Page 1

Troubleshooting Guide
Lightning Series
TRTS0580
January 2008
FRLO-14410C-T2
FRLO-15410C
FRLO-15410C-T2
FRLO-16410C
FRLO-16410C-T2
FRLOF-14410C
FRLOF-14410C-T2
FRLOF-15410C
FRLOF-15410C-T2
FRLOF-16410C
FRLOF-16410C-T2
Page 2

For parts or service call us
Pro Gear & Transmission, Inc.
1 (877) 776-4600
(407) 872-1901
parts@eprogear.com
906 W. Gore St.
Orlando, FL 32805
Page 3

General Warnings
General Warnings
Before starting a vehicle:
1. Sit in driver’s seat
2. Place shift lever in neutral
3. Set the parking brake
working on a vehicle or leaving the cab with engine run-
Before
g:
nin
1. Place shift lever in neutral
2. Set parking brake
3. Block wheels
not release the parking brake or attempt to select a gear un-
Do
the air pressure is at the correct level.
til
parking the vehicle or leaving the cab:
When
1. Place shift lever in neutral
2. Set the parking brake
not operate if alternator lamp is lit or if gauges indicate low
Do
.
voltage
Suggested Tools
• Volt/Ohm Meter
SPX
/ Kent-Moore 1 (800) 328-6657
P/N
5505027
• PC-based Service Tool “ServiceRanger”
Contac
t your OEM
• Data Link Tester
Ea
ton Service Parts 1 (800) 826-4357
P/N MF-KIT-04
• Eaton Test Adapter Kit
SPX
/ Kent-Moore 1 (800) 328-6657
P/N J-43318
• 6-Pin Deutsch Diagnostic Adapter
/ Kent-Moore 1 (800) 328-6657
SPX
P/N
J-38500-60A
Related Publications
• TRIG-0580 - Lightning Installation Guide
• TRDR-0580 - Lightning Driver Instructions
• TRSM-0580 - Lightning Service Manual
more information call 1-800-826-HELP (4357) or visit
For
Roadranger.com.
www.
Page 4

Table of Contents
Section 1: Basic Troubleshooting
Diagnostic Procedure for Lightning Models .............1-2
Operational Check List .............................................1-3
Basic System Troubleshooting ................................. 1-4
What To Do If The Transmission
Is Not Operating Properly ................................1-5
Retrieving Fault Information .....................................1-6
Fault Code Table for Lightning Transmission ...........1-7
Symptom Complaints ...............................................1-8
Air System Troubleshooting
Vehicle Air Supply Requirement .............................1-12
Air System - Overview ............................................1-13
Air System - ECU ...................................................1-14
Air System - Splitter Subsystem ............................1-15
Air System - Range Subsystem ..............................1-16
Clutch Housing Breather Leak Overview ................1-18
Clutch Housing Breather Leak ................................1-19
Transmission ECU Breather Leak Overview ............1-20
Transmission ECU Breather Leak ...........................1-21
Range Cylinder Test Overview ................................1-22
Range Cylinder Test ...............................................1-23
Splitter Cylinder Test Overview ..............................1-26
Splitter Cylinder Test ..............................................1-27
Electronic System Troubleshooting
Electrical System Requirements .............................1-30
Wiring Diagram ......................................................1-31
Pinouts ...................................................................1-32
Power-Up Sequence Test Overview .......................1-34
Power-up Sequence Test .......................................1-35
Electrical Pretest Overview .....................................1-38
Electrical Pretest ....................................................1-39
Shift Knob Test- No Fault Codes Overview .............1-42
Shift Knob Test- No Fault Codes ............................1-43
J-1587 Data Link Test Overview .............................1-46
J-1587 Data Link Test ............................................1-47
Section 2: Fault Isolation Procedures
Component Code 11(SID 254, FMI 12)
Transmission ECU ............................................ 2-1
Component Code 33 (PID 158 or 168, FMI 3 or 4)
System Voltage Fault ........................................ 2-3
Component Code 35 (SID 231, FMI 2)
J-1939 Data Link Test ...................................... 2-5
Component Code 36 (SID 48 or 49, FMI 2)
Position Sensor Test ...................................... 2-13
Component Code 43 (SID 36, FMI 4, 5, 6)
Low Range Solenoid ...................................... 2-15
Component Code 46 (SID 37, FMI 4, 5, 6)
Splitter Solenoid ............................................. 2-17
Component Code 48 (SID 35, FMI 4, 5, 6)
High Range Solenoid ...................................... 2-19
Component Code 58 (PID 191, FMI 2)
Output Shaft Speed Sensor ............................ 2-21
System Code 66 (SID 58, FMI 1)
Unconfirmed Torque Path .............................. 2-25
System Code 71 (SID 61, FMI 7)
Range or Splitter Stuck in Gear ...................... 2-29
Component Code 73 (SID 58, FMI 11)
Transmission Missed Synchronous ............... 2-31
System Code 74 (SID 14, FMI 7)
Engine Missed Synchronous .......................... 2-33
System Code 93 (SID 231, FMI 14)
J-1939 Engine Message Fault ......................... 2-33
Reverse Switch Test Overview ............................... 2-39
Reverse Switch Test .............................................. 2-40
Neutral Switch Test Overview ................................ 2-43
Neutral Switch Test ................................................ 2-44
Table of Contents
1-1
Page 5

Fault Isolation Procedures
Diagnostic Procedure for Lightning Models
Key On
Service light
comes on for a
few seconds
then turns off
Yes
Retrieve active
fault codes
Active Codes?
No
(Code 25)
Retrieve inactive
fault codes
No
Yes
- Perform vehicle electrical test
- Perform "No service light test"
- Solid service light? - Replace ECU
- Perform vehicle electrical test
- Follow troubleshooting guide
diagnostics for all Actives Codes
- Clear Inactive Codes/test drive &
confirm code(s) have not reset
1-2
Inactive
Codes?
No
(Code 25)
Symptom?
No
Test Complete
Yes
Yes
- Record & clear inactive fault codes
- Verify complaints / test drive
- If fault code is reset after clearing,
perform vehicle electrical test, and
following diagnostics for symptom
driven faults
- Perform vehicle electrical test
- Perform pneumatic test
- Isolate transmission / clutch issues
- Follow basic troubleshooting/symptom
driven diagnostic procedures
Page 6

Fault Isolation Procedures
Operational Check List
When operating properly, the lightning transmission will act in the following manner:
• Top-2 feature will not function with cruise control turned off.
• Service light flashes once at vehicle initial power up.
• Service light flickers at vehicle power down.
• Service light flashes continuously with an active fault code.
• Synchronizer will not trigger with key off.
• Synchronizer will not trigger in neutral with key on and vehicle stationary.
• Synchronizer will trigger with key on, vehicle stationary and lever moved into a high range gear.
• Synchronizer will not downshift into low range if lever is moved into a low range gear at too high of road speed.
• If started in a high range gear the vehicle accelerator pedal will be “dead”.
• If driver beats the range up-shift with lever movement to a high range gear the accelerator pedal is “dead” until synchronous is made.
• Splitter will not trigger with key off.
Fault Isolation Procedures
• Splitter will trigger with key on and in any lever position.
• Accelerator pedal is “dead” when splitter is up shifting if the driver attempts to accelerate before splitter synchronous is
made.
• Engine accelerates when splitter downshifts if the driver doesn’t control engine RPM for proper synchronous.
• Aggressive splitter shifts below 1100 engine RPMs and whenever the transmission has a fast deceleration of the output
shaft.
• Aggressive splitter shifts with clutch disengaged or foot resting on clutch pedal disengaging clutch switch.
• Aggressive splitter shifts with clutch switch wired improperly – check for engine brake and cruise control functionality.
1-3
Page 7
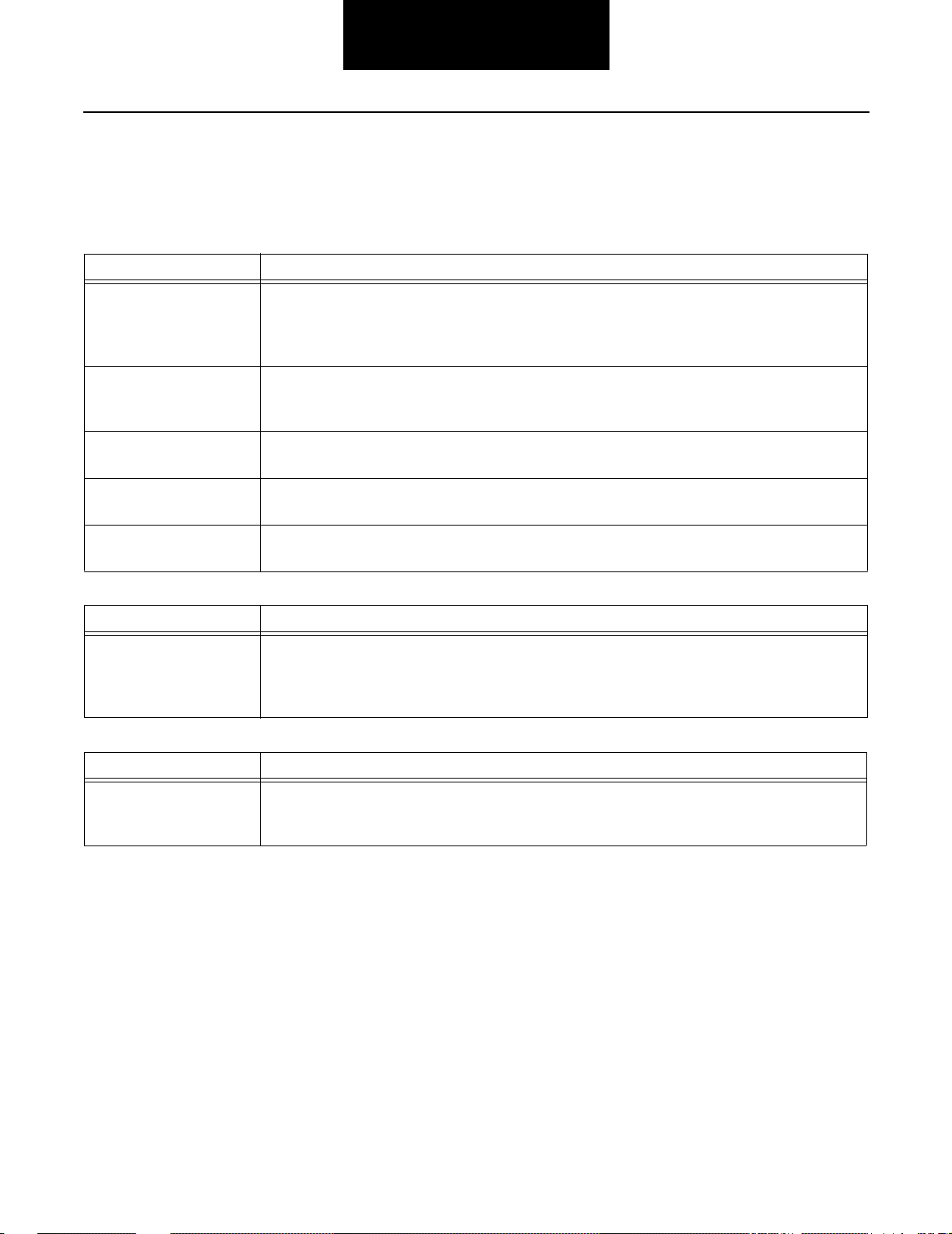
Fault Isolation Procedures
Basic System Troubleshooting
Following is information to help a vehicle operator start basic troubleshooting of the transmission system.This is not a complete
list. In many cases, the vehicle needs to be evaluated by a trained and experienced transmission technician.
Problem Possible Causes
Growl/Rattle in a “float” or
coast condition.
At idle Check for damaged or defective master clutch, master clutch release bearing, or clutch linkage,
Growl/Rattle on a “pull” Check for engine problem, which would result in noise or excessive vibration.Check master clutch
Lever Check for loose or damaged shift lever, which may vibrate and cause noise. Check for components
All other conditions Check for loose clutch housing bolts. Check transmission oil for excessive metal particles, which
Problem Possible Causes
Hard Lever Shifting Check for damaged or binding shift lever or shift control system.Check for lever interference with
Check for damaged, worn, or defective driveshaft, support bearing, or u-joints, which would result
in noise or vibration. Check for improper vehicle ride height, which would cause improper u-joint
operating angles. Check for axle problem, which would result in noise or vibration. Check for tire
problem, which would result in noise or vibration.
which would result in noise or vibration. Check for loose components, brackets, exhaust system,
and hoses in transmission area, which would result in noise or vibration.
for defects in dampening devices.
added to the shift lever; such as, cruise control, which may vibrate and cause noise.
may indicate internal problem. Check for damaged or worn gearing.
cab floor. Check for upper or lower shift boot tugging on shift lever. Check for a defective or damaged master clutch, which would result in clutch drag. Check for improper clutch brake engagement. Check that proper shifting procedures are followed.
Problem Possible Cause
Transmission is operating
at higher than normal temperature
1-4
If transmission is equipped with an internal cooler, check for pinched engine coolant hoses or
closed shut off valves. See section on Operating Temperatures with Coolers. Check oil level.
Page 8

