LG GSA-4040 Service Manual

website http://biz.LGEservice.com e-mail http://www.LGEservice.com/techsup.html
Super Multi DVD Drive
SERVICE MANUAL
MODEL: GSA-4040B
P/NO : 3828HS1044A
September, 2003
Printed in Korea
MODEL : GSA-4040B

|
TABLE OF CONTENTS |
|
INTRODUCTION ....................................................................................................................................................................... |
3 |
|
FEATURES............................................................................................................................................................................ |
3~4 |
|
SPECIFICATIONS................................................................................................................................................................. |
5~8 |
|
LOCATION OF CUSTOMER CONTROLS ......................................................................................................................... |
9~10 |
|
DISASSEMBLY ................................................................................................................................................................. |
11~12 |
|
1. CABINET and CIRCUIT BOARD DISASSEMBLY .......................................................................................................... |
11 |
|
1-1. Bottom Chassis.......................................................................................................................................................... |
11 |
|
1-2. Front Bezel Assy........................................................................................................................................................ |
11 |
|
1-3. Cabinet and Main Circuit Board ................................................................................................................................. |
11 |
|
2. MECHANISM ASSY DISASSEMBLY.............................................................................................................................. |
11 |
|
2-1. Pick-up Unit................................................................................................................................................................ |
11 |
|
2-2. Pick-up ...................................................................................................................................................................... |
12 |
|
GLOSSARY ............................................................................................................................................................................. |
16 |
|
EXPLODED VIEW ............................................................................................................................................................. |
13~14 |
|
MECHANICAL REPLACEMENT PARTS LIST ...................................................................................................................... |
15 |
|
THE DIFFERENCES OF CD-R/CD-RW DISCS AND GENERAL CD-ROM ........................................................................... |
17 |
|
1. |
Recording Layer .............................................................................................................................................................. |
17 |
2. |
Disc Specification ............................................................................................................................................................ |
17 |
3. |
Disc Materials .................................................................................................................................................................. |
18 |
4. |
Reading Process of Optical Disc ..................................................................................................................................... |
19 |
5. |
Writing Process of CD-R Disc ......................................................................................................................................... |
20 |
6. |
Writing Process of CD-RW Disc ...................................................................................................................................... |
20 |
7. |
Organization of the PCA, PMA and Lead-in Area ........................................................................................................... |
21 |
8. |
Function of PCA and PMA area ...................................................................................................................................... |
22 |
9. OPC and ROPC .............................................................................................................................................................. |
22 |
|
10. Writing Process of DISC................................................................................................................................................ |
23 |
|
THE DIFFERENCES OF DVD-R/RW, DVD+R/RW DISCS AND DVDD-ROM ....................................................................... |
24 |
|
1. |
Recording Layer .............................................................................................................................................................. |
24 |
2. |
Disc Specification ............................................................................................................................................................ |
25 |
3. |
Disc Materials .................................................................................................................................................................. |
25 |
4. |
Writing Pulse Waveform of DVD+R................................................................................................................................. |
28 |
5. |
Writing Pulse Waveform DVD+RW ................................................................................................................................. |
30 |
6. |
Organization of Inner Drive Area, Outer Drive Area, Lead-in Zone and Lead-out Zone ................................................. |
31 |
DVD & CD DATA PROCESSING...................................................................................................................................... |
33~36 |
|
1. |
Data Processing Flow...................................................................................................................................................... |
33 |
2. |
Copy Protection and Regional Code Management Block ............................................................................................... |
34 |
3. |
About Prevention the DVD-ROm from to be copy ........................................................................................................... |
35 |
4. |
About the DVD-ROM Regional Code .............................................................................................................................. |
36 |
INTERNAL STRUCTURE OF THE PICK-UP.................................................................................................................... |
37~39 |
|
1. |
Block Diagram of the Pick-up(HOP-8511T)..................................................................................................................... |
37 |
2. |
Pick up Pin Assignment................................................................................................................................................... |
38 |
3. |
Signal detection of the P/U .............................................................................................................................................. |
39 |
DESCRIPTION OF CIRCUIT............................................................................................................................................. |
40~47 |
|
1. |
ALPC Circuit .................................................................................................................................................................... |
40 |
2. |
Focus Circuit.................................................................................................................................................................... |
42 |
3. |
Tracking & Sled Circuit .................................................................................................................................................... |
43 |
4. |
Spindle Circuit ................................................................................................................................................................. |
43 |
MAJOR IC INTERNAL BLOCK DIAGRAM AND PIN DESCRIPTION............................................................................. |
48~73 |
|
TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE .......................................................................................................................................... |
74~90 |
|
BLOCK DIAGRAM .................................................................................................................................................................. |
92 |
|
PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD DIAGRAM ........................................................................................................................... |
93~96 |
|
ELECTRICAL REPLACEMENT PARTS LIST ........................................................................................................................ |
97 |
|
CAUTION - INVISIBLE LASER RADIATION WHEN OPEN AVOID EXPOSURE TO BEAM.

