Page 1

PowerFlex 20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter
Series A FRN 2.xxx
Series B FRN 4.xxx
User Manual
Page 2

20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Page 3

Important User Information
!
!
Solid state equipment has operational characteristics differing from those of
electromechanical equipment. Safety Guidelines for the Application,
Installation and Maintenance of Solid State Controls (Publication SGI-1.1
available from your local Rockwell Automation sales office or online at
www.rockwellautomation.com/literature) describes some important differences
between solid state equipment and hard-wired electromechanical devices.
Because of this difference, and also because of the wide v ariety of uses for solid
state equipment, all persons responsible for applying this equipment must
satisfy themselves that each intended application of this equipment is
acceptable.
In no event will Rockwell Automation, Inc. be respo nsible or li able for i ndirect
or consequential damages resulting from the use or application of this
equipment.
The examples and diagrams in this manual are included solely for illustrative
purposes. Because of the many variables and requirements associated with any
particular installation, Rockwell Automati on, Inc. cannot assu me responsibility
or liability for actual use based on the examples and diagrams.
No patent liability is assumed by Rockwell Automation, Inc. with respect to use
of information, circuits, equipment, or software described in this manual.
Reproduction of the contents of this manual, in whole or in part, without
written permission of Rockwell Automation, Inc. is prohibited.
http://
Throughout this manual, when necessary we use notes to make you aware of
safety considerations.
WARNING: Identifies information about practices or
circumstances that can cause an explosion in a hazardous
environment, which may lead to personal injury or death, property
damage, or economic loss.
Important: Identifies information that is critical for successful application and
understanding of the product.
ATTENTION: Identifies information about practices or
circumstances that can lead to personal injury or death, property
damage, or economic loss. Attentions help you identify a hazard,
avoid a hazard, and recognize the consequences.
Shock Hazard labels may be located on or inside the equipment
(e.g., drive or motor) to alert people that dangerous voltage may be
present.
Burn Hazard labels may be located on or inside the equipment
(e.g., drive or motor) to alert people that surfaces may be at
dangerous temperatures.
Allen-Bradley, Rockwell Software, Rockwell Automation, TechConnect, PowerFlex, SMC Flex, DPI, SCANport, Connected Components
Workbench, DriveExplorer, DriveExecutive, and DriveTools are trademarks of Rockwell Automation, Inc.
Trademarks not belonging to Rockwell Automation are property of their respective companies.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Page 4

20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Page 5

Summary of Changes
The information below summarizes the changes made to this manual since
its last release (October 2012):
Description of Changes Page
Added information about the compatible products. Throughout
Added information for use with PowerFlex Digital DC drives.
manual
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 6

soc-ii Summary of Changes
Notes:
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 7

Preface About This Manual
Conventions Used in This Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . P-1
Rockwell Automation Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . P-2
Additional Resources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . P -2
Chapter 1 Getting Started
Components. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
Compatible Products. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
Required Equipment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
Safety Precautions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-5
Quick Start . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-6
Chapter 2 Installing the Adapter
Preparing for an Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
Setting the Web Pages Switch (only Series B Adapter, Firmware 3.xxx or Later). . . . . . 2-2
Connecting the Adapter to the Drive. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
Connecting the Adapter to the Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-6
Applying Power. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-6
Commissioning the Adapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-8
Table of Contents
Chapter 3 Configuring the Adapter
Configuration Tools. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
Using the PowerFlex 7-Class HIM to Access Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
Using BOOTP Server to Set the IP Address, Subnet Mask, and Gateway Address. . . . . 3-3
Using Parameters to Set the IP Address, Subnet Mask, and Gateway Address . . . . . . . . 3-5
Setting the Data Rate. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-7
Setting the I/O Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-7
Selecting Master-Slave or Peer-to-Peer Hierarchy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-8
Setting the Reference Adjustment. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-13
Setting a Fault Action . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-14
Setting Web Access Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-15
Resetting the Adapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-16
Viewing the Adapter Status Using Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-17
Updating the Adapter Firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-17
Chapter 4 Configuring the I/O
Using RSLinx Classic Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
ControlLogix Controller Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-2
Limitations Using a PLC-5, SLC 500, or MicroLogix 1100/1400 Controller . . . . . . . . 4-22
PLC-5 Controller Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-23
SLC 500 Controller Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-31
MicroLogix 1100/1400 Controller Example. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-39
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 8

ii Table of Contents
Chapter 5 Using the I/O
About I/O Messaging. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-1
Understanding the I/O Image. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-2
Using Logic Command/Status. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-6
Using Reference/Feedback . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-6
Using Datalinks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-9
Example Ladder Logic Program Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-11
ControlLogix Controller Example. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-11
PLC-5, SLC 500, or MicroLogix 1100/1400 Controller Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-21
Chapter 6 Using Explicit Messaging
About Explicit Messaging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-2
Performing Explicit Messages. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-3
ControlLogix Controller Examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-4
PLC-5 Controller Examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-23
SLC 500 Controller Examples. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-29
MicroLogix 1100/1400 Controller Examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-53
Chapter 7 Troubleshooting
Understanding the Status Indicators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-1
PORT Status Indicator. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-2
MOD Status Indicator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-2
NET A Status Indicator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-3
NET B Status Indicator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-3
V iewing Adapter Diagnostic Items . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-4
Viewing and Clearing Events. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-6
Chapter 8 Viewing the Adapter Web Pages
Enabling the Adapter Web Pages. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-1
Viewing the Web Pages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-1
Process Display Pop-up Window. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-4
TCP/IP Configuration Web Page. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-5
Configure E-mail Notification Web Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-6
Device Information Pages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-9
Chapter 9 Using the Adapter in a DPI External Comms Kit (20-XCOMM-DC-BASE)
Installing the Adapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-1
I/O Board Option (20-XCOMM-IO-OPT1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-2
Understanding the I/O Image (Drive + I/O Option) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-2
Configuring the Adapter to Use the Optional I/O Data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-3
Viewing Optional I/O Diagnostic Items . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-4
Appendix A Specifications
Communications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-1
Electrical . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-1
Mechanical. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-2
Environmental . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-2
Regulatory Compliance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-2
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 9

Appendix B Adapter Parameters
Parameter List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-1
Appendix C EtherNet/IP Objects
Identity Object. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-2
Assembly Object. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-3
Register Object . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-4
Parameter Object. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-5
Parameter Group Object . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-7
PCCC Object. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-8
DPI Device Object . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-13
DPI Parameter Object . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-16
DPI Fault Object . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-22
DPI Alarm Object . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-24
DPI Diagnostic Object . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-26
DPI Time Object. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-28
Host DPI Parameter Object. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-30
TCP/IP Interface Object . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-36
Ethernet Link Object. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-37
Table of Contents iii
Appendix D Logic Command/Status Words
PowerFlex 70/700/700H, and 700L (with 700 Control) Drives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . D-1
PowerFlex 700S (Phase II Control) and 700L (with 700S Control) Drives . . . . . . . . . . . D-3
PowerFlex 750-Series Drives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . D-5
PowerFlex Digital DC Drives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . D-7
Glossary
Index
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 10

iv Table of Contents
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 11

Preface
About This Manual
Topic Page
Conventions Used in This Manual
Rockwell Automation Support P-2
Additional Resources P-2
This manual provides information about the adapter and using it wit h
PowerFlex 7-Class (Architecture-Class) drives. The adapter can be used
with other products that support a DPI™ adapter, such as the DPI External
Comms Kit (20-XCOMM-DC-BASE). See the documentation for your
product for specific information about how it works with the adapter.
P-1
Conventions Used in This
Manual
The following conventions are used throughout this manual:
• Parameter names are shown in the format Parameter xx - [*]. The xx
represents the parameter number. The * represents the parameter name—
for example Parameter 01 - [DPI Port].
• Menu commands are shown in bold type face and follow the format
Menu > Command. For example, if you read ‘Select File > Open’, you
should click the File menu and then click the Open command.
• The firmware revision number (FRN) is displayed as FRN X.xxx, where
‘X’ is the major revision number and ‘xxx’ is the minor revision number.
• The screen images in this manual resulted from using the following
software:
®
– RSLinx
– RSLogix™ 5 software, version 7.20
– RSLogix 500 software, version 7.20
– RSLogix 5000 software, version 16.00
Different versions of the software may have screens that vary in
appearance, and differences in procedures.
Classic software, version 2.51
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 12

P-2 About This Manual
Rockwell Automation Support
Rockwell Automation offers support services worldwide, with ov er 75 sales
and support offices, over 500 authorized distributors, and over 250
authorized systems integrators located through the United States alone. In
addition, Rockwell Automation representatives are in every major country
in the world.
Local Product Support
Contact your local Rockwell Automation representative for the following:
• Sales and order support
• Product technical training
• Warran t y support
• Support service agreements
Technical Product Assistance
For technical assistance, please review the information in Chapter 7,
Troubleshooting
Allen-Bradley Technical Support website at www.ab.com/support/abdrives
or contact Rockwell Automation.
, first. If you still have problems, then access the
Additional Resources
Resource Description
PowerFlex 7-Class DPI (Drive Peripheral Interface) Network Communication Adapter Installation
Instructions, publication 20COMM-IN004
EtherNet/IP Media Planning and Installation Manual, ODVA publication 148
EtherNet/IP Network Infrastructure Guidelines, ODVA publication 35
Ethernet Design Considerations Reference Manual, publication ENET-RM002
Connected Components Workbench website http://www.ab.com/support/abdrives/webupdate/
software.html, and online help
DriveExplorer website http://www.ab.com/drives/driveexplorer/
DriveExecutive website http://www.ab.com/drives/drivetools/
PowerFlex 20-HIM-A3/-A5/-C3S/-C5S HIM Quick Reference, publication 20HIM-QR001
PowerFlex 20-HIM-A6/-C6S HIM (Human Interface Module) User Manual, publication 20HIM-UM001
PowerFlex 70 User Manual, publication 20A-UM001
PowerFlex 70/700 Reference Manual, publication PFLEX-RM001
PowerFlex 70 Enhanced Control and 700 Vector Control Reference Manual, publication PFLEX-RM004
PowerFlex 700 Series A User Manual, publication 20B-UM001
PowerFlex 700 Series B User Manual, publication 20B-UM002
PowerFlex 70/700 Reference Manual, publication PFLEX-RM001
PowerFlex 70 Enhanced Control and 700 Vector Control Reference Manual, publication PFLEX-RM004
PowerFlex 700H Installation Instructions, publication PFLEX-IN006
PowerFlex 700H Programming Manual, publication 20C-PM001
These documents contain additional information concerning related
products from Rockwell Automation.
Information on the installation of PowerFlex
Network Communication Adapters.
(1)
, and online help
, and online help
(1)
(2)
(2)
Information on using the PowerFlex 20-HIM-A3, 20-HIM-A5,
Information on the planning, installation, and techniques used
to implement an EtherNet/IP network.
Information on the Connected Components Workbench™
software tool—and includes a link for free software download.
Information on using the DriveExplorer™ software tool.
Information on using the DriveExecutive™ software tool.
20-HIM-C3S, and 20-HIM-C5S HIMs.
Information on installing and using the PowerFlex 20-HIM-A6
and 20-HIM-C6S HIMs.
Information on installing and programming PowerFlex
standard control and enhanced control drives.
Information on installing and programming PowerFlex 700
standard control and vector control Series A drives, and
PowerFlex 700 vector control Series B drives.
Information on installing and programming PowerFlex 700H
drives.
®
20-COMM-x
70
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 13

Resource Description
PowerFlex 700S w/Phase I Control Installation Manual (Frames 1…6), publication 20D-IN024
PowerFlex 700S w/Phase I Control Installation Manual (Frames 9 and 10), publication PFLEX-IN006
PowerFlex 700S w/Phase I Control User Manual (All Frame Sizes), publication 20D-UM001
PowerFlex 700S w/Phase I Control Reference Manual, publication PFLEX-RM002
PowerFlex 700S w/Phase II Control Installation Manual (Frames 1…6), publication 20D-IN024
PowerFlex 700S w/Phase II Control Installation Manual (Frames 9…14), publication PFLEX-IN006
PowerFlex 700S w/Phase II Control Programming Manual (All Frame Sizes), publication 20D-PM001
PowerFlex 700S w/Phase II Control Reference Manual, publication PFLEX-RM003
PowerFlex 700L User Manual, publication 20L-UM001
PowerFlex 750-Series Drive Installation Instructions, publication 750-IN001
PowerFlex 750-Series Drive Programming Manual, publication 750-PM001
PowerFlex 20-750-ENETR Dual-port EtherNet/IP Option Module, publication 750COM-UM008
PowerFlex 755 Drive Embedded EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual, publication 750COM-UM001
20-750-20COMM and 20-750-20COMM-F1 Communication Carrier Cards Installation Instructions,
publication 750COM-IN001
PowerFlex Digital DC Drive User Manual, publication 20P-UM001
Getting Results with RSLinx Guide, publication LINX-GR001
RSLogix Emulate 5/500 Getting Results Guide, publication EMULAT-GR002
RSLogix 500 Getting Results Guide, publication LG500-GR002
RSLogix 5000 PIDE Autotuner Getting Results Guide, publication PIDE-GR001
EtherNet/IP Modules in Logix5000 Control Systems User Manual, publication ENET-UM001
Information on installing and programming PowerFlex 700L
Information on installing and programming PowerFlex Digital
, and online help
, and online help
(2)
, and online help Information on installing and navigating the RSLogix Emulate
(2)
, and online help
Information on using the ControlLogix® 1756-ENBT or
Enhanced and Ethernet PLC-5 Programmable Controllers User Manual, publication 1785-UM012
SLC 500 Modular Hardware Style User Manual, publication 1747-UM011
MicroLogix 1100 Programmable Controllers User Manual, publication 1763-UM001
MicroLogix 1400 Programmable Controllers User Manual, publication 1766-UM001
(1)
Use this link to the ODVA EtherNet/IP library: http://odva.org/Home/ODVATECHNOLOGIES/EtherNetIP/EtherNetIPLibrary/tabid/76/Default.aspx
(2)
The online help is installed with the software.
Information on installing, using, and troubleshooting the SLC
Information on installing and programming PowerFlex 700S
drives.
Liquid-Cooled AC drives.
Information on installing and programming PowerFlex
750-Series AC drives.
DC drives.
Information on using RSLinx Classic software.
software for ladder logic programming with Allen-Bradley
®
and SLC™ 500 processors.
PLC-5
Information on using RSLogix 500 software tool.
(2)
Information on using RSLogix 5000 software tool.
1756-EN2T EtherNet/IP communication modules with the
Logix5000 controller and communicating with various devices
on the EtherNet/IP network.
Information to help design, operate and maintain an Enhanced
and Ethernet PLC-5 programmable controller system.
500 controller with 1747-L5-xxx module.
Information on installing, using, and troubleshooting the
MicroLogix™ 1100 and MicroLogix 1400 controllers.
About This Manual P-3
®
Documentation can be obtained online at http://
literature.rockwellautomation.com. To order paper cop i es of technical
documentation, contact your local Rockwell Automation distributor or sales
representative.
To find your local Rockwell Automation distributor or sales representative,
visit http://www.rockwellautomation.com/locations
.
For information such as firmware updates or answers to drive-related
questions, go to the Drives Service & Support website at http://
www.ab.com/support/abdrives and click the Downloads or Knowledgebase
link.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 14

P-4 About This Manual
Notes:
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 15
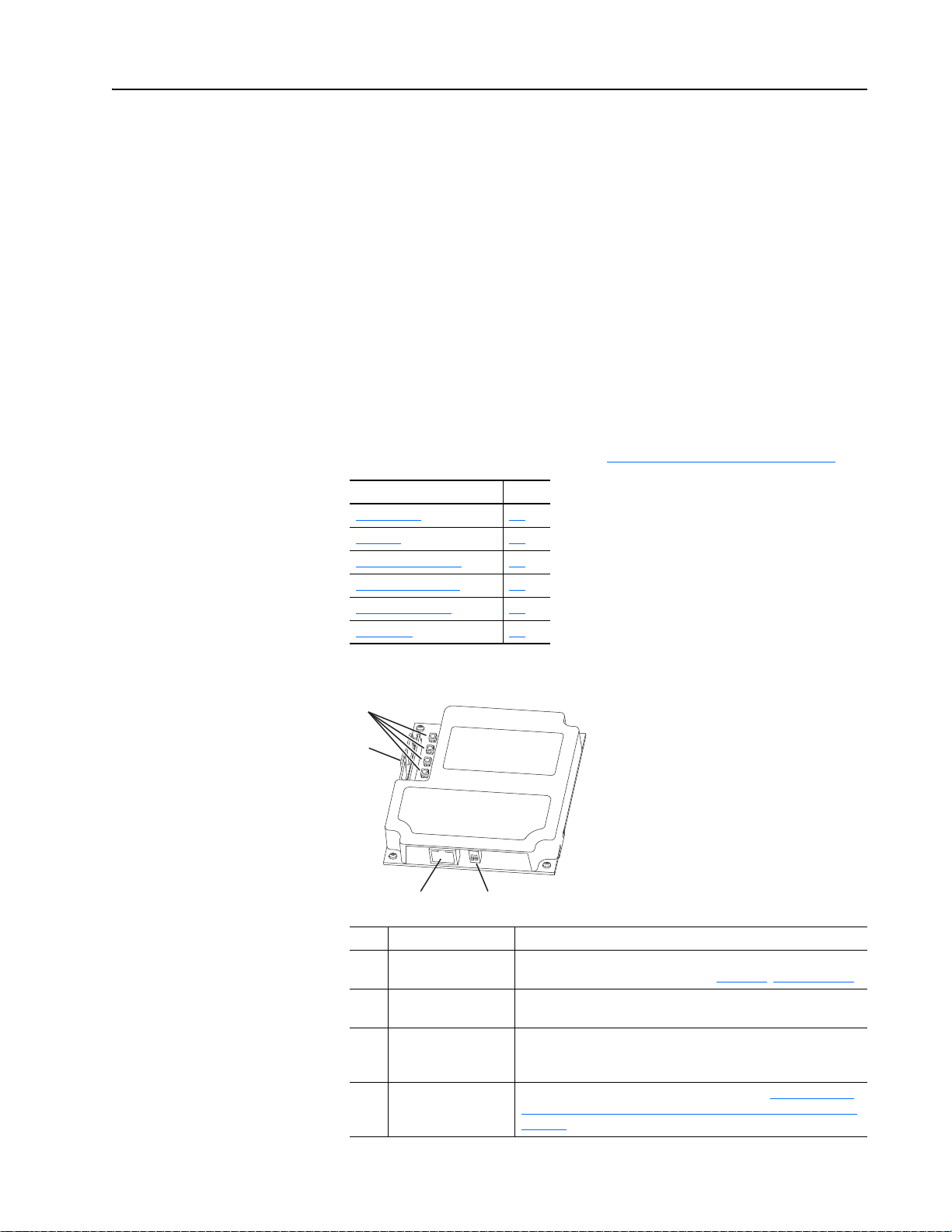
Not provided on Series A adapter
Chapter 1
Getting Started
The adapter is intended for installation in a PowerFlex 7-Class drive and is
used for network communication. The 20-COMM-E Series B adapter,
firmware 3.xxx or later, can also be installed in an External DPI Comms Kit
(20-XCOMM-DC-BASE).
For PowerFlex 750-Series driv es, we recommend using the 20-750-ENETR
Dual-port EtherNet/IP option module or the embedded EtherNet/IP adapter
(only in PowerFlex 755 drives) instead of the 20-COMM-E adapter.
However, this manual does include information about using the
20-COMM-E adapter with PowerFlex 750-Series drives—but there are
operating limitations. For details, see Compatible Products
Topic Page
Components
Features 1-2
Compatible Products 1-3
Required Equipment 1-3
Safety Precautions 1-5
Quick Start 1-6
1-1
on page 1-3.
Components
➊
➋
➌➍
Item Part Description
Status Indicators Four status indicators that indicate the status of the DPI, the
➊
DPI Connector A 20-pin, single-row shrouded male header. An Internal Interface
➋
Ethernet Connector RJ-45 connector for the Ethernet network cable. The connector is
➌
Web Pages Switch
➍
(SW2)
adapter, and network connection. See Chapter 7
cable is connected to this connector and a connector on the drive.
CAT-5 compliant to ensure reliable data transfer on 100Base-TX
Ethernet connections.
Enables or disables the adapter web pages. See Setting the Web
Pages Switch (only Series B Adapter, Firmware 3.xxx or Later) on
page 2-2. SW1 is unused.
, Troubleshooting.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 16