Fault Isolation Procedures
What to Do if the Transmission is Not Operating Properly
If a problem occurs with the transmission or vehicle system, the transmission may not shift correctly. These effects may include:
• Harsh, slow, or grinding button only shifts.
• No button shifts (5 gear ratios only).
• No range shift (low range or high range gear ratios only).
The Service Light on the Shift Knob may be on continuously, may be flashing, or may not illuminate at all.
If the Transmission is Not Operating Properly, Try the Following Steps:
1. Check the dash air gauge to make sure at least 90 PSI is available in both primary and secondary air systems.
2. Try resetting the Transmission Electronic Control Unit (ECU) - See procedure below.
3. If vehicle and road conditions permit, you may be able to operate the transmission as a 5 speed (no button shifts).
Transmission Reset Procedure
In some cases, “resetting” the transmission Electronic Control Unit (ECU) can restore proper transmission operation. Use the following procedure to reset the ECU.
• When it is safe to do so, stop the vehicle.
• Place the transmission shift lever in neutral and turn the ignition key to the “off” position.
• Wait 5 seconds.
• Restart the engine.
• If the problem continues, proceed to page 9 and identify the symptom.
Transmission Diagnostics
The Lightning Series Transmission ECU has self-diagnostic capability. The transmission recognizes when a problem occurs and
“stores” the information about these problems (faults) in the ECU memory. This information can be retrieved by the following
methods:
• Retrieve basic fault information (flash codes) by counting flashes of the service light.
• Some OEM vehicles have an electronic dashboard, which displays fault information. Refer to the specific OEM chassis
operator instructions for the procedure.
• Connect an applicable hand-held or PC diagnostic tool to the vehicle’s SAE J-1587 diagnostic connector.
Fault Isolation Procedures
1-5
Page 9

Retrieving Fault Information
Fault Isolation Procedures
The transmission Electronic Control Unit (ECU) turns on the
service lamp, located on the shift knob, in the event the ECU
detects an electronic fault and at initial power-up. Once the
ECU has successfully powered-up, the ECU turns off the service lamp. The power-up sequence usually takes a few seconds. The service lamp remains on continuously if the ECU
execution malfunctioned at power-up. The ECU begins code diagnostics only after the ECU has successfully powered-up. The
service lamp flashes steadily if the ECU has detected an Active
fault code.
Note: Any Active code detected at vehicle start-up immediately
starts flashing the service light on the shift knob.
The service light provides access to diagnostic fault information, which has been logged in the transmission ECU. The service light flashes a sequence of on/off pulses, which can be
translated into specific “flash codes”. The flash codes can then
be used to identify a specific fault in the transmission system.
Transmission faults are classified as either Active (current
problem) or In-Active (non-current problem). An Active fault is
logged when the ECU recognizes a problem with the transmission. During an Active fault, the service light flashes steadily or
may stay on continuously. If during vehicle operation, the
problem corrects itself, the service light stops flashing and the
fault is logged as an In-Active fault.
Retrieving In-Active Fault Codes:
1. Use the procedure to retrieve Active fault codes except, turn the key off and on four (4) times within five
seconds ending with the key in the on position.
2. Observe the flash sequence of the service light on the
shift knob. A one or two second pause separates each
stored code, and the sequence automatically repeats
itself after flashing all codes.
Clearing Fault Codes:
The following procedure clears all In-Active fault codes from
the ECU’s memory.
1. Place the shift lever in neutral.
2. Set the parking brakes.
3. Turn the ignition key on but do not start the engine.
4. Start with the key in the on position. Turn the key off
and on six (6) times within five seconds ending with
the key in the on position. The service light will flash
on for 5 seconds confirming the codes are cleared.
Example of Flash Codes
How to Retrieve Fault Codes
Retrieve Lightning fault codes by enabling the Lightning system’s self-diagnostic mode.
Note: You can also use a P.C. based diagnostic tool such as
ServiceRanger to retrieve fault codes.
Retrieving Active Fault Codes:
1. Place the shift lever in neutral.
2. Set the parking brakes.
3. Turn the ignition key on but do not start the engine.
4. Starting with the key in the on position. Turn the key
off and on two (2) times within five seconds ending
with the key in the on position.
5. Observe the flash sequence of the service light on the
shift knob. Flash codes may take 5 seconds to begin
flashing. A one or two second pause separates each
stored code, and the sequence automatically repeats
itself after flashing all codes.
Fault Code 35 Fault Code 11
Short Pause Long Pause Short Pause
Service Light
1-6
Page 10

Fault Isolation Procedures
Fault Code Table for Lightning Transmission
Component Fault Codes*
Flash
Code
11 Transmission ECU 130 254 12
25 No Codes 130
33 Ignition/Battery Voltage Low or High 130 158 or 168 3 or 4
35 Engine to Transmission J1939
36 Shift Lever Position Sensor 130 48 or 49 2
43 Low Range Shift Solenoid 130 36 4, 5, or 6
46 Splitter Shift Solenoid 130 37 4, 5, or 6
48 High Range Shift Solenoid 130 35 4, 5, or 6
58 Output Speed Sensor 130 191 2
Description MID PID SID FMI
130 231 2
Communication Link
System Fault Codes **
Flash Code Description MID PID SID FMI
66 Unconfirmed Torque Path (Input speed and
output speed do not equal known gear ratio)
71 Splitter or Range Stuck in Gear 130 61 7
130 58 1
Fault Isolation Procedures
73 Transmission Missed Synchronization 130 58 11
74 Engine/Transmission Missed
Synchronization
93 J-1939 Engine Message Fault 130 231 14
*Component Fault Codes specifically isolate problems that may arise with the electronic components used in the Lightning series
transmissions. These codes occur at initial vehicle power-up if not induced by intermittent vibration or heat problems.
**System Fault Codes specifically isolate problems that may arise from a mechanical or pneumatic problem that has prevented
or missed a shift in the Lightning transmission. System fault codes are only active during vehicle operation and are not detected
at initial vehicle power-up.
Note: System fault codes also indicate problems with other components that affect the performance of the transmission such as
low air pressure. Troubleshoot the code properly to isolate the component causing the fault to become active.
130 14 7
# Hand Held Codes
MID – Message ID Assignment. In this case, MID 130 represents the transmission.
PID – Parameter ID Assignment. Generally represents a status or value.
SID – Subsystem ID Assignment. Identifies a failure in a subsystem.
FMI – Failure Mode ID. Describes the type of failure detected in the subsystem
1-7
Page 11

Fault Isolation Procedures
Symptom Complaints
Symptom Possible Condition Remedy Reference
No service light Electrical circuit is open,
grounded, or blown VIGN fuse
or faulty light
Service light on continuously Light circuit grounded to VBATT,
transmission performance not
affected
Transmission ECU internal failure;
3 speed operation only;
No splitter or range shifts
Top 2 option not functioning Cruise control turned off Turn on cruise control.
Top 2 option stops functioning
as a result of another problem
No button shifts after cruise control if turned off while in Top 2
mode
Hold Mode Normal Operation. Lever must be
No fault codes set. Performance of
transmission not affected by nonfunctioning light. Check fuse then if
necessary, perform service light
test.
Repair vehicle wiring harness.
Perform vehicle electrical test, if OK
- replace transmission ECU.
Repair for other faults such as Output Speed Sensor Position Sensor.
Look for other complaints such as
engine brake or cruise not functioning.
cycled through neutral to regain button function.
Harsh or aggressive splitter shifts ECU Malfunction Active Fault Code 11. page 1
Before proceeding, see note at
bottom of page.
(any shift using the splitter button) Engine Missed Synchronization Active Fault Code 74. page 33
Grinding or Raking Splitter Shifts Out-Of-Synchronous or shifts
(Shifts from 1st to 2nd, 3rd. to 4
th, 5th to 6th, 7 th to 8 th, and 9 th
to 10th. Shift grinds but engages.)
Position Sensor Malfunction Active Fault Code 36. page 13
Lever/Splitter shifts attempted in an
Engine Synchronous speed outof-limit of operating range
Low or high air pressure Faulty Air Regulator.
Splitter leak or partial blocked air
system
Driver resting foot on Clutch
Pedal so as to disengage clutch
switch but still has clutch engaged
out-of-synchronous condition. Re-
view Driver Instruction Book -
TRDR-0580 - for proper driving
techniques.
Perform Splitter Cylinder Test. page 26
Remove foot from clutch pedal ex-
cept when necessary to shift, start or
stop the vehicle.
1-8
Page 12

Fault Isolation Procedures
Symptom Possible Condition Remedy Reference
Clutch Switch Contamination
built up on switch, for example,
dirt, ice, etc. or Mechanical
Clutch Linkage
Note: Aggressive splitter shifts may occur normally under the following conditions.
1. Low speed splitter shifts below 1100 RPMs. - This is normal operation.
2. Splitter shifts on grades with heavily loaded vehicle. - This is normal operation.
3. Anytime the vehicle has a fast deceleration of the transmission output shaft. For example, making a hard left-hand turn
and moving the splitter at the same time. - This is normal operation.
Symptom Possible Condition Remedy Reference
Harsh shifts (Lever Only) Out-Of-Synchronous Shifts Lever shifts attempted in an out-of-
(Skip shifts. i.e. 1 st to 3 rd., or 3
rd. to 5 th.)
Clutch Drag Adjust Clutch and check for clutch
Clutch Brake Check for improper clutch brake en-
Cruise control and engine brake is
also inoperative when the clutch
switch malfunctions. Refer to OEM
manual for troubleshooting clutch
switch.
synchronous condition. Review Driver’s Instruction Book for proper techniques.
slippage and drag.
gagement.
Fault Isolation Procedures
Slow/grinding/raking or inoperative Range Shift (Shift from 6 th to
7 th or from 7 th to 6 th.)
Five speed transmission. (Only
Even or Odd Numbered Gears.)
Low or High Air Pressure Perform Range Cylinder Test. page 22
Air System Leaks
Reduced Air Flow
Damaged Mechanical parts internal to the transmission
ECU Malfunction Active Fault Code 11. page 1
Unconfirmed torque path
through transmission
Splitter stuck in gear Active Fault Code 71. page 29
Output Speed Sensor Malfunction
Splitter System Air Leak Perform Splitter Cylinder test. page 26
Shift Knob Malfunction No Active Fault Codes. Perform Shift
Active Fault Code 66. page 25
Review Air System Overview. page 13
Repair for damaged internal parts.
Perform Output Shaft Speed Sensor
test.
Knob test.
page 21
page 42
1-9
Page 13

Fault Isolation Procedures
Symptom Possible Condition Remedy Reference
Six speed transmission. (Only 1st
through 6th gears.)
Splitter Solenoid Short or Open Active Fault Code 46. Perform Sole-
noid test.
Loss of communication with
engine
Range system air leak Perform Range Cylinder test. page 22
Position sensor malfunction Active Fault Code 36. page 13
Low Range Solenoid Malfunction
High Range Solenoid Malfunction
Range stuck in gear. Active Fault Code 71. page 29
Transmission missed synchronous.
High Range Synchronizer Mechanical Failure
Active Fault Code 35 and gears 1, 3, 5,
7, 9. J-1939 communication link broken.
Active Fault Code 43. page 15
Active Fault Code 48. page 19
Active Fault Code 73. page 31
Perform Range Cylinder test prior to
disassembly, then replace damaged
synchronizer parts if required. Refer
to “Synchronizer” repair strategy item
TRSM-0915 (Note: after 12/31/04 this
publication will be TRMT-0001) for
repair details.
page 17
page 5
page 22
Four Speed Transmission. (Only 7
th through 10 th gears.)
Three Speed Transmission (Only
1 st, 3 rd., 5 th gears)
Low Range Solenoid Malfunction
Range System Air Leak Perform Range Cylinder test. page 22
High Range Solenoid Malfunction
Range stuck in gear. Active Fault Code 71. page 29
Low Range Synchronizer Mechanical Failure
Low System Voltage Active Fault Code 33. page 3
Loss of air pressure to transmission.
ECU Malfunction. Active Fault Code 11. page 1
Active Fault Code 43. page 15
Active Fault Code 48. page 19
Perform air system test prior to disassembly, then replace damaged synchronizer parts if required. Refer to
“Synchronizer” repair strategy item
TRSM-0915 (Note: after 12/31/04 this
publication will be TRMT-0001) for
repair details.
Check vehicle air pressure.
Service light on continuously. Replace
ECU.
1-10
Page 14
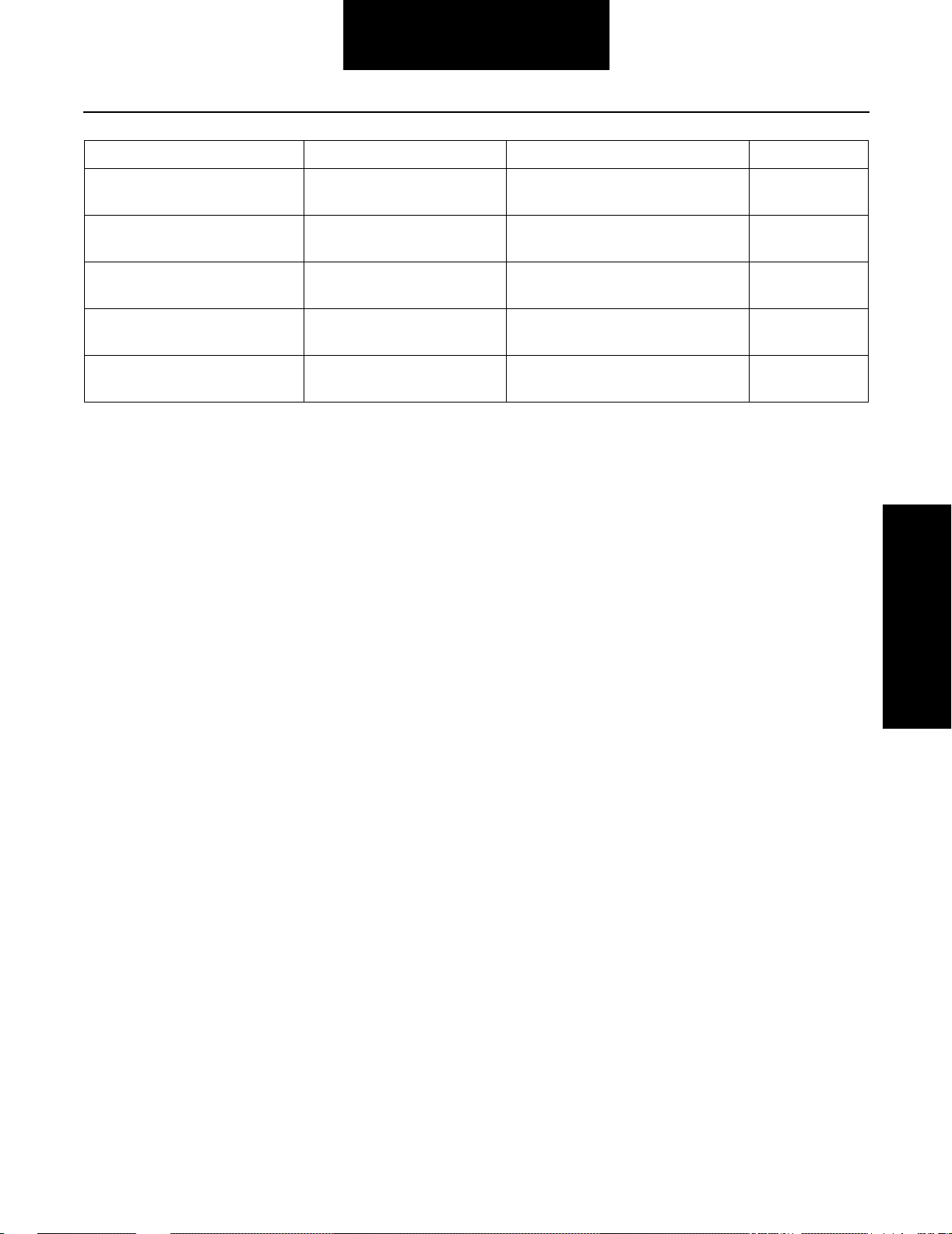
Fault Isolation Procedures
Symptom Possible Condition Remedy Reference
Software download unsuccessful
Two Speed Transmission (only 7
th, 9 th gears)
Neutral Switch Wheel Chair Lift / PTO etc. not
Reverse Switch Reverse Light / Beeper not
ECU malfunction service light
on continuously
operating
Engine will not crank (some applications)
functioning.
Replace ECU.
Replace ECU.
Perform Neutral Switch Test per OEM
recommendations.
Perform Neutral Switch Test per OEM
recommendations.
Perform Reverse Switch Test per
OEM recommendations.
Fault Isolation Procedures
1-11
Page 15

