Schneider Electric TAC Xenta 500, TAC Xenta 700, TAC Xenta 911, TAC Xenta 913 Users Manual
TAC Vista
TAC Pangaea
WorkStation
TAC Xenta 500/700/911/913
Product Manual


TAC Vista
TAC Xenta 500/700/911/913
Product Manual

Copyright © 2011 Schneider Electric Buildings AB. All rights reserved.
This document, as well as the product it refers to, is only intended for licensed users. Schneider Electric Buildings AB owns the copyright of
this document and reserves the right to make changes, additions or deletions. Schneider Electric Buildings AB assumes no responsibility for
possible mistakes or errors that might appear in this document.
Do not use the product for other purposes than those indicated in this document.
Only licensed users of the product and the document are permitted to use the document or any information therein. Distribution, disclosure,
copying, storing or use of the product, the information or the illustrations in the document on the part of non-licensed users, in electronic or
mechanical form, as a recording or by other means, including photo copying or information storage and retrieval systems, without the express
written permission of Schneider Electric Buildings AB, will be regarded as a violation of copyright laws and is strictly prohibited.
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.

TAC Xenta 500/700/911/913, Product Manual Contents
Contents
INTRODUCTION
1 About this Manual 11
1.1 Structure..................................................................................................................... 12
1.2 Typographic Conventions.......................................................................................... 12
1.3 Terminology............................................................................................................... 13
1.4 Related Documents .................................................................................................... 14
REFERENCE
2 TAC Xenta 500/700/911/913 17
2.1 Hardware.................................................................................................................... 17
2.1.1 Communication Interface........................................................................................... 18
2.1.2 Port Pins ..................................................................................................................... 21
2.1.3 Fail-Safe State............................................................................................................23
2.1.4 LEDs .......................................................................................................................... 23
2.2 Configuring the TAC Xenta 500/700/911/913 .......................................................... 25
2.2.1 Configuration Data..................................................................................................... 25
2.2.2 Configuring Windows HyperTerminal ...................................................................... 26
2.2.3 Configuring the TAC Xenta....................................................................................... 28
2.3 Verifying the TAC Xenta Communication................................................................ 31
2.3.1 Accessing the TAC Xenta.......................................................................................... 32
2.3.2 Changing the Root Password ..................................................................................... 34
2.4 Temporary Login ID.................................................................................................. 35
2.5 Upgrading the System Program................................................................................. 36
3 Connecting the TAC Xenta to Your Network 41
3.1 Alternative Port Settings............................................................................................ 42
3.1.1 HTTP and HTTPS...................................................................................................... 42
4 TAC Xenta 511 43
4.1 Configuration Phase................................................................................................... 43
4.1.1 Connections, configuration........................................................................................ 44
4.2 Engineering Phase...................................................................................................... 45
4.2.1 Connections, engineering........................................................................................... 46
4.3 Operating Phase ......................................................................................................... 47
4.3.1 Directly Connected..................................................................................................... 47
4.3.2 Connections, operation directly ................................................................................. 48
4.3.3 Dialed-Up, operation.................................................................................................. 49
4.3.4 Connections................................................................................................................, op-
eration dial-up ............................................................................................................ 50
Schneider Electric Buildings AB, Feb 2011 5 (134)
04-00071-04-en

Contents TAC Xenta 500/700/911/913, Product Manual
4.4 Port Usage ..................................................................................................... .... ..... .... 51
5 TAC Xenta 527 53
5.1 Configuration Phase ................................................................................................... 53
5.1.1 Connections................................................................................................................54
5.2 Engineering Phase ...................................................................................................... 55
5.2.1 Connections................................................................................................................56
5.3 Operating Phase.................................................................. ........................................ 58
5.3.1 Directly Connected..................................................................................................... 58
5.3.2 Connections................................................................................................................58
5.3.3 Dialed-Up................................................................................................................... 60
5.3.4 Connections................................................................................................................60
5.4 Port Usage ........................................................ .......................................................... 63
5.5 Connecting the TAC Xenta 527 to an I/NET Controller LAN .................................. 64
5.6 Using a Direct Connection to I/NET.......................................................................... 65
6 TAC Xenta 555 67
6.1 Configuration Phase ................................................................................................... 67
6.1.1 Connections................................................................................................................68
6.2 Engineering Phase ...................................................................................................... 69
6.2.1 Connections................................................................................................................70
6.2.2 RS485 LAN Wiring.................................................................................................... 72
6.3 Operating Phase.................................................................. ........................................ 73
6.3.1 Connections................................................................................................................73
6.4 Port Usage ..................................................................................................... .... ..... .... 75
6.5 Connecting the TAC Xenta 555 to a MicroNet Controller LAN............................... 76
6.5.1 Connecting to a MicroNet NCP network (MN MI not used)..................................... 77
6.5.2 Connecting to a MicroNet ARCNET network (MN MI used)................................... 78
6.5.3 Connecting to a Satchnet network (MIU not used).................................................... 78
7 TAC Xenta 701/711/721 79
7.1 Configuration Phase ................................................................................................... 79
7.1.1 Connections................................................................................................................80
7.2 Engineering Phase ...................................................................................................... 81
7.2.1 Connections................................................................................................................82
7.3 Operating Phase.................................................................. ........................................ 83
7.3.1 Directly Connected..................................................................................................... 83
7.3.2 Connections................................................................................................................84
7.3.3 Dialed-Up................................................................................................................... 85
7.3.4 Connections................................................................................................................86
7.4 Port Usage ..................................................................................................... .... ..... .... 87
8 TAC Xenta 731 89
8.1 Configuration Phase ................................................................................................... 89
8.1.1 Connections................................................................................................................90
8.2 Engineering Phase ...................................................................................................... 91
8.2.1 Connections................................................................................................................92
8.3 Operating Phase.................................................................. ........................................ 94
8.3.1 Directly Connected..................................................................................................... 94
8.3.2 Connections................................................................................................................95
8.3.3 Dialed-Up................................................................................................................... 97
8.3.4 Connections................................................................................................................98
6 (134) Schneider Electric Buildings AB, Feb 2011
04-00071-04-en

