Page 1

Model 520
Body Builder Manual
2017
Release Date 3/23/17
Page 2

This page intentionally left blank
Page 3

BODY BUILDER MA NUAL CONTENTS
SECTION 1: INTRODUCTION 1-1
SECTION 2: SAFETY AND COMPLIANCE
SAFETY SIGNAL S 2-1
FEDERAL MOT O R VEHI CLE SAFETY STANDA RD S AND COMPLIANCE 2-2
NOISE AND EMISSIO N S R EQU IREMENTS 2-3
FUEL SYSTEM 2-4
COMPRESSED AIR SYSTEM 2-4
EXHAUST AND EXHAUST AFTER-TREATMENT SYSTEM 2-5
COOLING SYSTEM 2-6
AIR INTAKE SYSTEM 2-6
CHARGE AIR COOLER SYSTEM 2-6
SECTION 3: DIMENSIONS
INTRODUCTION 3-1
ABBREVIATIONS 3-1
OVERALL DIMENSIONS 3-2
FRAME RAILS 3-9
FRAME HEIGHT CHARTS 3-11
REAR SUSPENSION LAYOUTS 3-18
Reyco 79KB Single 3-19
Reyco 102AR Single 3-20
Neway ADZ252 3-21
Neway ADZ369/378 3-22
Peterbilt Air Leaf 3-23
Peterbilt Air Trac Single 3-24
Peterbilt Air Trac Tandem 3-25
Peterbilt
Peterbilt Low Air Leaf 3-27
Chalmers 854 3-28
Hendrickson HMX 3-29
Hendrickson RT/RTE 3-30
Hendrickson HN 3-31
Hendrickson R 3-32
Hendrickson RS 3-33
PUSHER AND TAG LAYOUTS 3-34
Hendrickson 3-34
Watson-Chalin 3-38
EXHAUST HEIGHT CALCULATIONS 3-42
GROUND CLEARANCE CALCULATIONS 3-43
OVERALL CAB HEIGHT CALCULATIONS 3-44
FRAME COMPONENTS 3-45
Fuel Tanks 3-45
EXHAUST SYSTEM 3-46
Air Trac Tri-Drive 3-26
SECTION 4: BODY MOUNTING
INTRODUCTION 4-1
FRAME RAILS 4-1
CRITICAL CLEARANCES 4-2
BODY MOUNTING USING BRACKETS 4-3
Brackets 4-4
Mounting Holes 4-5
Frame Drilling 4-6
Peterbilt Motors Company ii
Page 4

TABLE OF CONTENTS
BODY MOUNTING USING U–BOLTS 4-7
Rear Body Mount 4-9
SECTION 5: FRAME MODIFICATIONS
INTRODUCTION 5-1
DRILLING RAILS 5-1
MODIFYING FRAME LENGTH 5-2
CHANGING WHEELBASE 5-2
CROSSMEMBERS 5-3
TORQUE REQUIREMENTS 5-4
SECTION 6: ELECTRICAL 520 FAMILY
CONTROL UNIT IDENTIFICATION 6-1
Functional Description-Cab Electronic Control Unit (CECU) 6-1
HOW MULTIPLEXED INSTRUMENTS WORK 6-2
CECU Architecture 6-2
Power On Self-Test 6-3
ELECTRICAL INTERFACE 6-4
Cab Harness 6-5
Chassis Harness 6-9
J1939 6-9
Body Builder Harness Extensions 6-9
Guidelines - J1939 Circuit Requirements 6-9
J1939 Access 6-9
J1939 Access Procedures 6-9
SECTION 8: PTO SECTION
INTRODUCTION 7-1
TRANSMISSION MOUTED PTO – GENERAL 7-1
Manu
al Transmission 7-1
Automatic Transmission 7-2
Installation Clearances 7-2
FRONT ENGINE PTO 7-3
REAR ENGINE PTO 7-4
PTO INSTALLATIONS 7-5
REMOTE PTO CONTROL (12 PIN CONNECTOR) 7-6
INSTALLTION OF PTO MODEL 7-7
CHELSEA 890 7-7
Peterbilt Motors Company iii
Page 5

SECTION 1 INTRODUCTION
The Peterbilt 520 Body Builder Manual was des igned to provide body builders with a comprehensive information set to
guide the body planning and installation process. Use this information when installing bodies or other associated
equipment.
This manual contains appropriat e dimensional information, guidelines for mounting bodies, modifying fr ames, electrical
wiring information, and other information useful in the body installation process.
The Peterbilt 520 Body Builder Manual c an be ver y usef ul whe n specif ying a ve hic le, partic ularl y when th e bod y builder is
involved in the vehicle definition and ordering proc ess. Information in this m anual will help reduce overall cos ts through
optimized integration of the body installation with vehicle se lection. Early in the process , professional body builders c an
often contribute valuable information that reduces the ultimate cost of the body installation.
In the interest of continuing product developm ent, Peterbilt reserves the right to change spec ifications or products at any
time without prior notice. It is the responsibility of the user to ensure that he is working with the latest released information.
Check Peterbilt.com for the latest released version.
If you require additional information or reference materials, please contact your local Peterbilt dealer.
Peterbilt Motors Company 1-1
Page 6

his page intentionally left blank
T
Page 7
2
SAFETY AND COMPLIANCE
SECTION 2 SAFETY AND COMPLIANCE
SAFETY SIGNALS
We’ve put a number of alerting messages in t his book. Please r ead and follow them. They are there for your
protection and information. These alerting m essages can h elp you avoid injury to yourself or other s and help
prevent costly dam - age to the vehicle.
Key symbols and “signal words” are used to indicate what kind of message is going to follow. Pay special attention
to comments prefaced by “WARNING”, “CAUTION”, and “NOTE.” Please don’t ignore any of these alerts.
Warnings, cautions, and notes
WARNING
Example:
WARNING! Be sure to use a circuit breaker designed to meet liftgate amperage requirements. An
incorrectly specified circuit breaker could result in an electrical overload or fire situation. Follow the
liftgate installation instructions and use a circuit breaker with the recommended capacity.
CAUTION
Example:
CAUTION: Never use a torch to make a hole in the rail. Use the appropriate drill bit.
NOTE
When you see this word and symbol, the message that follows is especially vital. It signals a
potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in death or serious injury.
This message will tell you what the hazard is, what can happen if you don’t heed the warning,
and how to avoid it.
Signals a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in minor or
moderate injury or damage to the vehicle.
Provides general information: for example, the note could war n you on how to avoid damaging
your vehicle or how to drive the vehicle more efficiently.
Example:
Note: Be sure to provide maintenance access to the battery box and fuel tank fill neck.
Please take the time to read these messages when you see them, and remember:
WARNING
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in death or serious injury.
CAUTION
Signals a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in minor or moderate
injury or damage to the vehicle.
NOTE
Useful information that is related to the topic being discussed.
Page 8

2
SAFETY AND COMPLIANCE
FEDERAL MOTOR VEHICLE SAFETY STANDARDS AND COMPLIANCE
As an Original Equipment Manufacturer, Peterbilt Motors Company ensures that our products comply with all applicable
U.S. or Canadian Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards. However, the fact that this vehicle has no fifth wheel and that a
Body Builder (Intermediate or Final Stage Manufacturer) will be doing additional modifications means that the vehicle was
incomplete when it left the build plant.
Incomplete Vehicle Certification
An Incomplete Vehicle Document is shipped with the vehicle, certifying that the vehicle is not complete. See Figure 2–1.
In addition, affixed to the driver’s side door frame or edge is an Incomplete Vehicle Certification label . See Figure 2–2.
NOTE
These documents list the U.S. or Canadian Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard regulations that the
vehicle complied with when it left the build plant. You should be aware that if you add, modify or alter any
of the components or systems covered by these regulations, it is your responsibility as the Intermediate or
Final Stage Manufacturer to ensure that the complete vehicle is in compliance with the particular
regulations upon completion of the modifications.
U.S. EPA Noise Label (U.S. registered vehicles only)
inal Stage Manufacturer
F
Label to be installed by
Final Stage Manufacturer
Chassis Serial
Number
Vehicle Emission Control
Information Label
FIGURE 2-1. Incomplete Vehicle Certification Document
Tire, Rim and
Weight Rating
Data label
Safety Mark (Canadian
Registry Only)
Incomplete Vehicle
Certification Label
Major Components and
Weights Label
FIGURE 2-2. Locations of Certification Labels - Driver’s Door and Frame
As the Intermediate or Final Stage Manufacturer, you should retain the Incomplete Vehicle Document for your records. In
addition, you should record and retain the manufacturer and serial number of the tires on the vehicle. Upon completion of
the vehicle (installation of the body and any other modifications), you should affix your certification label to the vehicle as
required by Federal law. This tag identifies you as the “Intermediate or Final Stage Manufacturer” and certifies that the
vehicle complies with Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards. (See Figure 2–2.) Be advised that regulations affecting the
intermediate and final stage manufacturer may change without notice. Ensure you are referencing the most updated copy
of the regulation during the certification and documentation processes.
In part, if the final stage manufacturer can complete and certify the vehicle within the instruction in the incomplete vehicle
document (IVD) the certification label would need a statement that reads, “This vehicle has been completed in accordance
with the prior manufacturers‚ IVD where applicable. This vehicle conforms to all applicable Federal Motor Vehicle Safety
Standards [and Bumper and Theft Prevention Standards if applicable] in effect in (month, year).”
However, if the vehicle cannot be completed and certified with in the guidance provided in the IVD, the final stage
manufacturer must ensure the vehicle conforms to all applicable Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards (FMVSS). The
final stage manufactures certification lab e l would need a statement that reads, “This vehicle conforms to all applicable
Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards [and Bumper and Theft Prevention Standards if applicable] in effect in (month,
Peterbilt Motors Company 2-2
Page 9

2
SAFETY AND COMPLIANCE
year).These statements are just part of the changes to the new certification regulation. Please refer to the Feb 15, 2005
final rule for all of the details related to this regulation. You can contact NTEA Technical Services Department at 1-800441- NTEA for a copy of the final rule (DocID 101760).
For Canadian final stage manufacturers see:
http://www.gazette.gc.ca/index-eng.html;
and http://www.tc.gc.ca/eng/acts-regulations/menu.htm for
the regulations.
Or contact:
Transport
Canada
Tower C, Place de Ville, 330 Sparks Street
Ottawa, Ontario K1A
0N5 (613) 990-2309
TTY: 1-888-675-6863
Noise and Emissions Requirements
NOTE
This truck may be equipped with specific emissions control components/systems* in order to
meet applicable Federal and California noise and exhaust emissions requirements. Tampering
with these emissions control components/systems* is against the rules that are established by the
U.S Code of Federal Regulations, Environment Canada Regulati ons a nd California Air Resources
Board (CARB). These emissions control componen ts /s ystems* may only be replaced with orig in al
equipment parts.
Additionally, most vehicles in North America will be equipped with a Greenhouse Gas (GHG)
“Vehicle Emission Control Information” door label indicating its certified configuration. The vehicle
components listed on this label are considered emission control devices.
Modifying (i.e. altering, substituting, relocating) any of the emissions control components/systems
defined above will affect the noise and emissions performance/certification. Modifications that
alter the overall s ha pe and aer odynamic performance of a tractor will also affect the emission
certification. If modifications are required, they must first be approved by the manufacturer.
Unapproved modifications could negatively affect emissions performance/certification. There is no
guarantee that proposed modifications will be approved.
Tires may be substituted provided the new tires possess a Coefficient of rolling resistance (Crr)
equal to or lower than Crr of the original tires. Consult with your tire supplier(s) for appropriate
• For Cummins Contact 1-800-DIESELS or your local Cummins distributor. Reference AEB 21.102.
It is possible to relocate the DEF tank; however the relocation requirements need to be followed. Any variances from the
relocation requirements may cause the emissions control components/systems to operate improperly potentially resulting
in engine de-rate.
Peterbilt Motors Company 2-3
replacement tires.
Contact the engine manufacturer for any requirements and restrictions prior to any modifications.
Page 10

2
SAFETY AND COMPLIANCE
NOTE
To ensure compliance to emissions regulations, the final configuration of certain features of the completed vehicle
must meet specific requirements. This section describes requirements relevant for only the most common or critical
modifications done by body builders. For a complete description of acceptable modifications, see the application
guidance available from the manufacturer of the engine installed in the chassis.
All 2017 engine emissions certified vehicles will be equipped with an On-Board Diagnostics
(OBD) system. The OBD system is designed to detect malfunctions of any engine or vehicle
component tha t may increase exhaust emissions or interfere with the proper performance of the
OBD system itself All diesel engines will be equipped with an On-Board Diagnostics (OBD)
system. The OBD system consists of computer program on one or more of the vehicle’s Electronic
Control Units (ECUs). This program uses information from the control system and from additional
sensors to detect malfunctions. When a malfunction is detected, information is stored in the
ECU(s) for diagnostic purposes. A Malfunction Indicator Light (MIL) is illuminated in the dash to
alert the driver of the need for service of an emission-related component or system.
Fuel System
The following are highlights of some of the more common or critical aspects of this system.
The overall system restriction may not exceed the restriction limitations set forth by the engine manufacturer for both
supply and return.
• Ensure that fuel lines are not pinched or can potentially be damaged when installed between body
and frame
• Fuel lines must be routed and secured without dips or sags
• There must be easy access to filter(s) and fill cap
• The tank vent may not obstructed
• Added accessories (heaters, generators) cannot introduce air into system
• Fuel tank must be located so that the full level is not above cylinder head
• “Ultra-Low Sulfur Fuel Only” labels must be present on the dash and fuel fill
• Modification of the pressure side secondary filter and plumbing is not allowed without engine
manufacturer approval
• Body installation of fuel tank or routing of lines must not cause significant increase in fuel temperature
• Fuel hoses shall meet or exceed OEM supplied hose material construction specifications
Compressed Air System
The following are highlights of some of the more common or critical aspects of this system.
• Air system modification must meet applicable FMVSS regulations
• Compressed Air tank may not be modified (exception – addition or removal of fittings or relocation of the
tank)
• Added devices or bodywork may not interfere with or rub air lines
Peterbilt Motors Company 2-4
Page 11

