Cisco Systems CCNA 2 User Manual

This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for noncommercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics course as part of an official Cisco Networking Academy Program.
I. Welcome
Welcome to the CCNA 2 version 3.1 Instructor Guide. Cisco Worldwide Education (WWE) has developed this guide to provide a helpful resource for instructors. This introduction will emphasize four themes:
•Student-centered, instructor-facilitated model
•One size does not fit all
•Hands-on, skills-based learning
•Global community of educators
Student-Centered, Instructor-Facilitated
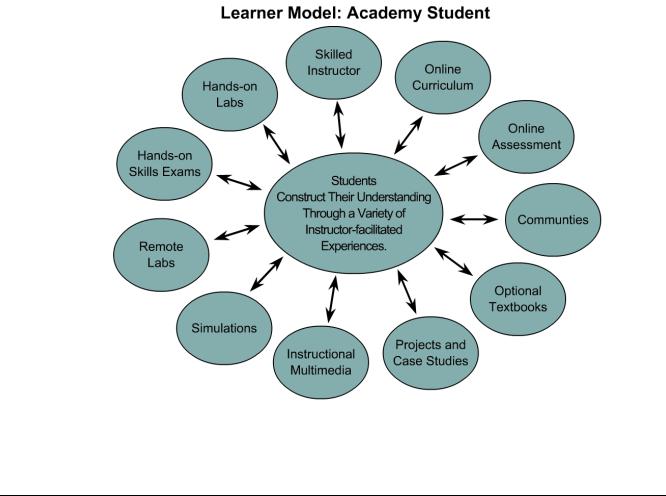
The CCNA curriculum has not been designed as a standalone e-learning or distance-learning course. The teaching and learning model of the Cisco Networking Academy® Program is based on instructor facilitation. The Learner Model: Academy Student diagram shows the emphasis that WWE puts on the learner. The model begins with the prior knowledge of students. The instructor guides learning events, which are built from a variety of resources, to help the students achieve their desired comprehension of networking.
1 - 238 |
CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v3.1 Instructor Guide – Welcome |
Copyright © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. |

One Size Does Not Fit All
The Cisco Networking Academy Program serves hundreds of thousands of students in almost 150 countries. Students range from early teens to mature adults and from advanced middle school students to undergraduate engineering students.
One curriculum cannot fit the needs of all students. WWE relies on local instructors to make the program work and to help their students achieve the learning goals of the program. There are three fixed reference points for each program that provide flexibility for the instructors:
•The mission of WWE to educate and train
•The requirements of the CCNA certification exam
•The hands-on skills that help prepare students for the industry and further education
The WWE policy allows instructors to "add anything, but subtract nothing" from the curriculum. WWE supports in-class differentiation, which is used to provide additional support for students who need it and additional challenges for advanced students. WWE also allows instructors to decide how much time to spend on various topics. Some topics can be skimmed, while others may need to be emphasized for different audiences. The local instructor must decide how to balance the need for hands-on labs with the realities of the local student-to-equipment ratio and time schedule. This Guide can be used to facilitate the preparation of lesson plans and presentations. Instructors are encouraged to research and use external sources to develop additional labs and exercises.
Core TIs have been highlighted for emphasis to assist the instructor in course and lesson planning. These are not the only TIs that need to be taught. Many core TIs will only make sense after the preceding TIs have been reviewed. It may be useful to have a map of the core TIs, which contain the most important knowledge and skills for success in the CCNA program.
The assessment process is multifaceted and flexible. A wide variety of assessment options exist to provide feedback to students and document their learning. The Academy assessment model is a blend of formative and summative assessments that include online and hands-on, skills-based exams.
Hands-On, Skills-Based
The core of the CCNA 2 experience is the sequence of hands-on labs. Labs are designated as either essential or optional. Essential labs include information that is fundamental to the CCNA Academy student experience. This information will help students prepare for the certification exam, succeed in job situations, and develop their cognitive abilities. In CCNA 2, students will learn about the following elements of basic router configuration:
•Hostnames, banners, and passwords
•Interface configuration
•IOS file system
•Static routes and dynamic routing (RIP version 1 and IGRP)
2 - 238 CCNA 2 Routers and Routing Basics v3.1 Instructor Guide – Welcome |
Copyright © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. |

•Standard and extended access-list configuration and placement
•show, debug, ping, trace, and telnet commands to verify and troubleshoot
Global Community
WWE instructors are members of a global community of educators. There are over 10,000 instructors that teach the same eight CCNA and CCNP courses in the program. Instructors should take advantage of the diversity and skills of this community through their Regional Academies, Cisco Academy Training Centers (CATCs), the Cisco Academy Connection (CAC), or through other forums. WWE is committed to the improvement of the curriculum, assessment model, and instructional resources such as this guide. Please submit any feedback through CAC. Check CAC for new releases of instructional materials.
Guide Overview:
Section II provides a scope and sequence overview of the course. Section III summarizes the most important learning objectives, target indicators, and labs, and offers teaching suggestions and background information. Section IV provides a case study related to network design, implementation, and troubleshooting. Instructors can also devise their own case studies. Section V includes four appendices:
•Cisco online tools and utilities
•CCNA assessment guidelines
•Evidence-centered design of assessment tasks in the Networking Academy program
•Instructional best practices
3 - 238 CCNA 2 Routers and Routing Basics v3.1 Instructor Guide – Welcome |
Copyright © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. |

