Page 1

GESTRA
GESTRA Steam Systems
NRG 16-42
Installation Instructions 810295-03
Level electrode NRG 16-42
1
Page 2

Contents
Page
Important Notes
Usage for the intended purpose ..............................................................................................................4
Safety note .............................................................................................................................................4
Danger ...................................................................................................................................................4
Attention .................................................................................................................................................4
ATEX (Atmosphère Explosible) .................................................................................................................4
Explanatory Notes
Scope of supply ...................................................................................................................................... 5
Description .............................................................................................................................................5
Function .................................................................................................................................................5
System components ...............................................................................................................................5
Design .................................................................................................................................................... 5
Technical data
NRG 16-42 .............................................................................................................................................
Corrosion resistance ............................................................................................................................... 7
Sizing .....................................................................................................................................................7
Name plate / marking .............................................................................................................................7
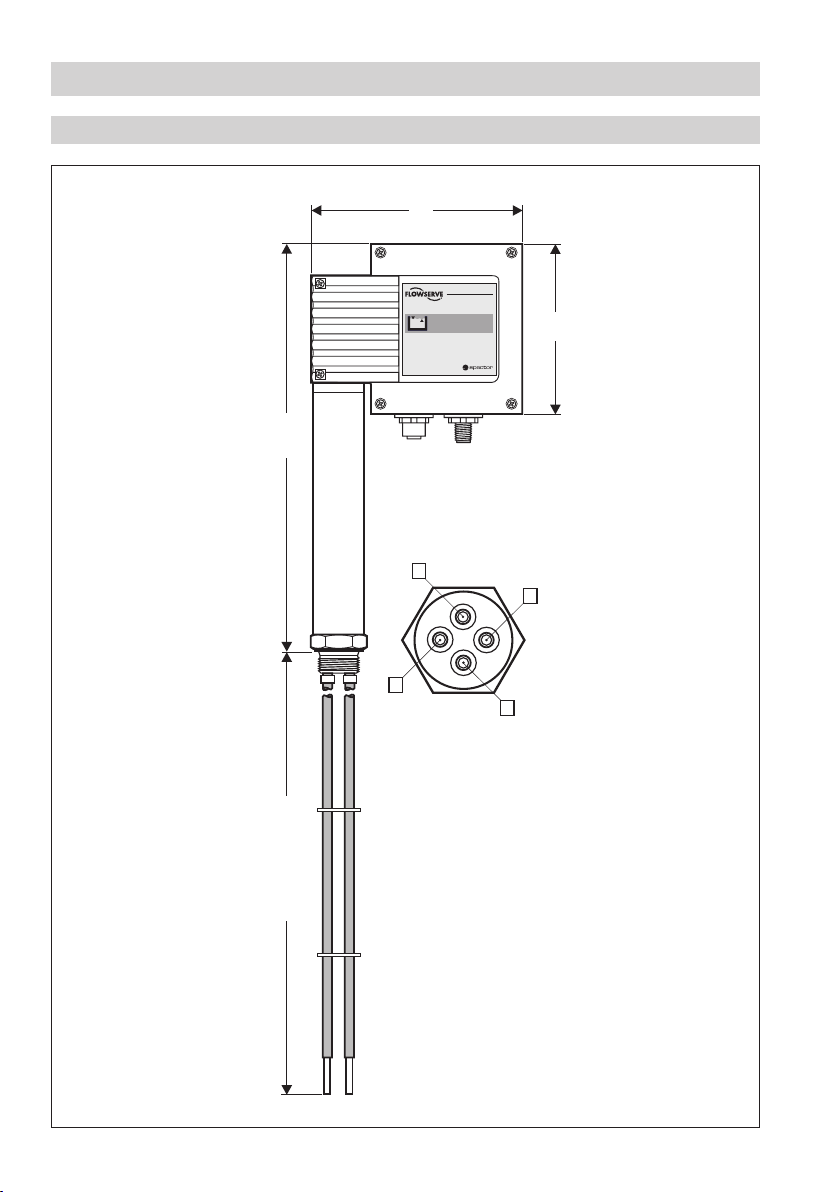
Dimensions NRG 16-42 ..........................................................................................................................
Design
NRG 16-42 .............................................................................................................................................9
Key .......................................................................................................................................................11
Functional Elements
NRG 16-42 ...........................................................................................................................................10
Key .......................................................................................................................................................11
Installation
NRG 16-42 ...........................................................................................................................................12
Attention ...............................................................................................................................................12
Note .....................................................................................................................................................12
Tools .....................................................................................................................................................12
Examples of installation NRG 16-42 ..................................................................................................... 13
Key .......................................................................................................................................................14
6
8
2
Page 3

