TOSHIBA TMP1942CYUE, TMP1942CZUE, TMP1942CXBG Technical data

32bit TX System RISC TX19 family
TMP1942CYUE
TMP1942CZUE/XBG
Rev1.0 March 29, 2007

TX1942CY/CZ
32-Bit RISC Microprocessor TX19 Family
TMP1942CYUE/CZUE/CZXBG
1.Outline and Features
The TX19 is a family of high-performance 32-bit microprocessors that offers the speed of a 32-bit RISC solution with the added advantage of a significantly reduce code size of a 16-bit architecture. The instruction set of the TX19 includes as a subset the 32-bit instructions of the TX39, which is based on the MIPS R3000ATM architecture. Additionally, the TX19 supports the MIPS16TM Application-Specific Extensions (ASE) for improved code density.
The TMP1942 is built on a TX19 core processor and a selection of intelligent peripherals. The TMP1942 is suitable for low-voltage, low-power applications.
Features of the TMP1942 include the following:
RESTRICTIONS ON PRODUCT USE |
070122EBP |
|
•The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. 021023_D
•TOSHIBA is continually working to improve the quality and reliability of its products. Nevertheless, semiconductor devices in general can malfunction or fail due to their inherent electrical sensitivity and vulnerability to physical stress. It is the responsibility of the buyer, when utilizing TOSHIBA products, to comply with the standards of safety in making a safe design for the entire system, and to avoid situations in which a malfunction or failure of such TOSHIBA products could cause loss of human life, bodily injury or damage to property.
In developing your designs, please ensure that TOSHIBA products are used within specified operating ranges as set forth in the most recent TOSHIBA products specifications. Also, please keep in mind the precautions and conditions set forth in the “Handling Guide for Semiconductor Devices,” or “TOSHIBA Semiconductor Reliability Handbook” etc.
021023_A
•The TOSHIBA products listed in this document are intended for usage in general electronics applications (computer, personal equipment, office equipment, measuring equipment, industrial robotics, domestic appliances, etc.). These TOSHIBA products are neither intended nor warranted for usage in equipment that requires extraordinarily high quality and/or reliability or a malfunction or failure of which may cause loss of human life or bodily injury (“Unintended Usage”). Unintended Usage include atomic energy control instruments, airplane or spaceship instruments, transportation instruments, traffic signal instruments, combustion control instruments, medical instruments, all types of safety devices, etc. Unintended Usage of TOSHIBA products listed in this document shall be made at the customer’s own risk. 021023_B
•The products described in this document shall not be used or embedded to any downstream products of which manufacture, use and/or sale are prohibited under any applicable laws and regulations. 060106_Q
•The information contained herein is presented only as a guide for the applications of our products. No responsibility is assumed by TOSHIBA for any infringements of patents or other rights of the third parties which may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patents or other rights of TOSHIBA or the third parties.
070122_C
•The products described in this document are subject to foreign exchange and foreign trade control laws. 060925_E
•For a discussion of how the reliability of microcontrollers can be predicted, please refer to Section 1.3 of the chapter entitled Quality and Reliability Assurance/Handling Precautions. 030619_S
TMP1942CY/CZ-1

TX1942CY/CZ
(1)TX19 core processor
1)Two instruction set architecture (ISA) modes: 16-bit ISA for code density and 32-bit ISA for speed
•The 16-bit ISA is object-code compatible with the code-efficient MIPS16TM ASE.
•The 32-bit ISA is object-code compatible with the high-performance TX39 family.
2)Combines high performance with low power consumption.
-High performance
•Single clock cycle execution for most instructions
•3-operand computational instructions for high instruction throughput
•5-stage pipeline
•On-chip high-speed memory
•DSP function: Executes 32-bit x 32-bit multiplier operations with a 64-bit accumulation in a single clock cycle.
-Low power consumption
•Optimized design using a low-power cell library
•Programmable standby modes in which processor clocks are stopped
3)Fast interrupt response suitable for real-time control
•Distinct starting locations for each interrupt service routine
•Automatically generated vectors for each interrupt source
•Automatic updates of the interrupt mask level
(2)Internal RAM: FDUE/FDXBG: 20KB,CYUE/CZUE/CZXBG: 16 KB
Internal ROM: FDUE/FDXBG: 512KB,CYUE/CZXBG: 384KB,CYUE: 256 KB ROM correction function (8 words x 4 blocks)
(For FDUE/FDXBG, only registers are available; data is not replaced.)
(3)External memory expansion
•16-Mbyte off-chip address space for code and data
•External bus interface with dynamic bus sizing for 8-bit and 16-bit data ports
(4)4-channel DMA controller
•Interruptor software-triggered
(5)6 channel 8-bit PWM timer
(12 channel 8-bit interval timer, 6 channel 16-bit interval timer, 6 channel 8-bit PPG output)
(6)14 channel 16-bit timer
(2 channels support 2-phase input pulse counter mode.)
(7)1 channel real-time counter (RTC)
(8)5 channel general-purpose serial interface
(Supports both UART and synchronous transfer modes)
(9)1 channel serial bus interface
Either I2C bus mode or clock-synchronous mode can be selected.
(10)16 channel 10-bit A/D converter (with internal sample/hold) Conversion time: 2 µs (throughput), 4 to 5 µs (latency)
(11)3 channel 10-bit D/A converter
(12)Watchdog timer
(13)4 channel chip select/wait controller
TMP1942CY/CZ-2

TX1942CY/CZ
(14) Interrupt sources
• |
4 CPU interrupts: |
software interrupt instruction |
•45 internal interrupts: 7 priority levels, with the exception of the watchdog timer interrupt
•29 external interrupts: 7 priority levels, with the exception of the NMI interrupt
The external sources include 14 KWUP sources, which are all assigned to a single interrupt vector, and 4 extended interrupts (INTB, INTC, INTD, and INTE), which are all assigned to a single interrupt vector with an identification flag. Thus, the actual number of external interrupt sources is 13.
(15)108 pin input/output ports
(16)Three standby function
•IDLE, SLEEP, and STOP
(17)Dual clocks
•RTC clock: Low-speed clock (32.768 kHz)
(18)Clock generator
•On-chip PLL (x4)
•Clock gear: Divides the operating speed of the CPU by 1/2, 1/4 or 1/8
(19)Operating voltage range: 2.7 to 3.6 V
PC and PF are 2.7 to 3.6 V or 4.5 to 5.25 V for 5 V-enabled ports.
(20)Operating frequency
•32 MHz (Vcc ≥ 3.0 V)
•28 MHz (Vcc ≥ 2.7 V)
(21)Package
•144-pin QFP (16 x 16 x 1.4 (t) mm, 0.4-mm pitch): FDUE/CZUE/CYUE
•177-pin CSP (13 x 13 x 1.4 (t) mm, 0.8-mm pitch): FDXBG/CZXBG
Note: TMP1942FDXBG (Package: 177-pin CSP) is under development.
TMP1942CY/CZ-3
|
|
|
|
|
|
TX1942CY/CZ |
|
|
|
|
|
TX19 Proccessor Core |
(*) |
MROM for the mask ROM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
version. |
|
|
|
|
TX19 CPU |
|
|
CZUE/XBG:384KB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MAC |
DSU |
|
|
|
|
|
|
256 KBROM |
16 KBRAM |
ROM correction |
|
|
|
|
|
(*) |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
X1 |
|
|
|
|
DMAC (4ch) |
|
|
X2 |
|
|
|
|
|
CG |
XT1 (PD6) |
||
|
|
|
|
|
XT2 (PD7) |
||
|
|
|
|
G-Bus |
|
SCOUT (P44) |
|
|
|
NMI |
|
|
PLLOFF* |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
INT0 (PF6) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
INT1 2 (PE6 7) |
INTC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
INT3 4 (PA0 1) |
|
EBIF |
|
|
|
|
|
INT5 6 (PA3 4) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
INT7 (PB7) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
INT8 A (PC0 2) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RESET* |
|
|
|
AN0 7 (P50 57) |
10-bit |
I/O Bus I/F |
|
BW0/1 |
|
|
AN8 15 (P60 67) |
|
|
INTLV (PE7) |
|||
|
|
ADTRG (P57) |
ADC (16ch) |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
AVCC/AVSS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VREFH/VREFL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DAOUT0 3 |
10-bit |
|
PORT0 |
|
|
|
|
DAVCC/DAVSS |
|
AD0 7 (P00 P07) |
|||
|
|
DAC (3ch) |
|
||||
|
|
DAREFH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TXD0 (PD0) |
|
|
PORT1 |
AD8/A8 AD15/A15 (P10 P17) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RXD0 (PD1) |
SIO0 |
|
|
|
|
|
SCLK0/CTS0 (PD2) |
|
|
PORT2 |
A0/A16 A7/A23 (P20 P27) |
||
|
|
TXD1 (PD3) |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RXD1 (PD4) |
SIO1 |
|
|
|
|
|
SCLK1/CTS1 (PD5) |
|
|
|
RD (P30) |
||
|
|
TXD3 (PE0) |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
WR (P31) |
||
|
|
RXD3 (PE1) |
SIO3 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
HWR (P32) |
|||
|
SCLK3/CTS3 (PE2) |
|
|
PORT3 |
WAIT (P33) |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
SCK (PF3) |
SERIAL |
|
|
BUSRD (P34) |
|
|
|
SO/SDA (PF4) |
|
|
BUSAK* (P35) |
||
|
|
BUS I/F |
|
|
R/W (P36) |
||
|
|
SI/SCL (PF5) |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
P37 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TXD4 (PE3) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RXD4 (PE4) |
SIO4 |
|
PORT4 |
CS0 CS3 (P40 P43) |
|
|
SCLK4/CTS4 (PE5) |
|
|
||||
|
|
TXD5 (PF0) |
SIO5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
RXD5 (PF1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
SCLK5/CTS5 (PF2) |
|
|
WDT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TB4IN1 (PB5), |
TB0IN0 1 (PA0 1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
TB7IN0 1 (P95 96), TB1IN0 1 (PA3 4) |
|
|
|
|
|
||
TB8IN0 1 (PC6 7), TB2IN0 1 (PB0 1) |
16-bit TMR0-D |
|
Real-Time |
|
|
||
TB9IN0 1 (PD0 1), TB3IN0 1 (PB3 4) |
|
Counter (RTC) |
|
|
|||
TBAIN0 1 (PD5 6), |
|
TB4IN0 (PB2) |
(14ch) |
|
|
|
|
TB0OUT (PA2), |
TB4OUT (P92) |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
TB1OUT (PA5), |
TB5OUT (P93) |
|
|
INTBCDE |
INTB C (PB0 1) |
||
TB2OUT (PB2), |
TB6OUT (P94) |
|
|
||||
|
|
INTD E (PB3 4) |
|||||
TB3OUT (PB5), |
TB7OUT (P97) |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
TA1OUT (PA6), |
TA7OUT (PC5) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA3OUT (PB6), |
TA9OUT (PC7) |
8-bit TMR0/1 |
|
|
|
|
|
TA5OUT (PC3), |
TABOUT (PD5) |
A/B |
|
KWUP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
TA0IN (PA7), |
TA6IN (PC1) |
(12ch) |
|
|
|
|
|
TA2IN (PB7), |
TA8IN (PC2) |
|
|
JTAG |
|
|
|
TA4IN (PC0), |
TAAIN (PC4) |
|
|
|
|
||
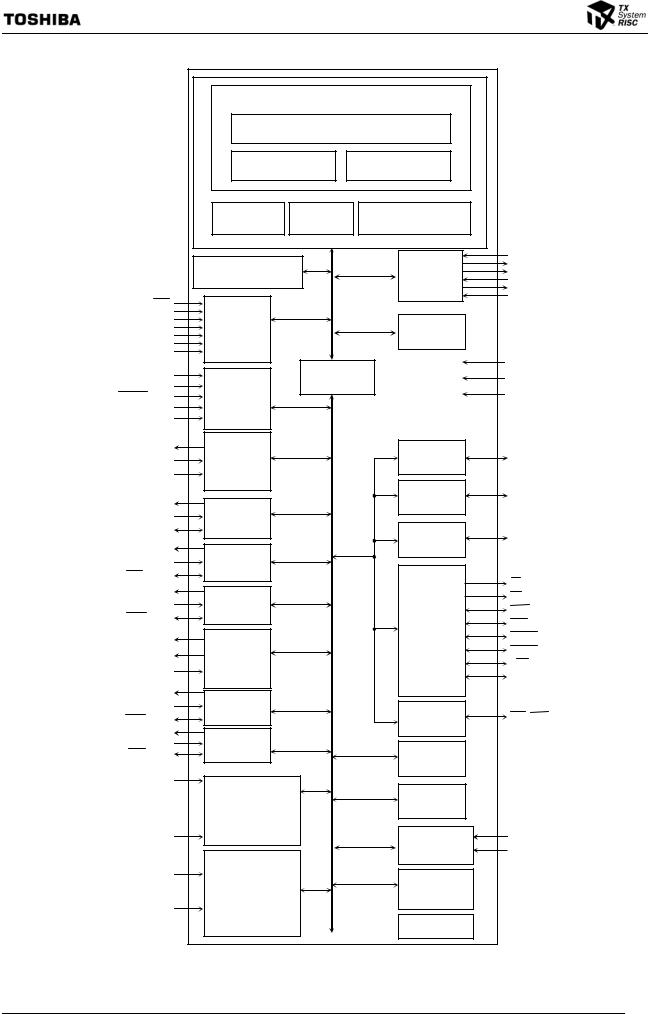
Figure 1.1 TMP1942 Block Diagram
TMP1942CY/CZ-4

