gsk GSK928TEa User Manual

This user manual describes all items concerning the operation of
the system in detail as much as possible. However, it is impractical to give
particular descriptions of all unnecessary and/or unavailable operations of
the system due to the manual content limit, product specific operations and
other causes. Therefore, the operations not specified herein shall be
considered impossible or unallowable.
All rights are reserved. It is against the law for any organization or individual
to publish or reprint this manual without the express written permission of
This user manual is the property of GSK CNC Equipment Co., Ltd.
GSK and the latter reserves the right to ascertain their legal liability.

GSK928TEa Turning CNC System User Manual
Foreword
Dear user,
We are really grateful for your patronage and purchase of this
GSK928TEa Turning CNC system made by GSK CNC Equipment Co., Ltd.
The manual describes the relative content and notes of the system.
Warning
This system can only be operated by authorized and qualified personnel as improper
operations may cause accidents. Please carefully read this user manual before use!
Notes before operating the system:
z Connect the emergency stop button of the system firmly and correctly, otherwise an
emergency stop alarm will occur when the system is switched on, so that the system cannot
work properly( it is not the system failure).
z Set the program reference point of the system according to the actual mounting position of
the tool of the machine that the system controls.
Note: The power supply of the system installed in the cabinet is exclusive to GSK’ CNC
systems.
Must not take the power supply as other uses, otherwise, there maybe cause
great accidence!
Chinese version of all technical documents in Chinese and English languages is
regarded as final.
All specifications and designs are subject to change without notice.
All rights reserved.
We are full of heartfelt gratitude to you for supporting us in the use of GSK’s products.
II

Suggestions for safety
Suggestions for Safety
The user must carefully read the suggestions for the system before installing and operating the
system.
The user must follow the suggestions of the system to ensure that the person is not hurt and the
equipments are not damaged.
The user must follow the related suggestions for safety described in the user manual, and must not
operate it until the manual is read completely.
The user must follow the suggestions of safety described in the user manual from the machine
manufacture.
The user can operate the machine or compile the program to control the machine after completely
reading the manual and the one from the machine manufacturer.
III
GSK928TEa Turning CNC System User Manual
Ⅰ. Graphic symbol
Caution Operation against the instructions may cause the operator serious
injuries.
Alarm Wrong operation may injure the operator and damage the system.
Warning Improper operation may result in damage to the machine, as well its
products.
Important information.
IV

Suggestions for safety
Ⅱ. Notes
1)Check before acceptance
Warning ● The damaged or defect product must not be used.
2)Delivery and storage
Warning ●Moistureproof measures are needed while the system is delivered and stored.
Never climb the packing box, neither stand on it, nor place heavy items on it. Do
not put over five packing boxes in piles. Take particular care of the front panel
and the display of the system.
3)Installation
Warning ●Protect the system from sunlight and raindrops. The shell of the system is not
waterproof.
Warning ●Prevent dust, corrosive air, liquid, conductors and inflammable substances
from entering the system.
●Keep the system away from inflammable and explosive substances. Avoid
places where there is powerful electromagnetic interference.
●Install the system firmly without vibration.
4)Wiring
Caution ●Only qualified persons can connect the system or check the connection. The
connecting wires cannot be damaged. Do not press or open the cover of the
system with power on.
Caution ●The voltage and the polarity of connecting plugs must accord with the user
manual.
●Wet hands are dangerous to grasp the plug or the switch.
Warning ●The connection must be proper and firm.
●The system must be earthed.
V

GSK928TEa Turning CNC System User Manual
5)Debugging
Warning ●Make sure that the parameters of the system is correct before the system runs.
●No parameter is beyond the setting limit in the manual.
6)Operation
Caution ●Only qualified operators can operate the system.
●Ensure the switch is OFF before connecting the power supply.
Warning ●The operator can not leave the system to work alone.
●Do not switch on the system until making sure the connection is correct.
●The emergency stop button is able to disconnect all power supplies when the
system breaks down. Do not switch on/off the system frequently
Warning ●Prevent the system from the environmental interference.
7)Troubleshooting
Caution ●Unqualified persons cannot repair the system.
Warning ●After alarms, do not restart the system until the breakdown is fixed.
VI

Ⅲ. Safety suggestions for programming
1) Setting a coordinate system
Incorrect coordinate system may cause the machine not to work as expected even if the
program is correct, which may injure the operator, and damage the machine as well as its
Suggestions for safety
tool and workpiece.
2) Rapid traverse (positioning)
When G00 rapid traverse performs the positioning( nonlinear motion to position between
its starting point and end point), make sure that the path for the tool is safe before
programming. The positioning is to perform the rapid traverse, and when the tool and the
workpiece are interfered, the tool, the machine and the workpiece may be damaged, and
even the operator injured.
3) Applicability of user manual
The manual introduces in detail all functions of the system, including optional functions
and max. controllable ranges, which are subject to change with the machine. If there is
any doubt, please read the instruction for the machine.
4) Functions of CNC system and machine
CNC machines depend on CNC systems, but also power voltage cabinets, servo systems,
CNC and the operator panels. It is hard to explain all the integrated functions,
programming and operation. Do not use integrated instructions not included in the manual
until they have been tested successfully.
VII

GSK928TEa Turning CNC System User Manual
Ⅳ. Notes and Safety Suggestions for Operating Machine
1)Test the machine without workpieces or tools. Make sure that the machine runs well before
it starts to work.
2)Check the input data of the system carefully before operating the machine. Incorrect input
data may cause the machine to work improperly, so as to damage the workpiece and the
tool, as well injure the operator.
3)Make sure that the input feedrate of the system is suitable for the expected operation.
Feedrate has a maximum for each machine, and the amount of the feed rate is subject to
change with operation. Choose the maximum according to the instructions of the machine.
Improper feedrate leads the machine to work wrongly, so as to damage the workpiece and
the tool, as well injure the operator.
4)When offset is needed, check the direction and the amount of the compensation. Improper
compensation causes the machine to work wrongly, so as to damage the workpiece and
the tool, as well injure the operator.
5)If the machine is to run in JOG working mode, check the current position of the tool and the
workpiece, and correctly specify the moving axis, moving direction and the feedrate.
MPG(Handwheel) control with great override, such as 100, may damage the machine and
its tool, even injure the operator.
6)If the tool is return to the reference point, make sure that the machine has been equipped
with the device to detect the reference point, otherwise, the tool can not reach the
VIII
reference point, which may damage the machine and its tool, and even injure the operator.