Contents continued
Page
Wiring
NRG 16-42 ...........................................................................................................................................15
Aligning terminal box ............................................................................................................................ 15
Note .....................................................................................................................................................15
Wiring diagram ..................................................................................................................................... 16
Attention ...............................................................................................................................................17
Tools .....................................................................................................................................................17
Basic Settings
CAN Bus ...............................................................................................................................................18
Node ID ................................................................................................................................................18
Attention ...............................................................................................................................................18
Factory setting ......................................................................................................................................18
Factory set default node IDs .................................................................................................................. 19
Assigning / changing node ID ................................................................................................................ 19
Attention ...............................................................................................................................................19
Code switch settings for node ID / baud rate .........................................................................................20
Commissioning
Check wiring ........................................................................................................................................21
Apply mains voltage..............................................................................................................................21
Operation
Level electrode with CAN bus................................................................................................................21
Note .....................................................................................................................................................21
Malfunctions
Fault finding list for troubleshooting ................................................................................................ 21-22
Decommissioning
Danger .................................................................................................................................................23
Disposal................................................................................................................................................23
Annex
Declaration of conformity ......................................................................................................................23
3
Page 4

Important Notes
Usage for the intended purpose
Use level electrode NRG 16-42 only in conjunction with level switch NRS 1-42.
Safety note
The equipment must only be installed and commissioned by qualified and adequately trained
personnel.
Maintenance and retrofitting must only by performed by entrusted personnel who – through adequate
training – have achieved a recognised level of competence.
Danger
When loosening the electrode live steam or hot water might escape.
This presents the danger of severe scalding. It is therefore essential not to dismantle
the electrode unless the boiler pressure is verified to be zero.
The electrode is hot during operation. This presents the risk of severe burns to hands
and arms. Installation and maintenance work should only be carried out when the
system is cold.
If the internal ceramic insulation breaks, hot steam can escape through the lateral vent
hole on the electrode body. This presents the risk of severe scalding. Do not stay near
the electrode during operation.
Attention
The name plate indicates the technical specification on the equipment.
Do not commission or operate equipment without a name plate.
ATEX (Atmosphère Explosible)
According to the European Directive 94/9/EC the equipment must not be used in explosion-risk areas.
4
Page 5

Explanatory Notes
Scope of supply
NRG 16-42
1 Level electrode type NRG 16-42
1 Joint ring (of stainless steel 1.4301) D 33 x 39 to DIN 7603, bright annealed
1 Terminating resistor 120
1 Installation manual
Description
Ω
The level electrode NRG 16-42 works according to the conductivity measurement principle.
With the NRG 16-42 a maximum of 4 levels can be signalled in conductive liquids:
■4 levels with one switchpoint each.
■ High level (MAX) alarm, Low level (MIN) alarm, pump ON, pump OFF with one switchpoint each.
Use level electrode NRG 16-42 in combination with level switch type NRS 1-42 or further system
components. The level data are transferred to the level switch or another system component via
CAN data bus, using the CANopen protocol.
Function
The conductivity of the liquid is used to signal the liquid level. Some liquids are conductive, which
means that they allow an electric current to flow through them.
For the safe functioning of this device a minimum conductivity of the liquid to be measured is required.
The conductivity measurement method can detect two conditions: electrode rod submerged or
exposed, meaning switchpoint reached (or exceeded) or not yet reached. Before installation, the
length of the electrode rod must be cut to the required switching levels, e. g. for max./min. alarm,
controlling of a valve or pump.
At regular intervals the level electrode NRG 16-42 sends a data telegram to the level switch NRS 1-42.
The data are transferred via a CAN bus to DIN ISO 11898 using the CANopen protocol.
System components
NRS 1-42
Data exchange: CAN bus to DIN ISO 11898, using CANopen protocol.
URB 1, URB 2
Control terminal & display unit.
Functions: Parameterization and visual display (LCD).
Data exchange: CAN bus to DIN ISO 11898, using CANopen protocol.
Design
NRG 16-42:
Screwed design 1" BSP, EN ISO 228-1. Fig. 2
5
Page 6