INTRODUCTION
This service manual provides a variety of service information.
It contains the mechanical structure of the Super Multi DVD Drive and the electronic circuits in schematic form. This Super Multi DVD Drive was manufactured and assembled under our strict quality control standards and meets or exceeds industry specifications and standards.
This Super Multi DVD drive is an internal drive unit designed for use with IBM PC, HP Vectra, or compatible computer. It can write as much as 700 Mbytes of digital data into CD-R/RW disc, and can
read as much as 700 Mbytes of digital data stored in a CD-ROM, CD-R and CD-RW disc.
It can write as much as 4.7Gbytes of digital data into DVD+R/RW disc, and can read as much as 4.7Gbytes of digital data stored in a DVD-ROM, DVD-R, DVD-RW, DVD+R and DVD+RW disc.
This Super Multi DVD Drive can easily meet the upcoming MPC level 3 specification, and its Enhanced Intelligent Device Electronics (E-IDE) and ATAPI interface allows Plug and play integration in the majority of today’s PCs without the need of an additional interface card.
GSA-4040B series *1)
Design Specifications
*1)
GMA-4040B does not apply to the record function of DVD+R/+RW. GRA-4040B does not apply to the record function of DVD-R/-RW/-RAM GWA-4040B does not apply to the record function of DVD-RAM. GDA-4040B does not apply to the record function of DVD+R/+RW and CD-R/RW.
FEATURES
1General
1)Enhanced IDE (ATAPI) interface.
2)Internal Half-height Drive.
3)CD-R/RW, DVD-R/RW/RAM/+R/+RW read and write compatible CD Family and DVD-ROM read compatible.
4)Buffer Under-run prevention function embedded.
5)2MB buffer memory.
6)Power loading and power eject of a disc. Bare media loading.
7)MTBF : 100,000 POH
8)Vertical and Horizontal installable.
2.Supported disc formats
1)Reads data in each CD-ROM, CD-ROM XA, CD-I, Video CD, CD-Extra and CD-Text.
2)Reads data in Photo CD (Single and Multi session).
3)Reads standard CD-DA.
4)Reads and writes CD-R discs conforming to “Orange Book Part 2”.
5)Reads and writes CD-RW discs conforming to “Orange Book Parts 3”.
6)Reads data in each DVD-ROM, DVD-R(Ver.1.0, Ver.2.0 for Authoring) and DVD-RAM(Ver.1.0)
7)Reads and writes in each DVD-R(Ver.2.0 for General), DVD-RW, DVD-RAM(Ver.2.1), DVD+R and DVD+RW
3
3.Supported write method
1)For CD-R/RW
Disc at once, Session at Once, Track at once and Packet Write.
2)For DVD-R
Disc at Once and Incremental Recording.
3)For DVD-RW
Disc at Once, Incremental Recording and Restricted Overwrite.
4)For DVD-RAM Random Write
5)For DVD+R Sequential Recording
6)For DVD+RW Random Write
4.Performance
1) |
Average access time : |
CD-ROM |
125ms |
|
|
(1/3 stroke) |
|
DVD-ROM |
145ms |
2) |
Write speed : |
|
CD-R |
4x, 8x CLV, 16x, 24x ZCAV |
|
|
|
CD-RW |
4x, 8x, 12x CLV, 16x ZCLV |
|
|
|
|
(High Speed CD-RW supported: 8x, 12x, |
|
|
|
|
Ultra Speed CD-RW supported: 16x) |
|
|
|
DVD-R |
1x, 2x, 4x CLV |
|
|
|
DVD-RW |
1x, 2x CLV |
|
|
DVD-RAM (Ver.2.1) |
2x, 3x ZCLV |
|
|
|
|
DVD+R |
2.4x, 4x CLV |
|
|
|
DVD+RW |
2.4 CLV |
3) |
Read speed: |
CD-ROM/R/RW |
32x/32x/24x Max. |
|
|
|
|
CD-DA(DAE) |
24x Max. |
|
|
DVD-ROM/R/RW |
12x/8x/8x Max. |
|
|
|
|
+R/+RW |
8x Max. |
|
DVD-Video(CSS Compliant Disc) |
|
||
|
|
(Single/Dual layer) |
8x Max. |
|
|
|
DVD-RAM(Ver. 1.0/2.1) |
2x/2x, 3x |
|
4) |
Sustained Transfer rate : |
CD-ROM |
4,800 kB/s (32x).Max. |
|
|
|
|
DVD-ROM |
16.62 Mbytes/s (12x)Max. |
5) |
Burst Transfer rate: |
|
Ultra DMA Mode2, Multi word DMA Mode2, PIO Mode4. |
|
6)Multimedia MPC-3 compliant
5.Audio
1)16 bit digital data output through ATA interface.
2)Software Volume Control
3)Equipped with audio line output for audio CD playback.
* Definition |
|
|
Transfer Rate : 1x (DVD) = 1.385 Mbytes/s, |
Mbytes/s = 106bytes/s |
|
|
1x(CD) = 150 kB/s, |
kB/s = 210 bytes/s |
Capacity : |
MB = 220 bytes, |
kB = 210bytes |
4
SPECIFICATIONS
1. SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS
-CPU: IBM Compatible Pentium 700MHZ (or faster) (For High speed, 700MHz or faster recommended.) -128MB Memory or greater
2. SUPPORTING OPERATING SYSTEM
* Operating System |
* Recording tool |
|
Window 98 Second Edition |
(1) |
RecordNow (Veritas) |
Windows Millennium Edition (Me) |
(2) |
DLA (Veritas) |
Window 2000 Professional |
(3) |
DVD-RAM Device driver software (Panasonic) |
Window XP Home Edition, Professional |
(4) |
WinCDR (Aplix) |
|
(5) |
B’s Recorder Gold (BHA) |
|
(6) |
B;s Clip (BHA) |
|
(7) |
Drag’n Drop (Easy System Japan) |
|
(8) |
Nero(Ahead) |
|
(9) |
In CD(Ahead) |
|
(10) |
Easy CD Creator (Roxio) |
|
(11) |
Direct CD (Roxio) |
2.1 Applicable disc formats |
|
|
DVD |
DVD-ROM: |
4.7GB (Single Layer) |
|
|
8.5GB (Dual Layer) |
|
DVD-R: |
3.95GB (Ver.1.0 : read only) |
|
|
4.7GB (Ver.2.0 for Authoring : read only) |
|
|
4.7GB (Ver.2.0 for General: read & write) |
|
DVD-RW: |
4.7GB (Ver.1.1) |
|
DVD-RAM: |
2.6GB/side (Ver.1.0) |
|
|
1.46GB/side, 4.7GB/side (Ver.2.1) |
|
DVD+R: |
4.7GB |
|
DVD+RW: |
4.7GB |
CD |
CD-ROM Mode-1 data disc |
|
|
CD-ROM Mode-2 data disc |
|
CD-ROM XA, CD-I, Photo-CD Multi-Session, Video CD
CD-Audio Disc
Mixed mode CD-ROM disc (data and audio)
CD-Extra
CD-Text
CD-R (Conforming to “Orange Book Part2”: read & write)
CD-RW (Conforming to “Orange Book Part3”: read & write)
2.2Writing method
(1)For CD-R/RW .......................Disc at Once (DAO)
|
Session at Once (SAO) |
|
Track at Once (TAO) |
|
Packet Writing |
(2) For DVD-R/RW |
.....................Disc at Once |
|
Incremental Recording |
|
Restricted Overwrite (DVD-RW only) |
(3)For DVD-RAM/+RW .............Random Write
(4)For DVD+R...........................Sequential Recording
5
2.3 Disc capacity............................................... |
120mm |
|
|
80mm (Horizontal only) |
|
2.4 Data capacity |
|
|
• User Data/Block |
DVD-ROM/R/RW/RAM/+R/+RW ...... |
2,048 bytes/block |
|
CD (Yellow Book) .......................................... |
2,048 bytes/block(Mode 1 & Mode 2 Form 1) |
|
|
2,336 bytes/block (Mode 2) |
|
|
2,328 bytes/block (Mode 2 Form 2) |
|
|
2,352 bytes/block (CD-DA) |
2.5 RPC (Regional Playback Control) Phase2, No Region
3.DRIVE PERFORMANCE
3.1 Host interface .................................................................. |
|
X3T13 ATA/ATAPI5/1321D |
|||
|
|
|
INF-8090i Rev.5.3 |
||
3.2 Read/Write & Rotational speed |
|
|
|
||
<Read> |
CD-ROM ........................................................ |
|
14x ~ 32x (CAV), Approx. 6,850r/min |
||
|
CD-RW data/CD-I/Video CD .......................... |
10x ~ 24x (CAV), Approx. 5,130 r/min |
|||
|
CD-DA (DAE) ................................................. |
|
10x ~ 24x (CAV), Approx. 5,130 r/min |
||
|
CD-DA (Audio out) ......................................... |
|
4.3x |
~ |
10x (CAV), Approx. 2,140 r/min |
|
DVD-ROM ............ |
Single layer...................... |
5.0x |
~ |
12x (CAV), Approx. 6,890 r/min |
|
|
Dual layer ........................ |
3.3x |
~ |
8x (CAV), Approx. 5,056 r/min |
|
DVD-R ................... |
3.95GB ............................ |
3.3x |
~ |
8x (CAV), Approx. 5,056 r/min |
|
|
4.7GB .............................. |
3.3x |
~ |
8x (CAV), Approx. 4,600 r/min |
|
DVD-RW................ |
4.7GB .............................. |
3.3x |
~ |
8x (CAV), Approx. 4,600 r/min |
|
DVD-RAM.............. |
Ver.1.0............................. |
2x (ZCLV)* |
||
|
|
Ver.2.1............................. |
2x, 3x (ZCLV)* |
||
|
DVD+R .................. |
4.7GB .............................. |
3.3x |
~ |
8x (CAV), Approx. 4,600 r/min |
|
DVD+RW............... |
4.7GB .............................. |
3.3x |
~ |
8x (CAV), Approx. 4,600 r/min |
<Write> |
CD-R .............................................................. |
|
