Page 1

1
Page 2

DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Information in this document is subject to change without notice.
© 2015 D-Link Corporation. All rights reserved.
Reproduction in any manner whatsoever without the written permission of D-Link Corporation is strictly
forbidden.
Trademarks used in this text: D-Link and the D-Link log o are tr ademark s of D-Link Corporation; Microsoft and
Windows are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Other trademarks and trade names may be used in this document to refer to either the entities claiming the
marks and names or their products. D-Link Corporation disclaims any proprietary interest in trademarks and
trade names other than its own.
FCC Warning
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to
Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses,
and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with this user’s guide, may
cause harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely
to cause harmful interference in which case the user will be required to correct the interference at his own
expense.
CE Mark Warning
This is a Class A product. In a domestic environment, this product may cause radio interference in which case
the user may be required to take adequate measures.
Warnung!
Dies ist ein Produkt der Klasse A. Im Wohnbereich kann dieses Produkt Funkstoerungen verursachen. In
diesem Fall kann vom Benutzer verlangt werden, angemessene Massnahmen zu ergreifen.
Precaución!
Este es un producto de Clase A. En un entorno doméstico, puede causar interferencias de radio, en cuyo case,
puede requerirse al usuario para que adopte las medidas adecuadas.
Attention!
Ceci est un produit de classe A. Dans un environnement domestique, ce produit pourrait causer des
interférences radio, auquel cas l`utilisateur devrait prendre les mesures adéquates.
Attenzione!
Il presente prodotto appartiene alla classe A. Se utilizzato in ambiente domestico il prodotto può causare
interferenze radio, nel cui caso è possibile che l`utente debba assumere provvedimenti adeguati.
VCCI Warning
May, 2015
ii
Page 3

DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Table of Contents
1. Introduction ................................................................................................................................................................... 1
Audience ............................................................................................................................................................................ 1
Standard Mode and Surveillance Mo de ............................................................................................................................. 1
Other Documentation ......................................................................................................................................................... 1
Conventions ....................................................................................................................................................................... 1
Notes, Notices, and Caut io ns ............................................................................................................................................ 2
2. Product Introduction ..................................................................................................................................................... 3
DGS-1100-10MP ............................................................................................................................................................... 4
Front Panel ................................................................................................................................................................... 4
Rear Panel .................................................................................................................................................................... 4
DGS-1100-10MPP ............................................................................................................................................................. 6
Front Panel ................................................................................................................................................................... 6
Rear Panel .................................................................................................................................................................... 6
DGS-1100-26MP ............................................................................................................................................................... 8
Front Panel ................................................................................................................................................................... 8
Rear Panel .................................................................................................................................................................... 9
DGS-1100-26MPP ........................................................................................................................................................... 10
Front Panel ................................................................................................................................................................. 10
Rear Panel .................................................................................................................................................................. 11
3. Hardware Installation .................................................................................................................................................. 12
Step 1: Unpacking ............................................................................................................................................................ 12
Packing Contents ........................................................................................................................................................ 12
Step 2: Switch Installation ................................................................................................................................................ 12
Desktop or Shelf Installation ....................................................................................................................................... 12
Rack Installation ......................................................................................................................................................... 12
Step 3: Plugging in the AC Power Cord ........................................................................................................................... 14
Power Failure .............................................................................................................................................................. 14
Grounding the Switch ................................................................................................................................................. 14
4. Web-based Switch Configuration .............................................................................................................................. 16
Management Options ....................................................................................................................................................... 16
Connecting using the Web User Interface ....................................................................................................................... 16
Logging onto the Web User Interface .............................................................................................................................. 17
Smart Wizard ................................................................................................................................................................... 18
Web User Interface (Web UI) ........................................................................................................................................... 22
Areas of the User Interface ......................................................................................................................................... 22
5. Device Information ...................................................................................................................................................... 23
6. System .......................................................................................................................................................................... 24
System Information Settings ............................................................................................................................................ 24
IPv4 Interface ................................................................................................................................................................... 24
IPv6 Interface ................................................................................................................................................................... 25
Port Configuration ............................................................................................................................................................ 25
Port Settings ............................................................................................................................................................... 25
Jumbo Frame .............................................................................................................................................................. 27
PoE .................................................................................................................................................................................. 28
iii
Page 4

DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch Web UI Reference Guide
PoE System ................................................................................................................................................................ 28
PoE Status .................................................................................................................................................................. 29
PoE Configuration ....................................................................................................................................................... 30
System Log ...................................................................................................................................................................... 31
System Log Settings ................................................................................................................................................... 31
System Log Server Settings ....................................................................................................................................... 31
System Log ................................................................................................................................................................. 32
Time ................................................................................................................................................................................. 33
Clock Settings ............................................................................................................................................................. 33
Time Zone Settings ..................................................................................................................................................... 33
SNTP Settings ............................................................................................................................................................ 34
Time Profile ...................................................................................................................................................................... 35
7. Management ................................................................................................................................................................ 36
User Account Settings ..................................................................................................................................................... 36
SNMP ............................................................................................................................................................................... 37
SNMP Global Settings ................................................................................................................................................ 38
SNMP Community Table Settings .............................................................................................................................. 38
SNMP Host Table Settings ......................................................................................................................................... 39
HTTP/HTTPS ................................................................................................................................................................... 40
D-Link Discovery Protocol ................................................................................................................................................ 40
8. Layer 2 Features .......................................................................................................................................................... 42
FDB .................................................................................................................................................................................. 42
Static FDB ................................................................................................................................................................... 42
MAC Address Table Settings...................................................................................................................................... 43
MAC Address Table .................................................................................................................................................... 44
VLAN ................................................................................................................................................................................ 45
802.1Q VLAN .............................................................................................................................................................. 45
Port-based VLAN ........................................................................................................................................................ 45
Management VLAN .................................................................................................................................................... 46
Asymmetric VLAN ....................................................................................................................................................... 46
VLAN Interface ........................................................................................................................................................... 46
Auto Surveillance VLAN ............................................................................................................................................. 49
Voice VLAN................................................................................................................................................................. 51
Spanning Tree ................................................................................................................................................................. 54
STP Global Settings ................................................................................................................................................... 55
STP Port Settings ....................................................................................................................................................... 55
ERPS ............................................................................................................................................................................... 56
Loopback Detection ......................................................................................................................................................... 57
Link Aggregation .............................................................................................................................................................. 59
L2 Multicast Control ......................................................................................................................................................... 62
IGMP Snooping .......................................................................................................................................................... 62
MLD Snooping ............................................................................................................................................................ 64
Multicast Filtering ........................................................................................................................................................ 66
LLDP ................................................................................................................................................................................ 67
LLDP Global Settings ................................................................................................................................................. 67
LLDP Neighbor Port Information ................................................................................................................................ 67
9. Quality of Service (QoS) ............................................................................................................................................. 68
iv
Page 5

DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch Web UI Reference Guide
802.1p Priority ............................................................................................................................................................. 68
Port Rate Limiting ....................................................................................................................................................... 69
10. Security ........................................................................................................................................................................ 70
DHCP Snooping ............................................................................................................................................................... 70
Safeguard Engine Settings .............................................................................................................................................. 71
Traffic Segmentation ........................................................................................................................................................ 71
Storm Control ................................................................................................................................................................... 72
DoS Attack Prevention Settings ....................................................................................................................................... 72
Zone Defense Settings .................................................................................................................................................... 73
SSL .................................................................................................................................................................................. 74
SSL Global Settings .................................................................................................................................................... 74
11. OAM .............................................................................................................................................................................. 75
Cable Diagnostics ............................................................................................................................................................ 75
12. Monitoring .................................................................................................................................................................... 76
Statistics ........................................................................................................................................................................... 76
Port Counters .............................................................................................................................................................. 76
Mirror Settings .................................................................................................................................................................. 77
13. Green ............................................................................................................................................................................ 78
Power Saving ................................................................................................................................................................... 78
EEE .................................................................................................................................................................................. 80
14. ONVIF ........................................................................................................................................................................... 81
Global Status.................................................................................................................................................................... 81
IP-Camera Information ..................................................................................................................................................... 82
IPC Settings ................................................................................................................................................................ 82
NVR Information .............................................................................................................................................................. 82
15. Save and Tools ............................................................................................................................................................ 84
Save Configuration .......................................................................................................................................................... 84
Firmware Information ....................................................................................................................................................... 84
Firmware Upgrade & Backup ........................................................................................................................................... 84
Firmware Upgrade from HTTP ................................................................................................................................... 85
Firmware Upgrade from TFTP .................................................................................................................................... 85
Firmware Backup to HTTP ......................................................................................................................................... 85
Firmware Backup to TFTP .......................................................................................................................................... 86
Configuration Restore & Backup ..................................................................................................................................... 87
Configuration Restore from HTTP .............................................................................................................................. 87
Configuration Restore from TFTP .............................................................................................................................. 87
Configuration Backup to HTTP ................................................................................................................................... 88
Configuration Backup to TFTP ................................................................................................................................... 88
Log Backup ...................................................................................................................................................................... 89
Log Backup to HTTP .................................................................................................................................................. 89
Log Backup to TFTP ................................................................................................................................................... 89
Ping .................................................................................................................................................................................. 90
Reset ................................................................................................................................................................................ 90
Reboot System ................................................................................................................................................................ 91
16. Appendix A - Ethernet Technology ........................................................................................................................... 92
Gigabit Ethernet Technology ........................................................................................................................................... 92
v
Page 6

DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Fast Ethernet Technology ................................................................................................................................................ 92
Switching Technology ...................................................................................................................................................... 93
17. Appendix B - Technical Specifications ..................................................................................................................... 94
Hardware Specifications .................................................................................................................................................. 94
Key Components / Performance ................................................................................................................................ 94
Port Functions ............................................................................................................................................................. 94
Physical & Environment .............................................................................................................................................. 94
Emission (EMI) Certifications...................................................................................................................................... 94
Safety Certifications .................................................................................................................................................... 94
Features ........................................................................................................................................................................... 94
L2 Features ................................................................................................................................................................. 94
L2 Multicasting ............................................................................................................................................................ 94
VLAN ........................................................................................................................................................................... 94
Quality of Service (QoS) ............................................................................................................................................. 95
Security ....................................................................................................................................................................... 95
Management ............................................................................................................................................................... 95
Power Saving .............................................................................................................................................................. 95
Surge Protection ......................................................................................................................................................... 95
18. Appendix C – Rack mount Instructions .................................................................................................................... 96
vi
Page 7

1. Introduction
This manual’s command descriptions are based on the software release 1.00. The commands listed
here are the subset of commands that are supported by the DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series switch.
Audience
This reference manual is intended for network administrators and other IT networking professionals
responsible for managing the switch by using the Web User Interface (Web UI). The Web UI is the
secondary management interface to the DGS-11 00 M P/M PP Series switch, which will be general l y
be referred to simply as ‘the switch’ within this manual. This manual is written in a way that assumes
that you already have the experience and knowledge of Ethernet and modern networking principles
for Local Area Networks.
Standard Mode and Surveillance Mode
The DGS-1100 MP/MPP series switches support Standard Mode and Surveillance Mode Web UI
types. Standard Mode is used to manage the network and system elements of the switch.
Surveillance Mode is a dedicated user interface designed for monitoring and managing the
surveillance and IP security devices on your network.
D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
To switch between the two types of interfaces, you can re-run the Smart Wizard that is presented
when you access the web interface of the device. For more information, please refer to the Web UI
Reference Guide for the appropriate mode.
Other Documentation
The documents below are a further source of information in regards to configuring and
troubleshooting the switch. All the documents are available either from the CD, bundled with this
switch, or from the D-Link website. Other documents related to this switch are:
• Getting started Guide
• D-Link Network Assistant (DNA) User Guide
• D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Surveillanc e Mo de Web UI Reference Guide
Conventions
Convention Description
Boldface Font
Indicates a button, a toolbar icon, menu, or menu item. For example:
Open the File menu and choose Cancel. Used for emphasis. May
also indicate system messages or prompts appearing on screen.
For example: You have mail. Bold font is also used to represent
filenames, program names and commands. For example: use the
copy command.
Initial capital letter Indicates a window name. Names of keys on the keyboard have
initial capitals. For example: Press Enter.
Menu Name > Menu
Option
Blue Courier Font
Indicates the menu structure. Device > Port > Port Properties
means the Port Properties menu option under the Port menu
option that is located under the Device menu.
This convention is used to represent an example of a screen
console display including example entries of CLI command input
with the corresponding output.
1
Page 8

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Notes, Notices, and Cautions
Below are examples of the three types of indicators used in this manual. When administering your
switch using the information in this document, you should pay special attention to these indicators.
Each example below provides an explanatory remark regarding each type of indicator.
NOTE: A note indicates important information that helps you make better use of
your device.
NOTICE: A notice indicates either potential damage to hardware or loss of data
and tells you how to avoid the problem.
CAUTION: A caution indicates a potential for property damage, personal injury,
or death.
2
Page 9

2. Product Introduction
The DGS-1100 MP/MPP series Smart Switch is the world’s first PoE switch with ONVIF support.
This allows it to recognize ONVIF devices and integrate seamlessly with your surveillance network.
Various power budgets, support for high powered PoE standards (MPP series) and 6 KV surge
protection make the DGS-1100 MP/MPP series a critical part of your surveillance infrastructure.
The DGS-1100 MP/MPP series switches can change modes between ‘Smart Switch’ and
‘Surveillance Switch’ modes, making them suitable for a variety of applications. An intuitive web user
interface makes advanced features avai lable in the Standard Mode, with full PoE capab ilit ies and
high link speeds improving deployment times for PoE devices.
The switches are designed to be energy efficient with support for IEEE 802.3az Energy Efficient
Ethernet (EEE) and D-Link Green Technologies. They include multiple features, such as cable
length detection, port status detection and the ability to hibernate under low utilization. If the switch
detects no activity on any of the switch ports, it can be hibernated to conserve power.
The DGS-1100 MPP series provides multiple PoE ports that support I EE E 802. 3bt, allowing the
latest high-powered PoE devices to be used with the switch. Automatic device identification, video
traffic optimization and health diagnostic tools provide an intelligent solution to your enterprise
network requirements.
D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
3
Page 10

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
DGS-1100-10MP
8-Port 10/100/1000 Mbps + 2-Port SFP 10 00 Mbps Po E switch
Front Panel
Figure 2-1 - DGS-1100-10MP Front Panel
Power LED: The Power LED lights up when the switch is connected to a power source.
Link/Act/Speed LED (Ports 1-8):
Solid Green: When there is a secure 1000Mbps connection at the port.
Blinking Green or Amber: Indicates that the switch is either sending or receiving data to the
port.
Solid Amber: Indicates that the port is running at 10/100Mbps.
Light off: No link.
PoE Mode (Ports 1- 8):
Green: Indicates that PoE mode is active.
Amber: Indicates that there is an issue with the PoE mode activating prop erly.
Light off: Indicates that PoE mode is not active.
Link/Act/Speed LED (Ports 9-10):
Solid Green: There is a secure 1000Mbps connection at the port.
Blinking Green: There is reception or transmission occurring at the port.
Light off: No link.
Reset: By pressing the Reset butt on until the power LED turns amber, the switch will change back to
the default configuration and all changes will be lost.
Rear Panel
Figure 2-2 – DGS-1100-10MP Rear Panel
4
Page 11

Power: The power port is where to connect the AC power cord.
CAUTION: The SFP ports should use UL listed Optical Transceiver product,
Rated Laser Class I. 3.3Vdc.
CAUTION: This equipment is to be connected only to PoE networks without
routing to the outside plant.
D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
5
Page 12

