
SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA
2–1
REV 3
Motorola, Inc. 1996
5/95
The MC10E/100E431 is a 3-bit flip-flop with differential clock, data
input and data output.
The asynchronous Set and Reset controls are edge-triggered rather
than level controlled. This allows the user to rapidly set or reset the
flip-flop and then continue clocking at the next clock edge, without the
necessity of de-asserting the set/reset signal (as would be the case with a
level controlled set/reset).
The E431 is also designed with larger internal swings, an approach
intended to minimize the time spent crossing the threshold region and
thus reduce the metastability susceptibility window.
The differential input structures are clamped so that the inputs of
unused registers can be left open without upsetting the bias network of
the device. The clamping action will assert the D
and the CLK sides of the
inputs. Because of the edge triggered flip-flop nature of the device
simultaneously opening both the clock and data inputs will result in an
output which reaches an unidentified but valid state. Note that the input
clamps only operate when both inputs fall to 2.5V below VCC.
• Edge-Triggered Asynchronous Set and Reset
• Differential D, CLK and Q; V
BB
Reference Available
• 1100MHz Min. Toggle Frequency
• Extended 100E V
EE
Range of – 4.2V to – 5.46V
PIN NAMES
Pin Function
D[0:2], D[0:2] Differential Data Inputs
CLK[0:2], CLK[0:2] Differential Clock
S[0:2] Edge Triggered Set Inputs
R[0:2] Edge Triggered Reset Input
V
BB
VBB Reference Output
Q[0:2], Q[0:2] Differential Data Outputs
3-BIT DIFFERENTIAL
FLIP-FLOP
FN SUFFIX
PLASTIC PACKAGE
CASE 776-02
CLK0 CLK0 D0D0R
0
D
2
D
2
CLK2CLK2V
BB
V
CCO
LOGIC DIAGRAM
CLK1
CLK1
R
1
V
EE
S
1
D
1
D
1
26
27
28
2
3
4
25 24 23 22 21 20 19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
115 6 7 8 9 10
R2S
2
Q
2
Q
2
V
CC
Q
1
Q
1
Q
0
Q
0
S
0
S
0
D
0
D
0
CLK0
CLK0
R
0
S
1
D
1
D
1
CLK1
CLK1
R
1
S
2
D
2
D
2
CLK2
CLK2
R
2
V
BB
Q
0
Q
0
Q
1
Q
1
Q
2
Q
2
S
Q
R
Q
D
S
Q
R
Q
D
S
Q
R
Q
D
1
Pinout: 28-Lead PLCC (Top View)
* All VCC and V
CCO
pins are tied together on the die.
MC10E431 MC100E431
MOTOROLA ECLinPS and ECLinPS Lite
DL140 — Rev 4
2–2
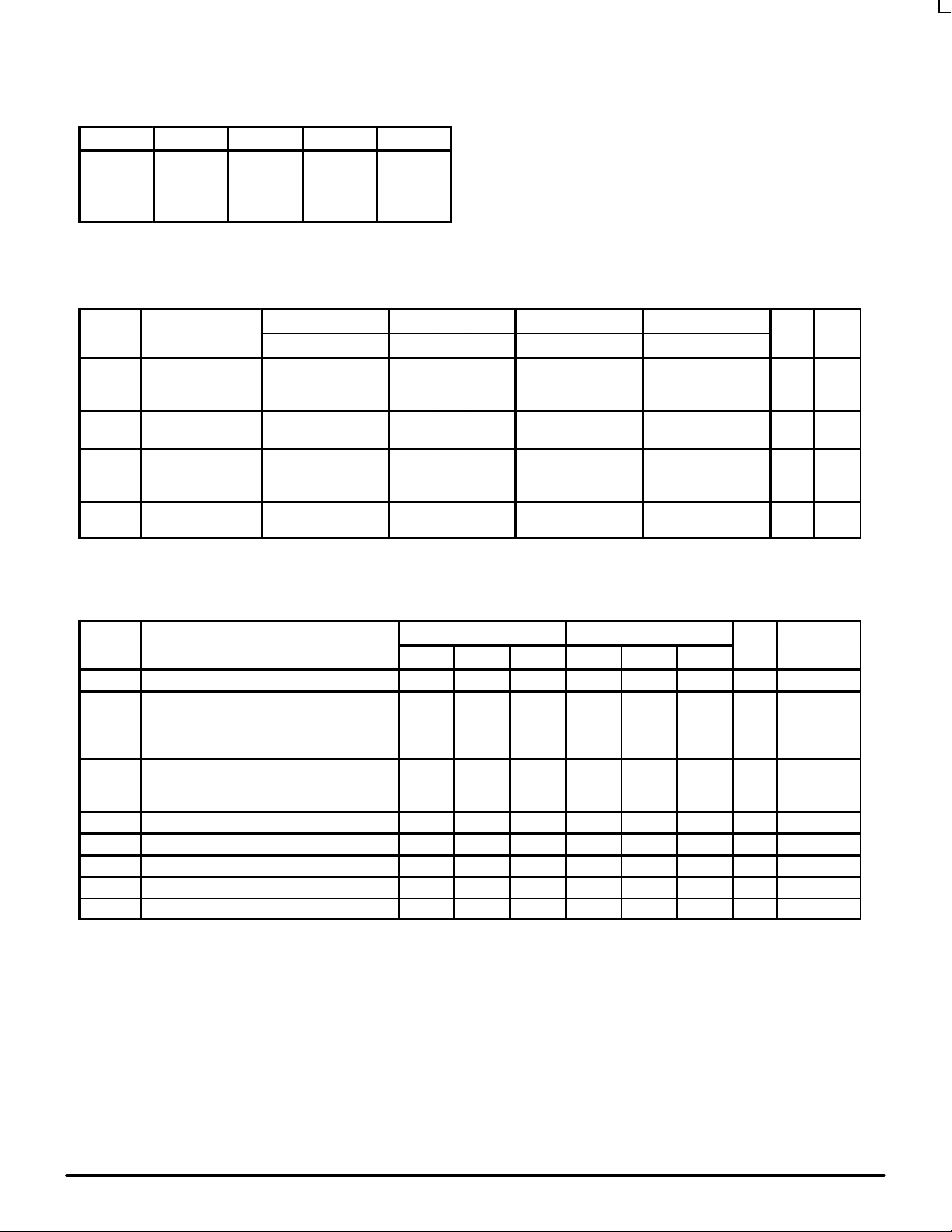
FUNCTION TABLE
Dn CLKn Rn Sn Qn
L Z L L L
H Z L L H
X X Z L L
X X L Z H
Z = Low to high transition
X = Don’t Care
DC CHARACTERISTICS (VEE = VEE(min) to VEE(max); VCC = V
CCO
= GND)
–40°C 0°C 25°C 85°C
