Page 1

900 Touch Control
Manual
8.900.8015EN / 2014-03-10
Page 2

Page 3

Metrohm AG
CH-9100 Herisau
Switzerland
Phone +41 71 353 85 85
Fax +41 71 353 89 01
info@metrohm.com
www.metrohm.com
900 Touch Control
Program version 5.900.0030
8.900.8015EN / 2014-03-10
Manual
ebe
Page 4

Teachware
Metrohm AG
CH-9100 Herisau
teachware@metrohm.com
This documentation is protected by copyright. All rights reserved.
Although all the information given in this documentation has been
checked with great care, errors cannot be entirely excluded. Should you
notice any mistakes please send us your comments using the address
given above.
Documentation in additional languages can be found on
http://documents.metrohm.com.
Melody for the BEEP command: excerpt from "En Altfrentsche", with kind
permission of the Laseyer Quartett, Appenzell.
Page 5

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Table of contents
1 Introduction 1
1.1 Instrument description ......................................................... 1
1.2 Titration and measuring modes .......................................... 1
1.3 About the documentation ................................................... 3
1.3.1 Symbols and conventions ........................................................ 3
2 Safety instructions 5
2.1 General notes on safety ....................................................... 5
2.2 Electrical safety ..................................................................... 5
2.3 Tubing and capillary connections ....................................... 6
2.4 Flammable solvents and chemicals ..................................... 6
2.5 Recycling and disposal ......................................................... 7
Table of contents
3 Overview of the instrument 8
4 Installation 10
4.1 Setting up the instrument .................................................. 10
4.1.1 Packaging .............................................................................. 10
4.1.2 Checks .................................................................................. 10
4.1.3 Location ................................................................................ 10
5 Titrations 11
5.1 Dynamic equivalence point titration (DET) ....................... 11
5.2 Monotonic equivalence point titration (MET) .................. 11
5.3 Endpoint titration (SET) ..................................................... 12
5.4 Water determination according to Karl Fischer (KFT) ..... 12
5.5 Endpoint titration with constant maintenance of the
measured value (STAT) ...................................................... 13
6 Operation 15
6.1 Switching the instrument on and off ............................... 15
6.2 Fundamentals of operation ............................................... 17
6.2.1 Touch-sensitive screen ........................................................... 17
6.2.2 Display elements and controls ................................................ 17
6.2.3 Status display ........................................................................ 18
6.2.4 Entering text and numbers ..................................................... 19
900 Touch Control
■■■■■■■■
III
Page 6

Table of contents
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
7 System settings 22
7.1 General system settings ..................................................... 22
7.1.1 Selecting the dialog language ................................................ 22
7.1.2 Setting the date, time and local time ..................................... 23
7.2 System-specific dialog options .......................................... 24
7.3 User administration ............................................................ 28
7.3.1 Editing the user configuration ................................................ 29
7.3.2 Creating an identification profile ............................................ 33
7.3.3 Defining login options ........................................................... 33
7.3.4 Password options .................................................................. 35
7.3.5 Modification options ............................................................. 37
7.3.6 Reasons ................................................................................. 38
7.3.7 Audit Trail .............................................................................. 39
7.4 Measured value display ..................................................... 40
7.5 Acoustic signals .................................................................. 40
8 Titrants 41
8.1 Adding a new titrant .......................................................... 42
8.2 Editing titrant data ............................................................. 43
8.3 Monitoring the working life .............................................. 45
8.4 Dosing unit .......................................................................... 46
8.4.1 Parameters for preparing (PREP) and emptying (EMPTY) ......... 47
8.4.2 Tubing parameters ................................................................. 48
8.4.3 Shift direction of the valve disk .............................................. 51
8.5 Exchange unit ..................................................................... 52
8.5.1 Parameters for the preparation (PREP) .................................... 53
8.5.2 Tubing parameters ................................................................. 54
8.6 GLP test for exchange unit and dosing unit .................... 56
8.7 Titer determination options and data .............................. 58
8.7.1 Titer validity ........................................................................... 58
8.7.2 Properties of the previous titer determinations ....................... 59
9 Reagents 61
9.1 Editing reagent data .......................................................... 62
9.2 Reagent monitoring ........................................................... 62
■■■■■■■■
IV
10 Sensors 66
10.1 Adding a new sensor ......................................................... 67
10.2 Editing the sensor data ...................................................... 68
10.3 Monitoring the working life .............................................. 69
900 Touch Control
Page 7

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
11 Device manager 79
Table of contents
10.4 Calibration data (for pH- and ISE electrodes and con-
ductivity measuring cells only) .......................................... 70
10.4.1 Properties of the previous calibrations .................................... 72
10.5 Limit values for the calibration data ................................. 75
10.6 Monitoring the calibration interval (only for pH and
ion-selective electrodes and conductivity measuring
cells) ..................................................................................... 77
11.1 Adding a new device .......................................................... 80
11.2 Configuring the instrument ............................................... 80
11.3 Touch Control ..................................................................... 81
11.3.1 E-mail .................................................................................... 82
11.3.2 PC/LIMS report ...................................................................... 83
11.3.3 Shared memory ..................................................................... 84
11.3.4 TCP/IP settings ....................................................................... 86
11.4 Metrohm control devices ................................................... 87
11.4.1 Properties – Control device .................................................... 88
11.4.2 Properties – Measuring input ................................................. 88
11.4.3 Properties – MSB connector ................................................... 90
11.4.4 Properties – Peripheral devices ............................................... 91
11.5 USB Sample Processor ....................................................... 91
11.5.1 Properties – Sample Processor ............................................... 92
11.5.2 Properties – Tower ................................................................ 93
11.5.3 Properties – Swing Head ........................................................ 94
11.6 Sample racks ....................................................................... 99
11.6.1 Editing rack data .................................................................. 101
11.6.2 Rack adjustment .................................................................. 107
11.7 Printer ................................................................................ 108
11.7.1 PDF settings ......................................................................... 109
11.7.2 Network printer ................................................................... 110
11.7.3 More options ....................................................................... 112
11.8 Balance .............................................................................. 112
11.9 USB/RS-232 adapter ......................................................... 114
11.10 PC keyboard ...................................................................... 115
11.11 Barcode reader ................................................................. 117
12 File manager 119
12.1 Managing files .................................................................. 119
12.1.1 Copying a file ...................................................................... 121
12.1.2 Renaming a file ................................................................... 121
12.1.3 File properties ...................................................................... 122
900 Touch Control
12.2 External storage medium ................................................ 123
■■■■■■■■
V
Page 8

Table of contents
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
12.3 Creating backups / Restoring data ................................. 125
12.3.1 Restoring data ..................................................................... 125
13 GLP manager 127
13.1 Automatic system test ..................................................... 128
13.2 Test tools .......................................................................... 128
13.3 GLP tests for measurement and titration ...................... 129
13.3.1 Parameter description .......................................................... 130
13.4 System validation ............................................................. 133
13.4.1 Parameter description .......................................................... 134
13.5 System monitoring ........................................................... 137
13.5.1 Service interval .................................................................... 137
13.5.2 Backup interval .................................................................... 138
14 Common variables 139
14.1 Editing common variables ............................................... 140
14.2 Properties of common variables ..................................... 141
14.3 Monitoring validity ........................................................... 142
14.4 Assigning a result automatically to a common varia-
ble ...................................................................................... 143
15 Templates 145
15.1 Sample data ...................................................................... 145
15.1.1 Sample identification list ...................................................... 146
15.1.2 Sample assignment table ..................................................... 147
15.2 Custom result templates .................................................. 149
15.2.1 Editing result templates ....................................................... 150
15.3 Input lines ......................................................................... 153
15.3.1 Editing the input signal ........................................................ 154
15.4 Output lines ...................................................................... 155
15.4.1 Editing the output signal ...................................................... 157
15.5 Custom calibration buffers .............................................. 158
15.5.1 Defining calibration buffers .................................................. 159
15.6 Report header ................................................................... 160
15.7 Custom electrode type ..................................................... 161
15.7.1 Limit values for the electrode rating ..................................... 162
■■■■■■■■
VI
16 Methods 165
16.1 Creating a new method ................................................... 165
16.2 Saving a method ............................................................... 166
16.3 Loading a method ............................................................ 167
900 Touch Control
Page 9

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
17 Electronic signatures 182
18 Control 184
19 Favorites 188
Table of contents
16.4 Editing a method .............................................................. 168
16.4.1 Inserting a command ........................................................... 169
16.5 Method options ................................................................ 170
16.5.1 Start options ........................................................................ 171
16.5.2 Stop options ........................................................................ 173
16.5.3 Sample data ........................................................................ 174
16.5.4 Method properties ............................................................... 178
16.5.5 Note .................................................................................... 180
16.5.6 Saving a determination automatically ................................... 180
17.1 Signing methods/determinations electronically ............ 182
17.2 Deleting electronic signatures ......................................... 183
19.1 Creating favorites ............................................................. 189
19.1.1 Editing favorites ................................................................... 189
20 Sample data 192
20.1 Entering sample data in the main dialog ....................... 192
20.2 Requesting sample data at the start of the determina-
tion .................................................................................... 193
21 Sample table 195
21.1 General .............................................................................. 195
21.2 Edit the sample data ........................................................ 198
21.3 Properties .......................................................................... 200
22 Determination run 203
22.1 Carrying out a single determination ............................... 203
22.2 Performing a sample series ............................................. 204
22.3 Canceling determinations manually ............................... 205
23 Live modifications 206
23.1 Editing the sample data of the running determina-
tion .................................................................................... 206
900 Touch Control
23.2 Editing the sample table while a determination is run-
ning .................................................................................... 207
23.3 Live display ....................................................................... 208
23.4 Live parameters ................................................................ 210
■■■■■■■■
VII
Page 10

Table of contents
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
24 Results and more determination data 212
24.1 More determination data ................................................ 213
24.1.1 Details ................................................................................. 214
24.2 Messages ........................................................................... 216
24.3 Local common variables .................................................. 217
24.4 Determination properties ................................................ 217
24.5 Loading a determination ................................................. 220
24.5.1 Determination list ................................................................ 221
24.6 Saving a determination .................................................... 225
24.7 Curves ................................................................................ 225
24.8 Recalculation and reevaluation ....................................... 227
25 Statistics 229
25.1 Displaying details for a result .......................................... 231
25.2 Deleting statistical data ................................................... 232
25.3 Adding a determination to a determination series ....... 232
26 Result table 234
26.1 Properties .......................................................................... 235
26.2 Saving the result table ..................................................... 239
26.3 Loading the result table ................................................... 239
27 Printing 240
27.1 General report options ..................................................... 242
27.2 Settings of the individual reports ................................... 243
27.3 List of all printable reports .............................................. 244
28 Manual control 248
28.1 Opening and closing the manual control ....................... 249
28.2 Measuring ......................................................................... 250
28.2.1 Parameter description .......................................................... 251
28.3 Dosing ............................................................................... 254
28.3.1 Continuous dosing .............................................................. 256
28.3.2 Dosing fixed volumes ........................................................... 258
28.3.3 Preparing ............................................................................. 260
28.3.4 Emptying ............................................................................. 261
28.3.5 Filling .................................................................................. 262
28.3.6 Replacing reagent ................................................................ 262
VIII
■■■■■■■■
28.4 Stirring ............................................................................... 263
900 Touch Control
Page 11

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
29 Parameters 276
Table of contents
28.5 Conditioning a titration cell ............................................ 264
28.5.1 Parameter description .......................................................... 265
28.6 Remote .............................................................................. 265
28.7 USB Sample Processor ..................................................... 266
28.7.1 Moving the lift ..................................................................... 268
28.7.2 Moving to a rack position .................................................... 270
28.7.3 External positions ................................................................ 272
29.1 Dynamic equivalence point titrations (DET) ................... 276
29.1.1 Start conditions ................................................................... 276
29.1.2 Titration parameters ............................................................ 279
29.1.3 Stop conditions ................................................................... 283
29.1.4 Potentiometric evaluation .................................................... 284
29.1.5 Control device ..................................................................... 289
29.1.6 Sensor ................................................................................. 290
29.1.7 Dosing device ...................................................................... 291
29.1.8 Stirrer .................................................................................. 292
29.2 Monotonic equivalence point titrations (MET) .............. 293
29.2.1 Start conditions ................................................................... 293
29.2.2 Titration parameters ............................................................ 296
29.2.3 Stop conditions ................................................................... 299
29.2.4 Potentiometric evaluation .................................................... 300
29.2.5 Control device ..................................................................... 305
29.2.6 Sensor ................................................................................. 306
29.2.7 Dosing device ...................................................................... 307
29.2.8 Stirrer .................................................................................. 308
29.3 Endpoint titrations (SET) .................................................. 309
29.3.1 Start conditions ................................................................... 309
29.3.2 Control parameters .............................................................. 310
29.3.3 Titration parameters ............................................................ 314
29.3.4 Stop conditions ................................................................... 315
29.3.5 Conditioning ....................................................................... 316
29.3.6 Cell ...................................................................................... 318
29.3.7 Control device ..................................................................... 318
29.3.8 Sensor ................................................................................. 318
29.3.9 Dosing device ...................................................................... 320
29.3.10 Stirrer .................................................................................. 321
29.4 Volumetric Karl Fischer titrations (KFT) ......................... 321
29.4.1 Start conditions ................................................................... 321
29.4.2 Control parameters .............................................................. 323
29.4.3 Titration parameters ............................................................ 326
29.4.4 Stop conditions ................................................................... 327
29.4.5 Conditioning ....................................................................... 328
29.4.6 Cell ...................................................................................... 330
29.4.7 Control device ..................................................................... 330
29.4.8 Sensor ................................................................................. 331
900 Touch Control
■■■■■■■■
IX
Page 12

Table of contents
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
29.4.9 Dosing device ...................................................................... 332
29.4.10 Stirrer .................................................................................. 333
29.5 Coulometric Karl Fischer titrations (KFC) ....................... 334
29.5.1 Control parameters .............................................................. 334
29.5.2 Titration parameters ............................................................ 336
29.5.3 Stop conditions ................................................................... 337
29.5.4 Conditioning ....................................................................... 337
29.5.5 Cell ...................................................................................... 340
29.5.6 Control device ..................................................................... 341
29.5.7 Sensor ................................................................................. 341
29.5.8 Stirrer .................................................................................. 342
29.6 Bromine index determination (BRC) ............................... 343
29.6.1 Control parameters .............................................................. 343
29.6.2 Titration parameters ............................................................ 346
29.6.3 Stop conditions ................................................................... 347
29.6.4 Conditioning ....................................................................... 347
29.6.5 Cell ...................................................................................... 349
29.6.6 Control device ..................................................................... 350
29.6.7 Sensor ................................................................................. 350
29.6.8 Stirrer .................................................................................. 351
29.7 STAT titrations (STAT) ..................................................... 352
29.7.1 Start conditions ................................................................... 352
29.7.2 Control parameters .............................................................. 354
29.7.3 Titration parameters ............................................................ 356
29.7.4 Stop conditions ................................................................... 358
29.7.5 Monitoring .......................................................................... 359
29.7.6 Control device ..................................................................... 366
29.7.7 Sensor ................................................................................. 366
29.7.8 Dosing device ...................................................................... 367
29.7.9 Stirrer .................................................................................. 370
29.8 Manual titrations (MAT) .................................................. 371
29.8.1 Dosing parameters .............................................................. 371
29.8.2 Control device ..................................................................... 372
29.8.3 Sensor ................................................................................. 372
29.8.4 Dosing device ...................................................................... 373
29.8.5 Stirrer .................................................................................. 376
29.9 Measurements (MEAS) ..................................................... 377
29.9.1 Measuring parameters ......................................................... 377
29.9.2 Standard addition ................................................................ 381
29.9.3 Control device ..................................................................... 385
29.9.4 Sensor ................................................................................. 385
29.9.5 Stirrer .................................................................................. 387
■■■■■■■■
X
29.10 Calibration of sensors (CAL) ............................................ 388
29.10.1 Calibration parameters (CAL pH) .......................................... 388
29.10.2 Calibration parameters (CAL Conc) ...................................... 391
29.10.3 Calibration parameters (CAL Cond) ...................................... 394
29.10.4 Control device ..................................................................... 397
900 Touch Control
Page 13

