Page 1

HP LaserJet 1022nw
Wireless Printer User Guide
Page 2

Page 3

HP LaserJet 1022nw Wireless Printer
User Guide
Page 4

Copyright information
© 2005 Copyright Hewlett-Packard
Development Company, L.P.
Reproduction, adaptation or translation
without prior written permission is
prohibited, except as allowed under the
copyright laws.
The information contained in this document
is subject to change without notice.
The only warranties for HP products and
services are set forth in the express
warranty statements accompanying such
products and services. Nothing herein
should be construed as constituting an
additional warranty. HP shall not be liable
for technical or editorial errors or omissions
contained herein.
Part number: Q5914-90904
Edition 1, 02/2005
Trademark credits
Microsoft® and Windows® are U.S.
registered trademarks of Microsoft
Corporation.
Energy Star® and the Energy Star logo®
are U.S. registered marks of the United
States Environmental Protection Agency.
Page 5

Table of contents
1 Networking basics
Manual contents and sources for support and information ......................................................2
WWW links for drivers, software, and support ...................................................................2
Where to look for more information ...................................................................................2
Wireless networking basics ......................................................................................................3
Channels and communication modes ...............................................................................3
Security ..............................................................................................................................4
Wireless profiles ................................................................................................................6
2 Support information for installing to a wireless network
Chapter overview .....................................................................................................................8
Printer Wireless light ................................................................................................................9
Configuration page .................................................................................................................10
Printing a configuration page ...........................................................................................10
General and wireless network settings ............................................................................10
Embedded Web server ..........................................................................................................13
To open the embedded Web server ................................................................................13
Information tab .................................................................................................................14
Settings tab ......................................................................................................................14
Networking tab .................................................................................................................14
Other links .......................................................................................................................14
Switching from wired to wireless ............................................................................................15
Resetting the printer to the factory default settings ................................................................16
Resetting the factory defaults ..........................................................................................16
3 Problem solving
Solving problems that occur during installation ......................................................................18
Computer is unable to discover a device .........................................................................18
Personal software firewall is blocking communication .....................................................18
Device is unable to connect to the network after removing cable (infrastructure
only) ..............................................................................................................................18
System Requirements Error: No TCP/IP error displays ..................................................18
Printer not found screen appears during installation .....................................................19
Unable to determine or verify network name during installation ......................................19
Verification fails at end of installation ..............................................................................20
Setup failed ......................................................................................................................21
Installation software does not install correctly .................................................................23
Solving infrastructure mode problems ...................................................................................24
The printer cannot find the WLAN ...................................................................................24
Printer cannot find your computer ...................................................................................24
Computer is unable to discover device ............................................................................24
ENWW Table of contents iii
Page 6

Solving ad-hoc mode problems .............................................................................................25
Printer cannot find your computer ...................................................................................25
Solving general wireless networking problems ......................................................................26
Check the Wireless light ..................................................................................................26
Printer has the wrong wireless network settings .............................................................27
To change the printer’s network settings: ........................................................................27
Computer's wireless card is set to the wrong wireless profile .........................................28
Radio signal is weak ........................................................................................................28
Wireless access point (WAP) filters MAC addresses ......................................................28
Appendix A Regulatory information
USA Federal Communications Commission (FCC) compliance ............................................29
Declaration of Conformity ......................................................................................................30
Regulatory statements ...........................................................................................................31
Laser safety statement ....................................................................................................31
Canadian regulations .......................................................................................................31
European Union regulatory notice ...................................................................................31
Laser statement for Finland .............................................................................................32
Environmental product stewardship program ........................................................................34
Protecting the environment ..............................................................................................34
Ozone production ............................................................................................................34
Power consumption .........................................................................................................34
Toner consumption ..........................................................................................................34
Paper use ........................................................................................................................34
Plastics ............................................................................................................................34
HP LaserJet printing supplies ..........................................................................................35
HP printing supplies returns and recycling program information .....................................35
Paper ...............................................................................................................................36
Material restrictions .........................................................................................................36
For more information .......................................................................................................36
Material safety data sheet ......................................................................................................37
OpenSSL License ..................................................................................................................38
Original SSLeay License ........................................................................................................39
Glossary
Index
iv ENWW
Page 7

Networking basics
This chapter provides information on the following topics:
●
Manual contents and sources for support and information
●
Wireless networking basics
ENWW 1
Page 8

Manual contents and sources for support and information
NOTE
Only the HP LaserJet 1022nw printer contains wireless capability.
This manual is a supplementary document to the HP LaserJet 1022 Series Printer User
Guide and to the HP LaserJet 1022nw Wireless Getting Started Guide. Both of these
documents are included with the printer. This manual provides the following information
about installing and connecting the printer to a wireless network:
● The
● The
● The
In addition, this manual contains an appendix of regulatory information, a glossary of
wireless terms, and an index.
Networking basics chapter contains overview information about wireless networking
and the wireless features of the HP LaserJet 1022nw printer.
Support information for installing to a wireless network chapter contains support
information that will be useful if you are installing the printer to a wireless network, or if
you wish to change printer or network settings after you have installed the printer. You
can find procedures for installing to a wireless network in the HP LaserJet 1022nw
Printer Wireless Start Guide packaged with the printer.
Problem solving chapter contains troubleshooting information.
WWW links for drivers, software, and support
If you need to contact HP for service or support, use the following link: http://www.hp.com/
support/lj1022/.
Where to look for more information
● CD user guide: Detailed information on using and troubleshooting the printer. Available
on the CD-ROM that came with the printer.
● Online Help: Information on printer options that are available from within printer drivers.
To view a Help file, access the online Help through the printer driver.
HTML (online) user guide: Detailed information on using and troubleshooting the printer.
Available at http://www.hp.com/support/lj1022. Once connected, select Manuals.
2 Chapter 1 Networking basics ENWW
Page 9

Wireless networking basics
The HP LaserJet 1022nw printer has an internal HP wireless print server that supports both
wired and wireless connectivity. However, the printer does not support simultaneous wired
and wireless connections. To connect to a wireless network, the printer uses wireless
protocol IEEE 802.11b/g that communicates data through radio transmission. After installing
the printer to a wireless network, cables are not required to communicate with the computers
or devices that are part of the network.
NOTE
The printer is compatible with 802.11b/g-compliant devices.
A wireless local area network (WLAN) is a collection of two or more computers, printers, and
other devices linked by radio waves. A WLAN uses high-frequency airwaves (radio) to
communicate information from one point to another.
To connect a computer or device to a wireless network, the computer or device must have a
wireless network adapter. The HP LaserJet 1022nw printer uses an internal networking
component that contains a wireless network adapter and radio. No cabling is necessary
between networked devices that use wireless technology, although it is possible to use a
cable to configure your printer for a wireless network. This is the recommended installation
method.
Common wireless network adapters include the following:
● USB adapter: An external device that connects to a USB port on the computer (typically
has a PCMCIA card attached to one end).
● Notebook adapter: A PCMCIA card that plugs directly into one of the PCMCIA slots on
your laptop or other portable computer.
● Desktop computer adapter: A dedicated ISA or PCI card, or a PCMCIA card with a
special adapter, that plugs into your desktop computer.
● AirPort adapter: A wireless card that plugs directly into the AirPort slot on your
Macintosh laptop or desktop computer. AirPort adapters eliminate the need for cable
connections to the computer.
The following sections contain overview information about wireless channels and
communication modes, networking profiles, and network security.
Channels and communication modes
The band of radio signals used for IEEE 802.11b/g wireless networking is segmented into
specific frequencies, or channels. For IEEE 802.11b/g wireless networks, 14 channels are
available. But each country/region specifies the channels that are authorized for use. For
example, in North America, only channels 1 through 11 are allowed. In Japan, channels 1
through 14 can be used. In Europe, except for France, channels 1 through 13 are allowed.
Because existing standards change frequently, you should check with your local regulatory
agencies for authorized channel use. In most countries/regions channels 10 and 11 may be
used without restriction.
Channel selection depends on the communication mode of the network. The communication
mode defines how devices, such as computers and printers, communicate on a wireless
network. There are two primary types of wireless communication modes: infrastructure and
ad-hoc.
ENWW Wireless networking basics 3
Page 10
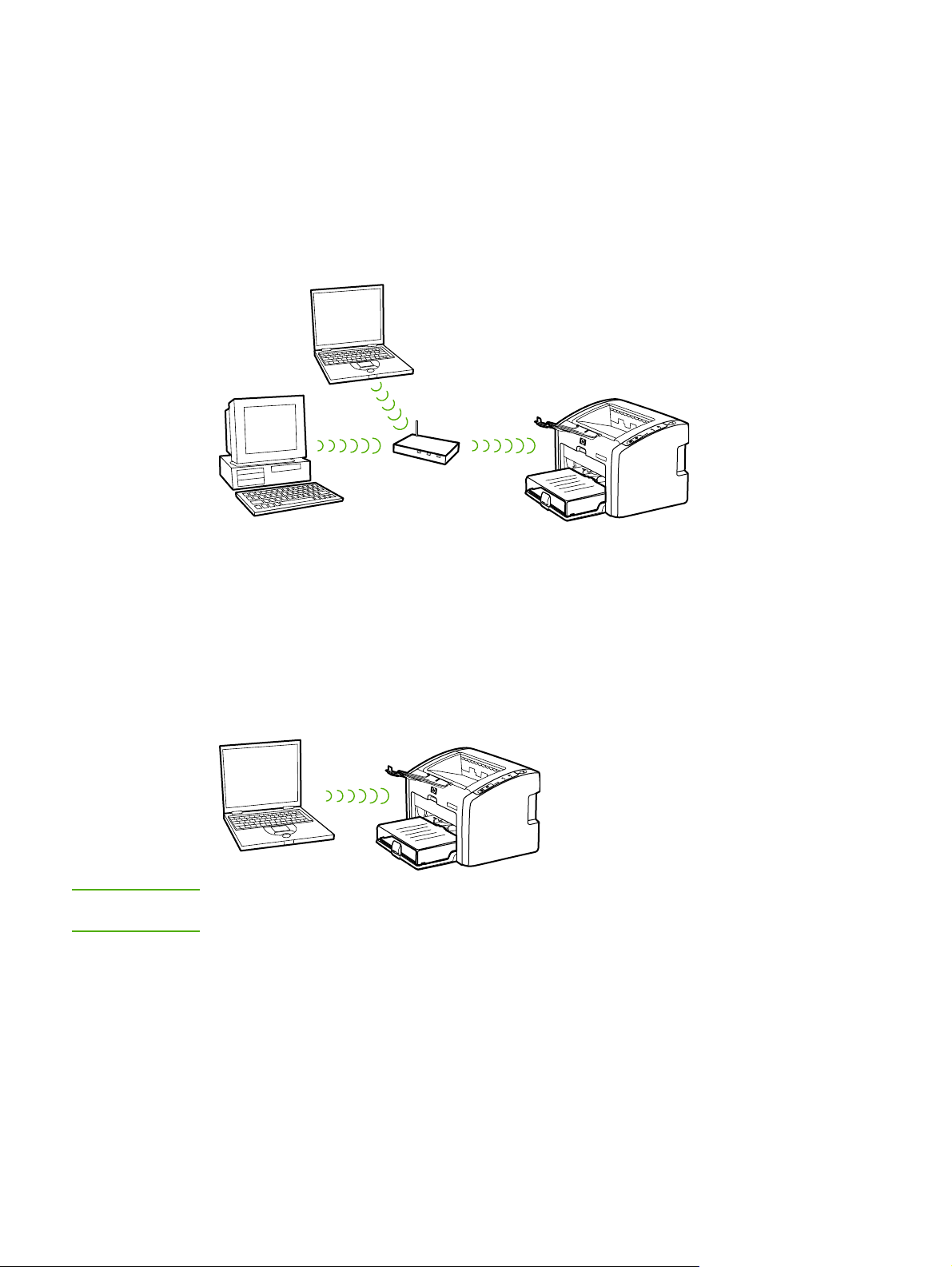
Infrastructure mode (preferred)
In infrastructure mode, the printer communicates with network computers through a wireless
access point (WAP) or a base station. The access point acts as a central hub or gateway
connecting wireless and, optionally, wired devices. (Most access points have an integrated
Ethernet controller to connect to an existing wired-Ethernet network.) If your printer connects
through a wireless residential gateway that provides access point functions, choose
infrastructure mode.
Ad-hoc mode
NOTE
In ad-hoc mode, which is sometimes called peer-to-peer mode, the printer communicates
with your computer directly, rather than through an access point or base station. Each device
on an ad-hoc network must have a wireless network adapter. The adapter enables each
device to communicate with the other devices on the network. Ad-hoc mode is usually
limited to simple, small wireless networks because performance degrades significantly after
connecting too many network devices. This option is most often used if you are connecting
only two network devices that are not sharing an Internet connection.
For maximum performance, HP recommends connecting the printer to a network that
communicates using the infrastructure mode.
Security
As with other networks, security for wireless networks focuses on access control and
privacy. Traditional wireless network security includes the use of Service Set Identifiers
(SSIDs), open or shared-key authentication, static Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) keys,
and optional Media Access Control (MAC) authentication. This combination offers a basic
level of access control and privacy.
4 Chapter 1 Networking basics ENWW
Page 11

