Cisco IR800 Service Manual

Cisco IR800 Integrated Services Router Software Configuration Guide
First Published: 2016-12-20
Last Modified: 2020-03-25
Americas Headquarters
Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-1706 USA http://www.cisco.com Tel: 408 526-4000
800 553-NETS (6387) Fax: 408 527-0883
THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. ALL STATEMENTS, INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS IN THIS MANUAL ARE BELIEVED TO BE ACCURATE BUT ARE PRESENTED WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. USERS MUST TAKE FULL RESPONSIBILITY FOR THEIR APPLICATION OF ANY PRODUCTS.
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE AND LIMITED WARRANTY FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PRODUCT ARE SET FORTH IN THE INFORMATION PACKET THAT SHIPPED WITH THE PRODUCT AND ARE INCORPORATED HEREIN BY THIS REFERENCE. IF YOU ARE UNABLE TO LOCATE THE SOFTWARE LICENSE OR LIMITED WARRANTY, CONTACT YOUR CISCO REPRESENTATIVE FOR A COPY.
The Cisco implementation of TCP header compression is an adaptation of a program developed by the University of California, Berkeley (UCB) as part of UCB's public domain version of the UNIX operating system. All rights reserved. Copyright © 1981, Regents of the University of California.
NOTWITHSTANDING ANY OTHER WARRANTY HEREIN, ALL DOCUMENT FILES AND SOFTWARE OF THESE SUPPLIERS ARE PROVIDED “AS IS" WITH ALL FAULTS. CISCO AND THE ABOVE-NAMED SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, THOSE OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT OR ARISING FROM A COURSE OF DEALING, USAGE, OR TRADE PRACTICE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS MANUAL, EVEN IF CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
All printed copies and duplicate soft copies of this document are considered uncontrolled. See the current online version for the latest version.
Cisco has more than 200 offices worldwide. Addresses and phone numbers are listed on the Cisco website at www.cisco.com/go/offices.
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: www.cisco.com go trademarks. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1721R)
© 2016-2019–2020 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.

C O N T E N T S
|
Full Cisco Trademarks with Software License ? |
|
|
Preface xi |
|
|
Preface xi |
|
C H A P T E R 1 |
Product Overview 1 |
|
|
General Description |
1 |
|
Hardware Overview |
2 |
IR829 Product Overview |
2 |
IR809 Product Overview |
4 |
Reset Button 5 |
|
Booting a Default IOS Image and Default Configuration - Method 1 |
6 |
Booting a Default IOS Image and Default Configuration - Method 2 |
7 |
Configuration Register 7 |
|
|
Auto-recovery of Corrupt Filesystems 9 |
|
||
|
Plug and Play Agent (PnP) support over 4G/Ethernet |
11 |
||
|
Plug and Play (PnP) Support on the IR829 LAN 12 |
|
||
|
Password Recovery |
14 |
|
|
|
Software Overview 15 |
|
|
|
|
Hardware Differences Between IR809, IR829, and C819HG |
16 |
||
|
Hardware Comparison |
17 |
|
|
|
Antenna Recommendations |
18 |
|
|
|
Features Supported in Different IOS Releases 18 |
|
||
|
Related Documentation |
22 |
|
|
C H A P T E R 2 |
Initial Configuration 23 |
|
|
|
Cisco IR800 Integrated Services Router Software Configuration Guide
iii

Contents
IR800 Bootstrap Sequence and Troubleshooting 23 |
||
Sequence 1 |
24 |
|
Example from a tftp server: 24 |
||
Example from USB to IOS flash: 25 |
||
Sequence 2 |
26 |
|
Setup Command Facility 27 |
||
Verifying the Initial Configuration 30 |
||
LEDs 30 |
|
|
Single Modem |
31 |
|
Dual Modem |
31 |
|
|
Software Bundle Installation |
34 |
|
|
|
|||
|
Displaing Digital Signature and Software Authenticity 34 |
|
||||||
|
show software authenticity file command |
34 |
|
|||||
|
verify command |
35 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bundle Installation Steps |
36 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
Additional Software Bundle Installation Options 37 |
|
||||||
|
Power Over Ethernet (PoE) |
38 |
|
|
|
|||
|
LLDP (Link Layer Discovery Protocol) Support for 3rd party PoE devices 39 |
|||||||
|
Serial Port Configuration |
41 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
Configuring Accelerometer and Gyroscope |
42 |
|
|||||
|
Auto-Negotiation Support for Gigabit-Ethernet 0 on the IR829 |
43 |
||||||
|
Where To Go From Here |
43 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
C H A P T E R 3 |
Cellular Interface Modules |
45 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cellular Interface 46 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4G LTE Dual SIM |
47 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AutoSim and Firmware Based Switching |
47 |
|
|||||
|
Dual Radio Configuration and Single Radio Configuration |
48 |
||||||
|
Verizon Profile |
52 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AT&T Profile |
53 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Creating a Cellular Profile for Verizon. 53 |
|
||||||
|
Creating a Cellular Profile for AT&T |
54 |
|
|||||
|
Other Useful Commands |
56 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
Accessing 4G Modem AT Commands |
57 |
|
|
||||
Cisco IR800 Integrated Services Router Software Configuration Guide
iv

Contents
|
|
Checking 4G Modem Firmware through AT Commands |
58 |
|
|||||||
|
|
Radio Frequency Band Select |
59 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Low Power Mode |
60 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Enhancement to Modem Crash Action |
60 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
IR800 Cellular Technology Selection |
61 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
GPS 64 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
GPS NMEA Multiple Stream |
66 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Setting up the Configuration |
66 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Troubleshooting the Cellular Interface |
67 |
|
|
|
|
||||
C H A P T E R |
4 |
IR829 AP803 Access Point Module |
71 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Hardware Overview |
71 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Software Overview |
72 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IOS Internal Interfaces |
72 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IR829 IOS – AP803 Console Access |
73 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
IR829 Service Module |
74 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AP803 Embedded Web Manager |
75 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Upgrading the Firmware on the AP803 |
76 |
|
|
|
|
||||
C H A P T E R |
5 |
Configuring Virtual-LPWA |
77 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configuring Virtual-LPWA Interface on the IR800 Series |
77 |
|
|
||||||
|
|
Configuring Ethernet Interface and Creating VLPWA Interface |
78 |
||||||||
|
|
Configuring IR809 for One Cisco LoRaWAN Gateway |
78 |
|
|||||||
|
|
Configuring IR809 for Multiple Cisco LoRaWAN Gateways |
79 |
||||||||
|
|
Configuring IR829 |
80 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configuring DHCP Pool for the Cisco LoRaWAN Gateway |
80 |
|
|||||||
|
|
Configuring SNMP TRAP for Modem Notifications |
82 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
Configuring VLPWA Interface and Associated Cisco LoRaWAN Gateway 83 |
|||||||||
|
|
Configuring IR809 for One Cisco LoRaWAN Gateway |
84 |
|
|
||||||
|
|
Configuring Cisco LoRaWAN Gateway Password 85 |
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
Configuring Console Access |
85 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Configuring Clock for the Cisco LoRaWAN Gateway |
86 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
Configuring NTP Server for the Cisco LoRaWAN Gateway |
86 |
|
|||||||
|
|
Configuring GPS as the Clock Source 87 |
|
|
|
|
|||||
Cisco IR800 Integrated Services Router Software Configuration Guide
v