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Table of contents
29.10.5 Sensor ................................................................................. 397
29.10.6 Stirrer .................................................................................. 398
29.11 Electrode test for pH electrodes (ELT) ............................ 399
29.11.1 Electrode test parameters .................................................... 400
29.11.2 Control device ..................................................................... 401
29.11.3 Sensor ................................................................................. 402
29.11.4 Stirrer .................................................................................. 403
29.11.5 Further information ............................................................. 403
29.12 Evaluations (EVAL) ........................................................... 405
29.12.1 Fixed endpoint evaluation (EVAL FIX-EP) .............................. 407
29.12.2 pK value and half neutralization potential evaluation (EVAL
pK/HNP) .............................................................................. 409
29.12.3 Minimum and maximum evaluation (EVAL MIN/MAX) .......... 410
29.12.4 Break point evaluation (EVAL BREAK) ................................... 411
29.12.5 Rate evaluation (EVAL RATE) ................................................ 414
29.13 Calculations ....................................................................... 415
29.13.1 Calculations (CALC) ............................................................. 415
29.13.2 Calculations (CALC LIVE) ...................................................... 422
29.13.3 Formula editor ..................................................................... 424
29.14 Reports (REPORT) ............................................................. 430
29.14.1 General report options ......................................................... 430
29.14.2 Settings of the individual reports .......................................... 431
29.14.3 List of reports ...................................................................... 432
29.15 Dosing and Liquid Handling ............................................ 435
29.15.1 Preparing an exchange or dosing unit (PREP) ........................ 435
29.15.2 Emptying a dosing unit (EMPTY) .......................................... 436
29.15.3 Dosing a specified volume (ADD) ......................................... 437
29.15.4 Liquid Handling (LQH) .......................................................... 442
29.15.5 Monitored dosing (DOS) ...................................................... 445
29.16 Communication ................................................................ 462
29.16.1 Scanning remote lines (SCAN) .............................................. 463
29.16.2 Setting remote lines (CTRL) .................................................. 464
29.16.3 Scanning the RS-232 interface (SCAN RS) ............................. 466
29.16.4 Defining RS-232 commands (CONTROL RS) .......................... 467
29.17 Automation ....................................................................... 467
29.17.1 Rotating sample rack (MOVE) .............................................. 467
29.17.2 Moving the lift (LIFT) ............................................................ 470
29.17.3 Controlling pumps (PUMP) ................................................... 471
29.17.4 Resetting the rack (RACK) .................................................... 472
29.17.5 Defining the sample variable (SAMPLE) ................................ 472
29.17.6 Creating a subsequence (SUBSEQ) ....................................... 473
900 Touch Control
29.18 Miscellaneous commands ................................................ 476
29.18.1 Controlling a stirrer (STIR) .................................................... 476
29.18.2 Pausing the method run (WAIT) ........................................... 477
29.18.3 Scan data (REQUEST) ........................................................... 477
29.18.4 Defining an acoustic signal (BEEP) ........................................ 478
■■■■■■■■
XI
Page 14

Table of contents
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
29.18.5 Signing a determination (SIGN) ............................................ 479
29.18.6 Canceling the method run (END) ......................................... 479
30 Operation and maintenance 480
30.1 System initialization ......................................................... 480
30.2 Quality management and qualification with
Metrohm ........................................................................... 481
31 Troubleshooting 482
31.1 Editing methods ............................................................... 482
31.2 Sample table ..................................................................... 482
31.3 Results/Statistics ............................................................... 482
31.4 Printing .............................................................................. 483
31.5 Manual control ................................................................. 483
31.6 Miscellaneous ................................................................... 484
31.7 SET titration ...................................................................... 484
31.8 Karl Fischer titration ........................................................ 485
31.9 STAT titration ................................................................... 487
32 Appendix 488
32.1 Dosing unit ........................................................................ 488
32.1.1 Maximum dosing and filling rate .......................................... 488
32.1.2 Default parameters for preparing (PREP) and emptying
(EMPTY) ............................................................................... 488
32.2 Exchange unit ................................................................... 489
32.2.1 Maximum dosing and filling rate .......................................... 489
32.2.2 Default parameters for preparing (PREP) .............................. 489
32.3 Stirring rate ....................................................................... 489
32.4 Balance .............................................................................. 490
32.5 Result variables as parameter setting ............................ 491
32.6 Electrode calibration with USB Sample Processors ....... 492
32.7 Stored buffer series for pH calibration ........................... 494
32.8 Using AuditTrailViewer .................................................... 498
32.8.1 Installing AuditTrailViewer ................................................... 498
32.8.2 Opening the Audit Trail ....................................................... 499
32.8.3 Contents of the Audit Trail ................................................... 500
32.8.4 Filtering the Audit Trail ......................................................... 502
32.8.5 Exporting the Audit Trail ...................................................... 502
XII
■■■■■■■■
32.9 Diagnosis ........................................................................... 503
32.9.1 LCD test .............................................................................. 503
32.9.2 Temperature monitoring ...................................................... 504
900 Touch Control
Page 15

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
33 Technical specifications 514
Table of contents
32.9.3 Formatting an external storage medium ............................... 504
32.9.4 Removing an external storage medium ................................ 505
32.9.5 Adjusting the touch screen .................................................. 505
32.9.6 Testing the touch screen ...................................................... 506
32.9.7 Software update (loading program versions and language
files) .................................................................................... 507
32.9.8 Simulating titration curves ................................................... 510
32.9.9 Service ................................................................................. 511
32.10 Arithmetic algorithms in the Titrando ............................ 512
33.1 Touch screen ..................................................................... 514
33.2 Interfaces .......................................................................... 515
33.3 Power supply .................................................................... 515
33.4 Safety specifications ........................................................ 515
33.5 Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) ............................. 516
33.6 Ambient temperature ...................................................... 516
33.7 Dimensions ........................................................................ 516
34 Warranty (guarantee) 517
35 Accessories 519
Index 521
900 Touch Control
■■■■■■■■
XIII
Page 16

Table of figures
Table of figures
Figure 1 Front 900 Touch Control ................................................................... 8
Figure 2 Rear 900 Touch Control .................................................................... 9
Figure 3 Reagent dosing for DET ................................................................... 11
Figure 4 Reagent dosing for MET .................................................................. 11
Figure 5 Reagent dosing for SET ................................................................... 12
Figure 6 Reagent dosing for KFT ................................................................... 13
Figure 7 Reagent dosing for STAT ................................................................. 14
Figure 8 Dosing unit – port assignment ......................................................... 51
Figure 9 Exchange unit – tubing connections ................................................ 56
Figure 10 Directory structure on the external storage medium ...................... 124
Figure 11 Live display "Preparing the dosing unit" ......................................... 261
Figure 12 Live display "Preparing the exchange unit" ..................................... 261
Figure 13 Equivalence point recognition and equivalence point numbering within
windows ....................................................................................... 288
Figure 14 Tubbs method for determining the equivalence point .................... 289
Figure 15 Equivalence point recognition and equivalence point numbering within
windows ....................................................................................... 304
Figure 16 Action "Exit method" or "Cancel command" .................................. 363
Figure 17 Action "Pause" .............................................................................. 363
Figure 18 Action "Wait" ................................................................................ 364
Figure 19 Evaluation of pK value / half neutralization potential ...................... 409
Figure 20 Evaluation of minimum and maximum ........................................... 410
Figure 21 Evaluation of a break point ............................................................ 411
Figure 22 Dosing criterion "Volume/Dosing rate" .......................................... 446
Figure 23 Dosing criterion "Volume/Dosing time" .......................................... 446
Figure 24 Dosing criterion "Dosing rate/Dosing time" .................................... 447
Figure 25 Action "Exit method" or "Cancel command" .................................. 455
Figure 26 Action "Pause" .............................................................................. 455
Figure 27 Action "Wait" ................................................................................ 455
Figure 28 Rotational speed depending on stirring rate .................................. 490
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
XIV
■■■■■■■■
900 Touch Control
Page 17

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
1 Introduction
1.1 Instrument description
The 900 Touch Control is an operating unit with a touch-sensitive screen.
You can operate the following control devices with the 900 Touch Control:
■ Titrandos
■ USB Sample Processors
■ 846 Dosing Interface
■ 867 pH Module
■ 856 Conductivity Module
With the 900 Touch Control, you can conveniently manage all of your
titrants, sensors, methods, etc. For example, you can connect a USB flash
drive to the USB connector as an external storage medium. You can use
this additional memory not only to store your methods and determinations, but also to create a backup together with all of the data and settings of your system. Thanks to the integrated Ethernet connector, the
device can be connected to your network, thus offering you the following
options, among others:
1 Introduction
■ Saving data to a PC within the network
■ Printing reports on a network printer
■ Sending displayed messages as e-mails
1.2 Titration and measuring modes
The 900 Touch Control supports the following titration and measuring
modes. Whether a particular mode is available or not depends on the type
of the control device connected.
■ DET
Dynamic equivalence point titration. The reagent is added in variable
volume steps.
Measuring modes:
– pH (pH measurement)
– U (potentiometric voltage measurement)
– Ipol (voltametric measurement with selectable polarization cur-
rent)
– Upol (amperometric measurement with selectable polarization
voltage)
900 Touch Control
■■■■■■■■
1
Page 18

1.2 Titration and measuring modes
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
■ MET
Monotonic equivalence point titration. The reagent is added in con-
stant volume steps.
Measuring modes:
– pH (pH measurement)
– U (potentiometric voltage measurement)
– Ipol (voltametric measurement with selectable polarization cur-
rent)
– Upol (amperometric measurement with selectable polarization
voltage)
■ SET
Endpoint titration at one or two specified endpoints.
Measuring modes:
– pH (pH measurement)
– U (potentiometric voltage measurement)
– Ipol (voltametric measurement with selectable polarization cur-
rent)
– Upol (amperometric measurement with selectable polarization
voltage)
■ STAT
Endpoint titration with constant maintenance of the measured value.
Measuring modes:
– pH (pH measurement)
– U (potentiometric voltage measurement)
■ KFT
Volumetric water content determination according to Karl Fischer.
Measuring modes:
– Ipol (voltametric measurement with selectable polarization cur-
rent)
– Upol (amperometric measurement with selectable polarization
voltage)
■ KFC
Coulometric water content determination according to Karl Fischer.
Measuring mode:
– Ipol (voltametric measurement with selectable polarization cur-
rent)
■ BRC
Coulometric bromine index determination. Determining the amount of
double bonds in e.g. mineral oils.
Measuring mode:
– Ipol (voltametric measurement with selectable polarization cur-
rent)
■■■■■■■■
2
900 Touch Control
Page 19

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
1 Introduction
■ MEAS
Measuring modes:
– pH (pH measurement)
– U (potentiometric voltage measurement)
– Ipol (voltametric measurement with selectable polarization cur-
rent)
– Upol (amperometric measurement with selectable polarization
voltage)
– T (temperature measurement)
– Conc (Concentration measurement with or without standard
addition)
– Cond (conductivity measurement)
■ CAL
Electrode calibration.
Measuring mode:
– pH (calibration of pH electrodes)
– Conc (calibration of ion-selective electrodes)
– Cond (calibration of conductivity measuring cells)
– ELT (Electrode test for pH electrodes)
1.3 About the documentation
CAUTION
Please read through this documentation carefully before putting the
instrument into operation. The documentation contains information
and warnings which the user must follow in order to ensure safe operation of the instrument.
1.3.1 Symbols and conventions
The following symbols and formatting may appear in this documentation:
Cross-reference to figure legend
The first number refers to the figure number, the second to the instrument part in the figure.
Instruction step
Carry out these steps in the sequence shown.
Method Dialog text, parameter in the software
900 Touch Control
File ▶ New Menu or menu item
[Next] Button or key
■■■■■■■■
3
Page 20

1.3 About the documentation
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
WARNING
This symbol draws attention to a possible life-threatening hazard or risk of injury.
WARNING
This symbol draws attention to a possible hazard due
to electrical current.
WARNING
This symbol draws attention to a possible hazard due
to heat or hot instrument parts.
WARNING
This symbol draws attention to a possible biological
hazard.
CAUTION
This symbol draws attention to possible damage to
instruments or instrument parts.
NOTE
This symbol highlights additional information and
tips.
■■■■■■■■
4
900 Touch Control
Page 21

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
2 Safety instructions
2.1 General notes on safety
WARNING
This instrument may only be operated in accordance with the specifications in this documentation.
This instrument has left the factory in a flawless state in terms of technical
safety. To maintain this state and ensure non-hazardous operation of the
instrument, the following instructions must be observed carefully.
2.2 Electrical safety
2 Safety instructions
The electrical safety when working with the instrument is ensured as part
of the international standard IEC 61010.
WARNING
Only personnel qualified by Metrohm are authorized to carry out service
work on electronic components.
WARNING
Never open the housing of the instrument. The instrument could be
damaged by this. There is also a risk of serious injury if live components
are touched.
There are no parts inside the housing which can be serviced or replaced
by the user.
Mains voltage
WARNING
900 Touch Control
An incorrect mains voltage can damage the instrument.
Only operate this instrument with a mains voltage specified for it (see
rear panel of the instrument).
■■■■■■■■
5
Page 22

2.3 Tubing and capillary connections
Protection against electrostatic charges
WARNING
Electronic components are sensitive to electrostatic charges and can be
destroyed by discharges.
Do not fail to pull the mains cable out of the mains connection socket
before you set up or disconnect electrical plug connections at the rear
of the instrument.
2.3 Tubing and capillary connections
CAUTION
Leaks in tubing and capillary connections are a safety risk. Tighten all
connections well by hand. Avoid applying excessive force to tubing
connections. Damaged tubing ends lead to leakage. Appropriate tools
can be used to loosen connections.
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Check the connections regularly for leakage. If the instrument is used
mainly in unattended operation, then weekly inspections are mandatory.
2.4 Flammable solvents and chemicals
WARNING
All relevant safety measures are to be observed when working with
flammable solvents and chemicals.
■ Set up the instrument in a well-ventilated location (e.g. fume cup-
board).
■ Keep all sources of flame far from the workplace.
■ Clean up spilled liquids and solids immediately.
■ Follow the safety instructions of the chemical manufacturer.
■■■■■■■■
6
900 Touch Control
Page 23