Fault Isolation Procedures
Vehicle Air Supply Requirement
The transmission filter/regulator assembly provides the inlet port for transmission supplied air. You will find the filter/regulator
located at the rear of the transmission on the driver’s side of the truck. The filter/regulator assembly regulates the transmission
supply to 80 PSI (551 kPa) maximum.
Filter / Regulator
Inlet Air Pressure Required 90-130 PSI (620-896 kPa)
Air Dryer Required
Inlet Port Size SAE 3/8” – 18 NPT
1-12
Page 16
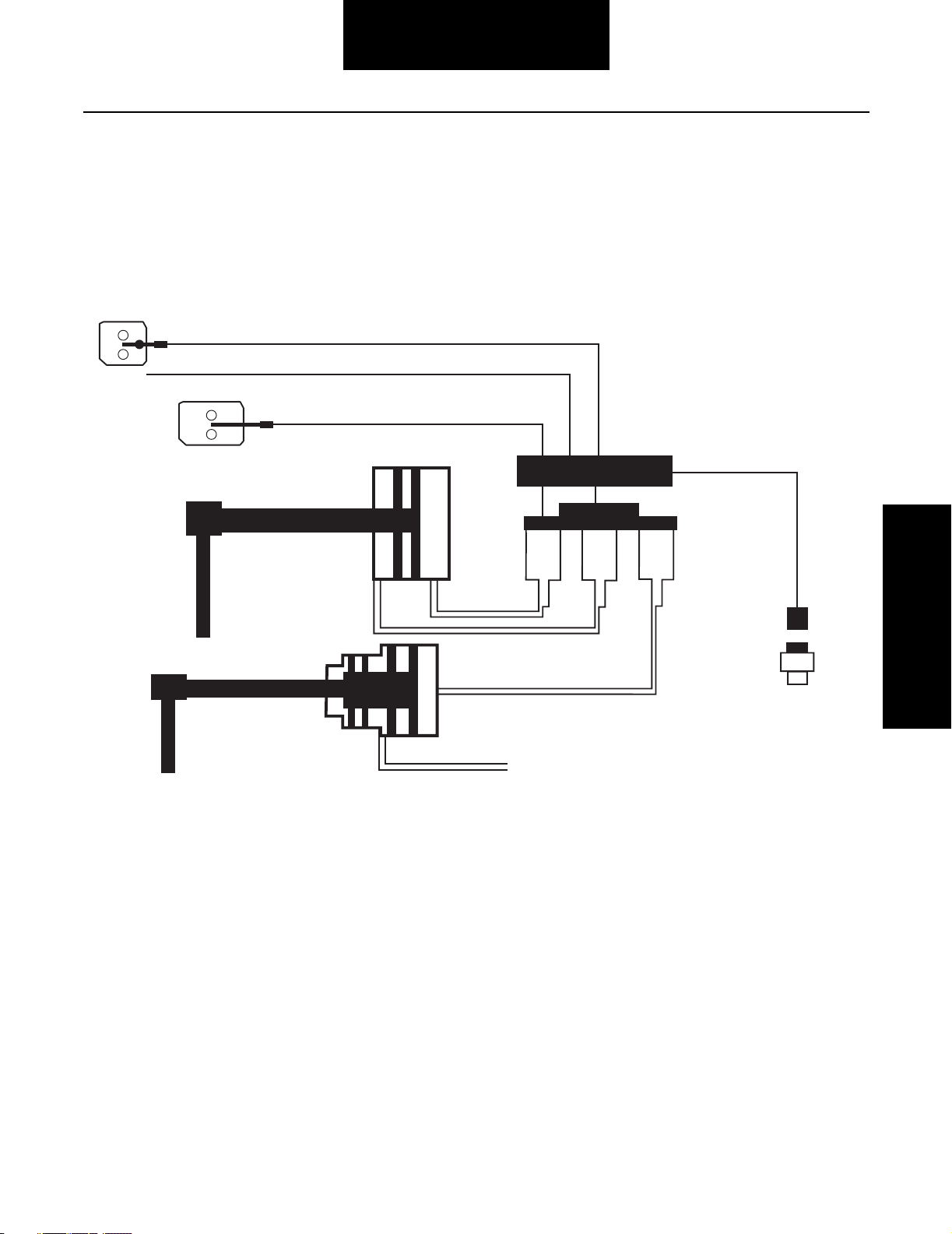
Fault Isolation Procedures
Air System - Overview
The Lightning series transmission uses an automatically controlled range cylinder to manage the air operated range shift between
6th and 7th gear. The button on the shift knob controls the splitter shift. Splitter shifts occur every time the transmission shifts
consecutive from one gear to the next gear or when the button is moved from one state to the next.
The simple block diagram below shows the relationship between the air system and electronic controls.
Splitter Signal from Shift Knob
Engine Communication (J1939)
Diagnostic Communication (J1587)
H
L
Non-Contacting Sensor to
sense desired range position
ECU
Splitter
Range
H L S
Charge Air
Constant Air
Solenoid
Pak
Output Speed
Sensor
The Lightning series transmission utilizes an electric over air concept for actuating the splitter and range cylinders. An electric
signal is sent to the ECU. The ECU then, enables a solenoid valve, which in turn directs air to the appropriate cylinder. A switch in
the shift knob directs the splitter shift. The position of the switch indicates to the ECU the desired splitter state. The ECU makes
the shift automatically when the proper conditions are achieved. The signal to the ECU for a range shift is automatically made when
the shift lever passes from the middle rail (6th gear) to the outside rail (7th gear). A sensor detects the movement and signals the
ECU to actuate the range valve. As with the splitter shift, the range shift only occurs when a specific set of conditions is achieved.
Fault Isolation Procedures
1-13
Page 17

Fault Isolation Procedures
Air System - ECU
The transmission’s electronic control unit (ECU) activates solenoids in the ECU, which opens up internal air passages. The transmission air filter/regulator is the only external air system component.
The air moves through passages internal to the transmission and the seal plate of the ECU. The illustration below shows the air
passages as viewed through the ECU.
Splitter Diagnostic Port
Supply to Valves
Range HI
Diagnostic Port
To HI Range
Splitter
80 PSI Supply
from Regulator /
Constant Air
to Splitter
To Splitter
Cylinder
Range Cylinder
O-ring
Seal Plate
Range
Supply to
Valves
HI Range Valve
LO Range Valve
Splitter Valve
From Splitter Valve
To LO Range
1-14
Splitter Cylinder
O-rings
Exploded View of Air System
Electronic Control Unit
(ECU)
Page 18

Fault Isolation Procedures
Air System - Splitter Subsystem
The ECU controls the operation of the splitter solenoid function, responding to driver input from the splitter button on the shift
knob or Top-2 operation.
The splitter cylinder has three distinct positions, forward (overdrive), rear (direct) and intermediate (neutral). The forward position
is achieved by activating the splitter solenoid valve, which applies air pressure to the rearward side of the piston. This is the splitter
state for the even numbered gears (2, 4, 6, 8 and 10)
The rearward position is achieved by de-activating the splitter solenoid valve, which exhausts the air pressure from the rearward
side of the splitter piston. The constant air pressure then forces the piston rearward. This is the splitter state for the odd numbered
gears (1, 3, 5, 7 and 9).
The intermediate or neutral state is achieved by the ECU rapidly turning on and off the splitter solenoid valve. This condition results
in a pressure on the rearward side of the splitter piston that is between 0 and full system pressure. This neutral state is used to
allow the gears to synchronize prior to engagement, thereby significantly improving the shift quality.
Constant Air Pressure
Splitter in
Direct
Constant Air Pressure
Constant Air Pressure
Signal Air Pressure
Splitter in
Overdrive
Fault Isolation Procedures
Signal Air Pressure
Splitter in
Neutral
1-15
Page 19

Fault Isolation Procedures
Air System - Range Subsystem
The ECU controls the operation of all range solenoid valve functions. The driver’s movement of the shift lever accomplishes a
change in the position of the range from high range to low range or vice versa.
The range piston has two distinct positions. Both the forward and rearward positions are a function of mechanical stops. Only one
side of the piston has air pressure at any one time. The ECU automatically selects either high or low range as the lever passes
through neutral when making an up-shift from 6th gear to 7th gear or the downshift from 7th gear to 6th gear.
In either case, the distinct sound of the range shifting is audible outside the cab, standing next to the stationary truck.
Air
Pressure
Low Range High Range
HI
R
LO
R
2
1
Low Range
3
5
8
4
7
10
6
9
High
Range
Pressure
Air
1-16
Page 20

Fault Isolation Procedures
This page left blank intentionally.
Fault Isolation Procedures
1-17
Page 21