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
DGS-1100-10MPP
8-Port 10/100/1000 Mbps + 2-Port SFP 10 00 Mbps Po E switch
Front Panel
Figure 2-3 – DGS-1100-10MPP Front Panel
Power LED: The Power LED lights up when the switch is connected to a power source.
Link/Act/Speed LED (Ports 1-8):
Solid Green: When there is a secure 1000Mbps connection at the port.
Blinking Green or Amber: Indicates that the switch is either sending or receiving data to the
port.
Solid Amber: Indicates that the port is running at 10/100Mbps.
Light off: No link.
PoE Mode (Ports 1- 8):
Green: Indicates that PoE mode is active.
Amber: Indicates that there is an issue with the PoE mode activating properly.
Light off: Indicates that PoE mode is not active.
Link/Act/Speed LED (Ports 9-10):
Solid Green: There is a secure 1000Mbps connection at the port.
Blinking Green: There is reception or transmission occurring at the port.
Light off: No link.
Reset: By pressing the Reset butt on until the power LED turns amber, the switch will change back to
the default configuration and all changes will be lost.
Rear Panel
Figure 2-4 – DGS-1100-10MPP Rear Panel
6
Page 13

Power: Connect the supplied AC power cable to this port.
CAUTION: The SFP ports should use UL listed Optical Transceiver product,
Rated Laser Class I. 3.3Vdc.
CAUTION: This equipment is to be connected only to PoE networks without
routing to the outside plant.
D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
7
Page 14

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
DGS-1100-26MP
24-Port 10/100/1000 Mbps + 2-Port Combo 1000BASE-T/SFP PoE switch
Front Panel
Figure 2-5 – DGS-1100-26MP Front Panel
Power LED: The Power LED lights up when the switch is connected to a power source.
Link/Act/Speed LED (Ports 1-24):
Solid Green: When there is a secure 1000Mbps connection at the port.
Blinking Green or Amber: Indicates that the switch is either sending or receiving data to the
port.
Solid Amber: Indicates that the port is running at 10/100Mbps.
Light off: No link.
PoE Mode (Ports 1- 24):
Green: Indicates that PoE mode is active.
Amber: Indicates that there is an issue with the PoE mode acti vat ing prop er ly.
Light off: Indicates that PoE mode is not active.
Link/Act/Speed LED (Ports 25-26):
Solid Green: There is a secure 1000Mbps connection at the port.
Blinking Green: There is reception or transmission occurring at the port.
Solid Amber: Indicates that the port is running at 10/100Mbps.
Light off: No link.
LED Mode Button: Pressing this button will change the LED behavior from Link mode, and PoE
Mode.
Reset: By pressing the Reset butt on until the power LED turns amber, the switch will change back to
the default configuration and all changes will be lost.
NOTE: The LED behavior for ports 1- 24 will switch between Link mode and PoE
mode when the PoE mode is active.
8
Page 15

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Rear Panel
Figure 2-6 – DGS-1100-26MP Rear Panel
Power: Connect the supplied AC power cable to this port.
CAUTION: The SFP ports should use UL listed Optical Transceiver product,
Rated Laser Class I. 3.3Vdc.
CAUTION: This equipment is to be connected only to PoE networks without
routing to the outside plant.
9
Page 16

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
DGS-1100-26MPP
24-Port 10/100/1000 Mbps + 2-Port Combo 1000BASE-T/SFP PoE switch
Front Panel
Figure 2-7 – DGS-1100-26MPP Front Panel
Power LED: The Power LED lights up when the switch is connected to a power source.
Link/Act/Speed LED (Ports 1-24):
Solid Green: When there is a secure 1000Mbps connection at the port.
Blinking Green or Amber: Indicates that the switch is either sending or receiving data to the
port.
Solid Amber: Indicates that the port is running at 10/100Mbps.
Light off: No link.
PoE Mode (Ports 1- 24):
Green: Indicates that PoE mode is active.
Amber: Indicates that there is an issue with the PoE mode acti vat ing prop er ly.
Light off: Indicates that PoE mode is not active.
Link/Act/Speed LED (Ports 25-26):
Solid Green: There is a secure 1000Mbps connection at the port.
Blinking Green: There is reception or transmission occurring at the port.
Solid Amber: Indicates that the port is running at 10/100Mbps.
Light off: No link.
LED Mode Button: Pressing this button will change the LED behavior from Link mode, and PoE
Mode.
Reset: By pressing the Reset butt on until the power LED turns amber, the switch will change back to
the default configuration and all changes will be lost.
NOTE: The LED behavior for ports 1- 24 will switch between Link mode and PoE
mode when the PoE mode is active.
10
Page 17

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Rear Panel
Figure 2-8 – DGS-1100-26MPP Rear Panel
Power: Connect the supplied AC power cable to this port.
CAUTION: The SFP ports should use UL listed Optical Transceiver product,
Rated Laser Class I. 3.3Vdc.
CAUTION: This equipment is to be connected only to PoE networks without
routing to the outside plant.
11
Page 18

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
3. Hardware Installation
This chapter provides unpacking and installation information for the D-Link switch.
Step 1: Unpacking
Open the shipping carton and carefully unpack its contents. Please consult the packing list located
below to make sure all items are present and undamaged. If any item is missing or damaged, please
contact your local D-Link reseller for a replacement.
Packing Contents
• One D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series switch
• One AC power cord
• Four rubber feet
• Screws and two mounting brackets
• One accessory kit for a ground screw
• One Multi-lingual Getting Started Guide
• One CD with User Manual
Step 2: Switch Installation
For safe switch installation and operation, it is recommended that you:
• Visually inspect the power cord to see that it is secured fully to the AC power connector.
• Make sure that there is proper heat dissipation and adequate ventilation around the switch.
• Do not place heavy objects on the switch.
Desktop or Shelf Installation
When installing the switch on a desktop or shelf, the rubber feet included with the device must be
attached on the bottom at each corner of the device’s base. Allow enough ventilation space between
the device and the objects around it.
Figure 3-1 – Attach the adhesive rubber pads to the bottom
Rack Installation
The switch can be mounted in an EIA standard size 19-inch rack, which can be placed in a wiring
closet with other equ ipment.
CAUTION: Ensure the power cable is disconnected before installing the switch.
12
Page 19
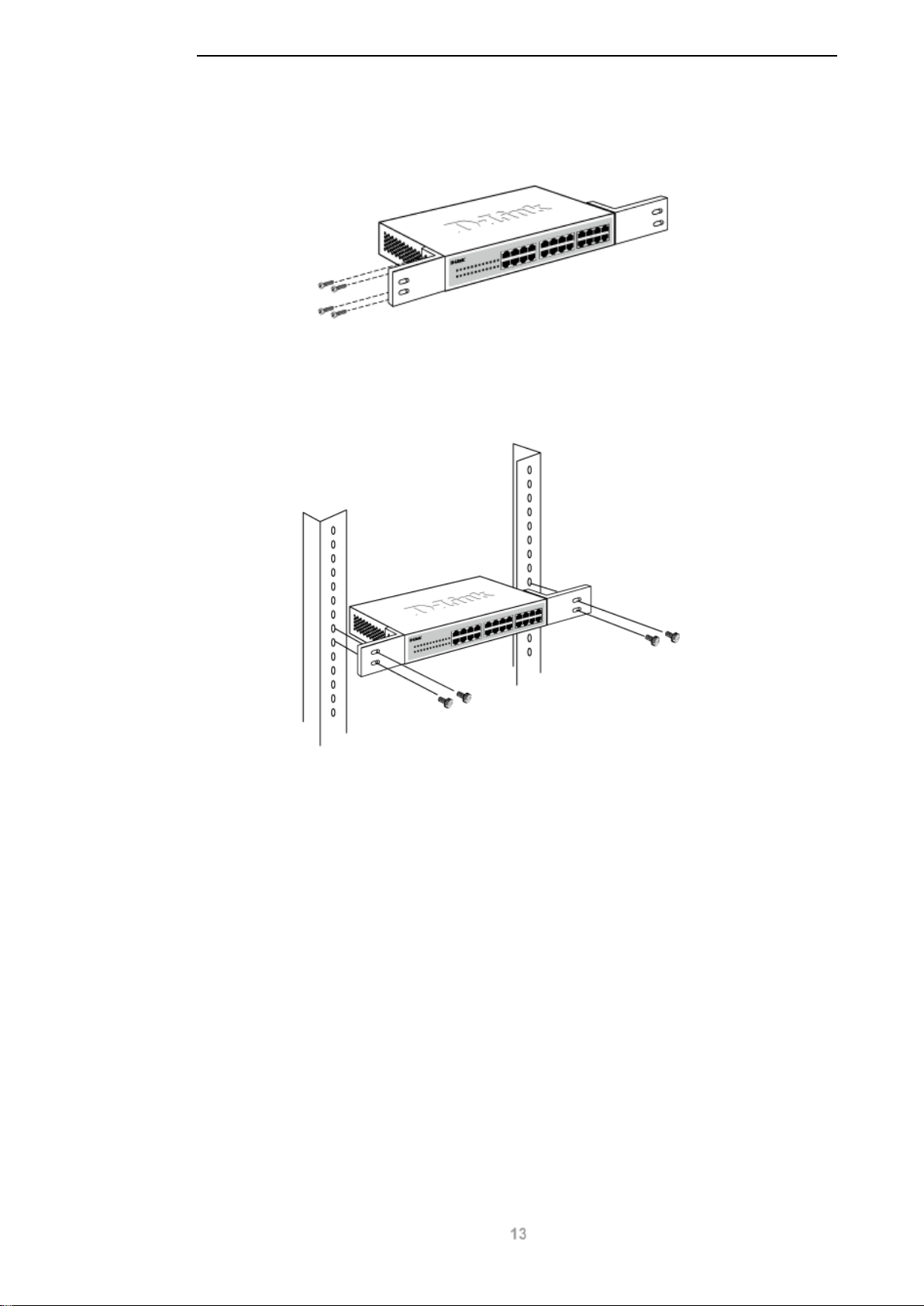
D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
To install, attach the mounting brackets to the switch’s side panels (one on each side) and secure
them with the screws provided.
Figure 3-2 – Attach the mounting brackets to the switch
Then, use the screws provided with the equipment rack to mount the switch in the rack.
Figure 3-3 – Mount the switch in the rack or chassis
Please be aware of following safety Instructions when installing:
A) Elevated Operating Ambient - If installed in a closed or multi-unit rack assembly, the operating
ambient temperature of the rack environment may be greater than room ambient. Therefore,
consideration should be given to installing the equipment in an environment compatible with the
maximum ambient temperature (Tma) specified by the manufacturer.
B) Reduced Air Flow - Installation of the equipment in a rack should be such that the amount of air
flow required for safe operation of the equipment is not compromised.
C) Mechanical Loading - Mounting of the equipment in the rack should be such that a hazardous
condition is not achieved due to uneven mechanical loading.
D) Circuit Overloading - Consideration should be given to the connection of the equipment to the
supply circuit and the effect that overloading of the circuits might have on overcurrent protection and
supply wiring. Appropriate consideration of equipment nameplate ratings should be used when
addressing this concern.
E) Reliable Earthing - Reliable earthing of rack-mounted equipment should be maintained. Particular
attention should be given to supply connections other than direct connections to the branch circuit
(e.g. use of power strips)."
13
Page 20

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Step 3: Plugging in the AC Power Cord
Users may now connect the AC power cord into the rear of the switch and to an electrical outlet
(preferably one that is grounded and surge protected).
Figure 3-4 – Plugging the switch into an outlet
Power Failure
As a precaution, the switch should be unplugged in case of power failure. When power is resumed,
the switch should be plugg ed back in.
Grounding the Switch
This section describes how to connect the DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series switch to ground. You must
complete this procedure before powering your switch.
Required Tools and Equipment
• Ground screws (included in the accessory kit): One M4 x 6 mm (metric) pan-head s c r ew
• Ground cable (not included in the accessory kit): The grounding cable should be sized
according to local and national installation requirements. Depending on the power supply
and system, a 12 to 6 AWG copper conductor is required for U.S installation. Commercially
available 6 AWG wire is recommended. The length of the cable depends on the proximity of
the switch to proper grounding facilities.
• A screwdriver (not included in the accessory kit)
Follow these steps to ground the switch:
Step 1: Verify that the switch is not connected to a power supply.
Step 2: Use the ground cable to place the #8 terminal lug ring on top of the ground-screw opening,
as seen in the figure below.
Step 3: Insert the ground screw into the ground-screw opening.
Step 4: Using a screwdriver, tighten the ground screw to secure the ground cable to the switch.
Step 5: Attach the terminal lug ring at the other end of the grounding cable to an appropriate
grounding stud or bolt on rack where the switch is installed.
Step 6: Verify if the connections at the ground connector on the switch and the rack are securely
attached.
14
Page 21