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
2.5 Recycling and disposal
This product is covered by European Directive 2002/96/EC, WEEE – Waste
from Electrical and Electronic Equipment.
The correct disposal of your old equipment will help to prevent negative
effects on the environment and public health.
More details about the disposal of your old equipment can be obtained
from your local authorities, from waste disposal companies or from your
local dealer.
2 Safety instructions
900 Touch Control
■■■■■■■■
7
Page 24
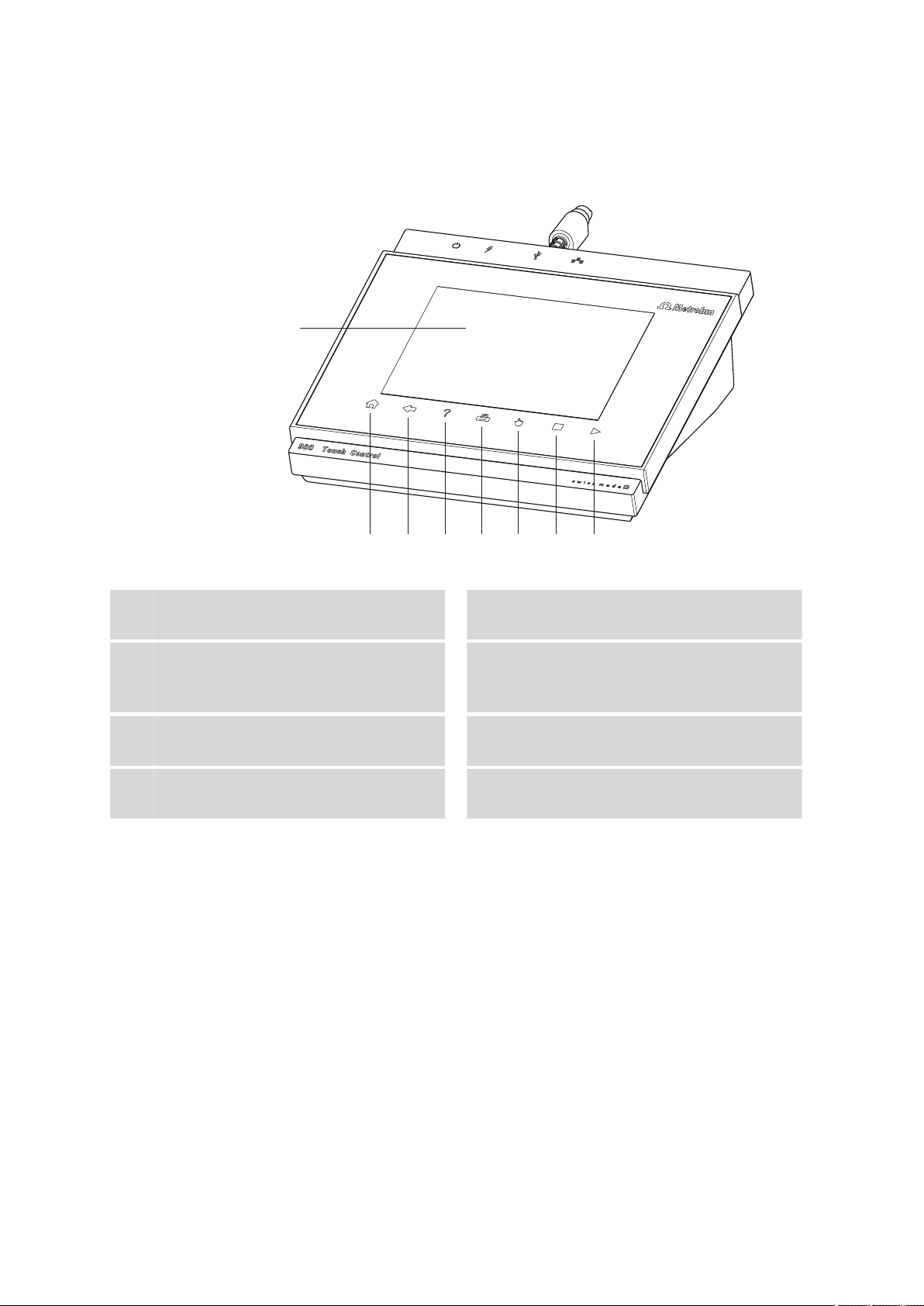
3 Overview of the instrument
8
6
5
3
1
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Figure 1 Front 900 Touch Control
Display
1
Touch screen.
Fixed key [Back]
3
Opens the next-higher dialog page.
Fixed key [Print]
5
Opens the print dialog.
Fixed key [STOP]
7
Cancels the running determination.
Fixed key [Home]
2
Opens the main dialog.
Fixed key [Help]
4
Opens the online help for the dialog displayed.
Fixed key [Manual]
6
Opens the manual control.
Fixed key [START]
8
Starts a determination.
■■■■■■■■
8
900 Touch Control
Page 25
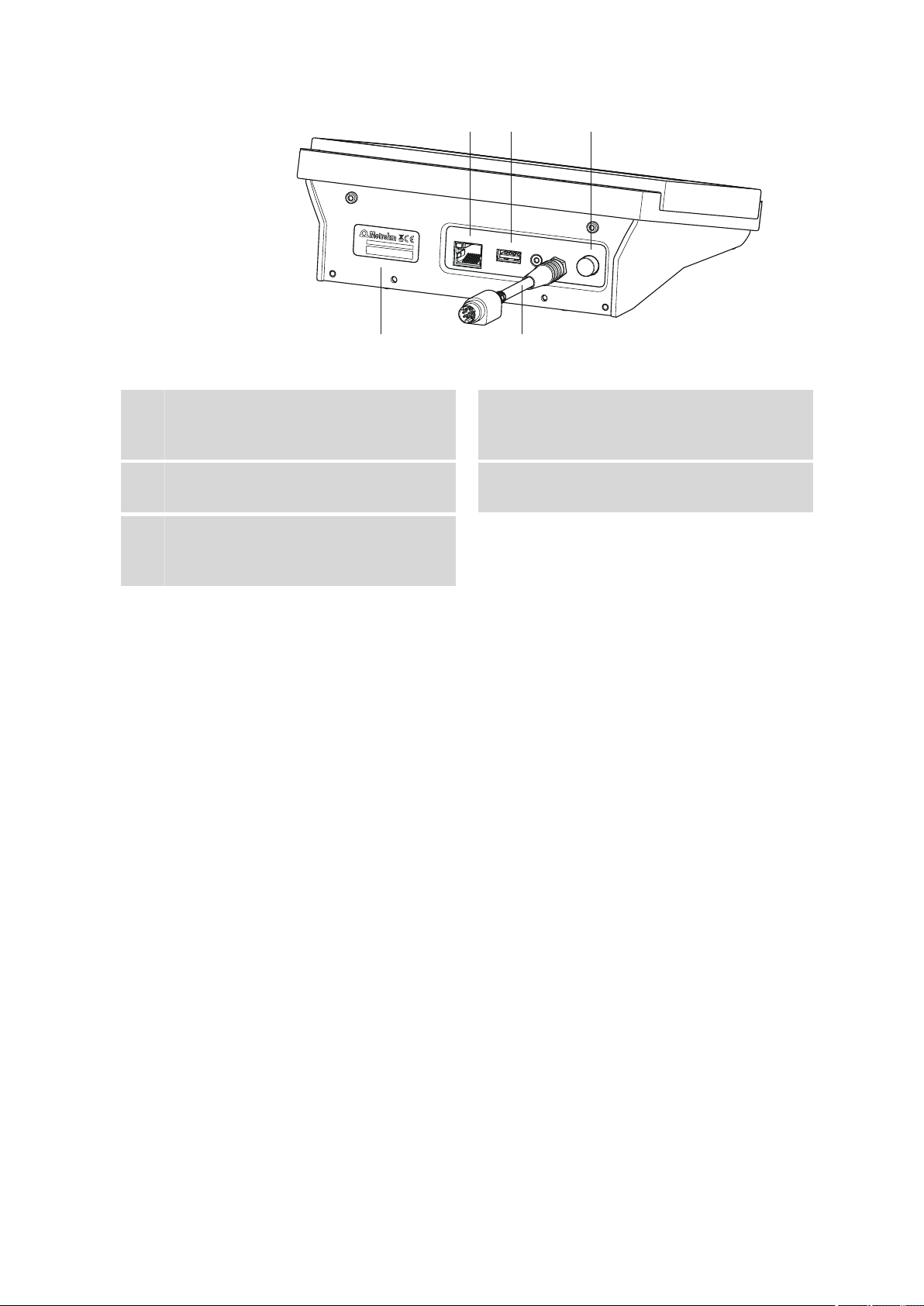
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
5
4
3
21
3 Overview of the instrument
Figure 2 Rear 900 Touch Control
Ethernet connector (RJ-45)
1
For connecting to a network.
Power switch
3
Switches the instrument on/off.
Connection cable
5
For the connection of the Touch Control to
a control device (socket "Controller").
USB connector (type A)
2
For connecting printers, USB sticks, USB
hubs, etc.
Type plate
4
Contains the serial number.
900 Touch Control
■■■■■■■■
9
Page 26