4x, 8x (CLV), 16x , 24x (ZCLV) |
||
|
CD-RW........................................................... |
|
4x(CLV), High speed Disc 8x, 12x (CLV) |
||
|
|
|
Ultra speed Disc 16x(ZCLV) |
||
|
DVD-R............................................................ |
|
1x, 2x, 4x (CLV) |
||
|
DVD-RW ........................................................ |
|
1x, 2x (CLV) |
||
|
DVD-RAM.............. |
Ver.2.1............................. |
2x, 3x (ZCLV) |
||
|
DVD+R........................................................... |
|
2.4x, 4x (CLV) |
||
|
DVD+RW ....................................................... |
|
2.4x |
(CLV) |
|
* Rotational speed (CLV, ZCLV) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
CD-ROM/R/RW.............................................. |
|
1x: Approx. 497 +38/-39 (Inside) |
||
|
(CLV = 1.2 - 1.4 m/s) |
|
to |
214 +17/-16 r/min (Outside) |
|
|
DVD-R/RW..................................................... |
|
1x: Approx. 1,390(Inside) ~ 575 r/min(Outside) |
||
|
(CLV = 3.49 m/s) |
|
|
|
|
|
DVD-RAM.............. |
Ver.1.0............................. |
1x: Approx. 2,387(Inside) ~ 1,014 r/min(Outside) |
||
|
|
Ver.2.1............................... |
2x: Approx. 3,246(Inside) ~ 1,375 r/min(Outside) |
||
|
DVD+R/RW.................................................... |
|
1x: Approx. 1,390(Inside) ~ 575 r/min(Outside) |
||
6
3.3Data transfer rate
3.3.1Sustained transfer rate
<Read> |
CD-ROM/R..................................................... |
|
2.07 |
~ 4.8 Mbytes/s (32x) Max. |
|
CD-RW........................................................... |
|
1.5 |
~ 3.6 Mbytes/s (24x) Max. |
|
CD-DA(DAE) .................................................. |
|
1.5 |
~ 3.6 Mbytes/s (24x) Max. |
|
DVD-ROM ............ |
Single layer...................... |
6.88 |
~ 16.2 Mbytes/s (12x) Max. |
|
|
Dual layer ........................ |
4.57 |
~ 11 Mbytes/s (8x) Max. |
|
DVD-R............................................................ |
|
4.57 |
~ 11 Mbytes/s (8x) Max. |
|
DVD-RW ........................................................ |
|
4.57 |
~ 11 Mbytes/s (8x) Max. |
|
DVD-RAM.............. |
Ver.1.0............................. |
2.77 |
Mbytes/s |
|
|
Ver.2.1............................. |
2.77, 4.155 Mbytes/s |
|
|
DVD+R........................................................... |
|
4.57 |
~ 11 Mbytes/s (8x) Max. |
|
DVD+RW ....................................................... |
|
4.57 |
~ 11 Mbytes/s (8x) Max. |
<Write> |
CD-R ..................... |
4x, 8x .............................. |
0.6, 1.2 Mbytes/s (Mode-1) |
|
|
|
16x, 24x (ZCLV) .............. |
1.8 ~ 2.4, 1.8 ~ 3.6 Mbytes/s (Mode-1) |
|
|
CD-RW .................. |
4x, 8x, 12x ....................... |
0.6, 1.2, 1.8 Mbytes/s (Mode-1) |
|
|
|
16x (ZCLV)...................... |
1.8 ~ 2.4, Mbytes/s (Mode-1) |
|
|
DVD-R ................... |
2x, 4x............................... |
2.77, 5.54 Mbytes/s |
|
|
DVD-RW................ |
1x, 2x............................... |
1.385, 2.77 Mbytes/s |
|
|
DVD-RAM.............. |
2x, 3x............................... |
2.77, 4.155 Mbytes/s(Ver.2.1):Without verify |
|
|
DVD+R .................. |
2.4x, 4x............................ |
3.32, 5.54 Mbytes/s |
|
|
DVD+RW............... |
2.4x.................................. |
3.32 |
Mbytes/s |
3.3.2 Burst transfer rate |
|
|
|
|
|
Ultra DMA Mode 2.......................................... |
|
33.3 |
Mbytes/s Max. |
|
Multiword DMA Mode 2.................................. |
16.6 |
Mbytes/s Max. |
|
|
PIO Mode 4 .................................................... |
|
16.6 |
Mbytes/s Max. |
3.4 Access time (1/3 stroke) |
|
|
|
|
* Typical value |
|
|
|
|
DVD-ROM ...................................................... |
145 ms Typ. |
DVD-RAM (Ver.2.1) ....................................... |
165 ms Typ. |
CD-ROM ........................................................ |
125ms Typ. |
(Note 1)
(Note 1)
Note :
1) Average random access time is the typcal value of more than 50 times including latency and error correction time.
Test Disc : DVD : ALMEDIO TDV-520 / TDR-820
CD : ALMEDIO TCDR-701 / HITACH HCD-1
*) Typical value defines a measured value in normal temperature (20 deg.C.) and horizontal position.
3.5 |
Data error rate (Measured with 5 retries maximum) |
|
|
DVD-RAM.............. |
<10 -12 |
|
DVD-ROM ............. |
<10 -12 |
|
CD-ROM................ |
<10-12 (Mode-1) |
|
|
<10-9 (Mode-2) |
|
Condition : It is assumed that the worst case raw error rate of the disc is 10-3 |
|
3.6 |
Data buffer capacity ....................................................... |
2Mbytes |
7
4. Quality and Reliability
4.1 MTBF.................................................. |
100,000 Power On Hours(Consecutive/Cumulative POH) |
|
|
Assumption : .......................... |
Used in a normall office environment at room temperature. |
|
-POH per year......................... |
3,000 |
|
-ON/OFF cycles per year........ |
600 |
|
-Operating duty cycle.............. |
20% of power on time (Seek: 5% of operating time) |
4.2 |
Tray cycle test................................... |
10,000 times |
4.3 |
Actuator mechanism |
No degeneration in the mechanical part after test |
1,000,000 full stroke seek |
||
4.4 MTTR (Mean Time To Repair) ........... |
0.5 h |
|
4.5 |
Component life ................................. |
5 years or 2,000 h of Laser radiating time |
|
Assumption : .......................... |
Used in a normall office environment. |
5.POWER REQUIREMENTS
5.1 Source voltage
|
+5V |
+ 5% tolerance, less than 150 mVp-p Ripple voltage |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
+12V + 10% tolerance, less than 300 mVp-p Ripple voltage |
|
|
|
|
|||||
5.2 Current |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Idle (Hold track state).............. |
+5V DC |
0.6A Typ. |
< 0.9 A Max. |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
+12V DC |
0.5A Typ. |
< 0.9 A Max. |
|
|
||
|
|
|
Read (Active) .......................... |
+5V DC |
0.7A Typ. |
< 1.3 A Max. |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
+12V DC |
0.6A Typ. |
< 1.2 A Max. |
|
|
||
|
|
|
Seek (Acess) .......................... |
+5V DC |
0.8A Typ. |
< 1.5 A Max. |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
+12V DC |
1.3A Typ. |
< 1.8 A Max. |
|
|
||
5.3 Standby |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Sleep mode (No disc) ............. |
1.0 W Typ. |
1.2 W Max. |
|
|
|
||
6. AUDIO PERFORMANCE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item |
Typical |
|
Test Signal |
|
Test Condition |
|
Note |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OUT |
|
Output Level |
0.7 Vrms |
|
1KHz 0 dB |
|
No Filter |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
at 47kΩ |
|
AUDIO |
|
Frequency response |
+/-3dB |
|
20-20kHz 0dB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
THD |
0.1% |
|
1KHz 0 dB |
with IHF-A + 20KHz LPF |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Headphone output level(Optional) |
- |
|
- |
|
- |
|
None |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7. Acoustic noise
Less than 50dB, A scale, at 0.5 m away from the drive Note : 1. Disc : Less than unbalance 0.5 x10-4 Nm
2.Installation : Horizontal
3.Ambient temperature : Normal temperature
4.Except loading, unloading and seek
8.Dimensions
External dimensions (W x H xD) |
146x41.3x184.6mm |
Front bezel (WxHxD) |
148.2x42x5 mm |
9. Mass ................................................. |
Approx. 0.92 kg |
*Which is not provided with Circuit Diagram of this model. Please Contact the friendly staff of LG Service Care at: Website http: //biz.LGEservice.com
e-mail http : //www.LGEservice.com/techsup.html
8