II. Course Overview
Target Audience
The target audience is anyone who desires a practical and technical introduction to the field of networking. This includes high school, community college, and lifelong-learning students who are interested in careers as network technicians, network engineers, network administrators, and network help-desk staff.
Prerequisites
The successful completion of this course requires the following:
•Reading age level of 13 or higher
•Successful completion of CCNA 1
The following prerequisites are beneficial, but not required:
•Prior experience with computer hardware and command line interfaces
•Background in computer programming
Course Description
CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics is the second of four CCNA courses that lead to the Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) designation. CCNA 2 focuses on initial router configuration, Cisco IOS Software management, routing protocol configuration, TCP/IP, and access control lists (ACLs). Students will learn how to configure a router, manage Cisco IOS software, configure routing protocols on routers, and set access lists to control access to routers.
Course Objectives
The CCNA certification indicates knowledge of networking for the small office, home office (SOHO) market and the ability to work in small businesses or organizations that use networks with fewer than 100 nodes. A CCNA-certified individual can perform the following tasks:
•Install and configure Cisco switches and routers in multiprotocol internetworks that use LAN and WAN interfaces
•Provide Level 1 troubleshooting service
•Improve network performance and security
•Perform entry-level tasks in the planning, design, installation, operation, and troubleshooting of Ethernet and TCP/IP Networks
4 - 238 |
CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v3.1 Instructor Guide – Course Overview |
Copyright © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. |

Students must successfully complete the CCNA 2 course before they can achieve CCNA certification.
Upon completion of this course, students will be able to perform tasks related to the following:
•Routers and their roles in WANs
•Cisco IOS Software Management
•Router configuration
•Router file management
•RIP and IGRP routing protocols
•TCP/IP error and control messages
•Router troubleshooting
•Intermediate TCP
•Access control lists
Lab Requirements
Please refer to the CCNA equipment bundle spreadsheets on the Cisco Academy Connection.
Certification Alignment
The curriculum is aligned with the following Cisco Internet Learning Solution Group (ILSG) courses:
•CCNA (Cisco Certified Network Associate)
•INTRO (Introduction to Cisco Networking Technologies)
The Course 2 claims state that students will be able to complete the following tasks:
•Identify the key characteristics of common wide-area network (WAN) configurations and technologies, and differentiate between these and common LAN technologies
•Describe the role of a router in a WAN
•Describe the purpose and operations of the router Internet Operating System (IOS)
•Establish communication between a terminal device and the router IOS, and use IOS for system analysis, configuration, and repair
•Identify the major internal and external components of a router, and describe the associated functionality
5 - 238 |
CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v3.1 Instructor Guide – Course Overview |
Copyright © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. |

•Connect router Fast Ethernet, serial WAN, and console ports
•Perform, save, and test an initial configuration on a router
•Configure additional administrative functionality on a router
•Use embedded data-link layer functionality to perform network neighbor discovery and analysis from the router console
•Use embedded Layer 3 through Layer 7 protocols to establish, test, suspend, or disconnect connectivity to remote devices from the router console
•Identify the stages of the router boot-up sequence and show how the configuration register and boot system commands modify that sequence
•Manage system image and device configuration files
•Describe the operation of the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) and identify the reasons, types, and format of associated error and control messages
•Identify, configure, and verify the use of static and default routes
•Evaluate the characteristics of routing protocols
•Identify, analyze, and show how to rectify inherent problems associated with distance vector routing protocols
•Configure, verify, analyze, and troubleshoot simple distance vector routing protocols
•Use commands incorporated within IOS to analyze and rectify network problems
•Describe the operation of the major transport layer protocols and the interaction and carriage of application layer data
•Identify the application of packet control through the use of various access control lists
•Analyze, configure, implement, verify, and rectify access control lists within a router configuration
Course Overview
The course has been designed for 70 contact hours. Approximately 35 hours will be designated to lab activities and 35 hours will be designated to curriculum content. A case study on routing is required. The format and timing should be determined by the Local Academy.
6 - 238 |
CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v3.1 Instructor Guide – Course Overview |
Copyright © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. |

The following changes have taken place since CCNA version 2.x:
•More emphasis on router configuration early in semester
•More efficient presentation and practice of IOS
•IGRP moved from CCNA 3 to CCNA 2
•Access lists moved from CCNA 3 to CCNA 2
•Revisions to TCP/IP coverage
•More focus on routing tables
•Case study is required with format and timing determined by the Local Academy
•More interactive flash activities
•Sequence of over 40 e-Labs
•Lab focus on two-router labs
7 - 238 |
CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v3.1 Instructor Guide – Course Overview |
Copyright © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. |