Contents
|
|
Configuring Cisco LoRaWAN Gateway Timezone 87 |
|
|
|||||||
|
|
Configuring IPSec on the Cisco LoRaWAN Gateway |
88 |
|
|||||||
|
|
Configuring SCEP on the Cisco LoRaWAN Gateway |
88 |
|
|||||||
|
|
Configuring Security Protection 90 |
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
Managing the Cisco LoRaWAN Gateway |
91 |
|
|
||||||
|
|
LoRaWAN Modem Firmware Upgrade |
92 |
|
|
||||||
|
|
Installing U-boot |
94 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
LoRaWAN Gateway FPGA Upgrade 94 |
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
Uploading a File to the LoRaWAN Gateway 95 |
|
|
|||||||
|
|
Monitoring the LoRaWAN Gateway |
95 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
Monitoring LED Status |
|
99 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Checking Connectivity |
99 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
Debugging the LoRaWAN Gateway |
99 |
|
|
|
|||||
C H A P T E R |
6 |
Alarms 101 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Finding Feature Information |
101 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
Information About Alarms |
|
101 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Alarm Port |
101 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Alarm Conditions |
102 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configuration Commands |
102 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
Configuration Examples |
|
103 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Enabling SNMP Traps |
104 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
MIBs 104 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C H A P T E R |
7 |
Guest Operating System (Guest OS) Installation and Configuration |
105 |
||||||||
|
|
Guest Operating System Overview |
105 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
Prerequisites |
106 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Guidelines and Limitations |
106 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
Default Settings |
107 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Installation and Upgrade |
108 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
Improvements in IOS and Guest-OS Clock Time Synchronization |
108 |
||||||||
|
|
Configuring Cisco IOS |
109 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
Configuring the IR800 Ethernet Interface |
109 |
|
|
||||||
|
|
IPv6 Gigabit Ethernet |
|
109 |
|
|
|
|
|||
Cisco IR800 Integrated Services Router Software Configuration Guide
vi

Contents
|
Enabling IPv4 Gigabit Ethernet |
110 |
|
|
||||||
|
Configuring DHCP Pool |
110 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Configuring Guest OS GigabitEthernet on Cisco IOS |
111 |
||||||||
|
Configuring Guest OS |
111 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Starting Guest OS |
111 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Guest OS persistent logging through reload 112 |
|
||||||||
|
Guest OS file system corruption detection and recovery 112 |
|||||||||
|
IOx Radius authentication |
113 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
IOXVM Storage Partition Enhancement |
113 |
|
|||||||
|
Configuring Network Address Translation (NAT) 114 |
|
||||||||
|
IR800 Guest-OS USB Access from IOS |
115 |
|
|||||||
|
New for IOS 15.6(1)T |
115 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
New for IOS 15.6(3)M |
116 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
USB Support |
116 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Serial Device Configuration |
116 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
Serial Relay Configuration 116 |
|
|
|
||||||
|
Memory Allocation Optimization |
117 |
|
|
||||||
|
New for IOS 15.7(3)M |
117 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Troubleshooting |
118 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Checking Connectivity |
119 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Related Documentation |
119 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
C H A P T E R 8 |
WAN Monitoring |
121 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Information About WANMon |
121 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Built-in Recovery Actions |
121 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Prerequisites |
122 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Guidelines and Limitations 122 |
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Configuring WANMon |
123 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Verifying WANMon Configuration |
124 |
|
|
||||||
|
Configuration Examples |
125 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
WANMon Cellular Interface Configuration Example |
125 |
||||||||
|
Multiple WAN Link Monitoring Example |
125 |
|
|||||||
|
Related Documentation |
126 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Cisco IR800 Integrated Services Router Software Configuration Guide
vii

Contents
C H A P T E R |
9 |
Ignition Power Management |
127 |
|
|
|||
|
|
Features of Ignition Power Management 127 |
|
|||||
|
|
Command Line Interface (CLI) |
128 |
|
||||
|
|
Configuration CLI |
128 |
|
|
|||
|
|
Status CLI |
128 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Troubleshooting CLI |
129 |
|
|
|||
|
|
Command Examples |
131 |
|
|
|||
|
|
Default Values |
132 |
|
|
|
|
|
C H A P T E R |
1 0 |
Licensing and Security |
133 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
Licensing 133 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Licensing CLI |
134 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hardware Crypto Support |
134 |
|
|
|||
C H A P T E R |
1 1 |
mSATA SSD as Additional Storage |
137 |
|
||||
|
|
mSATA Overview |
137 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
IR829M SKUs |
137 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Using the mSATA SSD |
138 |
|
|
|||
|
|
Displaying the Wear Leveling Data for the mSATA SSD |
139 |
|||||
|
|
IR829M: MIB support for mSATA Wear Ratio and Usage |
139 |
|||||
|
|
Example: Actual OID and output of SNMP get/walk on OID 140 |
||||||
|
|
Feature Details |
140 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Feature Assumptions |
140 |
|
|
|||
|
|
IR829M OIDs |
141 |
|
|
|
|
|
C H A P T E R 1 2
Client Information Signaling Protocol (CISP) 143
Client Information Signaling Protocol (CISP) 143
CISP Commands 143
CISP Prerequisites 144
Flow Diagrams 144
C H A P T E R 1 3 |
Dot1x Supplicant Support on the L2 interface 147 |
Cisco IR800 Integrated Services Router Software Configuration Guide
viii

Contents
|
Dot1x Supplicant Support on the L2 interface 147 |
|
||||
|
Sample Configuration to Support DOT1x Supplicant on the IR829 |
148 |
||||
C H A P T E R 1 4 |
Network Management Solutions |
151 |
|
|||
|
Cisco IoT Field Network Director (formerly referred to as CG-NMS) |
151 |
||||
|
IR809 and IR829: PNP Image Upgrade from FND 153 |
|
||||
|
Image Installation |
153 |
|
|
||
|
Feature Assumptions |
154 |
|
|||
|
Cisco Configuration Professional Express 155 |
|
||||
|
Cisco Kinetic |
155 |
|
|
|
|
|
Cisco Prime Infrastructure |
156 |
|
|||
|
Davra RuBAN |
156 |
|
|
|
|
|
Cisco IoT Fog Director |
156 |
|
|
||
|
About Cisco IOx |
156 |
|
|
||
|
About Cisco Fog Director |
156 |
|
|||
|
OID and Inventory |
|
157 |
|
|
|
Cisco IR800 Integrated Services Router Software Configuration Guide
ix

Contents
Cisco IR800 Integrated Services Router Software Configuration Guide
x

Preface
This preface describes the objectives, audience, organization, and conventions of this guide and describes related documents that have additional information.
Preface
This preface describes the objectives, audience, organization, and conventions of this guide and describes related documents that have additional information. It contains the following sections:
Objective
This guide provides an overview of the software features and explains how to perform the configuration steps for the Cisco IR800 Integrated Services Routers.
Audience
This guide is intended for people who have a high level of technical ability, although they may not have experience with Cisco software.
Conventions
This section describes the conventions used in this guide.
Note Means reader take note. Notes contain helpful suggestions or references to additional information and material.
Caution This symbol means reader be careful. In this situation, you might do something that could result in equipment damage or loss of data.
Tip Means the following information will help you solve a problem . The tip information might not be troubleshooting or even an action, but could be useful information.
Searching Cisco Documents
To search an HTML document using a web browser, press Ctrl-F (Windows) or Cmd-F (Apple). In most browsers, the option to search whole words only, invoke case sensitivity, or search forward and backward is also available.
To search a PDF document in Adobe Reader, use the basic Find toolbar (Ctrl-F) or the Full Reader Search window (Shift-Ctrl-F). Use the Find toolbar to find words or phrases within a specific document. Use the Full Reader Search window to search multiple PDF files simultaneously and to change case sensitivity and other options. Adobe Reader’s online help has more information about how to search PDF documents.
Cisco IR800 Integrated Services Router Software Configuration Guide
xi

