
GW
Gateway
User Manual
Software version G3
D13187-03
This document is not to be reproduced in whole or in part
without permission in writing from:

T ANDBERG Gateway
2

T ANDBERG Gateway
T rademarks and copyright
COPYRIGHT © 2005, TANDBERG
Philip Pedersensvei 22
1366 Lysaker, Norway, Tel: +47 67 125 125, Fax: +47 67 125 234
All rights reserved. This document contains information that is proprietary to TANDBERG. No part of this publication may be reproduced,
stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form, or by any means, electronically, mechanically, by photocopying, or otherwise, without
the prior written permission of TANDBERG. Nationally and internationally recognized trademarks and tradenames are the property of their
respective holders and are hereby acknowledged.
Disclaimer
The information in this document is furnished for informational purposes only, is subject to change without prior notice, and should not be
construed as a commitment by TANDBERG.
The information in this document is believed to be accurate and reliable, however TANDBERG assumes no responsibility or liability for any
errors or inaccuracies that may appear in this document, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties resulting from its
use. No license is granted under any patents or patent rights of TANDBERG.
This document was written by the Technical Support Department of TANDBERG, Norway. We are committed to maintaining a high level of
quality in all our documentation. Towards this effort, we welcome your comments and suggestions regarding the content and structure of this
document. Please fax or mail your comments and suggestions to the attention of:
TANDBERG
Attn: Product Support Department
P.O.Box 92
1325 Lysaker, Norway
Tel: +47 67 125 125
Fax: +47 67 125 234
Environmental Issues
Thank you for buying a product which contributes to a reduction in pollution and thereby helps save the environment.
Our products reduce the need for travel and transport and thereby reduce pollution.
Our products have either no or few consumable parts (chemicals, toner, gas, paper).
Our products are low energy consuming products.
Waste handling:
There is need to send material back to TANDBERG. Please contact your local dealer for information on recycling the product by sending the
main parts of the product for disassembly at local electronic waste stations.
Production of products:
Our factories employ the most efficient environmental methods for reducing waste and pollution by ensuring that the products are recyclable.
3

T ANDBERG Gateway
Operator Safety Summary
For your protection, please read these safety instructions completely before operating the equipment and keep this manual for future
reference. The information in this summary is intended for operators. Carefully observe all warnings, precautions and instructions both
on the apparatus and in the operating instructions.
Equipment Markings
The lightning flash symbol within an equilateral triangle is intended to alert the user to the
presence of uninsulated “dangerous voltages” within the product’s enclosure that may be of
sufficient magnitude to constitue a risk of electrical shock.
The exclamation mark within an equilateral triangle is intended to alert the user to the presence of
important operating and maintenance (servicing) instructions within literature accompanying the
equipment.
Warnings
Water and moisture - Do not operate the equipment under or near water - for example near a bathtub, kitchen sink, or laundry tub, in a wet
basement, near a swimming pool or in areas with high humidity.
Cleaning - Unplug the apparatus from the wall outlet before cleaning or polishing. Do not use liquid cleaners or aerosol cleaners. Use a lint-free
cloth lightly moistened with water for cleaning the exterior of the apparatus.
Ventilation - Do not block any of the ventilation openings of the apparatus. Install in accordance with the installation instructions. Never cover
the slots and openings with a cloth or other material. Never install the apparatus near heat sources such as radiators, heat registers, stoves, or
other apparatus (including amplifiers) that produce heat.
Grounding or Polarization - Do not defeat the safety purpose of the polarized or grounding-type plug. A polarized plug has two blades with one
wider than the other. A grounding type plug has two blades and a third grounding prong. The wide blade or third prong is provided for your
safety. If the provided plug does not fit into your outlet, consult an electrician.
Power-Cord Protection - Route the power cord so as to avoid it being walked on or pinched by items placed upon or against it, paying particular
attention to the plugs, receptacles, and the point where the cord exits from the apparatus.
Attachments - Only use attachments as recommended by the manufacturer.
Accessories - Use only with a cart, stand, tripod, bracket, or table specified by the manufacturer, or sold with the
apparatus. When a cart is used, use caution when moving the cart/apparatus combination to avoid injury from tip-over.
Lightning - Unplug this apparatus during lightning storms or when unused for long periods of time.
ISDN cables - CAUTION - To reduce the risk of fire, use only No. 26 AWG or larger telecommunication line cord.
Servicing - Do not attempt to service the apparatus yourself as opening or removing covers may expose you to
dangerous voltages or other hazards, and will void the warranty. Refer all servicing to qualified service personnel.
Damaged Equipment - Unplug the apparatus from the outlet and refer servicing to qualified personnel under the
following conditions:
When the power cord or plug is damaged or frayed
If liquid has been spilled or objects have fallen into the apparatus
If the apparatus has been exposed to rain or moisture
If the apparatus has been subjected to excessive shock by being dropped, or the cabinet has been damaged
If the apparatus fails to operate in accordance with the operating instructions
4

Content s
Introduction ........................................................................................ 7
The T ANDBERG Gateway ............................................................................10
NOTE
IMPORTANT
PLEASE READ THIS
SECTION
CAREFULLY
OPTIMAL
SET-UP.
FOR
SYSTEM
Installation ........................................................................................ 12
Precautions ...................................................................................................12
Unpacking .....................................................................................................12
Installation site preparations..........................................................................13
Rack Mounting (optional)...............................................................................13
Connecting cables ........................................................................................14
Gateway Configuration ..................................................................................15
Gateway start-up...........................................................................................16
Accessing the gateway .................................................................................16
Call Overview ................................................................................................17
Using the Gateway........................................................................... 17
Dial from ISDN ..............................................................................................21
Dial from IP....................................................................................................24
Manage the Phone Book ...............................................................................29
View System Status ......................................................................... 31
PRI Status .....................................................................................................31
H.323 St atus.................................................................................................. 33
System Information ....................................................................................... 33
Available Resources .....................................................................................34
Configure the Gateway.................................................................... 35
System Configuration....................................................................................35
IP Configuration.............................................................................................40
H.323 Configuration....................................................................................... 42
Dataport Configuration ..................................................................................45
SNMP Configuration ...................................................................................... 46
Miscellaneous Configuration .........................................................................47
Software Upgrade .........................................................................................49
File Management...........................................................................................50
ISDN Dial In Configuration.............................................................................51
T ANDBERG Gateway
5

T ANDBERG Gateway
H.323 Services..............................................................................................54
Gateway Features ......................................................................................... 57
Appendices ...................................................................................... 59
Appendix 1: Using the file system..................................................................59
Appendix 2: Declaration of Conformity .......................................................... 60
Appendix 3: Capacity.....................................................................................61
Index ................................................................................................. 62
6

T ANDBERG Gateway
Introduction
Introduction
The T ANDBERG Gateway enables sites on IP and sites on ISDN to p articipate in meetings with each other with
the quality and reliability found in all T ANDBERG equipment.
IP Services and Procedures
• Service Prefix.
• Dial Parameters.
Ne w Integrated ExpresswayTM firewall traversal technology .
Ne w H.235 Authentication at Gatekeeper and Border Controller .
Ne w Alternate Gatekeeper - Increased network reliability .
• Load balance.
N e w Bridging IP islands - Automatical call setup through two Gateways.
N e w Receives DTMF tones as audio tones or as control signals (H.245), converted into audio tones on ISDN.
N e w Possibility to request from the IP side two number 2x64k ISDN Dial-out (H.221)
ISDN Services
The T ANDBERG Gateway offers a variety of ISDN dial-in services:
• Direct Inward Dialing (DID) - The destination endpoint is determined from the dialed ISDN number .
• Interactive Voice Response (IVR) - The destination endpoint can be selected via touch tones.
• T erminal Control Session 4 (TCS-4) - The destination end point can be selected by endpoint signaling.
• Hotline/Operator Mode - The destination endpoint is a fixed one.
Ne w T elephone Dial-Ins can be disabled.
Ne w T wo number 2x64k ISDN Dial-in - Best interoperability with legacy equipment.
Security
• Secure Conference
Ne w Flexible encryption configuration - Transparent or independent.
• Secure Access - support XML/SOAP over HTTPS, Web (HTTP) encrypted password and the services that
can be disabled.
TF
- using standard based AES 128 and DES encryption on IP and ISDN.
7

T ANDBERG Gateway
Video Quality
• Natural VideoTF which provides 60 fields per second true interlaced picture.
• H.264, H.263 and H.261 video compression.
Presentations
Allows to watch a presenter on one video channel and simultaneously a second video channel (live presentation,
document camera and others).
• Duo VideoTF support.
Ne w Full ITU standard H.239 support.
N e w The Gateway allows to connect endpoints supporting Duo Video with endpoints supporting H.239 -
Automatic conversion.
Interoperability
• Worldwide compatibility with standards-based videoconferencing systems.
8

T ANDBERG Gateway
Management Interfaces
SOAP Simple Object Access Protocol is a lightweight protocol for exchange of information in a decentralized,
distributed environment
X M L Extensible Markup Language is a flexible way to create common information formats and share both the
format and the data on the World Wide Web, intranets, and elsewhere. This functionality can be used by
management systems like the T ANDBERG Management Suite to control the gateway .
HTTP Web-interface for system management, call management such as call transfer, diagnostics and
software uploads.
HTTPS Hypertext Transfer Protocol over Secure Socket Layer is a Web protocol that encrypts and decrypts
user page requests as well as the pages that are returned by the Web server . It uses Secure Socket
Layer (SSL) as a sublayer under its regular HTTP application layering. HTTPS uses port 443 instead of
HTTP port 80 in its interactions with the lower layer , TCP/IP. SSL uses a 40-bit key size for the RC4
stream encryption algorithm, which is considered an adequate degree of encryption for commercial
exchange.
Network and Features
• Up to 8 video sites and 8 telephony calls can be held at the same time.
• Call rate of up to 2 Mbps for each call is supported through the gateway .
• A maximum of 4 Mbps (2 Mbps standard) ISDN bandwidth is supported through the gateway.
• Downspeeding
TF
- Optimizes the end-to-end bandwidth automatically for the available network condition.
• Full H.243 Multipoint Control Unit (MCU) transparency , for seamless MCU connection through the gateway .
• Intelligent Packet Loss Recovery (IPLR).
• Far End Camera Control.
• T ext Chat (T.140).
9

