Page 1

HP LaserJet 1022, 1022n, 1022nw
Service Manual
Page 2

Page 3

HP LaserJet 1022 series printers
Service Manual
Page 4

Table of contents
1 Product Information
Product configurations............................................................................................................................2
HP LaserJet 1022 printer.......................................................................................................2
HP LaserJet 1022n printer.....................................................................................................2
HP LaserJet 1022nw printer..................................................................................................2
Overview of product...............................................................................................................................3
HP LaserJet 1022 series printers..........................................................................................3
Model and serial numbers.....................................................................................................5
Hardware description.............................................................................................................5
Firmware description ............................................................................................................5
Product specifications............................................................................................................................6
Physical specifications...........................................................................................................6
Printer performance...............................................................................................................6
Environmental specification...................................................................................................6
Electrical specifications..........................................................................................................7
Acoustic emissions................................................................................................................7
Extended warranty.................................................................................................................................8
Print-cartridge information .....................................................................................................................9
Refilled print cartridges ........................................................................................................9
Recycling print cartridges .....................................................................................................9
Regulatory information.........................................................................................................................10
FCC compliance..................................................................................................................10
Canadian DOC regulations..................................................................................................10
Korean EMI statement.........................................................................................................10
Laser statement for Finland.................................................................................................11
............................................................................................................................11
2 Installation and Operation
Operating environment ........................................................................................................................14
Identifying the control-panel components.............................................................................................15
Media specifications.............................................................................................................................16
Supported media sizes........................................................................................................16
Guidelines for using media...................................................................................................................17
Paper and transparencies ...................................................................................................17
Common media problems table ..........................................................................................17
Labels..................................................................................................................................17
Envelopes ...........................................................................................................................18
Envelopes with double-side seams.....................................................................18
Envelopes with adhesive strips or flaps..............................................................18
ENWW iii
Page 5

Loading media......................................................................................................................................20
Setting media types..............................................................................................................................21
3 Maintenance
Life expectancies of parts that wear ....................................................................................................24
Cleaning the product............................................................................................................................26
User-replaceable parts ........................................................................................................................30
Jams.....................................................................................................................................................37
Card stock and heavy media ..............................................................................................19
Card-stock construction......................................................................................19
Card-stock guidelines..........................................................................................19
Main input tray.....................................................................................................................20
Priority feed slot...................................................................................................................20
Specific types of media .......................................................................................................20
Set the media type...............................................................................................................21
Cleaning the print path.........................................................................................................26
Cleaning the print-cartridge area.........................................................................................27
Cleaning the pickup roller ...................................................................................................29
Replacing the pickup roller..................................................................................................30
Replacing the separation pad .............................................................................................33
Replacing the main input tray (paper-pickup tray assembly)...............................................35
Replacing the output-bin extension (delivery-tray assembly) .............................................36
Clearing jams.......................................................................................................................37
Typical media jam locations................................................................................37
Removing a jammed page..................................................................................38
4 Operational overview
Basic functions.....................................................................................................................................42
Formatter system.................................................................................................................................43
Central processing unit .......................................................................................................43
RAM.....................................................................................................................................43
USB interface.......................................................................................................................43
Control panel.......................................................................................................................43
Draft mode (EconoMode)....................................................................................................43
HP Memory Enhancement technology (MEt)......................................................................44
Enhanced I/O ......................................................................................................................44
Printer operation...................................................................................................................................45
Engine control system (engine control unit and power assembly).......................................46
Image-formation system......................................................................................................49
Printer-paper feed system...................................................................................................51
Jam detection .....................................................................................................................53
Solenoid, sensors, switches, and motor..............................................................................54
Basic sequence of operation (formatter-to-printer)..............................................................55
Printer-engine-control system.............................................................................46
Printer laser/scanner unit ...................................................................................47
Power system on the engine-power assembly....................................................48
The seven image-formation processes ..............................................................50
Print cartridge......................................................................................................51
Conditions of jam detection.................................................................................53
iv ENWW
Page 6

5 Removal and replacement
Removal and replacement strategy......................................................................................................58
Required tools .....................................................................................................................58
Before performing service....................................................................................................58
Print cartridge .....................................................................................................................59
Parts removal order ............................................................................................................60
User-replaceable parts ........................................................................................................................61
Replacing the pickup roller .................................................................................................61
Replacing the separation pad .............................................................................................64
Replacing the main input tray (paper-pickup tray assembly) ..............................................66
Replacing the output-bin extension (delivery-tray assembly) .............................................67
Covers..................................................................................................................................................68
Right-side cover...................................................................................................................68
Left-side cover.....................................................................................................................70
Rear panel and top-cover assembly....................................................................................70
Front cover...........................................................................................................................75
Internal assemblies..............................................................................................................................77
Transfer-roller assembly......................................................................................................77
Engine-power assembly......................................................................................................80
Fuser (fixing) assembly........................................................................................................82
Paper-pickup assembly.......................................................................................................84
Engine control unit (ECU) assembly....................................................................................85
Laser/scanner assembly......................................................................................................89
6 Troubleshooting
Basic troubleshooting...........................................................................................................................92
Reset the factory default settings (cold reset)......................................................................................94
Control-panel pages.............................................................................................................................94
Control-panel lights..............................................................................................................................95
Jams.....................................................................................................................................................97
Print-quality troubleshooting...............................................................................................................100
Solving paper-feed problems.............................................................................................................111
Functional checks...............................................................................................................................113
Troubleshooting tools.........................................................................................................................117
Basic troubleshooting..........................................................................................................92
Control-panel light patterns..................................................................................................95
Clearing jams.......................................................................................................................97
Typical media jam locations................................................................................97
Removing a jammed page..................................................................................98
Print-cartridge problems....................................................................................................100
Checking the print cartridge..............................................................................100
To redistribute toner in the print cartridge.........................................100
Solving print-quality problems............................................................................................100
Half self-test functional check............................................................................................113
To perform a half self-test check.......................................................................113
To perform other checks...................................................................................113
Drum-rotation functional check .........................................................................................114
High-voltage-contacts check..............................................................................................115
To check the print-cartridge contacts ..............................................................115
To check the printer high-voltage contacts ......................................................116
ENWW v
Page 7

Repetitive-image-defect ruler.............................................................................................117
Circuit diagram ..................................................................................................................118
Solenoid, sensors, switches, and motor.............................................................................................119
7 Parts and diagrams
Ordering parts and supplies...............................................................................................................122
Parts..................................................................................................................................122
Related documentation and software................................................................................122
Parts that wear ..................................................................................................................122
Accessories and consumables...........................................................................................................123
Accessories.......................................................................................................................123
Common hardware ...........................................................................................................124
How to use the parts lists and diagrams............................................................................125
Printer exchange/parts.......................................................................................................................126
External covers and panel..................................................................................................................128
Internal components...........................................................................................................................130
Alphabetical parts list.........................................................................................................................138
Numerical parts list.............................................................................................................................140
Index...................................................................................................................................................................143
vi ENWW
Page 8

List of tables
Table 1-1 Physical specifications....................................................................................................................6
Table 1-2 Performance....................................................................................................................................6
Table 1-3 Environmental specifications ..........................................................................................................6
Table 1-4 Power requirements........................................................................................................................7
Table 1-5 Power consumption (average, in watts)..........................................................................................7
Table 1-6 Acoustic emissions..........................................................................................................................7
Table 2-1 Media sizes...................................................................................................................................16
Table 3-1 Life expectancies of parts that wear..............................................................................................24
Table 4-1 Basic sequence of operation.........................................................................................................55
Table 6-1 Basic troubleshooting ..................................................................................................................92
Table 6-2 Control-panel pages: time ranges.................................................................................................94
Table 6-3 Control-panel light patterns...........................................................................................................95
Table 6-4 Solving print-quality problems.....................................................................................................100
Table 6-5 Solving paper-feed problems......................................................................................................111
Table 7-1 Technical support websites.........................................................................................................122
Table 7-2 Accessories.................................................................................................................................123
Table 7-3 Printer exchange.........................................................................................................................127
Table 7-4 External covers and panels.........................................................................................................129
Table 7-5 Internal components (1 of 3).......................................................................................................131
Table 7-6 Internal components (2 of 3).......................................................................................................133
Table 7-7 Internal components (3 of 3).......................................................................................................135
Table 7-8 Paper-pickup assembly...............................................................................................................137
Table 7-9 Alphabetical parts list..................................................................................................................138
Table 7-10 Numerical parts list......................................................................................................................140
ENWW vii
Page 9

viii ENWW
Page 10

List of figures
Figure 1-1 Front and right-side view.................................................................................................................3
Figure 1-2 Back and left-side view...................................................................................................................4
Figure 1-3 Model- and serial-number label.......................................................................................................5
Figure 2-1 Dimensions of product..................................................................................................................14
Figure 2-2 Control-panel lights and buttons...................................................................................................15
Figure 3-1 Main input tray...............................................................................................................................35
Figure 3-2 Output-bin extension.....................................................................................................................36
Figure 4-1 Basic configuration........................................................................................................................42
Figure 4-2 Printer functional-block diagram....................................................................................................45
Figure 4-3 Laser/scanner operation...............................................................................................................47
Figure 4-4 High-voltage power supply circuit.................................................................................................49
Figure 4-5 Image-formation block diagram.....................................................................................................50
Figure 4-6 Printer paper path ........................................................................................................................52
Figure 4-7 Solenoid, sensors, switches, and motor........................................................................................54
Figure 4-8 Printer timing diagram .................................................................................................................56
Figure 5-1 Removing the print cartridge.........................................................................................................59
Figure 5-2 Parts-removal block diagram........................................................................................................60
Figure 5-3 Remove the main input tray..........................................................................................................66
Figure 5-4 Output-bin extension.....................................................................................................................67
Figure 5-5 Remove the right-side cover (1 of 4).............................................................................................68
Figure 5-6 Remove the right-side cover (2 of 4).............................................................................................68
Figure 5-7 Remove the right-side cover (3 of 4).............................................................................................69
Figure 5-8 Remove the right-side cover (4 of 4).............................................................................................69
Figure 5-9 Remove the rear panel and top-cover assembly (1 of 6)..............................................................70
Figure 5-10 Remove the rear panel and top-cover assembly (2 of 6)..............................................................71
Figure 5-11 Remove the rear panel and top-cover assembly (3 of 6)..............................................................71
Figure 5-12 Remove the rear panel and top-cover assembly (4 of 6)..............................................................72
Figure 5-13 Remove the rear panel and top-cover assembly (5 of 6)..............................................................72
Figure 5-14 Remove the rear panel and top-cover assembly (6 of 6)..............................................................73
Figure 5-15 Reinstall the top-cover assembly (1 of 2)......................................................................................73
Figure 5-16 Reinstall the top-cover assembly (2 of 2)......................................................................................74
Figure 5-17 Remove the front cover (1 of 3)....................................................................................................75
Figure 5-18 Remove the front cover (2 of 3)....................................................................................................76
Figure 5-19 Remove the front cover (3 of 3)....................................................................................................76
Figure 5-20 Remove the transfer roller (1 of 3)................................................................................................77
Figure 5-21 Remove the transfer roller (2 of 3)................................................................................................78
Figure 5-22 Remove the transfer roller (3 of 3)................................................................................................78
Figure 5-23 Remove the engine-power assembly (1 of 2)...............................................................................80
Figure 5-24 Remove the engine-power assembly (2 of 2)...............................................................................81
Figure 5-25 Remove the fuser (fixing) assembly (1 of 2).................................................................................82
ENWW ix
Page 11

Figure 5-26 Remove the fuser (fixing) assembly (2 of 2).................................................................................83
Figure 5-27 Remove the paper pickup assembly.............................................................................................84
Figure 5-28 Remove the ECU assembly (1 of 6)..............................................................................................85
Figure 5-29 Remove the ECU assembly (2 of 6)..............................................................................................86
Figure 5-30 Remove the ECU assembly (3 of 6)..............................................................................................86
Figure 5-31 Remove the ECU assembly (4 of 6)..............................................................................................87
Figure 5-32 Remove the ECU assembly (5 of 6)..............................................................................................87
Figure 5-33 Remove the ECU assembly (6 of 6)..............................................................................................88
Figure 5-34 Removing the laser/scanner assembly.........................................................................................89
Figure 6-1 Printer-panel-lights legend............................................................................................................95
Figure 6-2 Check the fuser connections.......................................................................................................114
Figure 6-3 Print-cartridge high-voltage contacts...........................................................................................115
Figure 6-4 Printer high-voltage contacts.......................................................................................................116
Figure 6-5 Repetitive-image-defect ruler......................................................................................................117
Figure 6-6 Circuit diagram............................................................................................................................118
Figure 6-7 Solenoid, photosensors, switches, and motor.............................................................................119
Figure 7-1 External covers and panels.........................................................................................................128
Figure 7-2 Internal components (1 of 3).......................................................................................................130
Figure 7-3 Internal components (2 of 3).......................................................................................................132
Figure 7-4 Internal components (3 of 3).......................................................................................................134
Figure 7-5 Paper-pickup assembly...............................................................................................................136
x ENWW
Page 12

1 Product Information
This chapter provides general product information for HP LaserJet 1022 series printer.
●
Product configurations
●
Overview of product
●
Product specifications
●
Extended warranty
●
Print-cartridge information
●
Regulatory information
ENWW 1
Page 13