Preface
Preface
Cisco IR800 Integrated Services Router Software Configuration Guide
xii

C H A P T E R 1
Product Overview
This chapter provides an overview of the features available for the Cisco IR800 Integrated Services Routers (ISRs).
•General Description, on page 1
•Hardware Overview, on page 2
•Software Overview, on page 15
•Hardware Differences Between IR809, IR829, and C819HG, on page 16
•Antenna Recommendations, on page 18
•Features Supported in Different IOS Releases, on page 18
•Related Documentation, on page 22
General Description
The 800 Series Industrial Integrated Services Routers are compact, ruggedized, Cisco IOS Software routers. They offer support for integrated 4G LTE wireless WAN (both 809 and 829 models) and wireless LAN capabilities (829 model only). The IR829 offers an Internal WLAN Access Point which runs on-board the router. The AP803 runs its own IOS software independently from the IR829 IOS, and requires configuring. The AP803 works as a standalone access point or with a wireless controller.
They offer:
•Easily and rapidly deployable
•Highly available, highly secure, and reliable
•Designed for machine-to-machine (M2M) communication and for mobile vehicle communication in harsh environmental conditions
•Designed to withstand hostile environments, tolerating a wide temperature range
These industrialized routers deliver enterprise-class features, including highly secure data, voice, and video communications to stationary and mobile network nodes across wired and wireless links. They can deliver enterprise-grade, wireline-like functionality.
The routers also support Cisco IOx Software, providing an open, extensible environment for hosting additional operating systems and applications directly at the network edge. They can enhance other Cisco IoT System products across multiple industries, including transportation, manufacturing, electrical utilities, and others.
Cisco IR800 Integrated Services Router Software Configuration Guide
1
Product Overview
Hardware Overview
For a complete listing of the routers capabilities, see the Cisco 829 Industrial Integrated Services Routers Product Information .
Hardware Overview
This section covers the overview of the IR809 and IR829.
IR829 Product Overview
Figure 1: Cisco IR829 Integrated Services Router, on page 2 shows the IR829.
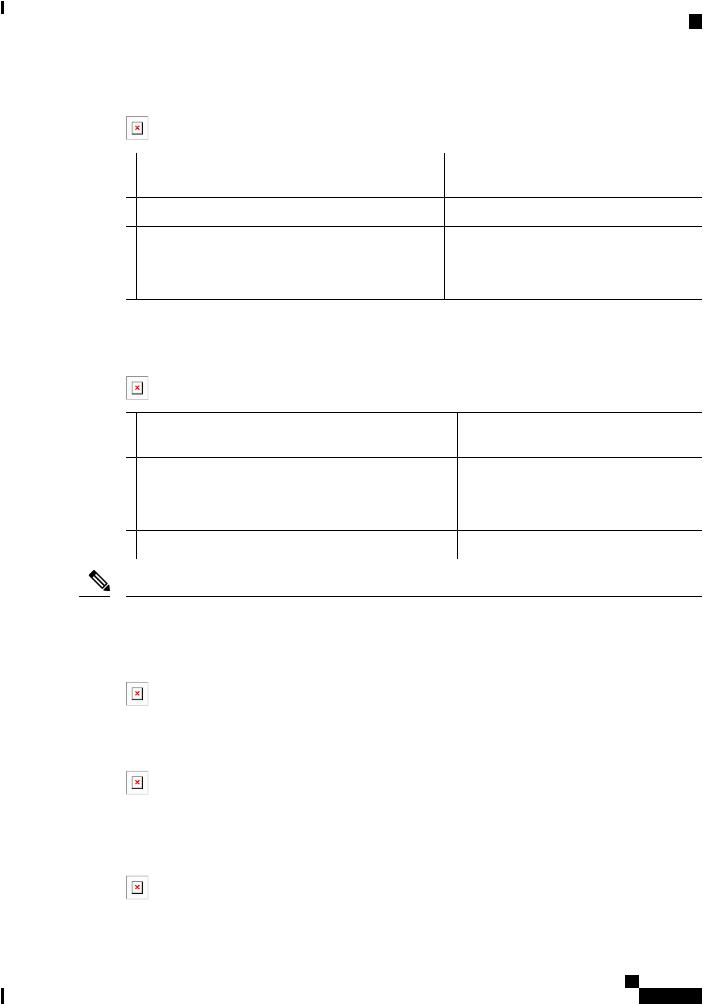
Figure 1: Cisco IR829 Integrated Services Router
Figure 2: Cisco IR829 Front Panel Single Modem, on page 2 shows the front panel details of the Cisco IR829 Single Modem.
Figure 2: Cisco IR829 Front Panel Single Modem
1 |
CELLULAR 0 AUX |
5 |
Serial Ports |
2 mSATA Slot |
6 |
USB-A Port |
|
3 |
Gigabit WAN (SFP) |
7 |
Power Input, Battery, and Ignition connector. Refer to the DC Power |
|
|
|
section for pin-outs. |
4 |
GigabitEthernetLAN/PoE(RJ45) |
8 |
WLAN ANT 0 2.4GHz |
Figure 3: Cisco IR829 Front Panel Duel Modem, on page 2 shows the front panel details of the Cisco IR829 Dual Modem.
Figure 3: Cisco IR829 Front Panel Duel Modem
1 |
CELLULAR 0 AUX |
5 |
Serial Ports |
2 mSATA Slot |
6 |
USB-A Port |
|
3 |
Gigabit WAN (SFP) |
7 |
Power Input, Battery, and Ignition connector. Refer to the DC Power |
|
|
|
section for pin-outs. |
4 |
GigabitEthernetLAN/PoE(RJ45) |
8 |
WLAN ANT 0 2.4/5GHz |
Figure 4: Cisco IR829 Back Panel Single Modem, on page 3 shows the back panels details of the Cisco IR829 Single Modem.
Cisco IR800 Integrated Services Router Software Configuration Guide
2
Product Overview
IR829 Product Overview
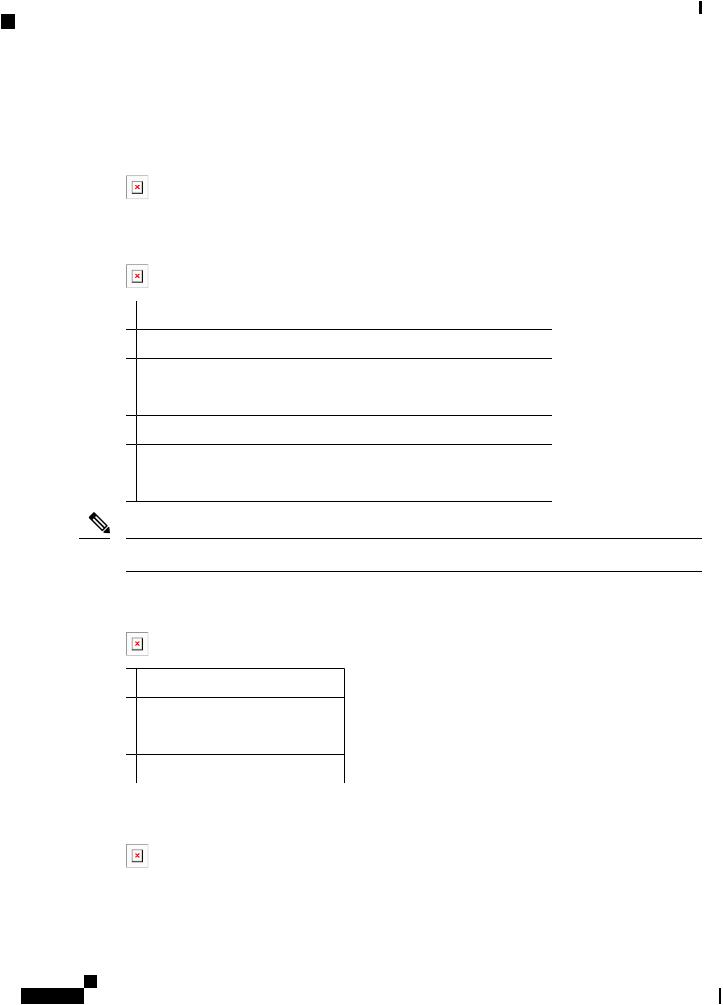
Figure 4: Cisco IR829 Back Panel Single Modem
1 WLAN ANT 0 |
5GHz |
5 Denotes SIM card order, SIM0 on top and |
|
|
SIM1 on bottom. |
2 WLAN ANT 1 |
2.4GHz |
6 WLAN ANT 1 5GHz |
3 CoveroverSIMcards,resetbuttonandconsoleportcover, 7 CELLULAR 0 MAIN see Figure 6: Behind the SIM Door, on page 3
4 GPS SMA
Figure 5: Cisco IR829 Back Panel Dual Modem, on page 3 shows the back panels details of the Cisco IR829 Dual Modem.
Figure 5: Cisco IR829 Back Panel Dual Modem
1 |
Cellular 1 Main |
5 |
Denotes SIM card order, SIM0 on top and |
|
|
|
SIM1 on bottom. |
2 |
WLAN ANT 1 2.4/5GHz |
6 |
Cellular 1 AUX |
3 |
CoveroverSIMcards,resetbuttonandconsoleportcover, |
7 |
CELLULAR 0 MAIN |
|
see Figure 6: Behind the SIM Door, on page 3 |
|
|
4 GPS SMA
Note Behind the SIM Door Assembly, there is a reset switch (1), Mini USB console port (2), and Dual SIM slots
(3). See Figure 6: Behind the SIM Door, on page 3 for details
Figure 6: Behind the SIM Door
Figure 7: Cisco IR829 Top Cover, on page 3 shows the top of the Cisco IR829.
Figure 7: Cisco IR829 Top Cover
Figure 8: Cisco IR829 LED Detail, on page 3 shows the LED detail from the Dual Modem SKU. Single Modem SKUs will only have Cellular0 LEDs.
Figure 8: Cisco IR829 LED Detail
Cisco IR800 Integrated Services Router Software Configuration Guide
3
Product Overview
IR809 Product Overview
IR809 Product Overview
The following figure shows the IR809.
Figure 9: Cisco IR809 Integrated Services Router
The following figure shows the front panel details of the Cisco IR809.
Figure 10: Cisco IR809 Front Panel
1 |
S0RS232DCE/RS485ComboPort |
8 |
Grounding Point |
2 |
S1 RS232 DTE only |
9 |
Mini type-B USB console/debug port |
3 |
GE0 (10/100/1000) |
10 |
SYS LED |
4 |
GE1 (10/100/1000) |
1 |
Alarm LED |
5 |
USB 2.0 (Type-A Host Port) |
12 |
WAN/WWAN LEDs |
6 |
RESET Button |
13 |
SIM Card LEDs |
7 |
DC Power/Alarm Connector |
|
|
Note LEDs are viewable from the top and from the front of the IR809.
The following figure shows the back panels details of the Cisco IR809.
Figure 11: Cisco IR809 Back Panel
1 DIV TNC connector for 4G Modem
2 SMA connector for GPS
3 SIM0 and SIM1 Card Slots
4 MAINTNCconnectorfor4GModem
The following figure shows the top cover details of the Cisco IR809.
Figure 12: Cisco IR809 Top Cover
Cisco IR800 Integrated Services Router Software Configuration Guide
4