T ANDBERG GatewayIntroduction
The T ANDBERG Gateway
Front view
The front of the gateway contains 24 Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) organized in three groups. These diodes
provide information about PRI-line status, LAN (Ethernet) connection and power.
GW
Green: Layer 1 OK
Red: Layer 1 Red Alarm
Red: D-Channel Down
Yellow: Layer 1 Yellow Alarm
Green: Layer 1 OK
Red: Layer 1 Red Alarm
Yellow: Layer 1 Yellow Alarm
Red: D-Channel Down
Green: Layer 1 OK
Red: Layer 1 Red Alarm
Yellow: Layer 1 Yellow Alarm
Red: D-Channel Down
Red: Layer 1 Red Alarm
Yellow: Layer 1 Yellow Alarm
Green: Layer 1 OK
Red: D-Channel Down
Green: Tx
Green: Rx
Green: Tx
Green: Rx
Green: Not in use
Green: Not in use
Green: Power on
Green: Not in use
Red Alarm or Loss of signal (LOS) indicates that there is no signal and thus no framing info received. The same
effect will be obtained by pulling out the PRI cable. This may also be caused by a broken connector in the receive
(RX) part of the cable.
Yellow Alarm or Remote Alarm Indicator (RAI) means that the gateway is receiving framing info, but in this
framing info the other side tells the gateway that it is not reading the gateway’s transmitted framing info. T ypically,
this may be a broken connector in the transmit (TX) part of the PRI cable. This could also indicate weak or noisy
signal in the transmit (TX) part of the PRI cable.
10
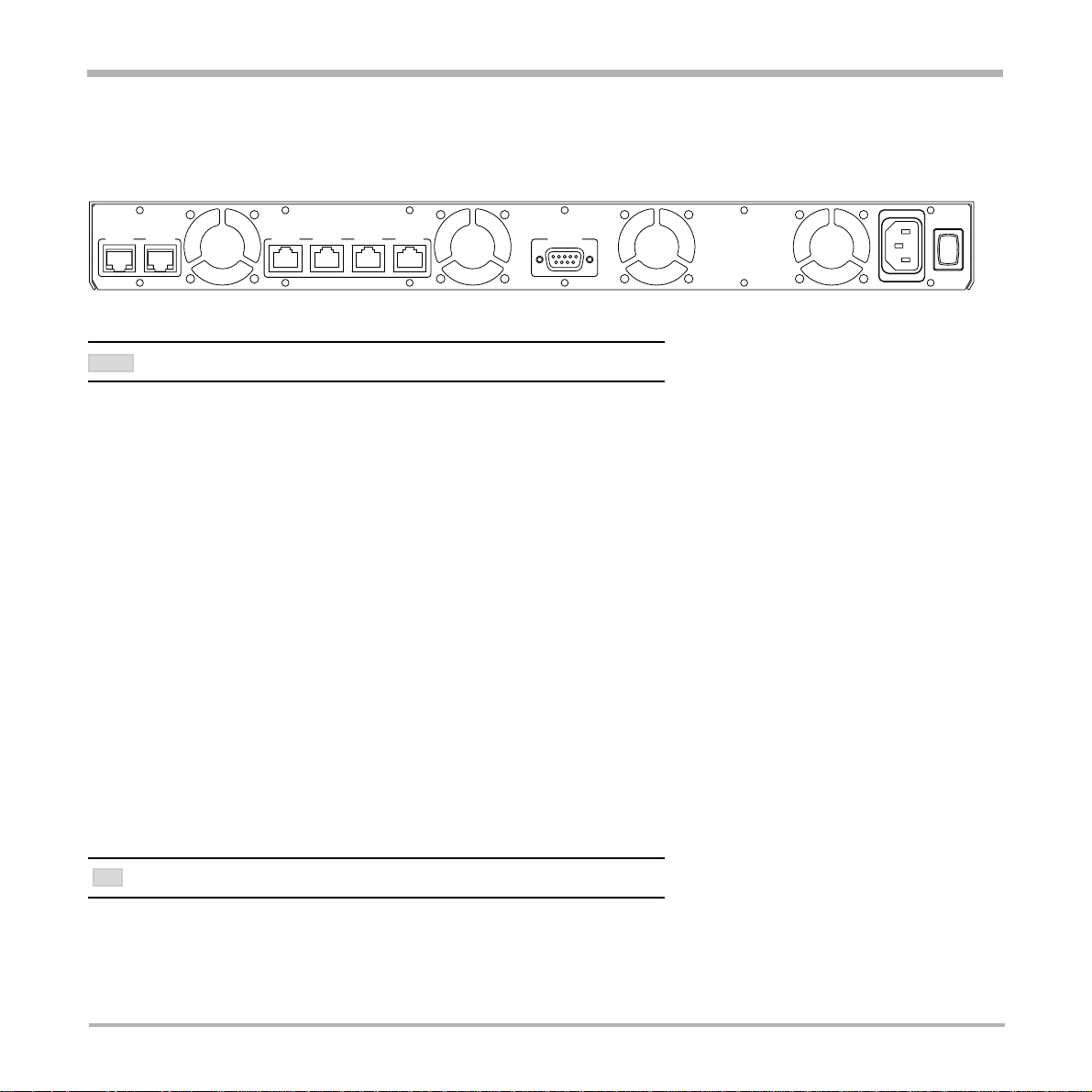
T ANDBERG Gateway
Introduction
Rear view
The back panel provides four PRI interfaces, two LAN interfaces and one RS 232 interface located together with
the power switch/connector and four cooling fans.
LAN 1 LAN 2 PRI 1 PRI 2 PRI 3 PRI 4 RS 232
THE ‘LAN 2’ CONNECTOR IS NOT USED.
NOTE
I
o
GA TEWAY Cap acity – typical scenarios (4 Mbp s option)
Below is an overview of the number of video calls possible to connect on different bandwidths, when 2xE1 (or
3xT1) PRI ISDN lines are connected. In addition to the video calls, telephone calls can also be made through the
gateway .
Bandwidth Non-encrypted Encrypted
128 kbps 8+8* 7+0
256 kbps 8+7 6+5**
384 kbps 8+4 5+5
512 kbps 7+4 5+0
768 kbps 5+0 3+8
1472 kbps (1.5 Mbps) 2+8 N/A
1920 kbps (2 Mbps) 2+0 N/A
* 8+8 indicates 8 video calls and 8 telephone calls.
** 6+5 indicates 6 encrypted video calls and 5 unencrypted telephone calls.
TIP
FOR MORE DETAILS ON CAPACITY, SEE ‘APPENDIX 3: CAPACITY’
11

T ANDBERG GatewayInstallation
Installation
Precautions
• Never install telephone wiring during a lightning storm.
• Never install telephone jacks in wet locations unless the jack is specifically designed for wet locations.
• Never touch uninstalled telephone wires or terminals unless the telephone line has been disconnected at the network interface.
• Use caution when installing or modifying telephone lines.
• Avoid using a telephone (other than a cordless type) during an electrical storm. There may be a remote risk of electrical shoc k from
lightning.
• Do not use the telephone to report a gas leak in the vicinity of the leak.
• The socket outlet shall be installed near to the equipment and shall be easily accessible.
• Never install cables without first switching the power OFF.
• This product complies with directives: LVD 73/23/EC, EMC 89/366/EEC, R&TTE 99/5/EEC.
• This product complies with the standards GR-63-CORE and GR-1089-CORE and is NEBS approved by UL .For NEBS compliance, the
product should be installed in the following manner:
- Use the enclosed rack brackets marked “NEBS”.
- There should be a clearance of 9.1cm between the product and any other product mounted in the rack.
Unpacking
T o avoid damage to the unit during transportation, the gateway is delivered in a special shipping box, which should
contain the following components:
• T ANDBERG GW.
• User Manual and other documentation on CD.
• Rack-ears, screws and screwdriver.
• Cables:
• Power cable
• Four ISDN PRI cables
• Ethernet cable
• RS232 cable
12
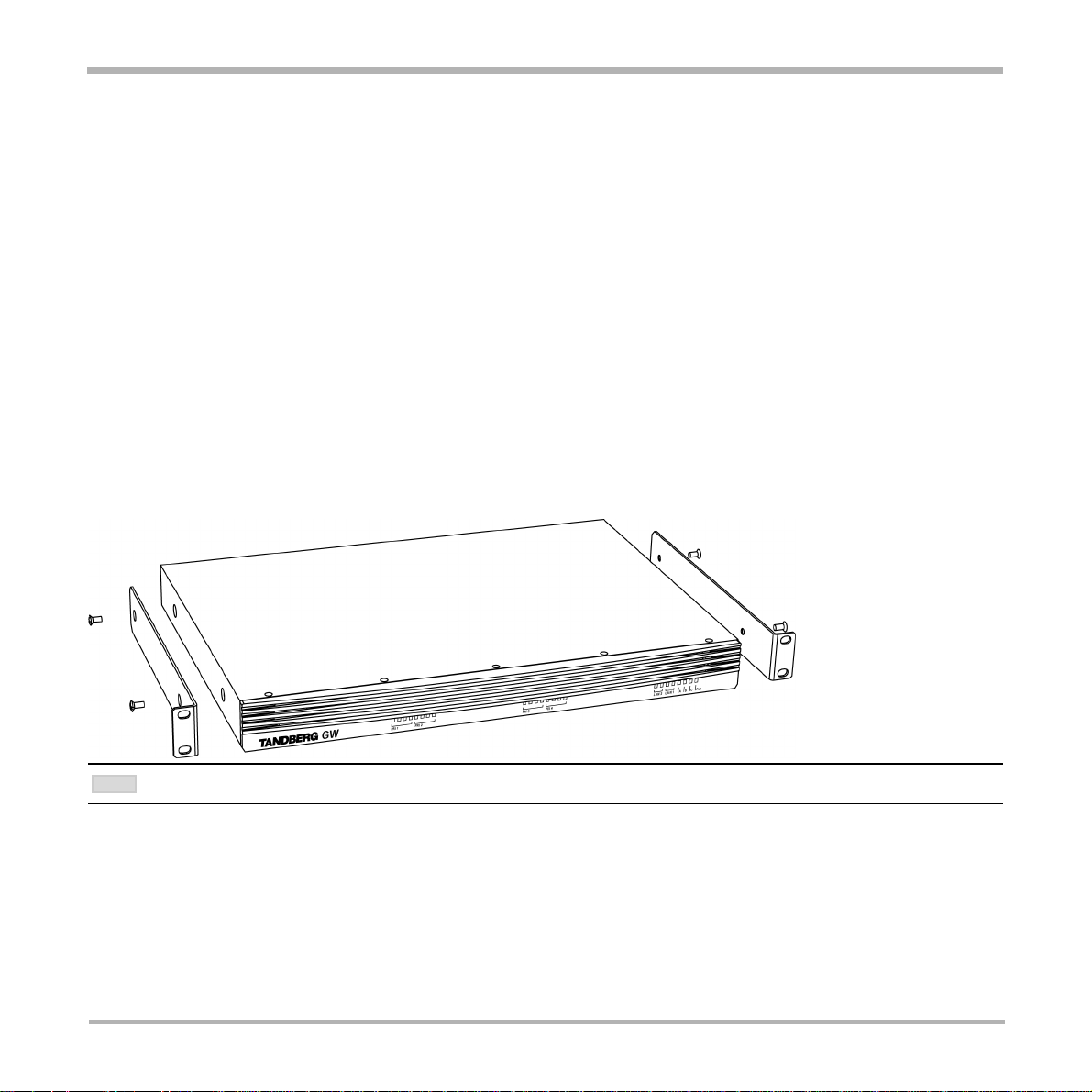
T ANDBERG Gateway
Installation
Installation site prep arations
• Make sure that the gateway is accessible and that all cables can be easily connected.
• For ventilation: Leave a space of at least 10cm (4 inches) behind the gateway’s rear panel and 10cm (4 inches)
in front of the front panel.
• The room in which you install the gateway should have an ambient temperature between 0oC and 35oC (32oF
and 95oF) and between 10% and 90% non-condensing relative humidity .
• Do not place heavy objects directly on top of the gateway .
• Do not place hot objects directly on top, or directly beneath the gateway .
• Use a grounded AC power outlet for the gateway.
• Y ou will need a CSU (Channel Service Unit) between your system and the PRI line from your network provider.
Rack Mounting (optional)
The gateway comes with brackets for mounting in standard 19” racks.
NOTE
BEFORE STAR TING THE RACK MOUNTING, PLEASE MAKE SURE THE T ANDBERG GW IS PLACED SECURELY ON A HARD, FLAT SURFACE.
1. Disconnect the AC power cable.
2. Make sure that the mounting space is according to the ‘Installation site preparations’ (see above).
3. Attach the brackets to the gateway on both sides of the unit.
4. Insert the gateway into a 19” rack, and secure with screws in the front (four screws).
13

Connecting cables
LAN 1 LAN 2
PRI 1 PRI 2 PRI 3 PRI 4
T ANDBERG GatewayInstallation
I
RS 232
o
Power
LAN 1
PRI 4
PRI 3
PRI 2
PRI 1
RS 232
Power cable
Connect the system power cable to an electrical distribution socket.
ISDN PRI cables
For each of the four PRI interfaces, the E1/T1 cable should be connected to a CSU (Channel Service Unit). Y ou will
need a CSU between your gateway and the PRI line from your network provider.
LAN cable
To use the gateway on IP, connect a LAN cable from the ‘LAN 1’ connector on the gateway to your network. The
LAN 2’ connector is not used and should be left open.
RS 232 cable
T o control the gateway using the dat aport, connect an RS 232 cable between the gateway’s RS 232 connector
and the COM-port on a PC. For further information, please refer to the ‘Dataport’ chapter in ‘Configure the
Gateway’.
14
T ANDBERG Gateway
Installation
Gateway Configuration
The gateway requires some basic configurations before it can be used. It will be necessary to find the IP-address
and program the ISDN-PRI Line numbers.
T o do this configuration, follow the instructions below:
1. Connect the RS232 cable between the gateway and a PC and then switch on the gateway .
2. Start a terminal program on the PC and configure it to: 9600, 8, 1, None.
3a. To assign a static IP-address, type ‘ipassign static’ and ‘ipaddress 1 static <IP-address>’.
3b. To assign an IP Subnetmask, type ‘ipaddress 1 subnetmask <subnetmask>’.
3c. To assign an IP Gateway address, type ‘ipaddress 1 gateway <gateway IP-address>’.
4. Restart the gateway.
TIP
DHCP ASSIGNED IP-ADDRESSES ARE SUPPORTED BY THE T ANDBERG GA TEWA Y (FACTORY DEFAUL T).
5. Start a WEB browser and enter the IP-address of the gateway. Default password: ‘TANDBERG’.
6. To configure the gateway for ISDN dial in, enter PRI numbers and dial in number(s). For details, see
the ‘PRI Configuration’ and the ‘ISDN Dial in Configuration’ section.
7. To configure the gateway for IP dial in, register the gateway to a gatekeeper and enter H.323
services. For details, see the ‘H.323 Services’ and ‘H.323 Configuration’ sections.
15

