3B Scientific Stages of Fertilization and of the Embryo User Manual [en, de, es, fr, it]
L01

Latin
1 Uterus
2 Cavitas uteri
3 Endometrium
4 Myometrium
5 Vagina
6 Corpus luteum
7 Corpus albicans
8 Folliculus ovaricus primordialis
9 Folliculus ovaricus primarius
10Folliculus ovaricus secundarius
11Folliculi ovarici vesiculosi
12Ovarium
13Folliculus ovaricus vesiculosus
14Ovulatio
15Impregnatio
16Spermatozoon
17Ovum cum pronuclei
18Duo blastomeri
19Quattuor blastomeri
20Tuba uterina
21Morula
22Bastocystis
23 |
Implantatio |
® |
24 |
Oocytus secundarius |
|
25 |
Corona radiata |
|
26 |
Zona pellucida |
|
27 |
Ovum |
|
28 |
Polocyti |
|
29 |
Blastomeri |
|
30 |
Trophoblastus |
|
31 |
Blastocelia |
|
32 |
Embryoblastus |
|
33 |
Decidua capsularis |
|
34 |
Saccus vitellinus |
|
35 |
Cavitas amniotica |
|
36 |
Mesoderma |
|
37 |
Coelom |
|

Stages of fertilisation and blastogenesis
English
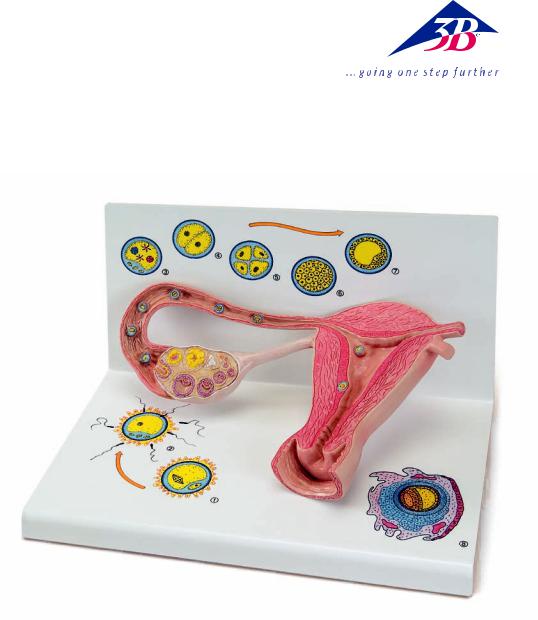
The model provides a schematic representation to illustrate the maturation of ova, ovulation, fertilisation and blastogenesis up until the embryo is implanted in the wall of the womb. The stages of development can be seen in large-scale models inside the ovary, the fallopian tubes and the womb. In some cases, even larger scale versions can be seen on the base.
Inside the ovary, primordial, primary, secondary and tertiary follicles can all be seen as well as a split tertiary follicle and a yellow body (corpus luteum).
In the fallopian tube near the ovary there is a recently split ovum with pellucid zone and corona radiata (part of the follicular epithelium) (Fig. 1).
Further along in the amplulla of the uterine tube (ampulla tuba uterina), a sperm is penetrating an ova (fertilisation) (Fig. 2)
Further along the fallopian tube a fertilised ovum (zygote) is shown with both a male and a female pronucleus (Fig. 3).
The following stages of cleavage are illustrated:
•Two-cell stage (Fig. 4)
•Four-cell stage (Fig. 5)
•Segmentation spheres (morula) (Fig. 6)
In the wonb (cavitas uteri) is a four-day-old blastocyst (Fig. 7) and an embryo of about 12 days old, that is now fully implanted into the mucous membrane of the womb (Fig. 8).
1 |
Uterus |
21 |
Morula |
2 |
Uterine cavity |
22 |
Blastocyst |
3 |
Endometrium |
23 |
Implanted embryo® |
4 |
Myometrium |
24 |
Split ovum |
5 |
Vagina |
25 |
Corona radiata |
6 |
Corpus luteum |
26 |
Pellucid zone |
7 |
Corpus albicans |
27 |
Ovum |
8 |
Primordial ovarian follicle |
28 |
Polar bodies |
9 |
Primary ovarian follicle |
29 |
Blastomere (segmentation sphere, |
10 |
Secondary ovarian follicle |
|
cleavage cell) |
11 |
Graafian follicles |
30 |
Trophoblast |
12 |
Ovary |
31 |
Cleavage, segmentation or subgerminal cavity |
13 |
Graafian follicle |
32 |
Embryoblast (inner cell mass) |
14 |
Ovulation |
33 |
Reflex decidua |
15 |
Fertilisation |
34 |
Yolk sack |
16 |
Spermatazoa |
35 |
Amniotic cavity |
17 |
Ovum with pronuclei |
36 |
Extraembryonic mesoderm |
18 |
Two-cell stage |
37 |
Coelom |
19Four-cell stage
20Uterine tube