TAC Xenta 500/700/911/913, Product Manual Contents
8.4 Port Usage.................................................................................................................. 100
9 Connecting the OP7 to Xenta 700 103
9.1 Connecting the OP7 ................................................................................................... 103
9.2 Remote (cabinet door) mounting ............................................................................... 103
9.3 Wall mounting............................................................................................................ 104
9.4 Handheld terminal...................................................................................................... 104
10 TAC Xenta 911 105
10.1 Configuration Phase................................................................................................... 105
10.1.1 Connections................................................................................................................ 105
10.2 Engineering Phase...................................................................................................... 106
10.2.1 Connections................................................................................................................ 106
10.3 Operating Phase ......................................................................................................... 107
10.3.1 LonTalk Adapter........................................................................................................ 107
10.3.2 Connections................................................................................................................ 107
10.3.3 IP Modem........................................................ .... ..... .................................................. 108
10.3.4 Connections................................................................................................................ 108
10.3.5 Serial Gateway ........................................................................................................... 110
10.4 Port Usage..................................................................................................................111
11 TAC Xenta 913 113
11.1 Configuration Phase................................................................................................... 113
11.1.1 Connections................................................................................................................ 114
11.2 Programming and Operating Phase............................................................................ 115
11.2.1 Connections................................................................................................................ 115
11.3 Port Usage..................................................................................................................117
12 Engineering TAC Xenta 911 119
12.1 Programming the TAC Xenta 911 ............................................................................. 119
APPENDIX
A Hardware 125
A.1 Adapters .....................................................................................................................125
A.1.1 DB9/Female-to-RJ45/Female Adapter....................................................................... 125
A.1.2 DB25/Female-RJ45/Female Adapter......................................................................... 126
A.1.3 RJ45/Female-to-DB25/Male Adapter........................................................................ 127
A.1.4 DB9/Female-to-DB25/Male Adapter......................................................................... 128
A.2 Cables......................................................................................................................... 129
A.2.1 RJ45-to-RJ45 Rollover Cable.................................................................................... 129
A.2.2 RJ45-to-RJ10 Cable ................................................................................................... 129
A.2.3 RJ-45-to-RJ-45 TAC Xenta-to-Xenta Cable.............................................................. 130
Schneider Electric Buildings AB, Feb 2011 7 (134)
04-00071-04-en

Contents TAC Xenta 500/700/911/913, Product Manual
8 (134) Schneider Electric Buildings AB, Feb 2011
04-00071-04-en

INTRODUCTION
1 About this Manual


TAC Xenta 500/700/911/913, Product Manual 1 About this Manual
1 About this Manual
This handbook describes
• The hardware interface of the Xenta 500/700/911/913 devices
• Cables required for various communication configurations for the
Xenta 500/700/911/913 devices
• The upgrading of the system program for the
Xenta 500/700/911/913 devices
• The engineering procedure of the Xenta 911
For more information on engineering Xenta 500/700/913, see
• TAC Xenta Server – TA C Networks, Technical Manual
• TAC Xenta Server – Web Server, Technical Manual
• TAC Xenta Server – Controller, Technical Manual
• TAC Xenta Server – Gateway, Technical Manual
For more information on the use of the OP7 operator panel, together
with the TAC Xenta 700 series, see
• TAC OP7 Operator Panel, Mini Manual
Notes
• We are continuously improving and correcting our documentation. This manual may have been updated.
• Please check ExchangeOnline at http://extranet.tac.com for the
latest version.
The Xenta devices as well as other products mentioned in this manual,
must not be used for any other purposes than those for which they were
designed.
Installation, connection and repair should only be carried out by authorized personnel.
Schneider Electric Buildings AB, Feb 2011 11 (134)
04-00071-04-en

1 About this Manual TAC Xenta 500/700/911/913, Product Manual
!
1.1 Structure
The manual is divided into the following parts:
• Introduction
The Introduction section contains information on how this manual
is structured and where to find additional information.
• Reference
The Reference section contains comprehensive information about
the products. It also provides you with information on mounting
and electrical installation.
1.2 Typographic Conventions
Throughout the manual the following specially marked texts may occur.
Warning
• Alerts you that failure to take, or avoid, a specific action might
result in physical harm to you or to the hardware.
Caution
• Alerts you to possible data loss, breaches of security, or other
more serious problems.
Important
• Alerts you to supplementary information that is essential to the
completion of a task.
Note
• Alerts you to supplementary information.
Tip
• Alerts you to supplementary information that is not essential to
the completion of the task at hand.
12 (134) Schneider Electric Buildings AB, Feb 2011
04-00071-04-en

TAC Xenta 500/700/911/913, Product Manual 1 About this Manual
1.3 Terminology
• DHCP – Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. A protocol for
assigning dynamic IP addresses to devices on a network. With
dynamic addressing, a device can have a different IP address every
time it connects to the network. In some systems, the device's IP
address can even change while it is connected. DHCP also supports a mix of static and dynamic IP addresses.
• DNS – Domain Name System (or Service), an Internet service that
translates domain names into IP addresses. Because domain names
are alphabetic, they are easier to remember. The Internet however,
is based on IP addresses. Consequently, every time you use a
domain name a DNS service must translate the name into the corresponding IP address.
• FTP – File Transfer Protocol. An application used to transfer files
from one host to another and to store the files on the requesting
host.
• IP Network – A network (for example Internet or Intranet) using
the Internet Protocol (IP) and IP addressing.
• LTA – LonTalk Adaptor . A computer interface with the LonWorks
network.
• NTP – Network Time Protocol. An Internet standard protocol
(used on top of TCP/IP) that assures accurate synchronization to
the millisecond of computer clock times in a network of computers.
• SNMP – Simple Network Management Protocol. A set of proto-
cols for managing complex networks. SNMP works by sending
messages, called protocol data units (PDUs), to different parts of a
network.
• SNTP – Simple Network Time Protocol. A simplified version of
NTP.
• SSL – Secure Sockets Layer. A protocol developed by Netscape
for transmitting private documents via the Internet. By convention,
URLs that require an SSL connection start with https: instead of
http:.
• TCP/IP – Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol. The
suite of protocols that when combined create the “language of the
Internet”.
Schneider Electric Buildings AB, Feb 2011 13 (134)
04-00071-04-en

1 About this Manual TAC Xenta 500/700/911/913, Product Manual
1.4 Related Documents
• TAC Xenta Server – TAC Networks, Technical Manual
Part No.: 04-00121
• TAC Xenta Server – Web Server, Technical Manual
Part No.: 04-00122
• TAC Xenta Server – Controller, Technical Manual
Part No.: 04-00123
• TAC Xenta Server – Gateway, Technical Manual
Part No.: 04-00124
• TAC OP7 Operator Panel, Mini Manual
Part No.: 04-00072
14 (134) Schneider Electric Buildings AB, Feb 2011
04-00071-04-en

REFERENCE
2 TAC Xenta 500/700/911/913
3 Connecting the TAC Xenta to Your
Network
4 TAC Xenta 511
5 TAC Xenta 527
6 TAC Xenta 555
7 TAC Xenta 701/711/721
8 TAC Xenta 731
10 TAC Xenta 911
11 TAC Xenta 913
12 Engineering TAC Xenta 911


