Milwaukee 6955-20 User Manual
OPERATOR'S MANUAL
MANUEL de L'UTILISATEUR
MANUAL del OPERADOR
Cat. No. No de Cat. 6955-20
RNI |
NG |
NT |
|
WA ISSEME |
|
AVERT |
CIA |
|
RTEN |
ADVE |
|
12" SLIDING DUAL BEVEL MITER SAW WITH DIGITAL FINE ADJUST
SCIE À ONGLETS COULISSANTE À DOUBLE BISEAU DE 305 mm (12 PO) AVEC FONCTION DE RÉGLAGE NUMÉRIQUE PRÉCIS
SIERRA INGLETEADORA DE BISEL DOBLE DESLIZABLE DE 305 mm (12 PULG.) CON AJUSTE FINO DIGITAL
TO REDUCE THE RISK OF INJURY, USER MUST READ OPERATOR'S MANUAL.
AFIN DE RÉDUIRE LE RISQUE DE BLESSURES, L'UTILISATEUR DOIT LIRE LE MANUEL DE L'UTILISATEUR.
PARA REDUCIR EL RIESGO DE LESIONES, EL USUARIO DEBE LEER EL MANUAL DEL OPERADOR.

GENERAL SAFETY RULES
WARNING
READ AND UNDERSTAND ALL INSTRUCTIONS
Failure to follow all instructions listed below, may result in electric shock, fire and/or serious personal injury.
SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS
WORK AREA
1.Keep work area clean and well lit. Cluttered, dark work areas invite accidents.
2.Avoid dangerous environments. Do not use your power tool in rain, damp or wet locations or in the presence of explosive atmospheres (gaseous fumes, dust or flammable materials). Remove materials or debris that may be ignited by sparks.
3.Keep bystanders away. Children and bystanders should be kept at a safe distance from the work area to avoid distracting the operator and contacting the tool or extension cord.
4.Protect others in the work area from debris such as chips and sparks. Provide barriers or shields as needed.
5.Make workshop child proof with padlocks, master switches, or by removing starter keys.
ELECTRICAL SAFETY
6.Grounded tools must be plugged into an outlet properly installed and grounded in accordance with all codes and ordinances. Never remove the grounding prong or modify the plug in any way. Do not use any adaptor plugs. Check with a qualified electrician if you are in doubt as to whether the outlet is properly grounded. If the tool should electrically malfunction or break down, grounding provides a low resistance path to carry electricity away from the user.
7.Double insulated tools are equipped
with a polarized plug (one blade is wider than the other). This plug will fit in a polarized outlet only one way. If the plug does not fit fully in the outlet, reverse the plug. If it still does not fit, contact a qualified electrician to install a polarized outlet. Do not change the plug in any way. Double insulation eliminates the need for the three wire grounded power cord and grounded power supply system.
8.Guard against electric shock. Prevent body contact with grounded surfaces such as pipes, radiators, ranges and refrigerators. When making blind or plunge cuts, always check the work area for hidden wires or pipes. Hold your tool by insulated nonmetal grasping surfaces. Use a Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) to reduce shock hazards.
9.Do not expose to rain or use in damp locations.
10.Do not abuse the cord. Never use the cord to carry the tools or pull the plug from an outlet. Keep cord away form heat, oil, sharp edges or moving parts. Replace damaged cords immediately.
Damaged cords increase the risk of electric shock.
PERSONAL SAFETY
11.Know your power tool. Read this manual carefully to learn your power tool’s applications and limitations as well as potential hazards associated with this type of tool.
12.Stay alert, watch what you are doing, and use common sense when operating a power tool. Do not use tool while tired or under the influence of drugs, alcohol, or medication. A moment of inattention while operating power tools may result in serious personal injury.
13.Dress properly. Do not wear loose clothing or jewelry. Wear a protective hair covering to contain long hair. These may be caught in moving parts. When working outdoors, wear rubber gloves and insulated non-skid footwear. Keep hands and gloves away from moving parts.
14.Reduce the risk of unintentional starting. Be sure your tool is turned off before plugging it in. Do not use a tool if the power switch does not turn the tool on and off. Do not carry a plugged-in tool with your finger on the switch.
15.Remove all adjusting keys and wrenches. Make a habit of checking that adjusting keys, wrenches, etc. are removed from the tool before turning it on.
16.Do not overreach. Maintain control.
Keep proper footing and balance at all times. Maintain a firm grip. Use extra care when using tool on ladders, roofs, scaffolds, etc.
17.Use safety equipment. Everyone in the work area should wear safety goggles or glasses with side shields complying with current safety standards. Everyday eyeglasses only have impact resistant lenses. They are not safety glasses. Wear hearing protection during extended use and a dust mask for dusty operations. Hard hats, face shields, safety shoes, etc. should be used when specified or necessary. Keep a fire extinguisher nearby.
18.Keep guards in place and in working order.
19.Never stand on tool. Serious injury could occur if the tool is tipped or if the cutting tool is unintentionally contacted.
20.Keep hands away from all cutting edges and moving parts.
TOOL USE AND CARE
21.Secure work. Use a clamp, vise or other practical means to hold your work securely, freeing both hands to control the tool.
22.Do not force tool. Your tool will perform best at the rate for which it was designed. Excessive force only causes operator fatigue, increased wear and reduced control.
23.Use the right tool. Do not use a tool or attachment to do a job for which it is not recommended. For example, do not use a circular saw to cut tree limbs or logs. Do not alter a tool.
24.Unplug tool when it is not in use, before changing accessories or performing recommended maintenance.
25.Store idle tools. When not in use, store your tool in a dry, secured place. Keep out of reach of children.
26.Never leave the tool running unattended. Turn power off. Do not leave the tool until it comes to a complete stop.
27.Check for damaged parts. Inspect guards and other parts before use. Check for misalignment, binding of moving parts, improper mounting, broken parts
and any other conditions that may affect operation. If abnormal noise or vibration occurs, turn the tool off immediately and have the problem corrected before further use. Do not use a damaged tool. Tag damaged tools “DO NOT USE” until repaired. A guard or other damaged part should be properly repaired or replaced by a MILWAUKEE service facility. For all repairs, insist on only identical replacement parts.
28.Use proper accessories. Consult this manual for recommended accessories. Using improper accessories may be hazardous. Be sure accessories are properly installed and maintained. Do not defeat a guard or other safety device when installing an accessory or attachment.
29.Maintain tools carefully. Keep handles dry, clean and free from oil and grease. Keep cutting edges sharp and clean. Follow instructions for lubricating and changing accessories. Periodically inspect tool cords and extension cords for damage. Have damaged parts repaired or replaced by a MILWAUKEE service facility.
30.Maintain labels & nameplates. These carry important information. If unreadable or missing, contact a MILWAUKEE service facility for a free replacement.
SERVICE
31.Tool service must be performed only by qualified repair personnel. Service or maintenance performed by unqualified personnel may result in a risk of injury.