2
SAFETY AND COMPLIANCE
• Air supply to the engine doser may not be restricted or disconnected
• Air lines should be routed, protected from heat, and properly secured to prevent damage
from other components
• Care should be taken so that air lines do not rub against other components
• Care should be taken to protect the air system from heat sources
Exhaust and Exhaust After-treatment System
The following are highlights of some of the more common or critical aspects of this system.
• The following after-treatment and exhaust system components may not be modified:
• DPF assembly
• SCR Catalyst assembly
• Exhaust pipes between the engine and after-treatment devices (DPF, SCR Catalyst) and between
after-treatment devices
• NO
• PM Sensor
• The following modifications may only be done within the guidelines of the “DEF System Relocation Guide.”
• Modifications to Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) throttle, s uction, or press ure lin es
• Modification or relocation of the DEF tank
• Modification of coolant lines to and from the DEF tank
• All DEF and coolant lines should be routed, protected, and properly secured to prevent damage during
• If relocation of the DCU or ACM is necessary, use existing frame brackets and mount inside of frame
• The DPF, the SCR catalyst, or their mounting may not be modified
• The NOx sensor may not be relocated or altered in any way; this includes re-clocking the
• Exhaust pipes used for tailpipes/stacks must be properly sized, and must prevent water from entering
• Ensure ade quat e clearance between the exhaust and body panels, hoses, and wire harnesses
• The body in the vicinity of the DPF must be able to withstand temperatures up to 400°C (750°F)
• Do not add thermal insulation to the external surface of the DPF
Sensors
x
vehicle operation or other components
flanges where necessary. Do not extend the harnesses
aftertreatement canister or reorienting the sensor(s)
• The SCR water drain hole may not be blocked
• Allow adequate clearance (25mm (1 inch)) for servicing the DPF sensors, wiring, and clamped joints
• Drainage may not come in contact with the DPF, SCR catalyst, sensors or wiring
Peterbilt Motors Company 2-5
Page 12

2
SAFETY AND COMPLIANCE
• Allow sufficient clearance for removing sensors from DPF. Thermistors require four inches. Other
sensors require one inch
• Wiring should be routed, protected from heat, and properly secured to prevent damage
from other components
• The exhaust system from an auxiliary power unit (APU) must not be connected to any part of the
vehicle after-treatment system or vehicle tail pipe.
Cooling System
The following are highlights of some of the more common or critical aspects of this system.
• Modifications to the design or locations of fill or vent lines, heater or defroster core, and surge tank are
not recommended
• Additional accessories plumbed into the engine cooling system are not permitted, at the risk of voiding
vehicle warranty
• Coolant level sensor tampering will void warranty
• When installing auxiliary equipment in front of the vehicle, or additional heat exchangers, ensure
that adequate air flow is available to the vehicle cooling system. Refer to engine manufacturer
application guide- lines for further detail
• When installing FEPTO drivelines, the lower radiator anti-recirculation seal must be retained with
FEPTO driveline clearance modification only
• Changes made to cooling fan circuit and controls are not allowed, with the exception of AC
minimum fan on time parameter
• See owner’s manual for appropriate winter front usage
Air Intake System
The following are highlights of some of the more common or critical aspects of this system.
• The air intake screen may not be blocked, either fully or partially
• Modification to the air intake system may not restrict airflow. For example, pipe dia meter may not be reduced
• All sensors must be retained in existing locations
• To retain system seal, proper clamp torque must be used. Refer to service manual for proper clamp torque
Charge Air Cooler System
The following are highlights of some of the more common or critical aspects of this system.
• The Charge Air Cooler may not be modified
• The installation of engine overspeed shutdown devices must not introduce restriction in the intake system
• All plumbing associated with the charge air cooler may not be modified
Peterbilt Motors Company 2-6
Page 13

SECTION 3 DIMENSIONS
INTRODUCTION
This section has been designed to provide enough information to successfully layout a chassis in the body planning
process. All dimensions a re inches unless otherwise noted. Optional equipm ent may not be depicted. Please contact
your local Peterbilt dealer if more dimensional information is desired.
ABBREVIATIONS
Throughout this sectio n and in other sections as wel l, abbreviations are used to describe certain character istics on your
vehicle. Table 3-1 below lists the abbreviated terms used.
TABLE 3-1. Abbre vi ati ons U sed
BFA Bumper to front axle
BOC Back of cab
CA Cab to axle. Measured from the back of the cab to the centerline of the rear axle(s).
EOF Frame rail overhang behind rear axle--measured from the centerline of tandems
FAX Front axle
FOF Front of frame
WB Wheelbase
Page 14
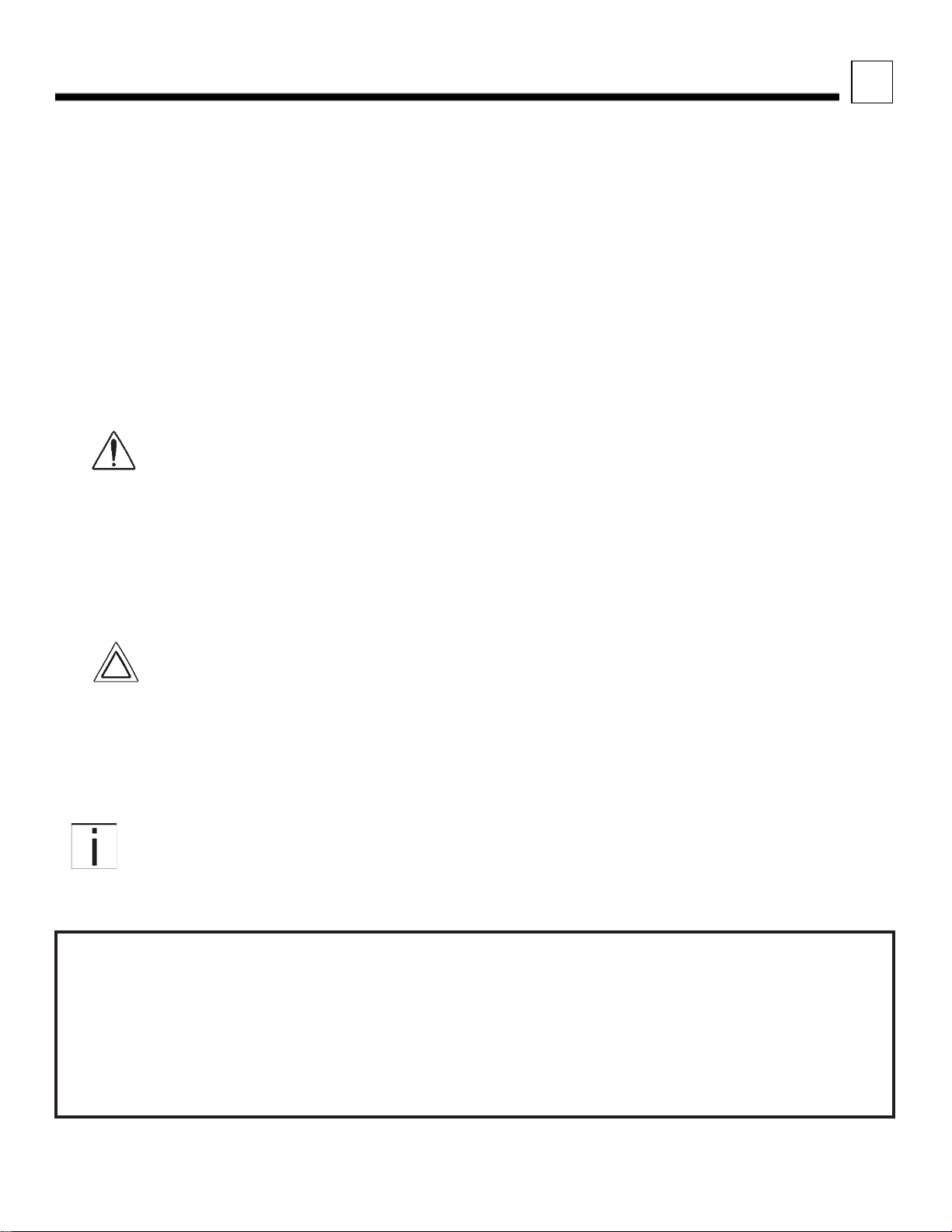
3
DIMENSIONS
OVERALL DIMENSIONS
This section includes drawings and charts of the Peterbilt Model 520.
On the pages that follow, detail drawings show particular views of the vehicle; all dim ensions are in inches (in). They
illustrate important measurements critical to designing bodies of all types. See the “Contents” at the beginning of the
manual to locate the drawing that you need.
All heights are given from the bottom of the frame rail.
Note that the Aftertreatment mounting is almost identical other than the use of a DEF tank (for diesels) and different
canister/catalyst but both use the same stanchions for mounting BOC.
FIGURE 3-1. Various Views of the Model 520
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 2
Page 15
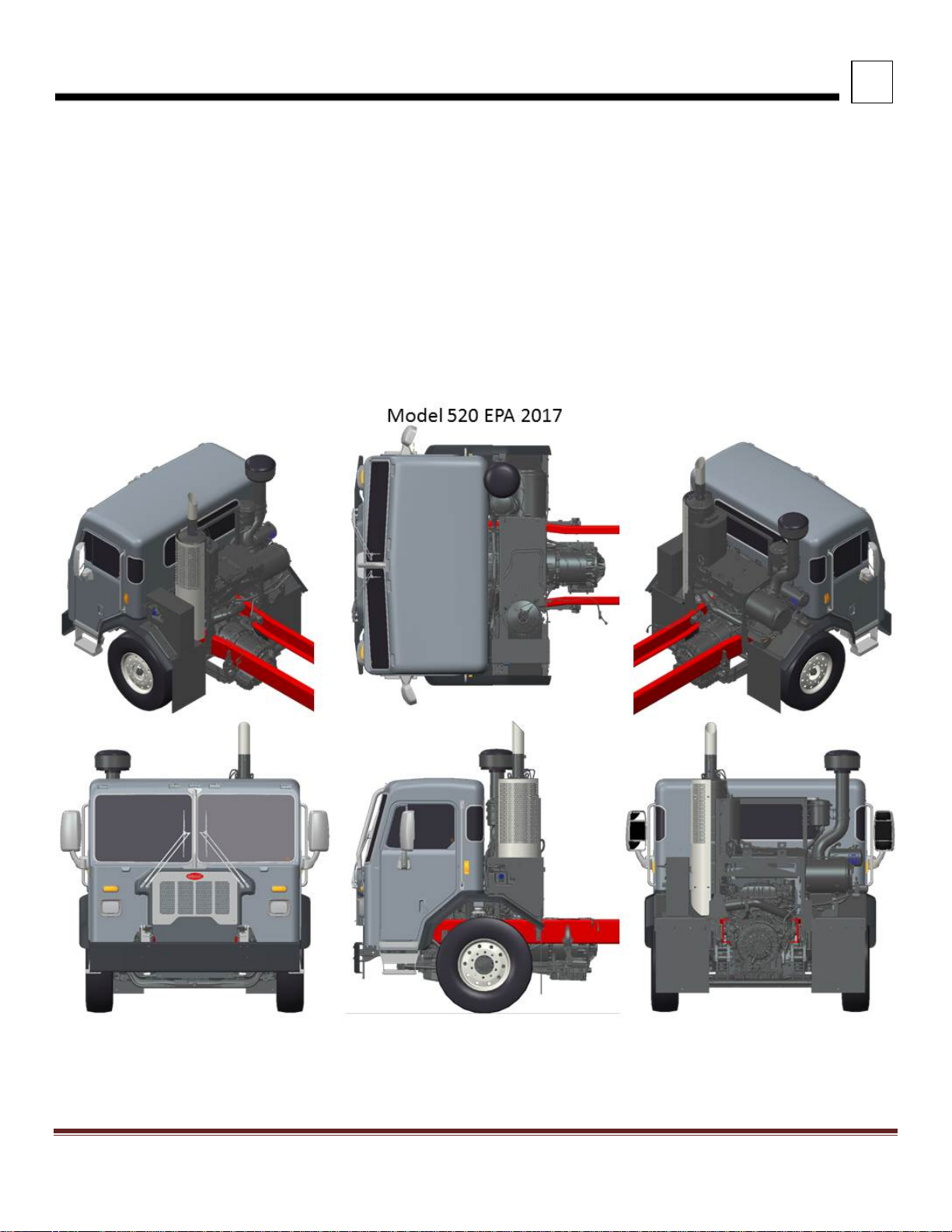
3
DIMENSIONS
EXTERIOR DIMENSIONS
FIGURE 3-2. 520 Cab Dimensions
Notes:
1. Shown with optional HD Air intake Pre-Cleaner
2. Shown with optional front cab guard
3. Door dimension is 33.4”W x 61”H
4. Diesel truck shown, but Natural Gas has same BOC dimension for Aftertreatement.
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 3
Page 16