More advanced levels of security (such as Wi-Fi protected access [WPA] and Pre-shared
key) are available through the printer’s embedded Web server. For introductory information
about the embedded Web server, see
about using the features, see the embedded Web server online help.
Embedded Web server. For detailed information
NOTE
NOTE
It is highly recommended that you implement a wireless security scheme (either WEP or
WPA) prior to setup. In addition, use an antivirus program to protect against computer
viruses, and follow basic security rules such as setting strong passwords and not opening
unknown attachments. Other network components, including firewalls, intrusion-detection
systems, and segmented networks, should also be considered as part of your network design.
Authentication and encryption are two different approaches to network security.
Authentication verifies the identity of a user or device before granting access to the network,
making it more difficult for unauthorized users to access network resources. Encryption
encodes the data being sent across the network, making the data unintelligible to
unauthorized users. Both of these security methods are common on wireless networks.
Authentication
The HP installation software supports Open System authentication. More advanced forms of
authentication are available through the embedded Web server.
A network with Open System authentication does not screen network users based on their
identities and usually involves supplying the correct SSID. Such a network might use Wired
Equivalent Privacy (WEP) encryption to provide a first level of security, or Wi-Fi protected
access (WPA) to provide security by encrypting data sent over radio waves from one
wireless device to another wireless device. The HP LaserJet 1022nw wireless printer allows
for either WEP or WPA.
Shared key and server-based authentication protocols are implemented through the
embedded Web server. For introductory information about the embedded Web server, see
Embedded Web server. For detailed information about using the features, see the
embedded Web server online help.
Network name (SSID)
Wireless devices are configured with the name of the network to which they will connect.
The network name is also called the SSID and identifies the ESS (Extended Service Set)
that is normally associated with larger infrastructure networks.
The SSID should not be considered a security feature because it can be easily identified.
However, as a network administration or management feature, it does provide basic network
access control.
Encryption
To reduce your network exposure to eavesdropping, establish a wireless security key for
your network. The printer installation software supports the WEP security scheme, which
hinders unauthorized users from accessing data transmitted over the radio waves. It is
based on the use of a single WEP key, in which case each computer or device is configured
with the same key to communicate on that network.
ENWW Wireless networking basics 5
Page 12

NOTE
Up to four WEP keys might be used on a wireless network for transmission of data. For
example, if you have three computers and an access point, each might be assigned a
distinct key for transmitting data. However, the remaining keys must also be entered on each
device so they can communicate with each other. The installation software for the
HP LaserJet 1022nw printer provides the option to type one WEP key. If you want to use
more than one WEP key, those keys must be entered into the printer’s embedded Web
server prior to installing the software. For introductory information about the embedded Web
server, see
the embedded Web server online help.
Embedded Web server. For detailed information about using the features, see
Media access control address authentication
Some WLAN vendors support authentication based on the physical address, or MAC
address, of the client Network Interface Card (NIC). In this scenario, an access point allows
association by a client only if that client’s MAC address matches an address in an
authentication table used by the access point. This is not configurable through the printer.
Wireless profiles
A wireless profile is a set of network settings unique to a given wireless network. Many
wireless devices have configuration utilities that allow the device to have wireless profiles for
several wireless networks. In order to use the printer, the printer's wireless settings must
match the computer's network settings for that wireless network.
NOTE
For example, a person uses the same wireless-enabled laptop at work and at home. Each
network has a unique set of wireless settings. The person creates the following wireless
profiles on the laptop:
● at_work: Contains the network settings for the office wireless network
● at_home: Contains the network settings for the home wireless network
When the laptop is being used at work, the person must set the wireless profile to at_work in
order to connect to the office network. Conversely, the laptop must be set to the at_home
wireless profile when the person is at home and wants to connect the laptop to the home
network.
The HP LaserJet 1022nw printer cannot be connected to a wired and wireless network at the
same time.
6 Chapter 1 Networking basics ENWW
Page 13

Support information for installing to a wireless network
This chapter provides information on the following topics:
●
Chapter overview
●
Printer Wireless light
●
Configuration page
●
Embedded Web server
●
Switching from wired to wireless
●
Resetting the printer to the factory default settings
ENWW 7
Page 14