Suggestions for safety
Safety Responsibility
Safety responsibility for manufacturer
——The manufacturer should be responsible for danger from clearing out or controlling
design and/or structure of the CNC system and its supplied accessories.
——The manufacture should be responsible for safety of the CNC system and its
supplied accessories.
——The manufacture should provide the user for use information and suggestion.
Safety responsibility for user
——The user should learn and master the safety operation content by studying and
training the CNC system safety operation.
——The user should be responsible for own adding, changing, or modifying the previous
CNC system and accessories.
——The user should be responsible for the danger caused by the operation, regulation,
maintenance, installation and storage and delivery which are not performed
according to the user manual.
IX

GSK928TEa Turning CNC System User Manual
X

Contents
CONTENTS
OPERATION ································································································································· 1
CHAPTER ONE OVERVIEW ··························································································································· 1
HAPTER TWO TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS····························································································· 3
C
2.1 Technical specifications····················································································································· 3
2.2 Functional difference between 928TEa and 928TCa turning CNC system·································· 4
HAPTER THREE OPERATION PANEL·········································································································· 6
C
3.1 LCD Display······································································································································· 6
3.2 LED Status Indicator ························································································································ 6
3.3 Keyboard············································································································································ 6
3.3.1 Character keys···························································································································· 6
3.3.2 Working mode selection key ······································································································ 7
3.3.3 Function keys ······························································································································ 7
3.3.4 Cycle start and cycle pause (feed hold)key···············································································8
3.3.5 Manual axis control key············································································································· 8
3.3.6 Manual auxiliary function key ·································································································· 9
3.3.7 Edit keys ···································································································································· 10
HAPTER FOUR SYSTEM OPERATION ········································································································11
C
4.1 System ON/OFF, Initial State, Modal, and Safe Protection··························································11
4.1.1 Power on·····································································································································11
4.1.2 Power off ····································································································································11
4.1.3 System, program initial and modal························································································· 12
4.1.3.1 Initial and modal ··············································································································· 12
4.1.3.2 Initial mode and modal of program················································································· 12
4.1.4 Safe protection ·························································································································· 13
4.1.4.1 Hardware limit protection ································································································ 13
4.1.4.2 Software limit safe protection··························································································· 14
4.1.4.3 Emergency stop alarm(emergently stopping the system) ·············································· 15
4.1.4.4 Drive unit alarm ················································································································ 16
4.1.4.5 Other alarms······················································································································ 16
4.1.4.6 Switching off power supply······························································································· 16
4.1.4.7 Reset operation ·················································································································· 17
4.2 CNC Working Mode Selection ······································································································· 17
4.3 EDIT Working Mode ······················································································································ 17
4.3.1 Part program catalog search··································································································· 18
4.3.2 Selecting, creating, deleting, renaming and copying a part program·································· 19
4.3.2.1 Selecting and creating a part program ············································································ 19
4.3.2.2 Delete a part program······································································································· 20
4.3.2.3 Deleting all part programs································································································ 20
4.3.2.4 Renaming a part program ································································································ 21
4.3.2.5 Copying a part program ··································································································· 21
4.3.3 Part program communication ································································································· 21
4.3.3.1 Sending part programs(CNC→PC, CNC→USB, CNC→CNC) ······························ 22
4.3.3.2 Receiving part programs(PC→CNC, USB→CNC, CNC→CNC) ··························· 22
4.3.3.3 TXT part program standard format in PC····································································· 23
4.3.4 Part program content input and edit······················································································ 24
4.3.4.1 Inputting program content ······························································································· 27
4.3.4.2 Inserting program line ······································································································ 27
4.3.4.3 Deleting a block ················································································································· 28
4.3.4.4 Inserting a character in a block························································································ 28
4.3.4.5 Deleting a character in a block························································································· 28
4.3.4.6 Modifying a block content ································································································ 28
4.3.4.7 Inserting a macro character string ·················································································· 29
4.3.4.8 Program stored space········································································································ 29
4.3.4.9 No. 253 program operation······························································································· 29
4.3.4.10 No. 254 program operation····························································································· 30
4.3.5 hp5 function ······························································································································ 30
XI

GSK928TEa Turning CNC System User Manual
4.3.5.1 Part program command help····························································································30
4.3.5.2 Relative parameter help for arc························································································30
4.3.5.3 Line number sort ··············································································································· 31
4.3.5.4 Replacing character string································································································ 31
4.3.5.5 Cursor position··················································································································· 32
4.3.5.6 MPG controlling cursor moving ·······················································································32
4.3.6 Part program compiling··········································································································· 32
4.3.6.1 hp3 compiling command ··································································································· 32
4.3.6.2 hp3 analog drawing ··········································································································· 33
4.3.6.3 Program compiling result analysis ··················································································· 34
4.3.6.4 Program compound check prompt··················································································· 35
4.4 JOG Working Mode ························································································································ 36
4.4.1 Coordinate axis movement······································································································· 38
4.4.1.1 JOG movement···················································································································38
4.4.1.2 Step movement ··················································································································· 39
4.4.1.3 MPG control······················································································································· 39
4.4.1.4 Rapid traverse speed selection·························································································· 40
4.4.1.5 Low speed feed speed selection ························································································· 41
4.4.1.6 Inputting field moving, setting feedrate···········································································41
4.4.1.7 Drive unit enabling control ······························································································· 43
4.4.1.8 Coordinate axis motion alarm prompt·············································································43
4.4.2 Creating coordinate system······································································································ 44
4.4.2.1 Creating machine coordinate system_machine zero return(machine reference point
return)················································································································································44
4.4.2.2 Creating machine coordinate system_without machine zero(no machine reference
point)·················································································································································· 46
4.4.2.3 Setting workpiece coordinate system ··············································································· 46
4.4.2.4 Setting program reference point······················································································· 47
4.4.2.5 Program reference point return ······················································································· 48
4.4.2.6 Recovering the workpiece coordinate system and program reference point················ 48
4.4.3 Spindle control function ··········································································································· 49
4.4.3.1 Spindle starting/stopping control ····················································································· 49
4.4.3.2 Spindle S command _gear shifting control ······································································ 50
4.4.3.3 Spindle S_ speed control···································································································· 51
4.4.3.4 Setting spindle working state ···························································································· 54
4.4.4 Cooling control··························································································································54
4.4.5 Manual tool change control ·····································································································55
4.4.6 Manual toolsetting operation··································································································· 57
4.4.7 Hydraulic chuck control function···························································································· 60
4.4.8 Hydraulic tailstock control function ······················································································· 62
4.4.9 Other option functions·············································································································· 64
4.4.9.1 Three-color indicator control···························································································· 64
4.4.9.2 Lubricating control············································································································ 65
4.4.9.3 Machine electricity delay power-on control·····································································65
4.4.9.4 External MPG operation···································································································66
4.4.9.5 Safety door check function································································································66
4.4.9.6 Pressure low alarm check function···················································································67
4.4.10 Searching run message in JOG working mode ····································································67
4.4.11 Appendix:: ···························································································································· 67
4.4.11.1 MDI input controlling M command table MDI·····························································67
4.4.12 Spindle turn function··············································································································68
4.5 AUTO Working Mode ····················································································································· 68
4.5.1 System working mode in AUTO working mode····································································· 70
4.5.2 Function key operation in AUTO working mode···································································70
4.5.2.1 SINGLE execution and CONTINUOUS execution switch············································· 70
4.5.2.2 Dry run and machining run switch ·················································································· 70
4.5.2.3 Switch between coordinate system and graph display····················································71
4.5.2.4 Running a part program from the first block ································································· 71
4.5.2.5 Running a part program from a specified block····························································· 72
4.5.3 Displaying in a part program running···················································································· 72
XII

