Page 1

Technical Description of
TANDBERG Gateway
with software version G2
TANDBERG
D13192 Rev. 02
Page 2

Technical Description of TANDBERG Gateway with software version G2
Table of contents
1 INTRODUCTION ............................................................................................................................................ 4
2 PRODUCT DESCRIPTION............................................................................................................................ 5
2.1 SOFTWARE...................................................................................................................................................... 5
3 OPERATION AND USER INTERFACE ...................................................................................................... 5
4 TANDBERG GATEWAY INTERFACES & FEATURES........................................................................... 6
4.1 NETWORK INTERFACES AND FEATURES.......................................................................................................... 6
4.1.1 Multiple Calls ........................................................................................................................................... 6
4.1.2 PRI E1/T1 ISDN ....................................................................................................................................... 7
4.1.2.1 ISDN number plan........................................................................................................................................... 7
4.1.2.2 PRI Trunk Grouping........................................................................................................................................ 7
4.1.2.3 PRI E1/T1 ISDN.............................................................................................................................................. 7
4.1.3 Dial In Services......................................................................................................................................... 9
4.1.3.1 Direct Inwards Dialing (DID).......................................................................................................................... 9
4.1.3.2 Interactive Voice Response (IVR) ................................................................................................................... 9
4.1.3.3 TCS-4 .............................................................................................................................................................. 9
4.1.3.4 Hotline........................................................................................................................................................... 10
4.1.4 IP Dial Out Services ............................................................................................................................... 10
4.1.4.1 Service Prefixes ............................................................................................................................................. 10
4.1.5 Ethernet / LAN Interface (H.323) ........................................................................................................... 10
4.1.5.1 Quality of Service features (QoS).................................................................................................................. 10
4.1.5.2 IP adaptive bandwidth management .............................................................................................................. 11
4.1.5.3 Dynamic playout buffering ............................................................................................................................ 12
4.1.5.4 Asymmetrical media capabilities ................................................................................................................... 12
4.1.5.5 Diagnostic tools for IP ................................................................................................................................... 12
4.1.5.6 Latency & Jitter ............................................................................................................................................. 12
4.1.5.7 Layer 4 Ports used in H.323 .......................................................................................................................... 13
4.1.5.8 IP packet sizes ............................................................................................................................................... 13
4.1.5.9 Intelligent Packet Loss Recovery (IPLR)....................................................................................................... 14
4.1.6 LEDs Description ................................................................................................................................... 15
4.1.6.1 Description of PRI Alarms............................................................................................................................. 15
4.1.7 Intelligent Call Management (ICM) ....................................................................................................... 16
4.1.8 TANDBERG Gateway Capacity.............................................................................................................. 17
4.1.8.1 TANDBERG Gateway Capacity – typical scenarios for 4Mb Option ........................................................... 18
4.1.9 Secure Conference (Encryption)............................................................................................................. 18
4.1.10 H.243 Multipoint Transparency......................................................................................................... 19
4.2 AGGREGATION STANDARDS.......................................................................................................................... 20
4.2.1 BONDING............................................................................................................................................... 20
4.2.1.1 ISDN channel set-up...................................................................................................................................... 20
4.2.2 H.221 ...................................................................................................................................................... 20
4.2.3 H0 ........................................................................................................................................................... 20
4.3 RS232 INTERFACE/APPLICATION PROGRAMMABLE INTERFACE (API) ......................................................... 21
4.3.1 API commands........................................................................................................................................ 21
4.4 VIDEO FEATURES ......................................................................................................................................... 22
4.4.1 Optimised Video Compression................................................................................................................ 22
4.4.2 Video Formats ........................................................................................................................................ 22
4.4.3 Asymmetric Video Formats..................................................................................................................... 22
4.4.4 Duo Video ............................................................................................................................................... 23
4.4.5 Custom pictures ...................................................................................................................................... 23
4.5 AUDIO FEATURES ......................................................................................................................................... 24
4.5.1 Custom Sounds........................................................................................................................................ 24
D13192 Rev. 02 2
Page 3