LOCATION OF CUSTOMER CONTROLS
Front Panel |
Emergency Eject Hole
Disc Tray
Stop/Eject Button
Drive Activity Indicators
1.Disc tray
This is the tray for the disc. Place the disc on the ejected disc tray, then lightly push the tray (or push the eject button) and the CD will be loaded.
NOTE: Don’t pull out or push in the disc tray forcibly. This might cause damage to the loading section of the drive.
2.Stop/Eject button
This button is pressed to open the CD tray.
This button works only when power is supplied to the drive.
If an Audio CD is playing, pressing this button will stop it, and pressing it again will open the tray.
3.Emergency Eject Hole
Insert a paper clip here to eject the Disc tray manually or when there is no power.
4.Drive activity indicator
Green colored LED is used to indicate the operation of Super Multi DVD Drive.
9

Rear Panel |
Analog Audio Output Connector |
|
IDE Interface Connector |
|
R G |
L |
|
C S M |
||
S |
L |
A |
|
POWER |
||
INTERFACE |
+5 |
GND |
+12 |
|
|
||
|
1 |
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
39 40
Jumper Connector
Power Connector
Digital Audio Output
Connector
1.Power Connector
Connects to the power supply (5-and 12-V DC) of the host computer.
NOTE : Be careful to connect with the proper polarity. Connecting the wrong way may damage the system (and is not guaranteed). Usually this connector can only be attached one-way.
2.IDE Interface Connector
Connect to the IDE (Integrated Device Electronics) Interface using a 40-pin flat IDE cable.
NOTE : Do not connect or disconnect the cable when the power is on, as this could cause a short circuit and damage the system. Always turn the power OFF when connecting or disconnecting the cable.
3.Jumper Connector
This jumper determines whether the drive is configured as a master or slave. Changing the master-slave configuration takes effect after power-on reset.
4.Analog Audio Output Connector
Provides output to a sound card (analog signal). Generally you need this to play a regular audio CD.
5.Digital Audio Output Connector
This connector is not supported.
10
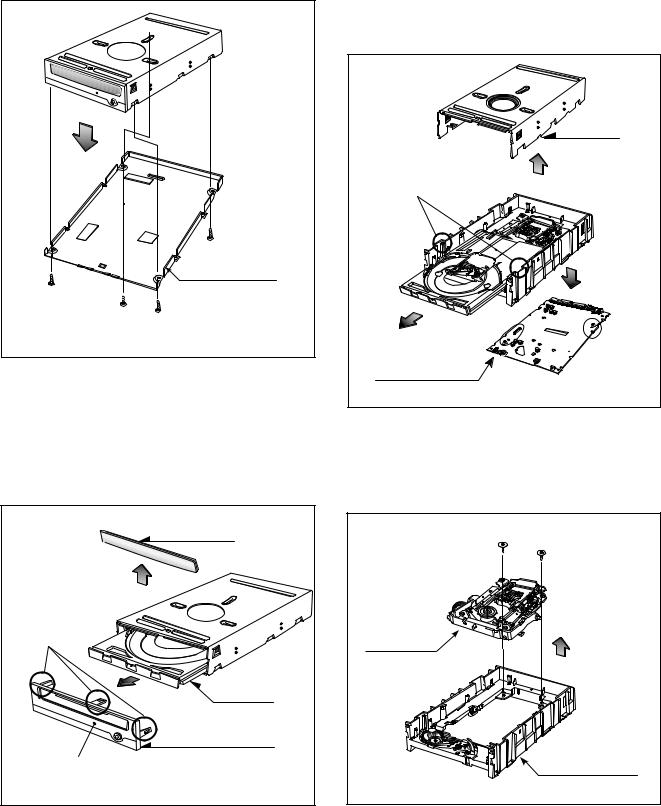
DISASSEMBLY
1.CABINET and CIRCUIT BOARD DISASSEMBLY
1-1. Bottom Chassis
A.Release 4 screws (A) and remove the Bottom Chassis in the direction of arrow (1). (See Fig.1-1)
(1)
(A)
Bottom Chassis
(A)
(A)(A)
Fig. 1-1
1-2. Front Bezel Assy
A.Insert and press a rod in the Emergency Eject Hole and then the CD Tray will open in the direction of arrow (2).
B.Remove the Tray Door in the direction of arrow
(3) by pushing the stoppers forward.
C.Release 3 stoppers and remove the Front Bezel Assy.
|
Tray Door |
(3) |
|
Stoppers |
|
(2) |
CD Tray |
|
Front Bezel Assy |
Emergency Eject Hole |
|
Fig. 1-2 |
|
11 |
|
1-3. Cabinet and Main Circuit Board
A.Remove the Cabinet in the direction of arrow (4). (See Fig. 1-3)
B.Release 2 hooks (a) and remove the CD Tray drawing forward.
C.Remove the Main Circuit Board in the direction of arrow (5).
D.At this time, be careful not to damage the 4 connectors, are positioned at left and bottom sides, of the Main Circuit Board.
|
Cabinet |
Hooks (a) |
(4) |
|
|
|
(5) |
Main |
|
Circuit Board |
|
|
Fig. 1-3 |
2. MECHANISM ASSY DISASSEMBLY
2-1. Pick-up Unit
A.Release screws (B).
B.Separate the Pick-up Unit in the direction of arrow (6).
(B) |
(B) |
|
|
Pick-up Unit |
|
|
(6) |
|
Mechanism Assy |
Fig. 2-1 |
|