TAC Xenta 500/700/911/913, Product Manual 2 TAC Xenta 500/700/911/913
2 TAC Xenta 500/700/911/913
The Xenta 500/700/911/913 all share the same hardware design and
hardware layout. For a more detailed description on each Xenta device,
see the Docnet site at
2.1 Hardware
The Xenta device is designed around a microprocessor. The module
consists of two parts, an electronics unit containing the circuit boards
and contacts, and a terminal part including the terminal blocks.
Fig. 2.1: The Xenta device – Electronics and terminal.
• Power Outage Protection – Settings like configurations and web
pages are stored in the non-volatile (flash) memory and will not be
lost in the event of a power outage. A built-in capacitor maintains
operation of the RAM memory for at least 72 hours in the event of
a power outage.
• Real Time Clock – The real time clock provides the internal event
log with a time stamp. The capacitor maintains operation of the
clock for at least 72 hours in the event of a power outage.
• Mounting – The Xenta device is cabinet mounted on a TS 35 mm
norm rail EN 50022.
To simplify commissioning, the terminal part can be pre-mounted
in the cabinet.
If the Xenta device is to be wall-mounted, a wide range of standardized boxes are available.
Schneider Electric Buildings AB, Feb 2011 17 (134)
04-00071-04-en
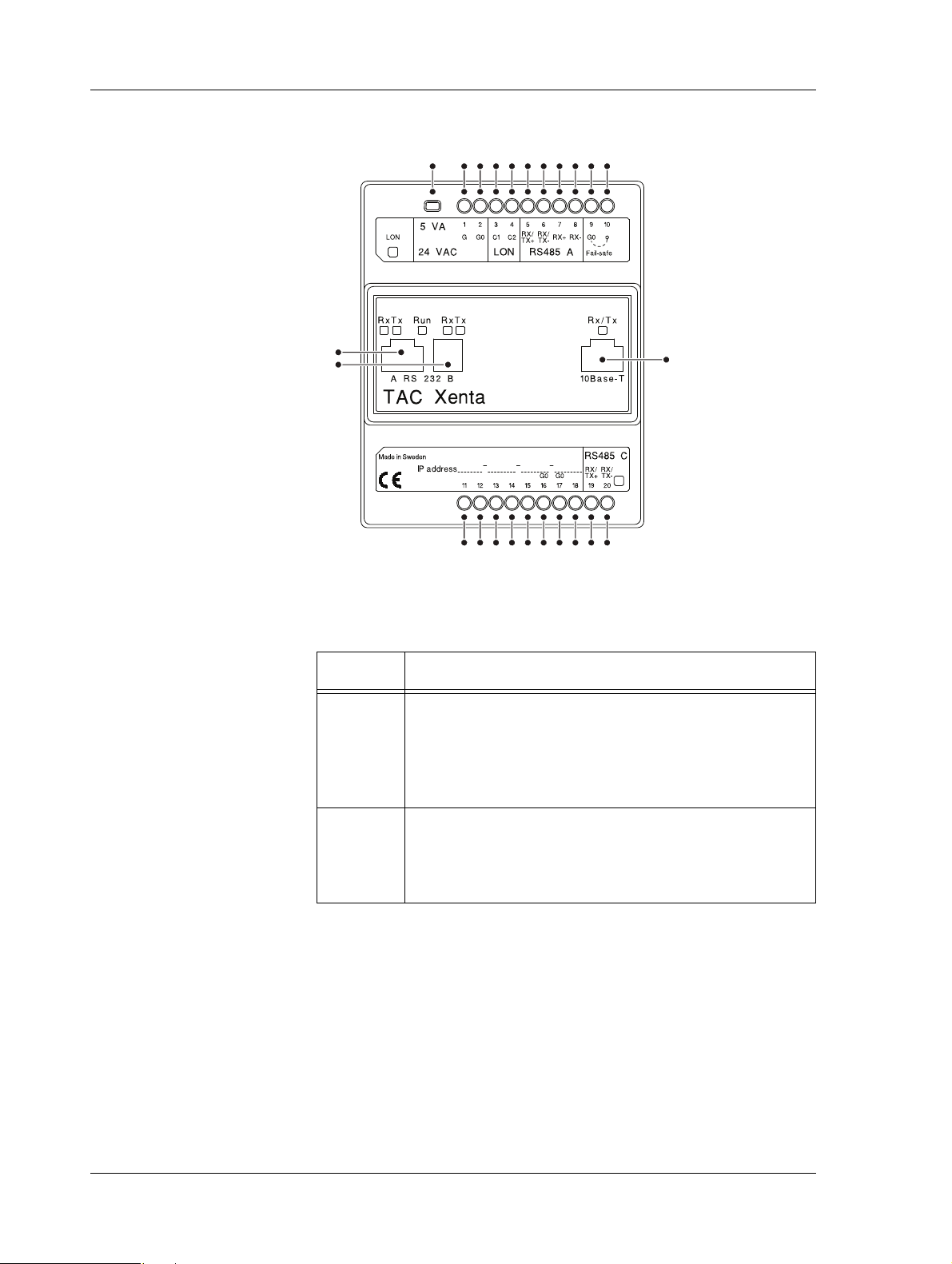
2 TAC Xenta 500/700/911/913 TAC Xenta 500/700/911/913, Product Manual