Technical Description of TANDBERG Gateway with software version G2
4.5.2 Telephony................................................................................................................................................ 24
4.5.3 Audio Compression Algorithms .............................................................................................................. 24
4.6 SYSTEM MANAGEMENT ................................................................................................................................25
4.6.1 Ethernet/LAN Interface........................................................................................................................... 25
4.6.2 Platform Requirements ........................................................................................................................... 25
4.6.3 Protocols Supported ............................................................................................................................... 26
4.6.4 System Management Functionality......................................................................................................... 27
4.6.4.1 Remote software upgrades using FTP: .......................................................................................................... 27
4.6.4.2 Management using a standard Web-browser: ................................................................................................ 27
4.6.4.3 Management using a standard Telnet-client: ................................................................................................. 27
4.6.4.4 Management using a terminal connected to the RS232 port:......................................................................... 27
4.6.5 Security ................................................................................................................................................... 27
4.6.5.1 HTTPS, TLS/SSL .......................................................................................................................................... 27
4.6.5.2 Telnet Challenge Service ............................................................................................................................... 28
4.6.5.3 Disable Services............................................................................................................................................. 29
4.6.5.4 Security Alert................................................................................................................................................. 29
4.6.6 Layer 4 ports used by the system ............................................................................................................ 30
5 MISCELLANEOUS FEATURES ................................................................................................................. 31
5.1 PHONE BOOK ................................................................................................................................................ 31
5.2 FILE SYSTEM (FTP) ...................................................................................................................................... 31
5.2.1 Picture files ............................................................................................................................................. 31
5.2.2 Sound files............................................................................................................................................... 31
5.2.3 Other files ............................................................................................................................................... 31
6 ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES ....................................................................................................................... 33
6.1 TANDBERG’S ENVIRONMENTAL POLICY ................................................................................................... 33
6.2 ENVIRONMENTAL CONSIDERATIONS............................................................................................................. 33
7 PRODUCT APPROVALS ............................................................................................................................. 34
7.1 CONNECTION OF TELE-TERMINAL EQUIPMENT............................................................................................. 34
7.2 EMC EMISSION - RADIATED ELECTROMAGNETIC INTERFERENCE ................................................................ 34
7.3 EMC IMMUNITY........................................................................................................................................... 34
7.4 ELECTRICAL SAFETY .................................................................................................................................... 34
7.5 EMC IMMUNITY........................................................................................................................................... 34
7.6 NEBS APPROVAL ......................................................................................................................................... 35
8 PRODUCT RELIABILITY ........................................................................................................................... 36
9 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION OF TANDBERG GATEWAY.............................................................. 37
9.1 MECHANICAL INFORMATION......................................................................................................................... 37
9.2 PACKAGING .................................................................................................................................................. 37
9.3 OPERATING TEMPERATURE AND HUMIDITY ................................................................................................. 38
9.4 STORAGE AND TRANSPORT TEMPERATURE.................................................................................................. 38
9.5 SYSTEM POWER CONSUMPTION.................................................................................................................... 38
10 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION SHEET ...................................................................................................39
D13192 Rev. 02 3
Page 4
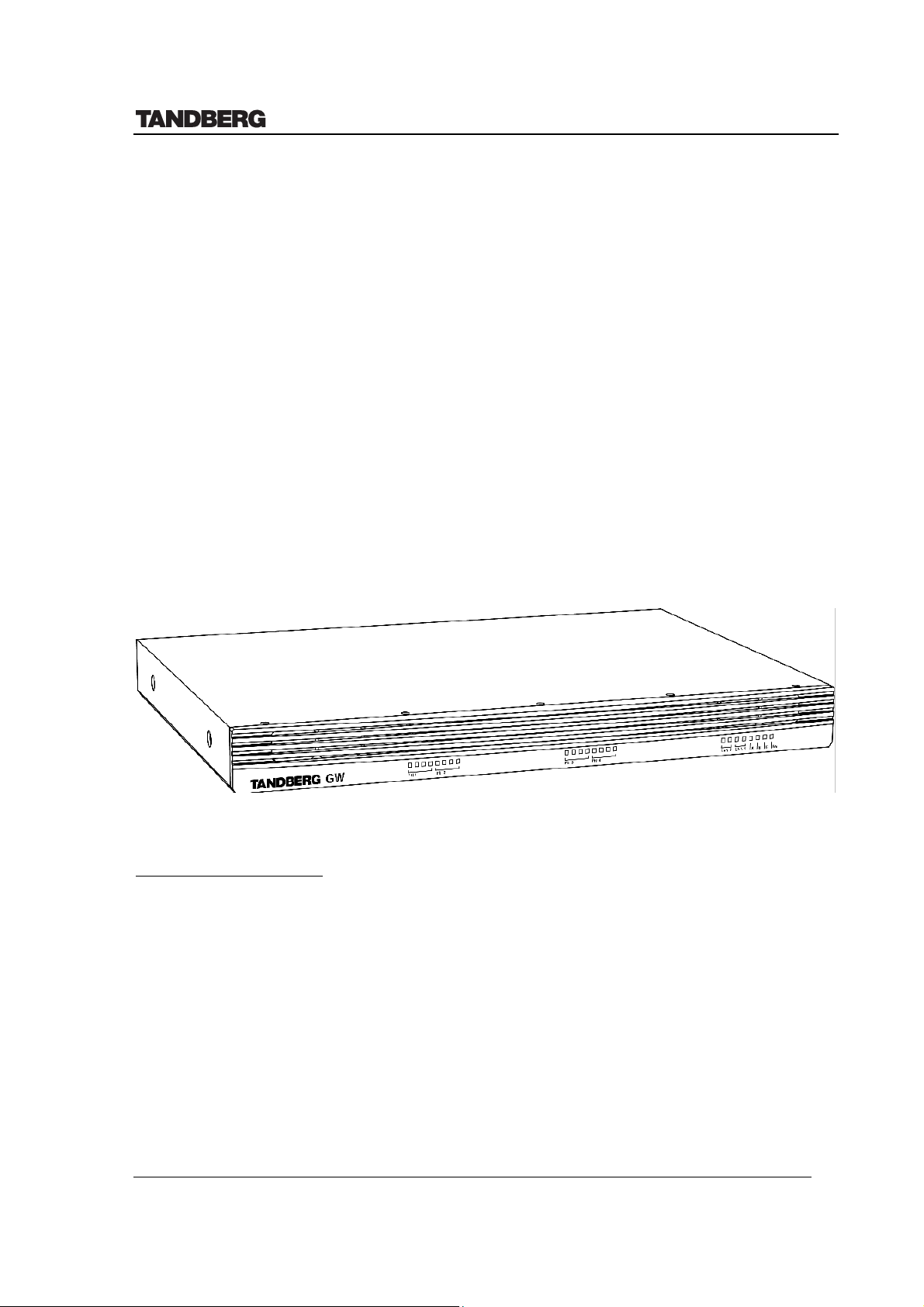
Technical Description of TANDBERG Gateway with software version G2
1 Introduction
The TANDBERG Gateway is designed to connect up to 8 videoconferencing calls and 8
telephone calls simultaneously between ISDN and IP Networks.
The TANDBERG Gateway supports the ITU-T H.320 standard and a combination of H.221 and
BONDING for communication on up to 30 ISDN B-channels as well as ITU-T H.323 v.4
standard for communication up to 2 Mbps over IP networks.
The TANDBERG Gateway is ‘configurationless’ in the sense that no extensive knowledge is
required for installation and maintenance. All features are included in the TANDBERG
Gateway – thus, there is no additional hardware required to use any of the inbuilt features.
All features of the TANDBERG Gateway are based on standards set by the ITU-T.
The TANDBERG Gateway is best utilised when used together with TANDBERG Management
Suite (TMS) and TANDBERG Scheduler, since they have incorporated features like System
Management and Scheduling (Optional).
Major features supported:
• Up to eight separate video and eight separate telephone calls
• Maximum bandwidth for all calls combined is 7680 kbps
• Flexible ISDN Dial-in Services
• Flexible IP Dial-out Services
• Call Transfer
• IP QoS Features
• H.243 Transparency
• H.264 Video Standard
• Custom video formats (e.g. XGA video resolution)
• Full implementation of Downspeeding
• Secure Conference (AES/DES Encryption)
D13192 Rev. 02 4
Page 5
Technical Description of TANDBERG Gateway with software version G2
• Dual Stream - supports Duo VideoTF on ISDN and IP, and People+Content on ISDN.
• Secure Access - Supports XML/SOAP over HTTPS
• Support for TANDBERG Scheduler and TANDBERG Management Suite - (Optional)
• ISDN Hotline
• Terminal Control Session (TCS-4)
• Interactive Voice Response (IVR)
• Direct Inward Dialing (DID)
2 Product Description
The TANDBERG Gateway is built on a standard 19-inch rack mounted chassis of only 1U in
height.
2.1 Software
In the standard version, the TANDBERG Gateway supports up to 2 Mbps bandwidth on ISDN.
With the bandwidth option installed, it can handle up to 4 Mbps bandwidth on ISDN.
3 Operation and User Interface
The TANDBERG Gateway is normally controlled via the web interface. The TANDBERG
Gateway can also be controlled via Telnet (or the RS232 port) by using a comprehensive set of
API commands
interface, such as an AMX or Crestron system.
For information on how to operate the system, please see the documents TANDBERG Gateway
User Manual or TANDBERG Gateway API supplied with the system.
1
Please, refer to document ‘
D13192 Rev. 02 5
1
. This enables the TANDBERG Gateway to be controlled by a different user
TANDBERG Gateway API’ (D13202)
Page 6
Technical Description of TANDBERG Gateway with software version G2
4 TANDBERG Gateway Interfaces & Features
Extensive use of industry standard interfaces and connectors ensure effortless integration of
external equipment with the TANDBERG Gateway. These interfaces can easily be controlled
via the web user interface.
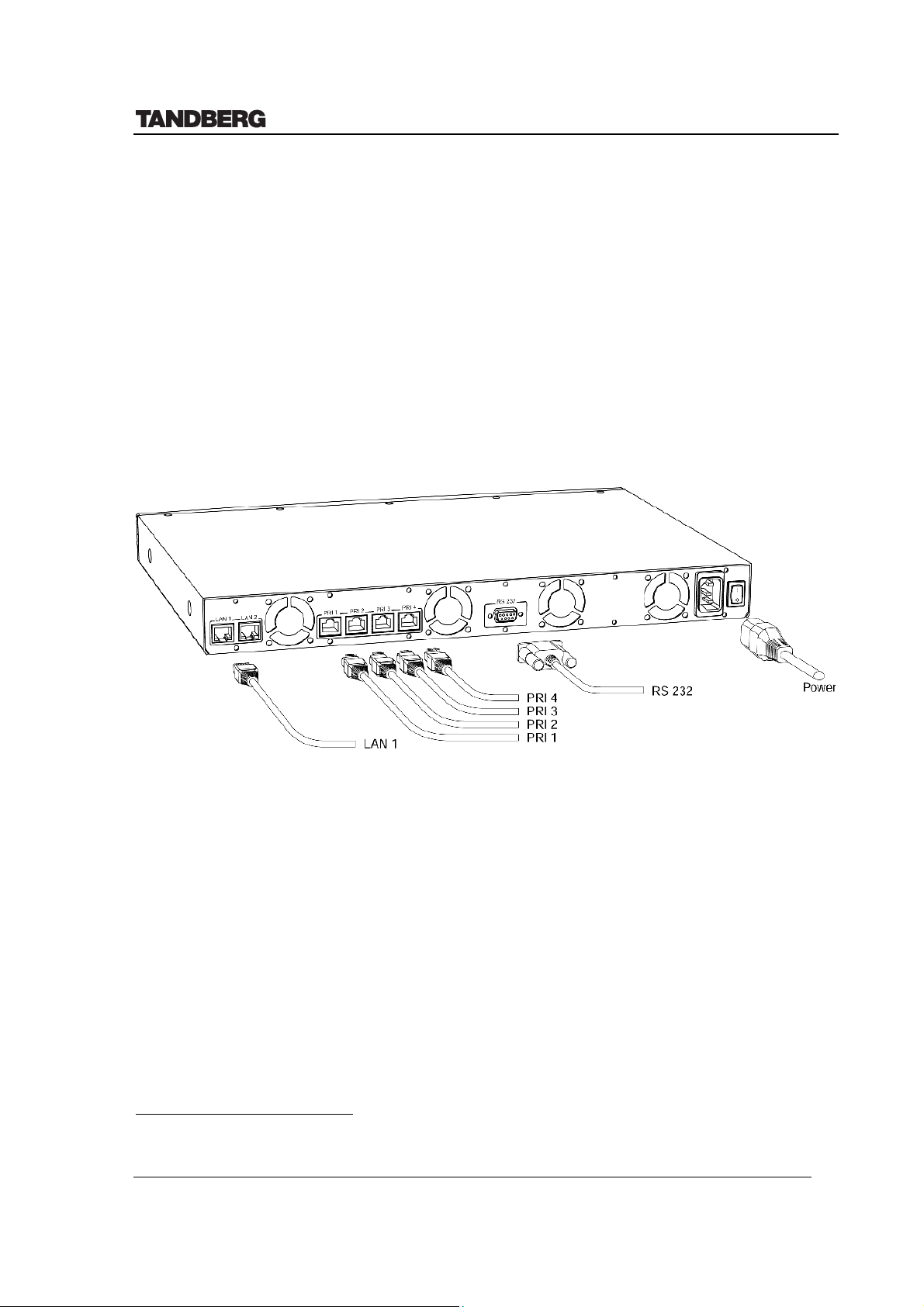
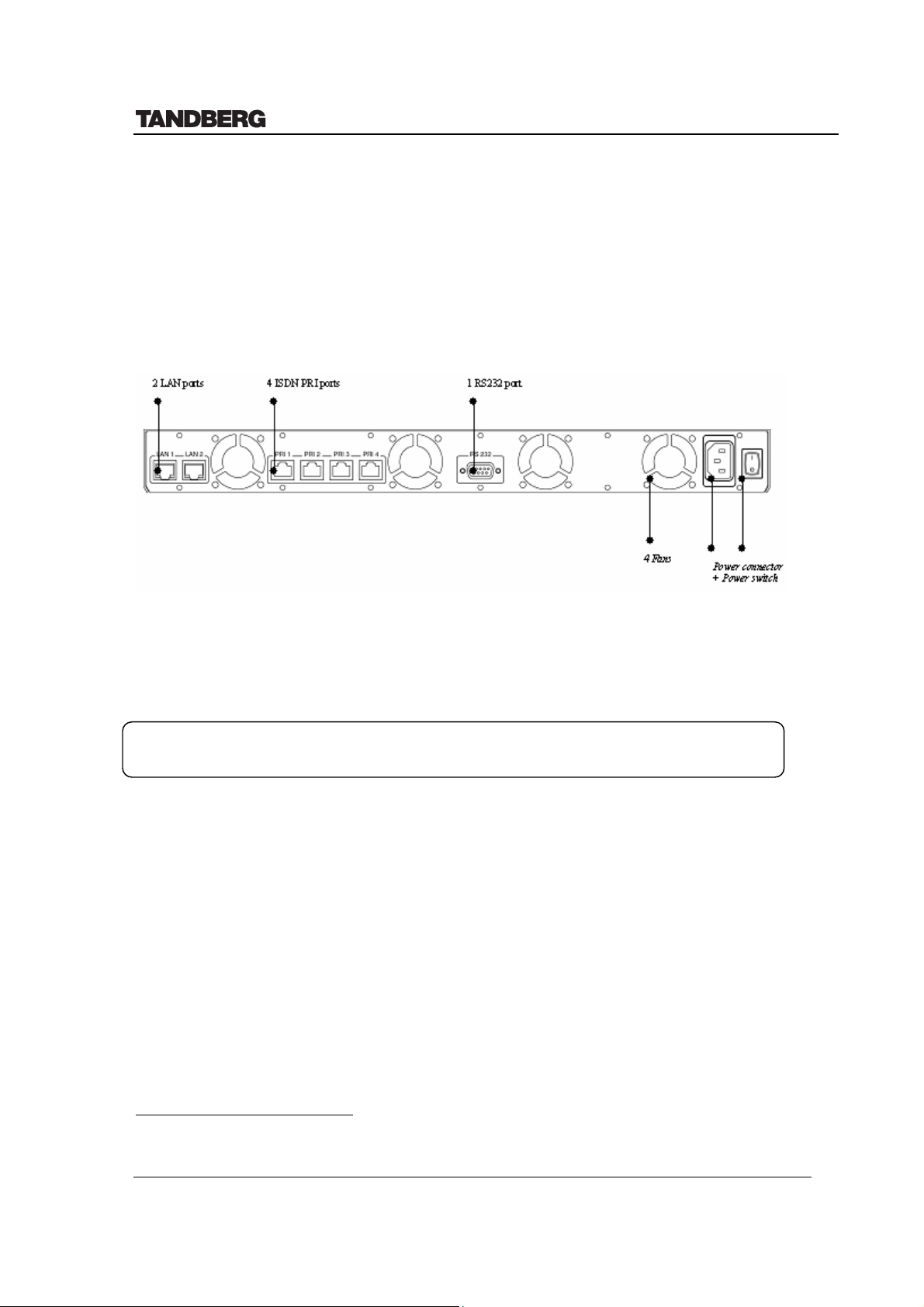
4.1 Network Interfaces and Features
Network Interfaces 4 x PRI (RJ-45 Jack) Primary Rate (G.703) Interfaces
2 x Ethernet (RJ-45 Jack) LAN interfaces (10/100 Mb)2
• 4 x PRI (RJ-45 jack) Primary Rate (G.703) interface for transmission speeds from 112
kbps up to 2 Mbps (1.5 Mbps PRI/T1).
• 2 x Ethernet (RJ-45 jack) Local Area Network interface (10/100Mb) for transmission
speeds up to 2 Mbps
4.1.1 Multiple Calls
The TANDBERG Gateway may run 8 separate simultaneous videocalls and 8 phone calls.
Please refer to the Capacity section for more information on available resources.
2
.
2
Only Ethernet port no. 1 is used in software version G2.
D13192 Rev. 02 6
Page 7