Chapter overview
This chapter contains information that will be useful if you are installing the printer to a
wireless network, or if you are changing printer or network settings after you have installed
the printer. Specifically, this chapter contains a description of the printer Wireless light and
the configuration page, and an overview of the embedded Web server (EWS). In addition,
this chapter contains procedures for resetting the printer network setting and for switching
between wireless and wired communications.
The procedure you follow for installing the printer to a wireless network depends on whether
the network communicates through an infrastructure mode or through an ad-hoc mode. You
can find procedures for installing the printer to a wireless network in the HP LaserJet
1022nw printer Wireless Getting Started Guide that was packaged with the printer. For more
information about infrastructure and ad-hoc networks, see
Wireless networking basics.
NOTE
NOTE
For maximum efficiency, HP recommends the printer be connected to a network that uses
the infrastructure communication mode.
The printer cannot be connected to a wired and wireless network at the same time.
8 Chapter 2 Support information for installing to a wireless network ENWW
Page 15
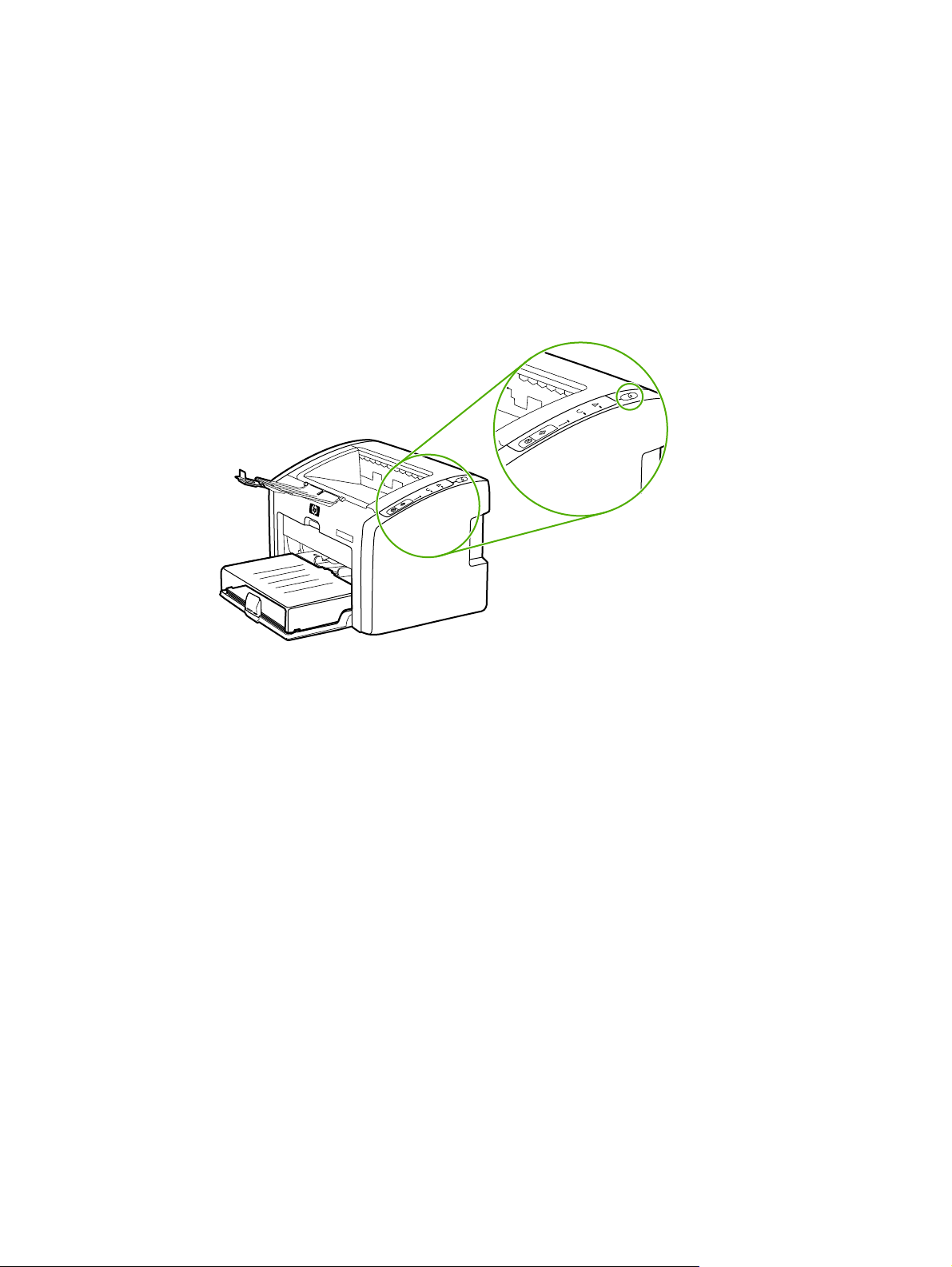
Printer Wireless light
The HP LaserJet 1022nw printer has an internal networking component that provides
wireless connectivity. To view the status of the wireless communications, the printer contains
a Wireless light.
● If the light is on, the printer is connected to a wireless network.
● If the light flashes, the printer is scanning for a wireless network.
● If the light is off, wireless networking is disabled.
ENWW Printer Wireless light 9
Page 16
Configuration page
The printer includes an internal component that provides networking capability for both wired
and wireless connectivity. This section contains a procedure for printing a configuration
page, as well as a description of the general network and wireless network fields that display
on the page.
Printing a configuration page
When the printer is in the Ready state, press and hold the GO button until the Ready light
starts blinking.
General and wireless network settings
NOTE
All of the settings on the configuration page should match the settings of the network with
which you are trying to connect. If any values are different, you might not be able to connect
to the network.
The following sections describe the various fields on the configuration page.
General network settings
Field Description
Hardware Address
Firmware Version
The Media Access Control (MAC) address that uniquely identifies
the printer. This is a unique 12-digit identification number assigned
to networking hardware for identification, like a digital fingerprint. No
two pieces of hardware have the same MAC address.
NOTE
Some ISPs require that you register the MAC address of the
Network Card or LAN Adapter that was connected to your cable or
DSL modem during installation.
The internal networking component and device firmware revision
code separated by a hyphen.
NOTE
You might be asked to provide the firmware revision code if you call
for support.
Host Name
The TCP/IP name assigned by the install software to the device. By
default, these are the letters NPI followed by the last six digits of the
MAC address. You can also configure the device name through the
embedded Web server.
10 Chapter 2 Support information for installing to a wireless network ENWW
Page 17
Field Description
IP Address
Config by
mDNS Name
The printer's Internet Protocol (IP) address. This address uniquely
identifies the device on the network.
IP addresses are assigned dynamically through DHCP or AutoIP.
You can also set up a static IP address, though this is not
recommended.
Manually assigning an invalid IP address during install will cause
your network components to not see the device.
The protocol used to assign the IP address to the device:
● AutoIP: the installation software determines the configuration
parameters.
● DHCP: the configuration parameters are supplied by a dynamic
host configuration protocol (DHCP) server on the network. On
small networks, this could be a router.
● Manual: the configuration parameters are set manually, such
as a static IP address.
● BOOTP: Bootstrap Protocol (BOOTP) is an Internet protocol
that enables a device to discover its own IP address, the IP
address of a BOOTP server on the network, and a file to be
loaded into memory to boot the machine. This enables the
device to boot without requiring a hard or floppy disk drive.
Multicast Domain Name Server Service Name. The name used by
Apple Rendezvous to identify the printer, which consists of the
device name and the MAC address.
Link Status
Apple Rendezvous is used with local and ad-hoc networks that do
not use central DNS servers. To perform name services,
Rendezvous uses a DNS alternative called mDNS.
With mDNS, your computer can find and use any printer connected
to your local area network. It can also work with any other Ethernetenabled device that appears on the network.
The protocol for transmitting data over a network:
● 802.11b and 802.11g: for wireless network
● 10T-Full: for wired network
● 10T-Half: for wired network
● 100TX-Full: for wired network
● 100TX-Half: for wired network
ENWW Configuration page 11
Page 18
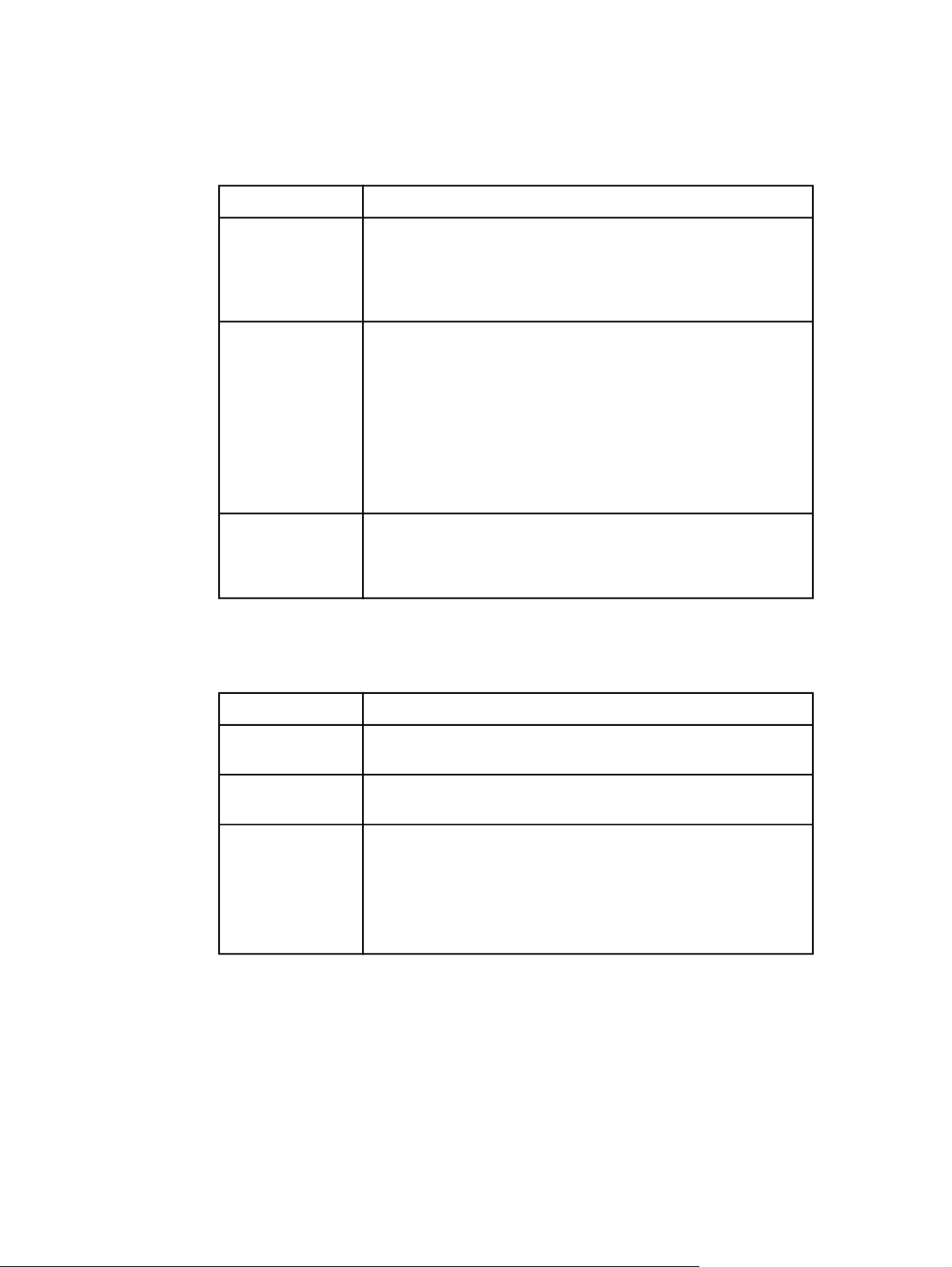
Wireless network settings
Field Description
Wireless Status
Communication
Mode
Network Name
(SSID)
Status of the wireless network:
● Disabled: the wireless 802.11b/g network is disabled when the
wired 802.3 network is active. This is the default setting.
● Enabled
An IEEE 802.11 networking framework in which devices or stations
communicate with each other:
● Infrastructure: the printer communicates with other network
devices through a wireless access point, such as a wireless
router or base station.
● Ad-hoc: the printer communicates directly with each device on
the network. No wireless access point is used. This is also
called a peer-to-peer network. On Macintosh networks, ad-hoc
mode is called computer-to-computer mode.
Service Set Identifier. A unique identifier (up to 32 characters) that
differentiates one wireless local area network (WLAN) from another.
The SSID is also referred to as the Network Name—the name of
the network to which the printer is connected.
Data transmission and receipt information
Field Description
Total Packets
Received
Bad Packets
Received
Total Packets
Transmitted
The number of packets received by the printer without error since it
has been turned on. The counter clears after the printer is turned off.
The number of packets received with errors since the printer has
been turned on. The counter clears after the printer is turned off.
The number of packets transmitted by the printer without error since
it has been turned on. The counter clears after the printer is turned
off.
When a message is transmitted over a packet-switching network, it
is broken up into packets. Each packet contains the destination
address as well as the data.
12 Chapter 2 Support information for installing to a wireless network ENWW
Page 19

