Page 1

Service Manual
Eaton Fuller® HD FR/FRO Transmissions
TRSM2400 EN-US
May 2013
FR-11210B
FR-12210B
FR-13210B
FR-14210B
FR-15210B
FR-9210B
FRF-11210B
FRF-12210B
FRF-13210B
FRF-14210B
FRF-15210B
FRF-9210B
FRO-11210B
FRO-11210C
FRO-12210B
FRO-12210C
FRO-13210B
FRO-13210C
FRO-14210B
FRO-14210C
FRO-15210B
FRO-15210C
FRO-16210B
FRO-16210C
FRO-17210C
FRO-18210C
FROF-11210B
FROF-11210C
FROF-12210B
FROF-12210C
FROF-13210B
FROF-13210C
FROF-14210B
FROF-14210C
FROF-15210B
FROF-15210C
FROF-16210B
FROF-16210C
Page 2

Warnings and Precautions
WARNING
!
WARNING
CAUTION
Warnings and Precautions
Before starting a vehicle, always be seated in the driver’s seat, place the Transmission in Neutral, set the Parking Brakes
and disengage the Clutch.
Before working on a vehicle, place the Transmission in Neutral, set the Parking Brakes and block the wheels.
Before towing the vehicle, place the Transmission in Neutral, and lift the rear wheels off the ground, remove the Axle Shafts,
or disconnect the Driveline to avoid damage to the Transmission during towing.
The description and specifications contained in this service publication are current at the time of printing.
Eaton reserves the right to discontinue or modify its models and/or procedures and to change specifications at any time
without notice.
Any reference to brand name in this publication is made as an example of the types of tools and materials recommended for use
and should not be considered an endorsement. Equivalents may be used.
This symbol is used throughout this manual to call attention to procedures where carelessness or failure to follow
specific instructions may result in personal injury and/or component damage.
Departure from the instructions, choice of tools, materials and recommended parts mentioned in this publication may jeopardize
the personal safety of the Service Technican or vehicle operator.
Failure to follow indicated procedures creates a high risk of personal injury to the Service Technician.
Failure to follow indicated procedures may cause component damage or malfunction.
Note: Additional service information not covered in the service procedures.
Tip: Helpful removal and installation procedures to aid in the service of this unit.
Always use genuine Eaton replacement parts.
i
Page 3

Introduction
Purpose and Scope of Manual .................................... 1
How to use this Manual............................................... 1
Disassemble Precautions ............................................ 1
Inspection Precautions................................................ 2
Assembly Precautions................................................. 4
Model Designations
Serial Tag Information and Model Nomenclature ........ 5
Model Options............................................................. 6
Lubrication
Transmission Lubrication ............................................8
Oil Leak Inspection Process ........................................ 9
Tools
Tool Specifications .................................................... 10
General Tools....................................................... 10
Special Tools Manufacturers................................ 12
Eaton Aftermarket Parts ....................................... 12
General Information
Torque Specifications ................................................ 13
Power Flow Diagrams ............................................... 15
Front Section Power Flow .................................... 16
Front Section Power Flow - Direct Gear ............... 17
Front Section Power Flow - Reverse Gear............ 18
Auxiliary Section Power Flow - Low Range .......... 19
Auxiliary Section Power Flow - High Range ......... 20
FR/FRO-1X210 ..................................................... 21
Air System Troubleshooting ...................................... 25
Air System Symptom - Air leak from Module
Base (Exhaust)..................................................... 26
Air System Symptom - No or Slow Range Shift
into High (Shift into Low Range is Good) ............ 27
Air System Symptom - No or Slow Range Shift
into Low (Shift into High is Good) ....................... 30
Air System Symptom - Constant Air Leak from
Shift Knob ............................................................ 33
Air System Symptom - Range Shift While
Transmission is in Gear ....................................... 34
Air System Symptom - Air Leak From Breather or
Case is Pressurized.............................................. 35
General Troubleshooting Chart ............................ 36
Air System Overview .................................................39
Air Module Part Nomenclature ............................. 41
Air Module Interlock............................................. 42
Air System Air Flow.............................................. 45
Air Module Operation ........................................... 48
Air System Nomenclature .................................... 51
Table of Contents
Timing Procedures
Timing Procedures ....................................................53
In-Vehicle Service Procedures
How to Disassemble the Roadranger Valve ...............55
How to Assemble the Roadranger Valve ....................57
How to Remove Compression Type Fittings ..............58
How to Install Compression Type Fittings .................59
How to Remove Push-To-Connect Type Fittings .......60
How to Install Push-To-Connect Type Fittings ...........61
How to Remove a Roadranger Valve .........................62
How to Install a Roadranger Valve .............................63
How to Remove the Gear Shift Lever/
Remote Shift Control .................................................64
How to Install the Gear Shift Lever/
Remote Shift Control .................................................65
In-Vehicle Service ProceduresHow to Adjust
the Remote Shift Control (LRC Type) ........................66
How to Remove the Detent Spring .............................68
How to Install the Detent Spring ................................69
Neutral Switch Operation and Testing ........................70
How to Remove the Neutral Switch ...........................71
How to Install the Neutral Switch ...............................72
Reverse Switch Operation and Testing ......................73
How to Remove the Reverse Switch ..........................74
How to Install the Reverse Switch .............................75
How to Install the Shift Bar Housing ..........................76
How to Remove the Shift Bar Housing ......................77
How to Remove the Oil Seal Mechanical/
Magnetic Speedometer ..............................................78
How to Install the Oil Seal Mechanical/
Magnetic Speedometer ..............................................80
How to Remove the Auxiliary Section in Chassis .......82
How to Install the Auxiliary Section in Chassis ..........84
How to Disassemble the Integral Oil Cooler ...............88
How to Assemble the Integral Oil Cooler ...................89
How to Remove the Air Module .................................90
How to Install the Air Module ....................................92
ii
Page 4

Table of Contents
Transmission Overhaul Procedures - Bench Service
How to Disassemble the Gear Shift Lever ................. 93
How to Assemble the Gear Shift Lever ...................... 95
How to Remove the Shift Bar Housing ...................... 97
How to Install the Shift Bar Housing ......................... 98
How to Disassemble the Shift Bar Housing ............... 99
How to Disassemble the Range Cylinder ................. 102
How Assemble the Range Cylinder ......................... 103
How to Assemble the Shift Bar Housing ................. 105
How to Remove the Input Shaft Assembly
(without Main Case disassembly) ........................... 109
How to Install the Input Shaft Assembly
(without Main Case disassembly) ........................... 111
How to Remove the Auxiliary Section ..................... 113
How to Disassemble the Auxiliary Section .............. 115
How to Disassemble the Range Yoke ...................... 118
How to Disassemble the Output Shaft ..................... 119
How to Disassemble the Synchronizer Assembly .... 120
How to Assemble the Synchronizer Assembly ........121
How to Remove the Clutch Housing ........................ 123
How to Assemble the Output Shaft ......................... 124
How to Assemble the Range Yoke .......................... 125
How to Disassemble the Auxiliary Countershaft ...... 126
How to Remove the Auxiliary Countershaft
Bearing Races ......................................................... 127
How to Install the Auxiliary Countershaft
Bearing Races ......................................................... 128
How to Assemble the Auxiliary Countershaft .......... 129
How to Remove the Auxiliary Drive Gear Assembly 130
How to Disassemble the Upper and Lower
Reverse Idler Gear Assembly .................................. 132
How to Remove the Countershaft Bearings and
Countershaft Assemblies ........................................ 134
How to Remove the Mainshaft Assembly ................ 136
How to Disassemble the Countershaft Assemblies . 138
How to Remove the Input Shaft and Main
Drive Gear ............................................................... 140
How to Prepare the Main Case for Reassembly ...... 142
How to Disassemble the Mainshaft Assembly ......... 143
How to Assemble the Mainshaft Assembly ............. 145
How to Install the Mainshaft Assembly ................... 148
How to Assemble the Countershaft Assemblies ...... 150
How to Assemble the Lower Reverse Idler
Gear Assembly ........................................................ 152
How to Install Countershaft Assemblies .................. 154
How to Install the Lower Countershaft Bearings ......155
How to Install the Input Shaft and Main Drive Gear .157
How to Install the Input Bearing Cover ....................159
How to Install the Upper Countershaft Bearings ......160
How to Install the Upper Reverse Idler
Gear Assembly .........................................................162
How to Install the Auxiliary Drive Gear Assembly ....164
How to Install the Clutch Housing ...........................165
How to Remove the Oil Pump ..................................166
How to Install the Oil Pump .....................................167
How to Install the Oil Seal ........................................168
How to Assemble the Auxiliary Section ...................169
How to Install the Auxiliary Section .........................173
Shim Procedure without a Shim Tool for
Tapered Bearings .....................................................175
iii
Page 5

Introduction
Introduction
Purpose and Scope of Manual
This Manual is designed to provide information necessary to service and repair the Eaton Fuller Transmissions listed on the front.
How to use this Manual
The service procedures have been divided into two sections: In-Vehicle Service Procedures and Transmission Overhaul
Procedures—Bench Service. In-Vehicle Service Procedures contain procedures that can be performed while the Transmission is
still installed in the vehicle. Transmission Overhaul Procedures contain procedures that are performed after the Transmission has
been removed from the vehicle.
The procedure sections are laid out with a general heading at the top outside edge of each page followed by more specific headings
and the procedures. To find the information you need in these sections, first go to the section that contains the procedure you
need. Then look at the heading at the top and outside edge of each page until you find the one that contains the procedure you need.
Transmission Overhaul Procedures follow the general steps for complete disassembly and then assembly of the Transmission.
Note: In some instances the Transmission appearance may be different from the illustrations, but the procedure is the same.
Disassemble Precautions
It is assumed in the detailed assembly instructions that the lubricant has been drained from the Transmission, the necessary
linkage and vehicle air lines disconnected and the Transmission has been removed from vehicle chassis. Removal of the Gear Shift
Lever Housing Assembly (or Remote Control Assembly) is included in the detailed instructions (How to Remove the Gear Shift
Lever). This assembly MUST be detached from the Shift Bar Housing before the Transmission can be removed.
Follow closely each procedure in the detailed instructions, make use of the text, illustrations, and photographs provided.
Assemblies
• When disassembling the various assemblies, such as the Mainshaft, Countershafts, and Shift Bar Housing, lay all parts
on a clean bench in the same sequence as removed. This procedure will simplify assembly and reduce the possibility of
losing parts.
Bearings
• Carefully wash and lubricate all usable bearings as removed and protectively wrap until ready for use. Remove bearings
planned to be reused with pullers designed for this purpose.
Cleanliness
• Provide a clean place to work. It is important that no dirt or foreign material enters the unit during repairs. Dirt is an
abrasive and can damage bearings. It is always a good practice to clean the outside of the unit before starting the planned
disassembly.
Input Shaft
• The Input Shaft can be removed from the Transmission without removing the Countershafts, Mainshaft, or Main Drive
Gear. Special procedures are required and provided in this Manual.
Snap Rings
• Remove Snap Rings with pliers designed for this purpose. Snap Rings removed in this manner can be reused, if they are
not sprung or loose.
When Using Tools to Move Parts
• Always apply force to shafts, housings, etc., with restraint. Movement of some parts is restricted. Never apply force to
driven parts after they stop solidly. The use of Soft Hammers, Soft Bars, and Mauls for all disassembly work is
recommended.
1
Page 6

For parts or service call us
Pro Gear & Transmission, Inc.
1 (877) 776-4600
(407) 872-1901
parts@eprogear.com
906 W. Gore St.
Orlando, FL 32805
Page 7

Introduction
Inspection Precautions
Before assembling the Transmission, check each part carefully for abnormal or excessive wear and damage to determine reuse or
replacement. When replacement is necessary, use only genuine Eaton® Fuller® Transmission parts to assure continued
performance and extended life from your unit.
Since the cost of a new part is generally a small fraction of the total cost of downtime and labor, avoid reusing a questionable part
which could lead to additional repairs and expense soon after assembly. To aid in determining the reuse or replacement of any
Transmission part, consideration should also be given to the unit's history, mileage, application, etc.
Recommended inspection procedures are provided in the following checklist.
Bearings
• Wash all bearings in clean solvent. Check balls, rollers, and raceways for pitting, discoloration, and spalled areas.
Replace bearings that are pitted, discolored, spalled, or damaged during disassembly.
• Lubricate bearings that are not pitted, discolored, or spalled and check for axial and radial clearances.
• Replace bearings with excessive clearances.
• Check bearing fit. Bearing inner races should be tight to shaft; outer races slightly tight to slightly loose in case bore.
If the bearing spins freely in the bore the case should be replaced.
Bearing Covers
• Check covers for wear from thrust of adjacent bearing. Replace covers damaged from thrust of bearing outer race.
• Check cover bores for wear. Replace those worn or oversized.
Clutch Release Parts
• Check clutch release parts. Replace yokes worn at cam surfaces and bearing carrier worn at contact pads.
• Check pedal shafts. Replace those worn at bushing surfaces.
Gears
• Check gear teeth for frosting and pitting. Frosting of gear teeth faces presents no threat of Transmission failure. Often in
continued operation of the unit, frosted gears "heal" and do not progress to the pitting stage. In most cases, gears with
light to moderate pitted teeth have considerable gear life remaining and can be reused, but gears in the advanced stage
of pitting should be replaced.
• Check for gears with clutching teeth abnormally worn, tapered, or reduced in length from clashing during shifting.
Replace gears found in any of these conditions.
• Check axial clearance of gears.
Gear Shift Lever Housing Assembly
• Check spring tension on Shift Lever. Replace Tension Spring if Lever moves too freely.
• If housing is disassembled, check Gear Shift Lever bottom end and Shift Finger Assembly for wear. Replace both gears
if excessively worn.
2
Page 8

Introduction
Introduction
Gray Iron Parts
• Check all gray iron parts for cracks and breaks. Replace parts found to be damaged.
Oil Return Threads and Seals
• Check oil return threads on the Input Shaft. If return action of threads has been destroyed, replace the Input Shaft.
• Check Oil Seal in Rear Bearing Cover. If sealing action of lip has been destroyed, replace seal.
O-Rings
• Check all O-rings for cracks or distortion. Replace if worn.
Reverse Idler Gear Assemblies
• Check for excessive wear from action of roller bearings.
Shift Bar Housing Assembly
• Check for wear on Shift Yokes and Block at pads and lever slot. Replace excessively worn parts.
• Check Yokes for correct alignment. Replace sprung Yokes.
• If housing has been disassembled, check Shift Shaft and all related parts for wear.
Sliding Clutches
• Check all Shift Yokes and Yoke Slots in Sliding Clutches for extreme wear or discoloration from heat.
• Check engaging teeth of Sliding Clutches for partial engagement pattern.
Splines
• Check splines on all shafts for abnormal wear. If Sliding Clutch Gears, Companion Flange, or Clutch Hub has wear marks
in the spline sides, replace the specific shaft effected.
Synchronizer Assembly
• Check Synchronizer for burrs, uneven and excessive wear at contact surface, and metal particles.
• Check Blocker Pins for excessive wear or looseness.
• Check Synchronizer contact surfaces on the Synchronizer Cups for wear.
Washers
• Check surfaces of all washers. Washers scored or reduced in thickness should be replaced.
3
Page 9