Symbol Characteristic Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Unit Cond
V
BB
Output Reference
Voltage 10E
100E
–1.43
–1.38
–1.30
–1.26
–1.38
–1.38
–1.27
–1.26
–1.35
–1.38
–1.25
–1.26
–1.31
–1.38
–1.19
–1.26
V
I
IH
Input HIGH
Current
150 150 150 150 µA
I
EE
Power Supply
Current 10E
100E
110
110
132
132
110
110
132
132
110
110
132
132
110
127
132
152
mA
V
CMR
Common Mode
Range
–1.5 0 –1.5 0 –1.5 0 –1.5 0 V 1
1. V
CMR
is referenced to the most positive side of the differential input signal. Normal specified operation is obtained when the input signals are
within the V
CMR
range and the input swing is greater than VPP.
AC CHARACTERISTICS (VEE = VEE(min) to VEE(max); VCC = V
CCO
= GND)
–40°C 0°C to 85°C
Symbol Characteristic Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Unit Condition
f
MAX
Maximum Toggle Frequency 1000 1400 1100 1400 MHz
t
PLH
t
PHL
Propagation Delay to Output CLK (Diff)
CLK (SE)
R
S
410
460
500
500
600
600
725
725
790
840
975
975
450
400
550
550
600
600
725
725
750
800
925
925
ps
t
S
Setup Time D
R
S
250
1100
1100
0
700
700
200
1000
1000
0
700
700
ps
1
1
t
H
Hold Time D 250 0 200 0 ps
t
PW
Minimum Pulse Width CLK 400 400 ps
t
skew
Within-Device Skew 50 50 ps 2
V
PP
Minimum Input Swing 150 150 mV 3
tr/t
f
Rise/Fall Times 250 450 700 275 450 650 ps 20–80%
1. These setup times define the minimum time the CLK or SET/RESET input must wait after the assertion of the RESET/SET input to assure the
proper operation of the flip-flop.
2. Within-device skew is defined as identical transitions on similar paths through a device.
3. Minimum input swing for which AC parameters are guaranteed.

MC10E431 MC100E431
2–3 MOTOROLAECLinPS and ECLinPS Lite
DL140 — Rev 4
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
FN SUFFIX
PLASTIC PLCC PACKAGE
CASE 776–02
ISSUE D
0.007 (0.180) T L
–M
SNSM
0.007 (0.180) T L
–M
SNSM
0.007 (0.180) T L
–M
SNSM
0.010 (0.250) T L
–M
SNSS
0.007 (0.180) T L
–M
SNSM
0.010 (0.250) T L
–M
SNSS
0.007 (0.180) T L
–M
SNSM
0.007 (0.180) T L
–M
SNSM
0.004 (0.100)
SEATING
PLANE
-T-
12.32
12.32
4.20
2.29
0.33
0.66
0.51
0.64
11.43
11.43
1.07
1.07
1.07
—
2
°
10.42
1.02
12.57
12.57
4.57
2.79
0.48
0.81
—
—
11.58
11.58
1.21
1.21
1.42
0.50
10
°
10.92
—
1.27 BSC
A
B
C
E
F
G
H
J
K
R
U
V
W
X
Y
Z
G1
K1
MIN MINMAX MAX
INCHES MILLIMETERS
DIM
NOTES:
1. DATUMS -L-, -M-, AND -N- DETERMINED
WHERE TOP OF LEAD SHOULDER EXITS
PLASTIC BODY AT MOLD PARTING LINE.