Embedded Web server
The embedded Web server provides a convenient way to manage your printer on a network.
The embedded Web server is available for the HP LaserJet 1022nw printer over the Internal
HP network connection. The following information applies to the embedded Web server:
● You do not need to install any software on the computer. You only need to have a
supported Web browser. To use the embedded Web server, you must have Microsoft
Internet Explorer 5.5 or later or Netscape Navigator 6.0 or later.
● The embedded Web server is available in English only.
● The embedded Web server does not provide e-mail or status alerts.
The embedded Web server allows you to view printer and network status and to manage
printing functions from your computer instead of from the printer control panel. The following
are examples of what you can do using the embedded Web server:
● View printer status information
● Order new supplies
● View and change the printer default configuration settings
● View and change the printer’s wired -or wireless network settings
The embedded Web server works when the printer is connected to an IP-based network.
The embedded Web server does not support IPX-based printer connections or AppleTalk.
NOTE
CAUTION
NOTE
Internet access is not required to open and use the embedded Web server. However, if you
click a link in the Other Links area, you must have Internet access in order to go to the site
associated with the link.
It is recommended that the printer and associated computers reside on the same subnet.
Printer installation across subnets can be problematic depending on the type of router used.
However, if the printer is on a different subnet than your computer, enter the printer's IP
address (for example, http://192.168.1.1) in the browser's Address fields to open the
embedded Web server. Also, if your computer uses a proxy server to access the Internet,
you might need to configure your browser to by-pass the proxy server in order to access the
embedded Web server.
To open the embedded Web server
1. In a supported Web browser, type the IP address or hostname for the printer. To find the
IP address, print a configuration page at the printer by pressing and holding the G
button until the Ready light starts blinking.
Once you open the URL, you can bookmark it so that you can return to it quickly in the future.
2. The embedded Web server has three tabs that contain settings and information about
the printer: the Information tab, the Settings tab, and the Networking tab. Click the tab
that you want to view.
O
ENWW Embedded Web server 13
Page 20

Information tab
The Information tab contains the following pages:
● Device Status. This page displays the printer and supplies status. This page also
displays product information such as the network name, network address, and model
information.
● Configuration. This page shows information found on the printer Configuration page.
Settings tab
This tab allows you to configure the printer from your computer. If this printer is networked,
always consult with the printer administrator before changing settings on this tab. The
Settings tab contains the Print Settings page. On the Print Settings page you can view
and change basic information about the printer.
Networking tab
This tab allows the network administrator to control network-related settings for the printer
when it is connected to an IP-based network.
Other links
CAUTION
This section contains links that connect you to the Internet. You must have Internet access in
order to use any of these links. If you use a dial-up connection and did not connect when
you first opened the embedded Web server, you must connect before you can visit these
Web sites. Connecting might require that you close the embedded Web server and reopen it.
● Product Registration. Connects you to the product registration page on the HP Web
site.
● Order Supplies. Click this link to connect to the Sure Supply Web site and order
genuine HP supplies from HP or a reseller of your choice.
● Product Support. Connects to the support site for the HP LaserJet 1022nw printer. You
can search for help regarding general topics.
● HP Instant Support. Connects you to the HP Web site to help you find solutions. This
service analyzes your printer error log and configuration information to provide
diagnostic and support information specific to your printer.
Use caution when changing the print server's wireless network settings. It is possible that the
printer could lose the connection, which might require resetting the printer to the factory
defaults and reinstalling the software.
14 Chapter 2 Support information for installing to a wireless network ENWW
Page 21

Switching from wired to wireless
If the printer is communicating with a wireless network and you plug a LAN cable into the
printer, it automatically switches to wired communications. For more information, see
Embedded Web server.
ENWW Switching from wired to wireless 15
Page 22

Resetting the printer to the factory default settings
Once the printer is configured for a network, its configuration settings are saved in its
memory. Resetting the printer to its factory default settings will clear all the settings from the
printer's memory for your network. This should only be done as a last resort when
troubleshooting the printer.
Resetting the printer to its factory default settings may require you to reinstall the printer
software. Additionally, you will also have to reconfigure the printer's security settings.
The printer's default settings are:
Option Default settings
Communication
mode
Network Name
(SSID)
Encryption None
Wireless Radio On, if no LAN cable is attached
ad-hoc
hpsetup
Resetting the factory defaults
When the printer is turned off, press and hold the GO and C
printer, and continue to hold the G
O
and C
ANCEL
buttons until all lights are blinking in unison.
ANCEL
buttons. Turn on the
16 Chapter 2 Support information for installing to a wireless network ENWW
Page 23

Problem solving
This chapter provides information on the following topics:
●
Solving problems that occur during installation
●
Solving infrastructure mode problems
●
Solving ad-hoc mode problems
●
Solving general wireless networking problems
ENWW 17
Page 24

Solving problems that occur during installation
This section contains solutions to problems that might occur while initially installing the
printer to a wireless network.
Computer is unable to discover a device
1. Verify that the following cables are connected properly:
● Power cables
● Cables between the printer and the hub or router
● Cables between the hub or router and your computer
● (If applicable) cables to and from your modem or Internet connection
2. Verify that you have an active network connection.
● Look at the light on the network connector. If the light is on, the printer is connected
to a wired network. If the light is off, check the cable connections from the printer to
the gateway, router, or hub to ensure connections are secure.
● If the connections are secure, recycle the power on the printer to initiate another
search for a wireless network.
Personal software firewall is blocking communication
The personal software firewall is a security program that protects a computer from intrusion.
However, the personal firewall might block communication between the computer and the
printer. If you cannot communicate with the printer, try disabling the personal firewall. If you
are still unable to communicate with the printer, then re-enable the firewall. If disabling the
firewall allows you to communicate with the printer, you might want to assign the printer a
static IP address and then re-enable the firewall. For information about firewalls that are
used in an HP environment, see http://www.hp.com/support/XP_firewall_information.
Device is unable to connect to the network after removing cable (infrastructure only)
If the access point/gateway has MAC filtering enabled, enter the MAC address of the printer
into the access point. The printer should then be able to connect to the wireless network. For
more information, see
Wireless access point (WAP) filters MAC addresses.
System Requirements Error: No TCP/IP error displays
Make sure your LAN card is installed properly and set up for TCP/IP (Windows only). For
more information, see
Computer is unable to discover a device.
18 Chapter 3 Problem solving ENWW
Page 25

Printer not found screen appears during installation
1. Verify that the printer is turned on.
2. Verify that you have an active network connection.
● Look at the light on the network connector on the back of the unit. If the light is on,
the printer is connected to a wired network. If the light is off, check the cable
connections from the printer to the gateway, router, or hub to ensure connections
are secure.
● Verify that the printer is connected to the network with the cable that is packaged
with the printer.
● If the connections are secure, recycle the power on your printer.
3. Print a configuration page. To print a configuration page, when the printer is in the
Ready state, press and hold the G
information, see
Configuration page.
4. Verify that the printer’s internal networking component is set to its factory default
settings. If the print server was previously configured, it might need to be reset to the
factory default settings.
● Communication mode: ad-hoc (peer-to-peer)
● Network name (SSID): hpsetup
● Encryption: disabled
O
button until the Ready light starts blinking. For more
You can check the print server's configuration by printing a configuration page. To
reset the printer to the factory settings, when the printer is turned off, press and
hold the G
and C
ANCEL
buttons. Turn on the printer, and continue to hold the G
buttons until all lights are blinking in unison.
O
O
and C
ANCEL
5. Move the printer and the computer closer together. If the distance between your
computer and the printer is significant, try reducing the distance. If possible, provide a
clear path between the computer and print server, and minimize sources of radio
interference. For more information, see
Radio signal is weak.
Unable to determine or verify network name during installation
Setup has either detected multiple networks or has been unable to read or verify the network
name from the access point.
In the Select Network Name screen, do one of the following:
● If the wireless access point or router was turned on after the printer was turned on, you
should turn the printer off and then on again to allow the printer to find the SSID.
● Enter a new SSID entry. If you choose to enter the wireless Network Name (SSID), also
select the Communication Mode (Ad-Hoc or Infrastructure).
● Select an existing network name from the list. Up to 12 SSIDs, detected at the time the
internal networking component booted up, might be listed.
NOTE
The SSID entry is case-sensitive and can be up to 32 alphanumeric characters long,
including spaces. You cannot leave the network name field blank.
ENWW Solving problems that occur during installation 19
Page 26

Verification fails at end of installation
Possible problem: You are using advanced forms of encryption, such as dynamic
encryption, WPA, or WPA-PSK, the encryption methods must be entered through the
embedded Web server. For more information, see
In dynamic encryption, each device has a different key and all keys change frequently.
Dynamic encryption is much harder for an intruder to circumvent, since the keys are likely to
change before the intruder can reverse engineer them.
Possible problem: Your SSID or WEP key might be incorrectly set. Complete the following
procedure to set the SSID or WEP key:
1. Print a configuration page. To print a configuration page, when the printer is in the
Ready state, press and hold the G
information, see
Configuration page.
O
button until the Ready light starts blinking. For more
2. Make sure the network SSID and WEP key on the device and the wireless network
match.
3. If one or both are incorrect, enter either the URL or device IP address from the
configuration page into the Address field on your Web browser. The printer EWS Home
page appears.
4. Select the Networking tab.
5. Click the Wireless option.
6. Enter the correct values in the appropriate sections (Network Name (SSID) and
Encryption).
Embedded Web server.
7. Click Apply.
Possible problem: Your network uses multiple WEP keys, and you have chosen the wrong
key for transmitting.
1. Print a configuration page. To print a configuration page, when the printer is in the
O
Ready state, press and hold the G
information, see
Configuration page.
button until the Ready light starts blinking. For more
2. Enter either the URL or device IP address from the configuration page into the Address
field on your Web browser. The EWS Home page appears, showing the printer device
information.
3. Click the Networking tab.
4. Click the Wireless option.
5. In the Encryption section, select the Static (WEP) option.
6. Under Static (WEP), enter the WEP keys used by your network. In static encryption, the
same key is used for all devices on the network and the key remains the same for long
periods of time.
7. Choose the key to be used to encrypt transmitted data. (The installer defaults to WEP
Key 1.)
8. Click Apply.
9. If the installation has terminated, restart the printer software CD-ROM.
Possible problem: You are using advanced authentication protocols that are not supported
by the installation software, such as LEAP, PEAP, EAP-MD5, EAP-TLS, or EAP-TTLS.
20 Chapter 3 Problem solving ENWW
Page 27