1-2 Getting Started
Features
The features of the adapter include the following:
• T ypical mounting in a PowerFlex 7-Class drive. The 20-COMM-E Series
B adapter, firmware 3.xxx or later , can also be installed in a DPI External
Comms Kit and used with the kit’s optional I/O board. See Chapter
Using the Adapter in a DPI External Comms Kit
(20-XCOMM-DC-BASE) for more information.
DPI External Comms Kit Compatibility
20-COMM-E Adapter Operation With
Firmware
Series
A 2.xxx and earlier No No
B 3.xxx and later Yes Yes
• Captive screws to secure and ground the adapter to the drive or, when
mounted in a DPI External Comms Kit, to the kit’s metal enclosure.
• Compatibility with various configuration tools to configure the adapter
and connected host drive, including the following tools:
– PowerFlex HIM (Human Interface Module) on the drive, if available
– Connected Components Workbench software, version 1.02 or later
– DriveExplorer software, version 2.01 or later
– DriveExecutive software, version 3.01 or later
Additionally, you can use a BOOTP server to configure the network
address for the adapter.
Revision
DPI External Comms Kit
(20-XCOMM-DC-BASE)
Optional I/O Board
(20-XCOMM-IO-OPT1)
9,
• Status indicators that report the status of the drive communications, the
adapter, and network. They are visible when the dri ve cov er is open or closed.
• Parameter-configured I/O (Logic Command/Reference and up to four
pairs of Datalinks) to accommodate application requirements.
• Explicit Messaging support.
• Master-Slave or Peer -to-Peer hierarchy that can be configured to transmit
data to and from either a controller or another PowerFlex drive on the
network.
• User-defined fault actions to determine how the adapter and connected
PowerFlex drive respond to the following:
– I/O messaging communication disruptions (Comm Flt Action)
– Controllers in idle mode (Idle Flt Action)
• Web pages, viewed by using a web browser, that show information about
the adapter, its connected host driv e, and DPI devices connected to the driv e.
• Configurable e-mail messaging to desired addresses when selected drive
faults occur and/or are cleared, and/or when the adapter takes a
communication or idle fault action.
• Access to any PowerFlex drive and its connected peripherals on the
network to which the adapter is connected.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 17
Getting Started 1-3
Compatible Products
Required Equipment
At the time of publication, the adapter is compatible with the following
products:
• PowerFlex 70 drives with standard or enhanced control • PowerFlex 750-Series drives
• PowerFlex 700 drives with standard or vector control • PowerFlex Digital DC drives
• PowerFlex 700H drives • DPI External Comms Kit
• PowerFlex 700S drives with Phase I or Phase II control • SMC™ Flex smart motor controllers
• PowerFlex 700L drives with 700 vector control or 700S control • SMC-50 smart motor controllers
(1)
The 20-COMM-E adapter can be used with PowerFlex 750-Series drives, but the drive must have firmware revision 4.001
or later. Also, the 20-COMM-E adapter has the following limitations and differences:
- Only the first 16 bits of the Logic Command and Logic Status words are used.
- Speed Reference and Feedback scaling are Hz (or RPM) x 1000 (depending on the setting of drive
parameter 300 - [Speed Units].
Instead of using the 20-COMM-E adapter with the PowerFlex 753 drive, the 20-750-ENETR Dual-port EtherNet/IP option
module should be used whenever possible. Please see the PowerFlex 750-Series AC Drives Programming Manual,
publication 750-PM001, for drive parameter information and the 20-750-ENETR Dual-Port EtherNet/IP Option Module User
Manual, publication 750COM-UM008, for network communication module information. For a PowerFlex 755 drive, it is
recommended to use its embedded EtherNet/IP adapter instead of the 20-COMM-E adapter and its inherent limitations.
Some of the equipment that is required for use with the adapter is shipped
with the adapter, but some you must supply yourself.
(1)
Equipment Shipped with the Adapter
When you unpack the adapter, verify that the package includes the follo wing:
❑ One 20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP adapter
❑ One 2.54 cm (1 in.) long and one 15.24 cm (6 in.) long Internal
Interface cable (only one cable is needed to connect the adapter to the
drive; for which cable to use, see Figure 2.2 on page 2-4
❑ One PowerFlex 7-Class DPI (Drive Peripheral Interface) Network
Communication Adapter Installation Instructions, publication
20COMM-IN004
TIP: When mounting the 20-COMM-E adapter in a PowerFlex 750-Series
drive, you must use a 20-750-20COMM or 20-750-20COMM-F1
Communication Carrier Card, publication 750COM-IN001—and the
20-COMM-E adapter must have firmware revision 4.001 or later.
User-Supplied Equipment
To install and configure the adapter, you must supply the following:
❑ A small flathead screwdriver
)
❑ Ethernet cable (for details, see the EtherNet/IP Media Planning and
Installation Manual, ODVA publication 148 available on the ODVA
website at http://odva.org/Home/ODVATECHNOLOGIES/EtherNetIP/
EtherNetIPLibrary/tabid/76/Default.aspx)
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 18

1-4 Getting Started
❑ Ethernet switch (for details, see the Ethernet Design Considerations
Reference Manual, publication ENET-RM002)
❑ Drive and adapter configuration tool, such as the following:
– PowerFlex 20-HIM-xx HIM
– Connected Components Workbench software, version 1.02 or later
Connected Components Workbench is the recommended
stand-alone software tool for use with PowerFlex drives. You can
obtain a free copy by:
• Internet download at http://www.ab.com/support/abdrives/
webupdate/software.html
• Requesting a DVD at http://www.ab.com/onecontact/controllers/
micro800/
Your local distributor may also have copies of the DVD available.
Connected Components Workbench software cannot be used to
configure SCANport-based drives or Bulletin 160 drives.
– DriveExplorer software, version 2.01 or later
This software tool has been discontinued and is now available as
freeware at http://www.ab.com/support/abdrives/webupdate/
software.html. There are no plans to provide future updates to this
tool and the download is being provided ‘as-is’ for users that lost
their DriveExplorer CD, or need to configure legacy products not
supported by Connected Components Workbench software.
– DriveExecutive software, version 3.01 or later
A Lite version of DriveExecutive software ships with RSLogix
5000, RSNetWo r x MD, FactoryTalk AssetCentre, and
ItelliCENTER software. All other versions are purchasable items:
• 9303-4DTE01ENE Drive Executive software
• 9303-4DTS01ENE DriveTools SP Suite (includes
DriveExecutive and DriveObserver software)
• 9303-4DTE2S01ENE DriveExecutive software upgrade to
DriveTools SP Suite (adds DriveObserver software)
DriveExecutive software updates (patches, and so forth) can be
obtained at http://www.ab.com/support/abdrives/webupdate/
software.html. It is highly recommended that you periodically check
for and install the latest update.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
– BOOTP Server, version 2.1 or later, for network setup only
❑ Controller configuration tool, such as RSLogix 5, RSLogix500, or
RSLogix 5000 software
❑ A computer connection to the EtherNet/IP network
Page 19
Getting Started 1-5
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
Safety Precautions
Please read the following safety precautions carefully.
ATTENTION: Risk of injury or death exists. The PowerFlex
drive may contain high voltages that can cause injury or death.
Remove all power from the PowerFlex drive, and then verify
power has been discharged before installing or removing an
adapter.
ATTENTION: Risk of injury or equipment damage exists. Only
personnel familiar with drive and power products and the
associated machinery should plan or implement the installation,
start up, configuration, and subsequent maintenance of the
product using an adapter. Failure to comply may result in injury
and/or equipment damage.
ATTENTION: Risk of equipment damage exists. The adapter
contains electrostatic discharge (ESD) sensitive parts that can be
damaged if you do not follow ESD control procedures. Static
control precautions are required when handling the adapter. If
you are unfamiliar with static control procedures, see Guarding
Against Electrostatic Damage, publication 8000-4.5.2.
A TTENTION: Risk of injury or equipment damage exists. If the
adapter is transmitting control I/O to the drive, the dri ve may f ault
when you reset the adapter. Determine how your drive will
respond before resetting an adapter.
ATTENTION: Risk of injury or equipment damage exists.
Parameters 21 - [Comm Flt Action], 22 - [Idle Flt Action], and
41 - [Peer Flt Action] let you determine the action of the adapter
and connected drive if communication is disrupted or the
controller is idle. By default, these parameters fault the driv e. You
may configure these parameters so that the dri v e continues to run,
howev er , precautions should be taken to v erify that the settings of
these parameters do not create a risk of injury or equipment
damage. When commissioning the drive, verify that your system
responds correctly to various situations (for example, a
disconnected cable or a controller in idle state).
ATTENTION: Risk of injury or equipment damage exists.
When a system is configured for the first time, there may be
unintended or incorrect machine motion. Disconnect the motor
from the machine or process during initial system testing.
ATTENTION: Risk of injury or equipment damage exists. The
examples in this publication are intended solely for purposes of
example. There are many variables and requirements with any
application. Rockwell Automation does not assume responsibility
or liability (to include intellectual property liability) for actual use
of the examples shown in this publication.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 20
1-6 Getting Started
Quick Start
This section is provided to help experienced users quickly start using the
adapter. If you are unsure how to complete a step, refer to the referenced
chapter.
Step Action See
1 Review the safety precautions for the adapter. Throughout this manual
2 Verify that the PowerFlex drive is properly installed. Drive User Manual
PowerFlex 7-Class DPI
Network Communication
Adapter Installation
Instructions, publication
20COMM-IN004, and
Chapter 2
Installing the Adapter
Chapter 2
Installing the Adapter
Chapter 3
Configuring the Adapter
Chapter 4,
Configuring the I/O
Chapter 5
Using the I/O
Chapter 6,
Using Explicit
Messaging
3 Install the adapter.
a. Verify that the PowerFlex drive is not powered.
b. Connect the adapter to the drive with the Internal Interface
cable.
c. Use the captive screws to secure and ground the adapter to
the drive.
d. Connect the adapter to the network with an Ethernet cable.
NOTE: When installing the adapter in either of the following
products, see the listed publication for instructions:
• DPI External Comms Kit—see the 20-XCOMM-DC-BASE
Installation Instructions, publication 20COMM-IN001, supplied
with the kit.
• PowerFlex 750-Series drive—see the 20-750-20COMM and
20-750-20COMM-F1 Communication Carrier Cards
Installation Instructions, publication 750COM-IN001, supplied
with the card.
4 Apply power to the adapter.
a. Verify that the adapter is installed correctly.
The adapter receives power from the drive.
b. Apply power to the drive.
The status indicators should be green. If they flash red, there
is a problem. See Chapter 7
c. Configure and verify key drive parameters.
5 Configure the adapter for your application.
Set adapter parameters for the following functions as required by
your application:
• IP address, subnet mask, and gateway address
• Data rate
• I/O configuration
• Master-Slave or Peer-to-Peer hierarchy
• Fault actions
6 Configure the controller to communicate with the adapter.
Use a controller configuration tool, such as RSLogix software, to
configure the master on the network to recognize the adapter and
drive.
7 Create a ladder logic program.
Use a controller configuration tool, such as RSLogix software, to
create a ladder logic program that enables you to do the
following:
• Control the connected drive, via the adapter, by using I/O.
• Monitor or configure the drive by using explicit messages.
, Troubleshooting.
,
,
,
,
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 21