2-2. Pick-up
A. Release 1 screw (C) and remove the Pick-up.
(C) |
Pick-up |
Pick-up Unit |
Fig. 2-2 |
12
|
|
|
|
|
|
005 |
035 |
004 |
|
|
5 |
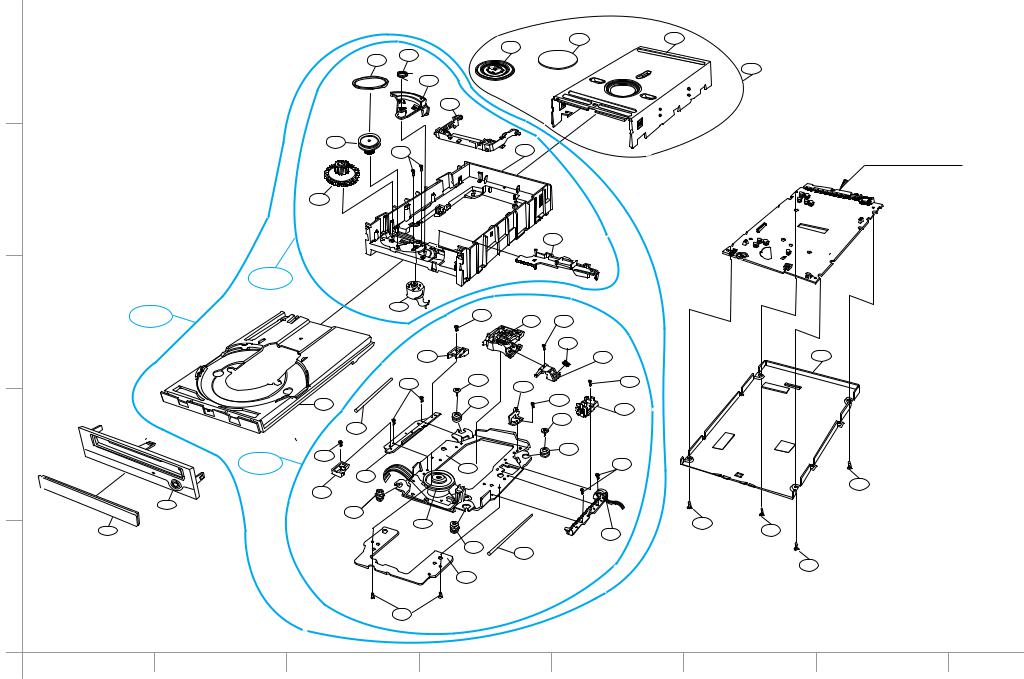
EXPLODED VIEW |
|
|
011 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
008 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
006 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
012 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
014 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
009 |
|
|
015 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
420 |
|
|
|
PBM00 (MAIN C.B.A) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
010 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
016 |
|
|
|
|
|
A03 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A01 |
|
|
013 |
401 |
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
025 |
471 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
027 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
018 |
|
026 |
|
001 |
|
|
|
|
|
401 |
430 |
028 |
|
401 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
007 |
|
020 |
|
401 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
022 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
023 |
|
|
|
430 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
A02 |
401 |
|
|
|
020 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
401 |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
050 |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
017 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
413 |
|
|
|
|
|
019 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
003 |
|
021 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
002 |
|
|
|
030 |
|
|
413 |
413 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
032 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
021 |
024 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
413 |
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
031 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
401 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A |
B |
C |
|
D |
|
E |
F |
G |
H |
|
|
|
|
|
13 |
|
14 |
|
|
|
|
GLOSSARY |
|
|
ATIP |
Absolute Time in Pre-groove. With an additional modulation of the “Wobble”, the “Groove” contains a time |
|
code information. |
|
|
Wobble |
The pre-groove in the Disc is not a perfect spiral but is wobbled. |
|
With : – A typical amplitude of 30 nm |
|
– A spatial peried of 54~64 µm |
|
|
CW |
Continuous Wave. The laser light output is at a constant level. |
|
|
DOW |
Direct Over-Write. The action in which new information is recored over previously recorded information in |
|
CD-RW disc. |
|
|
Overwrite |
The action in which new information is recorded over previously recorded information. |
|
|
(Pre-)Groove |
The guidance track in which clocking and time code information is stored by means of an FM |
|
modulated wobble. |
|
|
Land |
Land is characterized in the following way: |
|
When radial signals are concerned,land is defined as the area between the grooves. |
|
When HF signal are concerned,land is defined as the area between the marks(pits) in tangential |
|
direction. |
|
|
Hybrid Disc |
A Multisession disc of which the first Session is mastered. On a hybrid disc, recorded and |
|
mastered information may co-exist. |
|
|
Mastered |
Information,stored as pits on the disc during the manufacturing process of the disc. |
Information |
(when making the master) |
|
|
OPC |
Optimum Power Control. Procedure is determined optimum recording power according to CD- |
|
R/RW Media in recording start step. |
|
|
ROPC |
Running OPC. The purpose is to continuously adjust the writing power to the optimum power |
|
that is required. |
|
When the optimum power may change because of changed conditions of disc and change in |
|
operating temperature. |
|
|
Jitter |
The 16 value of the time variation between leading and trailing edges of a specific (I3 … I11) pit |
|
or land as measured by Time Interval Analysis. |
|
|
Deviation |
The difference between a fixed value of Pit length and Land length. |
|
|
TOC |
Table Of Contents : in the Lead-in Area the subcode Q-channel contains information about the |
|
Tracks on the disc. |
|
|
Packet |
A method of writing data on a CD in small increments. |
Writing |
Two kinds of packets can be written : Fixed-length and Variable-length. |
Write |
The shape of the HF write signal used to modulate the power of the laser. |
Strategy |
The Write Strategy must be used for recordings necessary for disc measurements. |
|
|
Information |
Wobble, ATIP, Disc Identification, Write Power, Speed Range OPC Parameters, etc are |
Area |
recorded in the Information area of CD-RW Disc |
Finalization |
The action in which (partially) unrecorded or logically erased tracks are finished and the Lead-in |
|
and/or Lead-out areas are recorded or overwritten with the appropriate TOC subcode. |
|
|
Logical Erase |
A method to remove information from a disc area by overwriting it with an EFM signal containing |
|
mode 0 subcode |
|
A logically erased area is equivalent to an unrecorded |
|
|
Physical Erase |
The action in which previously recorded information is erased by overwriting with a CW laser |
|
output. |
|
After a Physical Erase action, the erased area on the CD-RW disc is in the unrecorded state |
|
again. |
|
|
Session |
An area on the disc consisting of a Lead-in area, a Program area, a lead-out area. |
Multi session |
A session that contains or can contain more than one session composed Lead-in and Lead-out |
16
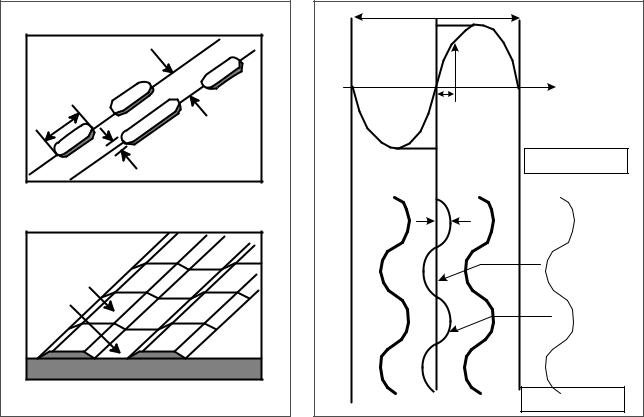
The differences of CD-R/CD-RW discs and General CD-ROM
1. Recording Layer
Recordable CD has a wobbled pre-groove on the surface of disc for laser beam to follow track.
CD-ROMRead(READ-only-ONLYDisc DISC) |
.6um |
1 |
3~11T |
0.4~0.5 um |
CD-R and CD-RW Disc |
(Pit)Groove |
Land |
|
Track pitch(p) |
a=30nm |
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
Iw |
|
|
O |
|
|
a |
Radial Direction |
|
|
|
|
|
Radial Error Signal |
Land |
Groove |
|
|
a |
|
|
|
Average center |
|
|
Actual center |
|
|
The Groove wobble |
2. Disc Specification
ITEM |
CD-ROM |
CD-R |
CD-RW |
|
|
|
|
Standard |
Yellow Book |
Orange Book II |
Orange Book III |
|
|
|
|
Record |
Not available |
Write once |
Re-Writeable |
|
|
|
|
Tracking Signal I11/Itop |
> 0.6 |
> 0.6 |
0.55 > M11> 0.70 |
(HF Modulation) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Read Laser Power(mW) |
< 0.5 mW |
< 0.7 mW |
< 1.0 mW |
|
|
|
|
Jitter |
< 35 nsec |
< 35 nsec |
< 35 nsec |
|
|
|
|
Reflectivity (Rtop) |
70 % |
65 % |
15 % ~ 25 % |
|
|
|
|
Remark) Write Laser Power(mW) |
|
14-65 mW |
6-45 mW |
|
|
|
|
17
3. Disc Materials
1)CD-ROM disc
•It is composed of Silver _ colored aluminum plate and Reflective layer.
•Groove (Pit) of aluminum plate make a track.
•Laser wavelength : 780 nm, Laser Power (Read): 0.5mW
•Signal is detected by the difference of reflective beam
intensity between “pit” and “Land” on the disc.
Label Printing
Protective Layer
 Reflective Layer
Reflective Layer
Substrate (Polycarbonate)
Pit
Laser Beam
2)CD-R disc
•It is so-called WORM (Write Once Read Many) CD.
•It is composed of polycarbonate layer, Organic dye layer, Reflective layer, and Protective layer.Gold/Silver Reflective layer is used to enhance the reflectivity
•According to the kinds of Organic dye layer, it is divided by Green CD, Gold CD, Blue CD.
•Laser Wavelength : 780 nm, Laser Power (read) : 0.7 mW
•Recording Power : 8x(14~20mW), 16x(25~35mW)
•When some part of dye layer is exposed to laser heat, it’s color changs black.Therefore, writing and reading is enabled by the difference of reflectivity between changed part and unchanged part.
•Polycarbonate layer has Pre_Groove which make a Track.
|
Pigment |
Reflective Layer |
Color |
|
|
|
|
|
Phtalocyanine |
Gold/Silver |
Yellow/White |
|
|
|
|
|
Cyanine |
Gold/Silver |
Dark Green/Bright Green |
|
|
|
|
|
Azo |
Gold/Silver |
Dark Blue |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Label Printing
Protective Layer
 Reflective Layer
Reflective Layer
Organic Dye Layer
Substrate (Polycarbonate)
Laser Beam |
Groove |
18