Introduction
IMPORTANT
Assembly Precautions
Make sure that case interiors and housings are clean. It is important that dirt and other foreign materials are kept out of the
Transmission during assembly. Dirt is an abrasive and can damage polished surfaces of bearings and washers. Use certain
precautions, as listed below, during assembly.
Bearings
• Use a Flange-End Bearing Driver for bearing installation. These special drivers apply equal force to both bearing races,
preventing damage to balls/rollers and races while maintaining correct bearing alignment with bore and shaft. Avoid
using a tubular or sleeve-type driver, whenever possible, as force is applied to only one of the bearing races.
Capscrews
• To prevent oil leakage and loosening, use Eaton Fuller Sealant #71205 on all capscrews.
Gaskets
• Use new gaskets throughout the Transmission as it is being rebuilt. Make sure all gaskets are installed. An omission of
any gasket can result in oil leakage or misalignment of bearing covers.
Initial Lubrication
• Coat all limit washers and shaft splines with Lubricant during assembly to prevent scoring and galling of such parts.
O-Rings
• Lubricate all O-rings with silicon lubricant.
Universal Joint Companion Flange or Yoke
• Pull the Companion Flange or Yoke tightly into place with the Output Shaft Nut, using 650–700 lb. ft. of torque. Make
sure the Speedometer Drive Gear or a replacement spacer of the same width has been installed. Failure to pull the
Companion Flange or Yoke tightly into place can result in damage to the Mainshaft Rear Bearing.
See the appropriate Illustrated Parts Lists (specified by model series) to ensure that proper parts are used during assembly
of the Transmission.
4
Page 10
Model Designations
Model Designations
FR
-
14210C
Ratio SetRatio Set
Forward SpeedsForward Speeds
This (x) 100 = Nominal Torque CapacityThis (x) 100 = Nominal Torque Capacity
= Helical Auxilary Gearing and = Helical Auxilary Gearing and
"Multi-Mesh" Front Gearing"Multi-Mesh" Front Gearing
EatonEaton Fuller Fuller Model Designation Prefix Model Designation Prefix
See options below:See options below:
Fuller Roadranger Twin CountershaftFuller Roadranger Twin Countershaft
FRFFRF w/ Forward Shift Bar Housingw/ Forward Shift Bar Housing
FROFRO w/ Overdrive w/ Overdrive
FROFFROF w/ Overdrive and Forward Shift Bar Housingw/ Overdrive and Forward Shift Bar Housing
PrefixPr ef ix
DefinitionDefin it ion
FRFR
2
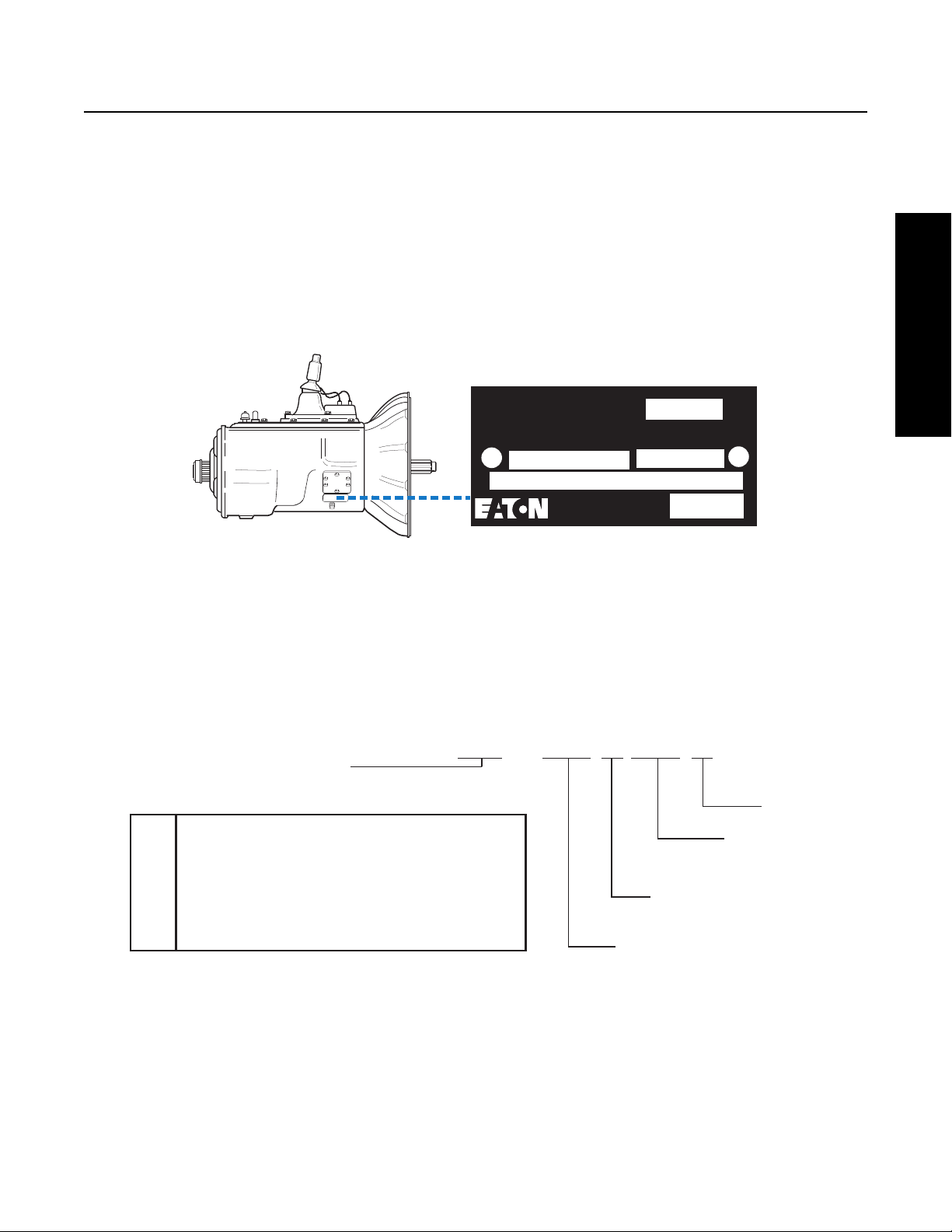
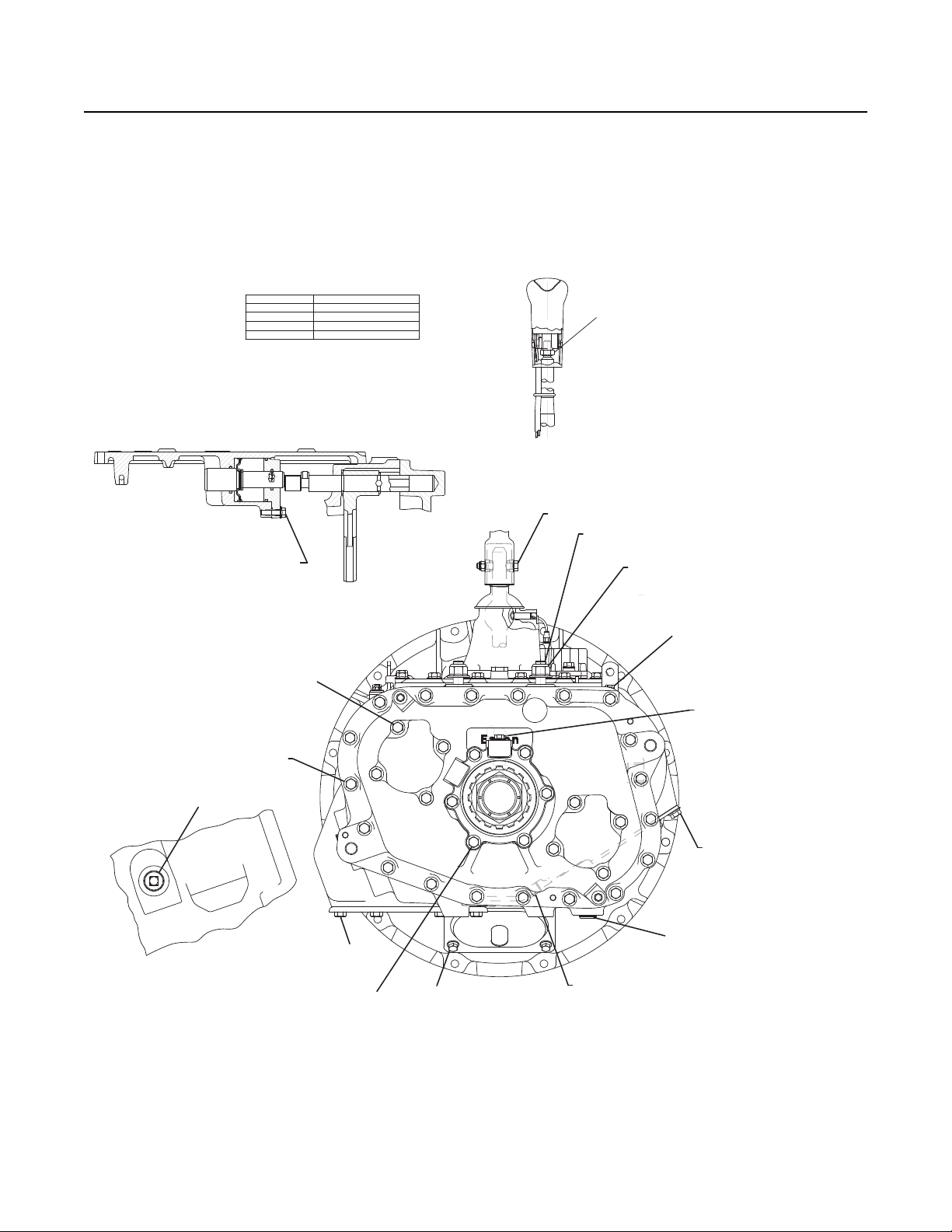
Serial Tag Information and Model Nomenclature
Transmission model designation and other Transmission Identification information are stamped on the Serial Tag. To identify the
Transmission Model and Serial Number, locate the Tag on the Transmission and then locate the numbers as shown. Figure 1-1
below shows the Tag which is located on the Transmission.
When calling for service assistance or parts, have the Model and Serial Numbers handy.
Do not remove or destroy the Transmission Identification Tag!
PTO Code
Eaton Fuller
Transmissions
Model
FRO-14210-C
Eaton Corporation
Transmission Div
Kalamazoo, MI 49003
Made
In
Serial
Fig 1-1
Transmission Tag and Location
Model Number
The Model Number gives basic information about the Transmission and is explained below. Use this number when calling for
service assistance or replacement parts.
Serial Number
The Serial Number is the sequential identification number of the Transmission. Before calling for service assistance, write the
number down as it may be needed.
Bill of Material or Customer Number
This number may be located below the Model and Serial Numbers. It is a reference number used by Eaton®.
5
Page 11
Model Designations
Model Options
Torque Rating
The torque rating of the Transmission specified in the Model Number is the Input Torque Capacity in lb. ft. Various torque ratings
are available. For more information, call the Roadranger Help Desk at 1-800-826-HELP (4357).
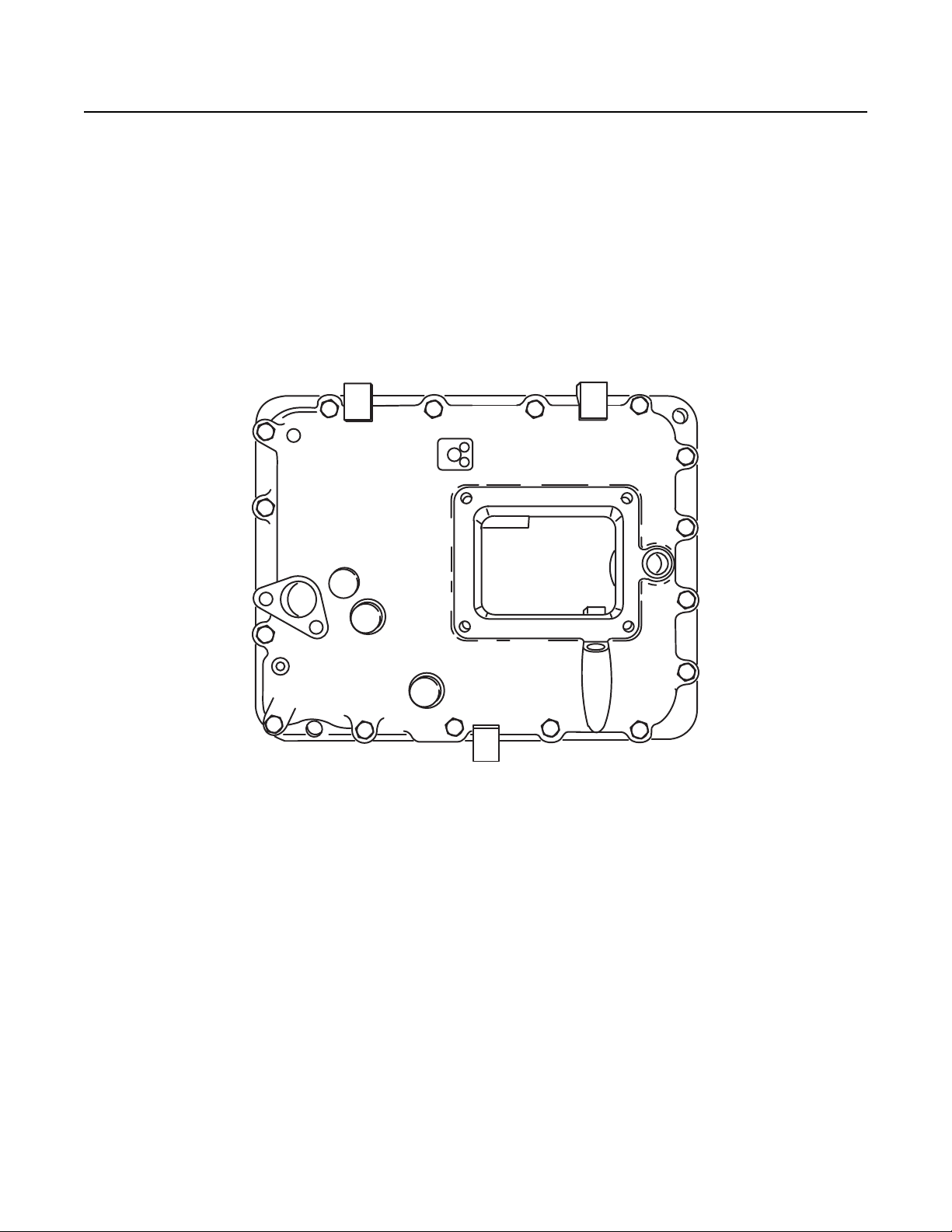
Two types of Shift Bar Housings are available for this Transmission. Both are described and shown below.
Shift Bar Housings
Standard: The standard Shift Bar Housing has a Gear Shift Lever opening that is located toward the rear of the Transmission. The
Housing is shown in figure 1-2.
Fig 1-2
6
Page 12
Model Designations
Model Designations
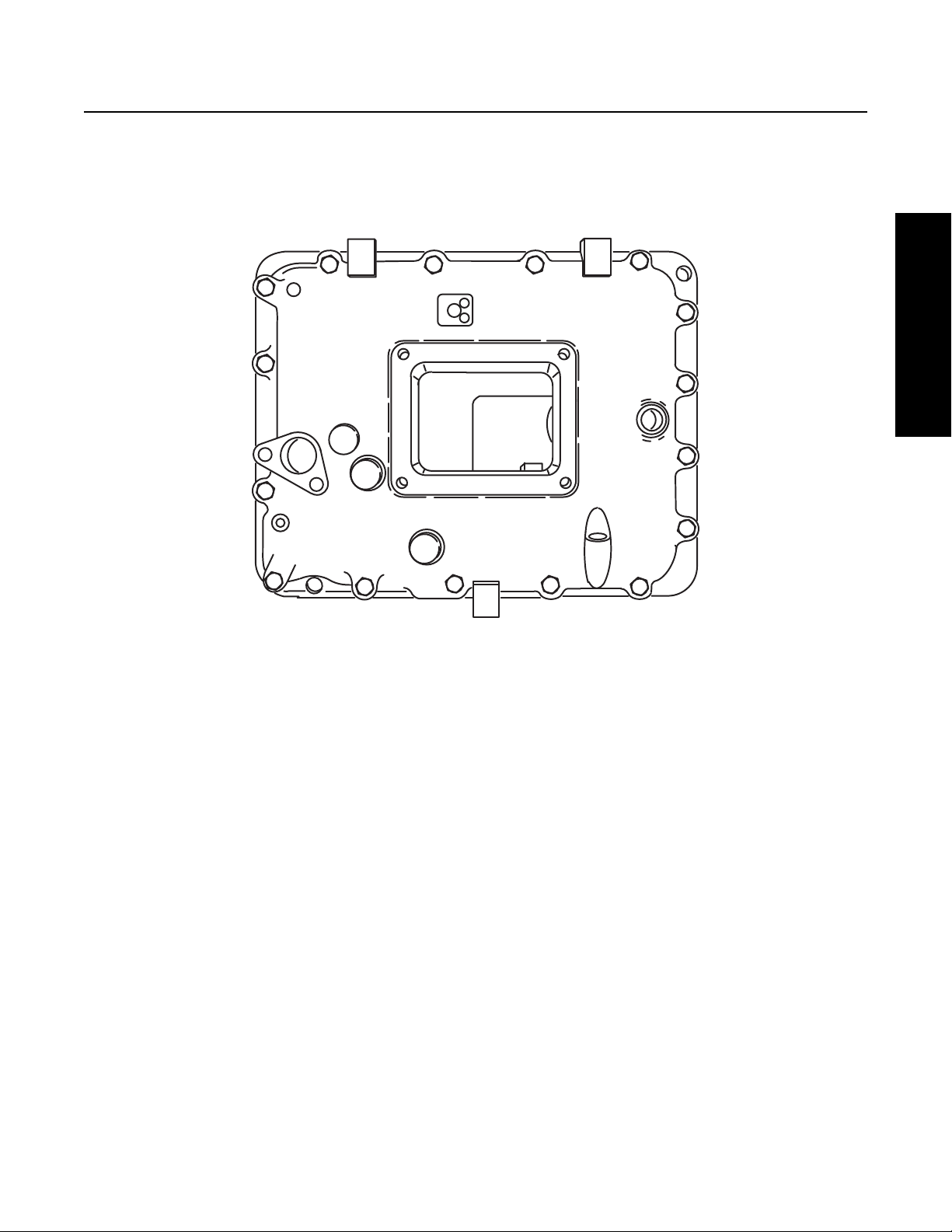
Forward Opening: The Forward Opening Shift Bar Housing has a Gear Shift Lever opening located three inches closer to the front
of the Transmission than the standard opening. This forward design allows greater flexibility in mounting the Transmission and
in indicated by an “F” in the Model Number. The Housing is shown in figure1-3.
Fig 1-3
Lubrication Pumps
Two types of lubrication pumps are available for use on this Transmission and are described below:
PTO Driven: A PTO Driven Pump is externally mounted on the 6 or 8 bolt PTO openings and driven off the PTO Gear.
Auxiliary Countershaft: An Auxiliary Countershaft Pump is mounted on the rear of the Transmission and driven off the
Auxiliary Countershaft.
Power Take Off (PTO) Usage
PTO’s can be mounted in the following ways:
6 or 8 Bolt: The 6 or 8 bolt openings are standard with the Transmission. The PTO is mounted to the opening and driven from the
PTO Gear on the Front Countershaft.
Thru-Shaft: The Thru-Shaft PTO mounts on the rear of the Transmission. It requires a special Auxiliary Housing and Main Case
Countershaft with internal splines.
7
Page 13

Lubrication
IMPORTANT
Transmission Lubrication
Reference Lubrication Manual TCMT-0021 on Roadranger.com or call 800-826-4357 for a list of approved transmission
lubricants.
Note: The use of lubricants not meeting these requirements will affect warranty coverage.
Transmission Filters should be changed during regular lube intervals. Inspection of the Transmission Filter should be
conducted during preventive maintenance checks for damage or corrosion. Replace as necessary.
8
Page 14
Lubrication
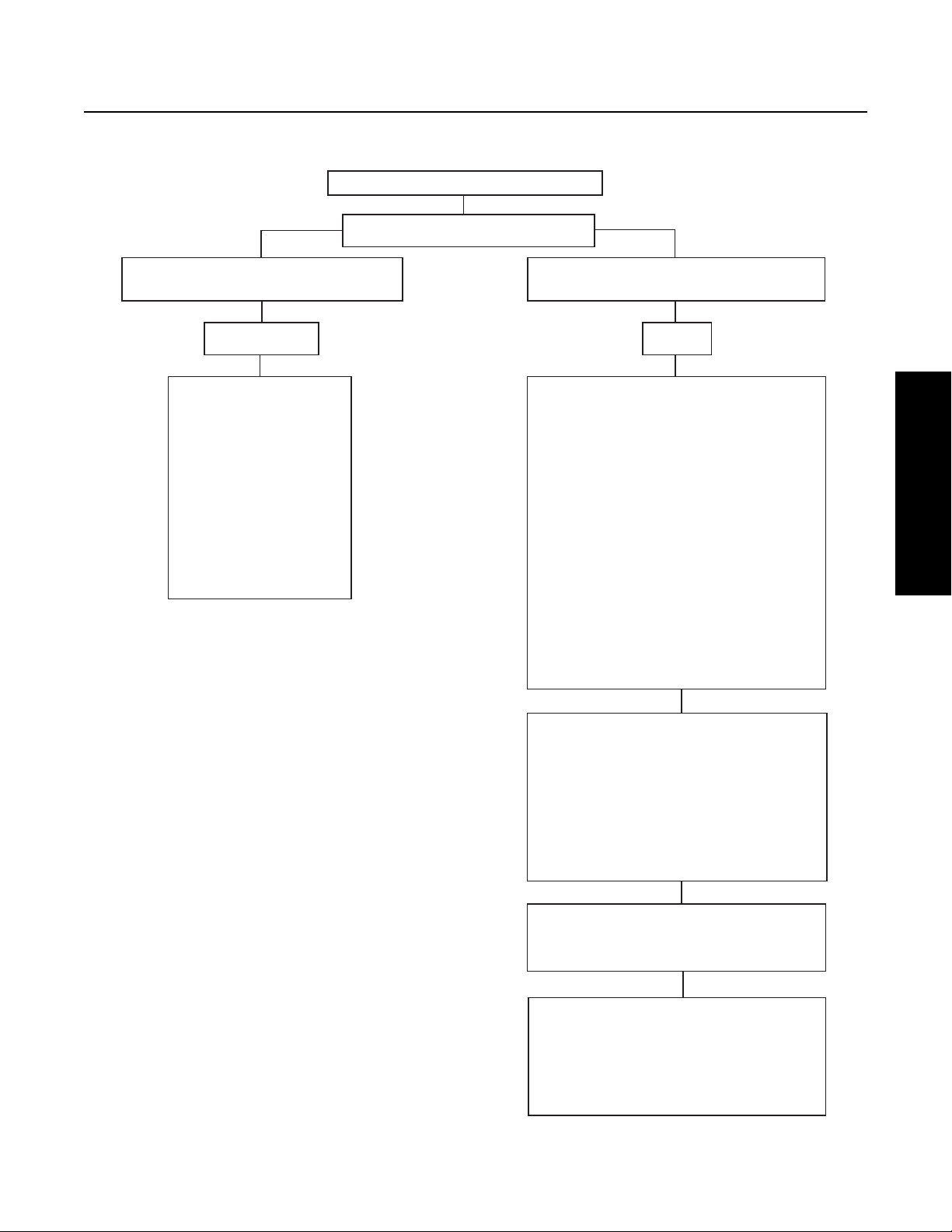
Oil Leak Inspection Process
Inspect for Oil Leak
Determine if it is a Weep or a Leak
Weep: Stained, damp, no drips, light oil film,
dirt adhered to the contaminated area.
Leak: Extremely wet or dripping of oil in the
contaminated area.
Gasket/Rear Seal Leak
1. Clean suspected oil weep
area with a clean dry cloth
or mild soluble degreaser.
2. Ensure lube is to proper
level.
3. Notify the customer that it
is only a weep and it is not
considered to be detrimental
to the life of the transmission.
4. Repair is complete.
1. Determine the origin of the leak path.
2. If origin of leak is obvious skip to Step 3.
3. If the origi
n of the oil leak is not obvious then
use either of the two following steps to determine
the oil leak:
Note: Do not use a high pressure spray washer to
clean the area. Use of a high pressure spray may
force contamination into the area of concern and
temporarily disrupt the leak path.
i. Clean area with a clean dry cloth or mild
soluble degr
easer and fill the transmission to
the proper lube level.
OR
ii. Clean the area as noted above and insert tracer
dye into the transmission lube and fill
transmission to proper lube level.
Operate vehicle to normal transmission operating
temperature and inspect the a
rea for oil leak(s)
visually or if tracer dye was introduced use an UVL
(Ultraviolet Light) to detect the tracer dye’s point
of origin.
Note: When inspecting for the origin of the leak(s)
make sure the assumed leak area is not being
contaminated by a source either forward or above
the identified area such as the engin
e, shift tower,
shift bar housing, top mounted oil cooler, etc...
Once the origin of the leak is identified, repair the
oil leak using proper repair procedures from the
designated model service manual.
After the repair is completed, verify the leak is
repaired and operate the vehicle to normal
transmission operatin
g temperature.
Inspect repaired area to ensure oil leak has been
eliminated. If the leak(s) still occurs, repeat steps
or contact the Roadranger Call Center at
1-800-826-4357.
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Lubrication
9
Page 15
Tools
Tool Specifications
Some repair procedures pictured in this manual show the use of specialized tools. Their actual use is recommended as they make
Transmission repair easier, faster, and prevent costly damage to critical parts.
For the most part, ordinary mechanic's tools such as socket wrenches, screwdrivers, etc., and other standard shop items such as
a Press, Mauls and Soft Bars are the only tools needed to successfully disassemble and reassemble any Eaton®Fuller®
Transmission.
The following tables list and describe the typical tools required to properly service this model Transmission above and beyond the
necessary basic wrenches, sockets, screwdrivers, and prybars.
General Tools
The following tools are available from several tool manufacturers such as Snap-On, Mac, Craftsman, OTC, and many others.
Tool Purpose
0–100 lb. ft. 1/2" drive Torque Wrench General torquing of fasteners (Typically 15–80 lb. ft.)
0–800 lb. ft. Torque Wrench Torque Output Nut to 650–700 lb. ft.
0–50 lb. in. 3/8" drive Torque Wrench General torquing of fasteners
0–30 lb. in. 1/4" drive Torque Wrench Torquing of capscrews to 7 lb. in. during auxiliary countershaft
bearing endplay setting procedure
70 MM or 2 3/4" Socket - Standard Depth To remove the output yoke nut
Snap Ring Pliers - Large Standard External To remove the snap rings at the auxiliary drive gear, input shaft
bearing, and countershaft bearings
Feeler Gauges To set mainshaft washer endplay and auxiliary tapered bearing
endplay
Crow's Foot Pry Bar To remove the auxiliary drive gear bearing
(2) Air Pressure Gauges 0–100 PSI To troubleshoot and verify correct operation of air system
Bushing Driver To remove and install clutch housing bushings.
Bushing OD = 1.125", ID = 1.000"
10
Page 16
Tools
Tools
Special Tools
The following Transmission Tools are available directly from K-Line Industries. To obtain any of these tools listed, contact K-Line
by phone or visiting the online store.:
K-Line Industries, Inc.
315 Garden Avenue
Holland, MI 49424
1-800-824-KLINE (5546)
http://www.klineind.com/
K-Line Part # Tool Tool Description
RR1001TR-1 Driver - Output Seal Slinger Used to install Output Seal Protective Slinger on FR & RT-series (Gen 9)
Transmission Output Yokes.
RR1001TR-2 Driver - Output Seal Used to install Output Seal in Rear Bearing Cover on RT-series (Gen 6 & 7)
Transmissions with 2.75" Output Shaft.
RR1001TR-8 Driver - Output Seal Used with Seal Driver RR1001TR-2 to install Output Seal in Rear Bearing
Cover on FR & RT-series (Gen 9) Transmissions.
RR1002TR Auxiliary Countershaft Support
Straps
RR1004TR Mainshaft Lifting Hook Used to remove/install Mainshaft Assembly into the Transmission Main Case.
RR1005TR Driver - Input Shaft Bearing Used to install the Input Bearing on Transmissions with 2" & 1.75" Input
RR1006TR Auxiliary Section Lifting Bracket Used to lift Transmission Auxiliary Sections.
RR1007TR Shimming Gauge - Auxiliary
Countershaft (0.100")
RR1010TR Slide Hammer Used to remove Bearing Races, Reverse Idler Shafts, and Seals.
RR1011TR-1 Slide Hammer Attachment Used for removing Output Seals.
RR1011TR-2 Slide Hammer Attachment Used for removing Bearing Races from the Transmission Case.
RR1011TR-3 Slide Hammer Attachment Used for removing Bearing Races from the Transmission Case.
RR1011TR-4 Slide Hammer Attachment Used for removing Reverse Idler Shafts on FR-series Transmissions.
RR1012TR-5 Driver - Auxiliary Countershaft
RR1013TR Timing Block - RT-series
RR1014TR Puller - Countershaft Front
RR1015TR Driver - Countershaft Front/Rear
RR1017TR Pusher - Countershaft Used to push the Countershaft Assembly rearward to create clearance for
RR1019TR Hand Maul Used with Bearing and Seal Drivers for part installation/removal.
RR1020TR Soft Bar Used with Hand Maul to remove parts from the Transmission.
RR1022TR Countershaft Support Tool Used to support the Upper Countershaft during Main Box disassembly on
RR1023TR Puller - Input Bearing Used to remove the Input Bearing on FR & RT-series Transmissions.
RR1024TR Driver - Output Bearing Used to install the Output Bearing on FR & RT-series Transmissions.
RR1025TR Timing Block - FR-series
Bearings
Countershaft
Bearings
Bearings
Countershaft
Used to support the Auxiliary Countershaft Assemblies when servicing the
Auxiliary Section on FR & RT-series (Gen 7 & 9) Transmissions.
Shafts.
Used for setting proper Auxiliary Countershaft Bearing clearance on
FR-series and RT-series (Gen 7 & 9) Transmissions.
Used to install Auxiliary Countershaft Bearings on FR &
RT-series Transmissions with Auxiliary Section Helical Gearing.
Used to support the Upper Countershaft during Main Box assembly on
RT-series Transmissions.
Used to remove Front Countershaft Bearing on FR-series Transmissions.
Used to install Front and Rear Countershaft Bearing on
FR-series Transmissions.
Bearing Puller on FR & RT-series Transmissions.
FR & RT-series Transmissions.
Used to support the Upper Countershaft during Main Box assembly on
FR-series Transmissions.
11
Page 17