Chapter 2
Installing the Adapter
This chapter provides instructions for installing the adapter in a PowerFlex
7-Class drive. The 20-COMM-E Series B adapter, firmware revision 3.xxx
or later, can also be installed in a DPI External Comms Kit. In this case, see
Chapter 9
publication 20COMM-IN001, supplied with the kit.
Topic Page
Preparing for an Installation
Setting the Web Pages Switch (only Series B Adapter, Firmware 3.xxx or Later) 2-2
Connecting the Adapter to the Drive 2-3
Connecting the Adapter to the Network 2-6
Applying Power 2-6
Commissioning the Adapter 2-8
or the 20-XCOMM-DC-BASE Installation Instructions,
2-1
Preparing for an Installation
Before installing the adapter, do the following:
• Make sure the Ethernet switch is the correct type. A ‘managed’ switch
that supports IGMP snooping is usually recommended. An ‘unmanaged’
switch can be used instead if RSLogix 5000 software, version 18.00 or
later, is used and all devices on the network are configured for ‘unicast’
I/O. For more details, see the following documents:
– EtherNet/IP Media Planning and Installation Manual,
ODVA publication 148
– EtherNet/IP Network Infrastructure Guidelines,
ODVA publication 35
– Ethernet Design Considerations Reference Manual,
publication ENET-RM002
• Understand IGMP Snooping/Ethernet Switches
The 20-COMM-E adapter is a multicast device. In most situations, an
IGMP snooping (managed) switch is required. If more than one or two
20-COMM-E adapters are connected to the switch, a managed switch is
required—otherwise the drive may fault on a DPI Port x network loss.
The 20-COMM-E Series B adapter, firmware 4.001 or later, RSLogix
5000 software, version 18.00 or later, and a ControlLogix or
CompactLogix controller will support unicast. Unicast setup is required
when adding the drive to the I/O. When all adapters are set up as unicast
devices, then an IGMP snooping (managed) switch is not needed.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 22
2-2 Installing the Adapter
!
Much of EtherNet/IP implicit (I/O) messaging uses IP multicast to
distribute I/O control data, which is consistent with the CIP producer/
consumer model. Historically, most switches have treated multicast
packets the same as broadcast packets. That is, all multicast packets are
re-transmitted to all ports.
IGMP snooping constrains the flooding of multicast traffic by
dynamically configuring switch ports so that multicast traffic is
forwarded only to ports associated with a particular IP multicast group.
Switches that support IGMP snooping (managed switches) ‘learn’ which
ports have devices that are part of a particular multicast group and only
forward the multicast packets to the ports that are part of the multicast
group.
Be careful as to what level of support a switch has of IGMP snooping.
Some layer 2 switches that support IGMP snooping require a router
(which could be a layer 3 switch) to send out IGMP polls to learn what
devices are part of the multicast group. Some layer 2 switches can use
IGMP snooping without a router sending polls. If your control system is
a standalone network or is required to continue performing if the router is
out of service, make sure the switch you are using supports IGMP
snooping without a router being present.
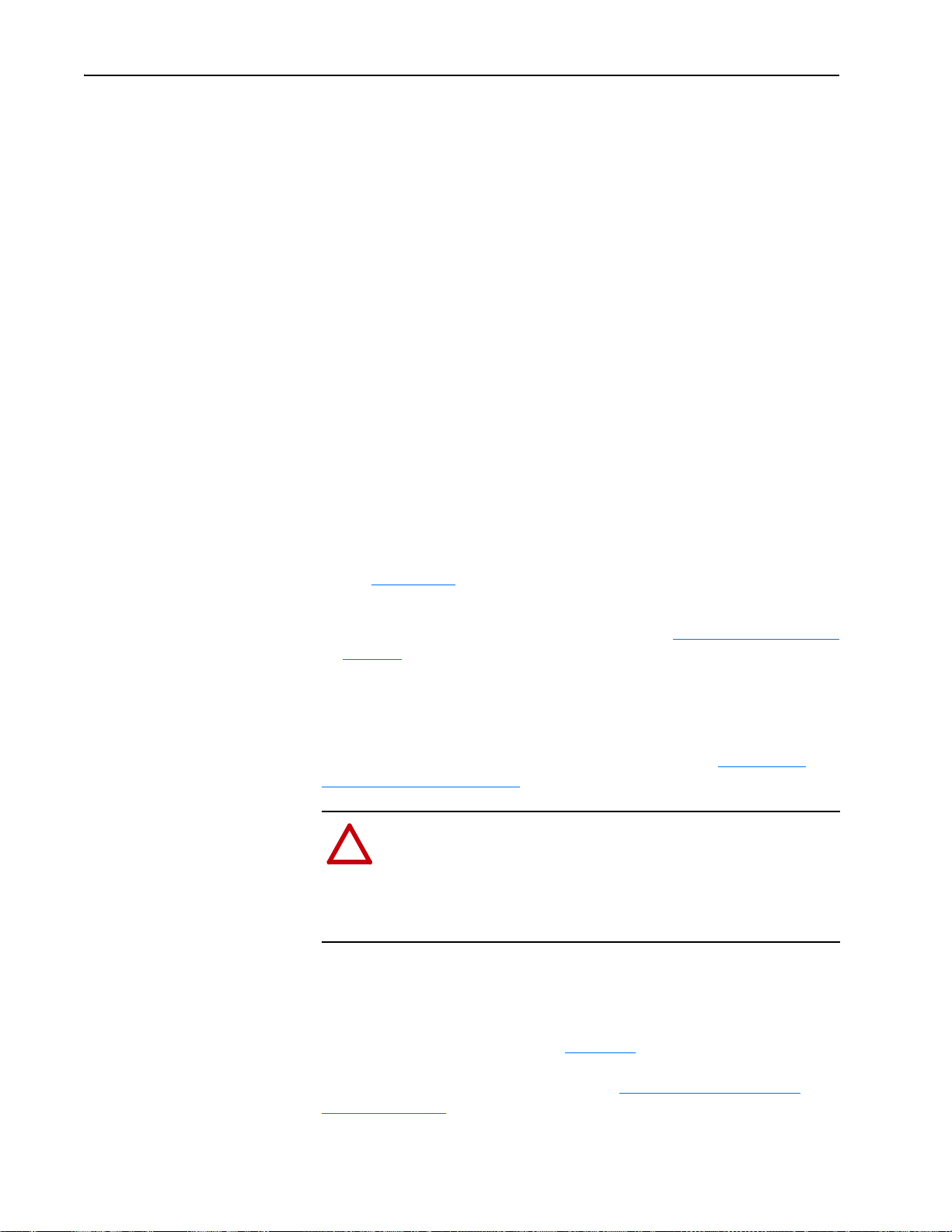
Setting the Web Pages Switch (only Series B Adapter, Firmware 3.xxx or Later)
• See Appendix
20-COMM-E adapter.
• Verify that you have all required equipment. See Required Equipment
page 1-3.
To use the adapter web pages, the Web Pages Switch (not supplied on the
Series A adapter) must be set to its ‘Enable Web’ position. For information
to enable or disable web pages for a Series A adapter, see Setting Web
Access Control on page 3-15.
ATTENTION: Risk of equipment damage exists. The adapter
contains electrostatic discharge (ESD) sensitive parts that can be
damaged if you do not follow ESD control procedures. Static
control precautions are required when handling the adapter. If you
are unfamiliar with static control procedures, see Guarding
Against Electrostatic Damage, publication 8000-4.5.2.
Important:A new switch setting is recognized only when po wer is applied
A for the number of CIP connections supported by the
on
to the adapter, or the adapter is reset. If you change a switch
setting, cycle power or reset the adapter to apply the change.
Set the Web Pages Switch (SW2 in Figure 2.1
adapter web pages. By default, the adapter web pages are disabled. For
complete details on adapter web pages, see Vi ewing the Adapter Web
Pages on page 8-1.
) to enable or disable the
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 23
Installing the Adapter 2-3
Unused
Switch
Web Pages
Switch
Enable Web
Position
Disable Web
Position
!
Figure 2.1 Setting Web Pages Switch (only Series B Adapter)
O
1
2
N
SW2 Setting Description
Down (OFF) position Disables the adapter web pages (default setting)
Up (ON) position Enables the adapter web pages
Connecting the Adapter to the Drive
ATTENTION: Risk of injury or death exists. The PowerFlex
drive may contain high voltages that can cause injury or death.
Remove power from the drive, and then verify po wer has been
discharged before installing or removing the adapter.
1. Remove power from the drive.
2. Use static control precautions.
3. Remove the drive cover or open the drive door.
4. Connect the Internal Interface cable to the DPI port on the drive and
then to the DPI connector on the adapter (see Figure 2.2
5. Secure and ground the adapter to the drive (see Figure 2.3
following:
– On a PowerFlex 70 dri ve, fold the Internal Interface cable behind the
adapter and mount the adapter on the drive using the four captive
screws.
– On a PowerFlex 700, PowerFlex 700H or PowerFlex 700S drive,
mount the adapter on the drive using the four captive screws.
).
) by doing the
Important:Tighten all screws to properly ground the adapter.
Recommended torque is 0.9 N•m (8.0 lb•in).
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 24
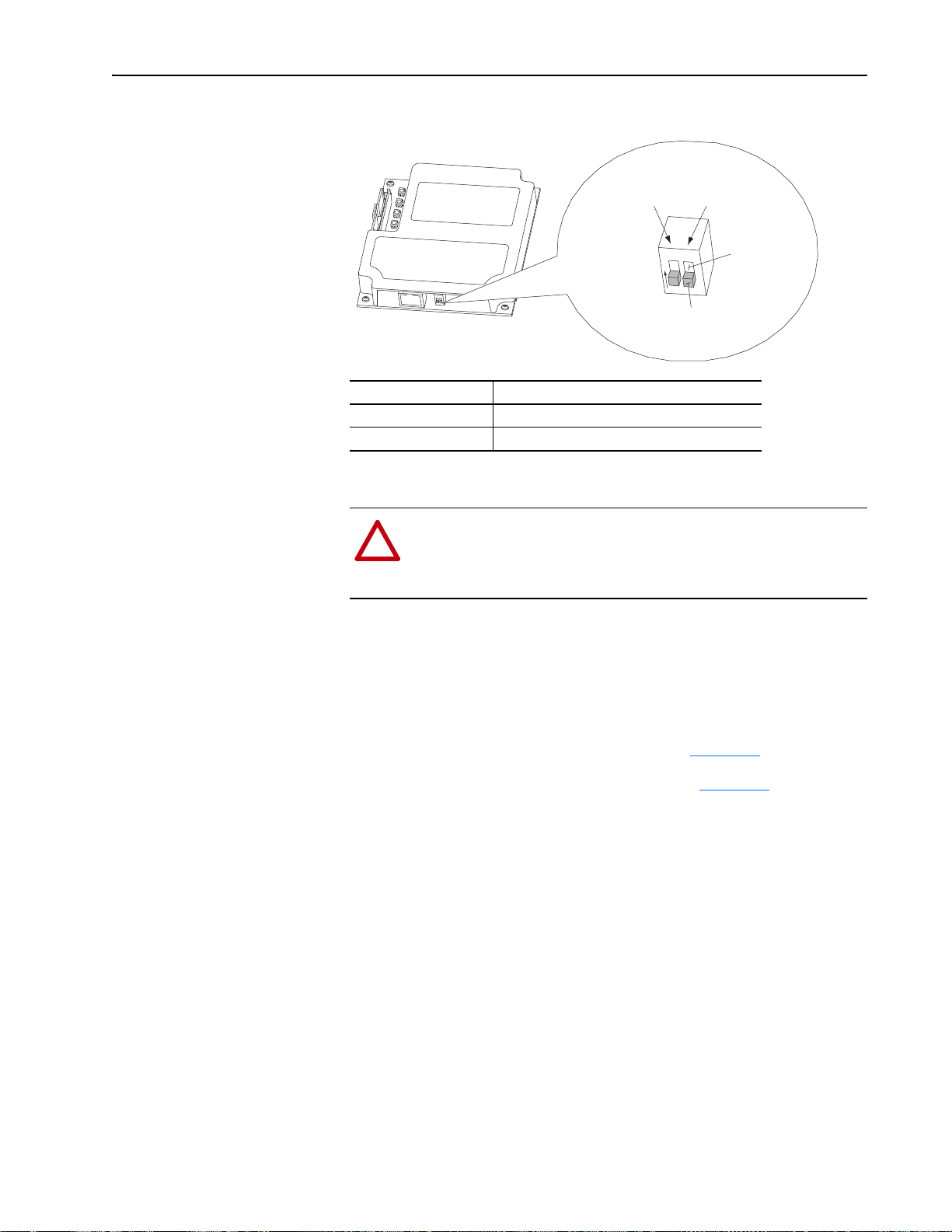
2-4 Installing the Adapter
20-COMM-E Adapter
PowerFlex 700 Frames 0 and 1
PowerFlex 700S Frames 0 and 1
PowerFlex 70 - All Frames
PowerFlex 700 Frames 2 and Larger
PowerFlex 700S Frames 2 through 6
HIM panel opens to
allow access to DPI
interface. To open
panel, remove screws
on left side of HIM
panel and swing open.
PowerFlex 700H Frames 9 and Larger
PowerFlex 700S Frames 9 and Larger
Figure 2.2 DPI Ports and Internal Interface Cables
➊
➋
➌
➍
Item Description
15.24 cm (6 in.) Internal Interface cable
➊
DPI Connector
➋
Ethernet cable
➌
2.54 cm (1 in.) Internal Interface cable
➍
X2
X1
➍
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 25
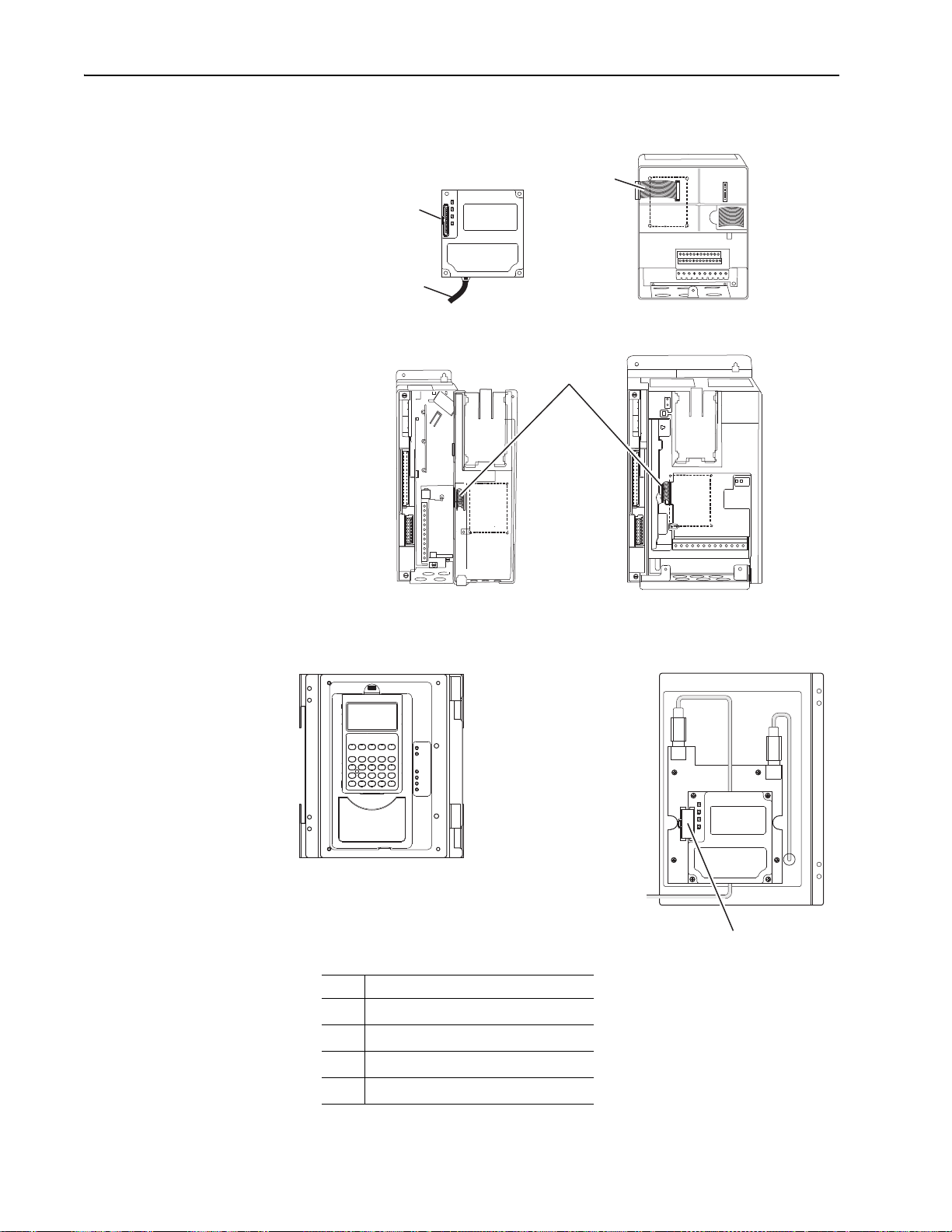
X1
X2
Drive
Adapter
Internal Interface Cable
folded behind the adapter
and in front of the drive.
PowerFlex 70 - All Frame Sizes
(Adapter mounts in drive.)
Verify metal ground tab is bent 90° and
is under the adapter before tightening
screw. After tightening the screw, verify
continuity exists between the head of
the screw and drive ground.
Ground Tab Detail
PowerFlex 700 Frames 0 and 1
PowerFlex 700S Frames 0 and 1
(Adapter mounts on door.)
PowerFlex 700 Frames 2 and Larger
PowerFlex 700S Frames 2 through 6
(Adapter mounts in drive.)
0.9 N•m
(8.0 lb•in)
4 Places
Verify metal ground tab is bent 90° and
is under the adapter before tightening
screw. After tightening the screw, verify
continuity exists between the head of
the screw and drive ground.
PowerFlex 700H Frames 9 and Larger
PowerFlex 700S Frames 9 and Larger
(Adapter mounts behind HIM panel.)
Ground Tab Detail
0.9 N•m
(8.0 lb•in)
4 Places
0.9 N•m
(8.0 lb•in)
4 Places
Installing the Adapter 2-5
Figure 2.3 Mounting and Grounding the Adapter
NOTE: When installing the adapter in a PowerFlex 750-Series drive, see
the 20-750-20COMM and 20-750-20COMM-F1 Communication Carrier
Cards Installation Instructions, publication 750COM-IN001, supplied with
the card.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 26
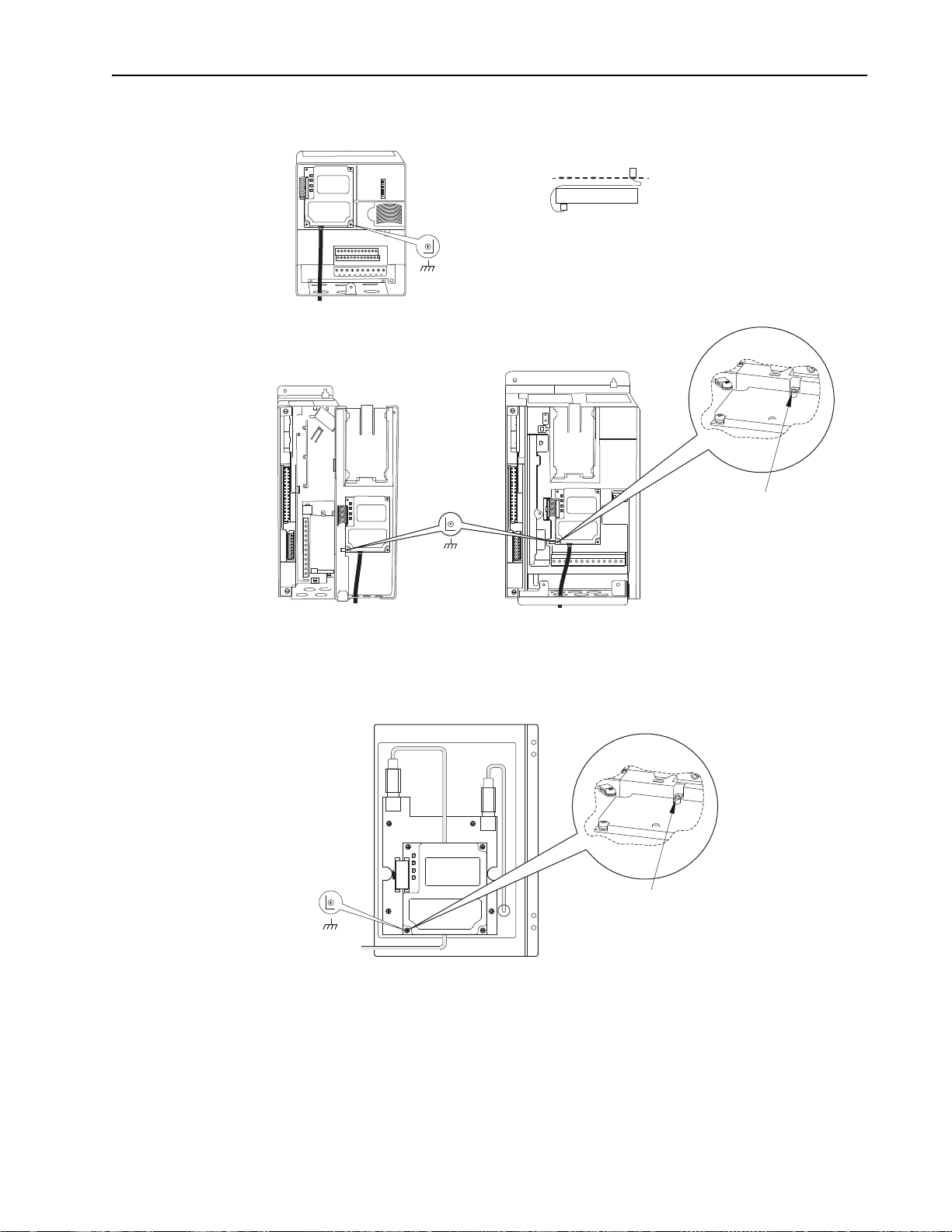
2-6 Installing the Adapter
!
Ethernet
Switch
Controller
(ControlLogix shown with
1756-ENBT Bridge)
PowerFlex 7-Class Drives
(each with a 20-COMM-E Adapter)
!
Connecting the Adapter to the Network
ATTENTION: Risk of injury or death exists. The PowerFlex
drive may contain high voltages that can cause injury or death.
Remove power from the drive, and then verify power has been
discharged before installing or removing the adapter.
1. Remove power from the drive.
2. Use static control precautions.
3. Connect one end of an Ethernet cable to the network.
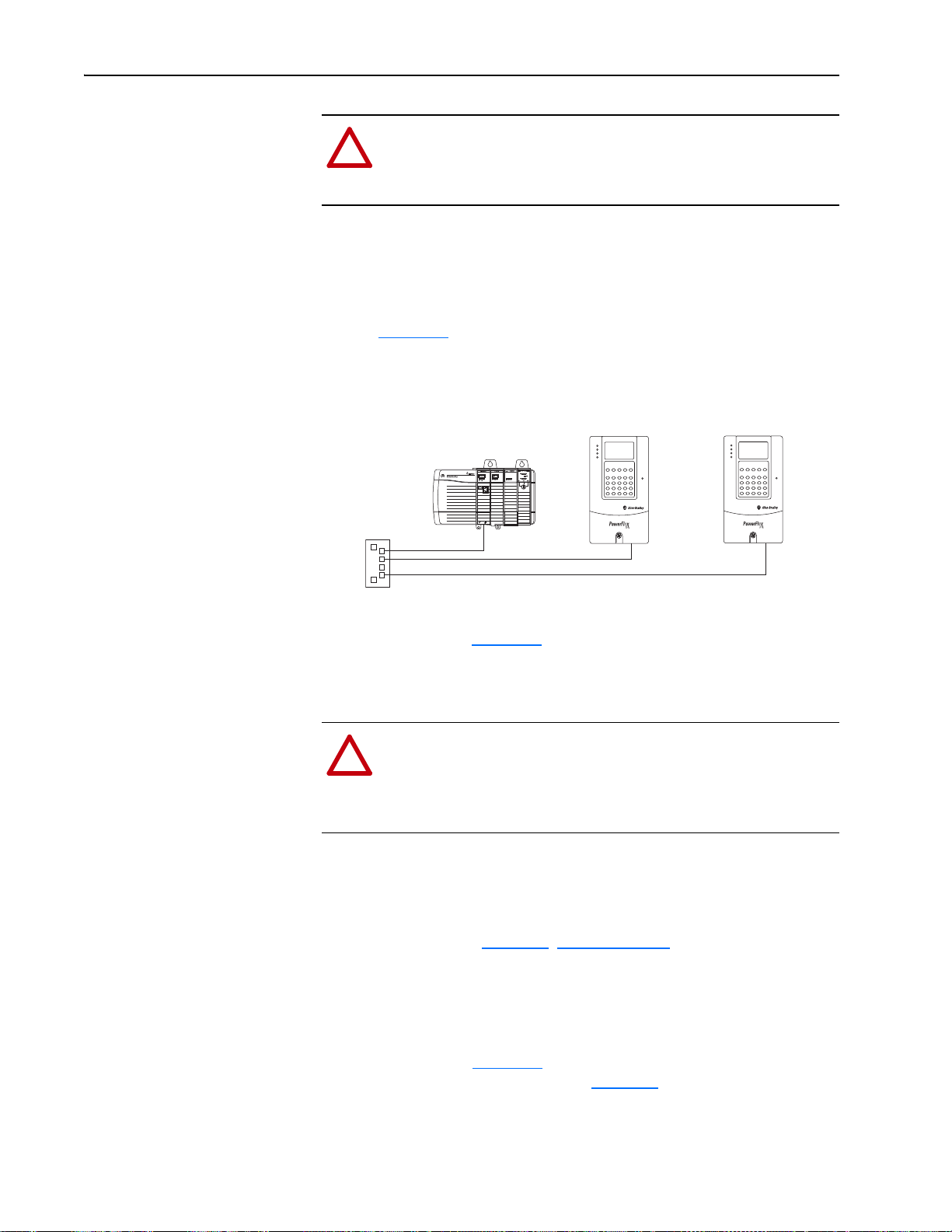
See Figure 2.4
Figure 2.4 Connecting the Ethernet Cable to the Network
for an example of wiring to an EtherNet/IP network.
Applying Power
4. Route the other end of the Ethernet cable through the bottom of the
PowerFlex drive (Figure 2.3
mating adapter connector.
ATTENTION: Risk of equipment damage, injury, or death
exists. Unpredictable operation may occur if you fail to verify
that parameter settings are compatible with your application.
Verify that settings are compatible with your application before
applying power to the drive.
Install the drive cover or close the drive door, and apply power to the drive.
The adapter receives its power from the connected drive. When you apply
power to the adapter for the first time, its topmost ‘PORT’ status indicator
should be steady green or flashing green after an initialization. If it is red,
there is a problem. See Chapter 7
Start-Up Status Indications
) and insert its Ethernet cable plug into the
, Troubleshooting.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Status indicators for the drive and communication adapter can be viewed on
the front of the drive (Figure 2.5
start-up status indications are shown in Table 2.A
) after power has been applied. Possible
.
Page 27
Installing the Adapter 2-7
Figure 2.5 Drive and Adapter Status Indicators (location on drive may vary)
PORT
MOD
➋
NET A
NET B
STS
Table 2.A Drive and Adapter Start-Up Status Indications
Item Name Color State Description
Drive STS Indicator
STS
➊
(Status)
PORT Green Flashing Normal operation. The adapter is establishing an I/O connection to
➋
MOD Green Flashing Normal operation. The adapter is operating but is not transferring I/O
NET A — Off Normal operation. BOOTP is enabled or a valid IP address is not set.
NET B — Off Normal operation. The adapter is properly connected but is idle.
Green Flashing Drive ready but not running, and no faults are present.
Steady Drive running, no faults are present.
Yellow Flashing,
drive stopped
Flashing,
drive running
Steady,
drive running
Red Flashing A fault has occurred.
Steady A non-resettable fault has occurred.
Steady Normal operation. The adapter is properly connected and
Steady Normal operation. The adapter is operating and transferring I/O data
Green Flashing Normal operation. BOOTP is disabled, the adapter is properly
Steady Normal operation. The adapter is properly connected and
Green Flashing Normal operation. The adapter is properly connected, BOOTP is
An inhibit condition exists – the drive cannot be started. Check drive
Parameter 214 - [Start Inhibits].
An intermittent type 1 alarm condition is occurring. Check drive
Parameter 211 - [Drive Alarm 1].
A continuous type 1 alarm condition exists. Check drive Parameter
211 - [Drive Alarm 1].
Adapter Status Indicators
the drive. It will turn steady green or red.
communicating with the drive.
data to a controller.
to a controller.
connected, has an IP address, and is connected to an EtherNet/IP
network but does not have an I/O connection.
communicating on the network to a controller.
enabled, and the adapter is transmitting data packets on the network.
➊
For more details on status indicator operation, see page 7-2 and page 7-3.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 28

2-8 Installing the Adapter
Configuring and Verifying Key Drive Parameters
The PowerFlex 7-Class drive can be separately configured for the control
and Reference functions in various combinations. For example, you could
set the drive to have its control come from a peripheral or terminal block
with the Reference coming from the network. Or you could set the drive to
have its control come from the network with the Reference coming from
another peripheral or terminal block. Or you could set the driv e to hav e both
its control and Reference come from the network.
The following steps in this section assume that the drive will receive the
Logic Command and Reference from the network.
1. Use drive Parameter 090 - [Speed Ref A Sel] to set the drive speed
Reference to ‘22’ (DPI Port 5).
2. If hard-wired discrete digital inputs are not used to control the drive,
verify that unused digital input driv e Parameters 361 - [Dig In1 Sel] and
362 - [Dig In2 Sel] are set to ‘0’ (Not Used).
3. Verify that drive Parameter 213 - [Speed Ref Source] is reporting that
the source of the Reference to the drive is ‘22’ (DPI Port 5).
Commissioning the Adapter
This ensures that any Reference commanded from the network can be
monitored by using drive Parameter 002 - [Commanded Speed]. If a
problem occurs, this verification step provides the diagnostic capability
to determine whether the drive/adapter or the network is the cause.
TIP: For PowerFlex 750-Series drives, use drive Parameter 545 [Speed Ref A Sel] to set the drive speed Reference:
a. Set the Port field to ‘0 - PowerFlex 75x’.
b. Set the Parameter field to point to the port (slot) in which the
20-COMM-E adapter/20-750-20COMM Communication Carrier
Card are installed (for this example, ‘876 - Port 6 Reference’).
The number ‘876’ in the Parameter field of the example is the
parameter in the drive that points to the port.
To commission the adapter, you must set a unique IP address on the
network. See the Glossary
adapter and applying power, you can set the IP address by using a BOOTP
server or adapter parameters. See Using Parameters to Set the IP Address,
Subnet Mask, and Gateway Address on page 3-5 for details.
By default, the adapter is configured so that you must set the IP address
using a BOOTP server. To use adapter parameters, you must disable the
BOOTP feature. For details, see Disable the BOOTP Feature
for details about IP addresses. After installing the
on page 3-5.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Important:New settings for some adapter parameters (for example,
Parameters 04 - [IP Addr Cfg 1] through 07 - [IP Addr Cfg
4]) are recognized only when po we r is applied to the adapter or
it is reset. After you change parameter settings, cycle power or
reset the adapter.
Page 29
Chapter 3
Configuring the Adapter
This chapter provides instructions and information for setting the
parameters in the adapter.
Topic Page
Configuration Tools
Using the PowerFlex 7-Class HIM to Access Parameters 3-2
Using BOOTP Server to Set the IP Address, Subnet Mask, and Gateway Address 3-3
Using Parameters to Set the IP Address, Subnet Mask, and Gateway Address 3-5
Setting the Data Rate 3-7
Setting the I/O Configuration 3-7
Selecting Master-Slave or Peer-to-Peer Hierarchy 3-8
Setting the Reference Adjustment 3-13
Setting a Fault Action 3-14
Setting Web Access Control 3-15
Resetting the Adapter 3-16
Viewing the Adapter Status Using Parameters 3-17
Updating the Adapter Firmware 3-17
3-1
Configuration Tools
For a list of parameters, see Appendix
definitions of terms in this chapter, see the Glossary
The adapter stores parameters and other information in its own nonvolatile
storage (NVS) memory. You must, therefore, access the adapter to view and
edit its parameters. The following tools can be used to access the adapter
parameters.
Tool See
PowerFlex 7-Class HIM page 3-2
BOOTP Server page 3-3
Connected Components Workbench
software, version 1.02 or later
DriveExplorer software,
version 2.01 or later
DriveExecutive software,
version 3.01 or later
B, Adapter Parameters. For
.
http://www.ab.com/support/abdrives/webupdate/
software.html, or online help (installed with the software)
http://www.ab.com/drives/driveexplorer
(installed with the software)
http://www.ab.com/drives/drivetools
(installed with the software)
, or online help
, or online help
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 30
3-2 Configuring the Adapter
ALT
Sel
F-> Stopped Auto
0.00 Hz
Main Menu:
Diagnostics
Parameter
Device Select
Por t 5 Device
20-COMM-E
Main Menu:
Diagnostics
Parameter
Device Select
Using the PowerFlex 7-Class HIM to Access Parameters
If your drive has either an LED or LCD HIM (Human Interface Module), it
can be used to access parameters in the adapter as shown below. We
recommend that you read through the steps for your HIM before performing
the sequence. For additional information, see the driv e documentation or the
PowerFlex 7-Class HIM Quick Reference, publication 20HIM-QR001.
Using an LED HIM
Step Example Screens
1. Press the key and then the Device (Sel) key to
display the Device Screen.
2. Press the or key to scroll to the adapter.
Letters represent files in the drive, and numbers represent
ports. The adapter is usually connected to port 5.
3. Press the (Enter) key to enter your selection.
A parameter database is constructed, and then the first
parameter is displayed.
4. Edit the parameters using the same techniques that you use
to edit drive parameters.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Using an LCD HIM
Step Example Screens
1. In the main menu, press the or key to scroll to
Device Select.
2. Press the (Enter) key to enter your selection.
3. Press the or key to scroll to the adapter
(20-COMM-E).
4. Press the (Enter) key to select the adapter.
A parameter database is constructed, and then the main
menu for the adapter is displayed.
5. Edit the parameters using the same techniques that you use
to edit drive parameters.
NOTE: All configuration procedures throughout this chapter use the
PowerFlex 7-Class LCD HIM to access parameters in the adapter and show
example LCD HIM screens.
TIP: When using a PowerFlex 20-HIM-A6 or 20-HIM-C6S HIM, see its
User Manual, publication 20-HIM-UM001.
Page 31

