Page 1

s
-
FANUC Series 30*/300*/300*
FANUC Series 31*/310*/310*s-MODEL A5
FANUC Series 31*/310*/310*s-MODEL A
FANUC Series 32*/320*/320*s-MODEL A
MODEL A
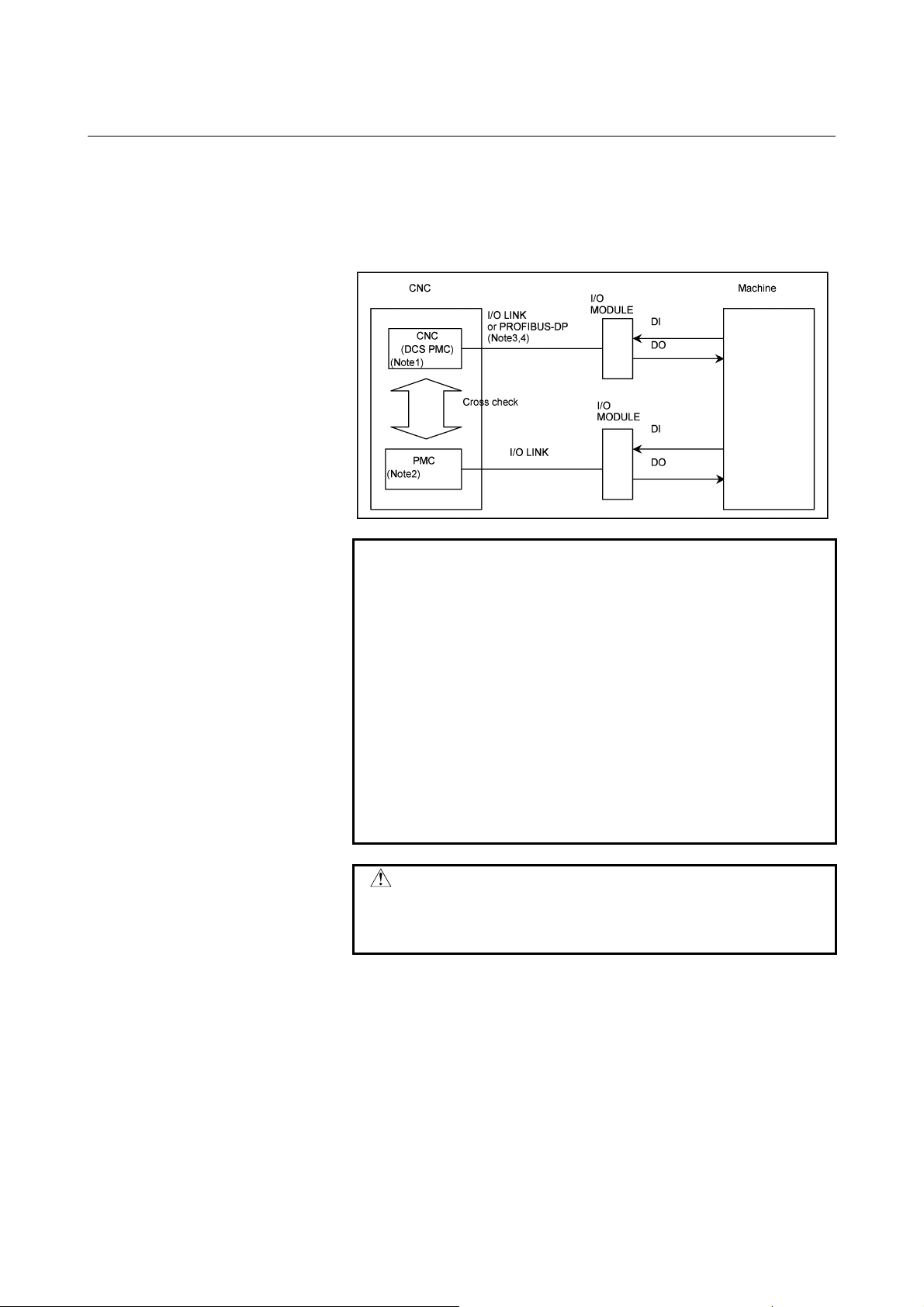
Dual Check Safety
OPERATOR’S MANUAL
B-64004EN/02
Page 2
• No part of this manual may be reproduced in any form.
• All specifications and designs are subject to change without notice.
The export of this product is subject to the authorization of the government of the country
from where the product is exported.
In this manual we have tried as much as possible to describe all the various matters.
However, we cannot describe all the matters which must not be done, or which cannot be
done, because there are so many possibilities.
Therefore, matters which are not especially described as possible in this manual should be
regarded as ”impossible”.
This manual contains the program names or device names of other companies, some of
which are registered trademarks of respective owners. However, these names are not
followed by or in the main body.
Page 3
B-64004EN/02 DEFINITION OF WARNING, CAUTION, AND NOTE
DEFINITION OF WARNING, CAUTION, AND NOTE
This manual includes safety precautions for protecting the user and
preventing damage to the machine. Precautions are classified into
Warning and Caution according to their bearing on safety. Also,
supplementary information is described as a Note. Read the Warning,
Caution, and Note thoroughly before attempting to use the machine.
WARNING
Applied when there is a danger of the user being
injured or when there is a danger of both the user
being injured and the equipment being damaged if
the approved procedure is not observed.
CAUTION
Applied when there is a danger of the equipment
being damaged, if the approved procedure is not
observed.
NOTE
The Note is used to indicate supplementary
information other than Warning and Caution.
• Read this manual carefully, and store it in a safe place.
s-1
Page 4

Page 5

B-64004EN/02 TABLE OF CONTENTS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
DEFINITION OF WARNING, CAUTION, AND NOTE .................................s-1
1 OVERVIEW .............................................................................................1
1.1 DIRECTIVE AND STANDARDS .................................................................... 3
1.1.1 Directives..................................................................................................................3
1.1.2 Related Safety Standards..........................................................................................3
1.1.3 Risk Analysis and Evaluation...................................................................................3
1.2 DEFINITION OF TERMS............................................................................... 4
1.2.1 General Definition of Terms ....................................................................................4
1.2.2 Definition of Terms Related to the Safety Function ................................................4
1.3 BASIC PRINCIPLE OF DUAL CHECK SAFETY ........................................... 5
1.3.1 Features of Dual Check Safety .................................................................................5
1.3.2 Compliance with the Safety Standard (EN954-1, Category 3) ................................5
1.3.2.1 Latent error detection and cross-check .................................................................................................. 7
1.3.2.2 Safety monitoring cycle and cross-check cycle ..................................................................................... 7
1.3.2.3 Error analysis.......................................................................................................................................... 8
1.3.2.4 Remaining risks...................................................................................................................................... 8
1.4 GENERAL INFORMATION ......................................................................... 10
2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION................................................................. 12
3 SAFETY FUNCTIONS...........................................................................14
3.1 APPLICATION RANGE ............................................................................... 15
3.2 BEFORE USING THE SAFETY FUNCTION ............................................... 17
3.2.1 Important Items to Check Before Using the Safety Function ................................17
3.2.2 MCC off Test of the Safe Stop Function................................................................17
3.3 STOP........................................................................................................... 18
3.3.1 Stopping the Spindle Motor ...................................................................................18
3.3.2 Stopping the Servo Motor ......................................................................................18
3.3.3 Stop States ..............................................................................................................19
3.4 SAFE-RELATED I/O SIGNAL MONITORING ............................................. 20
3.5 EMERGENCY STOP................................................................................... 29
3.6 SAFE SPEED MONITORING ...................................................................... 30
3.7 SAFE MACHINE POSITION MONITORING ............................................... 32
3.8 MCC OFF TEST .......................................................................................... 34
3.9 SAFETY POSITION SWITCH FUNCTION .................................................. 35
3.10 SAFETY RELATED PARAMETERS CHECK FUNCTION........................... 37
c-1
Page 6

TABLE OF CONTENTS B-64004EN/02
3.11 PARAMETER LOCK FUNCTION ................................................................ 37
3.12 SEFETY POSITION ERROR MONITORING FUNCTION ........................... 38
3.13 AMPLIFIER CIRCUIT MONITORING FUNCTION....................................... 39
3.14 SAFETY BRAKE SIGNAL OUTPUT FUNCTION ........................................ 40
3.15 CPU SELF TEST FUNCTION...................................................................... 41
3.16 RAM CHECK FUNCTION............................................................................ 42
3.17 CRC CHECK FUNCTION ............................................................................ 42
3.18 SAFE STOP MONITORING ........................................................................ 43
4 INSTALLATION .................................................................................... 44
4.1 OVERALL CONNECTION DIAGRAM ......................................................... 45
5 I/O SIGNALS ......................................................................................... 47
5.1 OVERVIEW ................................................................................................. 48
5.2 SIGNAL ADDRESS ..................................................................................... 49
5.3 SIGNALS ..................................................................................................... 53
5.4 GENERAL PURPOSE I/O SIGNAL ............................................................. 71
5.5 NOTE ON MULTI PATH CONTROL............................................................ 72
5.5.1 Machine Group And Multi Path Control................................................................72
6 PARAMETERS...................................................................................... 74
6.1 OVERVIEW ................................................................................................. 75
6.2 DATA TYPE................................................................................................. 76
6.3 REPRESENTATION OF PARAMETERS .................................................... 77
6.4 STANDARD PARAMETER STTING TABLES ............................................. 78
6.5 PARAMETERS ............................................................................................ 80
6.6 PROFIBUS-DP PARAMETER SETTINGS ................................................ 107
7 START-UP........................................................................................... 109
7.1 START-UP OPERATION........................................................................... 110
7.1.1 Acceptance test and report for safety functions ...................................................110
7.2 START-UP OF THE SAFETY FUNCTION ................................................ 112
7.2.1 Initial start-up .......................................................................................................112
7.2.2 Series start-up .......................................................................................................114
7.2.3 Troubleshooting ...................................................................................................114
8 ALARM MESSAGE.............................................................................115
9 DIAGNOSIS......................................................................................... 123
9.1 MCC OFF TEST STATUS SCREEN ......................................................... 124
9.2 CROSS CHECK DATA SCREEN .............................................................. 125
c-2
Page 7

B-64004EN/02 TABLE OF CONTENTS
9.3 FLOW MONITORING SCREEN ................................................................ 128
9.4 FEED LIMIT MONITORING SCREEN....................................................... 129
9.5 SAFE MACHINE POSITIONING MONITORING SCREEN ....................... 131
9.6 SAFETY POSITION ERROR MONITORING SCREEN............................. 132
10 SAMPLE SYSTEM CONFIGURATION............................................... 133
10.1 SAMPLE CONFIGURATION ..................................................................... 134
10.2 SAMPLE CONNECTIONS......................................................................... 135
10.2.1 Emergency Stop Signal (*ESP)............................................................................135
10.2.2 Guard Open Request Signal (ORQ) .....................................................................136
10.2.3 Test Mode Signal (OPT) ......................................................................................136
10.2.4 Guard Open Inhibit Signal (*OPIHB), Monitoring Result Signal (RSVx,RSPx),
Safety check Request Signal (*VLDVx,*VLDPs)...............................................137
10.2.5 MCC Off Signal (*MCF,*MCFVx,*MCFPs,*DCALM), MCC Contact State
Signal (*SMC)......................................................................................................139
11 COMPONENTS LIST .......................................................................... 140
11.1 HARDWARE COMPONENTS ................................................................... 141
11.1.1 Hardware Components for Series 30i/300i/300is-MODEL A .............................141
11.1.2 Hardware Components for Other Units................................................................141
11.2 SOFTWARE COMPONENTS.................................................................... 144
11.3 SERVO AMPLIFIER .................................................................................. 145
APPENDIX
A Directives, Standards and Technical Conditions for 3rd Party
Servo / Spindle Motors & Encoders when Applying FANUC /
GE Fanuc Dual-check Safety ............................................................ 153
A.1 GENERAL ................................................................................................. 154
A.2 MANDATORY STANDARDS AND DIRECTIVES ...................................... 155
A.3 SPINDLES ................................................................................................. 157
A.3.1 Spindle Motors – Driven by FANUC / GE Fanuc Spindle Amplifier..................157
A.3.2 Spindle Encoder – Speed / Position Feedback Sensor Embedded in Motor ........157
A.4 SERVO ...................................................................................................... 158
A.4.1 Servo Motors – Driven by FANUC / GE Fanuc Servo Amplifier .......................158
A.4.2 Servo Encoder – Speed / Position Feedback Sensor Embedded in
Motor ....................................................................................................................158
A.4.2.1 Encoder with FANUC / GE Fanuc Serial Interface........................................................................... 158
A.4.2.2 A/B-Phase Sine-wave Interface Connected to FANUC / GE Fanuc Interpolation Circuit............... 158
c-3
Page 8

Page 9

B-64004EN/02 1.OVERVIEW
1 OVERVIEW
Setup for machining, which includes attaching and detaching a
workpiece to be machined, and moving it to the machining start point
while viewing it, is performed with the protection door opened. The
dual check safety function provides a means for ensuring a high level
of safety with the protection door opened.
The simplest method of ensuring safety when the protection door is
open is to shut off power to the motor drive circuit by configuring a
safety circuit with a safety relay module. In this case, however, no
movements can be made on a move axis (rotation axis). Moreover,
since the power is shut off, some time is required before machining
can be restarted. This drawback can be corrected by adding a motor
speed detector to ensure safety. However, the addition of an external
detector may pose a response problem, and the use of many safety
relay modules results in a large and complicated power magnetic
cabinet circuit.
With the dual check safety function, two independent CPUs built into
the CNC monitor the speed and position of motors in dual mode. An
error in speed and position is detected at high speed, and power to the
motor is shut off via two independent paths. Processing and data
related to safety is cross-checked by two CPUs. To prevent failures
from being built up, a safety-related hardware and software test must
be conducted at certain intervals time.
The dual check safety system need not have an external detector added.
Instead, only a detector built into a servo motor or spindle motor is
used. This configuration can be implemented only when those
motors, detectors built into motors, and amplifiers that are specified
by FANUC are used. When an abnormality related to safety occurs,
the dual check safety function stops operation safely.
The dual check safety function ensures safety with the power turned
on, so that an operator can open the protection door to work without
turning off the power. A major feature of the dual check safety
function is that the required time is very short from the detection of an
abnormality until the power is shut off. A cost advantage of the dual
check safety function is that external detectors and safety relays can
be eliminated or simplified.
If a position or speed mismatch is detected by a cross-check using two
CPUs, the safety function of the Dual Check Safety works the power
to be shut off (MCC off) to the motor drive circuit.
- 1 -
Page 10