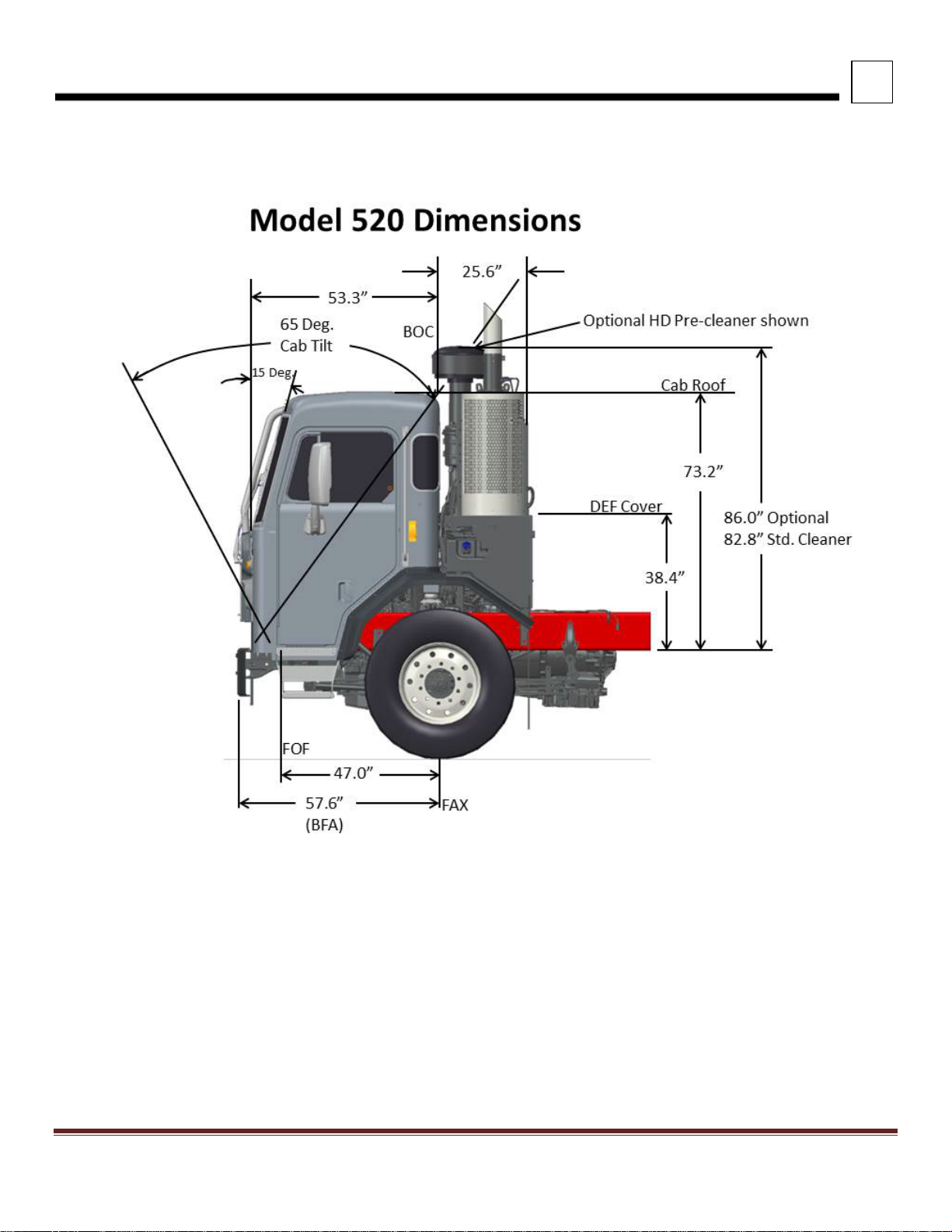
3
DIMENSIONS
INTERIOR DIMENSIONS
FIGURE 3-3. View Looking Through Cab to the Driver’s Side (LH Steer)
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 4
Page 17
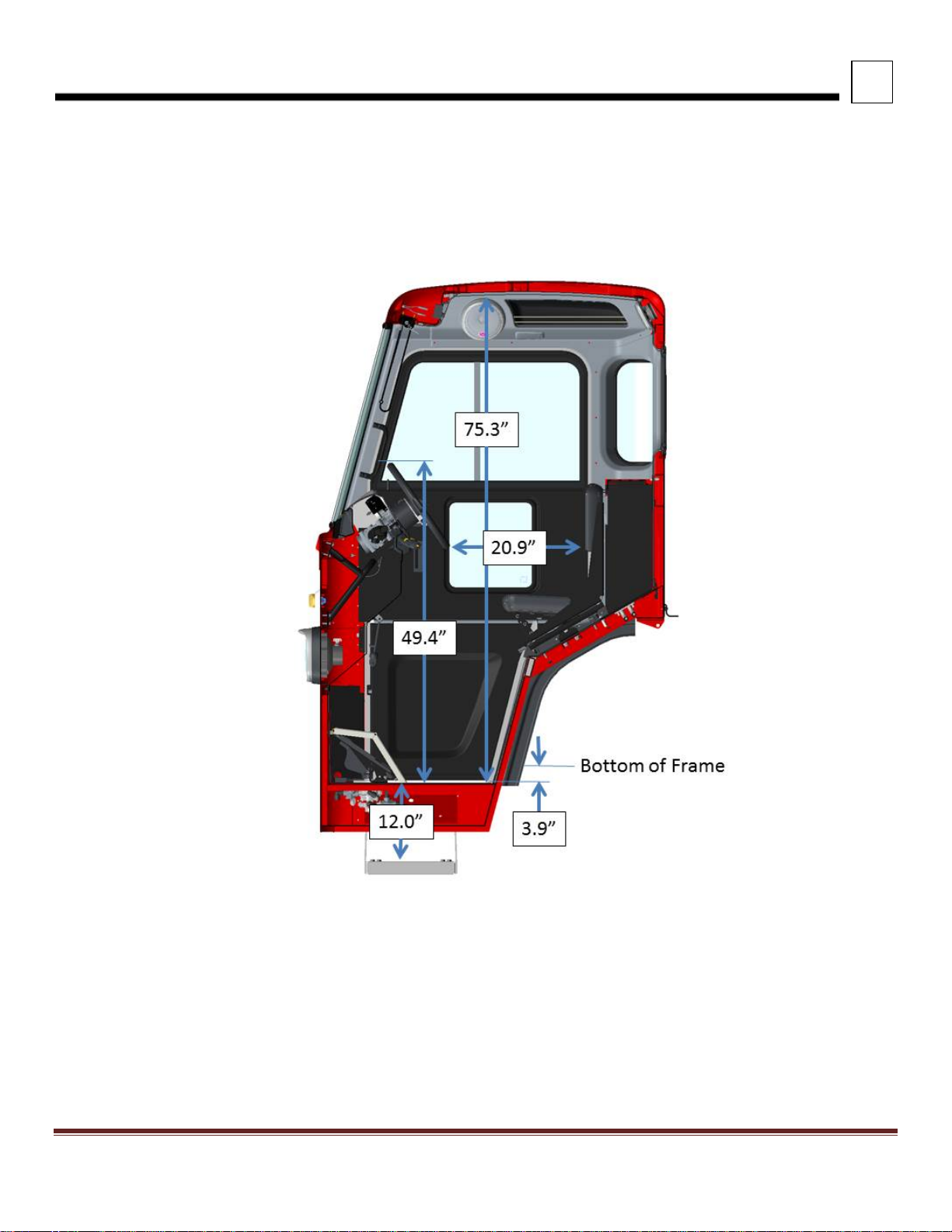
3
DIMENSIONS
INTERIOR DIMENSIONS
FIGURE 3-4. View Looking Through the Cab At The RH Drive Standup Version
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 5
Page 18