III. Teaching Guide for Each TI
Nomenclature
The CCNA curriculum uses the following hierarchy:
•Course
•Module
•Learning objective (LO)
•Target indicator (TI)
For example, 3.2.5 references Module 3, LO 2, and TI 5. The following terms are commonly used to describe the curriculum, instructional materials, and assessments in WWE and Cisco documentation:
•Certification-level claims
High-level statements about what a CCNA-certified person should know and be able to do. These claims are measured through certification exams.
•Course
A subset of a curriculum which is a collection of chapters to be offered as a scheduled course.
•Course-level claims
Medium-level statements about what a person who completes the CCNA 2 course should know and be able to do.
•Core TI
The TIs that apply most directly to the claims and learning objectives. Instructors should not skip over these TIs or move through them quickly.
•Curriculum
A predefined or dynamic path of learning events with an end goal such as certification or the acquisition of required job skills and knowledge.
•Hands-on skills
There is some overlap between hands-on skills and claims. These statements emphasize hands-on, lab-based learning.
8 - 238 |
CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v3.1 Instructor Guide – Teaching Guide: TI by TI Copyright © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. |

•Module
Logical groupings that comprise a course. Modules contain multiple lessons or LOs. Modules are also referred to as chapters.
•Learning objective (LO)
A statement that establishes a measurable behavioral outcome. LOs are used to organize content and to indicate how the acquisition of skills and knowledge will be measured. LOs are also referred to as terminal objectives or RLOs.
•Lesson
A set of TIs, or enabling objectives, that are grouped together and presented in a coherent format to meet an LO, or terminal objective. Lessons emphasize the role of the instructor. Learning objectives emphasize the role of the students.
•Module caution
Suggestions related to areas where difficulties may be encountered. These are especially important for syllabus development, lesson planning, and pacing.
•Optional lab
A lab that is for practice, enrichment, or differentiation.
•Essential lab
A lab that is fundamental to the course.
•Reusable Learning Object (RLO)
This is a Cisco Instructional Design term. RLOs typically consist of five to nine RIOs. In this guide, RLOs are equivalent to lessons or learning objectives.
•Reusable Information Object (RIO)
This is a Cisco Instructional Design term. In this guide, RIOs are equivalent to target indicators.
•Target indicator (TI)
TIs are also referred to as enabling objectives or RIOs. TIs typically consist of a text frame with graphics and several media content items.
9 - 238 |
CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v3.1 Instructor Guide – Teaching Guide: TI by TI Copyright © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. |

Module 1: WANs and Routers
Overview
When teaching Module 1, show the students how router configuration relates to the Internet, which is a global internetwork made possible by routers. Students will learn the difference between WANs and LANs, and will identify WAN connections, encapsulations, and protocols.
Module 1 Caution
WANs will be taught in detail in CCNA 4. In CCNA 2, it is important to teach students the fundamental basics of WANs and roles that routers play in the WAN connection. Inform the students that the serial interfaces will be used to simulate the DCE to DTE WAN connection. Do not spend too much time on this module.
Students who complete this module should be able to:
•Identify organizations responsible for WAN standards
•Explain the difference between WANs and LANs and the types of addresses they use
•Describe the role of a router in a WAN
•Identify internal components of a router and describe their functions
•Describe the physical characteristics of a router
•Identify common ports on a router
•Connect Ethernet, serial WAN, and console ports
10 - 238 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v3.1 Instructor Guide – Module 1 |
Copyright © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. |

1.1 WANs
Essential labs: |
None |
Optional labs: |
None |
Core TIs: |
All |
Optional TIs: |
none |
Course-level claim: Students can identify the important characteristics of common WAN configurations and technologies, differentiate between these and common LAN technologies, and describe the role of a router in a WAN.
Certification-level claim: Students can evaluate the important characteristics of WANs and implement simple WAN protocols.
Hands-on skills: none
1.1.1 Introduction to WANs
WANs differ from LANs in several ways:
•LANs connect workstations, peripherals, terminals, and other devices in a single building or several buildings that are located next to each other, and WANs connect large geographic areas.
•LANs connect devices and WANs connect data connections across a broad geographic area.
WANs operate at the physical and data-link layers of the OSI model. Devices used in a WAN are routers, switches, modems, and communication servers. The following topics are relevant to this TI:
•Discuss the various carriers and devices available for WAN connections.
•Show students what routers in a WAN look like.
•Explain what routers do.
Figure 3 is an important figure to review. Best instructional practices for this TI include online study sessions with study guides, group work, and mini-lectures. This TI provides essential background information for the CCNA exam.
1.1.2 Introduction to routers in a WAN
Routers and computers have four basic common components:
•CPU
•Bus
11 - 238 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v3.1 Instructor Guide – Module 1 |
Copyright © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. |