1.OVERVIEW B-64004EN/02
IMPORTANT
The dual check safety function cannot monitor the
stop state of the motors.
- 2 -
Page 11
B-64004EN/02 1.OVERVIEW
1.1 DIRECTIVE AND STANDARDS
1.1.1 Directives
Machine tools and their components must satisfy the EC directives
listed below.
The FANUC CNC systems with the dual check safety function are
compatible with all of these directives.
Directive
Directive 98/37/EC 1998 Safety of machinery
Directive 89/336/EEC 1989 Electromagnetic compatibility
Directive 73/23/EEC 1973 Low Voltage Equipment
1.1.2 Related Safety Standards
To be compatible with the directives, especially the machine directive,
the international standards and European standards need to be
observed.
Important safety standards
EN292-1 1991 Safety of machinery - Basic concepts, general principles for design – Part 1:
Basic terminology, methodology
EN292-2 1991 Safety of machinery - Basic concepts, general principles for design – Part 2:
Technical principles and specifications
EN954-1 1996 Safety of machinery - Safety-related parts of control systems –
Part 1: General principles for design
EN1050 1996 Safety of machinery - Principles for risk assessment
EN60204-1
1997
DIN V VDE0801 (1990) including
amendment A1(1994)
1.1.3 Risk Analysis and Evaluation
Safety of machinery - Electrical equipment of machines
Part 1: General requirements
Principles for computers in safety- related systems
According to the machine directive, the manufacturer of a machine or
machine components and a responsible person who supplies a
machine or machine components to the market must conduct risk
evaluation to identify all risks that can arise in connection with the
machine or machine components. Based on such risk analysis and
evaluation, a machine and machine components must be designed and
manufactured. Risk evaluation must reveal all remaining risks and
must be documented.
- 3 -
Page 12
1.OVERVIEW B-64004EN/02
1.2 DEFINITION OF TERMS
1.2.1 General Definition of Terms
Reliability and safety
Reliability and safety are defined by EN292-1 as follows:
Term Definition
Reliability Capability of a machine, machine component, or equipment to
perform its required function under a specified condition for a
specified period
Safety Capability of a machine to perform its function without injuring
the health under a condition of use for an intended purpose
specified in the operator's manual and allow its transportation,
installation, adjustment, maintenance, disassembly, and
disposal
1.2.2 Definition of Terms Related to the Safety Function
Safety-related I/O signal
Safety-related I/O signals are input/output signals monitored by two
systems. These signals are valid for each feed axis and spindle with
a built-in safety function, and are used with each monitoring system.
Example: Protection door state signal
Safety stop
When a safety stop occurs, power to the drive section is shut off.
The drive section can generate neither a torque nor dangerous
operation. The following are measures for incorporating the safety
stop feature:
Contactor between the line and drive system (line contactor)
Contactor between the power section and drive motor (motor
contactor)
If an external force is applied (such as a force applied onto a vertical
axis), an additional measure (such as a mechanical brake) must be
securely implemented to protect against such a force.
Safety limitation speed
When the drive system has reached a specified limitation speed, a
transition is made to the safe stop state.
A measure must be implemented to prevent a set limitation speed from
being changed by an unauthorized person.
Safety machine position
When the drive system has reached a specified positional limit, a
transition is made to the safety stop state. When a positional limit is
set, a maximum move distance traveled until a stop occurs must be
considered. A measure must be implemented to prevent a set
positional limit from being changed by an unauthorized person.
- 4 -
Page 13
B-64004EN/02 1.OVERVIEW
1.3 BASIC PRINCIPLE OF DUAL CHECK SAFETY
1.3.1 Features of Dual Check Safety
Dual Check Safety function has the following features.
- Two-channel configuration with two or more independent CPUs
- Cross-check function for detecting latent errors
Detection
A servo motor detector signal is sent via the servo amplifier and is
applied to the CNC through the FSSB interface. Then, it is fed to
two CPUs: a CNC CPU and a Servo CPU.
A spindle motor detector signal is sent via the spindle amplifier and is
applied to the CNC connected through the serial interface. Then, it is
fed to two CPUs: a CNC CPU and a CPU built into the spindle
amplifier.
The safety related signal such as guard signal is sent via the
independent I/O unit and is applied to the CNC through the I/O link
interface. Then, it is fed to two CPUs: a CNC CPU and a PMC CPU.
Evaluation
The safety function is monitored independently by a CNC CPU and
servo CPU or by a CNC CPU and spindle CPU. Each CPU
cross-checks data and results at certain intervals.
Response
If the monitoring function detects an error, the CNC CPU and the
servo/spindle CPU switch off the MCC via independent paths to shut
off the power to the feed axis and spindle.
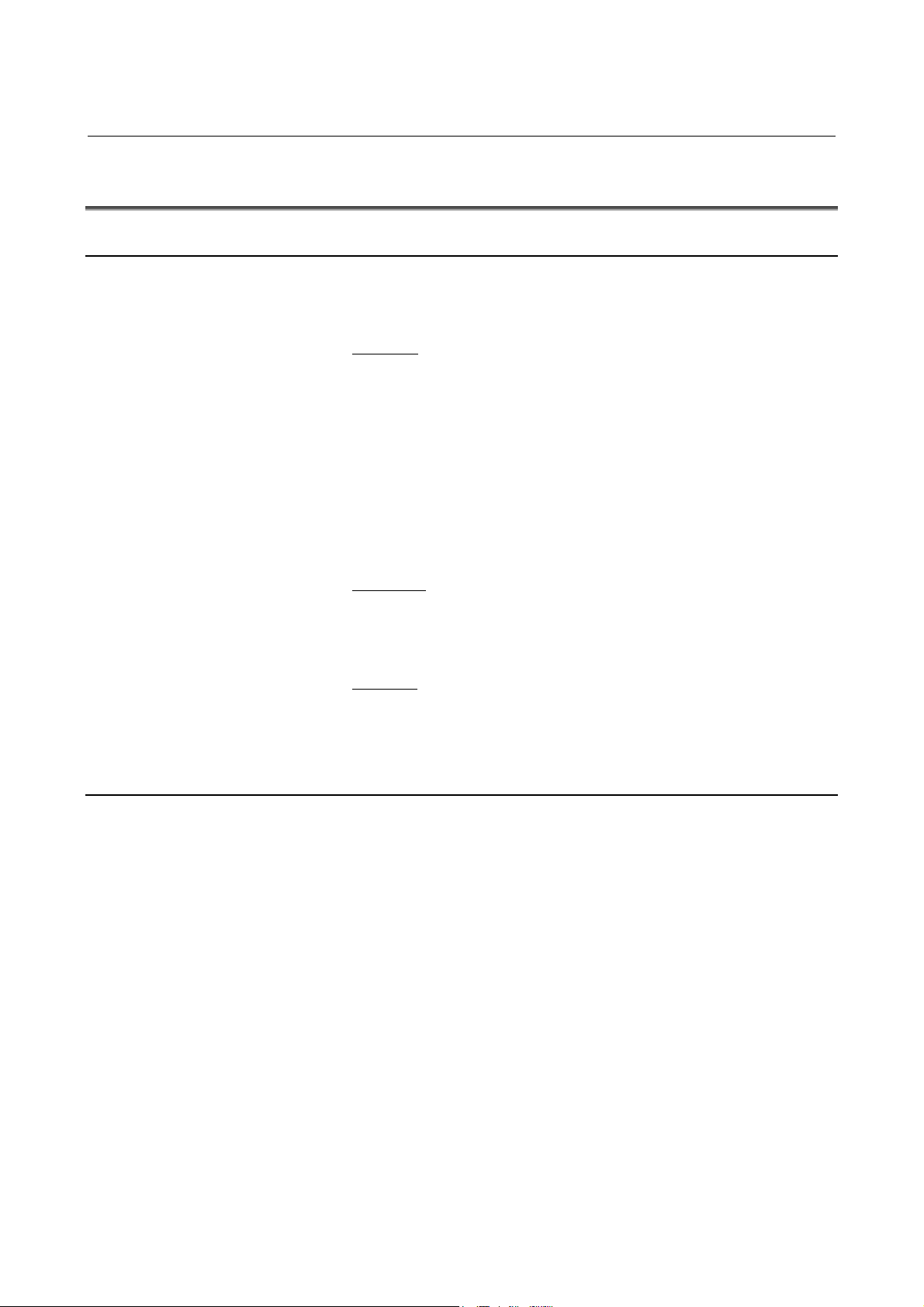
1.3.2 Compliance with the Safety Standard (EN954-1, Category 3)
The dual check safety function satisfies the requirements of Category
3 of the safety standard EN954-1.
Category 3 requires the following:
- The safety function of a safety-related portion must not degrade
- Single errors must be detected at all times when natural
To satisfy these requirements, the dual check safety function is
implemented using the two-channel configuration shown below.
when a single failure occurs.
execution is possible.
- 5 -
Page 14
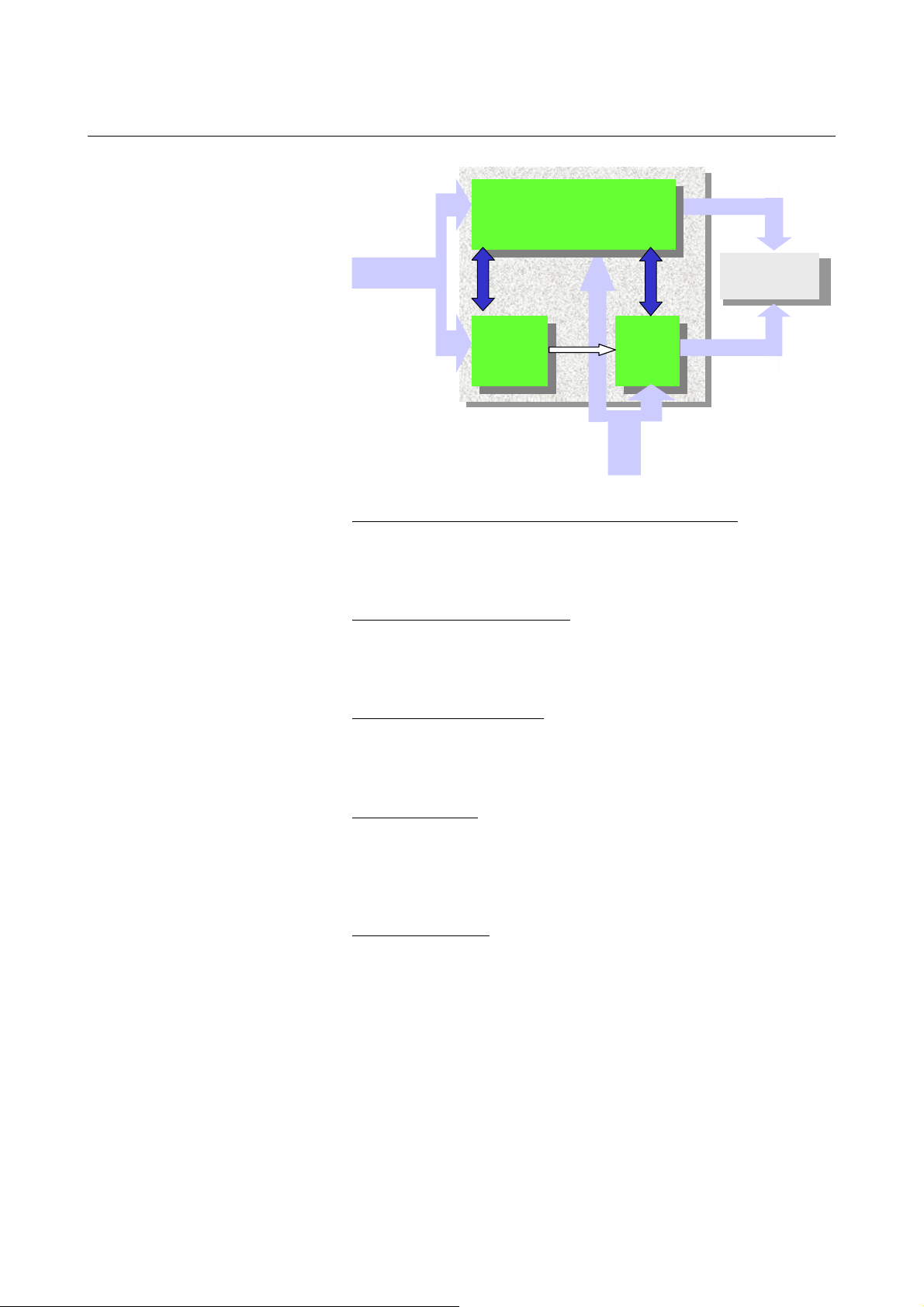
1.OVERVIEW B-64004EN/02
Shut off power
Magnetic
contactor
Shut off power
Motor detector
signal
Cross-check
of data and
results
Servo
Spindle
CPU
CNCCNC
CPU
CPU
Door switch signal
PMC
CPU
Monitoring of servo motor and spindle motor movement
Data output from the detector built into each motor is transferred to
the CNC through the amplifier. The safety of this path is ensured by
using motors and amplifiers specified by FANUC.
Cross-monitoring using 2 CPUs
Two CPUs built into the CNC are used to cross-monitor the safety
function. Each CPU is periodically checked for errors. If one
system fails, the servo system and spindle can be stopped safely.
Power shutoff via two paths
If an error is detected, the power is shut off via two power shutoff
paths. The paths need to be tested for built-up failures within a
certain time.
Input signal safety
Safety-related input signals such as the protection door lock/unlock
signal are monitored doubly. If a mismatch between the two
occurrences of a signal is detected, the power to the motor drive
circuit is shut off. This cross-check is constantly made.
Output signal safety
A signal is output (via two paths) to the relay used to shut off the
power to the motor drive circuit. An error is detected by a MCC off
Test. For detection of built-up failures, a MCC off Test needs to be
conducted at certain intervals. This MCC off Test is not mandatory
when machining is performed with the protection door closed. (The
MCC off Test should be performed, before the protection door is open
after the certain intervals.)
- 6 -
Page 15
B-64004EN/02 1.OVERVIEW
1.3.2.1 Latent error detection and cross-check
Detection of latent errors
This detection function can detect latent software and hardware errors
in a system that has a two-channel configuration. So, the
safety-related portions of the two channels need to be tested at least
once within an allowable period of time for latent errors.
An error in one monitoring channel causes a mismatch of results, so
that a cross-check detects the error.
CAUTION
Forced detection of a latent error on the MCC
shutoff path must be performed by the user
through a MCC off Test (after power-on and at
intervals of a specified time (within normally 24
hours)). When the system is operating in the
automatic mode (when the protection door is
closed), this detection processing is not requested
as mandatory. But, before the protection door
opens after the specified time, the detection
processing is required mandatory. If this has not
been performed, lock for the protection door should
not be released.
Cross-check
A latent safety-related error associated with two-channel monitoring
can be detected as a result of cross-checking.
For numeric data, an allowable difference between the two channels is
set in a parameter. (For example, an allowable cross-checked
difference is set for the actual position.)
NOTE
An error detected as the result of forced latent
error detection or cross-checking leads to a safety
stop state. (See Chapter 3.3.3).
1.3.2.2 Safety monitoring cycle and cross-check cycle
The safety function is subject to periodical monitoring in a monitoring
cycle.
The following functions are monitored at every 8ms.
- Safe speed monitoring (servomotor)
- Safe machine position monitoring (servomotor)
- Safe position error monitoring (servomotor)
The cross-check cycle represents a cycle at which all I/O data subject
to cross-checking is compared.
Cross-check cycle: 8 ms
- 7 -
Page 16

1.OVERVIEW B-64004EN/02
1.3.2.3 Error analysis
Error analysis
The table below indicates the results of system error analysis
controlled by the dual check safety function.
Error analysis when the protection door is open
Error Cause Action
Excessive speed
for Spindle axis
Excessive speed
for feed axis
Feed axis safety
machine position
error
Input/output signal
error
Amplifier or control unit failure,
operation error, etc.
Amplifier or control unit failure,
operation error, etc.
Amplifier or control unit failure,
operation error, etc.
Wiring error, control unit failure, etc. Safe-related I/O signal monitoring
Safety limitation speed monitoring function
EN60204-1 Category 1/0 stop
Safety limitation speed monitoring function
EN60204-1 Category 1/0 stop
Safety machine position monitoring
function
EN60204-1 Category 1/0 stop
function
EN60204-1 Category 1/0 stop
Error analysis when the protection door is closed
Error Cause Action
Input/output signal
error
Wiring error, control unit failure, etc. Safe-related I/O signal monitoring function
EN60204-1 Category 1/0 stop
1.3.2.4 Remaining risks
The machine tool builder is to make a failure analysis in connection
with the control system and determine the remaining risks of the
machine.
The dual check safety system has the following remaining risks:
a) The safety function is not active until the control system and
drive system have fully powered up. The safety function cannot
be activated if any one of the components of the control or drive
is not powered on.
b) Interchanged phases of motor connections, reversal in the signal
of encoder and reversal mounting of encoder can cause an
increase in the spindle speed or acceleration of axis motion. If
abnormal speed detected, system controlled to brake to zero
speed, but no effective for above error. MCC off is not activated
until the delay time set by parameter has expired. Electrical faults
(component failure etc.) may also result in the response described
above.
c) Faults in the absolute encoder can cause incorrect operation of
the safety machine position monitoring function.
d) With a 1-encoder system, encoder faults are detected in a single
channel, but by various HW and SW monitoring functions. The
parameter related to encoder must be set carefully. Depending on
the error type, a category 0 or category 1 stop function according
to EN60204-1 is activated.
- 8 -
Page 17

B-64004EN/02 1.OVERVIEW
e) The simultaneous failure of two power transistors in the inverter
may cause the axis to briefly (motion depend on number of pole
pairs of motor)
Example:
An 8-pole synchronous motor can cause the axis to move by
a maximum of 45 degrees. With a lead-screw that is directly
driven by, e.g.16mm per revolution, this corresponds to a
maximum linear motion of approximately 2.0mm.
f) When a limit value is violated, the speed may exceed the set
value briefly or the axis/spindle overshoot the set point position
to a greater or lesser degree during the period between error
detection and system reaction depending on the dynamic
response of the drive and the parameter settings (see Section
Safety-Functions)
g) The category 0 stop function according to EN60204-1 (defined
as STOP A in Safety Integrated) means that the spindles/axes are
not braked to zero speed, but coast to a stop (this may take a very
long time depending on the level of kinetic energy involved).
This must be noted, for example, when the protective door
locking mechanism is opened.
h) Amplifiers (drive power modules) and motors must always be
replaced by the same equipment type or else the parameters will
no longer match the actual configuration and cause Dual check
Safety to respond incorrectly.
i) Dual check Safety is not capable of detecting errors in
parameterization and programming made by the machine tool
builder. The required level of safety can only be assured by
thorough and careful acceptance.
j) There is a parameter that MCC off test is not to be made in the
self test mode at power-on as in the case of machine adjustment.
This parameter is protected, only changed by authorized person.
IF MCC off test is not conducted, MCC may not be off at stop
response is measured.
k) Safety machine position monitoring function does not apply to
the spindle axis.
l) During machine adjustment, an exact motion may be executed
incorrectly until the safety functions setup correctly and confirm
test is completely.
m) Before the reference point return is performed and the MCC off
test is performed, it may be dangerous because the correct
operation does not be guaranteed. So, the careful operations are
required when the machine is operated in the status that the
protection door opens.
n) The delay timer is prepared for the cross-checking of the safety
related input/output signals. When the inconsistency exists
between the signal from the 2 paths, system will recognize this
failure, after this time is passed. The system will start the
sequence of MCC shut-off, when this time is passed after the
inconsistency is detected.
- 9 -
Page 18

1.OVERVIEW B-64004EN/02
1.4 GENERAL INFORMATION
The following requirements must be fulfilled for the Dual-Check
System:
- All conditions of the certification report have to be respected.
- The procedures for the changes in the System (either HW or SW)
should be referred to maintenance manual (B-63945EN). When
safety related components are exchanged, confirmation test
regarding safety functions can be performed according to
Chapter 8.
- Programming in ladder logic should be referred to PMC
programming manual (B-63983EN).
Training
FANUC Training Center provides versatile training course for the
person who is concerned with hardware installation, maintenance and
operation. FANUC recommend studying and learning in the training
center how efficiently operate FANUC products.
There are 3 CNC training course.
[ CNC ELEMENTARY COURSE ]
Provides basics of CNC functions, operation and programming. The
course is recommended before taking more specialized training
courses to gain best effects.
MAIN ITEMS OF TRAINING
- CNC functions
- Configuration of CNC
- Configuration and function of servo system
- Basic programming of CNC
- Part programming of milling machine
- Part programming of turning machine
- Introduction of Custom Macro function
[ CNC MAINTENANCE COURSE ]
To master maintenance technique that permits you to maintain and
inspect CNC, also how to restore it promptly if a trouble should occur.
MAIN ITEMS OF TRAINING
- Function and configuration of Power Unit
- Function and configuration of CNC system
- include AC servo and AC spindle
- Self-diagnosis function
- Interface between CNC and the machine tools
- Data saving and restoring operation
- Trouble shooting
- 10 -
Page 19

B-64004EN/02 1.OVERVIEW
[ CNC SE INTERFACE COURSE ]
Training course offered to the engineers who design CNC machine
tools or CNC application system for the first time. This course is also
suitable for customers who provide to retrofitting, to develop an
original CNC machine tools or new application of CNC.
MAIN ITEMS OF TRAINING
- Configuration of CNC system
- Interface between CNC and machine tools
- Ladder programming of machine control sequence
- Setting of parameter related to machine
- Setting of parameter related to servo and spindle
More information and course registration
Yamanakako-mura, Yamanashi Prefecture : 401-0501, JAPAN
Phone : 81-555-84-6030
Fax : 81-555-84-5540
Internet:
www.fanuc.co.jp/eschool
- 11 -
Page 20

2.SYSTEM CONFIGURATION B-64004EN/02
2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
The dual check safety function has the following components.
Applicable CNC
FANUC Series 30i/300is/300i
FANUC Series 31i/310is/310i A5
FANUC Series 31i/310is/310i
FANUC Series 32i/320is/320i
Number of controlled axes
- Series 30i/300is/300i : 32 maximum
- Series 31i/310is/310i A5 : 20 maximum
- Series 31i/310is/310i : 20 maximum
- Series 32i/320is/320i : 9 maximum
Number of spindle controlled axes
- Series 30i/300is/300i : 8 maximum
- Series 31i/310is/310i A5 : 6 maximum
- Series 31i/310is/310i : 6 maximum
- Series 32i/320is/320i : 2 maximum
Amplifier
- α series servo amplifier
- α series spindle amplifier
- α series power supply module
- αi series servo amplifier
- βi series servo amplifier
- αi series spindle amplifier
- αi series power supply module
Motor
- α series servo motor
- α series spindle motor
- β series servo motor
- αi series servo motor
- αi series spindle motor
- αis series servo motor
- βis series servo motor
- Lis series linear motor
I/O
- I/O unit (I/O Link)
- 12 -
Page 21

B-64004EN/02 2.SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
Software
- Dual check safety software option
DETECTOR SYSTEM
The detectors below can be used.
Feed axis detector
-Pulsecoder αA1000, αA64,
- αA16000i, αA1000i, αI1000i, αA64i
- βA64B, βA32B
- βI64B, βI32B
- Separate type detector (A quard B)
Spindle detector
- M sensor
- MZ sensor
- BZ sensor
- Mi sensor
- MZi sensor
- BZi sensor
- CZi sensor
High Resolution Serial output circuit
- 13 -
Page 22