Technical Description of TANDBERG Gateway with software version G2
4.1.2 PRI E1/T1 ISDN
4.1.2.1 ISDN number plan
The TANDBERG Gateway’s PRI lines may use one or more numbers for dial in. If more than
one number is used, the numbers must be consecutive.
4.1.2.2 PRI Trunk Grouping
When using more than one PRI line, the same properties for PRI 1 can be used for all PRI's by
defining them all as a trunk group.
4.1.2.3 PRI E1/T1 ISDN
The PRI interface may require an external CSU depending on the network layout. ‘Cable
Length’ in the PRI set-up menu specifies the distance from the TANDBERG Gateway to the
CSU or last repeater.
A CSU is not required if the system is within 200 m (655 ft) of the last repeater.
The TANDBERG Gateway supports the PRI protocols AT&T Custom, National ISDN and
ETSI (Euro ISDN). The AT&T and National protocols will give a total of (23*4) = 92 channels
while the ETSI protocol will give a total of (30*4) = 120 channels.
Within these protocols the following switches are supported:
Switches
Protocols supported
4ESS (AT&T) AT&T Custom
5ESS (AT&T) AT&T Custom and National ISDN
3
DMS250 (Nortel) National ISDN
DMS100 (Nortel) National ISDN
(Any switch) ETSI (Euro ISDN)
Channel hunting is provided for outgoing calls. This feature is normally used when the number
of channels needs to be specified. When no value is specified for low or high channel, they
default to 1 (low), 23 (high US) and 30 (high Europe). Default search is from high to low.
3
Dependent on the configuration of the switch
D13192 Rev. 02 7
Page 8
Technical Description of TANDBERG Gateway with software version G2
Pinout of PRI E1/T1 Interface:4
PRI Pinout
1 TIP RX
2 RING RX
4 RING TX
5 TIP TX
NOTE: TANDBERG recommends always using category 5 cabling.
PRI T1 (US only):
Network Service Facility (NSF) can be configured as blank/no value (i.e. NSF not used –
default) or any value between 0 and 31, to describe the service facility on the PRI/T1 line.
AT&T
Service code (ref.1) Service
0 Disable
1 SDN (Including GSDN)
2 Toll Free Megacom (800)
3 Megacom
6 ACCUNET Switched Digital Service (incl. Switched Digital International)
7 Long Distance Service (incl. AT&T World Connect)
8 International Toll Free Service (1800)
16 AT&T MultiQuest
23 Call Redirection Service
Sprint
Service code (ref.2) Service
MCI
Service code (ref.2) Service
0 Reserved 1 VNET/Vision
1 Private 2 800
2 Inwatts 3 PRISM1, PRISMII, WATS
3 Outwatts 4 900
4 FX 5 DAL
5 TieTrunk
Ref. 1: AT&T TR 414859 Specification, June 1999, page 76
Ref. 2: Ascend Multiband Plus-T1/PRI, User Documentation, Page 6-8
4
The cable of use should be a straight through configuration.
D13192 Rev. 02 8
Page 9

Technical Description of TANDBERG Gateway with software version G2
4.1.3 Dial In Services
4.1.3.1 Direct Inwards Dialing (DID)
By enabling this feature, it is possible to make a direct mapping between ISDN numbers and
H323 aliases. This requires that the PRI lines connected to the TANDBERG Gateway are
configured with a range of numbers. This range of numbers should be large enough to associate
one ISDN number to each H.323 device that is intended to make use of the DID feature.
The H.323 aliases must be a portion of the ISDN number plus a prefix.
Example:
The TANDBERG Gateway is configured to use 4 digits of the ISDN Number, and 9 as the
H.323 prefix:
An endpoint dials the ISDN number 67117780
The TANDBERG Gateway transfers the call to the H.323 Alias 97780
4.1.3.2 Interactive Voice Response (IVR)
This feature is used when one 'main' ISDN number is used for the TANDBERG Gateway. When
dialing into the TANDBERG Gateway on this number, the user will be greeted with a welcome
picture and sound. The user can then enter the H.323 Alias of the site they wish to call using
DTMF tones.
IVR should be used when one single ISDN number is to be used for the TANDBERG Gateway
and when the endpoints using H.323 should be independent of the ISDN number used for the
TANDBERG Gateway.
4.1.3.3 TCS-4
TCS-4 uses the same ISDN number as IVR. The user can add the H.323 alias to the ISDN
number separated by a * . The TANDBERG Gateway will automatically transfer the call to the
H.323 alias.
Example:
Endpoint dials 6711111*1234
Gateway will transfer the call to the H.323 alias 1234
D13192 Rev. 02 9
Page 10