Technical data
NRG 16-42
Type Approval Nº
TÜV · WR · 04-399
Max. service pressure
32 bar g at 238°C
Connections
Screwed 1" BSP, DIN ISO 228-1
Flanged DN 50, PN 40, DIN 2635
Materials
Case: Die cast aluminium 3.2161 (G AlSi8Cu3)
Stem: S. S. 1.4571 (X6CrNiMoTi17-12-2)
Measuring electrodes: S. S. 1.4401 (X5CrNiMo17-12-2)
Electrode insulation: PEEK
Spacer disc: PTFE
Lengths supplied
500 mm
1000 mm
1500 mm
Supply voltage
18 – 36 V DC
Current consumption
65 mA
Fuse
Thermal fuse T
= 85°C
max
Hysteresis
-2 K
Electrode voltage
10 V
ss
Data exchange
CAN bus to DIN ISO 11898, CANopen protocol
Indicators and adjustors
1 green LED “C
1 red LED “b
an bus CommuniCation”
us fault”
1 10-pole code switch for node ID and baud rate settings
Electric connection
M 12 sensor connector, 5 poles, A-coded,
M 12 sensor jack, 5 poles, A-coded
Protection
IP 65 to DIN EN 60529
Max. admissible ambient temperature
70 °C
Weight
approx. 2.5 kg
6
Page 7
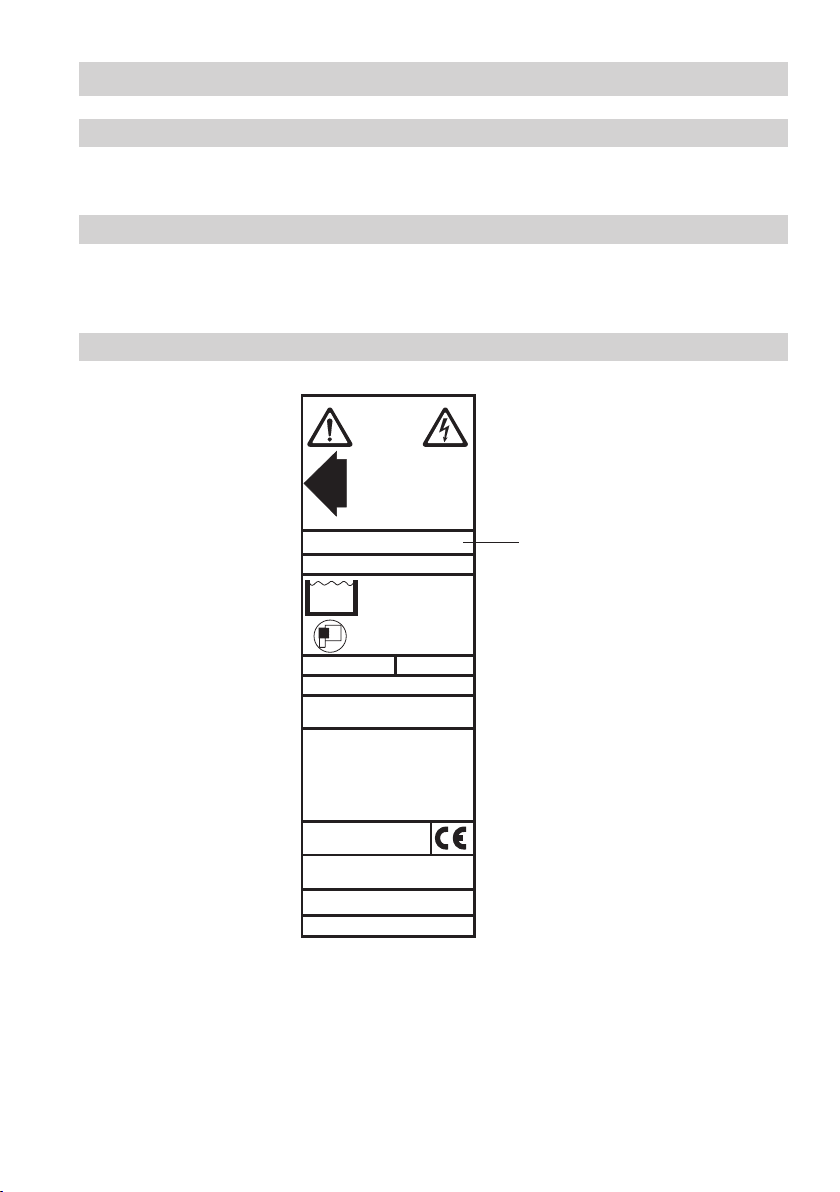
Technical Data continued
NRG 16-42
PN 40 G1 1.4571 IP 65
0,5 / 10µS/cm
Betriebsanleitung
beachten
See installation instructions
Voir instructions de
montage
32 bar ( 464 psi)
238 °C ( 453 °F)
Tmax = 70°C (133 °F)
Pmax
Tmax
IN/OUT: CAN-Bus
Münchener Str. 77,D-28215 Bremen
GB Reg. Design 2 053 113
US Pat. 5 719 342, 5 805 052,
Design 383 403
18-36 V DC
Node ID:__ __ __
TÜV.WR.99-399
GESTRA AG
SER Nr.:
Corrosion resistance
When used for its intended purpose the safe functioning of the electrode will not be impaired by
corrosion.
Sizing
The electrode body must not be subjected to sharp increases in pressure. Welds and flanges of the
electrode are designed to withstand dynamic loading (bending and alternating stress). The dimensional
allowances for corrosion reflect the latest state of technology.
Name plate / marking
Designation of
the equipment
Fig. 1
7
Page 8
4
3
GESTRAS teamSystems
GESTRA
NRG 16-42
4
3
1
2
Technical Data continued
Dimensions NRG 16-42
175
140
337.5
Depth: 70mm
500, 1000, 1500
Fig. 2
8
Page 9