3.SAFETY FUNCTIONS B-64004EN/02
3 SAFETY FUNCTIONS
- 14 -
Page 23
B-64004EN/02 3.SAFETY FUNCTIONS
3.1 APPLICATION RANGE
The dual check safety function assumes the following configuration:
A) At least, one protective door is provided.
B) If protective door is closed, safety is assured.
When the operator makes a request to open the protective door, the
safety functions are enabled, and the protective door can be unlocked.
While the protective door is open, the active safety functions assure
safety. When the request to open the protective door is canceled, the
protective door is locked, and the safety functions are disabled.
The dual check safety function provides these safety functions while
the protective door is open, as described above. Some of the safety
functions continue working while the protective door is closed.
WARNING
Each machine tool builder should take measures to
assure safety while the protective door is closed
and to ensure safety related to a rotation axis and
travel axis. At the same time, safety measures for
the FANUC servo motor or spindle motor need to
be taken, while the door is open.
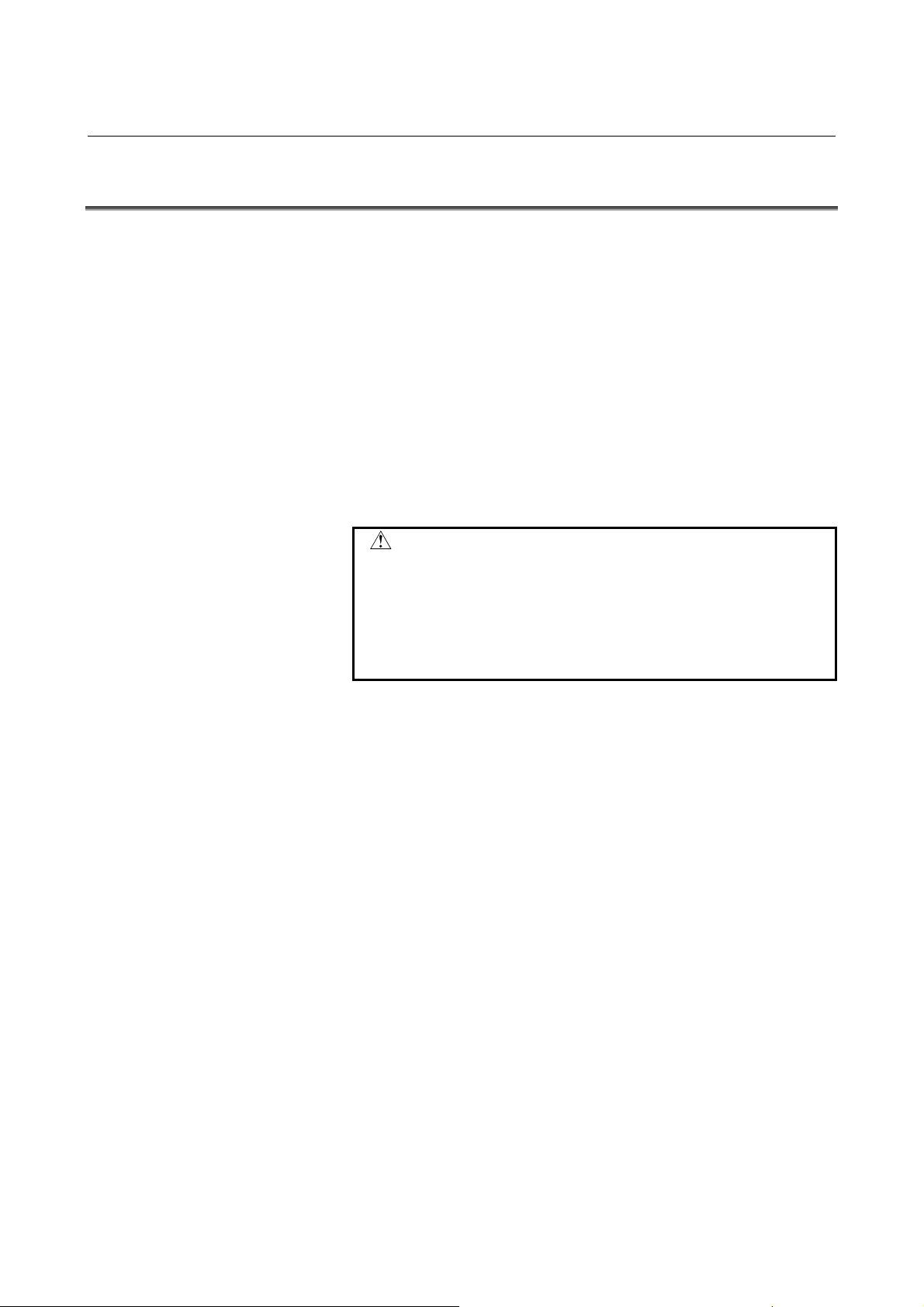
Safety function
The dual check safety function has the following safety functions:
• Safe-related I/O signal dual monitoring
Emergency stop input, protective door open/close state,
relay state for turning off the MCC
Output signal for shutting off the power (turning the MCC off)
To detect the latent cause of an abnormal state of this output, a
MCC off Test must be made.
• Spindle motor
Safe speed monitoring
• Servo motor
Safe speed monitoring
Safe machine position monitoring
Safe position error monitoring
- 15 -
Page 24
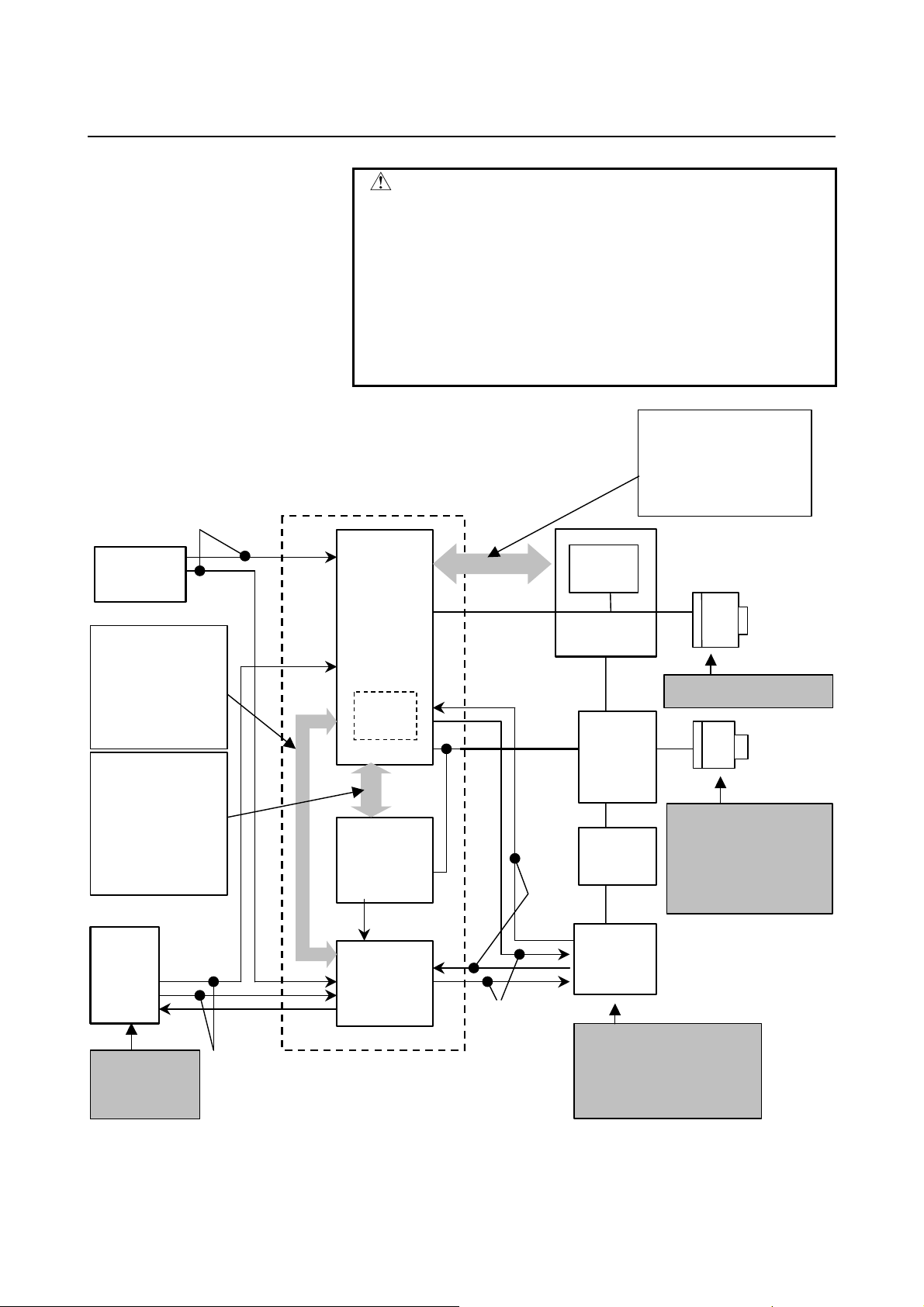
3.SAFETY FUNCTIONS B-64004EN/02
g
CAUTION
This safety function is enabled while the protective
door is open after a request to open the protective
door is made. If the request to open the protective
door is canceled and if the protective door is
closed, this safety function is disabled. The dual
input check of the safe-related I/O signal
monitoring function and the emergency stop
function are always active, regardless of whether
the protective door is opened or closed.
The CNC and the
spindle check the safe
speed of the spindle
motor in redundant
mode.
Dual monitoring of
ency stop signal
emer
CNC
Emergency
stop
Safety related
signal is checked
by the CNC(DCS
PMC) and the
PMC in redundant
mode
Safe speed of
servo motor and
machine position
are checked by
the CNC and the
Servo in
redundant mode
Protective
door
Door lock
open/close
monitoring
Protective door lock
signal
Dual monitoring of
protective door state
CNC
DCS
PMC
Cross
check
Servo
Power down direction
PMC
Cross
check
Power down
Spindle
Dual monitoring
of MCC
Dual monitoring of MCC
Dual power down
Detection of latent cause
of error by MCC off test
SPM
SVM
PSM
Power
down
(MCC)
Spi ndle
motor
Safe speed monitoring
Servo
motor
Safe speed monitoring.
Safe machine position
monitoring.
Safe position error
monitoring.
- 16 -
Page 25

B-64004EN/02 3.SAFETY FUNCTIONS
3.2 BEFORE USING THE SAFETY FUNCTION
3.2.1 Important Items to Check Before Using the Safety Function
When using the safety function for the first time upon assembly of the
machine, replacing a part, or changing a safety parameter (such as a
safe speed limit or safe range as described in Chapter 6), the user must
check that all safety parameters are correct and that all safety
functions are working normally. A return reference position must be
made on each axis. The user must also check the absolute position of
the machine. For details, see Chapter 7, “START UP.”
3.2.2 MCC off Test of the Safe Stop Function
An MCC off Test of the safe stop function monitors the contact state
of the electromagnetic contactor (MCC), compares the state with a
command to the electromagnetic contactor, and checks that the safe
stop function works normally. The user of the machine must carry out
the test. This test must be carried out when the CNC is turned on or
when 24 hours have elapsed after the previous test is completed. If the
CNC is turned on or if 24 hours have elapsed after the previous test is
completed, a guard open request (protective door open request) should
not be accepted until the test is performed. A machine tool builder
must make the ladder program to realize this sequence.
- 17 -
Page 26
3.SAFETY FUNCTIONS B-64004EN/02
3.3 STOP
3.3.1 Stopping the Spindle Motor
Because the spindle motor is an induction type motor, power-down
during rotation causes the motor to continue rotating for a certain
amount of time. From a safety standpoint, the motor may have to be
stopped immediately. If an error is detected and the spindle is judged
to be controlled, it is possible to stop spindle motor by the ladder
program. In case of emergency stop and abnormal condition of safety
related I/O, it is necessary to design the ladder program to shut off the
power after waiting the specified time elapses.
To speed down and stop the spindle, the PMC must input the spindle
Emergency Stop signals (*ESPA(G71.1), *ESPB(G75.1), and so on).
When this signal is input, the spindle slows down and stops. (A
Ladder program for inputting this signal in case of alarm must be
created.) The emergency stop input (connector CX4) of the PSM has
the same effect. If the Emergency Stop signal is connected to
emergency stop input (connector CX4) of the PSM, the spindle slows
down and stops in the emergency stop state. If the spindle does not
stop in spite of the stop command, the MCC is shut off.
If this processing is not performed, power-down causes the spindle
motor to continue rotating at the speed prior to power-down (and
eventually stopping in the end).
CAUTION
When the servo alarm related to the
communication error or position detector is caused,
MCC off signal corresponding to the spindle is
output. Shut off the MCC after executing
appropriate procedure such as spindle stop
operation. According to the setting value of the
parameter, MCC off signals of all axes, which
belong to the same path of the spindle that causes
an alarm, are output. Shut off the MCC after
executing appropriate procedure such as spindle
stop operation.
3.3.2 Stopping the Servo Motor
Because the servo motor is a synchronous motor, power-down results
in a dynamic brake stop. The dynamic brake stop is electric braking in
which the excited rotor is isolated from the power source and the
generated electric energy is used up in the winding. An internal
resistor provides additional braking. Unlike an induction motor, the
servo motor does not coast because of this function.
- 18 -
Page 27
B-64004EN/02 3.SAFETY FUNCTIONS
If the input of the Emergency Stop signal or an error of a safe-related
signal or speed monitoring is detected, the CNC automatically
specifies a command to zero the speed and reduces the speed to zero
(controlled stop). After the motor slows down and stops, the power is
turned off, and the motor is brought into the dynamic brake stop state.
To slow down and stop the motor, some parameters must be specified
in the CNC. If those parameters are not specified, the motor is
immediately brought into the dynamic brake stop state.
When abnormal state is detected in monitoring safety speed or so on, a
dynamic brake stop is made.
3.3.3 Stop States
The following stop states are possible.
Safe stop state
The power to the motor is shut off (MCC off state) in this state. If the
spindle motor can be controlled, the ladder program must shut off the
power after the spindle motor is slowed down to a stop. If the spindle
motor cannot be controlled, the power is immediately shut off.
If the servo motor can be controlled, the motor is slowed down to a
stop and then brought into the dynamic brake stop state. If the motor
cannot be controlled, the motor is immediately brought into the
dynamic brake stop state.
If the power is shut off immediately, the spindle motor continues at
the same speed prior to the abnormal event and eventually comes to a
stop. If the spindle motor can be slowed down to a stop, the operation
is performed as instructed by the PMC and then the power is shut off.
Controlled stop state
The power to the motor is not shut off. The servo motor and the
spindle motor are controlled to stop.
In the controlled stop state of either motor, the safety function is
active if the condition for enabling the safety function is satisfied (the
door is open). If a further abnormal event occurs, the motor is brought
into the safe stop state by the ladder program.
WARNING
1 The machine tool builder must design the machine
so that the machine is kept in the stop state if the
power to the servo motor driving circuit is shut off.
Example) Brake mechanism that would not drop
the vertical axis after the power is shut off
2 If the power to the spindle motor driving circuit is
shut off, the spindle motor continues rotating at the
speed before the power-down and eventually
comes to a stop. A measure must be taken so that
this coasting does not affect safety.
- 19 -
Page 28
3.SAFETY FUNCTIONS B-64004EN/02
3.4 SAFE-RELATED I/O SIGNAL MONITORING
A set of safe-related I/O signals are connected to the two channels of
the I/O respectively. As for safe-related I/O signals, a pair of signals
are prepared and connected to each I/O through different paths. The
two independent CPUs individually check the input signals. If a
mismatch between two corresponding signals is found, the system
enters the safe stop state. The following safe-related I/O signals are
monitored or output in redundant mode:
• Emergency stop input signal
• Protective door state input signal (Request to monitor for each
axis)
• Input signal for selecting safety speed monitoring and safety
position monitoring
• Input signal for monitoring the MCC contact state
• Output signal for turning off the MCC (power-down)
• Output signal for position switch
• Output signal for brake control
• User defined safe-related I/O signals
In order to setup double monitoring system, machine tool builder must
connect safety signals to both I/O Link #1, #2 and I/O Link#3, #4,
Profibus-DP.
IMPORTANT
If the safety input signals, except for Emergency
Stop input signals, are connected to the I/O
module, a Ladder program must be created to
establish a one-to-one relationship between the
actual input (X) and the input to the CNC (G).
The duplicated input/output signals are always checked for a
mismatch, regardless of whether the safety function is active or not.
When a signal state changes, the pair of signals may not match for
some period because of a difference in response. The dual check
safety function checks whether a mismatch between the two signals
continues for a certain period of time, so that an error resulting from
the difference in response can be avoided. The check period must be
specified as a safety parameter.
Parameter number Name
1945 Safe-related input/output signal check timer
The following signals are not defined as safe-related I/O signals and
are not duplicated. The signals, however, are necessary for the system.
- Input signal for making a protective door open request
- Input signal for starting the test mode
- Output signal for requesting a MCC off Test
- 20 -
Page 29
B-64004EN/02 3.SAFETY FUNCTIONS
This section briefly describes the signals. For details, see Chapter
5, “OPERATION.” For specific connections, see the sample
system configuration in Chapter 10.
NOTE
1 Dual Check Safety PMC (DCS PMC)
2 First path PMC, Second path PMC, Third path
PMC
Please refer to “FANUC Series
30i/300i/300is-MODEL A PMC
PROGRAMMING MANUAL (B-63983EN)”
3 When I/O Link and PROFIBUS-DP are connected
to DCS PMC at the same time, the X/Y signals
cannot be allocated to PROFIBUS-DP.
4 Please activate “Broken wire detection” of the
slave, which connect with PROFIBUS network as
Safety-related I/O. As for detail, please refer to
“6.6. PROFIBUS-DP parameter settings”.
CAUTION
Ladder functional instruction MOVB, MOVD and
MOVW cannot be used with ladder for Dual Check
Safety PMC. Use MOVN instead of them.
- 21 -
Page 30
3.SAFETY FUNCTIONS B-64004EN/02
I/O related with Dual Check Safety Function
PMC(n=path(0-9)) DCS PMC (m=path(0-9) x20)
Symbol Signal name I/O address
1 *ESP Emergency Stop signal <X008#4,0,1> (PMC)
<X008#4,0,1>(DCS PMC)
2 *SGOPN Guard State signal Machine side signal Dual input
*VLDVx Safety Check Request signal
3
*VLDPs Safety Check Request signal
SVAn/
SVBn
4
SPAn/
SPBn
5 *SMC MCC Contact State signal <Gn748#6>(PMC)
*DCALM MCC Off signal
*MCF MCC Off signal
6
*MCFVx MCC Off signal
*MCFPs MCC Off signal
7 BRKx Safety Brake signal <Fn754#0-#7>(PMC)
8 SPS Safety Position Switch signal <Fn755-Fn758>(PMC)
9
10 ORQ Guard Open Request signal <Gn191#3>(PMC) Input
11 OPT Test Mode signal <Fn191#2>(PMC) Input
12 *OPIHB Guard Open Inhibit signal <Fn191#0>(PMC)
13
14 RQT MCC Off Test Execution
15 POSEx Position Information Effect
Programmable Safety I/O
RSVx Monitoring result signal (Servo) <Fn750#0-#7>(PMC)
RSPs Monitoring result signal
Safety Speed / Safety Position
Selection signal (Servo)
Safety Speed Selection signal
(for each machine group)
(Servo)
(Spindle)
(Spindle)
(for all system)
(for each servo axis)
(for each spindle)
signals
(Spindle)
Request signal
signal
<Gn750#0-#7> (PMC)
<G(002+m)#0-#7>(DCS PMC)
<Gn751#0-#3>(PMC)
<G(003+m)#0-#3>(DCS PMC )
<Gn752/Gn753>(PMC)
<G(004+m)/G(005+m)>(DCS PMC)
<Gn754>(PMC)
<G(006+m)>(DCS PMC)
<G(000+m)#6>(DCS PMC)
<F0748#7>(PMC)
<F000#7>(DCS PMC)
<Fn748#1>(PMC)
<F(000+m)#1>(DCS PMC)
<Fn752#0-#7>(PMC)
<F(004+m)#0-#7>(DCS PMC)
<Fn753#0-#3>(PMC)
<F(005+m)#0-#3>(DCS PMC)
<F(006+m)#0-#7>(DCS PMC)
<F(007+m)-F(010+m)>(DCS PMC)
<F(019+m)#0>(DCS PMC)
<F(002+m)#0-#7>(DCS PMC)
<Fn751#0-#3>(PMC)
<F(003+m)#0-#3>(DCS PMC)
<Fn191#2>(PMC) Output
<Fn766#0-#7>(PMC)
<F(018+m)#0-#7>(DCS PMC)
Dual input
monitoring
Dual input
monitoring
Dual input
monitoring
Dual input
monitoring
Dual input
monitoring
Dual input
monitoring
Dual output
Dual output
Dual output
Dual output
Dual output
Dual output
Dual input
monitoring
Dual output
Dual output
Dual output
Dual output
Dual output
Safe-related I/O
1. *ESP Emergency Stop signal (input)
This signal is Emergency Stop signal and is monitored in redundant
mode.
The signal is connected to the *ESP input of the servo amplifier as
well.
- 22 -
Page 31

