Asus P5VDC-MX User’s Manual

.
nc
I
s
e
i
l
a
d
ogi
e
nt
r
i
hnol
VIA RAID Host Controller
c
e
T
User Manual
A
C
nf
o
I
V
For VT8251
D
N
de
i
A
qu
e
R
Preliminary Revision 0.1
November 1, 2005
VIA TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
Copyright Notice:
Copyright © 2002-2005 VIA Technologies Incorporated. All Rights Reserved. No part of this document may be
reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into any language, in any form or by
any means, electronic, mechanical, magnetic, optical, chemical, manual or otherwise without the prior written
permission of VIA Technologies Incorporated. The material in this document is for information only and is subject to
change without notice. VIA Technologies Incorporated reserves the right to make changes in the product design
without reservation and without notice to its users
Disclaimer Notice:
No license is granted, implied or otherwise, under any patent or patent rights of VIA Technologies. VIA Technologies
makes no warranties, implied or otherwise, in regard to this document and to the products described in this document.
The information provided by this document is believed to be accurate and reliable to the publication date of this
document. However, VIA Technologies assume no responsibility for any errors in this document. Furthermore, VIA
Technologies assume no responsibility for the use or misuse of the information in this document and for any patent
infringements that may arise from the use of this document. The information and product specifications within this
document are subject to change at any time, without notice and without obligation to notify any person of such change.
s
nc
I
.
e
Offices:
USA Office: Taipei Office:
940 Mission Court 1st Floor, No. 531
Fremont, CA 94539 Chung-Cheng Road, Hsin-Tien
USA Taipei, Taiwan ROC
Tel: (510) 683-3300 Tel: (886-2) 2218-5452
Fax: (510) 683-3301 or (510) 687-4654 Fax: (886-2) 2218-5453
Home Page: http://www.viatech.com
Home Page: http://www.via.com.tw
hnol
c
e
nf
o
A
T
C
I
ogi
nt
de
i
e
R
A
l
a
i
i
qu
d
e
r
V
D
N

User Manual – VIA RAID Controller For VT8251
Revision History
Document Release Date Revision Initials
0.1 11/1/05 Initial internal release SY
.
nc
I
s
e
V
I
A
T
c
e
C
hnol
nf
o
D
N
ogi
nt
de
i
R
A
a
i
qu
e
l
d
e
r
i
Preliminary Revision 0.1, November 1, 2005 i Revision History

User Manual – VIA RAID Controller For VT8251
Table of Contents
Revision History.................................................................................................................................................i
Table of Contents............................................................................................................................................... i
Introduction ....................................................................................................................................................... 1
RAID Basics...................................................................................................................................................1
RAID 0 (Striping) ........................................................................................................................................................................1
RAID 1 (Mirroring) ..................................................................................................................................................................... 1
RAID 0+1 (Striping/Mirroring) ...................................................................................................................................................2
RAID 5 (Striped with Rotating Parity) ........................................................................................................................................ 2
JBOD (Spanning)......................................................................................................................................................................... 3
Key Features .................................................................................................................................................. 3
Installing The Hard Drives ...............................................................................................................................4
BIOS Configuration Utility ............................................................................................................................... 5
Enter BIOS Configuration Utility ...............................................................................................................5
Create Disk Array ......................................................................................................................................... 7
Delete Disk Array........................................................................................................................................ 12
Create and Delete Spare Hard Drive ........................................................................................................13
Select Boot Array ........................................................................................................................................14
View Serial Number of Hard Drive........................................................................................................... 15
View Array Status ....................................................................................................................................... 15
Duplicate Critical RAID 1/0+1 Array ....................................................................................................... 16
Driver and RAID Software Installation.......................................................................................................... 17
Microsoft Windows Driver Installation .................................................................................................... 17
Verify Installation .......................................................................................................................................19
RAID Software................................................................................................................................................. 20
Getting Start ................................................................................................................................................ 20
View Online Help ........................................................................................................................................ 22
View Controller and Device Status............................................................................................................ 23
Create Disk Array ....................................................................................................................................... 24
Delete Disk Array........................................................................................................................................ 30
Add and Remove Spare Disk Drive........................................................................................................... 32
Add Spare Disk Drive................................................................................................................................................................ 32
Remove Spare Disk Drive.......................................................................................................................................................... 34
Check All Disks ...........................................................................................................................................35
View Event Log ...........................................................................................................................................36
Synchronize Mirror Disk............................................................................................................................ 38
Disk Error Detection...................................................................................................................................40
Duplicate Critical RAID 1/0+1/5 Array .................................................................................................... 40
Icon View...................................................................................................................................................... 42
I
V
T
A
hnol
c
e
nf
o
C
N
ogi
de
i
A
D
s
e
nt
e
R
nc
I
l
a
i
qu
.
d
e
r
i
Preliminary Revision 0.1, November 1, 2005 i Table of Contents
User Manual – VIA RAID Controller For VT8251
INTRODUCTION
This section gives a brief introduction on the RAID-related background knowledge and a brief introduction on the VIA IDE RAID
Host Controller. For users wishing to install their VIA IDE RAID driver and RAID software, please proceed to the Driver and
RAID Software Installation section.
RAID Basics
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a method of combining two or more hard disk drives into one logical unit. The
advantage of an Array is to provide better performance or data fault tolerance. Fault tolerance is achieved through data redundant
operation, where if one drives fails, a mirrored copy of the data can be found on another drive. This can prevent data loss if the
operating system fails or hangs. The individual disk drives in an array are called “members”. The configuration information of
each member is recorded in the “reserved sector” that identifies the drive as a member. All disk members in a formed disk array
are recognized as a single physical drive to the operating system.