Design
2
1
4
3
GESTRASt eamSystems
GESTRA
NRG 16-42
NRG 16-42
A
D
B
C
≥14
50
Fig. 3 Fig. 4
65-70
∅ 40
1" BSP, ISO 228-1
N 10
0.5
9
Page 10

Functional Elements
1
2
3
4
5
1 098765432
NO
MAX 70°C
MAX 95%
%
IP 65
GESTRA Steam Systems
GESTRA
NRG 16-42
NRG 16-42
MAX 70 °C
MAX 95 %
Fig. 5
M
E
Fig. 6
F
F
G
H
I
J
L K
10
Page 11

Design / Functional Elements continued
Key
A Thermal insulation, provided on site, d = 20 mm (outside of thermal insulation of the steam boiler)
B Seating surface
C Joint ring (of stainless steel 1.4301) D 33 x 39 to DIN 7603, bright annealed
D Electrode thread 1" BSP, EN ISO 228-1
E Housing screws M4
F M 12 sensor connector, 5 poles, A-coded
M 12 sensor jack, 5 poles, A-coded
G Housing cover
H 10-pole code switch (for setting node ID and baud rate)
I LED “Can bus CommuniCation” (flashes during data exchange), green
J LED “bus fault”, red
K Terminal strip
L PE connection
M Plug
11
Page 12

