed. The cursor moves to the block to be executed.
(7) Hereafter, automatic operation can be executed by repeating the steps(4) to (6)
3.3.4 Stopping and Terminating Memory Operation
The memory operation can be stopped using one of the follows two methods: Specifying a stop
command or Pressing a key on the machine operation panel.
(1) Program Stop(M00)
Memory operation is stopped when a block containing M00 command is executed, as in single block
operation, all existing modal information remains unchanged. The Memory operation can be restarted
by pressing the cycle start button.
(2) Program End (M30)
(a)Indicates the end of a program.
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
65
Page 71

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
(b)Terminates the memory operation and the reset state is entered.
(c)Return the control to the top of the program.
(3) Feed Hold
When feed hold button on the operation panel is pressed during memory operation, the tool
decelerates and stops at a time.
Feed hold key Cycle start key
When the feed hold button is pressed,
1) Feeding then stop if the tool is moving.
2) Dwell execution stops, if the Dwell is executing.
3) M,S, and T operation continues up to the end of the block.
When the cycle start button is press, the execution of the program is restarted again.
(4) Reset
The automatic operation can be stopped and the system can be made to the reset state by using the
[RESET] key on the LCD/MDI panel, is the tool is moving, the moving is stop with deceleration,
Reset key
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
66
Page 72

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
3.4 TEST OPERATION
3.4.1 All Axis Machine Lock
When this function is ON, move command pulse is suppressed. Consequently the position display is
updated as specified by the program, but the tool does not move, The M, S and T
function are still executed.
Machine lock indicator
This function is used to check the program, The state of this function can be switched between ON
and OFF by press the all axis machine lock key on the LCD/MDI panel. When it is ON, the machine
lock LED indicator is lighted.
3.4.2 Auxiliary Function Lock
When this function is ON, M, S and T function can not be executed, this function is used to check a
program together with the machine lock function.
This function is used to check the program.
Note: the M00, M30, M98 and M99 function are executed even when this function is ON.
3.4.3 Feedrate Override
Using the federate override and selected the desire percentage of the federate specified by program
during or before automatic operation.
Feedrate override selecting button
The federate override ranges from 0 to 150%.
Note: The federate override in test operation and automatic operation is in common used with
which in manual operation.
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
67
Page 73

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
3.4.4 Rapid Traverse Override
Rapid travel override selecting button
There are four steps of override(F0, 25%,50%,and 100%) can be applied to the following types of
(1) Rapid Positioning by G00.
(2) Rapid traverse rate in a canned cutting cycle.
(3) Rapid traverse rate in rate in G28 command.
(4) Manual rapid traverse rate.
(5) The rapid traverse rate of manual reference point return.
For example, if the rapid traverse rate is 6m/min and the rapid traverse override is 50%, the actual
rapid traverse is 3m/min.
3.4.5 Dry Running
While the Dry running switch is on, The tool is moved at the feederate specified by the following
table instead of the federate specified by the program.
Rapid traverse button
ON Rapid traverse rate The maximum JOG federate
OFF
Remark: Rapid traverse can be by parameter No.004 Bit RDRN.
Program command
Rapid traverse rate Feedrate
Jog federate or rapid
Traverse rate
JOG feedrate
3.4.6 Restart After Feed Hold
In automatic operation mode or MDI mode, press the cycle start button when the Feed hold switch is
on, the operation is restarted.
3.4.7 Single Block
When the single block switch is on, the single block LED is lighted. This function stops the machine
operation after executing on block of the program.
Press the cycle start button to execute the next block, the tool stops after the block is executed.
Note 1: IF G28 is specified, the single block function is effective at he intermediate point.
Note 2: IF single block switch is on during the executing of canned cycle G90, G92, G94, G70 to G75, the
single block stop points are as follows.
(· · · · · · · · · →Rapid traverse, Feedrate )
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
68
Page 74

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
G code Tool path Explanation
G90
3
3
2
3
6
4
2
4
2
1
5
1
1
4
4
3
4
3
2
4
3
2
1
2
3
1
2
Tool path 1 to 4 is assumed as
one cycle. The control is stop
after path 4 is finished.
1
Tool path 1 to 4 is assumed as
one cycle. The control is stop
after path 4 is finished.
1
Tool path 1 to 4 is assumed as
one cycle. The control is stop
after path 4 is finished.
4
Tool path 1 to 7 is assumed as
one cycle. The control is stop
after path 7 is finished.
Each tool path 1 to 4,5 to 8, 9 to
12, 13 to 16, and 17 to 20 is
assumed as on cycle, the control
is stop after each cycle is
finished.
Path 1 to 6 is assumed as a
cycle, the control is stop after
the cycle is finished.
Tool path 1 to 10 is assumed as
one cycle. The control is stop
after path 10 is finished.
3.5 Safety Operation
3.5.1 Emergency Operation
Press the Emergency Stop button on the machine panel, the machine movement stop immediately, all
output function such as spindle rotation and coolant control will be stitch off.
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
69
Page 75