T ANDBERG GatewayInstallation
Gateway start-up
To start the gateway, please make sure that the power cable is connected, and press the power switch button
to ‘1’.
GW
On the front panel of the system the power indicator LED, marked ‘Pwr’, will now turn GREEN.
Accessing the gateway
Y ou may access the gateway by entering the IP-address of the gateway in a standard WEB-browser . You will
then be asked to enter a password. It is not necessary to enter ‘User Name’. The default password for the
gateway is ‘T ANDBERG’. Remember that the password is case sensitive.
IF YOU DO NOT KNOW THE IP-ADDRESS, PLEASE FOLLOW THE
TIP
PROCEDURE IN ‘INSTALLA TION’, ‘SYSTEM CONFIGURATION’.
THE PASSWORD CAN BE CHANGED IN ‘SYSTEM CONFIGURATION’,
TIP
‘MISC’. SEE ALSO THE ‘CONFIGURE MISCELLANEOUS PARAMETERS’
SECTION IN ‘CONFIGURE THE GATEWAY’.
16
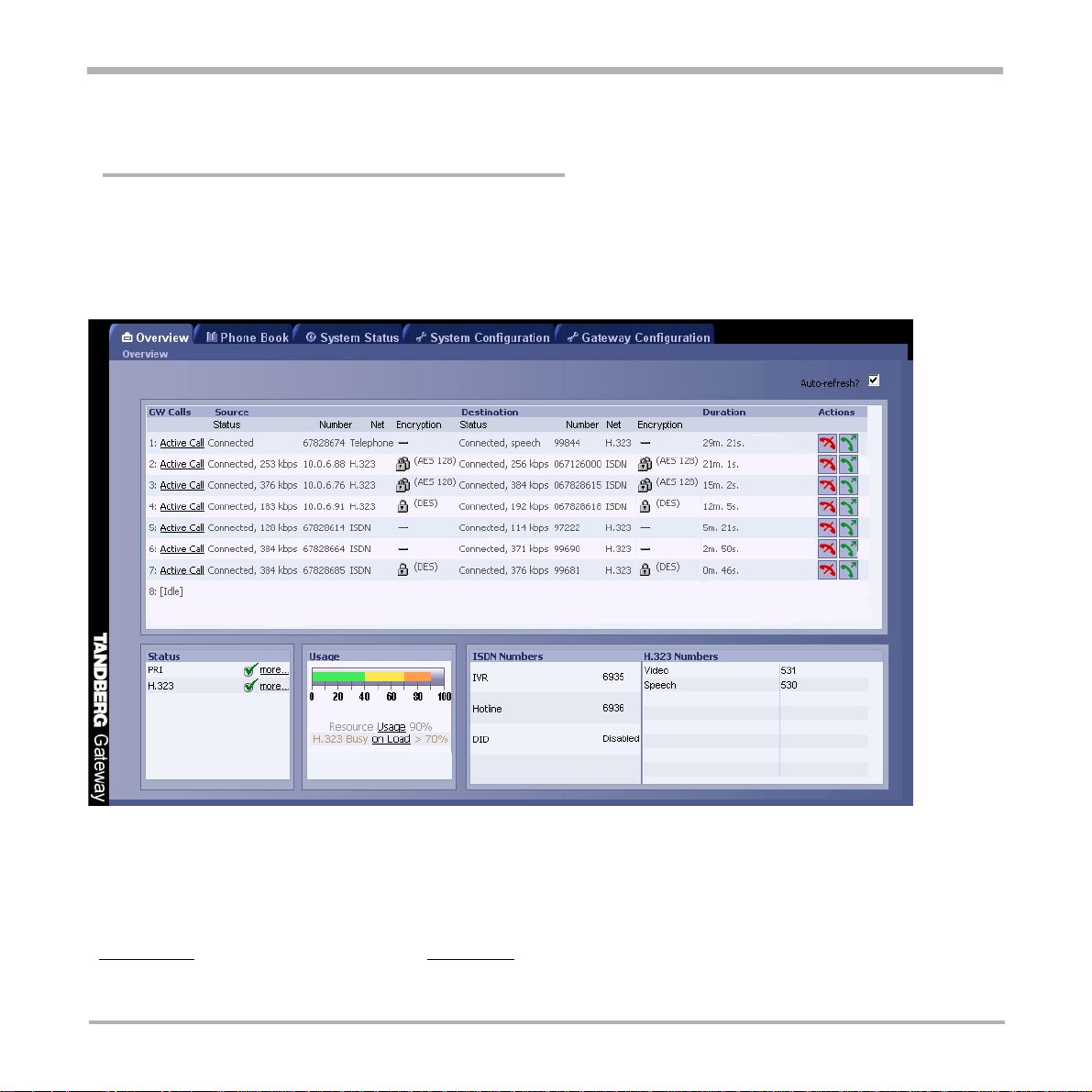
T ANDBERG Gateway
Installation
Using the Gateway
Call Overview
The following Web-page, called ‘Overview’ will be shown when the correct password has been entered and
shows all calls currently active through the gateway.
GW Calls
Shows each active call through the gateway.
[Idle] No call is active.
Active Call A call is active. Click on Active Call to see call info in details.
17
Using the Gateway
T ANDBERG Gateway
Source / Destination
Source shows the Status of the incoming call to the gateway, the number and which network the incoming call is
using.
Destination shows the Status of the outgoing call from the gateway, the number and which network the outgoing
call is using.
Idle No active call, call been disconnected.
Alerting Call is being connected.
Connected Call is connected.
Establ out Gateway is calling out to destination.
Clear out Call is being disconnected.
Number ISDN or IP number .
ISDN Call connected is using the H.320 protocol over ISDN.
IP/H.323 Call connected is using the H.323 protocol over IP .
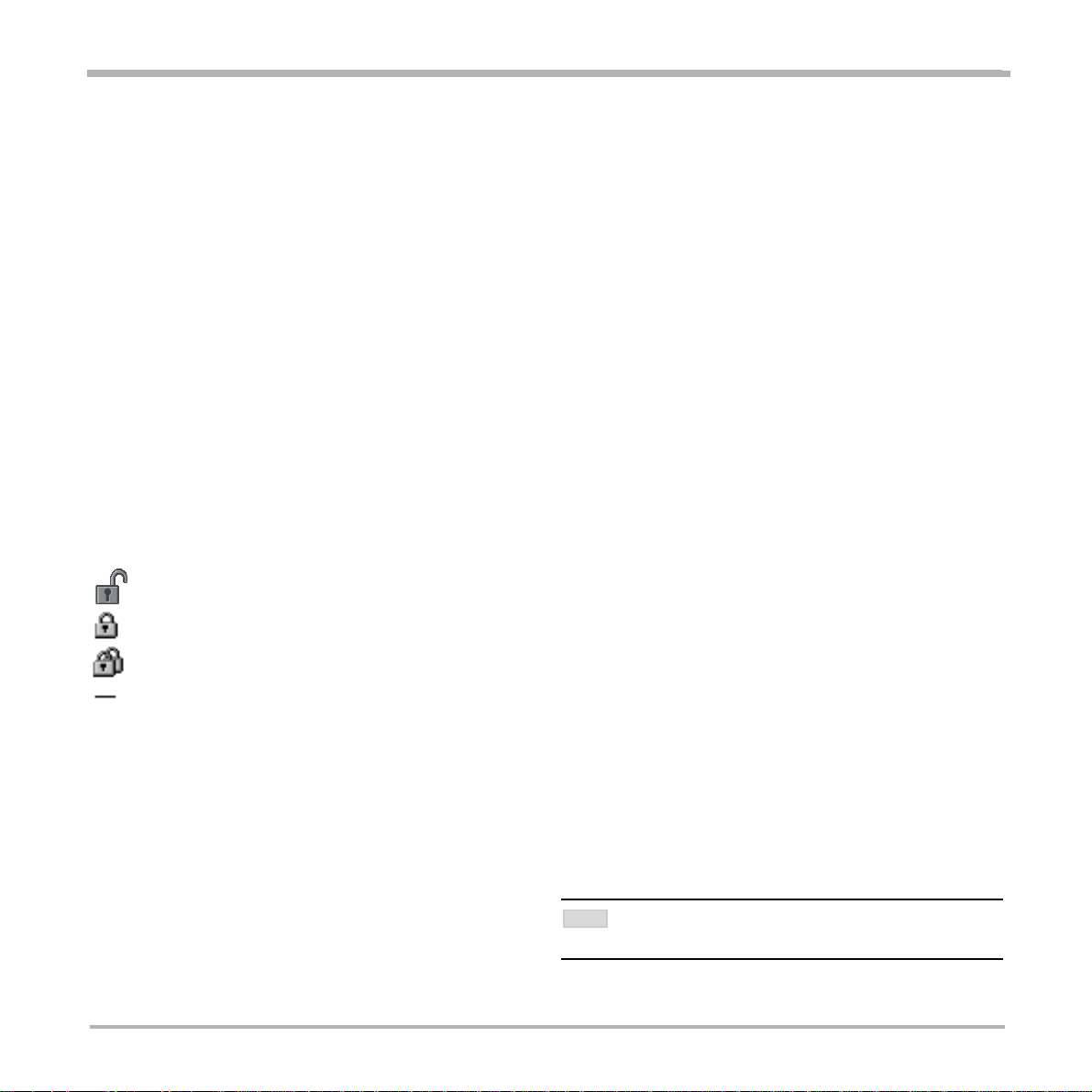
Encryption (Secure conferenceTF)
The gateway supports Secure Conference DES and AES.
The open padlock symbol indicates that the encryption is being established.
The single padlock symbol indicates that DES (56 bit) encryption is used.
The double padlock symbol indicates that AES (128 bit) encryption is used.
Indicates that the call is not encrypted.
Duration
Shows the length of the current call.
18
NOTE
ENABLING ENCRYPTION WILL REDUCE THE CAPACITY OF THE
GATEW A Y.

T ANDBERG Gateway
Using the Gateway
Actions
When a call is active, the Administrator or Operator has the possibility to disconnect the call, or transfer the call
from one IP endpoint to another .
Disconnect Gateway Call
Will disconnect the selected gateway call. A confirmation window will be shown.
Call Transfer
Will open the H.323 Call Transfer window . Here the Administrator or Operator can select an IP entry from
the Phone Book or enter a H.323 Alias/IP address and transfer the H.323 (IP) call to another IP endpoint.
If the transfer fails, the call will be disconnected.
Status
Shows current status on the PRI and IP status.
PRI:
Minimum one PRI line is synced and active. Click on More... to see status in detail.
No PRI lines are active. Click on More... to see status in detail.
IP/H.323:
The gateway is registered with a Gatekeeper. Click on More... to see st atus in detail.
The gateway is not registered with a Gatekeeper. Click on More... to see st atus in detail.
If encryption mode is set to “Independent”, then a warning is shown in the St atus area.
19

Using the Gateway
T ANDBERG Gateway
Usage
The usage bar shows the current status of all the available resources (CPU, ISDN channels and number of calls)
When the Resource Usage reaches the “Busy on Load”-limit, the gateway will try to route outgoing IP calls to
other gateways. This is done to maintain availability for incoming ISDN calls when using multiple gateways.
Resource Usage 90%. Click on Usage to see resource usage in detail.
H.323 Busy on Load> 70%. Click on on Load to adjust the value.
ISDN Numbers
FOR MORE INFO ABOUT IVR, HOTLINE OR DID, PLEASE READ THE
Shows the available ISDN dial-in numbers for IVR,
TCS-4, DID and Hotline.
TIP
‘DIAL FROM ISDN’ SECTION IN ‘USING THE GATEWAY’.
H.323 Numbers
Shows the available H.323 Services (dial-out prefixes)
for accessing/dialing the ISDN network.
20
FOR MORE INFO ABOUT H.323 SERVICES, PLEASE READ THE ‘DIAL
TIP
FROM IP’ SECTION IN ‘USING THE GATEWAY’.