Installation
NRG 16-42
1. Determine required measuring lengths of electrode rods and enter data in table “Functions”.
2. Cut electrode rods , , and accordingly, Fig. 3
2
1
3. Deburr faces of electrode tips.
4. Strip off 50 mm of PTFE insulation from the ends of electrode tips.
5. Check seating surfaces of threads or flange provided on vessel or boiler standpipe, Fig. 4
6. Place joint ring
C onto seating surface B of electrode, Fig. 3. Use only joint ring
(of stainless steel 1.4301) D 33 x 39 to DIN 7603 supplied with electrode.
7. Apply a light smear of silicone grease (e. g. Molykote
8. Screw level electrode into threads or flange provided on vessel or boiler standpipe and tighten with a
41 mm open-end spanner. The torque required is 140 Nm
Function Function Electrode rod Length [mm]
e.g. High level alarm 1
e.g. Feed pump ON 2
e.g. Feed pump OFF 3
e.g. First low-level alarm 4
Attention
■ The seating surfaces of the threads or flange provided on the vessel or boiler standpipe
must be accurately machined. Fig. 4
■ Do not bend electrode rod when mounting.
■ Use only the supplied joint ring D 33x 39 (of stainless steel 1.4301) to DIN 7603.
■ Do not lag electrode body.
■ Do not insulate electrode thread with hemp or PTFE tape.
4
3
Please enter data.
®
111) to electrode thread D.
when cold.
Please enter data.
Note
■ For the approval of the boiler standpipe with connecting flange the relevant local and
national regulations must be considered.
■ See four examples of installation on page 13.
Tools
■ Open-end spanner 17 mm A. F.
■ Open-end spanner 41 mm A. F.
Molykote® 111 is a registered trademark of DOW Corning Corp., Midland Michigan, USA
■ Hacksaw
■ Flat file, medium cut
12
Page 13

12
Installation continued
9
Examples of installation NRG 16-42
1" BSP
DN 50
4
8
≤90°
∅20
Fig. 7
1" BSP ¾" BSP
1" BSP
1
2
∅ 20
3
20
≤1500
DN
50
4
5
6
8
≥10
9
0
∅20
≥10
≤90°
1
2
∅ 20
3
20
5
6
9
0
Fig. 8
1" BSP
1
1
2
DN 20
≥20
4
3
Fig. 9
≤1500
DN 100
24,5 24,5
∅20
20
4
> 40
≥10
≤90°
∅20
5
7
8
9
!
DN 20
Fig. 10
ME
5
9
DN 20
13
Page 14

Installation continued
Key
1 Flange PN 40, DN 50 (2"), DIN 2527
Flange PN 40, DN 100 (4"), DIN 2527
2 For the approval of the boiler standpipe with connecting flange the
relevant regulations must be considered.
3 Vent hole Provide vent hole as close as possible to the boiler wall.
4 High water (HW)
5 Electrode rod d = 5 mm
6 Protection tube DN 80
7 Protection tube DN 100
8 Electrode distance ≥ 14 mm
9 Low water (LW)
0 Reducer K-88.9 x 3.2 – 42.4 x 2.6 W to DIN 2616, part 2
! Reducer K-114.3 x 3.6 – 48.3 x 2.9 W to DIN 2616, part 2
14
Page 15