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
Red
EMERGENCY STOP
The machine is locked when it is pressed, the button can be released by twisting it .
3.5.2 Overtravel
When the tool tries to move beyond the stroke end set by the parameter(Stored stroke limit inhibition
area), an over travel alarm is displayed and the tool slows down and stops. In this case, move the tool
to the safety direction by manual operation and then press the reset key to reset the alarm. Refer to the
operation manual issued by the machine tool builder for details.
3.6 Alarm
When abnormal running occurs, please confirm the following items:
(1) An alarm is displayed on the LCD screen.
See Appendix Alarm List to confirm the trouble. If P S □ □ □ is displayed, the trouble is caused
by program or data setting error, amend the program or concerned data to fit the trouble.
(2) No alarm is displayed on the screen.
According the display of the LCD screen to know the status of the CNC system. Refer to the CNC
status display.
3.7 Program Storage & Edit
Edit key
3.7.1 Preparation for Part Program Storage & Edit Operation
The following part of this Operation Manual describes the storage and editing operation of part
program, and the below preparation is necessary for the editing and the storage of the program:
1) Turn on the program protection switch.
2) Set the operation mode to Edit mode.
3) Press the [PRG] key and display the program.
When transiting the program via RS232 interface, the following preparation should be made:
1) Cabling the GSK928 CNC system with the PC(Personal computer)
2) Set the RS232C concerned switch parameter.
3) Turn on the program protection switch.
4) Set the operation mode to Edit mode.
5) Press the [PRG] key and display the program.
Note: In order to protect the program, There is a program switch on[SET] screen, the program can not
be edited when the switch is set off.
3.7.2 Registering Program to Memory
1) Registration by Operation Panel
a) Set the operation mode to Edit mode
b) Press[PRG] key
c) key in the program number
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
70
Page 76

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
e) Press [EOB] key
With the above procedure, the program number is registered to the memory, and then key in the words
of the program and press [INSRT] key to register(refer to the section of Inserting the Word).
2) Registration from PC
a) Set the operation mode to Edit mode.
b) Press[PRG] key and display the Program screen.
c) key in the address O and the program number.
d) Start the PC and set it to output mode.
e) Press[IN] key to register the program to memory, when registering is processing, [Input is
twinkling on the screen.
3.7.3 Program Number Searching
When there are many programs in the memory, when the[PRG] key is press, the pointer always point
to one of the program number, even though the power is turn off, the program pointer is not lose. The
desired program can be called by program number searching.
1) Searching Method 1
a) Set the operation mode to Edit mode
b) Press [PRG] key and display the program screen.
c) Press[O] key,
d) Key in the program number to be searched.
e) Push [↓] key .
f) When searching is over, the program number searched is displayed at the right top of the LCD
screen.
2) Searching Method 2
a) Set operation mode to Edit mode or Automatic Operation mode.
b) Press [PRG] key
c) Press[O] key
d) Press [↓] key, in the Edit mode, if the [O], [↓] keys are pushed tautologically, the registered
programs are displayed sequentially.
3.7.4 Deleting Program
The deleting operation is used to delete the program in the memory.
1) Set the operation mode to Edit mode.
2) Press the [PRG] key and display the program screen.
3) Press [O] key
4) Press[DEL] key, the program with the key in number is deleted.
3.7.5 Deleting All Program
The operation is used to delete the program in the memory.
1) Set the operation mode to Edit mode.
2) Press the [PRG] key and display the program screen .
3) Press[O]key,
4) Key in [--], [9], [9],[9],[9] and then press[DEL] key.
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
71
Page 77

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
3.7.6 Output a program
This operation is used to output a program in the memory to the PC.
1) Enabling the GSD980 and PC.
2) Setting the output code(ISO)
3) Set the operation mode to Edit mode.
4) Press[PRG] key to display the program screen.
5) Make the PC ready.
6) Press [O] key .
7) Key in the desired program number and then press[OUT] key.
3.7.7 Output All Programs
This operation is used to output all programs in the memory to the PC.
1) Enabling the GSK980 and PC.
2) Setting the output code(ISO).
3) Set the operation mode to Edit mode.
4) Press [PRG] key to display the program screen.
5) Make the PC ready.
6) Press[O] key .
7) Key in [--], [9],[9],[9],[9], and then press[OUT] key.
Note: pressing [∥] key can halt the outputting.
3.7.8 Sequence Number Search
This operation is used to find a sequence number in one program. It is usually used to edit or start the
program at the block of that sequence number.
The block or blocks skipped during the searching dose not affect the status of the CNC. It is to say
that the coordinate values, M, S, T code of the skipped do not affect the coordinate values and the
modal values of the CNC system. So specify the necessary M, S, T code and coordinate system
setting etc, in the first block of which the program is to be started or restart with the sequence number
searched. The block to be searched by sequence number search is usually at break point of the
procedure of the part. If it is necessary to search and start a program from a d3esired block during
program process, examine the condition of the CNC system and the machine tool. The specify of the
necessary M, S, T code, coordinate system setting, etc, can be made from MDI panel.
a) Set the operation mode to Edit mode.
b) Press [PRG] key to display the program screen.
c) Select the program number of which the sequence number to be searched
d) Press[N] key
e) Key in the desired sequence number.
f) Press [↓] key .
g) When the searching is over, the sequence number searched is displayed at the right top of the LCD
screen.
Note: During program search, M98××××(subprogram call) is not executed, so a search for a
sequence number within a subprogram called from a currently selected program in Automatic
Operation mode generates P/S alarm( alarm No060)
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
72
Page 78

