Page 1

Conext™ SW Inverter/Charger
Conext SW 2524 120/240 (865-2524)
Conext SW 4024 120/240 (865-4024)
Conext SW 4048 120/240 (865-4048)
Installation Guide
975-0639-01-01 Rev F
9-2018
solar.schneider-electric.com
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 2

Page 3

Conext SW Inverter/Charger
Conext SW 2524 120/240 (865-2524)
Conext SW 4024 120/240 (865-4024)
Conext SW 4048 120/240 (865-4048)
Installation Guide
solar.schneider-electric.com
Page 4

Copyright and Contact
Copyright © 2013-2018 Schneider Electric. All Rights Reserved. All trademarks are owned by Schneider Electric
Industries SAS or its affiliated companies.
Exclusion for Documentation
UNLESS SPECIFICALLY AGREED TO IN WRITING, SELLER
(A) MAKES NO WARRANTY AS TO THE ACCURACY, SUFFICIENCY OR SUITABILITY OF ANY TECHNICAL OR OTHER INFORMATION
PROVIDED IN ITS MANUALS OR OTHER DOCUMENTATION;
(B) ASSUMES NO RESPONSIBILITY OR LIABILITY FOR LOSSES, DAMAGES, COSTS OR EXPENSES, WHETHER SPECIAL, DIRECT,
INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL OR INCIDENTAL, WHICH MIGHT ARISE OUT OF THE USE OF SUCH INFORMATION.THE USE OF ANY
SUCH INFORMATION WILL BE ENTIRELY AT THE USER’S RISK; AND
(C) REMINDS YOU THAT IF THIS MANUAL IS IN ANY LANGUAGE OTHER THAN ENGLISH, ALTHOUGH STEPS HAVE BEEN TAKEN TO
MAINTAIN THE ACCURACY OF THE TRANSLATION, THE ACCURACY CANNOT BE GUARANTEED.APPROVED CONTENT IS
CONTAINED WITH THE ENGLISH LANGUAGE VERSION WHICH IS POSTED AT SOLAR.SCHNEIDER-ELECTRIC.COM.
Document Number: 975-0639-01-01 Revision: Rev F Date: 9-2018
Product Part Numbers: 865-2524, 865-4024, 865-4048
Contact Information solar.schneider-electric.com
Please contact your local Schneider Electric Sales Representative or visit our website at:
http://solar.schneider-electric.com/tech-support/
Information About Your System
As soon as you open your product, record the following information and be sure to keep your proof of purchase.
Serial Number
Product Number
Purchased From
Purchase Date
_________________________________
_________________________________
_________________________________
_________________________________
Page 5