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Figure 3-5 – Ground cable, screw and #8 terminal lug rings
CAUTION: This equipment is to be connected only to PoE networks without
routing to the outside plant.
15
Page 22
D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
4. Web-based Switch Configuration
Management Options
Connecting using the Web User Interface
Logging onto the
Smart Wizard
Web User Interface (Web UI)
Management Options
The switch provides multiple access platforms that can be used to configure, manage and monitor
networking features available on the switch. Currently there are three management platforms
available and they are described below.
Web-based Management Interface
After successfully installin g the switch, the user can configure the switch, monitor the LED panel, and
display statistics graphically using a Web browser, such as Microsoft® Internet Explorer, Opera
Firefox, Safari, or Google Chrome.
SNMP-based Management
The switch can be managed with an SNMP-compatible console program. The switch supports
SNMP version 1.0, and version 2c. The SNMP agent decodes the incoming SNMP messages and
responds to requests with MIB objects stored in the database. The SNMP agent updates the MIB
objects to generate statistics and counters.
D-Link Network Assistant
DNA (D-Link Network Assistant) included on the installation CD is a program for discovering DGS1100 MP/MPP Series switches with the same L2 network segment connected to your PC. This tool
can support windows 2000, XP, Vista, and Windows 7.
Connecting using the Web User Interface
Most software functions of the DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series switches can be managed, configured
and monitored via the embedded web-based (HTML) interface. Manage the switch from remote
stations anywhere on the network through a standard web browser. The web browser acts as a
universal access tool and can communicate directly with the switch using the HTTP or HTTPS
protocol.
You need the following equipment to begin the web configuration of your device:
• A PC with a RJ-45 Ethernet connection
• A standard Ethernet cable
Figure 4-1 – Connecting to a DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series switch
16
Page 23
D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Connect the Ethernet cable to any of the ports on the front panel of the switch and to the Ethernet
port on the PC.
Logging onto the Web User Interface
To access the Web UI, simply open a web browser and enter the switch’s default IP address into the
address bar. Make sure that the IP address of the management PC is in the same subnet as the IP
address of the switch you are trying to connect to.
NOTE: The default IP address of the switch is 10.90.90.90, with a subnet mask
of 255.0.0.0.
NOTE: The default username is ‘admin’ and password is ‘admin’.
After successfully connecting to the Web UI, the Smart Wizard will be launched.
17
Page 24
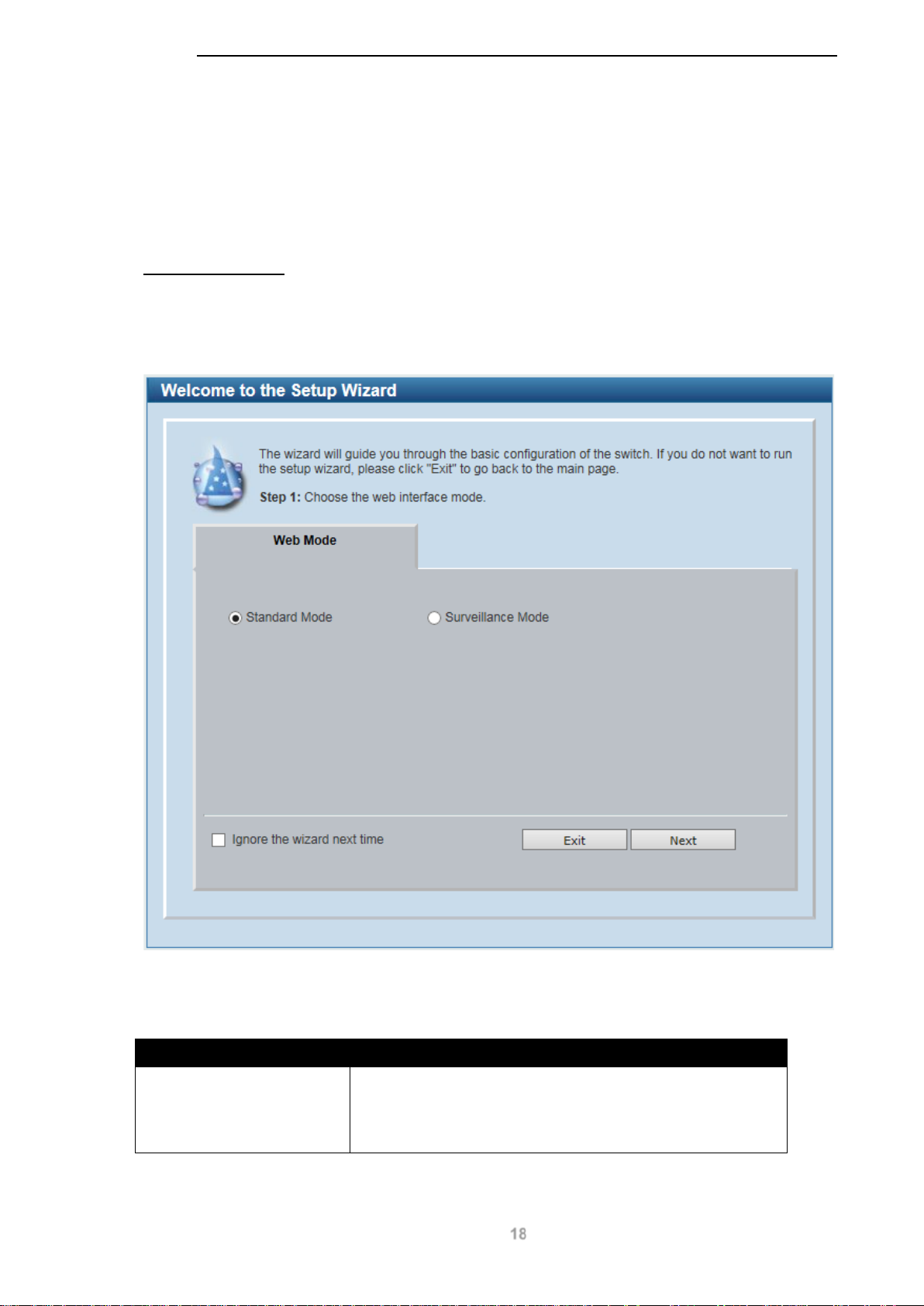
Smart Wizard
The Smart Wizard is a configuration utility that is launched the first time the Web UI is accessed. It
allows users to configure basic settings such as the switch mode, management IP and password. It
can also be used to switch between Standard Mode and Surveillance Mode Web UI types.
Step 1 – Web Mode
The initial page allows the user to choose between Standard Mode and Surveillance Mode on the
switch. This can be changed at any time by returning to the Smart Wizard.
For more information on the Surveillance Mode features of the switch, please refer to the
Surveillance Mode Web UI Reference Guide.
D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Figure 4-2 Web Mode window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
Web Mode Select the Standard Mode option to continue the Smart
Wizard in Standard Mode.
Please refer to the Surveillance Mode Web UI Reference
Guide for more information on Surveillance Mode.
Tick the Ignore the wizard next time option to skip the Smart Wizard on the next login.
18
Page 25
D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Click the Exit button to discard the changes made, exit the Smart Wizard, and continue to the Web
UI.
Click the Next button to accept the changes made and continue to the next step.
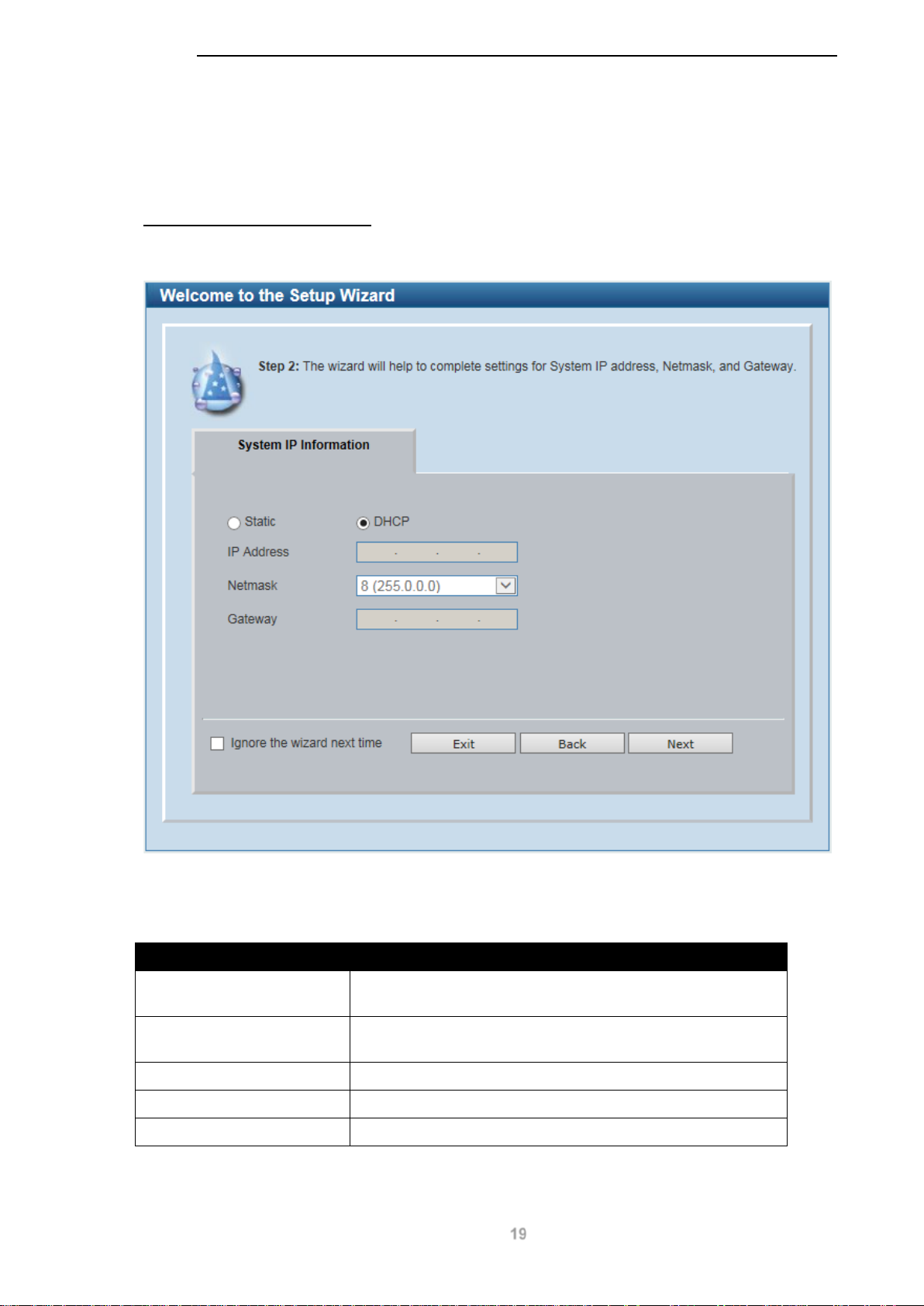
Step 2 – System IP Information
In this window, the user can configure the IP address assignment method, the static IP address,
netmask and gateway address.
Figure 4-3 System IP Information window
The fields that can be c onf i gur ed are des c ribed be lo w:
Parameter Description
Static
Select this option to manually configure and use IP address
settings on this switch.
DHCP
Select this option to obtain IP address settings from a DHCP
server.
IP Address
Netmask
Gateway
Enter the IP address of the switch here.
Select the netmask option here.
Enter the default gateway IP address here.
Tick the Ignore the wizard next time option to skip the Smart Wizard on the next login.
19
Page 26
D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Click the Exit button to discard the changes made, exit the Smart Wizard, and continue to the Web
UI.
Click the Next button to accept the changes made and continue to the next step.
Step 3 – Admin Password
In this window, the user can set the password used with the admin account.
Tick the Ignore the wizard next time option to skip the Smart Wizard on the next login.
Click the Exit button to discard the changes made, exit the Smart Wizard, and continue to the Web
UI.
Click the Next button to accept the changes made and continue to the next step.
Figure 4-4 Admin Password
20
Page 27
D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
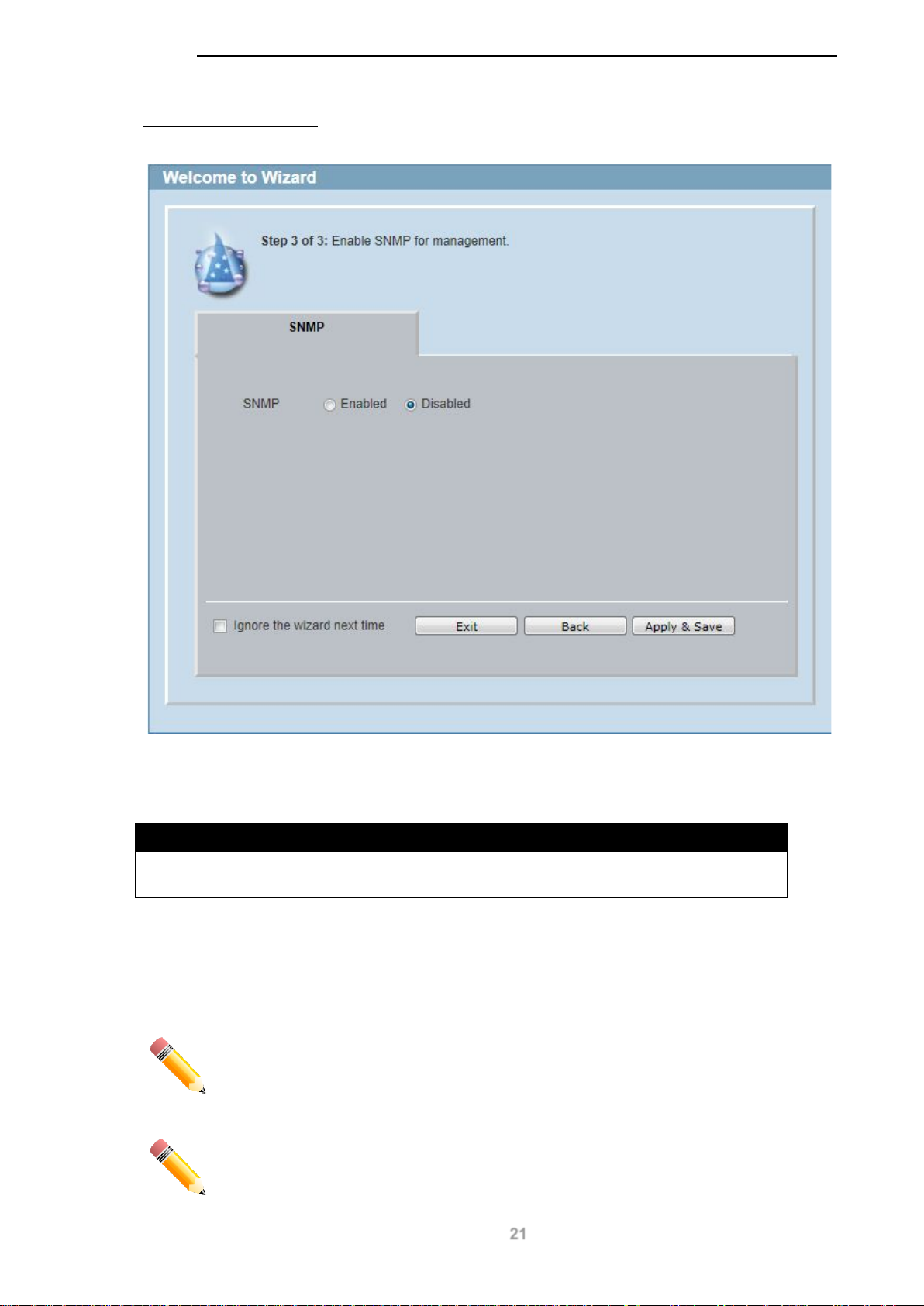
Step 4 – SNMP Settings
In this window, the user can enable or disable the SNMP function.
Figure 4-5 SNMP window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
SNMP Select the Enabled option to enable the SNMP function.
Select the Disabled option to disable the SNMP function.
Tick the Ignore the wizard next time option to skip the Smart Wizard on the next login.
Click the Exit button to discard the changes made, exit the Smart Wizard, and continue to the Web
UI.
Click the Apply & Save button to accept the changes made, and then continue to the Web UI.
NOTE: Standard Mode and Surveillance Mode Web UIs share the same
configuration files. Any features enabled in one interface will be made available
in the other interface.
NOTE: Settings are saved between interface types. It is possible to switch
interface types and re-run the Smart Wizard without losing settings saved in one
version of the interface.
21
Page 28
D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
AREA 1
AREA 2
Web User Interface (Web UI)
By clicking the Exit button in the Smart Wizard, you will enter the Web-based Management interface.
Areas of the User Interface
The figure below shows the user interface. Two distinct areas divide the user interface, as described
in the table.
Area Number Description
AREA 1
AREA 2
Figure 4-6 Main Web UI window
The navigation menu is displayed in this area. Click on the
links and navigate the folder structure to display information
on the main page.
This is the main page for displaying information and
configuration options for the switch. The page displayed here
is based on the selection in AR EA 1.
22
Page 29