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
O1000 ;
Subprogram
O8000 ;
M98 P8000 ;
N8888
M99 ;
In the above example, search for N8888 will generate an alarm.
3.7.9 Inserting, Amending and Deleting of word
This function is used to modify the content of a program in the memory.
a) Set the operation mode to Edit mode.
b) Press[PRG] key to display the program screen.
c) select the desired program.
d) Search the word to be modified. A scan or a word search can be used.
e) Inset, amend or delete the word .
(1) Wo rd Search
a) Word scan
Scan word by word.
N100 X100.0 Z120. 0 ; M 03; N110 M30 ;
1) Press the [↓] key, the cursor moves forward word by word on the screen. The cursor is displayed
below the address character of the selected word.
2) Press the [↑] key, the cursor moves backward word by word on the screen.
N100 X100.0 Z120. 0 ; M03 ; N110 M30 ;
3) Keep pressing the cursor key can move the cursor continuously.
4) Press the page change key ↓ to display the following page and search the first word of the page.
5) Press the page change key ↑to display the preceding page and search the first word of the page.
6) Keep press the page change key can display one page after another.
b) Word Search
A specified word is searched for from the current position in the forward or backward direction.
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
73
Page 79

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
N100 X100.0 Z120.0 ; S02 ; N110 M30 ;
Current cursor position
Word to be searched for
Searching direction
1) Key in address S.
2) Key in [0],[2].
Note1: Keying in only S0 does not execute a search for S02.
Note2: Keying in S1 dose not execute a search for S01, in searching of S01, “0” of S09 can not be omitted.
3) Press [↓] key to start the search. The cursor is displayed below S IN S02 at the end of the search.
If the [↑] key is pressed, the search is start from the current position in the backward direction.
c) Search by Address
By this method, a specified address is search for from the current position in the forward direction.
1) Key in address M.
2) Press[↓] key to start the search. The cursor is displayed below the address character of the word
searched at the end of the search. If the [↑] key is pressed, the search is start from the current
position in the backward direction.
d) Returning the cursor to the head of the program
N100 X100.0 Z120.0 ; S02 ; N110 M30 ;
Current cursor position
Word to be searched for
Searching direction
1) Method 1
Press Reset [∥] key (in program screen of Edit mode), the program will be displayed from the head
of the program after this operation is executed.
2) Method 2
Execute a program number search operation.
(2) Inserting a word
1) Search or scan a word which is before the insertion location,
2)Key in the address of the word to be inserted(in this example, T is the address to be inserted).
3) Key in [1],[5].
4) Press [INS] key.
Program
O0050 ;
N1234 X100.0-Z 20.0 ;
S02 ;
N5678 M03 ;
M30 ;
O0050 N1234
Addres
EDIT
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
74
S0000 T0200
Page 80

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
Z
Fug.3.7.9(1) The screen before insertion of T 15.
Program O0050 N1234
O0050 ;
N1234 X100.0-Z120.0 T15
S02 ;
N5678 M03 ;
M30 ;
Address
S0000 T0200
EDIT
Fig.3.7.9 (2) The screen after insertion of T15.
Insert Function A/B
In editing of program, When function A is selected, the insert operation is as described as above.
When the function B is selected, the insert operation is as follow:
After the address and value in word will be inserted with “;”(or“*”).
For example:
Key in X100. and then key in the other address Character, X100. Is inserted automatically, if [EOB]
key is pressed after X100; X100; are inserted at a time.
(3) Amending a word
a) Search for or scan the word to be changed.
N100 X100.0 Z120.0 T15 ; S02 ; N110 M30 ;
To be changed to M03
b) Key in the address to be changed, in this example, key in address[M].
c) Press [ALT] key to change the current word to M03.
N100 X100.0 Z120.0 T15 ; S02 ; N110 M30 ;
To be changed to M03
(4) Deleting a Word
N100 X100.0 Z120.0 T15; S02; N110 M30
a) Search for or scan the word to be deleted.
120.0 to be deleted
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
75
Page 81

Prog
B
b) Press [DEL] key.
GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
N100 X100.0 T15; S02; N110 M30
5) Deleting Blocks
By this operation, the blocks from the currently displayed word to the block with a specified sequence
number deleted.
N100 X100.0 M03; S02;……N2230 S02; N2300 M30;
ram after deletion
a) Key in address N.
b) Key in sequence number 2230.
c) Press [DEL] key, the program from the current cursor position up to the N2233 block is deleted.
The cursor moves to the address next to the block with specified sequence number.
locks to be deleted
3.7.10 Number of Registered Programs
Number of registered programs in this system: 63(standard configuration).
3.7.11 Capacity of System Memory
1) Capacity of program memory
32KB or 40 KB
2) Capacity of Offset Data Memory
15 Pairs.
3.8 Display and Setting Data
3.8.1 Offset Amount
(1) Setting and display of tool offset values([OFT] key)
The tool offset values can be set by absolute input of incremental input.
(a) Absolute Input
1) Press [OFT] key
2) Press page change keys to display the required page where the required offset numbe5r is give.
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
76
Page 82