•Memory
•Interfaces
However, the main purpose of a router is to route, not to compute. The main components of the router are as follows:
•RAM
•NVRAM
•Flash
•ROM
•Interfaces
The following topics should be covered in this TI:
•Discuss the similarities of computers and routers such as the software they use.
•Explain the components of the router and what each component contains.
•Open a router and let the students examine the inside. Point out the main components.
•Explain that just as a computer cannot work without an operating system and software, a router cannot work without an operating system and configurations.
1.1.3Router LANs and WANs
Routers function in both LANs and WANs. They are primarily used in WANs. Explain that routers have both LAN and WAN interfaces. Students should be able to identify the differences. The two main functions of a router are to select the best path and to forward packets to the correct outgoing interfaces.
Networking models are useful because they facilitate modularity, flexibility, and adaptability. Like the OSI model, the three-layer design model is an abstract picture of a network. Models may be difficult to comprehend because the exact composition of each layer varies from network to network.
Explain that each layer of a three-layer design model may include a router, a switch, a link, or some combination of these. Some networks may combine the function of two layers into a single device or may omit a layer entirely. The three-layer design model consists of the following:
•The core layer forwards packets as quickly as possible.
•The distribution layer provides a boundary by using filters to limit what gets to the core.
•The access layer feeds traffic into the network and controls entry into the network.
12 - 238 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v3.1 Instructor Guide – Module 1 |
Copyright © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. |

1.1.4 Role of Routers in a WAN
There are several encapsulations associated with serial lines:
•HDLC
•Frame Relay
•PPP
•SDLC
•SLIP
•LAPB
Some of the most common WAN technologies are as follows:
•POTS
•ISDN
•X.25
•Frame Relay
•ATM
•T1, T3, E1, and E3
•DSL
•SONET
Ask students to briefly explain each of the WAN technologies and discuss the differences between technologies and encapsulations. They will be covered in detail in CCNA 4.
It is important to encourage student interest and enthusiasm in this TI. The world of WAN technologies is briefly introduced. Many students will be familiar with one or more of the technologies used. Many of these topics will be covered in CCNA 4 and students should be encouraged to do additional research on one of these technologies and present it to the class.
1.1.5 Academy approach to hands-on labs
In the Networking Academy lab, all the networks are connected with a serial or Ethernet cable. This allows the students to see and touch all of the equipment. In a real network, the routers would not be in one physical location. In the Networking Academy lab, the serial cables are connected back-to-back. However, in the real world the cables would be connected through a CSU or DCE device.
Discuss the differences between real networking environments and the router lab setup. Help the students visualize the components between the V.35 connectors. If they can understand this picture, then they will realize that they are working with a complete WAN minus the carrier services.
13 - 238 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v3.1 Instructor Guide – Module 1 |
Copyright © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. |

Each student should build a complete topology and then take it apart and let the next student do the lab. These labs are a review of the cabling labs in CCNA 1. This may be one of the last opportunities students have to cable a network, so do not miss this opportunity to make sure students complete the CCNA 2 Lab setup. This is a good place to introduce troubleshooting and the Layer 1 issues that occur in CCNA 2. It is also a fairly simple and fun activity.
1.2 Routers
Essential Labs: |
1.2.5, 1.2.6, and 1.2.7 |
Optional Labs: |
None |
Core TIs: |
All |
Optional TIs: |
none |
CourseLevel Claim: Students can properly connect router Fast Ethernet, Serial WAN, and console ports.
Certification-Level Claim: Students can describe the components of network devices. They can also identify the major internal and external components of a router and describe the associated functionality.
Hands-on skills: none
1.2.1 Introduction to WANs
This section overviews the physical aspect of a router. The physical layer is always studied first in networking topics. The student will be able to identify internal components of the router and describe their functions, describe the physical characteristics of the router, identify common ports on a router, and properly connect FastEthernet, Serial WAN, and console ports.
The components in a router are essentially the same as those in a computer. In fact, a router can be thought of as a computer designed for the special purpose of routing. While the exact architecture of the router varies in different router series, this section will introduce the major internal components. The figures show the internal components of some of the Cisco router models.
Ask students the following questions:
•What are the common components of a router?
•What is NVRAM used for?
1.2.2Router physical characteristics
It is not necessary to know the location of the physical components inside the router to understand how to use the router. The exact components used and their locations vary in different router models.
14 - 238 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v3.1 Instructor Guide – Module 1 |
Copyright © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. |