Fault Isolation Procedures
Clutch Housing Breather Leak Overview
Overview
Air leaks out the breather located on top of clutch housing.
An air operated PTO with an air leak can pressurize the
transmission and cause air to leak out the transmission
breather.
Detection
Audible Air Leak
Fallback
There is no fallback mode for this failure.
Possible Leak Paths
Required Tools
• Basic Hand Tools
Possible Causes
• Splitter Cylinder O-Rings
• Range Cylinder O-Ring
• Air operated PTO leak
1-18
Splitter Cylinder Range Cylinder
Page 22
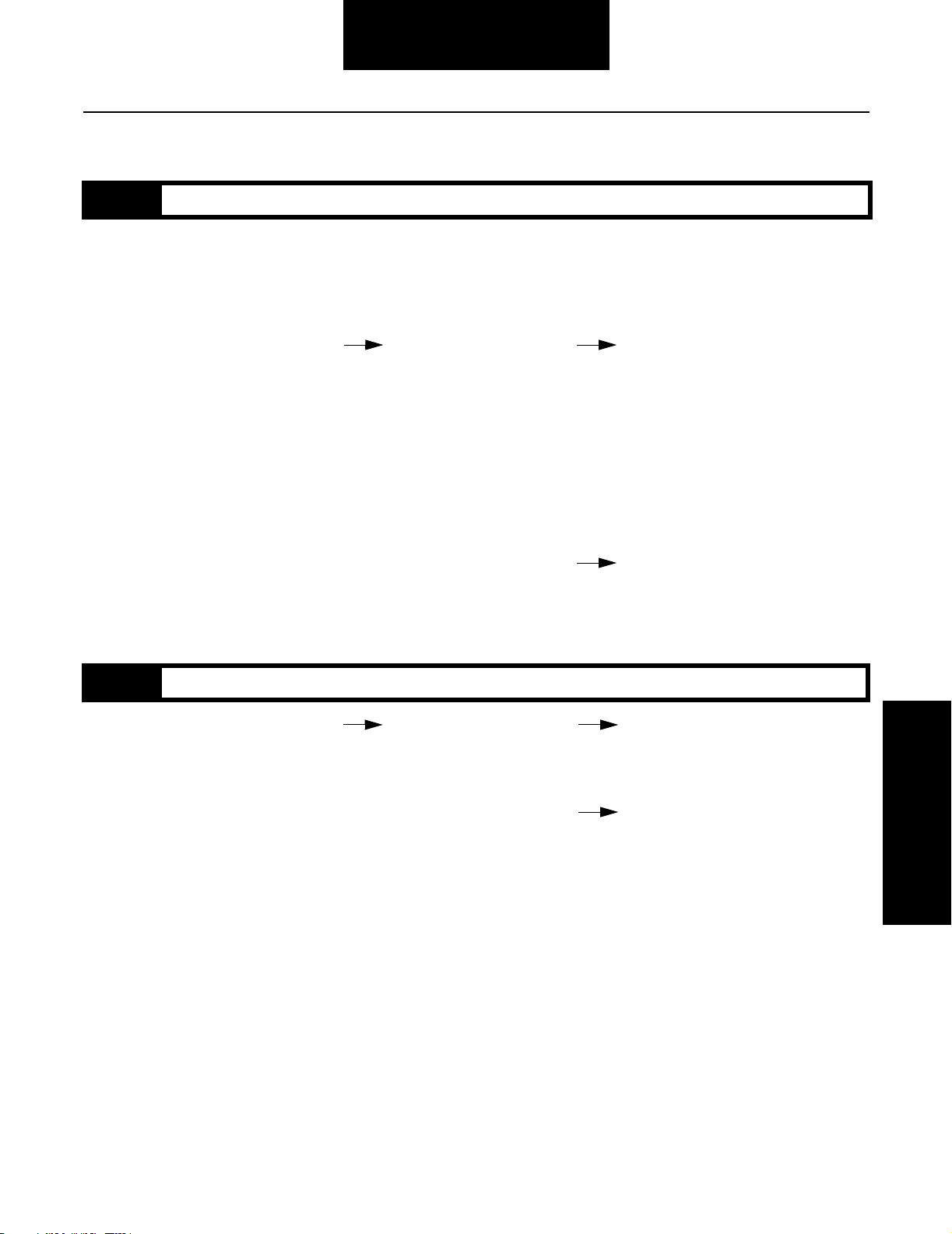
Fault Isolation Procedures
Clutch Housing Breather Leak
Step A Procedure Condition Action
1. Key on.
2. Vehicle stationary and secured,
air system fully charged, engine
not running.
3. Listen for air leaking
out the breather while
moving the shift lever
to make the range
cylinder shift from low
range to high range.
When stationary, the
lever must be moved
in and out of a high
range gear to make the
synchronizer shift.
Note: Oil leaking out the
breather may be a sign
indicating an air leak
internal to the
transmission.
Air leaks in both positions Repair the splitter cylinder, and
replace all cylinder o-rings. Go to
Step V.
Air leaks only in low
range
Repair the range cylinder, and
replace all cylinder o-rings. Go to
Step V.
Step V Procedure Condition Action
1. Fully charge air
system on vehicle and
check for
effectiveness of repair.
Breather still leaks Go to Step A.
Breather does not leak Test Complete.
Clutch Housing Breather
Leak
1-19
Page 23

Fault Isolation Procedures
Transmission ECU Breather Leak Overview
Overview
Air leaks out the breather on the ECU.
The breather exhausts a slight amount of air every time
the transmission makes a range shift and when the splitter
shifts to any odd numbered gear.
Detection
Audible Air Leak.
Fallback
There is no fallback mode for failure.
Possible Leak Paths
Required Tools
• Basic Hand Tools
Possible Causes
This fault can be caused by any of the following:
• Splitter or Range Cylinder O-rings
• Solenoid Seals or O-rings (ECU)
• Seal Plate
Possible Leak Path
1-20
Splitter Cylinder Range Cylinder
Solenoid
(Non-Serviceable - Inside ECU)
Page 24

Fault Isolation Procedures
Transmission ECU Breather Leak
Step A Procedure Condition Action
1. Key on, vehicle stationary and
secured, air system fully
charged, engine not running.
2. Cycle the splitter
cylinder by moving the
button on the shift
knob from the down
position to the up
position.
Leak stops with the
button in the up position.
Leaks in either position Go to Step B.
Replace the splitter cylinder orings and clean out any
contamination in the cylinder. If leak
continues after making this repair,
then replace the transmission ECU
and seal plate. Go to Step V.
Step B Procedure Condition Action
1. Key on, vehicle stationary and
secured, air system fully
charged, engine not running.
2. Cycle the range
cylinder by moving the
shift lever into high
range (the 7/8 gear
position) then back into
neutral. The
synchronizer makes a
distinct audible noise
when shifting.
Leak stops when in high
range.
Leak stops when in low
range.
Replace the range cylinder piston
and clean out any contamination in
the cylinder. If leak continues after
making this repair, then replace the
transmission ECU and seal plate.
Go to Step V
Replace the range cylinder piston
and clean out any contamination in
the cylinder. If leak continues after
making this repair, then replace the
transmission ECU and seal plate.
Go to Step V.
Transmission ECU
Breather Leak
Step V Procedure Condition Action
1. Charge the vehicle air
system and test
repairs for
effectiveness.
No Leaks Test Complete
Air still leaks out breather
on ECU.
Repeat test procedures for air leaks.
1-21
Page 25

Fault Isolation Procedures
Range Cylinder Test Overview
Overview
The range cylinder test does not relate to any specific fault
code, but must be performed prior to disassembly of the
transmission if a range system mechanical failure is suspected. The range cylinder test verifies the basic air system inputs are operating correctly, before proceeding with
disassembly. The driver complaint must be confirmed or
duplicated before preceding with the testing.
Detection
There is no detection process specifically for the Range
Cylinder. However, failures of this type are generally detected by the driver as a symptom such as the transmission range shift may grind, rake, or fail to operate.
Fallback
There is no fallback for the Range Cylinder Test.
Required Tools
• Basic Hand Tools
Possible Causes
This fault can be caused by any of the following:
• Truck air pressure out of range
• Faulty air/filter regulator
• Air system contamination
• Friction material worn or damaged on synchronizer
• Other internal mechanical failure
1-22
Page 26

Fault Isolation Procedures
Range Cylinder Test
Step A Procedure Condition Action
1. Start vehicle and
build up air pressure
to maximum. Shut off
vehicle.
Vehicle's primary and
secondary air supply is
less than 90 PSI or leaks
down
Vehicle air pressure is
Repair vehicle's air system and go
to Step V.
Go to Step B.
greater than 90 PSI and
no leaks.
Step B Procedure Condition Action
1. Drain air tanks to prevent injury.
2. Remove one of three plugs in
transmission filter/regulator and
insert pressure gauge.
3. Start vehicle and build
up air pressure to
maximum. Shut off
vehicle.
Front of
Transmission
Transmission filter/
regulator pressure less
than or greater than 77 to
82 PSI.
Regulator pressure
between 77 and 82 PSI.
Air Inlet
Port
Replace filter/regulator
assembly. Go to Step V.
Go to Step C.
Filter / Regulator
Range Cylinder Test
Regulated
Air Pressure
1-23
Page 27

Fault Isolation Procedures
Range Cylinder Test, continued
Step C Procedure Condition Action
1. Drain air tanks to prevent injury.
2. Remove either the plug for the
high range test port or low range
test port located on the top of
the transmission and insert
pressure gauge.
3. Start vehicle and build up air
pressure to maximum. Shut off
vehicle.
4. Key in the on position, do not
start vehicle.
5. Have an assistant move the
lever to cycle the range cylinder
by moving the lever in and out of
a high range gear position.
6. Watch the reaction of
the pressure gauge
and listen for the range
to shift.
Gauge response is
sudden and immediate.
Gauge reads between 77
to 82 PSI and the distinct
sound of the range
shifting is audible.
Gauge is slow to respond
or the range shift is not
audible.
Go to Step D.
Remove transmission ECU and
clean out any contamination in air
passages or cylinders. Go to Step
V.
Splitter Test Port
High Range Test Port
Low Range Test Port
1-24
Clean the area around the plugs prior
to removal to prevent dirt or other
contamination from falling into the
ports after removing the plugs.
Page 28
Fault Isolation Procedures
Range Cylinder Test, continued
Step D Procedure Condition Action
1. Remove and disassemble
transmission.
2. Inspect all
synchronizer parts.
Synchronizer parts
excessively worn or
damaged. Refer to
publication TRSM-0915
for synchronizer
replacement guidelines.
No parts worn or
damaged
Replace damaged parts. Go to Step
V.
Go to Step V.
Step V Procedure Condition Action
1. Start vehicle and road
test to determine
repair effectiveness.
Range shifts properly Test complete
Range still grinds/rakes
or inoperative
Repeat test procedures
1-25
Range Cylinder Test
Page 29

Fault Isolation Procedures
Splitter Cylinder Test Overview
Overview
The Splitter Cylinder Test does not relate to any specific
fault code, but must be performed prior to disassembly of
the transmission if a splitter system mechanical failure is
suspected. The splitter cylinder test verifies the basic air
system inputs are operating correctly, before proceeding
with transmission disassembly.
Required Tools
• Basic Hand Tools
Possible Causes
Detection
There is no detection process specifically for the splitter
cylinder. However, failures of this type are generally detected by the driver as a symptom such as the transmission splitter shift may grind, rake, or fail to operate. The
driver complaint must be confirmed or duplicated before
proceeding with the testing.
Fallback
There is no fallback for the Splitter Cylinder Test.
This fault can be caused by any of the following:
• Truck air pressure out of range
• Faulty air/filter regulator
• Air system contamination
• Faulty shift knob / splitter switch or
vehicle wiring
• Internal mechanical failure
1-26
Page 30
Fault Isolation Procedures
Splitter Cylinder Test
Step A Procedure Condition Action
1. Review driver's instruction for
proper driving technique.
2. Test drive truck with
operator.
Driver operating splitter
improperly
Driver operating splitter
Provide instruction and end test.
Go to Step B.
properly
Step B Procedure Condition Action
1. Start vehicle and build
up air pressure to
maximum. Shut off
vehicle.
Vehicle's primary and
secondary air supplies
less than 90 PSI or leaks
down
Vehicle air pressure is
greater than 90 PSI and
no leaks
Repair vehicle's air system and
go to Step V.
Go to Step C.
Step C Procedure Condition Action
1. Drain air tanks to prevent injury.
2. Remove one of three plugs in
transmission filter/regulator and
insert pressure gauge.
Splitter Cylinder Test
3. Start vehicle and build
up air pressure to
maximum. Shut off
vehicle.
Front of
Transmission
Regulated
Air Pressure
Filter / Regulator
Air Inlet
Port
Transmission filter/
regulator pressure less
than or greater than 77 to
82 PSI
Regulator pressure
between 77 and 82 PSI
Replace filter/regulator assembly.
Go to Step V.
Go to Step D.
1-27
Page 31

Fault Isolation Procedures
Splitter Cylinder Test, continued
Step D Procedure Condition Action
1. Drain air tanks to prevent injury.
2. Remove the plug for the splitter
test port located on the top of
the transmission and insert
pressure gauge. See illustration
below.
3. Start vehicle and build up air
pressure to maximum. Shut off
vehicle.
4. Key in the on position, do not
start vehicle.
5. Have an assistant move the
button to cycle the splitter
cylinder.
6. Watch the reaction of
the pressure gauge
and listen for the
splitter to shift.
Gauge response is
sudden and immediate.
Gauge reads between 77
to 82 PSI with button in
the up position and the
faint sound of the splitter
shifting is audible
Gauge is slow to respond
or the splitter shift is not
audible
No response on gauge.
Gauge reads “0”.
Go to Step E.
Remove transmission ECU and
clean out any contamination in air
passages or cylinders. Go to Step
V.
Perform “Shift Knob Test - No Fault
Codes Overview” on page 42.
1-28
Page 32

Fault Isolation Procedures
Splitter Cylinder Test, continued
Step D Procedure Condition Action
Splitter Test Port
High Range Test Port
Low Range Test Port
Clean the area around the plugs prior
to removal to prevent dirt or other
contamination from falling into the
ports after removing the plugs.
Step E Procedure Condition Action
1. Remove and disassemble
transmission.
2. Inspect all splitter
parts.
Splitter parts excessively
worn or damaged
No parts worn or
damaged
Replace damaged parts. Go to Step
V.
Go to Step V.
Step V Procedure Condition Action
1. Start vehicle and road
test to determine
repair effectiveness.
Splitter shifts properly Test Complete.
Splitter still grinds/rakes
or inoperative
Repeat test procedures.
Splitter Cylinder Test
1-29
Page 33

Fault Isolation Procedures
Electrical System Requirements
This transmission requires an electronically managed engine, which complies with current SAE J-1939 provisions. The transmission electronic control unit (ECU) communicates with the engine ECU over the J-1939 communication link. The OEM also provides
the J-1939 and J-1587 data-link to the transmission.
Shift Knob
Connection
Reverse Switch
Location
Neutral Switch
Location
ECU
Assembly
Output
Speed Sensor
18-pin
ECU Connector
Transmission Electrical Attachment Points
1-30
Page 34