Hard disk drives can be combined together through a few different methods. The different methods are referred to as different
RAID levels. Different RAID levels represent different performance levels, security levels and implementation costs. The RAID
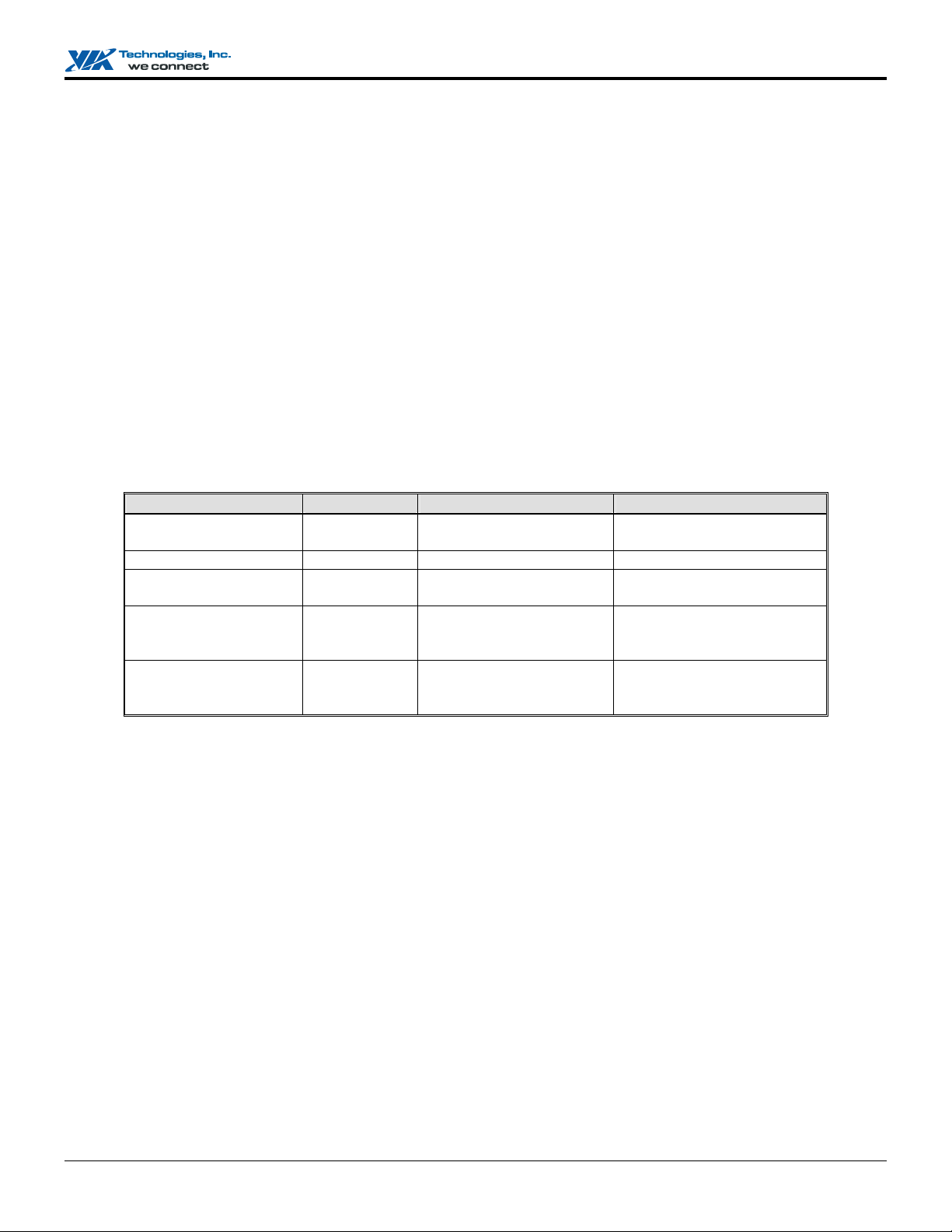
levels are RAID 0, 1, 0+1, 5 and JBOD. The table below briefly introduced these RAID levels.
RAID Level No. of Drives Capacity Benefits
RAID 0 (Striping) 2 to 4 Number drives * Smallest size Highest performance without
RAID 1 (Mirroring) 2 Smallest size Data protection
RAID 0+1
(Striping/Mirroring)
RAID 5
(Striped with Rotating
Parity)
JBOD (Spanning) 2 to 4 Sum of All drives No data protection and
4 2 * Smallest size Highest performance with data
3 (Number drives–1) * smallest
size
hnol
c
ogi
de
i
e
o
nf
A
D
T
RAID 0 (Striping)
RAID 0 reads and writes sectors of data interleaved between multiple drives. If any disk member fails, it affects the entire array.
The disk array data capacity is equal to the number of drive members times the capacity of the smallest member. The striping
block size can be set from 4KB to 64KB. RAID 0 does not support fault tolerance.
V
I
A
C
s
e
nt
e
R
nc
I
l
data protection
a
i
protection
Data protection and high disk
utilization
qu
performance improving, but disk
capacity fully used.
.
d
e
r
i
N
RAID 1 (Mirroring)
RAID 1 writes duplicate data onto a pair of drives and reads both sets of data in parallel. If one of the mirrored drives suffers a
mechanical failure or does not respond, the remaining drive will continue to function. Due to redundancy, the drive capacity of the
array is the capacity of the smallest drive. Under a RAID 1 setup, an extra drive called the “spare drive” can be attached. Such a
drive will be activated to replace a failed drive that is part of a mirrored array. Due to the fault tolerance, if any RAID 1 drive fails,
data access will not be affected as long as there are other working drives in the array.
Preliminary Revision 0.1, November 1, 2005 1 Introduction
User Manual – VIA RAID Controller For VT8251
RAID 0+1 (Striping/Mirroring)
RAID 0+1 is a combination of RAID 0 and RAID 1 array types. A minimum of four drives needs to be installed. With a four-drive
array, there must be two pairs of RAID 0 drives. Each pair mirrors the data on the other pair of striping drives. The data capacity is
two times the smallest drive.
In a four-drive array, a single drive failure will cause the whole array to become, in essence, a RAID Level 0 array. However, this
does not impact the data access. Another unique feature of RAID 0+1 is dual fault tolerance. In some cases, two drives can fail
simultaneously and still maintain the integrity of the data. The data can still be accessed and worked like a RAID 0 array.