Product configurations
The HP LaserJet 1022 series printers are designed to print documents easily and with the laser quality
that customers have come to expect from an HP LaserJet product. The following sections describe the
configurations of the HP LaserJet 1022 series printers.
HP LaserJet 1022 printer
The HP LaserJet 1022 (HP LJ 1022) is the base model of the HP LaserJet 1022 series printers. It offers
the following features:
■ Prints up to 18 pages per minute (ppm) for A4-sized media, and 19 ppm for letter-size media
■ 10 seconds or less to first page out
■ ProRes 1200 print quality setting that provides fine-line detail at 1200 x 1200 dots per inch (dpi)
■
250-sheet input capacity (75-g/m
■ Priority input slot
■ 125-sheet output bin capacity
■ Prints watermarks, booklets, and multiple pages per sheet (N-up), and can print the first page on
different media from the remainder of the document
■ 8 MB of RAM
■ Host-based and PCL5e printer driver
■ 26 PCL fonts
■ 2,000-page print cartridge
■ USB 2.0 Hi-Speed port
2
[20-lb] media)
HP LaserJet 1022n printer
The HP LaserJet 1022n (HP LJ 1022n) has all of the features of the HP LJ 1022, and also includes an
internal network port.
HP LaserJet 1022nw printer
The HP LaserJet 1022nw (HP LJ 1022nw) has all of the features of the HP LJ 1022n, and also includes
integrated 802.11b/g wireless connectivity.
NOTE For more information about this product, see the HP LaserJet 1022nw
Wireless User Guide.
2 Chapter 1 Product Information ENWW
Page 14
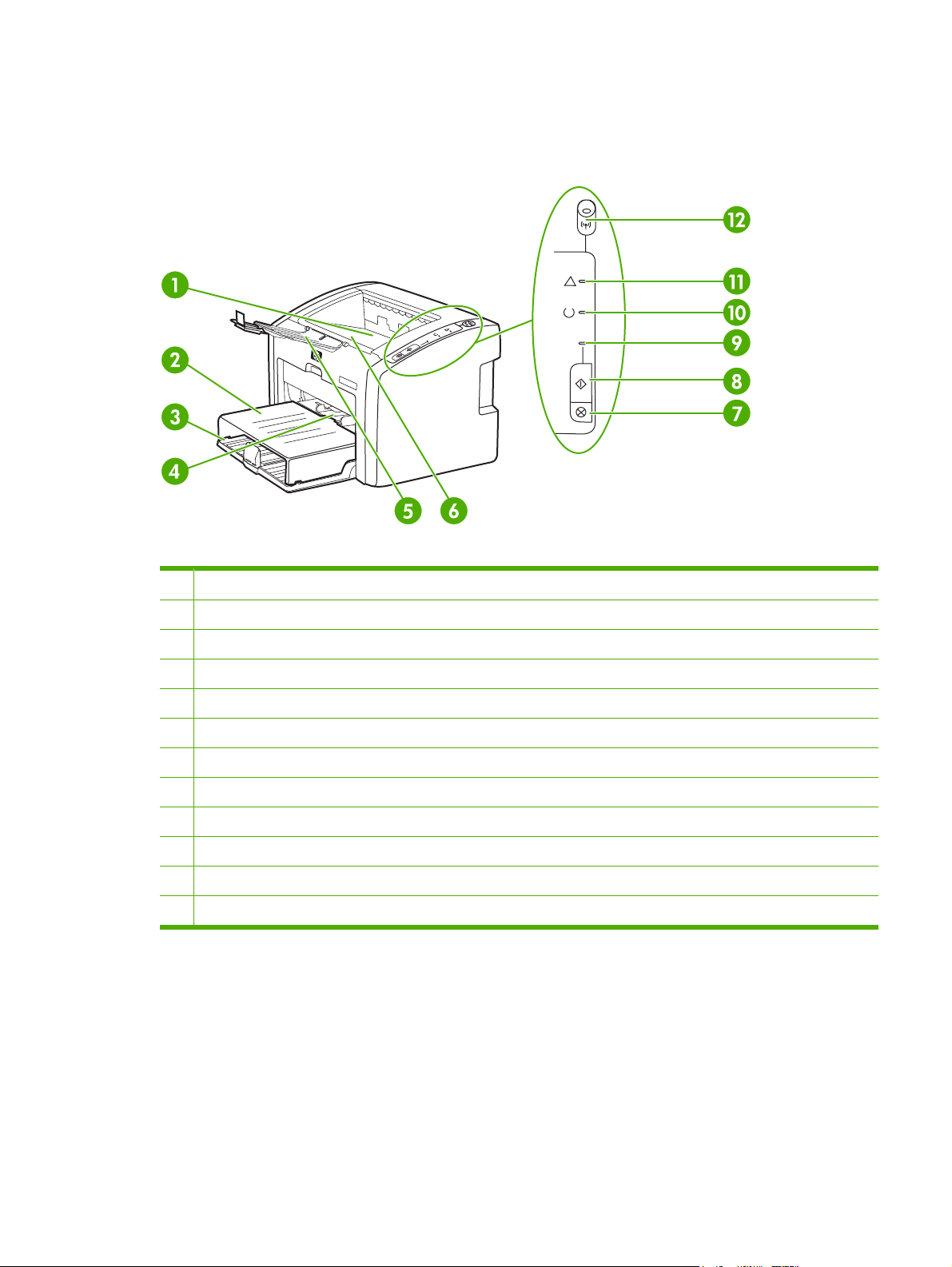
Overview of product
HP LaserJet 1022 series printers
Figure 1-1 Front and right-side view
1 Output bin
2 Input-tray cover
3 250-sheet main input tray
4 Priority feed slot
5 Output-media support
6 Print-cartridge door
7 C
ANCEL JOB
8 GO button
9 GO light
10 R
EADY
11 A
TTENTION
12 W
IRELESS
button
light
light
light (HP LJ 1022nw printer only)
ENWW Overview of product 3
Page 15
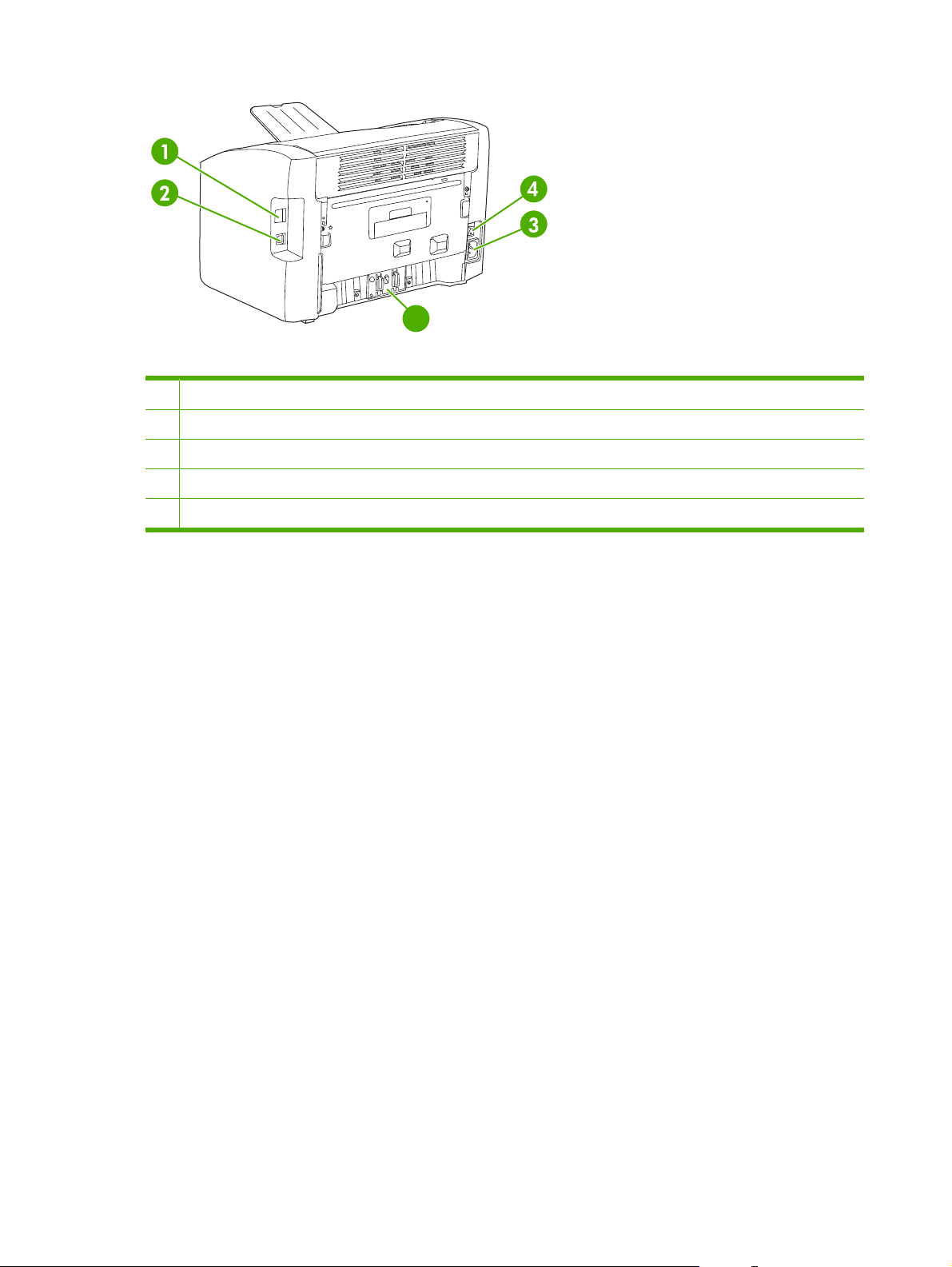
5
Figure 1-2 Back and left-side view
1 Internal network port (HP LJ 1022n and HP LJ 1022nw printers only)
2 USB port
3 Power receptacle
4 On/off switch
5 Separation pad
4 Chapter 1 Product Information ENWW
Page 16
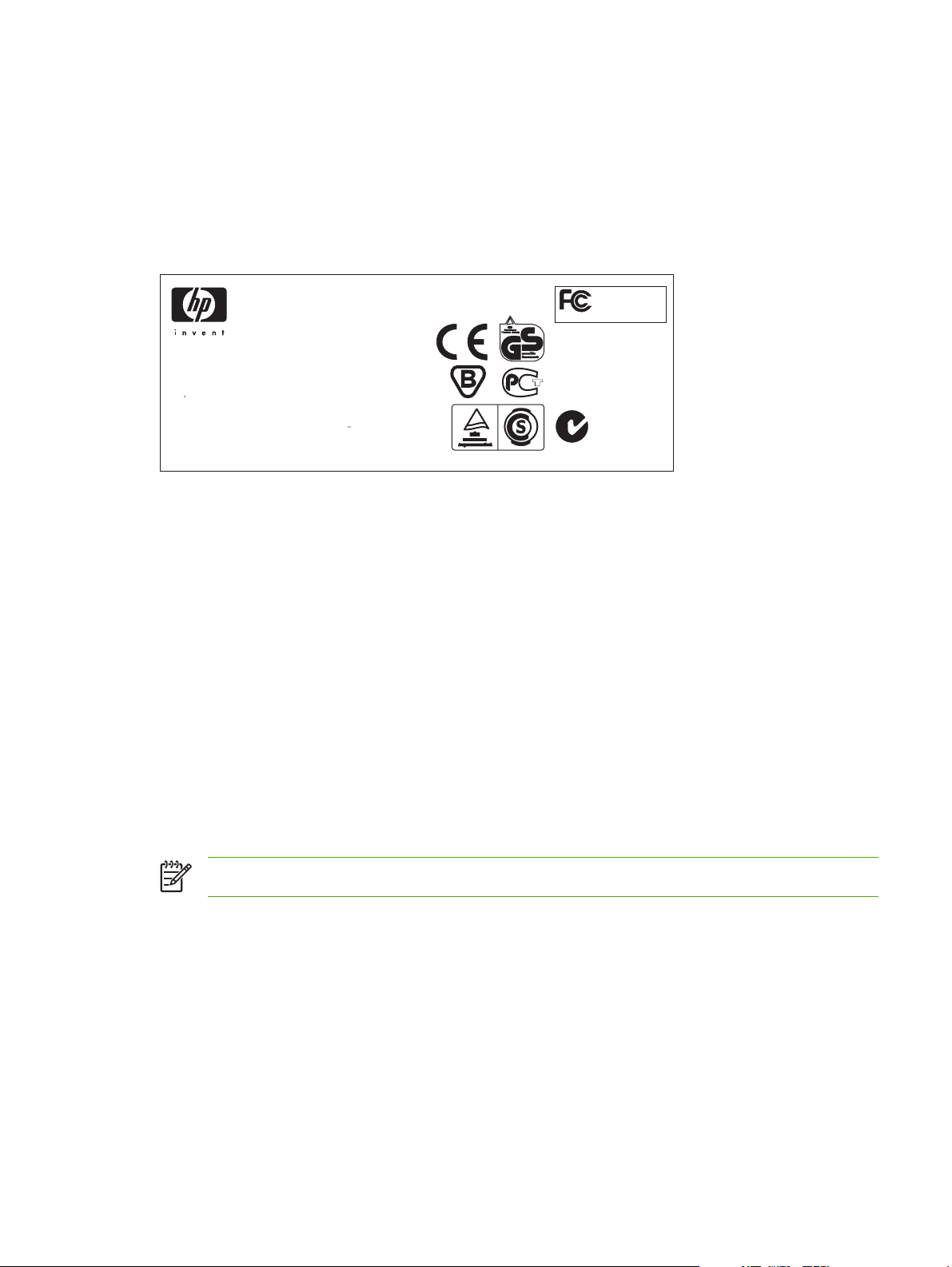
Model and serial numbers
The model number and serial number are listed on an identification label located on the back of the
product.
The serial number contains information about the country/region of origin and the revision level,
production code, and production number of the product.
The label also contains power-rating and regulatory information.
HEWLETT-PACKARD
11311 CHINDEN BLVD.
BOISE, IDAHO 83714
USA
Numero du produit
Product No.Q5912A
CNBR212347
CNBR212347
Nsmero de Serie
Serial No.
CNBR212347
CNBR212347
Made in China
Fabricado en China
CNBB123456
Manufacturado
Manufactured:
April 16, 2005
Numero reglementaire du modele
é
é
Regulatory Model Number BOISB-0405-00
220- 240V ~AC
50/60 Hz, 2.5A (2,5A)
Apparaten skall
anslutas till jordat
natuttag.
é
TestedTo Comply
With FCC Standards
FOR HOME OR OFFICE USE
This product conforms with
CDRH radiation performance
standard 21 CFR chapter 1,
sub-chapter J.
Complies with Canadian EMC
Class B requirements.
>PET< SITE:FR1
Figure 1-3 Model- and serial-number label
Hardware description
The HP LaserJet 1022 series printers provide ProRes technology for 1200 dpi resolution.
The product prints at 19 ppm for letter-size paper and 18 ppm for A4-size paper. With 1200 dpi printing,
the product has exceptional text and graphics print quality. The simple control panel and improved paper
handling make this product very easy to use.
2
The main input tray has a 250-sheet (75-g/m
printing. The priority input slot is used to manually feed single sheets of most recommended media. Both
the main input tray and the priority input slot are center-justified for all supported media sizes. The output
2
bin holds up to 100 sheets of 75-g/m
(20-lb) paper.
[20-lb] media) capacity for continuous, multiple-page
The product has a very fast first-page-out, at less than 8 seconds. The base memory contains 8 MB of
RAM and an embedded 133 MHz processor.
The print engine has an average duty cycle of 1,000 pages per month (7,000 peak) or 50,000 total pages
printed. The standard print-cartridge life is 2,000 pages, in accordance with ISO/IEC 19752.
NOTE Actual print cartridge life depends on specific usage.
Firmware description
The firmware in the product includes these features:
■ Host-based printing
■ PCL Level 5e
■ EconoMode functionality
ENWW Overview of product 5
Page 17