Ask students the following questions:
•What are the different types of RAM used by a router?
•Can the RAM be upgraded in a router?
1.2.3Router external connections
The three basic types of connections on a router are LAN interfaces, WAN interfaces, and management ports. LAN interfaces allow the router segment network boundaries within a LAN and reduce broadcast traffic within a LAN. WAN connections are provided through a service provider which connects two or more distant site through the Internet or PSTN. The LAN and WAN connections provide network connections through which frames are passed. The management port provides an ASCII or text-based connection for the configuration and troubleshooting of the router.
Ask students the following questions:
•What are the three basic types of connections on a router?
•What is the console connection used for?
1.2.4Management port connections
The management ports are asynchronous serial ports. They are the console port and the auxiliary port. Not all routers have an auxiliary port. These serial ports are not designed as networking ports. To prepare for initial startup and configuration, attach an RS-232 ASCII terminal or a computer that emulates an ACSII terminal to the system console port.
It is essential for students to understand the difference between network interfaces and nonnetwork interfaces. The instructor may need to talk about the differences extensively.
Discuss the following topics:
•The network ports use network encapsulation frames while the non-network ports are bit and byte oriented.
•There is no addressing involved in the serial management ports.
•The serial interface for management is asynchronous and the serial WAN interface is synchronous.
Ask students the following questions:
•Which port is preferred for troubleshooting and why?
•Do all routers have an auxiliary port?
1.2.5Console Port Connections
The console port is a management port used to provide out-of-band access to a router. It is used for the initial configuration of the router, monitoring, and disaster recovery procedures.
15 - 238 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v3.1 Instructor Guide – Module 1 |
Copyright © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. |

Students may not be familiar with the term out-of-band. Out-of-band refers to the fact that the management control communications use a different path or channel than the data communications.
Ask students the following questions:
•What type of terminal emulation must the PC or terminal support?
•What are the steps to connect the PC to a router?
1.2.6Connecting Router LAN interfaces
In most LAN environments, an Ethernet or FastEthernet interface is used to connect the router to the LAN. The router is a host that connects to the LAN through a hub or a switch. A straightthrough cable is used to make this connection. The correct interface must be used.
If the wrong interface is connected, the router or other networking devices may be damaged. This is generally not true within LAN interfaces. However, if LAN interfaces are connected to some form of WAN interface such as ISDN, damage can occur. The students should be taught to be observant and careful whenever connections are made.
Ask students the following questions:
•What type of cable is used to connect from the router Ethernet interface to a hub or switch?
•What type of cable is used to connect from the router Ethernet interface to a router Ethernet interface?
1.2.7Connecting WAN interfaces
There are many forms of WAN connections. A WAN uses many different types of technology to make data connections across a broad geographic area. WAN services are usually leased from service providers. The WAN connection types include leased line, circuit switched, and packet switched.
Many of the WAN interfaces use the same physical interfaces but different pinouts and electrical characteristics. This difference in electrical characteristics could potentially cause damage if the wrong connections were made. Again, the students should be taught to be observant and careful when they make any connections.
Ask students to perform the following tasks:
•List the physical layer standards that Cisco routers support.
•List the different types of WAN connections.
16 - 238 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v3.1 Instructor Guide – Module 1 |
Copyright © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. |

Module 1 Summary
Before students move on to Module 2, they must be able to cable the lab setup, identify all external relevant ports, and identify internal router components.
Online assessment options include the end-of-module online quiz in the curriculum and the online Module 1 exam. Consider introducing formative assessments, where the instructor supervises the students as they work on the router setup. The use of formative assessments can be very valuable while students work through this router-intensive and IOS-intensive course.
Students should understand the following main points:
•WAN and LAN concepts
•Role of a router in WANs and LANs
•WAN protocols
•How to configure console connections
•The identification and description of the internal components of a router
•The physical characteristics of a router
•The common ports on a router
•How to connect router console, LAN, and WAN ports
17 - 238 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v3.1 Instructor Guide – Module 1 |
Copyright © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. |

Module 2: Introduction to Routers
Overview
Consider the prior knowledge of students when teaching Module 2. Some students may be familiar with command-line interfaces (CLIs). Students who have only used GUIs may not know how to use CLIs to interact with a computer. Students should experiment with CLIs to learn how to interact with a router.
Module 2 Caution
Students need to know what the IOS is and what it does. They also need to know the difference between the configuration file and the IOS. It is also important for students to feel comfortable when they enter into and move around in the CLI. Do not move too quickly through these labs. If students are uncomfortable with the CLI, they will have difficulties with more complex labs.
Students who complete this module should be able to perform the following tasks:
•Describe the purpose of the IOS
•Describe the basic operation of the IOS
•Identify various IOS features
•Identify the methods to establish a command-line interface (CLI) session with the router
•Move between the user command executive (EXEC) and privileged EXEC modes
•Establish a HyperTerminal session on a router
•Log into a router
•Use the help feature in the command-line interface
•Troubleshoot command errors
18 - 238 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v3.1 Instructor Guide – Module 2 |
Copyright © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. |