Configuring the Adapter 3-3
Using BOOTP Server to Set the IP Address, Subnet Mask, and Gateway Address
By default, the adapter is configured so that you can set its IP address,
subnet mask, and gateway address with a BOOTP server. There is a variety
of BOOTP servers available. The following instructions use Rockwell
Automation’s BOOTP Server, version 2.3 or later, a free standalone
program that incorporates the functionality of standard BOOTP utilities
with a graphical interface. It is available from http://
www.software.rockwell.com/support/download/detail.cfm?ID=3390. See
the Readme file and online Help for directions and more information.
TIP: You can disable BOOTP and configure the IP address, subnet mask,
and gateway address with adapter parameters. For details, see Using
Parameters to Set the IP Address, Subnet Mask, and Gateway Address on
page 3-5.
1. On the adapter label, note the adapter’s hardware Ethernet Address
(MAC), which will be used in step 6.
2. On a computer connected to the EtherNet/IP network, start the BOOTP
software.
The BOOTP Server window appears.
3. Select Tools > Network Settings to display the Network Settings
window.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 32

3-4 Configuring the Adapter
To properly configure devices on your EtherNet/IP network, you must
configure settings in the BOOTP software to match the network.
4. Edit the following boxes as required by your application.
Box Setting
(1)
Subnet Mask
Gateway
Primary DNS The address of the primary DNS server to be used on the local end of
Secondary DNS Optional — the address of the secondary DNS server to be used on the
Domain Name The text name corresponding to the numeric IP address that was
(1)
5. Click OK to apply the settings.
Devices on the network issuing BOOTP requests appear in the BOOTP
Request History list.
(1)
For definitions of these terms, see the Glossary.
The subnet mask for the adapter’s network.
The IP address of the gateway device on the adapter’s network.
the link for negotiating with remote devices.
local end of the link for negotiating with remote devices when the primary
DNS server is unavailable.
assigned to the server that controls the network.
6. In the BOOTP Request History list, either double-click the adapter’s
Ethernet Address (MAC) noted in step 1, or click New in the Relation
List.
The New Entry dialog box appears.
In the first case, the Ethernet Address (MAC) is automatically entered.
In the latter case, you must manually enter it.
7. Edit the following:
Box Setting
IP Address
Host Name Optional
Description Optional
(1)
For a definition of this term, see the Glossary.
8. Click OK to apply the settings.
(1)
A unique IP address for the adapter
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 33

Configuring the Adapter 3-5
Val ue Sett ing
0 Disabled
1 Enabled (Default)
Por t 5 Device
20-COMM-E
Parameter #: 03
BOOTP
0
Disabled
The adapter appears in the Relation List with the new settings.
9. To assign this configuration to the adapter permanently, select the
device in the Relation List and click Disable BOOTP/DHCP.
When power is cycled on the adapter, it will use the configuration you
assigned it and not issue new BOOTP requests.
Using Parameters to Set the IP Address, Subnet Mask, and Gateway Address
TIP: To enable BOOTP for an adapter that has had BOOTP disabled,
first select the adapter in the Relation List, then click Enable BOOTP,
and lastly reset the adapter or power cycle the drive.
10. Select File > Save to save the Relation List.
By default, the adapter is configured so that you set its IP address, subnet
mask, and gateway address using a BOOTP server. To use adapter
parameters instead, you must first disable BOOTP and then set the adapter
address parameters.
Disable the BOOTP Feature
1. Set the value of Parameter 03 - [BOOTP] to ‘0’ (Disabled).
2. Reset the adapter (see Resetting the Adapter
After disabling the BOOTP feature, you can configure the IP address,
subnet mask, and gateway address using adapter parameters.
on page 3-16).
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 34

3-6 Configuring the Adapter
Por t 5 Device
20-COMM-E
Parameter #: 04
IP Addr Cfg 1
0
0 <> 255
Default = 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255
[IP Addr Cfg 1]
[IP Addr Cfg 2]
[IP Addr Cfg 3]
[IP Addr Cfg 4]
Por t 5 Device
20-COMM-E
Parameter #: 08
Subnet Cfg 1
0
0 <> 255
Default = 0.0.0.0
255.255.255.255
[Subnet Cfg 1]
[Subnet Cfg 2]
[Subnet Cfg 3]
[Subnet Cfg 4]
Por t 5 Device
20-COMM-E
Parameter #: 12
Gateway Cfg 1
0
0 <> 255
Default = 0.0.0.0
255.255.255.255
[Gateway Cfg 1]
[Gateway Cfg 2]
[Gateway Cfg 3]
[Gateway Cfg 4]
Set the IP Address
1. Verify that Parameter 03 - [BOOTP] is set to ‘0’ (Disabled).
2. Set the value of Parameters 04 - [IP Addr Cfg 1] through 07 - [IP
Addr Cfg 4] to a unique IP address.
3. Reset the adapter (see Resetting the Adapter
The NET A status indicator will be steady green or flashing green if the
IP address is correctly configured, and is connected to an operating
ethernet network.
Set the Subnet Mask
1. Verify that Parameter 03 - [BOOTP] is set to ‘0’ (Disabled).
2. Set the value of Parameters 08 - [Subnet Cfg 1] through 11 - [Subnet
Cfg 4] to the desired value for the subnet mask.
3. Reset the adapter (see Resetting the Adapter
on page 3-16).
on page 3-16).
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Set the Gateway Address
1. Verify that Parameter 03 - [BOOTP] is set to ‘0’ (Disabled).
2. Set the value of Parameters 12 - [Gateway Cfg 1] through 15 [Gateway Cfg 4] to the IP address of the gateway device.
3. Reset the adapter (see Resetting the Adapter
on page 3-16).
Page 35

Configuring the Adapter 3-7
Value Data Rate
0 Autodetect (default)
1 10 Mbps Full
2 10 Mbps Half
3 100 Mbps Full
4 100 Mbps Half
Por t 5 Device
20-COMM-E
Parameter #: 16
EN Rate Cfg
0
Autodetect
Bit Description
0 Logic Command/Reference (Default)
1Datalink A
2Datalink B
3Datalink C
4Datalink D
5…15 Not Used
Por t 5 Device
20-COMM-E
Parameter #: 23
DPI I/O Cfg
xxxxxxxxxxx0000
1
Cmd/Ref b00
Setting the Data Rate
By default, the adapter is set to autodetect, so it automatically detects the data
rate and duplex setting used on the network. If you need to set a specific data
rate and duplex setting, the value of Parameter 16 - [EN Rate Cfg]
determines the Ethernet data rate and duplex setting that the adapter will use
to communicate. For definitions of data rate and duplex, see the Glossary
1. Set the value of Parameter 16 - [EN Rate Cfg] to the data rate at which
your network is operating.
TIP: Auto detection of baud rate and duplex works properly only if the
device (usually a switch) on the other end of the cable is also set to
automatically detect the baud rate/duplex. If one device has the baud
rate/duplex hard-coded, the other device must be hard-coded to the
same settings.
.
Setting the I/O Configuration
2. Reset the adapter (see Resetting the Adapter
The I/O configuration determines the data that is sent to and from the driv e.
Logic Command/Status, Reference/Feedback, and Datalinks may be
enabled or disabled. (Datalinks allow you to read/write directly to
parameters in the drive using implicit I/O.) A ‘1’ enables the I/O and a ‘0’
disables the I/O.
1. Set the bits in Parameter 23 - [DPI I/O Cfg].
Bit 0 is the right-most bit. It is highlighted above and equals ‘1’.
2. If a controller is used to control the drive, set adapter Parameters 35 -
[M-S Input] and 36 - [M-S Output] for Master-Slave Hierarchy.
on page 3-16).
3. If Logic Command/Reference is enabled, configure the parameters in
For details, see Setting a Master-Slave Hierarchy (Scanner-to-Drive
Communication) on page 3-8.
the drive to accept the Logic Command and Reference from the adapter.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 36

3-8 Configuring the Adapter
Bit Description
0 Logic Command/Reference (Default)
1 Datalink A Input
2 Datalink B Input
3 Datalink C Input
4 Datalink D Input
5…15 Not Used
Por t 5 Device
20-COMM-E
Parameter #: 35
M-S Input
xxxxxxxxxxx0000
1
Cmd/Ref b00
For example, set Parameter 90 - [Speed Ref A Sel] in a PowerFle x 70 or
700 drive to ‘22’ (DPI Port 5) so that the drive uses the Reference from
the adapter. Also, verify that the mask parameters (for example,
Parameter 276 - [Logic Mask]) in the drive are conf igured to recei ve the
desired logic from the adapter. See the documentation for your drive for
details.
4. If you enabled one or more Datalinks, configure parameters in the drive
to determine the source and destination of data in the Datalinks.
When using Datalinks, up to 8 drive [Data In xx] parameters
(300…307) and/or up to 8 [Data Out xx] parameters (310…317) must
be assigned to point to the appropriate drive parameters for your
application. See Chapter 4
for an example.
Selecting Master-Slave or Peer-to-Peer Hierarchy
5. Reset the adapter (see Resetting the Adapter
The adapter is ready to receive I/O. You must now configure the adapter to
receive I/O from a master or peer device. See Select ing Master-Slave or
Peer-to-Peer Hierarchy. If you select a Master-Slave hierarchy, you must
also configure the master to communicate with the adapter. See Chapter
Configuring the I/O
A hierarchy determines the type of device with which the adapter exchanges
data. In a Master-Slave hierarchy, the adapter exchanges data with a master,
such as a scanner or bridge (1756-ENBT, 1756-EN2T , 1747-L 5-xxx, and so
forth). In a Peer-to-Peer hierarchy, the adapter exchanges data with one or
more EtherNet/IP adapters in other drives. (The drives must have
compatible Logic Command/Status words.)
For both Master-Sla v e and Peer -to-Pe er hierarchies, the de vices e xchanging
data must be on the same IP subnet. See ‘IP Addresses’ in the Glossary
information about IP subnets.
Setting a Master-Slave Hierarchy (Scanner-to-Drive Communication)
1. Enable the desired I/O in Parameter 23 - [DPI I/O Cfg].
See Setting the I/O Configuration
.
on page 3-7.
on page 3-16).
4,
for
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
2. Set the bits in Parameter 35 - [M-S Input].
This parameter determines the data received from the master by the
drive. A ‘1’ enables the I/O and a ‘0’ disables the I/O.
Page 37

Configuring the Adapter 3-9
Bit Description
0 Status/Feedback (Default)
1 Datalink A Output
2 Datalink B Output
3 Datalink C Output
4 Datalink D Output
5…15 Not Used
Por t 5 Device
20-COMM-E
Parameter #: 36
M-S Output
xxxxxxxxxxx00 0 0
1
Status/Fdbk b00
Value Setting
0 Off (Default)
1On
Por t 5 Device
20-COMM-E
Parameter #: 51
Peer Out Enable
0
Off
Por t 5 Device
20-COMM-E
Parameter #: 49
Peer A Output
1
Cmd/Ref
Value Description
0 Off (Default)
1 Logic Command/Reference
2…5 Datalink A, B, C, or D Input
6…9 Datalink A, B, C, or D Output
Bit 0 is the right-most bit. It is highlighted above and equals ‘1’.
3. Set the bits in Parameter 36 - [M-S Output].
This parameter determines the data transmitted from the drive to the
scanner. A ‘1’ enables the I/O and a ‘0’ disables the I/O.
Bit 0 is the right-most bit. It is highlighted above and equals ‘1’.
4. Reset the adapter (see Resetting the Adapter
The adapter is ready to receive I/O from the master (that is, scanner). You
must now conf igure the scanner to recognize and transmit I/O to the adapter.
See Chapter
Setting the Adapter to Transmit Peer-to-Peer Data (Drive-to-Drive Communication)
1. Verify that Parameter 51 - [Peer Out Enable] is set to ‘0’ (Off).
This parameter must be Off while you configure peer output
parameters.
2. Set Parameter 49 - [Peer A Output] to select the source of the data to
output to the network.
4, Configuring the I/O.
on page 3-16).
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 38

3-10 Configuring the Adapter
Por t 5 Device
20-COMM-E
Parameter #: 50
Peer B Output
2
DL A Input
Value Description
0 Off (Default)
1 Logic Command/Reference
2…5 Datalink A, B, C, or D Input
6…9 Datalink A, B, C, or D Output
Por t 5 Device
20-COMM-E
Parameter #: 52
Peer Out Time
2.00 s
0 <> 10.00
Por t 5 Device
20-COMM-E
Parameter #: 53
Peer Out Skip
2
1 <>16
Default = 10.00 s Default = 1
3. If desired, set Parameter 50 - [Peer B Output] to select an additional
source of the data to output to the network.
4. Set Parameters 52 - [Peer Out Time] and 53 - [Peer Out Skip] to
establish the minimum and maximum intervals between peer messages.
Because the adapter transmits peer messages when a change-of-state
condition occurs, minimum and maximum intervals are required.
– The minimum interval ensures that the adapter does not transmit
messages on the network too often, thus minimizing network traffic.
Set the minimum interval with Parameter 52 - [Peer Out Time].
– The maximum interval ensures that the adapter transmits messages
often enough so that the receiving adapter(s) can receive recent data
and verify that communications are working or, if communications
are not working, can timeout. The maximum interval is the value of
Parameter 52 - [Peer Out Time] multiplied by the value of
Parameter 53 - [Peer Out Skip].
In the example below, the minimum interval is set to 2.00 seconds
(Parameter 52 - [Peer Out Time]), and the maximum interval is set to
4.00 seconds (2.00 x ‘2’ setting of Parameter 53 - [Peer Out Skip]).
5. Set Parameter 51 - [Peer Out Enable] to ‘1’ (On).
The adapter will transmit the data selected in Parameters 49 - [Peer A
Output] and 50 - [Peer B Output] to the network. Another adapter
must be configured to receive the peer I/O data.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 39

Configuring the Adapter 3-11
Value Setting
0 Off (Default)
1On
Por t 5 Device
20-COMM-E
Parameter #: 47
Peer Inp Enable
0
Off
Por t 5 Device
20-COMM-E
Parameter #: 42
Peer Inp Addr 1
0
0 <> 255
Default = 0.0.0.0
255.255.255.255
[Peer Inp Addr 1]
[Peer Inp Addr 2]
[Peer Inp Addr 3]
[Peer Inp Addr 4]
IP Address of Node
Transmitting Peer I/O
Por t 5 Device
20-COMM-E
Parameter #: 38
Peer A Input
1
Cmd/Ref
Value Description
0 Off (Default)
1 Logic Command/Reference
2…5 Datalink A, B, C, or D Input
Setting the Adapter to Receive Peer-to-Peer Data
1. Verify that Parameter 47 - [Peer Inp Enable] is set to ‘0’ (Off).
This parameter must be Off while you configure the peer input
parameters.
2. Set Parameters 42 - [Peer Inp Addr 1] through 45 - [Peer Inp Addr
4] to the IP address of the node from which you want to receive data.
Valid nodes must have 20-COMM-E adapters connected to drives with
compatible Logic Command/Status words.
3. Set Parameter 38 - [Peer A Input] to select the destination of the data
that is input to the drive as Peer A.
With the Series A adapter, revision 2.xxx or earlier, if you select a
Reference or Datalink as an input, note the following:
– If a drive that uses a 32-bit Reference and 32-bit Datalinks receives a
16-bit Reference or Datalink, it uses the data in its most significant
word, and its least significant word is zero.
– If a drive that uses a 16-bit Reference and 16-bit Datalinks receives a
32-bit Reference or Datalink, it uses the data in the most significant
word of the 32-bit Reference or Datalink and ignores the data in the
least significant word.
With the Series B adapter , re vision 3.xxx and later , data is used from the
least significant word in the event of a mismatch in Reference or
Datalink sizes.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 40

3-12 Configuring the Adapter
Por t 5 Device
20-COMM-E
Parameter #: 39
Peer B Input
2
DL A Input
Value Description
0 Off (Default)
1 Logic Command/Reference
2…5 Datalink A, B, C, or D Input
Value Description
0 Ignore this command bit. (Default)
1 Use this command bit.
Por t 5 Device
20-COMM-E
Parameter #: 40
Peer Cmd Mask
000000000000000
0
Bit 0 B00
Por t 5 Device
20-COMM-E
Parameter #: 46
Peer Inp Timeout
5.00 s
0.01 <> 10.00
Default = 10.00 s
4. If desired, set Parameter 39 - [Peer B Input] to select the destination
of the data to input to the drive as Peer B.
5. If the adapter receives a Logic Command, set the bits in Parameter 40 [Peer Cmd Mask] that the drive should use.
The bit definitions for the Logic Command word will depend on the
drive to which the adapter is connected. See Appendix
documentation.
D or the drive
If the adapter receives a Logic Command from both a master device and
a peer device, each command bit must ha ve only one source. The source
of command bits set to ‘0’ will be the master device. The source of
command bits set to ‘1’ will be the peer device.
6. Reset the adapter (see Resetting the Adapter
changes to Parameter 40 - [Peer Cmd Mask] take effect.
7. Set Parameter 46 - [Peer Inp Timeout] to the maximum amount of
time the adapter will wait for a message before timing out.
Important:This value must be greater than the product of Parameter
52 - [Peer Out Time] multiplied by Parameter 53 - [Peer
Out Skip] in the adapter from which you are receiving I/O.
For example, if the value of Parameter 52 - [Peer Out Time] is 2.00
seconds and the value of Parameter 53 - [Peer Out Skip] is 2 (see
example screen in step 4 on page 3-10
Timeout] needs to have a value greater than 4.00, such as 5.00 in the
example screen below.
), then Parameter 46 - [Peer Inp
on page 3-16) so that
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 41

Configuring the Adapter 3-13
!
Por t 5 Device
20-COMM-E
Parameter #: 41
Peer Flt Action
0
Fault
Value Description
0 Fault (Default)
1Stop
2 Zero Data
3 Hold Last
4 Send Flt Cfg
!
Port 5 Device
20-COMM-E
Parameter #: 37
Ref Adjust
100.00 %
0.00 <> 200.00
Default = 100.00%
8. Set Parameter 41 - [Peer Flt Action] to the action that the adapter will
take if it times out.
ATTENTION: Risk of injury or equipment damage exists.
Parameter 41 - [Peer Flt Action] lets you determine the action
of the adapter and connected drive if peer communication is
disrupted. By default, this parameter faults the drive. You can set
this parameter so that the drive continues to run, however,
precautions should be taken to ensure that the setting of this
parameter does not create a hazard of injury or equipment
damage. When commissioning the drive, verify that your system
responds correctly to various situations (for example, a
disconnected cable).
Setting the Reference Adjustment
For more details, see Setting a Fault Action on page 3-14.
9. Set Parameter 47 - [Peer Inp Enable] to ‘1’ (On).
The adapter is now configured to receive peer I/O from the specified node.
Ensure that the specified node is configured to transmit peer I/O.
A Reference Adjustment is a percent scaling factor for the Reference from
the network. It can be set between 0.00…200.00% to allow the drive’s
Reference to either match the network Reference (equal to 100.00%), scale
below the network Reference (less than 100.00%), or scale above the
network Reference (more than 100.00%).
ATTENTION: To guard against equipment damage and/or
personal injury , note that changes to adapter Parameter 37 - [Ref
Adjust] take effect immediately. A drive receiving its Reference
from the adapter will receive the newly scaled Reference,
resulting in a change of speed.
If the adapter is receiving a Reference, set Parameter 37 - [Ref Adjust] to
the desired scaling factor.
The adjustment takes effect as soon as it is entered.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 42

3-14 Configuring the Adapter
!
Port 5 Device
20-COMM-E
Parameter #: 21
Comm Flt Action
0
Fault
Port 5 Device
20-COMM-E
Parameter #: 22
Idle Flt Action
0
Fault
Setting a Fault Action
By default, when I/O communication is disrupted (for example, a cable is
disconnected) or the controller is idle (in program mode or faulted), the
drive responds by faulting if it is using I/O from the network. You can
configure a different response to these faults:
• Disrupted I/O communication by using Parameter 21 - [Comm Flt
Action]
• An idle controller by using Parameter 22 - [Idle Flt Action]
ATTENTION: Risk of injury or equipment damage exists.
Parameters 21 - [Comm Flt Action] and 22 - [Idle Flt Action]
let you determine the action of the adapter and connected drive if
I/O communication is disrupted or the controller is idle. By
default, these parameters fault the drive. You can set these
parameters so that the drive continues to run, however,
precautions should be taken to verify that the settings of these
parameters do not create a risk of injury or equipment damage.
When commissioning the driv e, v erify th at your sy stem resp onds
correctly to various situations (for example, a disconnected cable
or faulted controller).
Changing the Fault Action
Set the values of Parameters 21 - [Comm Flt Action] and 22 - [Idle Flt
Action] to an action that meets your application requirements.
Value Action Description
0 Fault The drive is faulted and stopped. (Default)
1 Stop The drive is stopped, but not faulted.
2 Zero Data The drive is sent ‘0’ values for data. This does not command a stop.
3 Hold Last The drive continues in its present state.
4 Send Flt Cfg The drive is sent the data that you set in the fault configuration parameters
(Parameters 25 - [Flt Cfg Logic] through 34 - [Flt Cfg D2 In]).
Changes to these parameters take effect immediately. A reset is not
required.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
If communication is disrupted and then is re-established, the drive will
automatically take commands from the network again.
Page 43