Fault Isolation Procedures
Wiring Diagram
The Lightning transmission uses a single 18-pin connector at the ECU. The transmission receives input to manage splitter shifts,
into this connector from the engine, shift knob, and output speed sensor. The drawing below illustrates these connections:
T
R
A
N
S
M
I
S
S
I
O
N
E
C
U
A1
B1
Note: Power source connections must be reliable and as close to
the actual source as possible. Relay connections are not advisable.
10 AMP FUSE
10 AMP FUSE
A3
B3
VBATT
A = J1587(+)
A2
B2
B = J1587(-)
Sensor Supplied by Eaton
A A
B B
D1
D2
A = Speed Sensor (+)
B = Speed Sensor (-)
D3
F3
E3
E1
RESERVED FOR
E2
F1
ENGINE CRUISE CONTROL
AND ENGINE RETARDER
+ 12 V (VBATT)
SWITCHED
IGNITION (VIGN)
GROUND (GND1)
GROUND (GND2)
C
A
B
E
A
B
C
A = Service Light Power
B = Shift Knob Ground
C = Voltage Signal
ATA
J1587
Output Shaft
Speed Sensor
SHIFT
KNOB
Fault Isolation Procedures
F2
C3
C2
C1
Terminating
resistor
J-1939/11 data link
(OEM supplied)
Note: Shield Not Used with J1939 Lite.
C = Shield
B = J1939(-)
A = J1939(+)
+
Battery
Shield
termination
_
Engine ECM
Terminating
resistor
1-31
Page 35

Fault Isolation Procedures
18-way Pinout
Circuit Pin Location Description Notes
VBATT A1 Battery Positive Voltage 12 volt 10 Amp Fuse or auto reset (thermal) circuit
breaker required
VIGN B1 Switch Battery Positive Voltage
Switched Ignition - 12 volt
GND1 A3 Battery Negative Connection required at or near vehicle ground
GND2 B3 Battery Negative Connection required at or near vehicle ground
J-1939+ C1 Serial Communication- Engine J-1939 Configured per J-1939 physical layer specifi-
J-1939- C2 Serial Communication- Engine J-1939 Configured per J-1939 physical layer specifi-
CAN_Shield (J-
1939)
J-1587+ A2 Serial Communication - Diagnostics J-
J-1587- B2 Serial Communication - Diagnostics J-
SPD1+ D1 Transmission Output Speed
SPD1- D2 Transmission Output Speed
Knob_Gnd F3 Shift Knob Ground
C3 Serial Communication- Engine Configured per J-1939 physical layer specifi-
1587- High
1587- Low
10 Amp Fuse or auto reset (thermal) circuit
breaker required
point
point
cation
cation
cation
Srv_ Light D3 Power to Knob mounted service light
Splitter_SW E3 Voltage Signal to Splitter Switch
Cruise / Retarder E1, E2, F1, F2 Reserved for engine cruise / engine re-
tarder
Note: Always use the correct connector pin lead adapters from Eaton Test Adapter Kit when performing pin-out diagnostics. This
will prevent damage to the connector pins.
1-32
Not available as of January 1, 1999
Page 36

Fault Isolation Procedures
Fault Isolation Procedures
This page left blank intentionally.
1-33
Page 37

Fault Isolation Procedures
Power-Up Sequence Test Overview
Overview
The power-up Sequence Test is used to identify a faulty
component as the result of a failure during the transmission self-check.
Detection
The power-up self-check is performed automatically each
time the key is turned on. Turn the key on and watch the
service lamp located on the driver's side of the shift knob.
If power-up stops with the service lamp constantly on or
it never comes on, self-check has failed. There are no fault
codes to identify a failure of the self-check.
Fallback
If the self-check fails, the transmission may have full functionality or range and splitter function may be lost.
Required Tools
• Basic Hand Tools
Possible Causes
This fault can be caused by any of the following:
• Shift Knob
• Wiring harness or connectors from 18-way connector to shift knob
• Transmission ECU
Transmission ECU
Connection
OEM Interface
Connection
Typical OEM Wiring Harness
and Connections
Speed Sensor
Connection
Shift Knob
Connection
1-34
Page 38

Fault Isolation Procedures
Power-Up Sequence Test
Step A Procedure Condition Action
1. Key on.
2. Observe service lamp. If service lamp lights for
Test Complete.
one second and turns off.
Light comes on Go to Step B.
If test fails Go to Step V.
Step B Procedure Condition Action
1. Key off.
2. Remove 18-way connector from
transmission ECU.
3. Using a 1.5 volt DC
battery connect the
positive (+) side of the
battery to pin D3 and
the negative (-) side of
the battery to pin F3.
This should illuminate
the light.
Light comes on Replace Transmission ECU.
If test fails Go to Step C.
Power-up Sequence Test
A3
A2
A1
B3 C3
B2 C2
B1
E3
D3
D2
C1
D1
E2E1F2
F3
Dry Cell
F1
1.5 Volts
1-35
Page 39

Fault Isolation Procedures
Power-Up Sequence Test, continued
Step C Procedure Condition Action
1. Remove skirt from bottom of
shift knob and disconnect shift
knob from wiring harness
2. Using a 1.5 volt DC
battery, connect the
positive (+) side of the
battery to pin A and the
negative (-) side of the
battery to pin B. This
should illuminate the
light.
Note: Raised ribs on the
connector identify pin
locations
Dry Cell
1.5 Volts
A B C
Light comes on Repair or replace damaged wiring
harness.
If test fails Replace shift knob.
Step V Procedure Condition Action
1. Perform Electrical Pre-Test.
2. Using a 1.5 volt DC
battery, connect the
positive (+) side of the
battery to pin A and the
negative (-) side of the
battery to pin B. This
should illuminate the
light.
1-36
Pre-test fails Repair vehicle harness or electrical
system according to OEM
specifications.
Pre-test passes Replace Transmission ECU.
Page 40

Fault Isolation Procedures
Power-Up Sequence Test, continued
This page left blank intentionally.
Power-up Sequence Test
1-37
Page 41

Electrical Pretest Overview
Fault Isolation Procedures
Overview
The pretest does not relate to any specific fault code, but
must be completed before performing Fault Code Isolation Table procedures. The pretest verifies the basic electrical inputs before testing individual circuits.
Detection
There is no detection process specifically for the basic
electrical supply. However, failures of this type are generally detected by the transmission or driver as different
symptom or fault code.
Fallback
There is no fallback for the electrical pretest, however, it
may effect other systems.
Required Tools
• Basic Hand Tools
• Digital Volt/Ohm Meter
• Troubleshooting Guide
Possible Causes
This pretest can be used for any of the following:
• Corroded Power Contacts
• Blown Fuse
• Wiring Harness
• Low Batteries
1-38
Page 42

Fault Isolation Procedures
Electrical Pretest
Step A Procedure Condition Action
1. Key off.
2. Check VBATT and
ignition fuse or circuit
breaker.
Note: System has two fuses or
circuit breakers, one for
switched ignition and the
other for VBATT.
Fuses or circuit breakers
blown or tripped.
Fuses or circuit breakers
good.
Replace or reset the fuse. Check for
short to ground on VBATT or VIGN.
Go to Step V.
Go to Step B.
Step B Procedure Condition Action
1. Key on - Engine Running.
2. Check truck charging
system including
alternator, regulator
and batteries. Check
per OEM or
manufacturer
recommendations.
Truck charging system
does not meet OEM
specifications for
charging requirements.
Charging system meets
OEM specifications.
Repair charging system, i.e.
alternator, batteries, etc., and Go
to Step V.
Go to Step C.
Electrical Pretest
Step C Procedure Condition Action
1. Key off
2. Locate transmission
power and ground
connections (2 of
each) and inspect for
looseness or
corrosion.
Connections loose or
corroded
Connections clean and
tight
Repair connections and Go to Step
V.
Go to Step D.
1-39
Page 43

Fault Isolation Procedures
Electrical Pretest, continued
Step D Procedure Condition Action
1. Key off.
2. Disconnect 18-way connector
from transmission.
3. Disconnect negative (-) battery
cable from battery.
4. Measure resistance
between ECU
If resistance is 0 to 0.3
ohms
Go to Step E.
connector pin A3 and
negative battery cable
and between
connector pin B3 and
negative battery cable.
If resistance is outside of
range
Repair ground path for
transmission and repeat this step.
Step E Procedure Condition Action
1. Key off.
2. Reconnect negative (-) battery
cable removed from previous
test.
3. Leave 18-way connector
disconnected from
transmission.
4. Check voltage from A1
to A3 and from A1 to
B3.
Voltage across pins
greater than or less than
specified system voltage
or 12 to 13 volts.
Repair truck harness or electrical
system according to OEM
specification and go to Step V.
1-40
VOLTS
V COM
Voltage equals specified
system voltage of 12 to
13 volts.
E3
A3
B3 C3
A2
B2 C2
B1
A1
D3
F3
E2E1F2
D2
C1
D1
F1
Go to Step F.
Page 44

Fault Isolation Procedures
Electrical Pretest, continued
Step F Procedure Condition Action
1. Leave 18-way connector
disconnected from
transmission.
2. Key on.
3. Check voltage across
pins A1 to A3 and
across B1 to B3 of the
harness.
Voltage across pins
greater than or less than
specified system voltage
or 12 to 13 volts.
Voltage equals specified
system voltage of 12 to
Repair truck harness or electrical
system according to OEM
specification and go to Step V.
System OK. Go to Symptom
Driven/Trouble Code Diagnostics.
13 volts.
VOLTS
E3
A3
B3 C3
A2
B2 C2
B1
A1
V COM
Step V Procedure Condition Action
D3
F3
E2E1F2
D2
C1
D1
F1
Electrical Pretest
1. Road test vehicle for
repair effectiveness.
Condition does not
Test complete
reoccur
Condition reoccurs Repeat test procedures.
1-41
Page 45

Fault Isolation Procedures
Shift Knob Test - No Fault Codes Overview
Overview
Perform the Shift Knob test if there is no splitter function
when the splitter switch on the Shift Knob is moved up or
down, and no active fault codes are logged.
Detection
The splitter does not change from low to high or high to
low when the splitter switch on the shift knob is changed.
There are no fault codes for a splitter switch failure.
Fallback
Odd number gears only 1st, 3rd, 5th, 7th, and 9th.
Required Tools
• Basic Hand Tools
Possible Causes
This fault can be caused by any of the following:
• Faulty Shift Knob
• Harness Between Shift Knob and Transmission
ECU
• Transmission ECU
Transmission ECU
Connection
OEM Interface
Connection
Typical OEM Wiring Harness
and Connections
Speed Sensor
Connection
Shift Knob
Connection
1-42
Page 46

Fault Isolation Procedures
Shift Knob Test - No Fault Codes
Step A Procedure Condition Action
1. Key off.
2. Remove 18-pin connector from
the transmission ECU.
3. Measure resistance
across pins F3 and E3
of the harness with the
splitter button in the
down position then in
the up position.
OHMS
V COM
A3
B3 C3
A2
B2 C2
B1
A1
D3
D2
C1
D1
E3
E2E1F2
If the button down
position meter reads .5
Replace transmission ECU. Go to
Step V.
ohms or less and button
up position meter reads
infinite ohms
If either position falls
Go to Step B.
outside this range
Shift Knob Test - No Fault
F3
F1
Codes
1-43
Page 47

Fault Isolation Procedures
Shift Knob Test - No Fault Codes, continued
Step B Procedure Condition Action
1. Gently remove the shift knob
skirt being careful not to damage
electrical connections.
2. Disconnect 3-way connector
located under skirt.
3. Measure resistance
across pins B and C of
the connector with the
splitter button in the
down position then in
the up position.
Note: Raised ribs on the
connector identify pin
locations.
OHMS
V COM
In the button down
position meter reads .5
ohms or less and Button
up position meter reads
infinite ohms
If either position falls
outside this range
A B C
Replace or repair wiring harness
between shift knob and
transmission ECU. Go to Step V.
Replace shift knob. Go to Step V.
Step V Procedure Condition Action
1. Reconnect all connectors.
2. Key on.
3. Drive vehicle to test for
repair effectiveness.
1-44
Transmission has all
available gears
Transmission still has
only five available gears
Test Complete.
Review tests procedures and check
for any active fault codes. Re-run
necessary tests.
Page 48

Fault Isolation Procedures
Shift Knob Test - No Fault Codes, continued
This page left blank intentionally.
Shift Knob Test - No Fault
Codes
1-45
Page 49

Fault Isolation Procedures
J-1587 Data Link Test Overview
Overview
Does not affect transmission operation. Any tool connected to the ATA J-1587 Data Link connector does not work
correctly.
Detection
The service technician observes the failure when operating the PC-based Service Tool. To observe this failure,
simply connect the PC-based Service Tool to the transmission via the J-1587 diagnostic connector located in the
cab.
Fallback
There is no fallback mode for J-1587 Data Link. The PCBased Service Tool will not work correctly.
Required Tools
• Basic Hand Tools
• Digital Volt/Ohm Meter
• Troubleshooting Guide
• Service Tool
Possible Causes
This fault can be caused by any of the following:
• J-1587 data link
• Transmission ECU
• Service Tool
+12
volts
battery
J-1587 data link
GROUND
6-way
diagnostic connector
9-way
diagnostic connector
A Ground
A ATA+
B ATA–
C + Battery
D
E Ground
F
J
D
F
B
A
E
C
D
C
H
B
G
E
A
F
B + Battery
C
D
E
F ATA+
G ATA-
H
J
All OEM responsible wiring shown is "typical". Consult specific application.
+12 volt non-switched from battery
Communication from and to the ECU
1-46
Page 50