About This Guide
Purpose
The purpose of this Installation Guide is to provide explanations and procedures
for installing the Conext SW Inverter/Charger to a main AC power source such as
an AC generator for off-grid application or AC mains (main power grid) for power
backup application.
Scope
The Guide provides safety and installation guidelines as well as information on
tools and wiring. Complete balance of system installation is not covered. For a
complete balance of system installation using the Conext SW AC Switchgear, DC
Switchgear, and solar charge controllers, consult the Conext SW System Guide.
It does not provide details about particular brands of batteries. You need to
consult individual battery manufacturers for this information.
Audience
Organization
The Guide is intended for use by anyone who plans to install an off-grid/backup
system involving the Conext SW Inverter/Charger. The information in this manual
is intended for qualified personnel. Qualified personnel have training,
knowledge, and experience in:
• Installing electrical equipment and PV power systems (up to 1000 volts).
• Applying all applicable installation codes.
• Analyzing and reducing the hazards involved in performing electrical work.
• Selecting and using Personal Protective Equipment (PPE).
This Guide is organized into:
Chapter 1, “Installation” covers installation instructions.
Chapter 2, “Specifications” covers product specifications.
Chapter 3, “Wiring Diagrams” covers overviews of Conext SW BOS installations
and wiring diagrams.
975-0639-01-01 Rev F iii
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 6
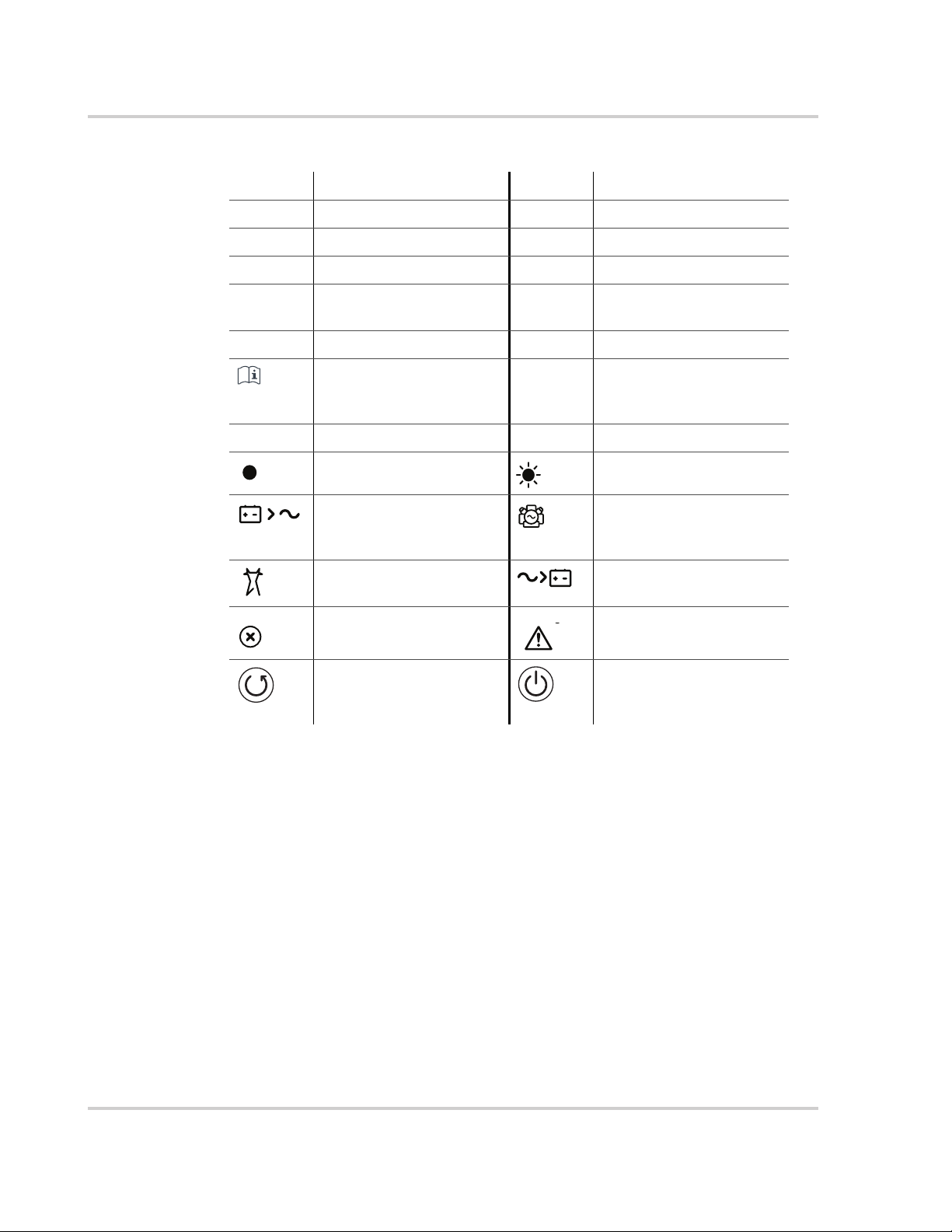
About This Guide
Abbreviations, Acronyms, and Symbols
AC Alternating Current LED Light Emitting Diode
AGS Automatic Generator Start SCP System Control Panel
BOS Balance of System SW Sine Wave
DC Direct Current VAC Volts, Alternating Current
PPE Personal Protective
Equipment
PV Photovoltaic IP20 Ingress protection rating
Reference to see guide
(or manual) for more
information
AC DC
Denotes a steady LED Denotes a flashing LED
Inv Enabled – see
Owner’s Guide for
definition.
AC IN – see Owner’s
Guide for definition.
Fault – see Owner’s Guide
for definition.
Clear Fault | Reset – see
Owner’s Guide for
definition.
VDC Volts, Direct Current
Ground
Gen Support – see
Owner’s Guide for
definition.
Charging – see Owner’s
Guide for definition.
Warning – see Owner’s
Guide for definition.
Inv Enable – see Owner’s
Guide for definition.
Related Information
You can find more information about Schneider Electric as well as its products
and services at solar.schneider-electric.com.
iv 975-0639-01-01 Rev F
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 7