Wiring
NRG 16-42
Note that screened multi-core twisted-pair control cable is required, e. g. UNITRONIC®
BUS CAN 2 x 2 x ... mm2 or RE-2YCYV-fl 2 x 2 x ... mm2.
Prefabricated control cables (with connector and coupler) of various lengths for connecting the
equipment are available as accessories.
The baud rate (data transfer rate) dictates the cable length between the bus nodes and the total power
consumption of the sensor dictates the conductor size.
S 8 S 9 S 10 Baud rate Cable length
OFF ON OFF 250 kBit/s 125 m
Factory setting
ON ON OFF 125 kBit/s 250 m 2 x 2 x 0.5
OFF OFF ON 100 kBit/s 335 m 2 x 2 x 0.75
ON OFF ON 50 kBit/s 500 m
OFF ON ON 20 kBit/s 1000 m
ON ON ON 10 kBit/s 1000 m
Number of pairs
and conductor size [mm2]
2 x 2 x 0.34
on request, dependent on
bus configuration
The baud rate is set via a code switch. Reduce baud if cable is longer than specified in the table above.
Make sure that all bus nodes feature the same settings.
To protect the switching contacts fuse circuit with 2.5 A (anti-surge fuse) or according to TRD
regulations (1.0 A for 72 hrs operation).
When a max. cable length of more than 125 m (up to 1000 m) is desired, make sure to modify
the baud rate accordingly. Refer to pages 19 and 20 for more details.
Aligning terminal box
1. Unscrew screws E, remove housing cover G. Fig. 5
2. Loosen screw M with 17 mm spanner but do not remove. Fig. 6
The electrode terminal can be turned through +/– 180°.
3. Turn electrode terminal into desired direction (+/–180°).
4. Tighten plug
M with a torque of 25 Nm.
5. Set node ID (see “Basic Settings”, “Configure level electrode”).
6. Replace housing cover G and fasten screws E.
Note
■ Wire the control cable according to the wiring diagram with connector and coupler.
UNITRONIC® is a registered trademark of LAPP Kabelwerke GmbH, Stuttgart
15
Page 16

1
2
3
4
NRG 16-42
_
1
2
3
4
5
S
+
C
L
H
C
24V DC
CAN - Bus
S
1 098765432
NO
C
L
C
H
Wiring continued
5 5 5 555
+
-
LCH
C
S
Wiring diagram
Electrode rod
Electrode rod
Electrode rod
Electrode rod
Terminating resistor 120 Ω, paired cable.
3
2 1 5 46 3 4 1 52
Code switch
e.g. UNITRONIC® BUS CAN 2 x 2 x...
e.g. UNITRONIC® BUS CAN 2 x 2 x...
1 Screen
2 Voltage supply 24V DC+
3 Voltage supply 24V DC-
4 CAN Data line C
5 CAN Data line C
6 Terminating resistor 120 Ω
2
2
H
L
Controller
NRS ...
LRR ...
TRS ...
Operating
device URB 1
Coupler with terminating
resistor 120
Fig. 11
UNITRONIC® is a registered trademark of LAPP Kabelwerke GmbH, Stuttgart
Ω
CEP
Central
earthing
point
16
Level electrode
Conductivity electrode
NRG ...
LRG ...
Temperature transmitter
TRV ...
Connector with terminating
resistor 120
Ω
Page 17

Wiring continued
Attention
■ Wire equipment in series. Star-type wiring is not permitted!
■ Interlink screens of control cables such that electrical continuity is ensured and
connect them once to central earthing point (CEP).
■ In a CAN bus network the first and the last equipment must be provided with a
terminating resistor of 120
■ The CAN bus network mut not be interrupted while operating.
An interruption will result in high/low level alarm!
Tools
■ Screwdriver for cross head screws, size 1
■ Screwdriver for slotted screws, size 2.5, completely insulated according to VDE 0680
■ Open-end spanner 17 mm A. F.
Ω. Fig. 11
17
Page 18

Basic Settings
CAN bus
All level and conductivity controllers and associated electrodes are interconnected by means of a CAN
bus adopting the CANopen protocol. Every item of equipment features an electronic address (Node ID).
The four-core bus cable serves as power supply and data highway for high-speed data exchange.
The CAN address (Node ID) can be set between 1 and 123.
The NRG 16-42 is configured at our works and ready for service with other GESTRA system
components without having to set the node ID.
If several systems of the same kind are to communicate in one CAN bus network, be sure to
assign one node ID for each individual system component (e. g. controller). Refer to the
following pages for more details.
Node-ID
Reserved NRS 1-42 NRG 16-42
X - 1
Attention
The node IDs of the individual units have to be adjusted manually.
For more information refer to the respective installation manuals.
Factory setting
The level electrode features the following factory set default values:
■ Baud rate: 250 kB/s
■ Sensitivity: 10 µS/cm
■Node ID: 021
X X + 1
20 21 Factory setting
Reserved area
18
Page 19