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
Offset 00001N0001
No. X Z R T
000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0
-001 10.000 10.000 10.000 1
002 -1.000 1.000 1.000 1
003 0.000 0.000 0.000 3
004 0.000 0.000 0.000 5
005 0.000 0.000 0.000 0
006 0.000 0.000 0.000 2
007 0.000 0.000 0.000 6
008 0.000 0.000 0.000 0
Position Relative)
U 0.000 W 0.000
Address S0000 T0200
MDI
3) Move the cursor to the offset number to be changed.
Scanning: Press the upward and downward cursor move key to move the cursor in sequence.
Searching: Using the following method to move the cursor to the desired position directly.
Key in P and offset number, and then press [IN] key.
4) Press address key [X] or [Z] and then input the offset value(input with decimal is also possible) by
press numerical keys.
5) The offset value is input and indicated on the LCD screen after press the [IN] key.
(b) Incremental Input
1) Move the cursor to the offset number to be changed (Same operation with(1)-3))
2) Input the address[U] if you need to change the value of X and [W] for Z.
3) Key in the incremental value with the data input keys.
4) Press[IN] key, the incremental value is added to the current offset value and the new value is
displayed on the screen.
Example:
The current offset value is 5.6.78
Key in incremental value 1.5
The new offset value is 7.178(=5.678+1.5)
Note: when the offset value is changed during automatic operation, the new offset value dose not become
effective immediately. It become effective after the T code specifying the offset number corresponding to it is
designated.
3.8.2 The setting of setting parameter
(1) Setting and display of setting parameter([SET] key)
a) Select MDI mode
b) Press [SET] Key to display the setting parameter.
c) Press the page change key to display to display the parameter switch and program sitch screen.
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
77
Page 83

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
N
Setting 02000
0100
-Not use = 0
Eia/ Iso = 1 (0:EIA 1:ISO)
Mm/inch = 0 (0:MM I:INCH)
Prg.seq = 0
No. REVS = S0000 T0200
MDI
(d) Press cursor move keys and move the cursor to the item to be changed.
(e) Input 1 or 0 according to the following description.
1) Not use
In reserved.
2) Eia/Iso
Setting code when input or output the program to or from the memory.
1: ISO code
0: EIA code
Note: when the programming unit special for 980T is used, the setting is ISO code.
3) mm/inch
Setting the program input unit, inch or metric system.
1: Inch
0: MM
4) Prg.seq
Setting sequence number insertion automatically when program input by keyboard.
0: Automatic sequence number insertion is not effective.
1: Automatic sequence number insertion is effective, the incremental value of the sequence
number can be set by parameter P042 in advance.
f) Press [IN] key, each parameter is set and displayed.
(2) The Setting of the Parameter Switch and Program Switch
(1) Press [SET] key
(2) Press the page change key to display the parameter switch and program witch screen.
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
78
Page 84

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
Setting 02000 N0100
Parm swt: off on
Prog key: off on
S0000 T0200
MDI
Press [W] key, and [D/L] key can change the Pram swt and Prog key between “off” and “on”. When
the parameter switch is set on, alarm P/S 100 is displayed on the LCD screen. Parameter can be
inputted when the parameter switch is on. After the parameter putting, the parameter switch should be
set to off. Press [∥] key can cancel the alarm No.P/S 100.
3.8.3 The Setting and Display of Custom Macro Variable
The common variable (#200~#231) can be displayed on the LCD screen.
When the value of the variable exceeds the value 9999999, ‘*******’ is displayed.
1) Press [OFT] key
2) Press Page Change Key to display the desired pages.
(2) Setting
1) Select the desired page.
Offset 00001N0001
No. Data No. Data
-200 10.000 208 10.000
201 -1.000 209 -1.000
202 0.000 210 0.000
203 0.000 211 0.000
204 0.000 212 0.000
205 0.000 213 0.000
206 0.000 214 0.000
207 0.000 215 0.000
Position (relative)
[ 0.000] W 0.000
address
MDI
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
79
Page 85

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
N
2) Move the cursor to the desired variable item.
3) Press the address keys (X, Z or U, W), and then input the desired value by press numeric keys.
4) Press [IN] key to set the variable.
3.8.4 Parameter
When the CNC is connected to the machine, Parameter must be set correctly so that the characteristics
of the driver unit the specification of the machine and the function of the machine can be fully bring
into display. Since the contents of the parameter depend upon the machine tool, refer to the attaché
parameter table of the operation manual issued by the machine tool builder for the detail of the
parameter setting.
(1) Parameter
(a) Press[PAR] key
(b) Press the page change keys to select the desired page.
In the parameter display screen, the detail information of the parameter in the cursor position is
displayed on the bottom of the LCD screen.
1) Bit parameter
Parameter No.004 to No.014 are bit parameter, there are two kinds of display method for the bit
parameter: one is used for display of the abbreviation name of the each bit. Another is used for display
of the detail information of each bit, press[CHG] key to change the display method. On above screen,
the display line will display the following message after [CHG] key is pressed.
Bit6: RDRN=1/0: Dry run G00 rapid travel/manual feed
In this case, press [D/L] key the display the detail message of the descending bit. Press[W] can
display the message of the ascending bit .
2) Data Parameter
Parameter O0010 N0010
No.. Data No. Data
001 00000001 011 11111010
002 11001000 012 11101111
003 01000100 013 00001000
_004 11000000 014 00000011
005 00000001 015 1
006 00000000 016 1
007 00001011 017 1
008 00000011 018 1
009 00000011 019 5
010 00000011 020 2
…RDRN DECI ORC TOC DCS PROD SCW
O. 004 = S0000 T02000
MDI
The display line for detail information of the current parameter
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
80
Page 86