Tools
Shop Equipment
20 Ton Capacity Press To press Countershaft Gears from Countershaft.
Eaton Aftermarket Parts
The following tools are available through Eaton Aftermarket Parts. To obtain any of the tools listed, contact your local Eaton
parts distributor:
Tool Purpose Eaton Part Number
5/32" Air Line Release Tool To remove 5/32" air lines from
push-to-connect fittings.
Air Line Cutting Tool To cut plastic air lines smoothly
and squarely.
P/N 4301157 included in Kit K-2394.
P/N 4301158 included in Kit K-2394.
12
Page 18
General Information
Torque Specifications
OUTPUT NUT
881-949 N.m [650-700 lb.ft.]
Install Output Nut onto a clean,
oil free shaft.
Note: DO NOT reuse Output Nut,
replace with new if removed
from shaft.
AUX DRIVE GEAR
BEARING RETAINER CAPSCREWS
54-61 N.m [40-45 lb.ft.]
M10x1.5 THREAD
SHIFT LEVER HOUSING CAPSCREWS
54-61 N.m [40-45 lb.ft.]
M10x1.5 THREAD
SHIFT BLOCK TO SHIFT ROD CAPSCREW
54-61 N.m [40-45 lb
.ft.]
M10x1.5 THREAD
COUNTERSHAFT FRONT BEARING
RETAINER CAPSCREWS
122-162 N.m [90-120 lb
.ft.]
.625-18-THREAD
CLUTCH HOUSING CAPSCREWS
ALUMINUM HOUSING
CAST IRON HOUSING
97-108 N.m [72-80 lb
.ft.]
M12x1.75 THREAD
FRONT BEARING COVER CAPSCREWS
54-61 N.m [40-45 lb
.ft.]
M10x1.5 THREAD
CLUTCH HOUSING STUDS
81 N.m [60 lb.ft.] MIN
M16x2 THREAD
DRIVEN UNTIL BOTTOMED
CLUTCH HOUSING NUTS
ALUMINUM HOUSING
CAST IRON HOUSING
244-271 N.m [180-200 lb
.ft.]
M16x1.5 THREAD
Torque Specifications
13
Page 19
Torque Specifications
.375 - 18
.250 - 18
PIPE THREAD SIZE
.0625 - 27 6.8-9.5 N.m [60-84 lb.in]
HYDRAULIC LINE SEALANT
20.3-27.1 N.m [180-240 lb.in]
33.9-47.5 N.m [300-420 lb.in]
.125 - 27 9.5-13.6 N.m [84-120 lb.in]
PIPE THREAD TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS. UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED:
MASTER VALVE JAM NUT
48-61 N.m [35-45 lb
.ft.]
.500-13 THREAD
SUPPORT STUDS
81 N.m [60 lb.
ft.]
M16x2 THREAD
DRIVE UNTIL BOTTOMED
SUPPORT STUD NUTS
230-257 N.m [170-190 lb
.ft.]
M16x1.5 THREAD
CAPTIVATED LIFTING EYE CAPSCREWS
54-61 N.m [40-45 lb
.ft.]
M10x1.5 THREAD
SPEEDO SENSOR CAPSCREW
27-31 N.m [20-23 lb
.ft]
M8x1.25 THREAD
SMALL PTO COVER CAPSCREWS
54-61 N.m [40-45 lb.ft.]
M10x1.5 THREAD
OIL DRAIN PLUG
61-74 N.m [45-55 lb
.ft.]
.750 PIPE THREAD
THERMOCOUPLE PLUG
54-67 N.m [40-50 lb
.ft.]
.500 PIPE THREAD
REAR BEARING COVER CAPSCREWS
54-61 N.m [40-45 lb
.ft.]
M10x1.5 THREAD
HAND HOLE COVER CAPSCREWS
19-24 N.m [14-18 lb
.ft.]
.3125-18 THREAD
LARGE PTO COVER CAPSCREWS
77-88 N.m [57-65 lb
.ft.]
M12x1.75 THREAD
AUX C'SHAFT REAR BEARING COVER CAPSCREWS
54-61 N.m [40-45 lb.ft.]
M10x1.5
AUX HOUSING CAPSCREWS
54-61 N.m [40-45 lb
.ft.]
M10x1.5 THREAD
OIL FILL PLUG
47-67 N.m [35-50 lb
.ft.]
1.0625-12 THREAD
RANGE COVER TO SBH
RANGE CYL CAPSCREWS
27-31 N.m [20-23 lb
.ft.]
M8x1.25 THREAD
SHIFT LEVER SHOULDER BOLT AND NUT
14-16 N.m [10-12 lb.ft.]
.3125-18 THREAD
14
Page 20
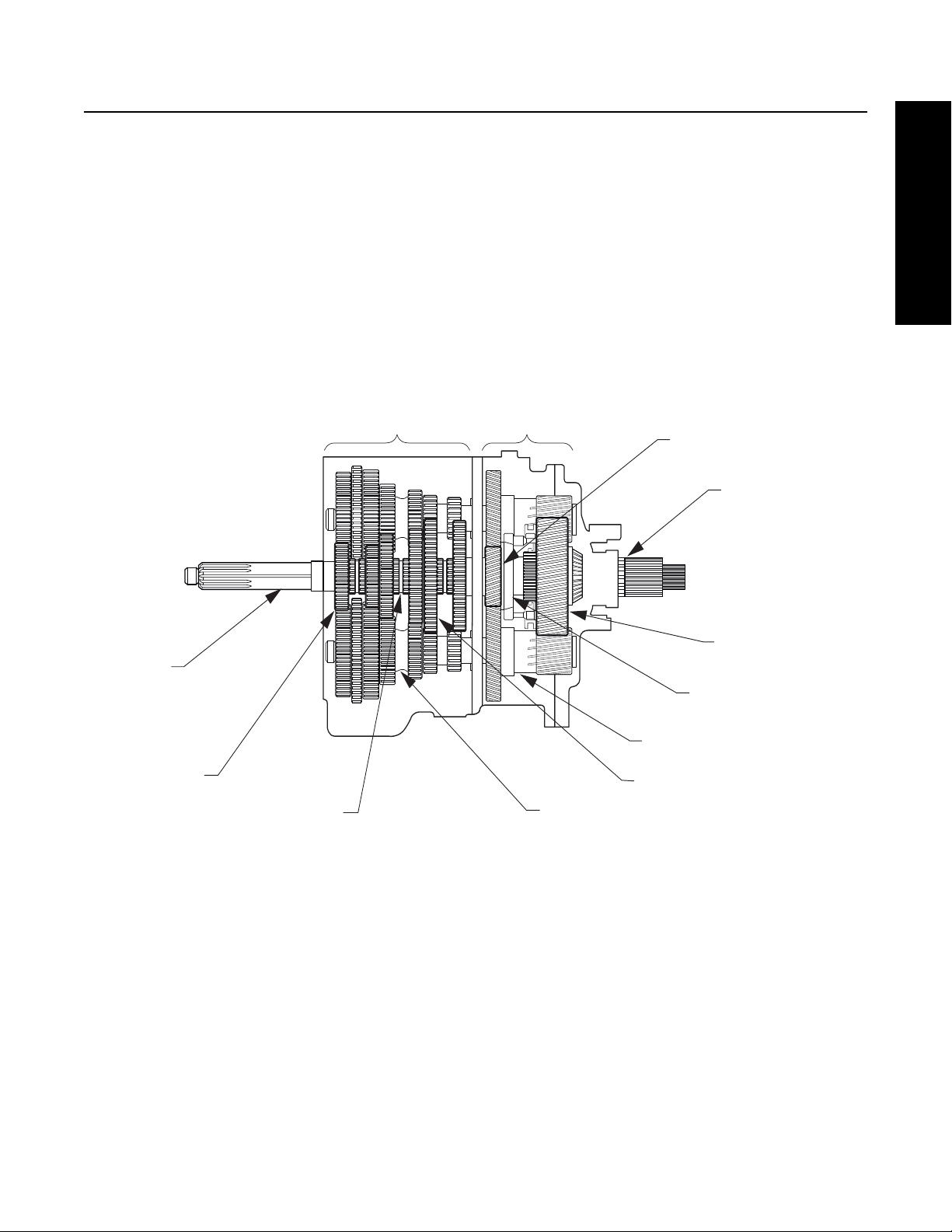
Power Flow
General Information
Front Section
Input Shaft
Main Drive Gear
Sliding Clutch
Countershaft
Mainshaft Gear
Auxiliary Countershaft
Range Sliding Clutch
Auxiliary Mainshaft
Reduction Gear
Output Shaft
(Auxiliary Mainshaft)
Auxiliary Drive Gear
Auxiliary Section
Power Flow Diagrams
An understanding of the engine’s power flow through a Transmission in each particular gear will assist the technician in
troubleshooting and servicing a Transmission.
The Eaton Fuller Roadranger Transmission can be thought of as two separate “Transmissions” combined into one unit. The first
“Transmission” or Front Section contains six gear sets which are shifted with the Gear Shift Lever. The second “Transmission”
called the Auxiliary Section, contains two gear sets and is shifted with air pressure.
Note: This Transmission is referred to as a constant mesh type Transmission. When in operation, all gears are turning even
though only some of them are transferring power.
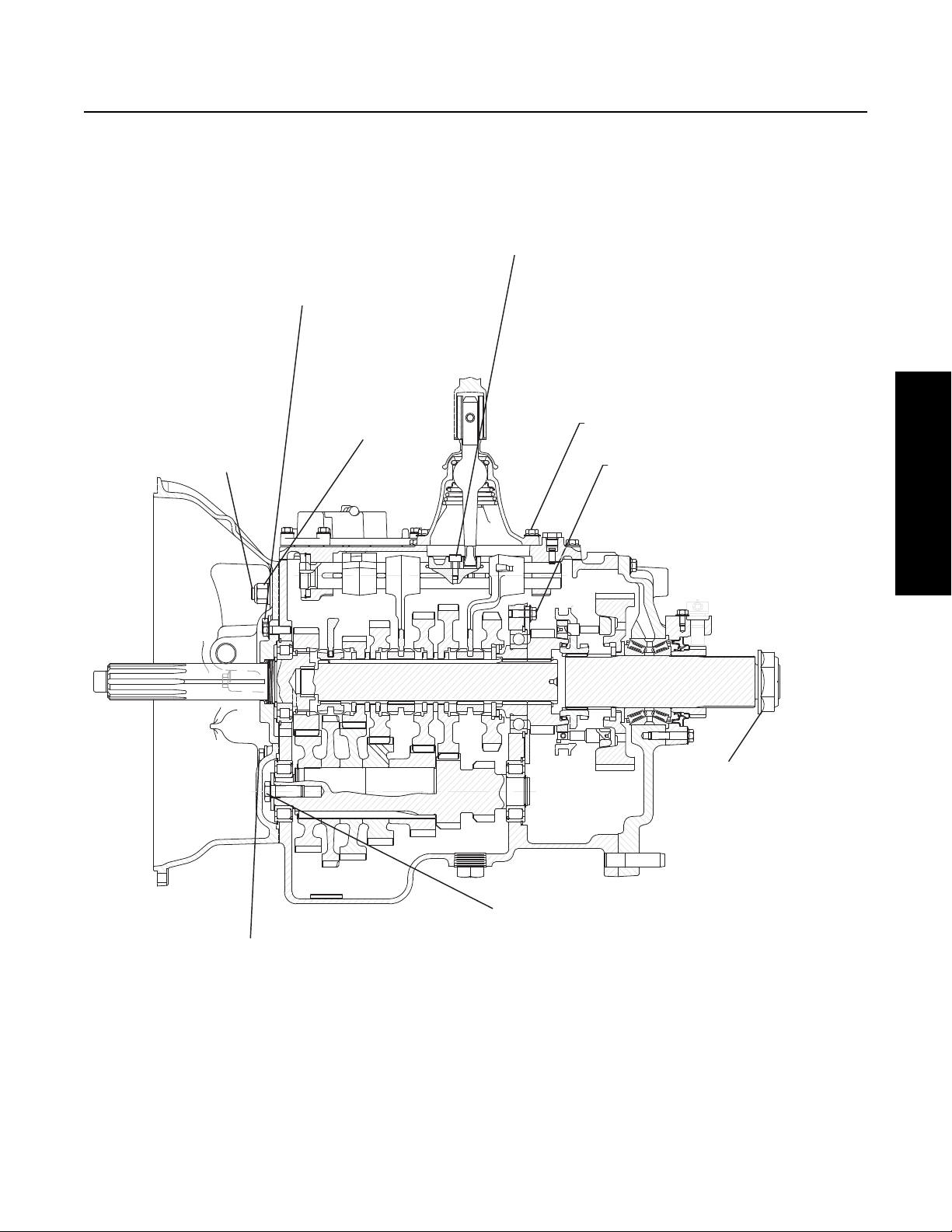
Figure 2-3 below shows the Transmission with the main components called out. Note that the Transmission is in the Neutral
position because the Sliding Clutches are all in their center positions and not engaged is any gears.
Figure 2-3. Transmission Components Important for Understanding Power Flow
15
Page 21

Power Flow
k
Front Section Power Flow
Note: The heavy lines in Figure 2-4 outline the power flow description below. For help in understanding the Transmission
components, refer to Figure 2-3.
1. Power (torque) from the vehicle’s engine is transferred to the Transmission’s Input Shaft.
2. The Input Shaft rotates the Main Drive Gear through internal splines in the hub of the gear.
3. The Main Drive Gear meshes with both Countershaft driven gears and the torque is split between both Countershafts.
4. Because the Countershaft Gears are in constant mesh with the Mainshaft Gears, all the Front Section gearing rotates.
However, only the engaged Mainshaft Gear will have torque. External clutching teeth on the Sliding Clutch will engage
internal clutching teeth on the selected Mainshaft Gear. Torque will now be provided from both opposing Countershaft
Gears, into the engaged Mainshaft Gear, and through the Sliding Clutch to the Front Section Mainshaft.
5. The rear of the Front Section Mainshaft is spined into the Auxiliary Drive Gear and torque is now delivered to the
Auxiliary Section.
Figure 2-4 Front Section Torque (1st Gear)
Sliding Clutch Forward
Sliding Clutch Bac
16
Page 22