32.When servicing a tool, use only identical replacement parts. Follow instructions in the maintenance section of this manual. Use of unauthorized parts or failure to follow maintenance instructions may create a risk of shock or injury.
SPECIFIC SAFETY RULES
1.Always keep hands away from the path of the saw blade.
2.Never reach around, under or across blade.
3.Do not place hands under the saw motor or in the path of the blade. Do not retrieve a piece of material that is cut off while the blade is rotating. Never place hands or fingers behind or in front of the saw blade.
4.Check guards for smooth operation before each use.
2 |
3 |

5.Do not defeat the guards or operate the tool without the guards in place.
6.Avoid kick back. Kick back is a violent reaction to a pinched or binding blade, which throws the saw head upward and towards the operator. Proper workpiece selection and support, proper blade selection and maintenance, and even feed rate are essential to reduce the risk of kick back.
7.Always support work properly. Use the fence, support blocks, auxiliary work support or clamps to keep workpiece secure. Always support the free end of the workpiece and support all small workpieces. Workpieces that bow and pinch the blade may result in kick back. Do not perform any operations freehand (unsupported).
8.Thin material tends to warp or sag and must be well-supported over its entire length to avoid pinching the blade.
9.Position fence properly. The fence can be adjusted for compound cuts and miter cuts. Always make sure the fence is adjusted for the intended cut. Never operate the saw without the fence in place.
10.Be sure the miter angle lock knob and the bevel adjustment lever are tightened securely before making cuts.
11.Use the right blade. Use only recommended blade types and sizes with proper mounting holes, rated at least 5500 RPM. Follow the rotation arrow on the blade to be sure you install it properly. Keep saw blades sharp to help prevent cracking and grabbing. Never use defective or incorrect washers or bolts.
12.Do not use abrasive wheels with the miter saw.
13.Keep blades clean and sharp. An unsharpened or improperly sharpened blade produces a narrow kerf and is likely to be pinched by the workpiece. A dull blade produces excessive friction which can cause the blade to warp or bind. Be sure the blade screw is tight to prevent slipping or loosening during operation.
14.Wait for the blade to reach full speed before lowering the saw head to make a cut.
15.Push the saw through the workpiece. Do not pull the saw through the workpiece. To make a cut, raise saw head and pull it out OVER the workpiece WITHOUT cutting, start the motor, wait a few seconds for the blade to reach full speed, press down on saw head, and push saw head through the cut.
16.If the blade stalls, do not turn the switch on and off. A dull blade or excess pressure may cause stalling. Release the switch immediately if the blade binds or the saw stalls and remove the saw from the cut.
17.Restarting in mid-cut. If you stop the saw in mid-cut, allow the blade to stop, then raise the saw out of the cut. Then restart the saw.
18.Do not lock the trigger in the on position.
19.Keep the cord away from the cutting area and position it so that it will not be tripped over or caught on the workpiece while you are cutting.
20.Avoid cutting nails. Inspect for and remove all nails before cutting.
21.Always wait for the blade to stop completely before changing positions, retrieving a cut-off piece, or preparing the next cut. Unplug the tool before tightening blade screw, servicing, making adjustments, transporting or moving the saw to another location.
22.Lock the saw head down and lock the sliding mechanism before transporting.
23.WARNING: Some dust created by power sanding, sawing, grinding, drilling, and other construction activities contains chemicals known to cause cancer, birth defects or other reproductive harm. Some examples of these chemicals are:
•lead from lead-based paint
•crystalline silica from bricks and cement and other masonry products, and
•arsenic and chromium from chemicallytreated lumber.
Your risk from these exposures varies, depending on how often you do this type of work. To reduce your exposure to these chemicals: work in a well ventilated area, and work with approved safety equipment, such as those dust masks that are specifically designed to filter out microscopic particles.
GROUNDING
WARNING
Improperly connecting the grounding wire can result in the risk of electric shock. Check with a qualified electrician if you are in doubt as to whether the outlet is properly grounded. Do not modify the plug provided with the tool. Never remove the grounding prong from the plug. Do not use the tool if the cord or plug is damaged. If damaged, have it repaired by a MILWAUKEE service facility before use. If the plug will not fit the outlet, have a proper outlet installed by a qualified electrician.
Grounded Tools:
Tools with Three Prong Plugs
Tools marked “Grounding Required” have a three wire cord and three prong grounding plug. The plug must be connected to a properly grounded outlet (See Figure A). If the tool should electrically malfunction or break down, grounding provides a low resistance path to carry electricity away from the user, reducing the risk of electric shock.
The grounding prong in the plug is connected through the green wire inside the cord to the grounding system in the tool. The green wire in the cord must be the only wire connected to the tool's grounding system and must never be attached to an electrically “live” terminal.
Your tool must be plugged into an appropriate outlet, properly installed and grounded in accordance with all codes and ordinances. The plug and outlet should look like those in Figure A.
Double Insulated Tools: Tools with Two Prong Plugs
Tools marked “Double Insulated” do not require grounding. They have a special double insulation system which satisfies OSHA requirements and complies with the applicable standards of Underwriters Laboratories, Inc., the Canadian Standard Association and the National Electrical Code. Double Insulated tools may be used in either of the 120 volt outlets shown in Figures B and C.
Fig. B |
Fig. C |
|
|
Symbology |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Double Insulated |
|
|
Underwriters Laboratories, Inc. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Amperes |
|
|
No Load Revolutions per |
|
|
|
Minute (RPM) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Volts Alternating Current |
|
|
Always keep hands away from |
|
|
|
the path of the saw blade. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
5 |
EXTENSION CORDS
Grounded tools require a three wire extension cord. Double insulated tools can use either a two or three wire extension cord.
As the distance from the supply outlet increases, you must use a heavier gauge extension cord. Using extension cords with inadequately sized wire causes a serious drop in voltage, resulting in loss of power and possible tool damage. Refer to the table shown to determine the required minimum wire size.
The smaller the gauge number of the wire, the greater the capacity of the cord. For example, a 14 gauge cord can carry a higher current than a 16 gauge cord. When using more than one extension cord to make up the total length, be sure each cord contains at least the minimum wire size required. If you are using one extension cord for more than one tool, add the nameplate amperes and use the sum to determine the required minimum wire size.
Guidelines for Using Extension Cords
•If you are using an extension cord outdoors, be sure it is marked with the suffix
“W-A” (“W” in Canada) to indicate that it is acceptable for outdoor use.
•Be sure your extension cord is properly wired and in good electrical condition. Always replace a damaged extension cord or have it repaired by a qualified person before using it.
•Protect your extension cords from sharp objects, excessive heat and
damp or wet areas.
