Cisco CCNA 2.0 User Manual

640-607
Cisco Certified Network Associate 2.0
CCNA 2.0
Version 3.0
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 1 -
640 - 607
Important Note
Please Read Carefully
This product will provide you questions and answers along with detailed explanations carefully compiled and written by our experts. Try to understand the concepts behind the questions instead of just cramming the questions. Go through the entire document at least twice so that you make sure that you are not missing anything.
We are constantly adding and updating our products with new questions and making the previous versions better so email us once before your exam and we will send you the latest version of the product.
Each pdf file contains a unique serial number associated with your particular name and contact information for security purposes. So if we find out that particular pdf file being distributed by you. Testking will reserve the right to take legal action against you according to the International Copyright Law. So don’t distribute this PDF file.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 2 -
640 - 607
Q. 1
Your Ethernet network, 172.30.1.0, shuts down. Which update message is seen in your router's debug ip rip output regarding that network?
A.subnet 172.30.1.0, metric 0
B.subnet 172.30.1.0, metric 1
C.subnet 172.30.1.0, metric 15
D.subnet 172.30.1.0, metric 16
Answer: D
Explanation: In RIP when a network in not reachable then its metric is change to 16.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; this is not a valid metric.
B is incorrect; this metric indicates that the network is up.
C is incorrect; this metric indicates that the network is up.
Q. 2
Which command displays the configuration register setting?
A.show register
B.show flash
C.show boot this IOS command displays the settings of the boot environment variables
D.show version
Answer: D
Explanation:
The show version command displays version information for the hardware and firmware. This includes the register settings.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; this is not a valid command.
B is incorrect; the show flash command displays information in relation to router memory and image file.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 3 -
640 - 607
C is incorrect; the show boot IOS command displays the settings of the boot environment variables.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 128-137. http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/lan/c3550/1214ea1/3550cr/ccimtoc.htm
Q. 3
When setting up Frame Relay for point-to-point subinterfaces, which of the following must not be configured?
A.The Frame Relay encapsulation on the physical interface
B.The local DLCI on each subinterface
C.An IP address on the physical interface
D.The subinterface type as point-to-point
Answer: C
Explanation:
When setting up Frame Relay for point-to-point subinterfaces it is recommend the network layer address, IP address be removed from the physical interface and assign this network layer address to the subinterface.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; when establishing a Frame Relay for point-to-point subinterfaces the Frame Relay encapsulation on the physical interface must be configured.
B is incorrect; when establishing a Frame Relay for point-to-point subinterfaces the local DLCI on each subinterface must be configured.
D is incorrect; when establishing a Frame Relay for point-to-point subinterfaces the subinterface must be configured as point-to-point.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 427-429.
Q. 4
Which IOS command is used to associate an ISDN phone number with the next hop router address?
A.isdn destination number
B.dialer map
C.isdn spid1
D.isdn line number
Answer: B
Explanation:
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 4 -
640 - 607
The dialer map command is used to define one or more dial-on-demand numbers to reach one or more destinations for a particular interface. This is the exact command to associate an ISDN phone number with the next hop router address.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; this is not a valid command.
C is incorrect; the isdn spid1 command specifies the SPID required for b channel to access the ISDN network when your router makes its call to the local ISDN exchange.
D is incorrect; this is not a valid command.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 397-406.
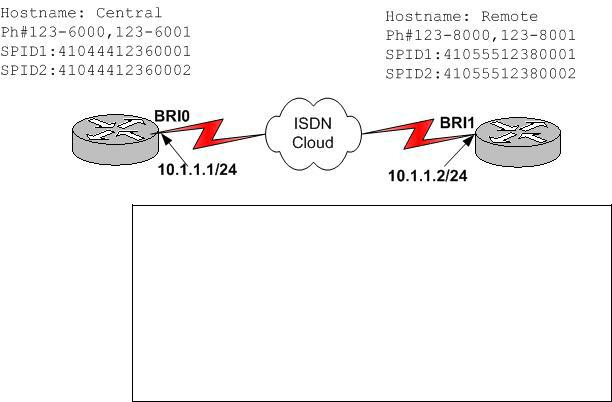
Q. 5
Exhibit:
Central Partial Configuration
isdn switch-type basic-ni username Remote password cisco interface bri0
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 encapsulation ppp
ppp authentication chap isnd spid1 51055512360001 isnd spid1 51055512360002
dialer map ip 10.1.1.2 name Remote 1238001 dialer-list 1 protocol ip permit
Use the partial BRI configuration and graphic shown. Which additional command must be issued on the Central router before interesting traffic will be sent to the Remote router?