Contents
4.5.3.1 Graphic display data definition························································································ 73
4.5.3.2 Inputting data of graph display························································································ 74
4.5.3.3 Machining workpiece count and timing·········································································· 75
4.5.4 Manual operation of miscellaneous function ········································································· 75
4.5.5 Speed override tune in AUTO working mode········································································ 76
4.5.5.1 Speed override tune··········································································································· 76
4.5.5.2 MPG speed control············································································································ 76
4.5.6 Interference operation in program execution process··························································· 77
4.5.6.1 Press key interference in program execution ·································································· 77
4.5.6.2 External feed hold knob···································································································· 78
4.5.6.3 External start and pause signal ························································································ 79
4.5.6.4 Feed device alarm function······························································································· 80
4.5.7 Modifying offset in program run ···························································································· 80
4.5.7.1 Modifying offset method in program run········································································ 80
4.5.7.2 Modifying tool compensation validity in program running··········································· 81
4.5.8 Searching run message in AUTO working mode··································································· 81
4.5.9 Program reference point return in AUTO working mode ···················································· 82
4.5.10 System reset and emergence stop signal processing in AUTO working mode ·················· 83
4.5.11 Regulating LCD brightness in AUTO, JOG working mode ··············································· 83
4.6 Parameter Working Mode ·············································································································· 84
4.6.1 Parameter overview·················································································································· 84
4.6.1.1 Parameter privilege··········································································································· 85
4.6.1.2 Entering operation level···································································································· 85
4.6.1.3 Parameter management···································································································· 85
4.6.2 Parameter modification ··········································································································· 87
4.6.2.1 Parameter search··············································································································· 87
4.6.2.2 Parameter modification ···································································································· 87
4.6.3 Parameter hp6 function ··········································································································· 88
4.6.3.1 Parameter communication and standard format ··························································· 88
4.6.3.2 Parameter draw and solidifying······················································································· 91
4.6.3.3 System software upgrade and memory update······························································· 92
4.6.3.4 Functional command privilege························································································· 93
4.6.4 Parameter explanation············································································································· 93
4.6.4.1 Reference point, software limit parameter bit parameter __ P000~P020··················· 93
4.6.4.2 Parameters related to zero return function __ P021~P026, P109~P111, P406~
P407 ··················································································································································· 94
4.6.4.3 Traverse speed, acceleration time parameter __P100~P108, P112~P118 ·············· 96
4.6.4.4 Parameters related to transmission and compensation __ P200~P209, P411,
P1000~P1905 ··································································································································· 97
4.6.4.5 Parameters related to spindle, cooling __ P300~P317, P326, P329, P410··················· 99
4.6.4.6 Parameters related to tool post __ P318~P325, P408 ·············································· 102
4.6.4.7 Parameters related to chuck tailstock __ P327~P328, P409 ······································ 104
4.6.4.8 Run and efficiency bit parameter __ P400~P401························································ 105
4.6.4.9 Relationship between path and run, efficiency parameter ·········································· 107
4.6.4.10 Safety and debugging bit parameter __ P402~P404················································· 108
4.6.4.11 Motor drive bit parameter __ P405···············································································112
4.6.4.12 Parameters related to other interfaces __ P412, P330~P332 ·································113
4.6.4.13 Miscellaneous parameter __ P413~P416, P333 ··························································114
4.6.4.14 Interface parameter __P500~P556··············································································116
4.6.4.15 Variable initial value __P600~P639·············································································116
4.6.4.16 Related parameter of G76 __P336~P339····································································117
4.6.5 Appendix: parameter list ········································································································117
4.6.5.1 Reference parameter list··································································································117
4.6.5.2 Motion parameter list·······································································································118
4.6.5.3 Transmission parameter list ····························································································118
4.6.5.4 Miscellaneous parameter list ···························································································119
4.6.5.5 Bit parameter····················································································································119
4.6.5.6 Variable initial value list ································································································· 120
XIII

GSK928TEa Turning CNC System User Manual
4.6.5.7 Pitch compensation parameter list················································································· 120
4.6.5.8 Interface parameter list··································································································· 121
4.6.5.9 Parameter list related to command forbidden ······························································ 122
4.6.5.10 Parameter list related to input interface release ·························································122
4.6.5.11 Parameter list related to output interface release ·······················································123
4.7 OFFSET Working Mode ··············································································································· 124
4.7.1 Tool offset value search···········································································································125
4.7.2 Input tool offset data by keyboard key ·················································································125
4.7.3 Offset value in each group clear ···························································································· 126
4.7.4 Tool offset hp6 function·········································································································· 126
4.7.4.1 Communication and standard format of tool offset data ············································· 126
4.7.4.2 Offset data clear ··············································································································· 127
4.8 Diagnosis Working Mode ·············································································································· 128
4.8.1 Interface signal search············································································································ 128
4.8.2 Interface signal name display explanations·········································································· 128
4.8.3 Input interface diagnosis explanation ··················································································· 129
4.8.4 Output interface diagnosis explanation ················································································ 129
4.8.5 Output interface operation function ·····················································································129
4.8.6 Spindle encoder and spindle speed check ············································································· 130
4.8.7 Diagnosis hp6 function ··········································································································· 130
4.8.8 Machine miscellaneous function control··············································································· 130
HAPTER FIVE RS232 AND USB SYSTEM COMMUNICATION ································································· 132
C
5.1 RS232 Communication·················································································································· 132
5.1.1 Communication between CNC and PC················································································· 132
5.1.2 Communication between CNC and CNC ·············································································133
5.2 USB Communication ····················································································································· 133
5.2.1 USB operation ·························································································································133
5.2.2 USB file catalog requirements ·······························································································134
PROGRAMMING ···················································································································· 135
CHAPTER ONE PROGRAMMING FUNDAMENTAL ·····················································································135
1.1 Coordinate Axis and its Direction ································································································ 135
1.2 Machine Coordinate System, Machine Zero··············································································· 136
1.3 Program Reference Point ·············································································································· 136
1.4 Machine 2nd, 3rd Program Reference Point··············································································· 136
1.5 Workpiece Coordinate System ····································································································· 136
1.6 Programming Coordinate ············································································································· 137
1.6.1 Absolute Coordinate Values··································································································· 137
1.6.2 Incremental (Relative)Coordinate Values············································································· 137
1.6.3 Compound Coordinate Values·······························································································138
1.7 Diameter Programming and Radius Programming ···································································138
1.8 Interpolation Function ··················································································································138
HAPTER TWO PROGRAM STRUCTURE··································································································· 140
C
2.1 Character········································································································································ 140
2.2 Block ··············································································································································· 140
2.3 Block Number ································································································································ 141
2.4 Block ··············································································································································· 141
2.5 Block Skip Symbol and Comment································································································ 142
2.6 Program Structure························································································································· 142
HAPTER THREE MSTF COMMANDS AND FUNCTIONS ·········································································· 144
C
3.1 M — Miscellaneous Function (Command List) ·········································································· 144
3.1.1 M00 — Pause··························································································································· 145
3.1.2 M02 — End of Program········································································································· 145
3.1.3 M20 — End of Program Cycle Machine···············································································145
3.1.4 M30 — End of Program Spindle OFF Cooling OFF ····················································· 146
3.1.5 M03, M04, M05 —Spindle Control······················································································· 146
XIV