3
DIMENSIONS
INTERIOR DIMENSIONS
FIGURE 3-5. Top View of LH Steer Model
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 6
Page 19
3
DIMENSIONS
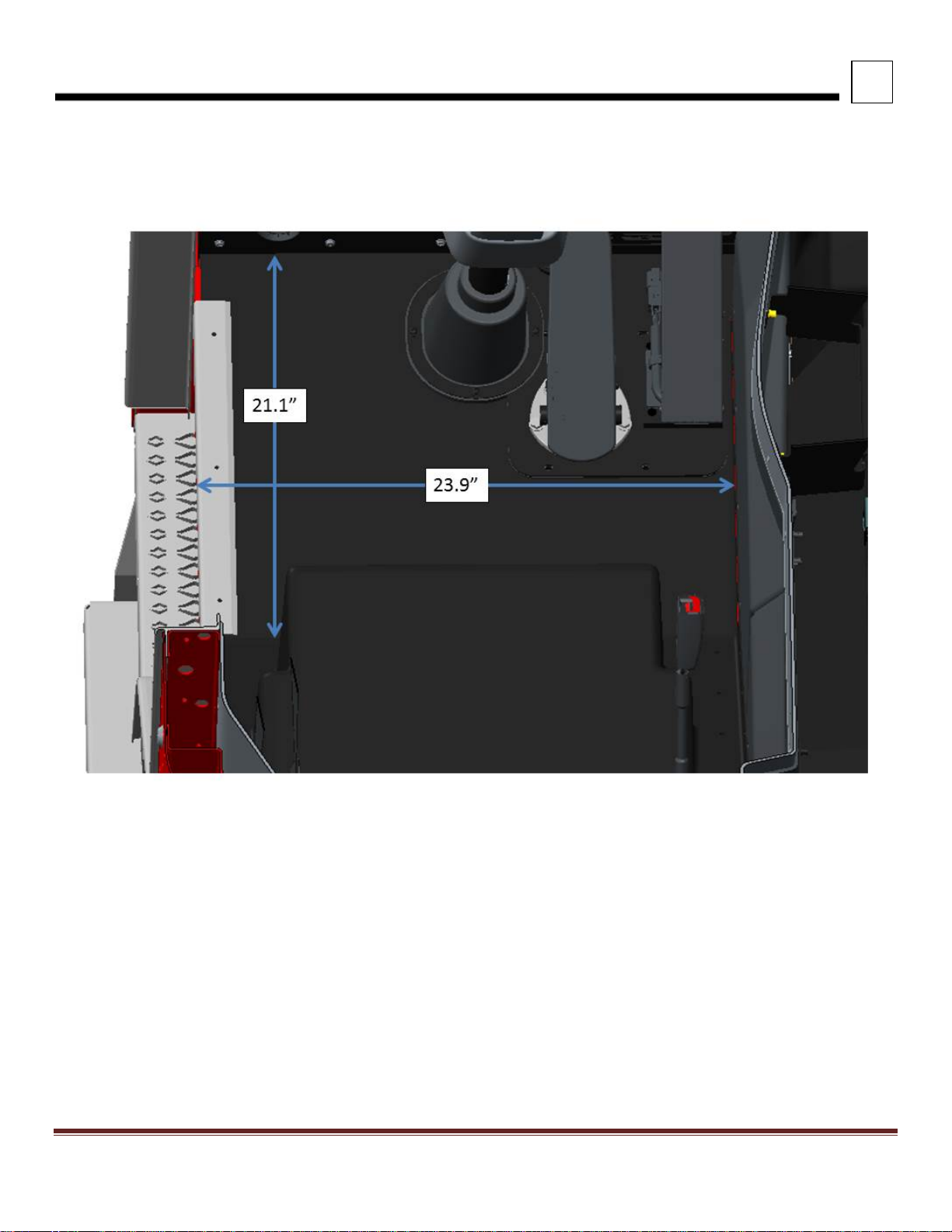
INTERIOR DIMENSIONS
FIGURE 3-6. Floor Dimensions for LH Floor
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 7
Page 20
3
DIMENSIONS
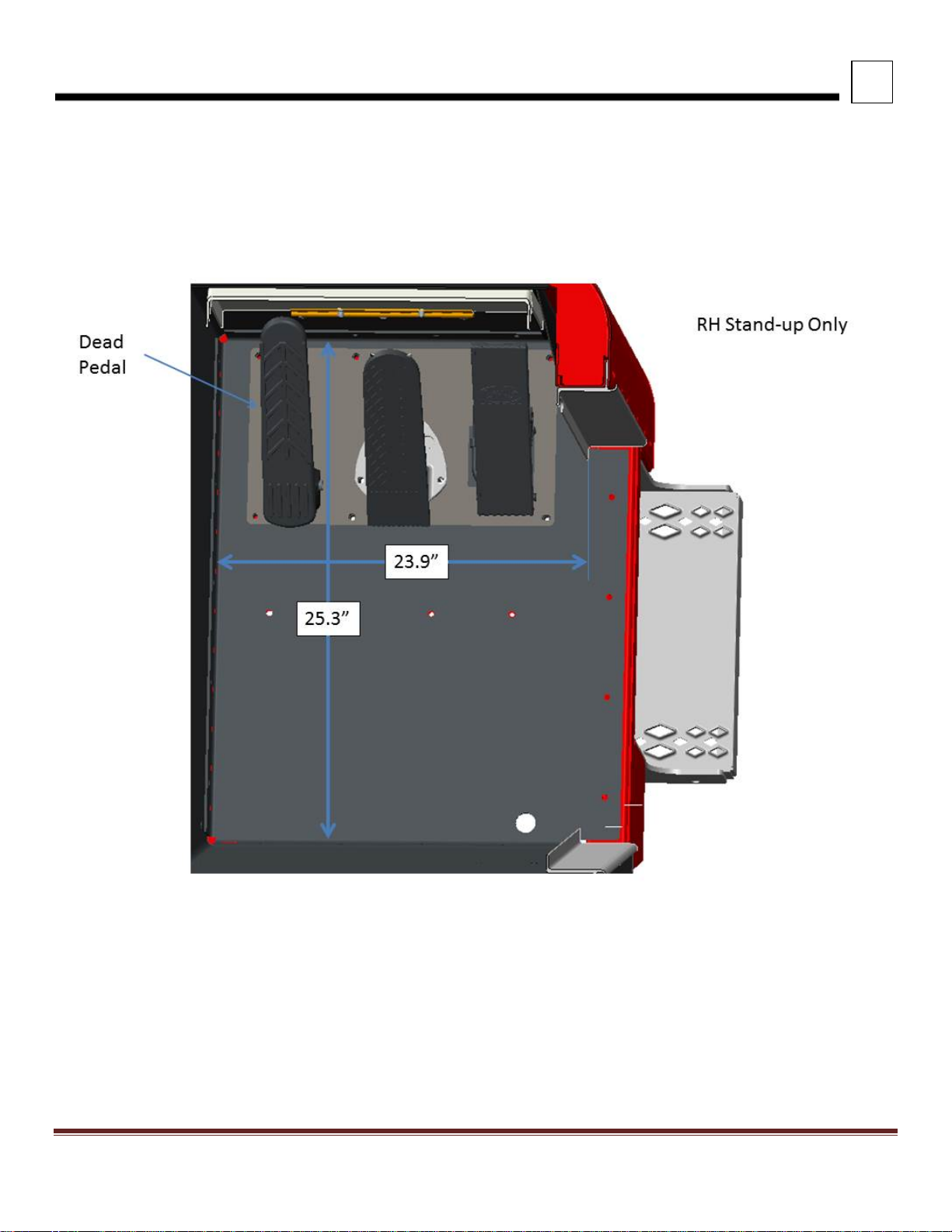
INTERIOR DIMENSIONS
FIGURE 3-7. Passenger Floor RH Stand Up
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 8
Page 21
3
DIMENSIONS
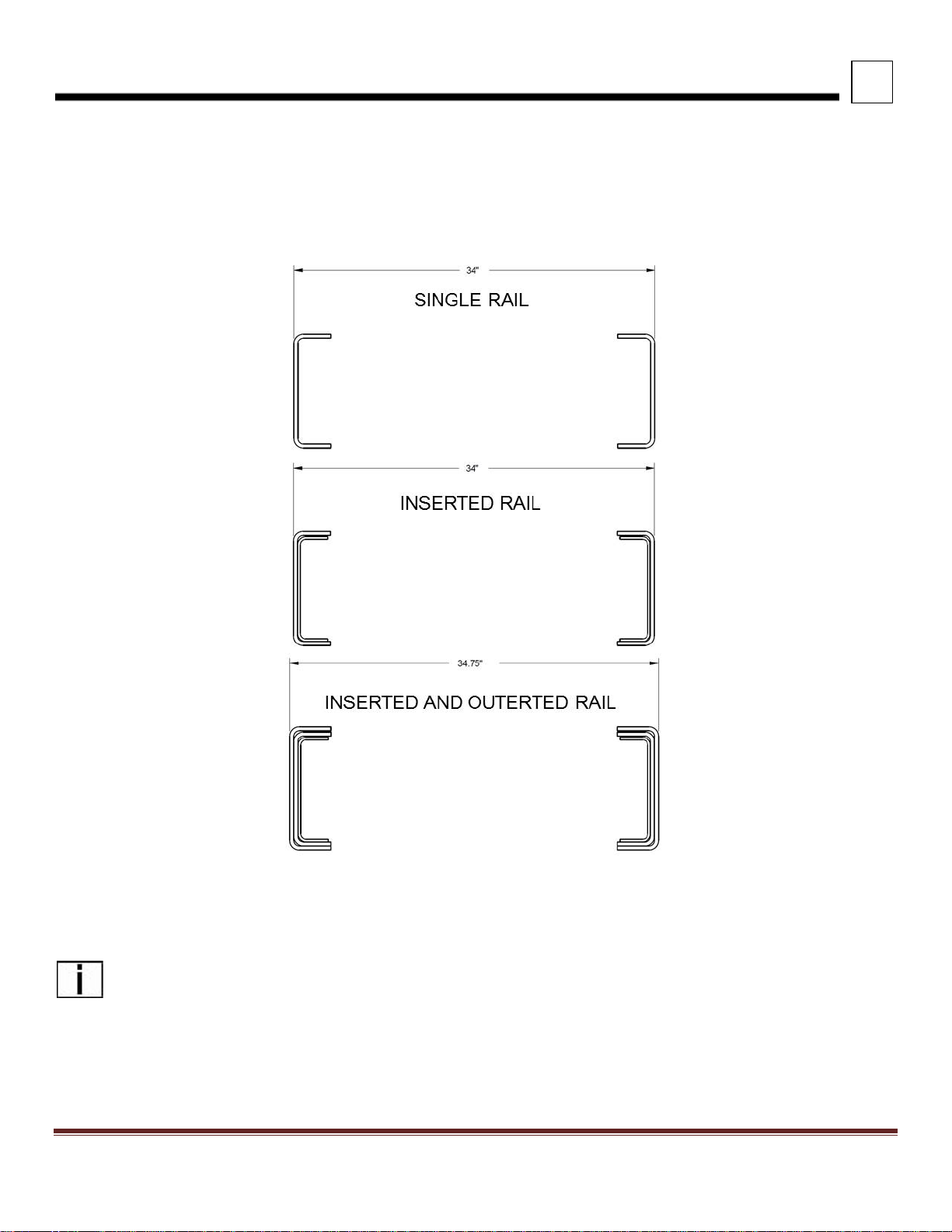
FRAME RAILS
Frame rail configurations are shown in Figure 3-8. The under cab area of the 520 frame rails are splayed as shown in
Figure 3-9. Frame height, flange and structural values can be found in the Body Mounting Section.
FIGURE 3-8. Frame Rail Configurations
NOTE: The outserted frame section does not extend through the rear suspension area. The outserted frame
section does not extend through the splayed area.
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 9
Page 22
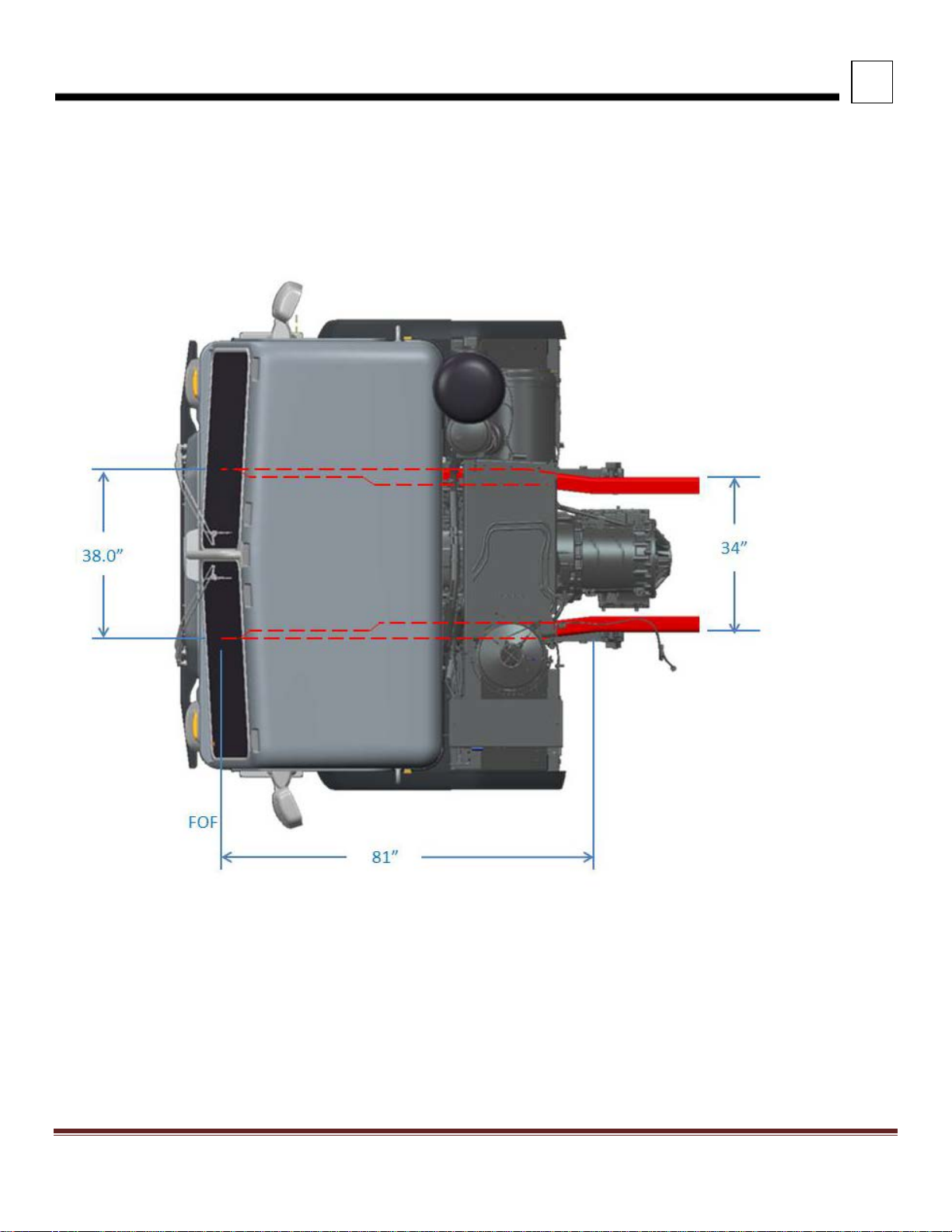
3
DIMENSIONS
FRAME RAILS
FIGURE 3-9. Model 520 Frame Rail
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 10
Page 23
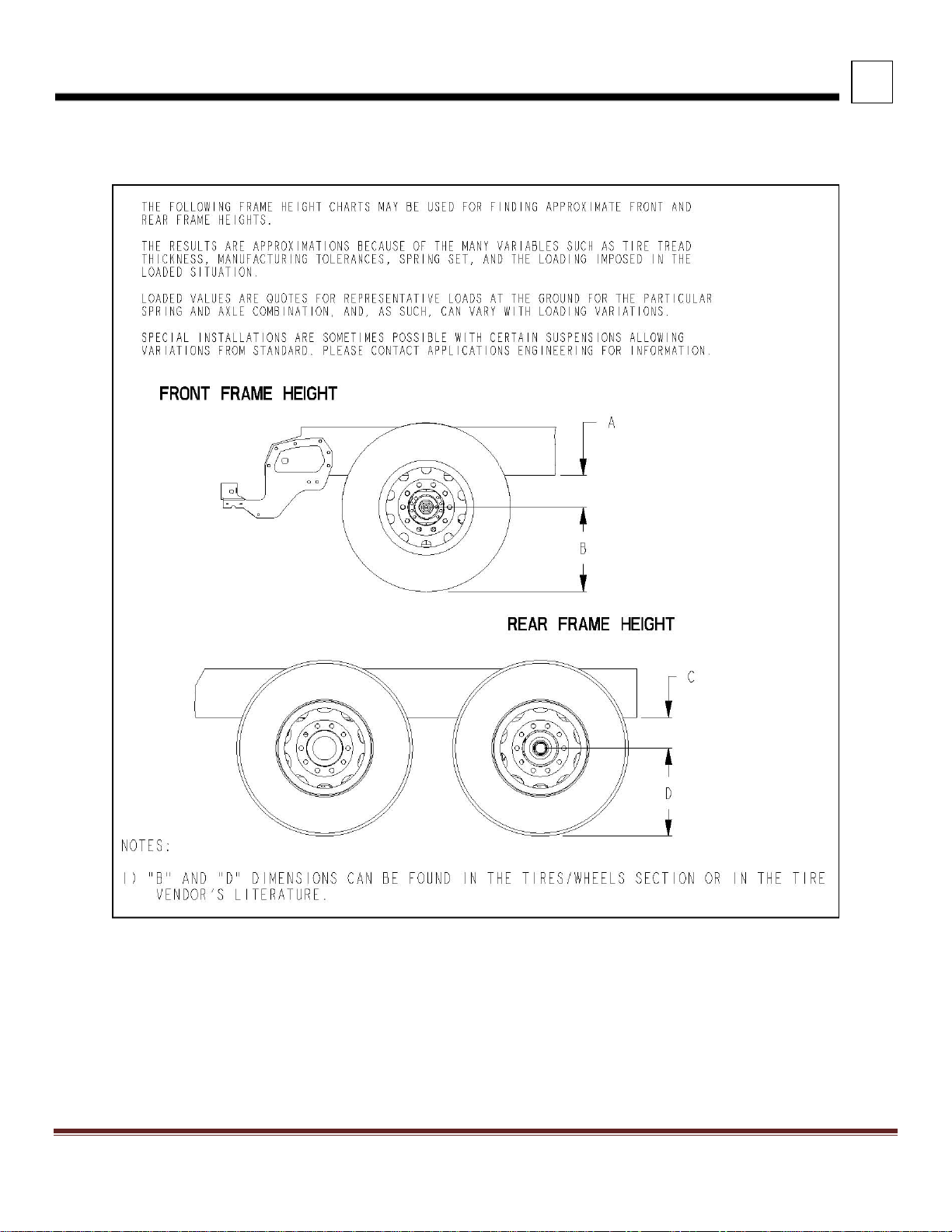
3
DIMENSIONS
FRAME HEIGHT CHARTS
FIGURE 3-4. Frame Height
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 11
Page 24
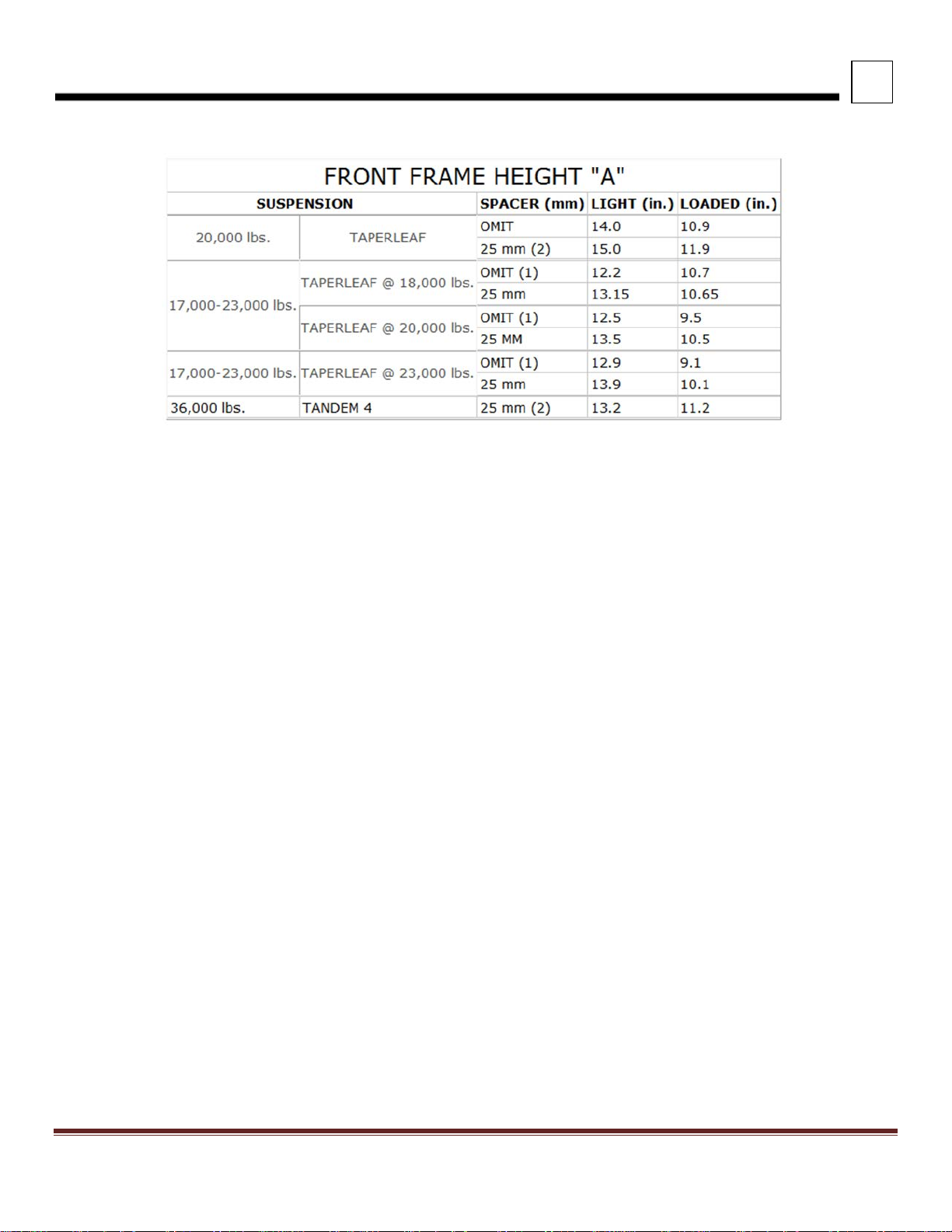
3
DIMENSIONS
TABLE 3-2. Front Frame Height “A” – 520
NOTES:
1) Omit spacer block standard.
2) 25mm spacer block standard and required.
3) Standard 3-1/2" drop axle heights shown, for 5" drop axles, subtract an additional 1-1/2".
4) Spacer blocks are used by Engineering to obtain level frame and are not options.
5) "A" dimension shown is to bottom of frame rail. Add frame rail height dimension for frame height.
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 12
Page 25
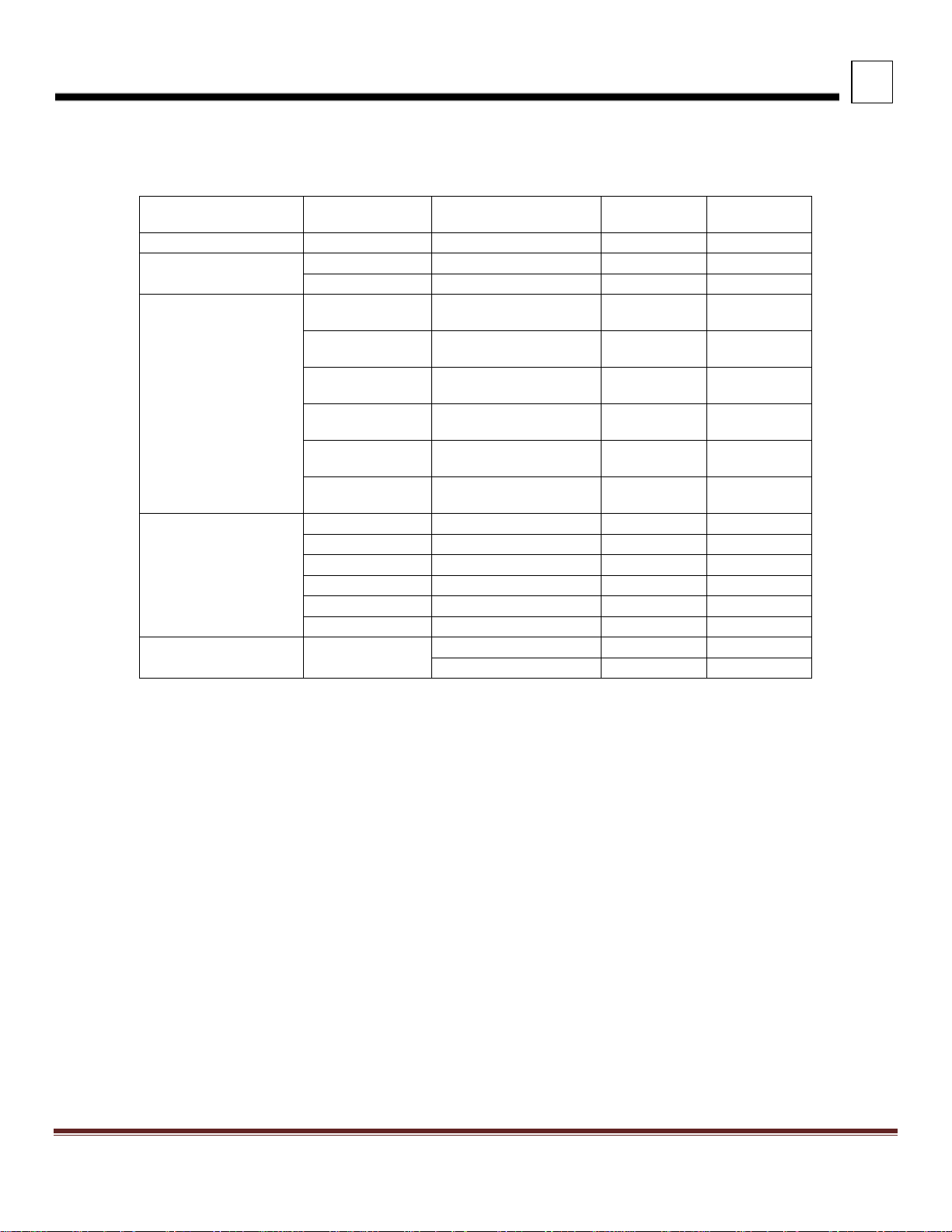
3
Suspension
Rating
Version
Light
Height
Laden
Height
LOW AIR LEAF
21,000 lbs.
Standard
6.8
6.5
20,000 lbs.
Standard
11.4
11.0
23,000 lbs.
Standard
11.4
11.0
Taper-leaf (3.38"
saddle)
Taper-leaf (1.38"
saddle)
Multi-leaf (1.38"
saddle)
Multi-leaf (1.38"
saddle)
Multi-leaf (1.38"
saddle)
Multi-leaf (1.38"
saddle)
23K-29K lbs.
4.38 saddle
12.0
10.2
23K-29K lbs.
4.63 saddle
12.2
10.4
29,000 lbs.
3.50 saddle
11.7
10.0
31,000 lbs.
3.50 saddle
12.2
10.5
31,000 lbs.
4.38 saddle
12.5
10.7
31,000 lbs.
4.63 saddle
12.7
10.9
Standard
9.3
9.3
Low
8.3
8.3
DIMENSIONS
REAR FRAME HEIGHTS "C"
AIR TRAC
TABLE 3-3. Single Drive Suspension Heights
REYCO 79KB
REYCO 102
REYCO 102AR (AIR) 17K -23K
20,000 lbs.
21,000 lbs.
23,000 lbs.
26,000 lbs.
28,000 lbs.
31,000 lbs.
9.4 11.8
7.4 9.8
8.8 11.6
9.2 11.8
9.6 12.3
10.7 13.3
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 13
Page 26
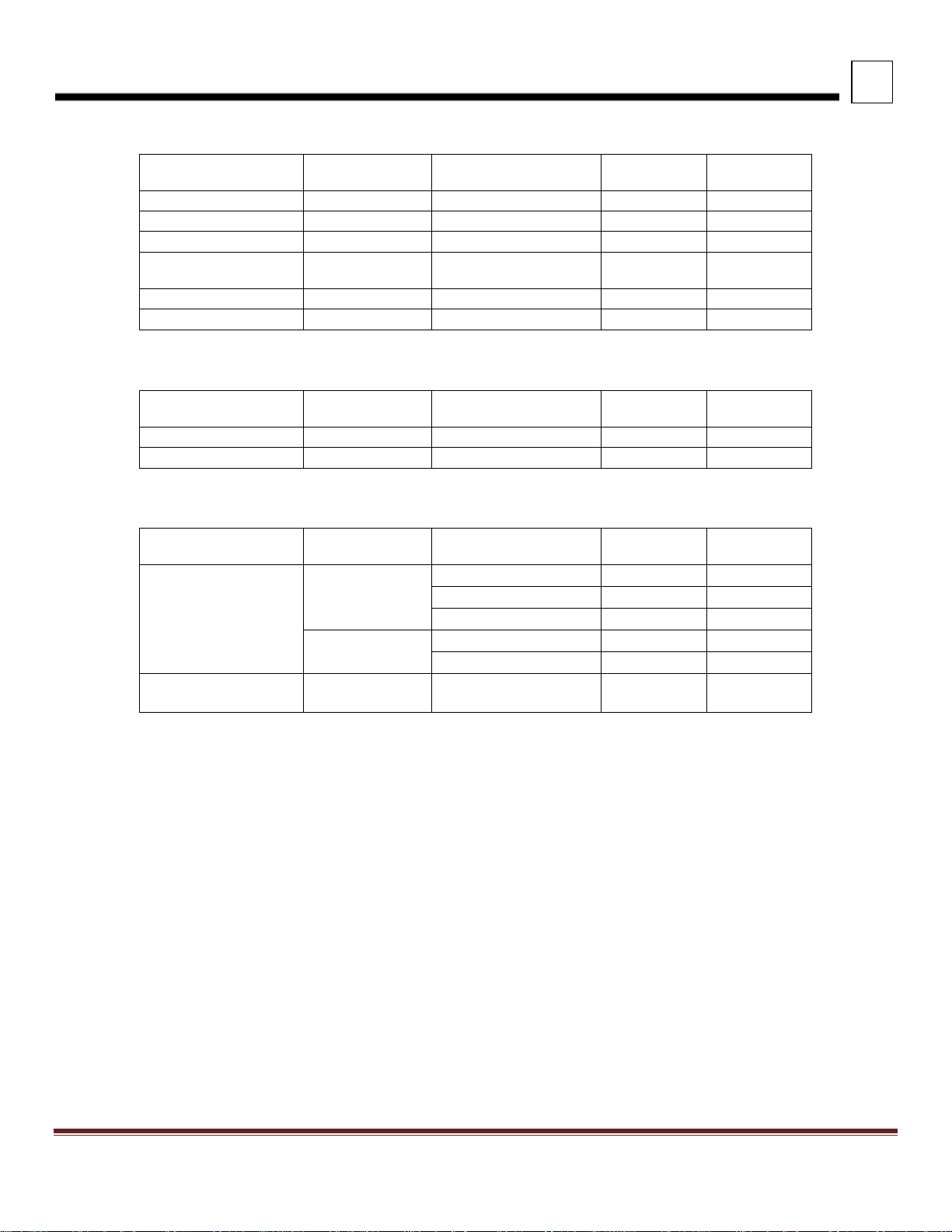
3
Suspension
Rating
Version
Light
Height
Laden
Height
AIR LEAF
38,000 lbs.
12.0
11.7
LOW AIR LEAF
40,000 lbs.
8.8
8.5
FLEX AIR
38,000 lbs.
8.8
8.5
LOW-LOW AIR
LEAF
AIR TRAC
40K-46K lbs.
11.4
11.0
QUADRAFLEX
38,000 lbs.
Taper-leaf
10.6
8.7
Suspension
Rating
Version
Light
Height
Laden
Height
NEWAY AD
52,000 lbs.
10.0
10.0
NEWAY ADZ
46K-52K lbs.
10.0
10.0
Suspension
Rating
Version
Light
Height
Laden
Height
1.75 saddle (STD)
11.7
9.8
1.38 saddle
10.2
8.3
3.38 saddle
13.4
11.5
1.75 saddle (STD)
11.7
9.8
1.38 saddle
11.5
9.7
REYCO 102AR
(AIR)
DIMENSIONS
TABLE 3-4. Tandem Drive Peterbilt Suspension Heights
40,000 lbs. 6.8 6.5
TABLE 3-5. Tandem Drive Neway Suspension Heights
TABLE 3-6. Tandem Drive Reyco Suspension Heights
REYCO 102
MULTILEAF
40,000 lbs.
44,000 lbs.
34K-40K STD LOW 8.3 8.3
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 14
Page 27
3
Suspension
Rating
Version
Light
Height
Laden
Height
LOW
11.1
8.9
HIGH
12.4
10.2
X-HIGH
14.5
12.2
XX-HIGH
17.2
14.9
LOW
11.3
8.9
HIGH
12.5
10.1
X-HIGH
14.7
12.2
XX-HIGH
17.3
14.9
LOW
11.3
8.9
HIGH
12.5
10.1
X-HIGH
14.6
12.1
XX-HIGH
17.3
14.8
LOW
11.2
8.8
HIGH
12.5
10.3
X-HIGH
14.6
12.2
XX-HIGH
17.3
14.9
LOW
11.2
8.8
HIGH
12.5
10.3
X-HIGH
14.6
12.1
XX-HIGH
17.3
14.8
DIMENSIONS
TABLE 3-7. Tandem Drive Chalmers Suspens ion Hei g hts
CHALMERS 854 &
860
CHALMERS 854 &
860
CHALMERS 854 &
860
CHALMERS 872 46,000 lbs.
CHALMERS 872 50,000 lbs.
NOTES:
1) Laden dimension shown with standard restrictor cans. Add 0.7” for #29 High Stability Restrictor Cans.
40,000 lbs.
46,000 lbs.
50K-52K
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 15
Page 28