Configuring the Adapter 3-15
Bit Description
0 Web Enable (Default = 1 = Enabled)
1 E-mail Config (Default = 0 = Disabled)
2…31 Not Used
Por t 5 Device
20-COMM-E
Parameter #: 54
Access Control
xxxxxxxxxxxxxx0
1
Web Enable b00
Setting the Fault Configuration Parameters
When setting Parameter 21 - [Comm Flt Action] or 22 - [Idle Flt Action]
to ‘Send Flt Cfg’, the values in the following parameters are sent to the driv e
after an I/O communication fault and/or idle fault occurs. You must set
these parameters to values required by your application.
Parameter Description
25 - [Flt Cfg Logic] A 16-bit value sent to the drive for Logic Command.
26 - [Flt Cfg Ref] A 32-bit value (0…4294967295) sent to the drive as a Reference or Datalink.
27 - [Flt Cfg x1 In]
through
34 - [Flt Cfg x2 In]
Changes to these parameters take effect immediately. A reset is not required.
Important: If the drive uses a 16-bit Reference or 16-bit Datalinks, the most
significant word of the value must be set to zero (0) or a fault will occur.
Setting Web Access Control
By using a web browser to access the IP address set for the adapter, you can
view the adapter’s web pages for information about the adapter, its
connected drive, and other DPI devices connected to the drive, such as
HIMs or converters. Additionally, the adapter can be configured to
automatically send e-mail messages to desired addresses when selected
drive faults occur and/or are cleared, and/or when the adapter takes a
communication or idle fault action. For more details on the adapter’s web
pages, see Chapter
TIP: Series A adapter web pages are accessed differently than Series B
web pages. Enabling and disabling e-mail configuration is also different.
Series A Adapter (Firmware Revision 2.002 or Earlier)
By default, the Series A adapter web pages are enabled. To disa ble the
adapter web pages, use Parameter 54 - [Access Control] to set the Web
Enable Bit 0 value to ‘0’ (Disabled). To protect the configured settings for
adapter e-mail messaging, use Parameter 54 - [Access Control] to set the
E-mail Config Bit 1 value to ‘0’ (Disabled). E-mail messaging will remain
active regardless of whether or not its settings are protected—unless e-mail
messaging was never configured. For more information about configuring
adapter e-mail messaging, see Configure E-mail Notification Web Page
page 8-6).
8, Viewing the Adapter Web Pages.
on
Bit 0 is the right-most bit. It is highlighted above and equals ‘1’.
Changes to this parameter take effect immediately. A reset is not required.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 44

3-16 Configuring the Adapter
Bit Description
0 E-mail Cfg (Default = 1 = Enabled)
1…7 Not Used
Por t 5 Device
20-COMM-E
Parameter #: 56
Web Features
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
1
E-mail Cfg b00
!
Value Description
0 Ready (Default)
1 Reset Module
2 Set Defaults
Port 5 Device
20-COMM-E
Parameter #: 20
Reset Module
1
Reset Module
Series B Adapter (Firmware Revision 3.xxx or Later)
By default, the Series B adapter web pages are disabled. See Figure 2.1 and
set the Web Pages Switch (SW2) to the ‘Enable Web’ (up) position.
Important:For a change to the switch setting to take effect, the adapter
must be reset (see Resetting the Adapter
Bit 0 of Parameter 56 - [Web Features] is used to protect the configured
settings for e-mail messaging. By default, settings are not protected and the
user can make changes. To protect the configured settings, set the value of
E-mail Cfg Bit 0 to ‘0’ (Disabled). You can unprotect the configuration by
changing Bit 0 back to ‘1’ (Enabled). E-mail messaging will always remain
active regardless of whether or not its settings are protected—unless e-mail
messaging was never configured. For more information about configuring
adapter e-mail messaging or to stop e-mail messages, see Configure E-mail
Notification Web Page on page 8-6.
on page 3-16).
Resetting the Adapter
Bit 0 is the right-most bit. It is highlighted above and equals ‘1’.
Changes to this parameter take effect immediately. A reset is not required.
Changes to switch settings and some adapter parameters require that you
reset the adapter before the new settings take effect. You can reset the adapter
by power cycling the drive or by using Parameter 20 - [Reset Module].
A TTENTION: Risk of injury or equipment damage e xists. If the
adapter is transmitting control I/O to the driv e, the dri ve may fault
when you reset the adapter. Determine how your drive will
respond before resetting a connected adapter.
Set Parameter 20 - [Reset Module] to ‘1’ (Reset Module).
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
When you enter ‘1’ (Reset Module), the adapter will be immediately reset.
When you enter ‘2’ (Set Defaults), the adapter will set all adapter
parameters to their factory-default values. After performing a Set Defaults,
enter ‘1’ (Reset Module) so that the new values take effect. The v alue of this
parameter will be restored to ‘0’ (Ready) after the adapter is reset.
Page 45

Configuring the Adapter 3-17
Bit
Definition
Not Used
Not Used
Not Used
Datalink D
Datalink C
Datalink B
Datalink A
Cmd/Ref
Default xxx00001
Bit 76543210
0 = I/O disabled
1 = I/O enabled
Viewing the Adapter Status Using Parameters
The following parameters provide information about the status of the
adapter. You can view these parameters at any time.
Parameter Description
17 - [EN Rate Act] The data rate used by the adapter.
18 - [Ref/Fdbk Size] The size of the Reference/Feedback. It will either be 16 bits or 32 bits. It
is set in the drive and the adapter automatically uses the correct size.
19 - [Datalink Size] The size of the Datalinks. It will either be 16 bits or 32 bits. It is set in the
drive and the adapter automatically uses the correct size.
24 - [DPI I/O Act] The Reference/Feedback and Datalinks used by the adapter. This value
is the same as Parameter 23 - [DPI I/O Cfg] unless the parameter was
changed and the adapter was not reset.
48 - [Peer Inp Status] The status of the consumed peer input connection.
Val ues
0 = Off
1 = Waiting
2 = Running
3 = Faulted
Updating the Adapter Firmware
The adapter firmware can be updated over the network or serially through a
direct connection from a computer to the drive using a 1203-USB or
1203-SSS serial converter.
When updating firmware over the network, you can use the Allen-Bradley
ControlFLASH software tool, the built-in update capability of
DriveExplorer Lite or Full software, or the built-in update capability of
DriveExecutive software.
When updating firmware through a direct serial connection from a
computer to a drive, you can use the same Allen-Bradley software tools
described above, or you can use HyperTerminal software set to the
X-modem protocol.
To obtain a firmware update for this adapter, go to http://www.ab.com/
support/abdrives/webupdate. This website contains all firmware updat e files
and associated Release Notes that describe the following items:
• Firmware update enhancements and anomalies
• How to determine the existing firmware revision
• How to update firmware using ControlFLASH, DriveExplorer,
DriveExecutive, or HyperTerminal software
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 46

3-18 Configuring the Adapter
Notes:
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 47

Chapter 4
Configuring the I/O
This chapter provides instructions on how to configure a Rockwell
Automation ControlLogix, PLC-5, SLC 500, or MicroLogix 1100/1400
controller to communicate with the adapter and connected PowerFlex driv e.
Topic Page
Using RSLinx Classic Software
ControlLogix Controller Example 4-2
Limitations Using a PLC-5, SLC 500, or MicroLogix 1100/1400 Controller 4-22
PLC-5 Controller Example 4-23
SLC 500 Controller Example 4-31
MicroLogix 1100/1400 Controller Example 4-39
4-1
Using RSLinx Classic
Software
RSLinx Classic software, in all its variations (Lite, Gateway, OEM, and so
forth), is used to provide a communication link between the computer,
network, and controller. RSLinx Classic software requires its
network-specific driver to be configured before communication is
established with network devices. To configure the RSLinx driver, follow
this procedure.
1. Start RSLinx Classic software and select Communications >
Configure Drivers to display the Configure Drivers screen.
2. From the Available Driver Types pull-down menu, choose EtherNet/IP
Driver.
3. Click Add New… to display the Add New RSLinx Driver screen.
4. Use the default name or type a new name and click OK.
The ‘Configure driver:’ screen appears.
5. Depending on your application, select either the browse local o r remote
subnet option.
6. Click OK.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 48

4-2 Configuring the I/O
IP Address 10.91.100.80
ControlLogix Controller
with 1756-ENBT Bridge
IP Address 10.91.100.79
PowerFlex 70 Drive with
20-COMM-E Adapter
Computer with
Ethernet Connection
Ethernet
Switch
The Configure Drivers screen reappears with the new driver in the
Configured Drivers list.
7. Click Close to close the Configure Drivers screen.
8. Keep RSLinx running and verify that the computer reco gnizes th e dri v e.
a. Select Communications > RSWho.
b. In the menu tree, click ‘+’ next to the Ethernet driver.
ControlLogix Controller Example
If the ‘EtherNet/IP driver’ cannot see your drive, as an alternative, use
either the ‘Ethernet devices’ or ‘Remote Devices via Linx Gateway’
RSLinx driver.
After the adapter is configured, the connected drive and adapter will be a
single node on the network. This section provides the steps needed to
configure a simple EtherNet/IP network (see Figure 4.1
will configure a ControlLogix controller with 1756-ENBT (Series A) bridge
to communicate with a drive using Logic Command/Status, Reference/
Feedback, and 16 Datalinks (8 to read and 8 to write) over the network.
Figure 4.1 Example ControlLogix Controller EtherNet/IP Network
). In our example, we
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
TIP: Information for PowerFlex 750-Series drives has been added to this
manual where it is applicable.
Page 49

Configuring the I/O 4-3
Adding the Bridge to the I/O Configuration
To establish communications between the controller and adapter over the
network, you must first add the ControlLogix controller and its bridge to the
I/O configuration. This procedure is similar for all RSLogix 5000 versions.
1. Start RSLogix 5000 software.
2. Select File > New to display the New Controller screen.
a. Choose the appropriate selections for the fields in the screen to
match your application.
b. Click OK.
The RSLogix 5000 window reappears with the treeview in the left
pane.
3. In the treeview, right-click the I/O Configuration folder and choose
New Module.
The Select Module screen appears.
4. Expand the Communications group to display all of the available
communication modules.
5. In the list, select the EtherNet/IP bridge used by your controller.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 50

4-4 Configuring the I/O
In this example, we use a 1756-ENBT EtherNet/IP Bridge (Series A),
so the 1756-ENBT/A option is selected.
6. Click OK.
7. In the Select Major Revision pop-up dialog box, select the major
revision of its firmware.
8. Click OK.
The bridge’s New Module screen appears.
9. Edit the following:
Box Setting
Name A name to identify the EtherNet/IP bridge.
Description Optional – description of the EtherNet/IP bridge.
IP Address The IP address of the EtherNet/IP bridge.
Host Name Not used.
Slot The slot of the EtherNet/IP bridge in the rack.
Revision The minor revision of the firmware in the bridge. (You already set the major
Electronic
Keying
Open
Module
Properties
10. Click OK.
The bridge is now configured fo r the EtherNet/IP netw ork and added to
the RSLogix 5000 project. It appears in the I/O Configuration folder. In
our example, a 1756-ENBT bridge appears under the I/O Conf iguration
folder with its assigned name.
revision by selecting the bridge series in step 5.)
Compatible Keying. The ‘Compatible Keying’ setting for Electronic Keying
ensures the physical module is consistent with the software configuration
before the controller and bridge make a connection. Therefore, be sure that
you have set the correct revision in this screen. See the online Help for
additional information on this and other Electronic Keying settings.
When this box is checked, clicking OK opens additional module properties
screens to further configure the bridge. When unchecked, clicking OK closes
the bridge’s New Module screen. For this example, uncheck this box.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
For convenience, keep the project open. Later in this chapter the project
will need to be downloaded to the controller.
Page 51

Configuring the I/O 4-5
There are three ways to add the adapter into the I/O configuration:
• Drive Add-on Profiles (RSLogix 5000 software, version 16.00 or later)
• Classic Profile (RSLogix 5000 software, versions 13.00…15.00)
• Generic Profile (RSLogix 5000 software, all versions)
These are described in separate sections below. If your version of RSLogix
5000 software supports drive Add-on Profiles, we recommend that you use
this method.
Using RSLogix 5000 Drive Add-on Profiles, Version 16.00 or Later
When compared to using the RSLogix 5000 Classic Profile (versions
13.00…15.00) or Generic Profile (all versions), the RSLogix 5000 drive
Add-on Profiles provide the following advantages:
• Profiles for specific drives that provide descriptive controller tags for
basic control I/O words (Logic Command/Status and Reference/
Feedback) and Datalinks. Additionally, Datalinks automatically take the
name of the drive parameter to which they are assigned. These profiles
virtually eliminate I/O mismatch errors and substantially reduce drive
configuration time.
• New Drive tab eliminates the need for a separate drive software
configuration tool.
• Drive configuration settings are saved as part of the RSLogix 5000
software, version 16.00 or later , project file (.A CD) and also do wnloaded
to the controller.
• Unicast connection (requires RSLogix 5000 software, version 18.00 or
later, and 20-COMM-E Series B adapter firmware 4.001 or later)
• Drive Add-on Profiles can be updated anytime. When a new drive is
used, or to benefit from new updates for Add-on Profiles, you will need
the newest Add-on Profile update. Go to http://www.ab.com/support/
abdrives/webupdate to download the latest RSLogix 5000 drive Add-on
Profile. To determine your drive Add-on Profile version, see
Allen-Bradley Knowledgebase document #65882.
Add the Drive/Adapter to the I/O Configuration
T o transmit data between the bridge and the dri ve, you must add the dri v e as
a child device to the parent bridge. In this example, RSLogix 5000 software,
version 16.00 is used with drive Add-on Profile version 3.01.
1. In the treeview, right-click on the bridge and choose New Module… to
display the Select Module screen.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 52

4-6 Configuring the I/O
In our example, we right-click on the 1756-ENBT/A bridge. Expand the
Drives group to display all of the available drives with their
communication adapters.
TIP: If the PowerFlex drive is not shown, go to http://www.ab.com/
support/abdrives/webupdate and download the latest RSLogix 5000
drive Add-on Profile.
2. From the list, select the drive and its connected adapter.
For this example, we selected ‘PowerFlex 70 EC-E’.
3. Click OK.
The drive’s New Module screen appears.
4. On the General tab, edit the following data about the drive/adapter.
Box Setting
Name A name to identify the drive.
Description Optional – description of the drive/adapter.
IP Address The IP address of the adapter.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
5. On the New Module screen in the Module Definition section, click
Change… to launch the Module Definition screen and begin the drive/
adapter configuration process.
Page 53

Configuring the I/O 4-7
In this example, Datalinks are used to do the following.
Read… Write to…
Output Current (Parameter 3) Accel Time 1 (Parameter 140)
DC Bus Voltage (Parameter 12) Decel Time 1 (Parameter 142)
Fault 1 Code (Parameter 243) High Resolution Reference (Parameter 308)
TIP: To get the latest RSLogix 5000 drive Add-on Profile, go to http://
www.ab.com/support/abdrives/webupdate.
6. In the Module Definition screen, edit the following information.
Box Setting
Revision The major and minor revision of the firmware (database) in the drive. If the
drive’s major and minor revision is not available, the drive database is not
installed on your computer. To get the correct database revision, use one of the
following buttons at the bottom left of the Module Definition screen:
• Create Database: Creates a database from an online network drive. Clicking
this button displays an RSLinx software RSWho window. Browse to the
online drive (for this example, PowerFlex 70 EC), select it, and click OK. The
database will be uploaded and stored on the computer. Thereafter, close the
Module Definition screen and then re-open it to display the new revision.
• Web Update: When a drive is not available online, opens the Allen-Bradley
Drives Web Updates website to download a specific database file. After
downloading the file, close the Module Definition screen and then re-open it
to display the new revision.
• Match Drive: Use this button when the drive being added to the network
matches the drive profile (revision, rating, configuration settings, and so forth)
of an existing online network drive. Click this button to conveniently create a
duplicate drive profile from the online drive, and automatically load this
identical information into the Module Definition screen. This eliminates the
need to manually enter the information each time a new drive with a
matching profile is added to the network.
Electronic
Keying
Compatible Module. The ‘Compatible Module’ setting for Electronic Keying
ensures that the physical module is consistent with the software configuration
before the controller and bridge make a connection. Therefore, ensure that you
have set the correct revision in this screen. See the online Help for additional
information on this and other Electronic Keying settings. If keying is not required,
select ‘Disable Keying’. Drives do not require keying, and so ‘Disable Keying’ is
recommended.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 54

4-8 Configuring the I/O
Box Setting
Drive
Rating
Connection Parameters via Datalinks. When selecting ‘Parameters via Datalinks’ (default),
Data
Format
Datalink
A, B, C, D
Sort Input/
Output
selection…
Use
Network
Reference
The voltage and current rating of the drive. If the drive rating is not listed, the
drive database is not installed on your computer. To get the correct drive rating,
use the Create Database, Web Update, or Match Drive button described
above.
the controller tags for the Datalinks use the drive parameter names to which
they are assigned. When selecting ‘Datalinks’, the controller tags for the
Datalinks have non-descriptive UserDefinedData[n] names like those used in
RSLogix 5000 software, version 15.00.
Parameters. When the Connection field is set to ‘Parameters via Datalinks’,
‘Parameters’ is automatically selected. When the Connection field is set to
‘Datalinks’, you must select the number of Datalinks required for your application
in the ‘Data Format’ field.
In the Input Data column, assigns selected drive parameters to be READ by the
controller. In the Output Data column, assigns selected drive parameters to be
WRITTEN by the controller.
When this box is checked, sorts the Input Data and Output Data assigned
parameters by name and then by number, and enables parameter search by
name. When unchecked, sorts the assigned parameters by parameter number
and then by name, and enables parameter search by number.
Conveniently selects the speed reference for the drive to come from the
network. This box is checked by default.
When a 32-bit parameter is selected for Input Data or Output Data for a
drive with 16-bit Datalinks, two contiguous Datalinks (for example, x1
and x2, where x = A, B, C or D) are automatically assigned as a pair to
represent that parameter. See Datali nk e xamples in the screen sho wn on
the previous page. For more information on Datalinks, see Using
Datalinks on page 5-9.
On the Module Definition screen, notice that the automatically-assigned
controller tags DriveStatus, OutputFreq, DriveLogicRslt, and
CommandedFreq are always used.
When a Datalink is enabled, the following 20-COMM-E adapter I/O
parameters are automatically set:
– Parameter 23 - [DPI I/O Cfg] turns on the enabled Datalink bit so
the 20-COMM-E adapter will communicate that Datalink’s
information with the drive.
– Parameter 35 - [M-S Input] turns on the enabled Datalink bit so the
20-COMM-E adapter will input that Datalink’ s information from the
controller.
– Parameter 36 - [M-S Output] turns on the enabled Datalink bit so
the 20-COMM-E adapter will output that Datalink’s information to
the controller.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
7. Click OK on the Module Definition screen to sa ve th e dri ve a nd adapter
configuration and close the screen.
The drive’s New Module screen reappears.
Page 55

Configuring the I/O 4-9
Screen for
RSLogix 5000
software, version
16.00 or 17.00
Screen for
RSLogix 5000
software, version
18.00 or later
8. On the New Module screen, click the Connection tab.
9. In the ‘Requested Packet Interval (RPI)’ box, set the value to 5.0
milliseconds or greater.
This value determines the maximum interval that a controller should
use to move data to and from the adapter. To conserve bandwidth, use
higher values for communicating with low priority devices.
The ‘Inhibit Module’ box, when checked, inhibits the module from
communicating with the RSLogix 5000 project. When the ‘Major Fault
on …’ box is checked, a major controller fault will occur when the
module’s connection fails while the controller is in the Run Mode. For
this example, leave the ‘Inhibit Module’ an d ‘Major Fa ult On …’ boxes
unchecked.
Important:Unicast support has been added to RSLogix 5000 software,
version 18.00 or later. Ho wever, to also support unicast, the
controller firmware must be version 18.00 or later, and the
20-COMM-E Series B adapter firmware must be revision
4.001 or later. Unicast is recommended whenever possible.
For the benefits of unicast operation, see Preparing for an
Installation on page 2-1. If unicast is selected and the
20-COMM-E adapter does not support it, the connection
will be rejected. In this case, either update the 20-COMM-E
firmware to revision 4.001 or later, or uncheck the ‘Use
Unicast Connection over EtherNet/IP’ checkbox.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 56

4-10 Configuring the I/O
10. On the New Module screen, click the Port Configuration tab.
11. In the Port Configuration tab screen, edit the following information.
Box Setting
IP Address The IP address of the adapter that was already set in the General tab. This
field is not configurable (grayed out).
Subnet Mask The Subnet Mask configuration setting of the network. This setting must
match the setting of other devices on the network (for example,
255.255.255.0).
Gateway
Address
Enable BootP When this box is checked, BOOTP is enabled in the adapter and will ignore
The Gateway Address configuration setting of the network. This setting must
match the setting of other devices on the network (for example, 10.91.100.1).
the IP address set in the General tab. When unchecked, the controller uses
the set IP address. This is another method to enable/disable BOOTP in the
adapter. For this example, leave this box unchecked.
12. Click Set to save the Port Configuration information which sets the
corresponding offline Subnet Cfg x and Gateway Cfg x parameters in
the adapter.
13. Click OK on the New Module screen.
The new node (‘My_PowerFlex_70_EC_Drive’ in this example) now
appears under the bridge (‘My_EtherNet_IP_Bridge’ in this example)
in the I/O Configuration folder. If you double-click the Controller Tags,
you will see that module-defined data types and tags have been
automatically created (Figure 4.2
and Datalinks include the assigned drive parameter name. After you
save and download the configuration, these tags allow you to access the
Input and Output data of the drive via the controller’s ladder logic.
). Note that all tag names are defined
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 57

Figure 4.2 Controller Tags
Configuring the I/O 4-11
Save the I/O Configuration to the Controller
After adding the bridge and drive/adapter to the I/O configuration, you must
download the configuration to the controller. You should also save the
configuration to a file on your computer.
1. In the RSLogix 5000 window, select Communications > Download.
The Download dialog box appears.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 58

4-12 Configuring the I/O
TIP: If a message box reports that RSLogix 5000 software is unable to
go online, select Communications > Who Active to find your
controller in the Who Active screen. After finding and selecting the
controller, click Set Project Path to establish the path. If your
controller does not appear, you need to add or conf igure the EtherNet/IP
driver with RSLinx software. See Using RSLinx Classic Software
page 4-1 and RSLinx online help for details.
2. Click Download to download the configuration to the controller.
When the download is successfully completed, RSLogix 5000 software
goes into the Online mode and the I/O Not Responding box in the
upper-left of the window should be flashing green. Also, a yellow
warning symbol should be displayed on the I/O Configuration folder
in the treeview and on the drive profile.
If the controller was in Run Mode before clicking Download, RSLogix
5000 software prompts you to change the controller mode back to
Remote Run. In this case, choose the appropriate mode for your
application. If the controller was in Program Mode before clicking
Download, this prompt will not appear.
on
3. Select File > Save.
If this is the first time you saved the project, the Save As dialog box
appears.
a. Navigate to a folder.
b. Type a file name.
c. Click Save to save the configuration to a file on your computer.
To be sure that the present project configuration values are saved,
RSLogix 5000 software prompts you to upload them. Click Yes to
upload and save the values.
Correlate the Drive with the Controller
You must now correlate the drive settings to the RSLogix 5000 project I/O
settings so that they match. This requires loading the project I/O settings
into the drive.
1. In the treeview under I/O Configuration, right-click on the drive profile
(for this example, My_PowerFlex_70_EC_Drive) and choose
Properties.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 59