2.1 Operating Cisco IOS Software
Essential Labs: |
None |
Optional Labs: |
None |
Core TIs: |
All |
Optional TIs: |
none |
Course-Level Claim: Students can describe the purpose and fundamental operation of the router IOS.
Certification-Level Claim: Students can establish communication between a terminal device and the router IOS and use it for system analysis, configuration, and repairs.
Hands-on skills: none
2.1.1 The purpose of Cisco IOS software
In this TI, students will be introduced to the fundamentals of the Cisco Internet Operating System (IOS). Student will learn about the show version command, which helps users gain information about the Cisco IOS. The IOS command line interface is introduced in another lesson, so there is no need to focus on the show command in this TI.
A router and switch cannot function without an operating system. Cisco IOS is the installed software in all Cisco routers and Catalyst switches.
A computer needs an operating system such as Windows or UNIX. Discuss how the hardware cannot function without this software. Make sure the students understand the role of the IOS.
2.1.2 Router user interface
Cisco IOS software uses a command-line interface (CLI) as its console environment. The CLI is accessible through several methods:
•Console port
•Auxiliary port
•Telnet session
Students should know the difference between these methods. They should also be comfortable with the term CLI.
2.1.3 Router user interface modes
The user EXEC mode allows a limited number of basic monitoring commands. This mode is often referred to as a view-only mode. The privileged EXEC mode provides access to all router commands. To enter the privileged mode from user mode the enable command must be entered. The privileged mode is used to access other modes to configure the router.
19 - 238 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v3.1 Instructor Guide – Module 2 |
Copyright © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. |

Students should be able to identify the router prompts. The user mode prompt is Router>. The privileged mode prompt is Router#.
2.1.4 Cisco IOS software features
Cisco IOS devices have three operating environments:
•ROM monitor
•Boot ROM
•Cisco IOS
ROM monitor is used to recover from system failures and recover a lost password. Boot ROM is used to modify the Cisco IOS image in flash. There is a limited subset of features in this mode. Normal operation of a router requires the full Cisco IOS image. Discuss the three operating environments. Students should be able to identify these environments. Students must be familiar with the IOS to control the router. Cisco technology is in the IOS, not in the hardware.
2.1.5 Operation of Cisco IOS software
There are numerous IOS images for different Cisco device models. Each devise uses a similar basic command structure for configuration. The configuration and troubleshooting skills acquired on a specific device will apply to a variety of products.
The naming convention for the different Cisco IOS Releases contains three parts:
•The platform on which the image runs
•The special capabilities and feature sets supported in the image
•Where the image runs and whether it has been zipped or compressed
One of the major constraints for the use of a new IOS image is compatibility with the router flash and RAM memory.
The students should also understand that the same IOS is used on the smallest to the largest Cisco products. This will assure students that the skills they develop on small Cisco routers can be applied to larger routers and switches.
Show students various naming conventions and identify the three parts of the naming convention. For example, in cpa25-cg-1, cpa25 is the Cisco Pro 2500 Router, cg is the feature capability such as communication server, remote-access server, or ISDN, and the 1 is the run location or compressed status.
Explain that it is important to install and maintain various IOS versions, especially newer versions with advanced features. Encourage the students to conduct research online at www.cisco.com for more information on how to obtain various IOS images.
20 - 238 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v3.1 Instructor Guide – Module 2 |
Copyright © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. |

2.2Starting a Router
Essential Labs: |
2.2.1, 2.2.4, and 2.2.9 |
Optional Labs: |
None |
Core TIs: |
All |
Optional TIs: |
none |
Course-Level Claim: Students can describe the purpose and fundamental operation of the router IOS
Certification-Level Claim: Students can establish communication between a terminal device and the router IOS and use it for system analysis, configuration, and repair
Hands-on skills: none
2.2.1 Initial startup of Cisco routers
This section teaches students about the startup process for a router. Students learn how to establish a HyperTerminal session and log into a router. Students will then be introduced to the help feature and enhanced editing commands.
When a Cisco router powers up, it performs a POST. This executes diagnostics from ROM on all hardware modules. After the POST, the following events occur as the router initializes:
•Bootstrap is loaded from ROM.
•IOS is loaded from flash, TFTP, or ROM.
•Config is loaded from NVRAM or TFTP into setup mode.
This section teaches students how to check the configuration during the boot process. Setup mode is intended to quickly install a router with minimal configuration. Discuss the initial startup of routers and explain why the IOS and configuration files can be loaded from several places.
2.2.2 Router LED indicators
Router LED indicators indicate the status of a router. If an interface is extremely busy, its LED will be on all the time. The green LED will be on after the router card initializes correctly.
Have the students view the LED indicators on the routers in the lab setup. Show them LEDs that work correctly and explain what they are. Make sure the students understand that the port status and link LEDs are the prime indicators of the physical layer status.
2.2.3 The initial router bootup
Bootup messages displayed by a router include messages such as “NVRAM invalid, possibly due to write erase”, which indicates that the router has not been configured or the backup configuration has been erased.
21 - 238 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v3.1 Instructor Guide – Module 2 |
Copyright © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. |