Recommended Minimum Wire Gauge
for Extension Cords*
Nameplate |
Extension Cord Length |
|||||
Amperes |
25' |
50' |
75' |
100' |
150' |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 - 2.0 |
18 |
18 |
18 |
18 |
16 |
|
2.1 |
- 3.4 |
18 |
18 |
18 |
16 |
14 |
3.5 |
- 5.0 |
18 |
18 |
16 |
14 |
12 |
5.1 |
- 7.0 |
18 |
16 |
14 |
12 |
12 |
7.1 - 12.0 |
16 |
14 |
12 |
10 |
|
|
12.1 |
- 16.0 |
14 |
12 |
10 |
|
|
16.1 |
- 20.0 |
12 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Based on limiting the line voltage drop to five volts at 150% of the rated amperes.
READ AND SAVE ALL INSTRUCTIONS FOR FUTURE USE.
Specifications
Cat. |
Volts |
|
No Load |
Arbor |
Blade |
|
No. |
AC |
Amps |
RPM |
Size |
Size |
Weight |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6955-20 |
120 |
15 |
3 200 |
5/8" |
12" |
65 lbs |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Capacities
|
Miter Cuts |
|
Compound Cuts |
||
Max Height |
Max Height |
Max Width |
Max Width |
45° Miter and 45° Bevel |
|
at 90° |
at 45° |
at 90° |
at 45° |
Left Bevel |
Right Bevel |
6.55" H at |
6.55" H at |
13.5" W at |
9.51" W at |
9.51" W at |
9.51" W at |
2.10" W |
.40" W |
4.02" H |
4.02" H |
2.25" H |
1.9" H |
|
|
|
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION |
|
|
||
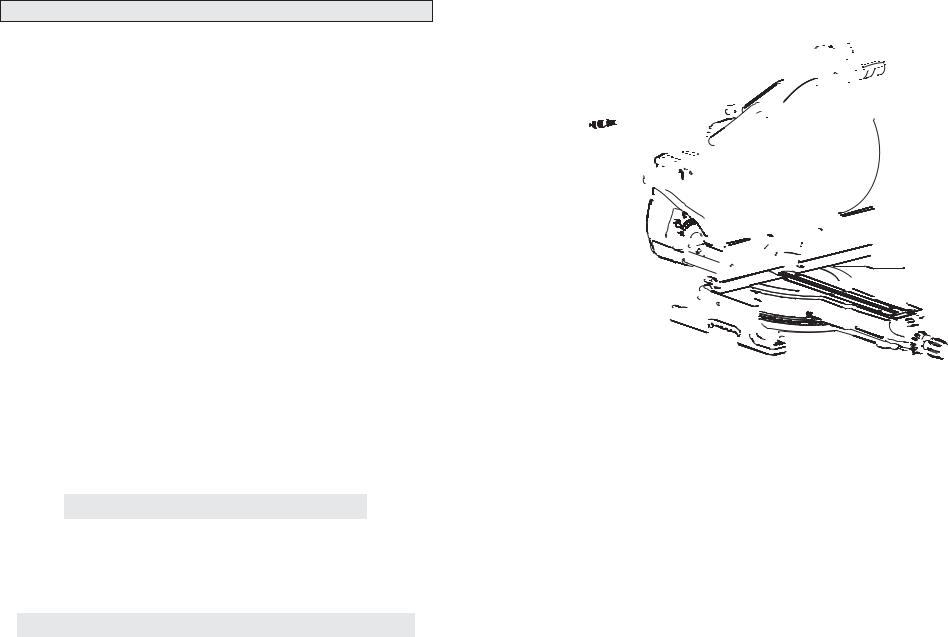
1. |
Saw head |
|
1 |
|
|
|
2 |
2. |
Light on/off switch |
|
|
|
|
||
3 |
On/Off trigger |
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. |
Upper guard |
|
27 |
|
|
|
3 |
5. |
Lower guard |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6. |
Guard bracket |
25 |
26 |
|
|
|
5 |
7. |
Lights |
24 |
|
|
|
|
6 |
8. |
Fence |
|
|
|
|
||
9. |
Turntable |
23 |
|
|
|
|
7 |
10. |
Digital miter |
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
angle readout |
|
|
|
8 |
||
11. |
Fine adjustment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
21 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
ring |
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
12. |
Miter angle |
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
lock knob |
19 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
||
13. |
Detent lever |
|
|
|
|
||
8 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
14. |
Adjustable kerf |
18 |
|
|
|
11 |
|
|
plates |
|
|
|
|
|
|
15. |
Miter angle pointer |
|
|
|
|
|
|
16. |
Miter angle scale |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17 |
16 |
15 |
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
13 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
17. |
Mounting holes (4) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
18. |
Fence lock knob |
|
|
|
|
|
|
19. |
Face board mounting |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
holes (4) |
28 |
|
|
|
|
|
20. |
Slide rails |
|
|
|
|
|
21. |
Bevel angle scale |
|
|
|
|
|
|
29 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
22. |
Depth stop paw |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
23. |
Head lock-down pin |
|
|
|
|
|
|
24. |
Dust ejection port |
|
|
|
|
|
|
25. |
Dust chute |
|
|
|
|
|
|
26. |
Bevel adjustment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
lever |
|
|
|
|
|
|
27. |
Depth stop adjust- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ment knob |
|
|
|
|
|
|
28. |
Spindle lock |
|
|
|
|
|
|
29. |
Dust elbow (Dust bag |
|
|
|
31 |
|
|
|
not shown) |
|
|
|
30 |
|
30. |
Slide rail lock |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
32 |
|
|
|
31. |
Wrench storage |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
32. |
Carrying handles |
6 |
7 |
FEATURES
Miter system
The Milwaukee 6955-20 Miter Saw uses a heavy duty steel plate with detents (stops). This steel plate is extremely durable and provides for repeatable accuracy at each detent. The miter angle can be set using detents for commonly cut angles at 0°, 15°, 22.5° 31.62°, 45° Right and Left and 60° Right. The 6955-20 has a miter range from 55° on the left to 60° on the right. An industrial grade bearing allows the turntable to be quickly and accurately adjusted to any angle across the miter range.
Miter Angle Fine Adjust
In certain finish carpentry applications like casing a window or door, it is necessary to compensate for a non-square situation by making a precision miter angle adjustment to the turntable. The Milwaukee miter angle fine adjust system makes this process quick and easy, especially when the saw is positioned near a miter detent (stop).
Digital Miter Angle Readout
The Milwaukee 6955-20 has a Digital Miter Angle Readout at the front of the turntable that displays the miter angle of the turntable to a resolution of 0.1°. The Digital Miter Angle Readout is based on the mechanical accuracy of the miter angle detent plate. It calibrates itself each time the turntable is placed in a miter detent and it requires no adjustment.
Using the Miter Angle Fine Adjust in conjunction with the Digital Miter Angle Readout, it is easy to make accurate minor angle adjustments anywhere along the miter range. Using these systems together makes it easy to re-position the turntable and repeat any miter angle setting.