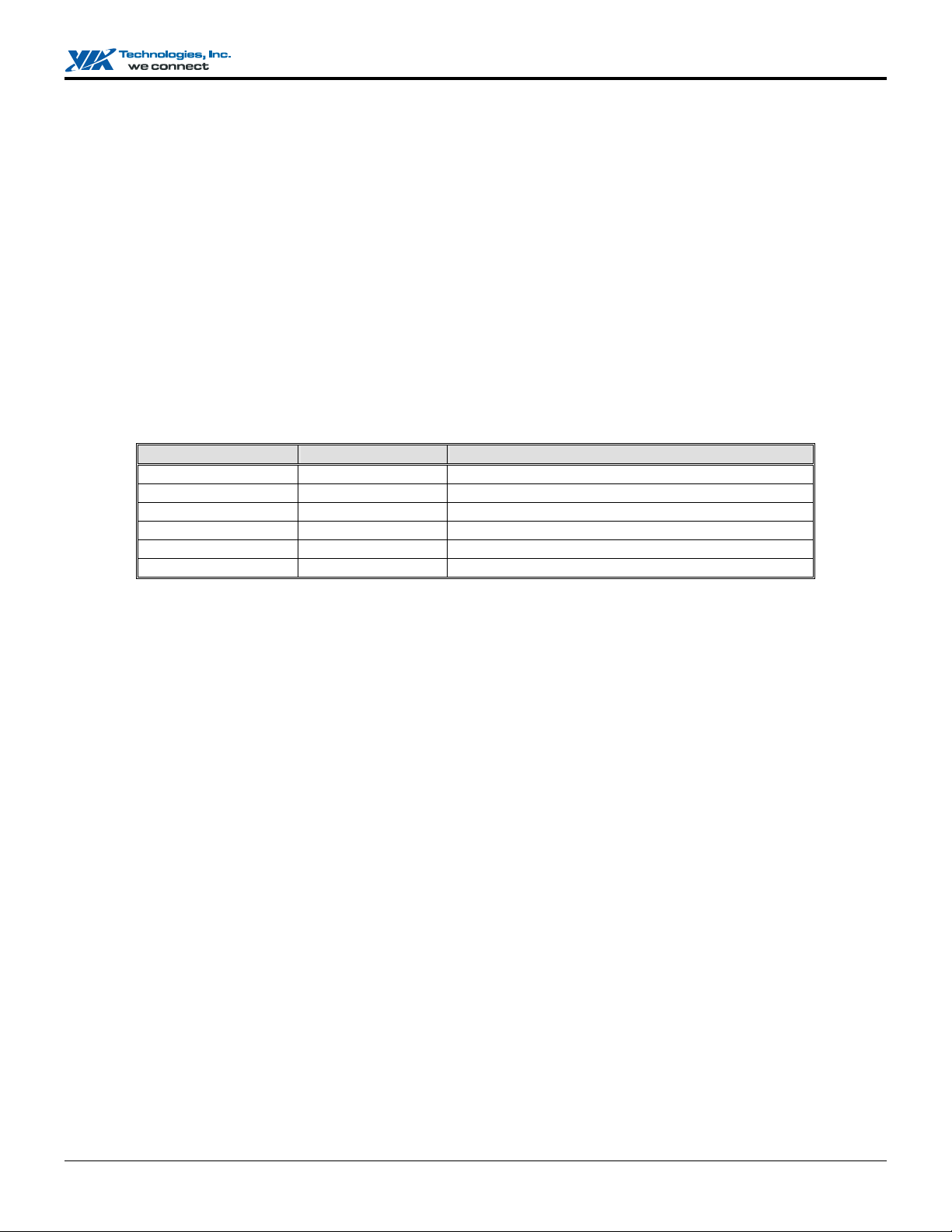
Assume the drives are configured as follows (M = Master, S = Slave, A/B indicates which striping pair the drive belongs to,
number indicates which part of stripe data):
IDE 1 IDE 2
M Drive A1 Drive A2
S Drive B1 Drive B2
In a RAID 0+1 array, the data integrity will remain if any of the 1, 2 combinations survives. The following table indicates the
possible combination of dual drive failure and the respective results of each case.
Failed Drives Array Status Note
A1, A2 Working B1, B2 retains array integrity
B1, B2 Working A1, A2 retains array integrity
A1, B2 Failure A2, B1 contains only half of array data
B1, A2 Failure B2, A1 contains only half of array data
A1, B1 Working A2, B2 retains array integrity
A2, B2 Working A1, B1 retains array integrity
ogi
s
e
nc
I
l
a
i
.
d
e
RAID 5 (Striped with Rotating Parity)
nt
RAID 5 Array uses block-level striping with parity data distributed across all member disks. It requires a minimum of 3 disks to
implement. It has highest read data transaction rate and medium write data transaction rate. When one of the disks in RAID 5 fails,
the data in RAID 5 can also be accessed, and the broken RAID 5 disk array can be repaired with a new disk. If more than one disk
fail, the RAID 5 array is corrupt and the data can not be recovered. RAID 5 can be created in Option ROM, Windows or other
operating system utilities, but it only can be initialized in Windows or other operating system utilities.
T
A
I
c
e
C
hnol
nf
o
de
i
A
qu
e
R
r
i
V
D
N
Preliminary Revision 0.1, November 1, 2005 2 Introduction

User Manual – VIA RAID Controller For VT8251
JBOD (Spanning)
A spanning disk array is equal to the sum of the all drives in the array. Spanning stores data on to a drive until it is full then
proceeds to store files onto the next drive in the array. When any disk member fails, the failure affects the entire array. JBOD is
not really a RAID and does not support fault tolerance.
Key Features
The VIA XXX RAID solution uses the storage chip as a RAID controller. The RAID software is a Windows-based software utility.
Its graphical user interface provides an easy way to configure and manage disk drives or disk arrays connected to the controller.
Listed below are the main features and benefits of VIA XXX RAID:
1. Supports four SATA ports at 3.0Gb/s (300MB/sec).
2. Supports AHCI mode of the VT8251 controller.
3. Supports hard disk drive larger than 137 GB (48-bits LBA).
4. Four independent AHCI ports and maximum connection of four hard disk drives are allowed.
5. Supports SATA I, SATA II, Ultra DMA mode 6/5/4/3/2/1/0, DMA mode 2/1/0, and PIO mode 4/3/2/1/0.
6. Supports PCI Plug and Play. PCI interrupt sharing and coexists with mainboard IDE controller.
7. Supports IDE bus master operation.
8. Supports RAID 0, 1, 0+1, 5 and JBOD (RAID 5 is only supported by VT8251).
9. 4 KB to 64 KB striping block size support.