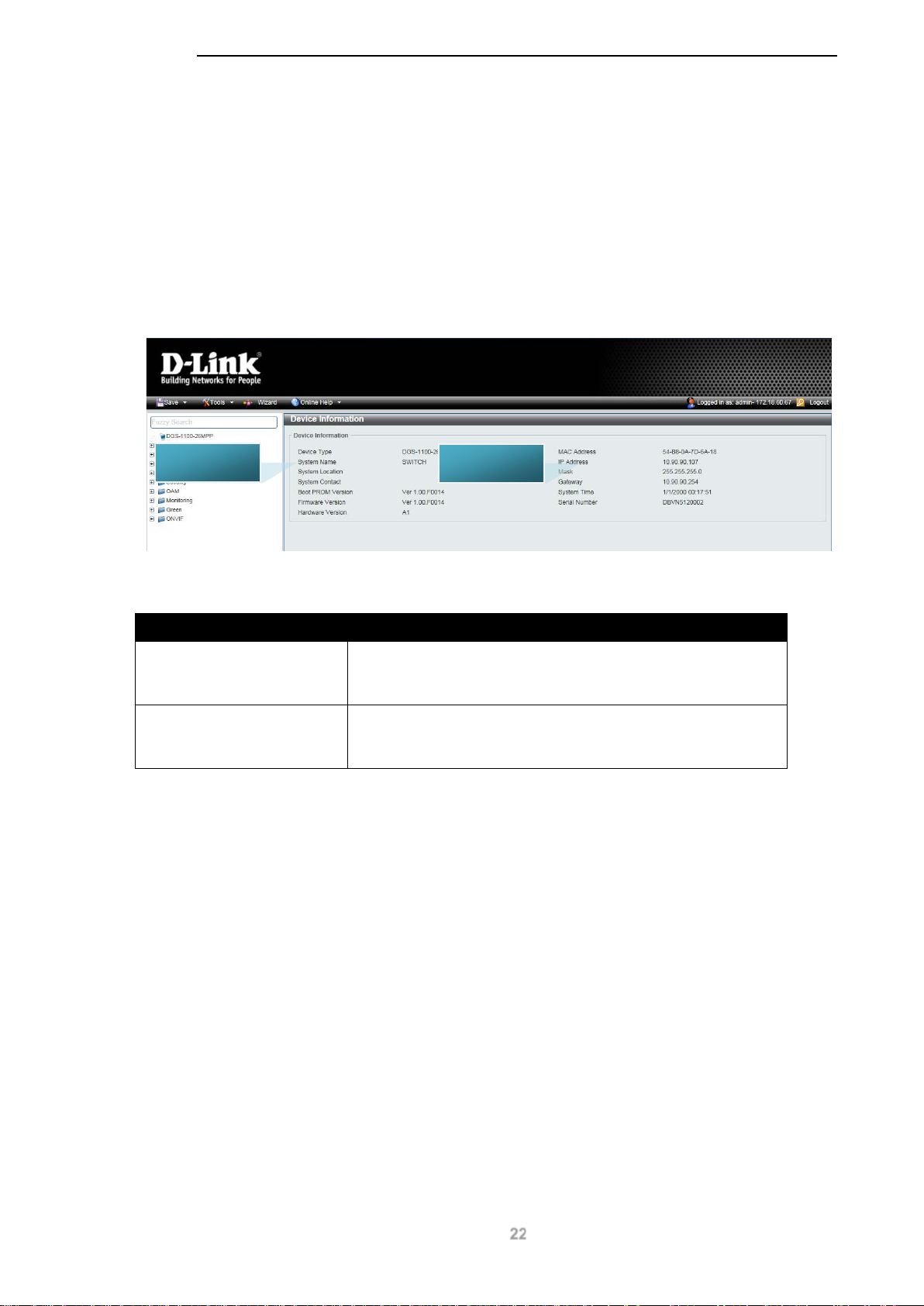
5. Device Information
Device information such as firmware version, MAC address and serial number are displayed in this
window. It appears automatically when you log in to the switch. To return to the Device Information
window after viewing other windows, click the model number of the switch at the top of the
navigation menu.
D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Figure 5-1 Device Information window
23
Page 30
6. System
System Information Settings
Port Configuration
PoE
System Log
Time
Time Profile
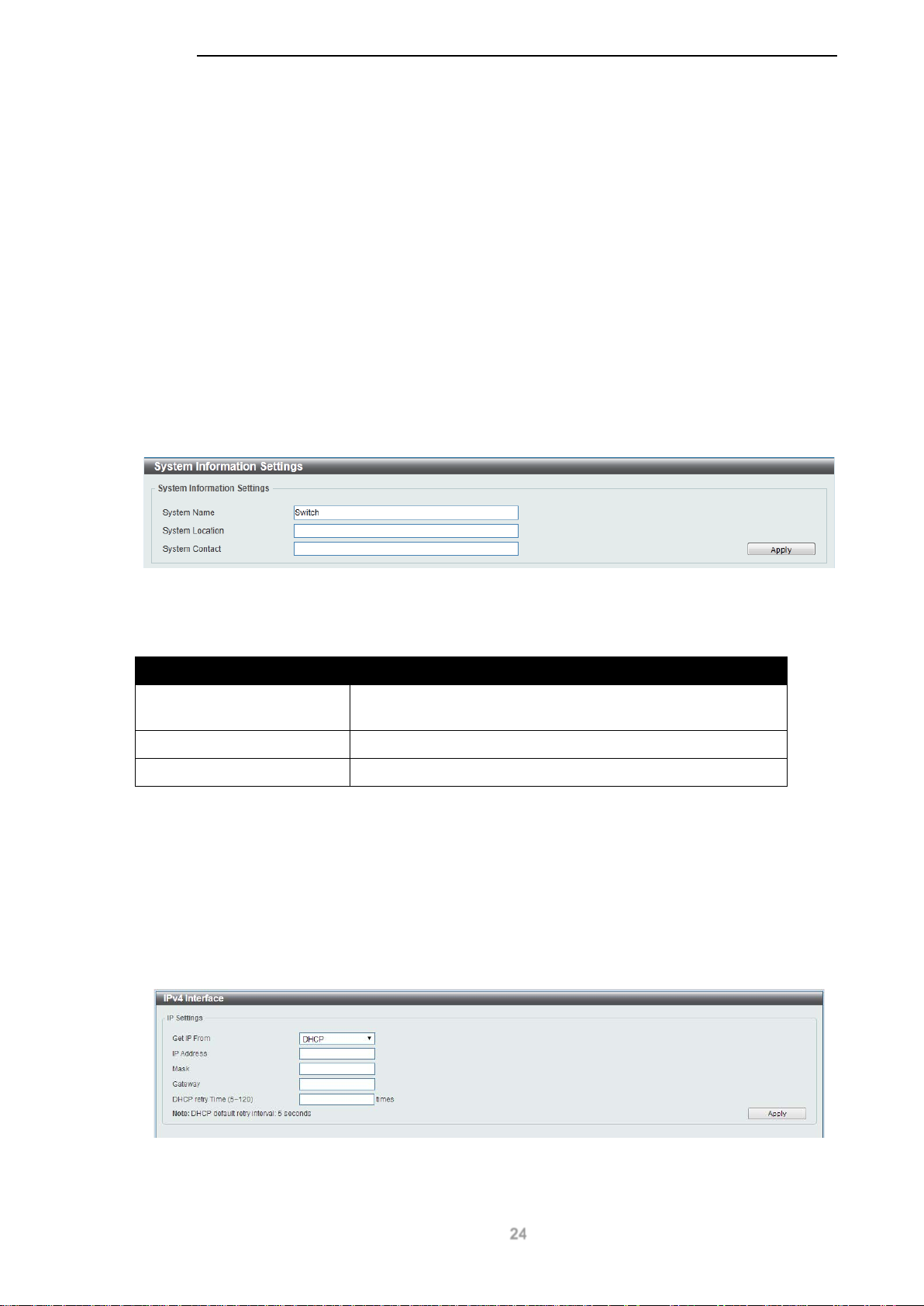
System Information Settings
The user can enter a System Name, System Location, and System Contact to aid in defining the
switch.
To view the following window, click System > System Information Settings, as shown below:
D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Figure 6-1 System Information Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
System Name
System Location
System Contact
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Enter a system name for the switch, if so desired. This name
will identify it on the switch network.
Enter the location of the switch, if so desired.
Enter a contact name for the switch, if so desired.
IPv4 Interface
This window is used to configure the IPv4 settings of the switch.
To view the following window, click System > System Information Settings > IPv4 Interface, as
shown below:
Figure 6-2 Peripheral Settings window
24
Page 31

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
Get IP From
IP Address
Mask
Gateway
DHCP retry Time
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Select DHCP to automatically obtain an IP address. Select
Static to manually configure the IP address settings. BOOTP
allows the switch to get an IP configuration using the BOOTP
protocol.
If Static is selected, enter the IP address of the switch. If
DHCP or BOOTP is selected, the automatically obtained IP
address will be displayed.
If Static is selected, enter the IP address of the switch. If
DHCP or BOOTP is selected, the automatically obtained
network mask will be displayed.
If Static is selected, enter the IP address of the switch. If
DHCP or BOOTP is selected, the automatically obtained
gateway will be displayed.
If DHCP is selected, enter the number of times to retry
obtaining an IP address.
IPv6 Interface
This window is used to configure the IPv6 settings of the switch.
To view the following window, click System > System Information Settings > IPv6 Interface, as
shown below:
Figure 6-3 Peripheral Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
IPv6 State Select whether to Enable or Disable IPv6 functionality.
Static IPv6 Address
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
If enabled, enter the static IPv6 address of the switch.
Port Configuration
Port Settings
This window is used to view and configure the switch’s port settings.
To view the following window, click System > Port Configuration > Port Settings, as shown below:
25
Page 32

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Figure 6-4 Port Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration
here.
Medium Type
Choose the medium type, either SFP or RJ45.
State Select this option to enable or disable the physical port
here.
MDIX
Select the Medium Dependent Interface Crossover (MDIX)
option here. Options to choose from are Auto, Normal, and
Cross.
Auto - Select this option for auto-sensing of the optimal type
of cabling.
Normal - Select this option for normal cabling. If this option
is selected, the port is in the MDIX mode and can be
connected to a PC’s NIC using a straight-through cable or a
port (in the MDIX mode) on another switch through a crossover cable.
Cross - Select this option for cross cabling. If this option is
selected, the port is in the MDI mode and can be connected
to a port (in the MDIX mode) on another switch through a
straight cable.
Flow Control Select to either turn flow control On or Off here. Ports
configured for full-duplex use 802.3x flow control, half-duplex
ports use back-pressure flow control, and Auto ports use an
automatic selection of the two.
Duplex
Select the duplex mode used here. Options to choose from
are Auto, Half, and Full.
Speed
Select the port speed option here. This option will manually
force the connected on the selected port to only connect at
the speed specified here. Options to choose from are Auto,
10M, 100M. 1000M speed is only available when Auto is
selected.
Description
Enter a 8 characters description for the corresponding port
here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Note: The SFP ports on the DGS-1100 MP/MPP series only support Auto for duplex and speed.
Also, the fiber ports on the DGS-1100 MP/MPP series do not support MDIX.
26
Page 33

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Jumbo Frame
This window is used to view and configure the Jumbo Frame size and settings. The switch supports
jumbo frames. Jumbo frames are Ethernet frames with more than 1,518 bytes of payload. The switch
supports jumbo frames with a maximum frame size of up to 9216 bytes.
To view the following window, click System > Port Configuration > Jumbo Frame, as shown below:
Figure 6-5 Jumbo Frame window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
From Port / To Port
Jumbo Frame Enable Select whether to Enable or Disable support for Jumbo
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration
here.
Frames on the switch.
27
Page 34

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
PSE provides power according to the following
PoE
The DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series switches support the IEEE 802.3af and 802.3at Power over Ethernet
(PoE) standards. The DGS-1100 MPP Series also support the IEEE 802.3bt standard.
The ports and power ratings per switch are as follows:
Switch Model Port Numbers Power Rating
DGS-1100-10MP 1 - 8 30W
DGS-1100-10MPP 1 – 8
7 - 8
30W
75W
DGS-1100-26MP 1 - 24 30W
DGS-1100-26MPP 1 – 24
21 - 24
30W
75W
Power can be supplied at 48 VDC to Powered Devices (PDs) over Category 5 or Category 3 UTP
Ethernet cables. The switches follow the standard PSE (Power Sourcing Equipment) pinout
Alternative A, wh e r e power is sent over pins 1, 2, 3 and 6.
The DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series switches include the following PoE features:
• Auto-discovery recognizes the connection of a PD (Powered Device) and automatically sends
power to it.
• The Auto-disable feature occurs under two conditions: firstly, if the total power consumption
exceeds the system power limit; and secondly, if the per port power consumption exceeds the
per port power limit.
• Active circuit protection automatically disables the port if there is a short. Other ports will remain
active.
Based on 802.3af/at PDs receive power according
to the following classification:
classification:
Class Maximum power used by PD Class Max power supplied by PSE
0 12.95W
1 3.84W
2 6.49W
3 12.95W
4 25.5W
0 16.2W
1 4.2W
2 7.4W
3 16.2W
4 31.6W
PoE System
This window is used to configure the PoE system, and display the detailed power information and
PoE Trap parameters for PoE modules.
To view the following window, click System > PoE > PoE System, as shown below:
28
Page 35

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Figure 6-6 PoE System window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
Usage Threshold
Trap State
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Enter the usage threshold to generate a log and send the
corresponding standard notification.
Select this option to enable or disable the sending of PoE
notifications.
PoE Status
This window displays the PoE status of each port.
To view the following window, click System > PoE > PoE Status, as shown below:
Note: For the PoE Status table, if the classification was shown as “Legacy PD”, it will be
classified to non-AF PD or Legacy PD.
Figure 6-7 PoE Status window
29
Page 36

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
PoE Configuration
This window is used to configure the PoE port.
To view the following window, click System > PoE > PoE Configuration, as shown below:
Figure 6-8 PoE Configuration window
The fields that can be configured are desc r ibed belo w:
Parameter Description
From Port / To Port
Priority
State
4-Pair State
Legacy
Power Limit
Max Wattage When selecting Auto in the Mode drop-down list, this option
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration
here.
Select the priority for provisioning power to the port. Options
to choose from are Critical, High and Low.
Select this option to enable or disable the PoE functionality.
Options to choose from are Disabled or Enabled.
This is used to enable 60 W PoE or 75 W PoE by utilizing all
4 pairs in a standard Ethernet cable. It can also be used to
disable this functionality. Options to choose from are
Disabled, 60W Enabled and 75W Enabled.
Use this to enable or disable PoE support for non-802.3af
devices. These will show up in the Legacy column as
Disabled or Enabled, depending on which option is chosen.
Options to choose from are Disabled or Enabled.
Select the power management mode for the PoE ports.
Options to choose from are Auto, Class 1, Class 2, Class 3,
and Class 4.
appears. Tick the check box and enter the maximum wattage
of power that can be provisioned to the auto-detected PD. If
the value is not entered, the class of the PD automatically
determines the maximum wattage which can be provisioned.
The valid range for maximum wattage is between 1000 mW
and 30000 mW.
Time Profile Select the Time Profile from the drop down list.
Note: The Time Profile drop down menu will only have
available options if a time profile has been created.
Click the Delete Time Range button to clear the setting in the corresponding Time Range field.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
30
Page 37

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Note: The Max Wattage option will only be available if the check box next to the input field is
enabled. When enabled, the Power Limit drop down menu will not be available.
Note: If the switch failed to supply power to the IEEE 802.3at PD (Powered Device),
1. Check if the PD connected to the port supports the IEEE 802.3at standard.
2. Manually configure the corresponding port’s power limit value to 30 Watts.
CAUTION: Before connecting the PD, make sure it supports IEEE 802.3bt, as
otherwise it will become damaged.
System Log
System Log Settings
This window is used to view and configure the system’s log settings.
To view the following window, click System > System Log > System Log Settings, as shown
below:
Figure 6-9 System Log Settings window
The fields that can be configured for Global State are described below:
Parameter Description
System Log
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for Buffer Log Settings are described below:
Parameter Description
Buffer Log State
Select this option to enable or disable the System Log
functionality.
Select whether the enable or disable the buffer log’s global
state here. Options to choose from are Enable, Disabled.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
System Log Server Settings
This window is used to view and configure system log’s server settings.
To view the following window, click System > System Log > System Log Server Settings, as
shown below:
31
Page 38