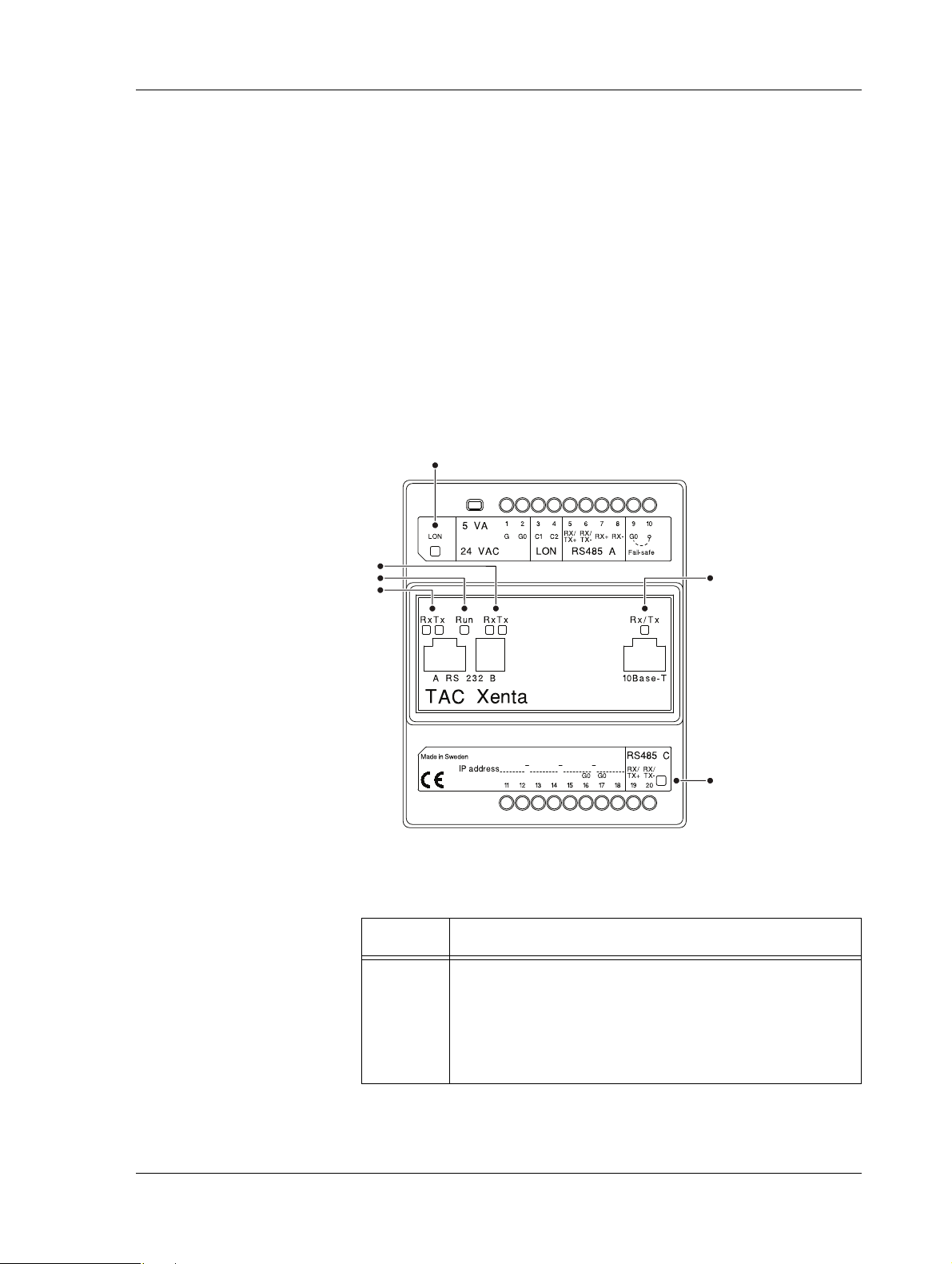
1 2345678910
11
12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
21
22
23
24
2.1.1 Communication Interface
Fig. 2.2: Connections on the Xenta device.
Table 2.1: Connections on the Xenta device.
Position Description
1–2 Power supply. Minimum cross-sectional area 0.75 mm2
(AWG-19).
• 1 (G) – 24 V AC (or DC+)
• 2 (G0) – Ground
3–4 LonWorks TP/FT-10 connection.
•3 (C1)
•4 (C2)
18 (134) Schneider Electric Buildings AB, Feb 2011
04-00071-04-en
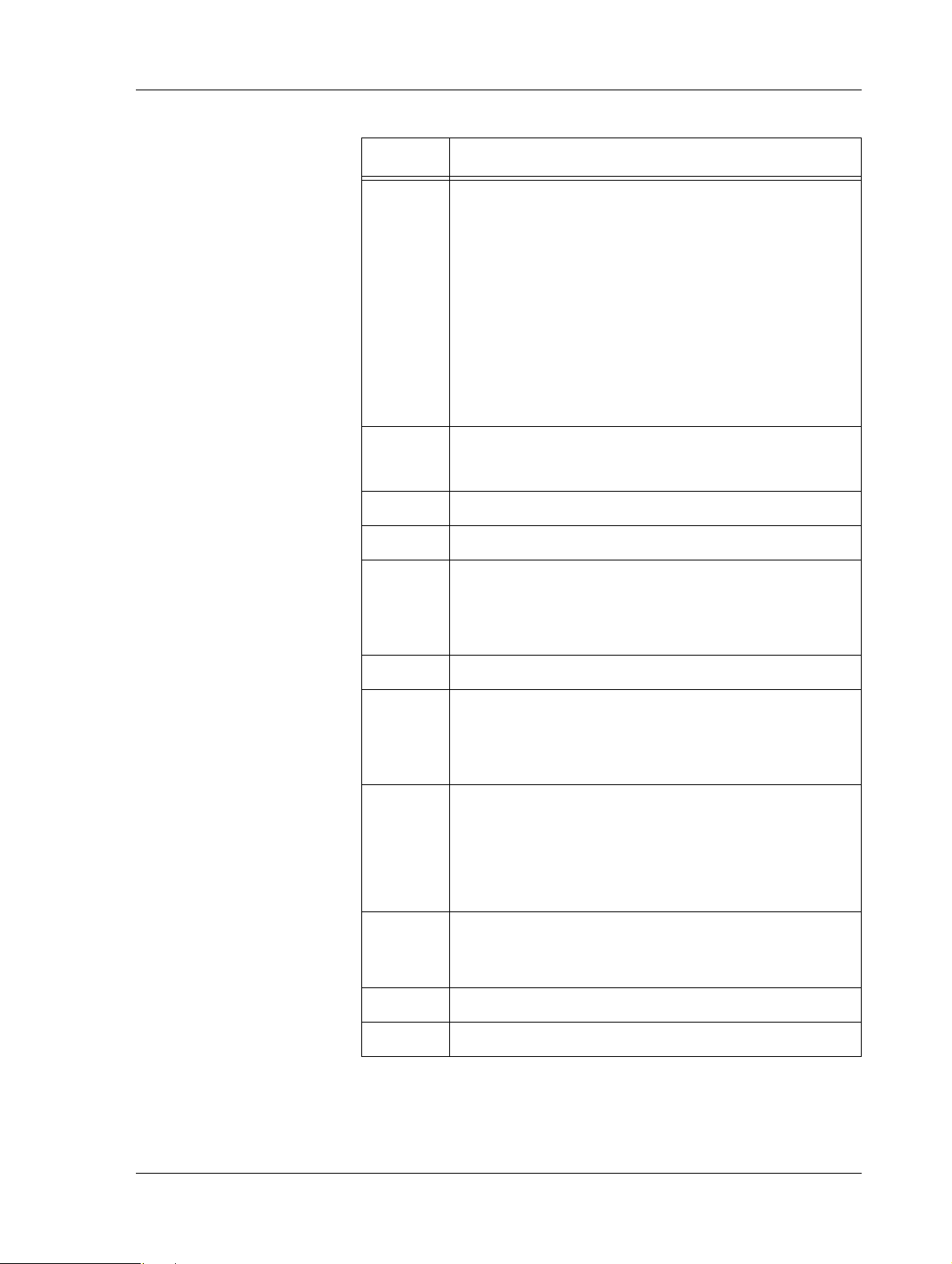
TAC Xenta 500/700/911/913, Product Manual 2 TAC Xenta 500/700/911/913
Table 2.1: Connections on the Xenta device. (Contd.)
Position Description
5–8
Internal
port A
RS-485 A connection.
•5 (RX/TX+)
• 6 (RX/TX-)
•7 (RX+)
•8 (RX-)
Note that the interface RS-232 A (position 21) and
interface RS-485 A (position 5–8) are internally connected to port A on the processor. Only one should be
connected.
9 Ground.
•9 (G0)
10 Fail-safe.
11–15 Unused.
16–17 Ground.
•16 (G0)
•17 (G0)
18 Unused.
19–20
Internal
port C
RS-485 C (SDLC) connection.
• 19 (RX/TX+)
• 20 (RX/TX-)
21
Internal
port A
RS-232 A connection.
Note that the interface RS-232 A (position 21) and
interface RS-485 A (position 5–8) are internally connected to port A on the processor. Only one should be
connected.
22
RS-232 B console connection.
Internal
port B
23 Ethernet 10Base-T connection.
24 Service pin.
Schneider Electric Buildings AB, Feb 2011 19 (134)
04-00071-04-en