B-64004EN/02 3.SAFETY FUNCTIONS
2. *SGOPN Guard State signal (Machine side input signal)
The signal is provided for double monitoring of the protective door
state. The signal is connected so that it is normally set to 1 while the
protective door is closed and locked (door closed) and set to 0
otherwise (door opened). These states are implemented by the
combination of the safety door and safety relays. The PMC ladder for
safety check must check the state of axes by asserting the Safety
Request signal, when a protective door is open.
3. *VLDVx, *VLDPs Safety Check Request signal (input)
These signals are monitored in redundant mode. These signals request
safety check when a protective door is open. These signals are
prepared for each axis and each spindle.
CNC monitors these signals. If safe speed range of a servo motor is
exceeded in the door open state, the system enters the controlled stop
state. If an axis is still not stopped, the system enters the safe stop
state.
If safe speed range of a spindle motor is exceeded in the door open
state, the spindle motor enters free run state. If the spindle motor is not
decelerated, the system enters the safe stop state.
4. SVAx/SVBx,SPAs/SPBs Safety Speed / Safety Position Selection signal (input)
These signals are monitored in redundant mode. SVA/SVB are the
signals to select safety speed / safety position for each servo axis.
SPA/SPB are the signals to select safety speed for each spindle.
(The values of safety speed / safety position are given by the
parameters.)
5. *SMC MCC Contact State signal (input)
The MCC contact state is monitored in redundant mode. In normal
operation, the MCC is closed, therefore whether the contact of a relay
is in an abnormally closed state cannot be detected. In the test mode, it
can be detected whether the contact of relay is abnormally closed.
6. *DCALM, *MCF, *MCFVx, *MCFPs MCC Off signal (output)
With these signals, the MCC is shut off by 2 channels I/O when either
one of these signals state is “0”.
*DCALM is to allow turning off MCC of all system when I/O cross
check alarm or some problems of safety check function are found.
*MCF is to allow turning on MCC of each machine group according
to emergency stop or MCC off Test.
*MCFVx is to allow turning on MCC of each axis according to
monitor safety speed of servo axis or so on. *MCFPs is to allow
turning on MCC of each spindle according to the result of monitoring
safety speed of spindle.
These signals are assigned on both PMC and DCS PMC. Machine tool
builder must output the signal to shut off MCC when either one of
these signal is “0”.
7. BRKx Safety Brake signal (output)
These signals are output to control the brake of each servo axis.
- 23 -
Page 32

3.SAFETY FUNCTIONS B-64004EN/02
8. SPS1 to SPS32 (SPS33 to SPS64 in case of 2 or more path) Safety Position Switch
(output)
These signals show whether the machine position of each axis is
stayed within the range specified by the parameters or not.
9. Programmable Safety I/O signals (input/output)
The 8 bytes (64 bit) programmable safe I/Os can be freely defined as
the different address from the above basic safe signals. Each byte of 8
byte programmable safe I/Os can be assigned on either address of X/Y
or R or D by parameter. Each byte of the programmable safe I/O
between the PMC and DCS PMC is cross-checked by the CNC and
PMC. The combinations of cross-checking these signals are defined
by using Safety parameters as follows.
Signal type Combination No. DCS PMC PMC
input
output
1 No.11950 No.11970
2 No.11951 No.11971
3 No.11952 No.11972
4 No.11953 No.11973
5 No.11954 No.11974
6 No.11955 No.11975
7 No.11956 No.11976
8 No.11957 No.11977
1 No.11960 No.11980
2 No.11961 No.11981
3 No.11962 No.11982
4 No.11963 No.11983
5 No.11964 No.11984
6 No.11965 No.11985
7 No.11966 No.11986
8 No.11967 No.11987
Signals other than safe-related I/O
The following signals are not safe-related signals (are not checked in
redundant mode) but are important signals in the dual check safety
system. The machine tool builder must create an appropriate Ladder
program with these signals.
IMPORTANT
The error of ladder program cannot be checked by
safety function itself. Please make sure to check
safety function (see Chapter 7).
10. ORQ Guard Open Request signal (input)
When this signal is input, the CNC set the Guard Open Inhibit signal
(*OPIHB) to “1” (Guard open accept). The PMC ladder program of a
machine tool builder confirms the safety machine position and the
safety speed. If both machine position and speed are judged within
safe range according to the result of confirmation, the guard unlock
signal is set to 1 (guard unlock enabled). The machine tool builder
- 24 -
Page 33

B-64004EN/02 3.SAFETY FUNCTIONS
must provide an output signal that opens the actual protective door
through the PMC.
11. OPT Test Mode signal (input)
When the signal is input, a MCC off Test is executed. The MCC off
Test checks whether the contact of the MCC is abnormally closed.
When carrying out the MCC off Test manually, input this signal after
the preparation of a MCC off Test is completed by the PMC.
12. *OPIHB Guard Open Inhibit signal (output)
When the Guard Open Request signal (ORQ) is input, the CNC sets
this signal to “1”. The machine tool builder must design the PMC
ladder logic by this signal.
If this signal is set to “1”, the PMC confirms safety machine position
and safety speed. If the result of confirmation is judged safe, PMC
turns on the signal to release guard lock and outputs the signal to open
the actual protective door.
If the protective door is unlocked (*SGOPN becomes “0”) while the
signal is set to 0, PMC will notify alarm occurrence to an operator by
lighting a lamp or so on and bring the motor into the safe stop state.
NOTE
This signal is not output while MCC off Test is
carried out.
13. RSVx, RSPs Monitoring Result signal (output)
These signals show the result of monitoring safety machine position
and safety speed of each axis and the result of monitoring safety speed
of each spindle. When Guard Open Inhibit signal (*OPIHB) is set to
“1”, a machine tool builder can judge whether the machine is in the
safety state or not according to these signals. If safety is confirmed as
a result, turn on the signal to unlock the guard lock and output the
signal to open the actual protective door.
14. RQT MCC Off Test Execution Request signal (output)
If the execution of a MCC off Test is required, this signal is output. At
power-on, this signal is always output. If this signal is output, a MCC
off Test must be executed.
15. POSEx Position Informaion Effect signal (output)
This signal is output when Dual Check Safety Function is effective
and the reference point is established. When the reference point is not
established, the machine system is in danger state because Safety
Machine Position Monitoring and Safety Position Error Monitoring
are not active. If this signal is “0”, Machine Tool Builder has to
control not to open the protective door.
- 25 -
Page 34

3.SAFETY FUNCTIONS B-64004EN/02
Guard Open Request signal and Guard Unlock signal
Door open request
24V
X
ORQ-I
The figure shows a sample connection of the protective door open
request switch and the guard unlock signal. In the normal state, the
door lock state is changed as follows before the safety monitoring
state is established.
Ladder
CNC(PMC)
*OPIHB
RSVx
RSPx
POSEx
F
F
F
G
ORQ
Ladder
Y
Protective
door lock
Protective door
Door lock state transition
ORQ-I ORQ *OPIHB RSVx
RSPs
POSEx Protective
door lock
(*SGOPN)
A
0 0 0 Locked A protective door open request is
not made, and the door is
locked.
B
1 0 0 Locked A guard open request is made.
C1
1 1 0 Locked The request is transferred to the
CNC.
C2
1 1 1 Locked The CNC receives the request.
D
1 1 1 1 1 Locked Reference point is established
and a safe speed check, a
machine position check and a
position error check prove that
there is no failure and that the
CNC can enter the safe state.
E
1 1 1 1 1 Unlocked
(*SGOPN=0)
The actual safety door is
unlocked.
Operations can be performed
with the door open.
D
1 1 1 1 1 Locked The door is closed and locked
again.
F
0 1 1 1 1 Locked The guard open request is
canceled.
G
0 0 1 1 1 Locked The request is transferred to the
CNC.
A
0 0 0 Locked The CNC receives the request
and exits from the safe state.
Normal
operating
state
Safety
function is
enabled.
- 26 -
Page 35

B-64004EN/02 3.SAFETY FUNCTIONS
IMPORTANT
The PMC ladder must be designed to monitor
whether the protective door is open (*SGOPN is
set to 0) while ORQ is set to 0. If the door open is
detected, the PMC ladder judges that an abnormal
event has occurred and enters the safe stop state.
This can occur, for instance, when the door
happens to open (or to be unlocked) while
machining is in progress with the protective door
closed.
Timing diagram from door close state to door open state
The following diagram shows the timings at which the door is opened
and closed again.
ORQ_P
ORQ
*OPIHB
RSVx
RSPs
POSEx
Actual door unlock signal
*SGOPN
(Safety re lated
I/O signal)
Actual door unlock signal
Door closed
Door opened
(1) (2) (3) (4)
t
Door closed
(5)
(1) When the Guard Open Request signal (ORQ) is input, the CNC
returns the answer signal (*OPIHB) to PMC.
(2) The PMC ladder program checks that the machine position,
speed and position error are within safe ranges by the Monitoring
Result signal (RSVx/RSPs) and the reference point is established
by the Position Information Effect signal (POSEx). Then, it turns
on the guard unlock signal. This example assumes that the
protective door has an electromagnetic lock mechanism. While
the door is open, the unlock signal is turned off.
(3) The door is open.
(4) The protective door is closed and locked. After this, the Guard
Open Request signal (ORQ) must be turned off.
(5) When the Guard Open Request signal (ORQ) is turned off, the
CNC turned off the answer signal (*OPIHB).
- 27 -
Page 36

3.SAFETY FUNCTIONS B-64004EN/02
CAUTION
Ensure a time of 100 ms or longer (“t” in the figure)
from when the door is closed (locked) until the
Guard Open Request signal (ORQ) goes off. If this
time requirement is not satisfied, an alarm may be
raised when the door is closed (locked).
Design an operator panel to inform an operator
that Guard Open Request signal (ORQ) is turned
on by lighting a lamp.
- 28 -
Page 37

B-64004EN/02 3.SAFETY FUNCTIONS
3.5 EMERGENCY STOP
The Emergency Stop signal is monitored in redundant mode. When
the emergency stop is input, the servo motor slows down to a stop
(*see the below caution) and enters the dynamic brake stop. The
spindle slows down to a stop (*see the below caution) as instructed by
the PMC (Ladder program), and then the power is shut off.
CAUTION
To enable the function to slow down and stop the
servo motor, the corresponding parameter must be
specified. If the parameter is not specified, the
motor immediately enters the dynamic brake stop
state. The spindle motor slows down and stops as
instructed by the PMC (Ladder program). If the
PMC does not instruct this, the motor maintains the
high speed prior to the power-down and coasts. If
an illegal speed is specified because of a failure on
the PMC side while the safety function is active
(the protective door is open), the CNC enters the
safe stop state.
WARNING
In the emergency stop state, the processing to
open or close the protective door depends on the
Ladder program created by the machine tool
builder. For instance, if the protective door should
not be opened in the emergency stop state, a
Ladder program of the processing must be
created.
IMPORTANT
Emergency Stop Button must fulfill the Standard
IEC60947-5-1. This is mandatory.
- 29 -
Page 38

3.SAFETY FUNCTIONS B-64004EN/02
3.6 SAFE SPEED MONITORING
If the safe speed range is exceeded while the protective door is open,
the dual check safety function immediately enters the stop state. If
each axis or spindle is not stopped, the dual check safety function
enters the safety stop state. For each feed axis and spindle, up to four
safe speed ranges can be specified in safety parameters.
Both the CNC and the SV/SP monitor whether a safe speed is kept on
each feed axis and spindle. Limit speed can be changed by the Safety
Speed / Safety Position Selection signals (SVAn/SVBn for feed axis,
SPAn/SPBn for spindle).
Safety Speed/Safety
Name
Safety speed 1 0 0 No.13821 No.4372
Safety speed 2 1 0 No.13822 No.4438
Safety speed 3 0 1 No.13823 No.4440
Safety speed4 1 1 No.13824 No.4442
Position Selection signal
SVAn/
SPAn
SVBn/
SPBn
When excess limit error is detected, Monitoring Result signal
(RSVx/RSPs) is set to “0”. In this situation, if Safety Check Request
signal (*VLDVx/ *VLDPs) is “0” and safety monitor is executed, an
alarm is generated.
Error detected CPU Alarm
CNC SV0494/SP0757
SV SV0476
SP SP9069(SPINDLE ALARM 69)
CAUTION
1 When an illegal speed is detected for the servo
axis, if the axis is not stopped after the time
specified in the parameter, the MCC Off signal
(*MCFVx) is turned to “0”.
2 When an illegal speed is detected for the spindle
axis, CNC checks whether the spindle speed
decelerates continuously or not. If acceleration is
detected, the MCC Off signal (*MCFPs) is turned
to “0”.
Safety speed parameter
Feedaxis Spindle
- 30 -
Page 39

B-64004EN/02 3.SAFETY FUNCTIONS
IMPORTANT
1 A gear ratio, ball screw, and the like must be
carefully selected so that a safe speed can be kept
on the feed axis.
2 Before inputting the Guard Open Request signal
(ORQ), reduce each axial speed and spindle speed
to a safe speed range or below. If a speed exceeds
the limit, do not unlock the protective door. The
PMC ladder must be designed that the power to
the driving circuit is shut off (safe stop state) if the
door is forced open.
WARNING
The safe speed monitoring function monitors
whether the traveling speed exceeds a specified
limit. The function cannot monitor the stop state
(zero speed). If an error causes a movement on
the feed axis at a speed lower than the safe speed
range while the protective door is open, for
instance, the function cannot detect this state. The
machine must be designed so that this state does
not affect the safety of the machine system.
- 31 -
Page 40

3.SAFETY FUNCTIONS B-64004EN/02
3.7 SAFE MACHINE POSITION MONITORING
While the door is open, the dual check safety function checks whether
the position on each feed axis is within the safe machine position
range defined by safety parameters. If it detects a machine position
beyond the safety range, the dual check safety function immediately
enters the stop state. If each axis is not stopped, the dual check safety
function enters the safety stop state.
For each feed axis, up to four safe positions can be specified in safety
parameters.
Both the CNC and the Servo monitor whether each axis is within the
safety position. The range of the safety machine position can be
changed by the Safety Speed / Safety Position Selection signals
(SVAn/SVBn for feed axis).
Safety Speed/Safety
Name
Safety machine
position 1
Safety machine
position 2
Safety machine
position 3
Safety machine
position 4
Position Selection signal
SVAn SVBn + direction - direction
0 0 No.13831 No.13832
1 0 No.13833 No.13834
0 1 No.13835 No.13836
1 1 No.13837 No.13838
When “out of position error” is detected, Monitoring Result signal
(RSVx) is set to “0”. In this situation, if Safety Check Request signal
(*VLDVx) is “0” and safety monitor is executed, an alarm is
generated.
Error detected CPU Alarm
CNC SV0495
SV SV0477
CAUTION
1 The safe machine position monitoring function
does not keep monitoring the specified range. Only
after the function detects that a position on a feed
axis exceeds the range, the system enters the stop
state. Accordingly, in the stop state, an over travel
has occurred on the feed axis. The travel distance
depends on the traveling speed and other
conditions.
2 When an “out of position error” is detected, if the
axis is not stopped after the time specified in the
parameter, the MCC Off signal (*MCFVx) is turned
to “0”.
Safety machine position
parameter
- 32 -
Page 41

B-64004EN/02 3.SAFETY FUNCTIONS
The user of the machine must first carry out a reference position return
in order to obtain the initial position. If the reference position return is
not carried out, the check function is disabled. This check function is
enabled after the reference position is established. (The function
cannot be disabled by any means after the reference position is
established.) A safe machine position limit on each feed axis is
specified in a safety parameter.
CAUTION
A machine operator must confirm whether the
machine reference position is established correctly
by checking the actual machine position and
position display of the CNC.
At power-on, the safety function does not work. After power-on, the
CNC checks whether a reference position return is completed. If the
reference position return is completed and if the protective door is
open, safe machine position monitoring, safe speed monitoring and
safety position error monitoring are performed. Then, the safety
functions start working. If the reference position return is not
completed, safe machine position monitoring cannot be performed
because the coordinates are not established. In this state, the machine
position monitoring function is disabled. After a reference position
return is made, this function is enabled. Depending on the safety
parameter setting, however, an alarm may be raised. To avoid this
alarm, specify the safe machine position parameters before making a
reference position return.
CAUTION
1 The machine coordinate of the safety function is
based on position feed back. So it does not always
indicate the same value as the machine coordinate
based on the summation of the command value.
2 This function is activated only in position control
mode. This function is not activated in torque
control mode.
- 33 -
Page 42

3.SAFETY FUNCTIONS B-64004EN/02
3.8 MCC OFF TEST
A MCC off Test must be carried out in intervals of 24 hours, so that
the safety functions would not be damaged by a possible cause of
failure. A message telling that the MCC off Test must be carried out is
displayed at power-on or when 24 hours have elapsed after the
previous MCC off Test. The machine tool builder must set up the
machine not to open the protective door before a MCC off Test is not
completed.
The protective door can be opened only after the MCC off Test is
carried out accordingly.
A MCC off Test performs the test to turn on and off MCC by
controlling *SMC signal in order to confirm whether the circuit to
shut off MCC is normal. The MCC off Test is performed both on
PMC and DCS PMC. If the MCC off Test is not completed within the
time specified by the parameter No.1946 (MCC off Test timer), servo
alarm SV0488 is generated. It is necessary to carry out the MCC off
Test before the protective door is open, when power is on or 24 hours
have elapsed after previous MCC off Test.
The PMC ladder program must be designed to carry out the following
control.
<1> When MCC off Test request signal (RQT) is set to “1” at
power-on or in case 24 hours are elapsed after the previous MCC
off Test, the protective door is locked till the MCC off Test is
performed. But the operator can operate the machine while the
protective door is closed.
<2> When the MCC off Test request signal (RQT) is turned to “0”,
the protective door can be unlocked.
Example) DO state during MCC off Test
Tes t N o .
*MCF (PMC)
*MCF (DCS PMC)
*SMC (PMC)
*SMC (DCS PMC)
Timer limit
Timer
1 2 3 4 5
Test completion Test st a r t
IMPORTANT
Carry out the MCC off Test with the protective door
closed. As the test shuts off the MCC, prepare the
system for mechanical MCC shut-off before
starting the MCC off Test.
- 34 -
Page 43

B-64004EN/02 3.SAFETY FUNCTIONS
3.9 SAFETY POSITION SWITCH FUNCTION
It is checked whether the machine position is within the range of
safety position switch. The checked result is outputted to the Safety
Position Switch signal. The correspondence between axes and each
signal is specified by the parameters. In case of 1 path system, up to
32 points can be specified. And in case of 2 or more paths, up to 64
points can be specified.
When a machine position of controlled axis is within a range, which is
specified by the safety parameters, this signal is output.
1
0
Parameter setting
value
Parameter setting
value
The signals are output after establishment of the reference position.
The signal is not output before the completion of return to reference
position.
The “machine position” is the actual machine position (which is
calculated using feedback of position detector), not the commanded
position.
The comparison of position for safe position switch is executed in
detection unit.
If the machine position equals parameter setting value, the safe
position switch signal is output.
The safe position switch signal is not output for axis which the Dual
Check Safety (No.1904#6(DCN=1)) is not applied to.
Safety Position switch can be assigned up to 16 points per 1 group to
the output signal (F area) and totally up to 4 groups can be used in the
CNC system.
Two areas per a path are provided to assign. It is possible to assign the
signal to an appropriate area.
Safe position switch signals can be assigned to arbitrary controlled
axes. (All points can be also assigned to one axis.) The assignment of
controlled axes is set by the safety parameters (No.13880 to No.13911,
No.10501 to No.10532).
And the signals can be also assigned to the rotary axes.
When inconsistency between the position switch on PMC and that on
DCS PMC is lasted for the time that is specified by the parameter
No.1945, the safety function sets MCC Off signal (*DCALM) to “0”
and generates the alarm “safe I/O cross check error”
(PW0010/PW0011) .
- 35 -
Page 44