10. Bootable disk or disk array support.
11. Windows-based RAID configure and management software tool. (Compatible with BIOS)
12. Real-time monitoring of device status and error alarm with popup message box and beeping.
13. Supports hot-swap failed disk drive in RAID 1, 0+1 and RAID 5 array.
14. Mirroring and RAID 5 automatic background rebuild support.
15. SATA and ATA SMART function support.
16. Microsoft Windows 98, Me, NT4.0, 2000, XP and Server 2003 operating systems support.
17. Event log for easy troubleshooting.
18. On-line help for easy operation for RAID software.
hnol
c
ogi
de
i
e
o
nf
A
I
A
T
C
s
e
nt
e
R
nc
I
l
a
i
qu
.
d
e
r
i
V
D
N
Preliminary Revision 0.1, November 1, 2005 3 Introduction
User Manual – VIA RAID Controller For VT8251
INSTALLING THE HARD DRIVES
Hard disk drives must be SATA II, SATA I, Ultra ATA/133, Ultra ATA/100, Ultra ATA/66, Ultra ATA/33, or ATA-3
compatible to operate with the XXXX XXX RAID controller. For optimal performance, it is recommended to install all identical
drives of the same model and capacity.
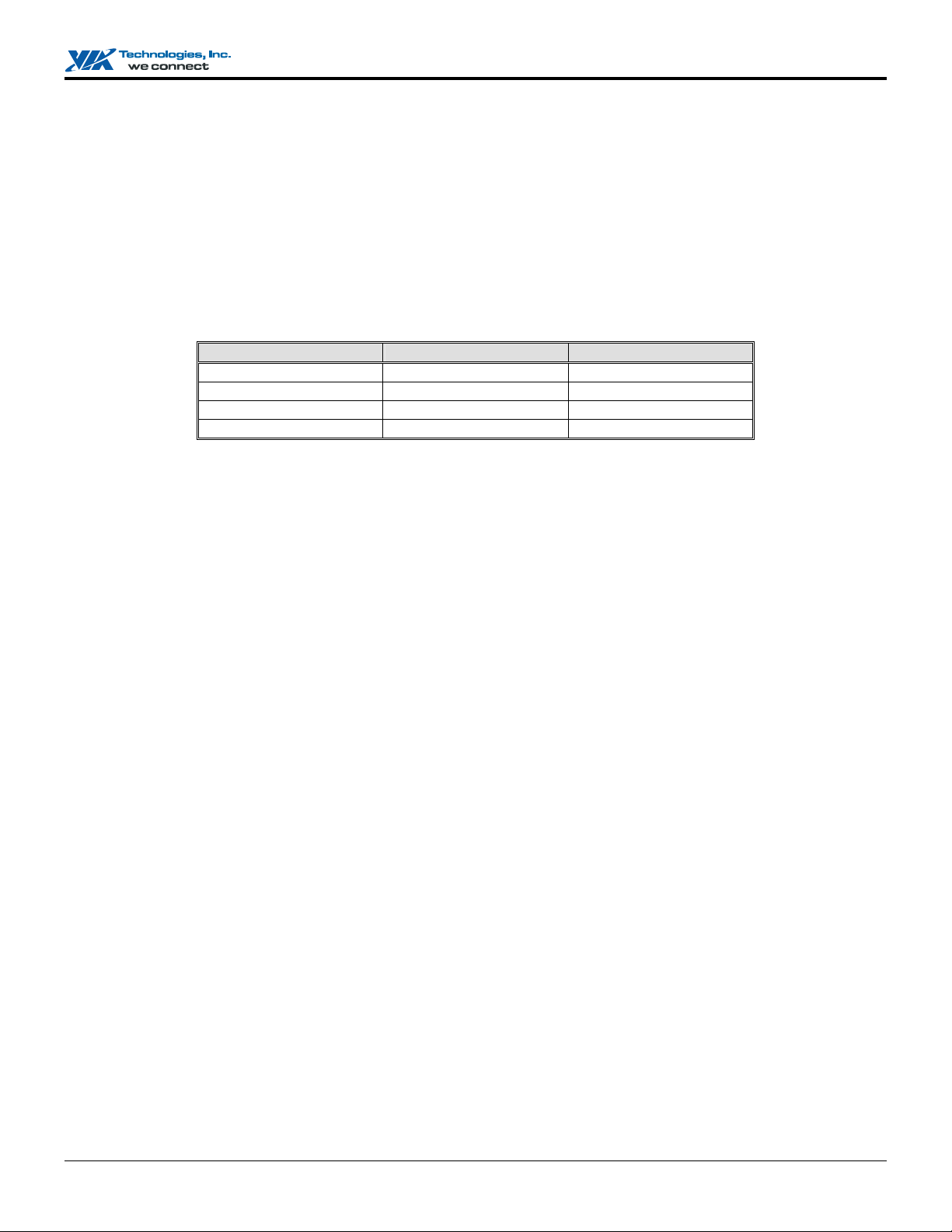
1. Striping (RAID 0) and JBOD require at least two drives and has a limit of four drives. Mirroring (RAID 1) requires two
drives. Striping and mirroring (RAID 0 +1) requires four drives. RAID 5 requires at least 3 drives and has a limit of four
drives. Set the jumpers of each hard drive to “Master” (“Device 0”) or “Slave” (“Device 1”) under PATA channel according
to the following table.
Number of Drives IDE Channel 1 IDE Channel 2
1 Master -----2 Master Master
3 Master & Slave Master
4 Master & Slave Master & Slave
2. Connect the IDE cables and the power cables to the hard drives. When connecting hard drives, pay attention to its Master –
Slave jumper setting. If two hard drives are connected to one IDE cable, then one drive must be set as master while the other
as slave.
3. Attach the SATA cables into the connectors on the XXXX RAID controller SATA port. Attach the IDE cables into the
connectors on the XXXX RAID controller PATA port.
ogi
s
e
nc
I
l
a
i
.