Product Overview
Reset Button
Note See the respective Hardware Installation Guides for detailed description of the LEDs.
Reset Button
The reset button resets the router configuration to the default configuration set by the factory. To restore the router configuration to the default configuration set by the factory, use a standard size #1 paper clip with wire gauge 0.033 inch or smaller and simultaneously press the reset button while applying power to the router.
Note On the IR829, the rear cover must be removed to expose the reset switch.
Starting with release 15.6(1)T, the IR809 and IR829 have changed the way the reset button works. The IR800 series platforms now perform in the same manner as the C819. The high level description of the functionality works like this:
•Press and hold the reset button while powering up the router
•During warm reboot this button has no impact on performance
•Simply pressing the button at any time does not reset the router
•The router will not react to the reset button if it is pressed after power-up because the button needs to be pushed before turning ON/inserting power – to make sure that the condition is detected.
•The push-button cannot be used to boot a IOS image from network. The golden image has to be on flash: only
Note For the location of the reset button, see the appropriate IR809 or IR829 Hardware Installation Guide.
Perform the following steps to use the reset button:
Procedure
Step 1 Unplug power.
Step 2 Press the reset button on the router.
Step 3 Power up the system while holding down the reset button.
Step 4 Check the “boot system” setting configuration in the default configuration file (prior to saving it to startup-config), and verify that it points to an existing IOS image on the flash: partition. Note: If that particular IOS image is not present, the device will drop in rommon-2 mode and you will need to manually boot an IOS image from there.
Step 5 Copy your desired default config file to the startup-config.
Step 6 Reloadtherouter. DoNOTenterYesifpromptedwhetheryouwanttosavetherunning-configtostartup-config.
Cisco IR800 Integrated Services Router Software Configuration Guide
5
Product Overview
Booting a Default IOS Image and Default Configuration - Method 1
Example
An example of the log activity after a reboot follows:
IR800# show log
*Nov 30 19:31:04.925: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface GigabitEthernet0, changed state to down
*Nov 30 19:31:10.651: %PLATFORM-5-RESET_BUTTON: Reset Button pressed during boot up.
*Nov 30 19:31:11.527: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Async0, changed state to up
*Nov 30 19:31:11.595: %SYS-5-RESTART: System restarted --
Cisco IOS Software, ir800 Software (ir800-UNIVERSALK9-M), Version 15.6(1)T, RELEASE
SOFTWARE (fc1)
What to do next
Note To simplify the boot process, the IR800 routers do not support the ROMMON configuration register and the associated CLI commands. The IR800 either boots the pre-configured images, or stops at the ROMMON prompt for user intervention. In the event of a boot failure, see Chapter 3, “Setup Command Facility” for additional information.
Booting a Default IOS Image and Default Configuration - Method 1
The IR800 differs from traditional IOS routers when booting a default IOS image and a default configuration. These steps apply on a device running 15.6(1)T or later.
Method 1:
Procedure
Step 1 Save a copy of your IR800 IOS image with the .default extension on flash. For example: ios-image.default.
Step 2 Save a copy of your IR800 Hypervisor image with the .default extension on bootstrap. For example: hypervisor-image.default.
Step 3 Save your desired default configuration file with the .cfg extension on flash. For example: config.cfg.
Step 4 Reset your IR800 router by powering it down, then press and hold the RESET button while powering up the device.
The IR800 router will automatically boot hypervisor-image.default, then ios-image.default, and load the config.cfg.
Step 5 Make sure there exists only one IOS image with a .default extension, only one configuration file with the .cfg extension on the flash, and only one hypervisor image with the .default extension on bootstrap.
Cisco IR800 Integrated Services Router Software Configuration Guide
6