Contents
3.1.6 M08, M09 — Cooling control································································································ 146
3.1.7 M10,M11, M12 — clamping/releasing workpiece, cancelling chuck output signal······· 147
3.1.8 M32, M33 — Lubricating ON/OFF ······················································································ 147
3.1.9 M41, M42, M44, M43 — Spindle Automatic Gear Shifting Control ································· 147
3.1.10 M78, M79, M80 —Tailstock going forward and retreating backward, cancelling tailstock
output signal········································································································································ 148
3.1.11 M96 —Cycle execution call·································································································· 148
3.1.12 M97 — Program transfer ···································································································· 149
3.1.13 M98, M99 — Subprogram call and subprogram return··················································· 149
3.1.14 M21, M22, M23, M24 —User Output Control ·································································· 150
3.1.15 M91, M92, M93, M94 — User input ··················································································· 151
3.1.16 M47, M48 — Setting spindle working state ······································································· 152
3.1.17 M60~M74 — Customized commands················································································· 152
3.2 S function — Spindle Function ···································································································· 152
3.2.1 Gear shifting controlling spindle motor ··············································································· 153
3.2.2 Spindle controlling conversion motor··················································································· 153
3.3 T function — Tool Function·········································································································· 154
3.3.1 Tool offset execution mode-moving slide ·············································································· 154
3.3.2 Tool offset execution mode- modifying coordinates····························································· 155
3.4 F function — Feedrate Function ···························································································· 156
HAPTER FOUR G COMMANDS AND FUNCTIONS ···················································································· 158
C
4.1 G00 —Rapid Traverse (Positioning)···························································································· 158
4.2 G01 — Linear Interpolation········································································································· 159
4.3 G02, G03, G05 —Circular interpolation····················································································· 161
4.4 Chamfering Function ···················································································································· 165
4.4.1 Linear chamfering·················································································································· 165
4.4.2 Circular chamfering··············································································································· 167
4.4.3 Special cases ···························································································································· 168
4.4.4 Chamfer supplementary explanation ··················································································· 170
4.5 Thread Cutting Command ··········································································································· 170
4.5.1 G33 —thread cutting·············································································································· 171
4.5.2 G34 — variable pitch thread cutting ···················································································· 178
4.6 G32 —Tapping Cycle ···················································································································· 180
4.7 G50 — Setting a Workpiece Coordinate System ········································································ 181
4.8 G51 — Recovering Workpice Coordinate System Setting························································· 182
4.9 G26 — X, Z, Y Reference Point Return ······················································································ 182
4.10 G28 — Return to Machine Zero(Machine Reference Point)··················································· 183
4.11 G30 — 2
4.12 G04 — Dwell ································································································································ 185
4.13 G96 —Constant Surface Speed Control, G97 —Constant Surface Speed Cancel ················ 185
4.14 Single Canned Cycle···················································································································· 188
4.14.1 G90 —outer cylinder face turning cycle (axial cutting cycle)··········································· 188
4.14.2 G92 —Thread cutting cycle································································································· 191
4.14.3 G94 —Inner/outer end face (taper) turning cycle ····························································· 198
4.14.4 G74 —Deep hole machining cycle on end face··································································· 200
4.14.5 G75 —Grooving cycle ·········································································································· 202
4.15 Compound Cycle ························································································································· 204
4.15.1 G71 —axial plane roughing compound cycle····································································· 204
4.15.2 G72 —End face roughing cycle ··························································································· 209
4.15.3 G73 — closed cutting cycle command group ····································································· 212
4.15.4 G76 — multi thread cutting cycle command group ·························································· 217
4.16 G22, G80 —Program Part Cycle ······························································································· 222
4.17 G98 —Feed per Minute(feed/m) , G99 —Feed per Rev(feed/r) ·············································· 223
4.18 G31 — Skip ·································································································································· 224
4.19 G52 — rotary axis coordinate clearing integer········································································· 225
4.20 Additional Axis(Y) Function······································································································· 226
4.20.1 Additional axis(Y) start········································································································ 226
4.20.2 Additional axis(Y) realizing motion···················································································· 226
4.21 Appendix: G function and its Explanation Table ····································································· 227
4.22 Appendix:G and its Relative Parameter Explanation ··························································· 229
nd
, 3rd Program Reference Point Return····································································· 184
XV

GSK928TEa Turnin g CNC System User Manual
CHAPTER FIVE TOOL NOSE RADIUS COMPENSATION (G41,G42)·························································· 230
5.1 Application ····································································································································· 230
5.1.1 Overview·································································································································· 230
5.1.2 Command format···················································································································· 231
5.1.3 Compensation direction ·········································································································231
5.1.4 Programming rules················································································································· 232
5.1.5 Application example ··············································································································· 233
5.1.6 Toolsetting and tool nose number of ball tool······································································· 234
5.2 Tool Nose Radius Compensation Offset Path Explanation ························································ 236
5.2.1 Inner and outer side················································································································ 236
5.2.2 Tool movement in start-up ····································································································· 237
5.2.3 Tool movement in OFFSET mode ························································································· 238
5.2.4 Tool movement in OFFSET canceling···················································································239
5.2.5 Tool interference check··········································································································· 241
5.2.6 Particulars ·······························································································································242
5.2.7 Radius compensation of compound cycle command ···························································242
HAPTER SIX PITCH ERROR COMPENSATION························································································· 244
C
6.1 Leading-Screw Error Curve ········································································································· 244
6.2 Constant Interval Description Method ························································································ 245
6.3 Inflection Point Description Method ···························································································· 246
6.4 Pitch Compensation Execution Method ······················································································ 247
HAPTER SEVEN GENERAL PROGRAMMING RULES AND EXAMPLES ····················································250
C
7.1 General Programming Rules ········································································································ 250
7.2 Programming Rules for Commands in One Block ·····································································251
7.3 Command Execution Sequence ···································································································· 252
7.4 Programming Example ················································································································· 254
7.4.1 Outer machining example ······································································································ 254
7.4.2 Thread machining example···································································································· 255
7.4.3 Compound machining example ····························································································· 257
HAPTER EIGHT ALARM MESSAGE········································································································· 262
C
8.1 Emergency Alarm·························································································································· 262
8.2 Alarm Table in PARAMETER, OFFSET Working Mode(i.e.E001~E009) ····························· 262
8.3 General Chart of Alarm in Working Mode(i.e. E100~ E199)··············································· 264
8.4 Emergency Alarm Program Alarm Table(i.e.E200~ E299, E600~ E699) ···························· 266
8.4.1 Alarm in program command(i.e. E200~299)·······································································266
8.4.2 Alarm in program command (i.e. E600~699)······································································· 269
8.5 Alarm Table in JOG OR AUTO Working Mode (i.e.E300~ E499)··································· 270
8.5.1 Alarm in Executing Relative Operations (i.e E300~E399)················································· 271
8.5.2 Relative alarm in executing statement(i.e.E400~ E499) ················································· 274
C
HAPTER NINE STATEM EN T PROGRAMMING·························································································· 276
9.1 Variable··········································································································································· 276
9.1.1 Variable expression method··································································································· 276
9.1.2 Classification of variable········································································································ 276
9.1.2.1 Command variable ··········································································································276
9.1.2.2 Pointer variable················································································································ 278
9.1.2.3 Interface variable············································································································· 279
9.1.2.4 Keyboard scan register R5001························································································ 281
9.1.2.5 Display window register r5002························································································282
9.1.2.6 r5003 display value register r5003·················································································· 284
9.1.2.7 Graph update register r5004··························································································· 285
9.1.2.8 Program control register r5008 ······················································································ 285
9.1.2.9 System special variable set 1 ··························································································· 286
9.1.2.10 System special variable set 2·························································································286
9.2 Statement········································································································································ 287
9.2.1 Assignment statement········································································································· 287
9.2.2 Conditional statement········································································································· 288
9.2.3 Statement program example······························································································ 289
9.3 Process Monitoring and Execution·······························································································290
9.3.1 Process monitor description (r7000) ·················································································291
XVI