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
In data parameter, only one data can be set. For example, when the cursor moves to parameter No.15,
the message is follow:
X command numerator.
(2) Parameter Setting
Parameter can be set by MDI panel or input from PC (personal computer).
(a) Parameter Setting by MDI Panel
1) Set the parameter switch to on.
2) Select MDI operation mode (or the emergency stop button is pressed)
3) Press[PAR] key to display parameter screen.
4) Press page change key to display the page with the desired parameter.
5) Move the cursor to the position of the desired parameter.
Method 1: Press [↓] or [↑] key to shift the cursor to the position of the desired parameter. If the
cursor key is depressed continuously, the cursor shifts sequentially. If the cursor exceeds a page, the
previous/next page appears on the screen.
Method 2: Input [P] [parameter number] and [IN] (step 4 can be omitted)
6) Key in the parameter by data input keys.
7) Press [IN] key, the parameter value is input and displayed.
8) After all parameter have been set and confirmed, select the parameter switch and program switch
screens and set the parameter switch to off.
9) Press the Reset [∥] key to cancel the alarm, when alarm No.000 has occurred, turn off the power
supply of the CNC system and turn it on..
(b) Input Parameter from PC
The method is effective only when the input /output interface option function is combined.
1) The file is head by “%LF”.
2) The format of parameter number and parameter value are as follows:
N__ P__ LF(N- parameter number, P-parameter value)
Step (b) can be repeated according to requirement. The leading zero of the parameter value can be
omitted.
3) The file is ended by “LF” or “%”.Data input is finished when these codes are input.
Parameter not specified on the file remains unchanged even if the parameter setting file is input from
PC. The parameter setting file prepared by the above procedure can be input according to the
following procedure:
1) Set the parameter switch to on.
2) Select Edit operation mode.
3) Select parameter screen, and make the programming unit stand by to output.(Refer to the Operation
Manual of the programming unit).
4) Press [ IN] key to input the parameter setting, when the input is being processed, “Input ” is
flickering in the status display line.
5) Set the parameter switch to off..
6) Press Reset key.
(If alarm No.000 occurred, turn off and on the power supply of the CNC system).
Note1: When any of the following alarm is detected, the input is halted:
1) An address other than N and P was input .
2) The value of N or P is not correct.
Note2: If it is desired to halt the parameter setting file input, press Reset key .
Note3: Apart of parameters do not become effective until the power supply is turn off and turn on (When
alarm No.000 occurred)
Note4: Parameter related to the RS232C interface must be set from MDI operation panel before inputting
parameter from PC.
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
81
Page 87

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
N
3.8.5 Diagnoses
The status of the DI/DO signal between CNC and machine tool, the internal data of CNC and the
signal status of the transmission between CNC and PC can be displayed by diagnosis function. By
corresponding setting, the signal can be output directly to machine tool and set the parameter related
to auxiliary function. Refer to the Maintenance Manual for detail of Diagnoses signal.
1) Display of diagnosis
2) Press page change key to selected the desired page.
(2) Setting of Parameter Related to Auxiliary Function
The setting of parameter related to auxiliary function can be made from MDI panel.
1) Select MDI mode and set the program switch to on.
2) Press [DGN] key to display the Diagnoses screen.
3) Press page change key to display the desired diagnosis page.
4) Move the cursor to the desired diagnosis.
Method 1: Press [↓] or [↑] key to move the cursor, if the cursor key is depressed, the cursor shifts
sequentially, if the cursor is exceeds a page, the precious/ next page appear on the Screen.
Method2: Key in [p] [diagnosis number] and [IN] key . (Step 4 can be omitted)
5) Key in the diagnosis data by input keys.
7) Press [IN]key, the diagnostic data is input and displayed.
Diagnosis O0010 N0010
No.. Data No. Data
_000 00101101 008 00110011
001 00110000 009 00000000
002 00000000 010 00000000
003 00000000 011 00000000
004 00100000 012 00000000
005 00000000 013 00000000
006 00000000 014 00000000
007 00000000 015 00000000
Diagnostic information
Input signal from machine tool
…Bit0:*TCP…*DECX.. T04 T03 T02 T01
O. 000 = S0000 T02000
MDI
Display line for detail diagnostic information.
3.9 Display
3.9.1 Status display
The display line above the soft key status display line on the screen is used as status display.
Not ready indicates the CNC system or the drive system is not ready.
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
82
Page 88