1. Print a configuration page. To print a configuration page, when the printer is in the
Ready state, press and hold the G
information, see
2. Enter either the URL or device IP address from the configuration page into the Address
field on your Web browser. The EWS Home page appears, showing the printer device
information.
3. Click the Networking tab.
4. Click the Wireless option.
5. In the Communication Mode section, select Infrastructure.
6. Select a network name (SSID) from the list of detected networks, or enter the name of a
new wireless network.
7. Select WPA/PSK, enter a pass phrase (from 8 to 63 characters in length, including
spaces) that will be used by the software to generate a pre-shared key.
Configuration page.
O
button until the Ready light starts blinking. For more
NOTE
All devices on the network must use the same pass phrase.
8. Click Apply.
Setup failed
Possible problem: No signal is being received by the device because it is not in range of
the access point (infrastructure) or computer (ad-hoc).
Move the printer and the computer closer together. If the distance between your computer
and the printer is significant, try reducing the distance. If possible, provide a clear path
between the computer and print server, and minimize sources of radio interference.
Possible problem: The setup program tried to change the computer’s wireless configuration
so that it can communicate to the printer, but was unable to reprogram the settings on the
computer’s wireless access card.
1. Quit all applications.
2. If your computer is connected to the Internet, disable the connection to your computer by
removing the Ethernet cable that connects the modem (cable, DSL, or dial-up) to your
computer.
3. Click Setup. The Setup menu appears.
4. Select 6. The Network menu appears.
5. Select 2. The wireless radio setting options appear.
NOTE
ENWW Solving problems that occur during installation 21
The default setting for the wireless radio is Off.
6. Use the up and down buttons to select On.
7. Select OK.
8. Open the configuration utility for your wireless network adapter.
9. Write down the existing wireless profile settings.
Page 28

10. Create a new wireless profile with the following values:
● Communication mode: Ad Hoc
● Network name (SSID): hpsetup
● Encryption: disabled
NOTE
NOTE
This is the default configuration for your printer’s internal networking component.
11. Activate the profile.
When the configuration change is complete, the computer is ready to communicate on
the printer’s network. (The computer is no longer part of its original network.)
Unless you change your computer settings, the computer will continue to communicate with
your existing wireless network. However, the wireless device that you need to configure is on
its own network (called hpsetup). To configure that device, you need to temporarily change
your computer to the printer’s network.
12. Print a configuration page and obtain the IP address of the printer. To print a
configuration page, when the printer is in the Ready state, press and hold the G
O
button until the Ready light starts blinking. For more information, see Configuration page.
13. Open your Web browser on your computer.
14. Type either the URL or device IP address from the configuration page into the Address
field in your browser. The EWS Home page appears.
15. Select the Networking tab.
16. Click the Wireless option.
17. In the appropriate section, enter the profile values you recorded in step 9.
18. Click Apply.
19. Exit the EWS by closing your browser.
20. Open the configuration utility for your wireless network adapter.
21. Restore the previous wireless profile settings.
22. Unplug the network cable from the printer.
23. Wait 60 seconds and then print a configuration page. The Wireless light should be on.
24. Open your Web browser on your computer.
25. Enter either the URL or device IP address from the configuration page into the Address
field in your browser. If the EWS Home page appears, your printer is properly configured.
26. Exit the EWS by closing your browser.
27. Insert the printer software installation CD into your computer's CD-ROM drive.
28. Run the installation software again.
22 Chapter 3 Problem solving ENWW
Page 29

Installation software does not install correctly
During a normal installation of the printer software, the following actions occur:
● The printer CD-ROM runs automatically
● The software installs
● Files are copied to your hard drive
● You are requested to plug in the printer
● You are requested to restart your computer
● The registration process runs
If any of these actions did not occur, there might be a problem with the installation. To check
the installation on a PC, verify the following:
● Open the Printers dialog box and check to see that the printer is listed.
● Look at the Task Tray for a printer icon. This indicates that the printer is ready.
If nothing happens when you insert the CD-ROM into the computer’s CD-ROM drive,
do the following:
1. From the Windows Start menu, choose Run.
2.
In the Run box, type d:\setup.exe (if your CD-ROM drive is not assigned to drive
letter d, use the appropriate drive letter), and then click OK.
If the minimum system checks screen appears, your system does not meet the minimum
requirements to install the software. Click Details to view the specific problem. Correct the
problem before attempting to install the software.
ENWW Solving problems that occur during installation 23
Page 30

Solving infrastructure mode problems
This section contains solutions to problems that might occur if the printer is connecting to a
wireless network that communicates using the infrastructure mode. For more information,
see Channels and communication modes.
The printer cannot find the WLAN
1. Verify your access point is broadcasting its network name (SSID).
a. See your access point User Guide and check the access point settings.
b. Turn on options, such as broadcast network name, and turn off silent broadcast.
2. Turn off the access point unit, and then turn it on. Then run the printer software setup
program again.
3. Move the access point and the printer closer together. Then run the printer software
setup program again. For more information, see
4. Check for firmware updates for your access point on the manufacturer’s Web site.
a. Update the firmware on the access point.
b. Run the printer software setup program again.
Radio signal is weak.
Printer cannot find your computer
1. Verify you have a functioning wireless network by using another wireless device.
2. Verify the printer is operational.
3. Verify the IP address and subnet mask of your printer and computer are similar (on the
same network).
4. Verify the encryption settings on your access point. The same encryption key and
settings must be used on both the access point and the printer.
For more information, see
Solving problems that occur during installation.
Computer is unable to discover device
1. Print a configuration page and verify you are connecting to the correct wireless network.
To print a configuration page, when the printer is in the Ready state, press and hold
the G
O
button until the Ready light starts blinking. For more information, see
Configuration page.
2. If you have a firewall, grant access permission to the printer.
3. Try temporarily disabling the firewall to determine whether the firewall is preventing the
printer from accessing your computer.
24 Chapter 3 Problem solving ENWW
Page 31

Solving ad-hoc mode problems
This section contains solutions to problems that might occur if the printer is connecting to a
wireless network that communicates using the ad-hoc mode. For more information, see
Channels and communication modes.
Printer cannot find your computer
1. Verify you have a functioning wireless ad-hoc network by using another wireless device.
2. Verify the printer is operational. For more information, see
during installation.
3. Verify the IP address and subnet mask of your printer and computer are similar (on the
same network).
4. Verify your computer’s wireless adapter is broadcasting its network name (SSID), which
can be found on the configuration page. To print a configuration page, when the
printer is in the Ready state, press and hold the G
blinking. For more information, see
5. Verify the encryption settings on your access point. The same encryption key and
settings must be used on both the access point and the printer. For more information,
see
Solving problems that occur during installation.
6. Check for firmware updates for your wireless adapter on the manufacturer’s Web site.
a. Update the firmware.
b. Run the printer software setup program again.
Configuration page.
O
button until the Ready light starts
Solving problems that occur
ENWW Solving ad-hoc mode problems 25
Page 32

Solving general wireless networking problems
For most wireless printing problems, the first step is to try printing a configuration page. To
print a configuration page, when the printer is in the Ready state, press and hold the G
button until the Ready light starts blinking. For more information, see Configuration page.
If the configuration page does not print, verify the following:
● Printer is set up and powered on
● Print cartridges are installed correctly
● Printer is on and the paper tray is loaded
● Printer is free of paper jams
● Network connections are secure
● Cable connections are secure
● Printer covers are closed
If any of the above are problems, see the HP LaserJet 1022 Series Printer User Guide.
If the configuration page does print, you can begin to solve the problem by checking the
Wireless light, as described below.
Check the Wireless light
O
Look at the printer's Wireless light. If the Wireless light is off, wireless networking has been
disabled. Verify the printer’s network settings match the network settings (see
wrong wireless network settings.) Then, verify the following:
● An Ethernet cable is not connected to the printer. Connecting an Ethernet cable to the
printer automatically turns off the wireless radio. Unplug the cable.
If the Wireless light is on, try reprinting the document, then look at the printer's Ready light.
If the Ready light is flashing, the printer’s wireless communications feature is working
correctly.
If the Wireless light is on steadily, the wireless radio is functioning, but the printer and the
computer cannot communicate.
● The printer's network settings do not match the settings for your network. See
has the wrong wireless network settings.
● The computer might be set to the wrong wireless profile. See
is set to the wrong wireless profile.
● A personal software firewall might block communication between the printer and the
computer. See
Radio signal is weak.
Computer's wireless card
Printer has the
Printer
26 Chapter 3 Problem solving ENWW
Page 33

Printer has the wrong wireless network settings
The printer's wireless network settings must match those of your network, which includes the
following:
● Communication mode
● Network Name (SSID)
● Channel (ad-hoc networks only)
● Authentication type
1. Reconnect the cable.
2. Compare the network settings to those that appear on the printer's configuration page.
To print a configuration page, when the printer is in the Ready state, press and hold
O
button until the Ready light starts blinking. For more information, see
the G
Configuration page.
3. Do one of the following to find the settings for your network:
● If the printer is communicating with the network using the infrastructure mode, open
the Wireless Access Point's (WAP) configuration utility.
● If the printer is communicating with the network using the ad-hoc mode, open the
configuration utility for the network card installed in your computer.
4. Compare the settings and note any settings that are different. Possible problems include:
● The WAP filters hardware addresses (MAC addresses). See
Wireless access point
(WAP) filters MAC addresses.
● One of these settings in the printer might be incorrect: communication mode,
network name (SSID), channel (ad-hoc networks only), or security settings. See
Printer has the wrong wireless network settings.
5. Reprint the configuration page.
To change the printer’s network settings:
1. Open the printer's embedded Web server.
2. Click the Networking tab. For wireless settings, click Wireless. For IP settings, click IP
Configuration.
3. Change the printer's settings to match the settings of the network, then click Finish.
4. Close the printer's EWS, then disconnect the Ethernet cable from the printer.
5. The control panel lights will cycle.
If the printer is still not working, verify the computer’s wireless profile. Then, as a last option,
reset the network settings to the factory defaults and use the printer software CD to reinstall
the printer software.
To reset the network settings to the factory defaults, when the printer is turned off, press
O
and C
ANCEL
and hold the G
C
ANCEL
buttons until all lights are blinking in unison.
buttons. Turn on the printer, and continue to hold the GO and
NOTE
If you reset the network settings, you will have to reconfigure all the network settings.
ENWW Solving general wireless networking problems 27
Page 34