Product Overview
Booting a Default IOS Image and Default Configuration - Method 2
Booting a Default IOS Image and Default Configuration - Method 2
If you do not have a config.cfg on flash, it will boot with the Cisco default configuration (aka: empty) startup-config.
Method 2:
Procedure
Step 1 Check the “boot system” setting configuration in the default configuration file (prior to saving it to startup-config), and verify that it points to an existing IOS image on the flash: partition.
Note If that particular IOS image is not present, the device will drop in rommon-2 mode and you will need to manually boot an IOS image from there.
Step 2 Copy your desired default config file to the startup-config.
Step 3 Reloadtherouter. DoNOTenterYesifpromptedwhetheryouwanttosavetherunning-configtostartup-config.
What to do next
An example of the log activity after a reboot follows:
IR800# show log
*Nov 30 19:31:04.925: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface GigabitEthernet0, changed state to down
*Nov 30 19:31:10.651: %PLATFORM-5-RESET_BUTTON: Reset Button pressed during boot up. *Nov 30 19:31:11.527: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Async0, changed state to up
*Nov 30 19:31:11.595: %SYS-5-RESTART: System restarted --
Cisco IOS Software, ir800 Software (ir800-UNIVERSALK9-M), Version 15.6(1)T, RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc1)
Configuration Register
To configure the register:
IR800#conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. IR800(config)#config-register 0x?
<0x0-0xFFFF> IR800(config)#config-register 0x102 IR800(config)#
Jul 26 22:10:22.790: Bootstrap Emulator called with code 62 Jul 26 22:10:22.790: Bootstrap Emulator called with code 61 IR800(config)#
To display the register:
IR800#sh ver …..
…..
…..
Configuration register is 0x2101 (will be 0x102 at next reload)
The Format for the configuration registers is 0 x _ _ _ _ (4 bytes)
For example:
Cisco IR800 Integrated Services Router Software Configuration Guide
7

Product Overview
Configuration Register
0x102, 0x2102, 0x2142, 0x142, 0x101, 0x2101
The Configuration Register 1st byte table shows the configuration register 1st byte values and descriptions.
Table 1: Configuration Register 1st byte |
|
Value |
Description |
0 |
Boots into rommon 2 on reload. |
|
Importance – access to rommon mode and rommon parameters can be |
|
changed. |
1 |
Ignores auto-boot and boots first image in flash. |
|
In case of failure to boot the first image, it will try a maximum of 3 times to |
|
boot the same image and then halt in rommon 2. |
|
Importance – Irrespective of auto-boot string it will boot first image from |
|
flash. |
|
Auto-boot is ignored. |
2 to F |
Checks auto-boot and if present, the device will boot with auto-boot string. |
|
If auto-boot is not present, then the device will boot first image from flash. |
In case of failure to boot the first image, it will try a maximum of 3 times to boot the same image and then halt in rommon 2.
Importance - Auto-boot has the higher priority, and if that fails then the device will boot-up with first image.
The Configuration Register 2nd byte table shows the configuration register 2nd byte values and descriptions.
Table 2: Configuration Register 2nd byte
Value |
Description |
|
0 |
On reload after the device boots up with an image, it will have all the |
|
|
configuration stored in startup config. |
|
4 |
On reload after the device boots up with an image, it will ignore the startup |
|
|
config and stays on config dialog box for user to enter configuration. |
|
|
Note |
startup-config is still present however not used by router |
|
Importance – Used for password recovery. |
|
The Configuration Register 3rd byte table shows the configuration register 3rd byte values and descriptions.
Table 3: Configuration Register 3rd byte
Value |
Description |
0 or 1 |
Allows the user to break and get into rommon mode by pressing Ctrl C. |
|
Importance – To debug or to set something in rommon mode. |
Cisco IR800 Integrated Services Router Software Configuration Guide
8

Product Overview
Auto-recovery of Corrupt Filesystems
The Configuration Register 4th byte table shows the configuration register 4th byte values and descriptions.
Table 4: Configuration Register4th byte
Value |
Description |
0 or 2 |
Doesn’t make any difference, behavior is decided by next 3 bytes. |
Auto-recovery of Corrupt Filesystems
On rare occasions, the router could get stuck in ROMMON to flash and bootstrap file system corruption caused by hard reloads. Hard reloads can be a consequence of fluctuating voltage or very low current. The file system (in flash: or bootstrap:) is completely inaccessible at this point.
Starting with 15.8(3)M, on the IR8x9 platforms, software will automatically recover the router if one or more filesystems are corrupt. This feature is enabled once the user executes bundle install, write memory, reload.
For example:
IR800#bundle install flash:ir800-universalk9-bundle.SSA.158-3.0m.M
Installing bundle image: /ir800-universalk9-bundle.SSA.158-3.0m.M......
...........................
updating Hypervisor image...
Sending file modes: C0444 25196401 ir800-hv.srp.SPA.3.0.55
SRP md5 verification passed!
updating IOS image...
Sending file modes: C0644 64486377 ir800-universalk9-mz.SSA.158-3.0m.M
IOS md5 verification passed! |
|
Done! |
Done! |
Performing image backup ......... |
During the bundle installation, the user will observe the message "Backup partition successful'. Once the bundle install is complete, the user can also verify if backup is successful using show platform bundle.
For example:
IR800#show platform bundle
Installed
Backup Success
This backup partition is taken from the Guest-OS data partition on the IR809, IR829, IR829GW, IR829B products.
The IR829M products mSATA SSD partition is unaffected.
If a previous user was already using up this extra partition in old software, the new software will NOT proceed with creating a backup partition. This ensures the user data is always intact. If the user wants to trigger a backup, ~300Mb needs to be cleaned up from Guest-OS /dev/sdb. In some routers, Guest-OS /dev/sdb may appear to have ~250Mb lesser, and some ~330Mb. This is due to the two different versions of eMMC on the IR8x9s, and there is no software cli to provide eMMC part number to distinguish.
Files Backed Up to the New Backup Partition
•IOS image
•Hypervisor image
•Guest-OS image (if IOX Recovery is enabled using conf t then iox recovery-enable)
Cisco IR800 Integrated Services Router Software Configuration Guide
9

Product Overview
Auto-recovery of Corrupt Filesystems
•Standard Files:
•Entire eem folder
•The entire managed folder, except managed/images
•All pnp* files (all PnP related files)
•vlan.dat
•Archive folder
•Field Network Director specific files:
•express-setup-config
•before-registration-config
•before-tunnel-config
•Sample file labeled additional_backup_file (This file is to ensure if a user wants to customize low sized (50 kbytes or less) configuration file copy, they can save it in this name and it will be backed up.
Files NOT Backed Up to the New Backup Partition
•Duplicates of software images in managed/images
•User generated files, folders and configurations
•FW of 4G modems
•IOx application data
Notes:
The backup partition is limited in space and only for basic device recovery, and to load startup -config [as SPI Flash: is intact]. In this manner, remote device reachability is back up again. Remaining files need to be restored again by end user.
If a user running old software would like to increase their current Guest-OS disk space, it is recommended to take a data backup, and execute the following command taking up larger disk space. Starting at IOS release 156(3)M3 and greater, the default disk space allocated to Guest-OS is Option 1 from the example below. For previous releases default used to be Option 6 from the example below.
IR800#guest-os 1 disk-repartition ?
1 disk1: 500MB vs disk2: 1800MB
2 disk1: 700MB vs disk2: 1600MB
3 disk1: 900MB vs disk2: 1400MB
4 disk1: 1100MB vs disk2: 1200MB
5 disk1: 1300MB vs disk2: 1000MB
6 disk1: 1500MB vs disk2: 800MB
7 disk1: 1700MB vs disk2: 600MB
Note: Actual storage available for applications will be less than the value chosen for all profiles. The disk2 partition displayed in the15.8(3)M release has to account for 300MB less space. For example: option1, disk2 is 1500MB not 1800MB. In future releases, this will be corrected.
Cisco IR800 Integrated Services Router Software Configuration Guide
10