Product specifications
This section details the specifications for the HP LaserJet 1022 series printers.
Physical specifications
Table 1-1 Physical specifications
Model Height Depth Width Weight
HP LaserJet 1022 series printers 241 mm (9.5
inches)
245 mm (9.6
inches)
370 mm (14.6
inches)
Printer performance
Table 1-2 Performance
Model Print resolution (normal) Print speed (A4-size
media)
HP LaserJet 1022 series printers 1200 dpi (ProRes) 18 ppm
Environmental specification
Table 1-3 Environmental specifications
Category Specification
Operating environment (unit plugged into an alternating
current [ac] outlet)
■ Temperature: 10° to 32.5°C (50° to 90.5° F)
■ Humidity: 20 to 80% relative humidity (no condensation)
6.3 kg (13.9 lb)
Storage environment (unit not plugged into an AC outlet) ■ Temperature: 0° to 40°C (32° to 104°F)
■ Humidity: 10 to 80% relative humidity (no condensation)
6 Chapter 1 Product Information ENWW
Page 18

Electrical specifications
Table 1-4 Power requirements
Specification 110-volt models 220-volt models
Power requirements 110–127 V (±10%)
50/60 Hz (±2 Hz)
220–240 V (±10%)
50/60 Hz (±2 Hz)
Rated current 4.0 amps 2.5 amps
WARNING! Power sources are not interchangeable.
Table 1-5 Power consumption (average, in watts)
Product model Printing
HP LaserJet 1022
300 W (110 V models)
series printers
250 W (220 V models)
1
Values are subject to change. See www.hp.com/support/lj1022 for current information.
2
Power reported is highest value measured for printing using all standard voltages. HP LaserJet 1022 printer print speed is
19 ppm (letter size) and 18 ppm (A4 size).
2
1
2
Ready
PowerSave Off
4 W 4 W 0 W
Acoustic emissions
Table 1-6 Acoustic emissions
Sound power level Declared per ISO 9296
1
Printing L
= <6.2 Bels (A) [62 dB (A)]
WAd
Ready Inaudible
Sound pressure level—Bystander position Declared per ISO 9296
Printing L
= ≤49 dB (A)
pAm
Ready Inaudible
1
Values are subject to change. See www.hp.com/support/lj1022 for current information. Configuration tested: HP LaserJet 1022
printer using the standard tray, A4 paper, and simplex, continuous printing. HP LaserJet 1022 printer print speed is 19 ppm
(letter size) and 18 ppm (A4 size). During other operations, acoustic emissions might vary.
ENWW Product specifications 7
Page 19

Extended warranty
In most countries/regions, HP Care Pack provides additional coverage, beyond standard warranty for
the HP device and for all HP-supplied internal components. This hardware maintenance can uplift the
standard warranty, for example, from next-day to same-day service, or extend it up to 5 years. The HP
Care Pack can provide Express Exchange or onsite service. For more information, see the support flyer
that came with the device for the appropriate phone numbers and information.
8 Chapter 1 Product Information ENWW
Page 20

Print-cartridge information
The print cartridge is designed to simplify replacement of the major consumable parts. The print cartridge
contains the printing mechanism and a supply of toner.
The standard print-cartridge life is 2,000 pages, in accordance with ISO/IEC 19752.
NOTE Actual print cartridge life depends on specific usage.
Refilled print cartridges
While Hewlett-Packard does not prohibit the use of refilled print cartridges during the warranty period
or while the product is under a maintenance contract, use of refilled cartridges is not recommended for
the following reasons:
■ Repairs resulting from the use of refilled cartridges are not covered under Hewlett-Packard warranty
or maintenance contracts.
■ Hewlett-Packard has no control or process to ensure that a refilled cartridge functions at the high
level of reliability of a new HP LaserJet print cartridge. Hewlett-Packard also cannot predict the longterm reliability effect on the product from using the different toner formulations that are found in
refilled cartridges.
■ The print quality of HP LaserJet print cartridges influences the customer’s perception of the product.
Hewlett-Packard has no control over the actual print quality of a refilled cartridge.
■ Parts that are critical to print quality might not be replaced when the cartridge is refilled with toner.
Recycling print cartridges
In order to reduce waste, Hewlett-Packard offers a recycling program. Cartridge components that do
not wear out are recycled. Plastics and other materials are recycled. Hewlett-Packard pays the shipping
costs from the user to the recycling plant (within the United States). To join this recycling effort, follow
the instructions inside the print cartridge box. See
www.hp.com/recycle for more information.
ENWW Print-cartridge information 9
Page 21

Regulatory information
FCC compliance
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant
to Part 15 of the FCC rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio
frequency energy. If it is not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, it may cause harmful
interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur
in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television
reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try
to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
■ Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
■ Increase separation between equipment and receiver.
■ Connect equipment to an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is located.
■ Consult your dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician.
NOTE Any changes or modifications to the printer that are not expressly approved by Hewlett-
Packard could void the user's authority to operate this equipment. Use of a shielded interface
cable is required to comply with the Class B limits of Part 15 of FCC rules.
Canadian DOC regulations
Complies with Canadian EMC Class B requirements.
«Conforme á la classe B des normes canadiennes de compatibilité électromagnétiques. «CEM».»
Korean EMI statement
10 Chapter 1 Product Information ENWW
Page 22

Laser statement for Finland
LASERTURVALLISUUS
LUOKAN 1 LASERLAITE
KLASS 1 LASER APPARAT
HP LaserJet 1022, HP LaserJet 1022n, HP LaserJet 1022nw -laserkirjoitin on käyttäjän
kannalta turvallinen luokan 1 laserlaite. Normaalissa käytössä kirjoittimen suojakotelointi
estää lasersäteen pääsyn laitteen ulkopuolelle. Laitteen turvallisuusluokka on määritetty
standardin EN 60825-1 (1994) mukaisesti.
VAROITUS!
Laitteen käyttäminen muulla kuin käyttöohjeessa mainitulla tavalla saattaa altistaa käyttäjän
turvallisuusluokan 1 ylittävälle näkymättömälle lasersäteilylle.
VARNING!
Om apparaten används på annat sätt än i bruksanvisning specificerats, kan användaren
utsättas för osynlig laserstrålning, som överskrider gränsen för laserklass 1.
HUOLTO
HP LaserJet 1022, HP LaserJet 1022n, HP LaserJet 1022nw-kirjoittimen sisällä ei ole
käyttäjän huollettavissa olevia kohteita. Laitteen saa avata ja huoltaa ainoastaan sen
huoltamiseen koulutettu henkilö. Tällaiseksi huoltotoimenpiteeksi ei katsota väriainekasetin
vaihtamista, paperiradan puhdistusta tai muita käyttäjän käsikirjassa lueteltuja, käyttäjän
tehtäväksi tarkoitettuja ylläpitotoimia, jotka voidaan suorittaa ilman erikoistyökaluja.
VARO!
Mikäli kirjoittimen suojakotelo avataan, olet alttiina näkymättömälle lasersäteilylle laitteen
ollessa toiminnassa. Älä katso säteeseen.
VARNING!
Om laserprinterns skyddshölje öppnas då apparaten är i funktion, utsättas användaren för
osynlig laserstrålning. Betrakta ej strålen. Tiedot laitteessa käytettävän laserdiodin
säteilyominaisuuksista:
Aallonpituus 785-800 nm
Teho 5 mW
Luokan 3B laser
ENWW Regulatory information 11
Page 23