Important Safety Instructions
READ AND SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS - DO NOT DISCARD
This guide contains important safety instructions for the Conext SW Inverter/
Charger that must be followed during operation and troubleshooting. Read and
keep this Installation Guide for future reference.
Read these instructions carefully and look at the equipment to become familiar
with the device before trying to install, operate, service or maintain it. The
following special messages may appear throughout this bulletin or on the
equipment to warn of potential hazards or to call attention to information that
clarifies or simplifies a procedure.
The addition of either symbol to a “Danger” or “Warning” safety label
indicates that an electrical hazard exists which will result in personal
injury if the instructions are not followed.
This is the safety alert symbol. It is used to alert you to potential
personal injury hazards. Obey all safety messages that follow this
symbol to avoid possible injury or death.
DANGER
DANGER indicates an imminently hazardous situation, which, if not avoided,
will result in death or serious injury.
WARNING
WARNING indicates a potentially hazardous situation, which, if not avoided,
can result in death or serious injury.
CAUTION
CAUTION indicates a potentially hazardous situation, which, if not avoided,
can result in moderate or minor injury.
NOTICE
NOTICE indicates a potentially hazardous situation, which, if not avoided, can
result in equipment damage.
975-0639-01-01 Rev F v
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 8

Safety
Safety Information
ELECTRICAL SHOCK AND FIRE HAZARD
Installation must be done by qualified personnel to ensure compliance with all
applicable installation and electrical codes and regulations. Instructions for
installing the Conext SW are provided here for use by qualified installers only.
Failure to follow these instructions will result in death or serious injury.
ELECTRICAL SHOCK AND FIRE HAZARD
• Read all instructions, cautionary markings, and all other appropriate
sections of this guide before installing the Conext SW.
• Exercise extreme caution at all times to prevent accidents.
• Do not cover or obstruct ventilation openings.
• Do not mount in a zero-clearance compartment. Overheating may result.
• Do not open nor disassemble the inverter/charger. There are no userserviceable parts inside.
• Do not expose to rain or spray.
• Disconnect and lockout all AC and DC sources before servicing. Servicing
includes maintenance or cleaning or working on any circuits connected to
the inverter/charger. See following note.
Failure to follow these instructions will result in death or serious injury.
DANGER
DANGER
NOTE: Turning off inverter mode using the Inv Enable switch on the front panel,
disabling the inverter and charger functions using the SCP, and putting the unit in
Standby mode will not reduce an electrical shock hazard.
vi 975-0639-01-01 Rev F
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 9