3.SAFETY FUNCTIONS B-64004EN/02
A
A
NOTE
The machine coordinate of the safety function is
based on position feed back. So it does not always
indicate the same value as the machine coordinate
based on the summation of the command value.
Two machine coordinates that are calculated by
two CPU independently are not always the same
because the position feedback is continuously
changed a little. As there is a possibility that the
condition of two signals is different from each other
near the boundary, do not stop an axis near the
boundary.
CAUTION
This function is activated only in position control
mode. This function is not activated in velocity
control mode and torque control mode.
• Hysteresis
Position switch sometimes turns on and off repeatedly near the
boundary of position switch area by very small vibration of a
servo motor. According to this problem, position switch is
inconvenient to use. So “hysteresis” described below is applied.
Minimum limit of
position switch
Maximum limit of
position switch
Width of hysteresis Width of hysteresis
ctivated area of position switch
Fig.3.9(a) Measuring area of position switch in case state of switch is “0”
Minimum limit of
position switch
ctivated area of position switch
Fig.3.9(b) Measuring area of position switch in case state of switch is “1”
Maximum limit of
position switch
The position switch is checked at every sampling period. When the
minimum and maximum limit of position switch are given like above
figure, activated area is checked by the area shown in the figure 3.9(a)
considering hysteresis if the state of position switch measured at last
time is “0”. And activated area is checked by the area shown in the
figure 3.9(b) not considering hysteresis if the state of position switch
measured at last time is “1”. According to this, it is possible to
suppress frequent changing of position switch.
- 36 -
Page 45

B-64004EN/02 3.SAFETY FUNCTIONS
3.10 SAFETY RELATED PARAMETERS CHECK FUNCTION
At every power-on, the CNC checks whether the safety related
parameters are destroyed and are transferred to the SV, the SP and the
PMC normally or not. The SV, the SP and the PMC also check
whether the safety related parameters are transferred from the CNC
normally or not.
If some problem is found in this check, an alarm is generated and the
MCC is shut off. (*DCALM=0)
3.11 PARAMETER LOCK FUNCTION
It is possible to lock the rewriting of the safety related parameters.
The parameter No.3225 and No.3226 unlock these parameters. The
following parameters are locked.
No.980, No.981, No.982, No.1023, No.1240, No.1838, No.1839,
No.1840, No.1841,No.1842, No.1902, No1904, No.1945, No.1946,
No.1948, No.1950, No.3021,No.3022, No.3225, No.3717, ,No.3797,
No.4372, No.4438, No.4440, No.4442, No.4448, No.10500-No.10596,
No.11950-No.11957, No.11960-No.11967, No.11970-No.11977,
No.11980-No.11987, No.13811, No.13821-No.13829,
No.13831-No.13838, No.13840-No.13843, No.13880-No.13911,
No.13920-No.13951, No.13960-No.13991
- 37 -
Page 46

3.SAFETY FUNCTIONS B-64004EN/02
3.12 SEFETY POSITION ERROR MONITORING FUNCTION
Both the CNC and the SV check whether the servo following error of
each axis exceeds the limit of deviation specified by the parameters.
If the servo following error exceeds, an alarm is generated and MCC
OFF signal (*MCFVx) is output immediately.
The relation between the safety monitoring state and the parameter of
limit of deviation is shown in the following table.
Safety monitoring is
activated
(In case *VLDVx =0)
Moving No.1838 No.1841
Stopping No.1839 No.1842
Servo-off No.1840 No.1840
Error detected CPU Alarm
CNC SV1072/SV1071/SV1069
SV SV0474/SV0475/SV1070
When position deviation exceeds the limit given by the parameter
(No.1839 in stop state, No.1838 in moving state and No.1840 in servo
off state) during safety monitoring, Monitoring result signal RSVx is
set to “0” regardless of the state of Safety check request signal
*VLDVx.
This function is valid after the reference position return is finished or
the follow-up of absolute position is finished in case an absolute
position coder.
CAUTION
This function is activated only in position control
mode. This function is not activated in torque and
velocity control mode.
Safety monitoring is not
activated
(In case *VLDVx =1)
- 38 -
Page 47

B-64004EN/02 3.SAFETY FUNCTIONS
3.13 AMPLIFIER CIRCUIT MONITORING FUNCTION
The SV and the SP transmit the data of plural axes to amplifiers
through one electronic circuit (LSI). The CNC, the SV and the SP
check whether this transmission is performed normally without
placing data on wrong address.
In case of servo amplifier, the CNC axis numbers kept by the CNC are
compared with the CNC axis numbers kept by the SV. In case of
spindle amplifier, the spindle numbers kept by the CNC are compared
with the spindle number kept by the SP. The checking sequence is as
follows.
[Checking sequence for servo amplifier]
<1> When a servo amplifier is set up at the first time, an alarm
SV0498 is generated. At that time, the CNC transfers the CNC
axis numbers to the SV and the SV keeps the data. Then the
power of all CNC system (amplifiers are included) must be
turned off and on.
When an alarm is generated after the configuration of servo
amplifiers is changed, it is necessary to carry out the operation to
send the CNC axis numbers to servo amplifiers. Set the
parameter No.2212#4 to “1” then return to “0”. Then turned off
the power of all CNC system (amplifiers are included.)
<2> After the power-on, the CNC and the SV start monitoring the
CNC axis numbers. The CNC monitors by comparing the CNC
axis number kept by the CNC itself with that kept by the SV. The
SV monitors by comparing the CNC axis numbers kept by the
SV with that sent by the CNC.
When some error is found, an alarm SV0478 or SV0496 is output,
and MCC Off signal (*DCALM) is turned to “0”.
[Checking sequence for spindle amplifier]
<1> When spindle is set up, the spindle numbers are transferred from
the SP to the CNC.
<2> The CNC compares the spindle numbers kept by the CNC itself
with that sent from spindle amplifier. If inconsistency is found,
an alarm SP0756 is output and MCC Off signal (*DCALM) is
turned to “0”.
<3> The SP compares the spindle numbers with that kept by the SP.
If inconsistency is found, alarm SP9070 (Spindle alarm 70) is
output, and MCC Off signal (*DCALM) is turned to “0”.
- 39 -
Page 48

3.SAFETY FUNCTIONS B-64004EN/02
3.14 SAFETY BRAKE SIGNAL OUTPUT FUNCTION
The CNC and the SV output the Safety Brake signal (*BRKx) to
control the mechanical brake. When this signal is “0”, mechanical
brake must be activated. When this signal is “1”, mechanical brake is
allowed to be released.
These signals cannot be used with the ignore v-ready off for all axes
signal <G
the same time.
When the inconsistency between the break signal on PMC and that on
DCS PMC is lasted for the time that is specified by the parameter
No.1945, the safety function sets MCC Off signal (*DCALM) to “0”
and generates the alarm “safe I/O cross check error”
(PW0010/PW0011).
066#0> and the ignore v-ready off for each axis <Gn192> at
n
- 40 -
Page 49

B-64004EN/02 3.SAFETY FUNCTIONS
3.15 CPU SELF TEST FUNCTION
The CNC, the PMC, the SV and the SP carry out the following
self-diagnosis. If the error is detected, the alarm is generated and sets
MCC Off signal (*DCALM) to “0”.
<1> CPU check
It is checked whether each CPU runs normally or not.
It is checked whether the instructions related to safety function is
executed normally or not.
Error detected CPU ALARM
CNC PW0014
PMC PW0009
SV SV0484
SP SP9074(Spindle alarm 74)
<2> Program monitoring
It is confirmed whether all safety related function run normally.
Error detected CPU ALARM
CNC PW0017 / SV0490
PMC PW0008(DCS PMC) PW0009(PMC)
SV SV0484
SP SP9076 (Spindle alarm 76)
SP0755
<3> Cross check
It is checked whether the result of the judgment about the safety
related function of a CPU is consistent with that of another CPU.
If some error is found, an alarm is output.
ALARM
SV relation SV0490/SV0484
SP relation SP9072(Spindle alarm 72)
SP9077(Spindle alarm 77)
SP9078(Spindle alarm 78)
SP0755
PMC relation PW0008(DCS PMC) PW0009(PMC)
- 41 -
Page 50

3.SAFETY FUNCTIONS B-64004EN/02
3.16 RAM CHECK FUNCTION
ECC (Error Check and Correct) function is applied to the battery
back-upped file memory. Then a single-bit error is corrected. And,
when an error that cannot be corrected occurs, memory parity error is
generated.
Other memory for dual check safety is checked as follows:(If the error
is detected, the alarm is generated and sets MCC Off signal
(*DCALM) to “0”)
1) Test at power-on
The several test patterns are written to the RAM area. It is checked
whether the written test data are read correctly. If read error occurs, an
alarm is generated.
2) Test during normal operation
RAM area is checked in turn at constant interval during normal
operation. The several test patterns are written to the RAM. It is
checked whether the written test data are read correctly. If read error
occurs, an alarm is generated.
Alarm detected CPU Alarm
CNC PW0016
SV SV0484
PMC PW0008(DCS PMC) PW0009(PMC)
SP SP9016(Spindle alarm 16)
3.17 CRC CHECK FUNCTION
At power-on and after power on, the data that are related to Dual
Check Safety and stored in the ROM area are checked. The CNC
software, the servo software, the PMC software and the spindle
software are checked. If some error is found, an alarm is generated.
After power on
Error detected Software Alarm
CNC software CRC CHECK ERROR: NC BASIC.
Servo software SERVO ROM TEST: CRC CHECK ERROR
PMC management software LED “6”
Spindle software Spindle alarm 75
After power on
Error detected Software Alarm
CNC software PW0018 CRC CHECK ERROR
PMC management software SYS-ALM199 NON MASK INTERRUPT
OTHER-CPU
- 42 -
Page 51

B-64004EN/02 3.SAFETY FUNCTIONS
3.18 SAFE STOP MONITORING
When a safety door is open, safe stop monitoring for servo axis and
spindle can be realized by the combination of several functions.
Safe stop monitoring for servo axis
According to the safe speed monitoring for servo axis and the safe
positing error monitoring, CNC and Servo monitor actual feedrate and
deviation of each axis. When a safety door is open, monitoring of stop
condition of each axis can be performed by the combination of the
following three functions.
a) By the safety speed monitoring function, check whether the
actual feed rate is lower than the safety level. If the feedrate
exceeds the safety limit, an alarm is generated.
Actual speed is calculated with the feedback of a position
detector. So, even if command feedrate is 0, actual feedrate may
be detected as not 0 when an axis is moved by external power.
Set the value of safety limit that does not cause an alarm when
feedrate command is 0.
b) By the safe positioning error monitoring function, check whether
position deviation is within a safety limit. If an axis is moved
unexpectedly, an alarm is generated.
c) According to “Axis moving signal MVx (Fn102)”, check
whether axis motion command is not given. (Axis moving signal
is prepared for PMC and is not double check signal.)
Safe stop monitoring for spindle
According to the safe speed monitoring for spindle, CNC and Spindle
monitor actual speed of each spindle. When a safety door is open,
monitoring of stop condition of each spindle can be performed by the
combination of the following two functions.
a) By the safety speed monitoring function, check whether the
actual speed is lower than the safety level. If the feedrate exceeds
the safety limit, an alarm is generated.
Actual speed is calculated with the feedback of a position
detector. So, even if command speed is 0, actual speed may be
detected as not 0 when a spindle is moved by external power. Set
the value of safety limit that does not cause an alarm when speed
command is 0.
b) There is a possibility that spindle rotate at speed lower than
safety speed limit. Then it is necessary to select the function to
make position control loop, such as spindle positioning, Cs
contouring control or spindle orientation.
- 43 -
Page 52

4.INSTALLATION B-64004EN/02
4 INSTALLATION
The hardware installation such as field wiring, power supply, etc.
should be referred to connection manual for CNC units and for servo
amplifier. EMC problem should be referred to EMC guideline manual.
Degree of IP protection:
Servo Motors: IP55
Spindle Motors: IP54 with oil-seal, IP40 without oil-seal
Servo and Spindle amplifiers: IP1x
CNC and other accessories: IPxx
NOTE
Servo/Spindle amplifiers, CNC are to be installed in
IP54 protected cabinets.
The peripheral units and the control unit have been designed on the
assumption that they are housed in closed cabinets.
As for the environmental conditions for each unit, such as CNC
controller, servo amplifier and etc, please refer to each connection
manual.
- 44 -
Page 53

B-64004EN/02 4.INSTALLATION
4.1 OVERALL CONNECTION DIAGRAM
CNC
Main board
I/O-LINK(JD51A)
I/O LINK #3
(Safety-related I/O)
In case of using the 2 channel I/O link
3ch I/O Link
branching
adapter
JD51B
JD44A-1
JD44A-2
JD1A
Distribution-type
I/O board
24VDC
CPD1
JD1B
JD1A
I/O LINK #1/#2
(general I/O, safety-related I/O)
Manual pulse
generator
JA3
Operator’s
panel
I/O UNIT etc
24VDC
24VDC
CPD1
JD1B
JD1A
I/O UNIT etc
CPD1
JD1B
JD1A
Power
magnetic
cabinet
Power
magnetic
cabinet
Above shows only the 2 channel I/O link for the safety-related I/Os of
the Dual Check Safety Function. As for the other connections, please
refer to the Connection manual.
- 45 -
Page 54

4.INSTALLATION B-64004EN/02
CNC
CNC
CNC
Main board
Main board
Main board
I/O-LINK(JD51A)
I/O-LINK(JD51A)
Profi-bus board
Profi-bus
(CN1)
In case of using the 1 channel I/O link and Profi-bus I/O
I/O LINK#1#2
(general I/O, safety-related I/O for PMC)
Manual pulse
generator
Operator’s
panel
Power
magnetic
cabinet
24VDC
24VDC
Distribution-type
I/O board
CPD1
JD1B
JD1A
I/O UNIT etc
CPD1
JD1B
JD1A
JA3
Profi-I/O
Profi-I/O
(general I/O, safety-related I/O for DCS PMC)
Above shows only the I/O link and Profi-bus for the safety-related
I/Os of the Dual Check Safety Function. As for the other connections,
please refer to the Connection manual.
- 46 -
Page 55

B-64004EN/02 5.I/O SIGNALS
5 I/O SIGNALS
- 47 -
Page 56

5.I/O SIGNALS B-64004EN/02
5.1 OVERVIEW
The Dual Check Safety Function provides two input paths and two
output paths for safe-related signals (safety signals).
For input signals (safety input signals), two paths are used: one path
for input to the CNC via I/O Link#3,#4 or Profibus-DP (Note1), and
another for input to the PMC via I/O Link#1,#2. The CNC (DCS
PMC) and the PMC exchange the safety input signals with each other
at all times to check each other. If a mismatch is found between a
safety input signal via one path and the same signal via another path
and such a state lasts for the period set in a parameter or more, the
CNC (DCS PMC) and the PMC independently detect an alarm.
(Dual-check for safety input signals)
For output signals (safety output signals), two paths are also used: one
path for output from the CNC via the I/O Link#3,#4 or Profibus-DP,
and another for output from the PMC via the I/O Link#1,#2. The
MCC Off signal (*MCF) is output via these two paths. When both a
signal via one path and the same signal via another path are 1, the
signal is assumed to be 1. If either is 0, the signal is assumed to be 0.
That is, if the signal (*MCF of DCS PMC)(Note2) via the I/O
Link#3,#4 or Profibus-DP and the signal (*MCF of PMC)(Note2)
via the I/O Link#1,#2 are both 1, the MCC may be turned on. If either
is 0, the MCC must be turned off.
In Subsection 5.3, a signal name is followed by its symbol and
addresses <via I/O Link#1,#2> and <via I/O Link#3,#4 or
Profibus-DP>. Then, for an input signal, its classification, function,
and operation are described, in this order. For an output signal, its
classification, function, and output condition are described in this
order.
For information about the emergency stop mode and MCC off Test
mode described in Subsection 5.3, see Subsection 5.3.
NOTE
1 I/O Link and Profibus-DP can not be used for the
safety X/Y signals at the same time.
2 DCS PMC : Dual Check Safety PMC PMC :
Normal PMC (First PMC, Second PMC, Third
PMC) Please refer to “FANUC Series
30i/300i/300is-MODEL A PMCPROGRAMMING
MANUAL(B-63983EN)”
- 48 -
Page 57

B-64004EN/02 5.I/O SIGNALS
5.2 SIGNAL ADDRESS
Via I/O Link#1/#2
PMC (n=0 to 9 (Path number-1))
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
X008
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
Gn008
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
Gn191 ORQ OPT
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
Gn748
*SMC
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
Gn749
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
Gn750
*VLDV8 *VLDV7 *VLDV6 *VLDV5 *VLDV4 *VLDV3 *VLDV2 *VLDV1
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
Gn751
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
Gn752
SVA8 SVA7 SVA6 SVA5 SVA4 SVA3 SVA2 SVA1
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
Gn753
SVB8 SVB7 SVB6 SVB5 SVB4 SVB3 SVB2 SVB1
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
Gn754
SPB4 SPB3 SPB2 SPB1 SPA4 SPA3 SPA2 SPA1
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
Fn191 RQT *OPIHB
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
Fn748 *DCALM *MCF
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
Fn749
*ESP *ESP *ESP
*ESP
*VLDP4 *VLDP3 *VLDP2 *VLDP1
- 49 -
Page 58

5.I/O SIGNALS B-64004EN/02
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
Fn750 RSV8 RSV7 RSV6 RSV5 RSV4 RSV3 RSV2 RSV1
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
Fn751 RSP4 RSP3 RSP2 RSP1
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
Fn752 *MCFV8 *MCFV7 *MCFV6 *MCFV5 *MCFV4 *MCFV3 *MCFV2 *MCFV1
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
Fn753 *MCFP4 *MCFP3 *MCFP2 *MCFP1
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
Fn754
*BRK8 *BRK7 *BRK6 *BRK5 *BRK4 *BRK3 *BRK2 *BRK1
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
Fn755
SPS08 SPS07 SPS06 SPS05 SPS04 SPS03 SPS02 SPS01
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
Fn756
SPS16 SPS15 SPS14 SPS13 SPS12 SPS11 SPS10 SPS09
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
Fn757
SPS24 SPS23 SPS22 SPS21 SPS20 SPS19 SPS18 SPS17
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
Fn758
SPS32 SPS31 SPS30 SPS29 SPS28 SPS27 SPS26 SPS25
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
Fn766 POSE8 POSE7 POSE6 POSE5 POSE4 POSE3 POSE2 POSE1
Via I/O Link#3,#4 or Profibus-DP
DCS PMC (m=path(0 to 9)×20) 0 to 9: Path number-1
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
X008
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
G000+m
*SMC
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
G001+m
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
G002+m
*VLDV8 *VLDV7 *VLDV6 *VLDV5 *VLDV4 *VLDV3 *VLDV2 *VLDV1
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
G003+m
*ESP *ESP *ESP
*VLDP4 *VLDP3 *VLDP2 *VLDP1
- 50 -
Page 59

B-64004EN/02 5.I/O SIGNALS
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
G004+m
SVA8 SVA7 SVA6 SVA5 SVA4 SVA3 SVA2 SVA1
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
G005+m
SVB8 SVB7 SVB6 SVB5 SVB4 SVB3 SVB2 SVB1
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
G006+m
SPB4 SPB3 SPB2 SPB1 SPA4 SPA3 SPA2 SPA1
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
G007+m
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
G008+m
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
G019+m
*ESP
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
F000+m *DCALM *MCF
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
F001+m
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
F002+m RSV8 RSV7 RSV6 RSV5 RSV4 RSV3 RSV2 RSV1
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
F003+m RSP4 RSP3 RSP2 RSP1
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
F004+m *MCFV8 *MCFV7 *MCFV6 *MCFV5 *MCFV4 *MCFV3 *MCFV2 *MCFV1
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
F005+m *MCFP4 *MCFP3 *MCFP2 *MCFP1
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
F006+m
*BRK8 *BRK7 *BRK6 *BRK5 *BRK4 *BRK3 *BRK2 *BRK1
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
F007+m
SPS08 SPS07 SPS06 SPS05 SPS04 SPS03 SPS02 SPS01
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
F008+m
SPS16 SPS15 SPS14 SPS13 SPS12 SPS11 SPS10 SPS09
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
F009+m
SPS24 SPS23 SPS22 SPS21 SPS20 SPS19 SPS18 SPS17
- 51 -
Page 60