3) CD-RW Disc
Label Printing
Protective Layer
Dielectric Layer(TL)














 Recording Layer
Recording Layer
 Dielectric Layer(UL)
Dielectric Layer(UL)
Substrate (Polycarbonate)
Laser Beam |
Groove |
•It is composed of polycarbonate layer, alloy(silver, arsenic) layer, aluminum reflectivity layer, protective layer.
•An crystalized alloy layer is transformed into noncrystalized by the laser heat. Therefore, writing and reading is enabled by the difference of reflectivity.
•It is possible to overwrite about 1000 times.
•Laser Wavelength : 780 nm, Laser Power (Read) : 1.0mW
•Recording Power : Erase (4~18mW), Write (6~45mW)
•When disc rewriting, new data is overwritten previously recorded data.
•Polycarbonate layer has a Pre-Groove which make a track.
4. Reading process of Optical Disc |
|
|
|
Lens |
H |
|
|
|
|
θ |
D |
|
|
|
|
|
Beam |
|
|
Spot |
Focusing |
Numerical aperture: |
NA=nsinθ, |
Lens |
|
n: Refractive index |
|
Focus depth : H = λ/NA |
|
Laser Spot |
laser spot diameter : D = λ/NA2 |
|
|
|
|
at Constant |
|
|
Read Intensity |
Previously Recorded Marks |
|
|
||
|
|
Groove |
Land |
Mirror |
Reflected |
|
|
|
|
Light |
|
|
|
|
Signal |
|
|
|
|
|
I11 |
IG |
IL |
I0 |
I3 |
Itop Laser Spot |
|
|
|
|
Position |
|
|
|
(Time)
19

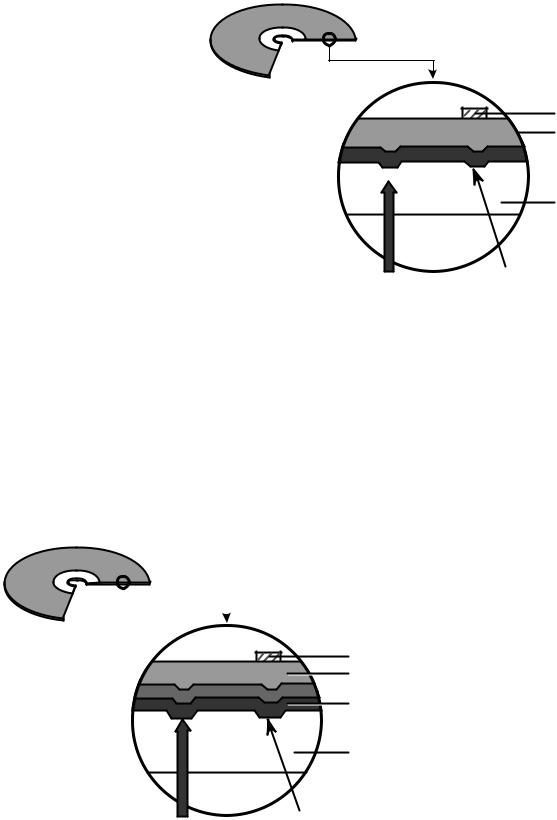
5. Writing Process of CD-R Disc
Incident |
(Write) |
|
Laser |
|
|
|
|
|
Power |
|
(Read) |
(Read) |
|
|
a |
b c d e f g |
Laser Spot |
Position |
||
|
|
(Time) |
|
a |
|
Laser |
b |
|
Spot |
|
Reflected |
|
c |
|
|
Light |
|
|
|
Signal |
|
d |
|
|
e |
|
|
f |
|
Recorded |
|
g |
Mark |
|
|
|
|
Reflected
Light
Signal
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Laser Spot |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
a b c d e f |
g |
|||||||||
Position |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Time) |
|
Below "ORP"– Mark Too Short
At Optimum Record Power ("ORP")
Above "ORP" – Mark Too Long
Time
6. Writing process of CD-RW Disc
Crystal phase |
Amorphous |
Write Power |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Melting/ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
quenching |
|
Erase Power |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Heating/ |
|
Read Power |
|
|
|
|
|
gradual cooling |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Erased state |
Recorded state |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(higher reflectivity) |
(lower reflectivity) |
Groove |
|
|
|
|
|
Crystal Amorphous
20