Safety
DANGER
ELECTRIC SHOCK HAZARD
• For indoor use only. This inverter/charger is designed for off-grid, solar,
backup, and hybrid applications.
• Do not operate the inverter/charger if it has been damaged in any way.
• Do not operate the inverter/charger with damaged or substandard wiring.
Wiring must be done by qualified personnel to ensure compliance with all
applicable installation codes and regulations.
Failure to follow these instructions will result in death or serious injury.
WARNING
EXPLOSION AND FIRE HAZARD
• Charge properly rated lead-acid (GEL, AGM, Flooded, or lead-calcium)
rechargeable batteries because other battery types may explode.
• When using Lithium-Ion batteries, ensure that the battery pack being used
includes a certified Battery Management System (BMS) with safety
controls.
• Do not work in the vicinity of lead-acid batteries. Batteries generate
explosive gases during normal operation. See note #1.
• Do not install and/or operate in compartments containing flammable
materials or in locations that require ignition-protected equipment. See
notes #2 and #3.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in death or serious injury.
NOTES:
1. Follow these instructions and those published by the battery manufacturer
and the manufacturer of any equipment you intend to use in the vicinity of the
battery. Review cautionary markings on these products.
2. This inverter/charger contains components which tend to produce arcs or
sparks.
3. Locations include any space containing gasoline-powered machinery like a
generator, fuel tanks, as well as joints, fittings, or other connections between
components of the fuel system.
CAUTION
FIRE AND BURN HAZARD
Do not cover or obstruct the air intake vent openings and/or install in a zeroclearance compartment.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in moderate or minor injury.
975-0639-01-01 Rev F vii
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 10

Safety
Precautions When Working With Batteries
IMPORTANT: Battery work and maintenance must be done by qualified
personnel knowledgeable about batteries to ensure compliance with battery
handling and maintenance safety precautions.
DANGER
ELECTRIC SHOCK HAZARD
• Determine if the battery is inadvertently earthed (grounded). If inadvertently
grounded, remove the source from ground.
• Avoid contact with any part of a grounded battery.
• Remove ground during installation and maintenance.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in moderate or minor injury.
WARNING
BURN AND FIRE HAZARD
• Always wear proper, non-absorbent gloves, complete eye protection, and
clothing protection.
• Remove all personal metal items, like rings, bracelets, and watches when
working with batteries. See CAUTION below.
• Never smoke or allow a spark or flame near batteries.
• Batteries can produce a short circuit current high enough to weld a ring or
metal bracelet or the like to the battery terminal, causing a severe burn.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in death or serious injury.
CAUTION
CHEMICAL, BURN, AND EXPLOSION HAZARD
• Never allow battery acid to drip when reading specific gravity or filling
battery.
• Make sure the area around the battery is well ventilated.
• Make sure the voltage of the batteries matches the output voltage of the
inverter/charger.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in moderate or minor injury.
viii 975-0639-01-01 Rev F
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 11

Safety
WARNING
LI
LIMITATIONS ON USE
Do not use in connection with life support systems or other medical
equipment.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in death or serious injury.
NOTICE
RISK OF INVERTER/CHARGER DAMAGE
• Never place the Conext SW Inverter/Charger unit directly above batteries;
gases from a battery will corrode and damage the inverter/charger.
• Never place the Conext SW Inverter/Charger unit in the same compartment
as batteries due to an explosive hazard.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in damage to equipment.
NOTICE
RISK OF BATTERY DAMAGE
Study and follow all of the battery manufacturer's specific precautions, such
as removing or not removing cell caps while charging, whether equalization is
acceptable for your battery, and recommended rates of charge.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in damage to equipment.
975-0639-01-01 Rev F ix
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 12

Safety
FCC Information to the User
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B
digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to
provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential
installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency
energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may
cause harmful interference to radio communications.
However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular
installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and
on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the
following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which
the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
x 975-0639-01-01 Rev F
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 13