T ANDBERG Gateway
Dial from ISDN
Dial from ISDN
The gateway supports four different ISDN Dial In services:
• IVR
TIP
• IVR + TCS4
• DID
• Hotline
Any of these services can be enabled or disabled, but at least one must be enabled for incoming call routing to
take place.
In order to enable parallel incoming calls, a PRI number range must be defined.
IVR
Interactive Voice Response (IVR), also called extention dial-in, is an automated answering system that direct s the
call to the IP endpoint indicated by the caller . The caller uses telephone tones (DTMF) to enter the H.323 Alias or
extention.
IVR is useful if you have limited PRI numbers on your PRI line.
Example:
• A videoconferencing system calls into the Extention Dial In number with IVR active.
• The gateway activates the ‘Welcome’ picture and sound.
• The videoconferencing system enters the extention (H.323 Alias) followed by the # (pound-sign) to
indicate end of number.
• The gateway starts to call the IP endpoint and the “Call proceeding” picture and sound are activated.
• When the call is connected audio and video are transmitted through the gateway .
FOR MORE DETAILS ON ISDN DIAL IN SERVICES, SEE ‘ISDN
DIAL IN CONFIGURATION’ UNDER ‘CONFIGURE THE GATEWAY’.
21
THE WELCOME PICTURE AND SOUND CAN BE CHANGED IN THE
TIP
‘FILE MANAGEMENT’ SECTION IN ‘CONFIGURE THE GATEWAY’.

Dial from ISDN
T ANDBERG Gateway
IVR + TCS-4
IVR + Terminal Control Session 4 (TCS-4) is an extention dial-in method that combines IVR with TCS-4. In this
mode the extention number can be indicated with IVR (see above) or TCS-4 signaling.
TCS-4 allows an ISDN based videoconferencing endpoint to dial an IP endpoint directly , without having to
(manually) enter the extention number by DTMF . If no TCS-4 extention is given from the end point, then IVR will be
used.
T o use TCS-4, it needs to be supported by the videoconferencing endpoint. Refer to the User Manual of the
videoconferencing endpoint to see how TCS-4 is supported.
Example:
• A videoconferencing endpoint calls into the Extention Dial In number with IVR + TCS-4 active, using
<Dial In number of gateway>*<party’s extention>.
• The gateway starts to call the IP endpoint and the “Call proceeding” picture and sound are activated.
• When the call is connected audio and video are transmitted through the gateway.
• TANDBERG end points allow to store the complete dial string in the phonebook to automate dial-
through.
NOTE
THE ‘*’ IS SPECIFIC TO T ANDBERG ENDPOINTS. OTHER
WILL HAVE DIFFERENT METHODS OF ENTERING THE
VENDORS
TCS-4 EXTENTION.
DID
Direct Inward Dialing (DID) will provide you with direct ISDN numbers for your IP endpoints. I.e. it will do a direct
mapping between your ISDN number and the H.323 Alias.
In order to use DID you will need to have assigned multiple ISDN numbers to your ISDN PRI line, as each ISDN
number will map to a single IP endpoint.
We also recommend that if more than one PRI line is used all PRI lines should have the same numbers (use trunk
groups).
Example:
• Y our ISDN PRI number range is from 67124000 to 67124050 and DID is enabled.
• Y ou want your IP endpoints to have the numbers (H.323 Alias) in the range 94000 - 94050.
• In the ISDN Dial In Configuration, set ‘No. Significant Digits’ to 4 and ‘Prefix (E.164)’ to 9.
• T o call an IP endpoint with H.323 Alias 94020 from ISDN, dial the ISDN number 67124020.
22

T ANDBERG Gateway
Dial from ISDN
• The gateway starts to call the IP endpoint and the “Call proceeding” picture and sound are activated.
• When the call is connected audio and video are transmitted through the gateway .
Hotline
Hotline is a service that allows incoming ISDN calls on a dedicated ISDN number, to be routed to an IP endpoint.
This is useful if you want to have an operator or helpdesk functionality together with DID, IVR and/or TCS-4.
Example:
• Y our ISDN PRI number range is from 67124000 to 67124050 and DID is enabled.
• Hotline number assigned is 67124050.
• An operator/helpdesk has got the H.323 Alias (extention) 98660.
• A videoconferencing end point calls ISDN number 67124050.
• The gateway starts to call the IP endpoint and the “Call proceeding” picture and sound are activated.
• When the call is connected audio and video are transmitted through the gateway .
• If needed, the Hotline operator can use Call Transfer to transfer the call to another IP endpoint.
Sequence of Services
To ensure best service to the incoming ISDN call, the gateway will first try to match the Hotline number, and then
the IVR/TCS-4 number before using DID (if enabled). If DID is disabled and no other number programmed, the call
will be routed to the IVR service (if enabled).
23

Dial from IP
T ANDBERG Gateway
Dial from IP
IP endpoints and MCUs can call out through the gateway by using one of the H.323 services defined on the
gateway .
H.323 Services
H.323 Service prefixes are used for IP endpoints to
access the ISDN network. Up to twenty prefixes can
be defined, but we recommend using one single
prefix for simplicity.
Example:
• An H.323 Service prefix for outgoing video calls is defined as “0” (default).
• The IP endpoint dials 067121212 to dial the ISDN number 67121212.
• The gateway starts to call the ISDN endpoint and the “Call proceeding” picture and sound are activated.
• Audio and video are transported through the gateway when the call is connected.
DEFAULT H.323 SERVICE FOR OUTGOING VIDEO CALLS IS ‘0’.
NOTE
DEFAULT H.323 SERVICE FOR TELEPHONE CALLS IS ‘1’.
24
THE BANDWIDTH USED FOR THE CALL WILL BE THE BANDWIDTH
NOTE
SELECTED ON THE IP ENDPOINT.
FOR MORE DETAILS ON H.323 SERVICES, SEE ‘H.323
TIP
SERVICES’ UNDER ‘CONFIGURE THE GA TEWAY’.
T ANDBERG Gateway
Features
Dial out to 2x64k ISDN (H.221)
For improved interoperability with legacy equipment, the two number 2x64k dial-out method can be selected from
the calling IP endpoint instead of using the standard BONDING method.
To instruct the Gateway to use this method, the calling IP endpoint has to combine the dialed number from:
• A Service Prefix of fering at least 128k callrate,
• The (first) ISDN number to dial out to,
• Two stars (“**”),
• The second ISDN number to dial out to.
Example:
• An H.323 Service prefix for outgoing video calls is defined as “0” (default).
• The user wants to dial the first ISDN number 67121212 and the second number 67121213.
• The user dials to “067121212**67121213”.
• Audio and video are transported through the gateway when the call is connected.
NOTE
NOT ALL ENDPOINTS WILL SEND OUT THE NEEDED NUMBER (INCLUDING THE ‘*’ CHARACTERS). TO MAKE OLDER TANDBERG EQUIPMENT
(CLASSIC SERIES, MXP UP TO F2) USING THIS SYNTAX, THE USER HAS TO SELECT H.323 AS THE NETWORK PROFILE TO BE USED. ALSO IF SUCH A
SHOULD BE STORED IN THE PHONEBOOK, THE H.323 PROFILE HAS TO BE SELECTED EXPLICITL Y . SOME ENDPOINTS MIGHT HAVE A
NUMBER
LIMITITATION ON THE LENGTH OF THE DIAL STRING.
25

Features
T ANDBERG Gateway
Bridging IP Islands
Organizations that uses IP based video conferencing internally in their LAN but not for external purposes can be
called “IP Islands”. If a user in one IP island wants to call another user in another IP island, both organizations
have to be connected with a Gateway . The TANDBERG Gateway can help the user to set up this type of call
automatically without the need of invoking touch tones under call setup.
T o dial to a remote IP endpoint through two Gateways, the calling IP end point has to combine the dialed number
from:
• A Service Prefix at the first Gateway ,
• The ISDN number of the second Gateway ,
• One star character (“*”),
• The extension address (E.164 alias) of the endpoint to dial.
NOTE
THE SECOND GATEWAY MUST HAVE TCS-4 DIAL-IN METHOD ENABLED: FOR INFORMATION ABOUT RESTRICTIONS OF THE DIAL STRING, SEE THE NOTE
IN THE PREVIOUS SECTION.
Example:
• An H.323 Service prefix for outgoing video calls is defined as “0” (default).
• The second gateway has the ISDN number 67121212.
• The user wants to dial to an endpoint in the other network that has a E.164 alias 5012345.
• The user dials to “067121212*5012345”.
• The user will get displayed poster from the first, then from the second Gateway .
• Audio and video are transported through the gateway when the call is connected.
26
T ANDBERG Gateway
Manage the Phone Book
The Expressway Solution
IP based video conferencing between organizations has been hindered by two major barriers:
· Firewalls which block audio and video traffic.
· Lack of a common dial plan for IP based video conferencing.
The Expressway solution solves both the firewall problem and the dial plan problem. Using Expressway , audio
and video can traverse firewalls securely . Expressway is natively supported in the T ANDBERG Gateway .
As part of an Expressway solution, a Gateway can be made accessible to e.g. home users and branch offices,
reducing the need to deploy ISDN at all locations.
Users on IP in home offices or branch offices can now use all the features of the enterprise Gateway and can be
reached by ISDN systems.
27