Fault Isolation Procedures
J-1587 Data Link Test
Step A Procedure Condition Action
1. Key on.
2. Measure voltage
between pins C and E
If voltage is within .6
volts of battery voltage
Go to Step B
on the 6-way
diagnostic connector
or pins B and A on the
9-way connector.
If voltage is outside of
range
Repair battery or ground line to
vehicle diagnostic connector. Go to
Step V.
VOLTS
F
B
A
E
C
D
V COM
H
JCD
B
G
E
A
F
VOLTS
V COM
Step B Procedure Condition Action
1. Disconnect Transmission ECU
18-way connector.
2. Measure resistance
across 18-way
connector pin A2 and
either 6-way diagnostic
connector pin A or 9way diagnostic
connector pin F.
If resistance is 0 to .3
ohms
If resistance is outside of
range
J-1587 Data Link Test
Go to Step C.
Repair vehicle's interface harness
and go to Step V.
1-47
Page 51

Fault Isolation Procedures
J-1587 Data Link Test, continued
Step C Procedure Condition Action
1. Measure resistance
across either 6-way
diagnostic connector
pin A or 9-way
diagnostic connector
pin F and ground.
OHMS
F
E
V COM
Ground
If resistance is greater
Go to Step D.
than 10K ohms or infinite
If resistance is less than
10K ohms
OHMS
B
A
C
D
V COM
Ground
H
JCD
B
G
E
A
F
Repair vehicle's harness and go to
Step V.
1-48
Page 52

Fault Isolation Procedures
J-1587 Data Link Test, continued
Step D Procedure Condition Action
1. Measure resistance
across 18-way
connector pin B2 and
either 6-way
diagnostic connector
pin B or 9-way
diagnostic connector
pin G.
E3
A3
B3 C3
A2
B2 C2
B1
A1
D3
E2E1F2
D2
C1
D1
If resistance is 0 to .3
Go to Step E.
ohms
If resistance is outside of
range
Repair vehicle's harness and go to
Step V.
OHMS
F3
F1
COM
V
F
B
A
E
C
D
J-1587 Data Link Test
OHMS
J
D
C
E3
D3
A3
B3 C3
A2
B2 C2
C1
B1
A1
F3
D2
E2E1F2
D1
F1
COM
V
H
E
B
A
G
F
1-49
Page 53

Fault Isolation Procedures
J-1587 Data Link Test, continued
Step E Procedure Condition Action
1. Measure resistance
between either 6-way
diagnostic connector
pin B or 9-way
diagnostic connector
pin G and ground.
OHMS
F
E
V COM
Ground
If resistance is greater
Go to Step F.
than 10K ohms or infinite
If resistance is less than
10K ohms
OHMS
B
A
D
V COM
Ground
H
JCD
B
G
E
A
F
Repair vehicle's harness and go to
Step V.
1-50
Page 54

Fault Isolation Procedures
J-1587 Data Link Test, continued
Step F Procedure Condition Action
1. Disconnect all data links to the
vehicle's diagnostic connector
leaving only the transmission
connected.
2. Connect the data link tester
across the diagnostic connector
pins A and B for the 6-way
diagnostic connector or F and G
of the 9-way diagnostic
connector.
3. Key on.
4. Place the Data Link
Tester in the
communication test
mode.
Black
B
F
A
C
H
E
JCD
B
G
D
A
F
Red
Red
E
Black
Data Link Tester
CONTINUITY TEST
SELF TEST
OFF
COMMUNICATION
TEST
Part No. 691582
Data Link Tester
CONTINUITY TEST
SELF TEST
OFF
COMMUNICATION
TEST
Part No. 691582
If test passes Problem exits with service tool in
one of the following area.
Communication Box, Cables or the
PC. Repair as required and go to
Step V.
If test fails Replace transmission ECU and go
to Step V.
OFF
J-1587 Data Link Test
OFF
Step V Procedure Condition Action
1. Key on.
2. Connect tool to J-
1587.
If service tool functions
correctly
If service tool does not
function correctly
Test Complete.
Return to Step A and
repeat procedure.
1-51
Page 55

Fault Isolation Procedures
Component Code 11 (SID 254, FMI 12) Transmission ECU
Overview
This fault code indicates an internal failure of the transmission ECU.
Detection
The transmission ECU detects an internal solenoid power
supply problem or three consecutive attempts to read or
write program memory information each time the ignition
key is turned on. Active fault code 11 cannot be accessed
using the key switch method to access flash codes. An
electronic diagnostic tool such as ServiceRanger or ProLink must be used to confirm active fault code 11.
Fallback
Required Tools
• Basic Hand Tools
• Diagnostic Tool
Possible Causes
This fault can be caused by any of the following:
• Transmission ECU
Depending on the failure mode, shift performance may
not be affected. The driver may have only odd number
gears in either low or high range, or he may have 6-speed
shifting with low range only.
Transmission ECU
2-1
Page 56

Fault Isolation Procedures
Code 11 (SID 254, FMI 12) Transmission ECU
Step A Procedure Condition Action
1. Key on.
2. Retrieve codes. Active Code Replace Transmission ECU.
In-Active Code Test Complete.
2-2
(SID 254, FMI 12)
SideTitle Code 11
Page 57

Fault Isolation Procedures
Component Code 33 (PID 158,168, FMI 3,4) System Voltage Fault
Overview
This fault code indicates vehicle ignition or battery voltage
supplied to the transmission ECU connector pins A1 or B1
is outside the acceptable operating range.
Required Tools
• Basic Hand Tools
Possible Causes
Detection
The fault code can be set during initial power up or during
normal operation if either of the following conditions occur:
1. Vehicle battery power supplied to transmission ECU
connector pin A1 falls below 9 volts for 5 seconds.
2. Vehicle ignition power is lost at transmission ECU connector pin B1 longer than 60 seconds and J1939 data link
remains active.
Fallback
Detection mode 1 results in fallback to 1st, 3rd, and 5th
gears only.
Detection mode 2 results in fallback to odd gears only 1st, 3rd, 5th, 7th, 9th.
This fault can be caused by any of the following:
• Truck charging system
• Battery or ground connections
• Fuses or circuit breakers
• Transmission ECU
2-3
Page 58

Fault Isolation Procedures
Code 33 (PID 158,168, FMI 3,4) System Voltage Fault
Step A Procedure Condition Action
1. Perform Vehicle
Electrical Pretest.
Vehicle Passes Test Go to Step V.
Vehicle Fails Test Repair according to manufacturers
recommendations. Go to Step V.
Step V Procedure Condition Action
1. All connectors secure and in
place on transmission
2. Clear all fault codes from
transmission ECU.
3. Key on.
4. Wait 5 minutes and
look for fault code 33 to
reappear.
Fault reoccurs Replace transmission ECU.
Fault does not reoccur Test complete.
PID 158,168, FMI 3,4)
Code 33
2-4
Page 59

Fault Isolation Procedures
Component Code 35 (SID 231, FMI 2) J-1939 Data Link Test
Overview
This fault code indicates J1939 data link communication
between the transmission and all other J1939 devices has
failed.
Detection
15 seconds after key-on and throughout vehicle operation
the transmission constantly monitors communication
with all other J1939 devices. If communication to or from
the engine or other devices is lost for more than a fraction
of a second and there is a shift request, Fault Code 35 will
be logged and the service light will begin flashing. If communication is lost and there is no shift request (steady
speed condition), the fault code will not be set as long as
communication is reestablished before a shift request. If
communication is reestablished after an active fault code
is set, the light will stop flashing and the fault will be
logged as inactive.
Required Tools
• Basic Hand Tools
• Digital Volt/Ohm Meter
• Troubleshooting Guide
• Data Link Tester
Possible Causes
This fault can be caused by any of the following:
• J-1939 data link
• J- 1939 data link connectors
• Engine ECM
• Transmission ECU
Fallback
An active J-1939 fault causes the transmission to default
to a 5-speed fallback mode in either low or high split depending on last known gear position. Range shift now
triggers in neutral with engine running and the vehicle stationary.
Engine ECM
Terminating
resistor
J-1939/11 data link
(OEM supplied)
+
termination
_
Shield
Terminating
resistor
2-5
Battery
Page 60

Fault Isolation Procedures
Code 35 (SID 231, FMI 2) J-1939 Data Link Test
Step A Procedure Condition Action
1. Key off
2. Disconnect transmission ECU
18-way connector.
3. Disconnect engine ECM's
connector, which contains the
J-1939 data link.
4. Measure resistance across
vehicle interface harness from:
• Transmission
ECU 18-way
connector and
engine ECM
+J-1939 pin
(See OEM
Engine pinout).
• Transmission
ECU 18-way connector C1
and ground.
A3
B3 C3
A2
B2
B1
A1
If resistance between pin
Go to Step B.
C1 and engine ECM
+J-1939 pin is 0 to .3
ohms and if resistance
between pin C1 and
ground is greater than
10K.
If resistance is outside of
this range
Repair J-1939 data link harness
between ECM and transmission
ECU, then go to Step V.
(SID 231, FMI 2)
OHMS
E3
D3
F3
D2
C2
E2E1F2
D1
F1
COM
V
A3
B3 C3
A2
B2 C2
B1
A1
E3
D3
F3
D2
E2E1F2
D1
F1
OHMS
V
Code 35
COM
Ground
J1939 (+)
J1939 (-)
Shield
EATON
Lightning
18-Way ECU
Connector
C1
C2
C3
Engine ECM
+ J1939 pin
2-6
Page 61

Fault Isolation Procedures
Code 35 (SID 231, FMI 2) J-1939 Data Link Test, continued
Step B Procedure Condition Action
1. Measure resistance across:
• Transmission
ECU 18-way
connector C2 and
Engine ECM -J1939 pin (See
OEM Engine
pinout).
• Transmission
ECU 18-way
connector C2 and
ground.
A3
A2
A1
B3 C3
B2
B1
If resistance between pin
C2 and engine ECM
-J-1939 pin is 0 to .3
If equipped with J-1939 Lite. Go to
Step D. If not equipped with J1939 Lite Go to Step C.
ohms and if resistance
between pin C2 and
ground is greater than 10K ohms.
If resistance is outside of
this range
Repair J-1939 data link harness
between ECM and transmission
ECU Go to Step V.
OHMS
E3
D3
F3
D2
E2E1F2
D1
C1
F1
COM
V
A3
B3 C3
A2
B2
B1
A1
C1
E3
D3
F3
D2
E2E1F2
D1
F1
OHMS
COM
V
Ground
J1939 (+)
J1939 (-)
Shield
EATON
Lightning
18-Way ECU
Connector
C1
C2
C3
Engine ECM
+ J1939 pin
2-7
Page 62

Fault Isolation Procedures
Code 35 (SID 231, FMI 2) J-1939 Data Link Test, continued
Step C Procedure Condition Action
1. Measure resistance
across Transmission
ECU 18-way
connector C3 and
Engine ECM Shield
pin (See OEM Engine
pinout).
J1939 (+)
J1939 (-)
Shield
If resistance between pin
C3 and engine ECM
Shield pin is 0 to .3
ohms.
If resistance is outside of
this range
EATON
Lightning
18-Way ECU
Connector
C1
C2
C3
Go to Step D. If working with Mack
engine Step E.
Repair J-1939 data link harness
between ECM and transmission
ECU, then go to Step V.
OHMS
B3 C3
B2
B1
D3
F3
D2
E2E1F2
D1
C1
F1
V
COM
Engine ECM
+ J1939 pin
A3
A2
A1
E3
(SID 231, FMI 2)
Code 35
2-8
Page 63

Fault Isolation Procedures
C1
Code 35 (SID 231, FMI 2) J-1939 Data Link Test, continued
Step D Procedure Condition Action
1. Key off.
2. Measure resistance on
vehicle interface
harness between
transmission 18-way
connector pins C1 and
C2.
B3 C3
A3
A2
B2
B1
A1
If resistance between pin
Go to Step E.
C1 and C2 is between 50
to 70 ohms
If resistance is outside of
range
Repair J-1939 data link harness and
go to Step V.
OHMS
E3
D3
F3
D2
E2E1F2
D1
C1
F1
COM
V
2-9
Page 64

Fault Isolation Procedures
Code 35 (SID 231, FMI 2) J-1939 Data Link Test, continued
Step E Procedure Condition Action
1. Key off.
2. Reconnect engine ECM
connector and transmission
ECU 18-way connector.
3. Disconnect the 3-way stub
connector, which connects the
transmission into the J-1939
data link.
4. Connect the data link tester to
the 3-way stub connector,
which connects the
transmission into the J-1939
data link.
5. Place the data link tester in
communication test mode.
6. Key on. If test passes Problem exists with the engine
ECM. Repair according to
manufacturer's recommendations
and go to Step V.
Note: If vehicle does not use a
3-way connector, then do
If test fails Replace transmission ECU and go
to Step V.
not reconnect the engine
ECM and connect the data
link tester across the +/J-1939 terminals.
Transmission
ECU
Data Link Tester
CONTINUITY TEST
SELF TEST
OFF
COMMUNICATION
TEST
Part No. 691582
OFF
Data Link Tester
CONTINUITY TEST
SELF TEST
OFF
COMMUNICATION
TEST
Part No. 691582
OFF
(SID 231, FMI 2)
Code 35
J1939 (+)
J1939 (-)
Shield
EATON
Lightning
18-Way ECU
Connector
C1
C2
C3
2-10
Page 65