1
2
3
4
5
1 098765432
NO
Basic Settings continued
NRS 1-40 ID: 001
NRS 1-40.1 ID: 001
NRS 1-41 ID: 006
NRS 1-42 ID: 020
NRS 2-40 ID: 039
NRR 2-40 ID: 040
LRR 1-40 ID: 050
NRG 16-40 ID: 002
NRG 16-40 ID: 003
NRG 16-41.1 ID: 004
TRV 5-40 ID: 005
NRG 16-41 ID: 007
NRG 16-42 ID: 021
NRG 26-40 ID: 041
LRG 16-40 ID: 051
Factory set default node IDs
Switching Controller Level Electrode
Assigning / changing node ID
If several systems of the same kind are to communicate in one CAN bus network, be sure to establish
one node ID for each individual system component (e. g. controller).
1. Undo screws
2. Change code switch
3. Re-attach housing cover
E and remove housing cover G.
H settings as required. For more information refer to page 20.
G and fix it with screws E.
Attention
■ Do not assign the same node ID twice within the CAN bus network.
Fig. 12
H
19
Page 20

1 098765432
NO
1 098765432
NO
Basic Settings continued
Code switch settings for node ID / baud rate
H H
▲
S1
OFFS2
OFFS4
OFFS6
OFFS7
Fig. 13 (Factory setting)
S8
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
OFF
Node ID
ON
ONS3
ONS5
S9 S0
OFFON
OFF
ON
ON
ON
1
2
4
8
16
32
64
Baud rate
250 kBit/s
125 kBit/s
100 kBit/s
ON 20 kBit/sONOFF 1000 m
ON 10 kBit/sONON 1000 m
Fig. 15 (Factory setting 250 kBit/s)
21
50 kBit/s
▲
S1
ON
ONS2
ONS3
OFFS4
OFFS5
OFFS6
ONS7
Fig. 14 (Example)
Length of cable
Node ID
125 m
250 m
335 m
500 m
71
1
2
4
8
16
32
64
20
Page 21

Commissioning
Check wiring
Check whether the level electrode NRG 16-42 and the associated level switch NRS 1-42 have been
wired according to the wiring diagram. Fig. 11
Apply mains voltage
Turn on the power for level switch NRS 1-42.
Operation
Level electrode with CAN bus
During operation the level switch detects the level electrode via CAN bus.
The communication via CAN bus is faultless – there are no fault messages.
Note
■
To analyse and eliminate malfunctions refer to “Fault finding list for troubleshooting” on
pages 21 - 22.
Malfunctions
Fault finding list for troubleshooting
Equipment fails to work – Indication of a malfunction
Fault: In spite of correct wiring and commissioning of the equipment an interference signal
is indicated.
Remedy: The interference signal is caused by H. F. interferences coming from the installation. For
interference suppression of the voltage supply we supply ferrite rings, stock code 147253.
The 230 V supply lines should be looped through the ferrite ring five to ten times.
If several controllers are used in the system, they can be fed from the interference
suppressed supply lines. For the interference suppression of the bus line we supply
hinged-shell ferrite rings, stock code 147254. The hinged-shell ferrite rings are clamped
onto the bus line close to the terminal strip of the controller.
21
Page 22

Malfunctions continued
Fault finding list for troubleshooting continued
The equipment fails to work – no function
Fault: LED “Power” does not light up.
Remedy: Apply mains voltage. Wire equipment according to the wiring diagram.
Fault: The thermal fuse has been triggered.
Remedy: The ambient temperature must not exceed 70°C.
Fault: The LED I does not light up. No data exchange.
Remedy: Check level switch NRS 1-42. Connect electode according to the wiring diagram.
Switchpoints reached / level below switchpoints – no function
Fault: The electric conductivity is too low.
Remedy: Set sensitivity of level switch NRS 1-42 to ≥ 0.5 µS/cm.
Fault: The electrode rods have earth contact.
Remedy: Change installation position.
Fault: The electrode housing does not have earth connection to the boiler.
Remedy: Clean seating surfaces and insert metal joint ring (of stainless steel 1.4301) 33 x 39 to
DIN 7603. Do not insulate compact system with hemp or PTFE tape!
Fault: The vent hole in the protection tube does not exist, is obstructed or flooded.
Remedy: Check protection tube and, if necessary, provide vent hole.
Fault: The isolating valves of the external measuring pot (optional) are closed.
Remedy: Open isolating valves.
Switchpoints reached / level below switchpoints – incorrect function
Fault: The switching function has not been correctly allocated. Electrode rods have been cut
to the wrong size.
Remedy: Identify electrode supply wire and reconnect the circuit board in the terminal box
accordingly.
Fault: The internal seal of the electrode rod is damaged.
Remedy: Replace level electrode.
If faults occur that are not listed above or cannot be corrected, please contact our service centre or
authorized agency in your country.
22
Page 23