4.1 Setting up the instrument
4 Installation
The connection between the Touch Control and the control device
(Titrando, etc.) is described in the respective manual, as is the configuration of the titration system with its peripheral devices, e.g. stirrers and
dosing devices.
4.1 Setting up the instrument
4.1.1 Packaging
The instrument is supplied in highly protective special packaging together
with the separately packed accessories. Keep this packaging, as only this
ensures safe transportation of the instrument.
4.1.2 Checks
Immediately after receipt, check whether the shipment has arrived complete and without damage by comparing it with the delivery note.
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
4.1.3 Location
The instrument has been developed for operation indoors and may not be
used in explosive environments.
Place the instrument in a location of the laboratory which is suitable for
operation, free of vibrations, protected from corrosive atmosphere, and
contamination by chemicals.
The instrument should be protected against excessive temperature fluctuations and direct sunlight.
■■■■■■■■
10
900 Touch Control
Page 27
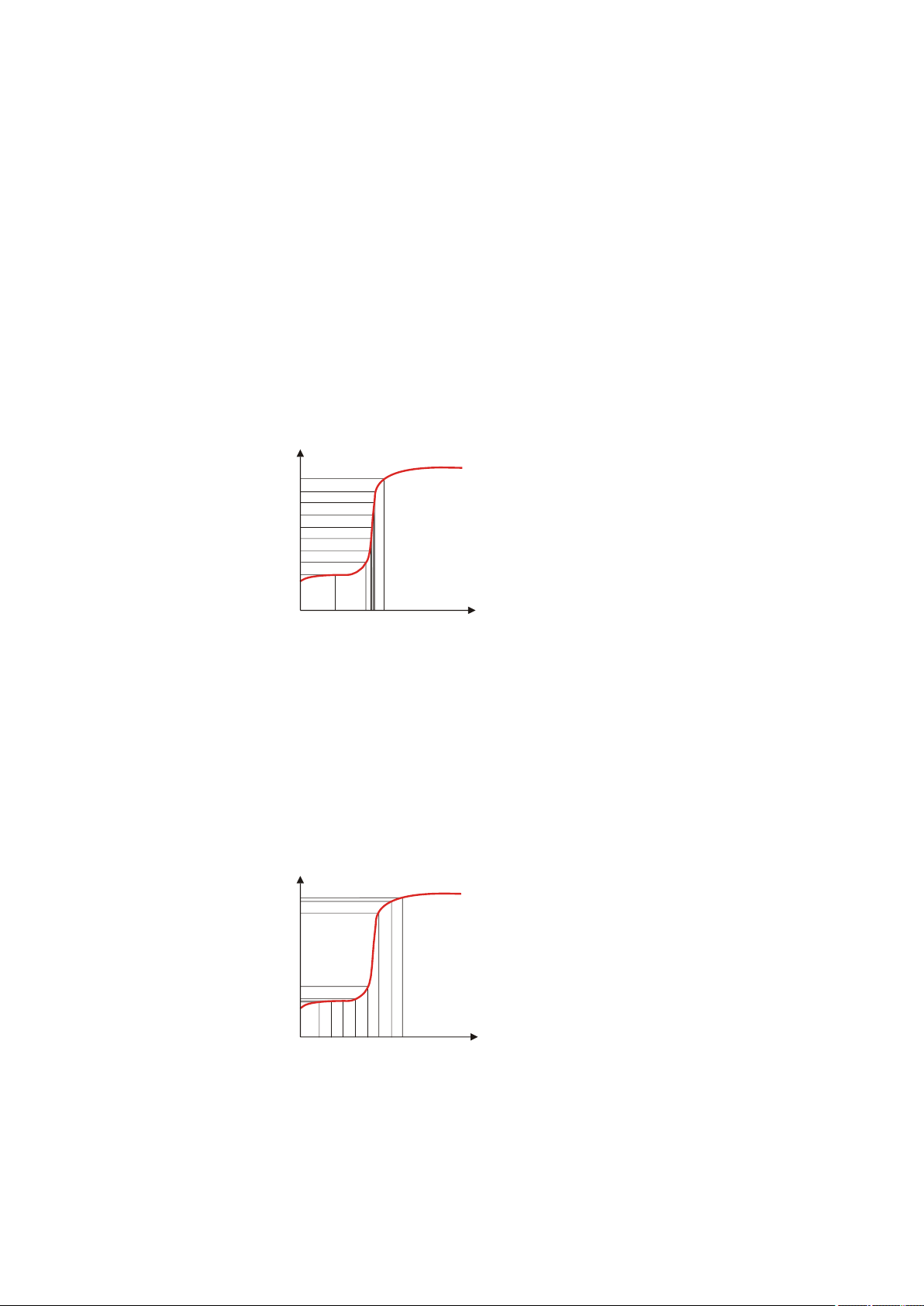
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
U/mV
V/mL
U/mV
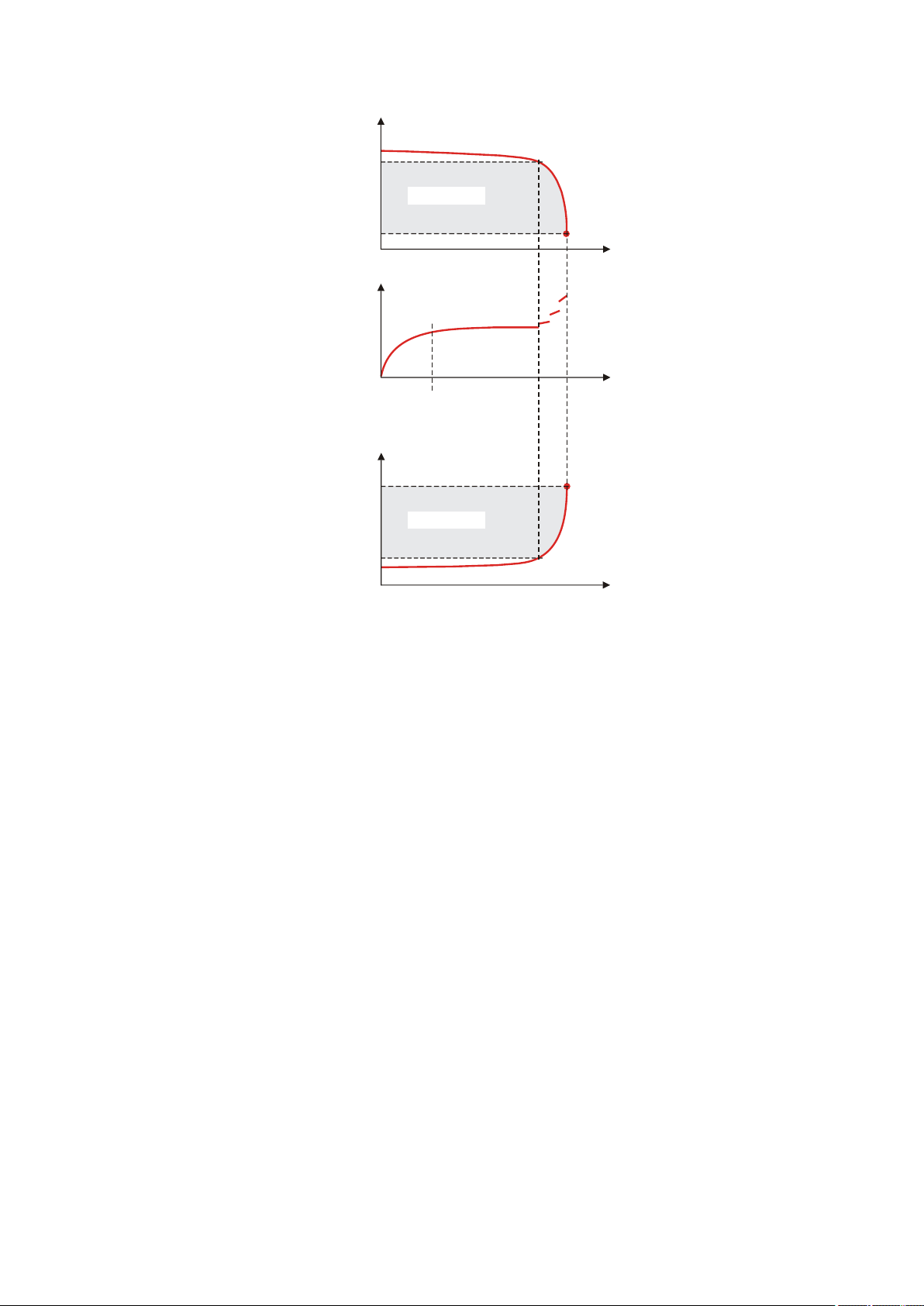
5 Titrations
5.1 Dynamic equivalence point titration (DET)
Dynamic equivalence point titration is a titration mode for all standard
titrations. The reagent is added in variable volume steps. The volume
increments vary as a function of the slope of the curve. An attempt is
made to achieve constant measured value alterations with each dosing.
The optimal volume for dosing is determined from the measured value
alterations of the previous dosings. Measured value acceptance is driftcontrolled (equilibrium titration) or after a waiting time. Equivalence points
are evaluated automatically.
5 Titrations
Figure 3
Reagent dosing for DET
5.2 Monotonic equivalence point titration (MET)
Monotonic equivalence point titration is a titration mode for titrations
with relatively high signal fluctuations or suddenly occurring potential
jumps and for slow titrations or slow-response electrodes. The reagent is
added in constant volume steps. Measured value acceptance is drift-controlled (equilibrium titration) or after a waiting time. Equivalence points are
evaluated automatically.
Figure 4
Reagent dosing for MET
900 Touch Control
■■■■■■■■
11
Page 28
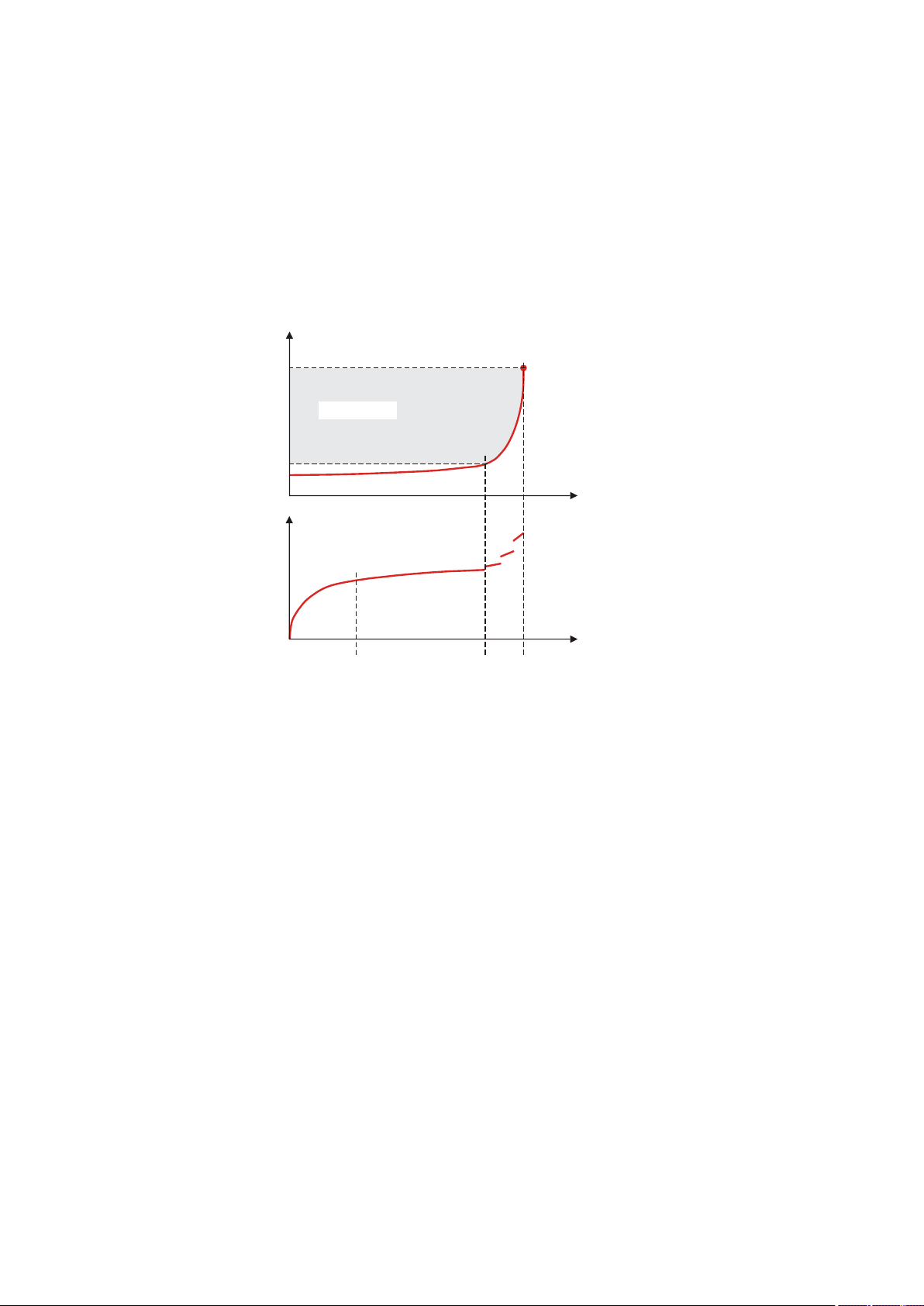
5.3 Endpoint titration (SET)
t/s
EP
Continuous
dosing
Initial
dosing
V/mL
V/mL
U/mV
Control range
5.3 Endpoint titration (SET)
Endpoint titration is a titration mode for rapid routine determinations to a
preset endpoint (e.g. titrations in accordance with special norms) and
titrations for which reagent overflow must be avoided. The titration termination at the endpoint takes place either drift-controlled or after a waiting
period. The volume dosed until the endpoint is used for calculating the
content of the sample.
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Figure 5 Reagent dosing for SET
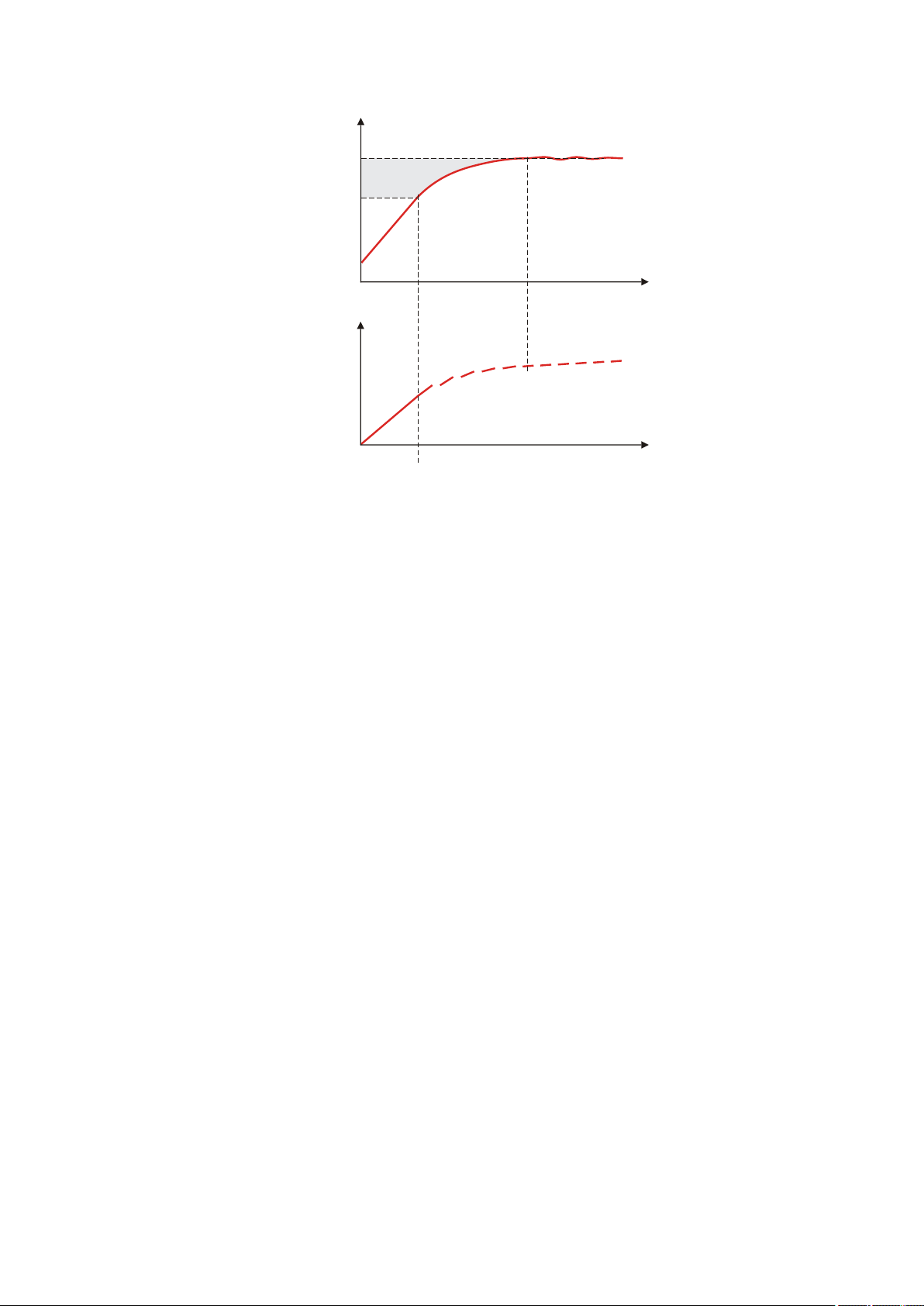
5.4 Water determination according to Karl Fischer (KFT)
Karl Fischer Titration is a method for volumetric water determination. Conditioning is carried out automatically both before and after the actual titration. The reagent dosing is controlled in such a way that a predefined
endpoint is reached as quickly and as accurately as possible. The volume
steps and the rate of reagent dosing are regulated by the difference
between the current measured value and the predefined endpoint. This
means that titration is performed more slowly in the control range and
that smaller volumes are added. The titration is stopped at the endpoint
either drift-controlled or after a waiting time. The volume dosed until the
endpoint is used to calculate the water content of the sample.
■■■■■■■■
12
900 Touch Control
Page 29
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
EP
KFT Ipol
KFT Upol
EP
V/mL
Continuous
dosing
Initial
dosing
V/mL
V/mL
U/mV
t/s
I/µA
Control range
Control range
5 Titrations
Figure 6 Reagent dosing for KFT
5.5 Endpoint titration with constant maintenance of the measured value (STAT)
The pH STAT titration is the one most frequently utilized. Reagent is added
until a preset measured value (control point) has been reached. This control point is kept stable by continuously titrating off the substance set free
by the reaction with the reagent. The STAT titration keeps the control
point constant until the preset stop criterion has been reached. The STAT
titration is applied, for example, in analysis of enzymes. The dosing rate
resulting from the the control point being kept stable provides insight into
the activity of an enzyme.
900 Touch Control
■■■■■■■■
13
Page 30
5.5 Endpoint titration with constant maintenance of the measured value (STAT)
Control point
U/mV
V/mL
Control range
V/mL
Initial
dosing
t/s
Incremental dosing
Figure 7 Reagent dosing for STAT
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
14
■■■■■■■■
900 Touch Control
Page 31

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
6 Operation
6.1 Switching the instrument on and off
Switching on the instrument
CAUTION
Peripheral devices (e.g. printers) must be switched on before you switch
on the 900 Touch Control.
Proceed as follows:
■ Press the mains switch on the left-hand side of the rear panel of
1
the 900 Touch Control.
The 900 Touch Control and the control device are initialized and a
system test is carried out. This process takes some time.
■ If a buret unit is attached, then a request appears to carry out the
Prepare function:
6 Operation
900 Touch Control
All tubings and the cylinder are rinsed with the
Prepare function.
The preparing of the buret unit is described in chapter 28.3.3,
page 260.
■ Confirm the message with [OK].
The main dialog is displayed:
■■■■■■■■
15
Page 32

6.1 Switching the instrument on and off
Switching off the instrument
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
CAUTION
The 900 Touch Control must be switched off by pressing the mains
switch on the rear of the instrument before the electricity supply is
interrupted. If this is not done, then there is a danger of data loss.
Because the power supply for the Touch Control is provided through
the control device (Titrando, etc.) you must never disconnect the control device from the mains (e.g. by switching off with a connector strip)
before you have switched off the Touch Control.
Proceed as follows:
■ Press the mains switch on the left-hand side of the rear panel of
1
the 900 Touch Control.
The current data is saved and the system is shut down. This process
takes just a short time. At the same time, all other devices connected
to the 900 Touch Control via a USB cable are also being switched
off.
■■■■■■■■
16
900 Touch Control
Page 33

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
6.2 Fundamentals of operation
6.2.1 Touch-sensitive screen
The entire Touch Control user interface is touch-sensitive. Simply touch a
few of the buttons on the interface to learn how a touch-sensitive screen
reacts. You can always return to the main dialog by touching [ ].
In order to activate an element on the Touch Control user interface, just
touch the screen with your fingertip, finger nail, the eraser of a pencil or a
stylus (special tool for operating instruments with touch-sensitive screens).
CAUTION
Never touch the touch screen with a pointed or sharp object such as a
ballpoint pen.
In the default setting, the software is configured in such a way that an
acoustic signal will be generated every time an active control is touched.
This setting can be deactivated in the system settings (see Chapter 7.5,
page 40).
6 Operation
6.2.2 Display elements and controls
The following display elements and controls are available:
Table 1
Fixed keys which are always available
[Home] always opens the main dialog.
900 Touch Control
■■■■■■■■
17
Page 34

6.2 Fundamentals of operation
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
[Back] saves the entry and opens the next-higher dialog
page.
[Help] opens the online help feature for the dialog displayed.
[Print] opens the printing dialog.
[Manual] opens the manual control.
[Stop] cancels the ongoing determination.
[Start] starts a determination.
The method loaded, the time and the system status are displayed in the
main dialog in the Title bar.
In the other dialogs, the title bar shows the headings of the next upper
level and of the displayed dialog. This is an aid for orientation during navigation through the user dialog.
Table 2
6.2.3 Status display
The current status of the system is displayed in the upper right-hand corner of the title bar:
Screen elements
Buttons open a new dialog when they are tapped.
Inactive buttons with gray lettering indicate
that the respective function is not available at the
moment.
Input fields open an input dialog when tapped
with the finger.
Tapping on the selection symbol opens a selection list.
A check box can also be activated or deactivated by tapping on it.
■■■■■■■■
18
The instrument is in normal status.
900 Touch Control
Page 35

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
6 Operation
The working medium is being conditioned.
Conditioning has been paused.
The working medium is conditioned.
A method has been started.
A method has been paused.
An action has been started in manual control.
6.2.4 Entering text and numbers
In the editing dialog for text or numerical input, enter the individual characters by tapping in the input field. The following functions are available:
Text editor
900 Touch Control
■■■■■■■■
19
Page 36

6.2 Fundamentals of operation
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Editing function Description
[OK] The modification is applied and the editing dialog
is exited.
[Cancel] The editing dialog is exited without applying the
modification.
[Delete entry] The content of the input field is deleted com-
pletely.
[⌫] The character in front of the cursor is deleted.
[⇦] The cursor within the input field is shifted to the
left by one character.
[⇨] The cursor within the input field is shifted to the
right by one character.
[a…z] The lower-case letters are displayed. The label
changes to [A…Z]. The upper case letters are
displayed by tapping again.
[0…9] Numbers and mathematical characters are dis-
played.
[Special characters]
Special characters are displayed. You can use the
button [More] to navigate through all available
characters.
Number editor
■■■■■■■■
20
Editing function
Description
[OK] The modification is applied and the editing dialog
is exited.
900 Touch Control
Page 37

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
6 Operation
Editing function Description
[Cancel] The editing dialog is exited without applying the
modification.
[Delete entry] The content of the input field is deleted com-
pletely.
[off] If not only numbers but also special values (e.g.
off) can be entered, then the corresponding but-
tons will be shown to the right of the numerical
keypad.
[R1] For many parameters, a result previously defined
in the method can also be entered in place of a
number (see Chapter 32.5, page 491). You can
select the result variable by touching [R1].
NOTE
A commercially available USB keyboard can be connected to make it
easier to enter text and numbers. The key assignment is described in
Chapter 11.10, page 115.
900 Touch Control
■■■■■■■■
21
Page 38

7.1 General system settings
7 System settings
Main dialog: System ▶ System settings
This chapter describes the various system settings and configurations.
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
■ Selecting the dialog language (see Chapter 7.1.1, page 22).
■ Setting the date and time (see Chapter 7.1.2, page 23).
■ Defining system-specific dialog options (see Chapter 7.2, page 24).
■ User administration (see Chapter 7.3, page 28).
■ Defining settings for the measured value display (see Chapter 7.4,
page 40).
■ Configuring settings for acoustic signals (see Chapter 7.5, page 40).
7.1 General system settings
7.1.1 Selecting the dialog language
The user interface is available in several languages. In addition to the two
default dialog languages English and German, additional languages can
be selected.
Proceed as follows to select the dialog language:
1
Open the system settings
■ In the main dialog, tap on [System].
■ Tap on [System settings].
■■■■■■■■
22
The dialog System / System settings is displayed.
900 Touch Control
Page 39