Contents
Important Safety Instructions
Safety Information ----------------------------------------------------------vi
Precautions When Working With Batteries ----------------------------------------viii
FCC Information to the User ---------------------------------------------------x
1 Installation
Materials List ------------------------------------------------------------1–2
Conext SW Front and Side Panels ------------------------------------------1–3
Front Panel Buttons and Status LEDs -------------------------------------1–4
Conext SW AC/DC/Ports Side Panel --------------------------------------1–5
Conext SW Supplied Accessories ------------------------------------------1–6
Conext SW Required Accessory --------------------------------------------1–7
Installation Information -----------------------------------------------------1–8
Before You Begin the Installation -------------------------------------------1–8
Installation Codes ------------------------------------------------------1–8
Xanbus Network System ----------------------------------------------------1–9
Xanbus System --------------------------------------------------------1–9
Xanbus-enabled Products and Other Accessories ------------------------------1–10
Installation Planning ------------------------------------------------------ 1–11
Planning Preparations -------------------------------------------------- 1–11
Components of the Inverter Power System ----------------------------------- 1–11
AC, DC, and Network Components -------------------------------------1–12
Unpacking and Inspecting the Conext SW Inverter/Charger -----------------------1–16
Installation Tools and Materials ------------------------------------------- 1–17
Tools ----------------------------------------------------------- 1–17
Materials -------------------------------------------------------- 1–17
Inverter/Charger Installation------------------------------------------------- 1–18
Overview -----------------------------------------------------------1–18
Step 1: Choosing a Location for the Inverter/Charger ---------------------------- 1–19
Step 2: Mounting the Inverter/Charger --------------------------------------1–20
Step 3: Connecting the AC Input and AC Output Wires -------------------------- 1–22
General AC Wiring Considerations -------------------------------------- 1–22
AC System Bonding --------------------------------------------------- 1–23
Step 4: Installing the DC Switchgear and Connecting the DC Cables ---------------- 1–25
DC Connection Precautions ------------------------------------------- 1–25
Installing the DC Switchgear next to Conext SW Inverter/Charger ---------------- 1–26
Connecting the DC Cables to the DC Switchgear --------------------------- 1–27
Step 5: Connecting the BTS and Xanbus-enabled Components -------------------- 1–29
Step 6: Performing Checks Prior to Initial Start-Up ------------------------------ 1–31
Step 7: Testing Your Installation ------------------------------------------- 1–31
Testing in Invert Mode ----------------------------------------------- 1–32
975-0639-01-01 Rev F xi
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 14

Contents
Testing in Charge Mode and AC Bypass Mode ----------------------------- 1–32
Installation Complete ----------------------------------------------- 1–33
Multiple Unit Configuration ------------------------------------------------- 1–34
DC Connections for Multiple Unit Configuration -------------------------------- 1–36
Configuring the System for Multiple Unit Operation ----------------------------- 1–37
Search Mode Operation in Multiple Unit Configuration --------------------------- 1–38
Wiring Schematic ----------------------------------------------------- 1–38
Battery Information ------------------------------------------------------- 1–39
Battery Bank Sizing --------------------------------------------------- 1–39
Estimating Battery Requirements ------------------------------------------ 1–40
Calculating Battery Size --------------------------------------------- 1–40
Battery Banks ----------------------------------------------------- 1–41
Battery Bank Sizing Worksheet ---------------------------------------- 1–41
Restrictions on Motor Size ----------------------------------------------- 1–42
Battery Cabling and Hook-up Configurations --------------------------------- 1–43
Battery Parallel Connection ------------------------------------------- 1–43
Battery Series Connection -------------------------------------------- 1–44
Battery Series-Parallel Connections ------------------------------------- 1–44
2 Specifications
Inverter Specifications ----------------------------------------------------- 2–2
Charger Specifications ----------------------------------------------------- 2–3
AC Transfer Specifications -------------------------------------------------- 2–4
Physical Specifications ----------------------------------------------------- 2–5
Environmental Specifications ------------------------------------------------ 2–5
Regulatory-------------------------------------------------------------- 2–6
3 Wiring Diagrams
Single-Inverter System (Off-Grid/Power Backup)----------------------------------- 3–3
Single-Inverter System Renewable Energy (Solar)---------------------------------- 3–5
xii 975-0639-01-01 Rev F
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 15