7. Organization of the PCA, PMA and Lead-in Area
1) Layout of CD-ROM disc
Disc Center |
Diameter 120 mm |
|
Diameter 46 mm
Diameter 15 mm
Center hole |
Clamping and Label Area |
|
Information Area |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Read Only Disc |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Lead-in Area |
Program Area |
|
Lead-out Area |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2) Layout of CD-R/RW disc
Disc Center |
Diameter 120 mm |
|
|
|
|
Diameter 45 mm
Diameter 15 mm
|
Center hole |
Clamping and Label Area |
|
|
|
Information Area |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Unrecorded Disc |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
PCA |
PMA |
|
Lead-in Area |
|
|
|
Program Area |
Lead-out Area |
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Test Area : for performing OPC procedures. |
||
|
Test Area |
|
Count Area |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Count Area : to find the usable area immediately in T.A |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Tsl : start time of the Lead-in Area, as encoded in ATIP |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
in |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
out |
PMA : Program Memory Area |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Tsl-00:35:65 Tsl-00:15:05 Tsl-00:13:25 Tsl |
99:59:74 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
00:00:00 |
|
|
|
|
||
21

8. Function of PCA and PMA area
1)PCA (Power Calibration Area)
•PCA area is used to determine the correct Laser Power for a disc.
–Method 1 : PCA area is divided by a track.
–Method 2 : The previous Calibration value is referred.
–Method 3 : ROPC is used to determine Laser Power value automatically in data writing.
•CD-R Disc can write maximum 99 Tracks but CD-RW Disc can write unlimited tracks because it has a rewritable function.
2)PMA (Program Memory Area)
•It has a track information (track No, track Start/End time) of every track before writing completed.
–PMA area has the last written point and the next writable point of a disc.
–In case of CD to CD copy, some writer may not write PMA area.
* When Disc is Finalized,
PMA information is transferred to the Lead_In area so that general Driver can read it.
* Because PCA and PMA area exist before Lead-In area, General CD Player or CD-ROM Drive can’t read these areas.
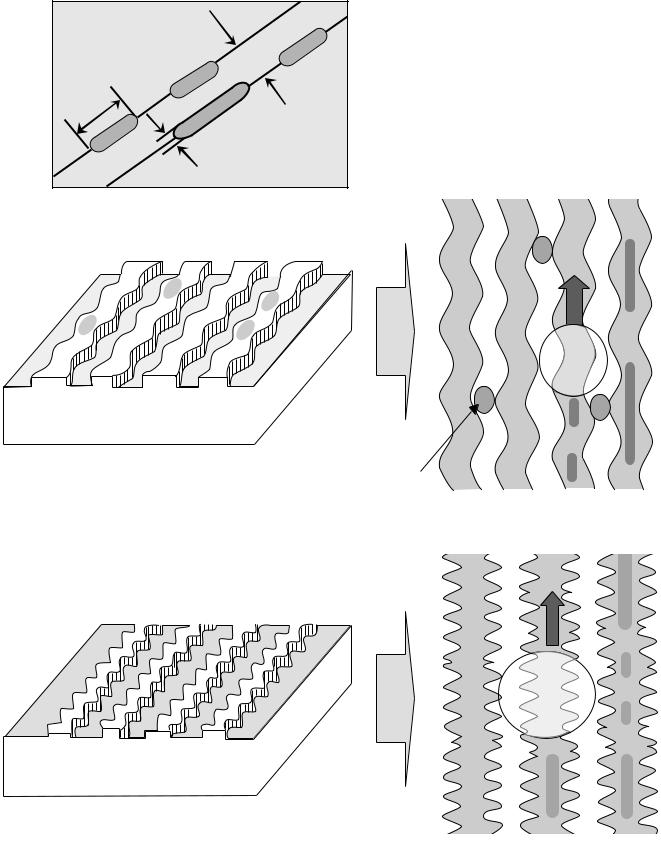
9. OPC and ROPC
1)OPC (Optimum Power Control)
•This is the first step of writing process, because CD writer has its own laser power value and media have different writing characteristics,
–This is determined by the Writing characteristic, speed, temperature, and humidity.
–Laser wavelength is determined by the environmental temperature (775~795nm) and Optical Laser Power is determined by the test and retry.
•Asymmetry and optimum writing Power
–EFM signal Asymmetry is determined by the writing power.
Therefore, Optical Power which has the same value to the preset power value can be estimated by measuring HF signal Asymmetry on the PCA area.
•Measurement of Asymmetry
*Parameter setting (Beta) : Using AC coupled HF signal before equalization Beta = (A1+A2)/(A1-A2)
Signal |
A1 |
|
0 |
|
|
HF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
A2 |
|
|
Time |
P << Po |
P = Po
Time
P >> Po |
Time |
22

2) ROPC (Running Optimum Power Control)
• Variable primary factor of Optimum Power
–Change of Power sensitivity on the Disc. (limited to 0.05 *Po)
–Wavelength shift of the laser diode due to the operating temperature change.
–Change of the Spot aberration due to the Disc skew,
Substrate thickness, Defocus.
– Change of Disc or Optics conditions due to the long term OPC
==> It is necessary to adjust continuously to obtain the Optimum Power.
• Principle of Running OPC |
Sampled timing B |
|
– To meet the factors mentioned above, |
|
|
a horizontal _ direction movement of a curve is uesd. |
|
|
– Beta = f(B-level) = constant on the Recorded Disc
–Procedure of ROPC
a. Reference B-level is determined during OPC Procedure.
b. During Recording, B-level value is controlled to have a close Reference B-level value.
c.Normalization of B-level is used to eliminate the effect of reflectivity fluctuation. ==> The reflected B-level value is normalized by the disc reflectivity itself.
|
B |
Sample Disc Reflectivity |
Level |
|
|
(Read power) |
|
11T
Sample B-level (Write Power)
 Sampled at timing B normalized to recording power
Sampled at timing B normalized to recording power
Level B with Pwo
Pwo decided by OPC
Recording Power
10. Writing Process of DISC |
|
|
|
|
CD-R/RW Media |
Program Area |
|
|
Write Strategy |
PMA Area |
ROPC |
|
Determination |
||
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
OPC |
PCA Test Area |
Lead-In Area |
|
|
|
||
PCA Count Area |
Lead-out Area |
* Recording Capacity of CD-R/RW (74Minute Recording media)
•(2048 Byte/Sector) X (75 Sector/Second) X (60 Second/Minute) X 74 Minute = 681,984,000 Bytes = 682 Mbytes
•But the actual recording capacity is about 650 Mbytes. (according to the ISO 9660 standard, approximately 30 Mbytes are used to make directory structure and volume names.)
23
The differences of DVD-R/RW, DVD+R/RW discs and DVD-ROM
1. Recording Layer
DVD-ROM (Read Only Disc)
um |
.74 |
0 |
T |
3 |
0.4 um |
DVD-R/RW Disc
LPP
(Land Pre-Pit)
DVD+R/RW Disc
24