2 TAC Xenta 500/700/911/913 TAC Xenta 500/700/911/913, Product Manual
Caution
• G0 equals GROUND.
• Only G0 may be connected to protective ground.
20 (134) Schneider Electric Buildings AB, Feb 2011
04-00071-04-en
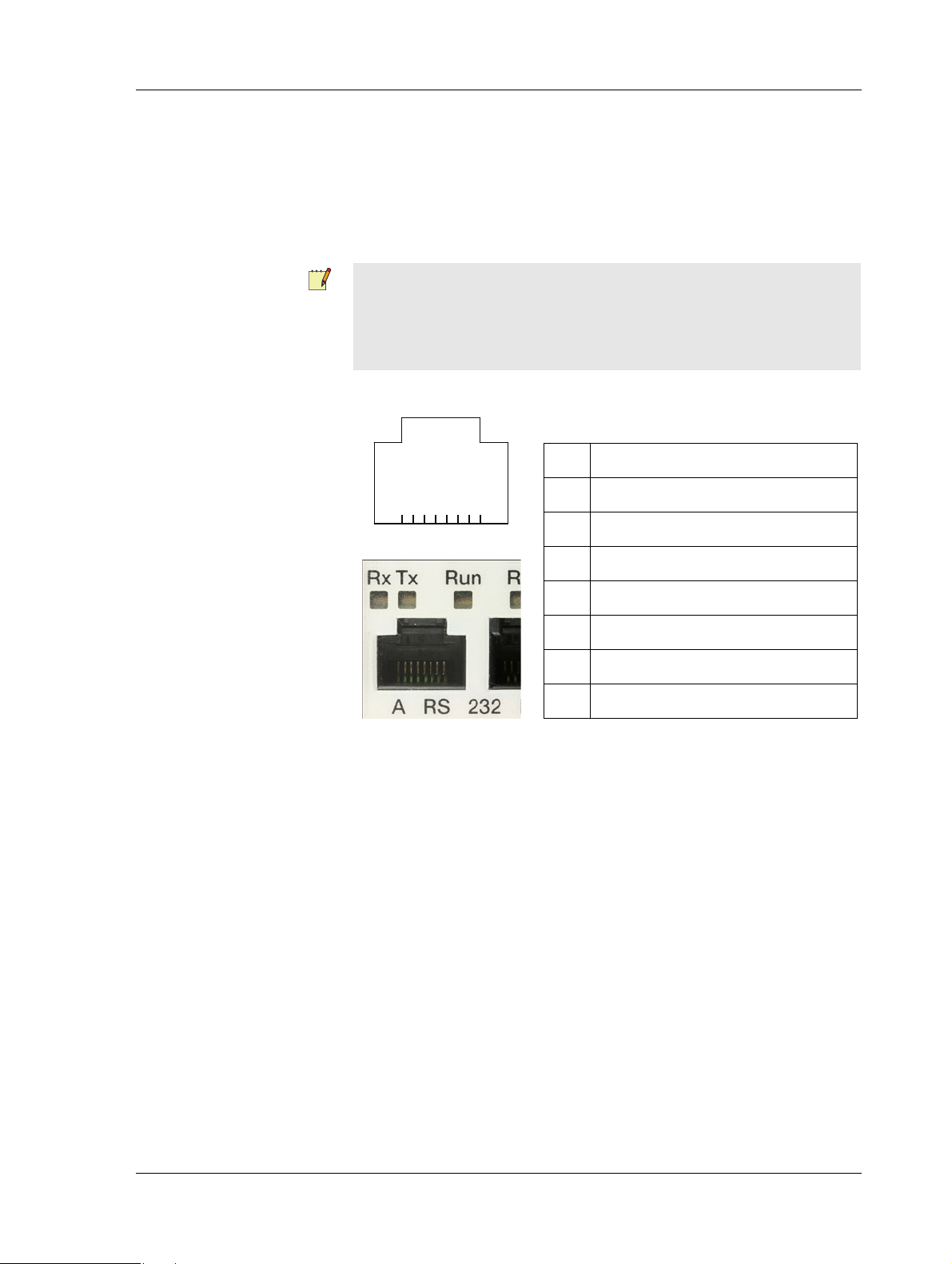
TAC Xenta 500/700/911/913, Product Manual 2 TAC Xenta 500/700/911/913
Table 2.2: Port pins – RS-232 A.
1 CTS/RI (input)
2 RTS (output)
3 TxD (output)
4 RxD (input)
5Ground
6 DSR (input)
7 DCD (input)
8DTR (output)
2.1.2 Port Pins
Serial Port – RS-232 A
The RS-232 A port (position 21) is used for serial communication
between the Xenta device and the connected unit. The connector is an
8-pin modular jack (RJ-45).
Note
• The interface RS-232 A (position 21) and interface RS-485 A
(position 5–8) are internally connected to port A on the processor. Only one should be connected.
The port uses the following signals:
87654321
Fig. 2.3: Connection using hardware signals for modem communication.
Schneider Electric Buildings AB, Feb 2011 21 (134)
04-00071-04-en