5.I/O SIGNALS B-64004EN/02
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
F010+m
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
F018+m POSE8 POSE7 POSE6 POSE5 POSE4 POSE3 POSE2 POSE1
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
F019+m *OPIHB
SPS32 SPS31 SPS30 SPS29 SPS28 SPS27 SPS26 SPS25
NOTE
1 The hatched signals are double-checking signals.
2 The Emergency Stop signals in X address are
double checking signals.
3 When the number of path is 1, 32 points signals
are provided in total. When the number of path is 2
or more, 64 points signals are provided in total.
4 The following signals are provided for each
machine group. Emergency Stop (*ESP: X0008),
Test Mode signal(OPT), Guard Open Request
signal(ORQ), Guard Open Inhibit signal(*OPIHB),
MCC Off signal (*MCF), MCC Contact State signal
(*SMC)
5 The signal (Fxxxx/Gxxxx), which is provided for
each machine group, is assigned in the path area
for the smallest path number of the paths in the
machine group.
Example) When the 3rd and 5th path belong to the
2nd machine group, test Mode signal (OPT) for the
2nd machine group is assigned at G2191#2 in 3rd
path area.
- 52 -
Page 61

B-64004EN/02 5.I/O SIGNALS
5.3 SIGNALS
Emergency Stop signal (input)
*ESP <PMC:X008#4, #0, #1><DCS PMC:X008#4, #0, #1> (for each machine group)
*ESP <PMC: Gn008#4> <DCS PMC: G(019+m)#4> (for each path)
This is Emergency Stop signal. The Emergency Stop signal must be
connected to the Emergency Stop input of the amplifier.
[Classification] Input signal (Dual signal)
[Function] Stops machine movement immediately in an emergency.
0: Emergency stop state
1: Normal state
[Operation] When Emergency Stop signal (*ESP) is set to 0, the CNC is reset, and
the system enters emergency stop state. A machine tool builder must
output a signal to shut off directly the MCC when “MCC Off signal”
(*MCF) is set to “0”.
In emergency stop state, a machine tool builder must check “MCC
Contact State signal” (*SMC). If *SMC signal is “0” (MCC is on), a
machine tool builder must not release the guard lock signal of
protective door.
In general, Emergency Stop signal (*ESP) is specified by the
pushbutton switch B contact. When an emergency stop occurs, the
servo ready signal SA is set to 0.
If the input of the Emergency Stop signal is detected, the CNC
automatically specifies a command to zero the speed of a servo motor
and reduces the speed to zero (controlled stop). (See below note) After
the servo motor slows down and stops, the power is turned off, and the
servo motor is brought into the dynamic brake stop state.
The spindle motor is slowed down by the PMC command (see below
note) and the power is shut off.
- 53 -
Page 62

5.I/O SIGNALS B-64004EN/02
CAUTION
1 The Emergency Stop signal for DCS PMC is
assigned to each machine group, like the signal for
PMC.
<X008#4> for 1st machine group
<X008#0> for 2nd machine group
<X008#1> for 3rd machine group
2 The related parameter must be set in order to
perform the controlled stop of a servo motor. If the
parameter is not set, a servo motor is stopped by
dynamic brake control just after an emergency stop
is detected.
3 A spindle motor is slowed down by the command
(PMC ladder program). If the PMC does not
command to slow down, the spindle motor
continues rotating at the speed prior to
power-down and runs by inertia (and eventually
stopping in the end). When safety function is active
(protective door is open) and abnormal speed is
given due to the trouble of PMC, the spindle is
brought into safe stop state.
4 The Emergency Stop signals for every machine
group, <X008#4> <X008#0> <X008#1>, are
checked doubly in PMC and DCS PMC.
WARNING
A machine tool builder must make the ladder to
control to open and shut protective door in
emergency stop state. For instance, a machine tool
builder must make the ladder program for
procedure to inhibit to open the protective door in
emergency stop state.
IMPORTANT
1 Emergency stop button must fulfill the Standard
IEC60947-5-1.This is mandatory.
2 As MCC Off signal (*MCF) is effective for each
machine group, MCC is controlled per a machine
group. Then, although the Emergency Stop signal
by G signal is effective for each path, design to
turn on Emergency Stop by G signal of all paths in
a machine group at the same time.
- 54 -
Page 63

B-64004EN/02 5.I/O SIGNALS
Example of protective door open/shut sequence
The following figure shows the sequence in case of emergency stop.
EMG_P
*ESP
*SMC
RSVx
RSPs
Actual door lock releasing sig nal
*SGOPN
(Safety re lated I/ O)
Actual door open/ close
signal
Door closed
Door opened
Door closed
A machine tool builder must design the ladder program as follows:
(1) In case Emergency Stop signal (*ESP) is input, the guard lock
signal is turned off after confirming safety machine position,
safety speed and safety position error by the Monitoring Result
signals RSVx/RSPs.
(2) In this example, it is assumed that a protective door with an
electronic door lock is applied. When a door is opened, door lock
releasing signal must be turned off. At the same time, Guard
State signal (*SGOPN: machine side signal) is changed to show
guard-releasing state.
(3) This is door open state
(4) Protective door is shut and locked. Then Emergency Stop signal
(*ESP) is released. Pay attention the time “t”.
(5) After Emergency Stop signal is released, CNC turns MCC Off
signal (*MCF) to “1”.
Test Mode signal (input)
OPT <PMC:Gn191#2> (for each machine group)
When this signal is input, MCC off Test is carried out. MCC off Test
checks whether the contact of the MCC is abnormally closed or not.
MCC Off Test Execution Request signal (RQT) notifies that MCC off
Test should be executed. Input this signal while servo ready signal
(SA) is set to “1”.
When MCC off Test is carried out by manual operation, input this
signal after preparing to carry out MCC off Test by PMC.
(1) (2) (3)
(4)
t
(5)
- 55 -
Page 64

5.I/O SIGNALS B-64004EN/02
[Classification] Input signal (Single signal)
[Function] This signal notifies CNC to enter MCC off Test mode.
0: not enter MCC off Test mode
1: enter MCC off Test mode
Test Mode signal (OPT) through I/O Link#3, 4, Profibus-DP is not
provided.
[Operation] When this signal (OPT) is set to “1”, CNC turns on/off MCC in
various combinations with MCC Off signals
*MCF(PMC)/*MCF(DCS PMC). And CNC checks whether MCC
Contact State signals *SMC(PMC)/ *SMC(DCS PMC) are input in
proper combination corresponding to the combination with MCC Off
signals.
However MCC off Test should not be carried out in case of
emergency stop state, servo alarm state or spindle alarm state.
Avoid VRDY OFF alarm by MCC off Test by using all axes of each
path VRDY off alarm ignore signal IGNVRY <Gn066#0> or each
axis VRDY off alarm ignore signal IGNVRY1 to IGNVRY8
<Gn192>.
If MCC off Test is not completed within the time specified by the
parameter No.1946, a servo alarm SV0488 occurs.
CAUTION
1 While MCC off Test is being carried out, do not
turn Test Mode signal (OPT) to “0”.
2 It is not permitted to carry out MCC off Test for
plural machine groups simultaneously. Carry out
MCC off Test for only one machine group
independently.
3 If MCC is shared between two or more machine
groups and MCC off Test is carried out in a
machine group, VRDY off alarm in another
machine group, which shared MCC, must be
ignored by using all axes of each path VRDY off
alarm ignore signal IGNVRY <Gn066#0> or each
axis VRDY off alarm ignore signal IGNVRY1 to
IGNVRY8 <Gn192>.
4 The MCC shall have forced guided contacts , and
must fulfill the standard IEC60204 and IEC 60255.
This is mandatory.
WARNING
While the MCC off Test processing is in progress,
the MCC Off signal (*MCF) goes high and low to
turn on and off the MCC. Carry out the MCC off
Test in such a state that the turning on or off of the
MCC will not cause a problem.
- 56 -
Page 65

B-64004EN/02 5.I/O SIGNALS
A
NOTE
If MCC off Test is executed when MCC is forced to
shut off in emergency stop state, servo alarm state
or spindle alarm state, the test cannot be executed
normally. MCC off Test should be executed only
when the test can be executed normally.
Test No.
*MCF (DCS PMC)
*MCF (PMC)
*SMC (DCS PMC)
*SMC (PMC)
Timer limit
Timer
12345
Test completion Test start
Example 1) Timing chart 1 of MCC off test (normal state)
Test No.
*MCF (DCS PMC)
*MCF (PMC)
*SMC (DCS PMC)
*SMC (PMC)
Timer limit
Timer
12 3 4
Test start
larm !!
Example 2) Timing chart 2 of MCC off test (abnormal state)
- 57 -
Page 66

5.I/O SIGNALS B-64004EN/02
Guard Open Request signal (input)
ORQ <PMC: Gn191#3>(for each machine group)
This signal is input when an operator intends to release the guard lock
and open the protective door.
[Classification] Input signal (Single signal)
[Function] In order to open the protective door, this signal requests CNC to
unlock the guard lock with the Dual Check Safety Function. Guard
Open Request signal (ORQ) is not input via the DCS PMC.
0: not request to open guard lock.
1: request to open guard lock
[Operation] When CNC detects that the Guard Open Request signal (ORQ) is 1,
CNC returns Guard Open Inhibit signal (*OPIHB). A machine tool
builder must design the PMC ladder program so that the guard lock is
released after judging the result of safety machine position check,
safety speed check, safety position error check to be safe or other
safety condition such as Dual Check alarm status signal to be safe.
This signal is not a safety signal that is checked doubly. But this is an
important signal to make up the safety system. Then a machine tool
builder must design the proper ladder program to deal with this signal.
IMPORTANT
The mistake of the ladder program cannot be
checked. So be sure to perform the confirmation of
the safety function. (refer to the chapter 7)
Guard State signal (Machine side input signal)
*SGOPN <PMC:X machine side signal><DCS PMC:X machine side signal> (for each safety
door)
Input the guard state of the protective door to this signal. When the
protective door is open (Guard State signal (*SGOPN) =0), set Safety
Check Request signal (*VLDVx, *VLDPs) to “0” in order to activate
the alarm monitoring of safety functions.
[Classification] Input signal (Dual signal)
[Function] Guard State signal informs CNC of the guard open/closed state for the
Dual Check Safety Function.
0: Guard open state
1: Guard closed state
[Operation] When Guard State signal (*SGOPN) is “0”, the ladder program turn
Safety Check Request signal (*VLDVx, *VLDPs) to “0” in order to
activate the alarm monitoring of safety speed, safety machine position
and safety position error. If the ladder program detects abnormal
condition in each CPU, it generates a safety related alarm and stops
motors.
IMPORTANT
As for the contacts for Guard State signal, it is
recommended to fulfill the Standard IEC60947-5-1.
- 58 -
Page 67

B-64004EN/02 5.I/O SIGNALS
MCC Contact State (input)
*SMC <PMC: Gn748#6><DCS PMC: G(000+m)#6> (for each machine group)
The state of MCC contact is checked doubly. It is not possible to
check whether the contact of MCC is melted and adhered abnormally
because MCC contact is closed during normal operation. The state of
MCC contact can be checked by performing MCC off Test.
[Classification] Input signal (Dual signal)
[Function] MCC Contact State signals (*SMC) inform CNC of the MCC state for
the Dual Check Safety Function.
0: MCC-on state
1: MCC-off state
[Operation] MCC Contact State signals (*SMC) is used to check if the MCC Off
signals (*MCF) operates normally in MCC off Test mode.
When the MCC Contact State signals (both *SMC(PMC) and
*SMC(DCS PMC)) are 1 in the emergency stop state (*ESP=0), it is
possible to design the ladder program to release the guard lock.
CAUTION
Input this signal according to the MCC state.
Safety Check Request signal (input)
*VLDVx <PMC:Gn750#0 to #7><DCS PMC:G(002+m)#0 to #7> (for each axis)
*VLDPs <PMC:Gn751#0 to #3><DCS PMC:G(003+m)#0 to #3> (for each spindle)
If these signals are set to “0” when Guard State signal (*SGOPN:
machine side signal) is “0”, the alarm monitoring of safety speed,
safety machine position and safety position error is activated.
[Classification] Input signal (Dual signal)
[Function] Safety Check Request signals request each CPU to carry out the safety
check for the Dual Check Safety Function.
These signals select a servo axis and a spindle that must be checked
when a protective door is open.
0: Alarm by safety check is monitored, as a protective door is open.
1: Alarm by safety check is not monitored, as a protective door is
closed
[Operation] Each CPU carries out the safety check of the servo axis and the
spindle that are selected by these signals. (Safety speed for a spindle,
safety speed, safety machine position and safety position error for a
servo axis.) If each CPU finds out any problem, it generates a safety
related alarm and stops motors.
- 59 -
Page 68

5.I/O SIGNALS B-64004EN/02
Guard Open Inhibit signal (output)
*OPIHB <PMC: Fn191#0><DCS PMC: F(019+m)#0> (for each machine group)
CNC returns these signals as answer when CNC detects that Guard
Open Request signal (ORQ) is set to “1”.
[Classification] Output signal (Not checked doubly)
[Function] When CNC receives Guard Open Request signal (ORQ) =1, CNC
returns these signal as answer. CNC outputs Guard Open Inhibit
signal (*OPIHB) through both PMC and DCS PMC.
0: Inhibit guard open
1: Permit guard open
[Operation] A machine tool builder can release a guard lock by his ladder program
when Guard Open Inhibit signal (*OPIHB) =1, Monitoring Result
signal (RSVx/RSPs) =1 and the condition of machine side is
confirmed to be safe.
IMPORTANT
The mistake of the ladder program cannot be
checked. So be sure to perform the confirmation of
the safety function. (refer to the chapter 7)
Monitoring Result signal (output)
RSVx <PMC:Fn750#0 to #7><DCS PMC:F(002+m)#0 to #7> (for each axis)
RSPx <PMC:Fn751#0 to #3><DCS PMC:F(003+m)#0 to #3> (for each spindle)
These signals show the result of monitoring safety speed, safety
machine position and safety position error.
By checking these signals, a machine tool builder can judge whether a
machine is in safe state or not. When a machine is judged to be in safe
state, it is necessary to turn on the signal for releasing a guard lock
and outputs a signal actually to open a protective door.
[Classification] Output signal (Output to both PMC but not checked doubly)
[Function] These signals show the result of monitoring of the Dual Check Safety
Function.
These signals notify that an abnormal condition is detected in safety
monitoring function of the Dual Check Safety Function, such as safety
speed check, safety machine position check and safety position error
check.
In the following case, these signals are turned to “0”.
0: In dangerous condition (Abnormal condition is detected by
safety function.)
In the following case, these signals are turned to “1”.
1: In safe condition (Abnormal condition is not detected.)
[Operation] Each CPU notifies PMC of the result of safety monitoring through
these signal.
A machine tool builder can release a guard lock by his ladder program
when Guard Open Inhibit signal (*OPIHB) =1, these Monitoring
Result signal (RSVx/RSPx) =1 and the condition of machine side is
confirmed to be safe.
- 60 -
Page 69

B-64004EN/02 5.I/O SIGNALS
MCC Off signal (output)
*DCALM <PMC: F0748#7><DCS PMC: F000#7> (for all system)
In case this signal is “0”, MCC is shut off through 2 channels of I/O
line respectively.
This signal is set to “0”, when a crosscheck alarm of safety related
signals or a CPU self-diagnosis alarm occurs.
A machine tool builder makes a ladder program to output a signal to
shut off MCC when this signal is turned to “0”. If necessary, control
DO signal for peripheral devices.
[Classification] Output signal (This signal output to both PMC but is not monitored
doubly)
[Function] This is a signal to turn on MCC when both a crosscheck alarm and a
CPU self-diagnosis alarm are not caused.
0: MCC off
1: MCC on
[Operation] When each CPU finds out any abnormal condition, it generates an
alarm and turns off this signal at the same time.
MCC Off signal (output)
*MCF <PMC: Fn748#1, DCS PMC: F(000+m)#1> (for each machine group)
In case this signal is “0”, MCC is shut off through 2 channels of I/O
Link line respectively.
This signal is set to “0”, when Emergency Stop signal (*ESP ) is “0”
or MCC off Test is carried out.
A machine tool builder makes a ladder program to output a signal to
shut off MCC when this signal is turned to “0”.
[Classification] Output signal (This signal output to both PMC but is not monitored
doubly)
[Function] When the Dual Check Safety Function is applied, this signal allows
turning on MCC.
When either MCC Off signal through PMC or that through DCS PMC
is “0”, MCC is turned off. When both MCC Off signal through PMC
and that through DCS PMC is “1”, MCC is turned on.
0: MCC off
1: MCC on
[Operation] When Emergency Stop signal is input, CNC turns off this signal.
When MCC off Test is carried out, CNC turns off this signal, too.
[Output condition] In the following case, this signal turns to “0” (not permit MCC on)
- MCC off Test is carried out.
- In emergency stop state
In other than the above case, this signal turns to “1” (permit MCC on).
- 61 -
Page 70

5.I/O SIGNALS B-64004EN/02
MCC Off signal (output)
*MCFVx <PMC: Fn752#0 to #7><DCS PMC: F(004+m)#0 to #7> (for each axis)
In case this signal is “0”, MCC is shut off through 2 channels of I/O
line respectively.
This signal is set to “0”, when an alarm occurs in safety speed check,
safety machine position check or safety position error check for each
servo axis.
A machine tool builder makes a ladder program to output a signal to
shut off the MCC of the path that the axis belongs, when this signal is
turned to “0”.
[Classification] Output signal (This signal output to both PMC but is not monitored
doubly)
[Function] When the Dual Check Safety Function is applied, this signal allows
turning on MCC.
0: MCC off
1: MCC on
[Operation] If each CPU finds out the abnormal state of the axis when Safety
Check Request signal for the axis (*VLDVx)=0, each CPU brings the
axis into controlled stop state at first. In case of an alarm of Safety
Speed Monitoring or Safety Machine Position Monitoring, each CPU
watches whether the axis is decelerated and stopped or not. If the axis
does not stop, each CPU turns this signal corresponding to the alarm
axis to “0”. In case of an alarm of Safety Position Error Monitoring,
each CPU turns this signal corresponding to the alarm axis to “0”
immediately.
In case of an alarm other than described above and related to data
communication or position detector, each CPU turns this signal
corresponding to the alarm axis to “0” immediately. But according to
the parameter setting, it is possible to turn to “0” this signals of all the
axes belonged to the path that involves the alarm axis in case of any
servo alarms.
MCC Off signal (output)
*MCFPs <PMC: Fn753#0 to #3><DCS PMC: F(005+m)#0 to #3> (for each spindle)
In case this signal is “0”, MCC is shut off through 2 channels of I/O
Link line respectively.
This signal is set to “0”, when an alarm occurs in safety speed check
for each spindle.
A machine tool builder makes a ladder program to output a signal to
shut off the MCC of the path that the spindle belongs, when this signal
is turned to “0”.
[Classification] Output signal (This signal output to both PMC but is not monitored
doubly)
[Function] When the Dual Check Safety Function is applied, this signal allows
turning on MCC.
0: MCC off
1: MCC on
[Operation] If each CPU finds out safety speed over alarm in safety speed
monitoring when Safety Check Request signal for the spindle
(*VLDPs)=0, each CPU brings the spindle into free run state at first.
- 62 -
Page 71

B-64004EN/02 5.I/O SIGNALS
After that, if the spindle is not decelerated, each CPU turns this signal
to “0”.
In case of an alarm other than described above and related to data
communication or position detector, each CPU turns this signal
corresponding to the alarm spindle to “0” immediately. But according
to the parameter setting (No.10500#1 = 1), it is possible to turn to “0”
this signals of all the spindles belonged to the path that involves the
alarm spindle in case of any spindle alarms.
MCC Off Test Execution Request signal (output)
RQT <PMC:Fn191#2> (for each machine group)
[Classification] Output signal (Single signal)
[Function] This signal notifies that MCC off Test mode is required and a check
should be made to determine whether the safety output signals (MCC
Off signal (*MCF)) operate normally. When MCC Off Test Execution
Request signal (RQT) is set to 1, set MCC off Test mode and carry out
a safety output signal MCC off Test as soon as possible.
When MCC Off Test Execution Request signal (RQT) is 1, a machine
tool builder must make ladder not to release a guard lock.
Once a guard is closed when MCC Off Test Execution Request signal
(RQT) is set to “1” while a guard is open by Guard Open Request
signal (ORQ), it is necessary not to release a guard lock until MCC off
Test request signal (RQT) turns to “0”.
When MCC Off Test Execution Request signal (RQT) is 1, the
following screen is displayed and the warning “EXECUTE MCC
TEST” is displayed.
MCC Off Test Execution Request signal (RQT) is not output via the
DCS PMC.
Make a ladder program to lock a protective door when MCC Off Test
Execution Request signal (RQT) =1.
- 63 -
Page 72