A. (config-if)# dialer-group 1
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 5 -
640 - 607
B.(config-if)# dialer-list 1
C.(config-if)# dialer map 1
D.(config-if)# dialer-route 1
Answer: A
Explanation:
Once the above commands have been entered to enabled DDR, then the last step required is to bind the traffic destination to an interface by linking the interesting traffic definition already created. This is done with the dialer-group command. In this case the proper command would be (config-if)# dialer-group 1.
Incorrect Answers:
B is incorrect; the interesting traffic was already identified the first time the dialer-list 1 command was used.
C is incorrect; the dialer map command is used to identify the router to be dialed. In this case this has already been done.
D is incorrect; there is no such thing as a dialer route command.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 398-405.
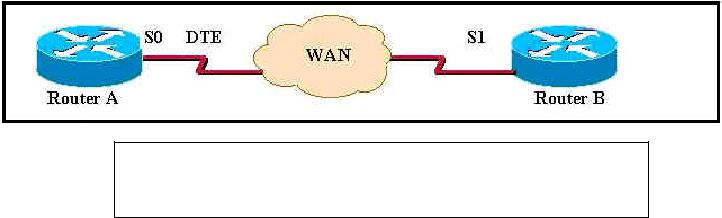
Q. 6
Exhibit:
RouterA# show interface s0
Serial 0 is up, line protocol is down
Hardware is HD64570
Internet address 10.1.1.1
Encapsulation HDLC, loopback not set, keepalive set (10sec)
Router A is connected to Router B, a non-Cisco router, through the network cloud. Using the command output shown what must be configured on Router A's interface s0 to change the line protocol from down to up?
A.no shutdown
B.encapsulation ppp
C.interface serial point-to-point
D.clock rate 56000
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 6 -

640 - 607
Answer: B
Explanation: To ensure that the line comes up the encapsulation type must be enabled. This is done with the encapsulation ppp command.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; the interface is already enable therefore this command in not required.
C is incorrect; the serial interface has already been created, this command would not solve the problem. D is incorrect; this will only set the clock rate and not bring solve the problem.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 381, 105, 432, and 407.
Q. 7
Exhibit:
Which Frame Relay feature allows the point-to-point Frame Relay PVC between Router A and Router B to be identified at Router A as 100 and at Router B as 200?
A.Locally significant DLCI
B.Globally significant DLCI
C.Locally significant LMI
D.Globally significant LMI
Answer: A
Explanation:
The DLCI (Data-Link Connection Identifier) is a number that identifies the logical circuit between the router and the Frame Relay switch. The Frame Relay switch maps the DLCIs between each pair of routers to create a PVC. DLCIs have local significance in that the identifier references the point between the local router and the Frame Relay switch, which it is connected.
Incorrect Answers:
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 7 -

640 - 607
B is incorrect; as the DLCI are significant to just the two routers involved in the exchange of information it is not proper to refer to globally significant DLCI.
C is incorrect; locally significant LMI is not the answer. LMIs are responsible for managing the connection between the routers and not the assignment of numbers.
D is incorrect; globally significant LMI is not the answer. LMIs are responsible for managing the connection between the routers and not the assignment of numbers.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 414-416.
Q. 8
During encapsulation in which order is information packaged?
A.Data, Packet, Segment, Frame
B.Segment, Data, Packet, Frame
C.Data, Segment, Packet, Frame
D.Packet, Data, Segment, frame
Answer: C.
Explanation: Data encapsulation is a process in which information is wrapped in the data section of another protocol. In the OSI model each layer encapsulates the layer immediately above as the data flows down the protocol stack. The order of encapsulation is
1. |
Application/Presentation/Session |
DATA |
2. Transport |
SEGMENT |
|
3. |
Network |
PACKET |
4. Data Link |
FRAMES |
|
5. |
Physical |
BITS |
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; with Data, Packet, Segment, Frame; packet and segment are inverted. B is incorrect; with Segment, Data, Packet, Frame; data and segment are inverted.
D is incorrect; with Packet, Data, Segment, frame; the only information package in the proper order is frame.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) page 13.