Technical Description of TANDBERG Gateway with software version G2
4.1.3.4 Hotline
When calling the Hotline number specified in the TANDBERG Gateway, the call is
automatically transferred to a predefined H.323 alias. This feature can be used when an operator
or helpdesk is needed.
All ISDN Dial In features (DID, IVR, TCS-4 and Hotline) can be used in any combination.
4.1.4 IP Dial Out Services
4.1.4.1 Service Prefixes
A Service Prefix is used when dialing from a H.323 endpoint to a ISDN endpoint. By dialling
the prefix, followed by the ISDN number, the call is transferred through the gateway, to the
remote site on ISDN. The service defines the type of call (telephone/video) and bandwidth for
the connection.
It is possible to define up to 20 different services on the TANDBERG Gateway.
The TANDBERG Gateway have two default services:
Service Prefix ‘0’ Video call with maximum bandwidth 384kbps
Service Prefix ‘1’ Telephone call
4.1.5 Ethernet / LAN Interface (H.323)
The TANDBERG Gateway has two RJ-45 jacks
5
for the Ethernet interface (manual or automatic
detection of 10/100Mb) and supports call rates up to 2 Mbps. The ITU-T standard H.323 v4
protocol is implemented in the TANDBERG Gateway.
The following features are specifically relevant for this network interface:
4.1.5.1 Quality of Service features (QoS)
4.1.5.1.1 IP precedence
IP precedence is a classification of packets from 0 (low priority) to 7 (high priority). The
values 6 and 7 are typically reserved for congestion control. IP precedence helps a router
select what kind of traffic to prioritise. By means of queue mechanisms, it can select
5
Ethernet port no.2 is not used in software version G2.
D13192 Rev. 02 10
Page 11

Technical Description of TANDBERG Gateway with software version G2
which packets to send first and which to throw away. Some information/traffic is time
critical while other is not, and classification is used to differentiate this traffic.
One may set separate IP precedence for Signalling, Audio, Video and Data (values 1 – 7)
as well as turn IP precedence off.
The auto setting uses the following values for IP precedence:
Signalling=6
Audio/Video=4
Data=3 (e.g. FECC commands)
This means that in auto, IP precedence has the value 6 (i.e. signalling value) while both
audio and video value is 4; data value is 3. Setting the IP precedence value in system’s
menu is actually setting the signalling value. The audio/video and data values are
changed accordingly in respect to the signalling value (i.e. audio/video value = - 2; data
value = - 3).
4.1.5.1.2 Diffserv
Diffserv is an extension of IP precedence, where values from 0 to 63 (63=Highest
priority) can be set.
4.1.5.1.3 IP type of service (TOS)
TOS helps a router select a routing path when multiple paths are available.
Delay- tells router to minimize delay
Throughput- tells router to maximize throughput
Reliability- tells router to maximize reliability
Cost- tells router to minimized cost
Off- Turns TOS off
4.1.5.1.4 Resource-Reservation Protocol (RSVP)
RSVP is a protocol that allows the TANDBERG Gateway to request the network to
reserve the bandwidth needed for the IP meeting.
4.1.5.2 IP adaptive bandwidth management
• The TANDBERG Gateway never produces more traffic than needed for better
utilization of network resources. Most of the data sent in a videoconference is video
data. Thus, by incorporating smart video algorithms, the codec sends no more video
data than necessary. Little movement in the picture gives low bit rate; while a lot of
movement gives higher bit rate.
• The TANDBERG Gateway regulates outgoing and incoming media bit rates by
means of flow control signalling.
D13192 Rev. 02 11
Page 12

Technical Description of TANDBERG Gateway with software version G2
An example of this is automatic adjustment of total bandwidth used when DuoVideo is
opened.
4.1.5.3 Dynamic playout buffering
Shapes the incoming data for better playout and re-sequencing of packet delivered out of
order. This ensures better lip sync.
4.1.5.4 Asymmetrical media capabilities
Audio and video protocols can be fully asymmetrical.
E.g., the TANDBERG Gateway can send H.263 and receive H.261 at the same time.
4.1.5.5 Diagnostic tools for IP
Q.931 To show Q.931 trace during a conference you need to issue the command syslog
on. One can get traces for RAS, Q.931 and H.245 with this command. It is a
complex trace and requires an extensive knowledge in H.323 signalling to be
understood.
Ping Ping is used to see if the TANDBERG Gateway is able to reach a specific IP-
address, using a mechanism in IP called ICMP. If the TANDBERG Gateway is
unable to register to its gatekeeper, or if it is unable to dial a specific endpoint,
one can use ping to see if there is at least an IP-route to the gatekeeper or to the
endpoint.
Traceroute Traceroute does exactly that; it traces the route an IP-packet takes to reach its
destination and displays all router hops. Traceroute is very useful for seeing
exactly where there is a routing-problem in the IP-network, and for checking
where transport-delay is introduced.
4.1.5.6 Latency & Jitter
Latency is defined as the time between a node sending a message and receipt of the
message by another node. The TANDBERG Gateway can handle any value of latencyhowever, the higher the latency, the longer the delay in video and audio. This may lead to
conferences with undesirable delays causing participants to interrupt and speak over each
other.
Jitter is defined as the variation in latency for packets sent between two nodes in the
network. Where constant latency simply produces delays in audio and video, jitter can
have a more adverse effect. Jitter causes packets to arrive out of order or at the wrong
times, which again leads to packet loss. The TANDBERG Gateway can manage packets
with jitter up to 100ms. If excessive packet loss is detected, the TANDBERG Gateway
will downspeed the connection until acceptable packet loss is achieved.
D13192 Rev. 02 12
Page 13

Technical Description of TANDBERG Gateway with software version G2
4.1.5.7 Layer 4 Ports used in H.323
The following tables describes which layer 4 ports are being used by the TANDBERG
Gateway when a call is made on an H.323 network.
TANDBERG Gateway meetings + Duo Video
Function Port Type
Gatekeeper Discovery (RAS) 1719 UDP
Q.931 Call Setup 1720 TCP
H.245 Range 5555—5587 TCP
Video Range 2326—2837 UDP
Audio Range 2326—2837 UDP
Data/FECC Range 2326—2837 UDP
4.1.5.8 IP packet sizes
Audio
The TANDBERG Gateway can receive up to 60 ms of audio in each packet. The
TANDBERG Gateway is sending 20 ms of audio in each packet, thus:
• G.711 – 160 bytes per packet
• G.728 – 40 bytes per packet
• G.722 – 160 bytes per packet
• G.722.1 – 60 bytes per packet
Video
The TANDBERG Gateway is sending maximum 1450 bytes of video per packet.
Note:
In addition, the system needs to add the following header information for each of the audio
and video packets above:
20 bytes IP-header, 8 bytes UDP-header and 12 bytes RTP-header (i.e. 40 bytes in total).
D13192 Rev. 02 13
Page 14

Technical Description of TANDBERG Gateway with software version G2
4.1.5.9 Intelligent Packet Loss Recovery (IPLR)
IPLR is an ITU standards based packet loss compensation for H.323 that improves received
video into the TANDBERG Gateway. IPLR supports all video protocols and resolutions that
TANDBERG Gateway already has implemented and is compatible with all terminals.
IPLR is a special algorithm developed at TANDBERG that will make efforts to reconstruct
the lost packets and reduce the visual effects caused by packet losses.
• If the TANDBERG Gateway experiences packet loss from an endpoint, it will ask the
endpoint to handle packet loss. This requires Intelligent Packet Loss Recovery
functionality on the endpoint.
• If an endpoint experiences packet loss from the TANDBERG Gateway, the
TANDBERG Gateway encoder will not start IPLR since this would affect the received
video quality for the other endpoint.
D13192 Rev. 02 14
Page 15

Technical Description of TANDBERG Gateway with software version G2
4.1.6 LEDs Description
The TANDBERG Gateway has 24 LEDs (Light Emitting Diodes) on the front panel. Each
giving various information, as shown below.
4.1.6.1 Description of PRI Alarms
A PRI cable consists of four wires (2 pairs of wires): One pair for Transmit (TX) and one pair
for Receive (RX) signals.
Red Alarm
Red alarm or Loss of signal (LOS) means that there is no signal and thus no framing info
received. (This has same effect as pulling out the PRI cable).
Yellow Alarm
Yellow alarm or Remote Alarm Indicator (RAI) means that the TANDBERG Gateway is
receiving framing info, but in this framing info the other side tells the TANDBERG Gateway
that it is not reading the TANDBERG Gateway’s transmitted framing info. Typically, this may
be a broken connector in the TX part of the TANDBERG Gateway PRI cable. This could also
indicate weak or noisy signal in the TX part of the TANDBERG Gateway PRI cable.
Blue Alarm
Blue alarm means that network on the far side of the CSU is unavailable.
D13192 Rev. 02 15
Page 16