Configuring the I/O 4-13
2. Click the Drive tab.
3. Click Connect to Drive to begin the correlation process.
The Connect To Drive screen appears.
4. Browse the communication path to the drive and select the drive.
5. Click OK.
After the drive configuration data has been verified, a pop-up dialog
box appears, which synchronizes ports from the online drive to the
project to be sure that correct Datalinks are assigned.
6. Click OK.
If the Differences Found screen appears—which is typical, click
Download. This will download the project settings from the controller
to the drive and its connected adapter. If Upload is clicked, the drive
and adapter settings are uploaded to the controller.
TIP: On subsequent connections to the drive (after initial download),
click Upload.
7. When the Reset Comm Module screen appears, click Yes to reset the
communication adapter so that the new I/O settings take effect.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 60

4-14 Configuring the I/O
After resetting the communication module, which may take up to a
minute to complete, the I/O OK box in the upper-left of the RSLogix
5000 window should now be steady green and the yellow warning
symbols in the treeview under the I/O Configuration folder and driv e
profile should be gone.
TIP: If the yellow warning symbol for your dri ve remains displayed,
first try power c ycling the drive. Otherwise, double-click the drive under
the I/O tree and click the Connection tab to find the cause of the problem.
8. The Module Properties Drive Tab screen re-appears.
You can view the drive’ s Pa rameter List, Diagnostic Items List, and lists
for any connected peripheral, including the 20-COMM-E adapter.
While connected to the drive, you can dynamically change values of
parameters. Diagnostic items and diagram views can be used for
troubleshooting. Table 7.A on page 7-4
troubleshooting the adapter.
9. Click OK when finished to close the Module Properties screen for the
drive.
provides diagnostic items for
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Using the RSLogix 5000 Classic Profile, Versions 13.00…15.00
When compared to using the RSLogix 5000 Generic Profile (all versions),
the RSLogix 5000 Classic Profile provides these advantages:
• Profiles for specific dri ves (Figure 4.3
tags for basic control I/O words (Logic Command/Status and Reference/
Feedback). The controller tags for Datalinks, however, have
non-descriptive UserDefinedData[n] names.
• Improved I/O configuration—no I/O assembly configuration required.
Basic control I/O is defined, but Datalinks still need to be configured/
mapped.
) that provide descriptive controller
Page 61

Configuring the I/O 4-15
• The Setup tab includes a DriveExecutive icon link to conveniently
launch DriveExecutive software (when installed on computer) to match
the adapter I/O configuration with the controller, and to assign the
Datalink parameters in the drive. This reduces I/O mismatches.
TIP: Because the RSLogix 5000 Classic Profile has been significantly
improved upon by RSLogix 5000 Drive Add-on Profiles, version 16.00 or
later, we recommend using RSLogix 5000 Drive Add-on Profiles to take
advantage of their benefits (more intuitive, time saving, and less likely to
make I/O configuration errors).
Figure 4.3 Classic Profile Screens for Drives
When Datalinks are used, you must enable the desired Datalinks and assign
names to their non-descriptive controller tags. When a Datalink is enabled,
you must set the following adapter I/O parameters:
• Parameter 23 - [DPI I/O Cfg] turns on the enabled Datalink bit so the
20-COMM-E adapter will communicate that Datalink’ s information with
the drive.
• Parameter 35 - [M-S Input] turns on the enabled Datalink bit so the
20-COMM-E adapter will input that Datalink’s information from the
controller.
• Parameter 36 - [M-S Output] turns on the enabled Datalink bit so the
20-COMM-E adapter will output that Datalink’s information to the
controller.
When using Datalinks, up to 8 drive [Data In xx] parameters (300…307)
and/or up to 8 [Data Out xx] parameters (310…317) must be assigned to
point to the appropriate drive parameters for your application.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 62

4-16 Configuring the I/O
Using the RSLogix 5000 Generic Profile, All Versions
We recommend that you use the basic RSLogix 5000 Generic Profile for
only the following reasons:
• A specific drive profile in other versions of RSLogix 5000 software is
unavailable.
• Users are already familiar with a drive Generic Pr ofile and do not w ant to
conver t an existing project to a Classic Profile, v ersions 13.00…15.00, or
to a drive Add-on Profile (RSLogix 5000 software, version 16.00 or
later).
• A project must maintain specific revision level control.
• The controller cannot be taken offline. RSlogix 5000 software, version
16.00 or later, enables the drive Generic Profile to be added while the
controller is online and in the Run mode.
Add the Drive/Adapter to the I/O Configuration
T o transmit data between the bridge and the dri v e, you must add the dri ve as
a child device to the parent bridge.
1. In the treeview, right-click the bridge and select New Module… to
display the Select Module screen.
In our example, we right-click on the 1756-ENBT/A bridge.
2. Expand the Communications group to display all of the available
communication modules.
3. Select ‘ETHERNET -MODULE’ from the list to conf igure the dri ve and
its connected 20-COMM-E adapter.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
4. Click OK.
Page 63

Configuring the I/O 4-17
The drive’s New Module screen appears.
5. Edit the following information about the drive and adapter.
Box Setting
Name A name to identify the drive and adapter.
Description Optional – description of the drive/adapter.
Comm Format Data - INT (This setting formats the data in 16-bit words.)
IP Address The IP address of the adapter.
Open Module
Properties
When this box is checked, clicking OK opens additional module properties
screens to further configure the drive/adapter. When unchecked, clicking
OK closes the drive’s New Module screen. For this example, check this box.
6. Under Connection Parameters, edit the following information.
Box Assembly Instance Size
Input 1 (This value is required.) The value will vary based on your application
Output 2 (This value is required.) The value will vary based on your application
Configuration 6 (This value is required.) 0 (This value is required.)
Depending on the size of the drive’s Reference/Feedback and the
number of Datalinks used in your I/O configuration, Table 4.A
Table 4.B
need to enter for the Input Size and Output Size boxes.
, or Table 4.C defines the number of 16-bit words that you
(setting of Parameters 23 - [DPI I/O Cfg] and 36
- [M-S Output]) and the size (16-bit or 32-bit) of
the Reference/Feedback and Datalinks in the
drive. See Tab l e 4 . A
page 4-18
(setting of Parameters 23 - [DPI I/O Cfg] and 35
- [M-S Input]) and the size (16-bit or 32-bit) of
the Reference/Feedback and Datalinks in the
drive. See Tab l e 4 . A
page 4-18
.
.
, Table 4.B, or Ta bl e 4 .C on
, Table 4.B, or Ta bl e 4 .C on
,
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 64

4-18 Configuring the I/O
Table 4.A Drives with 16-bit Reference/Feedback and 16-bit Datalinks
These products include the following:
• PowerFlex 70 drives with standard or enhanced control • SMC Flex smart motor controllers
• PowerFlex 700 drives with standard control • SMC-50 smart motor controllers
• PowerFlex 700H drives
Logic
Command/
Status
✔✔ 4 2 …0 0001 …0 0001 …0 0001
✔✔✔ 6 4 …0 0011 …0 0011 …0 0011
✔✔✔✔ 8 6 …0 0111 …0 0111 …0 0111
✔✔✔✔✔10 8 …0 1111 …0 1111 …0 1111
✔ ✔ ✔✔✔✔12 10 …1 1111 …1 1111 …1 1111
Logic
Command/
Status
✔✔ 4 2 …0 0001 …0 0001 …0 0001
✔✔✔ 8 6 …0 0011 …0 0011 …0 0011
✔✔✔✔ 12 10 …0 0111 …0 0111 …0 0111
✔✔✔✔✔16 14 …0 1111 …0 1111 …0 1111
✔✔✔✔✔✔20 18 …1 1111 …1 1111 …1 1111
Ref/Fdbk
(16-bit)
Table 4.B Drives with 16-bit Reference/Feedback and 32-bit Datalinks
These products include the following:
• PowerFlex 700 drives with vector control • PowerFlex Digital DC drives
• PowerFlex 700L drives with 700 control
Ref/Fdbk
(16-bit)
Datalinks (16-bit) User Configured Settings
ABCD
Datalinks (32-bit) User Configured Settings
ABCD
Size in Words Par. 23 -
Input Output
Size in Words Par. 23 -
Input Output
[DPI I/O Cfg]
[DPI I/O Cfg]
Par. 35 [M-S Input]
Par. 35 [M-S Input]
Par. 36 [M-S Output]
Par. 36 [M-S Output]
Table 4.C Drives with 32-bit Reference/Feedback and 32-bit Datalinks
These products include the following:
• PowerFlex 700S drives with Phase I or Phase II control • PowerFlex 753 drives
• PowerFlex 700L drives with 700S control • PowerFlex 755 drives
Logic
Command/
Status
✔✔ 6 4 …0 0001 …0 0001 …0 0001
✔✔✔ 10 8 …0 0011 …0 0011 …0 0011
✔✔✔✔ 14 12 …0 0111 …0 0111 …0 0111
✔✔✔✔✔18 16 …0 1111 …0 1111 …0 1111
✔ ✔ ✔✔✔✔22 20 …1 1111 …1 1111 …1 1111
Ref/Fdbk
(32-bit)
TIP: For instructions on configuring the I/O for the adapter using
Parameter 23 - [DPI I/O Cfg] and its Master-Slave Hiera r chy using
Parameters 35 - [M-S Input] and 36 - [M-S Output], see
Setting the I/O Configuration
Datalinks (32-bit) User Configured Settings
ABCD
Size in Words Par. 23 -
Input Output
on page 3-7.
[DPI I/O Cfg]
Par. 35 [M-S Input]
Par. 36 [M-S Output]
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 65

Configuring the I/O 4-19
When using Datalinks, up to 8 drive [Data In xx] parameters (300…307)
and/or up to 8 [Data Out xx] parameters (310…317) must be assigned to
point to the appropriate drive parameters for your application.
7. After setting the information in the drive’s New Module screen, click
OK.
The Module Properties screen appears.
8. Click the Connection tab.
9. In the ‘Requested Packet Interval (RPI)’ box, set the value to 5.0
milliseconds or greater.
This value determines the maximum interval that a controller should
use to move data to and from the adapter. To conserve bandwidth, use
higher values for communicating with low priority devices. For this
example, leave the ‘Inhibit Module’ and ‘Major Fault …’ boxes
unchecked.
10. Click OK.
The new node (‘My_PowerFlex_70_EC_Drive’ in this example) now
appears under the bridge (‘My_EtherNet_IP_Bridge’ in this example)
in the I/O Configuration folder . If you double-click the Controller Tags,
you will see that module-defined data types and tags have been
automatically created (Figure 4.4
configuration, these tags allow you to access the Input and Output data
of the drive via the controller’s ladder logic.
For this example, all Datalinks (A, B, C, and D) are enabled. The Input
Size is set to 12 words and the Output Size is set to 10 words. Also, the
following adapter I/O parameters are set to the following values.
Adapter Parameter No. Setting
23 - [DPI I/O Cfg] xxxx xxxx xxx1 1111
35 - [M-S Input] xxxx xxxx xxx1 1111
36 - [M-S Output] xxxx xxxx xxx1 1111
). After you save and download the
11. Reset the adapter (see Resetting the Adapter
cycle the drive.
on page 3-16) or power
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 66

4-20 Configuring the I/O
For the drive speed reference and Datalink parameter values and the
adapter setup parameter values, see Drive and Adapter Parameter
Settings on page 5-14.
Figure 4.4 Controller Tags
Save the I/O Configuration to the Controller
After adding the bridge and drive/adapter to the I/O configuration, you must
download the configuration to the controller. You should also save the
configuration as a file on your computer.
TIP: When using RSLogix 5000 software, version 16.00 or later, you can
add the I/O configuration of a Generic Profile while the controller is online
and in the Run mode.
1. In the RSLogix 5000 window, select Communications > Download.
The Download dialog box appears.
TIP: If a message box reports that RSLogix 5000 software is unable to
go online, select Communications > Who Active to find your
controller in the Who Active screen. After finding and selecting the
controller, click Set Project Path to establish the path. If your
controller does not appear, you need to add or conf igure the EtherNet/IP
driver with RSLinx software. See Using RSLinx Classic Software
page 4-1 and RSLinx online help for details.
on
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 67

Configuring the I/O 4-21
2. Click Download to download the configuration to the controller.
When the download is successfully completed, RSLogix 5000 software
goes into the Online mode and the I/O OK box in the upper-left of the
screen should be steady green.
3. Select File > Save.
If this is the first time you saved the project, the Save As dialog box
appears.
a. Navigate to a folder.
b. Type a file name.
c. Click Save to save the configuration as a file on your computer.
To be sure that the present project configuration values are saved,
RSLogix 5000 software prompts you to upload them. Click Yes to
upload and save the values.
4. Configure any Datalinks in the drive (for e xample, Datalink parameters
300…317 in PowerFlex 70/700 drives) that were enabled in the
controller and adapter during I/O configuration (Table 4.A
or Table 4.C
).
, Table 4.B,
Each Datalink being used must be assigned to a specific parameter in
the drive or connected peripheral. If this is not done, the controller will
receive or send placeholder data instead of actual drive or periphe r al
parameter values.
5. Place the controller in Remote Run or Run Mode.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 68

4-22 Configuring the I/O
Limitations Using a PLC-5, SLC 500, or MicroLogix 1100/1400 Controller
Controlling I/O with explicit messages is relatively complex compared to
normal implicit I/O control.
ControlLogix and CompactLogix controllers with EtherNet/IP provide the
easiest and most integrated form of implicit I/O control for a PowerFlex
drive. RSLogix 500 0 software, version 16.00 or later, for ControlLogix and
CompactLogix controllers contains integrated profiles for Po werFle x drives
that, with a few clicks of the mouse, automatically create all controller tags
and an implicit connection at the specified Requested Packet Interval to
control the drive. This connection is monitored at both ends to verify that
the controller and drive are communicating. A watchdog will cause a drive
fault if the drive does not respond within approximately 100 milliseconds.
Therefore, using a ControlLogix or CompactLogix controller is by far the
much preferred method of controlling drives on EtherNet/IP.
If you are not using either of these type of controllers, then PowerFlex
drives on EtherNet/IP can be controlled with explicit messages using
PLC-5, SLC 500, or MicroLogix 1100/1400 controllers with the following
limitations:
• An explicit message is a much slower form of control and is
non-deterministic. This means that you cannot guarantee how long the
drive will take to start up or stop when the command is given. Therefore,
all equipment used in this manner should be subject to a risk assessment,
taking into account the mechanical and electrical implementation.
• A timeout value (in seconds) in the EtherNet/IP adapter will issue a dri ve
fault if a message is not received from the controller within the specified
time. However, the controller has no way of detecting a loss of
communication to the drive until the next cycle of explicit messages.
This is another factor in the risk assessment.
• Any additional drives to be controlled will require additional explicit
messages for their control, and they need to be carefully sequenced.
Most controllers have small communication queues (see its User
Manual), which need to be carefully managed if messages are not to be
lost.
• Each controller has a limited number of communication connections (see
its User Manual for maximum connections), which will limit the number
of drives that can be connected.
In summary, unlike a ControlLogix or CompactLogix controller,
programming a PLC-5, SLC 500, or MicroLogix 1100/1400 controller by
using RSLogix 5 or RSLogix 500 software with explicit messages is more
difficult, and produces a more comp lex program.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 69

Configuring the I/O 4-23
IP Address 10.91.100.80
PLC-5/40E Controller with Embedded Ethernet
IP Address 10.91.100.79
PowerFlex 70 Drive with
20-COMM-E Adapter
Computer with
Ethernet Connection
Ethernet
Switch
PLC-5 Controller Example
Important:The PLC-5 controller must be Series E (Rev. D.1 or higher) to
support the MultiHop feature that routes messaging to the drive.
After the adapter is configured, the connected dri ve and adapter will be a
single node on the network. This section provides the steps needed to
configure a simple EtherNet/IP network (see Figure 4.5
will configure a PLC-5/40E controller to communicate with a dri v e using
Logic Command/Status, Reference/Feedback, and Datalinks over the network.
Figure 4.5 Example PLC-5 Controller EtherNet/IP Network
). In our example, we
TIP: Information for PowerFlex 750-Series drives has been added to this
manual where it is applicable.
Configuring Parameters for Network I/O
Because the I/O for the driv e is mes sage-based, there is no need to conf igure
any I/O inside the RSLogix 5 project, version 7.00 or later, until using the
I/O as described in Chapter 5
Howev er , to get the adapter to operate with the I/O created in Chapter 5
need to configure the adapter to accept the I/O and the drive to point to the
appropriate Datalinks.
1. Set adapter Parameters 23 - [DPI I/O Cfg], 35 - [M-S Input], and 36 [M-S Output] to values that meet your application requirements.
For this example, the adapter I/O parameters are set to these values.
Adapter Parameter No. Setting
23 - [DPI I/O Cfg] xxxx xxxx xxx1 1111
35 - [M-S Input] xxxx xxxx xxx1 1111
36 - [M-S Output] xxxx xxxx xxx1 1111
.
, you
2. Reset the adapter (see Resetting the Adapter
cycle the drive.
For the drive speed reference and Datalink parameter values and the
adapter setup parameter values, see Drive and Adapter Parameter
Settings on page 5-21.
on page 3-16) or power
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 70

4-24 Configuring the I/O
Creating RSLogix 5 Project, Version 7.00 or Later
T o transmit (read and write) data between the controller and dr iv e, you must
create message instructions that allocate data table addresses in the
controller for Logic Command/Status, Reference/Feedback, and Datalinks.
Note that three messages need to be configured. The timeout message has to
be executed first before the Logic Command, Reference, and Datalink In/
Out messages will work.
Select the Controller
1. Start RSLogix 5 software.
The RSLogix 5 window appears.
2. Select File > New to display the Select Processor Type screen.
3. Assign a name for the processor.
4. From the pull-down menus, choose the appropriate selections to match
your PLC-5 controller and application.
5. Click OK.
The RSLogix 5 project window appears.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 71

Configuring the I/O 4-25
Steps 2…5
Steps 6…9
Step 10
Create PLC-5 Ladder Logic for the Control Timeout
1. In the RSLogix 5 project window treeview under Program Files
double-click on LAD 2.
2. Insert a ladder rung.
3. Double-click the rung to display the rung editor.
4. Enter MSG MGxx:n, where:
xx is an unused data file number (for example, MG10:n), and
n is an unused element of the data file chosen for xx (for example, MG10:0
5. Press Enter.
6. Insert another separate rung.
7. Double-click the rung to display the rung editor.
8. Enter BST XIC MGxx:n/DN NXB XIC MGxx:n/ER BND OTU
MGxx:n/EN, where:
xx and n must correspond to the assigned data file number and element
(for example, MG10
:0) for the message created in steps 2…5.
)
Important:The information must be entered with appropriate numbers
for ‘xx’ and ‘n’ for your application, and with spaces and
forward slashes exactly as shown.
9. Press Enter.
10. In the MSG instruction (Figure 4.6
launch the message configuration screen (Figure 4.7
Figure 4.6 PLC-5 Ladder Logic for the Control Timeout
11. Configure the General tab fields by entering or verifying the
information shown in the message configuration screen.
), double-click Setup Screen to
).
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 72

4-26 Configuring the I/O
General Tab Box Setting
This PLC-5
Communication Command PLC-5 Typed Write. The controller type and command type for the controller to write the control
Data Table Address
Size in Elements
Por t Number 2. Controller port to which the network is connected.
Target Device (data for adapter/drive)
Data Table Address
MultiHop Ye s. Enables communication to allow network messaging to be routed to the adapter/drive. When
MultiHop Tab Box Setting
To Address 10.91.100.79. The IP address of the adapter connected to the drive.
(1)
For details on data table addresses for this example project, see Table 5.G…Table 5. J starting on page 5-23.
(2)
For details to determine element size for a specific drive, see Understanding Controller Data Table Addresses on page 5-22.
(3)
For details on setting the control timeout value and its function, see N-Files on page C-10. The Control Timeout (N42:3) is stored in RAM. If the
20-COMM-E adapter is power cycled, the Control Timeout Message must be re-sent. If the Control Timeout is not changed from a non-zero
value, the control message (page 4-29
(1)
(2)
(3)
Figure 4.7 PLC-5 Message Configuration Screens for the Control Timeout
timeout value to the drive.
N20:0. An unused controller data table address containing the control timeout value to be written.
1. Number of elements (words) to be transferred. Each element size is a 16-bit integer.
N42:3. Specific starting address of the destination file in the drive.
‘Yes’ is selected, a MultiHop tab appears on the message configuration screen.
) will error out.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
TIP: The Control Timeout (N42:3) must be changed to a non-zero value
(5…20 seconds recommended). If the Control Timeou t is not changed from
a non-zero value, the control message (page 4-29
Control Timeout is stored in RAM. If the adapter is power cycled, the
Control Timeout Message must be re-sent.
) will error out. The
Page 73

Configuring the I/O 4-27
Steps 1…4
Steps 5…8
Step 9
Create PLC-5 Ladder Logic for the Logic Status, Feedback, and Datalink Out
1. Insert another separate rung.
2. Double-click the rung to display the rung editor.
3. Enter MSG MGxx:n, where:
xx is an unused data file number (for example, MG11:n), and
n is an unused element of the data file chosen for xx (for example, MG11:0
4. Press Enter.
5. Insert another separate rung.
6. Double-click the rung to display the rung editor.
7. Enter BST XIC MGxx:n/DN NXB XIC MGxx:n/ER BND OTU
MGxx:n/EN, where:
xx and n must correspond to the assigned data file number and element
(for example, MG11
Important:The information must be entered with appropriate numbers
:0) for the message created in steps 1…4.
for ‘xx’ and ‘n’ for your application, and with spaces and
forward slashes exactly as shown.
)
8. Press Enter.
9. In the MSG instruction (Figure 4.8
launch the message configuration screen (Figure 4.9
Figure 4.8 PLC-5 Ladder Logic for the Logic Status, Feedback, and Datalink
Out
10. Configure the General tab fields by entering or verifying the
information shown in the message configuration screen.
), double-click Setup Screen to
).
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 74