12 Chapter 1 Product Information ENWW
Page 24

2 Installation and Operation
This chapter provides an overview of the appropriate operating environment, describes the control
panel, describes media requirements, and describes how to load print media.
Operating environment
●
●
Identifying the control-panel components
●
Media specifications
●
Guidelines for using media
●
Loading media
●
Setting media types
ENWW 13
Page 25
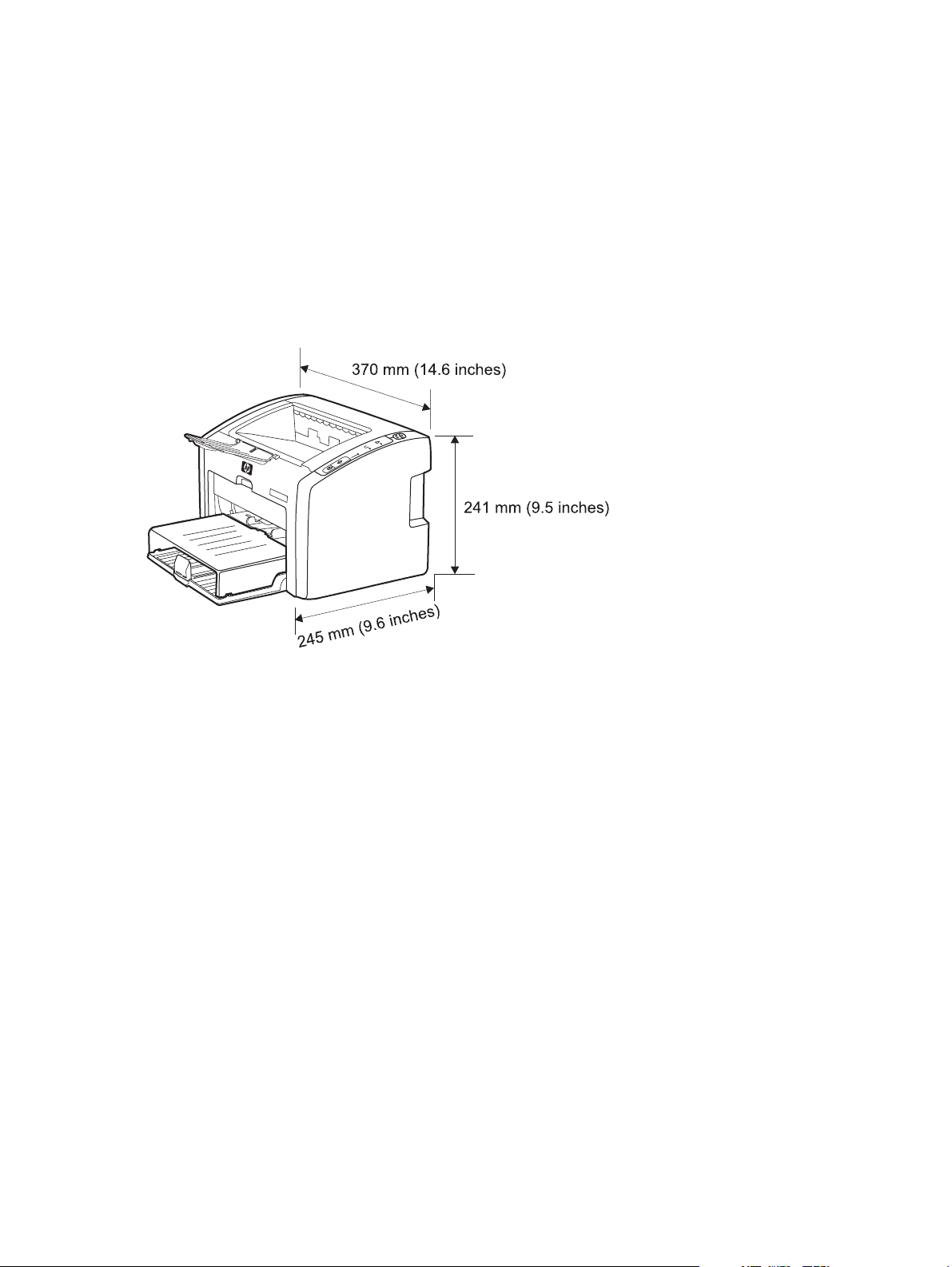
Operating environment
Place the product on a sturdy, level surface in a well-ventilated area that meets the following
environmental requirements:
■ Temperature: 10° to 32.5°C (50° to 90.5°F)
■ Humidity: 20 to 80% relative humidity (no condensation)
■ Away from direct sunlight, open flames, and ammonia fumes
■ With sufficient space around the product to accommodate proper access and ventilation
requirements
Figure 2-1 Dimensions of product
14 Chapter 2 Installation and Operation ENWW
Page 26
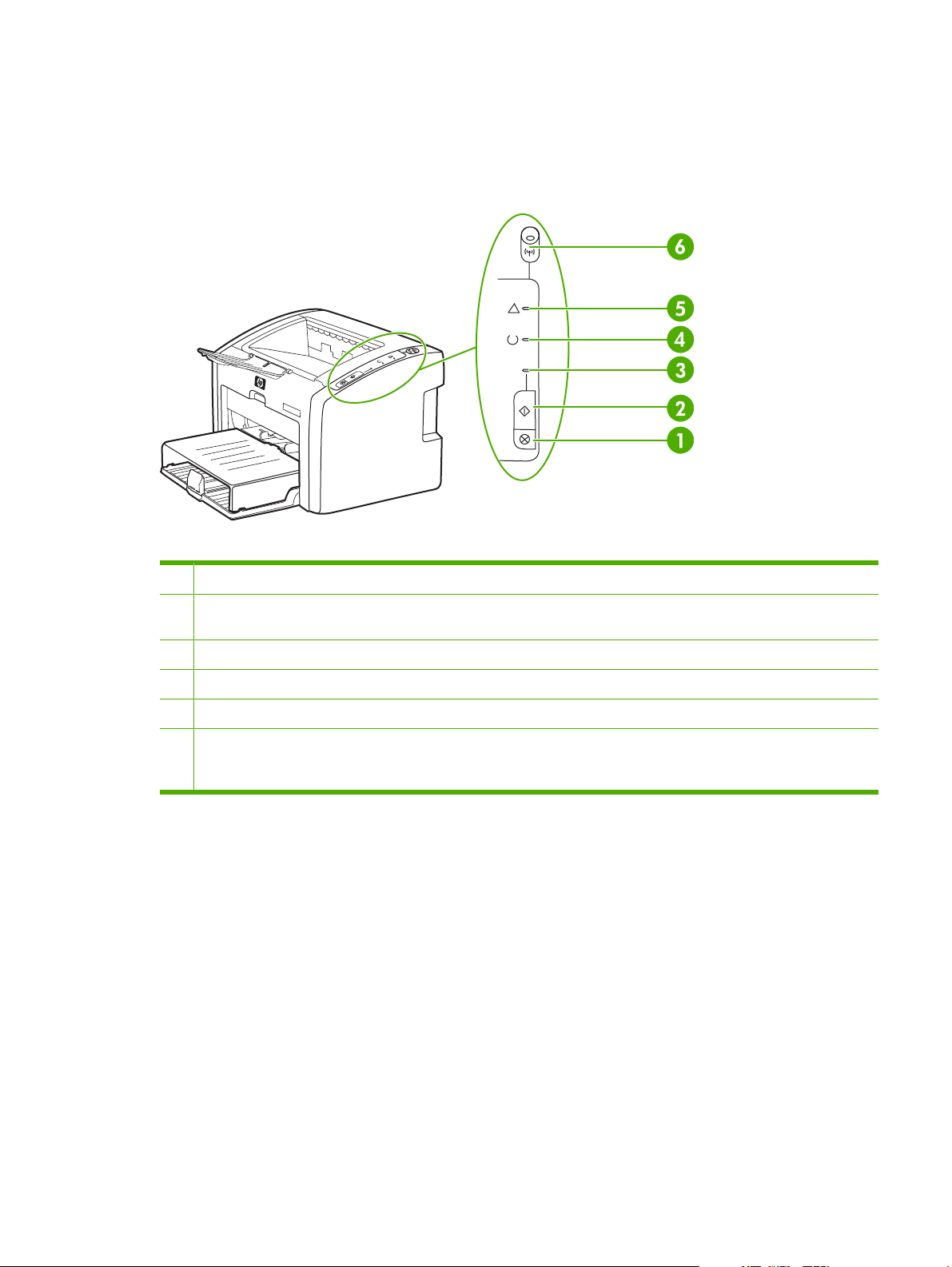
Identifying the control-panel components
The printer control panel has three lights and two buttons. The HP LaserJet 1022nw has an additional
light (W
IRELESS
status.
Figure 2-2 Control-panel lights and buttons
light) at the top of the control panel. These lights produce patterns that identify printer
1 C
ANCEL JOB
2 GO button: To print a demo page or to continue printing while in manual feed mode, press and release the GO button. To
print a configuration page, press and hold the G
3 GO light: Indicates that the product is receiving data when flashing.
4 R
EADY
5 A
TTENTION
6 W
IRELESS
established. When the wireless light is off, wireless operation is disabled. When the wireless light is flashing, the product
is trying to establish a wireless connection.
button: When the printer is processing data, press the C
O
button for 5 seconds.
light: Indicates that the product is ready to print.
light: Indicates that the input tray is empty, print-cartridge door is open, print cartridge is missing, or other errors.
light: (HP LJ 1022nw printer only) When the wireless light is on solid, a wireless connection has been
ANCEL JOB
button to cancel the print job.
ENWW Identifying the control-panel components 15
Page 27

Media specifications
The printers accept a variety of media. Properties such as weight, grain, and moisture content are
important factors that affect printer performance and output quality. Media should conform to the
guidelines in the user guide. Media that does not meet HP guidelines might cause poor print quality,
increased media jams, or premature wear on the product, which might require printer repair.
CAUTION Damage that is caused by using media that does not meet HP specifications is not
covered by the HP warranty or service agreements.
Supported media sizes
The printer supports media within this size range:
■ Minimum: 76 x 127 mm (3 x 5 inches)
■ Maximum: 216 x 356 mm (8.5 x 14 inches)
Table 2-1 Media sizes
Paper type Metric English
Letter 216 x 279 mm 8.5 x 11 inches
Legal 216 x 356 mm 8.5 x 14 inches
Executive 184 x 267 mm 7.25 x 10.5 inches
A4 210 x 297 mm 8.25 x 11.75 inches
COM10 envelopes 105 x 241 mm 4.13 x 9.5 inches
DL envelopes 110 x 220 mm 4.33 x 8.67 in
C5 envelopes 162 x 229 mm 6.4 x 9 inches
B5 envelopes 176 x 250 mm 6.9 x 9.85 inches
Monarch envelopes 98.5 x 191 mm 3.88 x 7.5 inches
Labels (216 x 279 mm) (8.5 x 11 inches)
Custom-size media custom (within acceptable range) custom (within acceptable range)
NOTE Narrow and heavy media can cause the printer to print more slowly.
16 Chapter 2 Installation and Operation ENWW
Page 28

Guidelines for using media
HP LaserJet printers produce documents that have excellent print quality. They can print on a variety
of media types, such as paper (including up to 100% recycled fiber content paper), envelopes, labels,
transparencies, and custom-sized media.
Paper and transparencies
Paper must be of good quality and free of cuts, nicks, tears, spots, loose particles, dust, wrinkles, holes,
and curled or bent edges. Check the label on the paper package for details about the type of paper
(such as bond or recycled).
Some paper causes print-quality problems, jamming, or damage to the printer.
NOTE Do not use letterhead that is printed with low-temperature inks, such as those used in
some types of thermography, raised letterhead, or colored paper or preprinted forms that use
inks incompatible with the printer temperature, which is 200°C (392°F) for 0.1 second.
Transparencies must be able to withstand 200°C (392°F), the maximum print temperature.
Common media problems table
Symptom Problem with paper Solution
Poor print quality or toner adhesion, or
problems with feeding
Dropouts, jamming, or curl Stored improperly Store paper flat in its moisture-proof
Increased gray background shading Might be too heavy Use lighter paper.
Excessive curl, or problems with feeding Too moist, wrong grain direction, or
Jamming, or damage to printer Cutouts or perforations Do not use paper that has cutouts or
Problems with feeding Ragged edges Make sure that the sliding media input
Moisture on the trailing edge of the paper Too moist (media is steaming when it
Too moist, too rough, too smooth, or
embossed faulty paper lot
short-grain construction
exits the printer)
Try another kind of paper that is between
100 and 250 Sheffield and has 4% to 6%
moisture content.
wrapping.
Use long-grain paper or change the
media type to light.
perforations.
guides on the input tray are correctly
adjusted.
Store paper in a low humidity area or air
tight container or change the media type
to light.
Labels
When selecting labels, consider the following factors:
■ Adhesives: The adhesive material should be stable at 200°C (392°F), the printer’s maximum
temperature.
■ Arrangement: Only use labels with no exposed backing between them. Labels can peel off sheets
that have spaces between the labels, causing serious jams.
■ Curl: Before printing, labels must lie flat with no more than 13 mm (0.5 inch) of curl in any direction.
ENWW Guidelines for using media 17
Page 29
■ Condition: Do not use labels with wrinkles, bubbles, or other indications of separation. Never use
a sheet of labels that has already been run through the printer.
Envelopes
Envelope construction is critical. Envelope fold lines can vary considerably, not only between
manufacturers but also within a box from the same manufacturer. Successful printing on envelopes
depends on the quality of the envelopes. When selecting envelopes, consider the following factors:
■
Weight: The weight of the envelope paper should not exceed 105 g/m
result.
■ Construction: Before printing, envelopes should lie flat with less than 6 mm (0.25 inch) curl and
should not contain air. Envelopes that trap air may cause problems.
■ Condition: Make sure that the envelopes are not wrinkled, nicked, or otherwise damaged.
■ Sizes: From 90 x 160 mm (3.5 x 6.3 inches) to 178 x 254 mm (7 x 10 inches).
Store envelopes flat. If air is trapped in an envelope, creating an air bubble, the envelope might wrinkle
during printing.
2
(28 lb), or jamming might
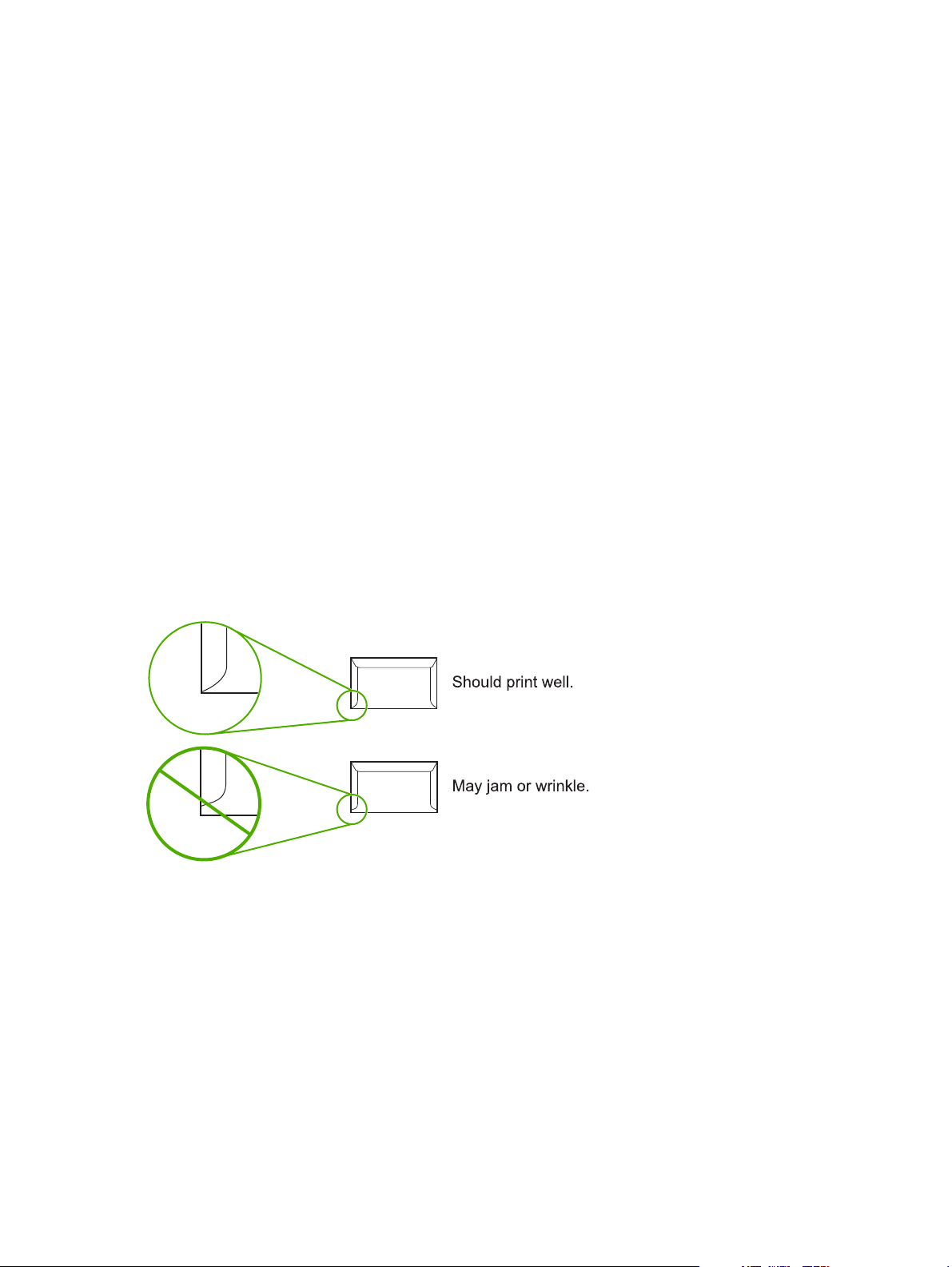
Envelopes with double-side seams
An envelope with double-side-seam construction (vertical seams at both ends of the envelope rather
than diagonal seams) is more likely to wrinkle. Make sure the seam extends all the way to the corner of
the envelope as shown in top figure of the following illustration:
Envelopes with adhesive strips or flaps
Envelopes with a peel-off adhesive strip or with more than one flap that folds over to seal must use
adhesives compatible with the heat and pressure in the printer: 200°C (392°F). The extra flaps and
strips might cause wrinkling, creasing, or jams.
18 Chapter 2 Installation and Operation ENWW
Page 30