If a router does not boot up correctly, issue the show version command to examine the configuration register to see if it is booting.
Remind the students that the router is a special purpose computer. It has a boot sequence that is similar to a standard computer. The router must load the IOS from one of several sources. The router must also obtain a configuration file. If a configuration file is not available, the router will enter setup mode, which prompts the user for a basic router configuration. Make sure the students understand what the router needs as basic configuration information. This provides a lot of information about how the router works. It is very important for students to understand the difference between the IOS and the configuration file.
2.2.4 Establish a console session
To establish a HyperTerminal Console session, students should complete the following steps:
1.Connect the terminal with an RJ-45-to-RJ-45 rollover cable and an RJ-45-to-DB-9 or RJ-45-to-DB-25 adapter
2.Configure the terminal or PC terminal emulation software for 9600 baud, 8 data bits, no parity, 1 stop bit, and no flow control
Instruct the students to connect the cables from the router to the PC and to connect with the HyperTerminal program. To configure a router, a connection must be established between the PC and a router. Make sure students understand that this is how routers need to be configured initially, but it is not the only way to configure a router.
2.2.5 Router login
There are two levels of access to commands in a router:
•User EXEC mode
•Privileged EXEC mode
The user EXEC mode is a view-only mode. Enter privileged EXEC mode with the enable command from the User prompt. Other modes can be accessed from privileged mode to configure a router. The students should have a lot of practice with hands-on activities in the lab setup. It is important for students to understand the various modes to be able to accurately configure a router. It is not necessary to memorize all commands. Students must understand each mode so they can make the configurations from the correct locations.
2.2.6 Keyboard help in the router CLI
At the user mode prompt, a question mark (?) should be typed to display a list of commands available in the router. From user mode, the enable command will switch the router into the privileged mode. If a question mark (?) is entered from the privileged mode prompt, many more commands are listed as available commands to use in the router. Students should briefly review the types of commands in each mode. There is no need to memorize all of the commands.
The context-sensitive help is one of the most useful features of the IOS. Teach the student that the question mark (?) is extremely helpful in the router.
22 - 238 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v3.1 Instructor Guide – Module 2 |
Copyright © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. |

To demonstrate the help feature, instruct students to set the clock without telling them which commands to use. The question mark (?) will guide students through the process.
2.2.7 Enhanced editing commands
Enhanced editing commands are on by default. To disable enhanced editing mode, the terminal no editing command can be used at the privileged mode prompt.
The editing command set provides a horizontal scrolling feature for commands that extend beyond a single line. When the cursor reaches the right margin, the command line shifts ten spaces to the left. The first ten characters of the line cannot be seen, but a user can scroll back to check the syntax. It is represented by a dollar sign ($).
Some of the editing commands are as follows:
•Ctrl-A moves to the beginning of the command line.
•Ctrl-B moves back one character.
•Ctrl-E moves to the end of the command line.
•Ctrl-F moves forward one character.
•Ctrl-Z moves back out of configuration mode.
•Esc and then B moves back one word.
•Esc and then F moves forward one word.
The syntax of IOS commands can be complex. Keyboard editing features can be used to correct text that has been entered. When a router is being configured, repetitive command statements, typing errors that need to be fixed, and commands that need to be reused may be encountered. Questions about the Ctrl key and Esc key sequences will probably appear on the CCNA exam.
2.2.8 Router command history
The user interface provides a history of commands that have been entered. This feature can be used to recall long or complex commands. The command history feature can be used to complete the following tasks:
•Set the command history buffer size
•Recall commands
•Disable the command history feature
By default, the command history records ten command lines in the history buffer. To recall commands, press Ctrl-P or the Up Arrow key to recall repeated commands. Press Ctrl-N or the Down Arrow key to recall more recent commands in the history. The Ctrl-P and Ctrl-N features are also likely to be tested on the CCNA exam.
23 - 238 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v3.1 Instructor Guide – Module 2 |
Copyright © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. |

The syntax of IOS commands can be complex. The feature used to recall commands can help students save time when they program or troubleshoot a router.
2.2.9 Troubleshooting command line errors
This troubleshooting lab allows students to log into the router and access various modes. Demonstrate the use of the question mark (?) as a helpful tool for students who do not know which command to enter.
Also demonstrate the use of the history command as a helpful tool for students to troubleshoot problems without retyping repeated commands.
2.2.10 The show version command
The show version command displays information about the Cisco IOS software version. This information includes the system image file name and the location from which it was booted. It also contains the configuration register and the boot-field setting. Explain that an important aspect of router and IOS maintenance is to know exactly which version of the IOS is being used.
Cisco has numerous major and minor IOS releases. There are many different versions and different features to meet the requirements of a network. Students should know that the show version command shows much more than just the version of the IOS. This is an important command. Explain to students is that this is the only command that can be used to examine the configuration register.
24 - 238 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v3.1 Instructor Guide – Module 2 |
Copyright © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. |

Module 2 Summary
Before students move on to Module 3, they must be able to interact with the router through a HyperTerminal session and the CLI.
Online assessment options include the end-of-module online quiz in the curriculum and the online Module 2 exam. Make sure students know how to access the command-line prompt. Formative assessments related to lab work are relevant to Module 2.
Students should understand the following main points:
•Understand the basic operation of IOS
•Identify various IOS features
•Identify methods to establish a CLI session with the router
•Use HyperTerminal to establish a CLI session
•Log into the router
•Use the help feature in the command line interface
•Use the enhanced editing commands
•Use the command history
•Troubleshoot command line errors
•Use the show version command
25 - 238 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v3.1 Instructor Guide – Module 2 |
Copyright © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. |