Decommissioning
Danger
Risk of severe burns and scalds to the whole body!
Before removing the level electrode make sure that the vessel and the measuring pot are
depressurised (O bar) and cooled down to room temperature (20 °C).
Disposal
Remove the level electrode and separate the waste materials, using the material specifications as a
reference. Electronic components (circuit boards) must be disposed of properly.
For the disposal of the level electrode observe the pertinent legal regulations concerning waste disposal.
Annex
Declaration of conformity
We hereby declare that the equipment NRG 16-42 conforms to the following European guidelines:
■
LV guideline 73/23/eec version 93/68/eec
■
EMC guideline 89/336/eec version 93/68/eec
■ ATEX Directive 94/9/EC of 23 March 1994
This declaration is no longer valid if modifications are made to the equipment without consultation
with us.
Dipl.-Ing. Uwe Bledschun
(Academically qualified engineer)
Head of the Design Dept.
Bremen, 3rd January 2005
GESTRA AG
Dipl.-Ing. Lars Bohl
(Academically qualified engineer)
Quality Assurance Manager
23
Page 24

Agencies all over the world:
www.gestra.de
GESTRA
España
GESTRA ESPAÑOLA S.A.
Luis Cabrera, 86-88
E-28002 Madrid
Tel. 00 34 91 / 5 15 20 32
Fax 00 34 91 / 4 13 67 47; 5 15 20 36
E-mail: aromero@flowserve.com
Great Britain
Flowserve Flow Control (UK) Ltd.
Burrel Road, Haywards Heath
West Sussex RH 16 1TL
Tel. 00 44 14 44 / 31 44 00
Fax 00 44 14 44 / 31 45 57
E-mail: gestraukinfo@flowserve.com
Italia
Flowserve S.p.A.
Flow Control Division
Via Prealpi, 30
l-20032 Cormano (MI)
Tel. 00 39 02 / 66 32 51
Fax 00 39 02 / 66 32 55 60
E-mail: infoitaly@flowserve.com
Polska
GESTRA POLONIA Spolka z.o.o.
Ul. Schuberta 104
PL - 80-172 Gdansk
Tel. 00 48 58 / 3 06 10 -02 od 10
Fax 00 48 58 / 3 06 33 00
E-mail: gestra@gestra.pl
Portugal
Flowserve Portuguesa, Lda.
Av. Dr. Antunes Guimarães, 1159
Porto 4100-082
Tel. 0 03 51 22 / 6 19 87 70
Fax 0 03 51 22 / 6 10 75 75
E-mail: jtavares@flowserve.com
USA
Flowserve GESTRA U.S.
2341 Ampere Drive
Louisville, KY 40299
Tel.: 00 15 02 / 4 95 01 54, 4 95 17 88
Fax: 00 15 02 / 4 95 16 08
E-mail: dgoodwin@flowserve.com
GESTRA AG
P. O. Box 10 54 60, D-28054 Bremen
Münchener Str. 77, D-28215 Bremen
Telephone +49 (0) 421 35 03 - 0
Fax +49 (0) 421 35 03- 393
E-Mail gestra.ag@flowserve.com
Internet www.gestra.de
810295-03/206cm · © 1998 GESTRA AG · Bremen · Printed in Germany
24
 Loading...
Loading...