TX1942CY/CZ
2.Signal Descriptions
This section contains pin assignments for the TMP1942 as well as brief descriptions of the functions of the TMP1942 input and output pins.
2.1Pin Assignment
Table 2.1.1 shows TMP1942 pin assignment.
144
 143
143
 142
142
 141
141
 140
140
 139
139
 138
138
 137
137
 136
136
 135
135
 134
134
 133
133
 132
132
 131
131
 130
130
 129
129
 128
128
 127
127
 126
126
 125
125
 124
124
 123
123
 122
122
 121
121
 120
120
 119
119
 118
118
 117
117
 116
116
 115
115
 114
114
 113
113
 112
112
 111
111
 110
110
 109
109
1 |
|
|
108 |
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
107 |
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
106 |
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
105 |
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
104 |
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
103 |
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
102 |
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
101 |
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
|
100 |
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
99 |
|
|
|
|
11 |
|
98 |
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
|
97 |
|
|
|
|
|
13 |
|
96 |
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
|
95 |
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
|
94 |
|
|
|
|
|
16 |
|
93 |
|
|
|
|
|
17 |
|
92 |
|
|
|
|
|
18 |
|
91 |
|
|
|
|
|
19 |
|
90 |
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
|
89 |
|
|
|
|
|
21 |
|
88 |
|
|
|
|
|
22 |
|
87 |
|
|
|
|
|
23 |
|
86 |
|
|
|
|
|
24 |
|
85 |
|
|
|
|
|
25 |
|
84 |
|
|
|
|
|
26 |
|
83 |
|
|
|
|
|
27 |
|
82 |
|
|
|
|
|
28 |
|
81 |
|
|
|
|
|
29 |
|
80 |
|
|
|
|
|
30 |
|
79 |
|
|
|
|
|
31 |
|
78 |
|
|
|
|
|
32 |
|
77 |
|
|
|
|
|
33 |
|
76 |
|
|
|
|
|
34 |
|
75 |
|
|
|
|
|
35 |
|
74 |
|
|
|
|
|
36 |
|
|
73 |
37 
 38
38 
 39
39 
 40
40 
 41
41 
 42
42 
 43
43 
 44
44 
 45
45 
 46
46 
 47
47 
 48
48 
 49
49 
 50
50 
 51
51 
 52
52 
 53
53 
 54
54 
 55
55 
 56
56 
 57
57 
 58
58 
 59
59 
 60
60 
 61
61 
 62
62 
 63
63 
 64
64 
 65
65 
 66
66 
 67
67 
 68
68 
 69
69 
 70
70 
 71
71 
 72
72
Figure 2.1.1 144-Pin LQFP Pin Assignment
TMP1942CY/CZ-5

TX1942CY/CZ
|
|
|
|
|
Table 2.1.1 |
Pin Assignment (144-pin LQFP) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
Pin |
Pin Name |
Pin |
Pin Name |
|
Pin |
Pin Name |
Pin |
Pin Name |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
No. |
No. |
|
No. |
No. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
1 |
VREFH |
37 |
P11/AD9/A9 |
|
73 |
P90/KEY8/DCLK |
109 |
CVCC |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
2 |
VREFL |
38 |
P12/AD10/A10 |
|
74 |
P91/KEY9/PCST2 |
110 |
X2 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
3 |
P50/AN0 |
39 |
P13/AD11/A11 |
|
75 |
P92/TB4OUT/PCST1 |
111 |
CVSS |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
4 |
P51/AN1 |
40 |
P14/AD12/A12 |
|
76 |
P93/TB5OUT/PCST0 |
112 |
X1 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
5 |
P52/AN2 |
41 |
P15/AD13/A13 |
|
77 |
P94/TB6OUT/SDSA0/TPC |
113 |
TEST1 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
6 |
P53/AN3 |
42 |
P16/AD14/A14 |
|
78 |
|
|
|
|
|
114 |
RESET |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
P95/TB7IN0/DBGE |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
7 |
DAVCC |
43 |
P17/AD15/A15 |
|
79 |
P96/TB7IN1/DINT |
115 |
PD6/XT1 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
8 |
DAVSS |
44 |
P20/A0/A16 |
|
80 |
P97/TB7OUT/DRESET |
116 |
PD7/XT2 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
9 |
DAREH |
45 |
P21/A1/A17 |
|
81 |
DVCC3 |
117 |
NMI |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
10 |
DAOUT0 |
46 |
P22/A2/A18 |
|
82 |
PA0/TB0IN0/INT3 |
118 |
BW0 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
11 |
DAOUT1 |
47 |
P23/A3/A19 |
|
83 |
PA1/TB0IN1/INT4 |
119 |
PB0/TB2IN0/INTB |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
12 |
DAOUT2 |
48 |
P24/A4/A20 |
|
84 |
PA2/TB0OUT |
120 |
PB1/TB2IN1/INTC |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
13 |
P54/AN4 |
49 |
P25/A5/A21 |
|
85 |
PA3/TB1IN0/INT5 |
121 |
PB2/TB2OUT/TB4IN0 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
14 |
P55/AN5 |
50 |
P26/A6/A22 |
|
86 |
PA4/TB1IN1/INT6 |
122 |
PB3/TB3IN0/INTD |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
15 |
P56/AN6 |
51 |
P27/A7/A23 |
|
87 |
PA5/TB1OUT |
123 |
PB4/TB3IN1/INTE |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
16 |
|
|
|
52 |
TEST0 |
|
88 |
PA6/TA1OUT |
124 |
PB5/TB3OUT/TB4IN1 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
P57/AN7/ADTRG |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
17 |
P60/AN8/KEY0 |
53 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
89 |
PA7/TA0IN/KEYA |
125 |
PB6/TA3OUT |
|||||||||||
PLLOFF |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
18 |
DVSS |
54 |
DVSS |
|
90 |
DVSS |
126 |
DVSS |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
19 |
P61/AN9/KEY1 |
55 |
ALE |
|
91 |
RSTPUP |
127 |
DVCC3 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
20 |
P62/AN10/KEY2 |
56 |
DVCC3 |
|
92 |
PC0/TA4IN/INT8 |
128 |
PB7/TA2IN/INT7/KEYB |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
21 |
P63/AN11/KEY3 |
57 |
BW1 |
|
93 |
PC1/TA6IN/INT9 |
129 |
PD0/TXD0/TB9IN0 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
22 |
P64/AN12/KEY4 |
58 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
94 |
PC2/TA8IN/INTA |
130 |
PD1/RXD0/TB9IN1 |
||||||||||||
P30/RD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
23 |
P65/AN13/KEY5 |
59 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
95 |
PC3/TA5OUT |
131 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
P31/WR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PD2/SCLK0/CTS0 |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
24 |
P66/AN14/KEY6 |
60 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
96 |
PC4/TAAIN |
132 |
PD3/TXD1/TBAIN0 |
|||||||||||||||
P32/HWR |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
25 |
P67/AN15/KEY7 |
61 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
97 |
PC5/TA7OUT |
133 |
PD4/RXD1/TBAIN1 |
||||||||||||||||
P33/WAIT |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
26 |
DVCC3 |
62 |
P34/BUSRQ |
|
|
98 |
PC6/TB8IN0/KEYC |
134 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
PD5/SCLK1/CTS1/TABOUT |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
27 |
P00/AD0 |
63 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
99 |
PC7/TB8IN1/TA9OUT |
135 |
PE0/TXD3 |
||||||||||||||||||
P35/BUSAK |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
28 |
P01/AD1 |
64 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
100 |
DVCC52 |
136 |
PE1/RXD3 |
|||||||||||||||||||
P36/R/W |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
29 |
P02/AD2 |
65 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
101 |
PF0/TXD5 |
137 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
P37/DSU |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PE2/SCLK3/CTS3 |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
30 |
P03/AD3 |
66 |
DVSS |
|
102 |
PF1/RXD5/KEYD |
138 |
PE3/TXD4 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
31 |
P04/AD4 |
67 |
DVCC3 |
|
103 |
|
|
|
139 |
PE4/RXD4 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PF2/SCLK5/CTS5 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
32 |
P05/AD5 |
68 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
104 |
PF3/SCK |
140 |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
P40/CS0 |
|
|
PE5/SCLK4/CTS4 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
33 |
P06/AD6 |
69 |
|
|
|
|
|
105 |
PF4/SO/SDA |
141 |
PE6/INT1/BOOT |
||||||||||||||||||||||
P41/CS1 |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
34 |
P07/AD7 |
70 |
P42/CS2 |
|
|
106 |
PF5/SI/SCL |
142 |
PE7/INT2/INTLV |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
35 |
DVSS |
71 |
P43/CS3 |
|
107 |
PF6/INT0 |
143 |
AVCC |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
36 |
P10/AD8/A8 |
72 |
P44/SCOUT |
|
108 |
DVCC51 |
144 |
AVSS |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
TMP1942CY/CZ-6
TX1942CY/CZ
Figure 2.1.2 shows pin assignment for the 177-pin model of the TMP1942.
A1 |
A2 |
A3 |
A4 |
A5 |
A6 |
A7 |
A8 |
A9 |
A10 |
A11 |
A12 |
A13 |
A14 |
A15 |
B1 |
B2 |
B3 |
B4 |
B5 |
B6 |
B7 |
B8 |
B9 |
B10 |
B11 |
B12 |
B13 |
B14 |
B15 |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
C5 |
C6 |
C7 |
C8 |
C9 |
C10 |
C11 |
C12 |
C13 |
C14 |
C15 |
D1 |
D2 |
D3 |
D4 |
D5 |
D6 |
D7 |
D8 |
D9 |
D10 |
D11 |
D12 |
D13 |
D14 |
D15 |
E1 |
E2 |
E3 |
E4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
E12 |
E13 |
E14 |
E15 |
F1 |
F2 |
F3 |
F4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
F12 |
F13 |
F14 |
F15 |
G1 |
G2 |
G3 |
G4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
G12 |
G13 |
G14 |
G15 |
H1 |
H2 |
H3 |
H4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
H12 |
H13 |
H14 |
H15 |
J1 |
J2 |
J3 |
J4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
J12 |
J13 |
J14 |
J15 |
K1 |
K2 |
K3 |
K4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
K12 |
K13 |
K14 |
K15 |
L1 |
L2 |
L3 |
L4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
L12 |
L13 |
L14 |
L15 |
M1 |
M2 |
M3 |
M4 |
M5 |
M6 |
M7 |
M8 |
M9 |
M10 |
M11 |
M12 |
M13 |
M14 |
M15 |
N1 |
N2 |
N3 |
N4 |
N5 |
N6 |
N7 |
N8 |
N9 |
N10 |
N11 |
N12 |
N13 |
N14 |
N15 |
P1 |
P2 |
P3 |
P4 |
P5 |
P6 |
P7 |
P8 |
P9 |
P10 |
P11 |
P12 |
P13 |
P14 |
P15 |
R1 |
R2 |
R3 |
R4 |
R5 |
R6 |
R7 |
R8 |
R9 |
R10 |
R11 |
R12 |
R13 |
R14 |
R15 |
Figure 2.1.2 177-Pin CSP Pin Assignment
TMP1942CY/CZ-7