Technical Description of TANDBERG Gateway with software version G2
Scenario: TANDBERG Gateway is connected via a CSU (i.e. a NT ‘Network Termination’) as
follows:
TANDBERG Gateway –cableA–CSU–cableB–Network
If a CSU loses framing/sync from the network (example: a bad cable B), it shall no longer send
valid framing out on cable A towards the TANDBERG Gateway. Instead it transmits "Blue
Alarm". Seen from the TANDBERG Gateway receiving blue alarm, this means that the network
on the far side of the CSU is unavailable.
4.1.7 Intelligent Call Management (ICM)
By using TANDBERG's inbuilt Intelligent Call Management (ICM), TANDBERG Gateway
conferences can be made from data rates up to 2 Mbps via ISDN networks.
ICM is a highly sophisticated feature provided by the TANDBERG Gateway that e.g. makes the
connection between two sites more reliable and safe. If the ISDN network drops channels
during a meeting, the conference will not shut down but adjust to the remaining number of
available channels
6
. This ability is called ‘Downspeeding’ and is in accordance to the
BONDING Mode 1 standard.
By defining a maximum bandwidth for the different services (DID, IVR, TCS-4, Hotline, H.323
services), all connections will be restricted to these bandwidths.
If the requested bandwidth is not available in the TANDBERG Gateway or in the receiving
endpoint, the TANDBERG Gateway will set up the connection using the available resources.
6
If the connected site does not support downspeeding, the site will drop out of the call.
D13192 Rev. 02 16
Page 17

Technical Description of TANDBERG Gateway with software version G2
4.1.8 TANDBERG Gateway Capacity
The total capacity of the TANDBERG Gateway is defined by the following rules.
I. Maximum 8 video calls and 8 telephones calls.
II. Total system bandwidth (IP + ISDN) of the TANDBERG Gateway is 7680 kbps. The
maximum bandwidth used for ISDN calls is depending on the number and type of
PRI's installed:
a) The maximum bandwidth for each ISDN E1 is 1920 kbps (30x64kbps).
b) The maximum bandwidth for ISDN T1 is 1472 kbps (23x64kbps).
III. In addition, each call has a Call Weight depending on bandwidth and encryption as
follows:
Video calls:
Bandwidth
Non-encr.
Encrypted
64
74 80 82 84 88 92 108 124 160 176 220
106 118 120 122 136 146 168 222 N/A N/A N/A
128 192 256 320 384 512 768 1152 1472 1920
Telephone calls:
Bandwidth Telephone
Non-encr.
Encrypted
22
N/A
The total sum of the Call Weights on the TANDBERG Gateway can not exceed 845.
(Users will be prevented from setting up calls that exceeds this limit).
Example of call weight calculation:
If the TANDBERG Gateway has made 1 encrypted call at 768kbps and two unencrypted calls at
384kbps the calculation will be:
222 + 2(92) = 222 + 184 = 406
Since 406 is less than 845, this will be OK.
D13192 Rev. 02 17
Page 18

Technical Description of TANDBERG Gateway with software version G2
4.1.8.1 TANDBERG Gateway Capacity – typical scenarios for 4Mb Option
In the table below some typical capacity scenarios are listed (they can be derived by the
calculation above):
Bandwidth Non-encrypted
(Max. no. of video
calls + telephone
Encrypted
(Max. no. of video
calls)
calls) IP & E1
128 kbps 8 + 8 7
256 kbps 8 + 7 6
384 kbps 8 + 4 5
512 kbps 7 + 4 5
768 kbps 5 + 0 3
1472 kbps
2 + 8 N/A
(1.5Mbps)
1920 kbps (2Mbps) 2 + 0* N/A
*) Limited by the maximum capacity 7680 kbps, see rule II a) above.
4.1.9 Secure Conference (Encryption)
The TANDBERG Gateway has built-in encryption of audio, video and data for both H.323
(based on ITU standard H.235) and H.320 (based on ITU standard H.233 and H.234).
The encryption algorithms used in the TANDBERG Gateway and all other TANDBERG
systems are:
- The Data Encryption Standard (DES) with a 56 bits session key
- The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) with a 128 bits session key
Although there are small differences between H.323 and H.320, a typical set-up of a secure call
can be defined as follow:
1. Establishement of a common shared secret and selection of a encryption algorithm.
2. Exchange of the keys according to the common shared secret and the selected encryption
algorithm.
3. Start the encryption.
The establishment of the common shared secret is done through the computation of the DiffieHellman (DH) algorithm. The DH method uses primes numbers of 512 bits length for DES and
1024 bits for AES. The shared secret is then used as a key for the selected encryption algorithm
D13192 Rev. 02 18
Page 19

Technical Description of TANDBERG Gateway with software version G2
which encrypts "the session keys". When the session are collected by the remote end, encryption
of the audio, video and data channels can start.
The encryption will be established automatically when both endpoints in the conference
supports encryption with automatic key generation (and the conference is set up for encryption
mode of operation).
Encryption is supported for meetings up to 768 kbps and for the TANDBERG feature
DuoVideo.
Note: For an encrypted call, the endpoints must support encryption (AES or DES).
If encryption is enabled, the TANDBERG Gateway accepts both AES and DES encryption.
If one of the sites does not support encryption, encryption on both sides is disabled.
4.1.10 H.243 Multipoint Transparency
All MCU commands and information signalling are transparent through the
TANDBERG Gateway. The most important commands and information signals are:
- Request/Release floor
- Site Naming
- Cascading Signalling
- OnAir Signalling
- Microphone Off signalling(not supported by IP endpoint)
D13192 Rev. 02 19
Page 20

Technical Description of TANDBERG Gateway with software version G2
4.2 Aggregation Standards
ISDN Aggregation H.221 Frame Structure from 64 (56
ISO 13871 BONDING, Mode 1 from 64 (56
H0 One 384 kbps channel
4.2.1 BONDING
• ISO 13871, BONDING Mode 1 for bit rates from 56 kbps up to 2 Mbps (1 to 30 channels).
• The maximum relative delay difference between B-channels is 0.5 second (i.e. to compensate
for different routing of channels).
The following are the standard bandwidths on H.320:
30ch – 24 – 23 – 18 – 12 – 8 – 6 – 5 – 4 – 3 – 2 – 1
4.2.1.1 ISDN channel set-up
The following is a description of how the ISDN channels are set up.
Incoming & Outgoing TANDBERG Gateway calls: Normally the TANDBERG Gateway will
set up only 1 channel from PRI 1 and build up the channels starting from the 'bottom' of the last
PRI in use.
This will ensure that the TANDBERG Gateway always have available channels on the first PRI
number (which normally should be the TANDBERG Gateway 's main number).
*
) kbps to 128 kbps
*
) kbps to 2 Mbps
4.2.2 H.221
• For bit rates from 56 kbps up to 128 kbps (1 or 2 channels).
• The maximum relative delay difference between the 2 B-channels is 0.6 second.
4.2.3 H0
H0 is an ITU defined 384 kbps service available for ISDN PRI. The TANDBERG Gateway
supports H0 on incoming ISDN calls. H0 is defined as a group of 6 ISDN channels multiplexed
to provide one 384 kbps channel. H0 may have a shorter connection time, since there is only
one channel to set up.
This service is sometimes called Switched 384 or ISDN H0.
D13192 Rev. 02 20
Page 21

Technical Description of TANDBERG Gateway with software version G2
4.3 RS232 Interface/Application Programmable Interface (API)
Data Standards Data TANDBERG Dynamic Data Channel (DDC)
Modem Standard modem commands
Data Interfaces 1 x Data port, RS-232 (9-pin D-sub), Up to 115200 Baud for Data & Control
The RS232 port on the TANDBERG Gateway is implemented as Digital Circuit Terminating
Equipment (DCE).
The connectors used are female 9-pin D-subs and the pin-out is shown in table below.
Signal Name Direction Pin number
Carrier detect, CD From DCE 1
Receive data, RXD From DCE 2
Transmit data, TXD To DCE 3
Data terminal ready, DTR From DCE 4
Signal ground, GND 5
Data set ready, DSR From DCE 6
Ready to send, RTS To DCE 7
Clear to send, CTS From DCE 8
Ring indicator, RI From DCE 9
Note: The API commands may also be accessed via Telnet, through the TANDBERG
Gateway’s Ethernet connection.
4.3.1 API commands
Please refer to the document ‘TANDBERG Gateway API’ (D13202) for details.
The RS232 port is used for local software upgrades, local control and diagnostics.
Also, refer to ‘TANDBERG SNMP’ (D12190) for SNMP implementation.
D13192 Rev. 02 21
Page 22