2. DIM G1, TRUE POSITION TO BE MEASURED
AT DATUM -T-, SEATING PLANE.
3. DIM R AND U DO NOT INCLUDE MOLD FLASH.
ALLOWABLE MOLD FLASH IS 0.010 (0.250)
PER SIDE.
4. DIMENSIONING AND TOLERANCING PER ANSI
Y14.5M, 1982.
5. CONTROLLING DIMENSION: INCH.
6. THE PACKAGE TOP MAY BE SMALLER THAN
THE PACKAGE BOTTOM BY UP TO 0.012
(0.300). DIMENSIONS R AND U ARE
DETERMINED AT THE OUTERMOST
EXTREMES OF THE PLASTIC BODY
EXCLUSIVE OF MOLD FLASH, TIE BAR
BURRS, GATE BURRS AND INTERLEAD
FLASH, BUT INCLUDING ANY MISMATCH
BETWEEN THE TOP AND BOTTOM OF THE
PLASTIC BODY.
7. DIMENSION H DOES NOT INCLUDE DAMBAR
PROTRUSION OR INTRUSION. THE DAMBAR
PROTRUSION(S) SHALL NOT CAUSE THE H
DIMENSION TO BE GREATER THAN 0.037
(0.940). THE DAMBAR INTRUSION(S) SHALL
NOT CAUSE THE H DIMENSION TO BE
SMALLER THAN 0.025 (0.635).
VIEW S
B
U
Z
G1
X
VIEW D-D
H
K
F
VIEW S
G
C
Z
A
R
E
J
0.485
0.485
0.165
0.090
0.013
0.026
0.020
0.025
0.450
0.450
0.042
0.042
0.042
—
2
°
0.410
0.040
0.495
0.495
0.180
0.110
0.019
0.032
—
—
0.456
0.456
0.048
0.048
0.056
0.020
10
°
0.430
—
0.050 BSC
-N-
Y BRK
D
D
W
-M-
-L-
28 1
V
G1
K1

MC10E431 MC100E431
MOTOROLA ECLinPS and ECLinPS Lite
DL140 — Rev 4
2–4
Motorola reserves the right to make changes without further notice to any products herein. Motorola makes no warranty , representation or guarantee regarding
the suitability of its products for any particular purpose, nor does Motorola assume any liability arising out of the application or use of any product or circuit, and
specifically disclaims any and all liability , including without limitation consequential or incidental damages. “Typical” parameters which may be provided in Motorola
data sheets and/or specifications can and do vary in different applications and actual performance may vary over time. All operating parameters, including “Typicals”
must be validated for each customer application by customer’s technical experts. Motorola does not convey any license under its patent rights nor the rights of
others. Motorola products are not designed, intended, or authorized for use as components in systems intended for surgical implant into the body, or other
applications intended to support or sustain life, or for any other application in which the failure of the Motorola product could create a situation where personal injury
or death may occur. Should Buyer purchase or use Motorola products for any such unintended or unauthorized application, Buyer shall indemnify and hold Motorola
and its officers, employees, subsidiaries, affiliates, and distributors harmless against all claims, costs, damages, and expenses, and reasonable attorney fees
arising out of, directly or indirectly, any claim of personal injury or death associated with such unintended or unauthorized use, even if such claim alleges that
Motorola was negligent regarding the design or manufacture of the part. Motorola and are registered trademarks of Motorola, Inc. Motorola, Inc. is an Equal
Opportunity/Affirmative Action Employer.
How to reach us:
USA/EUROPE/Locations Not Listed: Motorola Literature Distribution; JAPAN: Nippon Motorola Ltd.; Tatsumi–SPD–JLDC, 6F Seibu–Butsuryu–Center,
P.O. Box 20912; Phoenix, Arizona 85036. 1–800–441–2447 or 602–303–5454 3–14–2 Tatsumi Koto–Ku, Tokyo 135, Japan. 03–81–3521–8315
MFAX: RMFAX0@email.sps.mot.com – TOUCHTONE 602–244–6609 ASIA/PACIFIC: Motorola Semiconductors H.K. Ltd.; 8B Tai Ping Industrial Park,
INTERNET: http://Design–NET.com 51 Ting Kok Road, Tai Po, N.T., Hong Kong. 852–26629298
MC10E431/D
*MC10E431/D*
◊

WWW.ALLDATASHEET.COM
Copyright © Each Manufacturing Company.
All Datasheets cannot be modified without permission.
This datasheet has been download from :
www.AllDataSheet.com
100% Free DataSheet Search Site.
Free Download.
No Register.
Fast Search System.
www.AllDataSheet.com
 Loading...
Loading...