TX1942CY/CZ
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 2.1.2 Pin Assignment (177-pin CSP) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
Pin |
|
|
|
|
Pin Name |
Pin |
Pin Name |
Pin |
Pin Name |
Pin |
Pin Name |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
No. |
|
|
|
|
No. |
No. |
No. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
A1 |
VREFL |
D1 |
P50/AN0 |
H13 |
NC |
N4 |
P16/AD14/A14 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
A2 |
AVSS |
D2 |
DAVSS |
H14 |
NC |
N5 |
P21/A1/A17 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
A3 |
AVCC |
D3 |
P52/AN2 |
H15 |
DVSS |
N6 |
P25/A5/A21 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
A4 |
PE7/INT2/INTLV |
D4 |
P51/AN1 |
J1 |
P67/AN15/KEY7 |
N7 |
DVSS |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
A5 |
PE3/TXD4 |
D5 |
PE0/TXD3 |
J2 |
P65/AN13/KEY5 |
N8 |
TEST0 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
A6 |
TCK (JTAG) |
D6 |
PD3/TXD1/TBAIN0 |
J3 |
P66/AN14/KEY6 |
N9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
P30/RD |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
A7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
D7 |
PB7/TA2IN/INT7/KEYB |
J4 |
P64/AN12/KEY4 |
N10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
PD2/SCLK0/CTS0 |
|
P32/HWR |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
A8 |
PB5/TB3OUT/TB4IN1 |
D8 |
DVSS |
J12 |
PA6/TA1OUT |
N11 |
P37 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
A9 |
PB1/TB2IN1/INTC |
D9 |
PB2/TB2OUT/TB4IN0 |
J13 |
PA7/TA0IN/KEYA |
N12 |
DVSS |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
A10 |
PD7/TX2 |
D10 |
NMI |
J14 |
NC |
N13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
P41/CS1 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
A11 |
PD6/TX1 |
D11 |
NC |
J15 |
PA5/TB1OUT |
N14 |
P91/KEY9 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
A12 |
X1 |
D12 |
NC |
K1 |
P01/AD1 |
N15 |
NC |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
A13 |
X2 |
D13 |
PF1/RXD5/KEYD |
K2 |
DVCC3 |
P1 |
NC |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
A14 |
CVCC |
D14 |
PF3/SCK |
K3 |
NC |
P2 |
P10/AD8/A8 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
A15 |
NC |
D15 |
PF6/INT0 |
K4 |
NC |
P3 |
P12/AD10/A10 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
B1 |
NC |
E1 |
DAVCC |
K12 |
PA2/TB0OUT |
P4 |
P20/A0/A16 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
B2 |
NC |
E2 |
DAOUT0 |
K13 |
PA3/TB1IN0/INT5 |
P5 |
P22/A2/A18 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
B3 |
PE6/INT1 |
E3 |
DAREFH |
K14 |
PA4/TB1IN1/INT6 |
P6 |
P26/A6/A22 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
B4 |
PE4/RXD4 |
E4 |
P53/AN3 |
K15 |
PA1/TB0IN1/INT4 |
P7 |
TDO (JTAG) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
B5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
E5 |
NC (Bonding not applied) |
L1 |
P04/AD4 |
P8 |
ALE |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
TRST |
(JTAG) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
B6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
E12 |
PC6/TB8IN0/KEYC |
L2 |
P02/AD2 |
P9 |
BW1 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
PD5/SCLK1/CTS1/TABOUT |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
B7 |
PD0/TXD0/TB9IN0 |
E13 |
DVCC52 |
L3 |
TMS (JTAG) |
P10 |
P33/WAIT |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
B8 |
DVCC3 |
E14 |
PF0/TXD5 |
L4 |
P00/AD0 |
P11 |
TDI (JTAG) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
B9 |
PB4/TB3IN1/INTE |
E15 |
|
|
|
|
|
L12 |
P97/TB7OUT |
P12 |
P40/CS0 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
PF2/SCLK5/CTS5 |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
B10 |
PB0/TB2IN0/INTB |
F1 |
DAOUT1 |
L13 |
DVCC3 |
P13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
P42/CS2 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
B11 |
NC |
F2 |
P55/AN5 |
L14 |
PA0/TB0IN0/INT3 |
P14 |
P44/SCOUT |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
B12 |
RESET |
F3 |
P54/AN4 |
L15 |
P96/TB7IN1 |
P15 |
NC |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
B13 |
CVSS |
F4 |
DAOUT2 |
M1 |
P07/AD7 |
R1 |
P11/AD9/A9 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
B14 |
DVCC51 |
F12 |
PC2/TA8IN/INTA |
M2 |
P05/AD5 |
R2 |
NC |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
B15 |
NC |
F13 |
PC4/TAAIN |
M3 |
P03/AD3 |
R3 |
NC |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
C1 |
VREFH |
F14 |
PC5/TA7OUT |
M4 |
P14/AD12/A12 |
R4 |
P13/AD11/A11 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
C2 |
NC |
F15 |
PC7/TB8IN1/TA9OUT |
M5 |
P15/AD13/A13 |
R5 |
P17/AD15/A15 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
C3 |
|
|
|
G1 |
P56/AN6 |
M6 |
P24/A4/A20 |
R6 |
P23/A3/A19 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PE5/SCLK4/CTS4 |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
C4 |
|
|
|
G2 |
P61/AN9/KEY1 |
M7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
R7 |
P27/A7/A23 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
PE2/SCLK3/CTS3 |
|
PLLOFF |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
C5 |
PE1/RXD3 |
G3 |
NC |
M8 |
NC |
R8 |
NC |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
C6 |
PD4/RXD1/TBAIN1 |
G4 |
P60/AN8/KEY0 |
M9 |
DVCC3 |
R9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
P31/WR |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
C7 |
PD1/RXD0/TB9IN1 |
G12 |
PC0/TA4IN/INT8 |
M10 |
|
|
|
|
|
R10 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
P34/BUSRQ |
P35/BUSAK |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
C8 |
PB6/TA3OUT |
G13 |
PC1/TA6IN/INT9 |
M11 |
P36/R/W |
|
|
R11 |
DVCC3 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
C9 |
PB3/TB3IN0/INTD |
G14 |
NC |
M12 |
P93/TB5OUT |
R12 |
NC |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
C10 |
BW0 |
G15 |
PC3/TA5OUT |
M13 |
P94/TB6OUT |
R13 |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
P43/CS3 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
C11 |
NC |
H1 |
DVSS |
M14 |
P95/TB7IN0 |
R14 |
NC |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
C12 |
TEST1 |
H2 |
P63/AN11/KEY3 |
M15 |
P92/TB4OUT |
R15 |
P90/KEY8 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
C13 |
PF4/SO/SDA |
H3 |
|
|
|
N1 |
NC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
P57/AN7/ADTRG |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
C14 |
PF5/SI/SCL |
H4 |
P62/AN10/KEY2 |
N2 |
DVSS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
C15 |
NC |
H12 |
RSTPUP |
N3 |
P06/AD6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
TMP1942CY/CZ-8

TX1942CY/CZ
2.2Pin Usage Information
Table 2.2.1 lists the names and functions of the TMP1942’s input/output pins.
Table 2.2.1 Pin Names and Functions
|
|
|
Pin Name |
# of Pins |
Type |
Function |
||||||
|
P00~P07 |
8 |
Input/output |
Port 0: Individually programmable as input or output |
||||||||
|
AD0~AD7 |
|
Input/output |
Address (Lower): Bits 0-7 of the address/data bus |
||||||||
|
P10~P17 |
8 |
Input/output |
Port 1: Individually programmable as input or output |
||||||||
|
AD8~AD15 |
|
Input/output |
Address/Data (Upper): Bits 8-15 of the address/data bus |
||||||||
|
A8~A15 |
|
Output |
Address: Bits 8-15 of the address bus |
||||||||
|
P20~P27 |
8 |
Input/output |
Port 2: Individually programmable as input or output |
||||||||
|
A0~A7 |
|
Output |
Address: Bits 0-7 of the address bus |
||||||||
|
A16~A23 |
|
Output |
Address: Bits 16-23 of the address bus |
||||||||
|
P30 |
1 |
Output |
Port 30: Output-only |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Output |
Read Strobe: Asserted during a read operation from an external memory device |
|
RD |
|
||||||||||
|
P31 |
1 |
Output |
Port 31: Output-only |
||||||||
|
WR |
|
Output |
Write Strobe: Asserted during a write operation on D0-D7 |
||||||||
|
P32 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port 32: Programmable as input or output (with internal pull-up resister) |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Output |
Higher Write Strobe: Asserted during a write operation on D8-D15 |
|||
|
HWR |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
P33 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port 33: Programmable as input or output (with internal pull-up resister) |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Input |
Wait: Causes the CPU to suspend external bus activity |
||||
|
WAIT |
|
|
|
||||||||
|
P34 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port 34: Programmable as input or output (with internal pull-up resister) |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
BUSRQ |
|
Input |
Bus Request: Asserted by an external bus master to request bus mastership |
||||||||
|
P35 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port 35: Programmable as input or output (with internal pull-up resister) |
||||||||
|
BUSAK |
|
|
Output |
Bus Acknowledge: Indicates that the CPU has relinquished the bus in response to |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BUSRQ . |
|
P36 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port 36: Programmable as input or output (with internal pull-up resister) |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Output |
Read/Write: Indicates the direction of data transfer on the bus: 1 = read or dummy |
||||
|
R/W |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
cycle, 0 = write cycle |
|
P37 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port 37: Programmable as input or output (with internal pull-up resister) |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Input |
This pin is used to select the operating mode during reset. The TMP1940CYAF enters |
|||||
|
DSU |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NORMAL mode when this pin is sampled high at the rising edge of RESET . This pin |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
should not be pulled down to a logic 0 during a reset sequence. The TMP1940FDBF, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
which has an on-chip flash, uses this pin as an interface to the DSU tool. For details, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
refer to Part 4, TMP1940FDBF. |
|
P40 |
|
1 |
Input/output |
Port 40: Programmable as input or output (with internal pull-up resister) |
|||||||
|
CS0 |
|
Output |
Chip Select 0: Asserted low to enable external devices at programmed addresses |
||||||||
|
P41 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port 41: Programmable as input or output (with internal pull-up resister) |
||||||||
|
CS1 |
|
|
|
Output |
Chip Select 1: Asserted low to enable external devices at programmed addresses |
||||||
|
P42 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port 42: Programmable as input or output (with internal pull-up resister) |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
Output |
Chip Select 2: Asserted low to enable external devices at programmed addresses |
|||||||
|
|
CS2 |
|
|
|
|||||||
|
P43 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port 43: Programmable as input or output (with internal pull-up resister) |
||||||||
|
|
CS3 |
|
|
|
Output |
Chip Select 3: Asserted low to enable external devices at programmed addresses |
|||||
|
P44 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port 44: Programmable as input or output |
||||||||
|
SCOUT |
|
Output |
System Clock Output: Drives out a clock signal at the same frequency as the CPU |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
clock (high-speed or low-speed) |
|
P50~P57 |
8 |
Input |
Port 5: Input-only |
||||||||
|
AN0~AN7 |
|
Input |
Analog input: Input to the A/D converter |
||||||||
|
|
ADTRG |
|
|
Input |
External start request for the A/D converter (multiplexed with P57) |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P60~P67 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port 6: Input-only |
||||||||
|
AN8~AN15 |
|
Input |
Analog input: Input to the A/D converter |
||||||||
|
KEY0-KEY7 |
|
Output |
Key on wake-up input (with internal pull-up resister) (dynamic pull-up selectable) |
||||||||
|
P90 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port 90: Programmable as input or output |
||||||||
|
DSU (DCLK) |
|
Output |
DSU pin |
||||||||
|
KEY8 |
|
Input |
Key on wake-up input (with internal pull-up resister) (dynamic pull-up selectable) |
||||||||
TMP1942CY/CZ-9