When the turntable is positioned at a LEFT miter angle the digital readout will display with a (-) symbol in front of the angle (for example: -22.5° or -44.7°). When the turntable is positioned at a RIGHT miter angle the digital readout will display as follows: 22.5° or 44.7°.
Dual Bevel Adjustment System
The Dual Bevel Adjustment System allows for quick and accurate bevel adjustments to either the Right or the Left. The bevel angle can be set using detents (stops) for the following commonly cut angles 0°, 22.5°, 33.85°, 45° Right and Left. The bevel mechanism also has several degrees of overtravel beyond 45° on both the left and right.
Electronic Feedback Control Circuit
The Electronic Feedback Control Circuit (EFCC) helps improve the operation and life of the tool. It allows the tool to maintain constant speed and torque between no-load and load conditions. The soft start reduces the amount of torque reaction at startup to the tool and the user. It gradually increases the motor speed up from zero to the top no-load speed.
Electric Brake
The electric brake engages when the trigger is released, causing the blade to stop and allowing you to proceed with your work. Generally the saw blade stops in four to five seconds. However, there may be a delay between the time the trigger is released and the time the brake engages. Occasionally the brake may miss completely. If the brake misses frequently, the saw needs servicing by an authorized MILWAUKEE service station. The brake is not a substitute for the guards, so it is essential to always wait for the blade to stop completely before removing the blade from the kerf.
Lights
The Milwaukee 6950-20 Miter Saw has two high power lights positioned on either side of the blade to illuminate the workpiece cutting area so that it is easy to see blade approach the cutting line. An ON / OFF switch for the lights is conveniently located on the trigger handle. The bulb is designed to provide several years of service. Uses standard bulb size GE 193.
Dust Management System
The Milwaukee 6955-20 Miter Saw dust collection system uses a large dust chute on both sides of the blade to capture and direct dust to back of the saw. The saw comes with a Dust Elbow and a Dust Bag that attach to the back of the Dust Chute. The dust bag has a zipper located on the bottom of the bag that makes it easy to empty. When using the saw on a stand, the dust bag zipper can be left open to allow the waste to fall into a waste container.
Carrying Handles
For ease of transporting, multiple carrying handles are provided, one on each side of the table and one on top of the saw head. Always lock the saw head down when transporting.
8
TOOL ASSEMBLY
WARNING
To reduce the risk of injury, always unplug tool before attaching or removing accessories or making adjustments. Use only specifically recommended accessories. Others may be hazardous.
4.Move the bevel adjustment lever to the middle position and wedge in a tool (screw driver etc.) so the handle stay in the middle position. Move the saw head so that the bevel detent mechanism locks into the 0° bevel detent.
5.Loosen 2 screws (T25) on the front of the bevel arm, these screws are used to clamp the detent body.
Adjusting the Miter Saw
The 6955-20 Miter Saw is fully adjusted at the factory. If it is not accurate due to shipping and handling, please follow these steps to accurately set up your saw. Once the saw is properly adjusted, it should remain accurate under normal jobsite and transportation conditions.
Squaring the Blade (90°) to the Fence (0° Miter)
1.Unplug saw
2.Place a square against the fence and blade and ensure that the square is not touching blade teeth as this will cause an inaccurate measurement.
3.Loosen the miter lock knob and move the saw to the 0° miter position. Do not tighten the lock knob.
4.If the saw blade is not exactly perpendicular to the fence, use the supplied wrench to loosen the screws that hold the miter scale to the base. Move the scale left or right until the blade is perpendicular to the fence. Use the square to verify that the blade is perpendicular to the fence. Retighten the screws.
5.Loosen the miter pointer adjustment screw and reposition the pointer the so that it indicates exactly zero. Once the pointer is properly positioned, retighten the miter pointer adjustment screw.
Squaring the Blade (90°) to the Table (0° Bevel)
1.Unplug saw
2.Place a square against the table and blade and ensure that the square is not touching blade teeth as this will cause an inaccurate measurement.
3.Remove the 6 screws holding the dust chute together.
6.Using a T25 wrench you can adjust the bevel setting of the blade-to-table. Clockwise tilts blade to the right, counterclockwise tilts blade to the left.
7.When you have the blade set to the 0° bevel, torque the 2 screws to 85-100 in lbs.
8.Remove the tool used to wedge the bevel adjustment lever.
9.Move the bevel adjustment lever to "lock".
10.Reassemble the dust chute sides, tightening the 6 screws securely.
11.If necessary, loosen the left and right bevel pointer adjustment screws and reposition the pointers the so that they indicates exactly zero. Once the pointers are properly positioned, retighten the bevel pointer adjustment screw.
Mounting the Miter Saw
To prevent the tool from sliding, falling or tipping during operation, the saw can be mounted to a supporting surface such as a level, sturdy work table or bench. Position the saw and workbench to allow adequate room for cross-cutting long workpieces. To mount the saw, insert fasteners through the holes in the corners of the saw base.
Installing the Dust Bag
Use the dust bag to collect or divert sawdust.
Insert the dust elbow into the dust chute on the back of the saw. Then, attach the dust bag by hooking it onto the dust elbow. Always empty the dust bag before storing and frequently during use.
9

Raising and Lowering the Saw Head
The saw head must be locked down for transporting and storing the tool. The tool is shipped with the saw head locked down. To unlock it, press and hold down the saw head and simultaneously pull out the lock down pin. To lock the saw head, press and hold down the saw head and then push in the lock down pin.
Locking and Unlocking the Sliding Mechanism
Always lock the sliding mechanism before transporting or storing the saw. To unlock it, loosen the slide rail lock by turning it counterclockwise. To lock it, tighten the slide rail lock by turning it clockwise.
Lock-Off
There is a hole in the trigger through which a padlock will fit to lock the tool when it is not in use. Use a padlock with a 1/4" shackle and always unplug the tool before installing it (padlock not supplied with tool).
Selecting the Correct Miter Saw Blade
Use only sliding miter saw blades with the
MILWAUKEE Sliding Dual Bevel Miter Saw. Saw blades with a 0° hook angle or a negative hook angle work well for Sliding Miter saws. A negative hook angle means that teeth tip away from the direction of rotation, and a 0° degree hook angle means that the teeth are in line with the center of the blade. A low or negative hook angle will slow the feed rate and will also minimize the blade’s tendency to “climb” the material being cut.
Installing and Changing Blades
Always use clean, sharp blades because dull blades tend to overload the tool, bind and cause pinching. Use only 12" blades rated at least 5500 RPM.
1.Unplug the tool.
2.With the saw head up, use the wrench to loosen the guard bracket rear screw 1/4 turn using the wrench provided (1).
3.Raise the lower guard (2).
Fig. 1 |
1 |
Loosen guard |
bracket rear |
screw |
2 |
lower |
guard up |
4.Loosen (do not remove) the guard bracket front screw (3) until the guard bracket can be raised to expose the blade screw (4). Lower the lower guard until it rests on the guard bracket front screw. This will hold it up and out of the way during the blade change.