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Figure 6-10 System Log Server Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
Host IPv4 Address
UDP Port
Facility
Severity
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Enter the system log server’s IPv4 address here.
Enter the system log server’s UDP port number here. This
value must be between 1024 and 65535. By default, this
value is 514.
Specifies an application from which system logs are sent to
the remote server. Only one facility can be assigned to a
single server. If a second facility level is assigned, the first
facility is overwritten. There are up to eight facilities can be
assigned (Local 0 to Local 7).
Select the severity value of the type of information that will be
logged. Options to choose from are Warning, informational,
and All
The possible levels are:
Warning - The lowest level of a device warning. The device
is functioning, but an operational problem has occurred.
Informational - Provides device information.
All - Displays all levels of system logs.
System Log
This window is used to view and clear the system log.
To view the following window, click System > System Log > System Log, as shown below:
Click the Clear Log button to clear the system log entri es displayed in the table.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages
exist.
Figure 6-11 System Log window
32
Page 39

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Time
The Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) is a protocol for synchronizing computer clocks through
the Internet. It provides comprehensive mechanisms to access national time and frequency
dissemination services, organize the SNTP subnet of servers and clients, and adjust the system
clock in each participant.
Clock Settings
This window is used to configure the time settings for the switch.
To view the following window, click System > Time > Clock Settings, as shown below:
Figure 6-12 Clock Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
Time (HH:MM:SS)
Date (DD / MM / YYYY)
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Enter the current time in hours, minutes, and seconds.
Enter the current day, month, and year to update the system
clock.
Time Zone Settings
This window is used to configure time zones and Daylight Savings Time settings for SNTP.
To view the following window, click System > Time > Time Zone Settings, as shown below:
Figure 6-13 Time Zone Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
33
Page 40

Parameter Description
from 30 to 99999 seconds. The default interval is 720
D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Summer Time State
Time Zone
The fields that can be configured for Date Setting are described below:
Parameter Description
From: Date of the Month
From: Month
From: Year
From: Time (HH:MM)
To: Date of the Month
To: Month
To: Year
To: Time (HH:MM)
Offset
Select the summer time setting. Options to choose from are
Disabled, and Date Setting.
Disabled - Select to disable the summer time setting.
Date Setting - Select to configure the summer time that
should start and end on the specified date.
Select to specify your local time zone’s offset from
Coordinated Universal Time (UTC).
Select date of the month that summer time will start.
Select the month that summer time will start.
Enter the year that the summer time will start.
Select the time of the day that summer time will start.
Select date of the month that summer time will end.
Select the month that summer time will end.
Enter the year that the summer time will end.
Select the time of the day that summer time will end.
Enter the number of minutes to add during summer time. The
default value is 60. The range of this offset is 30, 60, 90 and
120.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
SNTP Settings
This window is used to configure the time settings for the switch.
To view the following window, click System > Time > SNTP Settings, as shown below:
Figure 6-14 SNTP Settings window
The fields that can be configured for SNTP Global Settings are described below:
Parameter Description
Current Time Source
This will indicate the current time source and will change
from System Clock to SNTP when SNTP is configured and
functioning.
SNTP State
Pool Interval
Select this option to enable or disable SNTP.
Enter the synchronizing interval in seconds. The value is
34
Page 41

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
seconds.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for SNTP Server Setting are described below:
Parameter Description
IPv4 Address
Click the Apply button to add the SNTP server.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
Enter the IP address of the SNTP server which prov id e s the
clock synchronization.
Time Profile
This window is used to view and configure the time range settings. The maximum number of time
profiles supported by the switch is 4.
To view the following window, click System > Time Profile, as shown below:
Figure 6-15 Time Range window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
Range Name
From Week / To Week
From Time / To Time
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
Enter the name of the time range. This name can be up to 8
characters long.
Select the starting and ending days of the week that will be
used for this time range. Tick the Daily option to use this
time range for every day of the week. Tick the End Week
Day option to use this time range from the starting day of the
week until the end of the week, which is Sunday.
Select the starting and ending time of the day that will be
used for this time range. The first drop-down menu selects
the hour and the second drop-down menu selects the
minute.
35
Page 42

7. Management
User Account Settings
SNMP
HTTP/HTTPS
D-Link Discovery Protocol
User Account Settings
This window is used to configure the user accounts. The active user account sessions can be
viewed.
There are several configuration options available in the Web User Interface (Web UI). The set of
configuration options avai la ble to the user dep ends on the accou nt’s Privilege Level.
NOTE: By default, the admin account is created on the switch.
D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
To view the following window, click Management > User Account Settings, as shown below:
Figure 7-1 User Management Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
User Name
Password
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified user account entry.
Select the user account name here.
Enter the password for the account here.
Note: Only one user can be logged into the switch at any tim e.
36
Page 43

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
SNMP
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an OSI Layer 7 (Application Layer) designed
specifically for managing and monitoring network devices. SNMP enables network management
stations to read and modify the settings of gateways, routers, switches, and other network devices.
Use SNMP to configure system features for proper operation, monitor performance and detect
potential problems in the switch, switch group or network.
Managed devices that support SNMP include software (referred to as an agent), which runs locally
on the device. A defined set of variables (managed objects) is maintained by the SNMP agent and
used to manage the device. These objects are defined in a Management Information Base (MIB),
which provides a standard presentation of the information controlled by the on-board SNMP agent.
SNMP defines both the format of the MIB specifications and the protocol used to access this
information over the network.
The switch supports the SNMP versions 1, and 2c. The two versions of SNMP vary in the level of
security provided between the management station and the network device.
In SNMP v.1 and v2c, user auth ent ic ati on is acc omplished using ‘community string’, which function
like passwords. The remote user SNMP application and the switch SNMP must use the same
community string. SNMP packets from any station that has not been authenticated are ignored
(dropped).
Traps
Traps are messages that alert network personnel of events that occur on the switch. The events can
be as serious as a reboot (someone accidentally turned OFF the switch), or less serious like a port
status change. The switch generates traps and sends them to the trap recipient (or network
manager). Typical traps include trap messages for Authentication Failure, and Topology Change.
MIBs
The switch in the Management Information Base (MIB) stores management and counter information.
The switch uses the standard MIB-II Management Information Base module. Consequently, values
for MIB objects can be retrieved from any SNMP-based network management software. In addition
to the standard MIB-II, the switch also supports its own proprietary enterprise MIB as an extended
Management Information Base. Specifying the MIB Object Identifier may also retrieve the proprietary
MIB. MIB values can be either read-only or read-write.
The switch supports the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) versions 1, and 2c. The
administrator can specify the SNMP version used to monitor and control the switch.
SNMP settings are configured using the menus located on the SNMP folder of the Web manager.
Workstations on the network that are allowed SNMP privileged access to the switch can be restricted
with the Management Station IP Address menu.
37
Page 44

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
SNMP Global Settings
This window is used to configure the SNMP global settings and trap settings.
To view the following window, click Management > SNMP > SNMP Global Settings, as shown
below:
Figure 7-2 SNMP Global Settings window
The fields that can be configured for SNMP Global Settings are described below:
Parameter Description
SNMP Global State
The fields that can be configured for Trap Settings are described below:
Parameter Description
Trap Global State
SNMP Authentication Trap
Port Link Up
Port Link Down
Coldstart
Warmstart
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Select this option to enable or disable the SNMP feature.
Select this option to enable or disable the sending of all or
specific SNMP notifications.
Tick this option to control the sending of SNMP
authentication failure notifications.
Tick this option to control the sending of port link up
notifications.
Tick this option to control the sending of port link down
notifications.
Tick this option to control the sending of SNMP ColdStart
notifications.
Tick this option to control the sending of SNMP WarmStart
notifications.
SNMP Community Table Settings
This window is used to create an SNMP community string to define the relationship between the
SNMP manager and an agent. The community string acts like a password to permit access to the
agent on the switch. One or more of the following characteristics can be associated with the
community string:
• Read/write or read-only level permiss ion f or the MI B o bj ects ac c ess ible to t he S N MP c om munity.
To view the following window, click Management > SNMP > SNMP Community Table Settings, as
shown below:
38
Page 45

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Figure 7-3 SNMP Community Table Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
Access Right
Community Name
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Select the access right here. Options to choose from are
Read Only, and Read Write.
Read Only - SNMP community members using the
community string created can only read the contents of the
MIBs on the switch.
Read Write - SNMP community members using the
community string created can read from, and write to the
contents of the MIBs on the switch.
Enter an alphanumeric string of up to 16 characters that is
used to identify members of an SNMP community. This
string is used like a password to give remote SNMP
managers access to MIB objects in the switch’s SNMP
agent.
SNMP Host Table Settings
This window is used to configure and display the recipient of the SNMP notification.
To view the following window, click Management > SNMP > SNMP Host Table Settings, as shown
below:
Figure 7-4 SNMP Host Table Settings
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
Host IPv4 Address
User-based Security
Model
Community String
Enter the IPv4 address of the SNMP notification host.
Select the security model here. Options to choose from are
SNMPv1, and SNMPv2c.
SNMPv1 - Select to allow the group user to use the SNMPv1
security model.
SNMPv2c - Select to allow the group user to use the
SNMPv2c security model.
Enter the community string to be sent with the notification
39
Page 46

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
packet.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
HTTP/HTTPS
This window is used to configure Web settings on the switch.
To view the following window, click Management > HTTP/HTTPS, as shown below:
Figure 7-5 HTTP/HTTPS window
The fields that can be configured for HTTP/HTTPS Settings are described below:
Parameter Description
Web Session
Web Session Timeout
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Note: If the switch is in HTTPS mode, the firmware or configuration cannot be upgraded using
regular HTTP.
Select this option to enable the configuration through HTTP
or HTTPS.
Note: When switching from HTTP to HTTPS mode, the
switch will take about 30 seconds to initialize the secured
HTTP environment.
Enter a value for the amount of time in seconds before the
web session expires.
D-Link Discovery Protocol
This window is used to configure and display D-Link Discovery Protocol (DDP).
To view the following window, click Management > D-Link Discovery Protocol, as shown below:
Figure 7-6 D-Link Discovery Protocol window
The fields that can be configured for D-Link Discovery Protocol are described below:
Parameter Description
D-Link Discovery Protocol
State
Report Timer
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Select this option to enable or disable DDP global state.
Select the interval in seconds between two consecutive DDP
report messages. Options to choose from are 30, 60, 90,120,
and Never.
40
Page 47

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
41
Page 48

8. Layer 2 Features
FDB
VLAN
Spanning Tree
ERPS
Loopback Detection
Link Aggregation
L2 Multicast Control
LLDP
FDB
Static FDB
Unicast Static FDB
This window is used to view and configure the static unicast forwarding settings on the switch.
D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
To view the following window, click L2 Features > FDB > Static FDB > Unicast Static FDB, as
shown below:
Figure 8-1 Unicast Static FDB window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
Port
VID
MAC Address
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Allows the selection of the port number on which the MAC
address entered resides.
Enter the VLAN ID on which the associated unicast MAC
address resides.
Enter the MAC address to which packets will be statically
forwarded or dropped. This must be a unicast MAC address.
Click the Delet e All button to delete all the entries found in the display table.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
42
Page 49

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Multicast Static FDB
This window is used to view and configure the multicast static FDB settings. To view the following
window, click L2 Features > FDB > Static FDB > Multicast Static FDB, as shown below:
Figure 8-2 Multicast Static FDB window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
From Port / To Port
VID
MAC Address
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delet e All button to remove all the entries.
Click the Delete button to remove the specific entry.
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration
here.
Enter the VLAN ID of the VLAN the corresponding MAC
address belongs to.
Enter the static destination MAC address of the multicast
packets. This must be a multicast MAC address. The format
of the destination MAC address is 01-XX-XX-XX-XX-XX.
MAC Address Table Settings
This window is used to view and configure the MAC address table’s global settings.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > FDB > MAC Address Table Settings, as shown
below:
Figure 8-3 MAC Address Table Settings (Global Settings) window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
Aging Time
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
After clicking the MAC Address Learning tab, at the top of the page, the following page will be
available.
Enter the MAC address table’s aging tim e value here. This
value must be between 10 and 1000000 seconds. Entering 0
will disable MAC address aging. By default, this value is 300
seconds.
43
Page 50

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Figure 8-4 MAC Address Table Settings (MAC Address Learning) window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
From Port / To Port
State
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Select the range of ports that will be used for this
configuration here.
Select to enable or disable the MAC address learning
function on the ports specified here.
MAC Address Table
This window is used to view the entries listed in the MAC address table.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > FDB > MAC Address Table, as shown below:
Figure 8-5 MAC Address Table window
Click the C l e a r Al l button to clear all dynamic MAC addresses.
44
Page 51

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
VLAN
802.1Q VLAN
This window is used to view and configure the VLAN settings on this switch.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > VLAN > 802.1Q VLAN, as shown below:
Figure 8-6 802.1Q VLAN window
The fields that can be configured for 802.1Q VLAN are described below:
Parameter Description
VID List
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Edit button to re-configure the specific entry.
Click the Delete button to remove the specific entry.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages
exist.
Enter the VLAN ID list that will be created here.
Port-based VLAN
This window is used to configure the asymmetric VLAN function.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > VLAN > Port-based VLAN, as shown below:
Figure 8-7 Asymmetric VLAN window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
VLAN State
From Port / To Port
VLAN Index
Select this option to enable or disable the Port-based VLAN
function.
Select the range of ports that will be used for this
configuration here.
VLAN Index is a unique number that identifies a particular
VLAN
45
Page 52

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete All button to delete all the entries found in the display table.
Management VLAN
This window is used to configure the asymmetric VLAN function.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > VLAN > Management VLAN, as shown below:
Figure 8-8 Asymmetric VLAN window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
Management VLAN State
VID
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Select this option to enable or disable the Management
VLAN function.
VLAN VID is a unique number (between 1 and 4094) that
identifies a particular VLAN.
Asymmetric VLAN
This window is used to configure the asymmetric VLAN function.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > VLAN > Asymmetric VLAN, as shown below:
Figure 8-9 Asymmetric VLAN window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
Asymmetric VLAN State
Select this option to enable or disable the asymmetric VLAN
function
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
VLAN Interface
This window is used to view and configure VLAN interface settings.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > VLAN > VLAN Interface, as shown below:
Figure 8-10 VLAN Interface window
46
Page 53

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Click the View Detail button to view more detailed information about the VLAN on the specific
interface.
Click the Edit button to re-configure the specific entry.
After clicking the VLAN Detail button, the follo wing pag e will app ear.
Figure 8-11 VLAN Interface Information window
More detailed information about the VLAN of the specific interface is displayed.
Click the Back button to return to the previous window.
After click the Edit button, the following window will appear. This is a dynamic window that will
change when a different VLAN Mode was selected. When Access was selected as the VL AN Mod e,
the following page will appear .
Figure 8-12 Configure VLAN Interface - Access window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
VLAN Mode
Select the VLAN mode option here. Options to choose from
are Access, Hybrid, and Trunk.
Acceptable Frame
Ingress Checking
VID
From Port / To Port
Select the acceptable frame behavior option here. Options to
choose from are Tagged Only, Untagged Only, and Admit
All.
Select this option to enable or disable the ingress checking
function.
Enter the VLAN ID used for this configuration here. This
value must be between 1 and 4094.
Select the appropriate port range used for the Clone
configuration here.
47
Page 54

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Back button to return to the previous window.
When Hybrid was selected as the VLAN Mode, the following page will appear.
Figure 8-13 Configure VLAN Interface - Hybrid window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
VLAN Mode
Select the VLAN mode option here. Options to choose from
are Access, Hybrid, and Trunk.
Acceptable Frame
Select the acceptable frame behavior option here. Options to
choose from are Tagged Only, Untagged Only, and Admit
All.
Ingress Checking
Select the check box to enable or disable t he ingress
checking function.
VID
Enter the VLAN ID used for this configuration here. This
value must be between 1 and 4094.
Action
Select the action that will be taken here. Options to choose
from are Remove, Tagged, and Untagged.
Allowed VLAN Range
From Port / To Port
Enter the allowed VLAN range information here.
Select the appropriate port range used for the Clone
configuration here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Back button to return to the previous window.
When Trunk is selected as the VLAN Mode, the following page will appear.
Figure 8-14 Configure VLAN Interface - Trunk window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
48
Page 55