Figures
Figure 1-1 Materials List------------------------------------------------------1–2
Figure 1-2 Conext SW Front and Side Panels---------------------------------------1–3
Figure 1-3 Front Panel Buttons and Status LEDs ------------------------------------1–4
Figure 1-4 AC and DC Terminals, Network and Communication Ports Panel-----------------1–5
Figure 1-5 Supplied Accessories -----------------------------------------------1–6
Figure 1-6 DC Switchgear ----------------------------------------------------1–7
Figure 1-7 Xanbus System Diagram Example -------------------------------------- 1–9
Figure 1-8 AC, DC, and Network Components ------------------------------------- 1–12
Figure 1-9 AC, DC, and Network Components ------------------------------------- 1–13
Figure 1-10 Conext SW Mounting Instructions --------------------------------------1–21
Figure 1-11 Conext SW AC INPUT and OUTPUT Connections--------------------------- 1–24
Figure 1-12 Installing the DC Switchgear------------------------------------------1–26
Figure 1-13 Conext SW DC Connections ------------------------------------------1–28
Figure 1-14 Conext SW BTS and Xanbus Connections -------------------------------- 1–30
Figure 1-15 Conext SW Front Panel---------------------------------------------- 1–32
Figure 1-16 Multiple (Dual) Unit Configuration Using Two Conext SW Units ----------------- 1–35
Figure 1-17 Connecting Battery Cables-------------------------------------------1–36
Figure 1-18 Multi Menu Screen ------------------------------------------------- 1–37
Figure 1-19 Batteries Connected in Parallel ----------------------------------------1–43
Figure 1-20 Batteries Connected in Series-----------------------------------------1–44
Figure 1-21 Batteries in Series-Parallel Connections----------------------------------1–44
Figure 2-1 Output Power versus Temperature Derating Graph --------------------------2–5
Figure 3-1 Single-Inverter System (Off-Grid/Backup) Overview --------------------------3–3
Figure 3-2 Single-Inverter System (Off-Grid/Backup) Wiring ----------------------------3–4
Figure 3-3 Single-Inverter System Renewable Energy (Solar) Overview --------------------3–5
Figure 3-4 Single-Inverter System Renewable Energy (Solar) Wiring ----------------------3–6
975-0639-01-01 Rev F xiii
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 16

xiv
Page 17

Tables
Table 1-1 AC Wire Size In and Out of the Inverter/Charger---------------------------- 1–14
Table 1-2 Recommended Battery Cable Sizes ------------------------------------ 1–15
Table 1-3 Recommended Fuse and Breaker Sizes --------------------------------- 1–15
Table 1-4 Battery Sizing Example --------------------------------------------- 1–41
Table 1-5 Battery Sizing Worksheet -------------------------------------------- 1–42
975-0639-01-01 Rev F xv
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 18