3
Suspension
Rating
Version
Light
Height
Laden
Height
6.00
9.9
8.9
7.188 (std.)
11.2
10.1
6.00
9.9
8.4
7.188 (std.)
11.2
9.5
12.80
5.8
5.8
15.81 (std.)
8.8
8.8
17.60
10.6
10.6
12.25
9.9
9.1
14.00 (std.)
11.7
10.8
15.25
12.9
12.1
16.5 (low)
10.6
9.5
18.5 (std.)
12.6
11.5
16.5 (low)
10.6
9.5
18.5 (std.)
12.6
11.5
HN462
46,000 lbs.
20.25 (high)
15.0
13.3
15.75 (std.)
8.8
8.8
20.50
13.5
13.5
12.25
9.7
8.9
14.0 (std.)
11.5
10.6
15.25
12.7
11.9
6.00
11.3
10.5
7.188 (std.)
13.0
11.4
11.00
16.3
15.2
7.188 (std.)
11.6
10.2
11.00
15.4
14.0
14.0 (std.)
11.7
10.8
15.25
12.9
12.1
7.188 (std.)
12.1
11.1
11.0 1
16.4
15.4
7.188 (std.)
11.6
10.2
11.00
15.4
14.0
RS-523
52,000 lbs.
14.0 (std.)
11.7
10.8
7.188 (std.)
12.1
11.1
11.00
16.4
15.4
HN522
52,000 lbs.
18.50 (std.)
12.6
11.5
15.00 (std.)
12.0 1
11.0 2
19.00
16.0 2
15.1 2
R650 *
65,000 lbs.
20.25 (std.)
12.5
12.5
R850 w/70K Meritor
20.25
12.0
12.0
R850 w/SISU 70K
20.25
12.1
12.1
RS850 w/SISU 70K
85,000 lbs.
16.75
11.5
10.6
DIMENSIONS
RT-403 40,000 lbs.
RTE-403 40,000 lbs.
R-403 40,000 lbs.
RS-403 40,000 lbs.
HMX 40,000 lbs.
HMX 46,000 lbs.
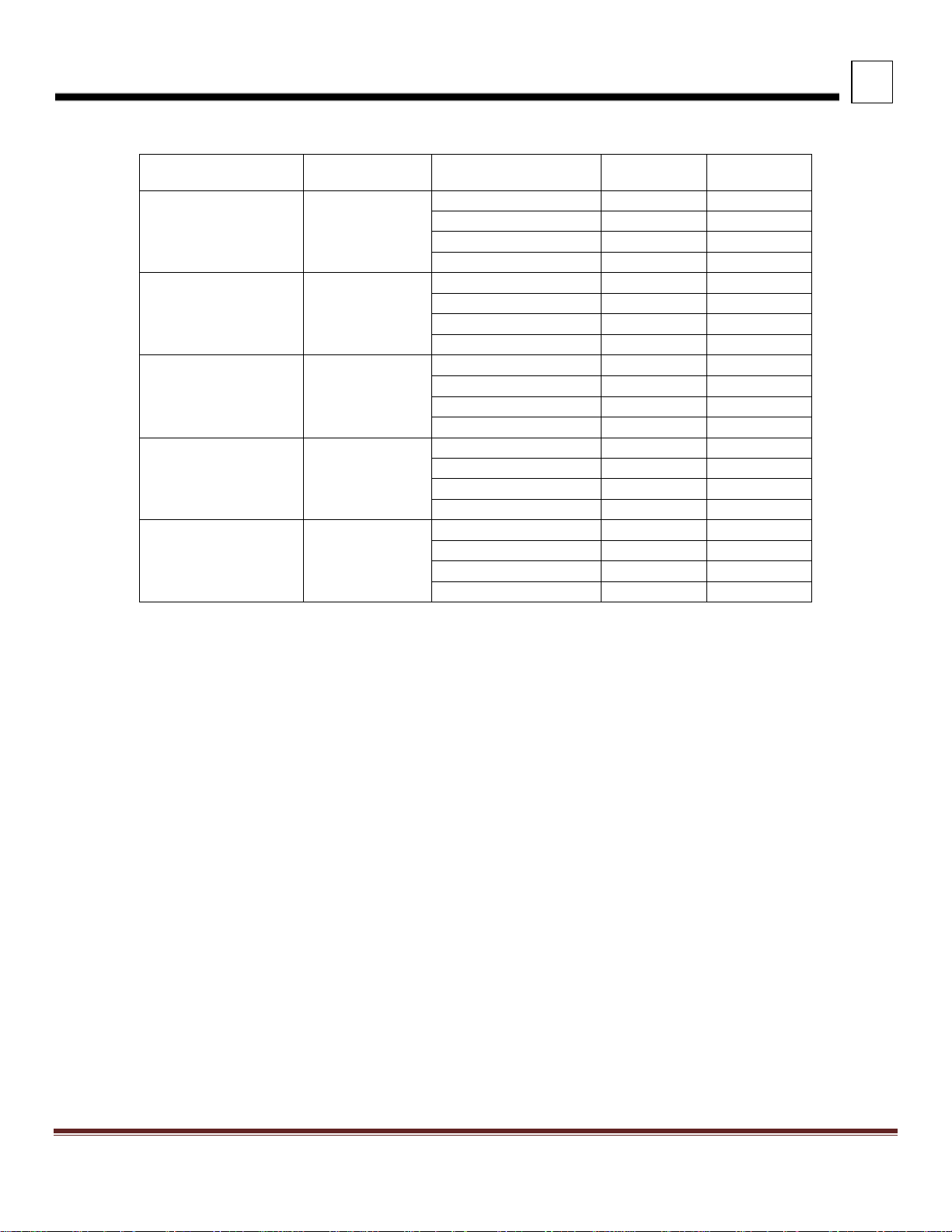
TABLE 3-8. Tandem Drive Hendrickson Suspension Heights
R-463 46,000 lbs.
RS-463 46,000 lbs.
RT-463 46,000 lbs.
RTE-463 46,000 lbs.
RS-503 50,000 lbs.
RT-503 50,000 lbs.
RTE-503 50,000 lbs.
RT-523 , RT-650 52K-65K
RS650 65,000 lbs.
NOTES:
1) With SISU 70k axle subtract 0.39” from light/laden
2) With SISU 70k axle subtract 0.28” from light and 0.39” from laden
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 16
85,000 lbs.
Page 29