2 TAC Xenta 500/700/911/913 TAC Xenta 500/700/911/913, Product Manual
Table 2.3: Port pins – RS-232 B
1 TxD (output)
2 RxD (input)
3 Not used
4Ground
Table 2.4: Port pins – 10Base-T
1TX+
2TX3RX+
4–5 Connected to ground via 75 ohms
6RX7–8 Connected to ground via 75 ohms
Serial Port – RS-232 B
The RS-232 B port is used for communication between the Xenta
device and a computer. It is used for configuration of the Xenta device
using Windows HyperTerminal. The connector is a 4-pin modular jack
(RJ-10).
The port uses the following signals:
4321
Fig. 2.4: Connection using basic RS-232 signals, primarily intended for a
computer running, for example Windows HyperTerminal during the
configuration phase.
Ethernet Port – 10Base-T
The Ethernet 10Base-T port is used for communication between the
Xenta device and the TCP/IP network.
The port uses the following signals:
87654321
Fig. 2.5: Connection for a LAN (Ethernet) cable.
22 (134) Schneider Electric Buildings AB, Feb 2011
04-00071-04-en
TAC Xenta 500/700/911/913, Product Manual 2 TAC Xenta 500/700/911/913
1
4
3
2
6
5
2.1.3 Fail-Safe State
The Xenta can enter a fail-safe state if a severe problem arises in the system program.
The unit can be forced into fail-safe mode by shorting terminals 9 and
10 in Fig. 2.2 during power-up. This can be useful if the system program
experiences problems.
The overall Run indicator (position 3 in Fig. 2.6) will show a steady red
light in the fail-safe state.
2.1.4 LEDs
A number of light-emitting diodes (LEDs) on the Xenta device indicate
that the application program is running and when communication is in
progress.
Fig. 2.6: LEDs on the Xenta device.
Table 2.5: LEDs on the Xenta device.
Position Description
1 Neuron status indicator
Schneider Electric Buildings AB, Feb 2011 23 (134)
04-00071-04-en
•Off – Normal mode
• Red, blinking – Unconfigured mode
• Red, steady – Hardware fault
2 TAC Xenta 500/700/911/913 TAC Xenta 500/700/911/913, Product Manual
Serial Ports
A
C
B
Processor
RS-232
RS-485
RS-232
RS-485
Por t 21
Port pins 5, 6 (7, 8)
Por t 22
Port pins 19, 20
Table 2.5: LEDs on the Xenta device. (Contd.)
Position Description
2 Serial RS-232 B port activity indicators:
• RX – Indicates that data is received
• TX – Indicates that data is transmitted
3 Overall Run indicator
• Green, steady – Normal mode
• Green, blinking – Start mode
• Red, steady – Fail-safe mode
(see description below)
• Red, blinking – Unit fault
4 Serial RS-232 A port activity indicators:
• RX – Indicates that data is received
• TX – Indicates that data is transmitted
5 Serial RS-485 C port activity indicator.
6 Ethernet 10Base-T activity indicator
Note
• The LEDs for the RS-232 A interface (position 4) do not indicate
communication when using the RS-485 A interface although
internal port A is used for both.
Fig. 2.7: Internal serial ports and RS-232/485 interfaces.
24 (134) Schneider Electric Buildings AB, Feb 2011
04-00071-04-en