Contents
9.3.2 The start and close of process monitor············································································· 292
9.3.3 Monitor program example································································································· 294
9.3.4 Pulse monitoring (r7100) ··································································································· 295
9.3.5 Pulse monitoring program example·················································································· 296
9.3.6 Variable transfer register (r7900)······················································································ 297
9.4 Attached List·································································································································· 298
9.4.1 ASCII list····························································································································· 298
9.4.2 Often used color and code value corresponding list ························································ 298
HAPTER TEN CUSTOMIZATION COMMAND PROGRAM ········································································ 299
C
10.1 Customization Command ··········································································································· 299
10.1.1 Customization command program format········································································· 299
10.2 Customization Command Store (P254) ··············································································· 300
10.2.1 Format and debugging of customization command storeroom········································ 300
10.2.2 Explanation of customized command storage···································································· 301
10.2.3 Customized command machining example········································································ 301
CONNECTION ·························································································································305
CHAPTER ONE INTERFACE······················································································································· 305
1.1 Rear Cover Interface Position Layout························································································· 305
1.2 Total Frame···································································································································· 306
HAPTER TWO INTERFACE GRAPH········································································································· 307
C
HAPTER THREE CNC DEVICE CONNECTION························································································ 309
C
3.1 Front Cover Communication Interface······················································································· 309
3.1.1 USB interface ·························································································································· 309
3.1.2 Serial RS232 technical specifications····················································································309
3.1.3 Serial RS232 signal definition ······························································································· 310
3.1.4 Connecting with external PC by RS232 ··············································································· 310
3.1.5 Connecting with another CNC system by RS232 communication interface
(communication connections between GSK928TEa) ······································································ 310
3.2 X1,X2 Interface·······························································································································311
3.2.1 X1 interface signal definition··································································································311
3.2.2 X2 interface signal definition································································································· 313
3.2.4 Connection method of output signal ····················································································· 316
3.2.5 Input/output signal technical specification ·········································································· 317
3.3 Machine Zero Return Function and Connection········································································ 317
3.4 Tool Exchange Control Function and Connection······································································ 319
3.4.1 Tool exchange control signal definition ················································································ 319
3.4.2 Signal connection···················································································································· 320
3.4.3 Function description··············································································································· 320
3.4.3.1 Tool change mode 0 ········································································································· 320
3.4.3.2 Tool change mode 1 ········································································································· 320
3.4.3.3 Tool change mode 2 ········································································································· 321
3.4.3.4 Tool change mode 3 ········································································································· 322
3.4.3.5 Tool change mode 4 ········································································································· 323
3.4.3.6 Tool change 9···················································································································· 324
3.4.4 Tool signal check and parameter setting ·············································································· 326
3.4.4.1 Default mode (P408_d7=0) ····························································································· 326
3.4.4.2 Table look-up mode (P408_d7=1)················································································ 327
3.5 X3 Motor Interface························································································································ 328
3.5.1 Signal definition······················································································································ 328
3.5.2 Technical specifications·········································································································· 328
3.5.3 Equivalent circuit ··················································································································· 328
3.5.3.1 Drive unit alarm signal XALM, ZALM, YALM························································ 328
3.5.3.2 Enabling signal XEN,ZEN····························································································· 329
3.5.3.3 Pulse signal and direction signal ···················································································· 329
3.5.4 Connection between CNC system and drive unit of compound stepper motor ················ 330
XVII

GSK928TEa Turnin g CNC System User Manual
3.5.5 Connecting between CNC and drive unit of reaction stepper motor································· 332
3.5.6 Connection layout between CNC and AC servo drive unit················································· 334
3.5.7 Connection layout between CNC and Panasonic drive unit ···············································336
3.5.8 Connection layout between CNC system and Japanese Yaskawa drive unit····················· 337
3.6 X4 Spindle Interface ······················································································································ 338
3.6.1 Signal definitions····················································································································· 338
3.6.2 Converter technical specification ·························································································· 338
3.6.3 Encoder technical specifications···························································································· 338
3.6.4 Connection layout of converter analog voltage ···································································· 339
3.6.5 Encoder interface method ······································································································ 339
3.6.6 Encode interface connection layout·······················································································339
3.6.7 Connection between CNC system Y and AC servo drive unit ············································340
3.6.8 Connection between CNC system Y and DAP03 spindle drive unit··································· 341
3.7 X5 MPG Interface·························································································································· 342
3.7.1 Signal definition ······················································································································ 342
3.7.2 Interface method····················································································································· 342
3.7.3 Connection layout ··················································································································· 342
HAPTER 4 USER USE AND MAINTENANCE ·····························································································343
C
4.1 Environmental Condition··············································································································343
4.2 Earthing·········································································································································· 343
4.3 Power Supply Requirements·········································································································343
4.4 Guard·············································································································································· 343
4.5 Use after Long-Time Unuse ·········································································································· 343
PPENDIX····················································································································································· 344
A
PPENDIX 1 CNC SYSTEM ELECTRICAL COMPONENT SYMBOL EXPLANATIONS···································· 344
A
PPENDIX 2 CNC SYSTEM TOOL POST CONTROLLER CIRCUIT METHOD LAYOUT ································· 345
A
PPENDIX 3 INTERFACE CIRCUIT METHOD LAYOUT ··············································································· 346
A
PPENDIX 4 EXTERNAL CONTROL CONNECTION LAYOUT ······································································ 349
A
PPENDIX 5 CNC SYSTEM APPEARANCE INSTALLATION DIMENSION····················································· 350
A
XVIII