|
|
|
|
TX1942CY/CZ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pin Name |
# of Pins |
Type |
Function |
|
P91 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port 91: Programmable as input or output |
|
DSU (PCST2) |
|
Output |
DSU pin |
|
KEY9 |
|
Input |
Key on wake-up input (with internal pull-up resister) (dynamic pull-up selectable) |
|
P92 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port 92: Programmable as input or output |
|
DSU (PCST1) |
|
Output |
DSU pin |
|
TB40UT |
|
Output |
16-Bit Timer 4 Output: Output from 16-bit Timer 4 |
|
P93 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port 93: Programmable as input or output |
|
DSU (PCST0) |
|
Output |
DSU pin |
|
TB5OUT |
|
Output |
16-Bit Timer 5 Output: Output from 16-bit Timer 5 |
|
P94 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port 94: Programmable as input or output |
|
DSU |
|
Output |
DSU pin |
|
(SDSA0/TPC) |
|
|
|
|
TB6OUT |
|
Output |
16-Bit Timer 6 Output: Output from 16-bit Timer 6 |
|
P95 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port 95: Programmable as input or output |
|
DSU (DBGE*) |
|
Input |
DSU pin |
|
TB7IN0 |
|
|
16-Bit Timer 7 Input 0: Count/capture trigger input to 16-bit Timer 7 |
|
P96 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port 96: Programmable as input or output |
|
DSU (DINT*) |
|
Input |
DSU pin |
|
TB7IN1 |
|
|
16-Bit Timer 7 Input 1: Capture trigger input to 16-bit Timer 7 |
|
P97 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port 97: Programmable as input or output |
|
DSU |
|
Input |
DSU pin |
|
(DRESET) |
|
|
|
|
TB7OUT |
|
Output |
16-Bit Timer 7 Output: Output from 16-bit Timer 7 |
|
PA0 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port A0: Programmable as input or output |
|
TB0IN0 |
|
Input |
16-Bit Timer 0 Input 0: Count/capture trigger input to 16-bit Timer 0 |
|
INT3 |
|
Input |
Interrupt Request 3: Programmable to be high-level, low-level, rising-edge or |
|
|
|
|
falling-edge sensitive |
|
PA1 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port A1: Programmable as input or output |
|
TB0IN1 |
|
Input |
16-Bit Timer 0 Input 1: Capture trigger input to 16-bit Timer 0 |
|
INT4 |
|
Input |
Interrupt Request 4: Programmable to be high-level, low-level, rising-edge or |
|
|
|
|
falling-edge sensitive |
|
PA2 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port A2: Programmable as input or output |
|
TB0OUT |
|
Output |
16-Bit Timer 0 Output: Output from 16-bit Timer 0 |
|
PA3 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port A3: Programmable as input or output |
|
TB1IN0 |
|
Input |
16-Bit Timer 1 Input 0: Count/capture trigger input to 16-bit Timer 1 |
|
INT5 |
|
Input |
Interrupt Request 5: Programmable to be high-level, low-level, rising-edge or |
|
|
|
|
falling-edge sensitive |
|
PA4 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port A4: Programmable as input or output |
|
TB1IN1 |
|
Input |
16-Bit Timer 1 Input 1: Capture trigger input to 16-bit Timer 1 |
|
INT6 |
|
Input |
Interrupt Request 6: Programmable to be high-level, low-level, rising-edge or |
|
|
|
|
falling-edge sensitive |
|
PA5 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port A5: Programmable as input or output |
|
TB1OUT |
|
Output |
16-Bit Timer 1 Output: Output from 16-bit Timer 1 |
|
PA6 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port A6: Programmable as input or output |
|
TA1OUT |
|
Output |
8-Bit Timer 0/1 Output: Output from 8-bit Timer 0 or 1 |
|
PA7 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port A7: Programmable as input or output |
|
TA0IN |
|
Input |
8-Bit Timer 0 Input: Input to 8-bit Timer 0 |
|
KEYA |
|
Input |
Key on wake-up input (with internal pull-up resister) (dynamic pull-up selectable) |
|
PB0 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port B0: Programmable as input or output |
|
TB2IN0 |
|
Input |
16-Bit Timer 2 Input 0: Count/capture trigger input/2-phase input pulse counter input to |
|
INTB |
|
Input |
16-bit Timer 2 |
|
|
|
|
Interrupt Request B: Programmable to be high-level, low-level, rising-edge or |
|
|
|
|
falling-edge sensitive |
TMP1942CY/CZ-10

|
|
|
|
|
TX1942CY/CZ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pin Name |
# of Pins |
Type |
|
Function |
|
PB1 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port B1: Programmable as input or output |
|
|
TB2IN1 |
|
Input |
16-Bit Timer 2 Input 1: Capture trigger input/2-phase input pulse counter input to 16-bit |
|
|
INTC |
|
Input |
|
Timer 2 |
|
|
|
|
Interrupt Request C: |
Programmable to be high-level, low-level, rising-edge or |
|
|
|
|
|
falling-edge sensitive |
|
PB2 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port B2: Programmable as input or output |
|
|
TB2OUT |
|
Output |
16-Bit Timer 2 Output: Output from 16-bit Timer 2 |
|
|
TB4IN0 |
|
Input |
16-Bit Timer 4 Input 0: Count/capture trigger input to 16-bit Timer 4 |
|
|
PB3 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port B3: Programmable as input or output |
|
|
TB3IN0 |
|
Input |
16-Bit Timer 3 Input 0: Count/capture trigger input/2-phase input pulse counter input to |
|
|
INTD |
|
Input |
|
16-bit Timer 3 |
|
|
|
|
Interrupt Request D: |
Programmable to be high-level, low-level, rising-edge or |
|
|
|
|
|
falling-edge sensitive |
|
PB4 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port B4: Programmable as input or output |
|
|
TB3IN1 |
|
Input |
16-Bit Timer 3 Input 1: Capture trigger input/2-phase input pulse counter input to 16-bit |
|
|
INTE |
|
Input |
|
Timer 3 |
|
|
|
|
Interrupt Request E: |
Programmable to be high-level, low-level, rising-edge or |
|
|
|
|
|
falling-edge sensitive |
|
PB5 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port B5: Programmable as input or output |
|
|
TB3OUT |
|
Output |
16-Bit Timer 3 Output: Output from 16-bit Timer 3 |
|
|
TB4IN1 |
|
Input |
16-Bit Timer 4 Input 1: Capture trigger input to 16-bit Timer 4 |
|
|
PB6 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port B6: Programmable as input or output |
|
|
TA3OUT |
|
Output |
8-Bit Timer 2/3 Output: Output from 8-bit Timer 2 or 3 |
|
|
PB7 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port B7: Programmable as input or output |
|
|
TA2IN |
|
Input |
8-Bit Timer 2 Input: |
Input to 8-bit Timer 2 |
|
INT7 |
|
Input |
Interrupt Request 7: Programmable to be high-level, low-level, rising-edge or |
|
|
KEYB |
|
Input |
|
falling-edge sensitive |
|
|
|
|
Key on wake-up input (with internal pull-up resister) (dynamic pull-up selectable) |
|
|
PC0 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port C0: Programmable as input or output |
|
|
TA4IN |
|
Input |
8-Bit Timer 4 Input: |
Input to 8-bit Timer 4 |
|
INT8 |
|
Input |
Interrupt Request 8: Programmable to be high-level, low-level, rising-edge or |
|
|
|
|
|
|
falling-edge sensitive |
|
PC1 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port C1: Programmable as input or output |
|
|
TA6IN |
|
Input |
8-Bit Timer 6 Input: |
Input to 8-bit Timer 6 |
|
INT9 |
|
Input |
Interrupt Request 9: Programmable to be high-level, low-level, rising-edge or |
|
|
|
|
|
|
falling-edge sensitive |
|
PC2 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port C2: Programmable as input or output |
|
|
TA8IN |
|
Input |
8-Bit Timer 8 Input: |
Input to 8-bit Timer 8 |
|
INTA |
|
Input |
Interrupt Request A: Programmable to be high-level, low-level, rising-edge or |
|
|
|
|
|
|
falling-edge sensitive |
|
PC3 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port C3: Programmable as input or output |
|
|
TA5OUT |
|
Output |
8-Bit Timer 4/5 Output: Output from 8-bit Timer 4 or 5 |
|
|
PC4 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port C4: Programmable as input or output |
|
|
TAAIN |
|
Input |
8-Bit Timer A Input: Input to 8-bit Timer A |
|
|
PC5 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port C5: Programmable as input or output |
|
|
TA7OUT |
|
Output |
8-Bit Timer 6/7 Output: Output from 8-bit Timer 6 or 7 |
|
|
PC6 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port C6: Programmable as input or output |
|
|
TB8IN0 |
|
Input |
16-Bit Timer 8 Input 0: Count/capture trigger input to 16-bit Timer 8 |
|
|
KEYC |
|
Input |
Key on wake-up input (with internal pull-up resister) (dynamic pull-up selectable) |
|
|
PC7 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port C7: Programmable as input or output |
|
|
TB8IN1 |
|
Input |
16-Bit Timer 8 Input 1: Capture trigger input to 16-bit Timer 8 |
|
|
TA9OUT |
|
Output |
8-Bit Timer 8/9 Output: Output from 8-bit Timer 8 or 9 |
|
|
PD0 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port D0: Programmable as input or output |
|
|
TXD0 |
|
Output |
Serial Transmit Data 0 |
|
|
|
|
|
Programmable as an open-drain output |
|
|
TB9IN0 |
|
Input |
16-Bit Timer 9 Input 0: Count/capture trigger input to 16-bit Timer 9 |
|
TMP1942CY/CZ-11

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TX1942CY/CZ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pin Name |
# of Pins |
Type |
|
Function |
||
|
|
PD1 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port D1: Programmable as input or output |
||||
|
|
RXD0 |
|
Input |
Serial Receive Data 0 |
|
|||
|
|
TB9IN1 |
|
Input |
16-Bit Timer 9 Input 1: Capture trigger input to 16-bit Timer 9 |
||||
|
|
PD2 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port D2: Programmable as input or output |
||||
|
|
SCLK0 |
|
Input/output |
Serial Clock Input/Output 0 |
|
|||
|
|
CTS0* |
|
Input |
Serial Clear-to-Send 0 |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Programmable as an open-drain output |
|
|
|
PD3 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port D3: Programmable as input or output |
||||
|
|
TXD1 |
|
Output |
Serial Transmit Data 1 |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Programmable as an open-drain output |
|
|
|
TBAIN0 |
|
Input |
16-Bit Timer A Input 0: Count/capture trigger input to 16-bit Timer A |
||||
|
|
PD4 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port D4: Programmable as input or output |
||||
|
|
RXD1 |
|
Input |
Serial Receive Data 1 |
|
|||
|
|
TBAIN1 |
|
Input |
16-Bit Timer A Input 1: Capture trigger input to 16-bit Timer A |
||||
|
|
PD5 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port D5: Programmable as input or output |
||||
|
|
SCLK1 |
|
Input/output |
Serial Clock Input/Output 1 |
|
|||
|
|
|
CTS1 |
|
|
|
Input |
Serial Clear-to-Send 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Programmable as an open-drain output |
|
|
|
TABOUT |
|
Output |
8-Bit Timer A/B Output: Output from 8-bit Timer A or B |
||||
|
|
PD6 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port D6: Programmable as input or open-drain output |
||||
|
|
XT1 |
|
Input |
Connection pin for a low-speed crystal |
||||
|
|
PD7 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port D7: Programmable as input or open-drain output |
||||
|
|
XT2 |
|
Output |
Connection pin for a low-speed crystal |
||||
|
|
PE0 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port E0: Programmable as input or output |
||||
|
|
TXD3 |
|
Output |
Serial Transmit Data 3 |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Programmable as an open-drain output |
|
|
|
PE1 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port E1: Programmable as input or output |
||||
|
|
RXD3 |
|
Input |
Serial Receive Data 3 |
|
|||
|
|
PE2 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port E2: Programmable as input or output |
||||
|
|
CTS3* |
|
Input/output |
Serial Clock Input/Output 3 |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Input |
Serial Clear-to-Send 3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Programmable as an open-drain output |
|
|
|
PE3 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port E3: Programmable as input or output |
||||
|
|
TXD4 |
|
Output |
Serial Transmit Data 4 |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Programmable as an open-drain output |
|
|
|
PE4 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port E4: Programmable as input or output |
||||
|
|
RXD4 |
|
Input |
Serial Receive Data 4 |
|
|||
|
|
PE5 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port E5: Programmable as input or output |
||||
|
|
SCLK4 |
|
Input/output |
Serial Clock Input/Output 4 |
|
|||
|
|
CTS4 |
|
|
Input |
Serial Clear-to-Send 4 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Programmable as an open-drain output |
|
|
|
PE6 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port E6: Programmable as input or output |
||||
|
|
INT1 |
|
Input |
Interrupt request 1: |
Individually programmable to be high-level, low-level, |
|||
|
|
BOOT |
|
|
|
rising-edge or falling-edge sensitive. |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Single-boot mode setting pin: Used when rewriting built-in flash memory (low active). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
During normal operation, this pin should be pulled up. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
This pin should always be pulled up for the mask ROM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
version. |
|
|
PE7 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port E7: Programmable as input or output |
||||
|
|
INT2 |
|
Input |
Interrupt request 2: |
Individually programmable to be high-level, low-level, |
|||
|
|
INTLV |
|
|
|
rising-edge or falling-edge sensitive. |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interleave mode setting pin: This pin should be pulled up when using interleave mode. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Otherwise, it should be pulled down. |
|
|
PF0 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port F0: Programmable as input or output |
||||
|
|
TXD5 |
|
Output |
Serial Transmit Data 5 |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Programmable as an open-drain output |
|
TMP1942CY/CZ-12