d
e
nt
r
i
hnol
de
i
A
qu
e
R
I
A
T
c
e
nf
o
C
V
D
N
Preliminary Revision 0.1, November 1, 2005 4 Installing The Hard Drives
User Manual – VIA RAID Controller For VT8251
BIOS CONFIGURATION UTILITY
Enter BIOS Configuration Utility
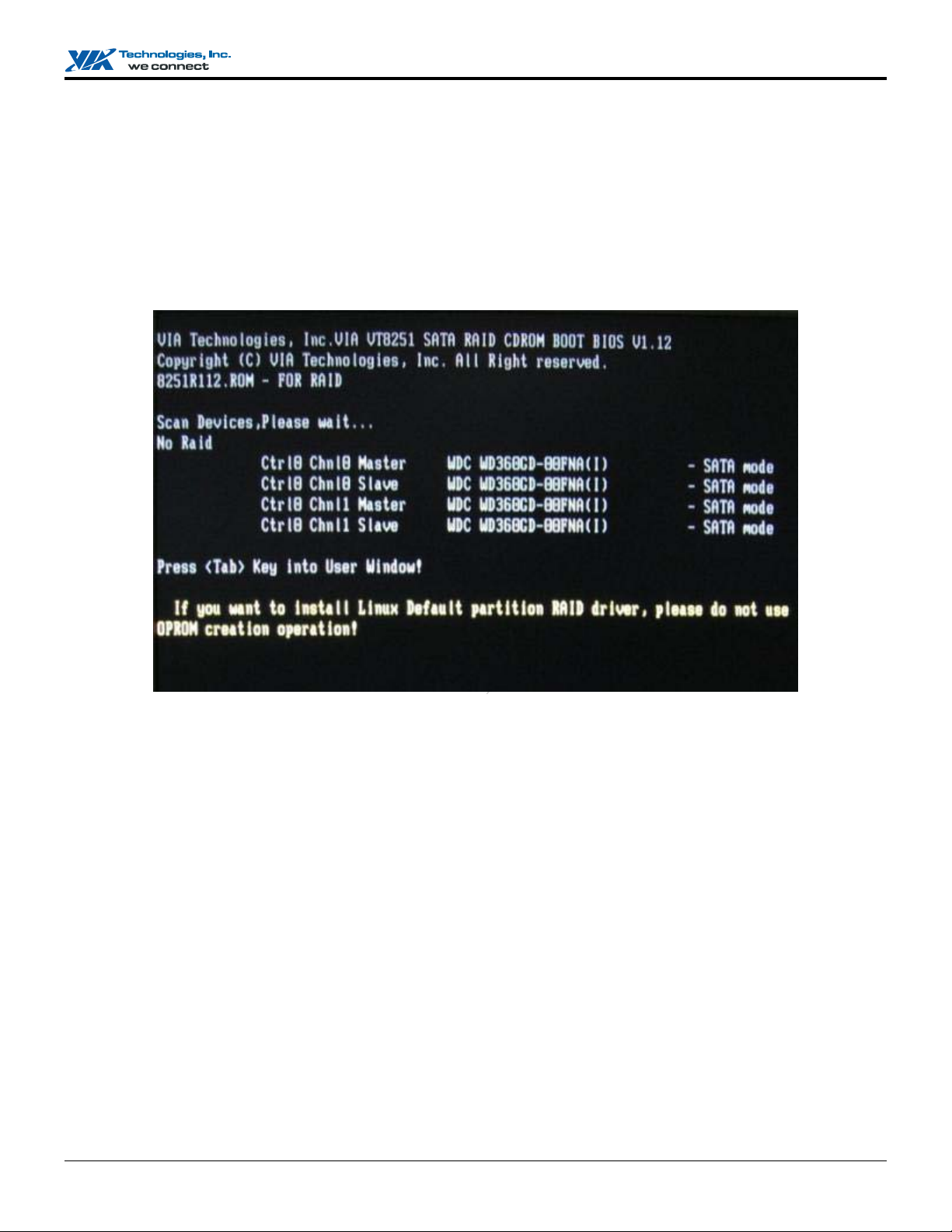
When the system powers on, the following information will appear on screen. Press the ‘Tab’ key to enter BIOS configuration
utility.
.
nc
I
s
e
hnol
c
e
A
T
o
C
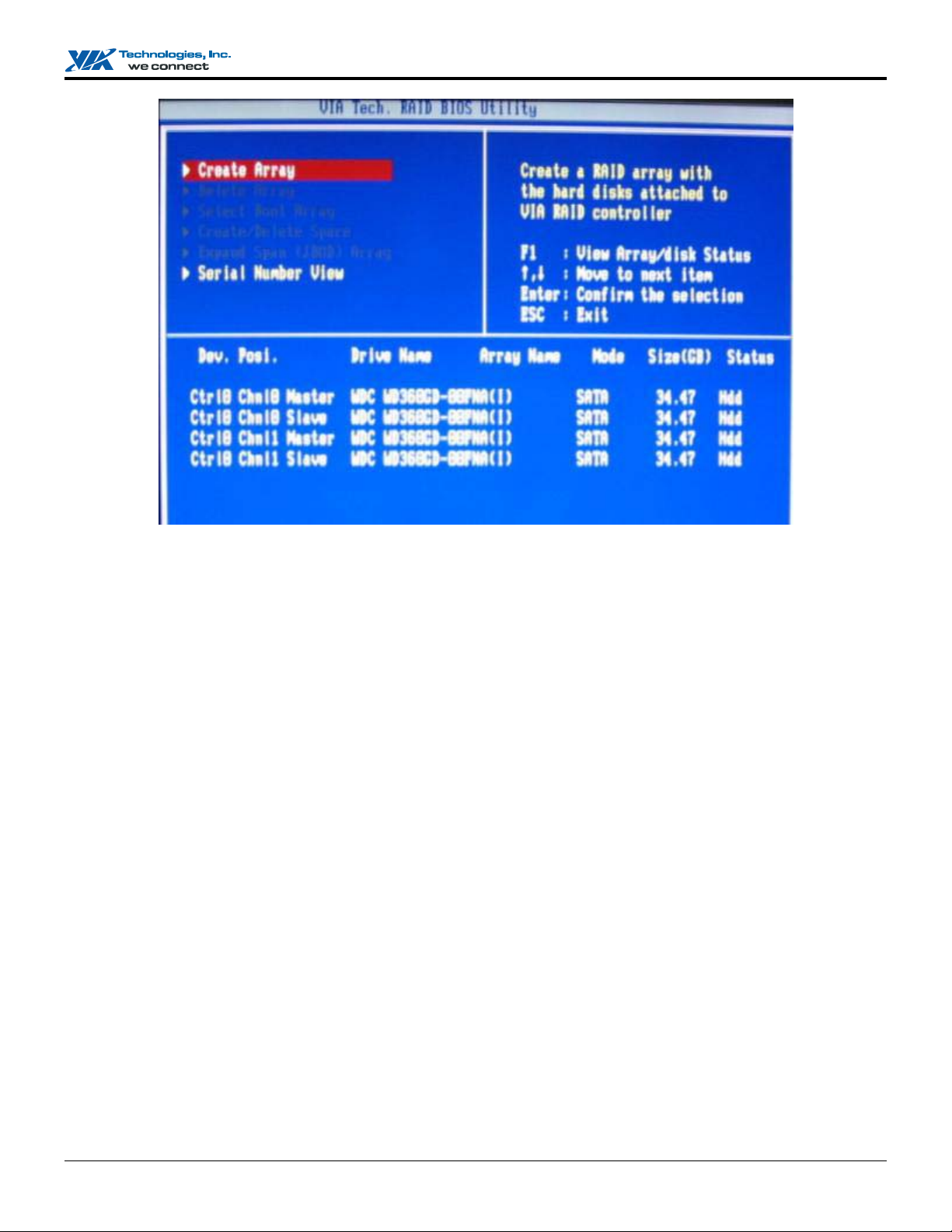
The main interface of BIOS configuration utility is as below:
I
V
N
i
nf
A
D
ogi
nt
de
e
R
l
a
i
i
qu
d
e
r
Preliminary Revision 0.1, November 1, 2005 5 BIOS Configuration Utility
User Manual – VIA RAID Controller For VT8251
.