Operation Chapter One Overview
Operation
Chapter One Overview
With 480×234 lattice TFT color graphic LCD, GSK 928TEa CNC system takes as key control the
high-speed CPU and the complex programmable logic device of super-large-scale integrated
circuit CPLD. ISO CNC code is used to write part programs. The system is characterized by a full
screen editing, Chinese operation interface, real time demonstration of the machining process,
simple operation. the system can be matched with stepper motors or AC servo drive unit to
machine outer cylinders, end faces, grooves, tapers, circular arcs and threads with high
cost-performance.
Technical Specifications:
9 X, Z link to realize the short linear high-speed smooth interpolation, 0.001mm
interpolation precision, max. rapid traverse speed 30m/min
9 Optional to Y(set by the parameter), Y not only realizes the rapid traverse,
feed(JOG/STEP/MPG feed) motion, alone tapping motion, but also sets the coordinate
system, program zero return, manual machine zero return and other operations
9 Control servo spindle
9 Flexible and convenient programming with statement programming function
9 USB interface communication to get the convenient and fast operation
9 Least command unit 0.001mm, command electronic gear ratio (1~99999)/(1~99999)
9 Control all kinds of automatic tool post, spindle automatic shifting gear
9 Pitch error compensation, backlash compensation, tool length compensation, tool
radius C compensation function
9 Exponential acceleration/deceleration control used to high-speed, high precise
machining
9 Automatic chamfering function
9 Tapping function
9 Course monitoring function
9 Cutting metric/inch thread, end face thread, variable pitch thread, continuous thread;
thread high-speed run-out
9 Full editing part programs, storing 255 machining programs; No. 253 program up to
4MB
9 Big screen color LCD, color configuration is selected by the parameter
9 MSTE state real-time display in machining
9 Multi-level operation password to conveniently manage devices
9 Parameter backup function
9 Parameter, offset data communication function
9 Bilateral communication between CNC and CNC, between CNC and PC, serial upgrade
CNC software
1

GSK928TEa Turnin g CNC System User Manual
9 Bilateral communication between CNC and USB, CNC is upgraded by USB
9 Installation dimension, electric characteristics, some interfaces are compatible to
GSK928TEa Turning CNC System
2
Operation Chapter Two Technical Specifications
Chapter Two Technical Specifications
2.1 Technical specifications
Controlled axes: X, Y, Z; simultaneous controlled axes(interpolation axes): 2 (X, Z)
Interpolation: X, Z linear, arc interpolation,Z/Y or X/Y linear interpolation
Position command range:-9999.999 mm~9999.999mm;least command unit: 0.001mm
Command multiplex coefficient 1~99999,command division coefficient 1~99999
Motion control
Rapid traverse speed:up to 30000mm/min; rapid override:F25%, 50%, 75%, 100% real-time
regulation
Cutting federate: up to 15000mm/min; federate override:0~150% 16 grades real-time regulation
MANUAL federate:: 0mm/min~1260mm/min 16-grade real-time regulation or it is defined extemporarily
MPG feed:0.001mm, 0.01mm, 0.1mm
Acceleration/deceleration: cutting feed can select exponential/linear acceleration/deceleration
G command
Thread
machining
Precision
compensation
M command
T command
Spindle speed
control
I/O
function
Statement
programming
Display window
Program edit
Communication
Optional drive
unit
32 commands:G00, G01, G02, G03, G04, G05, G26, G28, G30, G31, G32, G33, G34, G40, G41, G42,
G50, G51, G71, G72, G73, G74, G75, G76, G90, G92, G94, G96, G97, G98, G99
Tapping: metric/inch single/multiple straight thread, taper thread, end face thread; variable pitch thread;
thread run out length, angle and speed can be set, executing the high-speed thread run-out; pitch:
0.001mm~500mm or 0.06tooth/inch~25400tooth/inch; tapping function
Spindle encoder: lines can be set (100p/r~5000p/r); Drive ratio between encoder and spindle is 1:1
Backlash compensation: 0 mm~10.000mm
Pitch error compensation: 300 compensation points for each axis; use constant distance or inflection
point to create data; the system executes the delicate linear compensation
Offset: 16 tool selections, 64 groups tool length compensation and tool nose radius compensation (offset
C)
Toolsetting method: fixed-point, trial cutting
Offset executing method: traversing tool or modifying coordinate offset
M00, M02, M20, M30, M03, M04, M05, M08, M09, M10, M11, M12, M32, M33, M41, M42, M43, M44,
M47, M48, M78, M79, M80, M96, M97, M98, M99, M91, M92, M93, M94, M21, M22, M23, M24;M
commands are defined by operator: M60~M74 realize the special function control
Up to 16 tools (T01□□~T16□□),setting tool post type, parameters to select too change course
Tool post type is set to 0 when the line-up tool is used
Speed switching value control: S 4-gear directly controlling output range is S01~S04; or 16-gear BCD
output range is S00~S15
Speed analog voltage control: S specifies the spindle speed per minute or the cutting surface speed
(constant surface speed) , outputs 0~10V voltage to spindle converter, supports 4-gear spindle speed
M41~M44 with stepless shifting gear
Support DAP03 servo spindle speed/position control mode switch, realize spindle, Z or X link function
I/O function diagnosis display
I/O interface:23 input/18 output interfaces
Assignment statement: complete assignment, many arithmetic and logic operations
Conditional statement: complete conditional judgement and skip
Display: 480×234 lattice, color LCD,LED or CCFL light in poor
Display method: Chinese or English window set by a parameter, displaying machining path of workpiece
in real-time
Program capacity: max. 255 programs, No. 0~252, 254 with 800KB, No.253 with 4MB(FLASH)
Edit method: edit in full screen, relative/absolute coordinate and compound program call, subprogram
multi-level embedding
Program drawing check
USB, RS232 interface;bidirectionally transmitting programs, parameters and offset between CNC and
USB, CNC and PC, CNC and CNC
Supporting software RS232, USB to download and upgrade
DA98 Series Digital AC Servo or DY3 Series Stepper Drive unit with pulse + direction signal input
3
GSK928TEa Turning CNC System User Manual
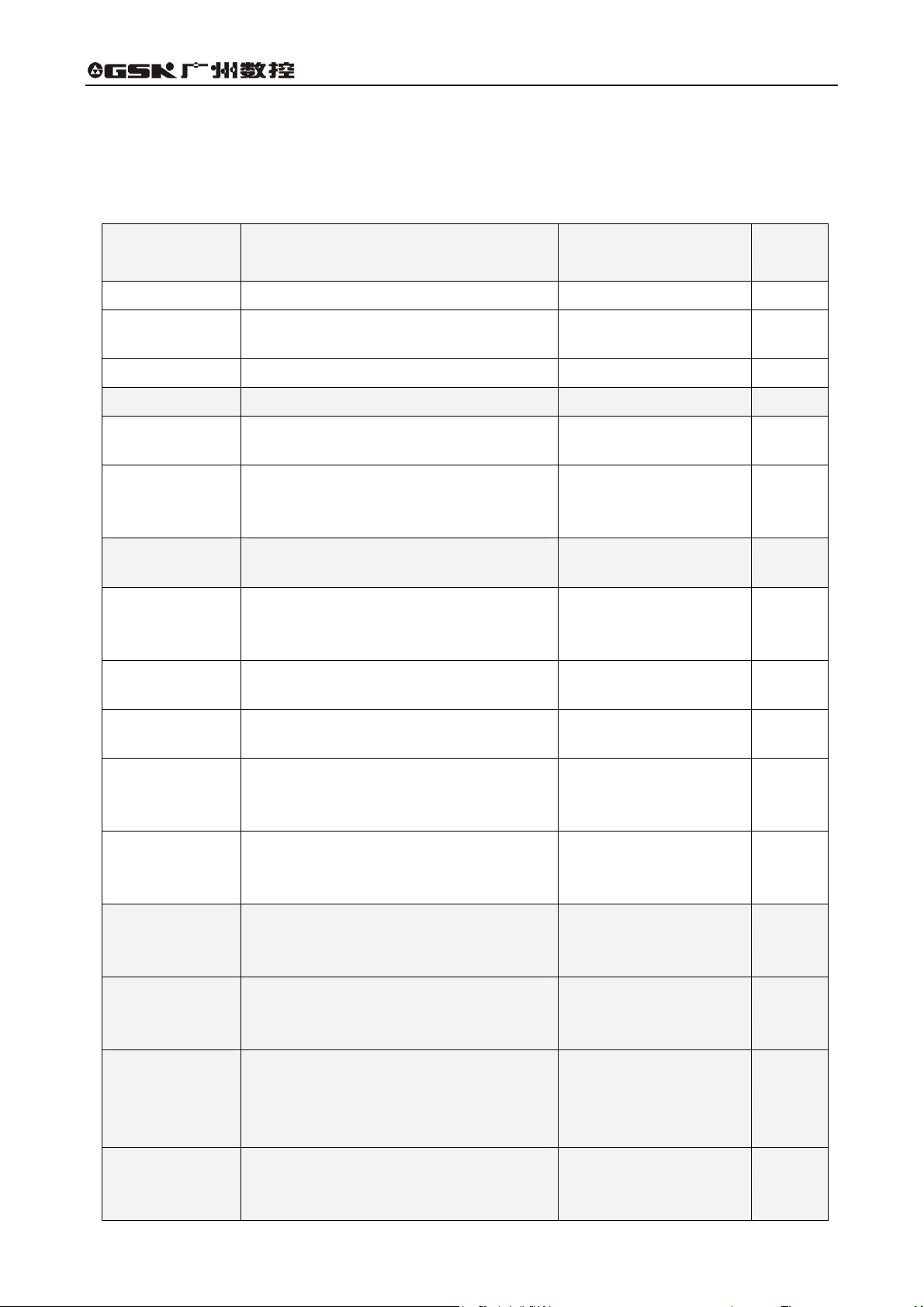
2.2 Functional difference between 928TEa and 928TCa turning CNC system
The manual is applied to two types of system: 928TEa, 928TCa. Functions of 928TCa turning CNC
system are less than those of 928TEa as follows:
Functional
928TEa 928TCa Remark
difference item
Controllable axis X, Y, Z X, Z
Rapid traverse
speed
Cutting speed
Max. radius of arc Max. machining: 1000m Max. machining: 100m
Tool nose radius
compensation
Pitch error
compensation
Automatic chamfer
function
Variable pitch
thread
Thread repair
function
Manual tapping
function
Spindle position
control
External MPG
control
Statement
programming
function
Program solid with
big capacity
Graph analog
function of program
run path, graph
zoom out function
M miscellaneous
function
C tool radius compensation,
Chapter 5 Tool Nose Radius Compensation
Fine linear pitch error compensation,
PROGRAMMING, Chapter 6 Pitch Error
Compensation
Automatic chamfer function,
Chapter 4.4 Chamfer Function
Variable pitch thread G34,
Chapter 4.5.2 G34-Variable Pitch Thread
Cutting
Manual tapping function,
4.4.12 Spindle Rotation Function
Switch position control and speed control,
OPERATION, Chapter 4.4.3.4 Setting Spindle
Working State
Support external MPG control function,
OPERATION, Chapter 4.4.9.4 External MPG
Operation
Statement programming function,
Chapter 9 Statement Programming
No. 253 program solid with big capacity,
OPERATION, Chapter 4.3.4.9 No.253 Program
Operation
Program movement path graph analog function,
graph zoom out function,
4.3.6.2 hp3 Analog Graph
Set Y permitted forbidding working state
(M47/M48),
Setting Spindle Working State
Max. 30000 mm /min Max. 15000 mm /min
(0.001~15000)mm/min (0.001~4000)mm/min
PROGRAMMING,
PROGRAMMING,
PROGRAMMING,
Thread repair function No the function
OPERATION, Chapter
OPERATION,
OPERATION, Chapter
OPERATION, Chapter 4.4.3.4
No the function
No the function
No the function
No the function
No the function
No the function
not support the function
No the function
No the function
No the function
not support the function
4