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TX1942CY/CZ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pin Name |
# of Pins |
Type |
Function |
||||
|
|
PF1 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port F1: Programmable as input or output |
||||||
|
|
RXD5 |
|
Input |
Serial Receive Data 5 |
||||||
|
|
KEYD |
|
Input |
Key on wake-up input (with internal pull-up resister) (dynamic pull-up selectable) |
||||||
|
|
PF2 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port F2: Programmable as input or output |
||||||
|
|
SCLK5 |
|
Input/output |
Serial Clock Input/Output 5 |
||||||
|
|
CTS5 |
|
|
Input |
Serial Clear-to-Send 5 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Programmable as an open-drain output |
|
|
PF3 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port F3: Programmable as input or output |
||||||
|
|
SCK |
|
Input/output |
Clock input/output pin when the serial bus interface is in SIO mode |
||||||
|
|
PF4 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port F4: Programmable as input or output |
||||||
|
|
SO |
|
Output |
Data transmission pin when the serial bus interface is in SIO mode |
||||||
|
|
SDA |
|
Input/output |
Data transmission/reception pin when the serial bus interface is in I2C mode |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Programmable as an open-drain output |
|
|
PF5 |
1 |
Input/output |
Port F5: Programmable as input or output |
||||||
|
|
SI |
|
Input |
Data reception pin when the serial bus interface is in SIO mode |
||||||
|
|
SCL |
|
Input/output |
Clock input/output pin when the serial bus interface is in I2C mode |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Programmable as an open-drain output |
|
|
PF6 |
|
Input/output |
Port F6: Programmable as input or output |
||||||
|
|
INT0 |
|
Input |
Interrupt request 0: Individually programmable to be high-level, low-level, rising-edge or |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
falling-edge sensitive. |
|
|
ALE |
1 |
Output |
Address Latch Enable |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(This signal is driven out only when external memory is accessed) |
|
|
TEST0 |
1 |
Input |
Test pin |
||||||
|
|
TEST1 |
1 |
Input |
Test pin |
||||||
|
|
RSTPUP |
1 |
Input |
When this pin is driven high (upon reset), pull-up for ports 3 and 4 is enabled. When this |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
pin is driven low, pull-up is disabled. |
|
|
DAOUT0-2 |
3 |
Output |
D/A converter output |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
Input |
Non-maskable Interrupt Request: Causes an NMI interrupt on the falling edge |
|
NMI |
||||||||||
|
|
BW0~1 |
2 |
Input |
Set both AM0 and AM1 to 1. |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
Input |
This pin should be tied to logic 1 when the frequency multiplied clock from the PLL is |
||||
|
|
|
PLLOFF |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
used; otherwise, it should be tied to logic 0. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
Input |
Reset (with internal pull-up resister): Initializes the whole TMP1940CYAF |
|||
|
RESET |
||||||||||
|
|
VREFH |
1 |
Input |
Input pin for high reference voltage for the A/D converter. |
||||||
|
|
VREFL |
1 |
Input |
Input pin for low reference voltage for the A/D converter. |
||||||
|
|
AVCC |
1 |
|
Power supply pin for the A/D converter. This pin should always be connected to power |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
supply even when the A/D converter is not used. |
|
|
AVSS |
1 |
|
Ground pin for the A/D converter. This pin should always be connected to ground even |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
when the A/D converter is not used. |
|
|
DAVCC |
1 |
|
Power supply pin for the D/A converter. This pin should always be connected to power |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
supply even when the D/A converter is not used. |
|
|
DAVSS |
1 |
|
Ground pin for the D/A converter. This pin should always be connected to ground even |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
when the D/A converter is not used. |
|
|
DAREFH |
1 |
|
Reference voltage input pin for the D/A converter |
||||||
|
|
X1/X2 |
2 |
Input/output |
Resonator connecting pin |
||||||
|
|
CVCC |
1 |
|
Power supply pin for the oscillator |
||||||
|
|
CVSS |
1 |
|
Ground pin for the oscillator (0 V) |
||||||
|
|
DVCC3 |
4 |
|
Power supply pins |
||||||
|
|
DVCC51 |
1 |
|
Power supply pin (port F) |
||||||
|
|
DVCC52 |
1 |
|
Power supply pin (port C) |
||||||
|
|
DVSS |
5 |
|
Ground pins (0 V) |
||||||
Port C becomes a 5 V port when a 5 V power supply is connected to DVCC52.
Port F becomes a 5 V port when a 5 V power supply is connected to DVCC51.
Note: When the DSU is enabled, port 9 functions as the processor probe interfacing signal regardless of the setting of the port 9 control register (P9CR).
TMP1942CY/CZ-13

TX1942CY/CZ
The following table lists the JTAG specific pins added to the CSP package:
Pin Name |
# of Pins |
Type |
Function |
||
|
|
|
1 |
Input |
JTAG reset pin (with internal pull-up resistor) |
TRST |
|||||
TCK |
1 |
Input |
JTAG clock pin (with internal pull-up resistor) |
||
TDI |
1 |
Input |
JTAG data input pin (with internal pull-up resistor) |
||
TDO |
1 |
Output |
JTAG data output pin |
||
TMS |
1 |
Input |
JTAG mode switching input pin (with internal pull-up resistor) |
||
TMP1942CY/CZ-14

TMP1942CY/CZ
3.Functional Description
This section describes the functions and basic operation of each individual circuit block in the TMP1942 series devices.
3.1Processor Core
The TX1942 contains a high-performance 32-bit processor core (the TX19 processor core). For details of the operation of the processor core, refer to “TX19 Family Architecture”.
Functions unique to the TMP1942, which are not explained in “TX19 Family Architecture”, are described below.
Recommended power-on sequence:
In powering up this device, it is recommended that the DVCC3 be turned on first.
At power-on, the pull-up resistors and input & output buffers pull-down resistors attached to the I/O ports of the 5V supply domain may rail become unstable or a through current may pass through the port until the DVCC3 has stabilized, when an injection order is not kept.
3.1.1Reset Operation
To reset the TMP1942, RESET must be input Low (at 0) for at least 12 system clock cycles while the power supply voltage is within the rated operating range and the internal high-frequency oscillator is oscillating stably. (With the device operating at 32 MHz, this period is equal to 3 μs if the PLL is being used and 6 μs if the PLL is not being used.) After a reset the PLL-multiplied clock is specified by the setting of the PLLOFF pin and the clock gear is initialized to 1/8 mode.
To reset the TMP1942, RESET must be asserted for at least 12 system clock periods after the power supply voltage and the internal high-frequency oscillator have stabilized. This time is typically 3 μs at 32 MHz when the on-chip PLL is utilized, and 6μs otherwise. After a reset, either the PLL-multiplied clock or an external clock is selected, depending on the logic state of the PLLOFF pin. By default, the selected clock is geared down to 1/8 for internal operation.
The following occurs as a result of a reset:
•The System control coprocessor (CP0) registers within the TX19 core processor are initialized. For details, refer to the Architecture manual.
•The Reset exception is taken. Program control is transferred to the exception handler at a predefined address. This predefined location is called an exception vector, which directly indicates the start of the actual exception handler routine. The Reset exception is always vectored to virtual address 0xBFC0_0000 (which is the same as for the Nonmaskable Interrupt exception).
•All on-chip I/O peripheral registers are initialized.
•All port pins, including those multiplexed with on-chip peripheral functions, are configured as either general-purpose inputs or general-purpose outputs.
TMP1942CY/CZ-15

