Fluke 113, 175, 177, 179 RMS, 289 Brochure
...
Fluke Digital Multimeters
Solutions for every need
How to choose the best DMM for your job
Choosing the right digital multimeter (DMM) requires thinking about what you’ll be using it for. Evaluate your basic measurement needs and job requirements and then take a look at special features/functions built into many multimeters. Think about whether you need to do basic measurements, or if you need the more advanced troubleshooting options offered by special features.
Factors to consider:
•Your work environment (voltage level, types of equipment, types of measurements, applications)
•Specialty features/functions (capacitance, frequency, temperature, non-contact voltage, low impedance mode, min-max record, data logging, trending)
•Resolution and accuracy (6,000, 20,000, or 50,000 count resolution)
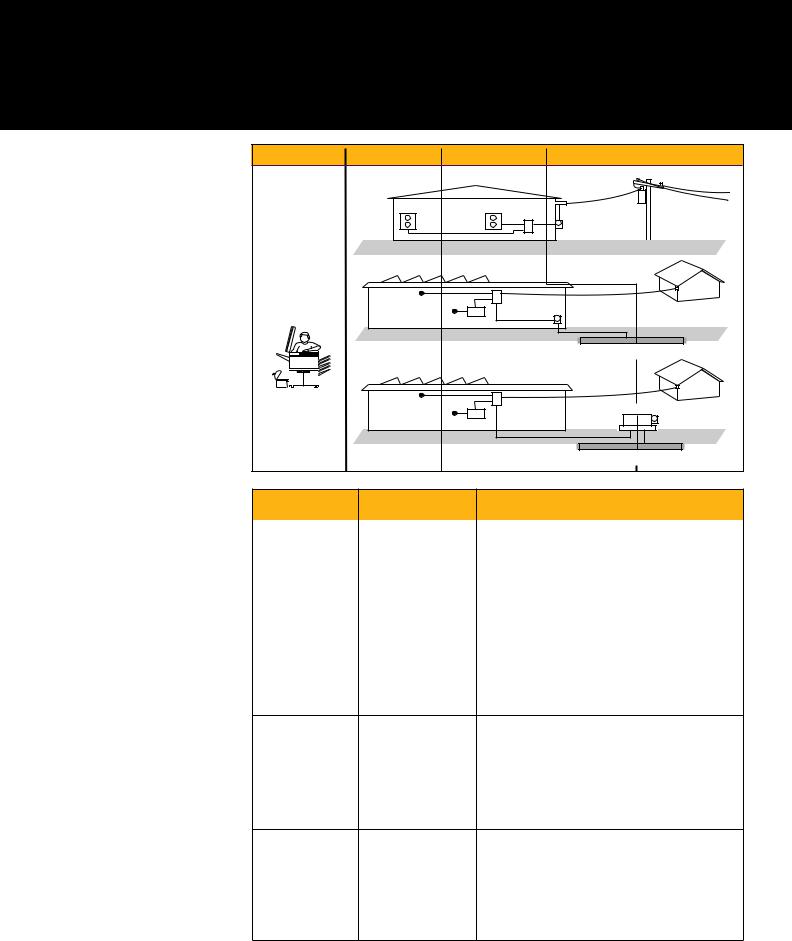
Safety
The increased occurrence and levels of transient overvoltages in today’s power systems have given rise to more stringent safety standards for electrical measurement equipment. Transients that ride on top of power sources (mains, feeder or branch circuits) can trigger a sequence of events that may lead to serious injury. Test equipment must be designed to protect people working in this high-voltage, high-current
environment.
CAT 0 |
CAT II |
CAT III |
CAT IV |
|
|
|
Service |
|
|
|
|
Entrance |
Meter |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Service |
|
Outbuilding |
|
|
Entrance |
Meter |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Underground Service |
|
|
|
Service |
Transformer |
Outbuilding |
|
|
Entrance |
Meter |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Underground Service |
|
Measurement |
In brief |
Examples |
category |
|
|
CAT 0 |
Electronic (Not directly |
•• Protected electronic equipment |
|
connected to mains) |
•• Equipment connected to (source) circuits in which |
|
|
measures are taken to limit transient overvoltages to |
|
|
an appropriately low level |
|
|
•• Any high-voltage, low-energy source derived from |
|
|
a high-winding resistance transformer, such as the |
|
|
high-voltage section of a copier |
CAT II |
Appliances, PCs, |
• Appliance, portable tools, and other household |
|
and TVs |
and similar loads |
•Outlet and long branch circuits
•Outlets at more than 10 meters (30 feet) from CAT III source
•Outlets more than 20 meters (60 feet) from CAT IV source
CAT III |
MC panels, etc. |
• Equipment in fixed installations, such as switchgear |
|
|
and polyphase motors |
•Bus and feeder in industrial plants
•Feeders and short branch circuits, distribution panel devices
•Lighting systems in larger buildings
•Heavy appliance outlets with short connections to service entrance
CAT IV |
Three-phase at utility |
• |
Refers to the “origin of installation,” i.e., where low- |
|
connection, any |
|
voltage connection is made to utility power |
|
outdoor conductors |
• |
Electricity meters, primary overcurrent protection |
|
|
|
equipment |
•Outside and service entrance, service drop from pole to building, run between meter and panel
•Overhead line to detached building, underground line to well pump
 Loading...
Loading...