Fig. 2 |
3 |
Loosen guard |
|
|
bracket |
|
|
front screw |
|
|
4 |
|
|
Rotate guard |
|
|
bracket up |
5.Press in the spindle lock and rotate the spindle until the lock engages.
6.Use the wrench to loosen and remove the left-hand thread blade screw clockwise.
7.Remove the outer blade flange, blade, blade washer, and inner blade flange.
Wipe the flanges, washer, and spindle to remove dust and debris. Inspect the parts for damage. Replace if needed.
Fig. 3 |
|
Blade |
Inner flange |
Blade |
|
screw |
|
Outer flange |
Blade |
|
washer |
8.Install the inner blade flange as shown.
9.Insert the blade washer into the blade arbor hole.
10.Match the arrow on the blade with the arrow on the lower guard. Slide the blade into the upper guard and onto the spindle.
11.Install the outer blade flange.
12.Press in the spindle lock and rotate the blade until the lock engages. Insert and securely tighten the blade screw counterclockwise with the wrench.
13.Rotate the guard bracket into position and securely tighten the two screws. Return the wrench to the wrench holder.
14.Lower the saw head and check the clearance between the blade and the adjustable kerf plates. Important: The lower guard must move freely. The blade should rotate freely (see "Adjusting the Kerf Plates").
Adjusting the Kerf Plates
Kerf plates reduce tear-out and splintering along the cut by providing edge support. Because blades vary in width, adjust the kerf plates with every blade change.
Never make a cut without the adjustable kerf plates installed. The kerf plates can be set at their maximum width to accommodate all blade widths and bevel angles if tear-out and splintering are not a concern.
1.Unplug the tool.
2.Install the blade to be used. Each time the blade is changed, check to be sure the kerf plates are adjusted properly.
3.Set the bevel angle. Each time the bevel is changed, check to be sure the kerf plates are adjusted properly.
4.Loosen the six kerf plate adjusting screws.
5.Lower the saw head to the full depth of cut (the point where the saw head will not lower any further).
6.Slide the kerf plates to the desired spacing and tighten the six screws.
7.Check to be sure the saw blade does not contact the kerf plates before starting the saw.
10 |
11 |

OPERATION
 WARNING
WARNING
To reduce the risk of injury, wear safety goggles or glasses with side shields. Always wait for the blade to stop completely and unplug the tool before changing accessories or making adjustments. Do not defeat the guards.
Using Face Boards
(Zero Clearance Sub Fences)
Support the Workpiece Properly
Always support the workpiece during operation. Otherwise, the workpiece may pull up and into the saw.
1.Use the Fence: Align the workpiece flush against the fence to provide a straight path for the saw blade. This will help eliminate the tendency for the blade teeth to bind. The fence can be used as a support for miter, bevel and compound cuts.
There are face board mounting holes in the fences for attaching face boards. Face boards place distance between the fence and the workpiece, providing improved support for some workpieces. Workpiece splintering can be reduced by using face boards.As the width of the face board increases, the height of the workpiece which can be cut increases slightly (but the width capacity decreases slightly). Similarly, if you place a face board on the saw table and place a workpiece on top of the face board, you can cut a workpiece with greater width (but with less height).
2.Use a clamp: Clamp the workpiece to the fence or base with a C-clamp.
Support of Longer Workpieces
Longer workpieces need support along their full length. If you are using the saw on a level work bench, prop up the workpiece to a height of 4-3/4" from the bottom of the saw feet. There are also many aftermarket work tables specifically designed for miter saws that provide supports for all types of workpieces.
Adjusting the Miter Angle
Guards
The tool is shipped with both the upper and lower guard installed. The lower guard should cover the blade when the saw head is up and it should move freely and open automatically as the saw head is lowered into the workpiece. If the lower guard appears loose, sticks, or if it does not move to cover the blade when the saw head is up, tighten the guard bracket screws. If it still does not move freely, take the saw to an authorized service center for repairs. Do not attempt to open the guard further than the automatic action permits.
Select the Workpiece Carefully
Be cautious of pitchy, knotty, wet or warped workpieces. These materials are likely to create pinching conditions. Workpieces that bow and pinch may result in kick back. Inspect for and remove nails before cutting. Always keep blades clean and sharp; otherwise the blade produces a narrow kerf and is likely to be pinched by the workpiece. This tool is not recommended for cutting ferrous metals such as iron and steel. See Applications for a more complete list of materials.
The miter angle can be set using detents for commonly cut angles, as well as finely adjusted to any angle. Use the miter angle pointer to adjust the turntable to any whole degree across the miter range. The digital miter angle readout shows the selected angle.
1.Loosen the miter angle lock knob.
2.To set the miter angle, pull up on the detent lever and rotate the turntable to the detent angle closest to the desired angle. The saw cuts miter angles from 55° on the left to 60° on the right. Detents are available at 0°, 15°, 22.5° 32.62°, 45°, and 60°.
3.Tighten the miter angle lock knob to use the miter angle set at the detent before making a cut.
4. To make a fine adjustment to the miter |
|
|
|
Fig. 5 |
|
||
angle: |
|
||
Detent Angles |
|
||
A. Pull up and hold the detent lever . |
Unlock |
||
|
|||
B. Push the fine adjustment ring forward |
|
|
|
until it locks to engage override. |
|
|
|
C. Rotate the fine adjustment ring left |
|
|
|
or right until the desired angle is |
|
|
|
displayed on the digital miter angle |
|
|
|
readout. ¼ turn = 1° change in miter |
|
|
|
angle. |
|
|
|
D. Tighten the miter angle lock knob |
Bevel |
|
|
to secure the table before making a |
Adjustment |
|
|
cut. |
Lever |
|
|
E. Pull up on the detent lever to release |
|
|
|
the fine adjustment ring. |
|
|
Fig. 4 |
|
|
|
|
|
B |
|
|
Lock |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Adjusting the Depth of Cut |
|||
|
|
The depth of the cut can be adjusted for |
|||
|
|
groove or rabbet cuts. |
|||
C |
D |
1. |
Unplug the tool. |
||
A E |
|
2. |
To set the depth of cut, swivel the depth |
||
|
|
stop paw toward the front of the saw. |
|||
Adjusting the Bevel Angle |
|
3. |
Lower the saw head to the desired depth |
||
|
|
of cut. |
|
||
The bevel angle can be set using detents for |
|
|
|||
4. Rotate the depth stop adjustment knob |
|||||
commonly cut angles, as well as adjusted |
|||||
|
until it contacts the paw. Lock in the |
||||
to any angle in between by using the bevel |
|
||||
|
depth using the lock nut. |
||||
angle scale. The bevel mechanism also has |
|
||||
several degrees of overtravel on both the left |
5. |
Plug in the tool and make a test cut to |
|||
and right. |
|
|
verify the depth of cut is correct. |
||
1. Unplug the tool. |
|
6. |
To remove the depth of cut limit, loosen |
||
2. To adjust the bevel angle, place one |
|
the lock nut by turning counterclockwise |
|||
hand on the front handle for better con- |
|
and swivel the paw away from the front |
|||
trol. |
|
|
of the saw. |
|
|
3. Using the other hand, lift the bevel ad- |
Fig. 6 |
|
|||
justment lever: |
|
Knob |
|||
|
|
|
|||
A. To use pre-set detents, lift the |
|
Lock nut |
|
||
bevel adjustment lever half-way |
|
|
|
||
up (until it "clicks") to move the |
|
|
|
||
saw head left or right, with stops at |
|
|
|
||
pre-set detents. |
|
|
|
Paw |
|
B. To freely move the head, lift the |
|
|
|||
bevel adjustment lever all the way |
|
|
|
||
up to freely move the saw head |
|
|
|
||
across the bevel range. |
|
|
|
|
|
4.Pull or push the saw head to the desired
angle using the bevel angle scale.