Product Overview
Plug and Play Agent (PnP) support over 4G/Ethernet
Once an auto-recovery is complete, the user will observe a small file in flash called fs_recovered.ios. It will contain the timestamp of the last recovery. This file is indication that backup was successful, and that there was indeed a corruption of the filesystem. This file is not persistent on soft reload of the router.
Alternatively, the user can also backup using:
IR800#hypervisor backup_images
WARNING - If you are running this command for the first time, it might delete all application data in IOx. This operation cannot be undone. Continue? [yes/no]: y
Performing image backup......... Done
This will ensure the latest sync of vlan.dat, pnp and managed configs.
The first time the command is executed, it will forcibly create the backup. If an IOx user was using up the 300Mb required for backup partition creation from an older IOS release, then it will be carved into backup and the user will loose data. The user can opt for 'no' and perform a manual backup of that data before proceeding with hypervisor backup_images command.
Plug and Play Agent (PnP) support over 4G/Ethernet
An option was added to the bundle install command:
bundle install <bundle_image_name> rom-autoboot
When this option is specified, the IOS system image to boot will NOT be written into the running-config. Instead, it will be set into the rommon BOOT variable (BOOT=<system_image>) ONLY.
After bundle install <bundle_image_name> rom-autoboot and write erase commands, when the device reloads it will automatically boot up the IOS image saved in rommon BOOT. This also ensures the device does not have any startup configuration when it boots up so it will allow PNP to start up.
PNP can be started either using Ethernet or cellular 4G. If connected to both, Ethernet will take precedence over Cellular 4G.
PNP using Ethernet can be done in three different ways:
1.Specifying OPTION 43 on DHCP ROUTER
Example: option 43 ascii 5A1D;B2;K4;I<APIC-EM_IP_ADDRESS>;J80
2.Specifying DNS on DHCP ROUTER
Example: domain-name test.com
#conf t
#ip host pnpserver.test.com <APIC-EM address>
3. Specifying CCO’s address by configuring devicehelper.cisco.com on DHCP ROUTER
#conf t
#ip host devicehelper.cisco.com <CCO_address>
PNP using 4G cellular can be done by configuring the device information (Serial number, PID and controller profile-APIC-EM) on CCO.
Once PNP is completed, issue a write mem command to save the configuration. PNP pushes the configuration but does not save it. The configuration must be saved after PNP is successfully completed.
To verify if PNP is completed or not, verify with the sh run command. At the bottom of the command output, there should be a pnp profile and the APIC EM address. This means the device was redirected to APIC-EM
Cisco IR800 Integrated Services Router Software Configuration Guide
11

Product Overview
Plug and Play (PnP) Support on the IR829 LAN
and the initial PNP was successfully done. Now once the configuration file is pushed from APIC-EM, verify this using the sh pnp task command and verify the Config-Upgrade Task should have Result: Success.
Note The device should not be interrupted until PNP is completed. If the device is interrupted, PNP will stop. If at any point something goes wrong, reload the router without saving the configuration and PNP will start once again. Once PNP is completed it is necessary to save the configuration by issuing the write mem command.
IR800#sh run | b pnp
pnp profile pnp-zero-touch
transport https ipv4 172.27.122.132 port 443 end
IR800#sh pnp task
------------------ show pnp tasks ---------------------
Certificate-Install Task - Last Run ID:5, ST:7201, Result:Success, LT:117562, ET:4 ms
Src:[-], Dst:[-] Device-Auth Task - Never Run
Device-Info Task - Last Run ID:9, ST:5301, Result:Success, LT:200634, ET:1 ms Src:[udi], Dst:[pnp-zero-touch]
Image-Install Task - Never Run SMU Task - Never Run
Config-Upgrade Task - Last Run ID:10, ST:5202, Result:Success, LT:267420, ET:984 ms Src:[https://192.168.1.1:443/api/v1/file/onetimedownload/1530b4e5-beb8-4db3-b4df-28dc016464fc], Dst:[running]
CLI-Config Task - Never Run
Licensing Task - Never Run File-Transfer Task - Never Run Redirection Task - Never Run
CLI-Exec Task - Last Run ID:12, ST:5401, Result:Success, LT:279464, ET:1 ms Src:[cli-exec request], Dst:[running-exec]
Script Task - Never Run
Additional Resources for Cisco Plug and Play can be found at the following links:
Plug and Play (PnP) Support on the IR829 LAN
Feature applies to the IR829 product series only
Starting with this release, PnP will be supported over LAN ports (G1 to G4). In previous releases, PnP was supported only over WAN port and 4G LTE.
Similar to WAN port, PnP over LAN Interfaces can be triggered by configuring either DHCP, DNS or CCO details on DHCP/DNS server. Since all the LAN interfaces default to Vlan1, when the router boots up in factory default mode, it acquires an IP address from either DHCP or DNS server through Vlan1. This is how PnP is initiated. Once the initial PnP discovery is successful and the router is discovered on the PnP Server (for example: any Network Management System such as Field Network Director, APIC-EM, DNAC to name a few), it will be in an unclaimed state. From here, the user can 'claim' the device and push required configurations from the PnP server to the router.
Note: Image upgrade from the PnP server is currently not supported.
PnP using Ethernet can be done in three different ways:
1. Specifying OPTION 43 on DHCP router
ip dhcp pool IOT_address
Cisco IR800 Integrated Services Router Software Configuration Guide
12

Product Overview
Plug and Play (PnP) Support on the IR829 LAN
network 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 default-router 192.168.1.1
option 43 ascii 5A1D;B2;K4;I172.23.165.116;J80 ntp master
2. Specifying DNS on DHCP router
ip dhcp pool IOT_DNS
network 192.168.2.0 255.255.255.0 default-router 192.168.2.1 domain-name pnp-agent-tb.cisco.com dns-server 192.168.2.1
ip host pnpserver.pnp-agent-tb.cisco.com 172.23.165.116 ip host pnpntpserver.pnp-agent-tb.cisco.com 172.23.165.116 ip dns server
3. Specifying CCO’s address by configuring devicehelper.cisco.com on DHCP router
ip dhcp pool IOT_dhcp
network 192.168.3.0 255.255.255.0 default-router 192.168.3.1 dns-server 192.168.3.1
ip host devicehelper.cisco.com 64.101.32.10 ip host time-pnp.cisco.com 192.168.3.1
ntp master
Note: Once PnP is completed, issue a write mem command to save the configuration. PnP pushes the configuration but does not save it. The configuration must be saved after PnP is successfully completed.
To verify if PnP is completed or not, verify with the show run command. At the bottom of the command output, there should be a PnP profile and the PnP controller IP address. This means the device was redirected to the PnP server and the PnP discovery was successfully done. Once the configuration file is pushed from the PnP server, verify this using the show pnp task command and verify the Config-Upgrade Task should show Result: Success.
You can further debug and verify the entire PnP process using the commands show pnp summary, show pnp trace and show pnp tech-support.
Note: The device should not be interrupted until PnP is completed. If the device is interrupted, PnP will stop. If at any point something goes wrong, reload the router without saving the configuration and PnP will start onceagain. OncePnPiscompleteditisnecessarytosavetheconfigurationbyissuingthe write mem command.
IR800#show running-config | begin pnp profile pnp profile pnp_redirection_profile transport https ipv4 128.107.248.237 port 443
!
end
IR800#show pnp task
------------------ show pnp tasks ---------------------
Certificate-Install Task - Last Run ID:5, ST:7201, Result:Success, LT:117562, ET:4 ms
Src:[-], Dst:[-] Device-Auth Task - Never Run
Device-Info Task - Last Run ID:9, ST:5301, Result:Success, LT:200634, ET:1 ms Src:[udi], Dst:[pnp-zero-touch]
Image-Install Task - Never Run SMU Task - Never Run
Config-Upgrade Task - Last Run ID:10, ST:5202, Result:Success, LT:267420, ET:984 ms Src:[https://192.168.1.1:443/api/v1/file/onetimedownload/1530b4e5-beb8-4db3-b4df-28dc016464fc], Dst:[running]
CLI-Config Task - Never Run
Cisco IR800 Integrated Services Router Software Configuration Guide
13