Q. 9
Exhibit:
Router# show ipx interface e0 Ethernet0 is up, line protocol is up
IPX address is 6F2C.0000.0c5d.b36e, NOVELL_ETHER [up] line-up, RIPPQ:0, SAPPQ: 0
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 8 -
640 - 607
Delay of this IPX network, in ticks is 1 throughput 0 link delay 0 IPXWAN processing not enabled on this interface.
IPX SAP update interval is 1 minute(s)
IPX type 20 propagation packet forwarding is disabled Incoming access list is not set
Outgoing access list is not set IPX helper access list is not set
SAP GNS processing enabled, delay 0 ms, output filter list is not set SAP Input filter list is not set
SAP Output filter list is not set SAP Router filter list is not set Input filter list is not set Output filter list is not set Router filter list is not set
Netbios Input host access list is not set Netbios Input bytes access list is not set Netbios Output host access list is not set Netbios Outpus bytes access list is not set
Updates each 60 seconds, aging multiple RIP: 3 SAP: 3
SAP interpacket delay is 55 ms, maximum size is 480 bytes RIP interpacket delay is 55 ms, maximum size is 432 bytes IPX accounting is disabled
IPX fast switching is configured (enabled) RIP packets received 0, RIP packets sent 1 SAP packets received 0, SAP packets sent 1
What is the Layer 2 address as shown in the output of the show ipx interface e0 command?
A.6F2C
B.0000.0c
C.5d.b35e
D.0c5d.b363
E.0000.0c5d.b363
F.6F2C.0000.0c5d.b363
Answer: E
Explanation:
An IPX address is composed of two parts: the network number and the node number. For IPX the node number is usually obtain from MAC address of the network interface. In this case the network number is 6F2C and the node number/MAC address is 0000.0c5d.b363
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; 6F2C is the network number which is a layer 3 address.
B is incorrect; this only part of the MAC address thus incorrect.
C is incorrect; this only part of the MAC address thus incorrect.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 9 -
640 - 607
D is incorrect; this only part of the MAC address thus incorrect.
F is incorrect; this is the IPX address. As stated previously this address is part layer 3 and part layer 2.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 332 and 345-6.
Q. 10
Which devices operate at all seven layers of the OSI model? (Choose three.)
A.Network host
B.Network management station
C.Transceiver
D.Bridge
E.Web server
F.Switch
Answer: A, B, E
Explanation: The three devices that operate at all seven layers of the OSI model are network hosts, network management station and web server. This is how these devices are able to perform their functions.
Incorrect Answers:
C is incorrect; a transceiver is not used in a network environment.
D is incorrect; a bridge is a Layer 2 device.
F is incorrect; a switch is a Layer 2 device.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 21-22.
Q. 11
With the hierarchical numbering of IP addresses what determines the portion of the address that will identify the network number?
A.Subnet Mask
B.Dots between octets
C.Class of first octet
D.Assignments of DHCP
E.Address Resolution Protocol
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 10 -
640 - 607
Answer: C.
Explanation:
In general, IP addresses contain two fields: one for the network and another for host. Class A address have a range of 1 to 126 and the network portion of the IP address is restricted to the first eight bits (octet). Class B address have a range of 128 –191.255.0.0 and the network portion of the IP address is contain in the first 2 octets. Class C IP addresses has a range of 192.223.255.255.0 and the network portion of the IP addresses is the first three octets of the IP address. Class D addresses include the range of 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255 and are used for multicast address. Class E addresses have a range of 224.0.0.0 to 247.255.255.255 and are reserved for experimental purposes.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; although the subnet mask is used by network devices to determine what part of the IP address is used for the network, the subnet and the host address but it is not part of the IP address hierarchy.
B is incorrect; the dots are used for making the IP address readable by humans, but have no determination of the network number.
D is incorrect; DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) provides a mechanism for allocating IP addresses dynamically so that addresses can be reused when hosts no longer need them.
E is incorrect; Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) determines the data link layer address of the destination devices for known destination IP addresses network number.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 215-227.
Q. 12
At which OSI layer does data translation and code formatting occur?
A.Physical
B.Data link
C.Network
D.Transport
E.Session
F.Presentation
Answer: F Explanation:
The presentation layer provides a variety of coding and conversion functions that are applied to application level data. These functions ensure that the data sent from the application layer of one system can be read the application layer of another system.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; the physical layer is what puts the actual data onto the wire.