5. Lock the bevel angle by pressing down the bevel adjustment lever before making a cut.
12 |
13 |

Adjusting the Fences
1.Loosen the fence lock knobs.
2.The left side fence can slide side-to-side to the desired position to allow for a left bevel or left compound miter cuts.
3.The right side fence can be removed for a right bevel or right compound miter cuts by pulling the fence up.
4.Always position the fences properly for maximum work support.
5.Tighten the fence lock knobs securely before making a cut.
NOTE: If either fence has any movement forward to backward, tighten the fence set screw, located on the back of each fence slot.
Lights
Use the on/off switch to turn on the turntable lights before making a cut. Turn off the lights when cutting is complete.
 WARNING
WARNING
To reduce the risk of injury, do not rely on the brake as a safety feature. Always wait until the blade stops completely before allowing anything near the blade.
 WARNING
WARNING
To reduce the risk of injury, make sure all adjustments are securely locked before making a cut.
Starting and Stopping the Tool
Always hold the trigger handle firmly because the starting and stopping action of the motor may cause the handle to move up or down slightly. Always secure the turntable by tightening the miter angle lock knob.
1.To start the motor, pull the trigger.
2.To stop the motor, release the trigger.
Making a Chop Cut
The sliding mechanism can be locked to use the saw for chop cuts (cuts not requiring the use of the slide mechanism). Cut workpieces with chop cuts whenever possible. A chop cut is always faster and easier to make than a sliding cut.
Fig. 7 |
3 |
1 |
2 |
1.Slide the saw head all the way back
(1).
2.Tighten the slide rail lock (2).
3.Plug in the tool. Raise the saw head completely.
4.Select the desired angles following the steps in "Adjusting the Miter Angle" and "Adjusting the Bevel Angle".
5.Place the workpiece on the turntable and line up the cut.
6.Support the workpiece using any of the methods described in "Support the Workpiece Properly".
7.Start the motor. Wait a few seconds for the blade to reach full speed. Then gently lower the saw head into the workpiece all the way through the cut (3).
8.Always allow the saw to do the work. Forcing the tool may stall or overheat the motor.
9.After the cut is complete, release the trigger and wait for the blade to stop completely. Then gently raise the saw head and remove the workpiece. Always unplug the tool before retrieving loose cut-off pieces from inside the guard area.
Making a Sliding Cut
Wider workpieces can be cut using the sliding mechanism.
Fig. 8
1
2
4
3
1.Make sure that the slide rail lock is loose and that the saw head moves freely back and forth.
2.Select the desired angle following the steps in "Adjusting the Miter Angle" and "Adjusting the Bevel Angle".
3.Place the workpiece on the turntable and line up the cut.
4.Raise saw head and pull it out OVER the workpiece WITHOUT cutting (1).
5.Start the motor. Wait a few seconds for the blade to reach full speed.
6.Press down on saw head (2).
7.Push saw through the cut (3).
8.After the cut is complete, release the trigger and wait for the blade to stop completely. Then gently raise the saw head (4) and remove the workpiece. Always unplug the tool before retrieving loose cut-off pieces from inside the guard area.
|
APPLICATIONS |
WARNING |
Cutting Non-Square Materials |
|
Cutting Round (Cylindrical) Materials |
Do not cut stone, brick, concrete, or ferrous metals (iron, steel, stainless steel, or alloys of these metals) with this saw.
Do not use abrasive wheels with this saw.
Dust created by cutting these materials and/or using abrasive cut-off wheels can jam the blade guard and possibly cause personal injury.
Recommended Materials and Applications
The following materials can be cut with the slide compound miter saw. There are many types of saw blades available. Always use the proper blade for the particular material and application.
Wood - solid wood, plywood, particle board, MDF (medium density fiberboard), HDF (high density fiberboard), melamine laminated particle board, formica laminates, hardboard (masonite).
Plastics - PVC, CPVC, ABS, solid surfacing materials (such as Corian®), and other plastic materials.
Nonferrous Metals - aluminum, brass, copper, and other non-ferrous materials.
"V" shaped blocks can be used to support round materials like closet rod and plastic pipe.
Aluminum Sash and Other Channel Type and Materials
Aluminum sash material can be supported with blocks to prevent it from deforming while it is being cut.
. 9 |
|
Clamp |
Fence |
|
Wood support |
|
block |
|
|
|
Aluminum |
|
|
material |
|
|
Wood support |
|
Base |
block |
|
|
14 |
15 |
Miter |
|
Miter |
|
Bevel |
|
Bevel |
|
Range |
Detents (Stops) |
|
Range |
|
Detents (Stops) |
||
0° to 55° Left |
0°, 15°, 22.5°, 31.62°, 45° Left |
|
0° to 45° Left |
0°, 22.5°, 33.85°, 45°, 48 Left |
|||
0° to 60° Right |
0°, 15°, 22.5°, 31.62°, 45° Right |
|
0° to 48° Right |
0°, 22.5°, 33.85°, 45°, 48 Right |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Base Molding |
|
Nested Crown |
|
||
|
|
Capacity |
|
Capacity |
|
||
|
|
6" at 0° |
|
6-5/8" |
|
||
|
|
6" at 45° Left and Right |
|
|
|
||
Two Methods for Cutting Crown Molding
The angles created on a piece of crown molding that fits flat against the ceiling and wall will, when added together, equal 90°
(A + B = 90°).The most common crown molding angles are :
52°/38°: A 52° angle against the ceiling (A) and a 38° angle against the wall (B). The miter saw has special miter settings at 31.6° left and right and a bevel setting at 33.9° to use when cutting 52°/ 38° crown molding flat on the miter saw table. These settings are identified with a diamond mark.
45°/45°: A 45° angle against the ceiling (A) and a 45° angle against the wall (B). The miter saw has special miter settings at 35.3° left and right and a bevel setting at 30° to use when cutting 45°/ 45° crown flat on the miter saw table. These settings are identified with a black circle.