Computer's wireless card is set to the wrong wireless profile
A wireless profile is a set of network settings unique to a given network. A single wireless
card might have several wireless profiles (for example, one for home and one for the office).
Open the configuration utility for the network card installed on your computer and verify that
the profile selected is the profile for the printer's network. If not, select the correct profile.
Radio signal is weak
If the printer is printing slowly, then the radio signal might be weak. Follow these guidelines
for reducing interference in a wireless network:
● Keep the wireless devices away from large metal objects, such as filing cabinets, and
other electromagnetic devices, such as microwaves and cordless telephones, as these
objects can disrupt radio signals.
● Keep the wireless devices away from large masonry structures and other building
structures as these objects can absorb radio waves and lower signal strength.
● For an infrastructure network, position the WAP in a central location in line of sight with
the wireless devices on the network.
● Keep all wireless devices on the network within range of one another.
Wireless access point (WAP) filters MAC addresses
MAC filtering is a security feature in which a Wireless Access Point (WAP) is configured with
a list of MAC addresses (also called hardware addresses) of devices that are allowed to gain
access to the network through the WAP.
If the WAP does not have the hardware address of a device attempting to access the
network, the WAP denies the device access to the network. If the WAP filters MAC
addresses, then the printer's MAC address must be added to the WAP's list of accepted
MAC addresses.
1. Print a configuration page. To print a configuration page, when the printer is in the
Ready state, press and hold the G
information, see
2. Find the printer's hardware address on the configuration page.
Open the WAP's configuration utility, then add the printer's hardware address to the list of
accepted MAC addresses.
Configuration page.
O
button until the Ready light starts blinking. For more
28 Chapter 3 Problem solving ENWW
Page 35

Regulatory information
USA Federal Communications Commission (FCC) compliance
CAUTION
Based on Section 15.21 of the FCC rules, changes or modifications to the operation of this
product without the expressed approval by Hewlett-Packard Company may invalidate its
authorized use.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital
device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC rules. These limits are designed to provide
reasonable protection against interference when the equipment is operated in a residential
installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if
it is not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will
not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to
radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on,
the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following
measures:
● Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
● Increase separation between the equipment and receiver.
● Connect equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is
connected.
● Consult your dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
This device complies with Part 15 of FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must
accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
Exposure to radio frequency radiation
CAUTION
ENWW USA Federal Communications Commission (FCC) compliance 29
The radiated output power of this device is far below the FCC radio frequency exposure
limits. Nevertheless, the device shall be used in such a manner that the potential for human
contact during normal operation is minimized.
In order to avoid the possibility of exceeding the FCC radio frequency exposure limits,
human proximity to the antenna shall not be less than 20 cm (8 inches) during normal
operation.
Page 36

Declaration of Conformity
Declaration of Conformity
according to ISO/IEC Guide 22 and EN 45014
Manufacturer's Name: Hewlett-Packard Company
Manufacturer's Address: 11311 Chinden Boulevard,
declares that the product
Product Name: HP LaserJet 1022nw
Regulatory Model
3)
:
Product Options: ALL
conforms to the following Product Specifications:
Safety: IEC 60950-1:2001 / EN60950-1:2001 +A11
IEC 60825-1:1993 +A1:1997 +A2:2001 / EN 60825-1:1994 +A1:2002 +A2:2001
(Class 1 Laser/LED Product)
EMC:
CISPR 22:1997 / EN 55022:1998 Class B
EN 61000-3-2:2000
EN 61000-3-3:1995 /A1:2001
EN 55024:1998/A1:2001
FCC Title 47 CFR, Part 15 Class B
4)
:
Radio
EN 301 489-1:2002 / EN 301 489-17:2002
EN 300 328 V1.4.1: (2003-04)
Boise, Idaho 83714-1021, USA
BOISB-0405-01
Toner Cartridge: Q2612A
1)
2)
/ ICES-003, Issue 4
FCC Title 47 CFR, Part 15 Subpart C (Section 15.247) / IC: RSS-210
Supplementary Information:
The product herewith complies with the requirements of the R&TTE Directive 1999/5/EC Annex IV, EMC Directive 89/336/EEC and the Low
Voltage Directive 73/23/EEC, and carries the CE-Marking accordingly
1) The product was tested in a typical configuration with Hewlett-Packard Personal Computer Systems. Compliance testing of product to
standard with exception of clause 9.5, which is not yet in effect.
2) This Device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two Conditions: (1) this device may not cause
harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
3) For regulatory purposes, this product is assigned a Regulatory model number. This number should not be confused with the product name
or the product number(s).
4) This product uses a Radio Module Device which Regulatory Model Number is: BOISB-0410-00
Boise, Idaho 83714, USA
10 February 2005
For Regulatory Topics ONLY, contact:
Australia Contact: Product Regulations Manager, Hewlett-Packard Australia Ltd. 31-41 Joseph Street, Blackburn, Victoria 3130, Australia
European Contact: Your Local Hewlett-Packard Sales and Service Office or Hewlett-Packard GmbH, Department HQ-TRE / Standards
Europe Herrenberger Straße 140, D-71034 Böblingen, Germany (FAX: +49-7031-14-3143)
USA Contact: Product Regulations Manager, Hewlett-Packard Company PO Box 15, Mail Stop 160, Boise, Idaho 83707-0015, USA
(Phone: 208-396-6000)
30 Appendix A Regulatory information ENWW
Page 37

Regulatory statements
Laser safety statement
The Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH) of the U.S. Food and Drug
Administration has implemented regulations for laser products manufactured since
August 1, 1976. Compliance is mandatory for products marketed in the United States. The
printer is certified as a “Class 1” laser product under the U.S. Department of Health and
Human Services (DHHS) Radiation Performance Standard according to the Radiation
Control for Health and Safety Act of 1968.
Since radiation emitted inside the printer is completely confined within protective housings
and external covers, the laser beam cannot escape during any phase of normal user
operation.
WARNING!
Using controls, making adjustments, or performing procedures other than those specified in
this user guide could result in exposure to hazardous radiation.
Canadian regulations
For Indoor Use. This digital apparatus does not exceed the Class B limits for radio noise
emissions from digital apparatus as set out in the radio interference regulations of the
Canadian Department of Communications. The internal wireless radio complies with
RSS 210 of Industry Canada.
Pour L'Usage D'intérieur. Le présent appareil numérique n'émet pas de bruits
radioélectriques dépassant les limites applicables aux appareils numériques de Classe B
prescribes dans le règlement sur le brouillage radioélectrique édicté par le Ministère des
Communications du Canada. Le composant RF interne est conforme à la norme CNR-210
d'Industrie Canada.
European Union regulatory notice
Radio Product for Indoor use in Home and Office environment operating in the 2.4 GHz band.
Radio product with the marking
complies with the R&TTE Directive (1999/5/EC) issues by the Commission of the European
Community.
Declaration of conformity
The Declaration of Conformity complies with ISO/IEC Guide 22 and EN45014. It identifies
the product, manufacturer’s name and address, and applicable specifications recognized in
the European community.
Selected EU, EU candidate and EFTA countries/regions
The radio functionality of this equipment (IEEE 802.11b/g wireless LAN) may be used in the
following EU, EU candidate and EFTA countries/regions:
ENWW Regulatory statements 31
Page 38

Austria, Belgium, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany,
Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, Latvia (1 May 2004), Liechtenstein, Lithuania,
Luxembourg, Malta, Netherlands, Norway, Poland (1 May 2004), Portugal, Slovak Republic,
Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland and United Kingdom.
Notice for use in France and Italy
Italy:
License required for use. Verify with your dealer or directly with General Direction for
Frequency Planning and Management (Direzione Generale Pianificazione e Gestione
Frequenze).
E’necessaria una concessione ministeriale anche per l’uso del prodotto. Verifici per favore
con il proprio distributore o direttamente presso la Direzione Generale Pianificazione e
Gestione Frequenze.
France: For 2.4 GHz Wireless LAN operation of this product certain restrictions apply: This
equipment may be used indoor for the entire 2400-2483.5 MHz frequency band (channels
1-13). For outdoor use, only 2454-2483.5 MHz frequency band (channels 10-13) may be
used. For the latest requirements, see http://www.art-telecom.fr.
Laser statement for Finland
LASERTURVALLISUUS
LUOKAN 1 LASERLAITE
KLASS 1 LASER APPARAT
HP LaserJet HP LaserJet 1022nw -laserkirjoitin on käyttäjän kannalta turvallinen luokan 1
laserlaite. Normaalissa käytössä kirjoittimen suojakotelointi estää lasersäteen pääsyn
laitteen ulkopuolelle.
Laitteen turvallisuusluokka on määritetty standardin EN 60825-1 (1994) mukaisesti.
VAROITUS!
Laitteen käyttäminen muulla kuin käyttöohjeessa mainitulla tavalla saattaa altistaa käyttäjän
turvallisuusluokan 1 ylittävälle näkymättömälle lasersäteilylle.
VARNING!
Om apparaten används på annat sätt än i bruksanvisning specificerats, kan användaren
utsättas för osynlig laserstrålning, som överskrider gränsen för laserklass 1.
HUOLTO
HP LaserJet 1022nw -kirjoittimen sisällä ei ole käyttäjän huollettavissa olevia kohteita.
Laitteen saa avata ja huoltaa ainoastaan sen huoltamiseen koulutettu henkilö. Tällaiseksi
huoltotoimenpiteeksi ei katsota väriainekasetin vaihtamista, paperiradan puhdistusta tai
muita käyttäjän käsikirjassa lueteltuja, käyttäjän tehtäväksi tarkoitettuja ylläpitotoimia, jotka
voidaan suorittaa ilman erikoistyökaluja.
VARO!
Mikäli kirjoittimen suojakotelo avataan, olet alttiina näkymättömälle lasersäteilylle laitteen
ollessa toiminnassa. Älä katso säteeseen.
32 Appendix A Regulatory information ENWW
Page 39

VARNING!
Om laserprinterns skyddshölje öppnas då apparaten är i funktion, utsättas användaren för
osynlig laserstrålning. Betrakta ej strålen.
Tiedot laitteessa käytettävän laserdiodin säteilyominaisuuksista:
Aallonpituus 785-800 nm
Teho 5 mW
Luokan 3B laser
ENWW Regulatory statements 33
Page 40

Environmental product stewardship program
Protecting the environment
Hewlett-Packard Company is committed to providing quality products in an environmentally
sound manner. This product has been designed with several attributes to minimize the
impact on our environment.
Ozone production
This product generates no appreciable ozone gas (O3).
Power consumption
Power usage drops significantly while in PowerSave/Sleep mode, which saves natural
resources and saves money without affecting the high performance of this product. This
product qualifies for ENERGY STAR® (Version 3.0), which is a voluntary program to
encourage the development of energy-efficient office products.
ENERGY STAR and the ENERGY STAR mark are U.S. registered marks. As an ENERGY
STAR partner, Hewlett-Packard Company has determined that this product meets ENERGY
STAR guidelines for energy efficiency. For more information, see http://www.energystar.gov/.
Toner consumption
Economode uses significantly less toner, which might extend the life of the print cartridge.
Paper use
This product’s manual duplex (two-sided printing) and N-up printing (multiple pages printed
on one page) features can reduce paper usage and the resulting demands on natural
resources.
Plastics
Plastic parts over 25 grams (0.9 ounces) are marked according to international standards
that enhance the ability to identify plastics for recycling purposes at the end of the product's
life.
34 Appendix A Regulatory information ENWW
Page 41