5.I/O SIGNALS B-64004EN/02
[Output condition] In the following case, this signal is set to “1”.
• MCC off Test is not completed after power-on (when bit 3 of
parameter No.10500 is 0).
• Twenty-four hours have elapsed since the completion of the last
MCC off Test.
In the following case, this signal sets to “0”.
• MCC off Test is completed.
CAUTION
1 Do not turn Test Mode signal (OPT) to “0” during
MCC off Test.
2 In case that there are plural machine groups in a
machine, carry out MCC off Test for each machine
group independently.
3 If MCC is shared between two or more machine
groups, do not carry out MCC off Test for those
machine groups at the same time.
4 If MCC is shared between two or more machine
groups and MCC off Test is carried out in a
machine group, VRDY off alarm in another
machine group, which shared MCC, must be
ignored by using all axes of each path VRDY off
alarm ignore signal IGNVRY <Gn066#0> or each
axis VRDY off alarm ignore signal IGNVRY1 to
IGNVRY8 <Gn192>.
WARNING
While the MCC off Test processing is in progress,
the MCC Off signal (*MCF) goes high and low to
turn on and off the MCC. Carry out the MCC off
Test in such a state that the turning on or off of the
MCC will not cause a problem.
Safety Brake signal (output)
*BRKx <PMC:Fn754#0 to #7><DCS PMC:F(006+m)#0 to #7> (for each axis)
This signal is used to control mechanical brake of each axis.
CNC and SV output Safety Brake signal (*BRKx) to control
mechanical brake. When *BRKx is “0”, mechanical brake is active.
When *BRKx is “1”, mechanical brake is not active. Note that *BRKx
cannot be used with all axes of each path VRDY off alarm ignore
signal IGNVRY <Gn066#0> or each axis VRDY off alarm ignore
signal IGNVRY1 to IGNVRY8 <Gn192>.
[Classification] Output signal (Dual signal)
[Function] When the Dual Check Safety Function is applied, this signal notifies
to activate a mechanical brake. When MCC is off, a brake should be
activated.
- 64 -
Page 73

B-64004EN/02 5.I/O SIGNALS
A
[Operation] In emergency stop state or alarm state, a mechanical brake is activated
by this signal.
A machine tool builder must connect this signal to a mechanical
brake.
[Output condition] In the following case, this signal is “1”.
• Releasing brake state
In the following case, this signal is “0”.
• Activating brake state
(a) In case *BRK signal is “0”
Emergency Stop state (*ESP signal is “0”)
*ESP
*BRK
Servo alarm occurs
larm
*BRK
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
Power-on
Power
*BRK
1
0
1
0
(b) In case BRK signal is “1”
When emergency stop is released (*ESP signal is “1”), MCC can
be enabled l (*MCF signal is “1”). After that, when MCC is
turned on, Safety Brake signal *BRK is turned to “1” after the
time specified by the parameter No.1950 is elapsed.
*ESP
*MCF
MCC
*BRK
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
Timer for brake signal
NOTE
Regular maintenance of a brake must be done.
- 65 -
Page 74

5.I/O SIGNALS B-64004EN/02
Safety Position Switch signal (output)
SPS1 to SPS32<PMC:Fn755 to Fn758><DCS PMC:F(007+m) to F(010+m)>
This signal shows whether the machine position of a servo axis is
within the range specified by the parameter or not.
[Classification] Output signal (Dual signal)
[Function] This signal notifies that the machine position of the axis specified by
the safety parameter (No.13880 to No.13911) is within the range
specified by the safety parameter (No.13920 to No.13951, No.13960
to No.13991). In case of single path system, up to 32 points can be
used.
In case of 2 or more path system, another 32 points in 2 path area can
be used. Then up to 64 points can be used at maximum. This signal
notifies that the machine position of the axis specified by the safety
parameter (No.10501 to No.10532) is within the range specified by
the safety parameter (No.10533 to No.10564, No.10565 to No.10596).
NOTE
In case of 3 or more path system, safety position
switch can be assigned up to 16 points per 1 group
to the output signal (F area) and totally up to 4
groups can be used in the CNC system.
Two areas per a path are provided to assign. It is
possible to assign the signal to an appropriate
area.
[Output condition] In the following case, this signal is set to “1”.
• The machine position of the axis is within the specified range.
In the following case, this signal is set to “0”.
• The machine position of the axis is out of the specified range.
[Note] When the axis is just on the boundary of the range (machine position
is equal to parameter setting value), it is regarded that the machine
position is within the range.
If the state of two Safety Position Switch of the signal of DCS PMC
side and the signal of PMC side is different more than the specified
period, each CPU shuts off MCC by DCS alarm (PW0010,PW0011).
- 66 -
Page 75

B-64004EN/02 5.I/O SIGNALS
NOTE
Position switch signal is activated when the
reference point correspond to the axis is
established after power-on. The state of position
switch is kept to “0” till then.
Once activating, position is always checked and
state of signal is changed according to the result of
checking. Even if the reference point is lost, the
state of signal is changed according to the
coordinate kept in both CNC and servo CPU. So if
the special procedure is required when the
reference point is lost, design the ladder program
by combining with Position Information Effect
signal (POSEx).
Safety Speed/Safety Position Selection signal A
SVAx <PMC:Gn752#0 to #7> <DCS PMC:G(004+m)#0 to #7> (for each axis)
SPAs <PMC:Gn754#0 to #3> <DCS PMC:G(006+m)#0 to #3> (for each spindle)
Safety speed/safety position selection signal B
SVBx <PMC:Gn753#0 to #7> <DCS PMC:G(005+m)#0 to #7> (for each axis)
SPBs <PMC:Gn754#4 to #7> <DCS PMC:G(006+m)#4 to #7> (for each spindle)
[Classification] Input signal (Dual signal)
[Function] When the Dual Check Safety Function is activated, it is possible to
select safety limit speed and safety machine position of each axis.
This signal is prepared for each axis and each spindle. The final
number in the signal name shows the number of the controlled axis
and spindle.
, SVBx
SVAx
1: Select safety speed/safety machine position of the 1st axis
x
2: Select safety speed/safety machine position of the 2nd axis
3: Select safety speed/safety machine position of the 3rd axis
: :
: :
, SPBy
SPAy
1: Select safety speed of the 1st spindle
y
2: Select safety speed of the 2nd spindle
: :
: :
- 67 -
Page 76

5.I/O SIGNALS B-64004EN/02
[Operation] According to the combination of Safety Speed/Safety Machine
Position Selection signal, safety speed and safety machine position are
selected as the following table.
Safety Speed/
Safety Machine Position
Selection signal
SVAn SVBn
SPAn SPBn
0 0
1 0
0 1
1 1
Safety limit speed Safety machine position
Parameter for
servo axis
Safety limit speed 1 Safety machine position 1
No.13821 No.4372 No.13831 No.13832
Safety limit speed 2 Safety machine position 2
No.13822 No.4438 No.13833 No.13834
Safety limit speed 3 Safety machine position 3
No.13823 No.4440 No.13835 No.13836
Safety limit speed 4 Safety machine position 4
No.13824 No.4442 No.13837 No.13838
Parameter
for spindle
+ direction
parameter
- direction
parameter
CAUTION
Safety Speed/Safety Machine Position Selection
signal is a safety signal. This signal is input through
both PMC and DCS PMC. Both CNC and PMC
check doubly inconsistency of this signal.
Position Information Effect signal
POSEx <PMC: Fn766#0 to #7><DCS PMC: F(018+m)#0 to #7> (for each axis)
This signal is output when Dual Check Safety function is activated
and the reference point is established. When the reference point is not
established, the machine system is in danger state because Safety
Machine Position Monitoring and Safety Position Error Monitoring
are not active. If this signal is “0”, Machine Tool Builder has to
control not to open the protective door.
[Classification] Output signal (This signal output to both PMC but is not monitored
doubly)
[Function] This signal informs whether the reference point is established or not.
0: The reference point is not established.
1: The reference point is established.
[Operation] Each CPU informs whether the reference point is established or not.
In the following case, this signal is turned to “1”.
• After the reference point is established.
• When the follow up operation of absolute pulse coder is finished
after power-on
In the following case, this signal is turned to “0”.
• When the reference point is lost
NOTE
In case that the reference point is re-established,
this signal is turned to “0” till the reference point is
re-established from the dog-signal is turned off.
- 68 -
Page 77

B-64004EN/02 5.I/O SIGNALS
Programmable Safety I/O signals
[Classification] Input/Output signal (Dual signal)
[Function] The 8 bytes (64 bit) programmable safe I/Os can be freely defined as
the different address from the above basic safe signals. Each byte of 8
byte programmable safe I/Os can be assigned on either address of X/Y
or R or D by parameter. Each byte of the programmable safe I/O
between the PMC and DCS PMC is cross-checked by the CNC and
PMC.
CNC CPU(DCS PMC) PMC CPU(PMC)
Input Signal 1
Input Signal 2
:
Input Signal 8
Output Signal 1
Output Signal 2
:
Output Signal 8
I/O Link
or
PROFIBUS-DP
CNC and PMC
monitor each
signal.
Input Signal 1
Input Signal 2
:
Input Signal 8
Output Signal 1
Output Signal 2
:
Output Signal 8
I/O Link
- 69 -
Page 78

5.I/O SIGNALS B-64004EN/02
[Operation] The combinations of cross-checking these signals are defined by using
Safety parameters as follows.
Signal type Combination No. CNC (DCS PMC) PMC(PMC)
input
output
1 No. 11950 No. 11970
2 No. 11951 No. 11971
3 No. 11952 No. 11972
4 No.11953 No.11973
5 No.11954 No.11974
6 No.11955 No.11975
7 No.11956 No.11976
8 No.11957 No.11977
1 No.11960 No.11980
2 No.11961 No.11981
3 No.11962 No.11982
4 No.11963 No.11983
5 No.11964 No.11984
6 No.11965 No.11985
7 No.11966 No.11986
8 No.11967 No.11987
- 70 -
Page 79

B-64004EN/02 5.I/O SIGNALS
5.4 GENERAL PURPOSE I/O SIGNAL
How to turn off general purpose signal
When it is confirmed that *DCALM, *MCF, *MCFVx and *MCFPs
is “0”, turn general purpose I/O signal off if necessary.
(a) In case MCC off Test is carried out,
When RQT=1 and OPT=1, ignore *MCF=0.
(b) In case of emergency stop (*ESP=0)
When *ESP=0, ignore *MCF=0.
- 71 -
Page 80

5.I/O SIGNALS B-64004EN/02
5.5 NOTE ON MULTI PATH CONTROL
This section describes cautions about safe-related I/O signals that
should be taken in multi-path control.
5.5.1 Machine Group And Multi Path Control
CNC can treat servo axes and spindles by dividing into two classes of
groups, machine group and path
In case that a machine has plural machine parts that are controlled
independently, machine group is provided to control a part of machine
in such machine. Emergency stop is prepared for each machine group.
The signals for MCC off Test and protective door open/close sequence
are provided for each machine group.
In case that a work piece is machined by plural cutters and plural
programs at the same time, multi path control is applied. An alarm is
checked by each path. If servo alarm occurs in a path, MCC of all axes
in the path is shut off.
In case of the alarm by safety check function, MCC of all axes in the
path are shut off. Then the safety area should be set for each path
basically.
When plural safety areas are defined in a path, MCC may be shut off
by an alarm that occurs in another safety area.
When the safety area is composed by the axes that change assignment
to a path, MCC of other axes are not always shut off. So wire the
MCC of all paths, which include the axes changed assignment to the
path, to shut off at the same time.
The safety signals that are cross-checked are provided both on PMC
and DCS PMC for each path. The state must be controlled to be equal.
- 72 -
Page 81

B-64004EN/02 5.I/O SIGNALS
NOTE
When “Composite control” or “Path speed control
of Multi path control” is specified, it is possible to
give a command to control a servo axis or a
spindle in another path. But in this case, the
correspondence between a path and a belonging
servo axis or spindle is not changed. An alarm
related to a servo axis or a spindle occurs in the
path that the axis and the spindle originally belong
to, and MCC shut off signal correspond to the axis
or spindle is output also in original path.
Then, as the path that gives a command and the
path that an axis and a spindle belongs to should
be regarded as the same group, it is necessary to
wire MCC off signal (*MCFVx, *MCFPs) to shut off
the MCC of both path at the same time when
“Composite control” or “Path speed control of Multi
path control” is specified.
- 73 -
Page 82

6.PARAMETERS B-64004EN/02
6 PARAMETERS
- 74 -
Page 83

B-64004EN/02 6.PARAMETERS
6.1 OVERVIEW
The parameters related to the dual check safety function (safety
parameters) are protected by a code (No. 3225) for the safety
parameters. The value of a safety parameter cannot be modified
unless the same value as the code for the safety parameters is set as the
key (No. 3226) for the safety parameters.
The safety parameters are stored in two locations on the CNC. The
CNC, PMC, servo and spindle software check the matching of the
parameters stored at the two locations. If a mismatch is found, an
alarm is issued.
If the setting of a safety parameter is modified, the power must be
turned off then back on. The new setting of the parameter becomes
effective after the power is turned back on.
- 75 -
Page 84

6.PARAMETERS B-64004EN/02
6.2 DATA TYPE
Parameters are classified by data type as follows:
Data type Valid data range Remarks
Bit
Bit machine group
Bit path
Bit axis
Bit spindle
Byte
Byte machine group
Byte path
Byte axis
Byte spindle
Word
Word machine group
Word path
Word axis
Word spindle
2-word
2-word machine group
2-word path
2-word axis
2-word spindle
Real
Real machine group
Real path
Real axis
Real spindle
Parameter Setting Tables.
NOTE
1 Each of the parameters of the bit, bit machine
group, bit path, bit axis, and bit spindle types
consists of 8 bits for one data number (parameters
with eight different meanings).
2 The machine group type allows data to be set
separately for each machine group.
3 The path type allows data to be set separately for
each path.
4 The axis type allows data to be set separately for
each control axis.
5 The spindle type allows data to be set separately
for each spindle axis.
6 The valid data range for each data type indicates a
general range. The range varies according to the
parameters. For the valid data range of a specific
parameter, see the explanation of the parameter.
0 or 1
-128 to 127
0 to 225
-32768 to 32767
0 to 65535
0 to ±999999999
See the Standard
Some parameters
handle these types of
data as unsigned
data.
Some parameters
handle these types of
data as unsigned
data.
Some parameters
handle these types of
data as unsigned
data.
- 76 -
Page 85

B-64004EN/02 6.PARAMETERS
6.3 REPRESENTATION OF PARAMETERS
Parameters of the bit type, bit machine group type, bit path type, bit axis type,
and bit spindle type
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
0000 EIA NCR ISP CTV TVC
Data No. Data (Data #0 to #7 are bit positions.)
Parameters other than the bit-type parameters above
1023 Number of the servo axis for each axis
Data No. Data
NOTE
1 The parameters, which are described here, are related directly to Dual Check Safety
function. As for the other parameters, please refer to the parameter manual
(B-63950EN).
2 A parameter usable with only one path control type, namely, the lathe system (T
series) or the machining center system (M series), is indicated using two rows as
shown below. When a row is blank, the parameter is not usable with the
corresponding series.
[Example 1]
Parameter HTG is a parameter common to the M and T series, but Parameters RTV
and ROC are parameters valid only for the T series.
#7 #6
1403
RTV
[Example 2]
The following parameter is provided only for the M series.
1411
3 When "to" is inserted between two parameter numbers, there are parameters with
successive numbers between the two starting and ending parameter numbers, but
those intermediate parameter numbers are omitted for convenience.
4 The lower-case letter "x" or "s" following the name of a bit-type parameter indicates
the following:
- ”
- ”
x” : Bit axis type parameters
s” : Bit spindle type parameters
#5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
ROC
HTG
HTG
Cutting feedrate
T series
M series
T series
M series
- 77 -
Page 86

6.PARAMETERS B-64004EN/02
6.4 STANDARD PARAMETER STTING TABLES
Overview
This section defines the standard minimum data units and valid data
ranges of the CNC parameters of the real type, real machine group
type, real path type, real axis type, and real spindle type. The data type
and unit of data of each parameter conform to the specifications of
each function.
Explanation
(A) Length and angle parameters (type 1)
Unit of data
mm
deg.
inch
Increment
system
IS-A 0.01 -999999.99 to +999999.99
IS-B 0.001 -999999.999 to +999999.999
IS-C 0.0001 -99999.9999 to +99999.9999
IS-D 0.00001 -9999.99999 to +9999.99999
IS-E 0.000001 -999.999999 to +999.999999
IS-A 0.001 -99999.999 to +99999.999
IS-B 0.0001 -99999.9999 to +99999.9999
IS-C 0.00001 -9999.99999 to +9999.99999
IS-D 0.000001 -999.999999 to +999.999999
IS-E 0.0000001 -99.9999999 to +99.9999999
(B) Length and angle parameters (type 2)
Unit of data
mm
deg.
inch
Increment
system
IS-A 0.01 0.00 to +999999.99
IS-B 0.001 0.000 to +999999.999
IS-C 0.0001 0.0000 to +99999.9999
IS-D 0.00001 0.00000 to +9999.99999
IS-E 0.000001 0.000000 to +999.999999
IS-A 0.001 0.000 to +99999.999
IS-B 0.0001 0.0000 to +99999.9999
IS-C 0.00001 0.00000 to +9999.99999
IS-D 0.000001 0.000000 to +999.999999
IS-E 0.0000001 0.0000000 to +99.9999999
Minimum
data unit
Minimum
data unit
Valid data range
Valid data range
- 78 -
Page 87

B-64004EN/02 6.PARAMETERS
(C) Velocity and angular velocity parameters
Unit of data
mm/min
degree/min
inch/min
Increment
system
IS-A 0.01 0.0 to +999000.00
IS-B 0.001 0.0 to +999000.000
IS-C 0.0001 0.0 to +99999.9999
IS-D 0.00001 0.0 to +9999.99999
IS-E 0.000001 0.0 to +999.999999
IS-A 0.001 0.0 to +96000.000
IS-B 0.0001 0.0 to +9600.0000
IS-C 0.00001 0.0 to +4000.00000
IS-D 0.000001 0.0 to +400.000000
IS-E 0.0000001 0.0 to +40.0000000
Minimum
data unit
Valid data range
(D)Acceleration and angular acceleration parameters
Unit of data
mm/sec2
deg./sec
inch/sec2
2
Increment
system
IS-A 0.01 0.00 to +999999.99
IS-B 0.001 0.000 to +999999.999
IS-C 0.0001 0.0000 to +99999.9999
IS-D 0.00001 0.00000 to +9999.99999
IS-E 0.000001 0.000000 to +999.999999
IS-A 0.001 0.000 to +99999.999
IS-B 0.0001 0.0000 to +99999.9999
IS-C 0.00001 0.00000 to +9999.99999
IS-D 0.000001 0.000000 to +999.999999
IS-E 0.0000001 0.0000000 to +99.9999999
Minimum
data unit
Valid data range
Notes
(1) Values are rounded up or down to the nearest multiples of the
minimum data unit.
(2) A valid data range means data input limits, and may differ from
values representing actual performance.
(3) For information on the ranges of commands to the CNC, refer to
Appendix, "List of Command Ranges," in the "USER’S
MANUAL" (B-63944EN).
(4) The setting value of the parameter related with length and angle
depends on whether the attribute of the axis is diameter
specification or radius specification. In case safety function, set
the parameter according to the attribute of the axis at power on.
Even if the attribute is changed after power on, changed value is
not used by each safety function. Each safety function refers to
the value that is specified at power on. .
- 79 -
Page 88