NOTE: Even though all of these angles are standard, rooms are very rarely constructed so the corners are exactly 90°. You will need to “fine tune” these settings and make necessary adjustments to the cutting angles.
Fig. 10 |
Ceiling |
Angle A 
Angle B
Wall
Outside Inside corner corner
Cutting Crown Molding Flat on the Miter Saw Table
The advantage of cutting crown molding flat on the table is that it is easier to secure the molding at the correct cutting position. Also larger pieces of crown molding may be cut laying flat on the miter saw table.
1.Set the bevel and miter angles using the Crown Molding Miter Angles chart. Tighten the miter lock knob and the bevel lock knob.
2.Using the Positioning section below, correctly positions the molding.
NOTE: Always make a test cut on scrap material to confirm all angles are correct.
3.Make the cut according to "Making a Chop Cut".
Cutting Crown Molding Angled Against the Fence (Nested – in position)
Always use a crown molding fence when cutting crown molding angled against the fence. When cutting crown molding angled against the fence does not require bevel settings. Small changes in the miter angle can be made without affecting the bevel angle. When using this method the saw can be quickly and easily adjusted for corners that are not 90° (square).
Positioning
Standard (U.S.) crown molding with 52° and 38° angles (set bevel angle to 33.85°)
Left side, inside corner
1.Top edge of molding against fence
2.Miter table set right 31.62°
3.Save left end of cut
Right side, inside corner
1.Bottom edge of molding against fence
2.Miter table set left 31.62°
3.Save left end of cut
Left side, outside corner
1.Bottom edge of molding against fence
2.Miter table set left 31.62°
3.Save right end of cut
Right side, outside corner
1.Top edge of molding against fence
2.Miter table set right 31.62°
3.Save right end of cut
Standard (U.S.) crown molding with 45° angles (set bevel angle to 0°)
Left side, inside corner
1.Top edge of molding against fence
2.Miter table set right 45°
3.Save left end of cut
Right side, inside corner
1.Bottom edge of molding against fence
2.Miter table set left 45°
3.Save left end of cut
Crown Molding Miter Angles
Wall Angle |
38˚ / 52˚ |
45˚/45˚ |
(B) |
Miter/Bevel |
Miter/Bevel |
67 |
42.93/41.08 |
46.89/36.13 |
68 |
42.39/40.79 |
46.35/35.89 |
69 |
41.85/40.50 |
45.81/35.64 |
70 |
41.32/40.20 |
45.28/35.40 |
71 |
40.79/39.90 |
44.75/35.15 |
72 |
40.28/39.61 |
44.22/34.89 |
73 |
39.76/39.30 |
43.70/34.64 |
74 |
39.25/39.00 |
43.18/34.38 |
75 |
38.74/38.69 |
42.66/34.12 |
76 |
38.24/38.39 |
42.15/33.86 |
77 |
37.74/38.08 |
41.64/33.60 |
78 |
37.24/37.76 |
41.13/33.33 |
79 |
36.75/37.45 |
40.62/33.07 |
80 |
36.27/37.13 |
40.12/32.80 |
81 |
35.79/36.81 |
39.62/32.53 |
82 |
35.31/36.49 |
39.13/32.25 |
83 |
34.83/36.17 |
38.63/31.98 |
84 |
34.36/35.85 |
38.14/31.70 |
85 |
33.90/35.52 |
37.66/31.42 |
86 |
33.43/35.19 |
37.17/31.14 |
87 |
32.97/34.86 |
36.69/30.86 |
88 |
32.52/34.53 |
36.21/30.57 |
89 |
32.07/34.20 |
35.74/30.29 |
90 |
31.62/33.86 |
35.26/30.00 |
91 |
31.17/33.53 |
34.79/29.71 |
92 |
30.73/33.19 |
34.33/29.42 |
93 |
30.30/32.85 |
33.86/29.13 |
94 |
29.86/32.51 |
33.40/28.83 |
95 |
29.43/32.17 |
32.94/28.54 |
96 |
29.00/31.82 |
32.48/28.24 |
97 |
28.58/31.48 |
32.02/27.94 |
98 |
28.16/31.13 |
31.58/27.64 |
99 |
27.74/30.78 |
31.13/27.34 |
10027.32/30.43 30.68/27.03
10126.91/30.08 30.24/26.73
10226.50/29.73 29.80/26.42
10326.09/29.38 29.36/26.12
10425.69/29.02 28.92/25.81
10525.29/28.67 28.48/25.50
10624.78/28.31 28.05/25.19
Left side, outside corner
1.Bottom edge of molding against fence
2.Miter table set left 45°
3.Save right end of cut
Right side, outside corner
1.Top edge of molding against fence
2.Miter table set right 45°
3.Save right end of cut
Wall |
38˚ / 52˚ |
45˚/45˚ |
Angle (B) |
Miter/Bevel |
Miter/Bevel |
10724.49/27.95 27.62/24.87
10824.10/27.59 27.19/24.56
10923.71/27.23 26.77/24.24
11023.32/26.87 26.34/23.93
11122.93/26.51 25.92/23.61
11222.55/26.15 25.50/23.29
11322.17/25.78 25.08/22.97
11421.79/25.42 24.66/22.65
11521.42/25.05 24.25/22.33
11621.04/24.68 23.84/22.01
11720.67/24.31 23.43/21.68
11820.30/23.94 23.02/21.36
11919.93/23.57 22.61/21.03
12019.57/23.20 22.21/20.70
12119.20/22.83 21.80/20.38
12218.84/22.46 21.40/20.05
12318.48/22.09 21.00/19.72
12418.13/21.71 20.61/19.39
12517.77/21.34 20.21/19.06
12617.42/20.96 19.81/18.72
12717.06/20.59 19.42/18.39
12816.71/20.21 19.03/18.06
12916.37/19.83 18.64/17.72
13016.02/19.45 18.25/17.39
13115.67/19.07 17.86/17.05
13215.33/18.69 17.48/16.71
13314.99/18.31 17.09/16.38
13414.65/17.93 16.71/16.04
13514.30/17.55 16.32/15.70
13613.97/17.17 15.94/15.36
13713.63/16.79 15.56/15.02
13813.30/16.40 15.19/14.68
13912.96/16.02 14.81/14.34
14012.63/15.64 14.43/14.00
14112.30/15.25 14.06/13.65
14211.97/14.87 13.68/13.31
14311.64/14.48 13.31/12.97
14411.31/14.09 12.94/12.62
14510.99/13.71 12.57/12.28
14610.66/13.32 12.20/11.93
16 |
17 |

Cutting Compound Miters
The chart below identifies miter and bevel settings for various types of compound miters. Always make trial cuts in scrap material prior to making the cut in the workpiece.