Technical Description of TANDBERG Gateway with software version G2
4.4 Video Features
The TANDBERG Gateway supports the ITU video standards H.261, H.263, H.263+ and H.264.
4.4.1 Optimised Video Compression
The ITU standard H.264 provides:
• Optimised compression and decompression of video at lower bandwidths.
• A sharper picture than provided by H.261 and H.263.
• Improved contrast and enhanced clarity of the finer details within an image.
• Improved motion handling that removes the characteristic blocking that tends to occur during
normal H.261 and H.263 movement.
4.4.2 Video Formats
The TANDBERG Gateway supports the following video formats:
Native NTSC:
• SIF, Source Input Format (352 x 240 pixels)
• 4SIF (704 x 480 pixels)
Native PAL:
• CIF, Common Intermediate Format (352 x 288 pixels)
• 4CIF (704 x 576 pixels)
• QCIF, Quarter CIF (176 x 144 pixels)
Native PC:
• VGA, Video Graphics Array (640 x 480 pixels)
• SVGA, Super VGA (800 x 600 pixels)
• XGA, eXtended VGA (1024 x 768 pixels)
4.4.3 Asymmetric Video Formats
The TANDBERG Gateway can send and receive asymmetric video formats. This means any
combination of the supported custom video formats may be sent/received to/from the
TANDBERG Gateway.
Changes in the video formats during the conference are done automatically either when one of
the sites changes its transmitting video format or if these formats are changed from the
TANDBERG Gateway itself.
D13192 Rev. 02 22
Page 23

Technical Description of TANDBERG Gateway with software version G2
4.4.4 Duo Video
The TANDBERG Gateway is capable of receiving/transmitting two simultaneous video signals
from/to the connected sites
7
on all call rates from 128kbps and above. When one of the sites
requests for Duo Video, the TANDBERG Gateway will open Duo Video towards the other
video site if capable of receiving it. If the other site requests for Duo Video the TANDBERG
Gateway will automatically transmit this site’s Duo Video to the first site.
The TANDBERG Gateway uses High Speed Data rates (HSD) for Duo Video.
The Video format of Duo Video is described in ch.4.4.2.
Duo Video Interoperability with other vendors
The TANDBERG Gateway is compatible with the Polycom feature ‘People + Content’.
The TANDBERG Gateway can receive Duo Video (from a TANDBERG endpoint) and transmit
it as People + Content to PolyCom iPower
8
(on H.320).
Note: This feature must be enabled in the TANDBERG Gateway configuration (Web page or
via Telnet) to work with the iPower. There is also a setting for enabling People + Content on the
iPower system.
4.4.5 Custom pictures
The TANDBERG Gateway has a variety of pictures that may be changed by storing new files on
the FTP file system of the TANDBERG Gateway.
Please, see ch.5.2 for details on file sizes.
Gateway Call Proceeding
The Call Proceeding image is shown while the TANDBERG Gateway connects to the second
participant in the call.
GW Extension Enquire picture
This is an image asking the calling site to enter the extension number to reach a site.
Downspeeding in progress
This is an image shown when a connection is downspeeding.
7
Depending on the connected sites ability to transmit/receive Duo Video.
8
This features is tested with: PictureTel iPower 680, 970 with software version 4.0.6.909 & Accord MCU with software version 4.01.448
D13192 Rev. 02 23
Page 24

Technical Description of TANDBERG Gateway with software version G2
4.5 Audio Features
4.5.1 Custom Sounds
The TANDBERG Gateway has a variety of sounds that may be changed by storing new files on
the FTP file system of the TANDBERG Gateway. Ref. Ch.5.2 for details.
4.5.1.1.1 Gateway Welcome
When endpoints are entering a conference, they will be greeted with a default welcome sound. It
is possible to customize this welcome sound by storing a WAV-file in the system.
4.5.1.1.2 Extension Enquire sound
When endpoints are entering a conference and a extension number is required, they will be
asked to enter the extension number by using DTMF tones. It is possible to customize this sound
by storing a WAV-file in the system.
4.5.2 Telephony
The TANDBERG Gateway may also be used to connect telephone calls. The TANDBERG
Gateway supports up to 8 simultaneous telephone calls. See also Ch. 4.1.8 for possible
connected telephone sites in a conference.
4.5.3 Audio Compression Algorithms
The following audio algorithms are supported on the TANDBERG Gateway:
• G.711 48/56/64 kbps, 3.1 kHz bandwidth.
• G.728 16 kbps, 3.1 kHz bandwidth.
• G.722 48/56/64 kbps, 7 kHz bandwidth.
• G.722.1 24 kbps or 32 kbps, 7 kHz bandwidth.
D13192 Rev. 02 24
Page 25

Technical Description of TANDBERG Gateway with software version G2
4.6 System Management
TANDBERG provides a comprehensive set of management tools, and is committed to the use of
standards-based tools.
The TANDBERG Gateway can be managed in many ways:
The internal web server allows for remote control of the TANDBERG Gateway using a
web interface from anywhere on the LAN/WAN/Internet (open browser
http://TANDBERG Gateway-ipaddress
The Application Program Interface (API) allows for connecting a computer directly to
the system via the RS232 port or from anywhere on the LAN/WAN/Internet via Telnet
or FTP.
The TANDBERG Management Suite (TMS) may also be used to manage the system and
the TANDBERG Scheduler may be used to schedule conference meetings (Optional).
4.6.1 Ethernet/LAN Interface
There are two Ethernet/LAN interfaces on the TANDBERG Gateway, of which only one is
currently in use. The LAN interface supported on the TANDBERG Gateway is 10base-T and
100base-T compatible, and is used for H.323 conferences as well as management features of the
TANDBERG Gateway, such as connecting to the internal web-server, Telnet and FTP-server.
The system supports the following settings of this interface:
• Auto The TANDBERG Gateway will auto-detect the speed/duplex on the LAN
• 10/Half The TANDBERG Gateway will connect to the LAN using 10Mbps
speed/Half Duplex
• 10/Full 10 Mbps speed/Full Duplex
• 100/Half 100 Mbps speed/Half Duplex
• 100/Full 100 Mbps speed/Full Duplex
‘DHCP’ (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) can be selected when a DHCP server is
present. When using DHCP, IP-address and IP-subnet mask and IP gateway are not used since
the DHCP server assigns these parameters.
If ‘Static’ is selected, the system’s IP-address and IP-subnet mask must be specified in the IP
configuration menu.
)
4.6.2 Platform Requirements
The management tools are based on standard protocols, obviating the need for special programs
running on the management computer.
The management computer may be any computer running a standard operating system (i.e. the
management computer may be a Personal Computer running the Windows 95/98/2000/NT
D13192 Rev. 02 25
Page 26

Technical Description of TANDBERG Gateway with software version G2
operating systems), which includes the necessary programs such as:
• An FTP client (please see ‘Upgrading software in TANDBERG Videoconferencing
units’- document D10238 - for details)
• A web-browser (please see ‘TANDBERG Gateway User Manual’- document D13187
- for details)
• A Telnet client (please see ‘TANDBERG Gateway API’- document D13202 - for
details)
• A terminal emulator for the RS232 port (please see ‘TANDBERG Gateway API’ -
document D13202 - for details)
4.6.3 Protocols Supported
TCP/UDP/IP - Transport Control Protocol/User Datagram Protocol/Internet
Protocol, providing connectivity over LAN/WAN to any
networked computer.
HTTP - HyperText Transport Protocol, providing a Web-browser interface
to the management computer. (‘Max. number of simultaneous
connections’ = unlimited, although only one is processed at a time)
HTTPS - Hypertext Transfer Protocol over Secure Socket Layer is a Web
protocol that encrypts and decrypts user page requests as well as
the pages that are returned by the Web server. It uses Secure
Socket Layer (SSL) as a sublayer under its regular HTTP
application layering. HTTPS uses port 443 instead of HTTP port
80 in its interactions with the lower layer, TCP/IP. SSL uses a 40bit key size for the RC4 stream encryption algorithm, which is
considered an adequate degree of encryption for commercial
exchange.
FTP - File Transfer Protocol, providing access to the ‘FTP file system’
of the TANDBERG Gateway. (‘Max. number of simultaneous
connections’ = 1)
TELNET - Provide a standard command-line interface to management
functions. (‘Max. number of simultaneous connections’ = 8)
TELNET CHALLENGE - An option to the standard Telnet service. Telnet Challenge offers a
telnet connection where the password is not sent over the network,
hence impossible to sniff.
SNMP
9
- Simple Network Management Protocol, standard for network
management and surveillance. (RFC1157 SNMPv1, RFC 1213
MIB-II).
DHCP - Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, enabling the system to
automatically be given IP address and Subnet Mask when
connected to a network with a DHCP server.
In addition to the above, TCP/IP based protocols allowing management to be performed
9
For further info on SNMP refer to document ‘TANDBERG SNMP’ (D12190)
D13192 Rev. 02 26
Page 27