2. Disc Specification
|
DVD-ROM |
DVD-R |
DVD-RW |
DVD+R |
DVD+RW |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Single-Layer |
Dual-Layer |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Media Type |
Read Only |
Read Only |
Dye |
Phase change |
Dye |
Phase change |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
User data capacity |
4.7GB |
8.54GB |
4.7GB |
4.7GB |
4.7GB |
4.7GB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Wavelength |
650nm |
650nm |
650nm |
650nm |
650nm |
650nm |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Reflectivity |
45~85% |
18~30nm |
45~85% |
18~30% |
45~85% |
18~30nm |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Track pitch |
0.74 |
0.74 |
0.74 |
0.74 |
0.74 |
0.74 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Minimum pit length |
0.4 |
0.44 |
0.4 |
0.4 |
0.4 |
0.4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Modulation |
>0.6 |
>0.6 |
>0.6 |
>0.6 |
>0.6 |
>0.6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Channel bitrate |
26.16MHz |
26.16MHz |
26.16MHz |
26.16MHz |
26.16MHz |
26.16MHz |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Wobble Frequency |
- |
- |
140KHz |
140KHz |
817.4KHz |
817.4KHz |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Addressing |
26.16MHz |
26.16MHz |
Wobble & LPP |
Wobble & LPP |
Wobble(ADIP) |
Wobble(ADIP) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Read Power (mW) |
|
|
|
|
0.7 + 0.1 |
0.7 + 0.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Write Power (mW) |
- |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
JItter |
<8% |
<8% |
<8% |
<8% |
<9% |
<9% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3. Disc Materials
1) DVD-ROM
<Single Layer >
 Label
Label
 Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate
 Bonding layer
Bonding layer
Reflective layer
 Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate
<Dual Layer >
 Label
Label
 Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate
 Reflective layer
Reflective layer
 Bonding layer
Bonding layer
Semi-reflective
 Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate
25

2) Recording format using organic dye material (DVD-R/DVD+R)
*The format that records data through the creation of recorded marks by changing the organic dye material with a laser beam.
> Disc structure
DVD-R |
DVD+R |
Adhesive layer |
Adhesive layer |
Protective layer |
Protective layer |
Reflective layer |
Reflective layer |
Recording layer(dye) |
Recording layer(dye) |
Disc substrate |
Disc substrate |
> Disc structure
[Recording]
Recording is done by changing the organic dye layer and the substrate with a laser when a strong is applied to a disc, the temperature of the ortanic dye material goes up, the dye is decomposed and the substrate changes at the same time. At this time, a durable bit is created as is the case with a CD-ROM.
[Playback]
Signals are read with the differences of the reflection of a laser from pits.
Adhesive layer
Protective layer
Reflective layer
Dye layer
Substrate
Laser beam
26

3) Recording format using phase-change recording material (DVD-RW/DVD+RW)
*Data is recorded by changing the recording layer from the amorphous status to the crystalline status, and played back by reading the difference of the reflection coefficient.
[ Amorphous : Non-crystalline ]
> Disc structure
DVD-RW |
DVD+RW |
Adhesive layer |
Adhesive layer |
Protective layer |
Protective layer |
Reflective layer |
Reflective layer |
Dielectric layer |
Dielectric layer |
Recording layer |
Recording layer |
(Phase change material) |
(Phase change material) |
Dielectric layer |
Dielectric layer |
Disc substrate |
Disc substrate |
> Recording principles
[Recording]
When a high-power laser is applied to the recording material, it melts and then becomes amorphous with a low reflection coefficient when it quickly cools off. When a mid-power laser is applied to heat gradually the recording material and then gradually cools it off, it becomes crystal with a high reflection coefficient.
[Playback]
A low-power laser is used for playback. The amount of reflected light depends on the status (amorphous or crystalline) of the recording material. This is detected by an optical sensor.
Substrate |
Laser beam
Crystalline status |
Amorphous status |
Recording data (Melting/Quick cooling)
Erasing data (Heating/Gradual cooling)
Data erased state |
Recorded state |
(High reflection coefficient) |
(Low reflection coefficient) |
27
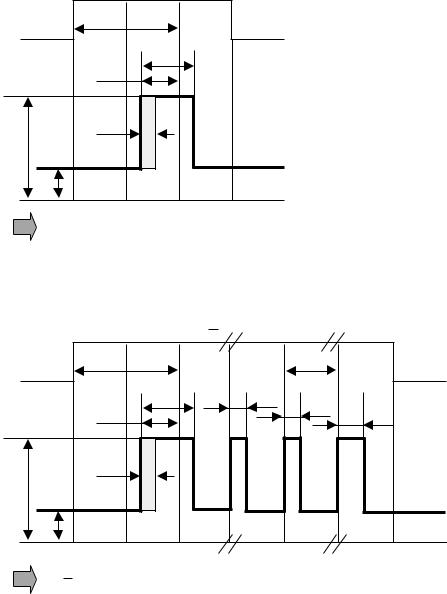
4. Writing Pulse Wave Form of DVD+R
For different speed ranges, different write strategies can be used. This document specifies 2 options:
-a pulsed write strategy, where each single mark is created by a number of subsequent separated short pulses.
-a blocked write strategy, where each single mark is created by one continuous pulse.
1) 1st Method : Using Pulsed Write Strategy
* 3T : |
|
|
|
T = 3 |
|
NRZI |
2Tw |
|
Channel bits |
||
|
||
|
Ttop |
|
|
dTtop |
|
Pp |
dTle |
|
Pb |
|
N = 3 : only the top pulse(Ttop ), first pulse lead-time dT top , dTle
* > 4T : |
|
|
|
|
|
|
T > 4 |
|
|
NRZI |
2Tw |
|
Tw |
|
Channel bits |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ttop |
Tmp |
Tmp |
Tlp |
|
dTtop |
|
||
|
|
|
||
Pp |
dTle |
|
|
|
Pb |
|
|
|
|
N > 4 : the top pulse (Ttop ), multi-pulse (Tmp ) and last pulse (Tlp ), first pulse lead-time dTtop, dTle
Pp : Actual write power
Pb : Bias Power
28

2) 2st Method : Using Blocked Write Strategy
NRZI |
|
|
2Tw |
Tw |
|
|||||||||
Channel bits |
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
dTtop |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Tlp |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ttop |
Tmp |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
dPp |
|
Pp |
dTle |
|
|
0mW |
Pb |
|
1.25Tw |
|
Pc |
Pb |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
dTtop,3 |
dPp3 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
3T mark |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.25Tw |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pb |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ttop,3 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
dTle |
|
|
Pc |
|||
dTtop,4 |
dPp4 |
4T mark |
1.25Tw |
|
|
Ttop,4 |
Tlp |
5T mark |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.25Tw |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
Ttop,4 |
|
Tmp |
Tlp |
|||||
|
|
||||||||||
Etc. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.25Tw |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
Ttop,4 |
|
Tmp |
|
|
Tmp Tlp |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
N = 3 : Ttop (cm = 3) can be optimized individually.
N > |
4 : T |
(cm > 4) + (N-3) x T |
+ T |
lp |
, |
T |
w |
= Tmp |
|
top |
w |
|
|
|
|
||
Pc |
shall be < 0.1mW |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pp : Actual write power Pb : Bias Power
dPp : Additional power ( Only be applied for the 3T and 4T marks)
Pc : Cooling power (Especially at higher recording speeds, optimum cooling down of the recording layer after writing a mark may be needed.)
29
 Loading...
Loading...