nc
I
s
e
V
I
A
T
c
e
C
hnol
nf
o
D
N
ogi
nt
de
i
R
A
a
i
qu
e
l
d
e
r
i
Preliminary Revision 0.1, November 1, 2005 6 BIOS Configuration Utility
User Manual – VIA RAID Controller For VT8251
Create Disk Array
1. Use the arrow keys to navigate the menu. Select Create Array and press <Enter> to call out the list of creation steps.
.
nc
I
s
e
l
ogi
nt
i
a
i
r
e
d
hnol
de
i
A
qu
e
R
V
I
A
T
c
e
nf
o
C
D
N
Preliminary Revision 0.1, November 1, 2005 7 BIOS Configuration Utility
User Manual – VIA RAID Controller For VT8251
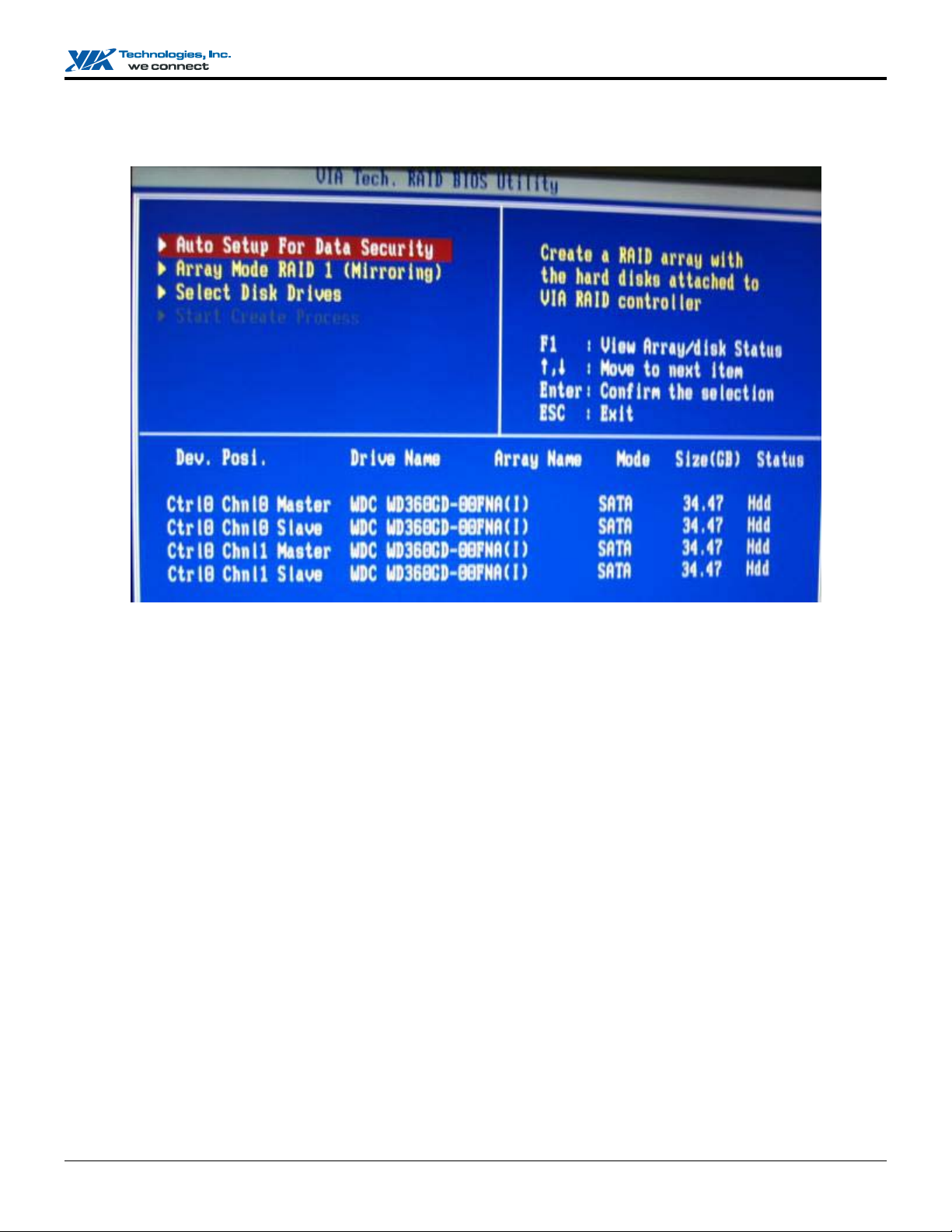
2. Select Array Mode and press <Enter>. A list of array modes will appear. Highlight the target array mode that you want to
create, and press <Enter> to confirm the selection. If RAID 1 or RAID 0/1 is selected, an option list will pop up and enable the
users to select Create only or Create and duplicate. Create only will allow BIOS to only create an array. The data on the
mirroring drive may be different from the source drive. Create and duplicate allows BIOS to copy the data from the source
to the mirroring drive.