TMP1942CY/CZ
3.2Memory Map
Figure 3.2.1 shows a memory map of the TMP1942.
Virtual address |
Physical address |
0xFFFF_FFFF |
16 Mbytes reserved |
16 Mbytes reserved |
|
Internal I/O |
0xFFFF_E000 |
0xFF00_0000 |
|
|
|
(Reserved) |
|
|
Kseg2 |
Kseg2 |
|
0xFFFF_AFFF |
|
|
|
Internal RAM (16KB) |
|||
0xC000_0000 |
(cacheable) |
(1 Gbyte) |
|
0xFFFF_7000 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
0xBFC0_0000 |
|
16 Mbytes reserved |
|
(Reserved) |
|
Kseg1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0xFF3F_FFFF |
|
|
(uncacheable) |
|
|
Reserved for |
|
0xA000_0000 |
Kseg0 |
Kuseg |
|
debugging (2 MB) |
0xFF20_0000 |
|
(2Gbyte) |
|
|
||
|
(cacheable) |
|
|
|
|
0x8000_0000 |
|
|
(Reserved) |
|
|
16 Mbytes reserved |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
0xFF00_0000 |
|
|
|
Internal ROM area |
0x4003_FFFF |
|
0x1FC3_FFFF |
|
|
reflected |
0x4000_0000 |
|
|
|
Kuseg |
Cannot be accessed |
User program area |
|
|
|
(cacheable) |
|
|
|
0x1FC0_0400 |
|
|
Internal ROM |
0x1FC3_FFFF |
Maskable interrupt |
|
|
|
|
|
||
0x0007_FFFF |
|
512 Mbytes |
0x1FC0_0000 |
area |
|
|
|
Exception vector area |
0x1FC0_0000 |
||
0x0000_0000 |
|
|
|
|
Figure 3.2.1 Memory Map
Note 1: The internal ROM is mapped into the memory space from 0x1FC0_0000 to 0x1FC3_FFFF (for a 256-KB ROM) or 0x1FC0_0000 to 0x1FC5_FFFF (for a 384-KB ROM). The internal RAM is mapped into the memory space from 0xFFFF_8000 to 0xFFFF_BFFF (for a 16-KB RAM).
Note 2: The memory space from 0xFFFF_4000 to 0xFFFF_BFFF is a reserved RAM area. Any area other than those shown above, where physical memory is located, should not be accessed.
Note 3: The internal memory data is stored in contiguous physical address locations starting at 0x1FC0_0000.
If exception vector addresses are placed in internal ROM, the system control coprocessor (CP0) Status register's BEV bit must be set to 1 (the default). (This is because exception vector addresses are dispersed if BEV = 0.) If memory is added externally, the BEV bit can be set to 0.
However, since a virtual address space of 0x0000_0000 ±32 KB is easier to access for reasons of code efficiency, this area is reflected in the contiguous physical address space from 0x4000_0000 upwards (as indicated by the shaded area) which corresponds to a virtual address space starting at 0x0000_0000 and which is equal in size to the internal memory. Hence, accessing this area is equivalent to accessing the internal memory.
Example: Using 32-bit ISA
• Access to the 0x0000_0000 ±32 KB area
ADDIU |
r2, r0, 7 |
; r 2 ← (0x0000_0007) |
SW |
r2, Io (_t) (r0) |
; 0x0000_xxxx ← (r2) |
↑
Can be accessed using a single instruction.
• Access to areas other than 0x0000_0000 ±32 KB
LUI |
r3, hi (_f) |
; ← Upper address is set to r3. |
ADDIU |
r2, r0, 8 |
; r2 ← (0x0000_0008) |
SW |
r2, Io (_f) (r3) |
; Memory is accessed after lower address has been set. |
Note 4: The TX1942 supports access to only 16 Mbytes of physical space as external address space. A 16-Mbyte physical address space can be placed in any chip-select area within the CPU's 3.5 Gbytes of physical address space.
However, when access to the internal memory, internal I/O space or a reserved area is performed, the external address space cannot be accessed simultaneously, since the other types of access have priority.
Note 5: Do not place an instruction in the last four words of the physical area.
•The relevant area of the internal ROM is 0x1FC3_FFF0 to 0x1FC3_FFFF (for a 256-KB ROM) or 0x1FC5_FFF0 to 0x1FC5_FFFF (for a 384-KB ROM).
•If ROM is added externally, this restriction applies to the last four words of the installed memory (system-dependent).
TMP1942CY/CZ-16
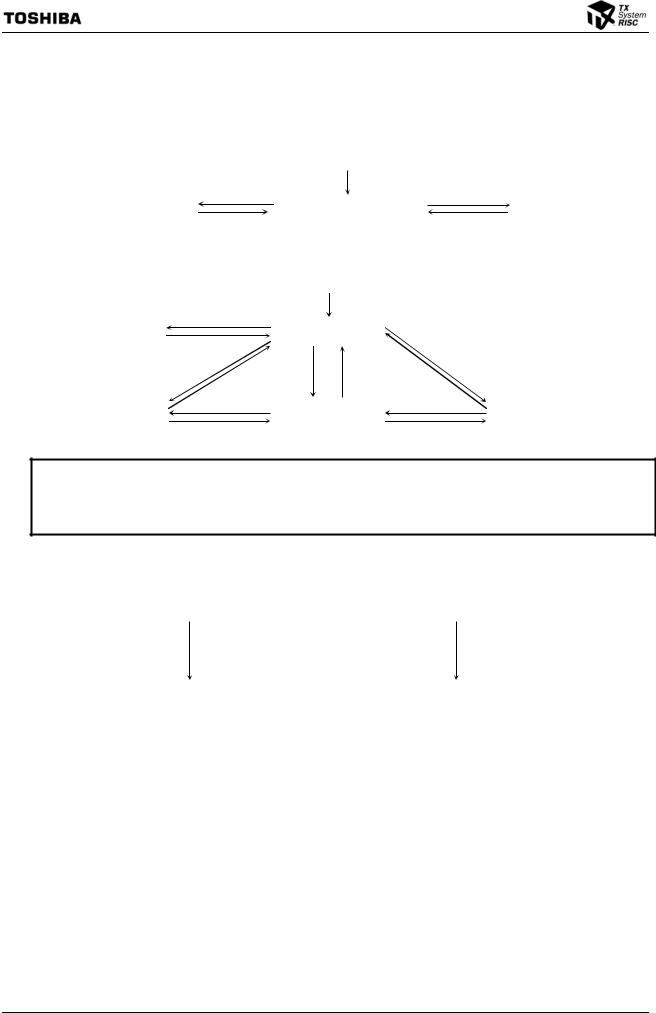
TMP1942CY/CZ
3.3Clock/Standby Control
There are essentially two modes of clock operation: single-clock mode (which uses only the X1 and X2 pins) and dual-clock mode (which uses the X1 and X2 pins as well as the XT1 and XT2 pins).
Figure 3.3.1 shows the state transition diagram for each operation mode.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Reset |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Reset terminated |
|
|
|
|||||
|
IDLE mode |
|
Instruction |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Instruction |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
NORMAL mode |
|
|
|
STOP mode |
|||||||||
|
(CPU halted) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
Interrupt |
|
|
|
(fc/gear value) |
|
|
Interrupt |
|
(all circuits turned off) |
|||||||
|
(I/O select operation) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
(a) State transition in single-clock mode |
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Reset |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Reset terminated |
|
|
|
||||||
|
IDLE mode |
|
|
Instruction |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NORMAL mode |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
(CPU halted) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
Interrupt |
|
|
(fc/gear value) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
(I/O select operation) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Instruction |
|
|
Instruction |
|
|
|
||||||
SLEEP mode (fc only) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
Instruction |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
Interrupt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interrupt |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(only real-time clock |
|
Instruction |
|
|
|
|
|
Instruction |
|
|
STOP mode |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
SLOW mode |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
timer operating) |
|
Interrupt |
|
|
|
(fs) |
|
|
Interrupt |
|
(all circuits turned off) |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Note 1: Before transition to SLOW/SLEEP mode can occur, the low-speed oscillator (fs) must be oscillating stably.
Note 2: When SLEEP mode is terminated, the device returns to the state in which it was placed before entering SLEEP mode.
Note 3: The state to which the device returns when STOP mode is terminated can be specified using system control register SYSCR0.
(b) State transition in dual-clock mode
Figure 3.3.1 State Transition Diagrams for Different Modes
|
|
Reset |
|
|
|
Reset |
|
|||
|
|
Reset terminated |
|
Reset terminated |
||||||
|
|
|
|
pin (High) |
|
|
|
pin (Low) |
||
|
|
|
PLLOFF |
|
|
PLLOFF |
||||
|
|
PLL clock used |
|
PLL not used |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NORMAL mode |
|
|
NORMAL mode |
|||||
|
|
fc = fpll = fosc × 4 |
|
|
fc = fosc/2 |
|||||
|
|
fsys = fc/8 |
|
|
fsys = fc/8 |
|||||
|
|
fsys = fosc/2 |
|
|
fsys = fosc/16 |
|||||
|
|
fperiph = fsys |
|
|
fperiph = fsys |
|||||
A. When a clock generated by the PLL is used |
B. When the PLL is not used |
|||||||||
Figure 3.3.32 Default States When the PLL is Used and Those When the PLL is Not Used
fosc: |
Clock frequency input via X1 and X2 pins |
||
fs: |
Clock frequency input via XT1 and XT2 pins |
||
fpll: |
Clock frequency multiplied (x4) by PLL |
||
fc: |
Clock frequency selected by setting of |
|
pin |
PLLOFF |
|||
fgear: |
Clock frequency selected by SYSCR1<GEAR1:GEAR0> |
||
System clock fsys: Clock frequency selected by SYSCR1<SYSCK> |
|||
fperiph: |
Input clock for peripheral I/O prescaler |
||
TMP1942CY/CZ-17
TMP1942CY/CZ
3.3.1Block Diagram of Clock Circuits
1.Main system clock
•A crystal can be connected between X1 and X2, or X1 can be externally driven with a clock.
•PLLOFF The on-chip PLL can be enabled or disabled (bypassed) during reset by using the PLLOFF pin. When the PLL is enabled, the input clock frequency is multiplied by four.
•The clock gear can be programmed to divide the clock by 2, 4 or 8. (The default is 1/8 on reset.)
•Input clock frequency
|
|
Input Frequency Range |
fmax |
fmin |
|
PLLON |
|
5~8 (MHz) |
32 MHz |
2.5 MHz |
|
(for both resonator and external input) |
|||||
|
|
|
|||
|
Resonator |
16~20 (MHz) |
20 MHz |
1 MHz |
|
PLLOFF |
External input |
16~20 (MHz) |
20 MHz |
1 MHz |
|
|
20 32 (MHz) |
16 MHz *1 |
1.25 MHz |
||
|
|
||||
*1. SYSCR1<DFOSC> must be 0. The default is 0.
2.Sub-system clock
•Generated using a 32.768-kHz resonator (external input also accepted).
•SLOW mode: The CPU runs at low speed.
•SLEEP mode: Only the timer for real-time clock, 2-phase pulse input counter, and dynamic pull-up operate.
TMP1942CY/CZ-18

TMP1942CY/CZ
3.Block diagram
SYSCR0<WUEF>
SYSCR2<WUPT1 : 0> SYSCR1 <FPSEL>
SYSCR3<LUPTM>
|
|
Warm-up timer |
|
|
fgear |
fperiph |
|
|
|
|
(to peripheral I/O) |
||
|
SYSCR0 |
|
|
|
||
|
Lock-up (PLL) timer |
|
|
|
|
|
|
<XTEN> |
fc |
|
|
|
fs |
|
|
fs |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
XT1 |
Low-speed |
|
|
|
|
|
XT2 |
oscillator |
Fpll = fosch × 4 |
|
|
|
fsys |
|
SYSCR0 |
Selector |
|
|
|
|
|
PLL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
<XEN> |
|
|
|
|
|
|
÷2 |
÷4 |
÷8 |
|
SYSCR1 <SYSCK> |
|
|
|
|
X1 |
High-speed |
÷2 |
|
|
SYSCR1 <GEAR1:0> |
X2 |
|
|
|||
oscillator |
fosc |
|
|
Divide by 8 after reset |
|
|
|
|
|
PLLOFF (default pin setting) |
|
|
|
SYSCR1 <DFOSC> |
|
||
|
fsys |
|
|
|
CPU |
|
|
|
SYSCR0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
<PRCK1:0> |
ROM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Peripheral I/O |
RAM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(prescaler input) |
DMAC |
|
|
|
|
TMRA/B, SIO |
|
|
fperiph |
÷2 |
÷4 |
|
|
|
SBI, ADC |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
INTC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Peripheral I/O
 ÷2
÷2  ADC,DA,TMRA/B, SIO,SBI,PIO, WDT, RTC
ADC,DA,TMRA/B, SIO,SBI,PIO, WDT, RTC
|
Timer for real-time clock |
|
fs |
2-phase pulse input counter |
|
KWUP |
||
|
||
|
SYSCR3 <SCOSEL> |
|
|
SCOUT |
Note 1: When using the clock gear to reduce the system clock frequency, make sure that φTn of the prescaler output for each peripheral I/O block satisfies the following relationship:
φTn<fsys/2
To this end, set the clock-related registers so that φTn is slower than fsys/2.
When selecting a low-speed system clock (fs), only the timer for real-time clock, 2-phase pulse input counter, and dynamic pull-up can operate.
Figure 3.3.3 Block Diagram of Dual-Clock and Standby Functions
TMP1942CY/CZ-19
TMP1942CY/CZ
3.3.2Clock Generator (CG) Registers
|
(1) Clock-related registers |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
0 |
SYSCR0 |
Bit Symbol |
XEN |
XTEN |
RXEN |
RXTEN |
RSYSCK |
WUEF |
PRCK1 |
PRCK0 |
(0xFFFF_EE00) |
Read/Write |
|
|
|
R/W |
|
|
|
|
|
After reset |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
Function |
High-speed |
Low-speed |
High-speed |
Low-speed |
Clock |
Oscillator |
Prescaler clock selection |
|
|
|
oscillator |
oscillator |
oscillator |
oscillator |
selection |
warm-up |
|
|
|
|
|
|
after exit |
after exit |
after exit |
timer (WUP) |
00: fperiph/4 |
|
|
|
|
|
from STOP |
from STOP |
from STOP |
control |
01: fperiph/2 |
|
|
|
|
|
mode |
mode |
mode |
Write 0: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
10: fperiph |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Don't care |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11: (reserved) |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Write 1: |
||
|
|
0: Turned off |
0: Turned off |
0: Turned off |
0: Turned off |
0: High speed |
|
|
|
|
|
WUP start |
|
|
|||||
|
|
1: Oscillating |
1: Oscillating |
1: Oscillating |
1: Oscillating |
1: Low speed |
Read 0: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
WUP finished |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Read 1: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
WUP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
operating |
|
|
|
|
15 |
14 |
13 |
12 |
11 |
10 |
9 |
8 |
SYSCR1 |
Bit Symbol |
|
|
SYSCK |
FPSEL |
DFOSC |
|
GEAR1 |
GEAR0 |
(0xFFFF_EE01) |
Read/Write |
|
|
R/W |
|
|
R/W |
||
|
After reset |
- |
- |
0 |
0 |
0 |
- |
1 |
1 |
|
Function |
|
|
System |
fperiph |
High-speed |
|
High-speed clock (fc) |
|
|
|
|
|
clock |
selection |
oscillator |
|
gear selection |
|
|
|
|
|
selection |
|
frequency |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
division |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
selection |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
00: fc |
|
|
|
|
|
0: High speed |
0: fgear |
0: Divide by 2 |
|
01: fc/2 |
|
|
|
|
|
(fc) |
1: fc |
1: Divide by 1 |
|
10: fc/4 |
|
|
|
|
|
1: Low speed |
|
|
|
11: fc/8 |
|
|
|
|
|
(fs) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
23 |
22 |
21 |
20 |
19 |
18 |
17 |
16 |
SYSCR2 |
Bit Symbol |
DRVOSCH |
DRVOSCL |
WUPT1 |
WUPT0 |
STBY1 |
STBY0 |
|
DRVE |
(0xFFFF_EE02) |
Read/Write |
|
|
R/W |
|
|
- |
R/W |
|
|
After reset |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
- |
0 |
|
Function |
High-speed |
Low-speed |
Oscillator warm-up time |
Standby mode selection |
|
1: Pins are |
||
|
|
oscillator |
oscillator |
selection |
|
|
|
|
also |
|
|
driving |
driving |
|
|
|
|
|
driven in |
|
|
capability |
capability |
00: 22/input frequency |
|
|
|
STOP |
|
|
|
control |
control |
00: Reserved |
|
mode. |
|||
|
|
|
|
01: 28/input frequency |
01: STOP mode |
|
|
||
|
|
0: Normal |
0: Normal |
10: 214/input frequency |
10: SLEEP mode |
|
|
||
|
|
1: Weak |
1: Weak |
11: 216/input frequency |
11: IDLE mode |
|
|
||
|
|
31 |
30 |
29 |
28 |
27 |
26 |
25 |
24 |
SYSCR3 |
Bit Symbol |
|
SCOSEL |
|
ALESEL |
|
|
LUPFG |
LUPTM |
(0xFFFF_EE03) |
Read/Write |
- |
R/W |
- |
R/W |
- |
- |
R |
R/W |
|
After reset |
- |
0 |
- |
1 |
- |
- |
0 |
0 |
|
Function |
|
SCOUT |
|
ALE output |
|
|
Lock-up flag |
Lock-up time |
|
|
|
output |
|
width |
|
|
|
selection |
|
|
|
selection |
|
selection |
|
|
0: LUP |
0: 216/input |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
finished |
frequency |
|
|
|
0: fs |
|
0: fsys × 0.5 |
|
|
1: LUP in |
1: 212/input |
|
|
|
1: fsys |
|
1: fsys × 1.5 |
|
|
operation |
frequency |
TMP1942CY/CZ-20