Power Flow
General Information
k
Front Section Power Flow - Direct Gear
In direct gear (5th/10th for FR model, 4th/9th for FRO model), the Front Sliding Clutch is moved forward and engages into the
back of the Main Drive Gear. Torque will flow from the Input Shaft to the Main Drive Gear, Main Drive Gear to Sliding Clutch, Sliding
Clutch straight into the Front Section Mainshaft which delivers the torque to the Auxiliary Drive Gear.
Note: All Countershaft and Mainshaft Gears will rotate, but the gears will not be loaded.
Sliding Clutch Forward
Figure 2-5 5th Gear FR, 4th Gear FRO
Sliding Clutch Forward
Figure 2-6 10th Gear FR, 9th Gear FRO
Sliding Clutch Bac
Sliding Clutch Forward
17
Page 23
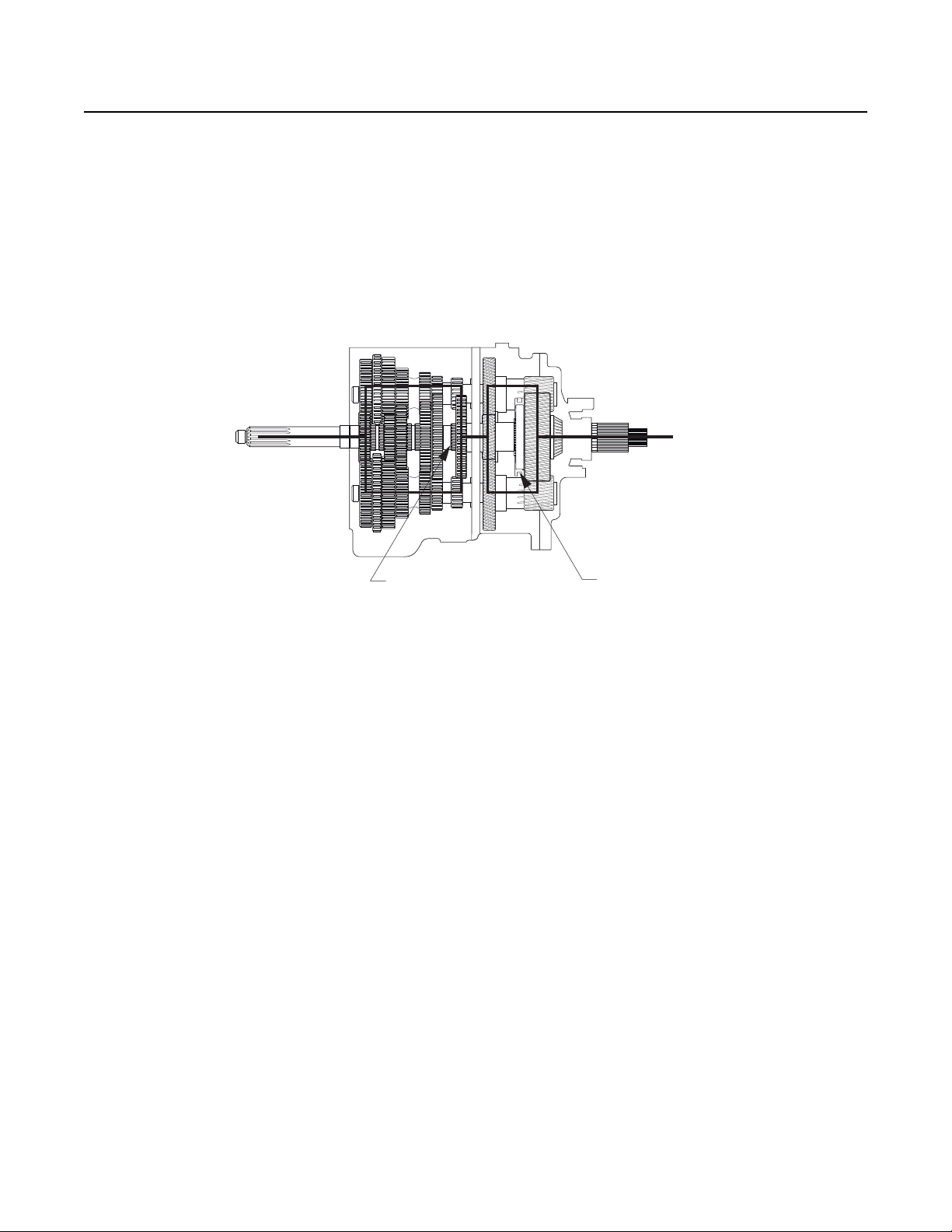
Power Flow
Sliding Clutch Back Sliding Clutch Back
Front Section Power Flow - Reverse Gear
Torque will flow from the Countershafts to the Reverse Idler Gears. Torque will then flow from the Reverse Idler Gears to the
Mainshaft Reverse Gear. Torque will now travel through the Mainshaft Reverse Gear, the Sliding Clutch in the Reverse position
and then to the Mainshaft and Auxiliary Drive Gear.
Note: The Idler Gears cause the reversal of rotation.
Figure 2-7 Reverse Gear - Low Range
18
Page 24
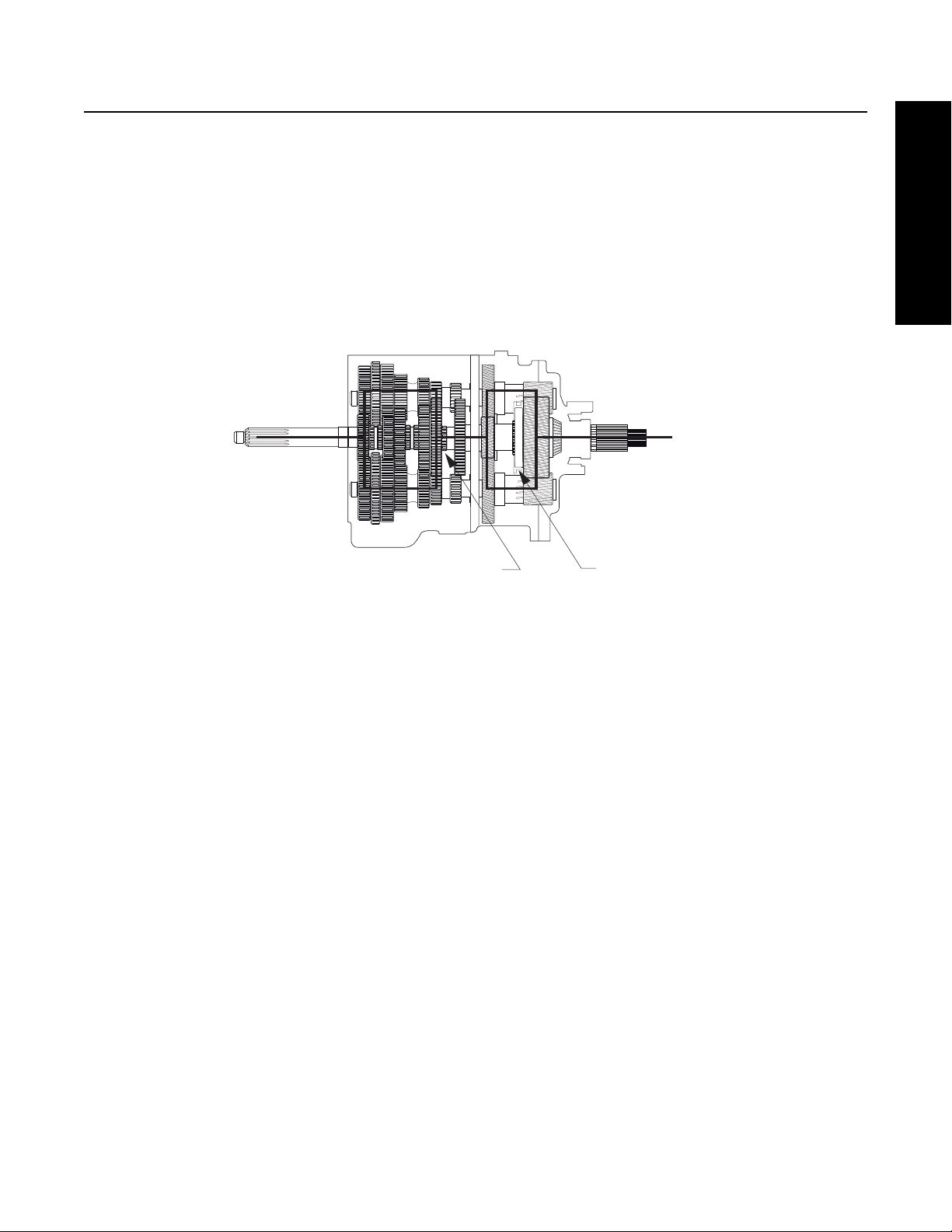
Power Flow
General Information
Auxiliary Section Power Flow - Low Range
The Auxiliary Drive Gear transfers torque to both Auxiliary Countershafts.
If the Auxiliary Section is in Low Range, the Range Sliding Clutch is rearward and engaged into the Auxiliary Mainshaft Reduction
Gear. Torque will flow from the Auxiliary Countershafts, into the Auxiliary Mainshaft Reduction Gear, through the Range Sliding
Clutch and then into the Output Shaft (Auxiliary Mainshaft).
Sliding Clutch Forward
Figure 2-8 Low Range (Sliding Clutch Back)
Sliding Clutch Back
19
Page 25
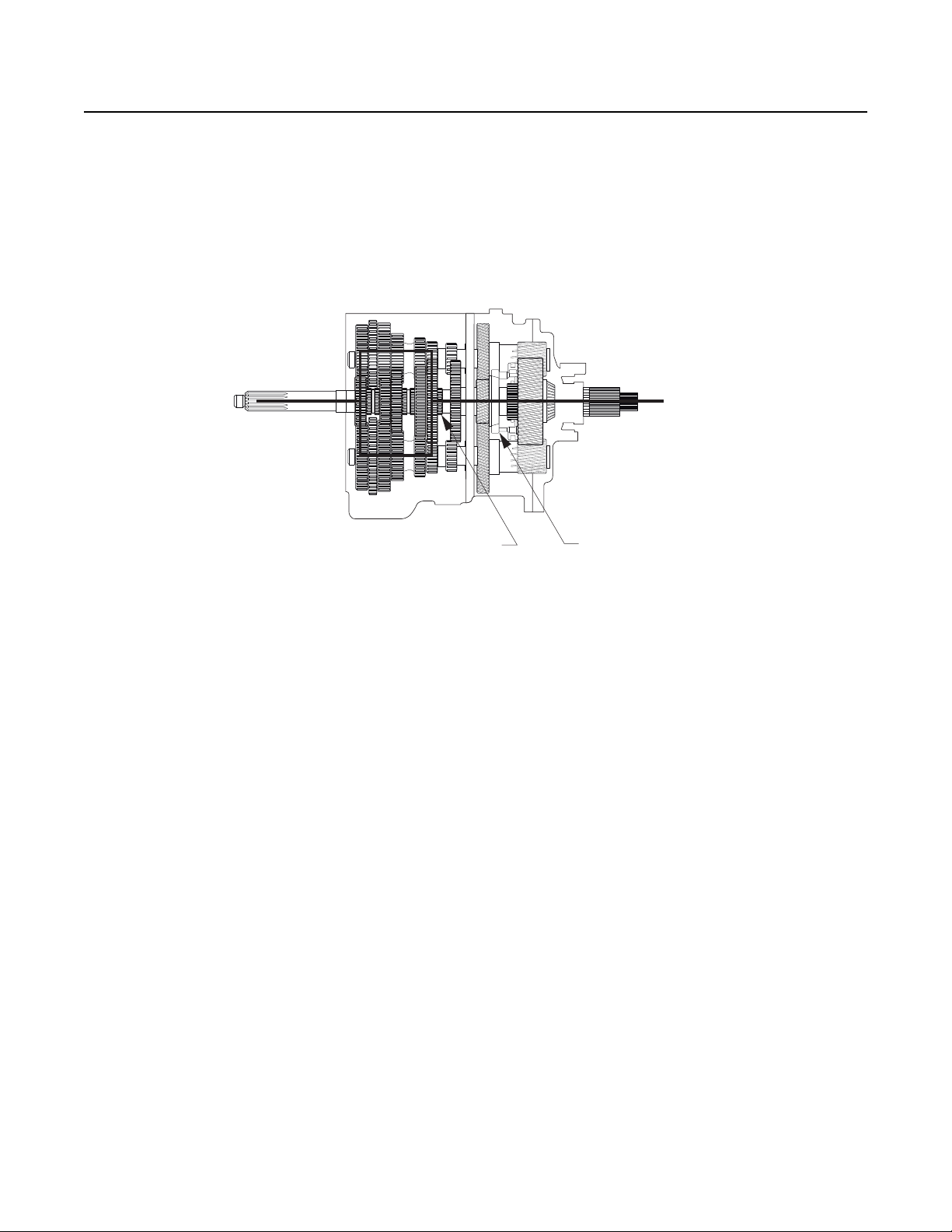
Power Flow
Auxiliary Section Power Flow - High Range
If the Auxillairy Section is in High Range, the Range Sliding Clutch is forward and engaged into the back of the Auxiliary Drive Gear.
Torque will flow from the Auxillairy Drive Gear to the Range Sliding Clutch. Because the Range Sliding Clutch has internal splines
which connect to the Output Shaft, torque will flow straight through the Auxiliary Section.
Note: The auxiliary gearing will still turn, but the gears will not be loaded.
Sliding Clutch Forward
Figure 2-9 High Range Selected (Sliding Clutch Forward)
Sliding Clutch Forward
20
Page 26
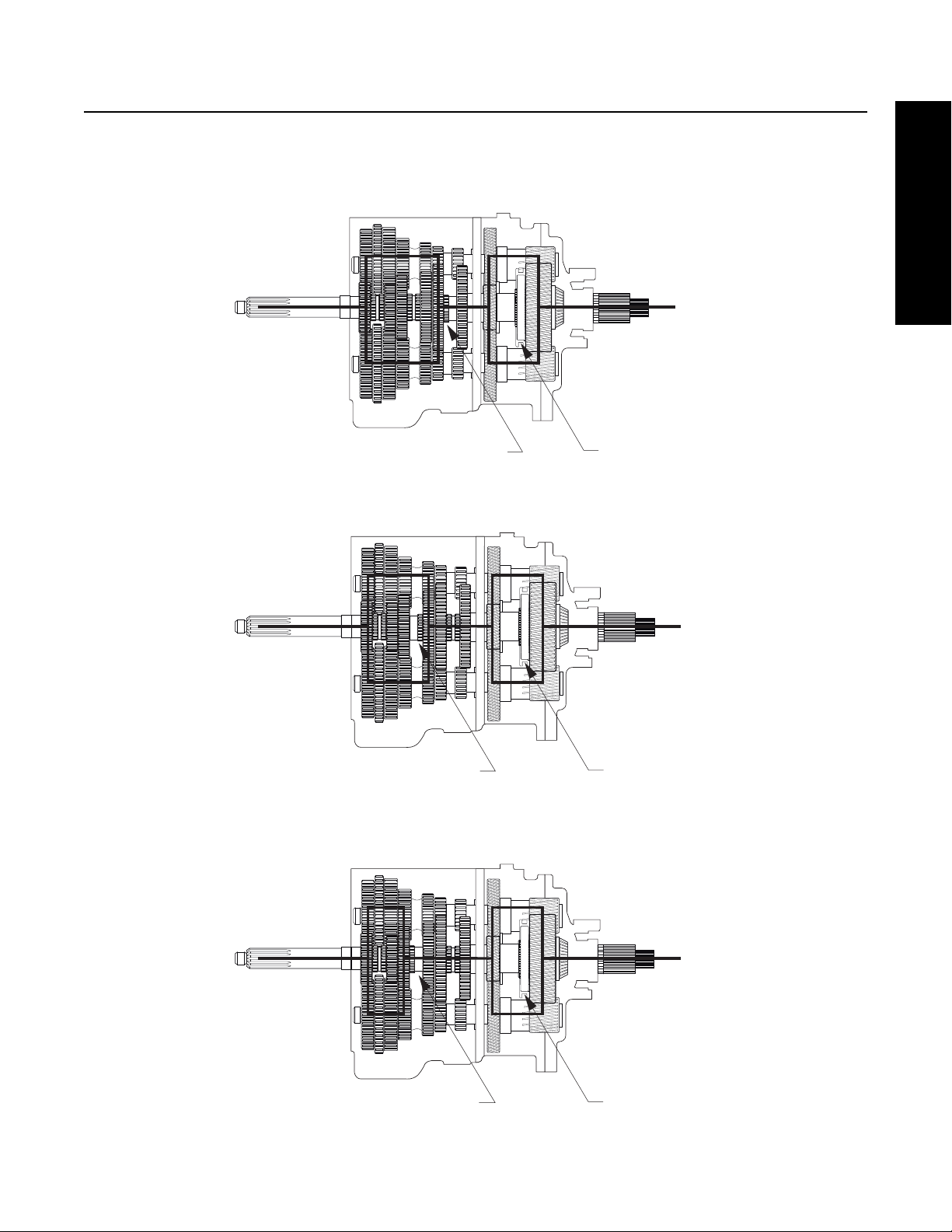
General Information
FR/FRO-1X210
Sliding Clutch Forward
Sliding Clutch Back
k
Sliding Clutch Forward
Sliding Clutch Back
1st Gear
2nd Gear
Power Flow
Sliding Clutch Back
3rd Gear
Sliding Clutch Bac
21
Page 27
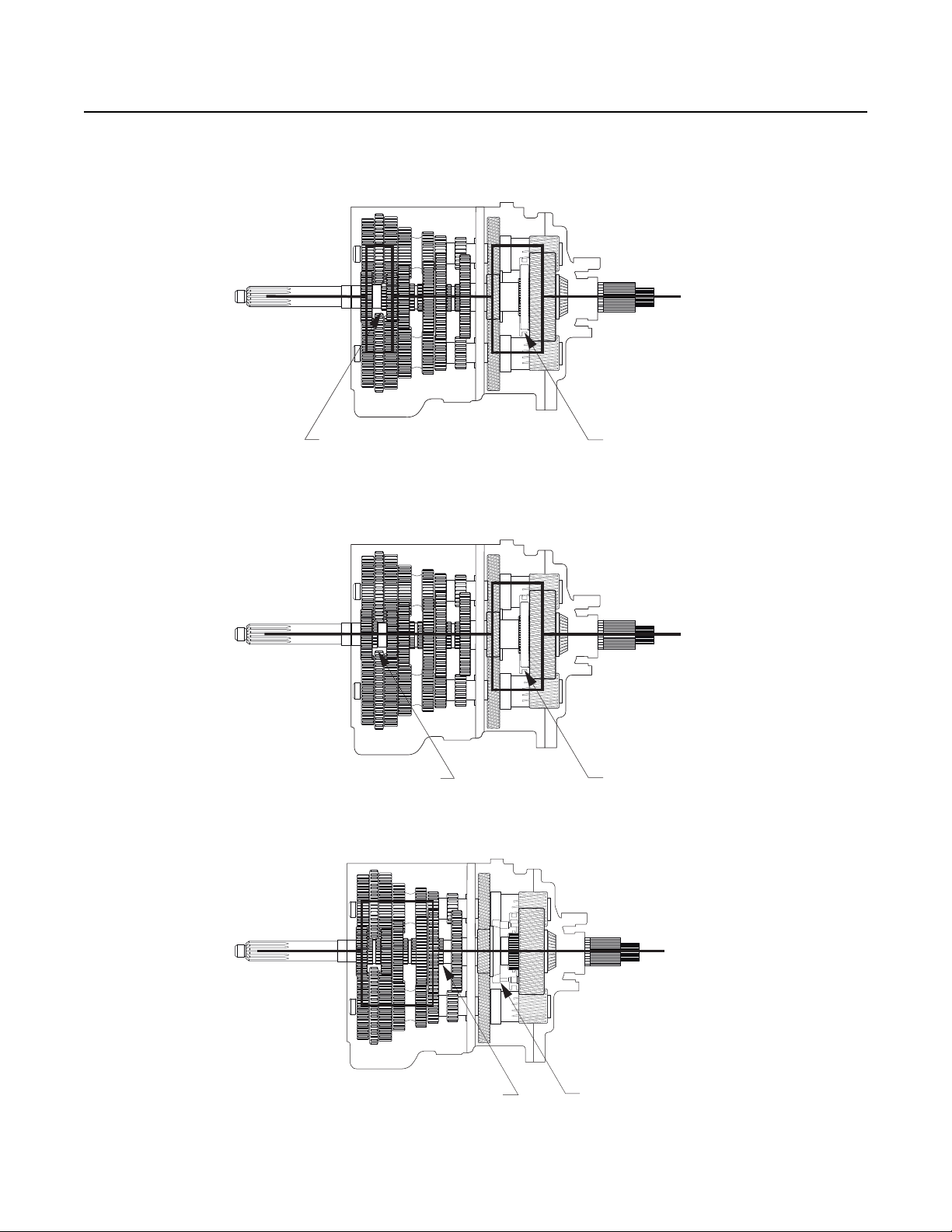
Power Flow
k
4th Gear-FR/Direct Drive Transmission
5th Gear- FRO/Overdrive Transmission
5th Gear- FR/Direct Drive Transmission
4th Gear FRO/Overdrive Transmission
Sliding Clutch Forward
6th Gear
Sliding Clutch Back
Sliding Clutch Back
Sliding Clutch Bac
22
Sliding Clutch Forward
Sliding Clutch Forward
Page 28