B is incorrect; the data link layer is involved in converting bits into bytes, converting bytes into frames and with error detection.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 11 -
640 - 607
C is incorrect; the network layer provides logical addressing so that routers can perform route determination. C is incorrect; the transport layer provides delivery of the data and error correction prior to retransmit.
E is incorrect; the session layer is responsible for establishing, managing, and terminating communications sessions between presentation layer entities.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 11-12.
Q. 13
A packet is the protocol data unit for which layer of the OSI model?
A.Data link
B.Session
C.Presentation
D.Network
E.Transport
Answer: D
Explanation:
The packet is the encapsulation type of the Network layer.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect, the data unit of the data link layer is the frame.
B is incorrect; the session layer in not involved in the data encapsulation process.
C is incorrect; the presentation layer ensures that the receiving system can read the data and is not involved in encasulation.
E is incorrect; the transport layer data unit is the segment.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 11-13.
Q. 14
What is the result of segmenting a network with a bridge?
A.It increases the number of collision domains.
B.It decreases the number of collision domains.
C.It increases the number of broadcast domains.
D.It decreases the number of broadcast domains.
Answer: A.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 12 -

640 - 607
Explanation:
Bridge networks have the following characteristics: each segment has its own collision domain, all connected devices are part of the same broadcast domain, and all segments must have the same data link layer implementation.
Incorrect Answers:
B is incorrect; when a network is segmented by a bridge the collisions domains increase and not decrease. C and D are incorrect; the addition of a bridge to a network has no effect on the number of domains.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 23-4.
Q. 15
Exhibit:
Router#show interface serial 0
Serial0 is down, line protocol is down Hardware is HD64570
Internet address is 172.22.5.1/30
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 1544 Kbit, DLY 20000 usec, rely 255/255, load 1/255 Encapsulation HDLC, loopback not set, keepalive set (10 sec)
Last input never, output 00:03:11, output hang never Last clearing of "show interface" counters never
Input queue: 0/75/0 (size/max(drops): Total output drops: 0 Queuing strategy: weighted fair
Output queue: 0/1000/64/0 (size/max active/threshold/drops) Conversations 0/2/256 (active/max active/max total) Reserved Conversations 0/0 (allocated/max allocated)
5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
0 packets input, 0 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 0 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored, 0 abort 11 packets output, 476 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 27 interface resets
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
11 carrier transitions
DCD=down DSR=down DTR=down RTS=down CTS=down
Based on the output of the show interface serial 0 command issued on a DTE router, which OSI layer is most likely source of the problem?
A.Physical layer
B.Data layer
C.Network layer
D.Transport layer
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 13 -

640 - 607
Answer: A
Explanation:
The key to answering this question is “Serial0 is down”. This indicates that the actual serial inerface is down. Thus there is a problem with the physical layer.
Incorrect Answers:
B is incorrect; the exhibit does not indicate a problem with the data link layer. C is incorrect; the exhibit does not indicate a problem with the network layer.
D is incorrect; if the output just indicated that “line protocol is down” then a their would be a
problem with the line protocol. If this was the only problem then there would’ve been a problem with the transport layer.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 107-110.
Q. 16
Exhibit:
Given the network diagram, assume that ports 1 through 3 are assigned to VLAN1 and ports 4 through 6 are assigned to VLAN2 on each switch. The switches are interconnected over a trunked link.
Which of the following conditions would verify proper VLAN and trunk operation? (Choose three.)
A.Host 1-1 can ping Host 1-2
B.Host 1-1 can ping Host 4-2
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 14 -
640 - 607
C.Host 1-1 can not ping Host 1-2
D.Host 4-1 can not ping Host 1-2
E.Host 4-1 can ping Host 4-2
Answer: A, B and E.
Explanation: If hosts from the different VLANs can ping each other then you can confirm the proper VLAN configuration and truck operation.
Incorrect Answers:
C is incorrect; if this occurred this would indicate a problem.
D is incorrect; if this occurred this would indicate a problem.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 191-193.
Q. 17
Which of the following statements are true regarding bridges and switches? (Choose three.)
A.Switches are primarily software based while bridges are hardware based.
B.Both bridges and switches forward Layer 2 broadcasts.
C.Bridges are frequently faster than switches.
D.Switches have a higher number of ports than most bridges.