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
2
Select the dialog language
■ Tap on the list box Dialog language and select the desired lan-
guage.
3
Save the settings
Tap on the fixed keys [ ] or [ ].
The main dialog is displayed in the respective dialog language.
7.1.2 Setting the date, time and local time
The Touch Control displays the date and time in accordance with ISO
standard 8601.
Proceed as follows to set the date and time:
1
Open the system settings
■ In the main dialog, tap on [System].
■ Tap on [System settings].
7 System settings
The dialog System / System settings is displayed.
2
Enter the date
■ Tap on the input field for the date.
The editor opens.
■ Enter the current date in the format YYYY-MM-DD and confirm
with [OK].
The arrow keys [⇦] and [⇨] are used to move the cursor to the
left or to the right by one character.
The input is saved and the editor is closed.
3
Enter the time
■ Tap on the input field for the time.
The editor opens.
■ Enter the current time in the format hh:mm:ss (24-hour format)
and confirm with [OK].
The arrow keys [⇦] and [⇨] are used to move the cursor to the
left or to the right by one character.
The input is saved and the editor is closed.
900 Touch Control
■■■■■■■■
23
Page 40

7.2 System-specific dialog options
4
Enter the local time
■ Tap on the list box Local time - UTC and select the difference
from the UTC (Coordinated Universal Time).
The selection off means that the time is saved with no difference
from the UTC.
5
Save the settings
Tap on the fixed keys [ ] or [ ].
The time settings are saved.
7.2 System-specific dialog options
Main dialog: System ▶ System settings ▶ Dialog options
A wide array of different titration systems can be operated with Touch
Control. Accordingly, the Touch Control displays far more functions than
are required for any particular system.
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Dialog
■■■■■■■■
24
If you work without a login function, in this dialog you can define
whether the system should generally be operated in expert mode or in
routine mode. If you work with the login function activated, you must
define this setting separately for each user (see Chapter 7.3.1, page 29).
Dialog mode in which the user may operate the system.
Selection Expert dialog | Routine dialog
Expert dialog
All functions that are supported by the connected system are available.
900 Touch Control
Page 41

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
[Command list]
[Fixed keys]
[Routine dialog]
7 System settings
Routine dialog
The user dialog can be limited for routine operations. Only selected
functions are available (see Configuring the routine dialog, page 26).
Block unneeded method commands (see "Blocking unneeded commands
and fixed keys", page 25).
Block unneeded fixed keys (see "Blocking unneeded commands and fixed
keys", page 25).
Configure functions for the routine dialog (see "Configuring the routine
dialog", page 26).
Selecting the dialog mode
Proceed as follows to change the dialog mode:
1
Select the dialog mode
Open the selection list Dialog and select either Expert dialog or
Routine dialog.
2
Save the settings
Tap on the fixed keys [ ] or [ ].
The setting will apply to all dialogs.
NOTE
If you have selected Routine dialog and if the routine dialog was
configured in such a way that the dialog System settings / Dia-
log options is blocked, then you can switch back over to the
expert dialog as follows:
■ Operation without login function:
In the main dialog, enter User = Metrohm.
■ Operation with login function:
A user who works with expert dialog must log in.
Blocking unneeded commands and fixed keys
This following configurations apply for both dialog modes: routine dialog
and expert dialog.
900 Touch Control
■■■■■■■■
25
Page 42

7.2 System-specific dialog options
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Blocking commands
Proceed as follows to block unneeded commands:
1
Display the command list
Tap on the button [Command list].
The list of all command groups is displayed.
2
Deactivate command groups
Deactivate those command groups which are not permitted to be
used.
3
Save the settings
Tap on the fixed keys [ ] or [ ].
All deactivated commands appear grayed out in the method editor
and cannot be used for creating methods.
Blocking fixed keys
Proceed as follows to block unneeded fixed keys:
1
Display fixed keys which can be blocked
Tap on the button [Fixed keys].
All fixed keys which can be blocked are displayed.
2
Deactivate fixed keys
Deactivate those fixed keys which are not permitted to be used.
3
Save the settings
Tap on the fixed keys [ ] or [ ].
Deactivated fixed keys cannot be used.
Configuring the routine dialog
A suitable Standard configuration has already been saved for routine
operations.
■■■■■■■■
26
■ Methods can only be loaded, but not modified or created.
■ Determinations cannot be recalculated.
You can readjust this standard configuration by disabling additional functions or re-enabling disabled functions.
900 Touch Control
Page 43

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
7 System settings
NOTE
The configuration of the routine dialog applies for all routine users. You
also have the option of defining user-specific routine settings. To do
this, you must work with the login function activated and create an
identification profile for each user (see Chapter 7.3.2, page 33).
Proceed as follows to modify the configuration for the routine dialog:
1
Open the dialog
Tap on the button [Routine dialog].
The list of all buttons in the main dialog, in the manual control, etc. is
displayed:
900 Touch Control
2
Deactivate buttons
Deactivate those buttons which are not permitted to be used.
All deactivated buttons will appear grayed-out, i.e. they are inactive.
3
Deactivate other functions
Many additional buttons and parameters can be disabled in the dialogs of [System], [Load method], [Control], [Edit parameters]
and [Results]. The corresponding option must be activated in order
to enable these buttons.
4
Save the settings
Tap on the fixed keys [ ] or [ ].
■■■■■■■■
27
Page 44

7.3 User administration
All deactivated functions will appear grayed-out, i.e. they are inactive.
7.3 User administration
Main dialog: System ▶ System settings ▶ User admin.
All of the functions of the user administration are described in this chapter. No user administration is mandatory for the simple operation of a
titration system. If, however, you wish to be in compliance with FDA
guideline 21 CFR Part 11, then you must use the functions of the user
administration. Additional information regarding the requirements of the
FDA guideline can be found in the Titrando Compliance Guide.
NOTE
If you work with the login function activated, then the user administration is accessible only for users with administrator rights. This means
that you must ensure that at least two users have administrator rights
so at least one of them will be available. Keep the access rights for a
user with administrator rights in a safe place so that they are accessible
in an emergency.
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
■■■■■■■■
28
The following data is displayed in the user list for each user:
■ Name
■ Dialog mode in which the user may operate the system.
■ Status
You can use the user list two different ways:
900 Touch Control
Page 45

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
[Login options]
[Create ID profile]
[New]
7 System settings
■ Operation with login function:
If you work with the login function activated, i.e. if each user must log
into the system before starting work, then only those users entered in
the list can log in. The user who is currently logged in is shown in the
main dialog.
■ Operation without login function:
If you work without the login function, the users whose names are
entered in the list can be selected in the main dialog or a user name
can be entered. This makes it possible to document who has operated
the titration system.
Define the settings for the login, Audit Trail, etc. (see Chapter 7.3.3, page
33).
Create an identification profile for the selected user on a storage medium
(see Chapter 7.3.2, page 33).
Add a new user to the list (see Chapter 7.3.1, page 29).
[Delete]
Delete the selected user from the list.
NOTE
Once you have worked with the login function and password protection, users can no longer be deleted, even if the password protection is
disabled again. The status of these users must be set to inactive
(requirement of FDA guideline 21 CFR Part 11).
The last user with administrator rights cannot be deleted.
[Edit]
Edit the data of the selected user (see Chapter 7.3.1, page 29).
7.3.1 Editing the user configuration
User list: User ▶ New / Edit
900 Touch Control
■■■■■■■■
29
Page 46

7.3 User administration
User
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
The designation of the user is used for unambiguous identification, e.g.
the company internal shorthand symbol or the personal number. The user
name is printed out in all reports containing determination data and
stored in the determination file. Each file always contains the name of the
user who created it and the name of the last user to edit it.
Full name
Dialog
Status
Entry 24 characters maximum
Default value empty
Complete name of the user.
Entry 24 characters maximum
Default value empty
Dialog mode in which the user may operate the system.
Selection Expert dialog | Routine dialog
Expert dialog
All functions that are supported by the connected system are available.
Routine dialog
The user dialog can be limited for routine operations. Only selected
functions are available (see Configuring the routine dialog, page 26).
Status of the user. Users can be deactivated. This function is useful, for
instance, if the user is no longer authorized to operate the system or no
longer works for the company.
■■■■■■■■
30
Selection active | inactive
Default value active
900 Touch Control
Page 47

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Admin. rights
[Favorites]
7 System settings
active
The user is authorized to operate the system.
inactive
The user is not authorized to operate the system and can no longer log
in.
on | off (Default value: off)
If this option is activated, then the user has administrator rights.
NOTE
The last user with administrator rights cannot be deleted anymore.
Save methods and sample tables as user specific favorites (see Chapter 19,
page 188).
[Signature method]
Assign the authorization to use and sign methods (see "Dialog "Edit user /
Signature method"", page 31).
[Signature determ.]
Assign the authorization to use and sign determinations (see "Dialog "Edit
user / Signature determination"", page 32).
Dialog "Edit user / Signature method"
User: Edit ▶ Signature method
Authorizations for using and signing methods can be defined in this dialog. These settings are only effective if you are working with the login
function enabled and password protection.
Use only released methods
on | off (Default value: off)
If this option is activated, then the user may only start methods that have
been released.
Review methods (signature level 1)
on | off (Default value: off)
900 Touch Control
If this option is activated, then the user may only sign methods which
have the status saved. The method is assigned the status reviewed.
■■■■■■■■
31
Page 48

7.3 User administration
Release methods (signature level 2)
on | off (Default value: off)
If this option is activated, then the user may only sign methods which
have the status reviewed. The method is assigned the status released.
NOTE
If the two options Review methods and Release methods are
selected for a user, then this user can sign different methods at either
level 1 or level 2, but not the same method at both level 1 and level 2.
Delete signatures
on | off (Default value: off)
If this option is activated, then the user may delete the signatures of a
method which has been released. The method is assigned the status
saved. The signatures of a method can only be deleted if it has the status
released.
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Dialog "Edit user / Signature determination"
User: Edit ▶ Signature determ.
Authorizations for signing determinations can be defined in this dialog.
These settings are only effective if you are working with the login function
enabled and password protection.
Review determinations (signature level 1)
on | off (Default value: off)
If this option is activated, then the user may only sign determinations at
the first level. The determination is assigned the status reviewed.
Release determinations (signature level 2)
on | off (Default value: off)
If this option is activated, then the user may only sign determinations at
the second level. The determination is assigned the status released.
Delete signatures
on | off (Default value: off)
If this option is activated, then the user may delete the signatures of a
determination which has been released. The signatures of a determination
can only be deleted if it has the status released.
■■■■■■■■
32
900 Touch Control
Page 49

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
7.3.2 Creating an identification profile
User list: User ▶ Create ID profile
If you plan to carry out the login with an identification profile (see Chapter
7.3.3, page 33), then you must first create an identification profile on a
storage medium for each user. A check can then be made at the time of
login as to whether or not the user does exist and whether or not he or
she is working in the expert dialog or in the routine dialog. After a successful login the routine dialog settings stored on the card are loaded.
NOTE
In addition to the user name, the current routine dialog settings are
also stored in this identification profile. This means you can define userspecific routine dialog settings for each user. However, you must configure them (see "Configuring the routine dialog", page 26), before
you create the identification profile.
7 System settings
Before you create the identification profile, check whether the desired
routine dialog settings are active.
1
Plug in a storage medium
Plug in the USB storage medium.
2
Select a user
In the user list, select the user for whom the profile is to be created.
3
Create the identification profile
Tap on [Create ID profile].
The user configuration and the current routine dialog settings are
saved.
7.3.3 Defining login options
Main dialog: System ▶ System settings ▶ User admin. ▶ Login
options
There are a number of different ways to log onto the system:
900 Touch Control
■ Without login
■ Login via user name
■ Login via user name and password
■ Login via identification profile
■ Login via identification profile and password
■■■■■■■■
33
Page 50

7.3 User administration
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
NOTE
If you work with the login function activated, then the user administration is accessible only for users with administrator rights. This means
that you must ensure that at least two users have administrator rights
so at least one of them will be available. Keep the access rights for a
user with administrator rights in a safe place so that they are accessible
in an emergency.
NOTE
If you exit this dialog with [ ] or [ ], and if you have selected one
of the login variants Login via user name or Login via identifica-
tion profile, then the login dialog will open automatically and you
must also log in to the system.
This means that you must make sure that you have first defined all the
users and created the identification profiles before you activate the
login function.
Login via user name
Login via identification profile
■■■■■■■■
34
on | off (Default value: off)
If this option is activated, then the user must log in with his or her unambiguous identification.
on | off (Default value: off)
If this option is activated, then the login will take place via USB storage
medium with the identification profile stored on it.
900 Touch Control
Page 51

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Password required
on | off (Default value: off)
If this option is activated, then the user must enter a password in addition
to his or her user name or identification profile.
Logout automatically
on | off (Default value: off)
If this option is activated, then the user will be logged out automatically
after the specified time.
Input range 1 - 60 min
Login only for the same user
on | off (Default value: off)
If this option is activated, then only the same user may log in again after
he or she has logged out. Users with administrator rights can, however,
log in at any time.
7 System settings
[Audit Trail]
Define the settings for recording an Audit Trail (see Chapter 7.3.7, page
39).
[Reasons]
Predefine a list of reasons that can be selected at the modification/signature of a method or determination (see Chapter 7.3.6, page 38).
[Modific. options]
Define for which modifications a reason is required (see Chapter 7.3.5,
page 37).
[Password options]
Define the settings for the password, see following chapter.
7.3.4 Password options
Main dialog: System ▶ System settings ▶ User admin. ▶ Login
options ▶ Password options
You can make various settings for password entry in the password
options.
900 Touch Control
■■■■■■■■
35
Page 52

7.3 User administration
Minimum password length
Minimum number of characters of the passwords.
Input range 1 - 10
Default value 1
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
No. of entry attempts
If the user has logged in incorrectly this many times, then it will automatically be deactivated. It can only be reactivated by a user with administrator rights.
Input range 2 - 5
Selection off
Default value off
Special characters required
on | off (Default value: off)
If this option is activated, then the password must contain one of the following special characters: ° § + ¦ @ * # ç % & ¬ ( ) = ' ^ ` ~ ] [ } { - _ : . ; , >
< £ !
Password expires
on | off (Default value: off)
If this option is activated, then the user must define a new password after
the time specified. A password that has already been used cannot be used
again.
■■■■■■■■
36
Input range 1 - 999 days
Default value 365 days
900 Touch Control
Page 53

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
7 System settings
Forgotten password
CAUTION
If a user has forgotten his password, a new user name must be defined.
The same user name can only be used again after a re-installation and
re-creating the user list.
Proceed as follows:
1
Create a backup
Create a backup (see Chapter 12.3, page 125).
2
Initialize the system
Switch off the Touch Control and carry out a system initialization (see
Chapter 30.1, page 480).
3
Restore backed-up data
Use the function Restore to reload the data from the backup into
your system (see Chapter 12.3.1, page 125).
Deactivate the options User list and System settings / User
admin..
4
Switch on the Touch Control
Switch the Touch Control back on again after a few seconds.
5
Restore the user list
Create the user list again and redefine the login options.
7.3.5 Modification options
Main dialog: System ▶ System settings ▶ User admin. ▶ Login
options ▶ Modific. options
In the dialog Login options / Modification options, you can define for
which actions a reason must be entered. These reasons are documented
in the Audit Trail (see Chapter 7.3.7, page 39) together with the modification. The reason for the last modification is shown in the properties of
the method or determination.
900 Touch Control
■■■■■■■■
37
Page 54