Deutsch |
Stadien der Befruchtung und Keimesentwicklung |
Das Modell veranschaulicht als schematische Darstellung die Reifung der Eizelle, des Eisprungs, die Befruchtung und die Keimesentwicklung bis hin zum eingenisteten Keim. Die Entwicklungsstadien sind zum einen vergrößert im Eierstock, Eileiter und in der Gebärmutter und zum anderen teilweise in einer weiteren Vergrößerung auf dem Sockel zu sehen.
Im Eierstock sind Primordial-, Primär-, Sekundärund Tertiärfollikel sowie ein gesprungener Tertiärfollikel und ein Gelbkörper (Corpus luteum) sichtbar.
Im Eileiter nahe dem Eierstock zeigt sich eine frisch gesprungene Eizelle mit Zona pellucida und Corona radiata (Teil des Follikelepithels) (Abb. 1).
Weiter aufwärts, in der Ausbuchtung des Eileiters (Ampulla tubae uterina), dringt ein Spermium in die Eizelle ein (Imprägnation) (Abb. 2).
Im weiteren Verlauf des Eileiters ist eine befruchtete Eizelle (Zygote) mit einem männlichen und einem weiblichen Vorkern abgebildet (Abb. 3).
Folgende Furchungsstadien sind zu sehen:
•Zweizellstadium (Abb. 4)
•Vierzellstadium (Abb. 5)
•Maulbeere (Morula) (Abb. 6)
In der Gebärmutterhöhle (Cavitas uteri) sind eine 4 Tage alte Blastozyste (Abb. 7) und ein ca. 12 Tage alter Keim, der vollständig in die Gebärmutterschleimhaut implantiert ist (Abb. 8), dargestellt.
1 |
Gebärmutter |
20 |
Eileiter |
|
2 |
Gebärmutterhöhle |
21 |
Maulbeere |
® |
3 |
Schleimhaut |
22 |
Blastozyste |
|
4 |
Muskelschicht |
23 |
Implantierter Keim |
|
5 |
Scheide |
24 |
Gesprungene Eizelle |
|
6 |
Gelbkörper |
25 |
Corona radiata |
|
7 |
Umgewandelter Gelbkörper |
26 |
Zona pellucida |
|
8 |
Primordialfollikel |
27 |
Ei |
|
9 |
Primärfollikel |
28 |
Polkörperchen |
|
10 |
Sekundärfollikel |
29 |
Blastomere |
|
11 |
Frühe Tertiärfollikel |
30 |
Trophoblast |
|
12 |
Eierstock |
31 |
Blastozystenhöhle |
|
13 |
Reifer Tertiärfollikel (Graaf‘scher Follikel) |
32 |
Embryoblast |
|
14 |
Eisprung |
33 |
Teil der Gebärmutterschleimhaut |
|
15 |
Befruchtung |
34 |
Dottersack |
|
16 |
Spermien |
35 |
Amnionhöhle |
|
17 |
Befruchtete Eizelle mit weiblichem und |
36 |
Extraembryonales Mesoderm |
|
|
männlichem Vorkern |
37 |
Chorionhöhle |
|
18Zweizellstadium
19Vierzellstadium
 Loading...
Loading...