Product Overview
Password Recovery
Licensing Task - Never Run
File-Transfer Task - Never Run
Redirection Task - Never Run
CLI-Exec Task - Last Run ID:12, ST:5401, Result:Success, LT:279464, ET:1 ms
Src:[cli-exec request], Dst:[running-exec]
Script Task - Never Run
Password Recovery
Use the following procedure in the event you have lost the router password.
Procedure
Step 1 Copy a ".cfg" configuration file in the router flash memory without any "username", "password", or "AAA" statements.
Example:
IR800# copy usb:default-config flash:default-config.cfg
Destination filename [default-config.cfg]?
In the router flash memory you must have only one ".cfg" at a time. If there are two or more the system will be confused resulting in unexpected behavior.
Step 2 Make a copy of the "startup-config" file in the router flash memory without an extension.
Example:
IR800# copy startup-config flash:startup-config
Destination filename [startup-config.cfg]?
Step 3 Power-off the router. Press the "Reset Button" and power-on the router, holding the button for 30sec. The router should boot with the new ".cfg" file.
Step 4 Copy the "startup-config" file over the "running-config".
Example:
IR800# copy flash:startup-config running-config
Destination filename [startup-config.cfg]?
Step 5 Change only the passwords necessary for your configuration. You can remove individual passwords by using the no in front of each statement. For example, entering the no enable secret command removes the enable secret password.
Step 6 Save the configuration changes.
Example:
IR800# write
building configuration...
Cisco IR800 Integrated Services Router Software Configuration Guide
14
Product Overview
Software Overview
Software Overview
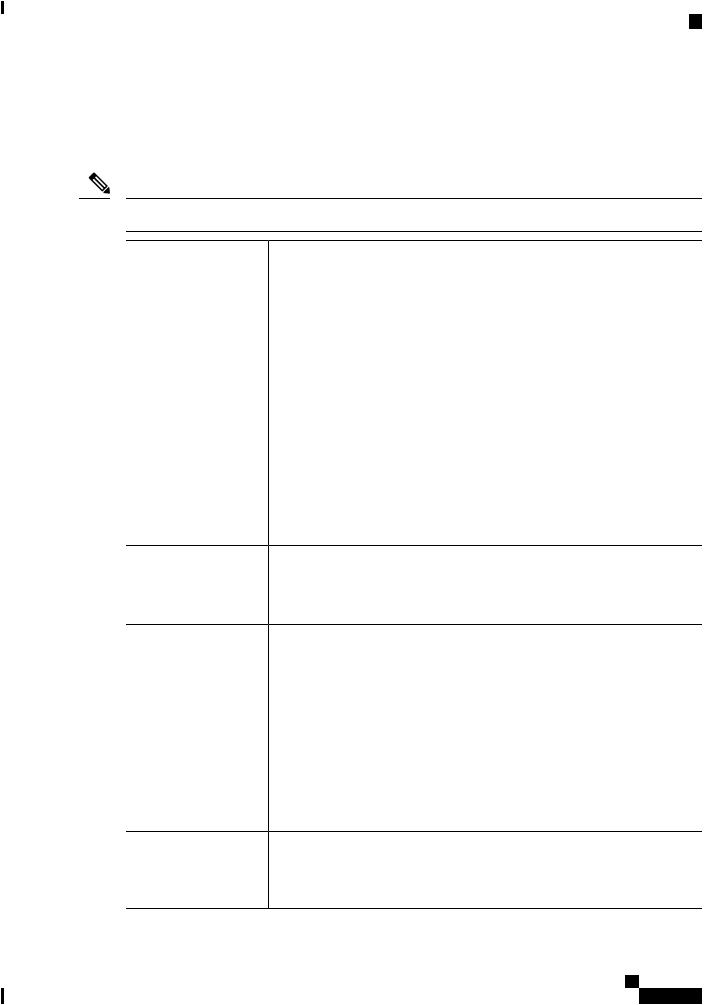
The IR800 series offers a rich IOS feature set. This section provides a brief overview of these features.
Note Features may be dependent of platform and releases
Feature |
Description |
Cellular Connectivity |
• 4G LTE, 3.7G, 3.5G, or 3G Cellular WAN link |
|
• External, dual 4G antennas with main and receive diversity for maximum |
|
signal strength connectivity |
|
• Dual subscriber identity module (SIM) capability |
|
• Auto-Sim |
|
• MPDN |
|
• Assisted GPS [for specific modems] |
|
• Dual-SIM |
|
• Dual-LTE (on dual LTE SKUs only) |
|
• Concurrentconnectionstotwocellularnetworksforhighreliability,enhanced |
|
data throughputs for mission critical services. |
Wi-Fi (829 only) |
• Dual radio 802.11n concurrent 2.4 GHz and 5.0 GHz with embedded 2X3 |
|
MIMO |
|
• Up to 300 Mbps data rate per radio |
Cisco IOx Application |
Provides an open, extensible environment for hosting OS and applications at the |
Support |
network edge. |
|
Application Hosting on Guest Operation System. |
Security |
Advanced security features that support: |
|
• Access control |
|
• Data confidentiality and data privacy |
|
• Threat detection and mitigation |
|
• Device and platform integrity |
Cisco IOT Field |
Available as the optional Cisco Industrial Operations Kit. This is a software |
Network Director |
platform that manages a multiservice network and security infrastructure for IoT |
|
applications such as transportation, smart grid, services, distribution automation |
|
and substation automation. |
Cisco IR800 Integrated Services Router Software Configuration Guide
15
Product Overview
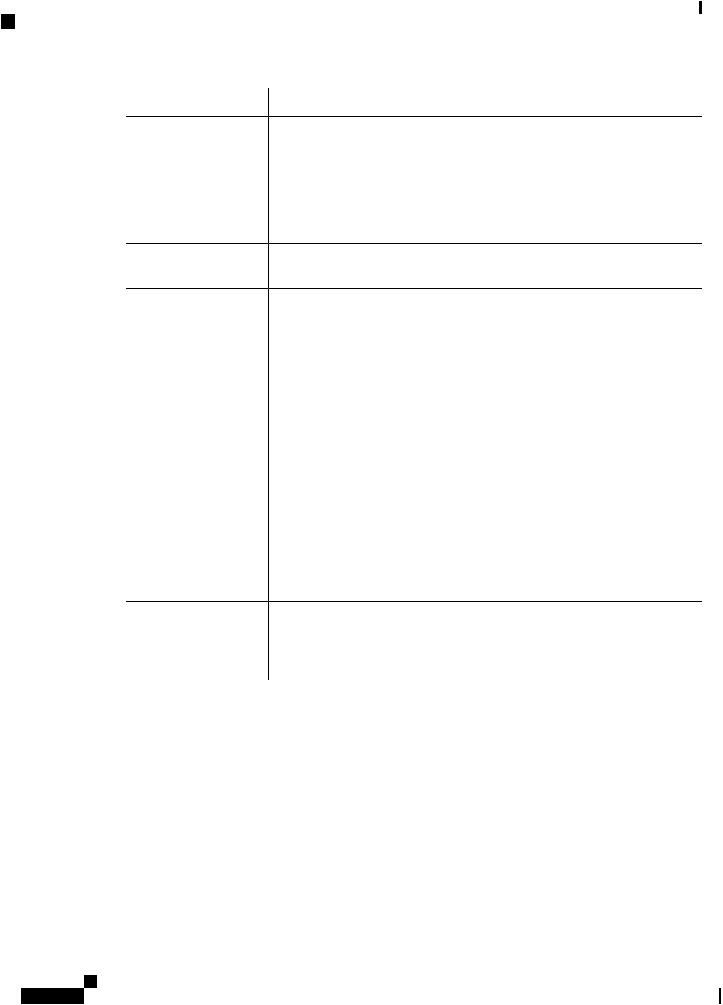
Hardware Differences Between IR809, IR829, and C819HG
Feature |
Description |
Cisco IOS Mobile IP |
• Mobile IP offers transparent roaming for mobile networks, establishing a |
Features |
transparent Internet connection regardless of location or movement. This |
|
enables mission-critical applications to stay connected even when roaming |
|
between networks. |
|
• Assigned IP addresses to the home network are maintained in private or |
|
public networks. |
Cisco IOS Mobile |
Allows an entire subnet or mobile network to maintain connectivity to the home |
Network Features |
network while roaming. |
QoS Features |
• Provides traffic precedence to delay-sensitive or prioritized applications. |
|
• Facilitates low-latency routing of delay-sensitive industrial applications. |
Management and |
• NetworkmanagerscanremotelymanageandmonitornetworkswithSNMP, |
Manageability |
Telnet, or HTTP/HTTPS/SSH, and locally through a console port. |
|
• Support for extensive 3G and 4G LTE-based MIBs allows for centralized |
|
management of remote devices and gives network managers visibility into |
|
and control over the network configuration at the remote site. |
|
• Network managers can reset to a predesignated golden image, as well as |
|
configure an 829 through Cisco IOS Software or through an external reset |
|
button. |
|
• Network managers can upgrade 3G, 3.5G, 3.7G, and 4G LTE firmware and |
|
router configurations remotely. |
|
The tight integration with Cisco IOS Software enables router to self-monitor the |
|
LTE WAN link and automatically recover from a radio link failure. |
Cisco IOS Software |
• Cisco IOS Software feature set: Universal Cisco IOS Software |
Requirement |
• Cisco IOS Software Release - 15.5(3)M, or later, and modem firmware - |
|
|
|
5.5.58, or later. (several features require later IOS releases) |
Hardware Differences Between IR809, IR829, and C819HG
The IR809s are very compact cellular (3G and 4G/LTE) industrial routers for remote deployment in various industries. They enable reliable and secure cellular connectivity for remote asset monitoring and machine-to-machine (M2M) solutions such as distribution automation, pipeline monitoring, and roadside infrastructure monitoring.
The IR829s are highly ruggedized compact cellular (3G and 4G LTE with GPS and dual SIM) and WLAN (2.4/5GHz) industrial routers supporting for scalable, reliable, and secure management of fleet vehicles and mass transit applications.
The 819HG-LTE-MNA-K9: Multimode Cisco LTE 2.0 for carriers that operate LTE 700 MHz (band 17), 1900 MHz (band 2 PCS), 850 MHz (band 5), 700 MHz (band 13), 1900 MHz (band 25 extended PCS)
Cisco IR800 Integrated Services Router Software Configuration Guide
16