4-28 Configuring the I/O
General Tab Box Setting
This PLC-5
Communication Command PLC-5 Typed Read. The controller type and command type for the controller to read data from the drive.
Data Table Address
Size in Elements
Port Number 2. Controller port to which the network is connected.
Target Device (data for adapter/drive)
Data Table Address
MultiHop Yes . Enables communication to allow network messaging to be routed to the adapter/drive. When ‘Yes’ is
MultiHop Tab Box Setting
To A d d r es s 10.91.100.79. The IP address of the adapter connected to the drive.
(1)
For details on data table addresses for this example project, see Table 5.G…Table 5.J starting on page 5-23.
(2)
For details to determine element size for a specific drive, see Understanding Controller Data Table Addresses on page 5-22.
(3)
For N-File details, see N-Files on page C-10.
Figure 4.9 PLC-5 Message Configuration Screens for the Logic Status,
Feedback, and Datalink Out
(1)
(2)
N20:1. An unused controller data table address containing the data to be read from the drive.
19. Number of elements (words) to be transferred. Each element size is a 16-bit integer.
(3)
N41:0. Specific starting address of the source file in the drive.
selected, a MultiHop tab appears on the message configuration screen.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 75

Configuring the I/O 4-29
Steps 1…4
Steps 5…8
Step 9
Create PLC-5 Ladder Logic for the Logic Command, Reference, and Datalink In
1. Insert another separate rung.
2. Double-click the rung to display the rung editor.
3. Enter MSG MGxx:n, where:
xx is an unused data file number (for example, MG12:n), and
n is an unused element of the data file chosen for xx (for example, MG12:0
4. Press Enter.
5. Insert another separate rung.
6. Double-click the rung to display the rung editor.
7. Enter BST XIC MGxx:n/DN NXB XIC MGxx:n/ER BND OTU
MGxx:n/EN, where:
xx and n must correspond to the assigned data file number and element
(for example, MG12
Important:The information must be entered with appropriate numbers
:0) for the message created in steps 1…4.
for ‘xx’ and ‘n’ for your application, and with spaces and
forward slashes exactly as shown.
)
8. Press Enter.
9. In the MSG instruction (Figure 4.10
launch the message configuration screen (Figure 4.11
Figure 4.10 PLC-5 Ladder Logic for the Logic Command, Reference, and
Datalink In
10. Configure the General tab fields by entering or verifying the
information shown in the message configuration screen.
), double-click Setup Screen to
).
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 76

4-30 Configuring the I/O
General Tab Box Setting
This PLC-5
Communication Command PLC-5 Typed Write. The controller type and command type for the controller to write data to the drive.
Data Table Address
Size in Elements
Por t Number 2. Controller port to which the network is connected.
Target Device (data for adapter/drive)
Data Table Address
MultiHop Ye s. Enables communication to allow network messaging to be routed to the adapter/drive. When ‘Yes’
MultiHop Tab Box Setting
To Address 10.91.100.79. The IP address of the adapter connected to the drive.
(1)
For details on data table addresses for this example project, see Table 5.G…Table 5. J starting on page 5-23.
(2)
For details to determine element size for a specific drive, see Understanding Controller Data Table Addresses on page 5-22.
(3)
For N-File details, see N-Files on page C-10.
Figure 4.11 PLC-5 Message Configuration Screens for the Logic Command,
Reference, and Datalink In
(1)
(2)
N20:20. An unused controller data table address containing the data to be written to the drive.
19. Number of elements (words) to be transferred. Each element size is a 16-bit integer.
(3)
N41:0. Specific starting address of the destination file in the drive.
is selected, a MultiHop tab appears on the message configuration screen.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
TIP: This message will error out if the Control Timeout value is not
changed from a non-zero value. See page 4-25
Control Timeout.
TIP: If the controller is controlling more than one drive, it is recommended
to intersperse the control I/O messaging for each drive to conserve network
bandwidth and decrease response time. That is, sequence the message
instructions for each drive so that its group of messages will occur at a
different time than those for another drive.
for writing a value to the
Page 77

Configuring the I/O 4-31
IP Address 10.91.100.80
SLC 500 Controller with Embedded Ethernet
IP Address 10.91.100.79
PowerFlex 70 Drive with
20-COMM-E Adapter
Computer with
Ethernet Connection
Ethernet
Switch
SLC 500 Controller Example
After the adapter is configured, the connected drive and adapter will be a
single node on the network. This section prov ides the steps needed to
configure a simple EtherNet/IP network (see Figure 4.12
we will configure a SLC 500 controller to communicate with a drive using
Logic Command/Status, Reference/Feedback, and Datalinks over the
network.
Figure 4.12 Example SLC 500 Controller EtherNet/IP Network
). In our example,
TIP: Information for PowerFlex 750-Series drives has been added to this
manual where it is applicable.
Configuring Parameters for Network I/O
Because the I/O for the driv e is mes sage-based, there is no need to conf igure
any I/O inside the RSLogix 500 project, version 7.00 or later , until using the
I/O as described in Chapter 5
Howev er, to get the adapter to operate with the I/O created in Chapter 5
need to configure the adapter to accept the I/O and drive to point to the
appropriate Datalinks.
1. Set adapter Parameters 23 - [DPI I/O Cfg], 35 - [M-S Input], and 36 [M-S Output] to values that meet your application requirements.
For this example, the adapter I/O parameters are set to these values.
Adapter Parameter No. Setting
23 - [DPI I/O Cfg] xxxx xxxx xxx1 1111
35 - [M-S Input] xxxx xxxx xxx1 1111
36 - [M-S Output] xxxx xxxx xxx1 1111
2. Reset the adapter (see Resetting the Adapter
cycle the drive.
.
on page 3-16) or power
, we
For the drive speed reference and Datalink parameter values and the
adapter setup parameter values, see Drive and Adapter Parameter
Settings on page 5-21.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 78

4-32 Configuring the I/O
Creating RSLogix 500 Project, Version 7.00 or Later
T o transmit (read and write) data between the controller and dr iv e, you must
create message instructions that allocate data table addresses in the
controller for Logic Command/Status, Reference/Feedback, and Datalinks.
Select the Controller
1. Start RSLogix 500 software.
The RSLogix 500 window appears.
2. Select File > New to display the Select Processor Type screen.
3. Assign a name for the processor.
4. In the list, select a 1747-L55x type controller.
5. Choose the appropriate selections for the fields in the screen to match
your application.
6. Click OK.
The RSLogix 500 project window appears.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 79

Configuring the I/O 4-33
Steps 6…9
Step 10
Steps 2…5
Create SLC 500 Ladder Logic for the Control Timeout
1. In the RSLogix 500 project window treeview under Program Files
double-click on LAD 2.
2. Insert a ladder rung.
3. Double-click the rung to display the rung editor.
4. Enter MSG WRITE 500CPU LOCAL Nxx:n, where:
xx is an unused data file number (for example, N10:n), and
n is an unused element of the data file chosen for xx (for example, N10:0
5. Press Enter.
6. Insert another separate rung.
7. Double-click the rung to display the rung editor.
8. Enter BST XIC Nxx:n/DN NXB XIC Nxx:n/ER BND OTU Nxx:n/
EN, where:
xx and n must correspond to the assigned data file number and element
(for example, N10
:0) for the message created in steps 2…5.
)
Important:The information must be entered with appropriate numbers
for ‘xx’ and ‘n’ for your application, and with spaces and
forward slashes exactly as shown.
9. Press Enter.
10. In the MSG instruction (Figure 4.13
launch the message configuration screen (Figure 4.14
Figure 4.13 SLC 500 Ladder Logic for the Control Timeout
), double-click Setup Screen to
).
11. Configure the General tab fields by entering or verifying the
information shown in the message configuration screen.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 80

4-34 Configuring the I/O
General Tab Box Setting
This Controller
Communication Command This setting is unavailable (grayed out) and is established when the message is created in the ladder rung.
Data Table Address
Size in Elements
Channel 1. Controller port to which the network is connected.
Target Device (data for adapter/drive)
Message Timeout 5. Message timeout duration in seconds.
Data Table Address
MultiHop Yes. Enables communication to allow network messaging to be routed to the adapter/drive. When ‘Yes’ is
MultiHop Tab Box Setting
To Address 10.91.100.79. The IP address of the adapter connected to the drive.
(1)
For details on data table addresses for this example project, see Table 5.G…Tabl e 5 . J starting on page 5-23.
(2)
For details to determine element size for a specific drive, see Understanding Controller Data Table Addresses on page 5-22.
(3)
For details on setting the control timeout value and its function, see N-Files on page C-10. The Control Timeout (N42:3) is stored in RAM. If the
20-COMM-E adapter is power cycled, the Control Timeout Message must be re-sent. If the Control Timeout is not changed from a non-zero value, the
control message (page 4-37
Figure 4.14 SLC 500 Message Configuration Screens for the Control Timeout
(1)
(2)
N20:0. An unused controller data table address containing the control timeout value to be written.
1. Number of elements (words) to be transferred. Each element size is a 16-bit integer.
(3)
N42:3. Specific starting address of the destination file in the drive.
selected, a MultiHop tab appears on the message configuration screen.
) will error out.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
TIP: The Control Timeout (N42:3) must be changed to a non-zero value
(5…20 seconds recommended). If the Control Timeou t is not changed from
a non-zero value, the control message (page 4-37
Control Timeout is stored in RAM. If the adapter is power cycled, the
Control Timeout Message must be re-sent.
) will error out. The
Page 81

Configuring the I/O 4-35
Steps 1…4
Steps 5…8
Step 9
Create SLC 500 Ladder Logic for the Logic Status, Feedback, and Datalink Out
1. Insert another separate rung.
2. Double-click the rung to display the rung editor.
3. Enter MSG READ 500CPU LOCAL Nxx:n, where:
xx is an unused data file number (for example, N11:n), and
n is an unused element of the data file chosen for xx (for example, N11:0
4. Press Enter.
5. Insert another separate rung.
6. Double-click the rung to display the rung editor.
7. Enter BST XIC Nxx:n/DN NXB XIC Nxx:n/ER BND OTU Nxx:n/
EN, where:
xx and n must correspond to the assigned data file number and element
(for example, N11
Important:The information must be entered with appropriate numbers
:0) for the message created in steps 1…4.
for ‘xx’ and ‘n’ for your application, and with spaces and
forward slashes exactly as shown.
)
8. Press Enter.
9. In the MSG instruction (Figure 4.15
launch the message configuration screen (Figure 4.16
Figure 4.15 SLC 500 Ladder Logic for the Logic Status, Feedback, and Datalink Out
10. Configure the General tab fields by entering or verifying the
information shown in the message configuration screen.
), double-click Setup Screen to
).
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 82

4-36 Configuring the I/O
General Tab Box Setting
This Controller
Communication Command This setting is unavailable (grayed out) and is established when the message is created in the ladder rung.
Data Table Address
Size in Elements
Channel 1. Controller port to which the network is connected.
Target Device (data for adapter/drive)
Message Timeout 5. Message timeout duration in seconds.
Data Table Address
MultiHop Ye s. Enables communication to allow network messaging to be routed to the adapter/drive. When ‘Yes’ is
MultiHop Tab Box Setting
To Address 10.91.100.79. The IP address of the adapter connected to the drive.
(1)
For details on data table addresses for this example project, see Table 5.G…Table 5.J starting on page 5-23.
(2)
For details to determine element size for a specific drive, see Understanding Controller Data Table Addresses on page 5-22.
(3)
For N-File details, see N-Files on page C-10.
Figure 4.16 SLC 500 Message Configuration Screens for the Logic Status,
Feedback, and Datalink Out
(1)
(2)
N20:1. An unused controller data table address containing the data to be read from the drive.
19. Number of elements (words) to be transferred. Each element size is a 16-bit integer.
(3)
N41:0. Specific starting address of the source file in the drive.
selected, a MultiHop tab appears on the message configuration screen.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 83

Configuring the I/O 4-37
Steps 1…4
Steps 5…8
Step 9
Create SLC 500 Ladder Logic for the Logic Command, Reference, and Datalink In
1. Insert another separate rung.
2. Double-click the rung to display the rung editor.
3. Enter MSG WRITE 500CPU LOCAL Nxx:n, where:
xx is an unused data file number (for example, N12:n), and
n is an unused element of the data file chosen for xx (for example, N12:0
4. Press Enter.
5. Insert another separate rung.
6. Double-click the rung to display the rung editor.
7. Enter BST XIC Nxx:n/DN NXB XIC Nxx:n/ER BND OTU Nxx:n/
EN, where:
xx and n must correspond to the assigned data file number and element
(for example, N12
Important:The information must be entered with appropriate numbers
:0) for the message created in steps 1…4.
for ‘xx’ and ‘n’ for your application, and with spaces and
forward slashes exactly as shown.
)
8. Press Enter.
9. In the MSG instruction (Figure 4.17
launch the message configuration screen (Figure 4.18
Figure 4.17 SLC 500 Ladder Logic for the Logic Command, Reference, and
Datalink In
10. Configure the General tab field by entering or verifying the information
shown in the message configuration screen.
), double-click Setup Screen to
).
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 84

4-38 Configuring the I/O
General Tab Box Setting
This Controller
Communication Command This setting is unavailable (grayed out) and is established when the message is created in the ladder rung.
Data Table Address
Size in Elements
Channel 1. Controller port to which the network is connected.
Target Device (data for adapter/drive)
Message Timeout 5. Message timeout duration in seconds.
Data Table Address
MultiHop Yes. Enables communication to allow network messaging to be routed to the adapter/drive. When ‘Yes’ is
MultiHop Tab Box Setting
To A d d r es s 10.91.100.79. The IP address of the adapter connected to the drive.
(1)
For details on data table addresses for this example project, see Table 5.G…Table 5.J starting on page 5-23.
(2)
For details to determine element size for a specific drive, see Understanding Controller Data Table Addresses on page 5-22.
(3)
For N-File details, see N-Files on page C-10.
Figure 4.18 SLC 500 Message Configuration Screens for the Logic Command,
Reference, and Datalink In
(1)
(2)
N20:20. An unused controller data table address containing the data to be written to the drive.
19. Number of elements (words) to be transferred. Each element size is a 16-bit integer.
(3)
N41:0. Specific starting address of the destination file in the drive.
selected, a MultiHop tab appears on the message configuration screen.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
TIP: This message will error out if the Control Timeout value is not
changed from a non-zero value. Refer to page 4-33
Control Timeout.
TIP: If the controller is controlling more than one drive, it is recommended
to intersperse the control I/O messaging for each drive to conserve network
bandwidth and decrease response time. That is, sequence the message
instructions for each drive so that its group of messages will occur at a
different time than those for another drive.
for writing a value to the
Page 85

Configuring the I/O 4-39
IP Address 10.91.100.81
MicroLogix 1100/1400 Controller
IP Address 10.91.100.79
PowerFlex 70 Drive with
20-COMM-E Adapter
Computer with
Ethernet Connection
Ethernet
Switch
MicroLogix 1100/1400 Controller Example
After the adapter is configured, the connected drive and adapter will be a
single node on the network. This section prov ides the steps needed to
configure a simple EtherNet/IP network (see Figure 4.19
we will configure a MicroLogix 1100 controller to communicate with a
drive using Logic Command/Status, Reference/Feedback, and Datalinks
over the network.
Figure 4.19 Example MicroLogix 1100/1400 Controller EtherNet/IP Network
). In our example,
TIP: Information for PowerFlex 750-Series drives has been added to this
manual where it is applicable.
Configuring Parameters for Network I/O
Because the I/O for the driv e is mes sage-based, there is no need to conf igure
any I/O inside the RSLogix 500 project, version 7.00 or later , until using the
I/O as described in Chapter 5
Howev er, to get the adapter to operate with the I/O created in Chapter 5
need to configure the adapter to accept the I/O and drive to point to the
appropriate Datalinks.
1. Set adapter Parameters 23 - [DPI I/O Cfg], 35 - [M-S Input], and 36 [M-S Output] to values that meet your application requirements.
For this example, the adapter I/O parameters are set to these values.
Adapter Parameter No. Setting
23 - [DPI I/O Cfg] xxxx xxxx xxx1 1111
35 - [M-S Input] xxxx xxxx xxx1 1111
36 - [M-S Output] xxxx xxxx xxx1 1111
2. Reset the adapter (see Resetting the Adapter
cycle the drive.
.
on page 3-16) or power
, we
For the drive speed reference and Datalink parameter values and the
adapter setup parameter values, refer to Drive and Adapter Parameter
Settings on page 5-21.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 86

4-40 Configuring the I/O
Creating RSLogix 500 Project, Version 7.00 or Later
To transmit (read and write) data between the controller and drive, you must
create message instructions that allocate data table addresses in the controller
for Logic Command/Status, Reference/Feedback, and Datalinks.
Select the Controller
1. Start RSLogix 500 software.
The RSLogix 500 window appears.
2. Select File > New to display the Select Processor Type screen.
3. Assign a name for the processor.
4. In the list, select the MicroLogix 1100 controller.
5. Choose the appropriate selections for the fields in the screen to match
your application.
6. Click OK.
The RSLogix 500 project window appears.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 87

Configuring the I/O 4-41
Steps 2…5
Steps 6…9
Step 10
Create MicroLogix 1100/1400 Ladder Logic for the Control Timeout
1. In the RSLogix 500 project window treeview under Program Files
double-click on LAD 2.
2. Insert a ladder rung.
3. Double-click the rung to display the rung editor.
4. Enter MSG MGxx:n, where:
xx is an unused data file number (for example, MG10:n), and
n is an unused element of the data file chosen for xx (for example, MG10:0
5. Press Enter.
6. Insert another separate rung.
7. Double-click the rung to display the rung editor.
8. Enter BST XIC MGxx:n/DN NXB XIC MGxx:n/ER BND OTU
MGxx:n/EN, where:
xx and n must correspond to the assigned data file number and element
(for example, MG10
:0) for the message created in steps 2…5.
)
Important:The information must be entered with appropriate numbers
for ‘xx’ and ‘n’ for your application, and with spaces and
forward slashes exactly as shown.
9. Press Enter.
10. In the MSG instruction (Figure 4.20
launch the message configuration screen (Figure 4.21
Figure 4.20 MicroLogix 1100/1400 Ladder Logic for the Control Timeout
11. Configure the General tab fields by entering or verifying the
information shown in the message configuration screen.
), double-click Setup Screen to
).
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 88

4-42 Configuring the I/O
General Tab Box Setting
This Controller (data for MicroLogix 1100 controller)
Channel 1 (integral). Controller port to which the network is connected.
Communication Command 500CPU Write. The controller type and command type for the controller to read or write data. Because
Data Table Address
Size in Elements
Target Device (data for adapter/drive)
Message Timeout 5. Message timeout duration in seconds.
Data Table Address
Routing Information File RI9:0. An unused routing information file for the controller.
MultiHop Tab Box Setting
To Address 10.91.100.79. The IP address of the adapter connected to the drive.
(1)
For details on data table addresses for this example project, see Ta bl e 5 . G …Table 5.J starting on page 5-23.
(2)
For details to determine element size for a specific drive, see Understanding Controller Data Table Addresses on page 5-22.
(3)
For details on setting the control timeout value and its function, see N-Files on page C-10. The Control Timeout (N42:3) is stored in RAM. If the
20-COMM-E adapter is power cycled, the Control Timeout Message must be re-sent. If the Control Timeout is not changed from a non-zero value, the
control message (page 4-45
Figure 4.21 MicroLogix 1100/1400 Message Configuration Screens for the
Control Timeout
the MicroLogix 1100 controller is part of the SLC-500 controller family, the ‘500CPU’ controller type
was selected. The ‘Write’ command type was selected to write the control timeout value to the drive.
(1)
(2)
(3)
N20:0. An unused controller data table address containing the control timeout value to be written.
1. Number of elements (words) to be transferred. Each element size is a 16-bit integer.
N42:3. Specific starting address of the destination file in the drive.
) will error out.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
TIP: The Control Timeout (N42:3) must be changed to a non-zero value
(5…20 seconds recommended). If the Control Timeou t is not changed from
a non-zero value, the control message (page 4-45
Control Timeout is stored in RAM. If the adapter is power cycled, the
Control Timeout Message must be re-sent.
) will error out. The
Page 89

Configuring the I/O 4-43
Steps 1…4
Steps 5…8
Step 9
Create MicroLogix 1100/1400 Ladder Logic for the Logic Status, Feedback, and
Datalink Out
1. Insert another separate rung.
2. Double-click the rung to display the rung editor.
3. Enter MSG MGxx:n, where:
xx is an unused data file number (for example, MG11:n), and
n is an unused element of the data file chosen for xx (for example, MG11:0
4. Press Enter.
5. Insert another separate rung.
6. Double-click the rung to display the rung editor.
7. Enter BST XIC MGxx:n/DN NXB XIC MGxx:n/ER BND OTU
MGxx:n/EN, where:
xx and n must correspond to the assigned data file number and element
(for example, MG11
Important:The information must be entered with appropriate numbers
:0) for the message created in steps 1…4.
for ‘xx’ and ‘n’ for your application, and with spaces and
forward slashes exactly as shown.
)
8. Press Enter.
9. In the MSG instruction (Figure 4.22
launch the message configuration screen (Figure 4.23
Figure 4.22 MicroLogix 1100/1400 Ladder Logic for the Logic Status, Feedback,
and Datalink Out
10. Configure the General tab fields by entering or verifying the
information shown in the message configuration screen.
), double-click Setup Screen to
).
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 90

4-44 Configuring the I/O
General Tab Box Setting
This Controller (data for MicroLogix 1100 controller)
Channel 1 (integral). Controller port to which the network is connected.
Communication Command 500CPU Read. The controller type and command type for the controller to read or write data.
Data Table Address
Size in Elements
Target Device (data for adapter/drive)
Message Timeout 5. Message timeout duration in seconds.
Data Table Address
Routing Information File RI9:1. An unused routing information file for the controller.
MultiHop Tab Box Setting
To Address 10.91.100.79. The IP address of the adapter connected to the drive.
(1)
For details on data table addresses for this example project, see Table 5.G…Table 5. J starting on page 5-23.
(2)
For details to determine element size for a specific drive, see Understanding Controller Data Table Addresses on page 5-22.
(3)
For N-File details, see N-Files on page C-10.
(1)
(2)
(3)
Figure 4.23 MicroLogix 1100/1400 Message Configuration Screens for the Logic
Status, Feedback, and Datalink Out
Because the MicroLogix 1100 controller is part of the SLC-500 controller family, the ‘500CPU’
controller type was selected. The ‘Read’ command type was selected to read data from the drive.
N20:1. An unused controller data table address containing the data to be read from the drive.
19. Number of elements (words) to be transferred. Each element size is a 16-bit integer.
N41:0. Specific starting address of the source file in the drive.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 91