6.PARAMETERS B-64004EN/02
6.5 PARAMETERS
0980 Machine group number of each path
NOTE
When this parameter is set, the power must be
turned off before operation is continued.
[Input type] Parameter input
[Data type] Byte path
[Valid data range] 1 to 3
Set the machine group number which each path belongs.
NOTE
When 0 is set, each path is assumed to belong to
machine group 1.
0981 Absolute path number of each axis
NOTE
When this parameter is set, the power must be
turned off before operation is continued.
[Input type] Parameter input
[Data type] Byte axis
[Valid data range] 1 to 10
Set the path to which each axis belongs.
NOTE
When 0 is set each axis is assumed to belong to path
1.
0982 Absolute path number of each spindle
NOTE
When this parameter is set, the power must be
turned off before operation is continued.
[Input type] Parameter input
[Data type] Byte spindle
[Valid data range] 1 to 10
Set the path to which each spindle belongs.
NOTE
When 0 is set each axis is assumed to belong to path
1.
- 80 -
Page 89

B-64004EN/02 6.PARAMETERS
1023 Servo axis number of each axis
NOTE
When this parameter is set, the power must be
turned off before operation is continued.
[Input type] Parameter input
[Data type] Byte axis
[Valid data range] 0 to Number of controlled axis
Set the servo axis for each control axis. Usually set to same number as
the control axis number.
The control axis number is the order number that is used for setting
the axis-type parameters or axis-type machine signals With an axis for
which Cs contour control/spindle positioning is to be performed, set
"-(spindle number)" as the servo axis number.
Example)
When performing Cs contour control on the fourth control axis by
using the first spindle, set -1.
1240
Coordinates value of the reference position in the machine coordinate
system
NOTE
When this parameter is set, the power must be
turned off before operation is continued.
[Input type] Parameter input
[Data type] Real axis
[Unit of data] mm, inch, degree (machine unit)
[Minimum unit of data] Depend on the increment system of the applied axis
[Valid data range] 9 digit of minimum unit of data (Refer to standard parameter setting
table(A). But in case that CMR≥1, data range becomes 1/CMR of 9
digits of minimum unit of data.)
(When the increment system is IS-B and CMR=1, -999999.999 to
+999999.999)
(When the increment system is IS-B and CMR=2, -499999.999 to
+499999.999)
NOTE
Whether to specify this parameter by using a
diameter value or radius value depends on whether
the corresponding axis is based on diameter
specification or radius specification.
Set the coordinate values of the reference position in the machine
coordinate system.
- 81 -
Page 90

6.PARAMETERS B-64004EN/02
1838 Position deviation limit for each axis in moving state during safety check
NOTE
When this parameter is set, the power must be
turned off before operation is continued.
[Input type] Parameter input
[Data type] 2-word axis
[Unit of data] Detection unit
[Valid data range] 0 to 99999999
Position deviation limit for each axis in moving state for safety check
of Dual Check Safety function is specified.
If position deviation of a moving axis exceeds position deviation limit
while Safety Check is carried out (Safety Monitoring Request
“*VLDVx” =0), a servo alarm (SV0475, SV1071) is generated and
axes are stopped immediately like emergency stop state.
In Dual Check Safety function, position deviation is always checked
by CNC and Servo. In case that Safety Check is carried out (Safety
Monitoring Request “*VLDVx” =0), the servo alarm
(SV0475,SV1071) is generated when each CPU finds out that the
deviation exceeds position deviation limit in moving state.
1839 Position deviation limit for each axis in stopped state during safety check
NOTE
When this parameter is set, the power must be
turned off before operation is continued.
[Input type] Parameter input
[Data type] 2-word axis
[Unit of data] Detection unit
[Valid data range] 0 to 99999999
Set the positioning deviation limit in stopped state for each axis for
Dual Check Safety function.
If the positioning deviation exceeds the positioning deviation limit
during stopped state while Safety Check is carried out (Safety
Monitoring Request “*VLDVx” =0), a servo alarm (SV0474,
SV1072) is generated, and operation is stopped immediately (as in
emergency stop).
In Dual Check Safety function, position deviation is always checked
by CNC and Servo. In case that Safety Check is carried out (Safety
Monitoring Request “*VLDVx” =0), servo alarm (SV0474,SV1072)
is generated when each CPU finds out that the deviation exceeds
position deviation limit in stopped state.
- 82 -
Page 91

B-64004EN/02 6.PARAMETERS
1840 Position deviation limit for each axis in servo-off state during safety check
NOTE
When this parameter is set, the power must be
turned off before operation is continued.
[Input type] Parameter input
[Data type] 2-word axis
[Unit of data] Detection unit
[Valid data range] 0 to 99999999
Set the positioning deviation limit in servo-off state for each axis for
Dual Check Safety function.
If the positioning deviation exceeds the positioning deviation limit
during servo-off, a servo alarm (SV1069,SV1070) is generated, and
operation is stopped immediately (as in emergency stop).
In Dual Check Safety function, position deviation is always checked
by CNC and Servo. In case that Safety Check is carried out (Safety
Monitoring Request “*VLDVx” =0), servo alarm (SV1069,SV1070)
is generated when each CPU finds out that the deviation exceeds
position deviation limit in servo-off state.
1841
Position deviation limit of each axis in moving state during other than Dual Check
Safety monitoring (for Dual Check Safety Function)
NOTE
When this parameter is set, the power must be
turned off before operation is continued.
[Input type] Parameter input
[Data type] 2 word axis
[Unit of data] Detection unit
[Valid data range] 0 to 99999999
Set the positioning deviation limit in moving state for each axis for
Dual Check Safety function, in case that Safety Check is not carried
out (Safety Monitoring Request “*VLDVx”=1).
In case that Safety Check is not carried out (Safety Monitoring
Request “*VLDVx” =1), servo alarm (SV0475,SV1071) is generated
and operation is stopped immediately (as in emergency stop), when
each CPU finds out that the deviation exceeds position deviation limit
in moving state.
If the value of this parameter is “0”, the parameter No.1828 is used for
the value of deviation limit in moving state.
In case that Safety Check is carried out (Safety Monitoring Request
“*VLDVx” =0), the parameter No.1838 is used for the value of
deviation limit in moving state.
- 83 -
Page 92

6.PARAMETERS B-64004EN/02
1842
Position deviation limit of each axis in stopped state during other than Dual
Check Safety monitoring (for Dual Check Safety Function)
NOTE
When this parameter is set, the power must be
turned off before operation is continued.
[Input type] Parameter input
[Data type] 2 word axis
[Unit of data] Detection unit
[Valid data range] 0 to 99999999
Set the positioning deviation limit in stopped state for each axis for
Dual Check Safety function, in case that Safety Check is not carried
out (Safety Monitoring Request “*VLDVx”=1).
In case that Safety Check is not carried out (Safety Monitoring
Request “*VLDVx” =1), servo alarm (SV0474,SV1072) is generated
and operation is stopped immediately (as in emergency stop), when
each CPU finds out that the deviation exceeds position deviation limit
in stopped state.
If the value of this parameter is “0”, the parameter No.1829 is used for
the value of deviation limit in stopped state.
In case that Safety Check is carried out (Safety Monitoring Request
“*VLDVx” =0), the parameter No.1839 is used for the value of
deviation limit in stopped state.
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
1902 DCE
[Input type] Parameter input
[Data type] Bit
NOTE
When this parameter is set, the power must be
turned off before operation is continued.
# 6 DCE Dual Check Safety function is
0: inactive.
1: active.
This parameter invalidates Dual Check Safety function temporarily.
In the system with Dual Check Safety function, this parameter is used
when the system set up without wiring and ladder related with Dual
Check Safety in order to set up other function.
- 84 -
Page 93

B-64004EN/02 6.PARAMETERS
NOTE
When Dual Check Safety function is used, this
parameter must be set to “1”. If Dual Check Safety
function is ordered and this parameter is “0”, an alarm
(DS0022) is displayed at power-on. This alarm can be
reset by pushing “CAN” and “RESET” key on MDI at
the same time.
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
1904 DCN
[Input type] Parameter input
[Data type] Bit axis
NOTE
When this parameter is set, the power must be
turned off before operation is continued.
# 6 DCN The checks of the target axis by Dual Check Safety function are:
0: carried out.
1: not carried out.
NOTE
1 It is not possible to inhibit each check of Dual
Check Safety Function of all axes by the parameter
DCN.
2 Set the DCN bit to 1 for the slave axis under
tandem control or for the tool axis of a simple
electronic gear box or electronic gear box 2-pair.
3 The checks by the dual check safety function are
not carried out on an axis for which the DCN bit is
set to 1. Set the DCN bit to 0 for normal axes.
1945 Safety input signal check timer
NOTE
When this parameter is set, the power must be
turned off before operation is continued.
[Input type] Parameter input
[Data type] Word machine group
[Unit of data] msec
[Valid data range] 0 to 1000
Input/output signals related to Dual Check Safety function (safety
double input/output signals) are transmitted through two paths, “I/O
Link #1 or #2” and “I/O Link#3, #4 or Profibus-DP”. CNC CPU and
PMC CPU exchange the input/output signals with each other at all
time to check each other. If a mismatch between double input/output
signals through two paths lasts greater than the time set in this
- 85 -
Page 94

6.PARAMETERS B-64004EN/02
parameter, alarm PW0010, PW0011, PW0012 or PW0013 is
generated.
If a value of less than 16 is specified, it is assumed that 16 ms is
specified.
If a value of more than 1000 is specified, it is assumed that 1000 ms is
specified.
NOTE
The same value is applied to each path that
belongs to a machine group.
1946 MCC off Test timer
NOTE
When this parameter is set, the power must be
turned off before operation is continued.
[Input type] Parameter input
[Data type] Word machine group
[Unit of data] msec
[Valid data range] 0 to 32767
When MCC off Test mode is selected with Dual Check Safety
function, CNC CPU carries out MCC off Test by the safety output
signal (*MCF). If MCC off Test is not completed within the time set
in this parameter, a servo alarm SV0488 is generated.
If a value of less than 0 is specified, it is assumed that 10000 ms is
specified.
NOTE
The same value is applied to each path that
belongs to a machine group.
1948 MCC off timer 2
NOTE
When this parameter is set, the power must be
turned off before operation is continued.
[Input type] Parameter input
[Data type] Word machine group
[Unit of data] msec
[Valid data range] 0 to 32767
CNC CPU and PMC CPU set MCC Off signal (*MCFVx) to 0, when
an axis is not stopped within the time set by this parameter after Safe
Speed Monitoring or Safe Machine Position Monitoring function of
Dual Check Safety function detects abnormal condition.
- 86 -
Page 95

B-64004EN/02 6.PARAMETERS
NOTE
The same value is applied for each path that
belongs to a machine group.
1950 Brake signal timer
NOTE
When this parameter is set, the power must be
turned off before operation is continued.
[Input type] Parameter input
[Data type] Word machine group
[Unit of data] msec
[Valid data range] 0 to 32767
Set a time period from when CNC CPU and Servo CPU in Dual
Check Safety function detects that the servo amplifier is ready (MCC
on state) until Safety Brake signal (*BRKx) goes 1 (brake release
enabled).
NOTE
The same value is applied for each path that
belongs to a machine group.
3021
Address to which an axis signal is assigned
NOTE
When this parameter is set, the power must be
turned off before operation is continued.
[Input type] Parameter input
[Data type] Byte axis
[Valid data range] 0 to 7, 10 to 17, 20 to 27, ... , 90 to 97
For each axis of the CNC, set a PMC interface address.
Set a value according to the tables below.
Value of parameter No. 3021 (tens digit)
Setting
value
0 G0000 to G0999 F0000 to F0999
1 G1000 to G1999 F1000 to F1999
9 G9000 to G9999 F9000 to F9999
Setting
value
0 #0 #0
1 #1 #1
7 #7 #7
Input signal address Output signal address
・・・
Value of parameter No. 3021 (ones digit)
Input signal address Output signal address
・・・
- 87 -
Page 96

6.PARAMETERS B-64004EN/02
[Example of setting]
Axis
number
1 0 +J1<G0100.0>, -J1<G0102.0>,
2 1 +J2<G0100.1>, -J2<G0102.1>,
3 2 +J3<G0100.2>, -J3<G0102.2>,
4 10 +J4<G1100.0>, -J4<G1102.0>,
5 11 +J5<G1100.1>, -J5<G1102.1>,
No.3021 Signal allocation
ZP1<F0090.0>, ...
ZP2<F0090.1>, ...
ZP3<F0090.2>, ...
ZP4<F1090.0>, ...
ZP5<F1090.1>, ...
If eight or less axes are used per path, the following signal allocation
results when 0 is set for all axes:
Axis 1 of path 1 = Setting equivalent to 0
Axis 2 of path 1 = Setting equivalent to 1
:
Axis 1 of path 2 = Setting equivalent to 10
:
NOTE
Set this parameter when more than eight axes are
used per path.
The valid data range varies, depending on the NC
system type.
3022 Address to which a spindle signal is assigned
NOTE
When this parameter is set, the power must be
turned off before operation is continued.
[Input type] Parameter input
[Data type] Byte spindle
[Valid data range] 0to3,10to13,20to23, ... ,90to93
For each axis of the CNC, set a PMC interface address.
Set a value according to the tables below.
Value of parameter No. 3022 (tens digit)
Setting value Input signal address Output signal address
0 G0000 to G0999 F0000 to F0999
1 G1000 to G1999 F1000 to F1999
9 G9000 to G9999 F9000 to F9999
Value of parameter No. 3022 (ones digit)
Setting value Input signal address Output signal address
0 Bit position A Bit position A
1 Bit position B Bit position B
2 Bit position C Bit position C
3 Bit position D Bit position D
・・・
- 88 -
Page 97

B-64004EN/02 6.PARAMETERS
(The bit positions A, B, C and D vary, depending on the type of
signal.)
[Example of setting]
Spindle number No.3022 Signal allocation
1 0 TLMLA<G0070.0>, TLMHA<G0070.1>,
ALMA<F0045.0>, ...
2 1 TLMLB<G0074.0>, TLMHB<G0074.1>,
ALMB<F0049.0>, ...
3 10 TLMLA<G1070.0>, TLMHA<G1070.1>,
ALMA<F1045.0>, ...
4 11 TLMLB<G1074.0>, TLMHB<G1074.1>,
ALMB<F1049.0>, ...
If four or less axes are used per path, the following signal allocation
results when 0 is set for all axes:
Axis 1 of path 1 = Setting equivalent to 0
Axis 2 of path 1 = Setting equivalent to 1
:
Axis 1 of path 2 = Setting equivalent to 10
NOTE
Set this parameter when more than four axes are
used per path.
The valid data range varies, depending on the
system software.
3225 Code for safety parameters
NOTE
When this parameter is set, the power must be
turned off before operation is continued.
[Input type] Parameter input
[Data type] 2-word
[Valid data range] 0 to 99999999
Set a code (password) for protecting against modifications to
parameters related to Dual Check Safety function (safety parameters).
When a code for safety parameters is set other than the value “0”, the
parameters are locked. In this state, the setting (code) is not displayed
but is blank, and safety parameter input is disabled.
If an attempt is made to input data in a locked safety parameter, the
result indicated in the table below is produced, depending on the
method of input. No attempt is successful.
Input method Result
MDI input Warning “WRITE PROTECT”
Input via reader/puncher interface No alarm is generated. But parameter
input is disabled.
Input through window function Completion code 7 (WRITE PROTECT)
If the value other than “0” is set to this parameter, the safety parameter
cannot be modified. The safety parameters can be set when the safety
- 89 -
Page 98

6.PARAMETERS B-64004EN/02
parameters are not locked, that is, when the code for safety parameters
is 0, or when the code for safety parameters is the same as the key for
safety parameters (No. 3226).
The following safety parameters are protected by a code for safety
parameters:
No.980, No.981, No.982, No.1023, No.1240, No.1838, No.1839,
No.1840, No.1841, No.1842, No.1902, No1904, No.1945, No.1946,
No.1948, No.1950, No.3021, No.3022, No.3225, No.3717, No.3797,
No.4372, No.4438, No.4440, No.4442, No.4448, No.10500,
No.10501-No.10596, No.11950-No.11957, No.11960-N0.11967,
No.11970-No.11977, No.11980-No-11987, No.13811,
No.13821-No.13829, No.13831~No.13838, No.13840-No.13843,
No.13880-No.13911, No.13920-No.13951, No.13960-No.13991
NOTE
Once parameters are locked, the lock must be
released or memory must be cleared before the
safety parameters can be modified. Moreover, the
code for the safety parameters cannot be modified
in locked condition. Be careful when setting a code
for safety parameters.
3226 Key for safety parameters
NOTE
When this parameter is set, the power must be
turned off before operation is continued.
[Input type] Parameter input
[Data type] 2-word
[Valid data range] 0 to 99999999
When the same value as the code for safety parameters No.3225 is set
in this parameter, the key is opened to enable modifications to the
safety parameters. The value set in this parameter is not displayed.
When the value other than 0 is set to the code for safety parameters
No.3225 and the value is different from this parameter, the key is
locked and the safety parameters can not be modified.
When the power is turned off, the value set in this parameter is cleared
to 0. Then the power-off results in the locked state.
- 90 -
Page 99

B-64004EN/02 6.PARAMETERS
3717 Motor number to each spindle
NOTE
When this parameter is set, the power must be
turned off before operation is continued.
[Input type] Parameter input
[Data type] Byte spindle
[Valid data range] 0 to Maximum number of controlled axes
Set a spindle amplifier number to be assigned to each spindle.
0: No spindle amplifier is connected.
1: Spindle motor connected to amplifier number 1 is used.
2: Spindle motor connected to amplifier number 2 is used.
to
n: Spindle motor connected to amplifier number n is used.
#7 #6 #5 #4 #3 #2 #1 #0
3797 DCN
[Input type] Parameter input
[Data type] Bit spindle
NOTE
When this parameter is set, the power must be
turned off before operation is continued.
# 0 DCN Each safety check of Dual Check Safety function for the specified
spindle is
0: carried out.
1: not carried out.
Set “1” to this bit for the spindle that is not required to apply Dual
Check Safety.
- 91 -
Page 100

6.PARAMETERS B-64004EN/02
4372 Safe speed 1 for each spindle
4438 Safe speed 2 for each spindle
4440 Safe speed 3 for each spindle
4442 Safe speed 4 for each spindle
NOTE
When this parameter is set, the power must be
turned off before operation is continued.
[Input type] Parameter input
[Data type] Word spindle
[Unit of data] min
-1
[Valid data range] 0 to 32767
Set a safe speed for each spindle in terms of motor speed. In case Dual
Check Safety function is activated, CNC and Spindle always check
the speed of each spindle motor. When it is detected that revolution
speed of spindle exceeds safety speed limit, Monitoring Result signal
(RSPs) is set to “0”. Moreover if the safety check is carried out
(Safety Check Request signal *VLDPs =”0”), an alarm SP0757(CNC
side) or SP9069(Spindle side) occurs.
Safety Speed can be set up to 4 data. Which speed should be selected
is decided by Safety Speed Selection signal (SPAs/SPBs). Please refer
more detail to the description about Safety Speed/Safety Position
Selection signal.
CAUTION
After Safety Speed parameters No.4372, No.4438,
No.4440 or No.4442 has been modified, the power
must be turned off then back on for the setting to
become effective.
4448 Stop check level
NOTE
When this parameter is set, the power must be
turned off before operation is continued.
[Input type] Parameter input
[Data type] Word spindle
[Unit of data] min
[Valid data range] 0 to 32767
-1
When a spindle motor is in free-run state because of excess of safety
speed, a motor is regarded as stop state if the speed of a spindle motor
becomes lower than the value set by this parameter. In this condition,
an alarm can be reset. The setting value must be lower than the
parameter “Safe Speed for each spindle”.
- 92 -
 Loading...
Loading...