.
nc
I
s
e
l
ogi
i
a
d
e
nt
T
A
I
V
c
e
C
hnol
nf
o
D
de
i
A
qu
e
R
r
i
N
Preliminary Revision 0.1, November 1, 2005 8 BIOS Configuration Utility
User Manual – VIA RAID Controller For VT8251
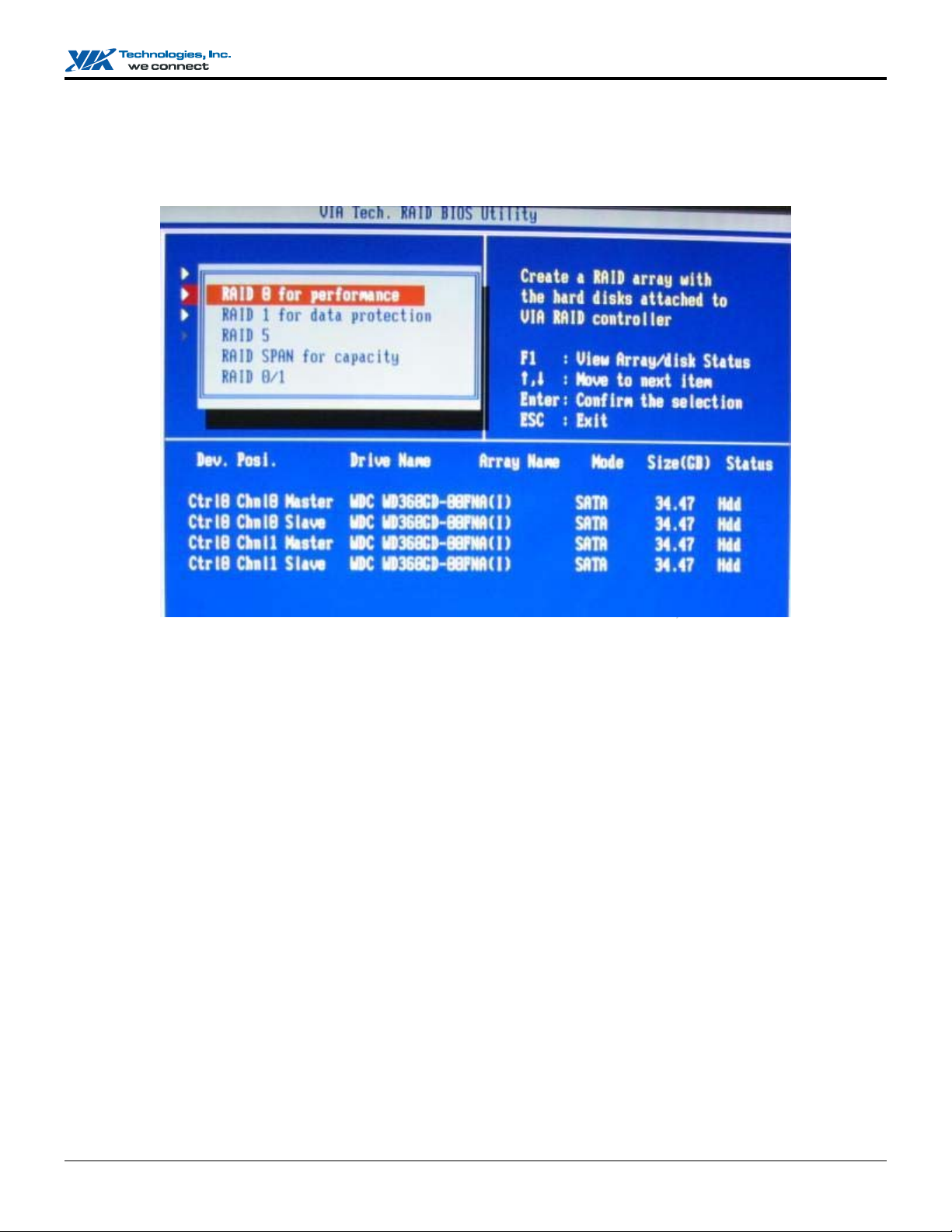
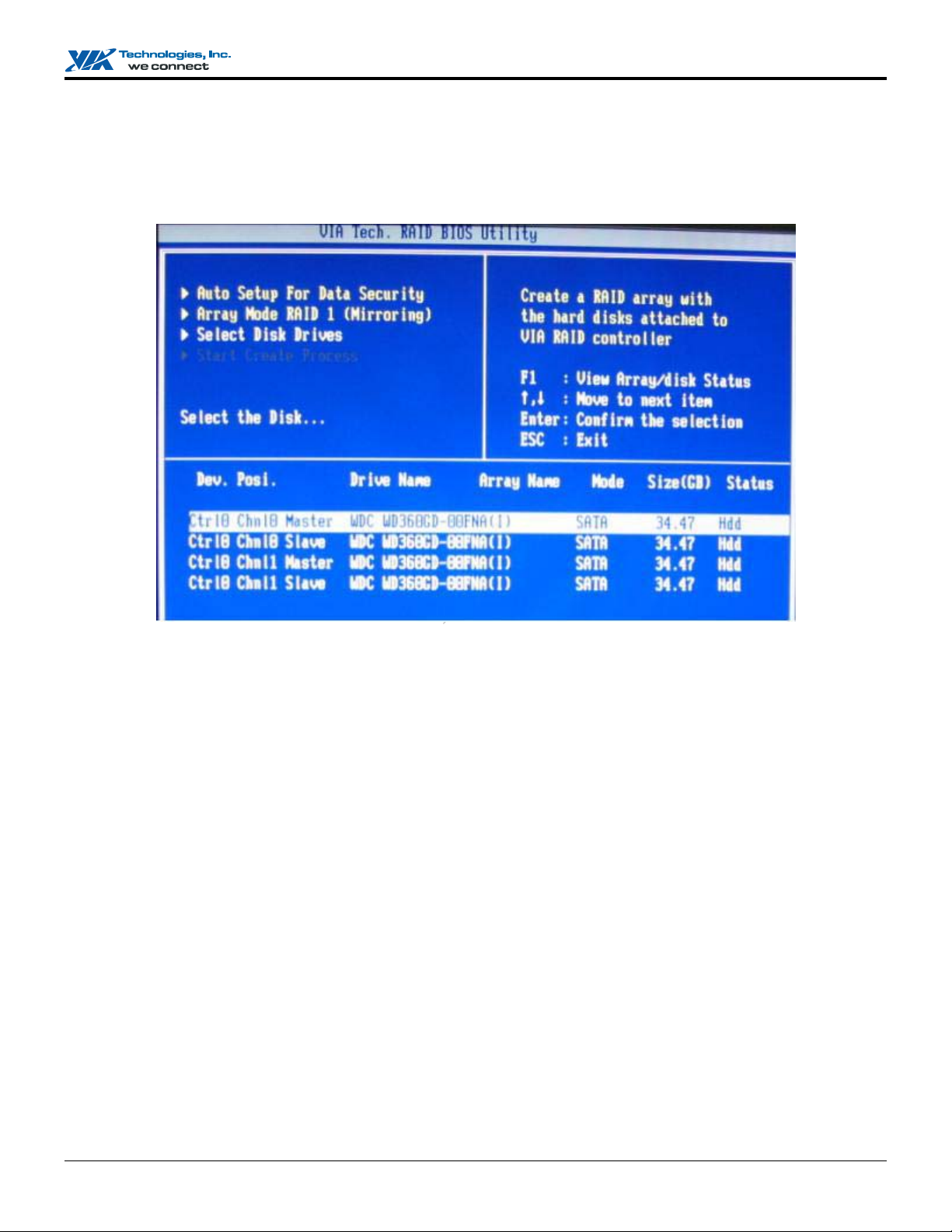
3. After array mode is selected, there are two methods to create a disk array. One method is “Auto Setup” and the other one is
“Select Disk Drives”. Auto Setup allows BIOS to select the disk drives and create arrays automatically but it does not
duplicate the mirroring drives even if the user selected Create and duplicate for RAID 1 or 0+1. It is recommended all disk
drives are new ones when wanting to create an array. Select Disk Drives lets the user select the array drives by their
requirements. When using Select Disk Drives, the channel column will be activated. Highlight the drives that you want to use
and press <Enter> to select them. After all drives have been selected, press <Esc> to go back to the creation steps menu.