Technical Description of TANDBERG Gateway with software version G2
remotely. Local management, control and software upgrade facilities are also available through
a standard RS232 interface.
4.6.4 System Management Functionality
4.6.4.1 Remote software upgrades using FTP:
This service is provided by the standard TCP/IP based FTP protocol. Any networked PC may
perform software upgrades either locally or over the Internet depending on the LAN connectivity
on the customer premises (firewalls etc.). By using any FTP-client software (such as the FTPclient bundled with the Windows operating system), it is possible to upload the new software
release to the TANDBERG Gateway. The software file is in binary format in order to decrease
upload time. All settings of the TANDBERG Gateway will be restored after a software upgrade.
4.6.4.2 Management using a standard Web-browser:
The web-browser is the most common way to manage the TANDBERG Gateway giving access
to all managing features of the TANDBERG Gateway. Using a standard Web-browser
(Netscape, MS Internet Explorer 3.0 or later), the user may perform all forms of meeting set-up
and control, but also diagnostics, troubleshooting and software upgrade.
4.6.4.3 Management using a standard Telnet-client:
(i.e. a Telnet program bundled with the Windows operating system)
This gives the user the same functionality as from the web interface and the RS232 port. It
provides advanced debug capabilities such as ISDN layer 3 (D-channel) traces on the Primary
Rate interfaces, low-level H.320 protocol diagnostics (e.g. H.221 traces), etc. This interface is a
command-line type interface, not a graphical interface like the Web-browser interface. The
system supports multiple simultaneous Telnet sessions. See chapter 4.3 and the document
‘TANDBERG Gateway API’ (D13202) for details of API commands available via
RS232/Telnet.
4.6.4.4 Management using a terminal connected to the RS232 port:
(i.e. using the HyperTerminal program bundled with the Windows operating system).
Provides the same services and features as the Telnet-interface does, but locally. See chapter 4.3
and the document ‘TANDBERG Gateway API’ (D13202) for details of API commands
available via RS232/Telnet.
4.6.5 Security
4.6.5.1 HTTPS, TLS/SSL
The TANDBERG Gateway supports HTTPS in order to ensure secure transmission of the
information displayed on the administrator’s PC (i.e. a secure connection between any Web
browser and the TANDBERG Gateway (the TANDBERG Gateway web server) will be
established if the HTTPS service on the TANDBERG Gateway is enabled). HTTPS allows for
password exchange which is especially important.
D13192 Rev. 02 27
Page 28

Technical Description of TANDBERG Gateway with software version G2
• SSL
Secure Sockets Layer, protocol developed by Netscape for transmitting private
documents via the Internet. SSL works by using a private key to encrypt data that is
transferred over the SSL connection.
• HTTPS - Web pages that require an SSL connection start with https: instead of http:.
• TLS - Transport Layer Security
• SOAP - Simple Object Access Protocol is a lightweight protocol for exchange of
information in a decentralized, distributed environment
• XML - Extensible Markup Language is a flexible way to create common information
formats and share both the format and the data on the World Wide Web, intranets, and
elsewhere.
To enable HTTPS, use the API command services https on. The HTTPS server will then be
activated at next restart.
If the TANDBERG Gateway’s HTTP service also is activated, the user will automatically be
redirected to HTTPS. If HTTP is de-activated, you will have to specify HTTPS. (In the latter
case https://10.0.5.203
will work, but not http://10.0.5.203).
4.6.5.2 Telnet Challenge Service
When password protection is enabled for a system, a user will be requested for a password when
connecting using normal telnet. The password provided is sent unencrypted, making it possible
to sniff the password on the network.
In order to avoid making it possible to obtain the password by sniffing, the telnet challenge
service is available. This service can be activated either on a separate IP port 57, or on IP port
23. When activated on IP port 23, the challenge service will override the normal telnet service.
The intention of the telnet challenge service is that the client will use the password with a server
provided string to generate a response that does not contain the password. Thus, the response
can not be used to deduct the password, but the server can use it to know whether the client
knows the correct password or not. This increases the security by not sending the password over
the network.
Notice that if password protection is disabled, there will be no challenge request when
connecting, and the service is equal to the normal telnet service.
D13192 Rev. 02 28
Page 29

Technical Description of TANDBERG Gateway with software version G2
It is also important to understand that only the password is protected with this service. The
actual connection is not encrypted, and can be sniffed as for a normal telnet connection.
4.6.5.3 Disable Services
There is no router inside the system that can route between the ISDN side and the IP side of the
TANDBERG Gateway. This means it is not possible to get access to the Ethernet port via an
ISDN conference. However, if wanted the following services may be disabled/enabled (with
API commands):
• Telnet Service
• Telnet Challenge Service
• HTTP Service
• HTTPS Service
• FTP Service
• SNMP Service (may also be set to read only or Traps Only)
4.6.5.4 Security Alert
The system will notify any management application when someone tries remote access over IP
with illegal password (via SNMP traps). Information about the intruder’s IP-address and the
service used (Web, Telnet and FTP) will be given.
When the (optional) TANDBERG Management Suite (TMS) is used, an email notification may
also be sent e.g. to the administrator of the network.
D13192 Rev. 02 29
Page 30

Technical Description of TANDBERG Gateway with software version G2
4.6.6 Layer 4 ports used by the system
The following TCP and UDP ports are relevant for the TANDBERG Gateway.
Function Port Type Direction
Gatekeeper RAS 1719 UDP
Gatekeeper Discovery 224.0.1.41:1718 UDP
Q.931 Call Setup 1720 TCP*
H.245/Q.931 Range 5555—5587 TCP
Video Range 2326—2837 UDP
Audio Range 2326—2837 UDP
Data/FECC Range 2326—2837 UDP
FTP (control) 21 TCP*
Telnet 23 TCP*
HTTP 80 TCP*
HTTPS 443 TCP
NTP 123 UDP*
⇐ (incoming to
⇔
⇔
⇔
⇔
⇔
⇔
⇔
⇔
⇔
⇔
⇔
TANDBERG Gateway)
SNMP (Queries) 161 UDP*
SNMP (Traps) 962 UDP
⇒ (outgoing from
⇔
TANDBERG Gateway)
Netlog 963 TCP
FTP (data) 1026 TCP
⇔
⇔
Outgoing H.323 call:
First call uses 5555 for outgoing Q.931 and 5556 for H.245, next uses 5557 for Q.931 and 5558
for H.245, etc.
Please see the TANDBERG and IP document (D12434) for more details.
Incoming H.323 call:
All incoming calls use 1720 for Q.931 messaging. First call uses 5555 for H.245, second 5556
etc.
Please see the TANDBERG and IP document (D12434) for more details.
(*) Listening sockets
D13192 Rev. 02 30
Page 31

Technical Description of TANDBERG Gateway with software version G2
5 Miscellaneous features
5.1 Phone book
The TANDBERG Gateway can store up to 100 numbers in the phonebook. The phonebook may
be edited through the web interface or by editing the dir.prm file, stored on file system of the
TANDBERG Gateway (FTP). It also interacts with the Phone book features in TANDBERG
Management Suite.
5.2 File system (FTP)
The TANDBERG Gateway incorporates an internal FTP-server where various files can be
stored.
The TANDBERG Gateway uses default files unless the administrator specifies/stores any of
these custom files (the default files are hidden). All the files described below are stored with the
filenames indicated in brackets. When storing any of these files directly from FTP the filenames
specified must be used. However, storing from the web page will change filenames
automatically.
Legal File Formats:
Pictures JPEG (.jpg) files that are not greyscale and non-progressive coded.
Sounds 16bit 8Khz mono Wave (.wav) files.
System Settings TANDBERG parameter (.prm) files
Recommended maximum size is 352x288.
5.2.1 Picture files
Gateway Call Proceeding - callproc.jpg
GW Extension Enquire Screen - extreq.jpg
Downspeeding In Progress - downspeed.jpg
5.2.2 Sound files
Gateway Welcome - callproc.wav
Extension Enquire Sound - extreq.wav
5.2.3 Other files
Parameter settings of TANDBERG Gateway - all.prm
This file contains the current TANDBERG Gateway parameter settings.
D13192 Rev. 02 31
Page 32

Technical Description of TANDBERG Gateway with software version G2
Directory - dir.prm
This file contains the directory/phonebook of the TANDBERG Gateway.
D13192 Rev. 02 32
Page 33