HP LaserJet printing supplies
It is easy to return and recycle your empty HP LaserJet print cartridges—free of charge—
with HP Planet Partners. HP is committed to providing inventive, high-quality products and
services that are environmentally sound, from product design and manufacturing to
distribution, operation and recycling processes. We ensure your returned HP LaserJet print
cartridges are recycled properly, processing them to recover valuable plastics and metals for
new products and diverting millions of tons of waste from landfills. Since this cartridge is
being recycled and used in new materials, it will not be returned to you. Your empty
HP LaserJet print cartridges are recycled responsibly when you participate in the HP Planet
Partners program. Thank you for being environmentally responsible!
In many countries/regions, this product's printing supplies (for example, print cartridge,
drum) can be returned to HP through the HP Printing Supplies Returns and Recycling
Program. An easy-to-use and free take back program is available in more than 35
countries/regions. Multi-lingual program information and instructions are included in every
new HP LaserJet print cartridge and supplies package.
HP printing supplies returns and recycling program information
Since 1992, HP has offered HP LaserJet supplies return and recycling free of charge. In
2004, HP Planet Partners for LaserJet Supplies was available in 85% of the world market
where HP LaserJet supplies are sold. Postage-paid and pre-addressed labels are included
within the instruction guide in most HP LaserJet print cartridge boxes. Labels and bulk boxes
are also available through the Web site: http://www.hp.com/recycle.
Use the label to return empty, original HP LaserJet print cartridges only. Please do not use
this label for, non-HP cartridges, refilled or remanufactured cartridges or warranty returns.
Printing supplies or other objects inadvertently sent to the HP Planet Partners program
cannot be returned.
More than 10 million HP LaserJet print cartridges were recycled globally in 2004 through the
HP Planet Partners supplies recycling program. This record number represents 26 million
pounds of print cartridge materials diverted from landfills. Worldwide, in 2004, HP recycled
an average of 59% of the print cartridge by weight consisting primarily of plastic and metals.
Plastics and metals are used to make new products such as HP products, plastic trays and
spools. The remaining materials are disposed of in an environmentally responsible manner.
U.S. returns
For a more environmentally responsible return of used cartridges and supplies, HP
encourages the use of bulk returns. Simply bundle two or more cartridges together and use
the single, pre-paid, pre-addressed UPS label that is supplied in the package. For more
information in the U.S., call 800-340-2445 or visit the HP Web site at http://www.hp.com/
recycle.
Non-U.S. returns
Non-US customers should visit the http://www.hp.com/recycle Web site for further
information regarding availability of the HP Supplies Returns and Recycling program.
ENWW Environmental product stewardship program 35
Page 42

Paper
This product is capable of using recycled papers when the paper meets the guidelines
outlined in the Print Media Guide. See the HP LaserJet 1022 Series Printer User Guide for
ordering information. This product is suitable for the use of recycled paper according to
EN12281:2002.
Material restrictions
This product does not contain added mercury.
This HP product does not contain batteries.
For more information
For more information on the following HP environmental programs:
● Product environmental profile sheet for this and many related HP products
● HP's commitment to the environment
● HP's environmental management system
● HP's end-of-life product return and recycling program
● Material safety data sheets
Visit: http://www.hp.com/go/environment or http://www.hp.com/hpinfo/community/
environment/productinfo/safety.
36 Appendix A Regulatory information ENWW
Page 43

Material safety data sheet
Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) for supplies containing chemical substances (for
example, toner) can be obtained by contacting the HP Web site at: http://www.hp.com/go/
msds or http://www.hp.com/hpinfo/community/environment/productinfo/safety.
ENWW Material safety data sheet 37
Page 44

OpenSSL License
Copyright© 1998-2000 The OpenSSL Project. All rights reserved.
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without modification, are permitted
provided that the following conditions are met:
1. Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, this list of
conditions and the following disclaimer.
2. Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice, this list of
conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials
provided with the distribution.
3. All advertising materials mentioning features or use of this software must display the
following acknowledgment:
“This product includes software developed by the OpenSSL Project for use in the
OpenSSL Toolkit. (http://www.openssl.org/)”
4. The names “OpenSSL Toolkit” and “OpenSSL Project” must not be used to endorse or
promote products derived from this software without prior written permission. For written
permission, please contact openssl-core@openssl.org.
5. Products derived from this software may not be called “OpenSSL” nor may “OpenSSL”
appear in their names without prior written permission of the OpenSSL Project.
6. Redistributions of any form whatsoever must retain the following acknowledgment:
“This product includes software developed by the OpenSSL Project for use in the OpenSSL
Toolkit (http://www.openssl.org/)”
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE OpenSSL PROJECT “AS IS” AND ANY
EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE
IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE OpenSSL PROJECT OR ITS
CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL,
EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO,
PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR
PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY
OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING
NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS
SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
This product includes cryptographic software written by Eric Young (eay@cryptsoft.com).
This product includes software written by Tim Hudson (tjh@cryptsoft.com).
38 Appendix A Regulatory information ENWW
Page 45

Original SSLeay License
Copyright© 1995-1998 Eric Young (eay@cryptsoft.com). All rights reserved.
This package is an SSL implementation written by Eric Young (eay@cryptsoft.com). The
implementation was written so as to conform with Netscape’s SSL.
This library is free for commercial and non-commercial use as long as the following
conditions are adhered to. The following conditions apply to all code found in this
distribution, be it the RC4, RSA, lhash, DES, etc., code; not just the SSL code. The SSL
documentation included with this distribution is covered by the same copyright terms except
that the holder is Tim Hudson (tjh@cryptsoft.com).
Copyright remains Eric Young's, and as such any Copyright notices in the code are not to be
removed.
If this package is used in a product, Eric Young should be given attribution as the author of
the parts of the library used.
This can be in the form of a textual message at program startup or in documentation (online
or textual) provided with the package.
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without modification, are permitted
provided that the following conditions are met:
1. Redistributions of source code must retain the copyright notice, this list of conditions and
the following disclaimer.
2. Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice, this list of
conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials
provided with the distribution.
3. All advertising materials mentioning features or use of this software must display the
following acknowledgement:
“This product includes cryptographic software written by Eric Young (eay@cryptsoft.com)”
The word ‘cryptographic’ can be left out if the routines from the library being used are
not cryptographic related.
4. If you include any Windows specific code (or a derivative thereof) from the apps
directory (application code) you must include an acknowledgement:
“This product includes software written by Tim Hudson (tjh@cryptsoft.com)”
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY ERIC YOUNG “AS IS” AND ANY EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE
ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHOR OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE
FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR
CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF
SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR
BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY,
WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR
OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF
ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
ENWW Original SSLeay License 39
Page 46

The license and distribution terms for any publicly available version or derivative of this code
cannot be changed, i.e., this code cannot simply be copied and put under another
distribution license [including the GNU Public License.]
40 Appendix A Regulatory information ENWW
Page 47

Glossary
10/100 Base-T
802.11a
802.11b
802.11g
Ad-hoc network
A technical term for Ethernet. 10/100 refers to the speed at which the
Ethernet network functions. 10 indicates 10 megabits per second (Mb/s) for
normal Ethernet, and 100 indicates 100 Mb/s for Fast Ethernet.
A type of wireless networking that provides up to 54 Mb/s transmission in the
5 GHz band.
A type of wireless networking that provides up to 11 Mb/s transmission (with
a fallback to 5.5, 2 and 1 Mb/s) in the 2.4 GHz band.
A type of wireless networking that provides up to 54 Mb/s transmission in the
2.4 GHz band.
A type of wireless network in which devices directly communicate with each
other rather than through a Wireless Access Point (WAP). Also referred to as
peer-to-peer. Ad-hoc networks are typically small and simple, for example, a
wireless PC and a wireless printer. Ad-hoc networks are independent basic
service stations (IBSS), or direct-connect wireless networks.
Authentication
AutoIP
BOOTP
Broadcast packet
Channel
Authentication is a wireless network security strategy. On a network with
authentication, devices use a shared key as a password and communicate
only with devices that know the key. Unlike WEP, authentication does not
encrypt the data sent between wireless devices. However, authentication
can be used in conjunction with WEP. Authentication keys and WEP keys
can be identical.
A process by which a device on a network automatically assigns an IP
address to itself.
Bootstrap Protocol (BOOTP) is an Internet protocol that enables a device to
discover its own IP address, the IP address of a BOOTP server on the
network, and a file to be loaded into memory to boot the machine. This
enables the device to boot without requiring a hard or floppy disk drive.
A packet sent from one device on a network to all devices on the network.
One of several pre-set frequencies at which 802.11b/g-enabled devices
communicate in order to reduce interference. The number of channels
available varies by country/region.
ENWW Glossary 41
Page 48

DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
A protocol used to automatically assign an IP address to each device on a
network.
DHCP server
This server dynamically manages a pool of IP addresses for use on a
network or the Internet. When a user logs in, the server “loans” the user an
IP address for the duration of the network connection. When a user logs off,
the IP address is returned to the pool for use by another device.
Digital Certificate
An electronic means of proving the identity of a network user or device.
Certificates contain detailed information about the user's device in a
standard format. Digital certificates are typically issued by a trusted thirdparty Certificate Authority (CA). Locally administered, or self-signed,
certificates are valid in some instances.
EAP
Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) is a general protocol for
authentication that also supports multiple authentication methods, such as
token cards, one-time passwords, certificates, and public key authentication.
Encryption keys
A sequence of characters or digits that a wireless device uses to encode
data. Encryption keys can be static (as they are in WEP) or dynamic (as they
are in WPA).
Encryption
Ethernet cable
Ethernet
EWS (embedded Web server)
Firewall
A network security that encodes the data sent across a wireless network
making the data unintelligible to unauthorized users. The printer supports
WEP and WPA.
There are two types of Ethernet cables. A straight-through cable is the most
common and is used to connect devices on a network to a hub or router. A
crossover cable is used to connect two devices that have Ethernet ports but
that are not hubs or routers. Use a CAT-5 straight-through cable with an
RJ-45 plug to connect the printer to an Ethernet network.
A popular form of wired computer networking for Local Area Networks.
A server that is completely contained within a device. An EWS provides
management information about the device. This is helpful for managing
single devices on a small network. By using a Web browser to access an
EWS, network users can perform such operations as obtaining network
printer status updates, simple troubleshooting, and changing device
configuration setting.
A combination of hardware and software tools that protects a network from
unwanted entry.
42 Glossary ENWW
Page 49