TAC Xenta 500/700/911/913, Product Manual 2 TAC Xenta 500/700/911/913
2.2 Configuring the TAC Xenta 500/700/911/913
The technician uses Microsoft Windows and HyperTerminal to initialize and configure the Xenta.
• For more information on how to connect the Xenta 511, see
Section 4.1, “Configuration Phase”, on page 43.
• For more information on how to connect the Xenta 527, see
Section 5.1, “Configuration Phase”, on page 53.
• For more information on how to connect the Xenta 555, see
Section 6.1, “Configuration Phase”, on page 67.
• For more information on how to connect the Xenta 701/711/721,
see Section 7.1, “Configuration Phase”, on page 79.
• For more information on how to connect the Xenta 731, see
Section 8.1, “Configuration Phase”, on page 89.
• For more information on how to connect the Xenta 911, see
Section 10.1, “Configuration Phase”, on page 105.
• For more information on how to connect the Xenta 913, see
Section 11.1, “Configuration Phase”, on page 113.
2.2.1 Configuration Data
To configure the Xenta, the following information should be obtained
from the network administrator:
• DHCP is used or not used
• IP address (only if DHCP is not used)
• Subnet mask (only if DHCP is not used)
• Default gateway
•DNS server
• Web site name (can be set later, using XBuilder)
• Domain name (only used as information)
• Host name (only used as information)
This information is used once you have connected to the Xenta using
HyperTerminal and a serial cable (null modem cable).
Schneider Electric Buildings AB, Feb 2011 25 (134)
04-00071-04-en
2 TAC Xenta 500/700/911/913 TAC Xenta 500/700/911/913, Product Manual
2.2.2 Configuring Windows HyperTerminal
When you use Windows HyperTerminal you need to set up a connection. Once created it can be used when required. In the example below
a Xenta 511 is configured.
To configure Windows HyperTerminal
1 Connect the Xenta to the engineering PC.
2 On the Start menu, point to All Programs, point to Accessories,
point to Communications, and then click HyperTerminal.
3 In the Connection Description dialog box, in the Name box, type
a name that describes the connection. In the example “Connection
to Xenta 511”.
4 In the Icon box, click the required icon.
5 Click OK.
6 In Connect To dialog box, in the Connect using list, click the
COM port used in step 1 above.
7 Click OK.
8 In the COM1 Properties dialog box, in the Bits per second list,
click 9600.
26 (134) Schneider Electric Buildings AB, Feb 2011
04-00071-04-en
TAC Xenta 500/700/911/913, Product Manual 2 TAC Xenta 500/700/911/913
9 In the Flow control list, click None.
10 Click OK.