Fault Isolation Procedures
Code 35 (SID 231, FMI 2) J-1939 Data Link Test, continued
Step V Procedure Condition Action
1. Key off.
2. Key on.
3. Clear codes.
4. Drive the vehicle in an attempt to
reset fault code.
5. Check for fault codes
and associated fall
back modes.
If no codes Test Complete.
Code reappears Return to Step A and retest.
If different code appears Go to fault code testing for isolation
procedure.
2-11
Page 66

Fault Isolation Procedures
Code 35 (SID 231, FMI 2) J-1939 Data Link Test, continued
This page left blank intentionally.
(SID 231, FMI 2)
Code 35
2-12
Page 67

Fault Isolation Procedures
Component Code 36 (SID 48,49, FMI 2) Position Sensor Test
Overview
This fault code indicates the transmission position sensor
is outside the acceptable operating range.
Detection
Required Tools
• Basic Hand Tools
Possible Causes
The transmission ECU monitors the Position Sensor values every 10 milliseconds. The fault code is set if the value
is outside the acceptable range 10 times within the last 1
second of operation.
Fallback
For SID 48 the transmission defaults to six speed shifting
(low range gears only). For SID 49 all gears remain functional, but all engine control is returned to the driver.
Shift Position Sensor has failed but is non-serviceable
(must replace complete transmission ECU).
2-13
Transmission ECU
Page 68

Fault Isolation Procedures
Code 36 (SID 48,49, FMI 2) Position Sensor Test
Step A Procedure Condition Action
1. Test drive vehicle to
verify active Fault Code
36.
Active code 36. Replace transmission ECU and
reset.
In-active code 36. Record and clear all in-active fault
codes. Test drive vehicle to verify
complaint. Perform diagnostic test
procedure for active fault code or
follow symptom complaint
procedure if no fault codes are
logged.
2-14
(SID 48,49, FMI 2)
Code 36
Page 69

Fault Isolation Procedures
Component Code 43 (SID 36, FMI 4,5,6) Low Range Solenoid
Overview
This fault code indicates an electrical failure of the Low
Range solenoid.
Detection
Required Tools
• Basic Hand Tools
Possible Causes
Starting at key-on and during normal operation, the transmission continuously measures the low range solenoid
circuit. Any condition resulting in an electrical short to
ground, open circuit, or low / high current for at least 1
second will set the fault code.
Fallback
Depending on the failure mode, the transmission defaults
to only odd number gears in either low or high range, or
high range gears only.
Low Range solenoid has failed but is non-serviceable
(must replace complete transmission ECU assembly).
2-15
Transmission ECU
Page 70

Fault Isolation Procedures
Code 43 (SID 36, FMI 4,5,6) Low Range Solenoid
Step A Procedure Condition Action
1. Test drive vehicle to
verify active Fault Code
43.
Active code 43 Replace transmission ECU and
retest.
In-active code 43 Record and clear all inactive fault
codes. Test drive vehicle to verify
complaint. Perform diagnostic
procedure for active fault codes or
follow symptom complaint
procedure if no faults are logged.
2-16
(SID 36, FMI 4,5,6)
Code 43
Page 71

Fault Isolation Procedures
Component Code 46 (SID 37, FMI 4,5,6) Splitter Solenoid
Overview
This fault indicates an electrical failure of the Splitter solenoid.
Detection
Required Tools
• Basic Hand Tools
Possible Causes
Starting at key-on and during normal operation, the transmission continuously measures the splitter solenoid circuit. Any condition resulting in an electrical short to
ground, open circuit, or low / high current for at least 1
second will set the fault code
Fallback
Depending on the failure mode, the transmission defaults
to only odd number gears in either low or high range, or
all odd number gears.
Splitter Solenoid has failed but is non-serviceable (must
replace complete transmission ECU assembly).
2-17
Transmission ECU
Page 72

Fault Isolation Procedures
Code 46 (SID 37, FMI 4,5,6) Splitter Solenoid
Step A Procedure Condition Action
1. Test drive vehicle to
verify active Fault Code
46.
Active code 46 Replace transmission ECU and
retest
In-active code 46 Record and clear all inactive fault
codes. Test drive vehicle to verify
complaint. Perform diagnostic
procedure for active fault codes or
follow symptom complaint
procedure if no faults are logged.
2-18
(SID 37, FMI 4,5,6)
Code 46
Page 73

Fault Isolation Procedures
Component Code 48 (SID 35, FMI 4,5,6) High Range Solenoid
Overview
This fault code indicates an electrical failure of the High
Range solenoid.
Detection
Required Tools
• Basic Hand Tools
Possible Causes
Starting at key-on and during normal operation, the transmission continuously measures the high range solenoid
circuit. Any condition resulting in an electrical short to
ground, open circuit, or low / high current for at least 1
second will set the fault code.
Fallback
Depending on the failure mode, the transmission defaults
to only odd number gears in either low or high range, or
low range gears only.
High Range solenoid has failed but is non-serviceable
(must replace complete transmission ECU assembly).
2-19
Transmission ECU
Page 74

Fault Isolation Procedures
Code 48 (SID 35, FMI 4,5,6) High Range Solenoid
Step A Procedure Condition Action
1. Test drive vehicle to
verify active Fault Code
48.
Active code 48 Replace transmission ECU and
retest.
In-active code 48 Record and clear all inactive fault
codes. Test drive vehicle to verify
complaint. Perform diagnostic
procedure for active fault codes or
follow symptom complaint
procedure if no faults are logged.
2-20
(SID 35, FMI 4,5,6)
Code 48
Page 75

Fault Isolation Procedures
Component Code 58 (PID 191, FMI 2) Output Shaft Speed Sensor
Overview
This fault code indicates an electrical problem has occurred in the output shaft speed sensor circuit.
Detection
Required Tools
• Basic Hand Tools
Possible Causes
This fault code can be set three ways:
1) With the truck stopped, at key-on the transmission ECU
performs a continuity check on the output speed sensor
circuit. The fault code will be set for an open circuit or a
short to ground condition.
2) While the truck is moving, in gear, engine speed
present, and clutch engaged - the fault code will be set if
the output speed signal is lost for at least six seconds.
3) With the truck stopped, key on, transmission in 4th
gear or higher, clutch engaged - the fault code will be set
if the clutch switch fails open after five seconds (clutch
state and output speed do not match).
Fallback
The transmission defaults to five speed shifting with odd
number gears only.
Transmission ECU
Connection
Typical OEM Wiring Harness
and Connections
This fault can be caused by any of the following:
• Faulty Output Speed Sensor
• Open or short in wiring Harness to Sensor
• Clutch Switch (at pedal) fails open
• Transmission ECU
Front View Side View
2-21
OEM Interface
Connection
Speed Sensor
Connection
Shift Knob
Connection
Seal Area
Non Threaded
Portion of Sensor
Page 76

Fault Isolation Procedures
Code 58 (PID 191, FMI 2) Output Shaft Speed Sensor
Step A Procedure Condition Action
1. Check for debris/contamination
around the output speed sensor
and connection.
2. Check for proper adjustment of
the speed sensor.
3. Check for loose
speedometer tone
wheel.
If any of these conditions
exist
Speed sensor location is
Repair, adjust, clean or tighten to
manufacturer's specification then
go to Step V.
Go to Step B.
free of contamination,
corrosion, and all cap
screws and output nut tight
Step B Procedure Condition Action
1. Key off.
2. Remove 18-way
connector from
transmission ECU and
measure resistance
across pins D1 to D2
and between pin D1 to ground.
If resistance between
pins D1 and D2 reads
between 2K and 5K ohms
and resistance from D1
to ground is greater than
10K
If resistance measures
outside the above ranges
than
Go to Step C.
Go to Step D.
(PID 191, FMI 2)
Code 58
OHMS
COM
V
OHMS
E3
B3 C3
B2
B1
D3
F3
D2
C2
C1
E2E1F2
D1
F1
A3
B3 C3
C2
A2
B2
B1
A1
C1
E3
D3
F3
D2
E2E1F2
D1
F1
COM
V
Ground
2-22
A3
A2
A1
Page 77

Fault Isolation Procedures
Code 58 (PID 191, FMI 2) Output Shaft Speed Sensor, continued
Step C Procedure Condition Action
1. Perform clutch pedal
switch diagnostics per
OEM instructions.
Clutch switch contacts
If clutch switch fails open
or installation issues
prevent the switch from
operating correctly
Adjust or replace clutch switch per
OEM instructions and go to Step V.
should be engaged
(pedal in the up
position) and closed
when clutch is
disengaged (pushed in).
If clutch switch test
passes and functions
Replace transmission ECU and go
to Step V.
100% of the time
Step D Procedure Condition Action
1. Disconnect transmission
harness from output speed
sensor.
2. Measure resistance
between output speed
sensor pins and each
pin to ground.
If output speed sensor
resistance is 2K to 5K
ohms and output sensor
pin to ground is greater
than 10K ohms
Repair or replace harness from
sensor to 18-way connector.
For ohm readings outside
the conditions above
OHMS
COM
V
OHMS
V
Replace output speed sensor and
go to Step V.
COM
Ground
2-23
Page 78

Fault Isolation Procedures
Code 58 (PID 191, FMI 2) Output Shaft Speed Sensor, continued
Step V Procedure Condition Action
1. Replace all connectors.
2. Clear any codes.
3. Drive vehicle to test
effectiveness of repair.
No fault codes Repair complete.
Code reappears or other
fault occurs
Return to appropriate test
procedure.
2-24
(PID 191, FMI 2)
Code 58
Page 79

Fault Isolation Procedures
System Code 66 (SID 58, FMI 1) Unconfirmed Torque Path
Overview
This fault code indicates that the current input and output
speeds do not match the current selected gear position ratio.
Required Tools
• Basic Hand Tools
Possible Causes
Detection
This fault code can only be set as an active fault code while
driving the vehicle. The transmission ECU constantly
monitors engine speed, output speed, shift lever position,
and splitter button position to confirm actual gear position. The ECU will set the fault when speed information
and gear position do not match for at least ten seconds
with the master clutch engaged
Fallback
The transmission defaults to five-speed shifting with either all odd or all even number gears.
This fault can be caused by any of the following:
• Slipping Clutch
• Clutch Switch Failure
• Electrical Interference with J-1939 link or Transmission ECU.
• Service work on the vehicle created high electrical current through the transmission such as improper arc welding techniques.
• Output Speed Sensor
• Transmission ECU
2-25
Page 80

Fault Isolation Procedures
Code 66 (SID 58, FMI 1) Unconfirmed Torque Path
Step A Procedure Condition Action
1. Test drive vehicle to
determine clutch
performance.
Clutch slips or has other
noticeable performance
problems.
Clutch performs
according to
manufacturer
specification
Repair clutch according to
manufacturer specification and
retest.
Go to Step B.
Step B Procedure Condition Action
1. Perform diagnostics on
clutch switch per OEM
or manufacturer
recommendation.
Note: Clutch switch failure also
results in an inoperable
engine brake and cruise
control.
Clutch switch does not
pass diagnostics test
Clutch switch passes
diagnostics test
Replace clutch switch per
manufacturer or OEM
recommendations
Go to Step C.
Step C Procedure Condition Action
1. Using a hand-held tool
or similar tool, drive
the vehicle and
monitor output speed
in 9th gear.
Output speed matches
engine rpm within 50
rpm
Output speed and engine
rpm do not match
Problem lies outside the
transmission. Contact vehicle or
engine manufacturer
Go to Step D.
(SID 58, FMI 1)
Code 66
Step D Procedure Condition Action
1. Perform Diagnostics
for Code 58 Output
Speed Sensor.
Output speed sensor test
passes
Output speed sensor test
fails
Go to Step E.
Perform Repairs and Go to Step V.
2-26
Page 81

Fault Isolation Procedures
Code 66 (SID 58, FMI 1) Unconfirmed Torque Path, continued
Step E Procedure Condition Action
1. Perform diagnostics
for Position Sensor
Code 36.
Position Sensor Test
Passes
Position Sensor Test
Fails
Replace Transmission ECU. Go to
Step V.
Perform Repairs and Go to Step V.
Step V Procedure Condition Action
1. Test drive vehicle to
test effectiveness of
repair.
Transmission operates
properly and code does
not reappear
Transmission fault code
reappears
Test Complete
Repeat test procedures for Active
Fault.
2-27
Page 82

Fault Isolation Procedures
This page left blank intentionally.
(SID 58, FMI 1)
Code 66
2-28
Page 83

Fault Isolation Procedures
System Code 71 (SID 61, FMI 7) Range or Splitter Stuck in Gear
Overview
This fault code indicates the transmission was unable to
move the front box to neutral during a shift request.
Detection
Required Tools
• Basic Hand Tools
Possible Causes
This fault code is set differently for Top 2 shifts and nonTop 2 shifts and it can only be set as an active fault code
while driving the vehicle.
1) For non-Top 2 shifts the fault code will be set during a
shift attempt after the engine has crossed through zero
torque five time and the transmission is unable to pull the
splitter or range out of gear.
2) For Top 2 shifts the transmission controls the throttle
and the fault code will be set if attempts to pull the splitter
out of gear have failed after nine seconds. The driver
should notice continuous engine throttle blips or surges
and no manual throttle control during this nine-second
period prior to setting the fault code.
Fallback
The transmission defaults to five-speed shifting with either all odd or all even number gears for an inoperable
splitter system or six speed shifting for an inoperable
range system.
This fault can be caused by any of the following:
• Air regulator malfunction
• Air cylinder malfunctions such as excessive air
leaks or contamination
• Solenoid Mechanical Malfunctions
• Transmission internal damage with components
such as range or splitter shift components
2-29
Page 84