Gateway
Host Name
Hub
ICS (Internet Connection Sharing)
Infrastructure network
Internet Sharing
A dedicated device (router or computer) that connects two different
networks. For example, a computer on an Ethernet network may act as a
gateway between the network and the Internet.
The name by which the printer identifies itself on the network. The printer's
host name appears on the configuration page. Use the host name to open
the printer's embedded Web server (EWS).
A simple device that acts as the center of an Ethernet network. Other
devices on the network are connected to the hub.
A Windows program that allows a computer to act as a gateway between the
Internet and a network. ICS uses DHCP to assign IP addresses. See
Windows documentation for more information about ICS.
A type of wireless network in which devices communicate with each other
through a Wireless Access Point (WAP), such as a wireless network hub,
router, or gateway.
A Macintosh OS X program that allows a computer to act as a gateway
between the Internet and a network. See Macintosh documentation for more
information about Internet Sharing.
IP address (Internet Protocol address)
Each computer that connects to a network or the Internet, must have a
unique address. A connection to the Internet provided by an Internet Service
Provider (ISP) uses a standard protocol called Internet Protocol (IP). This
protocol is also used on internal networks. IP address numbers are in the
form x.x.x.x—for example, 169.254.100.2. Most networks use DHCP or
AutoIP to dynamically assign IP addresses. However, a device can be
manually assigned a static IP address.
LAN (Local Area Network)
A high-speed type of computer network that connects devices that are a
relatively short distance from one another. An Ethernet network is one type
of LAN.
MAC address (Media Access Control address)
The hardware address for a device on a network. The printer's MAC address
appears on the configuration page.
Mb/s (megabits per second)
The measure for the rate at which a network functions. For example, 1 Mb/s
equals 1,000,000 bits per second (or 125,000 bytes per second).
ENWW Glossary 43
Page 50

mDNS
Network name
Node
Packet
Peer-to-peer
Protocol
As an alternative to a Domain Name Server, a device issues a Multicast
Domain Name Server (mDNS) notification to provide information regarding
its service. The notification includes the type of service (such as printing), the
name of the service (such as "your printer"), IP and port addresses, and
other necessary information. Each device on the network receives the
notification and stores the information in a personal DNS server.
A network name is an alphanumeric, case-sensitive character string that
provides basic access control to a wireless network. A network name is also
known as a Service Set Identifier (SSID).
A network connection point, typically a computer.
A message sent from one device on a network to other devices on the
network.
See Ad-hoc network.
Proxy server
Rendezvous
RJ-45
Router
Server
A language that devices on a network use to communicate with each other.
A popular network protocol is TCP/IP.
A proxy server acts as a security gate (such as a Web proxy) that restricts
traffic going through a network. The proxy intercepts requests to the network
to see if it can fulfill the requests itself. If not, it forwards the request to
another server. Proxy servers have two main purposes: improve
performance and filter requests.
Apple’s configuration technology that automatically discovers and connects
devices over Ethernet and wireless networks. Rendezvous is integrated into
the Mac OS X version 10.2 operating system.
The type of plug at the end of an Ethernet cable.
A complex networking device that directs packets from one network to
another network. A router can act as a gateway between a LAN and the
Internet.
A computer on a network that manages network resources. A network might
have a number of different server types. For example, a print server
manages one or more printers, a file server stores and manages files, and a
network server manages network traffic.
44 Glossary ENWW
Page 51

SSID (Service Set Identifier)
Static IP address
Subnet mask
Subnet
Switch
A unique identifier (up to 32 characters) attached to the header of packets
sent over a wireless LAN. An SSID provides basic access control to a
wireless network. It can also be used to logically segment a wireless
subgroup of users and devices. An SSID prevents access by any client
device that does not have the SSID. By default, an access point broadcasts
its SSID in its beacon. An SSID is also referred to as a Network Name
because it is a name that identifies a wireless network.
An IP address that is manually assigned to a device on a network. A static IP
address remains fixed until changed manually. Alternative methods for
assigning IP addresses are DHCP and AutoIP.
A number that identifies the IP addresses that belong to a subnet.
A small network that acts as part of a large network. It is recommended that
the printer and the computers that use the printer all be on the same subnet.
A network device that manages network traffic in order to minimize collisions
and maximize speed.
TCP/IP
TKIP
Unicast packet
WEP key
WEP
Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) is the network
communication protocol used on the Internet. The printer's built-in
networking feature supports LANs that use TCP/IP.
See WPA. Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP).
A packet sent from one device on a network to another device on the network.
A WEP key, or encryption key, is a sequence of alphanumeric characters or
hexadecimal digits. After creating a WEP key, you must remember it or store
it in a secure location. You may not be able to retrieve the WEP key if you
lose it. A WEP key is either 64 or 128 bits long. The first 24 bits of the key
are provided automatically. When creating the WEP key, the person creating
the key provides the remaining bits (40 bits in the case of a 64-bit key, or
104 bits in the case of a 128-bit key).
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) provides security by encrypting data sent
over radio waves from one wireless device to another wireless device. WEP
encodes the data sent across the network making the data unintelligible to
unauthorized users. Only devices that share the same WEP settings as the
printer will be able to communicate with the printer. WEP depends on
encryption keys that are static and provides less security than WPA (TKIP).
ENWW Glossary 45
Page 52

WiFi (Wireless Fidelity)
Wireless Access Point (WAP)
Wireless network adapter
Wireless profile
A term used generically when referring to any type of 802.11 network,
whether 802.11b/g, 802.11a, dual-band, or other. Any products tested and
approved as "Wi-Fi Certified" are certified as interoperable with each other,
even if they are from different manufacturers. Typically, however, any Wi-Fi
product using the same radio frequency (2.4 GHz for 802.11b or 11g; 5 GHz
for 802.11a) will work with any other Wi-Fi product, even if not Wi-Fi Certified.
A Wireless Access Point (WAP) is a device through which devices (for
example, computers and printers) on an infrastructure wireless network
communicate with one another. A WAP is also called a base station.
Each node (computer or device) on the WLAN uses a wireless network
adapter into which a wireless transceiver, with a small, integrated antenna, is
built. Wireless network adapters might be internal (inserted in a computer or
device), external (housed in a separate case), or built-in.
A wireless profile is a collection of wireless network settings that applies to a
particular wireless network. For example, a wireless LAN card can have one
profile for a home network and another profile for an office network. When
installing a device on a network, be sure to select the appropriate profile.
WPA
WPA (Wi-Fi protected access) provides security by encrypting data sent over
radio waves from one wireless device to another wireless device and by
controlling access to network resources through authentication protocols.
Only devices that share the same WPA settings as the printer will be able to
communicate with the printer. WPA uses encryption keys that change
frequently. WPA provides better security than WEP. WPA is also called TKIP.
46 Glossary ENWW
Page 53

Index
Symbols/Numerics
10/100 Base-T 41
802.11a 41
802.11b 41
802.11g 41
A
ad-hoc mode
cannot find computer 25
ad-hoc network 41
advanced authentication protocols 20
authentication 41
autoIP 41
B
BOOTP 41
broadcast packet 41
C
changing networks 15
channel 41
checking wireless light 26
communication modes
ad-hoc 4
infrastructure 4
peer to peer 4
configuration page
bad packets received 12
communication mode 12
configuration source 11
device IP address 11
firmware revision code 10
firmware version 10
hardware address 10
host name 10
link speed 11
mDNS service name 11
printing 10
Service Set Identifier (SSID) 12
TCP/IP name 10
total packets received 12
total packets transmitted 12
verification 26
wireless network status 12
copyright and trademark information 2
D
data information 12
DHCP 42
DHCP server 42
digital certificate 42
domain name server (DNS)
multicast service name 11
dynamic encryption 20
E
EAP 42
encryption 42
encryption keys 42
ENERGY STAR 34
Environmental Product Stewardship Program 34
ethernet 42
ethernet cable 42
EWS 42
F
FCC compliance 29
firewall 42
G
gateway 43
H
host name 43
hub 43
I
ICS 43
information
printer options 2
troubleshooting 2
infrastructure mode
cannot find computer 24
cannot find WLAN 24
computer unable to find device 24
infrastructure network 43
installation problems
authentication protocols not supported 20
cannot discover device 18
cannot find network name 19
device cannot connect 18
incorrectly set SSID or WEP key 20
no TCP/IP 18
ENWW Index 47
Page 54

printer not found 19
setup failed 21
signal not received by device 21
verification failure 20
wireless access card configuration 21
wrong WEP key 20
internet sharing 43
IP address
adding 11
L
LAN 43
link speed 11
M
MAC address 43
Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) 37
Mb/s 43
mDNS 44
media access control
address 10
address authentication 6
filtering 28
Media Access Control (MAC) 10
multiple WEP keys 20
N
network name 44
network settings
general 10
troubleshooting 27
wireless 12
node 44
P
packet 44
peer-to-peer 44
personal software firewall 18
power consumption 34
print cartridge
where to return for recycling 35
printer
IP address 11
unmatched network settings 27
printer drivers
sites for download 2
protocol 44
proxy server 44
R
recycling
HP printing supplies returns and environmental
program 35
where to return cartridges 35
regulatory statements
Canadian regulations 31
Declaration of Conformity statement 30
laser safety statement 31
laser statement for Finland 32
Rendezvous 44
RJ-45 44
router 44
S
security
wireless network 4
server 44
software
sites for download 2
speed
network transfer 11
SSID 45
static IP address 45
subnet 45
subnet mask 45
support, Web sites 2
switch 45
T
TCP/IP 45
TKIP 45
troubleshooting
ad-hoc mode 25
communication block 18
general wireless printing problems 26
installation 18
MAC filtering 28
network settings 27
weak radio signal 28
wireless infrastructure mode 24
wrong wireless profile 28
U
unicast packet 45
W
WAP 46
Web-based support 2
WEP 45
WEP key 45
WiFi 46
wired equivalent privacy (WEP) 5
wireless local area network (WLAN) 3
wireless network
authentication 5
communication modes 3
encryption 5
MAC address authentication 6
security 4
status 12
wireless network adapter 46
48 Index ENWW
Page 55

wireless profile 6, 46 WPA 46
ENWW Index 49
Page 56

50 Index ENWW
Page 57

Page 58

© 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
www.hp.com/support/lj1022
*Q5914-90904*
*Q5914-90904*
Q5914-90904
 Loading...
Loading...