Features
T ANDBERG Gateway
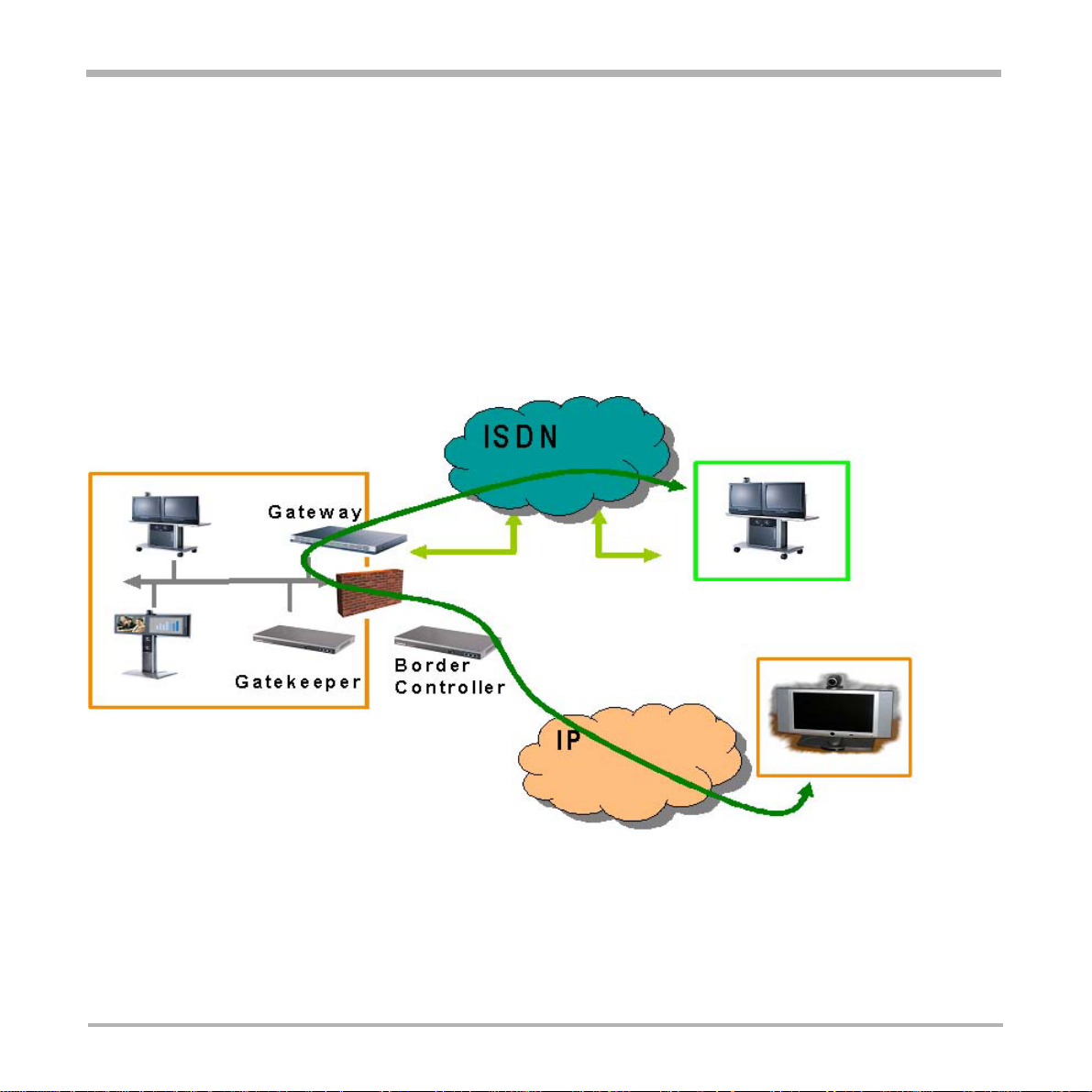
In a typical enterprise setup, such as the one in the previous figure, the Gateway is registered with a Gatekeeper,
and the Gatekeeper is registered with the Border Controller. In this scenario, the native Expressway functionality
in the Gateway enables media to be routed directly between the Gateway and the Border Controller, reducing
latency .
The native Expressway support in the Gateway also enables the Gateway to register directly to a border controller
through a firewall without the need for a Gatekeeper. Connecting the Gateway directly to a Border Controller
enables new deployment possibilities, e.g.:
· An organization may want to have a firewall between the Gateway and the rest of the IP video conferencing
infrastructure to add another layer of security .
· An organization may want to deploy Gateways at remote locations.
The figure below shows a scenario where IP is used between the enterprise and a remote location.
In this scenario, enterprise users can use a remotely deployed Gateway to do local calls on ISDN.
28

T ANDBERG Gateway
Features
Manage the Phone Book
By selecting the ‘Phone Book’ tab, you can add new or edit existing Phone Book entries in the gateway.
The Phone Book can be used when Transferring calls from one IP endpoint to another and can contain up to 99
single entries. They are listed alphabetically as can be seen in the figure below .
Add new entry
To add a new entry in the Phone Book, press the ‘Add New Entry’ button and the ‘Add New Entry’ will open, as
shown in the figure below.
Name Name of the IP endpoint.
Number IP number (E.164 Alias) of the IP endpoint.
Press ‘Create New’ to save the entry in the phone book.
29

Manage the Phone Book
T ANDBERG Gateway
Edit Entry
By selecting an existing Entry in the Phone Book and then pressing the ‘Edit’ button, you will be able to edit the
selected entry . The same fields as for the ‘Add New Entry’ will be available.
Save
The entry will be updated with the changes made.
Create New
This will create a new entry instead of replacing the old one. The old entry will still be stored in the Phone Book.
Cancel
Will discard all changes and display the ‘Edit Phone Book’ page.
Delete
By selecting an existing Entry in the Phone Book and then pressing the ‘Delete’ button, you will delete the
selected entry .
30

T ANDBERG Gateway
View System Status
T o view current gateway st atus, open ‘System S tatus’ as shown in the figure below.
PRI St atus
T o view st atus of the PRI, open ‘PRI S tatus’ as shown in the figure below.
System Status
If a site has been disconnected, the cause code can be viewed by pressing the link next to the PRI channel that
was disconnected. See next page for a cause code example.
31

System Status
T ANDBERG Gateway
Example of Location Codes:
A videoconferencing endpoint was connected to channel 1 and 2 on PRI Line 1. The status shows disconnected
with the cause code 2 : 16. The first part ( 2 ) is the Cause Location code and describes the origin of the cause
code.
Example of ISDN Cause Codes:
The second part ( 16 ) describes the reason for the disconnect. In this case, a normal call clearing.
PRI Alarms
Red Alarm or Loss of signal (LOS) indicates that there is no signal and thus no framing info received. The same
effect will be obtained by pulling out the PRI cable. This may also be caused by a broken connector in the receive
(RX) part of the cable.
Yellow Alarm or Remote Alarm Indicator (RAI) means that the gateway is receiving framing info, but in this
framing info the other side tells the gateway that it is not reading the gateway’s transmitted framing info. T ypically,
this may be a broken connector in the transmit (TX) part of the PRI cable. This could also indicate weak or noisy
signal in the transmit (TX) part of the PRI cable.
32

T ANDBERG Gateway
System Status
H.323 Status
T o view H.323 gatekeeper status, open ‘H.323 S tatus’ as shown in the figure below .
IT IS NOT POSSIBLE TO USE
NOTE
GW IP Address Shows the IP address of the gateway .
H.323 Gatekeeper Status Shows status and IP address of the Gatekeeper , the gateway is registered to.
‘Inactive’ means the gateway is not registered to a gatekeeper .
‘Registering’ means the gateway is having problems registering with selected
gatekeeper.
IP ADDRESS TO PLACE
THIS
CALLS THROUGH THE GA TEWA Y .
System Information
T o view gateway information, open ‘System Information as shown in the figure below . This p age provides
information on installed software and hardware.
33

System Status
T ANDBERG Gateway
Available Resources
T o view available resources on the gateway , open ‘Available Resources’ as shown in the figure below .
34
T ANDBERG Gateway
Configure the Gateway
Configure the Gateway
T o configure the gateway , open ‘System Configuration’ and ‘Gateway Configuration’. Shown in the figure below is
the ‘System Configuration’.
System Configuration
PRI Configuration
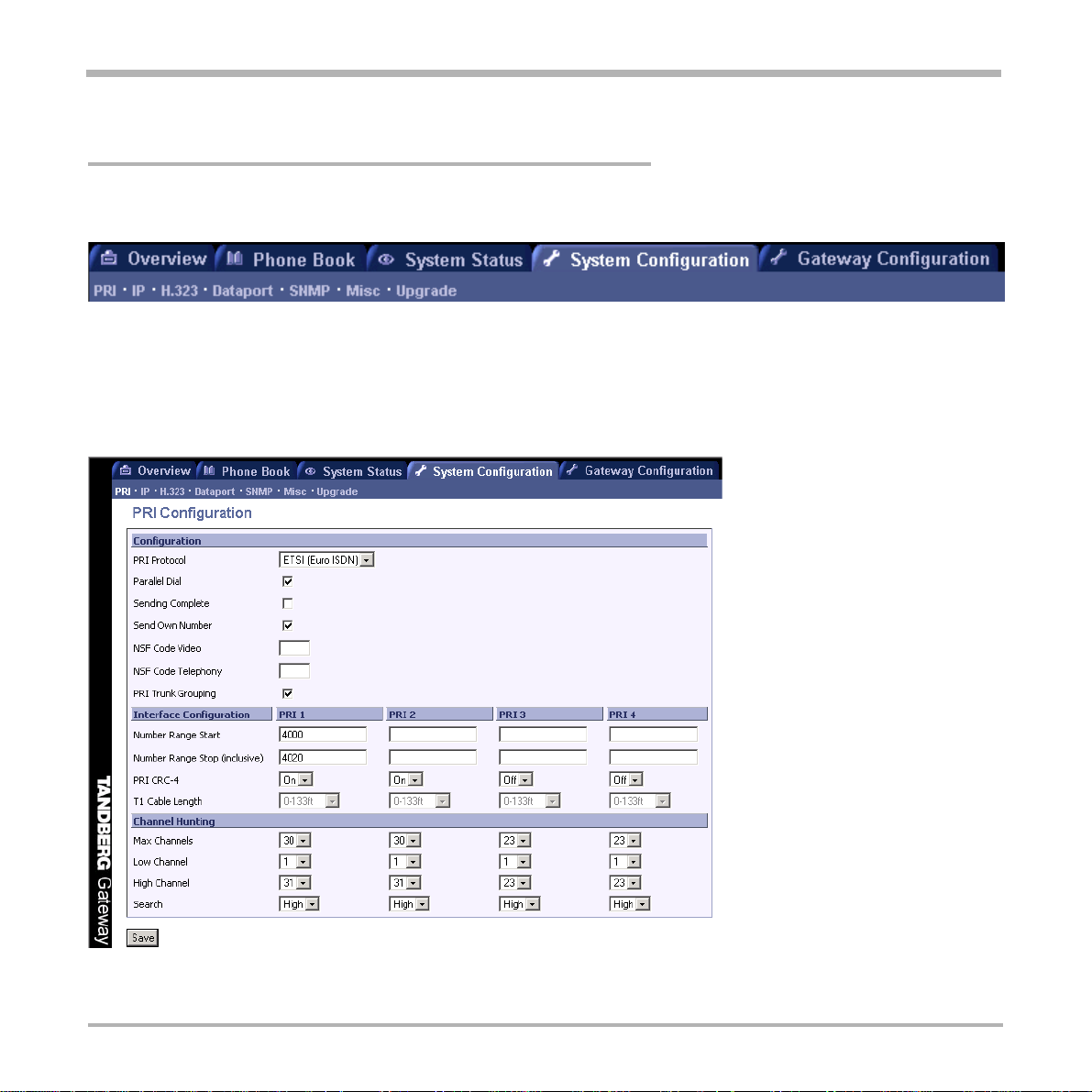
T o configure the PRI, select ‘System Configure - PRI’ as shown in the figure below .
35

Configure the Gateway
PRI Protocol
Select between the following PRI protocols:
T ANDBERG Gateway
• ETSI (Euro ISDN)
• National ISDN
• AT&T Custom
All PRI lines must use the same PRI Protocol.
Parallel Dial
On Channels will be dialed and connected in parallel when setting up a BONDING call.
Off Channels will be dialed sequentially , which may increase call setup time.
Sending Complete
On The system will send the ISDN message information element “Sending Complete”.
Off The system will not send “Sending Complete”.
Send Own Number
On The system will send its own number to the far end
Off The system will not send its own number to the far end, but please note that the network may still send
your number to the far end.
PRI Trunk Grouping
When Trunk Grouping is enabled, PRI 2, 3 and 4 will use the same number range as specified for PRI 1.
NSF - Non Standard Facility
Y our network provider may require a service selection in your ISDN configuration. Enter the Service code here.
V alid NSF service codes are from 1 to 31. Enter 0 to disable NSF service codes.
36
T ANDBERG Gateway
Configure the Gateway
NSF Example:
A T&T offers several digital switched services. These include SDN with service code 1 and ACCUNET with service
code 6.
Example:
Below is a list of common service profiles. As these profiles
may change, contact your service provider to get the correct
profile.
Service profiles for Sprint:
NSF Service
Reserved 0
Private 1
Inwatts 2
Service profiles for AT&T :
NSF Service
Disable 0
Outwatts 3
FX 4
TieTrunk 5
SDN (including GSDN) 1
Megacom 800 2
Megacom 3
Accunet 6
Long Distance 7
International 800 8
MultiQuest 16
Call Redirection Service 23
Service profiles for MCI:
NSF Service
VNET/Vision 1
800 2
PRISM1, PRISMII, WA TS 3
900 4
DAL 5
Save
When all settings are entered, please press the ‘Save’ - button to affect the new settings
37
Configure the Gateway
T ANDBERG Gateway
Interface Configuration
This section configures each of the four PRI interfaces individually . There is one column for each PRI Interface.
However, if PRI Trunk Grouping is enabled, the number range for PRI 1 will also apply for PRI 2, 3 and 4.
Number Range Start
The PRI lines connected to the gateway should have at least one number each, to allow dial in from ISDN.
In order for the gateway to handle two or more simultaneous incoming ISDN calls for the ISDN services IVR and
TCS-4, it is required to define a PRI number range in addition to the IVR number.
If the PRI line has a range of numbers, the start number
must be entered here. Please contact your IT manager to
obtain these numbers.
THE QUANTITY OF SIMULT ANEOUS INCOMING ISDN CALLS IS
NOTE
AS PRI NUMBER RANGE MINUS IVR AND HOTLINE
DEFINED
NUMBER (IF USED).
It is only necessary to enter the digits indicating the range. If the range is 67124000 to 67125000, then just enter
4000. Maximum amount of digits is 24.
Number Range Stop
Here is where the last number in the PRI number range is entered. If the range is 67124000 to 67125000, then
just enter 5000.
PRI CRC-4
Used for most E1-PRI configurations. If your network equipment does not support this feature, set PRI CRC-4 to
Off.
T1 Cable Length
Specifies the cable length between the gateway and the CSU for each of the PRI lines (only valid for T1 networks).
Possible values are:
• 0 to 133 feet
• 133 to 266 feet
• 266 to 399 feet
• 399 to 533 feet
• 533 to 655 feet
38