TMP1942CY/CZ
Note 1: Standby mode selection depends on the settings of the Doze and Halt bits in the CP0's internal Config register. If the Halt bit = 1, the device will enter the mode selected by STBY[1:0].
If the Doze bit = 1, the device will always enter IDLE mode.
Note 2: When the PLL is not used, set the LUPTM bit in the SYSCR3 register to 1 (i.e., select 212/input frequency).
Note3: The WURT1-WUPT0 bitys in the SYSCR2 must be not be changed during the oscillator warm-up event ( e.g. SLEEP-NORMAL-SLEEP)
Note 4: Do as follows to change the operating mode immediately after the device has warmed up from the clock stop state (e.g., from SLEEP mode to NORMAL mode to SLEEP mode).
•Warming up by hardware
(1)Moving from STOP or SLEEP mode to NORMAL mode
1) When the PLL is used
Before moving to the next operating mode, ensure that the lock-up bit, LUPFG, in the SYSCR3 register has been cleared to zero and wait for five or more instructions to complete (including the instruction to check the LUPFG flag).
2)When the PLL is not used
•When the oscillator warm-up time (SYSCR2<WUPT1:0>) is programmed as “01” (i.e., 28/input frequency). Before moving to the next operating mode, ensure that the lock-up bit, LUPFG, in the SYSCR3 register has been cleared to zero and wait for five or more instructions to complete.
•When the oscillator warm-up time (SYSCR2<WUPT1:0>) is programmed as “10” (214/input frequency) or “11” (216/input frequency). Before moving to the next operating mode, wait for five or more instructions to complete.
(2)Moving from STOP or SLEEP mode to SLOW mode
It is possible to move to SLOW mode immediately after the device has warmed up from STOP or SLEEP mode.
•Warming up by software
(1)Moving from SLOW mode to NORMAL mode
1)When the PLL is used
It is possible to move to NORMAL mode immediately after the device has warmed up. However, to move to another mode after that, ensure that the lock-up bit, LUPFG, in the SYSCR3 register has been cleared to zero and wait for five or more instructions to complete (including the instruction to check the LUPFG flag).
2)When the PLL is not used
•When the oscillator warm-up time (SYSCR2<WUPT1:0>) is programmed as “01” (i.e., 28/input frequency). It is possible to move to NORMAL mode immediately after the device has warmed up. However, to move to another mode after that, ensure that the lock-up bit, LUPFG, in the SYSCR3 register has been cleared to zero and wait for five or more instructions to complete.
•When the oscillator warm-up time (SYSCR2<WUPT1:0>) is programmed as “10” (214/input frequency) or “11” (216/input frequency). It is possible to move to NORMAL mode immediately after the device has warmed up. However, to move to another mode after that, wait for five or more instructions to complete.
(2)Moving from NORMAL mode to SLOW mode
Before moving to SLOW mode, ensure that the warm-up end flag (i.e., the WUEF bit in the SYSCR0 register) is cleared and wait for five or more instructions to complete.
TMP1942CY/CZ-21
TMP1942CY/CZ
|
(2) Standby (STOP/SLEEP mode) termination interrupts |
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
6 |
5 |
|
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
0 |
IMCGA0 |
Bit Symbol |
|
|
EMCG01 |
|
EMCG00 |
|
|
|
INT0EN |
(0xFFFF_EE10) |
Read/Write |
|
|
R/W |
|
|
|
R/W |
||
|
After reset |
|
|
1 |
|
0 |
|
|
|
0 |
|
Function |
|
|
Active state setting for |
|
|
|
INT0 |
||
|
|
|
|
INT0 standby termination |
|
|
|
request |
||
|
|
|
|
request |
|
|
|
|
input |
|
|
|
|
|
00: Low level |
|
|
|
|
0: Disable |
|
|
|
|
|
01: High level |
|
|
|
|
1: Enable |
|
|
|
|
|
10: Falling edge |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
11: Rising edge |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
15 |
14 |
13 |
|
12 |
11 |
10 |
9 |
8 |
|
Bit Symbol |
|
|
EMCG11 |
|
EMCG10 |
DFOSC |
|
|
INT1EN |
|
Read/Write |
|
|
R/W |
|
|
|
R/W |
||
|
After reset |
|
|
1 |
|
0 |
|
|
|
0 |
|
Function |
|
|
Active state setting for |
|
|
|
INT1 |
||
|
|
|
|
INT1 standby termination |
|
|
|
request |
||
|
|
|
|
request |
|
|
|
|
input |
|
|
|
|
|
00: Low level |
|
|
|
|
0: Disable |
|
|
|
|
|
01: High level |
|
|
|
|
1: Enable |
|
|
|
|
|
10: Falling edge |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
11: Rising edge |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
23 |
22 |
21 |
|
20 |
19 |
18 |
17 |
16 |
|
Bit Symbol |
|
|
EMCG21 |
|
EMCG20 |
|
|
|
INT2EN |
|
Read/Write |
|
|
R/W |
|
|
|
R/W |
||
|
After reset |
|
|
1 |
|
0 |
|
|
|
0 |
|
Function |
|
|
Active state setting for |
|
|
|
INT2 |
||
|
|
|
|
INT2 standby termination |
|
|
|
request |
||
|
|
|
|
request |
|
|
|
|
input |
|
|
|
|
|
00: Low level |
|
|
|
|
0: Disable |
|
|
|
|
|
01: High level |
|
|
|
|
1: Enable |
|
|
|
|
|
10: Falling edge |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
11: Rising edge |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
31 |
30 |
29 |
|
28 |
27 |
26 |
25 |
24 |
|
Bit Symbol |
|
|
EMCG31 |
|
EMCG30 |
|
|
|
INT3EN |
|
Read/Write |
|
|
R/W |
|
|
|
R/W |
||
|
After reset |
|
|
1 |
|
0 |
|
|
|
0 |
|
Function |
|
|
Active state setting for |
|
|
|
INT3 |
||
|
|
|
|
INT3 standby termination |
|
|
|
request |
||
|
|
|
|
request |
|
|
|
|
input |
|
|
|
|
|
00: Low level |
|
|
|
|
0: Disable |
|
|
|
|
|
01: High level |
|
|
|
|
1: Enable |
|
|
|
|
|
10: Falling edge |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
11: Rising edge |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TMP1942CY/CZ-22

TMP1942CY/CZ
|
|
7 |
6 |
5 |
|
|
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
0 |
IMCGB0 |
Bit Symbol |
|
|
EMCG41 |
|
EMCG40 |
|
|
|
INT4EN |
|
(0xFFFF_EE14) |
Read/Write |
|
|
|
R/W |
|
|
|
R/W |
||
|
After reset |
|
|
1 |
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
0 |
|
Function |
|
|
Active state setting for |
|
|
|
INT4 |
|||
|
|
|
|
INT4 standby termination |
|
|
|
request |
|||
|
|
|
|
request |
|
|
|
|
|
|
input |
|
|
|
|
00: Low level |
|
|
|
|
0: Disable |
||
|
|
|
|
01: High level |
|
|
|
|
1: Enable |
||
|
|
|
|
10: Falling edge |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
11: Rising edge |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
15 |
14 |
13 |
|
|
12 |
11 |
10 |
9 |
8 |
|
Bit Symbol |
|
|
EMCG51 |
|
EMCG50 |
|
|
|
KWUPEN |
|
|
Read/Write |
|
|
|
R/W |
|
|
|
R/W |
||
|
After reset |
|
|
1 |
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
0 |
|
Function |
|
|
These bits should always |
|
|
|
KWUP |
|||
|
|
|
|
be set to 01. |
|
|
|
|
request |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
input |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0: Disable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1: Enable |
|
|
23 |
22 |
21 |
|
|
20 |
19 |
18 |
17 |
16 |
|
Bit Symbol |
|
|
EMCG61 |
|
EMCG60 |
|
|
|
INTBCDEEN |
|
|
Read/Write |
|
|
|
R/W |
|
|
|
R/W |
||
|
After reset |
|
|
1 |
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
0 |
|
Function |
|
|
These bits should always |
|
|
|
INTBCDE |
|||
|
|
|
|
be set to 01. |
|
|
|
|
request |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
input |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0: Disable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1: Enable |
|
|
31 |
30 |
29 |
|
|
28 |
27 |
26 |
25 |
24 |
|
Bit Symbol |
|
|
EMCG71 |
|
|
EMCG70 |
|
|
|
INTRTCEN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Read/Write |
|
|
|
R/W |
|
|
|
R/W |
||
|
After reset |
|
|
1 |
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
0 |
|
Function |
|
|
These bits should always |
|
|
|
INTRTCEN |
|||
|
|
|
|
be set to 11. |
|
|
|
|
request |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
input |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0: Disable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1: Enable |
TMP1942CY/CZ-23
TMP1942CY/CZ
Note 1: When enabling an interrupt source as a means of terminating a standby mode, always set the active state for the corresponding interrupt request.
Note 2: When using an interrupt, always perform the following steps in order:
(1)Enable the input for the interrupt if the corresponding pin is also used for a general-purpose port or any other purpose.
(2)Set the active state for the interrupt during initialization.
(3)Clear the interrupt request.
(4)Enable the interrupt.
Note 3: The TMP1942 has eight interrupt sources (INT0~INT4, INTRTC, INTB/INTC/INTD/INTE, and KWUP0-KWUPD) which can be used as a means of terminating a standby mode. For INT0 to INT4, use the CG block to specify whether they are used to terminate a standby mode and to specify their active edge or level. For INTB/INTC/INTD/INTE and KWUP0-KWUPD, use the CG block to specify whether they are used to terminate a standby mode and use INTBCDEST and KWUPSTn, respectively, to specify their active edge or level. Set the active state for the corresponding interrupt source to High in the INTC block.
Example: Enable the INT0 interrupt
IMCGA0<EMCG01:00> = “10” IMCGA0<INT0EN> = “1” IMC0L<EIM11:10> = “01” IMC0L<IL12:10> = “101”
CG block
(Input is enabled on the falling edge.) INTC block
(A High-level interrupt is active and the interrupt level is 5.)
All interrupt sources other than those which are used to terminate STOP/SLEEP mode are set in the INTC circuit block.
Note 4: Among the above eight interrupt sources used to request the termination of a standby mode, INT0 to INT4 do not require settings in the CG block if they are used as normal interrupts. They still, however, require level or edge specification in the INTC. If INTB/INTC/INTD/INTE and KWUP0-KWUPD are used as normal interrupts, specify the active level or edge using INTBCDEST/KWUPSTn and specify the High level in the INTC. Settings in the CG are not required. INTRTC always requires settings in both the CG and INTC even if it is used as a normal interrupt.
All interrupt sources other than those which are used to terminate a standby mode are set in the INTC circuit block.
TMP1942CY/CZ-24