7.3 User administration
The reasons are only requested when working with activated login
function and password.
Saving modified method
on | off (Default value: off)
If this option is activated, then a reason must be given when saving a
method modification.
Recalculating determination
on | off (Default value: off)
If this option is activated, then a reason must be given when determinations are being recalculated.
7.3.6 Reasons
Main dialog: System ▶ System settings ▶ User admin. ▶ Login
options ▶ Reasons
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
NOTE
[New]
[Delete]
In the dialog Login options / Reasons, you can create a selection list
containing reasons from which a selection can be made when signing and
modifying methods and determinations. Some reasons have already been
provided.
Add a new reason to the list.
Delete the selected reason from the list.
■■■■■■■■
38
900 Touch Control
Page 55

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
[Edit]
7.3.7 Audit Trail
7 System settings
Change the designation of the selected reason.
Main dialog: System ▶ System settings ▶ User admin. ▶ Login
options ▶ Audit Trail
An Audit Trail is an automatically generated log of all user activities. An
Audit Trail contains precise logs of user actions (date, time, user, action,
etc.). Recording an Audit Trail is important for compliance with FDA
guideline 21 CFR Part 11 when using PC programs. A step-by-step
description of how you must proceed to remain in compliance with the
FDA guideline is included in the Titrando Compliance Guide. The Audit
Trail is saved to the internal memory.
You can also use the Audit Trail function specifically to record the data
which are of interest to you.
You can view, filter and export the Audit Trail on a PC with the supplied
software program AuditTrailViewer. Details concerning utilization of the
AuditTrailViewer can be found in the Appendix (chapter 32.8, page 498).
Security log
User administration log
Method log
If necessary, you can delete all of the entries in the Audit Trail with
[Delete Audit Trail]. Do not fail to create a backup before doing so,
however.
on | off (Default value: off)
If this option is activated, then the following events will be recorded: user
login/logout, password changes, automatic deactivation of users and messages displayed during the login procedure.
on | off (Default value: off)
If this option is activated, then all changes with respect to user administration will be recorded (modifying user list/user data, changing login
options, etc.).
on | off (Default value: off)
If this option is activated, then all changes with respect to methods and
determinations will be recorded (saving, deleting, renaming, copying and
loading methods; editing method parameters; starting, stopping, pausing
determinations).
900 Touch Control
■■■■■■■■
39
Page 56

7.4 Measured value display
Data log
on | off (Default value: off)
If this option is activated, then the following events will be recorded:
changing sample data; settings in the Control dialog, recalculating determinations, changing statistics data, changing the titer/concentration of a
titrant, changing the calibration data of a sensor, changing the value of a
common variable.
System log
on | off (Default value: off)
If this option is activated, then the program start and the displayed messages of the following types will be recorded:
■ : General warning messages
■ : Error messages
7.4 Measured value display
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Main dialog: System ▶ System settings ▶ Meas. value display
The number of decimal places can be defined for pH values and voltages.
This setting refers exclusively to the display of the measured values in the
live display and in the manual control. The values will, however, always be
stored with their full accuracy.
7.5 Acoustic signals
Main dialog: System ▶ System settings ▶ Acoustic signals
You can define acoustic signals in order to direct attention to particular
events. You can define signals for the following events:
■ Wrong manipulation
An acoustic signal will sound each time an invalid action is attempted
(e.g. pressing [
■ Display a message
A short beep will sound each time a message appears on the display.
This informs the user that the message must be confirmed.
■ Button contact
Each time a button is touched on the touch screen, this will be confirmed by an acoustic signal.
■ External data input
An acoustic signal will provide confirmation each time data is received
from external devices (e.g. balance, barcode reader).
] again when Help is open).
■■■■■■■■
40
900 Touch Control
Page 57

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
8 Titrants
8 Titrants
Main dialog: System ▶ Titrants
This chapter describes how you can create a list of titrants used in the system. Titrants can be used in intelligent buret units or in non-intelligent
buret units. Intelligent buret units have a built-in data chip on which the
data for the titrant is stored. This data is automatically read out during
attachment and entered in the titrant list.
The titrant list can contain a maximum of 30 titrants. The following data is
specified for each titrant:
■ Designation
■ Cylinder volume
■ Type
– EU: exchange unit without data chip
– IEU: exchange unit with integrated data chip
– DU: dosing unit without data chip
– IDU: dosing unit with integrated data chip
■ MSB connector of the dosing device/control device (only when
exchange unit/dosing unit is attached)
Titrants in exchange units/dosing units with integrated data chips are
depicted in green lettering.
The following titrant data is stored in the titrant list:
■ Name
Each titrant in the system is identified by its unambiguous name.
■ Concentration
■ Current titer
■ Working life
900 Touch Control
■■■■■■■■
41
Page 58

8.1 Adding a new titrant
[New]
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
■ Data on exchange/dosing unit:
– Parameters for the function PREP
– Length and diameter of the tubings
– Port assignment of the dosing unit
– Cylinder volume
– Serial number
– etc.
■ etc.
NOTE
If data is read out from the data chip, then a check is made whether
the titrant list already contains a titrant of the same type with the identical serial number. If this is the case, then the older data set will
always be overwritten by the new data set, no matter whether the
data set in the titrant list or the data set on the data chip is the most
recent one.
Add a new titrant to the list (see Chapter 8.1, page 42).
[Delete]
Delete the selected titrant from the list.
[Edit]
Edit the data of the selected titrant (see Chapter 8.2, page 43).
8.1 Adding a new titrant
Before you can use a titrant, you must add it to the titrant list. To do this,
use the button [New].
■ Exchange unit/dosing unit with data chip:
The exchange unit or dosing unit must be attached. All dosing devices
on which non-configured exchange or dosing units have been detected are included in a selection list. Tapping on the button [Edit] opens
the properties dialog, see following chapter.
■ Exchange unit/dosing unit without data chip:
The properties dialog is opened after the dosing unit type has been
selected, see following chapter.
■■■■■■■■
42
900 Touch Control
Page 59

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
8.2 Editing titrant data
Titrant list: Titrants ▶ New / Edit
All of the data for the selected titrant is displayed in the dialog Titrants /
Edit.
8 Titrants
Titrant
Concentration
Comment
Titer
The designation of the titrant is used for unambiguous identification.
Entry 24 characters maximum
Selection Selection of frequently used titrants
Concentration of the titrant.
Input range –999999999 - 9999999999
Default value 1.000
Unit of the concentration.
Entry 10 characters maximum
Selection µmol/mL | mmol/L | mol/L | g/L | mg/L | mg/mL |
µg/L | ppm | % | mEq/L
Default value mol/L
Entry 24 characters maximum
Titer of the titrant.
900 Touch Control
Input range –999999999 - 9999999999
Default value 1.000
■■■■■■■■
43
Page 60

8.2 Editing titrant data
Date titer det.
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Unit of the titer.
Entry 10 characters maximum
Default value empty
Selection µmol/mL | mmol/L | mol/L | g/L | mg/L | mg/mL |
µg/L | ppm | % | mEq/L
NOTE
If you modify the titer or the concentration of the titrant in a loaded
determination at a later date and would then like to recalculate the
determination with the corrected value, then you must modify the value
in the determination data under View data / Titrant data (see "Cali-
bration and titrant data", page 216).
Date and time of the last titer determination. For new titrants, the time
the preparation was made is specified until after the first time a titer determination has been carried out.
[Working life]
[Dosing unit]
[Exchange unit]
[Titer options]
Define the working life of the sensor (see Chapter 8.3, page 45).
This button is only displayed for Type = IDU or DU.
Define the properties of the dosing unit used (see Chapter 8.4, page
46).
This button is only displayed with Type = IEU or EU.
Define the properties of the exchange unit used (see Chapter 8.5, page
52).
Display the properties for the titer determination (see Chapter 8.7, page
58).
■■■■■■■■
44
900 Touch Control
Page 61

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
8.3 Monitoring the working life
Titrant: Edit ▶ Working life
In the dialog Edit titrant / Working life, you can define the time interval after which the titrant must be replaced. This is particularly important if
your titrant has a limited working life. If you do not wish to monitor the
working life, then you can enter only the date of manufacture for documentation purposes.
Preparation date
Date on which the reagent was manufactured or the bottle was opened.
For new titrants, the time the preparation was made will be specified.
Format: YYYY:MM:DD
Monitoring
on | off (Default value: off)
8 Titrants
Working life
Expiry date
Action
If this parameter is activated, then the working life will be monitored.
If you define a time interval for the working life, then the Expiry date will
be tracked automatically.
Input range 1 - 999 days
Default value 999 days
If you define an expiry date, then the Working life will be tracked automatically.
Format: YYYY:MM:DD
Selection of the action which is carried out when the time interval has
expired.
Selection Display message | Document message | Cancel
determination
Default value Display message
For all three options it is documented in the determination data (see dialog More determination
data / Messages), that the time interval has been
expired.
900 Touch Control
■■■■■■■■
45
Page 62

8.4 Dosing unit
Display message
A message is displayed. You can select whether you want to continue
with the determination or cancel the run.
Document message
In the determination data it will be documented, that the time interval
has been expired.
Cancel determination
The determination is stopped.
8.4 Dosing unit
Titrant: Edit ▶ Dosing unit
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Name
Order number
Serial number
You can edit data for the dosing unit of the titrant in this dialog.
Designation of the exchange or dosing unit.
Entry 24 characters maximum
Default value empty
Order number of the exchange or dosing unit. It will be read out automatically on units with integrated data chips.
Entry 24 characters maximum
Default value empty
Serial number of the exchange or dosing unit. It will be read out automatically on units with integrated data chips.
Entry 8 digits maximum
■■■■■■■■
46
900 Touch Control
Page 63

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Cylinder volume
Serial no. cyl.
[Valve disk]
[GLP test]
[PREP param.]
8 Titrants
Cylinder volume of the dosing unit. It will be read out automatically on
dosing units with integrated data chips.
Selection 2 | 5 | 10 | 20 | 50
Default value 20
Serial number of the dosing cylinder. It will be read out automatically on
exchange or dosing units with integrated data chips. The number can be
changed manually at any time, e.g. when a cylinder is replaced.
Entry 8 digits maximum
Specify the shift direction of the valve disc (see Chapter 8.4.3, page 51).
Define the time interval for the GLP test (see Chapter 8.6, page 56).
Enter the parameters for the preparation (see Chapter 8.4.1, page 47).
[Tubing param.]
Enter the parameters for the connected tubings (see Chapter 8.4.2, page
48).
8.4.1 Parameters for preparing (PREP) and emptying (EMPTY)
Titrant: Edit ▶ Dosing unit ▶ PREP param.
In the dialog Dosing unit / PREP parameters, you can adjust the
parameters for the execution of the Prepare (command PREP) and
Empty (command EMPTY) functions. The Prepare function is used to
rinse the cylinder and tubing of the dosing unit and fill it air bubble-free.
You should carry out this function before the first determination or once
per day. The EMPTY function empties the cylinder and the tubings of the
dosing unit.
Dosing port PREP/EMPTY
Dosing port through which the cylinder contents are ejected.
Selection Dosing port 1 | Dosing port 2 | Fill port | Spe-
cial port
Default value Dosing port 1
Dosing rate Dos. port 1
900 Touch Control
Rate used for the aspiration and ejection of the reagent via dosing port 1.
Input range 0.01 - 166.00 mL/min
■■■■■■■■
47
Page 64

8.4 Dosing unit
Dosing rate Dos. port 2
Dosing rate Fill port
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Selection maximum
Default value maximum
maximum
The maximum dosing rate depends on the cylinder volume (see Chapter 32.1, page 488).
Rate used for the aspiration and ejection of the reagent via dosing port 2.
Input range 0.01 - 166.00 mL/min
Selection maximum
Default value maximum
maximum
The maximum dosing rate depends on the cylinder volume (see Chapter 32.1, page 488).
Rate used for the aspiration and ejection of the reagent via fill port.
Input range 0.01 - 166.00 mL/min
Selection maximum
Default value maximum
maximum
The maximum dosing rate depends on the cylinder volume (see Chapter 32.1, page 488).
Dosing rate Spec.port
Rate used for the aspiration and ejection of the reagent via the special
port.
Input range 0.01 - 166.00 mL/min
Selection maximum
Default value maximum
maximum
The maximum dosing rate depends on the cylinder volume (see Chapter 32.1, page 488).
8.4.2 Tubing parameters
Titrant: Edit ▶ Dosing unit ▶ Tubing param.
You can enter the length and diameter of the connected tubings in the
dialog Dosing unit / Tubing parameters. The values which have
already been entered correspond to the dimensions of the supplied standard tubings. In addition, the port assignment can be modified.
■■■■■■■■
48
900 Touch Control
Page 65

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Dosing port 1
Port
Length
8 Titrants
NOTE
These parameters are important for the correct execution of the Preparing (PREP command) and Emptying (EMPTY command) functions,
because the volumes of the tubing connections are taken into account.
Port to be used as dosing port 1 for the PREP and EMPTY (see Figure 8,
page 51) functions.
Selection Port 1 | Port 2 | Port 3 | Port 4
Default value Port 1
Length of the tubing.
Diameter
Dosing port 2
Port
Length
Input range 0.0 - 999.9 cm
Default value 40.0 cm
The setting 0.0 means that this tubing will neither
be rinsed nor emptied.
Diameter of the tubing.
Input range 0.0 - 9.9 mm
Default value 2.0 mm
Port to be used as dosing port 2 for the PREP and EMPTY functions (see
Figure 8, page 51).
Selection Port 1 | Port 2 | Port 3 | Port 4
Default value Port 3
Length of the tubing.
900 Touch Control
Input range 0.0 - 999.9 cm
Default value 0.0 cm
The setting 0.0 means that this tubing will neither
be rinsed nor emptied.
■■■■■■■■
49
Page 66

8.4 Dosing unit
Diameter
Fill port
Port
Length
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Diameter of the tubing.
Input range 0.0 - 9.9 mm
Default value 2.0 mm
Port to be used as fill port for the PREP and EMPTY functions (see Figure
8, page 51).
Selection Port 1 | Port 2 | Port 3 | Port 4
Default value Port 2
Length of the tubing.
Input range 0.0 - 999.9 cm
Default value 25.0 cm
The setting 0.0 means that this tubing will neither
be rinsed nor emptied.
Diameter
Special port
Port
Length
Diameter of the tubing.
Input range 0.0 - 9.9 mm
Default value 2.0 mm
Port to be used as special port for the PREP and EMPTY functions (see
Figure 8, page 51).
Selection Port 1 | Port 2 | Port 3 | Port 4
Default value Port 4
Length of the tubing.
Input range 0.0 - 999.9 cm
Default value 0.0 cm
The setting 0.0 means that this tubing will neither
be rinsed nor emptied.
■■■■■■■■
50
Diameter
Diameter of the tubing.
900 Touch Control
Page 67

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
5
4
3
2
1
8 Titrants
Input range 0.0 - 9.9 mm
Default value 2.0 mm
Figure 8 Dosing unit – port assignment
VENT
1
This port is set up for the deaeration of the
reagent bottle. An adsorber tube (filled with
desiccant) is usually mounted here.
Port 2
3
The default definition of this port is the filling port. A riser tube is usually mounted to
it.
Port 3
5
The default definition of this port is dosing
port 2.
8.4.3 Shift direction of the valve disk
Titrant: Edit ▶ Dosing unit ▶ Valve disk
In this dialog, you can specify the shift direction of the valve disc.
Direction
Shift direction of the valve disc.
Port 1
2
The default definition of this port is dosing
port 1.
Port 4
4
Air is suctioned through this port during the
Emptying function.
Selection descending | ascending | automatic | not over
Default value automatic
descending
The ports are moved to in descending order.
900 Touch Control
■■■■■■■■
51
Page 68

8.5 Exchange unit
ascending
The ports are moved to in ascending order.
automatic
The ports are moved to by the shortest path.
not over
Define a protected port.
Not over port
This parameter can only be edited with Direction = not over.
Define a protected port if the valve disc is not to be rotated over this port
(useful with pipetting functions). The protected port can, however, be
moved to directly.
Selection 1 | 2 | 3 | 4
Default value 4
8.5 Exchange unit
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Name
Titrant: Edit ▶ Exchange unit
You can edit data for the exchange unit of the titrant in this dialog.
Designation of the exchange or dosing unit.
Entry 24 characters maximum
Default value empty
Order number
■■■■■■■■
52
Order number of the exchange or dosing unit. It will be read out automatically on units with integrated data chips.
900 Touch Control
Page 69