Parameter Description
resumes during the aging time, the aging timer will be reset
D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
VLAN Mode
Acceptable Frame
Ingress Checking After selecting Trunk as the VLAN Mode the following
Action
Allowed VLAN Range
From Port / To Port
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Back button to return to the previous window.
Select the VLAN mode option here. Options to choose from
are Access, Hybrid, and Trunk.
Select the acceptable frame behavior option here. Options to
choose from are Tagged Only, Untagged Only, and Admit
All.
parameter will be available. Select to enable or disable the
ingress checking function.
Select the action that will be taken here. Options to choose
from are Remove, Tagged, and Untagged.
Enter the allowed VLAN range information here.
Select the appropriate port range used for the Clone
configuration here.
Auto Surveillance VLAN
Auto Surveillance Properties
This window is used to configure the auto surveillance VLAN global settings and display the ports
surveillance VLAN information.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > VLAN > Auto Surveillance VLAN > Auto
Surveillance Pro perties, as shown below:
Figure 8-15 Auto Surveillance Properties window
The fields that can be configured for Global Settings are described below:
Parameter Description
Surveillance VLAN
Surveillance VLAN ID
Surveillance VLAN CoS
Aging Time
Select this option to enable or disable the surveillance VLAN
state
Enter the surveillance VLAN ID. The range is from 2 to 4094.
Select the priority of the surveillance VLAN from 0 to 7.
Enter the aging time of surveillance VLAN. The range is from
1 to 65535 minutes. The default value is 720 minutes. The
aging time is used to remove a port from surveillance VLAN
if the port is an automatic surveillance VLAN member. When
the last surveillance device stops sending traffic and the
MAC address of this surveillance device is aged out, the
surveillance VLAN aging timer will be started. The port will
be removed from the surveillance VLAN after expiration of
surveillance VLAN aging timer. If the surveillance traffic
49
Page 56

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
and stop.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
MAC Settings and Surveillance Device
This window is used to configure the user-defined surveillance device OUI and display the
surveillance VLAN information.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > VLAN > Auto Surveillance VLAN > MAC
Settings and Surveillance Device, as shown below:
Figure 8-16 User -defined MAC Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
Component Type
Description
MAC Address
Mask
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
After clicking the Auto Surveillance VLAN Summary tab, the following page will appear.
Select the surveillance component type. Options to choose
from are Video Management Server, VMS Client/Remote
Viewer, Video Encoder, Network Storage, and Other IP
Surveillance Device.
Enter the description for the user-defined OUI with a
maximum of 8 characters.
Enter the OUI MAC address.
Enter the OUI MAC address matching bitmask.
Figure 8-17 Auto Surveillance VLAN Summary window
50
Page 57

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Voice VLAN
Voice VLAN Global
Voice VLAN is a VLAN used to carry voice traffic from IP phone. Because the sound quality of an IP
phone call will be deteriorated if the data is unevenly sent, the quality of service (QoS) for voice
traffic shall be configured to ensure the transmission priority of voice packet is higher than normal
traffic.
The switches determine whether a received packet is a voice packet by checking its source MAC
address. If the source MAC addresses of packets comply with the organizationally unique identifier
(OUI) addresses configured by the system, the packets are determined as voice packets and
transmitted in voice VLAN.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > VLAN > Voice VLAN > Voice VLAN Global, as
show below:
Figure 8-18 Voice VLAN Global window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
Voice VLAN State
Voice VLAN ID
Voice VLAN CoS
Aging Time
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made for each individual section.
Select this option to enable or disable the voice VLAN.
Enter the voice VLAN ID. The value is range from 2 to 4094.
Select the priority of the voice VLAN from 0 to 7.
Enter the aging time of surveillance VLAN. The range is
from 1 to 65535 minutes. The default value is 720 minutes.
The aging time is used to remove a port from voice VLAN if
the port is an automatic VLAN member. When the last voice
device stops sending traffic and the MAC address of this
voice device is aged out, the voice VLAN aging timer will be
started. The port will be removed from the voice VLAN after
expiration of voice VLAN aging timer. If the voice traffic
resumes during the aging time, the aging timer will be reset
and stop.
51
Page 58

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Voice VLAN Port
This window is used to configure the user-defined voice traffic’s port.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > VLAN > Voice VLAN > Voice VLAN OUI, as
show below:
Figure 8-19 Voice VLAN Port window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
From Port / To Port
State
Mode Choose the Voice VLAN mode for the port. This can be Auto
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Select the range of ports that will be used for this
configuration here.
Select this option to enable or disable the Voice VLAN state
of the port.
untagged, Auto Tagged, or Manually configured.
52
Page 59

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Voice VLAN OUI
This window is used to configure the user-defined voice traffic’s OUI. The OUI is used to identify the
voice traffic. There are a number of pre-defined OUIs. The user can further define the user-defined
OUIs if needed. The user-defined OUI cannot be the same as the pre-defined OUI.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > VLAN > Voice VLAN > Voice VLAN OUI, as
show below:
Figure 8-20 Voice VLAN OUI window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
OU I Add r ess
Mask
Description
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
Enter the OUI MAC address.
Enter the OUI MAC address matching bitmask.
Enter the description for the user-defined OUI with a maximum of 8
characters.
Voice VLAN Device
This window is used to show voice devices that are connected to the ports. The start time is the time
when the device is detected on this port, the activate time is the latest time saw the device sending
the traffic.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > VLAN > Voice VLAN > Voice VLAN Device, as
show below:
Figure 8-21 Voice VLAN Device window
53
Page 60

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Spanning Tree
This switch supports two versions of the Spanning Tree Protocol: 802.1D-1998 STP, 802.1D-2004
Rapid STP. 802.1D-1998 STP will be familiar to most networking professionals. However, since
802.1D-2004 RSTP has been recently introduced to DGS-1100 MP/MPP switches, a brief
introduction to the technology is provided below followed by a description of how to set up 802.1D1998 STP, 802.1D-2004 RSTP.
802.1D-2004 Rapid Spanning Tree
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) as defined by the IEEE 802.1D-2004 specification and a
version compatible with the IEEE 802. 1D-1998 STP. RSTP can operate with legacy equipment
implementing IEEE 802.1D-1998; however the advantages of using RSTP will be lost.
The IEEE 802.1D-2004 Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) evolved from the 802.1D-1998 STP
standard. RSTP was developed in order to overcome some limitations of STP that impede the
function of some recent switching innovations, in particular, certain Layer 3 functions that are
increasingly handled by Ethernet switches. The basic function and much of the terminology is the
same as STP. Most of the settings configured for STP are also used for RSTP. This section
introduces some new Spanning Tree concepts and illustrates the main differences between the two
protocols.
Edge Port
The edge port is a configurable designation used for a port that is directly connected to a segment
where a loop cannot be created. An example would be a port connected directly to a single workstation. Ports that are designated as edge ports transition to a forwarding state immediately without
going through the listening and learning states. An edge port loses its status if it receives a BPDU
packet, immediately becoming a normal spanning tree port.
Note: If Spanning Tree protocol is used, loopback detection will not be available. If Loopback
Detection is enabled, the Spanning Tree protocol will not be available.
54
Page 61

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
STP Global Settings
This window is used to view and configure the STP global settings.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > Spanning Tree > STP Global Settings, as
shown below:
Figure 8-22 STP Global Settings window
The field that can be configured for Spanning Tree State is descr ibed be lo w:
Parameter Description
Spanning Tree State
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for Spanning Tree Mode are described below:
Parameter Description
Spanning Tree Mode
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for STP Traps are described below:
Parameter Description
STP New Root Trap
STP Topology Change
Trap
Select this option to enable or disable the STP global state
here.
Select the STP mode used here. Options to choose from are
RSTP, and STP.
Select this option to enable or disable the STP new root trap
option here.
Select this option to enable or disable the STP topology
change trap option here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
STP Port Settings
This window is used to view and configure the STP port settings.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > Spanning Tree > STP Port Settings, as shown
below:
55
Page 62

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Figure 8-23 STP Port Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
From Port / To Port
Port Fast
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration
here.
Select the port fast option here. Options to choose from are
Network, Disabled, and Edge. In the Network mode the
port will remain in the non-port-fast state for three seconds.
The port will change to the port-fast state if no BPDU is
received and changes to the forwarding state. If the port
received the BPDU later, it will change to the non-port-fast
state. In the Disable mode, the port will always be in the
non-port-fast state. It will always wait for the forward-time
delay to change to the forwarding state. In the Edge mode,
the port will directly change to the spanning-tree forwarding
state when a link-up occurs without waiting for the forwardtime delay. If the interface receives a BPDU later, its
operation state changes to the non-port-fast state. By default,
this option is Edge.
ERPS
Ethernet Ring Protec ti on Sw itchi ng (ERPS) is a system for preventing Layer 2 loops in an Ethernet
ring topology. One link between Ring Protection Link (RPL) nodes is blocked and un-blocked in the
event of a link failure elsewhere in the network. It uses G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection (ERP)
protocol, which is part ITU-T G.8032.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > Loopback Detection, as shown below:
Figure 8-24 ERPS window
The fields that can be configured are desc r ibed belo w:
Parameter Description
Ring Name
Enter the name of the ERPS ring here.
56
Page 63

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Loopback Detection
The Loopback Detection (LBD) function is used to detect the loop created by a specific port. This
feature is used to temporarily shut down a port on the switch when a CTP (Configuration Testing
Protocol) packet has been looped back to the switch. When the switch detects CTP packets received
from a port, this signifies a loop on the network. The switch will automatically block the port and send
an alert to the administrator. The Loopback Detection port will restart (change to normal state) when
the Loopback Detection Recover Time times out. The Loopback Detection function can be
implemented on a range of ports at a time. The user may enable or disable this function using the
drop-down menu.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > Loopback Detection, as shown below:
Figure 8-25 Loopback Detection window
The fields that can be configured for Loopback Detection Global Settings are described below:
Parameter Description
Loopback Detection State
Trap State
Enabled VLAN ID List
Action
Function Version
Select to enable or disable loopback detection. The default is
Disabled.
Select to enable or disable the loopback detection trap state.
The default is Disabled.
This is the range of VLANs that Loopback Detection is
enabled on. The range is from 1 to 4094.
The action to perform when a CTP packet is detected on a
port. The actions are as follows:
Shutdown: shut the port down.
None: perform no action.
This is the version of Loopback Detection software running
57
Page 64

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
on the switch.
Mode
Interval (1-32767) Set a Loop detection Interval between 1 and 32767 seconds.
Recover Time (0, 60-
1000000)
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for Loopback Detection Port Settings are described below:
Parameter Description
From Port / To Port
State
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
This is the Loopback Detection mode running on the switch.
The modes are:
Port-based: perform port-based Loopback Detection
VLAN-based: perform VLAN-based Loopback Detection.
The default is 10 seconds.
Time allowed (in seconds) for recovery when a Loopback is
detected. The Loop Detection Recover Time can be set at 0
seconds, or 60 to 1000000 seconds. Entering 0 will disable
the Loop Detection Recover Time. The default is 60 seconds.
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration
here.
Select this option to enable or disable the state of the port.
Note: If Spanning Tree protocol is used, loopback detection will not be available. If Loopback
Detection is enabled, the Spanning Tree protocol will not be available.
58
Page 65

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Link Aggregation
Understanding Port Trunk Groups
Port trunk groups are used to combine a number of ports together to make a single high-bandwidth
data pipeline.
Figure 8-26 Example of Port Trunk Group
The switch treats all ports in a trunk group as a single port. Data transmitted to a specific host
(destination address) will always be transmitted over the same port in a trunk group. This allows
packets in a data stream to arrive in the same order they were sent.
Link aggregation allows several ports to be grouped together and to act as a single link. This gives a
bandwidth that is a multiple of a single link's bandwidth.
Link aggregation is most commonly used to link a bandwidth intensive network device or devices,
such as a server, to the backbone of a network.
All of the ports in the group must be members of the same VLAN, and their STP status, static
multicast, traffic control; traffic segmentation and 802.1p default priority configurations must be
identical. Further, the LACP aggregated links must all be of the same speed and should be
configured as full duplex.
Load balancing is automatically applied to the ports in the aggregated group, and a link failure within
the group causes the network traffic to be directed to the remaining links in the group.
59
Page 66

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
The Spanning Tree Protocol will treat a link aggregation group as a single link, on the switch level.
On the port level, the STP will use the port parameter s of the Master Port in the calcul ati on of port
cost and in determining the state of the link aggregation group. If two redundant link aggregation
groups are configured on the switch, STP will block one entire group; in the same way STP will block
a single port that has a redundant link.
NOTE: If any ports within the trunk group become disconnected,
packets intended for the disconnected port will be load shared
among the other linked ports of the link aggregation group.
This window is used to view and configure the link aggregation settings.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > Link Aggregation, as shown below:
Figure 8-27 Link Aggregation window
The fields that can be configured for Channel Group Information are described below:
Parameter Description
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration
here.
Group ID
Enter the channel group number here. The system will
automatically create the port-channel when a physical port
first joins a channel group. An interface can only join one
channel-group.
Mode Select the mode option here. Options to choose from are On,
Active, and Passive. If the mode On is specified, the
channel group type is static. If the mode Active or Passive is
specified, the channel group type is LACP. A channel group
can only consist of either static members or LACP members.
Once the type of channel group has been determined, other
types of interfaces cannot join the channel group.
Active - Active LACP ports are capable of processing and
sending LACP control frames. This allows LACP compliant
devices to negotiate the aggregated link so the group may be
changed dynamically as needs require. In order to utilize the
ability to change an aggregated port group, that is, to add or
subtract ports from the group, at least one of the participating
devices must designate LACP ports as active. Both devices
must support LACP.
Passive - LACP ports that are designated as passive cannot
initially send LACP control frames. In order to allow the
linked port group to negotiate adjustments and make
changes dynamically, one end of the connection must have
"active" LACP ports
Click the Add button to add a new entry based on the information entered.
Click the Delete Member Port button to remove the specific member port.
Click the Delete Channel button to remove the specific entry.
Click the Channel Detail button to view more detailed information about the channel.
60
Page 67

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
After clicking the Chan nel Detai l b utto n, the fol lo wing page will be avai lab le.
Figure 8-28 Port Channel window
Click the Back button to return to the previous window.
61
Page 68

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
L2 Multicast Control
IGMP Snooping
Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) snooping allows the switch to recognize IGMP queries
and reports sent between network stations or devices and an IGMP host.
IGMP Snooping Settings
To view the following window, click L2 Features > L2 Multicast Control > IGMP Snooping > IGMP
Snooping Settings, as shown below:
Figure 8-29 IGMP Snooping Settings windo w
The field that can be configured for Global Settings is described below:
Parameter Description
Global State
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for VLAN Status Settings are described below:
Parameter Description
VID
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for VLAN Querier Status Settings are described below:
Parameter Description
VID
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages
exist.
Select this option to enable or disable IGMP Snooping global
state.
Enter a VLAN ID from 1 to 4094, and select to enable or
disable IGMP Snoop in g on the VL AN.
Enter a VLAN ID from 1 to 4094, and select to enable or
disable IGMP Snoop in g on the VL AN.
62
Page 69