E.Bridges define broadcast domains while switches define collision domains.
F.Both bridges and switches make forwarding decisions based on Layer 2 addresses.
Answer: B, D, F
Explanation: Switches and bridges are both Data Link layer devices and make their forwarding decision based on Layer 2 addresses. As a result they have a number of similar attributes. Switched have a higher port density.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; switches are hardware based.
C is incorrect; switches are most often faster than bridges.
E is incorrect; both define broadcast domains.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 21-22.
Q. 18
You need to add a new VLAN, named ACCOUNTS, to your switched network. Which of the following are true regarding configuration of this VLAN? (Choose three.)
A. The VLAN must be created.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 15 -
640 - 607
B.The VLAN must be named.
C.An IP address must be configured for the ACCOUNTS VLAN.
D.The desired ports must be added to the new VLAN:
E.The VLAN must be added to the STP domain.
Answer: A, B, D
Explanation: To add a VLAN there are a number of things that must be done. First it must be created, then named and assigned ports.
Incorrect Answers:
C is incorrect; IP addresses do not need to be configured for VLANs.
D is incorrect; the VLAN does not need to be added to the STP domain.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 195-199.
Q. 19
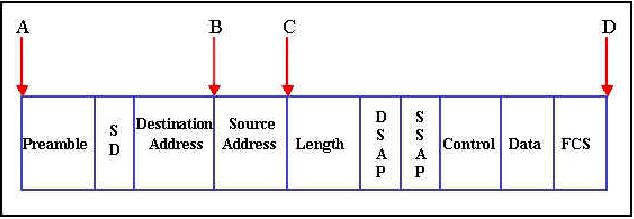
Exhibit:
At what point in the frame shown in the diagram is the store-and-forward switching decision made?
A.A
B.B
C.C
D.D
Answer: D
Explanation: When store-and-forward is employed the complete frame must be first received.
Incorrect Answers:
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 16 -
640 - 607
A is incorrect; in a switched environment the frame will not be immediately sent.
B is incorrect; this is the point at which the cut-through mode will start sending a frame. C is incorrect; this is the point at which the fragment-free mode start sending a frame.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 162-163.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 17 -
640 - 607
Q. 20
Which commands could be used at the command line interface to troubleshoot LAN connectivity problems on a router? (Choose three.)
A.ping
B.tracert
C.ipconfig
D.show ip route
E.winipcfg
F.show interfaces
Answer: A, D, F
Explanation: There are a number of commands that can be used to troubleshoot connectivity problems on a router. The ping command verifies connectivity, the show ip route command shows a great deal of information that is useful for troubleshooting connectivity, and the show interfaces command displays statistics for the network interfaces on the router.
Incorrect Answers:
B is incorrect; tracert is not a valid command. The Cisco command is trace.
C and E are incorrect; these are great Microsoft troubleshooting commands but they are not valid Cisco commands.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 124, 107-110, and 406407.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 18 -
640 - 607
Q. 21
What are the effects of sustained, heavy collisions in CSMA/CD LANs? (Choose three.)
A.Increased broadcast traffic
B.Delay
C.Low throughput
D.High throughput
E.Congestion
F.Higher bandwidth
Answer: B, C, E
Explanation: Whenever there is sustained high collision environment the results are longer delays, congestion and low throughput.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; this will not increase broadcast traffic.
D is incorrect; due to the collision the throughput will decrease.
F is incorrect; the bandwidth will not be effected.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 16-17.
Q. 22
Modem networks are often described as using 100Base-TX components. What is meant by the term 'Base' in this definition?
A.It describes the signaling method for communication on the network.
B.It refers to the type of media used in the network.
C.It relates to the speed of transmission of network signals.
D.It defines the allowable length of media that can be used.
E.It defines half-duplex or full-duplex operation.
Answer: A
Explanation: There are two main signaling types: Baseband and Broadband.
Incorrect Answers:
B is incorrect; TX represents the media type. TX r= Cat 5 cable.
C is incorrect; the speed of the transmission is represented by the 100 (mbps).
D is incorrect; the maximum cable length for 100BaseTX is 100 m and is not represented in the standard name. E is incorrect; 100BaseTX is for full-duplex operation. This cannot be interrupted from the name.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 19 -
640 - 607
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 45-48.
Q. 23
Which of the following are unique characteristics of half-duplex Ethernet as compared to full-duplex Ethernet? (Choose two.)