11 On the File menu, click Save to save the HyperTerminal connec-
tion. The HyperTerminal for the Xenta is now ready to use.
12 Press ENTER to activate the command prompt.
Tips
• To reopen the HyperTerminal connection to the Xenta, click
Start, point to All Programs, point to Accessories, point to
Communications, point to HyperTerminal and then click Connection to Xenta 511. ht .
• You can also click Open on the File menu in HyperTerminal.
Schneider Electric Buildings AB, Feb 2011 27 (134)
04-00071-04-en
2 TAC Xenta 500/700/911/913 TAC Xenta 500/700/911/913, Product Manual
2.2.3 Configuring the TAC Xenta
The configuration parameters for the Xenta are entered using HyperTerminal. The parameters enable the Xenta to communicate using its
TCP/IP port.
Important
• Because the Xenta’s TCP/IP default parameters are set at the factory, you can immediately access it using a web browser and
change the parameters without having to use HyperTerminal.
The default parameters are:
• IP address: 192.168.255.2
• Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
To configure the TAC Xenta
1 Start Windows HyperTerminal using the connection created in
Section 2.2.2, “Configuring Windows HyperTerminal”, on
page 26.
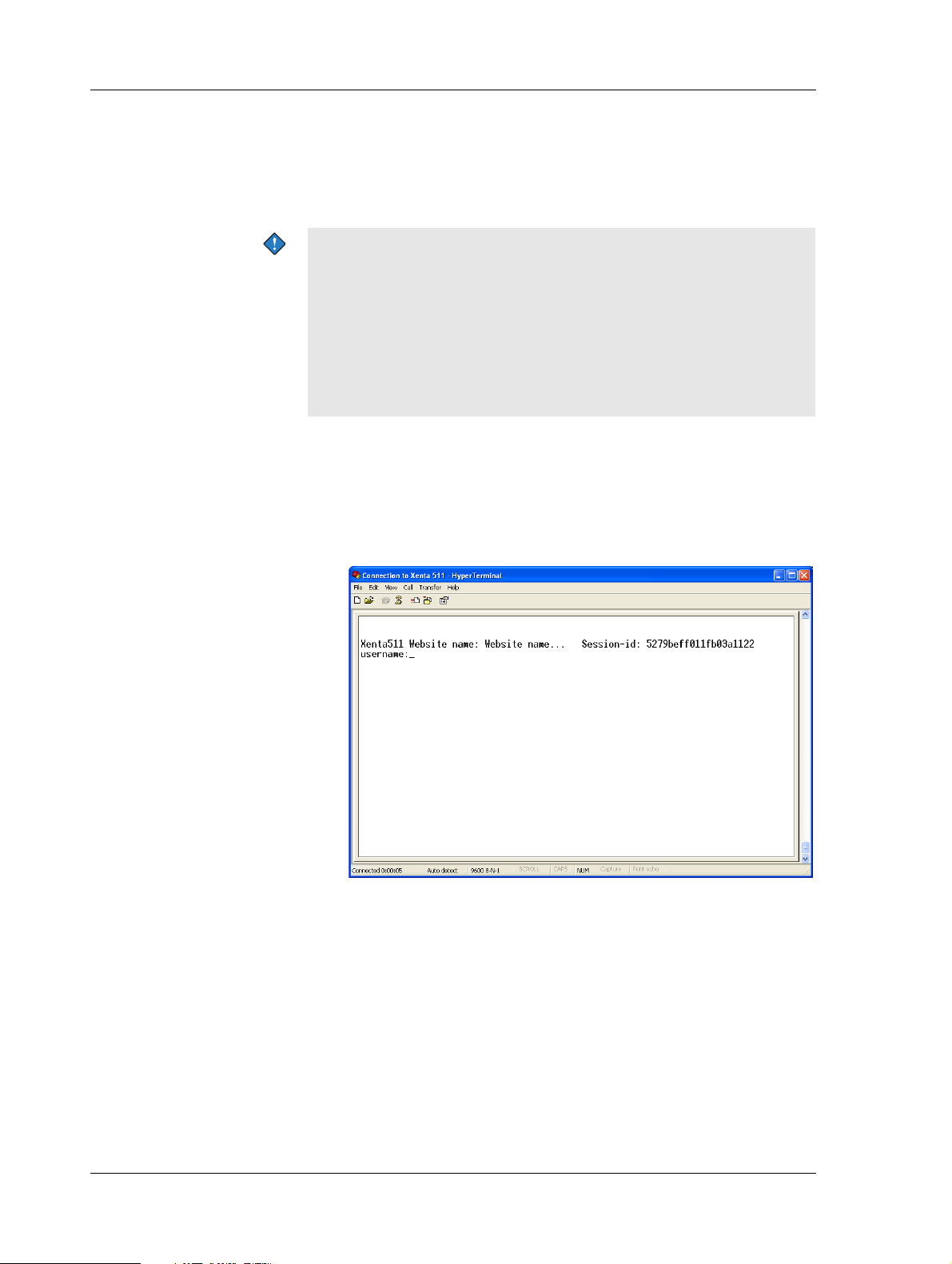
2 Press ENTER to activate the command prompt.
3 Type the user name “root” and press ENTER.
28 (134) Schneider Electric Buildings AB, Feb 2011
04-00071-04-en
TAC Xenta 500/700/911/913, Product Manual 2 TAC Xenta 500/700/911/913
4 Type the password “root” and press ENTER.
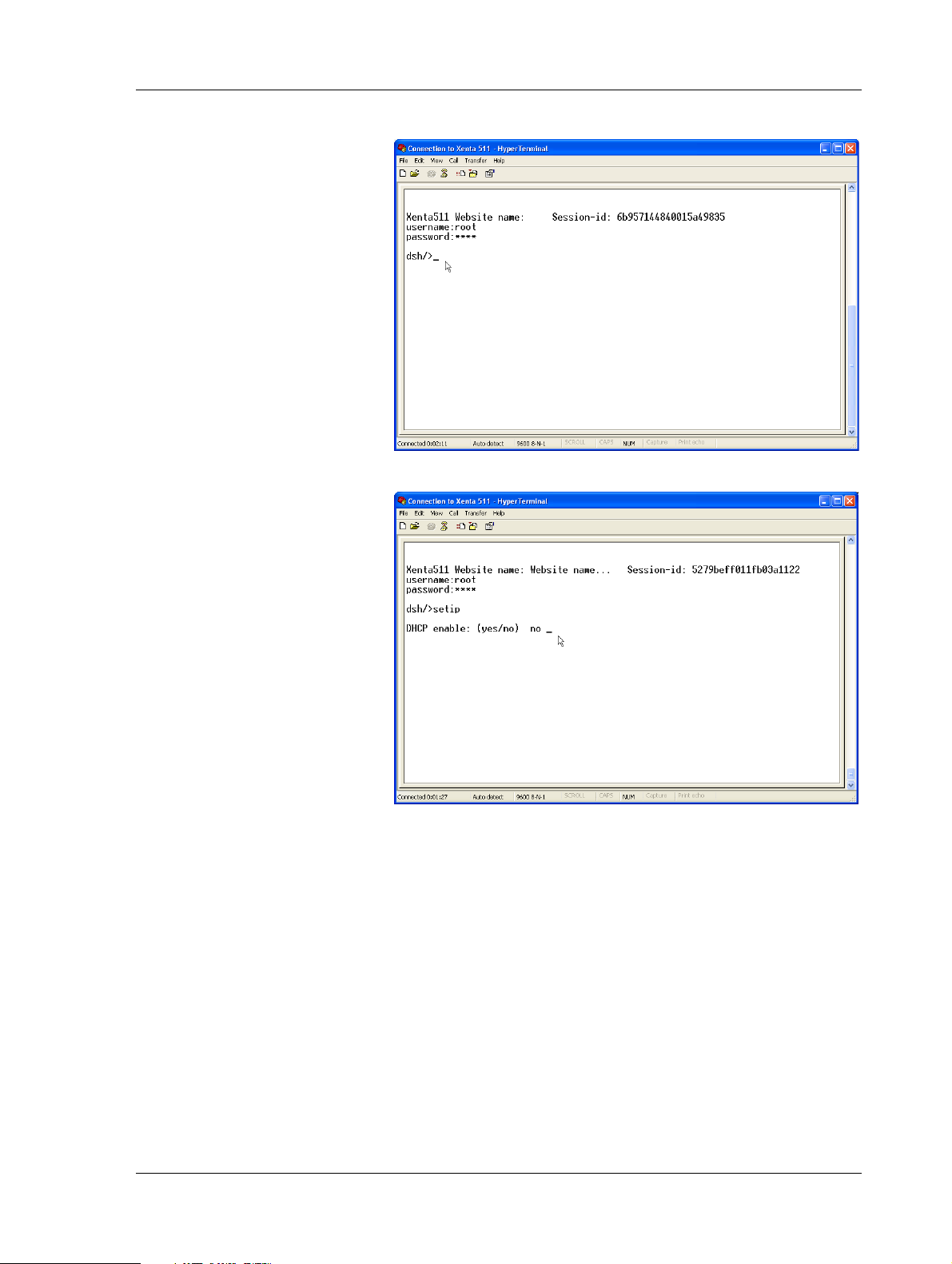
5 Type the command “setip” and press ENTER.
6 Type the configuration parameters, collected in Section 2.2.1,
“Configuration Data”, on page 25. Press ENTER after each entry.
Schneider Electric Buildings AB, Feb 2011 29 (134)
04-00071-04-en
2 TAC Xenta 500/700/911/913 TAC Xenta 500/700/911/913, Product Manual
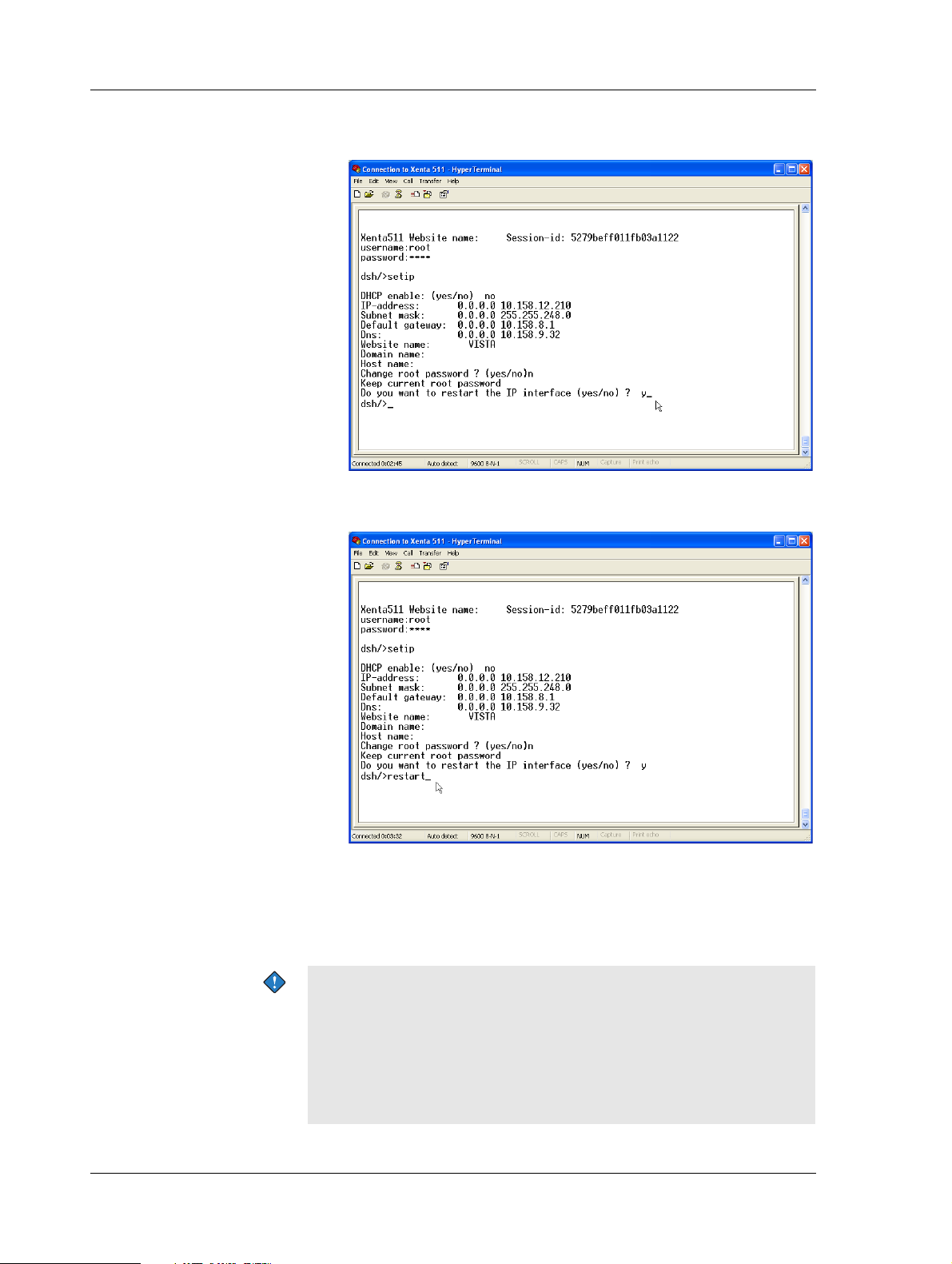
In the example, the configuration parameters appear as follows.
The root password is not changed.
7 T ype the command “restart” and press ENTER, to activate the new
configuration parameters.
8 Quit HyperTerminal.
The Xenta is now configured to communicate over TCP/IP, this means
that you can access the Xenta through a web browser and that you can
send web pages to the Xenta using XBuilder.
Important
• The password can be changed from a configuration page on the
web site in the Xenta.
• The user name and the password are used by the operator when
logging on to the web site and by XBuilder when sending the
project to the Xenta.
30 (134) Schneider Electric Buildings AB, Feb 2011
04-00071-04-en
 Loading...
Loading...