General Information
7th Gear
Sliding Clutch Back
Sliding Clutch Forward
Sliding Clutch Back
Sliding Clutch Forward
8th Gear
Power Flow
Sliding Clutch Forward
9th Gear-FR/Direct Drive Transmission
10th Gear-FRO/Overdrive Transmission
Sliding Clutch Forward
23
Page 29

Power Flow
Sliding Clutch Forward
Sliding Clutch Forward
10thGear-FR/Direct Drive Transmission
9th Gear-FRO/Overdrive Transmission
24
Page 30

Air System Troubleshooting
General Information
WARNING
Air System Troubleshooting
The symptoms listed below are covered on the following pages. Before beginning any of those troubleshooting procedures, place
the Transmission in Neutral and move the Range Selection Lever from Low to High. Listen for any constant air leak from the Shift
Knob, Air Module Base (exhaust), or Transmission Breather. If a constant leak is heard, go to that particular leak troubleshooting
procedure first.
If you do not see the symptom you need to correct, refer to the General Troubleshooting Chart.
Symptom
• Air Leak from Air Module Base (Exhaust Leak)
• No or Slow Range Shift into High (Shift into Low Range is good)
• No or Slow Range Shift into Low (Shift into High Range is good)
• Constant Air Leak from Shift Knob
• Range Shifts in Gear
• Air Leak from Transmission Breather or Transmission Case is Pressurized
Note: Use the Air System Troubleshooting Procedures for part replacement only if the symptom can be duplicated. If the problem
is intermittent, parts that are not defective could be replaced.
Note: During all testing, the vehicle air pressure must be greater than 90 PSI (620 kPa). If during testing the pressure falls below
90 PSI (620 kPa), make sure the Transmission is in Neutral, start the engine and let the pressure build to governor cutoff.
After the pressure reaches the governor cutoff, continue testing. The pressure is critical if the vehicle is equipped with a
Vehicle Air System Pressure Protection Valve that would shut off the air supply to certain air circuits if the system pressure
dropped below a preset level.
Note: A 0–150 PSI (0–1034 kPa) Air Gauge with a 1/16" male pipe thread fitting attachment is required for some of the test
procedures.
Note: Regulated air pressure is 75–85 PSI (517–586 kPa).
Prior to removing the Air Module, exhaust the air from it. Failure to exhaust the Air Module may result in personal injury or
damage to parts from the sudden release of air.
Use care when removing the Test Port Pipe Plugs. If air pressure is present on the plug, it can become a projectile during
removal. When removing the “L” plug or “H” plug, pressure can be shut off by selecting the opposite range mode. If
removing the “F” plug, exhaust the air to the Module Inlet.
25
Page 31

Air System Troubleshooting
WARNING
Air System Symptom - Air leak from Module Base (Exhaust)
Short bursts of air leakage from the Module Base (exhaust) are normal as the Range System is shifted. The Module Base is defined
as both the interface of the Module Cover and Module Base and the extreme underside of the Module. Leakage is a problem when
it is audible and constant. Air leakage from the Module Base may result from either a defective Air Module or a defective Range
Piston. The following procedure will identify the defective component.
Test Procedure:
1. Check for air leakage from the Module Base (exhaust) in each of the four following conditions. (Make sure the range is shifted
when the Shift Lever is shifted into Neutral.)
a. Range Selection Lever in Low and Shift Lever in neutral.
b. Range Selection Lever in Low and Shift Lever in gear.
c. Range Selection Lever in High and Shift Lever in neutral.
d. Range Selection Lever in High and Shift Lever in gear.
Record the findings (constant leak or no leak) in the following table:
Range Selector in LOW Range Selector in HIGH
Lever in Neutral
Lever in Gear
2. If the information you recorded at step 1 matches one of the following tables, replace the Air Module. If your table does not
match either of the tables, it will be necessary to isolate and test the Air Module separately, continue to Step 3.
Range Selector in LOW Range Selector in HIGH
Lever in Neutral No Leak Constant Leak
Lever in Gear No Leak Constant Leak
Range Selector in LOW Range Selector in HIGH
Lever in Neutral Constant Leak Constant Leak
Lever in Gear Constant Leak Constant Leak
Failure to exhaust the air pressure may cause personal injury or damage to parts.
3. Exhaust the air pressure from the Air Module. To do so, the vehicle’s Air Tanks may need to be exhausted.
4. Leaving all Air Lines connected to the Module, remove the four capscrews attaching the Air Module to the Shift Bar Housing.
Lift the Air Module and tilt it to gain access to the two air holes at the underside on the rear capscrew location. Do not damage
or lose the two O-rings used to seal the holes.
5. Block off the Air Ports on the underside of the Module. Use a piece of gasket material or rubber material to seal the bottom of
the Module as shown in Figure 4-4 “Air System Nomenclature”.
6. Repressurize the Air module with an inlet supply pressure of over 90 PSI (620 kPa). To repressurize the Air Module, the vehicle
may need to be started and air pressure allowed to build up.
7. Check for air leakage in both High and Low Range. If air continues to leak constantly from the exhaust, the Air Module is
defective. If air does not leak, a Range Cylinder Piston or Piston Seal failure has occurred. Remove the Shift Bar Housing to gain
access to the Range Shift Cylinder.
26
Page 32

Air System Troubleshooting
General Information
Air System Symptom - No or Slow Range Shift into High (Shift into Low Range is Good)
This Transmission contains a SynchroSaver feature to protect the High Range Synchronizer. When High Range is selected and a
Front Section Gear is engaged, air pressure is supplied to both sides of the Range Piston, which reduces Synchronizer force.
Therefore, if the driver engages a Front Section Gear before the High Range Synchronizer engages, the High Range Synchronizer
will remain in Neutral. When a Front Section Gear engages before the Synchronizer Shift completes, the driver must shift the Lever
back to Neutral to allow the High Range Synchronizer to complete its shift. Once the Range Shift is complete, the driver can
complete the Front Section shift.
If the High Range Synchronizer hangs up or is slow to synchronize, the Front Section may engage first. The driver complaint will
be that the Transmission “neutralizes” on a shift to High Range. If this condition occurs, perform the following test of the Air
System to eliminate the Air System as the source of the problem. If the Air System performs properly, then the problem is internal
to the Transmission Range Synchronizer System.
Note: The driver must preselect all Range Shifts.
Note: If a capscrew or stud is installed too far into the right side (Air Module side) rear support hole, the fastener can extend too
far into the Transmission. The fastener may contact the Range Yoke and bind the Range Synchronizer Assembly during the
Range Shift.
Test Procedures:
1. Check the Shift Knob operation.
On the Shift Knob, remove the screws holding the Plastic Skirt. Slide the Skirt down and out of the way. Move the Range Selection
Lever up into High Range. Disconnect the black line connected to the “P” port on the Knob.
Question Result What to do next
Does air come out of the “P” port on
the Knob?
Yes Repair or replace the Knob
No Reconnect the Air Line to the Knob, and
continue to the next Step.
27
Page 33

Air System Troubleshooting
2. Test the Regulator pressure. (Regulator pressure should be between 75–85 PSI (517–586 kPa)).
Reconnect the “P” line at the Shift Knob. Locate the two small Pipe Plugs on the rear of the Air Module. One is labeled “H” the
other “L”. (See figure 4-1 “Air System Nomenclature”). Install a 0–150 PSI (0–1034 kPa) Air Gauge in the port marked “H.”
Note: Prior to removing the Pipe Plug, turn off the air flow by flipping the Range Selector down into the Low Range position. The
Transmission must be in Neutral.
Move the Range Selector up to the High Range position and record the pressure on the Gauge. Match the pressure to one of those
on the chart on the next page, and follow the corresponding instructions.
Question Result What to do Next
What is the air pressure at
the “H” port?
3. Check the Spool Valve function.
With the Shift Lever in Neutral, move the Range Selector from Low to High several times. Answer the question on the chart below,
and follow the instructions corresponding to the result.
75–85 PSI (517–586
kPa) (to specification)
Less than 75 PSI
(517 kPa)
Greater than 85 PSI
(586 kPA)
Continue to the next Step.
Warning: The Pipe Plug to be removed in this procedure is
pressurized and could be expelled with great force. To prevent
personal injury or damage to parts, exhaust the air Module before
removing the Plug, and repressurize the Air Module after installing
the Gauge.
On the top of the Air Module, remove the Test Port Pipe Plug for
filtered vehicle air. (Marked “F” as shown in figure 4-1.)
Install the Test Gauge in the “F” port, and check the pressure. If the
pressure is less than 90 PSI (620 kPa), repair the Vehicle Air System
to achieve full vehicle air pressure at the Air Module Inlet, and repeat
the test. If the pressures greater than 90 PSI (620 kPa) and no
external air leaks were detected from the Air Module, Shift Knob, or
Transmission, replace the Air Module.
Replace the Air Module.
Question Result What to do Next
Does the Gauge rapidly go from
75–85 PSI (517–586 kPa) in High to
0 PSI in Low?
28
Yes Air System performs properly.
Go to Step 5.
No Continue to the next Step.
Page 34

Air System Troubleshooting
General Information
WARNING
4. Isolate and test the Air Module. Refer to Figure 4-4 “Air System Nomenclature” to see an example of an isolated Air Module.
Failure to exhaust the Air Module may cause personal injury or damage to parts due to the rapid release of air.
Exhaust the air pressure from the Air Module. To do so, the vehicle air tanks may need to be exhausted. Remove the four
capscrews attaching the air module to the shift bar housing. Lift the air module and tilt it to gain access to the two air holes at the
underside at the rear capscrew location. Do not damage or lose the two O-rings used to seal the holes. Block off the air ports on
the underside of the module. Repressurize the air module with an inlet supply pressure of over 90 PSI (620 kPa). To repressurize
the air module, the vehicle may need to be started and the air pressure allowed to build. With the shift lever in neutral and the
gauge still in the “H” test port, move the range selection lever from high to low (down) position.
Answer the question on the chart below, and follow the instructions corresponding to the result.
Question Result What to do Next
Does the Gauge rapidly go from
75–85 PSI (517–586 kPa) in High to
0 PSI in Low?
5. Install the Air Module, and remove the Range Alignment Lock Cover (Figure 4-3 “Air System Nomenclature”). Then move the
Range Selection Lever from the Low to High (up) position. If range now shifts properly, inspect and correct the source of
binding between Lock Cover and Range Yoke Bar.
NOTE: To prevent binding, Range Alignment Lock Cover Capscrews must be tightened when Transmission is in Low Range.
If the Transmission does not shift properly, continue to Step 6.
6. Remove the Auxiliary Section and inspect the Range Synchronizer, Range Yoke, Range Yoke Bar, Range Yoke Snap Ring, Range
Sliding Clutch, and mating gears for excessive wear, binding, or damage. Repair as necessary. If these components do not need
repair, continue to Step 7.
7. Remove the Shift Bar Housing and inspect the Range Piston, Piston Bar, and Cylinder for excessive wear, binding, or damage.
Repair as necessary.
Yes Continue to the next Step.
No Replace the Air Module.
29
Page 35

Air System Troubleshooting
Air System Symptom - No or Slow Range Shift into Low (Shift into High is Good)
Test Procedures:
1. Check the Shift Knob operation.
On the Shift Knob, remove the two screws holding the Plastic Skirt. Slide the Skirt down and out of the way. Move the Range
Selector up into High Range. Disconnect the black line connected to the “P” port on the Knob. Move the Range Selector down into
Low. Answer the question on the chart below and follow the instructions corresponding to the result:
Question Result What to do Next
Does air come out of the “P” port on the
Knob?
2. Check the air supply to the Shift Knob.
Disconnect the red line from the “S” port on the Shift Knob. Answer the question on the chart below and follow the instructions
corresponding to the result:
Question Result What to do Next
Is air coming out of the red line? Yes Repair or replace the Shift Knob.
Yes Go to Step 3.
No Reconnect the Air Line to the Knob, and
continue to the next Step.
No Loosen the air fitting for the line that
supplies vehicle air to the Module Inlet. If no
air is available here, repair the vehicle air to
the Air Module. If air is available at the Inlet,
check the red line going from the Air
Module to the Shift Knob for obstructions
or damage. If the line is clear, replace the
Air Module.
3. Check the black line for obstruction.
Reconnect the black line at the Shift Knob. At the Air Module, disconnect the black air line from the “P” port. Answer the question
on the chart below and follow the instructions corresponding to the result:
Question Result What to do Next
Is air available on the line when the
Range Selector is in the Low position?
30
Yes Continue to next Step.
No Repair the black line for damage or
obstruction.
Page 36

Air System Troubleshooting
General Information
4. Check the Regulator pressure.
Reconnect the “P” line at the Air Module. Locate the two small Pipe Plugs on the rear of the Air Module. One is labeled “H,” and
the other is labeled “L”. (See Figure 4-1 “Air System Nomenclature”). Install a 0–150 PSI (0–1034 kPa) Air Gauge in the port
marked “L”.
Note: Prior to removing the Pipe Plug, turn off the air flow by placing the Range Selector up into the High Range position. The
Transmission must be in Neutral.
Move the Range Selector down to the Low position and record the pressure on the Gauge. Match the air pressure to one of those
described on the chart on the next page, and follow the corresponding instructions:
Question Result What to do Next
What is the air pressure at the “L” port? 75–85 PSI (517–586 kPa)
(To specification.)
Less than 75 PSI (517 kPa) Warning: The Pipe Plug to be removed in
Greater than 85 PSI (586 kPa) Replace the Air Module.
Continue to the next Step.
this procedure is pressurized and could be
expelled with great force. To prevent
personal injury or damage to parts, exhaust
the Air Module before removing the plug,
and repressurize the Air Module after
installing the Gauge
On the top or the Air Module, remove the
Test Port Pipe Plug for filtered vehicle air.
(Marked “F” as shown in figure 4-1 “Air
System Nomenclature”).
Install the Test Gauge in the “F” port, and
check the pressure. If the pressure is less
than 90 PSI (620 kPa), repair the Vehicle Air
System to achieve full vehicle air pressure
at the Module Inlet, and repeat the test. If
the pressure is greater than 90 PSI
(620spa) and no external air leaks were
detected form the Air Module, Shift Knob,
or Transmission, replace the Air Module.
5. Check the Spool Valve function.
With the Shift Lever in Neutral, move the Range Select from Low to High several times. Answer the question on the chart below
and follow the instructions corresponding to the result:
Question Result What to do Next
Does the Gauge rapidly go from
75–85PSI (517–586 kPa) in Low to
0 PSI in High
Yes Air System performs properly. Go to Step 7.
No Continue to the next Step.
31
Page 37

Air System Troubleshooting
WARNING
6. Isolate the Air Module from the Transmission. Refer to Figure 4-4 “Air System Nomenclature” to see an example of an isolated
Air Module.
Failure to exhaust the Air Module may cause personal injury or damage to parts due to the rapid release of air.
Exhaust the air pressure from the Air Module. To do so, you may have to exhaust the vehicle air. Remove the four capscrews
attaching the Air Module to the Shift Bar Housing. Lift the Air Module and tilt it to gain access to the two air holes on the underside
at the rear capscrew location. Do not lose or damage the two small O-rings that seal the holes. Block off the air ports at the
underside of the module. Repressurize the Air Module with an inlet supply pressure of over 90 PSI (620 kPa). To repressurize the
Air Module, the vehicle may have to be started and the air pressure allowed to build. With the Shift Lever in Neutral and the Gauge
still in the “L” Test Port, move the Range Selector from Low to High (up) position.
Answer the question on the chart below, and follow the corresponding instructions:
Question Result What to do Next
Does the Gauge rapidly go from
75–85PSI (517–586 kPa) in Low to
0 PSI in High
7. Install the Air Module, and remove Range Alignment Lock Cover (Figure 4-4 “Air System Nomenclature”). Then move the Range
Selector from Low to High (up) position. If range now shifts properly, inspect and correct source of binding between Lock Cover
and Range Yoke Bar.
NOTE: To prevent binding, Range alignment Lock Cover Capscrew must be tighten when Transmission is in Low Range.
If Transmission does not shift properly, continue to Step 8.
8. Remove the Auxiliary Section, and inspect Range Synchronizer, Range Yoke, Range Yoke Bar, Range Yoke Snap Rings, Range
Sliding Clutch, and mating gears for excessive wear, binding, or damage. Repair as necessary. If these components do not need
repair, continue to Step 9.
9. Remove Shift Bar Housing and inspect Range Piston, Piston Bar, and Cylinder for excessive wear, binding, or damage. Repair
as necessary.
Yes Continue to next Step.
No Replace the Air Module.
32
Page 38

Air System Troubleshooting
General Information
Air System Symptom - Constant Air Leak from Shift Knob
In normal operation, a burst of air will be exhausted from the Shift Knob when moving the Range Selector from Low to High Range.
If a constant air leak is detected, first check for a leaking fitting. If the leak occurs when both High and Low Range are selected
and the leak is from the exhaust “E” port on the Shift Knob. Repair or replace the Shift Knob.
If the leak only occurs in High Range, check for reversed hook up of “P” and “S” air lines. If the air lines are connected properly,
repair or replace the Shift Knob.
33
Page 39

Air System Troubleshooting
WARNING
Air System Symptom - Range Shift While Transmission is in Gear
The Interlock Mechanism allows the driver to move the Range Selection Lever while still in gear (preselect). The range will then
shift when the Shift Lever moves into Neutral. If the driver preselects a Range Shift and the shift occurs while the Shift Lever is in
gear, a problem is present.
Test Procedures:
Failure to exhaust the Air Module may cause personal injury or damage to parts due to the rapid release of air.
1. Exhaust air pressure from the Air Module. To do so, the vehicle air may need to be exhausted.
2. Remove the four capscrews attaching the Air Module to the Shift Bar Housing. Lift the Air Module and tilt it to gain access to
the Module Interlock Finger. Do not lose or damage the two O-rings at the rear mounting capscrew.
3. Inspect the Module Interlock Finger for excessive wear. Replace, if necessary.
4. Shine a bright light into the hole the Interlock Finger engages. Inspect the Chamfer on the Shift Shaft for excessive wear. To
inspect the Chamfer, the Transmission may need to be shifted into gear so both the forward and rearward Chamfers are visible.
If the Chamfer is excessively worn, remove the Shift Bar Housing, disassemble, and replace the worn parts.
5. If the Shift Shaft is not excessively worn, replace the Air Module.
34
Page 40

Air System Troubleshooting
General Information
WARNING
Air System Symptom - Air Leak From Breather or Case is Pressurized
If the air leak occurs when the Transmission is in High Range, the problem is with the Range Cylinder in the Transmission. Remove
the Shift Bar Housing, and disassemble and inspect the Range Cylinder for worn or missing O-rings. Also, inspect the Shift Bar
Housing for cracks or porosity.
If the leak only occurs when the Transmission is shifted to Low Range, the Air Module may be leaking into the Transmission at
the Interlock Finger location. Prior to removing the Shift Bar Housing, perform the following test to determine the problem:
Test Procedures:
Failure to exhaust the Air Module may cause personal injury or damage to parts due to the rapid release of air.
Exhaust the air pressure from the Air Module. To do so, the vehicle air may need to be exhausted. Remove the four capscrews
attaching the Air Module to the Shift Bar Housing. Lift the Air Module and tilt it to gain access to the two air holes at the underside
at the rear capscrew location. Do not lose or damage the two small O-rings near the rear capscrew location. Block off the air ports
on the underside of the Module (Figure 4-4 “Air System Nomenclature”). Repressurize the Air Module with an inlet supply pressure
of over 90 PSI (620 kPa). Repressurizing the Air Module may require starting the vehicle and allowing the air pressure to build.
Shift the Transmission into Low Range. Answer the question on the chart below, and follow the instructions corresponding to
the result:
Question Result What to do Next
Can any air leakage be detected at the
Module Interlock Finger?
Yes Replace the Air Module
No Air leak is at the Range Cylinder. Remove
the Shift Bar Housing, and disassemble
and inspect the Range Cylinder for worn
or missing O-rings. Also inspect the Shift
Bar Housing for cracks or porosity.
35
Page 41