3
SUSPENSION
RATING (lbs.)
LIGHT (in.)
LOADED
(in.)
TRI-DRIVE SUSPENSION
AIR TRAC
40K-46K
11.4
11.0
NEWAY ADZ369
69,000
10.0
10.0
NEWAY ADZ378
78,000
10.0
10.0
DIMENSIONS
TABLE 3-9. Tri-Drive Suspension Heights
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 17
Page 30

3
DIMENSIONS
REAR SUSPENSION LAYOUTS
The rear suspension l ayouts are provided as a to ol to help layout bodies prior to arrival. The applica ble dimensions are
shown. Verify the axle spac ing that is shown, as a lternate spacing ma y exist and could chang e some of the dimens ions.
The dimensions shown below are the most typical installations, in special cases some hole locations will move.
If the holes shown will be used for body installation, please confirm with the local Peterbilt dealer the drawing below will be
the installation used on the specific t ruck. In this case, ordering the frame layout of the chassis is advised. This can be
done on any Peterbilt truck, and will be provided ahead of the build schedule. Ensure proper torque to reinstall any
suspension components. See Tables 5-1 and 5-2 on page 5-4.
For hole locations not detailed, please work with the local Peterbilt Dealer to request that information.
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 18
Page 31

3
DIMENSIONS
FIGURE 3-5. Reyco 79KB Frame Drilling (Dimensions In Millimeters)
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 19
Page 32

3
DIMENSIONS
FIGURE 3-6. Reyco 102AR Frame Drilling (Dimensions In Millimeters)
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 20
Page 33

3
DIMENSIONS
FIGURE 3-7. Neway ADZ 252 Frame Drilling (Dimensions In Millimeters)
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 21
Page 34

3
DIMENSIONS
FIGURE 3-8. Neway ADZ 369/378 Frame Drilling (Dimensions In Millimeters)
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 22
Page 35

3
DIMENSIONS
FIGURE 3-9. Peterbilt Air Leaf Tandem Frame Drilling (Dimensions In Millimeters)
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 23
Page 36

3
DIMENSIONS
FIGURE 3-10. Peterbilt Air Trac Single Frame Drilling (Dimensions In Millimeters)
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 24
Page 37

3
DIMENSIONS
FIGURE 3-11. Peterbilt Air T rac Tandem Frame Drilling (Dimensions In Millimeters)
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 25
Page 38

3
DIMENSIONS
FIGURE 3-12. Peterbilt Air Trac Tri-Drive Frame Drilling (Dimensions In Millimeters)
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 26
Page 39

3
DIMENSIONS
FIGURE 3-13. Peterbilt Low and Low-Low Air Leaf Tandem Frame Drilling (Dimensions In Millimeters)
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 27
Page 40

3
DIMENSIONS
FIGURE 3-14. Chalmers 854 Tandem Frame Drilling
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 28
Page 41

3
DIMENSIONS
FIGURE 3-15. Hendrickson HMX Tandem Frame Drilling
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 29
Page 42

3
DIMENSIONS
FIGURE 3-16. Hendrickson RT/RTE Tandem Frame Drilling
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 30
Page 43

3
DIMENSIONS
FIGURE 3-17. Hendrickson HN Tandem Frame Drilling (Dimensions In Millimeters)
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 31
Page 44

3
DIMENSIONS
FIGURE 3-18. Hendrickson R Tandem Frame Drilling (Dimensions In Millimeters)
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 32
Page 45

3
DIMENSIONS
FIGURE 3-19. Hendrickson RS Tandem Frame Drilling (Dimensions In Millimeters)
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 33
Page 46

3
DIMENSIONS
PUSHER AND TAG AXLE LAYOUTS
The rear pusher axle la youts are provided as a to ol to help layout bo dies prior to arriva l. The applicable dim ensions are
shown. When using the pusher layouts to d eterm ine availabl e frame s pace pleas e be aware c learanc es required are not
shown. For information tha t may not be detailed in these drawings, work with your local Peterbilt Dealer to request tha t
information.
FIGURE 3-20. Hendrickson SC8, SC10, SC13, SCO13, FX or FXO Pusher or Tag
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 34
Page 47

3
DIMENSIONS
FIGURE 3-21. Hendrickson SC20 Pusher or Tag
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 35
Page 48

3
DIMENSIONS
FIGURE 3-22. Hendrickson HLR2 Pusher
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 36
Page 49

3
DIMENSIONS
FIGURE 3-23. Hendrickson HLM Pusher or Tag
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 37
Page 50

3
DIMENSIONS
FIGURE 3-24. Watson-Chalin SL2065 Pusher or Tag
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 38
Page 51

3
DIMENSIONS
FIGURE 3-25. Watson-Chalin AL2200 Pusher or Tag
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 39
Page 52

3
DIMENSIONS
FIGURE 3-26. Watson-Chalin SL0893SSR or SL1093SSR Pusher or Tag
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 40
Page 53

3
DIMENSIONS
FIGURE 3-27. Watson-Chalin SL1190SSR Pusher or Tag
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 41
Page 54

3
DIMENSIONS
“Y” Dimension
Location
2013
Zero
81.2”
EXHAUST HEIGHT CALCULATIONS
The exhaust height calculations are provided as a tool to help layout bodies prior to arrival as well as aid in exhaust
configuration selection.
ase work with the local Peterbilt Dealer to request additional information if required.
Ple
The ov
erall exhaust height (EH) can be estimated based on the following formula: EH = Y + SPL + (A + B + C + D) / 2
TABLE 3-10. Exhaust Heights
ISX12
Exhaust
BOC Vertical 67.2” 74.2” 80.5” 84.4”
NOTES:
1) For “A” and “C” values, reference the FRAME HEIGHTS section for front or rear suspension height.
2) For “B” and “D” values, reference the tire manufacturer’s website or catalog for static loaded radius (SLR).
3) For Stand Pipe Length (SPL) values, reference the truck sales order.
4) Not applicable to horizontal exhaust.
EPA
ISLG
ISLG
Near
MX-11
PX-9 HHP
PX-9 MHP
79.7”
GURE 3-27. Exhaust Height Calculations
FI
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 42
Page 55

3
FRAME TO BOTTOM OF COMPONENT
Component
Y
Fender Mounted Battery Box
(ISX12 EPA13 and Natural Gas)
DIMENSIONS
GROUND CLEARANCE CALCULATIONS
The ground clearance tables are provided as a tool as a tool to help layout bodies prior to arrival, not all optional
equipment is included.
The ground clearance (GC) can be estimated based on the following formula: GC = (A + B + C + D) / 2 - Y
TABLE 3-11. Ground Clearance
Y = DISTANCE FROM BOTTOM OF
Cab Access Step 13.7”
Alum Space Saver ( Show n Belo w) 10.0”
Steel Space Saver Battery Box 11.8”
Narrow Space Saver Battery Box 11.9”
4.4”
20" Diameter Fuel Tank 12.4”
23" Diameter Fuel Tank 15.2”
26" Diameter Fuel Tank 18.0”
FIGURE 3-28. Ground Clearance Calculations
FIGURE 3-29. Space Saver Battery Box
NOTES:
1) For “A” and “ C” values, reference the FRA ME HEIGHTS section for front s uspension height or rear sus pension
height.
2) For “B” a nd “D” values, ref erence the tire m anufacturer’s website or catalog for over all diameter or s tatic loaded
radius (SLR).
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 43
Page 56

3
FIGURE 3-30. Overall Cab Height Calculations
DIMENSIONS
OVERALL CAB HEIGHT CALCULATIONS
The overall cab height tables are provided as a tool as a tool to help layout bodies prior to arrival, no roof mounted
equipment is included.
The overall cab height (CH) can be estimated based on the following formula: CH = (A + B + C + D) / 2 + 73.2”
NOTES:
1) For “A” and “ C” values, reference the FRA ME HEIGHTS section for front s uspension height or rear sus pension
height.
2) For “B” a nd “D” values, ref erence the tire m anufacturer’s website or catalog for overall diameter or s tatic loaded
radius (SLR).
3) Roof mounted content such as horns and antennas are not included.
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 44
Page 57

3
DIMENSIONS
20"
TANK
23"
TANK
26"
TANK
60
67
51.3
40.7
31.5
120
131
N/A
77.3
60.0
DIMENSIONS
FRAME COMPONENTS
This section includes dra wings and charts related to c ommon frame m ounted components. O ptional equipment m ay not
be depicted.
Please work with the local Peter bilt Dealer to request additional information if requir ed. At the dealer’s request, Peterb ilt
can provide frame layouts for individual vehicles prior to delivery.
FUEL TANKS
FIGURE 3-31. Fuel Tanks
TABLE 3-12. Fuel Tank Dimensions
A B C D
22.7 12.4 10.3 27.5
24.5 15.2 10.5 31.0
27.2 18.0 10.6 33.7
TABLE 3-13. Fuel Tank Data
GALLONS TANK LENGTH
USEABLE TOTAL 20" 23" 26"
40 46 33.3 N/A N/A
50 57 43.2 34.5 26.7
70 78 57.3 46.8 36.2
80 89 65.3 52.9 41.0
90 99 N/A 59.0 45.7
100 110 N/A *65.1 50.5
110 121 N/A N/A 55.2
135 147 N/A N/A 66.8
150 163 N/A N/A *74.0
NOTES:
1) * Largest capacity without a weld seam.
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 45
Page 58

3
DIMENSIONS
EXHAUST SYSTEMS
FIGURE 3-32. Exhaust Transverse DPF/SCR for ISX12 EPA 2013 Only (ISX12 didn’t convert to 2017 Exhaust)
See figure 3-1 for 2017 exhaust views showing all other engine configurations.
Peterbilt Motors Company 3- 46
Page 59