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
IGMP Snooping Groups Settings
This window is used to configure and view the IGMP snooping static group, and view IGMP
snooping group.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > L2 Multicast Control > IGMP Snooping > IGMP
Snooping Groups Settings, as shown below:
Figure 8-30 IGMP Snooping Groups Settings
The fields that can be configured for IGMP Snooping Static Groups Settings are described below:
Parameter Description
VID
Group Address
From Port / To Port
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
Enter a VLAN ID of the multicast group.
Enter an IP multicast group address.
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration
here.
63
Page 70

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
MLD Snooping
Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) Snooping allows the switch to listen to IPv6 multicast traffic and
forward it only to Layer 2 ports that have requested to participate in the multicast group.
MLD Snooping Settings
To view the following window, click L2 Features > L2 Multicast Control > MLD Snooping > MLD
Snooping Settings, as shown below:
Figure 8-31 MLD Snooping Settings windo w
The field that can be configured for Global Settings is described below:
Parameter Description
Global State
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for VLAN Status Settings are described below:
Parameter Description
VID
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for VLAN Querier Status Settings are described below:
Parameter Description
VID
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages
exist.
Select this option to enable or disable MLD Snooping global
state.
Enter a VLAN ID from 1 to 4094, and select to ena bl e or
disable MLD Snoop in g on the VLAN.
Enter a VLAN ID from 1 to 4094, and select to enable or
disable MLD Snoop in g on the VLAN.
64
Page 71

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
MLD Snooping Static Groups Settings
This window is used to configure and view the MLD Snooping static group, and view MLD Snooping
group.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > L2 Multicast Control > MLD Snooping > MLD
Snooping Groups Settings, as shown below:
Figure 8-32 MLD Snooping Groups Settings
The fields that can be configured for IGMP Snooping Static Groups Settings are described below:
Parameter Description
VID
Group Address
From Port / To Port
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
Enter a VLAN ID of the multicast group.
Enter an IP multicast group address.
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration
here.
65
Page 72

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Multicast Filtering
This window is used to view and configure the Layer 2 multicast filtering settings.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > L2 Multicast Control > Multicast Filtering, as
shown below:
Figure 8-33 Multicast Filtering window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
Multicast Filter Mode
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Select the multicast filter mode here. Options to choose from
are Forward Unregistered, and Filter Unregistered. When
selecting the Forward Unregistered option, registered
multicast packets will be forwarded based on the forwarding
table and all unregistered multicast packets will be flooded
based on the VLAN domain. When selecting the Filter
Unregistered option, registered packets will be forwarded
based on the forwarding table and all unregistered multicast
packets will be filtered.
66
Page 73

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
LLDP
LLDP Global Settings
LLDP (Link Layer Discovery Protocol) provides IEEE 802.1AB standards-based method for switches
to advertise themselves to neighbor devices, as well as to learn about neighbor LLDP devices.
This window is used to configure the LLDP global settings.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > LLDP > LLDP Global Settings, as shown below:
Figure 8-34 LLDP Global Settings window
The fields that can be configured for LLDP Global Settings are described below:
Parameter Description
LLDP State
LLDP Trap State
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Select this option to enable or disable the LLDP feature
Select this option to enable or disable the LLDP trap state.
LLDP Neighbor Port Information
This window is used to display the information learned from the neighbors. The switch receives
packets from a remote station but is able to store the information as local.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > LLDP > LLDP Neighbor Port Information, as
show below:
Figure 8-35 LLDP Neighbor Port Information window
67
Page 74

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
9. Quality of Service (QoS)
802.1p Priority
Port Rate Limiting
802.1p Priority
This window is used to view and configure the port’s default CoS settings.
To view the following window, click QoS > 802.1p Priority, as shown below:
Figure 9-1 Port Default CoS window
The fields that can be configured for Port Scheduler Method are described below:
Parameter Description
From Port / To Port
Scheduler Method SP - Denoting a Strict Priority scheduling will set the highest
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured Port Default CoS are described below:
Parameter Description
From Port / To Port
Default CoS
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration
here.
queue to be emptied first while the other queues will follow
the weighted round-robin scheduling scheme
WRR - Use the weighted round-robin ( WRR ) algorithm to
handle packets in an even distribution in priority classes of
service.
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration
here.
Select the default CoS option for the port(s) specified here.
The priorities are Highest, High, Medium and Low.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
68
Page 75

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Port Rate Limiting
This window is used to view and configure the port rate limiting settings.
To view the following window, click QoS > Port Rate Limiting, as shown below:
Figure 9-2 Port Rate Limiting window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
From Port / To Port
Direction
Rate Limit
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration
here.
Select the direction option here. Options to choose from are
Input and Output. When Input is selected, the rate limit for
ingress packets is configured. When Output is selected, the
rate limit for egress packets is configured.
Select the rate limit value here.
When Direction is Input, this drop-down menu allows you to
select data rate from 8Kbps to 512Mbps.
When Direction is Output, this drop-down menu allows you
to select data rate from 64Kbps to 512Mbps.
69
Page 76

10. Security
DHCP Snooping
Safeguard Engine Settings
Traffic Segmentation
Storm Control
DoS Attack Prevention Settings
Zone Defense Settings
SSL
DHCP Snooping
DHCP Snooping monitors DHCP bindings to verify the IP address allocated to each device and port.
The DHCP Snooping database can be view ed b y acce s sing the table below.
To view the following window, click Security > DHCP Snooping, as shown below:
D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
The field that can be configured for DHCP Snooping Global Settings is described below:
Parameter Description
DHCP Snooping
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages
exist.
Figure 10-1 DHCP Snooping Settings window
Select this option to enable or disable DHCP Snooping
globally on the switch.
70
Page 77

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Safeguard Engine Settings
D-Link’s Safeguard Engine is a robust and innovative technology that automatically throttles the
impact of packet flooding into the switch's CPU. This function helps protect the Smart switch from
being interrupted by malicious viruses or worm attacks.
This window is used to view and configure the safeguard engine settings.
To view the following window, click Security > Safeguard Engine > Safeguard Engine Settings,
as shown below:
Figure 10-2 Safeguard Engine Settings window
The fields that can be configured for Safeguard Engine Settings are described below:
Parameter Description
Safeguard Engine State
Select to enable or disable the safeguard engine feature
here.
Traffic Segmentation
This window is used to view and configure the traffic segmentation settings. When the traffic
segmentation forwarding domain is specified, packets received by the port will be restricted in Layer
2 packet forwarding to interfaces within the domain. When the forwarding domain of a port is empty,
Layer 2 forwarding for packets received by the port is not restricted.
To view the following window, click Security > Traffic Segmentation Settings, as shown below:
Figure 10-3 Traffic Segmentation Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
From Port / To Port
From Forward Port / To
Forward Port
Click the Add button to add a new entry based on the information entered.
Click the Delete button to remove an entry based on the information entered.
Select the receiving port range used for the configuration
here.
Select the forward port range used for the configuration here.
71
Page 78

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Storm Control
This window is used to view and configure the storm control settings. Once a packet storm has been
detected, the switch will drop packets coming into the switch until the storm has subsided.
To view the following window, click Security > Storm Control, as shown below:
Figure 10-4 Storm Control window
The fields that can be configured for Storm Control Port Settings are described below:
Parameter Description
From Port / To Port
Type
Rate Limit
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration
here.
Select the type of storm attack that will be controlled here.
Options to choose from are Broadcast, Multicast, and
Unicast.
Select a data rate from 512Kbps to 512Mbps.
DoS Attack Prevention Settings
This window is used to view and configure the Denial-of-Service (DoS) attack prevention settings.
The following well-known DoS types which can be detected by most switches:
• Land Attack: This type of attack involves IP packets where the source and destination
address are set to the address of the target device. It may cause the target device to reply to
itself continuously.
• Blat Attack: This type of attack will send packets with the TCP/UDP source port equal to the
destination port of the target device. It may cause the target device to respond to itself.
• TCP-Null: This type of attack involves port scanning by using specific packets which contain
a sequence number of 0 and no flags.
• TCP-Xmas: This type of attack involves port scanning by using specific packets which
contain a sequence number of 0 and the Urgent (URG), Push (PSH), and FIN flags.
• TCP SYN-FIN: This type of attack involves port scanning by using specific packets which
contain SYN and FIN flags.
• TCP SYN SrcPort Less 1024: This type of attack involves port scanning by using specific
packets which contain source port 0 to 1023 and SYN flag.
• Ping of Death Attack: A ping of death is a type of attack on a computer that involves
sending a malformed or otherwise a malicious ping to a computer. A ping is normally 64
bytes in size (many computers cannot handle a ping larger than the maximum IP packet size)
which is 65535 bytes. The sending of a ping of this size can crash the target computer.
Traditionally, this bug has been relatively easy to exploit. Generally, sending a 65536 byte
ping packet is illegal according to networking protocol, but a packet of such a size can be
sent if it is fragmented; when the target computer reassembles the packet, a buffer overflow
can occur, which often causes a system crash.
• All Types: All of above types.
72
Page 79

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
To view the following window, click Security > DoS Attack Prevention Settings, as shown below:
Figure 10-5 DoS Attack Prevention Settings window
The fields that can be configured for DoS Attack Prevention Settings are described below:
Parameter Description
DoS Type Selection
State
Action
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Tick the DoS type option that will be prevented here.
Select to enable or disable the DoS attack prevention
feature’s global state here.
Select the action that will be taken when the DoS attack was
detected here. The only option to select here is Drop.
Zone Defense Settings
This window is used to view and configure the Zone Defense setting.
To view the following window, click Security > Zone Defense Settings, as shown below:
Figure 10-5 Zone Defense Settings window
The fields that can be configured for Zone Defense Settings are described below:
Parameter Description
State
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Select to enable or disable the Zone Defense feature’s global
state here.
73
Page 80

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
SSL
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) is a security feature that will provide a secure communication path
between a host and client through the use of authentication, digital signatures and encryption.
SSL Global Settings
This window is used to view and configure the SSL feature’s global settings.
To view the following window, click Security > SSL > SSL Global Settings, as shown below:
Figure 10-6 SSL Global Settings window
The fields that can be configured for SSL Global Settings are described below:
Parameter Description
SSL Status
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Select to enable or disable the SSL feature’s global status
here.
74
Page 81

11. OAM
Cable Diagnostics
The cable diagnostics feature is designed primarily for administrators or customer service
representatives to verify and test copper cables; it can rapidly determine the quality of the cables and
the types of error.
To view the following window, click OAM > Cable Diagnostics, as shown below:
D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Figure 11-1 Cable Diagnostics window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
From Port / To Port
Click the Test button to test the specific port.
Click the Clear button to clear all the information for the specific port.
Click the C l e a r Al l button to clear all the information in this table.
Note: The Cable Diagnostics feature is only supported on the copper ports on all DGS-1100
MP/MPP Series switches.
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration
here.
75
Page 82

12. Monitoring
Statistics
Mirror Settings
Statistics
Port Counters
This window is used to display port counter statistics.
To view the following window, click Monitoring > Statistics > Port Counters, as show below:
D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Figure 12-1 Port Counters window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
From Port / To Port
TxOK: Number of packets transmitted successfully.
RxOK: Number of packets received successfully.
TxError: Number of transmitted packets resulting in error.
RxError: Number of received packets resulting in error
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click the Refresh button to refresh the display table.
Click the Clear button to clear all the information for the specific port.
Click the C l e a r Al l button to clear all the information in this table.
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration
here.
76
Page 83

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Mirror Settings
This window is used to view and configure the mirror feature’s settings. The switch allows users to
copy frames transmitted and received on a port and redirect the copies to another port. Attach a
monitoring device to the mirroring port, such as a sniffer, to view details about the packets passing
through the first port. This is useful for network monitoring and troubleshooting purposes.
To view the following window, click Monitoring > Mirror Settings, as shown below:
Figure 12-2 Mirror Settings window
The fields that can be configured for Mirror Settings are described below:
Parameter Description
Destination
Source Select From Port number and the To Port number as
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to delete an existing mirror entry based on the information entered.
Select one destination port from drop-down menu.
source port from drop-down menu. Lastly select the Frame
Type option. Options to choose from as the Frame Type are
Both, RX, and TX. When selecting Both, traffic in both the
incoming and outgoing directions will be mirrored. When
selecting RX, traffic in only the incoming direction will be
mirrored. When selecting TX, traffic in only the outgoing
direction will be mirrored.
77
Page 84

13. Green
Power Saving
EEE
Power Saving
This window is used to configure the power saving settings of the switch.
To view the following window, click Green > Power Saving, as shown below:
D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Figure 13-1 Power Saving window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
Link Detection Power
Saving
Scheduled Port-shutdown
Power Saving
Scheduled Hibernation
Power Saving
Scheduled Dim-LED Power
Saving
Administrative Dim-LED
Type
Time Profile
Select this option to enable or disable the link detection
state. When enabled, a port which has a link down status
will be turned off to save power to the switch. T his wi ll not
affect the port’s capabilities when the port status is link up.
Select this option to enable or disable applying the power
saving by scheduled port shutdown.
Select this option to enable or disable applying the power
saving by scheduled hibernation power.
Select this option to enable or disable applying the power
saving by scheduled dimming LEDs.
Select this option to enable or disable the port LED function.
Select the type of power saving. Option to choose from is
Dim-LED or Hibernation.
If a Time Profile was previously created, select the desired
profile from the drop down list.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made for each individual section.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
After clicking the Power Saving Shutdown Settings tab, the following page will appear.
78
Page 85

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Figure 13-2 Power Saving Shutdown Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
From Port / To Port
Time Range
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration
here.
If a Time Profile was previously created, select the desired
profile from the drop down list.
79
Page 86

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
EEE
Energy Efficient Ethernet (EEE) is defined in IEEE 802.3az. It is designed to reduce the energy
consumption of a link when no packets are being sent.
To view the following window, click Green > EEE, as shown below:
Figure 13-3 EEE window
The fields that can be confi gur ed are des c ribed be lo w:
Parameter Description
From Port / To Port
State
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Note: The EEE feature is only supported on the copper ports on all DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series
switches.
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration
here.
Select this option to enable or disable the state of this feature
here.
80
Page 87

14. ONVIF
Global Status
IP-Camera Information
NVR Information
Global Status
ONVIF is a global standard for improving inter-operability between IP-based security products. It is
an effort between various hardware and software vendors to define a specification for the exchange
of information between physical security products. The DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series support the
ONVIF protocol and its settings can be configured below.
The ONVIF Global Status page enables ONVIF support globally on the switch and allows you to
configure ONVIF settings. It also displays global ONVIF statistics for the switch.
To view the following window, click ONVIF > Global Settings, as shown below:
D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Figure 14-1 ONVIF Global Status window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
Global State
VLAN ID (2-4094)
VLAN CoS
Discover Port (554,1025-
65535)
Trap State
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Select this option to enable or disable ONVIF globally on the
switch. This will over-write Auto Surveillance VLAN, QoS,
and Power Saving settings.
This is the VLAN that is used for surveillance devices on the
switch and can be manually configured to be a VLAN created
in the VLAN section of this document.
This is the VLAN Class of Service and can be set to a value
between 0 and 7. It uses the IEEE 802.1p Priority Levels to
classify traffic.
This is the port that is used to discover ONVIF-compatible
devices on the VLAN. The default is TCP port 554.
Select this option to enable or disable SNMP traps for
ONVIF. This SNMP host can be configured in the SNMP
Global Settings section of this document.
81
Page 88