A.Shared collision domain.
B.Private collision domain
C.Higher effective throughput
D.Lower effective throughput
E.Private broadcast domain
Answer: A, D
Explanation: Half-duplex Ethernet have a lower effective throughput due to shared collision domain the a fullduplex Ethernet.
Incorrect Answers:
B is incorrect; the collision domain is shared not private.
C is incorrect; half-duplex as a lower effective throughput.
E is incorrect; it is a shared collision domain not a private broadcast domain.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 180-182.
Q. 24
From the DOS command prompt, you are able to ping a router but are unable to telnet it. What is the most likely cause of the problem?
A.The PC has a bad network interface card.
B.The IP address of the router is on a different subnet.
C.No password has been set on the router vty lines.
D.The default gateway is not set on the PC.
E.The IP address of the workstation is incorrect.
Answer: C
Explanation: In order to telnet to a router a password must be set on the router’s vty line.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; you could not ping if there was a bad NIC.
B is incorrect; telnet is design to allow remote connections.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 20 -
640 - 607
D is incorrect; there is no need to a default gateway to telnet
E is incorrect; you would not be able to ping id the IP address was wrong.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) page 103.
Q. 25
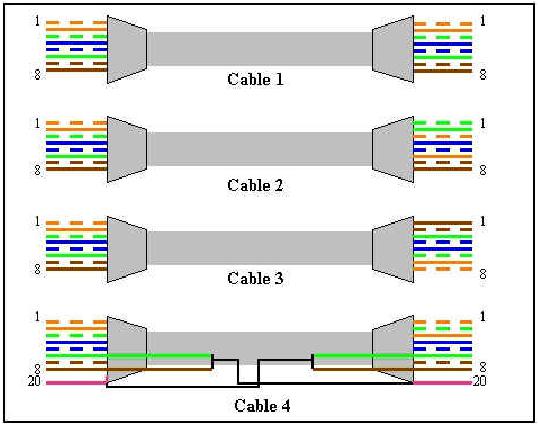
Exhibit:
Choose the correct cable to directly connect a router to another router over the Ethernet.
A.Cable #1
B.Cable #2
C.Cable #3
D.Cable #4
Answer: C
Explanation: A crossover cable must be used to connect similar devices. A crossover cable crosses the critical pairs in order to align, transmit, and receive signals.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 21 -
640 - 607
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; the critical pairs are not twisted.
B is incorrect; the critical pairs are not twisted.
D is incorrect; the critical pairs are not twisted.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) page 51.
Q. 26
Which two commands allow you to verify address configuration in your internetwork?
A.Ping
B.Trace
C.Verify
D.Test IP
E.Echo IP
F.Config IP
Answer: A, B
Explanation: The ping command will confirm connectivity and trace will determine the routes an outgoing packet will take.
Incorrect Answers:
C – F are incorrect; these are not valid commands.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) page 124.
Q. 27
Exhibit:
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 22 -
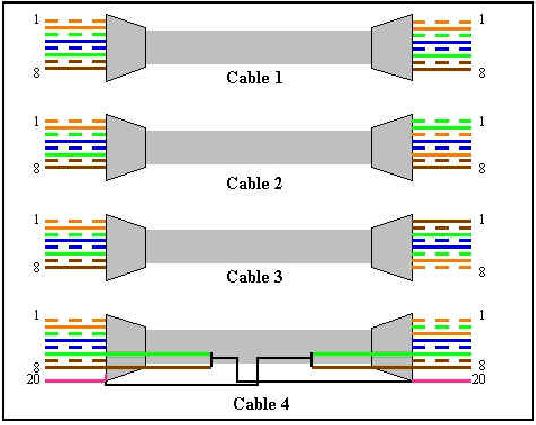
640 - 607
Choose the correct cable to connect an Ethernet switch to another Ethernet switch.
A.Cable #1
B.Cable #2
C.Cable #3
D.Cable #4
Answer: C
Explanation: A crossover cable must be used to connect similar devices. A crossover cable crosses the critical pairs in order to align, transmit, and receive signals.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; the critical pairs are not twisted.
B is incorrect; the critical pairs are not twisted.
D is incorrect; the critical pairs are not twisted.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) page 51.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 23 -
640 - 607
Q. 28
Which command displays all routed protocols and the interfaces on which the protocol is enabled?