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Serial number
Cylinder volume
Serial no. cyl.
8 Titrants
Entry 24 characters maximum
Default value empty
Serial number of the exchange or dosing unit. It will be read out automatically on units with integrated data chips.
Entry 8 digits maximum
Cylinder volume of the exchange unit. It will be read out automatically on
exchange units with integrated data chips.
Selection 1 | 5 | 10 | 20 | 50
Default value 20
Serial number of the dosing cylinder. It will be read out automatically on
exchange or dosing units with integrated data chips. The number can be
changed manually at any time, e.g. when a cylinder is replaced.
Entry 8 digits maximum
[GLP test]
Define the time interval for the GLP test (see Chapter 8.6, page 56).
[PREP param.]
Enter the parameters for the preparation (see Chapter 8.5.1, page 53).
[Tubing param.]
Enter the parameters for the connected tubings (see Chapter 8.5.2, page
54).
8.5.1 Parameters for the preparation (PREP)
Titrant: Edit ▶ Exchange unit ▶ PREP param.
In the dialog Exchange unit / PREP parameters, you can adjust the
parameters for the execution of the Prepare function (command PREP).
This function is used to rinse the cylinder and tubings of the exchange unit
and fill it air bubble-free. You should carry out this function before the
first determination or once per day.
Volume
900 Touch Control
Volume of titrant dosed during a rinsing cycle.
Input range 0.00000 - 99999.9 mL
Selection Cylinder volume
Default value Cylinder volume
■■■■■■■■
53
Page 70

8.5 Exchange unit
Cycles
Dosing rate
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Cylinder volume
The entire cylinder volume is being dosed.
Number of rinsing cycles. We recommend carrying out at least two rinsing
cycles in order to remove all air bubbles.
Selection 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9
Default value 2
Rate at which it is dosed.
Input range 0.01 - 166.00 mL/min
Selection maximum
Default value maximum
maximum
The maximum dosing rate depends on the cylinder volume (see Chapter 32, page 488).
Filling rate
Rate at which the dosing cylinder is filled.
Input range 0.01 - 166.00 mL/min
Selection maximum
Default value maximum
maximum
The maximum filling rate depends on the cylinder volume (see Chapter
32, page 488).
8.5.2 Tubing parameters
Titrant: Edit ▶ Exchange unit ▶ Tubing param.
You can enter the length and diameter of the connected tubings in the
dialog Exchange unit / Tubing parameters. The values which have
already been entered correspond to the dimensions of the supplied standard tubings.
Dosing tip
Tubing to the dosing tip (9-2).
■■■■■■■■
54
Length
Length of the tubing.
Input range 0.0 - 999.9 cm
Default value 40.0 cm
900 Touch Control
Page 71

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Diameter
Dosing cylinder
Length
Diameter
8 Titrants
Diameter of the tubing.
Input range 0.0 - 9.9 mm
Default value 2.0 mm
Tubing to the dosing cylinder (9-3).
Length of the tubing.
Input range 0.0 - 999.9 cm
Default value 13.0 cm
Diameter of the tubing.
Input range 0.0 - 9.9 mm
Default value 2.0 mm
Reagent bottle
Length
Diameter
Tubing to the reagent bottle (9-1).
Length of the tubing.
Input range 0.0 - 999.9 cm
Default value 25.0 cm
Diameter of the tubing.
Input range 0.0 - 9.9 mm
Default value 2.0 mm
900 Touch Control
■■■■■■■■
55
Page 72

8.6 GLP test for exchange unit and dosing unit
1
2
3
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Figure 9 Exchange unit – tubing connections
Tubing to the reagent bottle
1
Tubing to the dosing cylinder
3
Tubing to the dosing tip
2
8.6 GLP test for exchange unit and dosing unit
Titrant: Edit ▶ Dosing unit / Exchange unit ▶ GLP test
In the dialog Exchange unit / GLP test or Dosing unit / GLP test,
respectively, you can define the time interval after which a GLP test must
be carried out again for the exchange unit or dosing unit.
GLP test date
Date on which the last GLP test was carried out.
Format: YYYY:MM:DD
Monitoring
on | off (Default value: off)
If this parameter is activated, then the time interval after which a GLP test
has to be carried out again will be monitored.
■■■■■■■■
56
900 Touch Control
Page 73

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
GLP test interval
Next GLP test
Action
8 Titrants
If you define a time interval for the GLP test, then the date in Next GLP
test will be tracked automatically.
Input range 1 - 999 days
Default value 999 days
If you define a date for the next GLP test, then the GLP test interval will
be tracked automatically.
Format: YYYY:MM:DD
Selection of the action which is carried out when the time interval has
expired.
Selection Display message | Document message | Cancel
determination
Default value Display message
For all three options it is documented in the determination data (see dialog More determination
data / Messages), that the time interval has been
expired.
Display message
A message is displayed. You can select whether you want to continue
with the determination or cancel the run.
Document message
In the determination data it will be documented, that the time interval
has been expired.
Cancel determination
The determination is stopped.
900 Touch Control
■■■■■■■■
57
Page 74

8.7 Titer determination options and data
8.7 Titer determination options and data
Titrant: Edit ▶ Titer options
Detailed information concerning the titer determination is displayed in the
dialog Edit titrant / Titer options:
■ Titer method
Method by which the titer was determined. If the titer was entered
manually, then manual will be displayed.
■ User
User who carried out the titer determination.
■ Statistical data
The following information is also displayed for automatically assigned
titers if the mean value of the results has been saved as the titer (see
"Save as titer", page 151):
– n (titer det.)
Number of titer determinations.
– s abs
Absolute standard deviation
– s rel
Relative standard deviation
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
[Validity]
Define the time interval for the titer validity (see Chapter 8.7.1, page
58).
[History]
Display information about the last ten titer determinations (see Chapter
8.7.2, page 59).
8.7.1 Titer validity
Titrant: Edit ▶ Titer options ▶ Validity
In the dialog Titer options / Validity, you can define the time interval
after which the titer must be determined again.
Date titer det.
Date and time of the last titer determination. For new titrants, the time
the preparation was made is specified until after the first time a titer determination has been carried out.
Monitoring
on | off (Default value: off)
■■■■■■■■
58
If this parameter is activated, then the titer validity will be monitored.
900 Touch Control
Page 75

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Titer validity
Next titer determ.
Action
8 Titrants
If you define a time interval for the validity of the titer, then the date in
Next titer determ. will be tracked automatically.
Input range 1 - 999 days
Default value 999 days
If you define a date for the next titer determination, then the time interval
for the Titer validity will be tracked automatically.
Format: YYYY:MM:DD
Selection of the action which is carried out when the time interval has
expired.
Selection Display message | Document message | Cancel
determination
Default value Display message
For all three options it is documented in the determination data (see dialog More determination
data / Messages), that the time interval has been
expired.
Display message
A message is displayed. You can select whether you want to continue
with the determination or cancel the run.
Document message
In the determination data it will be documented, that the time interval
has been expired.
Cancel determination
The determination is stopped.
8.7.2 Properties of the previous titer determinations
Dialog "Titer options / History"
Titrant: Edit ▶ Titer options ▶ History
The date, time and titer of the last ten titer determinations are displayed in
tabular form in the dialog Titer options / History. Titers that were
determined automatically will be displayed in green; manually entered titer
values will be displayed in black with the designation (m). You can delete
these entries, e.g. if you have opened a new bottle.
900 Touch Control
■■■■■■■■
59
Page 76

8.7 Titer determination options and data
If multiple determinations have been carried out in order to determine
the titer, then only one entry will be made in the history.
[Delete History]
Delete the entire history.
[Graph]
Open the diagram of the titer values, see following chapter.
Dialog "History / Graph"
Titrant: Edit ▶ Titer options ▶ History ▶ Graph
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
NOTE
[Limits]
■■■■■■■■
60
In this diagram, titer values are plotted against the date of the titer determination. You can define warning limits (blue dashed lines) and intervention limits (red dashed lines). These limits will not, however, be monitored.
Define warning and intervention limits.
900 Touch Control
Page 77

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
9 Reagents
9 Reagents
Main dialog: System ▶ Reagents
This chapter describes how you can create a list of the reagents used in
the system. Depending on the usage a distinction is made between two
types of reagents:
■ Reagent for volumetric determinations
■ Reagents for coulometric determinations
[New]
[Delete]
[Edit]
The list of reagents gives the designation and type of each reagent.
Add a new reagent to the list, see following chapter.
Delete the selected reagent from the list.
Edit the data of the selected reagent, see following chapter.
900 Touch Control
■■■■■■■■
61
Page 78

9.1 Editing reagent data
9.1 Editing reagent data
Main dialog: System ▶ Reagents ▶ New / Edit
Reagent
The designation of the reagent is used for unambiguous identification.
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Entry 24 characters maximum
Comment
Entry 24 characters maximum
[Reagent monitoring]
Set the parameters for the reagent monitoring, see following chapter.
9.2 Reagent monitoring
The conditions for the monitoring of the reagent are defined in the dialog
Edit reagent / Reagent monitoring.
■■■■■■■■
62
900 Touch Control
Page 79

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Number of determ.
9 Reagents
If one of the following values is reached, then the reagent must be
replaced. The values are checked in the following cases:
■ at the start of the determination.
■ at the end of the determination.
The number of determinations to be carried out with a certain amount of
reagent depends on the type of sample and its amount.
Working life
Volume
Reagent capacity
Input range 1 - 999
Selection off
Default value off
Working life of the reagent.
Input range 1 - 999 days
Selection off
Default value off
This parameter is only visible for volumetric reagents.
Volume of titrant dosed.
Input range 1.0 - 999.9 mL
Selection off
Default value off
This parameter is only visible with coulometric reagents.
900 Touch Control
Water capacity of the reagent.
Input range 1 - 9999 mg
■■■■■■■■
63
Page 80

9.2 Reagent monitoring
Drift
[Status]
[Reagent replacement]
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Selection off
Default value off
This parameter is only visible with coulometric reagents.
During conditioning the measured drift has to be in the following range
for 2 min: 'specified drift value + 50 µg/min'.
Input range 1 - 999 µg/min
Selection off
Default value off
Display the status overview of the current values of the reagent monitoring.
Edit the parameters for the reagent exchange.
Dialog "Reagent monitoring / Status"
The current reagent monitoring values are displayed in this dialog.
[Reset]
Reagent replacement
Memory
Reset the values to zero.
Dialog "Reagent monitoring / Reagent replacement"
The parameters for the reagent exchange are defined in this dialog.
The reagent can either be exchanged manually or automatically.
Selection manual | auto
Default value manual
manual
If a monitored parameter has reached the limit set, a message is being
displayed. Then the reagent has to be exchanged manually.
auto
If a monitored parameter has reached the limit set, the method defined
below is started automatically.
This parameter can only be edited with Reagent replacement = auto.
■■■■■■■■
64
Memory location the method is loaded from. All memory locations are
selectable, even if they are currently not accessible.
900 Touch Control
Page 81

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Method
9 Reagents
Selection Internal memory | External memory 1 | Exter-
nal memory 2 | Shared memory
Default value Internal memory
Shared memory
Shared directory in the network.
This parameter can only be edited with Reagent replacement = auto.
Method used for emptying the titration cell.
NOTE
Make sure that the memory is accessible.
Entry 32 characters maximum
Selection Selection of stored methods
900 Touch Control
■■■■■■■■
65
Page 82

10 Sensors
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Main dialog: System ▶ Sensors
This chapter describes how you can create a list of the sensors used in the
system.
Five standard sensors are defined in the sensor list: pH electrode, Metal
electrode, Fluoride electrode, Temperature sensor and Conductivity sensor. These sensors cannot be deleted or renamed. A maximum of
25 additional sensors can be added to these sensors.
For each sensor, the following data is displayed in the sensor list:
■ Designation
■ Type
– pH: pH electrode
– Metal: Metal electrode
– ISE: Ion-selective electrode
– Temp.: Temperature sensor
– Cond.: Conductivity measuring cell
■ Measuring input/control device (only for intelligent sensors if they are
connected)
Intelligent sensors are also indicated by IS and are depicted in green lettering.
The following sensor data is stored in the list of sensors:
■ Name
Each sensor in the system is identified by its unambiguous name.
■ Calibration data (for pH electrodes, ISE electrodes and conductivity
measuring cells only)
■■■■■■■■
66
900 Touch Control
Page 83

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
[New]
[Delete]
10 Sensors
■ Calibration interval (for pH electrodes, ISE electrodes and conductivity
measuring cells only)
■ Working life
■ etc.
NOTE
If data is read out from the data chip of an intelligent sensor, then a
check is made whether the sensor list already contains a sensor of the
same serial number. If this is the case, then the older data set will
always be overwritten by the new data set, no matter whether the
data set in the sensor list or the data set on the data chip is the most
recent one.
Add a new sensor to the list (see Chapter 10.1, page 67).
Delete the selected sensor from the list.
[Edit]
Edit the data of the selected sensor (see Chapter 10.2, page 68).
10.1 Adding a new sensor
Before you can use a sensor, you must add it to the sensor list. To do this,
use the button [New].
■ Conventional sensors:
The properties dialog is opened after the sensor type has been
selected, see following chapter. The following sensor types can be
selected:
– pH electrode
– Metal electrode (Pt electrode, Ag Titrode, Ag/AgCl reference
electrode, etc.)
– Ion-selective electrode
– Other sensor, e.g. Spectrosense
– Temperature sensor
– Conductivity measuring cell
■ Intelligent sensors (also known as iTrodes):
If the 854 iConnect with iTrode is connected to a control device, then
the sensor is automatically entered in the sensor list and can be configured, see following chapter.
900 Touch Control
■■■■■■■■
67
Page 84

10.2 Editing the sensor data
10.2 Editing the sensor data
Sensor list: Sensor ▶ New / Edit
All of the data for the selected sensor is displayed in the dialog Sensors /
Edit.
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Sensor
Ion
Order number
Serial number
The designation of the sensor is used for unambiguous identification.
Entry 24 characters maximum
This parameter is only visible for electrodes of the type ISE.
Display of the ion and its charge.
Order number of the sensor. With intelligent sensors it is read out automatically.
Entry 24 characters maximum
Default value empty
Serial number of the sensor. With intelligent sensors it is read out automatically.
Entry 8 digits maximum
Comment
■■■■■■■■
68
Entry 24 characters maximum
900 Touch Control
Page 85

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
[Working life]
[Limit values]
[Calibration interval]
[Calibration data]
10 Sensors
Define the working life of the sensor (see Chapter 10.3, page 69).
This button is displayed only for pH and ISE electrodes and conductivity
measuring cells.
Define the limit values for monitoring the slope, the electrode zero point
or the cell constant (see Chapter 10.5, page 75).
This button is displayed only for pH and ISE electrodes and conductivity
measuring cells.
Define the time interval for the next calibration (see Chapter 10.6, page
77).
This button is displayed only for pH and ISE electrodes and conductivity
measuring cells.
Display the properties for titer determination (see Chapter 10.4, page
70).
10.3 Monitoring the working life
Sensor: Edit ▶ Working life
In the dialog Edit sensor / Working life, you can define the time interval after which the sensor must be replaced. If you do not wish to monitor
the working life, then you can enter only the date of manufacture for documentation purposes.
Start-up
Date on which the sensor was used for the first time.
Format: YYYY:MM:DD
Monitoring
on | off (Default value: off)
If this parameter is activated, then the working life will be monitored.
Working life
If you define a time interval for the working life, then the Expiry date will
be tracked automatically.
900 Touch Control
Input range 1 - 999 days
Default value 999 days
■■■■■■■■
69
Page 86

10.4 Calibration data (for pH- and ISE electrodes and conductivity measuring cells only)
Expiry date
If you define an expiry date, then the Working life will be tracked automatically.
Format: YYYY:MM:DD
Action
Selection of the action which is carried out when the time interval has
expired.
Selection Display message | Document message | Cancel
determination
Default value Display message
For all three options it is documented in the determination data (see dialog More determination
data / Messages), that the time interval has been
expired.
Display message
A message is displayed. You can select whether you want to continue
with the determination or cancel the run.
Document message
In the determination data it will be documented, that the time interval
has been expired.
Cancel determination
The determination is stopped.
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
10.4 Calibration data (for pH- and ISE electrodes and conductivity measuring cells only)
Sensor: Edit ▶ Calibration data
■■■■■■■■
70
900 Touch Control
Page 87