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
N
N
N
N
N
N
N
N
N
N
r
ALM: When an alarm occurs and ALM is displayed, pressing the [ALM] key displays the detail alarm
message.
Operation mode: Display the current operation mode: AUTO, EDIT, JOG, Handle, MDI, Mach ZRN
and Pro ZRN.
3.9.2 Display of key in data
The display line above the status display line is used as display of key in data.
Prompt: The prompt appears in the imputable screen.
(1) Display program in Edit mode.
Address------only address can be keyed in.
Numeral-----only numerical value can be keyed in
(2) Parameter, Offset and Diagnosis screen:
No.005 = … Numerical value input is effective.
No.005 … Numerical value input is not effective.
No.005 (flickering ) … key in the sequence number searched ( such as parameter number)
The keyed in value is displayed follows the prompt, When [I NS] or [IN] key is pressed, the value
disappears.
3.9.3 Program Number, Sequence Number Display
The program number and the sequence number are displayed at the top right of the screen as seen in
below figure.
When the program is being edited in the EDIT mode, the program number being edited and the
sequence number just prior to the cursor are indicated.
In case other than program edit mode, the program number and the sequence number search, the
program number and the sequence number searched are displayed.
Program 02000 N0100
02000;
100 G50 X0 Z70.;
110 G00 X70.;
120 Z-70.;
130 G01 X17.5 F200;
140 Z7.5
150 G03 X-17.5 Z17.5 R17.5;
160 G01 X-25
170 G02 X27.5 W 27.5 R27.5;
180 G01 X-15.;
190 G00 X0 Z0
Address S0000 T0200
AUTO
Program number
and sequence
numbe
Key in data
Status
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
83
Page 89

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
3.9.4 The Display of Program Memory Used.
The display of the program memory used can be preformed by proceed as follows.
(1) Select the other mode than EDIT mode.
(2) Push the [PRG] key.
(3) Keep pushing the page change over key until the program table is display.
(4) The content of the table:
(a)PROGRAM NO. USED: The number of programs registered(including the Subprogram)
FREE: The number of the program which can be registered additionally
(b)MEMORY ARED USED: The capacity of the program memory in witch program data is
Registered(indicated by the number of characters).
FREE: the capacity of the program memory, which can be used additionally.
(c)PROGRAM LIST: Displays the Program number in turn.
3.9.5 Display of Command Value ([PRG] key)
(1) Press the [PRG] key.
(2) Press the Page Change Over Key, the following two pages will be displayed:
1) Command values being executed and modal values previously specified are displayed.
Note: this page can not be displayed in EDIT mode.
2) One page including a block currently executed in the program is displayed:
Program 0200 N0100
(current T) (Modal)
X 10.000 F 100
G00 Z 2.000 G01 M
U G97 S
W T
R G69
F G98
M G21
S
T
P
Q SACT 2000
Address S0000 T0200
MDI
Program 0200 N0100
02000;
N100 G50 X70. Z0 ;
N110 G00 X20. ;
N120 W-30.;
N130 G01 X-25.;
N140 G02 X27.5 Z27.5 R27.5;
N150 G01 X-15.;
N160 G00 X0 Z0;
Address S0000 T0200
AUTO
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
84
Page 90

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
3.9.6 Current position display ([POS] key)
(1) Push [POS] key
(2) Push a page change over key, data will be displayed in one of the following three pages:
1) Absolute position in the work coordinate system.
Note1: 1024 Pulse spindle encoder is required for displaying of actual spindle speed display.
Note2: Actual federate = F commanded federate × federate override.
Note3: The unit of feed per revolution and thread cutting federate is 0.00001mm/min, but the displaying unit
of these federate is 0.01mm/rev, so that the value of the third and fourth digits after decimal point can not be
displayed.
For example:
G99 F20.2568
When this command is being executed, the federate is displayed as 2025
G99 F 10
When this command is being executed, the federate is displayed as 1000.
When the Programmed federate exceeds 500.00,“***” is displayed.
When thread is being cutting, the actual federate equal to programmed federate ( federate
override is not effective).
Note4: For feed per minute, When the programmed feedrate exceeds 15000mm/min, “***”is displayed.
2) Position in relative coordinate system
Position (Absolute)
O0008 N0000
X 16.000
Z 56.000
Prg feed: 500 G code: G01, G98
Act feed: 500 Mach No. 10
Fed Ovri: 100% Cut time: 05:28:08
Rap ovri: 100% S0000 T0200
MDI
Position (Relative)
O0008 N0000
U 16.000
W 56.000
Prg feed: 500 G code: G01, G98
Act feed: 500 Mach No. 10
Fed Ovri: 100% Cut time: 05:28:08
Rap ovri: 100% S0000 T0200
MDI
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
85
Page 91