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
IP-Camera Information
The IP-Camera Information page shows the devices that have been discovered through ONVIF.
These are ONVIF-compatible devices that have been detected in the VLAN defined in the ONVIF
Global Status page. The system probes for new IP-Cameras every 30 seconds.
To view the following window, click ONVIF > IP-Camera Information, as shown below:
Figure 14-2 IP-Camera Information window
IPC Settings
This menu is accessible by clicking on the Edit button on the IP-Camera Information page.
The fields that can be configured for IPC Settings are described below:
Parameter Description
IPC State Select the state of the IP-Camera, either Enabled or
Disabled.
Description
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Use this to enter a description for the IP-Camera. This will be
displayed on the IP-Camera Information page.
NVR Information
This is a list of the NVR devices that have been detected in the ONVIF VLAN. The switch port, IP
address of the device, the number of IP-Cameras connected, throughput, group number, and port
description. A group number will be assigned if multiple ONVIF devices have been recognized on a
port.
To view the following window, click ONVIF > NVR Information, as shown below:
Figure 14-3 NVR Information window
82
Page 89

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
The fields that can be configured for NVR Information are described below:
Parameter Description
Description Edit this by pressing the Edit button next to the entry in the
table. This is the description for the NVR that has been
detected as being connected to the port.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
83
Page 90

15. Save and Tools
Save Configuration
Firmware Information
Firmware Upgrade & Backup
Configuration Restore & Backup
Log Backup
Ping
Reset
Reboot System
Save Configuration
This window is used to save the running configuration to the start-up configuration of the switch. This
is to prevent the loss of configuration in the event of a power failure.
To view the following window, click Save > Save Configuration, as shown below:
D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Figure 15-1 Save Configuration window
Click the Apply button to save the configuration to the switch’s flash memory.
Firmware Information
This window is used to show firmware information.
To view the following window, click Tools > Firmware Information, as shown below:
Figure 15-2 Firmware Information window
Boot Up: Clicking the Boot Up button will set that firmware image as the active image to use upon
the next system start up.
Note: Changing the firmware only happens after the switch has been manually rebooted. In order to
boot with the newly selected firmware, make sure that the switch is rebooted.
Firmware Upgrade & Backup
Note: When upgrading the firmware on the DGS-1100 MP/ MPP Series switch, only the
image not currently active can be upgraded. All DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series switches
come with two images, however only one can be active at any time. (e.g. If image 1 is
currently in use, only image 2 can be upgraded, and vice versa.)
Note: If the switch is in HTTPS mode, the firmware or configuration cannot be
84
Page 91

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
upgraded using regular HTT P.
Firmware Upgrade from HTTP
This window is used to initiate a firmware upgrade from a local PC using HTTP.
To view the following window, click Tools > Firmware Upgrade & Backup > Firmware Upgrade
from HTTP, as shown below:
Figure 15-3 Firmware Upgrade from HTTP window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
Source File
Click the Upgrade button to initiate the firmware upgrade.
Enter the source filename and path of the firmware file
located on the local PC. Alternatively click the Browse button
to navigate to the location of the firmware file located on the
local PC.
Firmware Upgrade from TFTP
This window is used to initiate a firmware upgrade from a TFTP server.
To view the following window, click Tools > Firmware Upgrade & Backup > firmware Upgrade
from TFTP, as shown below:
Figure 15-4 Firmware Upgrade from TFTP window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
TFTP Server IP
Source File
Click the Upgrade button to initiate the firmware upgrade.
Enter the TFTP server’s IPv4 address here.
Enter the source filename and path of the firmware file
located on the TFTP server here.
Firmware Backup to HTTP
This window is used to initiate a firmware backup to a local PC using HTTP.
85
Page 92

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
To view the following window, click Tools > Firmware Upgrade & Backup > Firmware Backup to
HTTP, as shown below:
Figure 15-5 Firmware Backup to HTTP window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
Source
Click the Backup button to initiate the firmware backup.
Select the source image to use for the firmware backup.
Firmware Backup to TFTP
This window is used to initiate a firmware backup to a TFTP server.
To view the following window, click Tools > Firmware Upgrade & Backup > Firmware Backup to
TFTP, as shown below:
Figure 15-6 Firmware Backup to TFTP window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
TFTP Server IP
Source
Destination File
Click the Backup button to initiate the firmware backup.
Enter the TFTP server’s IPv4 address here.
Select the source image to use for the firmware backup.
Enter the destination path and location where the firmware
file should be stored on the TFTP server.
86
Page 93

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Configuration Restore & Backup
Configuration Restore from HTTP
This window is used to initiate a configuration restore from a local PC using HTTP.
Note: If the switch is in HTTPS mode, the firmware or configuration cannot be upgraded using
regular HTTP.
To view the following window, click Tools > Configuration Restore & Backup > Configuration
Restore from HTTP, as shown below:
Figure 15-7 Configuration Restore from HTTP window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
Source File
Click the Restore button to initiate the configuration restore.
Click Effective immediately (running-config) to have the uploaded configuration loaded
immediately.
Click Take effect after the next boot (startup-config) to load the configuration after the switch has
been rebooted.
Enter the source filename and path of the configuration file
located on the local PC. Alternatively click the Browse button
to navigate to the location of the configuration file located on
the local PC.
Configuration Restore from TFTP
This window is used to initiate a configuration restore from a TFTP server.
To view the following window, click Tools > Configuration Restore & Backup > Configuration
Restore from TFTP, as shown below:
Figure 15-8 Configuration Restore from TFTP window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
TFTP Server IP
Source File
Enter the TFTP server’s IPv4 address here.
Enter the source filename and path of the configuration file
located on the TFTP server here.
87
Page 94

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Click the Restore button to initiate the configuration restore.
Click Effective immediately (running-config) to have the uploaded configuration loaded
immediately.
Click Take effect after the next boot (startup-config) to load the configuration after the switch has
been rebooted.
Configuration Backup to HTTP
This window is used to initiate a configuration file backup to a local PC using HTTP.
To view the following window, click Tools > Configuration Restore & Backup > Configuration
Backup to HTTP, as shown below:
Figure 15-9 Configuration Backup to HTTP window
Select Include username password to save the switch user accounts and passwords to the backup
file.
Select Exclude username password to save the switch user accounts and passwords to the
backup file.
Click the Backup button to initiate the configuration file backup.
Configuration Backup to TFTP
This window is used to initiate a configuration file backup to a TFTP server.
To view the following window, click Tools > Configuration Restore & Backup > Configuration
Backup to TFTP, as shown below:
Figure 15-10 Configuration Backup to TFTP window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
TFTP Server IP
Destination File
Enter the TFTP server’s IPv4 address here.
Enter the destination path and location wher e the
configuration file should be stored on the TFTP server.
Select Include username password to save the switch user accounts and passwords to the backup
file.
Select Exclude username password to save the switch user accounts and passwords to the
backup file.
Click the Backup button to initiate the configuration file backup.
88
Page 95

Log Backup
Log Backup to HTTP
This window is used to initiate a system log backup to a local PC using HTTP.
To view the following window, click Tools > Log Backup > Log Backup to HTTP, as shown below:
Click the Backup button to initiate the system log backup.
Log Backup to TFTP
D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Figure 15-11 Log Backup to HTTP window
This window is used to initiate a system log backup to a TFTP server.
To view the following window, click Tools > Log Backup > Log Backup to TFTP, as shown below:
Figure 15-12 Log Backup to TFTP window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
TFTP Server IP
Destination File
Click the Backup button to initiate the system log backup.
Enter the TFTP server’s IPv4 address here.
Enter the destination path and location where the
configuration file should be stored on the TFTP server
89
Page 96

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Ping
Ping is a small program that sends ICMP Echo packets to the IP address you specify. The
destination node then responds to or “echoes” the packets sent from the switch. This is very useful
to verify connectivity between the switch and other nodes on the network.
To view the following window, click Tools > Ping, as shown below:
Figure 15-13 Ping window
The fields that can be configured for IPv4 Ping are described below:
Parameter Description
Target IPv4 Address
Ping Times
Timeout
After clicking the Start button in IPv4 Ping section, the following IPv4 Ping Result section will
appear:
Select and enter an IP address to be pinged.
Enter the number of times desired to attempt to Ping the IPv4
address configured in this window. Users may enter a
number of times between 1 and 255. Tick the Infinite check
box to keep sending ICMP Echo packets to the specified IP
address until the program is stopped.
Select a timeout period between 1 and 99 seconds for this
Ping message to reach its destination. If the packet fails to
find the IP address in this specified time, the Ping packet will
be dropped.
Figure 15-14 Ping - IPv4 Ping Result window
Click the Stop button to halt the Ping Test.
Click the Back button to return to the IPv4 Ping section.
Reset
This window is used to reset the switch’s configuration to the factory default settings.
To view the following window, click Tools > Reset, as shown below:
90
Page 97

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Figure 15-15 Reset window
Select the The Switch will be reset to its factory defaults including IP address and stacking
information, and the will save, reboot option to reset the switch’s configuration to its factory
default settings.
Select the The Switch will be reset to its factory default except IP address, and then will save,
reboot option to reset the switch’s configuration to its factory default settings. This option will
exclude the IP address from being changed.
Select the The Switch will be reset to its factory defaults including IP address option to reset
the switch’s configuration to its factory default settings.
Click the Apply button to initiate the factory default reset and reboot the switch.
NOTE: Performing a factory reset in one version of the interf ac e (Standar d Mo de
or Surveillance Mode) will cause settings to be reset in the other version of the
interface.
Reboot System
This window is used to reboot the switch and alternatively save the configuration before doing so. To
view the following window, click Tools > Reboot System, as shown below:
Figure 15-16 Reboot System window
When rebooting the switch, any configuration changes that was made during this session, will be lost
unless the Yes option is selected when asked to save the settings.
Click the Reboot button to alternatively save the settings and reboot the switch.
Figure 15-17 Reboot System - Rebooting window
91
Page 98

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
16. Appendix A - Ethernet Technology
This chapter will describe the features of the D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series switch and provide
some background information about Ethernet/Fast Ethernet/Gigab it Eth er net swit ching tec hn olo g y.
Gigabit Ethernet Technology
Gigabit Ethernet is an extension of IEEE 802.3 Ethernet utilizing the same packet structure, format,
and support for CSMA/CD protocol, full duplex, and management objects, but with a tenfold increase
in theoretical throughput of over 100-Mbps Fast Ethernet and a hundredfold increase over 10-Mbps
Ethernet. Since it is compatible with all 10-Mbps and 100-Mbps Ethernet environments, Gigabit
Ethernet provides a straightforward upgrade without wasting existing investments in hardware,
software, or trained personnel.
The increased speed and extra bandwidth offered by Gigabit Ethernet is essential to help solving
network bottlenecks that frequently develop as more advanced computer users and newer
applications continue to demand greater network resources. Upgrading key components, such as
backbone connections and servers to Gigabit Ethernet technology can greatly improve network
response times as well as significantly speed up the traffic between subnets.
Gigabit Ethernet enables fas t optical fiber connections to support video conferencing, complex
imaging, and similar data-intensive applications. Likewise, since data transfers occur 10 times faster
than Fast Ethernet, servers outfitted with Gigabit Ethernet NIC’s are able to perform 10 times the
number of operations in the same amount of time.
In addition, the phenomenal bandwidth delivered by Gigabit Ethernet is the most cost-effective
method to take advantage of today and tomorrow’s rapidly improving switching and routing
internetworking technologies. And with expected advances in the coming years in silicon technology
and digital signal processing that will enable Gigabit Ethernet to eventually operate over unshielded
twisted-pair (UTP) cabling, outfitting your network with a powerful 1000-Mbps-capable
backbone/server connection whic h will create a flexible foundation for the next generation of network
technology products.
Fast Ethernet Technology
The growing importance of LANs and the increasing complexity of desktop computing applications
are fueling the need for high performance networks. A number of high-speed LAN technologies have
been proposed to provide greater bandwidth and improve client/server response times. Among
them, 100BASE-T (Fast Ethernet) provides a non-disruptive, smooth evolution from the current
10BASE-T technology. The non-disruptive and smooth evolution nature, and the dominating
potential market base, virtually guarantees cost-effective and high performance Fast Ethernet
solutions.
100Mbps Fast Ethernet is a standard specified by the IEEE 802.3 LAN committee. It is an extension
of the 10Mbps Ethernet standard with the ability to transmit and receive data at 100Mbps, while
maintaining the CSMA/CD Ethernet protocol. Since the 100Mbps Fast Ethernet is compatible with all
other 10Mbps Ethernet environments, it provides a straightforward upgrade and utilizes existing
investments in hardware, software, and personnel training.
92
Page 99

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
Switching Technology
Another approach to push beyond the limits of Ethernet technology is the development of switching
technology. A switch bridges Ethernet packets at the MAC address level of the Ethernet protocol
transmitting among connected Ethernet or Fast Ethernet LAN segments.
Switching is a cost-effective way of increasing the total network capacity available to users on a local
area network. A switch increases capacity and decreases network loading by dividing a local area
network into different segments which won’t compete with each other for network transmission
capacity.
The switch acts as a high-speed selective bridge between the individual segments. The switch,
without interfering with any other segments, automatically forwards traffic that needs to go from one
segment to another. By doing this the total network capacity is multiplied, while still maintaining the
same network cabling and adapter cards.
93
Page 100

D-Link DGS-1100 MP/MPP Series Switch User Manual
17. Appendix B - Technical Specifications
Hardware Specifications
Key Components / Performance
Switching Capacity:
- DGS-1100-10MP: 20Gbps
- DGS-1100-10MPP: 20Gbps
- DGS-1100-26MP: 52Gbps
- DGS-1100-26MPP: 52Gbps
Max. Forwarding Rate:
- DGS-1100-10MP: 14.88Mpps
- DGS-1100-10MPP: 14.88Mpps
- DGS-1100-26MP: 38.69Gbps
- DGS-1100-26MPP: 38.69Gbps
Forwarding Mode: Store and Forward
Packet Buffer memory:
- DGS-1100-10MP: 1.5Mb ytes
- DGS-1100-10MPP: 1.5Mbytes
- DGS-1100-26MP: 1.5Mb ytes
- DGS-1100-26MPP: 1.5Mbytes
Flash Memory: 16M Byte
Port Functions
Physical & Environment
Power input: 100~240 VAC, 50/60Hz,
internal universal power supply
Acoustic Value:
- DGS-1100-10MP: 45.4dB
- DGS-1100-10MPP: 53dB
- DGS-1100-26MP: 56dB
- DGS-1100-26MPP: 56dB
Operation Temperature: -5-50°C
Storage Temperature: -40-70°C
Operation Humidity: 0% ~ 95% RH
Storage Humidity: 0% ~ 95% RH
Emission (EMI) Certifications
FCC class A
CE Class A
VCCI Class A
BSMI
CCC
Safety Certifications
CUL, LVD, CB, CCC, BSMI
10/100/1000BaseTX ports complia nt w ith
the following standards:
- IEEE 802.3
- IEEE 802.3u
- IEEE 802.3ab
- IEEE 802.3at
- IEEE 802.3af
- IEEE 802.3bt (DGS-1100 MPP Series
only)
- Supports Full/half-Duplex operations at
10/100Mbps
- Supports Full-Duplex operation at
1000Mbps
- Supports IEEE 802.3x Flow Control
- Support Auto-Negotiation
- Compliant to IEEE 802.3az Energy
Efficiency Ethernet.
SFP ports compliant with the following
standards:
- IEEE 802.3z compliance
Features
L2 Features
16K MAC address
Loopback Detection
Port Mirroring
Link Aggregation
Cable Diagnostics
Spanning Tree
Ethernet Ring Protection Switching
(ERPS)
L2 Multicasting
IGMP Snooping
VLAN
802.1Q VLAN standard
Port-Based VLAN
Surveillance VLAN
Voice VLAN
94
 Loading...
Loading...