General Troubleshooting
General Troubleshooting Chart
The chart on the following pages contains some of the most common problems that may occur with this Transmission along with
the most common causes and solutions:
Complaint Cause Corrective Action
Noise - Growl/Rumble Torsional Vibration.
[Noise may be most pronounced when
Transmission is in a “float” (low torque)
condition. May also be confined to a
particular vehicle speed.]
Transmission bearing or gear failure.
[Noise may be most pronounced under
hard pull or coast (high torque).]
Noise - Growl / Rumble at Idle
(Idle Gear Rattle)
Noise - High Pitched Whine Gear Noise.
Excess engine torsional vibration at idle. Check for low engine RPM.
Isolate as to axle or transmission noise.
If transmission, isolate to specific gear
or gears.
Check Driveline angles for proper U-joint
working angles.
Check Driveline for out of balance or
damage.
Check U-joints for proper phasing.
Check Clutch Assembly for broken
damper springs.
Check for inadequate clutch disc
damping.
Check Transmission Oil for excessive
metal particles.
Check for uneven engine cylinder
performance.
Check for proper clutch damper
operation.
Check for worn or defective shift lever
isolator.
Check for direct cab or bracket contact
with transmission (“grounding”).
Check for proper driveline u-joint
working angles.
Check for damaged or worn gearing.
36
Page 42

General Information
General Troubleshooting Chart (cont)
Complaint Cause What to do next
General Troubleshooting
Hard Lever Shifting
(Shift Lever is hard to gear into or out
of gear)
Shift Lever Jumpout
(Shift Lever comes out of gear on rough
roads)
Master Clutch dragging. Check Master cCutch for proper
disengagement.
Check Master Clutch for proper
adjustment (both release bearing travel
and Clutch Brake height).
Shift linkage problem. (Remote shifter) Check Shift Linkage or Cables for proper
adjustment, binding, lubrication, or
wear.
Shift Bar Housing problem. Check Shift Bar Housing components for
binding, wear, or damage.
Transmission Mainshaft problem. Check mainshaft for twist.
Check Sliding Clutches for binding,
damage, or excessive wear.
Driver technique. Driver not familiar or skilled with proper
double-clutching technique.
Driver contacting the Clutch Brake
during shifts.
Loose or worn engine mounts. Check engine mounts for damage, wear,
or excessive looseness.
Shift Lever problem. Check Shift Lever Floor Boot for binding
or stretching.
Check Shift Lever Isolator for excessive
looseness or wear.
Check for excessive offset or overhang
on the Shift Lever.
Check for extra equipment or extra
weight added to Shift Lever or knob.
Worn or broke Detent Spring or
Mechanism.
Check for broken Detent Spring.
Check for excessive wear on the Detent
Key of Detent Plunger.
Replace Detent Spring with heavier
spring or add additional spring.
37
Page 43

General Troubleshooting
General Troubleshooting Chart (cont)
Complaint Cause Corrective Action
Shift Lever Slipout
(Transmission comes out of gear under
torque)
Transmission goes to Neutral
(Shift lever doesn’t move)
No Range Shift or Slow Range Shift
(Also see Air System Troubleshooting)
Internal Transmission problem. Check for excessively worn or damaged
Sliding Clutches or Shift Yokes.
Low air pressure. Check Air Regulator pressure.
Internal Transmission problem. Check for excessively worn or damaged
Range Sliding Clutch or Yoke.
Transmission Air System problem. Preform Air System troubleshooting
procedure.
Check for proper air signal from Master
Valve.
Check Air Module Test Ports for proper
air delivery.
Range Cylinder problem. Check for failed or damaged Range
Piston, Piston Bar, or Cylinder.
Check for failed or loose Range Piston
Snap Ring.
Range Yoke Assembly problem. Check for failed or damaged Range
Yoke.
Check for failed or loose Range Yoke
Snap Rings.
Check for excessively long fastener
installed in rear support hole.
Check for binding between Range Yoke
Bar and Range Alignment Lock Cover.
Range Synchronizer problem. Check for failed or damaged Range
Synchronizer, Sliding Clutch, or Mating
Gear.
Check for excessively worn Range
Synchronizer Friction Material.
Grinding Noise on Range Shift Driver not preselecting Range Shift. Instruct driver to preselect Range Shifts.
Range Synchronizer worn or defective. Check Range Synchronizer and mating
parts for excessive wear or damage.
38
Page 44

Air System
General Information
Air Module
Shift Knob
(Master Control Valve)
Range Cylinder
Range Piston
Range Yoke Bar
Range Yoke
Low Range
Synchronizer
Range Sliding
Clutch
High Range
Synchronizer
Piston
Range
Bar
Range Selector
Air System Overview
The Range Shift Air System uses pressurized air to allow the operator to shift the Auxiliary Section between Low Range and High
Range. The operator controls this shift with a switch on the Shift Knob.
The Range Shift Air System components are described below in figure 2-10, which shows the Transmission with the Air System
components labeled.
Shift knob (Master Control Valve)
Located in the Shift Knob, the Master Control Valve is an operator controlled switch. When the Range Selector is in the down
position, Low Range is selected. When the Range Selector is in the up position, High Range is selected.
Air Module
Located on the top of the Transmission, this module contains an Air Filter, and Air Pressure Regulator, a Spool Valve, and an
Interlock Mechanism. Depending on the position on the Range Selector, the Air Module directs air flow to the Low Range or High
Range side of the Range Piston to complete a Range Shift.
The Range Shift Interlock feature of the Air Module allows the driver to preselect Range Shifts (place the Range Selector in the up
or down position) while the Transmission is still in gear. The System Interlock will prevent the Range Shift until the Shift Lever
and Transmission are in Neutral. The Range Shift will complete as the Shift Lever passes through Neutral, This feature prevents
Transmission damage and smooths shifting. The Air Module Interlock operation is described in greater detail later in this section.
Figure 2-10 Transmission Air System Components
39
Page 45

Air System
Range Cylinder and Piston
The Range Cylinder is located on the underside of the Shift Bar Housing. It contains the Range Piston and Bar Assembly. The
Range Piston and Bar Assembly is connected with the Range Yoke Bar to move the Range Sliding Clutch back and forth.
Depending on the position of the Range Selector, pressurized air is supplied to the front or back of the Range Piston to shift the
Auxiliary Section into Low or High Range.
Range Bar and Yoke
Located in the Transmission Auxiliary Section, the Range Yoke Bar and Yoke move the Range Sliding Clutch to Low or High Range.
The Range Yoke Bar extends into the Main Case where it is connected with the Range Piston Bar. The Range Yoke is positioned
in the slot of the Range Sliding Clutch. When the Range Cylinder moves the Range Bar and Yoke, the Yoke moves the Sliding
Clutch into the High or Low Range position.
Range Sliding Clutch and Synchronizer
The Range Sliding Clutch and Synchronizer are located on the Auxiliary Mainshaft (Output Shaft). The Range Sliding Clutch
connects the Auxiliary Mainshaft to either the Auxiliary Drive Gear (in High Range) or the Auxiliary Reduction Gear (in Low Range).
The Synchronizer allows the Sliding Clutch to move into gear without grinding.
40
Page 46

Air System
General Information
Low Range
Port
Supply
Port
Base Plate
Manifold
Gasket
Base
Plate
High Range
Port
High Range
Exhaust Port
Air Module Base
Exhaust
Filter
Spool Valve
End Cap
Spool Return
Spring Rest
Spool Return
Spring
Air Module
Cover
Spool
Valve
Spool Valve
Housing
Interlock
Return Spring
Interlock
Balls
Interlock/
Slave Piston
Housing
Interlock
End Cap
Slave Piston
Guide
Interlock
Finger
Slave
Piston
Low Range
Exhaust Port
"P" Pilot
Signal Port
Air Module Part Nomenclature
Figure 2-11 shows the Air Module with its components labeled. Refer to this figure as necessary while reading about the
Air System.
Figure 2-11 Air Module Part Nomenclature
41
Page 47

Air System
Interlock
Return Spring
Interlock
Balls
(Only Two
Shown)
Interlock/
Slave Piston
Housing
Interlock
End Cap
Slave Piston
Guide
Interlock
Finger
Air Module Interlock
Purpose
The Air Module Interlock allows the range to shift only when the Transmission is in Neutral. The Interlock prevents a Range Shift
when a front section gear is engaged.
This feature allows the driver to preselect the Range Shift (move the Range Selector on the Shift Knob) while a front section gear
is still engaged. The Range Shift will start and finish as the Shift Lever is moved through Neutral. The Range Shift must occur with
the front section in Neutral to prevent damage to the Range Synchronizers.
Interlock Construction
The Air Module Interlock Finger extends out of the bottom of the Air Module and through a hole in the Shift Bar Housing where it
contacts the Shift Shaft. The Interlock Return Spring continuously forces the Interlock Finger against the Shift Shaft.
The Shift Shaft contains a groove that corresponds with the Neutral shift position. The groove provides clearance so that the
Interlock Finger and Interlock End Cap can move to the relaxed position when the Transmission front section is in Neutral.
Four Interlock Balls are contained in four separate holes in the Slave Piston Guide. The Slave Piston end of the Interlock End Cap
contains a relief that provides clearance for the Interlock Balls.
Figure 2-12 Air Module Interlock Components
42
Page 48

Air System
General Information
Interlock balls
are held down
against slave piston.
Spring is compressed
as interlock end cap
is forced to the right.
NOTE: Interlock finger pushed left
due to contact with shift shaft.
(Shift shaft is in shift bar housing.)
Interlock Operation
When the Transmission front section is shifted into gear, the Shift Shaft is moved either forward of rearward. When the Shift Shaft
moves, the Interlock Finger rides up a ramp and out of the Shift Shaft Neutral Notch. The Interlock Finger pivots into the Air Module
and forces the Interlock End Cap to the right, compressing the Interlock Return Spring. The four Interlock Balls are forced down
into their respective holes. In this position, the Interlock Balls drop into a groove on the Slave Piston and prevent fore and aft
movement of the Slave Piston. This effectively locks the Slave Piston and Spool Valve in position. Figure 2-13 shows the
positioning of the Air Module Interlock components when the Shift Lever is in gear.
Figure 2-13 Interlock with Shift Lever in Gear
43
Page 49

Air System
Interlock Balls
can move away
from Slave Piston.
Spring forces
Interlock End Cap
and Finger to the left.
NOTE: Interlock Finger
in relaxed position against
Shift Shaft Notch.
When the Transmission is shifted to Neutral, the Interlock Return Spring forces the Interlock End Cap to the left as the Interlock
Finger pivots into the Neutral Notch on the Shift Shaft. The Interlock Balls can now move up out of the groove on the Slave Piston
and the Slave Piston can move freely. Figure 2-14 shows the positioning of the Air Module Interlock components when the Shift
Lever is in Neutral.
Figure 2-14 Interlock with Shift Lever in Neutral
44
Page 50

Air System
General Information
Shift Knob
Air
Module
Vehicle Supply
Air Inlet
Filtered Air
Test Port
"H"
"L"
Filter
Pressure
Regulator
120 PSI (827 kPa)
80 PSI (551 kPa)
"F"
SP
Air System Air Flow
Supply Air Flow
Vehicle air is supplied to the Air Module Inlet at the vehicle air pressure of 90–130 PSI (620–896 kPa). The air passes through the
Inlet Filter inside the Air Module and goes to a Pressure Regulator, which regulates the air pressure to 80 PSI (551kPa). Through
internal passages of the Air Module, the regulated air is available at the “S” supply port on the Air Module Cover and the supply
port on the Shift Knob Master Valve through 1/8” or 5/32” plastic air line. Figure 2-14 shows the supply air flow through the
Air Module.
Figure 2-14 Supply Air Flow
45
Page 51

Air System
Shift Knob
Air
Module
Vehicle Supply
Air Inlet
Filtered Air
Test Port
Range C
y
linder
High Range
Test Port
Low Range
Test Port
SP
"H"
"L"
"F"
120 PSI (827 kPa)
80 PSI (551 kPa)
0 PSI
Low Range Air Flow
When Low Range is selected, supply air will flow through the Air Module Spool Valve to the Low Range Port. Air flows through
the Low Range passages in the Air Module and exits the Module near the rear attaching capscrew. After exiting the Air Module,
the air flows into a passage in the Shift Bar Housing and is supplied to the front side of the Range Cylinder Piston. The Range
Piston, Yoke, and Sliding Clutch move rearward to shift the Auxiliary into Low Range. Figure 2-15 shows the Low Range air flow
through the Air Module.
Figure 2-15 Low Range Air Flow
46
Page 52

Air System
General Information
Shift Knob
Air
Module
Range Cylinder
High Range
Test Port
Low Range
Test Port
SP
"F"
120 PSI (827 kPa)
80 PSI (551 kPa)
0 PSI
Vehicle Supply
Air Inlet
Filtered Air
Test Port
"H"
"L"
High Range Air Flow
When High Range is selected, supply air will flow through the Air Module Spool Valve to the High Range Port. Air flows through
the High Range passages in the Air Module and exits the Module near the rear attaching capscrews. After exiting the Air Module,
the air flows into a passage in the Shift Bar Housing and is supplied to the back side of the Range Cylinder Piston. The Range
Piston, Yoke, and Sliding Clutch move forward to shift the Auxiliary into High Range. Figure 2-16 shows the High Range air flow
through the Air Module.
Figure 2-16 High Range Air Flow
47
Page 53

Air System
Air Module Operation
Low Range - Shift Lever in Neutral
When the Range Lever on the Shift Knob is placed in the down (Low Range) position, air flows through the Master Control Valve
and back to the Air Module through 5/32” air line. This signal air will enter the Air Module at the “P” port where it will enter the
Slave Piston Chamber. With the Shift Lever in Neutral, the air pressure will move the Slave Piston and Spool Valve to the full right
position as shown in figure 2-17, and the Spool Return Spring will be compressed. At this point, the Supply Port will be connected
with the Low Range Port, and the High Range Port will be exhausted. Pressurized air will move the Range Piston, Bars, Range
Yoke, and Range Sliding Clutch to the Low Range position.
"P" Pilot Signal
ExhaustExhaust
Low Range
High Range
Supply
Figure 2-17 Air Flow for Low Range with Shift Lever in Neutral
Low Range - Shift Lever in Gear
When the Transmission is shifted into gear, the Interlock Mechanism will shift to the right as shown in Figure 2-18, locking the
Slave Piston and Spool Valve into position. Air flow through the Air Module is not affected.
"P" Pilot Signal
ExhaustExhaust
Low Range
Supply
Figure 2-18 Air Flow for Low Range with Shift Lever in Gear
48
High Range
Page 54

Air System
General Information
Low Range - Shift Lever in Gear, High Range Preselected
With the Shift Lever still in gear, the driver will preselect High Range by switching the Range Lever on the Shift Knob to the up
position. When the Range Lever is in the up position, the air supply is shut off to the “P” port. The “P” air line will be exhausted
at the Shift Knob. The Spool Valve and Slave Piston will not move due to the Interlock Mechanism and the Transmission being in
gear. Figure 2-19 shows the air flow with High Range preselected.
"P" Pilot Signal
ExhaustExhaust
Low Range
High Range
Supply
Figure 2-19 Air Flow for Low Range with high Range Preselected
High Range - Shift Lever in Neutral
With High Range preselected, the Interlock Mechanism will release as soon as the Shift Lever is moved to Neutral. The Spool
Return Spring will move the Spool Valve and the Slave Piston to the full left position. Supply air will be provided to the High Range
Port. The Low Range Port will be exhausted. Pressurized air will move the Range Piston, Bars, Range Yoke, and Range Sliding
Clutch to the High Range position. Figure 2-20 shows the air flow with High Range selected and the Shift Lever in Neutral.
"P" Pilot Signal
ExhaustExhaust
Low Range
High Range
Supply
Figure 2-20 Air Flow for High Range with Shift Lever in Neutral
49
Page 55

Air System
High Range - Shift Lever in Gear
When the Shift Lever is moved into gear, the Interlock Finger moves the Interlock End Cap to the right, which activates the Interlock
Mechanism. It also moves the Slave Piston and Spool Valve partially to the right. The partial travel of the Spool Valve exposes the
Low Range Port to pressurized air from the Supply Port. Supply air is available to both the Low and High Range Ports, and both
Exhaust Ports are sealed. Equal air pressure is available on both sides of the Range Cylinder Piston. Because the High Range side
of the Piston has more available surface area than the Low Range side, the range remains in High Range. Figure 2-21 shows the
air flow with High Range selected and the Shift Lever in gear.
"P" Pilot Signal
ExhaustExhaust
Low Range
Supply
Figure 2-21 Air Flow for High Range with Shift Lever in Gear
High Range
50
Page 56

Air System
General Information
41
P
21
S
22
F
1
IN
23
H
25
L
P
ilot Signal Port
S
upply Port
Vehicle Supply
Air Inlet
H
igh Range
Test Port (1/16" NPT)
L
ow Range
Test Port (1/16" NPT)
F
iltered Vehicle
Supply Air Test Port (1/16" NPT)
Auxiliary Section
Housing
Indication Notch
Range
Alignment
Lock Cover
Air System Nomenclature
Figures 4-1 through 4-3 below show the Air Module, Shift Knob, and Range Alignment Lock Cover (earlier models) with their
components labeled. These are the primary components used during troubleshooting. If necessary, refer to these figures while
troubleshooting the Air System.
Selector
Figure 4-1 Air Module Ports
Range
Shift
Figure 4-2 Shift Knob Components Figure 4-3 Range Alignment Lock Cover
Knob
51
Page 57

Air System
Gasket Material*
1/2" Flat Washer
5/16" Flat Washer
5/16" Flat Washer
5/16" X 1 1/2"
Capscrew
5/16" Nut
* Gasket material must be used to seal the two
holes in the bottom of Air Module.
Figure 4-4 below shows how to isolate the Air Module. If necessary, refer to this figure when isolating the Air Module.
Figure 4-4 Air Module Isolation
The table below shows which air lines connect to which ports on the Shift Knob and Air Module. If necessary, refer to this table
when connecting the air lines.
SSRed
PPBlack
Port on Knob Port on Air Module Air Line Color (Typical)
52
Page 58

Timing
Timing
Timing Procedures
Special Instructions
It is essential that both Countershaft Assemblies of the Front and Auxiliary Sections are “timed.” This assures proper tooth contact
is made between Mainshaft Gears seeking to center on the Mainshaft during torque transfer and mating Countershaft Gears that
distribute the load evenly. If not properly timed, serious damage to the Transmission is likely to result from unequal tooth contact
causing the Mainshaft Gears to climb out of equilibrium.
Timing is a simple procedure of marking the appropriate teeth of a gear set prior to installation and placing them in proper mesh
while in the Transmission. In the Front Section, it is necessary to time only the Drive Gear Set. And depending on the model, only
the LO Range, Deep Reduction, or Splitter Gear Set is timed in the Auxiliary Section.
Procedure - Front Section
1. Marking Countershaft Drive Gear teeth: Prior to placing
each Countershaft Assembly into the Case, clearly mark the
tooth located directly over the Drive Gear Keyway as shown.
This tooth is stamped with an "0" to aid identification.
2. Marking Main Drive Gear teeth: Mark any two adjacent
teeth on the Main Drive Gear.
Mark the two adjacent teeth located directly opposite the
first set marked on the main drive gear. As shown to the left,
there should be an equal number of unmarked gear teeth on
each side between the marked sets.
3. Meshing marked Countershaft Drive Gear teeth with
marked Main Drive Gear teeth: After placing the Mainshaft
Assembly into the Case, the Countershaft Bearings are
installed to complete installation of the Countershaft
Assemblies.
When installing the bearings on the Left Countershaft, mesh
the Countershaft Drive Gear marked tooth with either set of
Main Drive Gear two marked teeth.
Repeat the procedure when installing the bearings on the
Right Countershaft, make use of the remaining set of Main
Drive Gear two marked teeth to time Assembly.
53
Page 59

Timing
6
5
Procedure - Auxiliary Section
4. Marking the helical Auxiliary Countershafts: Mark any two
teeth on the LO Range Gear. Then mark two teeth located
directly opposite the first marked.
Prior to placing each Auxiliary Countershaft Assembly
into housing, mark the tooth on each Auxiliary Countershaft
Assembly LO Range Gear stamped with the two "0"s.
Repeat the procedure on each Auxiliary Countershaft
Reduction Gear.
Follow the assembly procedures in the “Auxiliary Section”.
54
Page 60