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
After power on, the current relative position will be displayed as far as the machine is moved and can
be reset at any moment.
Reset operation of relative position: Press the [U] or [W] key, the address on the display will flicker,
then press the[CAN] key. The relative position of the flickering address will be reset to zero.
3) Overall display
Position
(Relative) (Absolute)
U 18 X 0.000
W 38.000 Z 0.000
(Machine) (Dis to go)
X 0.000 X 0.000
Z 0.000 Z 0.000
S0000 T0200
MDI
The current position in the following coordinate system is displayed simultaneously:
(A) Position in the relative coordinate system(RELATIVE).
(B) Position in the work coordinate system (ABSOLUTE).
(C) Position in the machine coordinate system (MACHINE).
(D) Residual movement amount (effective in Auto and MDI mode)
4) Programmed federate, override and actual federate display.
The actual federate of machine can be displayed on the current position display screen.
3.9.7 Display of Run Time and Parts Count
The run time and parts count are displayed on the position display screen:
Prg feed: The actual federate after federate override is calculated.
Fed Ovri: The federate override specified by federate override select button.
G Code: The current G code of group 01 or group 03.
Mach No.: Indicates the number of parts, When M30 is executed, it is increased by +1. When the
power supply is turn on, it is preset to “0”.
Cut time: indicates the run time of automatic operation, If is preset to “0” by turn off the power
supply.
3.9.8 Alarm Display([ALM] key)
When an alarm occurs, ALM is displayed at the bottom of the LCD screen. Pressing the [ALM] key
displays the alarm numbers and the alarm message. Refer to the appendix for details of the alarm. In
the alarm screen below, the alarm message is displayed at the bottom of the LCD screen
Indicates the current P/S alarm number and detail message. The detail message of the other alarm,
such as driver alarm, over heat alarm is displayed at the middle part of the LCD screen.
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
86
Page 92

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
Note: When an alarm occurs, the alarm message is automatically displayed on the screen.
Alarm 02000 N0100
Program/ operation error: 007
P/S alarm: decimal point input error
Alarm MDI
3.9.9 Adjusting Brightness of LCD
There are two kind of methods for adjusting brightness of the LCD:
1) Classifying adjusting:
In the first page of Position screen (Relative Coordinate), Depress [U] key or [W] until Address U
or W is flickering, Then press.
[↓] key: become dark, (for the first time, the screen becomes light, afterwards, when the [↑] key is
pressed once, the screen becomes darker)
[↓] key: become lighter gradually
2) Adjust by adjustable resistor (option)
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
87
Page 93

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
IV CONNECTION
4.1 SYSTEM CONNECTION DIAGRAM
4.1.1 Layout diagram of interfaces
XS2 power supply
XS30 X axis
XS36 PC
XS39 IO
XS31 Z axis
XS37 frequency
conversion
XS32 encoder
XS38
handwheel
XS40 IO
4.1.2 Descriptions of Interfaces
(1) XS2: Power supply interface (+5V、+24V、+12V、-12V、0V)
9 Pins connector, Power supply interface for main modules and interface.
(2) XS30, XS31: X, Z axis control signal interface
15 pole female D connecter.
(3) XS32: Spindle encoder interface (incremental encoder 1024pulse/revolution)
15 pole female D connector.
(4) XS36: Standard RS232 interface.
9 pole female D connector.
(5) XS37: Analogue signal interface for Frequency convertor(0—10V)
9 pins D connector.
(6) XS38: Handwheel interface.
9 pins D connector.
(7) XS39, XS40 Input/ output interface.
XS39: 25-contact female D connector plug.
XS40: 25-pin D connector plug.
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
88
Page 94

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
4.1.3 Connection Diagram
XS30
XS31 XS32 XS36 XS37 XS38 XS39 XS40
Spindle encoder
Z axis driver
X axis driver
GSK980T
Frequency convertor
Personal computer
Input/ output interface
Handwheel
XS2
Power supply
4.2 Detail of connection
4.2.1 From CNC to Axis Driver
(1) Interface Diagram of CNC Side:
AM26LS31
220
CP+ 1 CP- 9 DIR+ DIR-
10
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
*SE
T
+5V
EN1
7
89
4。
EN28PC
12V
4。
3
DAL
M
Page 95

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
(2) Signal list
XS30: DB15F (X axis) XS31: DB15F (Z axis)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
XCP+
XDIR+
XPC
XDALM
*XSET
XEN1
XEN2
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
XCP-
XDIR-
0V
+5V
+5V
0V
0V
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
ZCP+
9
ZDIR+
10
ZPC
11
12
ZDALM
13
*ZSET
14
ZEN1
15
ZEN2
(Single pulse)
XS30: DB15F (X axis) XS31: DB15F (Z axis)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
LPAX
LPBX
LPCX
*XSET
XDALM
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
0V
0V
0V
0V
+5V
+5V
XPC
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
LPAZ
9
LPBZ
10
LPCZ
11
12
13
*ZSET
14
15
ZDALM
(3 phases loop pulse distribution)
ZCP-
ZDIR-
0V
+5V
+5V
0V
0V
0V
0V
+5V
+5V
ZPC
4.2.2 Description of Signal
(1) Single Pulse Movement Command Signal
XCP+ XCP- ZCP_, ZCP-: command pulse signals.
XDIR+, XDIR-, ZDIR+, ZDIR_: Move direction command signal. These two groups of signal are
differential output.
Equivalent circuit diagram:
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
90
Page 96