Module 3: Configuring a Router
Overview
When teaching Module 3, emphasize the empowerment that students will gain from the ability to configure routers and the importance of familiarity with the IOS through extensive practice. There are many tools available to teach IOS:
•The curriculum text and graphics are used to introduce command syntax and context.
•The online command references are integrated.
•CiscoPedia is the IOS command reference in the form of a Windows help file. All CCNA and CCNP commands are included.
•Integrated e-Labs provide guided practice of command syntax.
•Standalone e-SIMs provide more open-ended practice of CCNA 2-level router configuration.
•Hands-on labs are integrated PDF files that should be the core of the learning experience.
Module 3 Caution
Spend a lot of time on this module. Students have wanted to program routers since the first day of CCNA 1. This module presents the core skills that the students will use to build all Cisco device configurations. From this point in the CCNA 2 curriculum through the end of the CCNA 4 curriculum, students may be deprived of the opportunity to learn about the IOS if the student-to-equipment ratio is high. Only the local instructor can decide what mix of lab equipment, group work, creative rotations, lab access, remote access through NetLabs or other solutions, e-Labs, e-SIM, CiscoPedia, and other tools can be used to give students adequate opportunities to learn IOS.
After completing this module, students should be able to perform the following tasks:
•Name a router
•Set passwords
•Examine show commands
•Configure a serial interface
•Configure an Ethernet interface
•Make changes to a router
•Save changes to a router
26 - 238 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v3.1 Instructor Guide – Module 3 |
Copyright © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. |

•Configure an interface description
•Configure a message-of-the-day banner
•Configure host tables
•Understand the importance of backups and documentation
27 - 238 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v3.1 Instructor Guide – Module 3 |
Copyright © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. |

3.1 Configure a Router
Essential Labs: |
3.1.2, 3.1.3, 3.1.4, 3.1.5, 3.1.6, and 3.1.7 |
Optional Labs: |
None |
Core TIs: |
All |
Optional TIs: |
none |
Course-Level Claim: Students can perform, save, and test an initial configuration on a router.
Certification Level Claim: Students can perform an initial configuration on a router.
Hands-on skills: none
3.1.1 CLI command modes
The students need to understand that the router does not know what routing to do until it is configured. This section will help students begin the configuration of a router.
To gain access to a router, a login is required. After login, there is a choice of modes. The modes interpret the commands that are typed and perform the operations. There are two EXEC modes:
•User EXEC mode
•Privileged EXEC mode
The first configuration mode is referred to as global configuration mode or global config. The following configuration modes are available in global configuration mode:
•Interface
•Subinterface
•Controller
•Map-list
•Map-class
•Line
•Router
Global configuration commands are used in a router to apply configuration statements that affect the entire system. Use the privileged EXEC command configure terminal to enter global configuration mode.
Explain that Cisco IOS is modal. Emphasize that in the CLI that there are different modes to accomplish different tasks. There are several advantages to this. One is that the commands are generally shorter because the object of the mode, i.e., the interface, or routing protocol, to
28 - 238 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v3.1 Instructor Guide – Module 3 |
Copyright © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. |

be changed does not need to be specified in the command. Another advantage is that only the parameters, or objects of the mode, i.e., the interface, or routing protocol, can be modified by the command. This helps prevent accidental configuration of the wrong object. There are shortcuts to show students at a later time:
• config t for configure terminal
•int fa0/0 for interface fastethernet 0/0
Students commonly enter the correct command at the incorrect prompt. If the students are unable to enter a command, check the mode. The prompt will be either Router(config)# or
Router(config-if)#.
Ask students the following questions:
•Which mode is the user in when first logging into the router?
•What mode is the user in after entering the enable command?
3.1.2Configuring a router name
One of the first basic configuration tasks is to name a router. This task helps with network management and uniquely identifies each router within a network. Use global configuration mode to name a router. The name of a router is called the hostname and will be displayed as the system prompt. If a router is not named, then the system default will be “Router”.
Students need to understand that the name is an important part of the configuration process. Much of the configuration and troubleshooting will be performed remotely. Users will telnet into different routers. For practice, ask students to name the routers. When instructors are asked to help troubleshoot a lab, they can easily identify the different routers. The router name at the prompt confirms the student has completed this task. Students should also understand that names should be chosen to represent a location or a function. In many organizations, there are naming conventions to be followed.
Ask students the following questions:
•What is the default name of the router?
•In which mode can the user name the router?
•What is the command to name a router?
3.1.3Configuring router passwords
Passwords can be used to secure a router and restrict access. Passwords can be established for virtual terminal lines and the console line. The privileged EXEC mode may also have a password. From global configuration mode use the enable password command to restrict access to the privileged mode. The line configuration mode can be used to establish a login password on the console terminal. Use the command line vty 0 4 to establish a login password on incoming Telnet sessions.
29 - 238 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v3.1 Instructor Guide – Module 3 |
Copyright © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. |
 Loading...
Loading...