In-Vehicle Service Procedures
How to Disassemble the Roadranger Valve
Special Instructions
None
Special Tools
• Typical service tools
In-Vehicle Service Procedures
1
7
2
2
6
6
2
8
3
8
2
5
4
5
Component Nomenclature and Auxiliary Countershaft Sectional View
1. Medallion
2. Spring
3. Lever
4. Cover
5. Screw
6. Ball 5/32”
7. Retainer
8. O-Ring
5
5
55
Page 61

In-Vehicle Service Procedures
Procedure -
1. Remove the two screws holding the bottom cover to the
valve and slide the cover down the Gearshift Lever to expose
air line fittings. Disconnect the air lines.
2. Loosen the Jam Nut and turn the Roadranger Valve from the
Gear Shift Lever.
3. Pry the Medallion from the recess in the Top Cover.
4. Turn out the two screws to remove the Top Cover from the
Valve Housing.
5. Turn out the two screws in the side of the Valve Housing to
separate the Housing.
6. Remove the Range Selection Lever from the Left Housing
along with the Position Balls and Guide.
7. If necessary, remove the spring and O-ring from the bores
in the Left Housing.
8. If necessary, remove the springs, O-ring and sleeve from the
bores in the Right Housing.
56
Page 62

In-Vehicle Service Procedures
How to Assemble the Roadranger Valve
Special Instructions
None
Special Tools
• Typical service tools
In-Vehicle Service Procedures
1
7
2
2
6
6
2
8
3
8
2
5
4
5
Component Nomenclature and Auxiliary Countershaft Sectional View
1. Medallion
2. Spring
3. Lever
4. Cover
5. Screw
6. Ball 5/32”
7. Retainer
8. O-Ring
Procedure -
1. Refer to the drawing for proper reassembly. Use a very small
amount of silicone lubricant on the O-rings to avoid clogging
the ports. A small amount of grease on the Position Springs
and Balls will help to hold them in place during reassembly.
5
5
2. Reinstall Roadranger Valve on Gear Shift Lever and tighten
the Jam Nut.
3. Attach the air lines and reinstall the Bottom Cover.
57
Page 63

In-Vehicle Service Procedures
WARNING
CAUTION
How to Remove Compression Type Fittings
Special Instructions
A sudden release of air pressure can cause personal injury or damage to equipment. To prevent injury or equipment damage,
exhaust the vehicle air tanks.
Small air lines are available in 1/8" or 5/32" sizes. Make sure 1/8" air lines are used with 1/8" fittings and 5/32" air lines are
used with 5/32" fittings. Mixing sizes can cause air leaks or damage to fittings.
Before removing the air lines and hoses, label or record their location.
Special Tools
• Typical service tools
58
Procedure -
1. Exhaust the vehicle air tanks before continuing.
2. Loosen the Nut on the fitting, and slide it back out of the way.
3. Pull the Air Line and attached Collet from the fitting.
4. Inspect the fitting, Air Line, Collet, and Nut for damage or
wear. Replace as necessary.
Page 64

In-Vehicle Service Procedures
In-Vehicle Service Procedures
WARNING
CAUTION
How to Install Compression Type Fittings
Special Instructions
A sudden release of air pressure can cause personal injury or damage to equipment. To prevent injury or equipment damage,
exhaust the Vehicle Air Tanks
Small air lines are available in 1/8" or 5/32" sizes. Make sure 1/8" air lines are used with 1/8" fittings and 5/32" air lines are
used with 5/32" fittings. Mixing sizes can cause air leaks or damage to fittings.
Special Tools
• Typical service tools
Procedure -
1. Check the threads of the fitting for thread sealant. If no
sealant is present, apply Eaton® Fuller® Thread Sealant
#71205 or equivalent.
2. Install the fitting.
Note: Do not overtighten the nut. Overtightening can
compress the Collet too much and cause an air line
restriction.
3. Install the Air Line, Collet, and Nut. If installing a new fitting,
place the Collet in the fitting and loosely install the Nut. (Do
not tighten the Nut yet.) Insert the Air Line through the Nut
and into the Collet. Tighten the Nut as usual.
4. Enable the Vehicle Air System. Allow the air tanks to
pressurize, and check for leaks. Repair as necessary.
59
Page 65

In-Vehicle Service Procedures
WARNING
CAUTION
How to Remove Push-To-Connect Type Fittings
Special Instructions
A sudden release of air pressure can injure you or damage equipment. To prevent injury or equipment damage, exhaust the
Vehicle Air Tanks.
Make sure only 5/32” air lines are used with push-to-connect fittings. Using sizes other than 5/32” can cause air leaks or
damage to fittings.
Special Tools
• Release Tool - 4301157
Procedure -
2
1. Exhaust the Vehicle Air Tanks before continuing.
2. Use the Air Line Release Tool to press the Release Sleeve
down while pulling the Air Line from the fitting as shown
at right.
3. Inspect the fitting for damage or wear. Remove and replace
2
as necessary.
60
Page 66

In-Vehicle Service Procedures
How to Install Push-To-Connect Type Fittings
Special Instructions
None
Special Tools
• Cutting Tool - 4301158
Procedure -
1. Check the threads of the fitting for thread sealant. If no
sealant is present, apply Eaton®Fuller® Thread Sealant
#71205 or equivalent.
2. Install the fitting.
3. Inspect Air Line ends for burrs or deformed areas, trim as
needed with Air Line Cutter Tool. The cut must be smooth
and square. If the tubing end is deformed or burred, the
internal O-ring in the fitting will be damaged when the Air
Line is inserted.
In-Vehicle Service Procedures
3
4. Push the Air Line into the fitting. It should insert
approximately 3/4”. If it does not insert far enough or is
difficult to insert, the fitting may be damaged and should be
replaced. After inserting, give the Air Line a slight tug to
make sure the line stays in place. If line does not stay in
place, replace the fitting.
5. Enable the Vehicle Air System. Allow the air tanks to
pressurize, and check for leaks.
61
Page 67

In-Vehicle Service Procedures
WARNING
How to Remove a Roadranger Valve
Special Instructions
A sudden release of air pressure can injure you or damage equipment. To prevent injury or equipment damage, the Vehicle
Air Tanks must be exhausted.
Special Tools
• Typical service tools
Procedure -
1. From the Roadranger Valve Cover, remove the two (2)
Mounting Screws.
2. Slide the Roadranger Valve Cover down.
3. From the air fittings, disconnect the Air Lines.
4. From the Roadranger base, loosen the Jam Nut. Rotate the
Roadranger Valve until the valve is removed.
5. Inspect the parts: Nut, Valve Cover, Air Lines, Sheathing,
and O-rings from the Lever Shaft.
6. In the Roadranger Valve, inspect the air fittings, and remove
if damaged.
62
Page 68

In-Vehicle Service Procedures
In-Vehicle Service Procedures
How to Install a Roadranger Valve
Special Instructions
To position the Roadranger Valve, the Range Lever must be to the front or the Splitter Button to the left when facing forward.
Special Tools
• Typical service tools
Procedure -
1. Make sure the Nut, Valve Cover, Air Lines, Sheathing, and
O-rings are in position on the Lever Shaft.
2. If previously removed, replace the Air Fittings and torque to
84–120 lb. in.
3. Place the Roadranger Valve on the Lever Shaft and rotate so
the Range Selector faces the vehicle front.
4. From the Roadranger Valve bottom, tighten the Jam Nut to
35–45 lb. ft. of torque.
5. Connect the Air Lines to the Air Fittings.
6. Slide the Cover into position on the Roadranger Valve.
7. Install the Roadranger Valve Cover Mounting Screws.
Note: Make sure the Air Lines are seated fully.
63
Page 69

In-Vehicle Service Procedures
CAUTION
How to Remove the Gear Shift Lever/Remote Shift Control
Special Instructions
The air lines must be disconnected from the Transmission or from the Roadranger Valve.
Different Detent Springs are available to increase or decrease shifting effort. Note and record specific locations for specific springs.
In some cases, a stiffer spring is installed in the top rail position.
Remote Control Housings are removed the same way as Gear Shift Levers.
Procedure -
1. From the Gear Shift Lever Base/Shift Control Housing,
remove the four (4) Retaining Capscrews.
2. To break the gasket seal, lightly jar the Gear Shift/Shift
Control Housing.
3. Remove the Gear Shift Lever Housing.
Make sure the Detent Springs do not fall into the
Transmission.
4. Remove Detent Springs as needed.
5. Remove the gasket and clean the area the replacement
gasket will contact.
64
Page 70

In-Vehicle Service Procedures
In-Vehicle Service Procedures
How to Install the Gear Shift Lever/Remote Shift Control
Special Instructions
Remote Control Housings are installed the same way as Gear Shift Levers.
For standard and forward Shift Bar Housings, make sure the Detent Springs and Balls are in the Shift Bar Housing top bores.
Make sure the Shift Block and Yoke notches are aligned in the neutral position.
Procedure -
1. Thoroughly clean mounting surface.
2. Position a new gear Shift Lever/Shift Control Housing
Gasket on the Gear Shift Lever mounting surface.
3. Install the Detent Springs.
4. Install the Shift Lever/Shift Control Housing. Make sure the
tip (finger) of the Gear Shift Lever fits into the slots in the
Shift Block.
5. Apply Eaton/Fuller Sealant #71205 or equivalent to the
retaining capscrews.
6. Install the retaining capscrews, tighten to 35–45 lbs.ft. of
torque.
Note: Make sure the capscrews are properly torqued.
Note: Make sure you can shift the Transmission.
65
Page 71

In-Vehicle Service Procedures
In-Vehicle Service ProceduresHow to Adjust the Remote Shift Control (LRC Type)
Special Instructions
The following is a typical adjustment procedure for an LRC type Slave Control. It is recommended that the OEM Chassis Service
Manual be consulted first.
Procedure -
1. Move the Gear Shift Lever forward or backward to the
neutral position.
2. Move the Gear Shift Lever sideways, toward reverse, until
you feel resistance from the Reverse Plunger Spring. DO
NOT shift to reverse. The Shift Finger must remain in this
position while you are making all the adjustments.
3. Remove the Cotter Pin, Castle Nut and Ball Joint A (see
figure A) from the Selection Lever. Do not remove the ball
joint from the pivot link.
4. Loosen the Capscrew B (see figure A) and remove the Shift
Arm from the inner shift shaft. Do not disconnect the
Selection Lever from the Shift Arm.
5. Turn the Shift Arm until it is at a right angle (90°) to the
Selection Lever as viewed from the side (see figure B).
Note: Ideally, the Shift Arm should be adjusted 90° to the
Selection Lever as described, but in some chassis
configurations, it may be necessary to index the Shift
Arm in the vertical position. Indexing the Shift Lever
is done to prevent shift lever jump out. This type of
adjustment will cause an unequal amount of gear shift
lever travel between neutral and a forward lever
position as compared to neutral and a rearward lever
position.
66
Page 72

In-Vehicle Service Procedures
6. Install the Shift Arm on the splines of the Inner Shift Shaft.
You may have to move the Shift Arm 4° or 5° to align the
splines of the two parts. Disregard any movement of the
Gear Shift Lever at this point. The Gear Shift Lever will be
adjusted later.
7. Tighten the Capscrew B (see figure A) on the Shift Arm.
8. Connect the Pivot Link Assembly Ball Joint to the Selection
Lever. Secure it with the Castle Nut and Cotter Pin.
9. Loosen the Jam Nuts C (see figure C) on the Pivot Link.
10. Check to be sure the Inner Shift Finger is still in place.
11. Rotate the Pivot Link until the curved end of the Selection
Lever is parallel with the Shift Arm as viewed from the rear
(see figure C).
12. Tighten the Pivot Link Jam Nuts C (see figure C).
In-Vehicle Service Procedures
13. Loosen both capscrews on the Turnbuckle D (see figure A).
14. Check to be sure Inner Shift Finger is still in place.
15. Rotate the Turnbuckle to obtain the proper forwardbackward neutral position of the Gear Shift Lever in the cab.
16. Tighten one Turnbuckle D capscrew (see figure A).
17. Move the Gear Shift Lever to the desired position.
18. Turn the second Turnbuckle D Capscrew.
19. Check for linkage obstructions in all gear positions.
67
Page 73

In-Vehicle Service Procedures
Detent Plunger
Detent Spring
Capscrew
Shift Block
Optional Spring
Design
2
3
How to Remove the Detent Spring
Special Instructions
None
Procedure -
1. Remove the Shift Lever or Remote Shift Control according
to the “Shift Lever/Remote Shift Control Removal”
instructions in this section.
2. Remove the Shift Block Socket Head Capscrew using an
8 mm or 5/16” hex driver.
3. Gently pry the Shift Block loose, and lift it straight up to
prevent the Detent Plunger and Spring from falling into the
Transmission Case.
4. Remove the Detent Plunger and Spring(s).
Note: Some Transmissions may have two springs to
increase the detent force.
68
Page 74

In-Vehicle Service Procedures
How to Install the Detent Spring
Detent Plunger
Detent Spring
Capscrew
Shift Block
Optional Spring
Design
2
3
Special Instructions
None
Special Tools
• Torque Wrench, 50 lb. ft. Capacity
Procedure -
1. Place the Detent Spring(s) and Detent Plunger in the
Shift Block.
In-Vehicle Service Procedures
2. Place the Shift Block on the Shift Shaft using the following
3. Install the Socket Head Capscrew to secure the Shift Block.
4. Install the Shift Lever or Remote Shift Control according to
procedure:
a. Tilt the Shift Block so the Plunger faces slightly upward.
b. Place the Plunger in the center of the Detent Notch, and
press the Detent Plunger in to compress the Detent
Springs.
c. While the springs are compressed, roll the Shift Block
into place on the Shift Shaft. If the Shift Shaft has been
moved or otherwise disturbed, it may be necessary to
slide the Shift Shaft fore or aft to properly install the
Shift Block.
Apply Thread Sealant/Adhesive and Torque the screw to
40–45 lb. ft. (54–61 N•m)
the “Shift Lever/ Remote Shift Control Installation”
instructions in this section.
Note: Transmissions with Shift Shaft Part Number 4308006
with register neutral side to side in all three Shift
Gates. Part Number 4305078 is central neutral
position only.
69
Page 75

In-Vehicle Service Procedures
Neutral Switch Operation and Testing
Special Instructions
The Neutral Switch is a normally closed switch. An electrical current flows through it when the Transmission Shifter is in the center
neutral position. When the Transmission Shifter is in gear or a side neutral position, the switch is open and no current flows
through it.
Special Tools
• Ohm Meter
Center Neutral Position
(Neutral Switch Active)
R
1
6
2
7
3
8
Shift Position
Diagram
Procedure -
1. Disconnect the wiring from the switch by lifting the
Connector Locking Tab and pulling the Connector out
of the Switch.
4
9
5
10
2. Connect an Ohm Meter to check for continuity or a
small reading.
3. Place the Transmission Shift Lever in the center neutral
position. The Ohm Meter should register continuity or a
small reading. If it does, go to the next step. If it does not,
remove the Switch and replace it according to the removal
instructions below.
4. Shift the Transmission into all gear positions. The Ohm
Meter should read open or infinity. If it does not, remove the
Switch, recheck it for continuity, and replace it as necessary.
Also, check for the presence of the Neutral Switch Pin.
Note: Shift Shaft part number 4308006 will register
Neutral Switch continuity in all three Shift Gates.
All FR-series Transmissions built after 3/2013
contain Shift Shaft 4308006.
70
Page 76

In-Vehicle Service Procedures
In-Vehicle Service Procedures
Reverse Switch
Reverse Pin
O-ring
Neutral Switch
O-ring
Neutral Pin
How to Remove the Neutral Switch
Special Instructions
If the Ohm Meter responds as indicated in the test procedure, do not perform this procedure as the Switch is in good working
condition.
Special Tools
• Typical service tools
Procedure -
1. Remove the Switch using a 22 mm or 7/8” deep well socket
or box end wrench.
2. Check for the presence of the Neutral Pin in the bore under
the Switch.
3. While watching the Neutral Pin, move the Transmission in
and out of gear. The Pin should raise up when the
Transmission is in gear and lower when the Transmission is
in neutral. If the Pin does not operate properly, remove the
Pin with a magnet and check it for wear. Also, remove the
Shift Bar Housing and check the Shift Shaft for wear.
4. Remove the Pin from the bore with a magnet and check it for
excessive wear. If it is worn, replace it.
5. If the Pin is present and not worn, replace the Switch with a
new one.
71
Page 77

In-Vehicle Service Procedures
Reverse Switch
Reverse Pin
O-ring
Neutral Switch
O-ring
Neutral Pin
How to Install the Neutral Switch
Special Instructions
None
Special Tools
• Torque Wrench, 25 lb. ft. Capacity
Procedure -
1. Insert the Neutral Pin in the neutral switch bore. (The Neutral
Pin is shorter than the Reverse Pin).
2. Lubricate the O-ring on the Switch.
3. Install the Neutral Switch. Tighten it to 15–20 lb. ft.
(20–27 N•m) of torque.
4. Connect the Wiring Connector to the Switch, making sure
the Locking Tab engages properly.
72
Page 78

In-Vehicle Service Procedures
In-Vehicle Service Procedures
Reverse Switch Operation and Testing
Special Instructions
The Reverse Switch is a normally open ball switch. When the Transmission is shifted into reverse, a ramp on the Reverse Shift
Yoke contacts and raises a pin. The pin depresses the ball on the switch, which closes the switch contact, allowing current to flow
through the switch and light up the vehicle’s backup lights.
Special Tools
• Ohm Meter
Procedure -
1. Disconnect the wiring from the Switch by lifting the
Connector Locking Tab and pulling the connector out of
the Switch.
2. Connect an Ohm Meter to test for continuity.
3. Place the Transmission Shift Lever in any position except
reverse. If the Switch is working properly, the Ohm Meter
should read open or infinity. If it is not, remove the Switch
and recheck it for continuity. Replace it as necessary.
4. Place the Transmission Shift Lever in the reverse position. If
the Switch is working properly, the Ohm Meter should
register continuity, or a small reading. If it does not, remove
the Switch and recheck it for continuity. Replace it as
necessary. Also, check for the presence of the Reverse Pin.
Neutral Switch
O-ring
Neutral Pin
Reverse Pin
O-ring
Reverse Switch
73
Page 79

In-Vehicle Service Procedures
Reverse Switch
Reverse Pin
O-ring
Neutral Switch
O-ring
Neutral Pin
How to Remove the Reverse Switch
Special Instructions
If the Ohm Meter responds as indicated in the test procedure, do not perform this procedure as the switch is in good working
condition.
Special Tools
• Typical service tools
Procedure -
1. Remove the Reverse Switch using a 22 mm or 7/8” deep
well socket or box end wrench.
2. Check for the presence of the Reverse Pin in the bore under
the Switch.
3. While watching the Reverse Pin, move the Transmission
Shifter between the reverse position and any gear. The pin
should raise when the Transmission is shifted to reverse and
lower when the Transmission is in neutral. If the pin does
not raise and lower, inspect it to see if something is causing
it to stick, and inspect it for wear. Also, remove the Shift
Tower and check for wear on the Reverse Yoke Ramp. This
ramp can be seen through the Shifter opening.
4. Remove the pin from the bore with a magnet and check it for
excessive wear. If it is worn, replace it.
5. If the pin is present and not worn, replace the Reverse
Switch with a new one.
74
Page 80

In-Vehicle Service Procedures
How to Install the Reverse Switch
Reverse Switch
Reverse Pin
O-ring
Neutral Switch
O-ring
Neutral Pin
Special Instructions
None
Special Tools
• Torque Wrench, 25 lb. ft. Capacity
Procedure -
1. Insert the Reverse Pin in the Reverse Switch bore.
(The Reverse Pin is longer than the Neutral Pin.)
2. Lubricate the O-ring on the Switch.
3. Install the Reverse Switch. Tighten it to 15–20 lb. ft.
(20–27 N•m) of torque.
4. Connect the Wiring Connector, making sure the Locking Tab
engages properly.
In-Vehicle Service Procedures
75
Page 81