Card stock and heavy media
For optimum performance, do not use paper heavier than 157-g/m 2 (42-lb). Paper that is too heavy
might cause misfeeds, stacking problems, jams, poor toner fusing, poor print quality, or excessive
mechanical wear.
Card-stock construction
■
Smoothness: 135- to 157-g/m
to 180 Sheffield. 60- to135-g/m
to 250 Sheffield.
■ Construction : Card stock should lie flat with less than 5 mm (0.2 inch) of curl.
■ Condition: Make sure that the card stock is not wrinkled, nicked, or otherwise damaged.
■ Sizes: Only use card stock within the following size ranges:
■ Minimum: 76 x 127 mm (3 x 5 inches)
■ Maximum: 216 x 356 mm (8.5 x 14 inches)
2
(36- to 42-lb) card stock should have a smoothness rating of 100
2
(16- to 36-lb) card stock should have a smoothness rating of 100
Card-stock guidelines
■ Set margins at least 2 mm (0.08 inch) away from the edges.
ENWW Guidelines for using media 19
Page 31

Loading media
Loading media in the HP LaserJet 1022 series printers is simple and straightforward.
This section describes loading bulk media to print.
Main input tray
The main input tray holds up to 250 sheets of 75-g/m 2 (20-lb) paper or a 25 mm (0.98 inch) stack of
heavier media. Load media with the top forward and the side to be printed on facing up. To prevent jams
and skew, always adjust the side and rear media guides.
Priority feed slot
The priority feed slot is used to feed a single sheet of recommended media for manual feeding and
special operations. It can hold one page of 75-g/m
of heavy paper (163-g/m
the top forward and the side to be printed on facing up. To prevent jams and skew, always adjust the
side media guides.
If you try to print on media that is wrinkled, folded, or damaged in any way, a jam might occur. See the
user guide for more information. See
NOTE When adding new media, make sure to remove all of the media from the input tray and
straighten the stack of new media. This helps prevent multiple sheets of media from feeding
through the printer at one time, and therefore reduces jams.
2
[42-lb]) or card stock, or a single envelope or transparency. Load media with
Jams on page 37.
2
(20-lb) paper, but is best used to feed a single sheet
Specific types of media
■ Transparencies and labels: Load transparencies and labels with the top forward and the side to
be printed facing up. See the user guide on the product CD for more information.
■ Envelopes: Load envelopes with the narrow, stamp side forward and the side to be printed facing
up. See the user guide for more information.
■ Letterhead or preprinted forms: Load with the top forward and the side to be printed facing up.
See the user guide for more information.
■ Cards and custom-sized media: Load with the narrow side forward and the side to be printed
facing up. See the user guide for more information.
20 Chapter 2 Installation and Operation ENWW
Page 32

Setting media types
Use the procedure in this section to select the correct type of media for the print job. An incorrect media
type setting might cause image-quality problems.
Set the media type
1 Open the Printer Properties dialog box.
2 Click Printer Preferences.
3 Select the correct media type from the Type Is drop down menu.
4 Click OK to close the Printer Preferences dialog box.
5 Click OK to close the Printer Properties dialog box.
ENWW Setting media types 21
Page 33

22 Chapter 2 Installation and Operation ENWW
Page 34

3 Maintenance
This chapter describes the life expectancy of parts that wear, printer cleaning, printer maintenance, and
the replacement of user-replaceable parts.
Life expectancies of parts that wear
●
●
Cleaning the product
●
User-replaceable parts
●
Jams
ENWW 23
Page 35

Life expectancies of parts that wear
Inspect any parts that wear when servicing the product. Replace them as needed, based on failure or
wear rather than on usage.
The following table lists approximate schedules for replacing consumables.
Table 3-1 Life expectancies of parts that wear
Description Part number Life (estimated) Remarks
Print cartridge (userreplaceable)
Pickup roller RL1-0266-000CN 50,000 pages Affects paper pickup
Printer separation pad RC1-2048-000CN 50,000 pages Affects paper separation
Fuser assembly (110-127 V) RM1-2049-000CN 50,000 pages Can affect print quality and
Fuser assembly (220-240 V) RM1-2050-030CN 50,000 pages Can affect print quality and
HP LJ 1022 printer 110 V Q5912-67056 (replacement)
HP LJ 1022n printer 110 V Q5913-67056 (replacement)
Q2612A 2,000 pages
NOTE The
declared cartridge
yield value is stated
in accordance with
ISO/IEC 19752. For
more information,
see
pageyield.
50,000 pages Maximum life
Q5912-69056 (refurbished)
Q5912-67001 (exchange
engine w/formatter)
50,000 pages Maximum life
When print becomes faint,
redistribute the toner in the
cartridge by gently rotating the
cartridge from side to side, or
replace the cartridge.
www.hp.com/go/
(feeding one page at a time)
paper movement
paper movement
Q5913-69056 (refurbished)
Q5913-67001 (exchange
engine w/formatter)
HP LJ 1022nw printer 110 V Q5914-67056 (replacement)
Q5914-69056 (refurbished)
Q5914-67001 (exchange
engine w/formatter)
HP LJ 1022 printer 220 V Q5912-67055 (replacement)
Q5912-69055 (refurbished)
Q5912-67002 (exchange
engine w/formatter)
HP LJ 1022n printer 220 V Q5913-67055 (replacement)
Q5913-69055 (refurbished)
50,000 pages Maximum life
50,000 pages Maximum life
50,000 pages Maximum life
24 Chapter 3 Maintenance ENWW
Page 36

Table 3-1 Life expectancies of parts that wear (continued)
Description Part number Life (estimated) Remarks
Q5913-67002 (exchange
engine w/formatter)
HP LJ 1022nw printer 220 V Q5914-67055 (replacement)
Q5914-69055 (refurbished)
Q5914-67002 (exchange
engine w/formatter)
50,000 pages Maximum life
ENWW Life expectancies of parts that wear 25
Page 37

Cleaning the product
WARNING! Before you perform these steps, unplug the product to avoid shock hazard.
To maintain quality, thoroughly clean the product at the following times:
■ Any time a new print cartridge is installed
■ After printing approximately 2,000 pages
■ Whenever print-quality problems appear
Clean the outside of the product with a water-dampened cloth. Clean the inside with a dry, lint-free cloth
(such as a lens tissue).
WARNING! Avoid touching the heating element in the fuser. It might be very hot and can cause
burns.
CAUTION To avoid permanent damage to the product, do not use ammonia-based or ethyl
alcohol-based cleaners on or around the product.
CAUTION Do not touch the surface of the black-sponge transfer roller. Contaminants on the
roller can cause print-quality problems.
Cleaning the print path
The HP LJ 1022 series feature a special cleaning mode to clean the paper path.
NOTE This process requires a transparency to remove dust and toner from the print paper path.
Do not use bond or rough paper.
Make sure that the transparency used in this cleaning process meets the media requirements for
the printer.
2
If transparency film is unavailable, you can use copier-grade paper (70- to 90-g/m
lb) with a smooth surface. If you must use paper, perform the procedure two or three times to
ensure thorough cleaning.
1 Make sure that the printer is idle and the R
2 Load the transparency in the input tray.
3 Open the Printer Properties dialog box. Click the Configure tab, and then select Start in the
Cleaning Page box. Follow the instructions in the Cleaning Utility dialog box.
NOTE The cleaning process takes approximately 3 minutes. The cleaning page will stop
periodically during the cleaning process. Do not turn the printer off until the cleaning process has
been completed. You might need to repeat the cleaning process several times to thoroughly clean
the printer.
EADY
light is on.
, or 18- to 24-
26 Chapter 3 Maintenance ENWW
Page 38

Cleaning the print-cartridge area
You do not need to clean the print-cartridge area often. However, cleaning this area can improve the
quality of your printed sheets.
1 Turn off the printer, unplug and remove the power cord. Wait for the printer to cool.
2 Open the print-cartridge door, and remove the print cartridge.
CAUTION To prevent damage, do not expose the print cartridge to light. Cover the print
cartridge, if necessary. Also, do not touch the black-sponge transfer roller inside the printer.
By doing so, you can damage the printer.
3 With a dry, lint-free cloth, wipe any residue from the media-path area and the print-cartridge cavity.
ENWW Cleaning the product 27
Page 39

4 Replace the print cartridge, and close the print-cartridge door.
5 Plug in the printer, and then turn it on.
28 Chapter 3 Maintenance ENWW
Page 40

Cleaning the pickup roller
If you want to clean the pickup roller rather than replace it, use the following instructions.
Remove the pickup roller as described in steps 1 through 5 of
on page 30. With the roller outside the printer, use the following steps to complete the cleaning.
1 Dampen a lint-free cloth with water and scrub the roller.
2 Using a dry, lint-free cloth, wipe the pickup roller to remove loosened dirt.
3 Allow the pickup roller to dry completely before you reinstall it in the printer. To reinstall the pickup
roller, see steps 6 through 9 of
Replacing the pickup roller on page 30.
Replacing the pickup roller
ENWW Cleaning the product 29
Page 41

User-replaceable parts
To order a new pickup roller or separation pad, go to www.partsdirect.hp.com.
Replacing the pickup roller
If the printer regularly misfeeds (no media feeds through) and cleaning the pickup roller does not fix the
problem, replace the pickup roller.
CAUTION Failure to complete all of the steps in this procedure might damage the product.
1 Turn off the printer, unplug and remove the power cord. Wait for the printer to cool.
2 Open the print-cartridge door, and remove the print cartridge.
30 Chapter 3 Maintenance ENWW
Page 42

3 Locate the pickup roller.
4 Gently release the small, white tabs on each side of the pickup roller by pushing them away from
the roller, and then rotate the pickup roller toward the front.
CAUTION Use gentle pressure to release the small, white tabs to avoid breaking them.
5 Gently pull the pickup roller up and out.
6 Position the new pickup roller in the slot of the previous pickup roller.
NOTE Circular and rectangular pegs on each side prevent you from incorrectly positioning
the pickup roller.
ENWW User-replaceable parts 31
Page 43

7 Rotate the top of the new pickup roller into position until the white tabs on each side of the roller
snap the roller into place.
8 Reinstall the print cartridge and close the print cartridge door.
9 Plug in the printer, and then turn it on.
32 Chapter 3 Maintenance ENWW
Page 44

Replacing the separation pad
If the printer grabs more than one page at a time, you might have to replace the printer separation pad.
Recurring feed problems indicate that the separation pad is worn.
Normal use with good-quality media causes wear. The use of poor-quality media might require more
frequent replacement of the separation pad.
NOTE Before you change the separation pad, clean the pickup roller. See Cleaning the pickup
roller on page 29 for instructions. To order parts, go to www.partsdirect.hp.com.
1 Turn off the printer, unplug and remove the power cord. Wait for the printer to cool.
2 At the back of the printer, use a #2 Phillips screwdriver to unscrew the two screws that hold the
separation pad in place.
ENWW User-replaceable parts 33
Page 45

3 Remove the separation pad.
4 Insert the new separation pad, and screw it in place.
5 Plug the printer in, and then turn it on.
34 Chapter 3 Maintenance ENWW
Page 46

Replacing the main input tray (paper-pickup tray assembly)
If you break or damage the main input tray (also called the paper-pickup tray assembly), you can replace
it. To order parts, go to
1 Carefully flex the main input tray just enough to release one side.
NOTE Be careful not to break the hinge points.
www.partsdirect.hp.com.
1
3
2
Figure 3-1 Main input tray
2 Remove the main input tray.
ENWW User-replaceable parts 35
Page 47