SECTION 4 BODY MOUNTING
(in.)
(in.)
(in)
Section
(cu. In.)
(in.-lbs)
(lbs/in.)
10 3/4
3.50
0.375
17.8
2,136,000
1.74
Main Rail
(in.)
Insert
Outsert
Section
(cu. In.)
(in.-lbs)
(lbs/in.)
10 3/4
9.875 x 2.87 x .250
None
28.9
3,468,000
2.78
10 3/4
9.875 x 2.87 x .250
11.63 x 3.87 x .375
45.7
5,484,000
4.67
INTRODUCTION
This section has be en designed to provid e guidelines to aid in body m ounting. This is not intended a complete guide,
rather as general inf ormation. Bod y mounting strateg ies are unique to eac h body type and bo dy builder mus t determine
the appropriate method.
Please contact your local Peterbilt dea ler if mor e information is desired.
FRAME RAILS
Frame rail information is provided in Table 4-1 and Table 4-2.
TABLE 4-1. Single Frame Rails
Rail Height
Flange Width
TABLE 4-2. Built-up Frame Rails
Height
Web Thickness
Modulus
Modulus
RBM (per rail)
RBM (per rail)
Weight (per rail)
Weight (per rail)
(1)
Page 60

4
BODY MOUNTING
CRITICAL CLEARANCES
REAR TIRES AND CAB
CAUTION: Insufficient clearance between rear tires and body structure could cause damage to the body during
suspension movement.
Normal suspension m ovement could cause contact b etween the tires and the bo dy. To prevent this, mount the body so
that the minimum clearance betwee n the top of the t ire and the bottom of the bod y is 8 inches (20 3 mm). This shou ld be
measured with the body empty. See Figure 4-1.
FIGURE 4-1. Minimum Clearance Between Top of Rear Tires and Body Structure Overhang
CAUTION: Maintain adequate clearance between back of cab and the front (leading edge) of m ount ed body . It is
recommended the body leading edge be mounted 4 in. behind the cab. See Figure 4-2.
NOTE: Be sure to provide access to all maintenance and service components.
FIGURE 4-2. Minimum Back of Cab Clearance
Peterbilt Motors Company 4-2
Page 61

4
BODY MOUNTING
BODY MOUNTING USING BRACKETS
CAUTION: Always install a spacer between the body subframe and the top flange of the frame rail. Installation of
a spacer between the body subframe and the top flange of the frame rail will help prevent premature wear of the
components due to chafing or corrosion.
WARNING! When mounting a body to the chassis, DO NOT drill holes in the upper or lower flange of the
frame rail. If the frame rail flanges are modified or damaged, the rail could fail prematurely and cause an
accident. Mount the body using body mounting brackets or U–bolts.
FRAME SILL
If the body is mounted to the frame with brackets, we recommend a frame sill spacer made from a strip of rubber or plastic
(delrin or nylon). Thes e materials will n ot undergo larg e dimensional cha nges during per iods of high or lo w humidity. The
strip will be less likely to fall out during extreme relative motion between body and chassis. See Figure 4-3.
FIGURE 4-3. Spacer Between Frame Sill and Body Rail – Rubber or Plastic
Peterbilt Motors Company 4-3
Page 62

4
BODY MOUNTING
BRACKETS
When mounting a bod y to the chassis with brac kets, we recom mend designs that of fer limited relativ e movement, bolted
securely but not too rigid. Brack ets should allow for slight movem ent between the body and the chassis. For instance,
Figure 4-4 shows a high compression s pring between the bolt and the bracket and Figure 4-5 shows a rubber s pacer
between the brackets . These designs will allo w relative movem ent between the body and the chassis during extreme
frame racking situatio ns. Mount ings th at are to o rigid c ould caus e dam age to the bod y. T his is partic ularl y true with t ank er
installations.
FIGURE 4-4. Mounting Brackets FIGURE 4-5. Mounting Brackets
Peterbilt Motors Company 4-4
Page 63

4
BODY MOUNTING
MOUNTING HOLES
When installing brac kets on the fr ame rails, the mount ing holes in the chas sis frame br acket and fram e rail must compl y
with the general spacing and location guidelines illustrated in Figure 4-6.
FIGURE 4-6. Hole Location Guidelines for Frame Rail and Bracket
FIGURE 4-7. Crossmember Gusset Hole Patterns (Additional Holes Available in 50 mm Horizontal Increments)
Peterbilt Motors Company 4-5
Page 64

4
BODY MOUNTING
FRAME DRILLING
WARNING! When mounting a body to the chassis, DO NOT drill holes in the upper or lower flange of the frame
rail. If the frame rail flanges are modified or damaged, the rail could fail prematurely and cause an accident.
Mount the body using body mounting brackets or U–bolts.
FIGURE 4-8. Frame Rail Flange Drilling Prohibited
WARNING! DO NOT drill closely spaced holes in the frame rail. Hole centers of two adjacent holes should be
spaced no less than twice the diameter of the largest hole. Closer spacing could induce a failure between the
two holes.
CAUTION: An appropriately sized bolt and nut must be installed and torqued properly in all unused frame holes.
Failure to do so could result in a frame crack initiation around the hole.
CAUTION: Use care when drilling the frame web so the wires and air lines routed inside the rail are not
damaged. Failure to do so could cause an inoperable electrical or air system circuit.
CAUTION: Never use a torch to make holes in the rail. Use the appropriate diameter drill bit. Heat from a torch
will affect the material properties of the frame rail and could result in frame rail cracks.
CAUTION: The hole diameter should not exceed the bolt diameter by more than .060 inches (1.5mm).
Peterbilt Motors Company 4-6
Page 65

4
BODY MOUNTING
BODY MOUNTING USING U–BOLTS
If the body is mounted to the frame with U–bolts, use a hardwood sill (m inimum 1/2 inch (12.7 mm) thick) between the
frame rail and body frame to protect the top surface of the rail flange.
WARNING! Do not allow the frame rails or flanges to deform when tightening the U–bolts. It will weaken the
frame and could cause an accident. Use suitable spacers made of steel or hardwood on the inside of the frame
rail to prevent collapse of the frame flanges.
Use a hardwood spacer between the bottom f lange and the U–bolt to prevent the U–bolt from notching the fr ame flange .
See Figure 4-9.
FIGURE 4-9. Acceptable U-Bolt Mounting with Wood and Fabricated Spacers
Peterbilt Motors Company 4-7
Page 66

4
BODY MOUNTING
WARNING! Do not allow spacers and other body mounting parts to interfere with brake lines, fuel lines, or wiring
harnesses routed inside the frame rail. Crimped or damaged brake lines, fuel lines, or wiring could result in loss
of braking, fuel leaks, electrical overload or a fire. Carefully
clearances for air brake lines, fuel lines, and wiring. See Figure 4-10.
inspect the installation to ensure adequate
FIGURE 4-10. Clearance Space for Air Lines and Cables
WARNING! Do not notch frame rail flanges to force a U–bolt fit. Notched or
damaged frame flanges could result in premature frame failure. Use a larger size U-bolt.
CAUTION: Mount U–bolts so they do not chafe on frame rail, air or electric lines.
Peterbilt Motors Company 4-8
Page 67

4
BODY MOUNTING
REAR BODY MOUNT
When U–bolts are us e d t o mount a body we recom mend that the last b ody attachment be m ade with a “ f ishp late” bracket.
See Figure 4-11. This provides a firm attaching point and helps prevent any relativ e fore or aft movement between the
body and frame. For hole location guidelines, See Figure 4-7.
FIGURE 4-11. Fishplate Bracket at Rear End of Body
Peterbilt Motors Company 4-9
Page 68

This page intentionally left blank
Page 69

SECTION 5 FRAME MODIFICATIONS
FIGURE 5-1. Wheelbase Customization
INTRODUCTION
Peterbilt offers cus tomer specified wheelbas es and frame overhangs. S o, in most cases fram e modifications should not
be necessary.
However, some body installations may require slight modifications, while other installations will require extensive
modifications. Sometimes an existing dealer stock chassis may need to have the wheelbase changed to better fit a
customer’s application. T he modifications may be as simple as m odifying the frame cutoff, or as complex as modif ying
the wheelbase.
DRILLING RAILS
If frame holes need to be drilled in the rail, see SECTION 4 BODY MOUNTING for more information.
Page 70

5
FRAME MODIFICATIONS
MODIFYING FRAME LENGTH
The frame overhang after the rear ax le can be shorte ned to match a particular bod y length. Using a torch is acc eptable;
however, heat from a tor ch will affect the material char acteristics of the fram e rail. The affected material will normall y be
confined to within 1 to 2 inc hes (25 to 50mm) of the flam e cut and m ay not advers ely affec t the strength of the chass is or
body installation.
CHANGING WHEELBASE
Changing a chassis’ wheelbase is not recommended. Occasionally, however, a chassis wheelbase will need to be
shortened or lengthened. Before this is done there are a few guidelines that should to be considered.
WARNING! When changing the wheelbase, be sure
to follow the driveline manufacturer’s
recommendations for driveline length or angle
changes. Incorrectly modified drivelines can fail
prematurely due to excessive vibration. This can
cause an accident and severe personal injury.
Before changing the wheelbase, the driveline angles of the proposed wheelbase need to be examined to ensure no
harmful vibrations are created. Consult with the driveline manufacturer for appropriate recommendations.
Before the rear susp ension is relocated, check the ne w location of the s pring hanger brackets. The new ho les for the
spring hanger brack ets must not overlap existi ng holes and should adhere to the guidelines in the “ FRAME DRILLING”
section of this manual.
When shortening the wheelbase, the suspension should be moved forward and relocated on the original rail. The rail
behind the suspension can then be cut to achieve the desired frame overhang. See Figure 5-1.
Welding:
Frame rails are heat treated. Do Not Weld the frame rails.
Peterbilt Motors Company 5-2
Page 71

5
FRAME MODIFICATIONS
CROSSMEMBERS
After lengthening a wheel base, an additio nal crossm ember may be required to m aintain the or iginal fram e strength. Contact Dealer for crossmember locations.
• The maximum allowable di stance bet ween th e for ward sus pensio n cros smem ber and the next c rossm em ber for ward
is 47.2 inches (1200 mm). If the distance exc eeds 47.2 i nches (1200 mm ) after the wheelbase is lengthened, add a
crossmember between them. See Figure 5-2. See Figure 4-7 on page 4-5 for crossmember hole patterns.
FIGURE 5-2. Crossmember Spacing Requirements
Peterbilt Motors Company 5-3
Page 72

5
Fastener
Torque
Size
Nm
Lb.-Ft
5/16
22–30
16–22
1-1/4
1877–2217
1380–1630
Fastener
Torque
Size
Nm
Lb-Ft
M6
9–15
7–11
M10
33–43
24–32
M12
75–101
55–75
M20
352–460
260–340
FRAME MODIFICATIONS
TORQUE REQUIREMENTS
Torque values apply to fasteners with clean thr ea ds , lightly lubricated, with hardened steel washer s, and n ylon-insert nuts.
TABLE 5-1. Customary Grade 8 UNF or UNC.
3/8 41–54 30–40
7/16 75–88 55–65
1/2 109–122 80–90
9/16 156–190 115-140
5/8 224–265 165–195
3/4 394–462 290–340
7/8 517–626 380–460
1 952–1129 800–830
1-1/8 1346–1591 990–1170
TABLE 5-2. U.S. Customary - Grade 8 Metric Class 10.9
M8 23–31
M14 134–164
M16 163–217
17–23
99–121
120–160
Peterbilt Motors Company 5-4
Page 73

CECU Located Below Body Builder Access Panel
SECTION 6 ELECTRICAL 520 FAMILY
CONTROL UNIT IDENTIFICATION
This section is written to provide information to the body builder when installing equipment into vehicles built with
Multiplexed instrum entation. The new technology pres ented by NAMUX 2-level instrumentatio n integrates J-1939 CAN
data communications to various components on the vehicle. This book is intended to address how to integrate
aftermarket equipment while still maintaining full functionality of the OEM vehicle.
The most impor tant advanc em ent of NAMUX 2 instrumentation is the im plem entation of the CE CU contr ol ling af term arket
devices. While it is s til l poss ible to wire c om pletel y outside of the C ECU s ystem, uti lizing t he CECU f unction s wil l m ake a
cleaner installatio n and will maintain OEM f unctionality. NAMUX 2 expands controls to devices by receivin g input from
dash switches, remote (aftermarket) switches, sensors mounted to the aftermarket equipment and other vehicle
parameters (engine spee d, tr ansmission status etc.) W ith the proper pr ogramming, the CECU will then pro ces s the inputs
and will create a J-1939 Data instruction.
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION - CAB ELECTRONIC CONTROL UNIT (CECU)
The heart of the m ultip lexed instrumentation system is the CECU. T he C ECU is inside the center console belo w th e c ov er
panel. See Figure 6-1.
FIGURE 6-1. CECU Location
This manual provides servi ce information covering trucks equipped w ith the multiplexed instrumentation s ystem. Before
attempting to make service repairs, the technician should be knowledgeable about the system design, components,
operation and troubleshooting procedures for diagnosing multiplexed instrumentation problems.
Page 74

6
Electrical 520 Family
HOW MULTIPLEXED INSTRUMENTS W ORK
Multiplexed gauges and devices send and receiv e signals through the CECU located in the center console. The CECU
receives sensor s ignals either through the J1 939 data bus or via c onventional wiring sen ding signals from sensors that
read actual pressures or temper atures. T he CECU in terprets th is data and m onitors or controls vehicle o peratio n throu gh
the CECU software. The CECU then sends data to the gauges, warning lamps, audible alarms, and displays located
inside the gauge clusters.
CECU ARCHITECTURE
The software programming of the control module can be grouped into three main types:
• Run Time (RT) - which acts as the operating system where all communication takes place.
• Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) Code - manufacturer specific programmed code and software that is
developed, accessible and editable.
• Vendor Module - blocks of code that are developed for specific manufacturers to allow other features to be
implemented more efficiently.
See Multiplexed Instrumentation Block Diagram (Figure 6-2).
To better understand how Electronic Service Analyst (ESA) f unc tio ns an d why there are curr ent limitations on some of the
multiplexed features, b y explaining what ESA can see. Current ly ESA can look at all inform ation that is communicated
between the RT and PLC Code p ortions of the programm ing. Most signals, be they inputs, out puts, or databus signals,
sent between the RT and P LC Code are visible to ES A . T hes e ar e the s ignals t hat may be monitored and sim ulat ed us ing
ESA.
Limitations with the ESA program are found in the communications that go to the pre-developed Vendor Modules.
Currently this information is not available for ESA to look at. That is why some features that have Vendor Module
programming, such as the odometer and the message display, are not available to monitor and/or simulate through ESA.
Peterbilt Motors Company 6-2
Page 75