Product Overview
Hardware Comparison
networks; or 1700/2100 MHz (band 4 AWS) networks; backward-compatible with UMTS and HSPA+: 850 MHz (band 5), 900 MHz (band 8), 1900 MHz (band 2 PCS), and 1700/2100 MHz (band 4 AWS), with EVDO Rev A/CDMA 1x BC0, BC1, BC10.
Hardware Comparison
Feature |
IR809 |
IR829 |
OIR of SIM |
Yes |
Yes |
Guest OS Support |
Yes |
Yes |
2G/3G/4G Support |
Yes, dual SIM support, SKUs available per region |
|
|
See Cellular Interface Modules, on page 45 for |
|
|
additional information. |
|
USB Flash |
Yes |
Yes |
USB type A Interface |
Yes |
Yes |
Console Port |
Mini USB |
Mini USB |
Alarm Port |
One Alarm input on |
No |
|
IR809 |
|
IEEE 802.11a/b/g/n WiFi |
No |
Yes, depending on the |
|
|
platform type. |
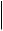 C819HG
C819HG
Yes
Yes
819(H)G-4G supports dual-SIM Different SKU’s per region.
SW MC 7750,7700,7710
No
No
RJ-45
No
No
Power Requirements |
Nominal voltage: 12-48V |
Nominal voltage: 12V, |
Nominal voltage: 12V, |
|
DC |
24V DC |
24V DC |
|
Min/max voltage: 9.6 – |
Min/max voltage: 9-32V |
Min/maxvoltage:10-36V |
|
60V DC input |
DC input |
DC |
|
Max, Min current: 3A, |
Max/Min current: 7.8 A, |
Maximum power |
|
0.5A |
2.8 A |
consumption: 26W |
|
|
Maximum power |
|
|
|
consumption: 40 W (no |
|
|
|
PoE) and 70W (PoE) |
|
Ethernet Ports |
2xRJ4510/100/1000Mbs |
4xRJ4510/100/1000Mbs |
4 x RJ45 10/100 Mbs |
|
|
1 x SFP 1000Mbs |
1 x GE 10/100/1000Mbs |
Serial Ports |
2 x RJ45 (1xRS-232 and 1xRS232/RS-485) |
12 in 1 Smart Serial |
|
Antenna: Main, Diversity |
Yes |
Yes |
819(H)G-4G has Active |
and GPS |
|
|
GPS SMA Connector and |
|
|
|
option for 2 4G antennas |
Cisco IR800 Integrated Services Router Software Configuration Guide
17

Product Overview
Antenna Recommendations
Antenna Recommendations
Neither the IR809 or IR829 is shipped with antennas. These antennas must be ordered separately. The IR829 must be installed with 2 antennas (Main & Aux) to guarantee the best performance level. Using a single antenna may impact the downlink performance by a minimum 3dB, and can be much greater (10-20dB) due to multipath fading (destructive interference between direct and reflected radio waves).
In case of 3G UMTS, a solo antenna would not be able to switch to the diversity port.
With the IR829, it must be guaranteed >15dB isolation between the WiFi and LTE antennas at all frequencies of 4G LTE and WiFi operation, for minimum impact to performance. This is ideally 20-25dB.
The Sierra Wireless MC73xx modem series supports MIMO on LTE. WCDMA UMTS HSPA DC-HSPA+ is diversity only, without MIMO.
Note Poorly installed MIMO antennas, such that the two (or more in case of 3x3, 4x4 MIMO) antennas have a strong correlation coefficient. This may cause the two streams to interfere with each other (otherwise known as lack of diversity), since the system has trouble separating the two. The multi-element antennas (5-in-1, 3-in-1, 2-in-1) have good diversity
For detailed information about Cisco Antennas, please refer to the following guides:
Cisco Industrial Routers Antenna Guide:
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/routers/connectedgrid/antennas/installing-combined/industrial-routers-antenna-guide.html
Cisco Aironet Antennas and Accessories Reference Guide
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/wireless/aironet-antennas-accessories/product_data_sheet09186a008008883b.html
Features Supported in Different IOS Releases
The IR800 series was originally released with IOS software version 15.5(3)M. The following lists the software releases with the features added.
15.5(3)M (initial release)
• Software based Crypto
15.5(3)Mx
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/routers/access/800/829/IR8xx-Release-Notes.html
• Hardware based Crypto
15.6(1)T
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/routers/access/800/829/15-6-1TIR8xx-Release-Notes.html
• IR809 Input alarm port, including SNMP Trap support
Cisco IR800 Integrated Services Router Software Configuration Guide
18
 Loading...
Loading...