In-Vehicle Service Procedures
4
5
How to Install the Shift Bar Housing
Special Instructions
None
Special Tools
• Torque Wrench, 50 lb. ft. capacity
Procedure -
1. Clean the gasket mounting surface of the Main Case and
Shift Bar Housing, and place a new gasket on the Main Case.
2. Place the Shift Bar Housing Shift Shaft in the neutral position
so the yokes will be positioned to fit over the Mainshaft
Sliding Clutches.
3. In the Main Case of the Transmission, place the Mainshaft
Sliding Clutches in their neutral positions.
4. If the Auxiliary Section is in place, slide the Range Piston Bar
forward or rearward to align the notch in the Piston Bar with
the notch in the Range Yoke Bar.
5. With all parts properly aligned, lower the Shift Bar Housing
straight down into position. Position can be verified thru
Shift Tower opening.
6. Apply Eaton® Fuller® thread sealant #71205 or equivalent
to the retaining capscrews.
7. Install the 16 retaining capscrews. Tighten the screws in
sequence per numbers on Shift Bar Housing to 40–45 lb. ft.
(54–61 N•m) of torque.
7
76
Page 82

In-Vehicle Service Procedures
In-Vehicle Service Procedures
How to Remove the Shift Bar Housing
Special Instructions
The Air Module does not have to be removed in order to remove the Shift Bar Housing.
Special Tools
• Typical service tools
Procedure -
1. From the Shift Bar Housing rim, remove the 16 retaining
capscrews.
2. Insert a screwdriver into the pry slots near the dowel pins
and pry the housing off the dowel pins.
TIP: Light upward hammering on the three tabs may help
loosen the Shift Bar Housing. Do not hammer
excessively as the housing may crack.
3. Lift the Shift Bar Housing straight off the Transmission Case
and set it on a bench.
4. Remove the gasket, and clean all mounting surfaces of
gasket material.
Dowel
Pin
Pry Slot
2
1
Dowel
Pin
Pry Slot
77
Page 83

In-Vehicle Service Procedures
How to Remove the Oil Seal Mechanical/Magnetic Speedometer
Special Instructions
Prior to replacing the seal, carefully inspect the Transmission to make sure the oil leakage is coming from the seal. Pay particular
attention to the gasketed surfaces of the Rear Bearing Cover, Rear Countershaft Bearing Covers, and Shift Bar Housing.
Special Tools
• Output Yoke Puller
1. Bushing
2. Rear Bearing Cover Assembly
3. Capscrew
4. Speedometer Drive Gear
5. Oil Seal with Slinger
6. O-Ring
7. Speedometer Spacer Assembly
78
1. Rear Bearing Cover
2. Sensor Retaining Capscrew
3. O-Ring
4. Speedometer Sensor
5. Capscrew
6. Oil Seal
7. Slinger
8. O-Ring
9. Speedometer Spacer Assembly
10. Slinger
Page 84

In-Vehicle Service Procedures
Procedure -
4
5
6
1. Disconnect the Driveshaft and U-joint from the Output Yoke
according to the OEM or driveshaft manufacturer’s
instructions.
2. Shift the Transmission into 1st gear or low gear or use a
Yoke Holding Tool to prevent the Output Yoke from turning
when you loosen the Output Yoke Nut.
3. Remove the Output Yoke Nut using a 70 mm or 2 3/4”
socket.
4. Remove the Output Yoke. Use Yoke Puller if needed.
a. For Magnetic Speedometers:
Remove the Speedometer Sensors from the rear
bearing cover.
TIP: If the Sensor is a thread in type, note the number
of threads exposed so that the Sensor can be
reinstalled to the same depth. If the Sensor is a
push in type, remove the Hold Down Capscrew and
pull the Sensor out of the bore.
In-Vehicle Service Procedures
Remove the Speedometer Rotor/Seal Sleeve and the
O-ring.
b. For Mechanical Speedometers:
Remove the Seal Sleeve and O-ring
5. For Transmissions with Magnetic Speedometers, pry the
seal out as shown using a large screwdriver or prybar in the
metal groove of the seal. For Transmissions with Mechanical
Speedometers, use a Slide Hammer with a hook attachment
to remove the seal.
Note: The seal will be damaged during removal and must be
replaced.
6. Remove Seal Slinger from the Speedometer Rotor/Seal
Sleeve using a Brass Drift and hammer. Remove Seal
Slinger from the Speedometer Rotor/Seal Sleeve using a
Brass Drift and hammer.
7. Inspect all parts of the Oil Seal according to the instructions
in the “General Service Practices” section of the manual.
79
Page 85

In-Vehicle Service Procedures
2
How to Install the Oil Seal Mechanical/Magnetic Speedometer
Special Instructions
Clean Seal Driver before installing new seals to prevent damage and future leaks.
Special Tools
• RR1001TR-2 Seal Driver
• RR1001TR-8 Seal Driver Adapter
• RR1001TR-1 Seal Slinger Driver
• RR1019TR Hand Maul
• Torque Wrench, 700 lb. ft. capacity
Procedure -
1. Place Driver Adapter RR1001TR-8 on Seal Driver
RR1001TR-2 and use a Hand Maul to install a new seal in the
Output Bearing Cover. The seal is fully installed when the
flange on the seal is flush with the shoulder in the bore.
1
2. Install new Seal Slinger on the Speedometer Rotor using
RR1001TR-1 Slinger Driver and Hand Maul.
80
Page 86

In-Vehicle Service Procedures
3. If previously removed, install the O-ring over the
3
4
CAUTION
Output Shaft.
To avoid creating oil leaks, make sure the Speedometer
Rotor/Seal Sleeve is free from contaminants.
4. Install the Speedometer Rotor/Seal Sleeve over the Output
Shaft, and install the Speedometer Sensors.
5. Install the Output Yoke over the Output Shaft. The Yoke
should slide on and stop before contacting the Speedometer
Rotor. As the Output Shaft Nut is installed, the Output Yoke
will contact the Speedometer Rotor.
6. Install Output Nut and torque to 650–700 lb. ft.
(881.28-949.07 N•m).
7. Connect the Driveshaft and U-joint according to the OEM or
Driveshaft manufacturer’s instructions.
In-Vehicle Service Procedures
81
Page 87

In-Vehicle Service Procedures
WARNING
How to Remove the Auxiliary Section in Chassis
Special Instructions
The following procedure covers the removal of the Auxiliary Section with the Transmission remaining in the Chassis. If the
Transmission has been removed, refer to “Auxiliary Section Removal (Bench Procedure)” for removal procedures.
Important: The Lock Cover was removed on new units, so the Shiftbar needs to be removed to unlock the Range Cylinder and
remove the Auxiliary Section.
Special Tools
• Floor Jack
• M10 x 1.5 thread tap
• RR1002TR Auxiliary Countershaft Support Straps
Procedure -
1. Place the Range Selector on the Shift Knob in the down
position to shift the Transmission into Low Range.
Removing the Auxiliary Section when the Transmission is in
Low Range will aid in reassembly.
2. Drain the transmission oil.
3. Disconnect the Driveshaft and U-joint from the Output Yoke.
4. If the Auxiliary Section is to be disassembled, remove the
Output Nut using a 70 mm or 2 3/4” socket. To prevent the
Output Shaft from rotating while removing the nut, shift the
Transmission to 1st gear or use a yoke holding tool.
If the Shift Bar Housing is still installed, you MUST
perform steps 5 and 6 if the Lock Cover is present. New
designs no longer use the Lock Cover and the Shiftbar
Housing must be removed for Auxiliary Section removal.
5. Remove the capscrews from the Range Bar Lock Cover, and
rotate the Lock Cover counterclockwise until the notch on
the cover lines up with the unlock symbol.
Note: The top picture is the old style cover and the bottom
picture is the new style cover.
Note: If the system still contains air pressure, greater force
is required to turn the Lock Cover.
6. Insert the right capscrew to secure the cover in the unlock
position.
82
Note: This step unlocks the Range Yoke Bar in the Auxiliary
from the Range Piston Bar in the Shift Bar Housing.
Page 88

In-Vehicle Service Procedures
7. Drive the two Dowel Pins forward, and remove them.
7
7
8
9
9
9
WARNING
CAUTION
8. Remove 18 of the 19 capscrews that secure the Auxiliary
Section to the Main Section. Leave one capscrew to secure
the Housing until it is ready to be removed.
Note: Capscrews are different lengths. Note their locations
for reassembly purposes.
9. Clean and oil the three threaded pusher holes in the Auxiliary
Section flange. To clean them, thread an M10x1.5 tap into
each hole to remove paint, rust, and other debris.
Use the proper equipment with safety chains attached to
remove the Auxiliary Section. The Auxiliary Section can slide
rearward and could fall, causing you serious injury and/or
damage to the Auxiliary Section.
10. Attach the chain and Lifting Device to the Auxiliary
Section Hanger.
In-Vehicle Service Procedures
Remove the Auxiliary Countershaft Bearing Covers and
install RR1002TR Auxillary Countershaft Support Straps.
11. Thread capscrews into each of the three previously cleaned
pusher holes in the Auxiliary Section Flange. Run the
capscrews in evenly to break the gasket seal and move the
Auxiliary Housing rearward approximately 1/4.” After
breaking the gasket seal, remove the Pusher Screws.
The weight of the Auxiliary Section must be supported during
removal to avoid damage to the Range Yoke Bar.
12. Support the weight of the Auxiliary Section with the Lifting
Device or Support Jack and move the Auxiliary Section
rearward until it is free from the front section of the
Transmission.
83
Page 89

In-Vehicle Service Procedures
CAUTION
1
1
2
Shoulder
4
3/8"-1/2"
CAUTION
How to Install the Auxiliary Section in Chassis
Special Instructions
The Lock Cover was removed on new units, so the Shiftbar Housing must remain off during Auxiliary Assembly to attach the
Range Cylinder.
Special Tools
• Floor Jack
• Torque Wrench, 700 lb. ft. capacity
• Torque Wrench, 100 lb. ft. capacity
• RR1002TR Auxiliary Countershaft Support Straps
Procedure -
1. Install the RR1002TR Auxiliary Countershaft Support Straps
on the Auxiliary Section Countershafts to center and hold the
Countershafts in position.
2. Install the Output Yoke over the Output Shaft. The Yoke
should slide on and stop before contacting the Speedometer
Rotor. As the Output Shaft Nut is installed, the Output Yoke
will contact the Speedometer Rotor.
Note: To prevent the Output Shaft from rotating while
installing the nut, place a clean shop rag in the gear
mesh or use a yoke holding tool.
Note: Due to chassis interference, it may not be possible to
install the Yoke at this step. However, the Output
Shaft must be drawn fully into position to prevent it
from sagging when the Auxiliary Section is installed in
the Chassis. If the Chassis causes interference, the
Yoke can be temporarily installed to draw up the
Output Shaft and then removed before the Auxiliary
Section is installed.
3. Use a wire wheel to clean rust and paint from the Dowel Pins
before installing them.
If the Dowel Pins are not installed in the Main Case to the
proper depth in Step 4, the Auxiliary Section will not
properly align with the Main Case and Bearing or
Synchronizer failure may occur.
4. Install the dowel pins into the Main Case so that 3/8”–1/2”
of the shoulder is exposed.
84
Page 90

In-Vehicle Service Procedures
5. Clean all rust and paint from the dowel pin holes in the
6
CAUTION
Auxiliary Section Housing, and lightly grease the Dowel Pins
on the Main Case and the dowel pin holes on the Auxiliary
Section Housing.
6. Make sure the Auxiliary Section is in Low Range. If not, use
one or two large screwdrivers or prybars to apply even
rearward pressure to the Range Sliding Clutch to move it
into the Low Range position.
In-Vehicle Service Procedures
7. Make sure the Range Bar Lock Cover is in the unlock
position. If not, rotate it counterclockwise until the notch on
the cover is aligned with the unlock symbol, and secure it in
that position.
The Lock Cover has been removed on newer models, so the
Shiftbar Housing needs to remain removed until the Range
Cylinder and Auxiliary Section are assembled.
Note: Old style Auxiliary Cover is shown in the top picture
and the new style cover in the bottom picture.
8. Position the gasket onto the Main Case mounting surface.
9. Mount the Auxiliary Section on the Lifting Device or Jack.
85
Page 91

In-Vehicle Service Procedures
CAUTION
14
15
16
10. Position the Auxiliary Section in line with the Main Case, and
perform the following steps:
a. Insert the Range Yoke Bar into the bore.
b. Mesh the Countershafts with the Auxiliary Drive Gear.
Rotate the Output Yoke and Shaft slightly to help the
gears mesh.
The Auxiliary Section should slide into place fairly easily.
DO NOT force it on or pull it into place with the capscrews.
Excessive force may damage the Transmission. If
excessive force is necessary, the gearing is likely out of
time. Remove the Auxiliary Section, tighten the
Countershaft Support Tools, and try again.
11. While rotating the Output Shaft, slide the Auxiliary Section
forward as far as it can go.
12. Apply Eaton®Fuller® thread sealant #71205 or equivalent to
the capscrew threads.
13. Install the 19 retaining capscrews to secure the
Auxiliary Section to the Main Case. Torque the capscrews
to 40–45 lb. ft. (54–61 N•m).
14. Remove the capscrew securing the Range Bar Lock Cover in
the unlock position, and remove the Lock Cover. Check the
O-ring on the inside of the cover to be sure it is in position,
and look for signs of wear or damage. Replace it if
necessary. Apply Eaton®Fuller® thread sealant #71205 or
equivalent to the capscrews used to secure the cover.
15. Install the Range Bar Lock Cover, and rotate it clockwise
until the notch on the cover aligns with the lock symbol.
Note: The cover should rotate fairly easily. If it does not
rotate, the Range Piston Bar and the Range Yoke Bar
may not be in the same range position (Low Range).
Move the Range Lever from low to high and back to
low, while rotating the Lock Cover.
16. Secure the cover in the locked position with the capscrews,
and torque them to 20–23 lb. ft. (27–31 N•m).
86
Note: To properly align the Lock Cover the Transmission
must be in Low Range prior to tightening the
capscrews.
Page 92

In-Vehicle Service Procedures
17. If the Countershaft, Countershaft Bearings, or Auxiliary
Housing have been replaced, or if the Countershafts,
Bearings, or Shims were not marked and reassembled in the
same location, the Bearing endplay must be checked and set
by shimming. Shim the Countershaft Bearings using the
shim procedure in Transmission Overhaul ProcedureBench Service.
18. If shimming is not required, remove the Support Tools, and
install the original shim in the proper location, new gasket
and Countershaft Bearing Cover. Secure the Bearing Covers
with the capscrews. Tighten the capscrews to 40–45 lb. ft.
(54–61 N•m)
19. Connect the Driveshaft and U-joint, and refill the
Transmission with the recommended lubricant. For
lubrication instructions, refer to the Lubrication section
of this manual.
In-Vehicle Service Procedures
87
Page 93

In-Vehicle Service Procedures
How to Disassemble the Integral Oil Cooler
Special Instructions
None
Special Tools
• Typical service tools
Procedure -
1. Remove capscrews retaining the internal Cooler Cover.
2. Remove the Cooler Cover, taking care not to damage the
steel beaded gasket.
3. Loosen the Cooler Fittings from the Cooler Cover Plate.
4. Remove the capscrews retaining the rear of the Cooler to the
Cover Plate.
88
Page 94

In-Vehicle Service Procedures
How to Assemble the Integral Oil Cooler
Special Instructions
None
Special Tools
• Typical service tools
Procedure -
1. Thoroughly clean the gasket surface of the Transmission
Case and Cover Plate. Be sure the Cooler Fitting threads and
Flare Seat are free of dirt and debris.
2. Install Cooler to Cover Plate and tighten Cooler Fittings to
75 lb. ft. (102 Nm).
In-Vehicle Service Procedures
3. Install capscrews to rear of Cooler and tighten to 9–10 lb. ft.
(12–14 Nm).
4. Install Cooler Cover Plate gasket and Cover Plate. Install
capscrews and tighten to 40–45 lb. ft. (54–61 Nm).
89
Page 95

In-Vehicle Service Procedures
WARNING
1
2
3
How to Remove the Air Module
Special Instructions
A sudden release of air pressure can cause personal injury or damage to equipment. To prevent injury or equipment damage,
exhaust the Vehicle Air System or shut off the air supply to the Transmission before removing the Air Module.
Note: For air line removal and replacement instructions, refer to the “Air Line and Fitting” portion of In-Vehicle Service Procedures.
Special Tools
• Typical service tools
Air inlet
Capscrew
(x4)
Air Fittings
O-rings
Interlock
Finger
Interlock
Finger O-ring
Procedure -
1. Disconnect the supply air line from the Inlet Port of the Air
Module.
2. Tag the two air lines connected to the ports on the top of the
Air Module with location information, and remove them.
3. From the Air Module, remove the four (4) capscrews, and lift
the Module from the Shift Bar Housing.
90
Page 96

In-Vehicle Service Procedures
4. From the Air Module Interlock Finger, remove the O-ring,
and inspect if for damage or wear. Replace it if necessary.
5. From the two small recesses in the Shift Bar Housing Top,
remove the two (2) O-rings and inspect them for damage or
wear. Replace them if necessary.
Note: The O-rings may stick to the bottom of the Air Module.
In-Vehicle Service Procedures
4
5
91
Page 97

In-Vehicle Service Procedures
2
2
4
5
4
7
8
8
How to Install the Air Module
Special Instructions
None
Special Tools
• Torque Wrench, 25 lb. ft. Capacity
Procedure -
1. Clean all rust, paint, or other debris from the Air Module
mounting surfaces of the Shift Bar Housing.
2. To help prevent corrosion between the aluminum Air Module
and the cast iron Shift Bar Housing, apply a light film of high
temperature grease to the Air Module mounting surfaces of
the Shift Bar Housing.
3. Lightly apply Eaton®Fuller® silicone lubricant #71206 or
equivalent to all O-rings so a film covers the entire surface
of each O-ring.
4. Install the large O-ring on the Air Module Interlock Finger
Boss, and position the two (2) small O-rings in the recesses
in the Shift Bar Housing.
5. Position the Air Module on the Shift Bar Housing.
6. Apply Eaton®Fuller® thread sealant #71205 or equivalent to
the four (4) retaining capscrews.
7. Install the four (4) retaining capscrews, and tighten them to
20–23 lb. ft. (27–31 N•m) of torque.
8. Reconnect the air lines to the inlet port and the other ports
on the top of the Air Module.
9. Return air to the system, and check for leaks.
92
Page 98

Transmission Overhaul Procedures - Bench Service
Transmission Overhaul
Procedures-Bench Service
How to Disassemble the Gear Shift Lever
Special Instructions
If total disassembly is needed, the Roadranger Valve, must be removed first.
Release the spring, one coil at a time.
Special Tools
• Vise with brass jaws or wood blocks
1. Pin
2. Bushing
3. Upper Lever
4. Snap Ring
5. Rubber Boot
6. Spade Pin
7. Housing
8. Capscrew
9. Gasket
10. O-Ring
11. Washer
12. Lower Lever
13. Stepped Washer
14. Tension Spring
93
Page 99

Transmission Overhaul Procedures - Bench Service
Procedure -
1. On a non-isolated Shift Lever, remove the Roadranger Valve
using the “How to Remove the Roadranger Valve”
instructions in In-Vehicle Service Procedures. If the Shift
Lever is equipped with a Lever Isolator, remove the Snap
Ring, bushing, and Cross Pin to disconnect and remove the
upper lever.
2. Slide the rubber boot up and off the Shift Lever Shaft.
3. With housing bottom facing up, secure the assembly in a
vise.
4. Use large screwdriver to twist between the spring and
housing, forcing the spring from under the Housing Lugs
one coil at a time.
5. From inside the Housing Tower, remove the Tension Spring,
Washer, and Gear Shift Lever.
6. In models so equipped, from the housing bore, remove the
nut and washer.
7. From the Housing Tower Spade Pin bore, remove and
inspect the Spade Pin, discard if damaged.
8. From the Housing Tower inside groove, inspect the O-ring,
discard if damaged.
94
Page 100

Transmission Overhaul Procedures - Bench Service
Transmission Overhaul
Procedures-Bench Service
How to Assemble the Gear Shift Lever
Special Instructions
Inspect Tension Spring and washer for wear.
Apply Eaton rust preventative lubricant #71212 or equivalent to the Shift Lever Pivot Ball. A rust preventative lubricant film should
cover all surfaces between and including the Pivot Ball.
Seat the Tension Spring one coil at a time.
Special Tools
• Vise with brass jaws or wood blocks
• Large Screwdriver or Prybar
1. Pin
2. Bushing
3. Upper Lever
4. Snap Ring
5. Rubber Boot
6. Spade Pin
7. Housing
8. Capscrew
9. Gasket
10. O-Ring
11. Washer
12. Lower Lever
13. Stepped Washer
14. Tension Spring
95
 Loading...
Loading...