Technical Description of TANDBERG Gateway with software version G2
6 Environmental Issues
6.1 TANDBERG’s Environmental Policy
• TANDBERG’s Research and Development is continuously improving TANDBERG’s
products towards less use of environmentally hazardous components and substances as
well as to make the products easier to recycle.
• TANDBERG's products are Video Conferencing Solutions. The idea of Video
Conferencing is to reduce the need for expensive, time demanding and polluting
transport of people. Through people’s use of TANDBERG’s products, the environment
will benefit from less use of polluting transport.
• TANDBERG’s wide use of the concepts of outsourcing makes the company itself a
company with a low rate of emissions and effects on the environment.
• TANDBERG’s policy is to make sure our partners produce our products with minimal
influence on the environment and to demand and audit their compatibility according to
applicable agreements and laws (national and international).
6.2 Environmental Considerations
Like other electronic equipment, the TANDBERG Gateway contains components that may have
a detrimental effect on the environment.
• Printed-wiring boards made of plastic, with flame-retardants like Chloride or Bromide.
• Component soldering that contains lead.
• Smaller components containing substances with possible environmental effect.
After the product’s end of life cycle, it should be returned to authorized waste handling and
should be treated according to National and International Regulations for waste of electronic
equipment.
D13192 Rev. 02 33
Page 34

Technical Description of TANDBERG Gateway with software version G2
7 Product Approvals
The product has been approved by various international approval agencies, among others: UL,
BABT and NEMKO. According to their Follow-Up Inspection Scheme, these agencies also
perform production inspections at a regular basis, for all production of TANDBERG’s
equipment.
The test reports and certificates issued by the approval agencies show that the TANDBERG
Gateway complies with the following standards.
7.1 Connection of Tele-Terminal Equipment
• TBR 4
(Comply with EU’s Commission Decision 1999/5/EC).
7.2 EMC Emission - Radiated Electromagnetic Interference
• EN55022:1994 + A1:1995 + A2:1997 (CISPR 22:1993 + Corr. and Am.1 and Am.2)
Class B (Comply with EU’s Commission Decision 89/336/EEC).
•
FCC Rules and Regulations Part 15, Subpart B, Class A.
7.3 EMC Immunity
• EN 55024:1998
•
EN 61000-3-2:1995 + A12:1995
EN 61000-3-3:1995
•
(Comply with EU’s Commission Decision 89/336/EEC).
7.4 Electrical Safety
• IEC 60950:1991 + Amd.1:1992 + Amd.2:1993 + Amd.3:1995 + Amd.4:1996
•
EN 60950:1992 + Amd.1:1993 + Amd.2:1993 + Amd.3:1995 + Amd.4:1997 +
Amd.11:1997 (Comply with EU’s Commission Decision 73/23/EEC).
•
UL 1950 3. Edition
•
CSA C22.2 No. 950-M95
7.5 EMC Immunity
• EN 55024:1998
D13192 Rev. 02 34
Page 35

Technical Description of TANDBERG Gateway with software version G2
7.6 NEBS approval
This product complies with the standards GR-63-CORE and GR-1089-CORE and is NEBS
approved by UL. For NEBS compliance, the product should be installed in the following
manner:
- Use the enclosed rack brackets marked "NEBS".
- There should be a clearance of 9.1cm between the product and any other
product mounted in the rack.
D13192 Rev. 02 35
Page 36

Technical Description of TANDBERG Gateway with software version G2
8 Product Reliability
The predicted reliability of the TANDBERG Gateway is expressed in the expected random
Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) for the electronic components based on the Power On
Hours (POH).
• The POH for the TANDBERG Gateway is > 69 000 hours.
The MTBF value is dependent on correct handling (e.g.: ESD protective measures are used), installation and
use of the TANDBERG Gateway.
• The Useful Life Cycle for the TANDBERG Gateway is in excess of 6 years.
• TANDBERG is in a position to identify batches of products with possibly less reliability than
stated above ('product tracking') and will in such an event inform their customers.
• ISO 9001 certificate is available upon request from the manufacturer.
D13192 Rev. 02 36
Page 37

Technical Description of TANDBERG Gateway with software version G2
9 Technical specification of TANDBERG Gateway
9.1 Mechanical information10
TANDBERG
Gateway
Height
Width
Depth
Weight
The TANDBERG Gateway is a standard 19 inch rack mountable with 1U height.
Standard cables for
TANDBERG Gateway
PRI cables (4) 111890 M1,M2,M3,M4 5.0 m 16.7 ft
Ethernet cable 112083 5.0 m 16.7 ft
RS232 cable 112489 3.0 m 10.0 ft
Power cables (International
package)
Power cable (US only) 110210 2.0 m 6.7 ft
4.4 cm 1.7 in
44.2 cm 17.4 in
31.8 cm 12.5 in
5.15 kg 11.3 lbs
Part no. Length
110207 (EU)
110208 (UK)
110209 (SW)
110212 (AUS)
2.5 m 8.3 ft
9.2 Packaging
The following table shows the approximate measurements on the cardboard packaging of the
TANDBERG Gateway system- as shipped from production.
Height 29 cm
Width 68 cm
Depth 56 cm
Weight 13 kg
10
All figures are subject to change without any further notice.
D13192 Rev. 02 37
Page 38

Technical Description of TANDBERG Gateway with software version G2
9.3 Operating Temperature and Humidity
• 0° C to 35° C (32° F to 95° F) ambient temperature.
• 10% to 90 % Relative Humidity (RH)
9.4 Storage and Transport Temperature
• -20° C to 60° C (-4° F to 140° F) at RH 10-90 % (non-condensing)
9.5 System Power Consumption
• Maximum power consumption for TANDBERG Gateway is 90 W.
D13192 Rev. 02 38
Page 39

Technical Description of TANDBERG Gateway with software version G2
10 Technical Specification sheet
System Capacity
Maximum number of video conferencing calls: 8
Maximum number of audio calls: 8
Endpoints Supported
H.320 conferencing endpoints
H.323 conferencing endpoints
Analogue/ IP telephones
Bandwidth
H.320 up to 3840 kbps
H.323 up to 3840 kbps
Video Standards
H.261, H.263, H.263+, H.263++, H.264
Audio Standards
G.711, G.728, G.722, G.722.1
Live Video Resolutions
Native PAL:
QCIF (176 x 144 pixels)
CIF (352 x 288 pixels)
4CIF (704 x 576 pixels)
Native NTSC:
SIF (352 x 240 pixels)
4SIF (704 x 480 pixels)
Native PC resolutions:
VGA (640 x 480 pixels)
SVGA (800 x 600 pixels)
XGA (1024 x 768 pixels)
Network Interfaces
4 x E1/T1 G.703 (RJ-45) for ISDN PRI
2 x LAN/Ethernet (RJ-45) 10/100 Mbit
Ethernet / Internet / Intranet Connectivity
TCP/IP,DHCP,SSL,ARP,FTP,Telnet,HTTP, HTTPS
SNMP Enterprise Management
XML/SOAP
Embedded WEB server
Support for TANDBERG Management Suite
10/100Mbit full/half duplex (manual or auto detect
selection)
Other Supported ITU Standards
H.320, BONDING (ISO 13871), H.231, H.243,
H.221, H.242, H.245
TANDBERG
Dial in / dial out capabilities
ISDN & IP Downspeeding at call setup
ISDN Downspeeding in call
H.243 Terminal names
Embedded Encryption
Standards based on ISDN, IP and mixed ISDN / IP:
H.235, H.233, H.234, DES 56 bit key, AES 128 bit
key
Automatic key generation and exchange
Audio Features
Automatic Gain Control
Custom Welcome Sound (WAV)
Custom Extension Enquire Sound (WAV)
Video Features
Custom “Welcome” Picture (JPEG)
Custom "Extension Enquire" Picture (JPEG)
Custom "Downspeed" Picture (JPEG)
Frame Rates
Up to 30fps
Dual Stream
DuoVideo (all video resolutions supported)
Support for “People + Content”
Security Features
IP Administration passwords
Management via HTTPS
IP password
Services may be disabled: FTP, Telnet, SNMP,
HTTP, HTTPS
H.323 Network Features
DiffServ
IP Precedence
TOS
RSVP
IPLR TF
Gateway Features
D13192 Rev. 02 39
Page 40

Technical Description of TANDBERG Gateway with software version G2
System Management
Total management via embedded WEB server using
HTTPS, SNMP, Telnet and FTP
1 x RS-232 for local software upgrades, local control
and diagnostics
Management using TANDBERG Management Suite
Call scheduling via TANDBERG Scheduler and
TANDBERG Management Suite (Optional)
Embedded WEB server
Total Conference and Call control
System diagnostics
Environmental Data
Operating Temperature:
0° C to 35° C (32° F to 95° F) ambient temperature
Relative Humidity(RH): 10% to 90%
Storage and Transport Temperature:
-20° C to 60° C (-4° F to 140° F) at RH 10-90 %
(non-condensing)
Physical Dimensions
Height 4,4 cm (1,7 inches)
Width 44,2 cm (17,4inches) Depth 31,8cm (12,5
inches)
Weight Net 5,15 kg (11,3lbs)
Power 100-240 VAC, 50/60 Hz
90W max. power consumption
19 inch rack mountable
D13192 Rev. 02 40
 Loading...
Loading...