T ANDBERG Gateway
Configure the Gateway
Channel Hunting
Should be used if your PRI is limited e.g.:
• If only channels 1 through 18 are digital, and the rest are analogue. Use Low = 1, High = 18.
• If you have a PRI with only 12 channels. Set Max channel to 12.
Max Channels
Indicates the maximum number of B-channels the system is allowed to use for each of the PRI-interfaces. For E1
(ETSI/Euro ISDN), the maximum number of channels is 30. For T1 (National ISDN and A T&T Custom), the
maximum number of channels is 23.
Low Channel
Indicates the lowest numbered E1/T1 B-channel the system is allowed to use for each PRI-line when selecting
channels for outgoing calls.
High Channel
Indicates the highest numbered E1/T1 B-channel the system is allowed to use for each PRI-line when selecting
channels for outgoing calls.
Search
Specifies where the system will start searching for available B-channels for each PRI-line. If ‘Search’ is set to
‘High’, the system will start to search for available B-channels at the highest numbered B-channel. If ‘Search’ is
set to ‘Low’, the system will start searching for available B-channels at the lowest numbered B-channel.
39
Configure the Gateway
T ANDBERG Gateway
IP Configuration
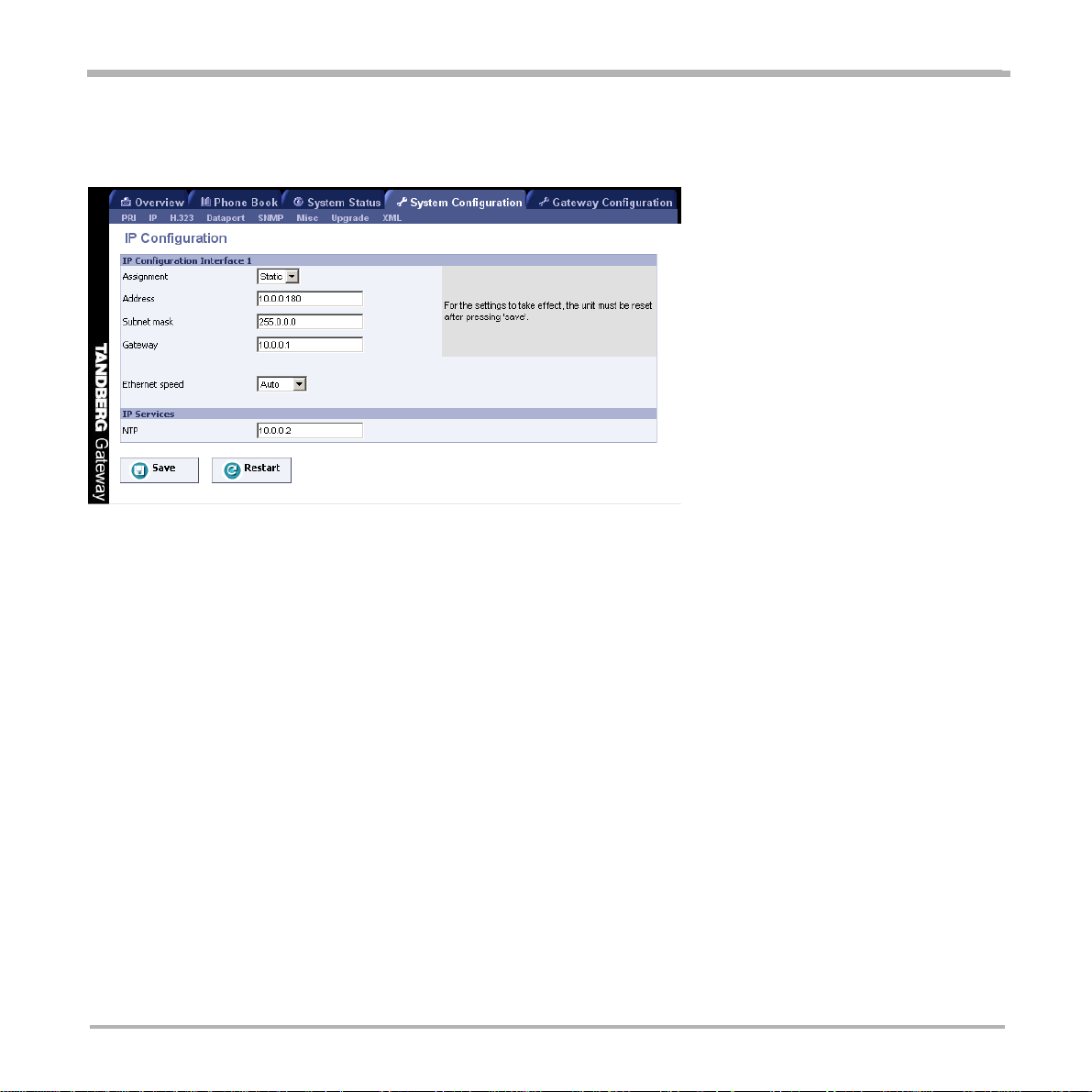
T o configure the IP settings on the gateway , open ‘IP’ as shown in the figure below .
Configuration
IP Address Assignment
DHCP: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol can be selected when a DHCP server is present.
St atic IP Address, S t atic IP Subnet Mask and Static IP Gateway are ignored because these parameters
are assigned by the DHCP server .
Static: If Static assignment is used, the gateway’s IP-address and IP-subnet mask must be specified in the
IP-address field.
IP Ethernet Speed
Auto The gateway will automatically detect the speed/duplex on the LAN.
10Half The gateway will connect to the LAN using 10 Mbps/Half Duplex.
10Full The gateway will connect to the LAN using 10 Mbps/Full Duplex.
100Half The gateway will connect to the LAN using 100 Mbps/Half Duplex.
100Full The gateway will connect to the LAN using 100 Mbps/Full Duplex.
40

T ANDBERG Gateway
Configure the Gateway
Static IP Address
The St atic IP Address defines the network address of the gateway. This address is only used in static mode. Your
LAN administrator will provide you with the correct address for this field.
Static IP Subnet Mask
The St atic IP Subnet Mask defines the type of network. Your LAN administrator will provide the correct value for
this field.
Static IP Gateway
The Static IP Gateway defines the Gateway address. Y our LAN administrator will provide the correct value for this
field.
NTP
The NTP Service defines the address of the NTP server . Y our LAN administrator will provide the correct value for
this field.
Save
When ready to store the new settings, press ‘Save’. These settings will take effect when the system is restarted.
Restart
This button will restart the gateway . Any changes made in IP Configuration and IP Service will then take effect.
41

Configure the Gateway
T ANDBERG Gateway
H.323 Configuration
T o dial out from IP to ISDN, through the gateway , requires the use of H.323 numbers (E.164 aliases). This means
that the gateway must be registered to a Gatekeeper.
H.323 GATEKEEPER STA TUS SHOWS
TIP
NOTE
STATUS OF GATEKEEPER
CURRENT
REGISTRATION.
IF THE GATEKEEPER IS CONFIGURED
AN ALTERNATIVE GATEKEEPER,
WITH
THE STATUS AREA MIGHT REPORT A
REGISTRATION
OF THE ALTERNATIVE GATEKEEPER.
TO THE IP ADDRESS
H.323 Configuration
Gatekeeper
Gatekeeper Enables the gateway to register to a Gatekeeper. The Gatekeeper IP Address must also be
filled in. When registered, the H.323 Gatekeeper Status shows Registered, Gatekeeper’s IP
address and what port used.
Problems with registration will be shown in the Status area and as a Red alarm on the
‘Overview’ page.
Direct No Gatekeeper registration will be preformed, hence it is not possible to dial through the
Gateway . The H.323 Gatekeeper S tatus window will show ‘Inactive’.
42

T ANDBERG Gateway
Configure the Gateway
Gatekeeper IP Address
Enter the Gatekeeper IP Address that the gateway should register to.
THE GATEWA Y MAY BE REGISTERED WITH A BORDER CONTROLLER IN THE SAME WAY IT IS REGISTERED WITH A GATEKEEPER . USE THE IP ADDRESS OF
NOTE
THE BORDER CONTROLLER IN THE GATEKEEPER ADDRESS FIELD.
Authentication Mode
Off Register to the Gatekeeper without authentication.
Auto Register to the Gatekeeper with H.235 authentication using ID/Password given below .
Authentication ID, Password
Enter the ID and password required to perform H.235 authentication at the Gatekeeper .
T o register to a Gatekeeper that requires authentication, an NTP server has to be configured.
Quality of Service
The network must support Quality of Service for these settings to work.
RSVP
Off No RSVP Quality of Service is initiated for any connections.
Auto Resource Reservation Protocol enables the gateway to request the optimal amount of bandwidth for
the duration of an IP video call.
QoS Mode
Off No QoS is used
Diffserv Diffserv QoS method is used. Please see ‘QoS Mode Configuration’ for details.
Precedence IP Precedence QoS method is used. Please see ‘QoS Mode Configuration’ for details.
43

Configure the Gateway
T ANDBERG Gateway
QoS Mode Configuration
Diffserv is used to define which priority audio, video, data and signaling packets should have in an IP network. The
priority ranges from 0 to 63 for each type of packets.
Precedence is used to define which priority audio, video, data and signaling should have in the network. The
higher the number, the higher the priority. The priority ranges from 0 (off) - 7 for each type of packets.
In addition to Precedence, T ype of Service can be used and enables the user to define what type of connection
that should be chosen for the IP traffic. Helps a router select a routing path when multiple paths are available.
Off Service not active.
Min. Delay Will choose a route where minimum delay is prioritized.
Max. Throughput Will choose the route with highest bandwidth.
Max. Reliable Will choose the route with highest reliability.
Min. Cost Will choose the route with minimum cost.
44

T ANDBERG Gateway
Configure the Gateway
Dataport Configuration
T o configure the Data port on the gateway, open ‘Dataport’ as shown in the figure below.
WHEN CONNECTING TO A PC
NOTE
THE CONNECTING CABLE
BE A STRAIGHT THROUGH
RS232 CABLE .
Dataport Configuration is used to configure the RS 232 serial port on the gateway . If you want to connect a PC to
the dataport, you must ensure that the PC and the gateway are identically configured.
Configuration
Baudrate
Possible values are: 1200 bps, 2400 bps, 4800 bps, 9600 bps, 19200 bps, 38400 bp s 56600 bps and 115200 bps.
MUST
Parity
Select ‘None’, ‘Odd’ or ‘Even’.
Databits
Select 7 or 8 databits.
Stopbits
Select 1 or 2 stopbits.
Save
Press ‘Save’ to activate the new settings.
45
THERE ARE NO HARDWARE OR SOFTWARE
NOTE
HANDSHAKE
PC HANDSHAKING IS TURNED OFF.
OPTIONS. MAKE SURE THE