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Slope
pH(0)
10 Sensors
Detailed information concerning calibration is displayed in this dialog Edit
sensor / Calibration data.
Slope of the electrode.
pH electrodes:
Input range –999.9 - 999.9 %
Default value 100.0 %
ISE electrodes:
Input range –999.9 - 999.9 mV
The default value depends on the charge of the ion.
This parameter is only visible with pH electrodes.
pH value of the electrode at 0 mV. Apart from the slope, pH(0) is the second characteristic of the calibration curve.
E(0)
c(blank)
Variance
Input range –20.000 - 20.000
Default value 7.000
This parameter is only visible with ISE electrodes.
Electrode zero point. Apart from the slope, E(0) is the second characteristic of the calibration curve.
Input range –2000.0 - 2000.0 mV
Default value 0.0 mV
This parameter is only visible with ISE electrodes.
Blank value concentration.
Input range –999999999 - 9999999999
Default value 0.00
This parameter is only visible with ISE electrodes.
The variance is only calculated, if the calibration has been carried out with
at least three standards.
Cell constant
900 Touch Control
This parameter is only visible for conductivity measuring cells.
Cell constant.
■■■■■■■■
71
Page 88

10.4 Calibration data (for pH- and ISE electrodes and conductivity measuring cells only)
Input range 0.001 - 500.000 /cm
Default value 1.000 /cm
The following data cannot be edited:
■ Electrode test (only with intelligent sensors)
Result of the electrode test.
■ Calibration temp
Temperature at which the calibration was carried out.
If the temperature was measured manually during the calibration, then
(manual) will also be displayed. If the temperature was measured with
a connected temperature sensor, then the sensor type ((Pt1000) or
(NTC)) will be displayed.
■ Calibration date
Date and time of the last calibration. For new sensors, the time the
preparation was made is specified until after the first time a calibration
has been carried out.
■ Cal. method
Method with which the sensor was calibrated. If the calibration data
was entered manually, then manual will be displayed.
■ User
User who carried out the calibration.
■ Measuring input (only with intelligent sensors)
The type and the serial number of the measuring input with which the
calibration was carried out.
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
[Initial data]
This button is only displayed for intelligent sensors.
Display the initial calibration data determined at the time of the Metrohm
quality control.
[GLP test]
This button is displayed only for pH electrodes.
Define the time interval for the GLP test (see "Dialog "Calibration data /
GLP test"", page 73).
[History]
Display information about the last ten calibrations (see "Dialog "Calibration data / History"", page 72).
10.4.1 Properties of the previous calibrations
Dialog "Calibration data / History"
Sensor: Edit ▶ Calibration data ▶ History
The date, time and calibration data of the last ten calibrations are displayed in tabular form in the dialog Calibration data / History. Calibrations that were carried out automatically will be displayed in green; man-
■■■■■■■■
72
900 Touch Control
Page 89

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
[Delete History]
[Graph slope]
[Graph pH(0)]
[Graph E(0)]
[Graph cell const.]
10 Sensors
ually entered calibration data will be displayed in black with the designation (m).
Delete the entire history.
Open the diagram of the electrode slopes, see following chapter.
Open the diagram of the electrode zero points, see following chapter.
Open the diagram of the electrode zero points, see following chapter.
Open the diagram of the cell constants, see following chapter.
Dialog "History / Graph"
Sensor: Edit ▶ Calibration data ▶ History ▶ Graph Slope / pH(0) /
E(0) / Cell const.
[Limits]
900 Touch Control
In this diagram, either slope, pH(0), E(0) or the cell constant is plotted
against the date of the calibration. You can define warning limits (blue
dashed lines) and intervention limits (red dashed lines). These limits will
not, however, be monitored.
Define warning and intervention limits.
Dialog "Calibration data / GLP test"
Sensor: Edit ▶ Calibration data ▶ GLP test
In the dialog Calibration data / GLP test, you can define the time interval after which a GLP test must be carried out again for the sensor.
■■■■■■■■
73
Page 90

10.4 Calibration data (for pH- and ISE electrodes and conductivity measuring cells only)
GLP test date
Date on which the last GLP test was carried out. After you have carried
out an electrode test (ELT command), the date of the electrode test is
automatically entered into this field. However, you also can enter the date
manually.
Format: YYYY:MM:DD
Monitoring
on | off (Default value: off)
If this parameter is activated, then the time interval after which a GLP test
has to be carried out again will be monitored.
GLP test interval
If you define a time interval for the GLP test, then the date in Next GLP
test will be tracked automatically.
Input range 1 - 999 days
Default value 999 days
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Next GLP test
Action
If you define a date for the next GLP test, then the GLP test interval will
be tracked automatically.
Format: YYYY:MM:DD
Selection of the action which is carried out when the time interval has
expired.
Selection Display message | Document message | Cancel
determination
Default value Display message
For all three options it is documented in the determination data (see dialog More determination
data / Messages), that the time interval has been
expired.
Display message
A message is displayed. You can select whether you want to continue
with the determination or cancel the run.
Document message
In the determination data it will be documented, that the time interval
has been expired.
Cancel determination
The determination is stopped.
■■■■■■■■
74
900 Touch Control
Page 91

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
10.5 Limit values for the calibration data
Sensor: Edit ▶ Limit values
You can define the following limit values in the dialog Edit sensor /
Limit values:
10 Sensors
Monitoring slope
Lower limit
■ Slope (pH and ion-selective electrodes)
■ Electrode zero point (pH and ion-selective electrodes)
■ Cell constant (conductivity measuring cells)
These values are monitored during the calibration. If these limits are
infringed, then a message will be displayed and you can decide whether
to accept the calibration data or not.
on | off (Default value: off)
If this parameter is activated, then the slope will be monitored.
pH electrodes:
Input range –999.9 - 999.9 %
Default value 96.0 %
ISE electrodes:
Input range –999.9 - 999.9 mV
The default value depends on the charge of the ion:
–25.0 mV (–2), –55.0 mV (–1), 55.0 mV (+1), 25.0
mV (+2).
900 Touch Control
■■■■■■■■
75
Page 92

10.5 Limit values for the calibration data
Upper limit
pH electrodes:
Input range –999.9 - 999.9 %
Default value 101.0 %
ISE electrodes:
Input range –999.9 - 999.9 mV
Monitoring pH(0)
on | off (Default value: off)
This parameter is only available with pH electrodes.
If this parameter is activated, then the electrode zero point pH(0) will be
monitored.
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
The default value depends on the charge of the ion:
–31.0 mV (–2), –61.0 mV (–1), 61.0 mV (+1), 31.0
mV (+2).
Lower limit
Upper limit
Monitoring E(0)
Lower limit
Upper limit
Input range –20.000 - 20.000
Default value 6.750
Input range –20.000 - 20.000
Default value 7.250
on | off (Default value: off)
This parameter is only available with ISE electrodes.
If this parameter is activated, then the electrode zero point E(0) will be
monitored.
Input range –2000.0 - 2000.0 mV
Default value –2000.0 mV
Input range –2000.0 - 2000.0 mV
Default value 2000.0 mV
Monitoring cell constant
■■■■■■■■
76
on | off (Default value: off)
This parameter is only available for conductivity measuring cells.
900 Touch Control
Page 93

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
If this parameter is activated, then the cell constant will be monitored.
Lower limit
Input range 0.001 - 500.000 /cm
Default value 0.850 /cm
Upper limit
Input range 0.001 - 500.000 /cm
Default value 1.150 /cm
10 Sensors
10.6 Monitoring the calibration interval (only for pH and ion-selective electrodes and conductivity measuring cells)
Sensor: Edit ▶ Calibration interval
In the dialog Edit sensor / Calibration interval, you can define the time
interval after which the sensor must be recalibrated.
Calibration date
Monitoring
Calibration interval
Next calibration
Action
Date of the last calibration.
on | off (Default value: off)
If this parameter is activated, then the validity of the calibration will be
monitored.
If you define a time interval for the validity of the calibration, then the
date in Next calibration will be tracked automatically.
Input range 1 - 999 days
Default value 7 days
If you define a date for the next calibration, then the Calibration inter-
val will be tracked automatically.
Format: YYYY:MM:DD
Selection of the action which is carried out when the time interval has
expired.
900 Touch Control
■■■■■■■■
77
Page 94

10.6 Monitoring the calibration interval (only for pH and ion-selective electrodes and conductivity
measuring cells)
Selection Display message | Document message | Cancel
determination
Default value Display message
For all three options it is documented in the determination data (see dialog More determination
data / Messages), that the time interval has been
expired.
Display message
A message is displayed. You can select whether you want to continue
with the determination or cancel the run.
Document message
In the determination data it will be documented, that the time interval
has been expired.
Cancel determination
The determination is stopped.
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
■■■■■■■■
78
900 Touch Control
Page 95

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
11 Device manager
Main dialog: System ▶ Device manager
This chapter describes how you can configure the Touch Control, the control instruments (Titrando, USB Sample Processor etc.) and the connected
peripheral devices. A detailed description of the hardware installation can
be found in the installation manual for the control instrument.
11 Device manager
[New]
[Delete]
[Edit]
The instrument list gives the name and type of every instrument. Connected control instruments (Titrando, Dosing Interface, USB Sample Processor, etc.) with the peripheral devices (dosing devices, stirrers, etc.) connected to the MSB connector are entered in the list automatically. A USB/
RS-232 adapter will also be automatically recognized and entered in the
instrument list with default settings. A printer is entered in the instrument
list in the default settings. You must enter a PC keyboard, a barcode
reader or a balance in the instrument list yourself.
Add a new device to the list (see Chapter 11.1, page 80).
Delete the selected device from the list.
NOTE
Devices which are recognized automatically cannot be deleted from the
list while they are still connected.
Configure the selected device (see Chapter 11.2, page 80).
900 Touch Control
■■■■■■■■
79
Page 96

11.1 Adding a new device
11.1 Adding a new device
Of the following device types, you can enter one device each in the device
list, even if it is not yet connected:
■ Titrando (three instruments maximum)
■ USB Sample Processor
■ Balance
■ Barcode reader
■ USB/RS-232 adapter
■ PC keyboard
Proceed as follows to do this:
1
Displaying the device selection
Tap on [New].
2
Selecting the instrument
Tap on the button for the desired device.
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
The new device is entered in the list.
11.2 Configuring the instrument
Instrument list: Instrument ▶ Edit
The data stored for an instrument depends on the type of instrument. You
can define an instrument name and a comment for each instrument. The
instrument name of the Touch Control is printed out in the standard
report header.
The description of the individual instruments can be found in the following specific chapters:
■ Touch Control (see Chapter 11.3, page 81)
■ Metrohm control instruments (see Chapter 11.4, page 87)
■ USB Sample Processor (see Chapter 11.5, page 91)
■ Printer (see Chapter 11.7, page 108)
■ Balance (see Chapter 11.8, page 112)
■ PC keyboard (see Chapter 11.10, page 115)
■ USB/RS-232 adapter (see Chapter 11.9, page 114)
■ Barcode reader (see Chapter 11.11, page 117)
■■■■■■■■
80
900 Touch Control
Page 97

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
11.3 Touch Control
Instrument list: 900 Touch Control ▶ Edit
Device name
This designation is used for identification purposes when selecting control
devices (command, manual control).
11 Device manager
Comment
Switch off display
Program version
Serial number
Control Remote Box
Entry 24 characters maximum
Entry 24 characters maximum
If this time interval has expired without the Touch Control having been
operated, then the display will be switched off. Touching the display will
switch it back on again at any time.
Input range 1 - 999 min
Default value 60 min
Selection off
Program version of the software.
Shows the serial number of the device.
Shows to which control device and MSB connector the Remote Box is
connected.
900 Touch Control
■■■■■■■■
81
Page 98

11.3 Touch Control
11.3.1 E-mail
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
The "Control Remote Box" is the interface via which the system can be
started and stopped externally. If multiple Remote Boxes are connected,
then the one that is recognized first when the program starts will be used
as the "Control Remote Box."
Selection Name of the control device / Number of the
MSB connector | Not available
900 Touch Control: Edit ▶ E-mail
The system allows you to send displayed messages as e-mails. The Touch
Control must be connected to a network for this to function. The following types of messages can be sent:
: general warning messages
■
: error messages
■
Configuring e-mail dispatch
Proceed as follows so that messages can be sent as e-mails:
1
Activating the option
■ In the instrument properties of the 900 Touch Control, tap on the
[E-mail] button.
■ In the Edit device / E-mail dialog, activate the Send the fol-
lowing messages as e-mail: option.
2
Configuring e-mail addresses
■ Tap on the [E-mail settings] button.
The E-mail / Settings dialog is displayed.
■ Enter the addresses of the mail server, the sender and the desired
recipient.
Parameter description
Send the following messages as e-mail:
on | off (Default value: off)
If this parameter is activated, then messages with the following symbols
will be sent as e-mails:
■■■■■■■■
82
■ : General warning messages
■ : Error messages
900 Touch Control
Page 99

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Send only during running determination
on | off (Default value: on)
If this parameter is activated, then messages will be sent as e-mails only if
a determination is running. Deactivate this parameter if messages are also
to be sent in normal status.
Mail server
Address of the mail server for outgoing mail, e.g. mail.metrohm.ch. You
can find the address of the mail server either in your e-mail program settings or obtain it from your IT department.
Entry 24 characters maximum
Default value empty
Sender
E-mail address of the sender. This address must be formatted as an e-mail
address, but need not necessarily correspond to an existing e-mail
account, e.g. touchcontrol@metrohm.com.
11 Device manager
Entry 24 characters maximum
Default value empty
Recipient
The messages will be sent to this e-mail address.
Entry 24 characters maximum
Default value empty
11.3.2 PC/LIMS report
900 Touch Control: Edit ▶ PC/LIMS report
You can generate a machine-readable report with all of the important
data concerning a determination, which is referred to as a PC/LIMS report.
This report can be saved as a TXT file or sent to a terminal program or a
LIMS via an RS-232 interface:
■
manually with the [ ] fixed key (see Chapter 27, page 240).
■ automatically at the end of a determination (see Chapter 16.5.6, page
180).
The file name of the TXT file is constructed as follows: PC_LIMS_ReportID1-YYYYMMDD-hhmmss.txt. A detailed description of the contents of
the PC/LIMS report can be found in the PC/LIMS Report Guide.
Memory
900 Touch Control
Memory location where the PC/LIMS report is stored as a TXT file. The
report will be saved in the directory pc_lims_report. This directory will be
■■■■■■■■
83
Page 100

11.3 Touch Control
RS-232
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
created the first time a PC/LIMS report is generated. All three memory
locations are listed as possible selections, even if they cannot be accessed
at the moment.
Selection off | External memory 1 | External memory 2 |
Shared memory
Default value off
off
The report will not be saved as a TXT file.
Shared memory
The report will be saved in a shared directory on the network. The
shared directory is selected in the Edit device / Shared memory dialog (see Chapter 11.3.3, page 84).
The RS-232 interface via which the PC/LIMS report is sent. The interface
parameters are adjusted in the Edit device / Port parameters dialog
(see Chapter 11.9, page 114).
Selection off | COM 1 | COM 2
Default value off
off
The report will not be sent via an RS-232 interface.
COM 2
This interface is inactive.
Coding
Format in which the PC/LIMS report is coded and stored.
Selection ISO 8859-1 | UTF-8
Default value ISO 8859-1
ISO 8859-1
This format is recommended for all languages that use the extended
ASCII code (e.g. German, English, Spanish, etc.).
UTF-8
This format is required for all languages that do not use the extended
ASCII code (e.g. Russian, Chinese, Korean, etc.).
11.3.3 Shared memory
900 Touch Control: Edit ▶ Shared memory
If you have your Touch Control connected to your network, then you can
specify in this dialog a shared memory location on a PC within your network for the purpose of saving data (methods, determinations, etc.).
■■■■■■■■
84
900 Touch Control
 Loading...
Loading...