Fault Isolation Procedures
Code 71 (SID 61, FMI 7) Range or Splitter Stuck in Gear
Step A Procedure Condition Action
1. Key on, vehicle running
2. Test drive vehicle in a safe area
then place the lever into 3rd
gear.
3. Drive the vehicle and
attempt to make an upshift to 4th gear.
Transmission completes
shift
Transmission does not
complete shift to 4th gear
Go to Step V.
Perform Splitter Cylinder Test.
Step V Procedure Condition Action
1. Key on, vehicle running
2. Test drive vehicle in a safe area
then place the lever into 6th gear
3. Drive the vehicle and
attempt to make an upshift to 7th gear.
Transmission does not
complete shift to 7th.
Transmission goes back
to 6th or 3rd/4th gear
when vehicle has slowed
down to 3rd/4th gear
road speed.
Transmission completes
shift
Perform Range Cylinder Test.
Repeat test procedures to isolate
problem.
(SID 61, FMI 7)
Code 71
2-30
Page 85

Fault Isolation Procedures
System Code 73 (SID 58, FMI 11) Transmission Missed Synchronous
Overview
An indication the transmission has failed to achieve complete ratio synchronization on splitter or range shifts
where engine control is involved. The code can only be set
as an active code while driving the vehicle and it can not
be set while in Top 2 (auto) mode.
Detection
This fault code can only be set as an active fault code while
driving the vehicle. Upon completion of an engine controlled non-Top 2 range or splitter shift, the transmission
monitors gear ratio match information while the engine is
reapplying torque. This fault code will be set if the ratio information fails to remain constant during the engine
torque ramp-up on any three shift attempts during one vehicle key-on cycle.
Required Tools
• Basic Hand Tools
Possible Causes
This fault can be caused by any of the following:
• Clutch or clutch switch malfunction
• Air system malfunction such as low pressure,
contamination, or leaks
• Transmission ECU
Fallback
All gears remain available but engine control is fully returned to the driver.
Transmission ECU
2-31
Page 86

Fault Isolation Procedures
Code 73 (SID 58, FMI 11) Transmission Missed Synchronous
Step A Procedure Condition Action
1. Test drive vehicle to
determine clutch
performance.
Clutch slips or has other
noticeable performance
problems
Clutch performs
according to
manufacturer
specification
Repair clutch according to
manufacturer specification and
retest.
Go to Step B.
Step B Procedure Condition Action
1. Perform diagnostics on
clutch switch per OEM
or manufacturer
recommendation.
Note: Clutch switch failure also
results in an inoperable
engine brake and cruise
control.
Clutch switch does not
pass diagnostics test
Clutch switch passes
diagnostics test
Replace clutch switch per
manufacturer or OEM
recommendations and retest.
Go to Step C.
Step C Procedure Condition Action
1. Test drive vehicle and
attempt to duplicate
complaint by
performing splitter
shifts and range shifts.
Fault code is set while
performing splitter shifts
Perform Splitter Cylinder Test.Go
to Step V.
Transmission Missed
SynchronousCode 73
Note: The fault code will be set if
the gear ratio match
information fails to remain
constant during engine
torque ramp-up on any
three shifts during one
key-on cycle.
Fault code is set while
performing range shifts
Perform Range Cylinder Test. Go
to Step V.
Step V Procedure Condition Action
1. Determine if air system
tests for Range or
Splitter systems pass
for air related issues.
Tests fail for air related
problems
Tests pass up to point
where you are instructed
to remove and
disassemble transmission
Repair per procedures and retest.
Replace Transmission ECU and
retest.
2-32
Page 87

Fault Isolation Procedures
System Code 74
(SID
14, FMI 7)
Eng
ine Missed Synchronous
Overview
This fault code indicates the engine failed to respond to
transmission
Detection
requests during a splitter shift.
Required Tools
• Eaton Data Link Tester (MF-KIT-04)
Possible Causes
This fault code can only be set as an active fault code while
ing the vehicle. This fault code is set differently for Top
driv
2 shifts and non-Top 2 shifts
For Top 2 shifts, the code will be set if the engine fails
1)
respond to transmission requests for engine control for
to
seconds during any one shift.
nine
For non-Top 2 shifts the code will be set if the engine
2)
to respond to transmission requests for engine con-
fails
for three separate three second occurrences during
trol
vehicle key-on cycle.
one
Fallback
All gears remain available but engine control is returned to
driver for all shifts.
the
This fault can be caused by any of the following:
• J-1939 Communication Link
• Vehicle Dynamics
• Electrical Harness Interface
• Transmission ECU
2-33
Page 88

Fault Isolation Procedures
Code 74 (SID 14, FMI 7) Engine Missed Synchronous
Step A Procedure Condition Action
1. Perform J-1939
communication link
test.
Link passes test Go to Step B.
Link does not pass test Repair link according to test
procedure. Test Complete.
Step B Procedure Condition Action
1. Key on and vehicle running and
parking brakes set.
2. Disengage clutch and place lever
into 7th/8th gear position.
3. Listen for the distinct noise of
the range shifting into high
range.
4. Depress accelerator
pedal.
Vehicle accelerates
above engine idle.
Vehicle does not
accelerate or accelerator
pedal is "dead"
Replace transmission ECU and
position sensor.
Go to Step V.
Note: This is the expected
condition.
(SID 14, FMI 7)
Code 74
2-34
Page 89

Fault Isolation Procedures
Code 74 (SID 14, FMI 7) Engine Missed Synchronous, continued
Step V Procedure Condition Action
1. Key on and vehicle running.
2. Drive vehicle normally until 7th
gear.
3. "Rush" the shift from 7th to 8th
gear by:
• Bringing the
engine to
governed RPM
• Move the splitter
button into the
up position.
• Release the
accelerator and
quickly reapply
Engine accelerates Dynamic communication link
problem. Repair for faulty harness
connections.
Vehicle does not
accelerate or accelerator
pedal is "dead" until shift
is complete
Note: This is the expected
condition.
Contact engine or vehicle
manufacturer to check for proper
vehicle performance characteristics
including:
a. Electrical harness
interface
b. Vehicle dynamics, such as
driveline setup
c. Engine performance
characteristics
2-35
Page 90

Fault Isolation Procedures
Code 74 (SID 14, FMI 7) Engine Missed Synchronous, continued
This page left blank intentionally.
(SID 14, FMI 7)
Code 74
2-36
Page 91

Fault Isolation Procedures
System Code 93 (SID 231, FMI 14) J-1939 Engine Message Fault
Overview
This fault code indicates the transmission Electronic Control Unit (ECU) is broadcasting J-1939 messages and receiving J-1939 messages, but has not received J-1939
messages from the engine or another required devices
such as the chassis control module.
Required Tools
• Basic Hand Tools
• Troubleshooting Guide
Possible Causes
Detection
The fault detected if J-1939 communication from the engine or other required device is lost for 5 seconds.
Fallback
If the fault occurs while moving it will cause a 5-speed fallback in either low or high split depending on last known
gear position. If the fault occurs at system initialization
(key-on), it causes a 5-speed fallback in low split.
J1939 Data Link
(OEM Supplied)
Chassis
ECU
Terminating
Resistor
This fault can be caused by any of the following:
• OEM Supplied J-1939 Harness
• Engine ECM
• Chassis ECM
Terminating
Resistor
2-37
Engine
Engine
ECM
Page 92

Fault Isolation Procedures
Code 93 (SID 231, FMI 14) J-1939 Engine Message Fault
Step AA Procedure Condition Action
1. Key on.
2. If fault code 93 is present,
inactive or active.
3. Inspect OEM J-1939 harness.
If problem found Repair OEM J-1939 harness. Go
to Step V.
If no problem is found Go to Step V.
Step V Procedure Condition Action
1. Key off.
2. Reconnect all connectors.
3. Key on.
4. Clear codes.
5. Test drive vehicle to test
effectiveness of repair.
6. Check for codes. If no codes Test complete.
If code 93 appears Return to Step A to find error in
testing.
If code other than 93 appears Go to Fault Code Table on page
1-7 to diagnose.
(SID 231, FMI 14)
Code 93
2-38
Page 93

Reverse Switch Test Overview
Overview
Fault Isolation Procedures
The reverse switch is a normally open switch. When the
shift lever is in the reverse gear position the switch closes
and electrical current flows through the switch.
Detection
The reverse switch normally provides an electrical signal
to the vehicle back-up lights or alarm when the transmission shift lever is in the reverse gear position. The reverse
switch is indepentent from the transmission controls. A
failure of the switch or vehicle wiring running to the switch
will not effect transmission operation.
Fallback
No Fallback Condition.
Required Tools
• Basic Hand Tools
• Digital Volt/Ohm Meter
• Troubleshooting Guide
Possible Causes
This fault can be caused by any of the following:
• Shorted or failed open switch
• Actuating pin failure
Reverse Switch
Location
Neutral Switch
Location
Shift Knob
Connection
ECU
Assembly
Output
Speed Sensor
18-pin
ECU Connector
Transmission Electrical Attachment Points
2-39
Page 94

Fault Isolation Procedures
Reverse Switch Test
Step A Procedure Condition Action
1. Key off.
2. Disconnect connector from
reverse switch and place shift
lever in reverse.
3. Measure resistance
between the two pins
If resistance is between 0
to .3 ohms
Go to Step B.
on the reverse switch.
If resistance is outside of
Go to Step V.
range or open
Step B Procedure Condition Action
1. Key off.
2. Place shift lever in any gear
position other than reverse.
3. Measure resistance
between the two pins
on the reverse swich.
VOLTS
B
A
V
COM
A
If resistance is open Reverse switch is functioning.
Repair vehicle wiring harness.
If resistance is not open
Go to Step V.
or infinite
Reverse Switch Test
2-40
Page 95

Fault Isolation Procedures
Reverse Switch Test, continued
Step V Procedure Condition Action
1. Remove reverse switch from
transmission.
2. Inspect reverse switch
opening checking for
actuating pin
movement while
moving the shift lever.
The pin should drop
deeper in the hold with
the transmission in
any non-reverse gear
position and move out
in the hold when
reverse gear is selected.
If pin moves in and out
freely
If pin does not move
freely or sticks
Replace reverse switch and retest.
Remove actuating pin and inspect.
Then repair or replace any faulty
parts.
2-41
Page 96

Reverse Switch Test, continued
Fault Isolation Procedures
Reverse Switch Test
2-42
Page 97

Fault Isolation Procedures
Neutral Switch Test Overview
Overview
The neutral switch is a normally closed switch. When the
shift lever is in the neutral position the switch is closed
and electrical current flows through the switch.
Detection
This may cause a malfunction of accessory equipment
powered by the Power Take Off (PTO) gear.
Fallback
No Fallback Condition.
Required Tools
• Basic Hand Tools
• Digital Volt/Ohm Meter
• Troubleshooting Guide
Possible Causes
This fault can be caused by any of the following:
• Shorted or failed open switch
• Actuating pin failure
Reverse Switch
Location
Neutral Switch
Location
Shift Knob
Connection
ECU
Assembly
Output
Speed Sensor
18-pin
ECU Connector
Transmission Electrical Attachment Points
2-43
Page 98

Fault Isolation Procedures
Neutral Switch Test
Step A Procedure Condition Action
1. Key off.
2. Disconnect wire connector from
neutral switch and place shift
lever in neutral.
3. Measure resistance
between the two pins
If resistance is 0 to .3
ohms
Go to Step B.
on the neutral switch.
If resistance is outside of
Go to Step V.
range or open
Step B Procedure Condition Action
1. Key off.
2. Place shift lever in any gear
position other than neutral.
3. Measure resistance
between the two pins
on the neutral switch.
VOLTS
B
A
V
COM
A
If resistance is open Neutral switch passes, inspect
vehicle wiring harness.
If resistance is not open Go to Step V.
Neutral Switch Test
Step V Procedure Condition Action
1. Remove neutral switch from
transmission.
2. Inspect neutral switch
opening checking for
actuating pin
movement while moving the
shift lever.
If pin moves in and out
freely
If pin does not move
freely or sticks
Replace neutral switch and retest.
Remove actuating pin and inspect.
Then repair or replace any faulty
parts.
2-44
Page 99

Copyright Eaton Corporation, 2012.
Eaton hereby grant their customers,
vendors, or distributors permission
to freely copy, reproduce and/or
distribute this document in printed
format. It may be copied only in
its entirety without any changes or
modifications. THIS INFORMATION
IS NOT INTENDED FOR SALE OR
RESALE, AND THIS NOTICE MUST
REMAIN ON ALL COPIES.
Note: Features and specifications
listed in this document are subject to
change without notice and represent
the maximum capabilities of the
software and products with all options
installed. Although every attempt has
been made to ensure the accuracy of
information contained within, Eaton
makes no representation about the
completeness, correctness or accuracy
and assumes no responsibility for
any errors or omissions. Features and
functionality may vary depending on
selected options.
For spec’ing or service assistance,
call 1-800-826-HELP (4357) or visit
www.eaton.com/roadranger.
In Mexico, call 001-800-826-4357.
Roadranger: Eaton and trusted partners
providing the best products and services in the
industry, ensuring more time on the road.
Eaton Corporation
Vehicle Group
P.O. Box 4013
Kalamazoo, MI 49003 USA
800-826-HELP (4357)
www.eaton.com/roadranger
Printed in USA
Page 100

For parts or service call us
Pro Gear & Transmission, Inc.
1 (877) 776-4600
(407) 872-1901
parts@eprogear.com
906 W. Gore St.
Orlando, FL 32805
 Loading...
Loading...