Configure the Gateway
T ANDBERG Gateway
SNMP Configuration
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is used for monitoring and configuring different units in a network.
The gateway’s SNMP Agent responds to requests from SNMP Managers (a PC program etc.). SNMP traps are
generated by the agent to inform the manager about important events.
THE SNMP COMMUNITY NAME
NOTE
IS CASE SENSITIVE.
Configuration
SNMP Community Name
SNMP Community names are used to authenticate SNMP requests. SNMP requests must have this ‘password’
in order to receive a response from the SNMP agent in the gateway .
SNMP Trap Host (1, 2 and 3)
Identifies the IP-address of the SNMP manager . Up to three different SNMP Trap Host s can be defined. Y our LAN
administrator should provide the correct values for these fields.
System Contact
Used to identify the system contact via SNMP tools such as HPOpenView or TANDBERG Management Suite.
Location
Used to identify system location via SNMP tools such as HPOpenView or TANDBERG Management Suite.
Save
Press ‘Save’ to activate the new settings.
46

T ANDBERG Gateway
Configure the Gateway
Miscellaneous Configuration
T o configure the miscellaneous settings on the gateway, open ‘Misc’ as shown in the figure below.
Configuration
To change the system name of the gateway, enter the new system name in the ‘System Name’.
Password
T o change the system p assword of the gateway , enter the new p assword in the ‘New Administrator Password’.
To delete the existing password, select ‘Delete Password’.
Services
The different IP services on the gateway - Telnet, T elnet Challenge, HTTP, HTTPS, SNMP and FTP can be
independently disabled to prevent access to the system.
In addition, the SNMP Service Read Only/Traps Only will make it possible to read SNMP messages in addition to
enable/disable SNMP .
47

Configure the Gateway
T ANDBERG Gateway
SNMP Security alert
This function will notify any Management Application (such as T ANDBERG Management Suite) if anyone tries to
perform Remote Management on the gateway using an illegal password. The Security alert that is sent to the
Management Application will cont ain information about the IP address and the service (WEB, Telnet, FTP) being
used for the attempt.
If T ANDBERG Management Suite is used, email notifications or alarms about the attempt can be sent to
specified persons.
Save
Press ‘Save’ and then the ‘Restart’.
48

T ANDBERG Gateway
Configure the Gateway
Software Upgrade
Software upgrade is where new software to the gateway can be installed from. It also shows current software
version and the gateway’s hardware serial number .
TO UPGRADE THE GATEWA Y , A
NOTE
RELEASE KEY AND
VALID
SOFTWARE FILE IS REQUIRED.
CONT ACT YOUR TANDBERG
REPRESENTA TIVE FOR MORE
INFO.
System Information
Software Version Shows the currently installed Software version.
Hardware Serial Number This unique identifier number for the gateway must be provided when ordering
Software Upgrade.
Installed Options Shows the currently installed Options.
Current Option Key Shows the current Option Key .
Software Option
Bandwidth Option Key Enter the bandwidth option key in the Key field and press ‘Enable Option’. The
gateway will validate the key, and if valid a rest art would be requested for the
new bandwidth option to take effect.
Install Software
Release Key Enter the release key in the Key field and press ‘Install Software’. You will be
presented with a new page where you select the software package file to upload.
49

Configure the Gateway
T ANDBERG Gateway
File Management
The File Management allows viewing or changing of pictures and sounds shown to the caller when connecting to
the gateway .
PLEASE REFER TO THE
NOTE
‘LEGAL FILE TYPES’
FIELD AT THE BOTTOM OF
PAGE FOR
THE
INFORMATION
LEGAL FILE FORMATS.
T o view/hear the currently inst alled files, press the name of the ‘File’ on the left side of the window . The file will
then be shown/played. At the bottom of the p age, custom file requirements are listed for each of the file-types.
ABOUT
The following can be specified:
• Encryption Required Picture
• Gateway Call Proceeding Picture
• Gateway Extension Enquire Screen Picture
• Downspeeding In Progress Picture
• Gateway Call Welcome Sound
• Gateway Extension Enquire Sound
• System Parameters
• Directory
To add a new file, press ‘Browse...’ to find the file, and then press ‘Upload’.
For each of the customized files, a ‘Delete’ button will be added in the ‘Type’ column. By pressing ‘Delete’, the
default file will replace the custom file.
Pressing ‘System Parameters’ allow you to do backup and restore the settings on the gateway.
Pressing ’Directory’ allow you to upload a Phone Book to the gateway. The Phone Book is used for the Call
Transfer function.
50
T ANDBERG Gateway
Configure the Gateway
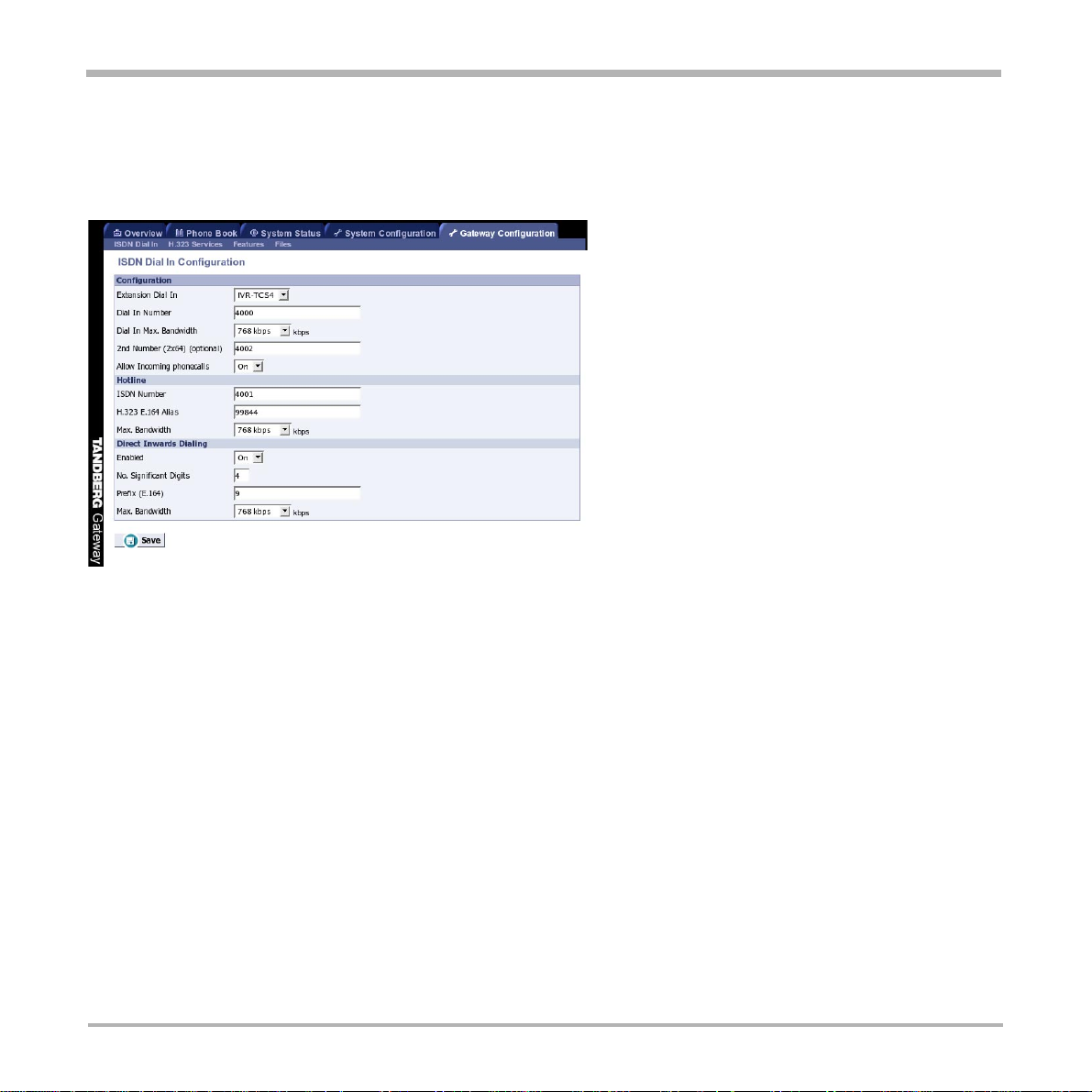
ISDN Dial In Configuration
The ISDN Dial In Configuration allows you to configure and enable the ISDN services used to access your IP
endpoints.
Configuration
Extension Dial In
Select between Off, IVR, IVR + TCS-4:
Off: Incoming calls will not be allowed, except those specified under Hotline and Direct Inwards
Dialing.
IVR: Incoming calls will be prompted with the Gateway Extension Enquire Screen and Sound,
except those specified under Hotline and Direct Inwards Dialing. The Gateway will wait for DTMF
input (touch tones) that specifies the address of the outgoing call.
IVR + TCS-4: Incoming calls will be prompted with the Gateway Extension Enquire Screen and
Sound, except those specified under Hotline and Direct Inwards Dialing. The Gateway will wait
simultaneously for DTMF input (touch tones) and TCS-4 signalling that specifies the address of the
outgoing call.
51

Configure the Gateway
T ANDBERG Gateway
Dial In Max. Bandwidth
The call rate (bandwidth) for incoming calls will automatically be determined by the endpoint. However , you can
use this setting to restrict the call rate for incoming DID/TCS-4 calls.
Calls above the Dial In Max. Bandwidth will be downspeeded
NOTE
REQUIRE SUPPORT OF DOWNSPEEDING ON THE ENDPOINT.
to the call rate specified in Dial In Max. Bandwidth.
Calls below the Dial In Max. Bandwidth will be connected at the requested call rate.
Dial In Number
All incoming calls received on this number will use the IVR/TCS-4 service.
2nd Dial In Number
This is the second number used for the 2x64k (H.221) dial in method. Most modern equipment used the default
BONDING method and don’t need the configuration of this number.
Allow Incoming Phonecalls
Incoming phonecalls can be disabled.
Hotline
ISDN Number
All incoming calls received on this number will be forwarded to the IP endpoint specified in ‘H.323 E.164 Alias’
field.
H.323 E.164 Alias
All incoming calls received to the Hotline ISDN number will be forwarded to this H.323 Alias.
Max. Bandwidth
The call rate for incoming calls will automatically be determined by the endpoint. However , you can use this
setting to restrict the call rate for incoming Hotline calls.
52
NOTE
REQUIRE SUPPORT OF DOWNSPEEDING ON THE ENDPOINT.

T ANDBERG Gateway
Calls above the Max. Bandwidth will be downspeeded to the
call rate specified in Max. Bandwidth.
Calls below the Max. Bandwidth will be connected at the requested call rate.
Configure the Gateway
Direct Inwards Dialing
When DID is enabled, all incoming calls within the PRI number range will be forwarded to an IP/H.323 endpoint
except calls received to the IVR and Hotline ISDN numbers.
No. Significant Digits
Specify the number of significant digit s in the PRI Number range that should be used to generate an H.323 Alias
(IP number).
Example:
• Y our ISDN PRI number range is from 67124000 to 67124050.
• Y ou want your IP endpoint s to have the numbers (H.323 Alias) in the range 4000 - 4050.
• Set ‘No. Significant Digits’ to 4.
• To call an IP endpoint with H.323 Alias 4020 from ISDN, dial the ISDN number 67124020.
Prefix (E.164)
When receiving an incoming call, a number prefix can be added to the range of digits specified under ‘No.
Significant Digits’. This is useful where the IP end points also use H.323 Prefix for placing calls on IP.
Example:
• Y our ISDN PRI number range is from 67124000 to 67124050.
• Y ou want your IP endpoints to have the numbers (H.323 Alias) in the range 94000 - 94050.
• In the ISDN Dial In Configuration, set ‘No. Significant Digits’ to 4 and ‘Prefix (E.164)’ to 9.
• T o call an IP endpoint with H.323 Alias 94020 from ISDN, dial the ISDN number 67124020.
Max. Bandwidth
The call rate for incoming calls will automatically be determined by the endpoint. However , you can use this
setting to restrict the call rate for Direct Inwards Dialing calls.
REQUIRE SUPPORT OF DOWNSPEEDING ON THE ENDPOINT.
Calls above the Max. Bandwidth will be downspeeded to the
call rate specified in Max. Bandwidth.
Calls below the Max. Bandwidth will be connected at the requested call rate.
53
NOTE

Configure the Gateway
T ANDBERG Gateway
H.323 Services
H.323 Service prefixes are used for IP endpoints to access the ISDN network. Up to twenty prefixes can be
defined, but we recommend using one single prefix for simplicity.
Default H.323 Services are ‘0’ for Video calls and ‘1’ for Telephone calls. Should other H.323 Services be required,
they can be entered here.
Description
Used to identify the H.323 Service.
Service
Specifies the gateway service prefix that all IP endpoints must use when dialing from IP to ISDN. There can be up
to 20 different H.323 Services.
If you have multiple gateways they should use the
same Service prefixes. Then it can be useful to use
“H.323 Load Balance” to balance resource usage
between the gateways.
54
TIP
IF YOU HAVE PROBLEMS DIALING A CONFIGURED H.323 SERVICE,
CHECK THAT THE SERVICE PREFIX IS REGISTERED ON THE
GATEKEEPER AS A GA TEWAY SERVICE. IT COULD ALREADY BE
REGISTERED AS ANOTHER SERVICE.