.
nc
I
s
e
l
ogi
i
a
d
e
nt
c
e
C
hnol
nf
o
D
de
i
A
qu
e
R
T
A
I
V
i
r
N
Preliminary Revision 0.1, November 1, 2005 9 BIOS Configuration Utility
User Manual – VIA RAID Controller For VT8251
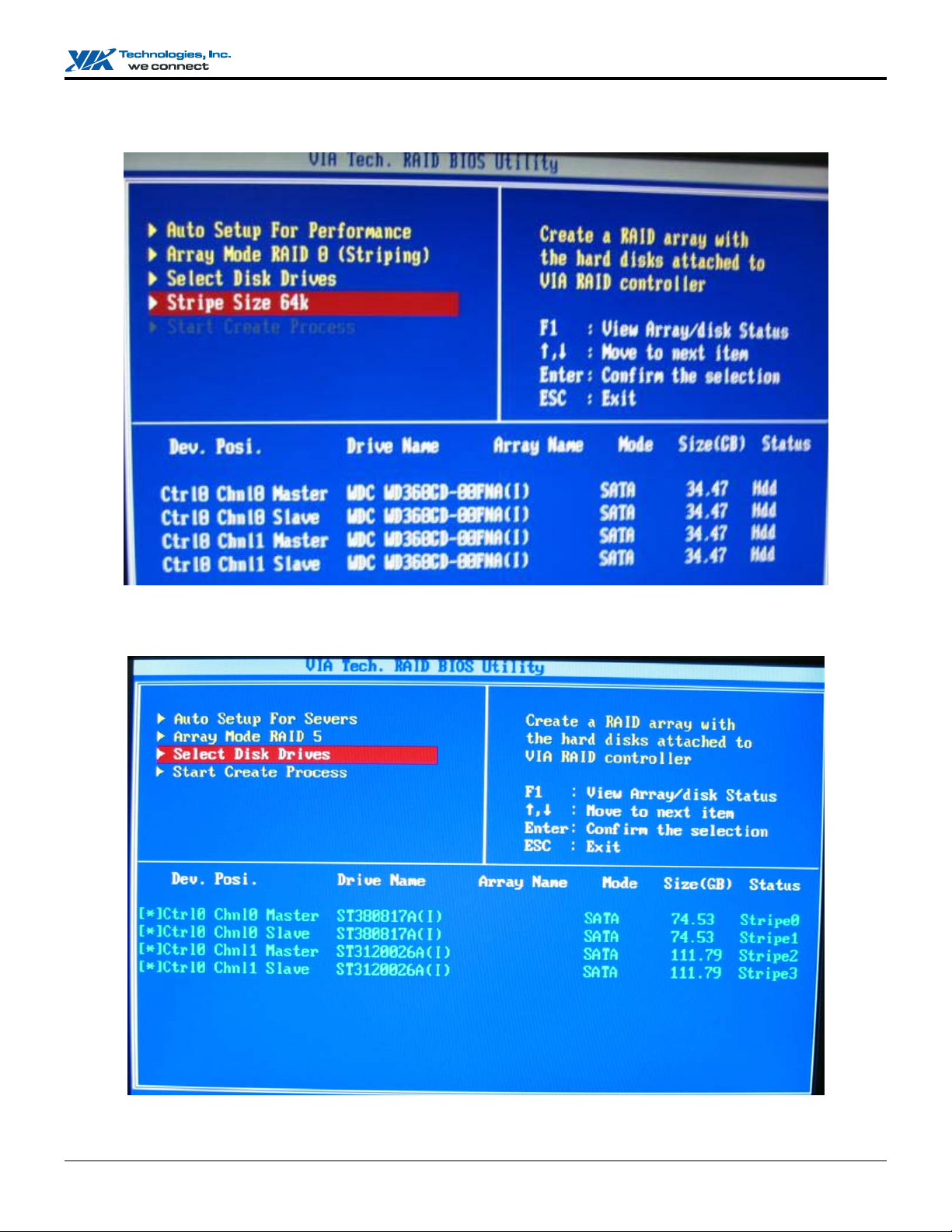
4. If RAID 0 or RAID 0+1 was selected in step 2, the block size of the array can also be selected. Use the arrow key to highlight
Block Size and press <Enter>. Then select a block size from the popup menu. The block size can be 4KB to 64KB.
.
nc
I
s
e
ogi
5. If RAID 5 was selected in step 2, then Select Disk RAID 5 Array is created.
hnol
c
de
i
nt
e
o
nf
R
A
D
V
I
A
T
C
N
a
i
qu
e
l
i
r
e
d
Preliminary Revision 0.1, November 1, 2005 10 BIOS Configuration Utility
 Loading...
Loading...