TMP1942CY/CZ
|
(3) Interrupt request clear register |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
|
|
0 |
EICRCG |
Bit Symbol |
|
|
|
|
|
ICRCG2 |
ICRCG1 |
|
ICRCG0 |
|
(0xFFFF_EE20) |
Read/Write |
|
|
|
|
|
|
W |
|
||
|
After reset |
|
|
1 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
|
|
|
|
|
Clear interrupt request |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
000: INT0 |
100: INT4 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
001: INT1 |
101:KWUP |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
010: INT2 |
110: INTB/C/D/E |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
011: INT3 |
111: INTRTC |
|
||
Note : To clear any of the eight interrupt sources which are used for terminating a standby mode:
(1)For KWUP, use KWUPCLR.
(2)For extended interrupts INTB/INTC/INTD/INTE, use INTFLG.
(3)For INT0 to INT4 and INTRTC, perform the clearing operation twice, first in the CG block and then in the INTC block.
(4)For all other interrupt sources, use the INTC block.
3.3.3System clock control unit
When reset, the device enters single-clock mode with the result that XEN = 1, XTEN = 0 and GEAR1:0 = 11; the system clock fsys is set to fc/8 (= fc × 1/8). (Since the PLL multiplies the original oscillation frequency by 4, fc equals to fosc × 4, where fosc is the original oscillation frequency.) For example, if the X1 and X2 pins are connected to an 8-MHz resonator, a reset will set fsys to 4 MHz (= 8 MHz × 4 × 1/8).
To disable the system from using a PLL-multiplied clock as the system clock by default, drive the PLLOFF pin Low. In this case, too, the system clock fsys will be set to fc/8 (= fc × 1/8) by a reset. However, since SYSCR1<DFOSC> is initialized to 0 by a reset (so that fc = fosc × 1/2), if the X1 and X2 pins are connected to a 25-MHz resonator, fsys will be 1.25 MHz. Also, if the device is clocked by an external oscillator and no internal resonator is connected, fc = fosc can be selected by setting SYSCR1<DFOCS> to 1 after a reset, so that the system clock frequency fsys is twice the frequency obtained with an internal resonator.
(1) Oscillation settling time (switchover between NORMAL and SLOW modes)
If a resonator is connected to the resonator-connecting pins, the device uses the built-in warm-up timer to check whether resonator oscillation has settled. The warm-up time can be set to suit the characteristics of the resonator using SYSCR2<WUPT1:WUPT0>. The value of SYSCR0<WUEF> must be checked in software (using instructions) to determine the start and completion of the warm-up time.
Table 3.3.1 shows warm-up times for mode switching.
TMP1942CY/CZ-25
TMP1942CY/CZ
Note 1: Warm-up is unnecessary when the clock generator uses an oscillator so that its oscillation is stable.
Note 2: Since the warm-up timer is clocked by an oscillating clock, it will not be exact if the oscillation frequency fluctuates. The warm-up time should, therefore, be considered to be an approximate value.
Note 3: Before starting the warm-up timer, first confirm that the PLL lock-up flag <LUPFG> is 0.
Note 4: The following precautions must be observed when a low-speed oscillator is being used:
When a low-speed oscillator is connected to ports PD6 and PD7, the corresponding register must be set as shown below in order to reduce the device's power consumption.
(When using a resonator)
Set PDCR<PD6C, PD7C> to 11 and PD<PD6, PD7> to 00.
(When using an external clock)
Set PDCR<PD6C, PD7C> to 11 and PD<PD6, PD7> to 10.
Table 3.3.1 Warm-Up Time
Warm-Up Time Selection |
High-Speed Clock |
Low-Speed Clock (fs) |
|
SYSCR2<WUPT1:0> |
(fosc) |
||
|
|||
|
|
|
|
(22/oscillation frequency) |
0.5 [μs] |
122 [μs] |
|
(28/oscillation frequency) |
32 [μs] |
7.8 [ms] |
|
(214/oscillation frequency) |
2.048 [ms] |
500 [ms] |
|
(216/oscillation frequency) |
8.192 [ms] |
2000 [ms] |
The values calculated are for when
fosc = 8 MHz
and fs = 32.768 kHz.
Note: When returning from STOP/SLEEP mode to NORMAL or SLOW mode, set the warm-up time to 122 μs or greater beforehand.
Example: If the device will return from SLEEP mode to SLOW mode, set SYSCR2<WUPT1:0> to 00, that is, a warm-up time of 122 μs, before entering SLEEP mode.
(2) Outputting the system clock from a pin
The system clock fsys or fs can be output from the P44/SCOUT pin to an external device. The P44/SCOUT pin can be set to function as the SCOUT pin by setting the registers which relate to port 4 as follows: P4CR<P44C> = 1 and P4FC<P44F> = 1. Use SYSCR3<SCOSEL> to select which clock will be output from this pin.
Table 3.3.2 shows the pin state for each standby mode when the P44/SCOUT pin is set to function as SCOUT.
Table 3.3.2 SCOUT Output State for Each Standby Mode
Mode |
NORMAL, |
|
Standby Mode |
|
SCOUT Selection |
SLOW |
IDLE |
SLEEP |
STOP |
<SCOSEL> = “0” |
Outputs fs clock. |
Fixed to 0 or 1 |
|
<SCOSEL> = “1” |
Outputs fsys clock. |
|
|
|
|
||
Note: This function does not guarantee a particular phase difference (AC timing) between the internal clock and the system clock output from SCOUT.
TMP1942CY/CZ-26

TMP1942CY/CZ
(3) Reducing the driving capability of oscillators
If a resonator is connected to the resonator-connecting pins of an oscillator, this function can suppress oscillation noise output from the oscillator, while reducing power consumption by the oscillator.
Setting SYSCR2<DRVOSCH> to 1 causes the driving capability of the high-speed oscillator to degrade (Weak). Similarly, setting SYSCR2<DRVOSCL> to 1 causes the driving capability of the low-speed oscillator to degrade (Weak).
Because both bits are initialized to 0 upon a system reset, both oscillators start oscillating with their normal driving capability (Normal) when the power is turned on. The oscillators must be placed in the Normal state (<DRVOSCL> or <DRVOSCH> = 0) when they start oscillating in any other cases, such as when STOP/SLEEP mode is terminated.
1) Reducing the driving capability of the high-speed oscillator
|
fOSC |
|
C1 |
X1 pin |
|
Oscillation enable |
||
|
||
Resonator |
|
|
|
SYSCR2<DRVOSCH> |
|
C2 |
|
|
|
X2 pin |
2) Reducing the driving capability of the low-speed oscillator
C1 |
XT1 pin |
|
Oscillation enable |
||
|
||
Resonator |
|
|
|
SYSCR2<DRVOSCL> |
|
C2 |
fS |
|
|
XT2 pin |
3.3.4Prescaler clock control unit
The internal I/O blocks (TMRA01 to TMRAAB, TMRB0 to TMRBD, SIO0 to SIO5, SBI, and ADC) each incorporate a prescaler for dividing the clock frequency. The clock φT0 fed into these prescalers is derived from the clock fperiph. fperiph is either fgear or fc (as specified by the value of SYSCR1<FPSEL>) divided by either 4 or 2, or not divided (as specified by the value of SYSCR0<PRCK1:PRCK0>. By default, fperiph is set to fgear and φT0 to fperiph/4.
3.3.5Clock multiplication circuit (PLL)
This circuit multiplies the high-speed oscillator output clock, fosc, by 4 and outputs the result as the clock fpll. This enables the oscillator to yield a fast internal clock with a low oscillator frequency. The PLL is halted by a reset. To use the PLL, hold the PLLOFF pin High when terminating a reset.
Note: If a reset is terminated while the PLLOFF pin is held Low, the PLL will not work and the internal clock chosen will be the original oscillating clock (i.e., it will not be multiplied by 4).
TMP1942CY/CZ-27
TMP1942CY/CZ
Since the PLL is configured as an analog circuit, it requires a certain settling time (a lock-up time) after it has been activated, as does the oscillator.
The same timer is used for both warm-up and lock-up. The lock-up time must be set using SYSCR3<LUPTM> so that it satisfies the following relationship:
Lock-up time ≥ warm-up time
By default, the lock-up time is 216/input frequency.
The lock-up timer is initiated as the high-speed oscillator starts warm-up, and the lock-up flag SYSCR3<LUPTM> remains 1 until the PLL is locked in phase and cleared to 0 upon the completion of lock-up.
If, for example, the PLL gets out of lock in a standby mode and control which depends on the software's execution speed, such as real-time processing, is to be performed, the software must check the lock-up flag after operation has started (i.e., after warm-up has been completed) to ensure that the clock has settled, before it starts processing.
On the other hand, various hardware settings and static processing, such as register and memory initialization, can be executed before the lock-up flag has been cleared.
Note: The LUPFG bit is undefined when the PLLOFF pin is Low (the PLL is not used).
Precautions to be observed when switching clock gear:
Clock gear switchover is performed by writing a value to SYSCR1<GEAR1:GEAR0>. The clock gear is not switched immediately after the write: a execution time equal to several clock cycles is required. Therefore, one or more instructions following the clock gear switchover instruction may be executed using the old clock gear value. If these instructions need to be executed using the new clock gear value, insert a dummy instruction (which executes a write cycle only) after the clock gear switchover instruction.
When using a clock gear, make sure that the prescaler output φTn in each peripheral I/O block satisfies the following relationship:
φTn < fsys/2
For this purpose set the clock-related registers so that φTn is slower than fsys/2.
3.3.6Standby control unit
If the Halt bit in the TX19 processor core's Config register is set in NORMAL mode, the device enters one of the standby modes - IDLE, SLEEP or STOP - as determined by the contents of SYSCR2<STBY1:STBY0>. If the Config register's Doze bit is set, the device enters IDLE mode regardless of the setting of SYSCR2<STBY1:STBY0>.
Features of the IDLE, SLEEP and STOP modes are described below.
1) IDLE: In this mode, only the CPU stops.
In the register corresponding to each module there is an IDLE mode run/stop setup bit for internal I/O. This allows each module to be set independently to run or stop while the device is in IDLE mode. Table 3.3.3 lists the IDLE setup registers available for each internal I/O module.
TMP1942CY/CZ-28

TMP1942CY/CZ
Table 3.3.3 IDLE Mode Internal I/O Setup Registers
Internal I/O |
IDLE Mode Setup Register |
TMRA01 |
TA01RUN<I2TA01> |
TMRA23 |
TA23RUN<I2TA23> |
TMRA45 |
TA45RUN<I2TA45> |
TMRA67 |
TA67RUN<I2TA67> |
TMRA89 |
TA89RUN<I2TA89> |
TMRAAB |
TAABRUN<I2TAAB> |
TMRB0 |
TB0RUN<I2TB0> |
TMRB1 |
TB1RUN<I2TB1> |
TMRB2 |
TB2RUN<I2TB2> |
TMRB3 |
TB3RUN<I2TB3> |
TMRB4 |
TB4RUN<I2TB4> |
TMRB5 |
TB5RUN<I2TB5> |
TMRB6 |
TB6RUN<I2TB6> |
TMRB7 |
TB7RUN<I2TB7> |
TMRB8 |
TB8RUN<I2TB8> |
TMRB9 |
TB9RUN<I2TB9> |
TMRBA |
TBARUN<I2TBA> |
TMRBB |
TBBRUN<I2TBB> |
TMRBC |
TBCRUN<I2TBC> |
TMRBD |
TBDRUN<I2TBD> |
SIO0 |
SC0MOD1<I2S0> |
SIO1 |
SC1MOD1<I2S1> |
SIO3 |
SC3MOD1<I2S3> |
SIO4 |
SC3MOD1<I2S4> |
SIO5 |
SC4MOD1<I2S5> |
SBI |
SBI0BR1<I2SBI0> |
A/D converter |
ADMOD1<I2AD> |
WDT |
WDMOD<I2WDT> |
Note 1: In Halt mode (entered when the Halt bit in the Config Register is set), the TX19 processor core stops processor operation while maintaining the pipeline status. Since it does not respond to requests for control of the bus from internal DMA, it retains control of the bus.
Note 2: In Doze mode (entered when the Doze bit in the Config Register is set), the TX19 processor core stops processor operation while maintaining the pipeline status. In this mode, it can respond to requests for control of the bus from devices external to the processor core.
2) SLEEP: Only the internal low-speed oscillator, timer for real-time clock, 2-phase pulse input counter, and KWUP (dynamic pull-up) operate.
3) STOP: The CPU runs with the low-speed clock. The INTC, timer for real-time clock, WDT, 2-phase pulse input counter, KWUP (dynamic pull-up), PIO, and EBIF can operate. Operation of other peripheral functions is not guaranteed.
4) SLOW: All of the internal circuits stop.
TMP1942CY/CZ-29
 Loading...
Loading...