T ANDBERG Gateway
Configure the Gateway
Max. Rate
The call rate for outgoing calls will automatically be determined by the call rate used by the endpoint. Use this
setting to restrict the call rate for outgoing calls.
Possible configurations are Telephone, 64 kbps, 128 kbps, 192 kbps, 256 kbps, 320 kbps, 384 kbps, 512 kbp s,
768 kbps, 1 152 kbp s, 1472 kbps and 1920 kbp s.
We recommend having one service prefix for Video and one for T elephone calls unless Q.931 S peech signaling on
IP/H.323 is supported by the endpoint.
ISDN Prefix
Can be used as an option to pick specific carriers or “outside”-lines and is automatically added to the ISDN
number.
Restrict
Select ‘Restrict’ if the H.323 Service always should force restricted (56k) ISDN calls. If ‘Restrict’ is not selected,
the gateway will dial an unrestricted call and downspeed to 56 kbps if necessary .
Create New
When Description, Service, Max. Rate, ISDN Prefix, Restrict (56k) has been entered, press ‘Create New’ to
activate the new H.323 Service.
Save Changes
To modify a H.323 Service, click on it, change the necessary settings and press ‘Save Changes’ to activate the
new settings.
Clear
Press ‘Clear’ to empty any entries done under Entry.
Save
Press ‘Save’ to activate the new settings.
55

Configure the Gateway
T ANDBERG Gateway
Signal Busy on Load
When the Resource Usage reaches the “Busy on Load”-limit, the gateway will try to route outgoing IP/H.323 calls
to other gateways. This is done to maintain availability for incoming ISDN calls when using multiple gateways.
V alue can be set from 0% to 100%.
Press ‘Save’ to activate the new settings.
56

T ANDBERG Gateway
Configure the Gateway
Gateway Features
Experience has shown that some features - even though they are standardized - might cause interoperability
problems with legacy video conferencing products. If you disable features on this page, the gateway can be used
as a filter to ensure interoperability with legacy products.
T o configure the gateway features, open ‘Gateway Configuration - Features’ as shown in the figure below .
Natural Video
Allows video formats and capabilities such as interlaced video (iCIF/iSIF) to be transmitted through the gateway .
When disabled no interlaced video capabilities will be transmitted.
Custom Video Formats
Allows H.263 custom video formats and capabilities such as SIF, 4SIF and VGA resolution to be transmitted
through the gateway . When disabled no H.263 custom video formats or capabilities will be transmitted.
Duo Stream (Duo Video / H.239)
Allows an additional video stream to be transmitted through the gateway using Duo Video or the H.239 protocol.
When disabled no Duo Video or H.239 capabilities will be transmitted.
57
Configure the Gateway
T ANDBERG Gateway
Encryption
NOTE
The gateway will allow DES and AES 128 encrypted
conferences to take place. Encryption can operate in two
modes.
WHEN ‘ENCRYPTION’ IS ENABLED, THE CAPACITY OF THE
MAY BE REDUCED. SEE APENDIX 3 FOR MORE
GATEWAY
INFO.
When set to Transp arent, the Gateway will forward the encryption modes of the connected devices
transparently . The encryption modes seen on each side of the Gateway are similar . The gateway will only encrypt
calls if both sides support encryption. The settings for H.320 and H.323 doesn’t have any meaning in this mode.
When set to Independent, the Gateway will use the settings made for the H.320 (ISDN) and H.323 (IP) side. The
encryption modes on each side of the Gateway are independent of each other. One end point might show that the
call is encrypted will the other endpoint shows an unencrypted call.
On Encryption is required. Gateway connection is only established if encryption can be established on this
side.
Off No encryption. Gateway connection will be established without any encryption on this side.
Auto Use encryption if available. Gateway will try to establish an encrypted connection, the connection will be
established regardsless if encryption on this side is available.
A typical application of this feature is when an external crypto device is used on the ISDN interface. In this case
might an administrator want to set the Gateway’s encryption on the H.320 side to Off and on the H.323 side to
On.
H.264
Allows H.264 video capabilities to be transmitted through the gateway . When disabled no H.264 video capabilities
will be transmitted.
Save
Press ‘Save’ to activate the new settings.
58

T ANDBERG Gateway
Appendices
Appendix 1: Using the file system
It is possible to access a file system within the TANDBERG GATEWAY by using ftp:
DOS-window: ftp <IP-address of gateway>, or
Web-browser: ftp:// <IP-address of gateway>
Description of the different folders
user - a folder to be used for custom files, images and audio files etc.
tmp - not used in the Gateway
Description of the different files
all.prm - all settings in the system (including directory)
dir.prm - directory entries
event.log - logs fault situations etc.
sw.pkg - the system software
user/relkeys.v1 - storage for the last used release keys (when upgrading to a newer version)
Appendices
What can be done by using the file system?
· upload of custom images
· upload software
59

T ANDBERG GatewayAppendices
Appendix 2: Declaration of Conformity
60

T ANDBERG Gateway
Appendices
Appendix 3: Capacity
Gateway capacity - calculation
The total capacity in the gateway is defined by the following rules:
1) A maximum of 8 video calls and 8 telephone calls.
2) Software version defines maximum ISDN bandwidth:
2 Mbps -> Maximum ISDN bandwidth is 1920 kbps (30x64 kbps).
4 Mbps -> Maximum ISDN bandwidth is 3840 kbps (60x64 kbps).
3) In addition, each call has a weight depending on bandwidth/encryption:
Bandwidth Teleph. 64 128 19 2 25 6 32 0 3 84 5 1 2 76 8 115 2 1472 1920
Non-encr. 22 74 80 82 84 8 8 9 2 108 124 160 176 220
Encrypted N/A 106 118 120 122 136 146 168 222 N/A N/A N/A
The sum of the call weights cannot exceed 845 and max. bandwidth. Users will be prevented from setting up calls that
exceeds these limits.
When encryption mode is set to Independent, the Gateway calls may be weighted as encrypted calls even though on side
of the connection might not be encrypted.
Example (4 Mbps version):
If the gateway has made 3 calls at 768, 2 calls at 384, and 2 encrypted calls at 192 the calculation will be:
3x124 + 2x92 + 2x120 = 372 + 184 + 240 = 796. Since 796 is less than 845 and the total bandwidth 3456 kbps, do not
exceed the maximum bandwidth limit, this will be possible.
Gateway capacity – typical scenarios (4 Mbps version)
Below some typical capacity scenarios are listed. They can be derived by the calculation above:
Bandwidth Non-encrypted Encrypted
128 kbps 8+8* 7+0
256 kbps 8+7 6+5**
384 kbps 8+4 5+5
512 kbps 7+4 5+0
768 kbps 5+0 3+8
1472 kbps (1.5 Mbps) 2+8 N/A
1920 kbps (2 Mbps) 2+0 N/A
* 8+8 indicates 8 video calls and 8 telephone calls.
** 6+5 indicates 6 encrypted video calls and 5 unencrypted telephone calls.
61

T ANDBERG GatewayIndex
Index
A
Accessing the gateway 16
Actions 19
Add new entry 29
Authentication 7, 43
Available Resources 34
B
Bandwidth Option Key 49
Battery handling 3
Baudrate 45
BONDING 36
Border Controller 7, 28, 43
C
Cables 14
Call Overview 17
Call Transfer 19
Capacity 61
Channel Hunting 39
Configuration 15
Configure the Gateway 35
Connecting cables 14
Copyright 3
CRC-4 38
Current Option Key 49
Custom Video Formats 57
D
Databits 45
Dataport Configuration 45
Declaration of Conformity 60
DHCP 40
Dial from IP 24
Dial from ISDN 21
Dial In Max. Bandwidth 52
Dial In Number 52
Diffserv 43
Direct Inward Dialing (DID) 22
Direct Inwards Dialing 53
Directory 50
Disconnect Gateway Call 19
Downspeeding In Progress Picture 50
Duo Stream (Duo Video / P+C) 57
Duration 18
E
Edit Entry 30
Enable H.264 58
Encryption 58
Encryption (Secure conference) 18
Environmental Issues 3
ETSI (Euro ISDN) 36, 51
Example of ISDN Cause Codes 32
Example of Location Codes 32
Expressway 7, 27
Extension Dial In 51
F
File Management 50
File system 59
Firewall Traversal 7, 27
Front view of gateway 10
G
Gatekeeper 42
Gatekeeper IP Address 43
Gateway Call Proceeding Picture 50
Gateway Call Proceeding Sound 50
GATEWAY Capacity 11
Gateway capacity 61
Gateway capacity - calculation 61
Gateway Configuration 15
Gateway Extension Enquire Screen Picture
50
Gateway Extension Enquire Sound 50
Gateway Features 57
Gateway start-up 16
H
H.264 58
H.323 Configuration 42
H.323 E.164 Alias 52
H.323 Numbers 20
H.323 Services 24, 54
H.323 Status 33
Hardware Serial Number 49
High Channel 39
Hotline 23, 52
I
Install Software 49
Installation 12
Installation site preparations 13
Installed Options 49, 52
Interface Configuration 38
Introduction 7
IP Address Assignment 40
IP Configuration 40
IP Ethernet Speed 40
IP Gateway 41
IP Precedence 43
IP Subnet Mask 41
IP/H.323 Status 19
ISDN Dial In Configuration 51
ISDN Numbers 20
ISDN Prefix 55
ISDN PRI cables 14
IVR 21
IVR + TCS-4 22
L
LAN cable 14
LED 10
Location 46, 58
Low Channel 39
M
Manage the Phone Book 29
Max Channels 39
62

T ANDBERG Gateway
Index
Max. Rate 55
Miscellaneous Configuration 47
N
National ISDN 51
Natural Video 40, 57
No. Significant Digits 53
NSF - Non Standard Facility 36
NSF Example 37
Number Range Start 38
Number Range Stop 38
P
Parallel Dial 36
Parity 45
Password 16, 47
Power cable 14
Power on 16
Precautions 12
Prefix (E.164) 53
PRI Alarms 32
PRI Configuration 35
PRI CRC-4 38
PRI Protocol 36
PRI Status 19, 31
PRI Trunk Grouping 36
Production of products 3
Q
QoS Mode 43
QoS Mode Configuration 44
Quality of Service 43
R
Rack Mounting (optional) 13
Rear view of gateway 11
Red Alarm 32
Release Key 49
Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP) 43
Restart 48
Restrict 55
RS 232 45
RS 232 cable 14
S
Secure conference 18
Send Own Number 36
Sending Complete 36
Sequence of Services 23
Services 47
Signal Busy on Load 56
Site preparations 13
SNMP 46
SNMP Agent 46
SNMP Community 46, 55, 57
SNMP Community Name 46
SNMP Community name 46, 54, 57
SNMP Configuration 46
SNMP Manager 46
SNMP Security alert 48
SNMP Trap Host 46, 54, 57
SNMP traps 46
Software Option 49
Software Upgrade 49
Software Version 49
Sound 50
Source 18
Start-up 16
Static 40
Static IP Address 41
Static IP Gateway 41
Static IP Subnet Mask 41
Stopbits 45
System Configuration 35
System Contact 46, 55, 57
System Information 33, 49
System Name 47
System Parameters 50
T
T1 38
T1 Cable Length 38
The TANDBERG Gateway 10
Trademarks 3
Type of Service (TOS) 44
U
Unpacking 12
Usage 20
Using the file system 59
Using the Gateway 17
V
View System Status 31
W
Waste handling 3
Y
Yellow Alarm 32
63
 Loading...
Loading...