A.show protocols
B.show protocol brief
C.show interfaces protocol
D.show interfaces
E.show routed
F.show routed interfaces
Answer: D
Explanation: The show interfaces command displays statistics fro all interfaces configured on the switch. This information is displayed by interface and includes the routing protocols.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; this is not a valid command.
B is incorrect; this is not a valid command.
C is incorrect; this is not a valid command.
E is incorrect; this is not a valid command.
F is incorrect; this is not a valid command.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 80-81.
Q. 29
If windows size is changed from 3000 to 4000 during the data transfer stage of a TCP session, what can a sending host do?
A.Transmit 3000 bytes before waiting for an acknowledgement.
B.Transmit 4000 packets before waiting for an acknowledgement.
C.Transmit 4000 bytes before waiting for an acknowledgement.
D.Transmit 4000 segments before waiting for an acknowledgement.
E.Transmit 3000 frames before waiting for an acknowledgement.
F.Transmit 3000 packets before waiting for an acknowledgement.
Answer: C
Explanation: For TCP a window size is in bytes. When a window size increases the sending device can increase transmission to the new size. In this case the new size 4000 bytes.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 24 -
640 - 607
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; prior to the increase in bytes the old window size was 3000 bytes.
B is incorrect; window size is bytes not packets.
D is incorrect; window size is bytes not segments
E is incorrect; window size is bytes not frames.
F is incorrect; window size is bytes not packets.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 213-214.
Q. 30
Users on network 192.168.69.0/28 are complaining that they cannot access the corporate intranet server at www.inhouse.com. In troubleshooting this problem, you find that you are able to telnet a workstation on this network to the internal webserver via its IP address.
What is the likely cause of this problem?
A.TCP/IP failure
B.DNS failure
C.FTP failure
D.SNMP failure
Answer: B
Explanation: When you combined the fact that user cannot connect to the intranet with its domain but you can telnet to it using the IP address, there must be a problem with the DNS. DNS translates names into addresses.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; if there was a problem with TCP/IP then you would not have been able to Telnet to web server. C is incorrect; a problem with FTP would not cause this problem.
D is incorrect; a SNMP failure would not cause this problem.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 239-240.
Q. 31
Given the network 199.141.27.0 with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.240, identify the valid host addresses. (Choose three.)
A.199.141.27.33
B.199.141.27.112
C.199.141.27.119
D.199.141.27.126
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 25 -

640 - 607
E.199.141.27.175
F.199.141.27.208
Answer: A, C, D
Explanation: When you base your calculations on the network address and the provided subnet mask the valid host addresses are 199.141.27.33, 199.141.27.119, and 199.141.27.126.
Incorrect Answers:
B, E and F are incorrect; these are not valid host addresses.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 233-236.
Q. 32
The network 172.12.0.0 needs to be divided into subnets where each subnet has the capacity of 458 IP addresses. What would be the correct subnet mask to accomplish this division keeping the number of subnets at the maximum.
Type the correct value in each box below.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 26 -

640 - 607
Answer:
Explanation: In order for a Class B IP, such as 172.12.0.0, to have 458 IP available on each subnet then a subnet mask of 255.255.254.0. This subnet mask provides for 126 subnets and 510 IPs.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) page 234.
Q. 33
Exhibit:
Router_B#show ip route
Codes: C-connected,s-static,I-IGRP,R-RIP,M-Mobile,B-BGP,D-EIGRP,EIGRP external, O-OSPF,IA-OSPFinter area,EI-OSPF external type 1,E2-OSPF external type 2, E-EGP, i-IS-IS,L1-IS-IS level-1,L2-IS-IS level-2,*-candidate default,U-per-user static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
R 192.168.8.0/24 [120/1] via 192.168.2.2, 00:00:10, Serial0
C 192.168.9.0/24 is directly connected, Serial 1
R 192.168.10.0/24 [120/7] via 192.168.9.1, 00:00:02, Serial1
R 192.168.11.0/24 [120/7] via 192.168.9.1, 00:00:03, Serial1
C 192.168.1.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0
C 192.168.2.0/24 is directly connected, Serial0
R 192.168.3.0/24 [120/1] via 192.168.2.2, 00:00:10, Serial0
R 192.168.4.0/24 [120/15] via 192.168.2.2, 00:00:10, Serial0
R 192.168.5.0/24 [120/15] via 192.168.2.2, 00:00:10, Serial0
R 192.168.6.0/24 [120/15] via 192.168.2.2, 00:00:10, Serial0
R 192.168.7.0/24 [120/1] via 192.168.2.2, 00:00:10, Serial0
Which route will not be entered into the routing table of the receiving router?