Replacing the output-bin extension (delivery-tray assembly)
If you break or damage the output-bin extension (also called the delivery-tray assembly), you can replace
it. To order parts, go to
1 Carefully flex the sides of output-bin extension just enough to release the hinge pins.
NOTE
Be careful not to break the hinge pins (callout 1).
www.partsdirect.hp.com.
1
Figure 3-2 Output-bin extension
2 Remove the output-bin extension.
36 Chapter 3 Maintenance ENWW
Page 48

Jams
Clearing jams
CAUTION Do not use sharp objects, such as tweezers or needle nose pliers, to remove jams.
Damage caused by sharp objects will not be covered by the warranty.
CAUTION Always pull jammed media in the direction it would travel through the paper path.
Do not pull jammed media against the direction of travel through the paper path to avoid damage
to the printer.
To prevent damage to the printer when clearing jams, including jams in the output bin, always open the
print-cartridge door and remove the print cartridge. Keep the door open and the cartridge out until the
jam has been cleared. Opening the print-cartridge door and removing the print cartridge relieves tension
on the printer rollers, which prevents damage to the printer and makes the removal of jammed pages
easier.
Occasionally, media becomes jammed during a print job. You are notified of a media jam by an error
from the software and the printer control panel lights. See
The following are some of the causes of media jams:
Control-panel lights on page 95.
■ The input trays are loaded improperly or are too full. See
NOTE When you add new media, always remove all of the media from the input tray and
straighten the stack of new media. This helps prevent multiple sheets of media from feeding
through the printer at one time, reducing media jams.
■ The media does not meet HP specifications. See Media specifications on page 16.
Loading media on page 20.
Typical media jam locations
■ Print cartridge area: See Removing a jammed page on page 38.
■ Input tray area: If the page is still sticking out of the input tray, gently try to remove it from the input
tray without tearing the page. If you feel resistance, see
on page 38.
■ Output path: If the page is sticking out of the output bin, see
on page 38.
NOTE There might be loose toner in the printer after a media jam. This toner clears up after
a few sheets are printed.
Removing a jammed page
Removing a jammed page
ENWW Jams 37
Page 49

Removing a jammed page
Use the procedures in this section to remove a jam.
CAUTION Media jams might result in loose toner on the page. If you get any toner on your
clothes, wash them in cold water. Hot water will permanently set the toner into the fabric.
CAUTION To prevent damage to the printer when clearing jams, including jams in the output
bin, always open the print cartridge door and remove the print cartridge.
To prevent damage to the print cartridge, minimize its exposure to direct light. Cover the print
cartridge with a sheet of paper.
1 Open the print cartridge door, and remove the print cartridge.
2 Grasp the middle edge of the side of the media that is most visible, and carefully pull it free from
the printer.
CAUTION Do not use sharp objects, such as tweezers or needle nose pliers, to remove
jams. Damage caused by sharp objects will not be covered by the warranty.
CAUTION Always pull jammed media in the direction it would travel through the paper path.
Do not forcefully pull jammed media against the direction of travel through the paper path to
avoid damage to the printer.
38 Chapter 3 Maintenance ENWW
Page 50

3 When you have removed the jammed media, replace the print cartridge, and close the print cartridge
door.
After clearing a media jam, you might need to turn the printer off then on again.
NOTE When you add new media, remove all of the media from the input tray and straighten
the stack of new media.
ENWW Jams 39
Page 51

40 Chapter 3 Maintenance ENWW
Page 52

4 Operational overview
This chapter describes the general components of the HP LaserJet 1022 series printers, and the theory
of operation.
Basic functions
●
●
Formatter system
●
Printer operation
ENWW 41
Page 53

Basic functions
The following are the major systems of the printer:
■ Formatter and I/O functions
■ Formatter system
■ Printer functions and operation
■ Engine control system (engine control unit [ECU] and engine power assembly)
■ Image-formation system
■ Paper-feed system
PRINTER
FORMATTER
COMPUTER
ENGINE UNIT
Figure 4-1 Basic configuration
ECU
42 Chapter 4 Operational overview ENWW
Page 54

Formatter system
The formatter coordinates the major systems. It is responsible for the following tasks:
■ Receiving and processing print data from the printer interface (the computer)
■ Monitoring the control panel and relaying printer-status information
■ Coordinating image formation and timing with the print engine
■ Communicating with the host computer through the bidirectional interface
The formatter receives print data from the universal serial bus (USB) interface and converts it into a dot
image. The ECU synchronizes the image-formation system with the paper-feed system and signals the
formatter to send the print-image data to the laser system. The formatter sends the print-image data
(dots) in the form of a video signal, and the printing process begins.
Central processing unit
The formatter uses an embedded Coldfire V4 microprocessor operating at 133 MHz.
RAM
■ One bank of nonvolatile RAM (NVRAM) stores parameters.
■ Dynamic random access memory (DRAM) provides temporary storage of the product program code
and print data.
■ The HP LaserJet 1022 series printers have 8 MB of RAM.
USB interface
The formatter receives incoming data through the USB interface. This interface provides high-speed,
two-way communication between the printer and the host, allowing applications on the host computer
to change printer settings and monitor printer status. The USB interface is compatible with the USB 2.0
specification.
Control panel
The control panel consists of the following components:
■ Three status lights (the HP LaserJet 1022nw printer has a fourth W
O
and C
■ G
ANCEL JOB
buttons
IRELESS
status light).
Draft mode (EconoMode)
Depending on which driver is used, selecting draft or EconoMode from the driver allows the product to
use less toner, extending the life of the print cartridge. There is a change in print quality when this setting
is used.
NOTE HP does not recommend the full-time use of EconoMode. If EconoMode is used full-time
when the average toner coverage is very low, it is possible that the toner supply will outlast the
mechanical parts of the print cartridge.
ENWW Formatter system 43
Page 55

HP Memory Enhancement technology (MEt)
HP (MEt) effectively doubles the standard memory through a variety of font- and data-compression
methods.
Enhanced I/O
The Enhanced I/O feature uses printer memory to store data that the printer received from the host
computer. When Enhanced I/O is enabled, you can send more data to the product in less time, so that
you can return to your application sooner. Enhanced I/O has the following options:
■ Auto: The product uses Enhanced I/O memory allocation to increase the speed of data transfer
from the host computer to the product, if necessary. The default setting is Auto.
■ Off: The product uses the minimum amount of product memory for storing data that the host
computer sends.
■ Page protect: The formatter creates the entire page image in page-buffer memory before physically
moving the media through the printer. This process ensures that the entire page is printed.
Page complexity (ruling lines, complex graphics, or dense text) can exceed the printer’s ability to create
the page image quickly enough to keep pace with the image-formation process. If the page protect
feature is disabled and a page is too complex, the page might print in parts (for example, the top half
on one page and the bottom half on the next page). Some print-data loss is likely in these instances,
and the A
TTENTION
light on the control panel will illuminate.
44 Chapter 4 Operational overview ENWW
Page 56

Printer operation
Printer functions are divided into five groups:
■ Engine control
■ Formatter
■ Image formation
■ Laser/scanner
■ Pickup and feed
The following figure is a block diagram of the printer:
Figure 4-2 Printer functional-block diagram
ENWW Printer operation 45
Page 57

Engine control system (engine control unit and power assembly)
The engine control system coordinates all print engine activities. The engine control system includes
both the engine control unit (ECU) PCA and the engine power-assembly-PCA.
NOTE In other HP LaserJet products, the ECU and power functions are combined onto one
PCA known as the controller PCA or the dc controller PCA. In the HP LaserJet 1022 series
printers, the control functions are primarily relegated to the ECU PCA and the power functions
to the engine-power-assembly PCA.
The ECU controls the following systems and functions:
■ Printer-engine control
■ Paper-motion monitoring and control (printing)
■ Motor
■ Printer laser/scanner unit
The engine power assembly provides the following features in the power system:
■ AC power distribution
■ DC power distribution
■ Overcurrent/overvoltage protection
■ High-voltage power distribution
Printer-engine-control system
Paper motion monitoring and control
The ECU controls paper motion in the printer by continuously monitoring the two paper sensors and
coordinating the timing with the other print processes.
For a detailed explanation of paper movement and the interaction of the sensors and pickup solenoid
with the paper-movement process, see
Motor
The ECU controls the motor. The motor drives all of the paper movement in the printer.
Printer-paper feed system on page 51.
46 Chapter 4 Operational overview ENWW
Page 58

Printer laser/scanner unit
The ECU sends signals to the laser/scanner assembly to modulate the laser diode on and off modes
and to drive the laser/scanner motor.
Laser driver PCB
/BDI
VDO1
/VDO1
VDO2
/VDO2
BD
sensor
CNT0
CNT1
CNT2
/BD
Cylindrical lens
/ACC
/DEC
Formatter
Engine
controller
PCB
Figure 4-3 Laser/scanner operation
Four-sided
mirror
Scanner motor
Photosensitive
drum
Focusing lens
ENWW Printer operation 47
Page 59

Power system on the engine-power assembly
The engine-power assembly provides the ac, dc, and high-voltage power supply circuits.
AC power distribution
The ac power circuitry supplies ac voltage whenever the power cord is connected to the ac power source
and the power switch is on. The ac voltage is distributed to the dc power supply circuitry and to the ac
driver circuitry, which controls ac voltage to the fuser-assembly heating element.
DC power distribution
The dc power distribution circuitry, located on the engine power assembly, distributes +3.3 Vdc, +5 Vdc,
and +24 Vdc as follows:
■ +3.3 Vdc ECU, sensors, formatter
■ +5 Vdc ECU
■ +24 Vdc Main motor, laser/scanner motor, solenoid, high-voltage power
supply, fuser, safety circuit, door switch
Overcurrent/overvoltage
Two overvoltage devices are in this product:
■ Fuse F101 provides overcurrent protection for the fusing-system circuitry.
■ Fuse F102 (110 V products only) provides overcurrent protection to the printer dc power supply
circuitry.
You can check or replace the fuses by removing the left cover. If either of these fuses fails, replace the
engine-power assembly.
High-voltage power distribution
The high-voltage power supply applies an overlap of dc and ac voltage to the primary charging roller
and to the developing roller. This circuit also applies a positive or negative dc voltage to the transfer
roller according to the instructions from the engine control unit.
This circuit also controls the image density by changing the primary ac voltage and the developing ac
bias according to the print density setting. See
Setting media types on page 21.
The high-voltage power supply is disabled when the print-cartridge door is open.
To change the print density, open the Printer Properties dialog box, Select the Configure tab. Use the
slide bar in the Print Density area of the dialog box to change the print density setting. Click OK to
close the Printer Properties dialog box.
48 Chapter 4 Operational overview ENWW
Page 60

Engine controller PCB
Power supply PCB
IC902
CPU
PRPWM
J201-14J902-12
PRAC
J201-15J902-11
DVAC
J201-16J902-10
High-voltagepowersupply circuit
Primary chargingbias circuit
IC301
IC301IC301
Developing bias circuit
IC301
DC voltage
generation
circuit
Combined
AC voltage
generation
circuit
DC voltage
generation
circuit
Combined
AC voltage
generation
circuit
PR1
DEV
charging roller
J304
Photosensitive
J303
J301
Primary
drum
Developing
cylinder
TRPDC
J201-18J902-8
TRNDC
J201-17J902-9
TRCRNT
J201-22J902-4
Transfer charging bias circuit
Positive voltage
generation circuit
Negative voltage
IC501
generation circuit
TRS
J302
Transfer
charging roller
Figure 4-4 High-voltage power supply circuit
Image-formation system
Laser printing requires the interaction of several different technologies, including electronics, optics, and
electrophotographic, to provide a printed page. Each process functions independently and must be
coordinated with the other printer processes. Image formation consists of seven processes, which are
described in the following section.
ENWW Printer operation 49
Page 61

The seven image-formation processes
Paper direction
Direction of drum rotation
Paper delivery
Fusing stage
1. Primary charging
7. Drum cleaning
6. Fusing
2. Scanning exposure
4. Transfer5. Separation
Transfer stage
3. Developing
Developing stage
Paper Pickup
Figure 4-5 Image-formation block diagram
1 Conditioning stage (primary charging)—This process applies a uniform negative charge to the
surface of the drum with the primary charging roller, which is located in the print cartridge. The
primary charging roller is coated with conductive rubber. An ac bias is applied to the roller to erase
any residual charges from any previous image. In addition, the primary charging roller applies a
negative dc bias to create a uniform negative potential on the drum surface. The print density setting
modifies the dc voltage.
2 Writing stage (scanning exposure)—During this process, a modulated laser diode projects the
beam onto a rotating scanning mirror. As the mirror rotates, the beam reflects off the mirror, first
through a set of focusing lenses, then off a mirror, and finally through a slot in the top of the print
cartridge, and onto the photosensitive drum. The beam sweeps the drum from left to right,
discharging the negative potential wherever the beam strikes the surface. This creates a latent
electrostatic image, which later is developed into a visible image. Because the beam sweeps the
entire length of the drum while the drum rotates, the entire surface area of the drum can be covered.
At the end of each sweep, the beam strikes the beam-detect lens, generating the beam-detect signal
(BD signal). The BD signal is sent to the ECU where it is converted to an electrical signal used to
synchronize the output of the next scan line of data.
3 Developing stage—During this process, the latent electrostatic image is present on the drum. The
toner particles obtain a negative surface charge by rubbing against the developing cylinder, which
is connected to a negative dc supply. The negatively charged toner is attracted to the discharged
(exposed, grounded) areas of the drum, and it is repelled from the negatively charged (unexposed)
areas.
4 Transfer stage—During this process, the toner image on the drum surface is transferred to the
media. The transfer roller applies a positive charge to the back of the media, which attracts the
negatively charged toner on the drum surface to the media. After separation, the drum is cleaned
and conditioned for the next image.
5 Separation stage—During this process, the media separates from the drum. To stabilize the feed
system and prevent toner dropouts on the printed image at low temperature and humidity, the static
eliminator reduces the charge on the back of the media.
50 Chapter 4 Operational overview ENWW
Page 62