Operation Chapter Two Technical Specifications
M customize
command
Support M60~M74 customize to realize special
function control, PROGRAMMING, Chapter 10
Customize Command Programming
not support the function
5

GSK928TEa Turning CNC System User Manual
Chapter Three Operation Panel
The turning CNC system(system or CNC) uses the aluminum alloy three-D operation panel and its
appearance is as follows:
3.1 LCD Display
LCD display: CNC man-machine dialogue interface. Resolution 480×234 lattice TFT color LCD
display.
3.2 LED Status Indicator
LED indicates that the current working state of the system. There are 16 function keys with LED
indicators, the function executed by the corresponding key is valid when LED is ON, and it is invalid
when LED is OFF.
3.3 Keyboard
Based on GB/T 3168-1993 Numerical Control of Machine-Symbol, the system sets the following
symbol function keys which complete the corresponding functions when they are pressed as follows:
3.3.1 Character keys
Character keys include all required valid digit, letter, mathematic symbol and logic symbol.
In EDIT working mode, each letter key can switch into 2 or 3 letter keys; in other working mode, each
6

Operation Chapter Three System Operation Panel
letter key only expresses one letter key. (For example, I and I are on one key, the operator directly
press the key when “I” or “P” is required, and the system automatically indentifies other letters.)
Digit key: input all kind of data (0~9);
Letter key: input field, address, English letter;
Symbol key: +, -, *, /, minus sign, decimal and so on;
Logic key: >, =, <, and, or, ()and so on.
3.3.2 Working mode selection key
Marking with the symbols and characters, the working mode selection keys are pressed to
complete the corresponding function, and their definitions are as follows:
: select EDIT working mode
: select JOG working mode
: select AUTO working mode
: select PARAMETER working mode
: select OFFSET working mode
: select DIAGNOSIS working mode
3.3.3 Function keys
Press function keys with the visualization symbol and letter to complete the corresponding functions
and each symbol definition is as follows:
INCREASING RAPID OVERRIDE Increase rapid traverse override in JOG working mode
and G00 rapid traverse override in AUTO working mode.
REDUCING RAPID OVERRIDE: Reduce rapid traverse override in JOG working mode and
G00 rapid traverse override in AUTO working mode.
INCREASING FEEDRATE OVERRIDE: Increase feedrate override in JOG working mode and
G01 feedrate override in AUTO working mode.
REDUCING FEEDATE OVERRIDE: Reduce feedrate override in JOG working mode and
7