Configuring the I/O 4-45
Steps 1…4
Steps 5…8
Step 9
Create MicroLogix 1100/1400 Ladder Logic for the Logic Command, Reference, and
Datalink In
1. Insert another separate rung.
2. Double-click the rung to display the rung editor.
3. Enter MSG MGxx:n, where:
xx is an unused data file number (for example, MG12:n), and
n is an unused element of the data file chosen for xx (for example, MG12:0
4. Press Enter.
5. Insert another separate rung.
6. Double-click the rung to display the rung editor.
7. Enter BST XIC MGxx:n/DN NXB XIC MGxx:n/ER BND OTU
MGxx:n/EN, where:
xx and n must correspond to the assigned data file number and element
(for example, MG12
Important:The information must be entered with appropriate numbers
:0) for the message created in steps 1…4.
for ‘xx’ and ‘n’ for your application, and with spaces and
forward slashes exactly as shown.
)
8. Press Enter.
9. In the MSG instruction (Figure 4.24
launch the message configuration screen (Figure 4.25
Figure 4.24 MicroLogix 1100/1400 Ladder Logic for the Logic Command,
Reference, and Datalink In
10. Configure the General tab fields by entering or verifying the
information shown in the message configuration screen.
), double-click Setup Screen to
).
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 92

4-46 Configuring the I/O
General Tab Box Setting
This Controller (data for MicroLogix 1100 controller)
Channel 1 (integral). Controller port to which the network is connected.
Communication Command 500CPU Write. The controller type and command type for the controller to read or write data.
Data Table Address
Size in Elements
Target Device (data for adapter/drive)
Message Timeout 5. Message timeout duration in seconds.
Data Table Address
Routing Information File RI9:2. An unused routing information file for the controller.
MultiHop Tab Box Setting
To Address 10.91.100.79. The IP address of the adapter connected to the drive.
(1)
For details on data table addresses for this example project, see Table 5.G…Table 5.J starting on page 5-23.
(2)
For details to determine element size for a specific drive, see Understanding Controller Data Table Addresses on page 5-22.
(3)
For N-File details, see N-Files on page C-10.
(2)
Figure 4.25 MicroLogix 1100/1400 Message Configuration Screens for the Logic
Command, Reference, and Datalink In
Because the MicroLogix 1100 controller is part of the SLC-500 controller family, the ‘500CPU’
controller type was selected. The ‘Write’ command type was selected to write data to the drive.
(1)
(3)
N20:20. An unused controller data table address containing the data to be written to the drive.
19. Number of elements (words) to be transferred. Each element size is a 16-bit integer.
N41:0. Specific starting address of the destination file in the drive.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
TIP: This message will error out if the Control Timeout value is not
changed from a non-zero value. Refer to page 4-41
Control Timeout.
TIP: If the controller is controlling more than one drive, it is recommended
to intersperse the control I/O messaging for each drive to conserve network
bandwidth and decrease response time. That is, sequence the message
instructions for each drive so that its group of messages will occur at a
different time than those for another drive.
for writing a value to the
Page 93

Chapter 5
!
Using the I/O
This chapter provides information and examples that explain how to
control, configure, and monitor a PowerFlex 7-Class drive using the
configured I/O.
Topic Page
About I/O Messaging
Understanding the I/O Image 5-2
Using Logic Command/Status 5-6
Using Reference/Feedback 5-6
Using Datalinks 5-9
Example Ladder Logic Program Information 5-11
ControlLogix Controller Example 5-11
PLC-5, SLC 500, or MicroLogix 1100/1400 Controller Example 5-21
5-1
About I/O Messaging
ATTENTION: Risk of injury or equipment damage exists. The
examples in this publication are intended solely for purposes of
example. There are many variables and requirements with any
application. Rockwell Automation does not assume responsibility
or liability (to include intellectual property liability) for actual
use of the examples shown in this publication.
On CIP-based networks, including EtherNet/IP, I/O connections are used to
transfer the data which controls the PowerFlex drive and sets its Reference.
I/O can also be used to transfer data to and from Datalinks in PowerFlex
7-Class drives.
The adapter provides many opti ons for conf iguring and using I/O, including
the following:
• Configuring the size of I/O by enabling or disabling the Logic
Command/Reference and Datalinks.
• Setting a Master-Slave or Peer-to-Peer hierarchy.
Chapter 3
discuss how to configure the adapter and controller on the network for these
options. The Glossary
how to use I/O after you have configured the adapter and controller.
, Configuring the Adapter, and Chapter 4, Configuring the I/O,
defines the different options. This chapter discusses
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 94

5-2 Using the I/O
Understanding the I/O Image
The terms ‘input’ and ‘output’ are defined from the controller’s point of
view. Therefore, output I/O is data that is produced by the controller and
consumed by the adapter. Input I/O is status data that is produced by the
adapter and consumed as input by the controller. The I/O image will vary
based on the following:
• Size (either 16-bit or 32-bit) of the Reference/Feedback words and
Datalink words used by the drive. To determine the size of the
Reference/Feedback and Datalinks, view adapter Parameters 18 - [Ref/
Fdbk Size] and 19 - [Datalink Size]. For information to access
parameters, see Using the PowerFlex 7-Class HIM to Access
Parameters on page 3-2.
• Configuration of I/O (Parameter 23 - [DPI I/O Cfg]). If all I/O is not
enabled, the image is truncated. The image always uses consecutive
words starting at word 0.
• ControlLogix/CompactLogix Contr o llers only—The drive prof i le
used in RSLogix 5000 software (driv e Add-on Prof ile in ve rsion 16.00 or
later, Classic Profile in versions 13.00…15.00, or Generic Profile in all
versions).
ControlLogix Controller Image
Because the drive Add-on Profile in RSLogix 5000 software, version 16.00
or later, and the Classic Profile, versions 13.00…15.00, provide descriptive
controller tags, the I/O image (tag size and location) is automatically
configured based on the drive being used. When using the Generic Profile
(page 4-16
descriptive or defined.
) in RSLogix 5000 software, however, controller tags are not
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
The ControlLogix controller I/O image changes depending on the size of
the drive’s Reference/Feedback and Datalinks, and the number of Datalinks
used. Table 5.A
various PowerFlex drives, and all Datalinks enabled.
, Table 5.B, and Table 5.C show the I/O image when using
Page 95

Using the I/O 5-3
Table 5.A ControlLogix Controller I/O Image for Drives with 16-bit Reference/
Feedback and 16-bit Datalinks – Using Generic Profile
These products include the following:
• PowerFlex 70 drives with standard or enhanced control • SMC Flex smart motor controllers
• PowerFlex 700 drives with standard control • SMC-50 smart motor controllers
• PowerFlex 700H drives
Word Output I/O Word Input I/O
0 Logic Command 0 Pad Word
1 Reference 1 Pad Word
2 Datalink In A1 2 Logic Status
3 Datalink In A2 3 Feedback
4 Datalink In B1 4 Datalink Out A1
5 Datalink In B2 5 Datalink Out A2
6 Datalink In C1 6 Datalink Out B1
7 Datalink In C2 7 Datalink Out B2
8 Datalink In D1 8 Datalink Out C1
9 Datalink In D2 9 Datalink Out C2
10 Datalink Out D1
11 Datalink Out D2
Table 5.B ControlLogix Controller I/O Image for Drives with 16-bit Reference/
Feedback and 32-bit Datalinks – Using Generic Profile
These products include the following:
• PowerFlex 700 drives with vector control • PowerFlex Digital DC drives
• PowerFlex 700L drives with 700 control
Word Output I/O Word Input I/O
0 Logic Command 0 Pad Word
1 Reference 1 Pad Word
2 Datalink In A1 (LSW) 2 Logic Status
3 Datalink In A1 (MSW) 3 Feedback
4 Datalink In A2 (LSW) 4 Datalink Out A1 (LSW)
5 Datalink In A2 (MSW) 5 Datalink Out A1 (MSW)
6 Datalink In B1 (LSW) 6 Datalink Out A2 (LSW)
7 Datalink In B1 (MSW) 7 Datalink Out A2 (MSW)
8 Datalink In B2 (LSW) 8 Datalink Out B1 (LSW)
9 Datalink In B2 (MSW) 9 Datalink Out B1 (MSW)
10 Datalink In C1 (LSW) 10 Datalink Out B2 (LSW)
11 Datalink In C1 (MSW) 11 Datalink Out B2 (MSW)
12 Datalink In C2 (LSW) 12 Datalink Out C1 (LSW)
13 Datalink In C2 (MSW) 13 Datalink Out C1 (MSW)
14 Datalink In D1 (LSW) 14 Datalink Out C2 (LSW)
15 Datalink In D1 (MSW) 15 Datalink Out C2 (MSW)
16 Datalink In D2 (LSW) 16 Datalink Out D1 (LSW)
17 Datalink In D2 (MSW) 17 Datalink Out D1 (MSW)
18 Datalink Out D2 (LSW)
19 Datalink Out D2 (MSW)
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 96

5-4 Using the I/O
Table 5.C ControlLogix Controller I/O Image for Drives with 32-bit Reference/
Feedback and 32-bit Datalinks – Using Generic Profile
These products include the following:
• PowerFlex 700S drives with Phase I or Phase II control • PowerFlex 753 drives
• PowerFlex 700L drives with 700S control • PowerFlex 755 drives
Word Output I/O Word Input I/O
0 Logic Command 0 Pad Word
1 Not Used 1 Pad Word
2 Reference (LSW) 2 Logic Status
3 Reference (MSW) 3 Not Used
4 Datalink In A1 (LSW) 4 Feedback (LSW)
5 Datalink In A1 (MSW) 5 Feedback (MSW)
6 Datalink In A2 (LSW) 6 Datalink Out A1 (LSW)
7 Datalink In A2 (MSW) 7 Datalink Out A1 (MSW)
8 Datalink In B1 (LSW) 8 Datalink Out A2 (LSW)
9 Datalink In B1 (MSW) 9 Datalink Out A2 (MSW)
10 Datalink In B2 (LSW) 10 Datalink Out B1 (LSW)
11 Datalink In B2 (MSW) 11 Datalink Out B1 (MSW)
12 Datalink In C1 (LSW) 12 Datalink Out B2 (LSW)
13 Datalink In C1 (MSW) 13 Datalink Out B2 (MSW)
14 Datalink In C2 (LSW) 14 Datalink Out C1 (LSW)
15 Datalink In C2 (MSW) 15 Datalink Out C1 (MSW)
16 Datalink In D1 (LSW) 16 Datalink Out C2 (LSW)
17 Datalink In D1 (MSW) 17 Datalink Out C2 (MSW)
18 Datalink In D2 (LSW) 18 Datalink Out D1 (LSW)
19 Datalink In D2 (MSW) 19 Datalink Out D1 (MSW)
20 Datalink Out D2 (LSW)
21 Datalink Out D2 (MSW)
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
PLC-5, SLC 500, or MicroLogix 1100/1400 Controller Image
The I/O image for these controllers always has 19 words of output and 19
words of input. Howe ver, depending on the size of the drive’s Reference/
Feedback and Datalinks, and the number of Datalinks used, specific words
in the I/O image may not be used. Table 5.D
the I/O image when using various PowerFlex drives, and all Datalinks
enabled.
, Table 5.E, and Tabl e 5.F show
Page 97

Using the I/O 5-5
Table 5.D PLC-5, SLC 500, or MicroLogix 1100/1400 Controller I/O Image for Drives
with 16-bit Reference/Feedback and 16-bit Datalinks
These products include the following:
• PowerFlex 70 drives with standard or enhanced control • SMC Flex smart motor controllers
• PowerFlex 700 drives with standard control • SMC-50 smart motor controllers
• PowerFlex 700H drives
Word Output I/O Word Input I/O
0 Logic Command 0 Logic Status
1 Not used 1 Not used
2 Reference (MSW) 2 Feedback (MSW)
3 Not used 3 Not used
4 Datalink In A1 (MSW) 4 Datalink Out A1 (MSW)
5 Not used 5 Not used
6 Datalink In A2 (MSW) 6 Datalink Out A2 (MSW)
7 Not used 7 Not used
8 Datalink In B1 (MSW) 8 Datalink Out B1 (MSW)
9 Not used 9 Not used
10 Datalink In B2 (MSW) 10 Datalink Out B2 (MSW)
11 Not used 11 Not used
12 Datalink In C1 (MSW) 12 Datalink Out C1 (MSW)
13 Not used 13 Not used
14 Datalink In C2 (MSW) 14 Datalink Out C2 (MSW)
15 Not used 15 Not used
16 Datalink In D1 (MSW) 16 Datalink Out D1 (MSW)
17 Not used 17 Not used
18 Datalink In D2 (MSW) 18 Datalink Out D2 (MSW)
Table 5.E PLC-5, SLC 500, or MicroLogix 1100/1400 Controller I/O Image for Drives
with 16-bit Reference/Feedback and 32-bit Datalinks
These products include the following:
• PowerFlex 700 drives with vector control • PowerFlex Digital DC drives
• PowerFlex 700L drives with 700 control
Word Output I/O Word Input I/O
0 Logic Command 0 Logic Status
1 Not used 1 Not used
2 Reference (MSW) 2 Feedback (MSW)
3 Datalink In A1 (LSW) 3 Datalink Out A1 (LSW)
4 Datalink In A1 (MSW) 4 Datalink Out A1 (MSW)
5 Datalink In A2 (LSW) 5 Datalink Out A2 (LSW)
6 Datalink In A2 (MSW) 6 Datalink Out A2 (MSW)
7 Datalink In B1 (LSW) 7 Datalink Out B1 (LSW)
8 Datalink In B1 (MSW) 8 Datalink Out B1 (MSW)
9 Datalink In B2 (LSW) 9 Datalink Out B2 (LSW)
10 Datalink In B2 (MSW) 10 Datalink Out B2 (MSW)
11 Datalink In C1 (LSW) 11 Datalink Out C1 (LSW)
12 Datalink In C1 (MSW) 12 Datalink Out C1 (MSW)
13 Datalink In C2 (LSW) 13 Datalink Out C2 (LSW)
14 Datalink In C2 (MSW) 14 Datalink Out C2 (MSW)
15 Datalink In D1 (LSW) 15 Datalink Out D1 (LSW)
16 Datalink In D1 (MSW) 16 Datalink Out D1 (MSW)
17 Datalink In D2 (LSW) 17 Datalink Out D2 (LSW)
18 Datalink In D2 (MSW) 18 Datalink Out D2 (MSW)
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 98

5-6 Using the I/O
Table 5.F PLC-5, SLC 500, or MicroLogix 1100/1400 Controller I/O Image for Drives
with 32-bit Reference/Feedback and 32-bit Datalinks
These products include the following:
• PowerFlex 700S drives with Phase I or Phase II control • PowerFlex 753 drives
• PowerFlex 700L drives with 700S control • PowerFlex 755 drives
Word Output I/O Word Input I/O
0 Logic Command 0 Logic Status
1 Reference (LSW) 1 Feedback (LSW)
2 Reference (MSW) 2 Feedback (MSW)
3 Datalink In A1 (LSW) 3 Datalink Out A1 (LSW)
4 Datalink In A1 (MSW) 4 Datalink Out A1 (MSW)
5 Datalink In A2 (LSW) 5 Datalink Out A2 (LSW)
6 Datalink In A2 (MSW) 6 Datalink Out A2 (MSW)
7 Datalink In B1 (LSW) 7 Datalink Out B1 (LSW)
8 Datalink In B1 (MSW) 8 Datalink Out B1 (MSW)
9 Datalink In B2 (LSW) 9 Datalink Out B2 (LSW)
10 Datalink In B2 (MSW) 10 Datalink Out B2 (MSW)
11 Datalink In C1 (LSW) 11 Datalink Out C1 (LSW)
12 Datalink In C1 (MSW) 12 Datalink Out C1 (MSW)
13 Datalink In C2 (LSW) 13 Datalink Out C2 (LSW)
14 Datalink In C2 (MSW) 14 Datalink Out C2 (MSW)
15 Datalink In D1 (LSW) 15 Datalink Out D1 (LSW)
16 Datalink In D1 (MSW) 16 Datalink Out D1 (MSW)
17 Datalink In D2 (LSW) 17 Datalink Out D2 (LSW)
18 Datalink In D2 (MSW) 18 Datalink Out D2 (MSW)
Using Logic Command/ Status
Using Reference/Feedback
The Logic Command is a 16-bit word of control data produced by the
controller and consumed by the adapter. The Logic Status is a 16-bit word
of status data produced by the adapter and consumed by the controller.
PowerFlex 750-Series drives have a 32-bit Logic Command/Status—but
when using a 20-COMM-E adapter, only the first 16 bits can be used.
This manual contains the bit definitions for most compatible products
available at the time of publication in Appendix
Words. For other products, see their documentation.
The Reference is produced by the controller and consumed by the adapter.
The Feedback is produced by the adapter and consumed by the controller.
The size of the Reference/Feedback is determined by the drive and
displayed with adapter Parameter 18 - [Ref/Fdbk Size].
Size Valid Values
16-bit -32768 to 32767
32-bit -2147483648 to 2147483647
When the Reference and Feedback are enabled and a ControlLogix
controller with a drive Add-on Profile or Classic Profile is used, specific
controller tags are automatically created, sized (16-bit or 32-bit), and placed
in the I/O image.
D, Logic Command/Status
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 99

Using the I/O 5-7
0
0 Hz
Par. 82 - [Maximum Speed]
130 Hz
90 Hz
60 Hz
327672268515123
Scaling = (Parameter 82 ÷ Parameter 55) * 32767
PowerFlex 70/700/700H and PowerFlex 700L Drives with 700 Control
The Reference/Feedback value is a scaled engineering value; it is not in
Hertz or RPM. The Reference uses a ‘32767’ scale. The ‘32767’ endpoint
of the scale is equal to the value of drive parameter 55 - [Maximum Freq],
which has a default value of 130 Hz. For these drives, default scaling is
0…15123 which is equal to 0…60.0 Hz. This is based on the formula
shown below. Reference/Feedback scaling is limited by drive parameter 82 [Maximum Speed]. If the default value of 60 Hz. for parameter 82 [Maximum Speed] is changed, the speed Reference/Feedback scaling also
changes. To determine Refe rence/Feedback scaling, use the following
formula:
(Parameter 82 ÷ Parameter 55) * 32767 = Scaling
Using drive parameter 82 and 55 default values, speed Reference/Feedback
scaling is:
(60 Hz ÷ 130 Hz) * 32767 = 15123
Therefore, 0…15123 = 0…60.0 Hz.
If parameter 82 - [Maximum Speed] is changed to 90 Hz, then:
(90 Hz ÷ 130 Hz) * 32767 = 22685
Therefore, 0…22685 = 0…90.0 Hz.
A graphic representation of this Reference/Feedback scaling is shown below.
For PowerFlex 70 drives with enhanced control, firmware 2.xxx or later, or
PowerFlex 700 drives with vector control, firmware 3.xxx or later, drive
parameter 298 - [DPI Ref Select] was added to simplify scaling for the
speed Reference/Feedback. When drive parameter 298 - [DPI Ref Select] is
set to its default ‘0’ (Max Freq), the speed Reference/Feedback scaling is as
shown above. However, when parameter 298 - [DPI Ref Select] is set to ‘1’
(Max Speed), the speed Reference/Feedback scaling is equal to parameter
82 - [Max Speed]:
Parameter 82 = Scaling
Using the parameter 82 default value, speed Reference/Feedback scaling is:
0…32767 = 0…60.0 Hz.
If parameter 82 - [Maximum Speed] is changed to 90 Hz, then:
90 Hz = 32767
Speed Feedback uses the same scaling as the speed Reference.
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
Page 100

5-8 Using the I/O
TIP: For PowerFlex 7 00 driv es with vector control, f irmware 3.xxx or later ,
parameter 299 - [DPI Fdbk Select] enables you to select the feedback data
coming from the drive o v er DPI. The def ault is ‘Speed Fdbk’ in Hz or RPM
determined by parameter 079 - [Speed Units]. The data selection for
parameter 299 is also displayed on the 1st line of the HIM and on
DriveExplorer and DriveE xecutive software screens in the drive status area
of the screen.
PowerFlex 700S and PowerFlex 700L Drives with 700S Control
The Reference/Feedback value is:
32767 = Base Motor Speed
The base speed is set using drive parameter 4 - [Motor RPM]. To set a speed
Reference/Feedback above base speed, a value greater than 32767 must be
entered.
For 16-bit processors, such as PLC-5 and SLC 500 controllers, the data
requires manipulation to set a speed Reference above 32767 or below
-32767. Please see the PowerFlex 700S AC Drives Phase II Control
Reference Manual, publication PFLEX-RM003, in the Chapter 1
‘Communications’ section. Then go to the ‘PLC 5 or SLC System’
subsection and see the ‘Reference/Feedback Programming’ sub-subsection.
PowerFlex 753/755 Drives
The Reference/Feedback value is Hz x 1000 or RPM x 1000. Drive
parameter 300 - [Speed Units] determines whether the scaling is Hz or
RPM. The default scaling is Hz, where 0…60,000 equates to 0…6 0.000 Hz.
When parameter 300 is set to RPM, then 0…1,765,000 equates to
0…1765.000 RPM.
For 16-bit processors, such as PLC-5 and SLC 500 controllers, the data
requires manipulation to set a speed Reference above 32767 or below
-32767. Please see the PowerFlex 700S AC Drives Phase II Control
Reference Manual, publication PFLEX-RM003, in the Chapter 1
‘Communications’ section. Then go to the ‘PLC 5 or SLC System’
subsection and see the ‘Reference/Feedback Programming’ sub-subsection.
PowerFlex Digital DC Drives
The Reference/Feedback value is:
25000 = Maximum Reference Speed
The maximum Reference speed is set using drive parameter 45 - [Max Ref
Speed].
20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM010G-EN-P
 Loading...
Loading...