|
|
|
|
|
Sides |
|
|
|
|
Pitch |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
||
0° |
Miter |
45.00° |
36.00° |
30.00° |
25.71° |
22.50° |
20.00° |
18.00° |
|
Bevel |
0.00° |
0.00° |
0.00° |
0.00° |
0.00° |
0.00° |
0.00° |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5° |
Miter |
44.89° |
35.90° |
29.91° |
25.63° |
22.42° |
19.93° |
17.94° |
|
Bevel |
3.53° |
2.94° |
2.50° |
2.17° |
1.91° |
1.71° |
1.54° |
||
10° |
Miter |
44.56° |
35.58° |
29.62° |
25.37° |
22.19° |
19.72° |
17.74° |
|
Bevel |
7.05° |
5.86° |
4.98° |
4.32° |
3.81° |
3.40° |
3.08° |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15° |
Miter |
44.01° |
35.06° |
29.15° |
24.95° |
21.81° |
19.37° |
17.42° |
|
Bevel |
10.55° |
8.75° |
7.44° |
6.45° |
5.68° |
5.08° |
4.59° |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20° |
Miter |
43.22° |
34.32° |
28.48° |
24.35° |
21.27° |
18.88° |
16.98° |
|
Bevel |
14.00° |
11.60° |
9.85° |
8.53° |
7.52° |
6.72° |
6.07° |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25° |
Miter |
42.19° |
33.36° |
27.62° |
23.56° |
20.58° |
18.26° |
16.41° |
|
Bevel |
17.39° |
14.38° |
12.20° |
10.57° |
9.31° |
8.31° |
7.50° |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30° |
Miter |
40.89° |
32.18° |
26.57° |
22.64° |
19.73° |
17.50° |
15.72° |
|
Bevel |
20.70° |
17.09° |
14.48° |
12.53° |
11.03° |
9.85° |
8.89° |
||
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
35° |
Miter |
39.32° |
30.76° |
25.31° |
21.53° |
18.74° |
16.60° |
14.90° |
|
Bevel |
23.93° |
19.70° |
16.67° |
14.41° |
12.68° |
11.31° |
10.21° |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
40° |
Miter |
37.45° |
29.10° |
23.86° |
20.25° |
17.60° |
15.58° |
13.98° |
|
Bevel |
27.03° |
22.20° |
18.75° |
16.19° |
14.24° |
12.70° |
11.46° |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
45° |
Miter |
35.26° |
27.19° |
22.21° |
18.80° |
16.32° |
14.43° |
12.94° |
|
Bevel |
30.00° |
24.56° |
20.70° |
17.87° |
15.70° |
14.00° |
12.62° |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
50° |
Miter |
32.73° |
25.03° |
20.36° |
17.20° |
14.91° |
13.17° |
11.80° |
|
Bevel |
32.80° |
26.76° |
22.52° |
19.41° |
17.05° |
15.19° |
13.69° |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
55° |
Miter |
29.84° |
22.62° |
18.32° |
15.44° |
13.36° |
11.79° |
10.56° |
|
Bevel |
35.40° |
28.78° |
24.18° |
20.82° |
18.27° |
16.27° |
14.66° |
||
60° |
Miter |
26.57° |
19.96° |
16.10° |
13.54° |
11.70° |
10.31° |
9.23° |
|
Bevel |
37.76° |
30.60° |
25.66° |
22.07° |
19.35° |
17.23° |
15.52° |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
65° |
Miter |
22.91° |
17.07° |
13.71° |
11.50° |
9.93° |
8.74° |
7.82° |
|
Bevel |
39.86° |
32.19° |
26.95° |
23.16° |
20.29° |
18.06° |
16.26° |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
70° |
Miter |
18.88° |
13.95° |
11.17° |
9.35° |
8.06° |
7.10° |
6.34° |
|
Bevel |
41.64° |
33.53° |
28.02° |
24.06° |
21.08° |
18.75° |
16.88° |
||
75° |
Miter |
14.51° |
10.65° |
8.50° |
7.10° |
6.12° |
5.38° |
4.81° |
|
Bevel |
43.08° |
34.59° |
28.88° |
24.78° |
21.69° |
19.29° |
17.37° |
||
|
|||||||||
80° |
Miter |
9.85° |
7.19° |
5.73° |
4.78° |
4.11° |
3.62° |
3.23° |
|
Bevel |
44.14° |
35.37° |
29.50° |
25.30° |
22.14° |
19.68° |
17.72° |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
85° |
Miter |
4.98° |
3.62° |
2.88° |
2.40° |
2.07° |
1.82° |
1.62° |
|
Bevel |
44.78° |
35.84° |
29.87° |
25.61° |
22.41° |
19.92° |
17.93° |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
90° |
Miter |
0.00° |
0.00° |
0.00° |
0.00° |
0.00° |
0.00° |
0.00° |
|
Bevel |
45.00° |
36.00° |
30.00° |
25.71° |
22.50° |
20.00° |
18.00° |
||
MAINTENANCE
WARNING
To reduce the risk of injury, always unplug your tool before performing any maintenance. Never disassemble the tool or try to do any rewiring on the tool's electrical system. Contact a MILWAUKEE service facility for ALL repairs.
Maintaining Tools
Keep your tool in good repair by adopting a regular maintenance program. Before use, examine the general condition of your tool. Inspect guards, switches, tool cord set and extension cord for damage. Check for loose screws, misalignment, binding of moving parts, improper mounting, broken parts and any other condition that may affect its safe operation. If abnormal noise or vibration occurs, turn the tool off immediately and have the problem corrected before further use. Do not use a damaged tool. Tag damaged tools “DO NOT USE” until repaired (see “Repairs”).
Under normal conditions, re-lubrication is not necessary until the motor brushes need to be replaced. After six months to one year, depending on use, return your tool to the nearest MILWAUKEE service facility for the following:
•Lubrication
•Brush inspection and replacement
•Mechanical inspection and cleaning (gears, spindles, bearings, housing, etc.)
•Electrical inspection (switch, cord, armature, etc.)
•Testing to assure proper mechanical and electrical operation
WARNING
To reduce the risk of injury, electric shock and damage to the tool, never immerse your tool in liquid or allow a liquid to flow inside the tool.
Cleaning
Clean dust and debris from vents. Keep the tool handles clean, dry and free of oil or grease. Use only mild soap and a damp cloth to clean your tool since certain cleaning agents and solvents are harmful to plastics and other insulated parts. Some of these include: gasoline, turpentine, lacquer thinner, paint thinner, chlorinated cleaning solvents, ammonia and household detergents containing ammonia. Never use flammable or combustible solvents around tools.
Repairs
If your tool is damaged, return the entire tool to the nearest service center.
ACCESSORIES
WARNING
To reduce the risk of injury, always unplug the tool before attaching or removing accessories. Use only specifically recommended accessories. Others may be hazardous.
For a complete listing of accessories refer to your MILWAUKEE Electric Tool catalog or go on-line to www.milwaukeetool.com. To obtain a catalog, contact your local distributor or a service center.
18 |
19 |
 Loading...
Loading...