GSK928TEa Turning CNC System User Manual
G01 feedrate override in AUTO working mode.
X PROGRAM REFERENCE POINT(PROGRAM ZERO) RETURN : It is valid in JOG /AUTO
working mode. (program zero is called program reference point in the user manual.)
Z PROGRAM REFERENCE POINT (PROGRAM ZERO) RETURN : It is valid in JOG /AUTO
working mode.
X MACHINE ZERO (MACHINE ZERO) RETURN : It is valid in JOG /AUTO working mode.
(machine zero is called machine reference point in the user manual.)
Z or Y MACHINE ZERO(MACHINE REFERENCE POINT) RETURN: It is valid in JOG
/AUTO working mode.
DRY RUN: In AUTO working mode, whether M, S, T are valid is determined by the
parameter (bit parameter P401_d7), each axis coordinates automatically recover to the
previous ones before the system enters the DRY RUN working mode.
SINGLE BLOCK: A single block runs in AUTO working mode. It is hp function in other
working modes.
3.3.4 Cycle start and cycle pause (feed hold)key
Start and pause programs in AUTO working mode and each key symbol definition is as follows:
CYCLE START: Start to run programs in AUTO working mode; move coordinate axis in
JOG working mode.
CYCLE PAUSE (FEED HOLD ): pause the running in JOG or AUTO working mode; hp
function in other working modes.
【Note】
There is “hp(help) at top right on some keys, and there are 7 help keys hp0~hp6;hp is valid
when the main key is invalid in different working modes.
3.3.5 Manual axis control key
Manual key symbol definitions in JOG working mode are as follows:
X axis moves negatively in JOG working mode.
X axis moves positively in JOG working mode.
8

Operation Chapter Three System Operation Panel
Z or Y moves negatively in JOG working mode.
Z or Y moves positively in JOG working mode.
RAPID TRAVERSE/FEED Switching rapid traverse and feed in JOG working mode.
JOG STEP Selecting each step width or MPG feed in STEP/ MPG(Handwheel) working
mode; hp function in other working modes.
MPG(Handwheel) MPG control selection and axis selection in JOG working mode; hp
function in other working modes.
Z/Y selection in JOG working mode; hp function in other working modes.
STEP/JOG mode Switch STEP/JOG mode in JOG working mode.
3.3.6 Manual auxiliary function key
The following press keys are used to controlling and completing all miscellaneous function of the
machine and each key symbol definition is as follows:
Spindle rotation (CW) Spindle rotates clockwise.
Spindle stop Spindle stops.
Spindle rotation (CCW) Spindle rotates counterclockwise.
Cooling control Switch cooling ON/OFF.
Spindle gear shifting Select the speed of each gear when the machine is equipped
with multi-gear (up to 16 gears) spindle motor and control
loops.
Tool change Select the next tool number neighboring to the current one.
9
GSK928TEa Turning CNC System User Manual
3.3.7 Edit keys
Press key Name Function explanation
ENTER key Press it after the corresponding operation is performed.
INPUT key Input the required content.
ALTER key
DELETE key
ESCAPE
key
HOME key
END key
Switch character insert/alter state in EDIT working mode;
Special definition in other working modes.
Delete digit, letter, block or whole program in EDIT working
mode;
Special definition in other working modes.
Cancel the current input data or escape from the working
state;
escape from the current operation or setting.
“DRY RUN” in AUTO working mode;
Cursor moving the end of the line in EDIT working mode.
“STEP” in JOG working mode;
Cursor moving the end of the line in EDIT working mode.
“SINGLE/CONTINUOUS” executing programs in AUTO
SINGLE
hp0
hp1
BLOCK key
Cursor
movement
key
PAGE
UP/DOWN
working mode;
“SINGLE/CONTINUOUS” analog executing programs in
AUTO working mode;
hp function in other working modes.
Control cursor movement in EDIT/PARAMETER/OFFSET
working mode;
Hp function or other special definitions in other working
modes.
Display page up/down in EDIT/PARAMETER/OFFSET;
Special definition in JOG /AUTO working mode.
10

Operation Chapter Four System Operation
Chapter Four System Operation
This chapter introduces operations and notes of the system. Please read carefully before operation.
4.1 System ON/OFF, Initial State, Modal, and Safe Protection
4.1.1 Power on
There is not a power switch on the operation panel of the system. The operator installs it according to
the different machine to avoid bad effects to CNC system owing to the impaction of power supply.
Check before the system is turned on:
1) Ensure the machine state is normal;
2) Ensure the voltage meets the requirements;
3) Ensure the wiring is correct and firm.
The system is turned on as follows:
1) The master power switch of machine is turned on.
Switch on the power switch of the CNC system, and the system displays as Fig. 4-1. Press
any keys except for
2) The system orderly completes the following work after power-on:
z The system controls the program loading.
z The system automatically check itself and executes the initialization.
z The system loads and checks parameters.
z I/O interface initialization.
z The system loads and checks the operator programs.
, and the system enters into EDIT working mode.
Fig. 4-1 System initialization display window
【Note】
1)Must not press any keys on the system panel when the system is turned on, press
RESET key when the system enters the press key test window at the moment.
4.1.2 Power off
The system is turned off as follows:
11

GSK928TEa Turning CNC System User Manual
1) The power switch of the CNC is turned off.
2) The power switch of the machine is turned off.
Check before the system is turned off:
1) X, Z, Y are in the stop state;
2) Miscellaneous function(spindle, cooling) OFF;
3) Turn off the power supply.
【Note】
1) The system should be checked itself and initialized when it is turned on firstly( it is
completed by the machine manufacturer, and the operator cannot execute the operation,
otherwise, the parameter set by the machine manufacture will lose).
2) Operations related to turn off the machine power supply are referred to the operator manual
machine manufacturer.
4.1.3 System, program initial and modal
4.1.3.1 Initial and modal
The initial mode of the system is defined to be a special initial state of all functions set by itself when
the system is turned on; all auxiliary functions do not execute the actual output.
The modal of the system is defined to be their kept states after the system executes all functions.
Initial mode and modal of the system:
System state Initial mode Modal
Machine coordinate system
of the system
Tool nose coordinate system
of the system
Conversion spindle speed:S
Spindle gear
MANUAL slow feed/rapid feed state Slow feed Keep till being changed
Feedrate override Keep last power-on state Keep till being changed
Rapid override Keep last power-on state Keep till being changed
Spindle state M05 spindle stop Keep till being changed
Cooling state M09 cooling OFF Keep till being changed
Chuck state M11 chuck release Keep till being changed
Lubricating state M33 lubricating OFF Keep till being changed
T number state Keep last power-on state Keep till being changed
Tailstock state M79 tailstock run-out state Keep till being changed
Set spindle speed/position mode M48 Keep till being changed
Keep last power-on state Keep till being changed
Keep last power-on state Keep till being changed
In Auto mode:30mm/min Cutting feedrate:F
JOG mode: Keep last power-on state
In
Keep last power-on state Keep till being changed
Shifting gear spindle gear:S0
Conversion spindle gear:M41
Keep till being changed
Keep till being changed
4.1.3.2 Initial mode and modal of program
The initial mode is the automatic initialization setting state before the system executes the machining
program; i.e. the initial default state of the default programming word and speed word.
Program initialization state of the system:
G command:G00, G40, G97, G98;
Cutting speed:30mm/min;
Miscellaneous function: current state;
System coordinates: current coordinates are those of the last automatic executing
program or manual operation
12
 Loading...
Loading...