A.R 192.168.3.0/24 [120/1] via 192.168.2.2, 00:00:10, Serial0
B.R 192.168.11.0/24 [120/7] via 192.168.9.1, 00:00:03, Serial1
C.C 192.168.1.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0
D.R 192.168.5.0/24 [120/15] via 192.168.2.2, 00:00:10, Serial0
Answer: D
Explanation: This route has the lowest metric of those listed and as such will not be shared with the neighbor.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; this has the best metric thus it will be shared.
B is incorrect; this route has a better metric therefore it will be shared.
C is incorrect; this is a directly connected network thus it will be shared.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 27 -
640 - 607
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 258-260.
Q. 34
Given the following routing table entry, which of the following are used by default in the calculation of the number 1200? (Choose two.)
172.16.0.0 [100/1200] via 192.168.16.3, 00:00:55, Ethernet1
A.MTU
B.bandwidth
C.administrative distance
D.hop count
E.metric
F.delay
Answer: B, F
Explanation: By default, only bandwidth and delay are used by the IGRP metric. In this case the metric is 1200.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; MTU can be used but it is not a default.
C is incorrect; administrative distance is not used by IGRP.
D is incorrect; hop count is not used by IGRP.
E is incorrect; 1200 is the metric value.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 283-284.
Q. 35
Which method does a Cisco Catalyst switch use to identify the VLAN membership of a frame over trunked links?
A.Frame filtering with VLAN ID
B.Frame tagging with VLAN ID
C.Frame filtering with trunk ID
D.Frame tagging with trunk ID
E.Frame filtering with VTP port ID
Answer: B
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 28 -
640 - 607
Explanation: One form of frame tagging that VLANs use is ISL tagging. The ISL tag includes the VLAN ID.
Incorrect Answers:
A, C and E are incorrect; frame filtering will not achieve the desired result.
D is incorrect; frame tagging does not include the trunk ID.
Wendell Odom. Cisco CCNA Exam #640-507 Certification Guide. (Cisco Press: 2000) page 175.
Q. 36
A routing table contains static, RIP, and IGRP routes for the same destination network. Which route would normally be used to forward data?
A.The IGRP route.
B.The static route.
C.The RIP route.
D.All three will load balance.
Answer: B
Explanation: If there are several routing sources providing common routing information, an administrative distance value is used to rate the trustworthiness of each routing source. The lower the administrative distance the more trustworthy it is. Static routes have a default distance of 1, IGRP has a default distance of 100, and RIP has a default distance of 120.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; IGRP does not have the lowest administrative distance.
C is incorrect; RIP does not have the lowest administrative distance in fact it has the highest. D is incorrect; as the administrative distance differ there can be no load balancing.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 256-258.
Q. 37
Which parameter must be supplied when initializing the IGRP routing process?
A.connected network numbers
B.IP address mask
C.metric weights
D.autonomous system number
E.registered administrative id
Answer: D
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 29 -

640 - 607
Explanation: IGRP requires an autonomous system number. The autonomous system number must be entered directly after the router igrp command and before the network command.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; the network command is used to identify the directly connected networks but this is done after the autonomous system number.
B is incorrect; the IP address mask is not required. C is incorrect; metric weights are not required.
E is incorrect; registered administrative id is not required.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) page 285.
Q. 38
Which of the following protocols utilizes features of both distance-vector and link-state routing?
A.RIP
B.OSPF
C.EIGRP
D.IGRP
Answer: C
Explanation: EIGRP is an example of a balanced hybrid routing protocol. It uses distance vectors with more accurate metrics to determine the best paths to destination networks. However, it differs from most distance vector protocols as it also has some features of link-state protocols.
Incorrect Answers:
A and D are incorrect; these are examples of distance vector routing protocol.
B is incorrect; OSPF is an example of a link-state routing protocol.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 275-276 and 259.
Q. 39
A host with a MAC address of 021f.2cfe.8322 is to be inserted into IPX network 4ad1.
Enter the IPX address for this host.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 30 -
 Loading...
Loading...