6 Fusing stage—During this process, the heat and pressure fuse the toner into the media to produce
a permanent image. The media passes between a heated fusing element and a soft pressure roller,
which melt the toner and press it into the media.
7 Drum-cleaning stage—During this process, the cleaning blade is in contact with the surface of the
drum at all times. As the drum rotates during printing, the cleaning blade wipes excess toner off the
drum and stores it in the waste toner receptacle.
Print cartridge
As the focal point of the image-formation system, the print cartridge contains toner and houses the
cleaning, conditioning, and developing stages of the process. The print cartridge contains the
photosensitive drum, primary charging roller, developing station, toner cavity, and cleaning station. By
including these components (which wear, degrade, or are consumed) in the replaceable print cartridge,
the need for many service calls is eliminated. The special photosensitive properties of the drum form
an image on the drum surface and then transfer the image to media.
CAUTION The print cartridge does not include a light-blocking shutter. Do not expose the drum
to light, which can permanently damage the drum. Protect the print cartridge whenever you
remove it by covering it with paper.
Printer-paper feed system
The main input tray and the priority feed slot merge into one main input area. The printer senses the
media as it enters the paper-feed path and passes the top of page sensor (PS801). It does not sense
the presence of media before the beginning the print cycle. The following steps occur when the product
receives a print job.
Step 1 The ECU activates the motor (M1). Paper motion begins when the ECU energizes the pickup
solenoid (SL1).
Step 2 The paper pickup roller rotates once. The paper-lift plate pushes the media against the pickup roller.
Step 3 Using friction, the pickup roller grabs the top sheet and advances it to the feed-assembly drive-rollers.
To ensure that only one sheet is fed, a main separation pad holds the remainder of the stack in place.
Step 4 The feed-assembly drive-rollers advance the media to the top-of-page sensor (PS801). This sensor
Step 5 The feed-assembly drive-rollers then advance the media to the transfer area where the toner image
Step 6 After the image is transferred, the media enters the fuser assembly where heat from the fuser and
Step 7 The fuser-assembly exit rollers deliver media to the output bin face-down.
informs the ECU of the exact location of the leading edge of media, so that the image being written
on the photosensitive drum can be precisely positioned on the page.
on the photosensitive drum is transferred to the media.
pressure from the pressure roller permanently bond the toner image to media. The paper-delivery
sensor (PS803) determines that the media has successfully moved out of the fusing area.
ENWW Printer operation 51
Page 63

BD OUTPUT signal (/BD)
P SOLENOID DRIVE signal (CPUD)
PICKU
Formatter
DETECTION sigunal (/PW2SNS)
FUSER DELIVERY PAPER WIDTH
PS804
Engine controller PCB
(/POSNS)
PAPER DELIVERY DETECTION signal
Face-down delivery
roller
MAIN MOTOR DRIVE signals
OF-PAGE-DETECTION signal (/PISNS)
P-
TO
PAPER WIDTH DETECTION signal (/PWSNS)
PS803
Transfer
charging
roller
SL1
Separation
pad
Fuser pressure
roller
Fuser film unit
Photosensitive
drum
PS801
PS802
Pick-up roller
PS801: Top-of-page sensor
PS802: Paper width sensor
PS803: Paper delivery sensor
-
-
PS804: Fuser delivery paper width sensor
M1: Main motor
SL1: Pickup solenoid
M1
Manual feed tray
Pickup tray
Figure 4-6 Printer paper path
52 Chapter 4 Operational overview ENWW
Page 64

Jam detection
The top-of-page sensor (PS801) and the paper-delivery sensor (PS803) detect media moving through
the printer. If a jam is detected, the ECU immediately stops the printing process and the jam light on the
control panel illuminates.
Conditions of jam detection
■ Pickup-delay jam—Paper does not reach the top-of-page sensor (PS801) within 1.4 seconds after
the pickup solenoid (SL1) has been turned on, a second pickup operation is attempted, and paper
again does not reach the top-of-page sensor within 1.4 seconds.
■ Pickup stationary jam—The top-of-page sensor (PS801) does not detect the trailing edge of media
within 4.6 seconds of detecting the leading edge.
■ Delivery-delay jam—The paper-delivery sensor (PS803) does not detect the leading edge of media
within 2.1 seconds after the top-of-page sensor (PS801) detects the leading edge.
■ Wrapping jam—The paper-delivery sensor (PS803) does not detect the trailing edge of the media
within 1.5 seconds after the top-of-page sensor (PS801) detects the leading edge and within ten
seconds after the paper-delivery sensor (PS803) detects the leading edge.
■ Delivery-stationary jam—The paper delivery sensor (PS803) does not detect the leading edge of
media within 2.2 seconds after the top-of-page sensor (PS801) detects the trailing edge.
■ Residual media jam—The top-of-page sensor (PS801) or the paper-delivery sensor (PS803)
detects media during the initial rotation period.
■ Door-open jam—The top-of-page sensor (PS801) or the paper-delivery sensor (PS803) detect
media while the print cartridge door is open.
ENWW Printer operation 53
Page 65

Solenoid, sensors, switches, and motor
The following figure shows the locations of the solenoid, sensors, switches, and motor.
Figure 4-7 Solenoid, sensors, switches, and motor
1 The door switch detects whether or not the print-cartridge door is closed. Printing cannot continue until the print-cartridge
door is closed.
2 Power switch
3 The paper-width sensor senses the width of the paper.
4 The paper-delivery sensor senses when paper has successfully moved out of the fusing area.
5 Top-of-page sensor detects the leading and trailing edges of the paper. It synchronizes the photosensitive drum and the
top of the paper.
6 Fuser delivery paper-width sensor
7 Motor
8 Solenoid
54 Chapter 4 Operational overview ENWW
Page 66

Basic sequence of operation (formatter-to-printer)
The microprocessor (CPU) on the ECU controls the printer operation sequence. The following events
take place during normal printer operation.
Table 4-1 Basic sequence of operation
Period Purpose Remarks
WAIT: After the product is turned on until
the end of the initial rotation of the main
motor.
STBY (Standby): From the end of the
WAIT period or the LSTR period until the
pickup command is sent from the
formatter. Or, from the end of the LSTR
period until the product is turned off.
INTR (Initial Rotation Period): After the
pickup command has been sent from the
formatter until the media reaches the topof-page sensor (PS801).
PRINT (Print): From the end of the initial
rotation until the primary voltage goes
OFF.
LSTR (Last Rotation Period): After the
primary voltage goes OFF until the main
motor stops rotating.
To clear the drum surface of potential
and to clean the primary charging roller.
To pause until the product is ready to
print.
To stabilize the photosensitive drum
sensitivity in preparation for printing, and
to clean the primary charging roller.
To form images on the photosensitive
drum based on the VIDEO signals (/
VDO, VDO) sent from the formatter and
to transfer the toner image onto the
media.
To deliver the last page, and to clean the
primary charging roller.
Detects whether or not the cartridge is
installed.
When the pickup command is sent from
the video controller, the printer enters the
INTR period immediately after the end of
the LSTR period.
ENWW Printer operation 55
Page 67

Figure 4-8 Printer timing diagram
NOTE The timing chart is for one sheet of A4-size media.
56 Chapter 4 Operational overview ENWW
Page 68

5 Removal and replacement
This chapter describes the removal and replacement of field-replaceable units (FRUs) only.
●
Removal and replacement strategy
●
User-replaceable parts
●
Covers
●
Internal assemblies
ENWW 57
Page 69

Removal and replacement strategy
This chapter contains detailed steps and images that show parts removal. Replacement is generally the
reverse of removal. Occasionally, notes are included to provide directions for difficult or critical
replacement procedures.
WARNING! Remove the power cord before attempting to service the product. If this warning is
not followed, severe injury can result, as well as damage to the device. Certain functional checks
during troubleshooting must be performed with power supplied to the product. However, the
power supply should be disconnected during removal of any parts.
Sheet metal and plastic edges in the product can be sharp. Use caution when working on the
product.
Never operate or service the printer with the protective cover removed from the laser/scanner
assembly. The reflected beam, although invisible, can damage your eyes.
CAUTION Some parts are sensitive to electrostatic discharge (ESD). Always perform service
work at an ESD-protected workstation. If an ESD workstation is not available, ground yourself by
touching the sheet-metal chassis before touching an ESD-sensitive part.
NOTE To install a self-tapping screw, first turn it counterclockwise to align it with the existing
thread pattern, and then carefully turn it clockwise to tighten. Do not overtighten. If a self-tapping
screw-hole becomes stripped, repair the screw-hole or replace the affected assembly.
Required tools
■ #2 Phillips screwdriver with magnetic tip
■ Small flat-blade screwdriver
■ Needle-nose pliers
■ ESD mat (if one is available)
CAUTION Do not use a pozidrive screwdriver or any motorized screwdriver. These can damage
screws or screw threads on the product.
CAUTION Do not pull directly on the wires when a connector is disconnected. Always pull on
the plastic body of a connector to avoid damaging the connector wires.
Before performing service
■ Remove all media.
■ Unplug the power cable.
■ Place the product on an ESD mat (if available).
■ Remove the input-tray cover.
■ Remove the print cartridge.
58 Chapter 5 Removal and replacement ENWW
Page 70

Print cartridge
1 Open the print-cartridge door on the top of the printer.
2 Remove the print cartridge.
CAUTION To prevent damage, do not expose the print cartridge to light. Cover it with a piece
of paper.
Figure 5-1 Removing the print cartridge
ENWW Removal and replacement strategy 59
Page 71

Parts removal order
Use the following illustration to determine which parts must be removed before removing other parts.
START
Transfer-roller
assembly
Right-side cover
Front-cover
assembly
ECU assembly
Laser/scanner
assembly
Figure 5-2 Parts-removal block diagram
Left-side cover
Rear-panel
assembly
Engine-power
assembly
Fuser (fixing)
assembly
Paper-pickup
assembly
User-replaceable parts:
Output bin
Main input tray
Pickup roller
60 Chapter 5 Removal and replacement ENWW
Page 72

User-replaceable parts
To order a new pickup roller or separation pad, go to www.partsdirect.hp.com.
Replacing the pickup roller
If the printer regularly misfeeds (no media feeds through) and cleaning the pickup roller does not fix the
problem, replace the pickup roller.
CAUTION Failure to complete all of the steps in this procedure might damage the product.
1 Turn off the printer, unplug and remove the power cord. Wait for the printer to cool.
2 Open the print-cartridge door, and remove the print cartridge.
ENWW User-replaceable parts 61
Page 73

3 Locate the pickup roller.
4 Gently release the small, white tabs on each side of the pickup roller by pushing them away from
the roller, and then rotate the pickup roller toward the front.
CAUTION Use gentle pressure to release the small, white tabs to avoid breaking them.
5 Gently pull the pickup roller up and out.
6 Position the new pickup roller in the slot of the previous pickup roller.
NOTE Circular and rectangular pegs on each side prevent you from incorrectly positioning
the pickup roller.
62 Chapter 5 Removal and replacement ENWW
Page 74

7 Rotate the top of the new pickup roller into position until the white tabs on each side of the roller
snap the roller into place.
8 Reinstall the print cartridge and close the print cartridge door.
9 Plug in the printer, and then turn it on.
ENWW User-replaceable parts 63
Page 75

Replacing the separation pad
If the printer grabs more than one page at a time, you might have to replace the printer separation pad.
Recurring feed problems indicate that the separation pad is worn.
Normal use with good-quality media causes wear. The use of poor media might require more frequent
replacement of the separation pad.
NOTE Before you change the separation pad, clean the pickup roller. See Cleaning the pickup
roller on page 29 for instructions. To order parts, go to www.partsdirect.hp.com.
1 Turn off the printer, unplug and remove the power cord. Wait for the printer to cool.
2 At the back of the printer, use a #2 Phillips screwdriver to unscrew the two screws that hold the
separation pad in place.
64 Chapter 5 Removal and replacement ENWW
Page 76

3 Remove the separation pad.
4 Insert the new separation pad, and screw it in place.
5 Plug the printer in, and then turn it on.
ENWW User-replaceable parts 65
Page 77

Replacing the main input tray (paper-pickup tray assembly)
If you break or damage the main input tray (also called the paper-pickup tray assembly), you can replace
it.
1 Carefully flex the main input tray just enough to release one side.
NOTE Be careful not to break the hinge points.
1
3
2
Figure 5-3 Remove the main input tray
2 Remove the main input tray.
66 Chapter 5 Removal and replacement ENWW
Page 78