6
Electrical 520 Family
FIGURE 6-2. CECU Block Diagram
The Driver Warning Information Mo dule (DWIM) receives in put data from the CECU via the I-CAN databus. W hen the
ignition key is first turned ON, the DWIM performs a calibration power on self-test.
POWER ON SELF-TEST
• Ignition key turned ON.
• The speedom eter and tachom eter gauge pointers move fr om pointing at zero t o their mechanical lim its, remain
there for 1 second and return to pointing at zero.
• At the same time, all LED indicators and telltales are switched on together, and then switched off together.
• A warning sound sequence is also activated.
• The warning lamps are all activated by the CECU.
NOTE: Before replaci ng the CECU or any gauges, c heck the wiring and fuses, and perform the diagnostic tests using
ESA to verify that you are not replacing a good component.
Peterbilt Motors Company 6-3
Page 76

6
Electrical 520 Family
ELECTRICAL INTERFACE
The multiplexed 520 electrical systems features factory installed connections for the body builder to interface the system.
These connections comply with RP-170A. Diesel Engines have access to the J1939 through the O-CAN connector and
gas engines have access through the V-CAN connector. This design limits the need for splicing harnesses.
CAB HARNESS
The two body builder interface connections inside the cab of the 520 are located near the CECU under the cover panel of
the center console (see Figure 6-4). The first body builder connection is pinned per Figure 6-6. Note that cavity 5 is only
for dual steer applications. The second body builder connection is pinned per Figure 6-8. The Cab body builder harness
part number is S92-6160. Note that J1939 cavities 5 and 6 will be dead with gas engine configuration and the J1939
signal will be on a separate harness S92-6160 with a two pin connection shown in Figure 6-11 and 6-12.
FIGURE 6-3. Center Console
FIGURE 6-4. Body Builder Connections in Cab
Peterbilt Motors Company 6-4
Page 77

6
Electrical 520 Family
CAB HARNESS
FIGURE 6-5. Body Builder Connections in Cab
Figure 6-6. Cab Body Builder Connection 1
Figure 6-7. Cab Body Builder Connection 1 Pin Assignm ent
CAB HARNESS
Peterbilt Motors Company 6-5
Page 78

6
Electrical 520 Family
FIGURE 6-8. Cab Body Builder Connection 2
Figure 6-9. Cab Body Builder Connection 2 Pin Assignm ent
Peterbilt Motors Company 6-6
Page 79

6
Electrical 520 Family
CAB HARNESS
FIGURE 6-10. Harness S92-6160 Body Builder Connectors
Peterbilt Motors Company 6-7
Page 80

6
Engine
CAN Bus
Connector
Gas
V-CAN
2-way
Electrical 520 Family
CAB HARNESS
The gas engines have a separate harness S92-6160 for the J1939 signal as shown in Figure 6-11 and 6-12. The gas
engine harness S92-6160 is located in the same location as the other body builder cab harnesses in Figure 6-5 under the
center console panel.
Engine
FIGURE 6-11. Harness S92-6160 Body Builder Connectors
(250Kbd)
Connector
FIGURE 6-12. Harness S92-6160 Body Builder Connectors
Peterbilt Motors Company 6-8
Page 81

6
Electrical 520 Family
CHASSIS HARNESS
The body builder connection that interfaces the chassis harness is located inside the right hand frame rail adjacent to the
transmission per Figure 6-13. The chassis body builder connection is pinned per Figure 6-14.
FIGURE 6-13. Chassis Body Builder Interface Location
FIGURE 6-14. Chassis Body Builder Connecti on
Peterbilt Motors Company 6-9
Page 82

6
Electrical 520 Family
BODY BUILDER HARNESS EXTENSIONS
Extension harnesses have been designed to ease in t he inst al lat ion of af termarket electrical com ponents. The extensions
can be utilized to prevent the need to cut and splice the production harnesses. These extensions have a mating
connector for the cor responding factory harnes s on one end and open wires on the other end. T he extensions can be
purchased from PACCAR Parts. The harness a vailable to extend from the second body builder connector (J844) of the
cab harness is P92-9276.
J1939
Warning! The J1939 databus is the communication link between the engine and the Anti-Lock Br aking System
(ABS). Only J1939 compatible devices shoul d b e ad de d t o t he data bus . Some J1939 compatible af t ermarket devices ma y
disrupt the ability of the databus to communic ate. If t h e dat abus is d is r upte d by an aftermarket device, it must be removed
from the databus.
GUIDELINES - J1939 CIRCUIT REQUIREMENTS
• Circuits added must be a twisted pair consisting of a minimum of 1 twist per inch.
• Individual breakout length of circuits added cannot exceed 118 inches.
• Do not splice into existing J1939 circuits. Use the connection points provided.
• J1939 circuits are for data transmission only and are not to be used for power or ground circuits.
• Any modifications must conform to SAE J1939-15.
J1939 ACCESS
All Peterbilt vehicles equipped with 2017 Emissions and later compliant engines incl ude J1939-15 circuitry. The J1 939
circuit can be accessed under the cover panel of the center console with the body builder cab harness connections
(reference Figure 6-3 for access location).
J1939 ACCESS PROCEDURES
1. Identify J1939 Access Connector
2. Disconnect connection
FIGURE 6-15. J1939 Access
Peterbilt Motors Company 6-10
Page 83

6
Electrical 520 Family
3. Make connection in between original connection.
FIGURE 6-16. J1939 Access
Peterbilt Motors Company 6-11
Page 84

SECTION 7 POWER TAKE-OFF (PTO)
INTRODUCTION
A Power Take Off ( PTO) provides a way to divert some or all of the tr ucks engine power to another com ponent. There
are a wide variety of PTO options available on a Peterbilt that are described below.
FIGURE 7-1. Power Take-Off Locations
TRANSMISSION MOUTED PTO – GENERAL
MANUAL TRANSMISSIONS
This is the most comm on t ype of PT O that is us ed. O n a manual trans mission there are two locations f or PTO ’s. There is
a 6 bolt PTO on the right and an 8 bolt PTO on the bottom left (Figure 7.2). For more information go to
www.roadranger.com and enter “PTO Installation Guide” in the search bar in the upper right corner.
FIGURE 7-2. HD Manual Transmission
Page 85

7
POWER TAKE-OFF (PTO)
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSIONS
On Allison transm issions th ere are t wo l ocations for PT O’s. T he Allison 400 0 ser ies has PT O locatio ns at 1 and 8 o’c lock
viewed from the back of the transmission. See Figur e 7-3. The 4000HS transm issions do not have any PT O locations.
The 3000 series Allis on tra nsm issions have PTO loc ations a t 4 a nd 8 o ’clock ( Figure 7-4). F or m ore inf orm ation on us ing
PTO’s with an Allison tran smission go to www.allisontransm ission.com and refer to the “Rugged Duty Seri es Brochure”
and “PTO Request Flyer” which is available in a 1000/2000 version and a 3000/4000 version.
FIGURE 7-3. Allison 4000 Series FIGURE 7-4. Allison 3000 Series
INSTALLATION CLEARANCES
Some PTO configurations will have cleara nce issues with other components on t he truck. W ith manual transmiss ions, a
6-bolt PTO on the right will typical ly clear m os t com ponents. T his is also tr ue when 3 0 and 4 5 degr ee ada pters are used.
The 8-bolt bottom m ount PTO will not ha ve any issue s. On Allison 40 00 series transm issions, m ost PTO’s will f it in the 1
o’clock position without interfer ing with the cab. If a wet kit is use d here, the dips tick housing will most likel y need to be
modified as it runs over the top of the tr ansmission to the driver s ide of the vehicle. The PTO in the 8 o’cloc k position is
typically ok. There ar e som e sc enarios where the PTO will be very close to or could interf ere with the re ar spring s hackle
on the front suspension.
Peterbilt Motors Company 7-2
Page 86

7
POWER TAKE-OFF (PTO)
FRONT ENGINE PTO
Front engine PTO (FEPTO) is sometimes used in vocational applications. When a FEPTO is spec’d on a truck, the
cooling module has a pass-thru to allow for a shaf t to be bolted to the fr ont of the c ranks haft and ex tend out to the f ront of
the truck. The bumper will be extended out to mount the customer installed aftermarket device. See Figure 7-5 and
Figure 7-6 for radiator installations with and without FEPTO provisions.
FIGURE 7-5. Cooling Module With FEPTO Provision FIGURE 7-6. Cooling Module Without FEPTO Provision
Peterbilt Motors Company 7-3
Page 87

7
POWER TAKE-OFF (PTO)
REAR ENGINE PTO
Rear Engine PTO (REPT O) is also sometimes used in vocatio nal applications. The REPTO is driven off the rear gear
train on the engine. T here is a 135 0/1410 f lange o n the bel l housin g in the 1 o’clo ck position that c an be us ed to att ach a
hydraulic pump or driveshaft. See Figur e 7-7 for an example. T he REPT O f lange will a lwa ys be turn ing wh en the en gine
is running and the output rotat ion is the same as the engine. The Cummins ISL9 and PX-9 REPT O turns at a rate of
1.15:1. The Cummins ISX-12 REPTO turns at a rate of 1.32:1.
FIGURE 7-7. REPTO Flywheel Housing
Peterbilt Motors Company 7-4
Page 88

7
POWER TAKE-OFF (PTO)
PTO INSTALLATIONS
Standard PTO operation is also called cab PTO. With this feature, the operator can set the engine to pre-programmed set
speed(s) and ramp the engine speed up and down with the set/resume switch. To control the PTO there are dash
switches that we offer . Standard with every vehicle is the Cruis e Control/PTO on/off switch an d the set/resume switch.
There are also additional PTO control switches th at can be used. The PTO c ontrol switch will be plumbed with a ir lines
that will be plugged at the bulkhead. See Figure 7-8 for PT O dash switch plumbing. The cab air manifold is located
where the floor meets the firewall on the LH side of the cab. When the cruise control switch is activated and all
parameters set in the ECM for PTO mode are met, the engine will go into PTO mode. In this mode, the engine will
respond to all PTO mode param eters that have been programm ed into the software. T hese parameters c an be changed
with INSITE. There is a PT O light on the dash that s hould be wired to the PT O to inform the oper ator whe n the PTO has
engaged or disengag ed. T his should be wired t o the PTO output, not just a dash s witch or PT O enabl e circ uit. The wir e
can be found in the right hand rail in the area of the transmission.
On Allison transmis sions, the PTO’s will require an el ectric signal. We do not current ly offer an electric PTO switch but
there are several options ava ilabl e. T he m ost c omm on method of gett ing an elec tric s ignal f or the PTO is to get a fac tory
air switch and instal l a pressure switch on the air line . It is recomm ended to provide a 12 vo lt signal to the tr ansmission
control module (TCM) and have the TCM programmed to check for specific requirements such as engine speed, g ear
selection, output s peed etc. before eng aging the PTO. If the TCM logic is bypassed and the PTO is engaged dir ectly it
could cause damage to the PTO and the transmission. Contact your local Allison rep for more information.
FIGURE 7-8. (1) Single acting PTO Controls Diagram
Peterbilt Motors Company 7-5
Page 89

7
Pin
Cummins
1
Not Used
2
Not Used
3
Common Return #1 (Switch)
4
Remote Throttle Signal
5
PTO On/Off
6
Remote Throttle Enable
7
Keyed Switch Power
8
Ground
9
Torque Limit Switch
10
5V Supply
11
Common Return #3 (Sensor)
12
Remote Throttle On/Off
POWER TAKE-OFF (PTO)
REMOTE PTO CONTROL
When a truck is or dered the option code for w ith remote PTO and thrott le controls, a 12 pin connec tor will be provided.
For all heavy duty models this wil l be a breakout of the main engine harness lo cated on the left side of the back of the
engine. See Figure 7-9. See Table 1 for the pin out descriptions on the 12 pin connec tor .
CUMMINS REMOTE PTO OPERATION
For Cummins engines a nd the Paccar PX-9, there ar e 2 d if f er ent modes of operation throug h the 12 pin connec tor . If you
put the engine in PTO m ode by appl ying comm on s witch retur n (ground) pin 3 to PTO on/off pin 5 the en gine RPM will go
to the first set speed. If the connection between pin 3 and 5 is broken and reapplied within ½ second, the engine will go to
the second set speed. If this is done agai n, it will go to t he 3rd s et s peed an d s o on. Ther e are up to 5 pr es et s peeds t hat
can be modified with IN SIT E. If the c onn ectio n is br oken long er th an ½ s econd a nd th en reapp lied, the RP M w ill go b ack
to the first set spee d. In th is mode, the e ngine wil l not respon d to an y throttle inputs unless the throttle ped al override is
engaged using INSIT E. The second m ode of operation is rem ote throttle which is en gaged by appl ying common switch
return (ground) pin 3 to r emote throttle on/off pin 12. In this mode the engin e will respond to the remote throttle signal.
The throttle works off a variable 5V source. T o control th e throttle, you would use a potentiom eter with pin 10 for the 5V
source, pin 11 for th e c ommon sensor retur n (gr o und) and output the var iab le 5V s ign al to t he r emote throttle signal p in 4.
In this mode the engine will not respond to the cab pedal unless the accelerator pedal override is engaged using INSITE.
TABLE 7-1. 12 Pin Connector
Peterbilt Motors Company 7-6
FIGURE 7-9. Connector Location
Page 90

7
POWER TAKE-OFF (PTO)
INSTALLATION OF PTO BY MODEL
CHELSEA 890
The installation shown below in figures 7-10 through 7-12 are of the model 520 with a Chelsea 890 PTO.
FIGURE 7-10. Bottom View FIGURE 7-11. Rear View
FIGURE 7-11. Isometric View with Enhanced View
Peterbilt Motors Company 7-7
 Loading...
Loading...