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
CNC side
CP+
CP-
6N137
(2) Pulse Distribution
LPAX, LPBX, LPCX, LPAZ, LPBZ, LPCZ are three phases six steps pulse distribution signals, TTL
level.
(3) Driver Alarm Signal ALM( input)
The receiving circuit of this signal is as fig. 4-2-2a. Alarms when the signal is logic 1 or logic 0 is
determined by parameter.
+5V +12V
R=2K
Input signal
XDALM
Fig 4-2-2a
(4) NC ready signal EN1、EN2(contact output)
When this contact closed, indicates that the CNC system is ready to operation. When alarm is detected
by CNC system, this signal is turn off.
(5) Setting signal*SET(output)
When movement command is output, this signal is at logic“1”, otherwise logic“0”.
(6) Reference Point Return Signal PC
The receiving circuit in the system side is as fig.4-2-2b.
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
91
Page 97

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
PC
R=4.7K
Input signal
Fig. 4-2-2b
4.3 Connection between CNC and Axis Driver
(1) GSK980T and DF3 stepping motor driver
Plug XS30,XS3
1
Signal Ping No.
CP+ 1
CP- 9
DIR+ 2
DIR- 10
0V 11
+5V 12
DALM 5
EN1 7
EN2 8
0V 14
Pin No. Signal
1 CP/CW
2 CP-/CW-
3 DIR/CCW
4 DIR-/CCW-
9 OUT COM
8 DC5-24V
7 ALM OUT
5 FREE-
DF3
Note: Soldering the shielding is metal covers of the connector.
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
Short connect
Figure4.3.1
92
Page 98

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
t
t
(2) GSK980T and Sinano/Panasonic Axis Servo Driver Unit
CN1 socket of Sinano side GSK980 XS30、31 Panasonic MINAS V series XS40
Signal Pin No. Signal Pin No. Pin No., Signal
PP 14 ←----- CP+ 1 -----→ 4 PULS+
PD 15 ←----- CP- 9 -----→ 3 PULS-
DD 16 ←----- DIR+ 2 -----→ 6 SIGN+
DN 17 ←----- DIR- 10 -----→ 5 SIGN-
PC 39 -----→ PC 3 ←----- 23 OZ+
DG 46 ←----- 0V 11 -----→ 13 GND
ALM 19 -----→ DALM 5 ←----- 37 ALM
SON 1 ←----- EN1 7 -----→ 29 SRV-ON
FSTP EN2 2
RSTP 0V
DG
DG 47、49 ←----- 0V 15 -----→ 34
PC- 40 串 300Ω 0V 15 7 COM+ 24V(23)
FG
Shielding
4
Shot connec
5
48
50 25、50 FG
33
8
14
CCWL
Short connect
1
CCW
Shot connec
INH
COM-
Shielding
Remark: For full digital AC servo connection, the Resistor R(R14, R15) should be 470Ω.Soldering
the shielding to the metal cover of connector 980TXS30.31
4.4 Spindle Encoder
This GSK90T CNC system requires an incremental rotary Position encoder with 1024 pulses per
revolution. *PCS, PCS, *PBS, PBS*PAS, PAS showed in below figure corresponding to /Z, Z, /B,
B, /A, A.
XS32: DB15F (Spindle positionn encoder)
1
9
2
10
11
12
13
14
15
0V
+5V
+5V
0V
0V
3
4
5
6
7
8
*PCS
PCS
*PBS
PBS
*PAS
PAS
4.5 RS232-C Serial Interface(Optional)
The communication between the CNC system and the personal computer is made via the serial
interface.(The communication software for 980T must be provided)
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
93
Page 99

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
Connecting diagram:
XS36 COM1/COM2 (9 pole D female connector)
DCD
RXD
TXD
DTR
GND
DSR
CNC SIDE
RTS
CTS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
3
TXD
2
RXD
4
DTR
5
GND
6
DSR
1
DCD
PERSONAL COMPUTER
7
RTS
8
CTS
REMARKS: The shielding of the cable must be firmed at the metal cover of the connector.
Figure 4.5
4-6 Spindle Analogue Control Interface(Optional)
Spindle analogue control interface, output range: SVC 0-10V
Connecting diagram:
XS37:(DB9M) CNC SIDE
1
2
3
4
5
0V
SVC
6
7
8
9
0V
XS37
Frequency
converter
Analogue control signal
Remarks: soldering the shielding of the cable on the metal of the connector.
Figure 4-6
4-7 Handwheel
Connecting diagram:
input interface
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
94
Page 100

GSK980T CNC SYSTEM USER MANUAL
XS38:(DB9M) CNC SIDER
1
2
3
4
5
HA
+5V
+5V
HB
6
7
8
9
0V
0V
XS38
HANDWHEEL
4.8 Connection of power supply
The are four groups of power supply inputs for this system: +5V, +12V, -12V and +24V.
+5V(5A): for logical circuit of CNC system.
+12V(1A): for internal I/O interface circuit.
-12V(1A): for analogue output interface circuit.
+12V(2A): For external I/O interface.
COM: the command terminal.
Connecting diagram:
Power supply box side
2
L
N
V
2
0
GND
+24V
+12
-12
COM
+5V
XS2
1
5
3
2/4/6
7/8/9
GUANGZHOU CNC EQUIPMENT CO., LTD.
95
 Loading...
Loading...