Replacing the output-bin extension (delivery-tray assembly)
If you break or damage the output-bin extension (also called the delivery-tray assembly), you can replace
it. To order parts, go to
1 Carefully flex the output-bin extension just enough to release the hinge pins.
NOTE Be careful not to break the hinge pins (callout 1).
www.partsdirect.hp.com.
1
Figure 5-4 Output-bin extension
2 Remove the output-bin extension.
ENWW User-replaceable parts 67
Page 79

Covers
Remove the covers to access the internal replaceable parts.
Right-side cover
1 Before removing the cover, examine Figure 5-5 Remove the right-side cover (1 of 4)
on page 68 and note the location of tabs on the cover.
Figure 5-5 Remove the right-side cover (1 of 4)
2 Remove one screw (callout 1) and then release one tab (callout 2)
1
2
Figure 5-6 Remove the right-side cover (2 of 4)
68 Chapter 5 Removal and replacement ENWW
Page 80

3 Open the print-cartridge door. Grasp the cover, and carefully pry up on the cover to release one tab.
Figure 5-7 Remove the right-side cover (3 of 4)
4 Slightly rotate the back of the cover away from the product, and then slide the cover forward to
remove it.
NOTE If the cover cannot be removed easily, release one additional tab that is located on
the bottom of the printer near the center of the cover.
Figure 5-8 Remove the right-side cover (4 of 4)
1
2
ENWW Covers 69
Page 81

Left-side cover
Removing the left-side cover is similar to removing the right-side cover. Use the steps and figures for
removing the right-side cover, except start the procedure by examining the tabs on the left side and
removing the screw on the left side.
NOTE If the cover cannot be removed easily, release one additional tab that is located on the
bottom of the printer near the center of the cover.
Rear panel and top-cover assembly
NOTE This procedure removes the rear panel and the top-cover assembly (the assembly
consists of the print-cartridge door and the fuser cover).
1 Remove the following assemblies.
● Right-side cover. See
● Left-side cover. See
2 Open the print-cartridge door.
3 Remove one screw (callout 1).
Right-side cover on page 68.
Left-side cover on page 70.
Figure 5-9 Remove the rear panel and top-cover assembly (1 of 6)
70 Chapter 5 Removal and replacement ENWW
Page 82

4 Squeeze the two retaining tabs on the plastic door-link clip to release it from the hinge arm on the
print-cartridge door.
Figure 5-10 Remove the rear panel and top-cover assembly (2 of 6)
Hint Reinsert the plastic door-link clip in the hinge arm or store it with the screws to prevent
losing it.
Figure 5-11 Remove the rear panel and top-cover assembly (3 of 6)
ENWW Covers 71
Page 83

5 Remove one screw (callout 1) from the back of the product.
2
Figure 5-12 Remove the rear panel and top-cover assembly (4 of 6)
6 The top-cover assembly and metal rear panel are interlocked with plastic tabs. Plastic tabs also
secure the metal rear panel at the bottom. Lift up the top cover assembly at the top and pull it back
slightly. Lift the rear panel up off the tabs on the bottom.
Figure 5-13 Remove the rear panel and top-cover assembly (5 of 6)
72 Chapter 5 Removal and replacement ENWW
Page 84

7 Lift up on the top-cover assembly to remove it.
Hint When the cover is reinstalled, make sure that the tab on the left side of the assembly
is fitted into the slot in the printer chassis.
Figure 5-14 Remove the rear panel and top-cover assembly (6 of 6)
Reinstalling the top-cover assembly
1 To reinstall the top-cover assembly, raise the two pressure-release levers.
Figure 5-15 Reinstall the top-cover assembly (1 of 2)
ENWW Covers 73
Page 85

2 Position the top-cover assembly over the pressure-release levers (callout 1), and lower it onto the
chassis. Make sure that the pressure-release levers are inserted through the slots (callout 2) on the
top-cover assembly.
1
2
Figure 5-16 Reinstall the top-cover assembly (2 of 2)
CAUTION Make sure that the two plastic antistatic tabs are correctly positioned. The tabs
must protrude into the output bin area.
74 Chapter 5 Removal and replacement ENWW
Page 86

Front cover
1 Remove the following assemblies.
● Right-side cover. See
● Left-side cover. See
2 Before removing the cover, examine
and note the locations of the plastic tabs at the top of the front cover. Open the print-cartridge door.
Right-side cover on page 68.
Left-side cover on page 70.
Figure 5-17 Remove the front cover (1 of 3) on page 75
Figure 5-17 Remove the front cover (1 of 3)
ENWW Covers 75
Page 87

3 Release the tab on the bottom right side of the front cover, and then pull the bottom of the cover
away from the chassis. Repeat this step for the left side of the front cover.
2
Figure 5-18 Remove the front cover (2 of 3)
4 With the bottom of the front cover released, pull up and back at the top of the cover while gently
rocking it to release all of the tabs at the top and remove the cover.
1
Figure 5-19 Remove the front cover (3 of 3)
Hint When reinstalling the front cover, make sure the tabs on the top of the cover are
securely in place, and then press the bottom of the cover into place.
76 Chapter 5 Removal and replacement ENWW
Page 88

Internal assemblies
When replacing internal assemblies, make sure to transfer any component parts that are not provided
with the new assembly from the failed assembly to the new assembly. For example, sensor PCBs are
not included with the fuser assembly or the paper-pickup assembly. The sensor PCB from the failed
assembly must be transferred to the new assembly
Transfer-roller assembly
Before proceeding, make sure it is absolutely necessary to remove the transfer roller.
CAUTION Be very careful not to break the paper guide that is removed during replacement of
the transfer roller. This is not a service part. If the paper guide is broken, the entire printer must
be replaced.
CAUTION Do not touch the black-sponge portion of the transfer roller. Skin oils and finger prints
can cause print-quality problems.
1 Open the print-cartridge door, and then release the two tabs on the paper guide and rotate it up.
Figure 5-20 Remove the transfer roller (1 of 3)
ENWW Internal assemblies 77
Page 89

2 The clamps on the paper guide fit over the bearings on each end of the transfer roller. Do not touch
the black-sponge portion of the transfer roller. Grasp the right end of the paper guide and pull the
clamp off the right bearing. Slide the paper guide slightly to the right, and the left clamp will slide off
the left bearing.
Figure 5-21 Remove the transfer roller (2 of 3)
3 Use needle-nose pliers or your fingers to squeeze the two small tabs on the transfer roller.
Figure 5-22 Remove the transfer roller (3 of 3)
4 Angle the transfer roller up while holding on to the gear on the right side. Slide the roller toward right
side of the printer, and lift both the transfer roller and the transfer-roller guide out of the printer.
78 Chapter 5 Removal and replacement ENWW
Page 90

Reinstallation tip A small grounding spring is under the right transfer-roller bearing. When
reinstalling the transfer roller, position this spring correctly under the right bearing. Reverse
the removal process to install the new transfer roller. Then reinstall the paper guide by gently
pressing the two ends of the guide onto the transfer-roller bearings until the clamps snap into
place. Rotate the paper guide down until the tabs on both ends engage.
ENWW Internal assemblies 79
Page 91

Engine-power assembly
1 Remove the following assemblies.
● Right-side cover. See
● Left-side cover. See
● Top-cover assembly. See
● Front cover. See
2 Disconnect the six cables (callout 1) near the top of the power assembly.
CAUTION Do not pull directly on the wires when a connector is disconnected. Always pull
on the plastic body of a connector to avoid damaging the connector wires.
3 Remove four screws (callout 2).
Right-side cover on page 68.
Left-side cover on page 70.
Rear panel and top-cover assembly on page 70.
Front cover on page 75.
1
Figure 5-23 Remove the engine-power assembly (1 of 2)
2
80 Chapter 5 Removal and replacement ENWW
Page 92

4 Remove two screws from the back of the printer (callout 3), disconnect the high-voltage wire (callout
4) and then remove the power supply.
NOTE Be careful not to lose the two springs that are behind the engine-power assembly.
4
3
Figure 5-24 Remove the engine-power assembly (2 of 2)
Reinstallation tip When reinstalling the engine-power assembly, make sure that the cable
guide is correctly installed by clipping it onto the PCB at the top, back corner and onto the
metal casing.
ENWW Internal assemblies 81
Page 93

Fuser (fixing) assembly
1 Remove the following assemblies.
● Right-side cover. See
● Left-side cover. See
● Top-cover assembly. See
2 Disconnect cables, as necessary, from near the top of the engine-power assembly and disconnect
the high-voltage wire (callout 1) from the back of the printer.
CAUTION Do not pull directly on the wires when a connector is disconnected. Always pull
on the plastic body of a connector to avoid damaging the connector wires.
Right-side cover on page 68.
Left-side cover on page 70.
Rear panel and top-cover assembly on page 70.
1
Figure 5-25 Remove the fuser (fixing) assembly (1 of 2)
3 Remove the wire harnesses from the plastic harness retainers.
82 Chapter 5 Removal and replacement ENWW
Page 94

4 Remove three screws (callout 2). (This figure shows the delivery-sensor PCB removed, but it is not
necessary to remove this PCB in order to remove the fuser).
2
Figure 5-26 Remove the fuser (fixing) assembly (2 of 2)
5 Lift the end of the fuser assembly from the right side of the printer, and then remove it.
Reinstallation tip When replacing the fuser assembly, be sure to transfer the delivery sensor
PCB from the old fuser to the new one.
NOTE When reinstalling the fuser assembly, be careful not to break the plastic tab on the
assembly.
ENWW Internal assemblies 83
Page 95

Paper-pickup assembly
1 Remove the following assemblies.
● Right-side cover. See
● Left-side cover. See
● Top-cover assembly. See
● Front cover. See
● Transfer-roller assembly. See
● Fuser (fixing) assembly. See
2 Disconnect and unwind any additional wires as necessary to release the paper-pickup assembly.
Unplug and unwind the wire from the solenoid to the formatter.
CAUTION Do not pull directly on the wires when a connector is disconnected. Always pull
on the plastic body of a connector to avoid damaging the connector wires.
3 Remove six screws (callout 1), and then remove the paper-pickup assembly.
Right-side cover on page 68.
Left-side cover on page 70.
Rear panel and top-cover assembly on page 70.
Front cover on page 75.
Transfer-roller assembly on page 77.
Fuser (fixing) assembly on page 82.
1
Figure 5-27 Remove the paper pickup assembly
Reinstallation tip When replacing the paper-pickup assembly, be sure to transfer the
sensor PCB and, if necessary, the separation-pad assembly to the new paper-pickup
assembly.
84 Chapter 5 Removal and replacement ENWW
Page 96

Engine control unit (ECU) assembly
1 Remove the following assemblies.
● Right-side cover. See
● Left-side cover. See
● Top-cover assembly. See
● Front cover. See
2 Disconnect the flat flexible (ribbon) cable (callout 1) from the formatter, which is on the right side of
the product.
Right-side cover on page 68.
Left-side cover on page 70.
Rear panel and top-cover assembly on page 70.
Front cover on page 75.
1
Figure 5-28 Remove the ECU assembly (1 of 6)
ENWW Internal assemblies 85
Page 97

3 Disconnect the flat flexible (ribbon) cable (callout 2) from the engine-power assembly.
Figure 5-29 Remove the ECU assembly (2 of 6)
4 Remove four screws (callout 3).
3
Figure 5-30 Remove the ECU assembly (3 of 6)
5 Lift the ECU cover up just enough to free it, and then tilt it back as far as it will go without forcing it.
86 Chapter 5 Removal and replacement ENWW
Page 98

6 Two sheet-metal hook hinges (one on each side) secure the cover. Use a screwdriver to push both
hooks free, and then remove the ECU cover.
2
1
Figure 5-31 Remove the ECU assembly (4 of 6)
7 Release the plastic wire-retainer tab (arrow 1), and rotate the retainer up and away from the chassis
(arrow 2).
2
1
Figure 5-32 Remove the ECU assembly (5 of 6)
ENWW Internal assemblies 87
Page 99

8 Disconnect one flat flexible (ribbon) cable and the connector to the step motor (callout 4). Remove
two screws (callout 5). Loosen the tape (callout 6) that secures the cable to the chassis. As you
remove the ECU, unplug the additional connector to the laser/scanner assembly.
CAUTION Do not pull directly on the wires when a connector is disconnected. Always pull
on the plastic body of a connector to avoid damaging the connector wires.
4
5
6
Figure 5-33 Remove the ECU assembly (6 of 6)
Reinstallation tip When reinstalling the ECU metal casing, make sure that the laser/
scanner shutter lever is inserted correctly through the plastic guide.
88 Chapter 5 Removal and replacement ENWW
Page 100

Laser/scanner assembly
1 Remove the following assemblies.
● Right-side cover. See
● Left-side cover. See
● Top-cover assembly. See
● Front-cover. See
● Engine control unit assembly. See
2 Remove four screws (callout 1) and then remove the laser/scanner assembly.
Right-side cover on page 68.
Left-side cover on page 70.
Rear panel and top-cover assembly on page 70.
Front cover on page 75.
Engine control unit (ECU) assembly on page 85.
1
Figure 5-34 Removing the laser/scanner assembly
Reinstallation tip When replacing the laser/scanner assembly, be sure to transfer the laser
shutter arm from the old assembly to the new one.
ENWW Internal assemblies 89
 Loading...
Loading...