xvi
Page 19

1 Installation
The following topics will be covered in this
chapter.
• Materials List
• Installation Information
• Xanbus Network System
• Installation Planning
• Inverter/Charger Installation
• Multiple Unit Configuration
• Battery Information
• Wiring Diagrams
975-0639-01-01 Rev F 1–1
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 20
Installation
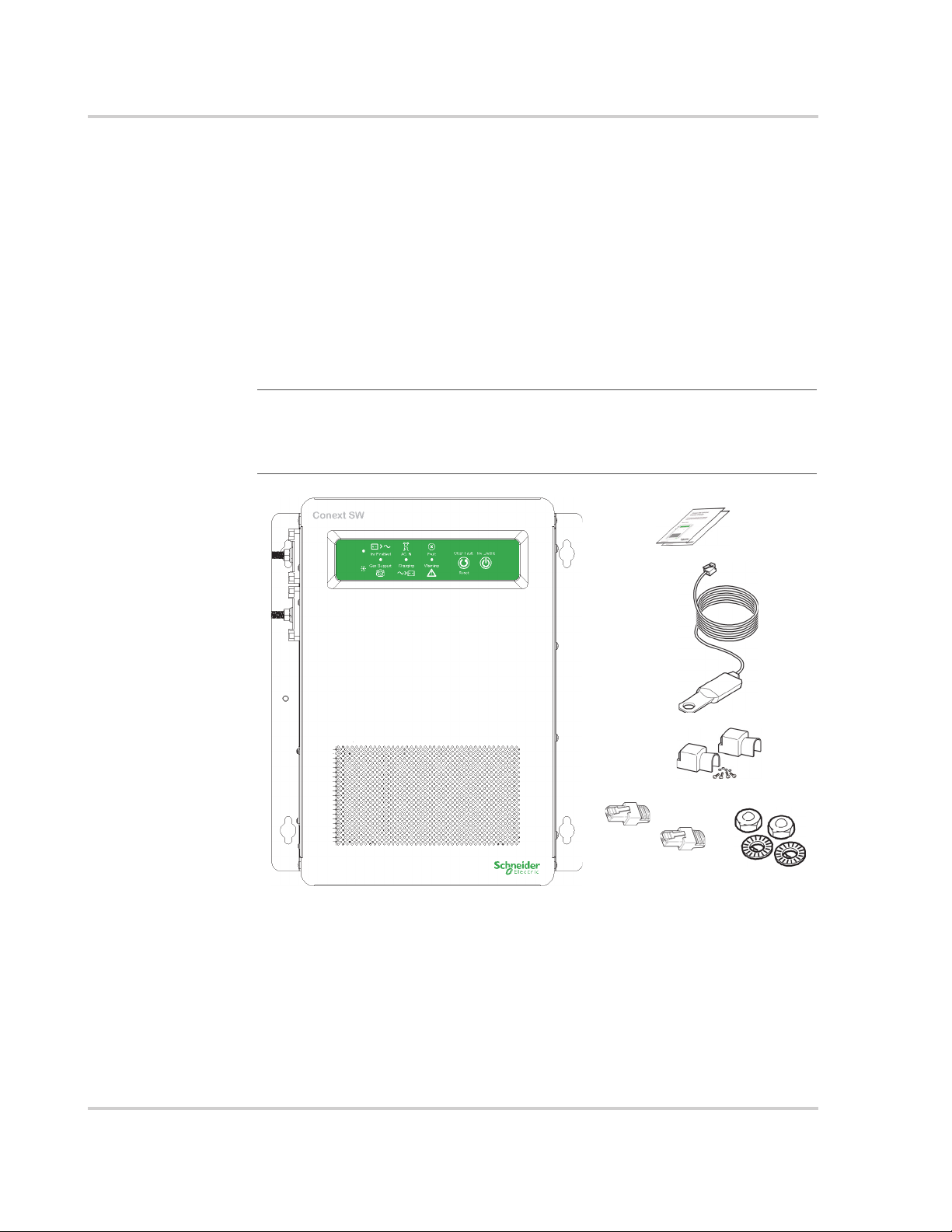
Materials List
The Conext SW ships with the following items:
• One Conext SW unit
• One set of owner’s and installation guides
• One Battery Temperature Sensor (BTS)
• Two Xanbus network terminators
• Two sets of 5/16
• Two DC terminal covers (red and black) with two sets of #6-32 screws
• One Installation bracket with one set of M6 nuts for mounting (not shown)
NOTE: If any of the items are missing, contact your dealer and/or sales
representative. For code-compliant installations in Canada and USA, the DC
Switchgear accessory is required. See “Conext SW DC Switchgear*” on
page 1–10.
"-8
nuts and washers for the DC terminals,
Figure 1-1 Materials List
1–2 975-0639-01-01 Rev F
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 21
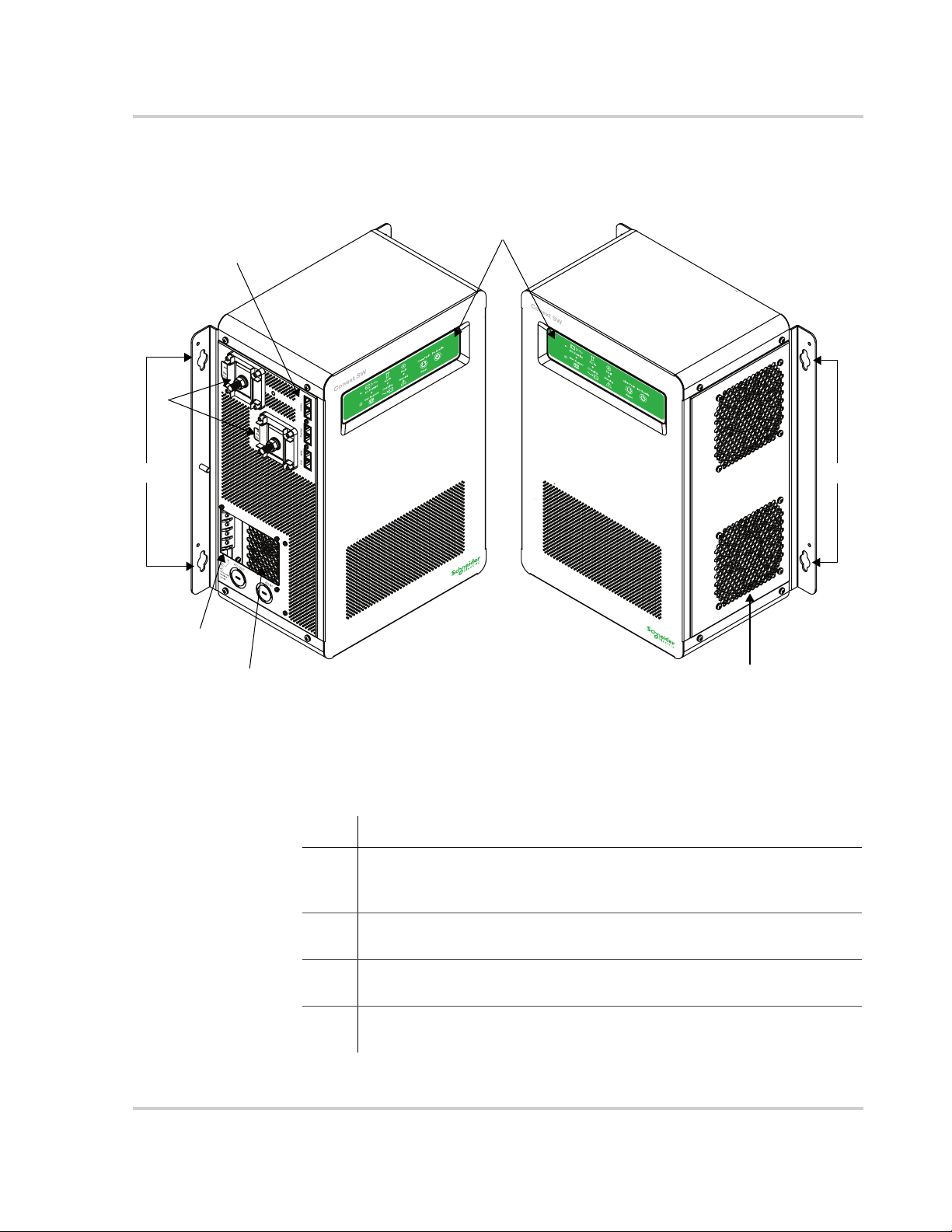
Conext SW Front and Side Panels
2
TOP TOP
3
Materials List
1
77
4
5
Figure 1-2 Conext SW Front and Side Panels
Before you begin to operate the Conext SW after installation, review the front
panel features shown in Figure 1-3 and described in the next table. A detailed
view of the lights and buttons on the front panel is also shown.
Item Description
1 Front Panel contains the Inv Enable and Clear Fault | Reset buttons, as
well as various LEDs (status indicator lights). See “Front Panel Buttons
and Status LEDs” on page 1–4.
2 Network and communications ports. See “AC and DC Terminals,
Network and Communication Ports Panel” on page 1–5.
3 DC battery terminals. See “AC and DC Terminals, Network and
Communication Ports Panel” on page 1–5.
4 AC Ground terminals. See “AC and DC Terminals, Network and
Communication Ports Panel” on page 1–5.
6
975-0639-01-01 Rev F 1–3
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 22
Installation
Item Description
5 AC line terminals. See “AC and DC Terminals, Network and
Communication Ports Panel” on page 1–5.
6 Two variable-speed cooling fans maintain a cool internal temperature
of critical components. The two fans control airflow through the
transformer and power compartments of the unit. Ensure at least
10" (254 mm) of clearance for proper ventilation.
7 Mounting holes for permanent installation. See “Step 2: Mounting the
Inverter/Charger” on page 1–20.
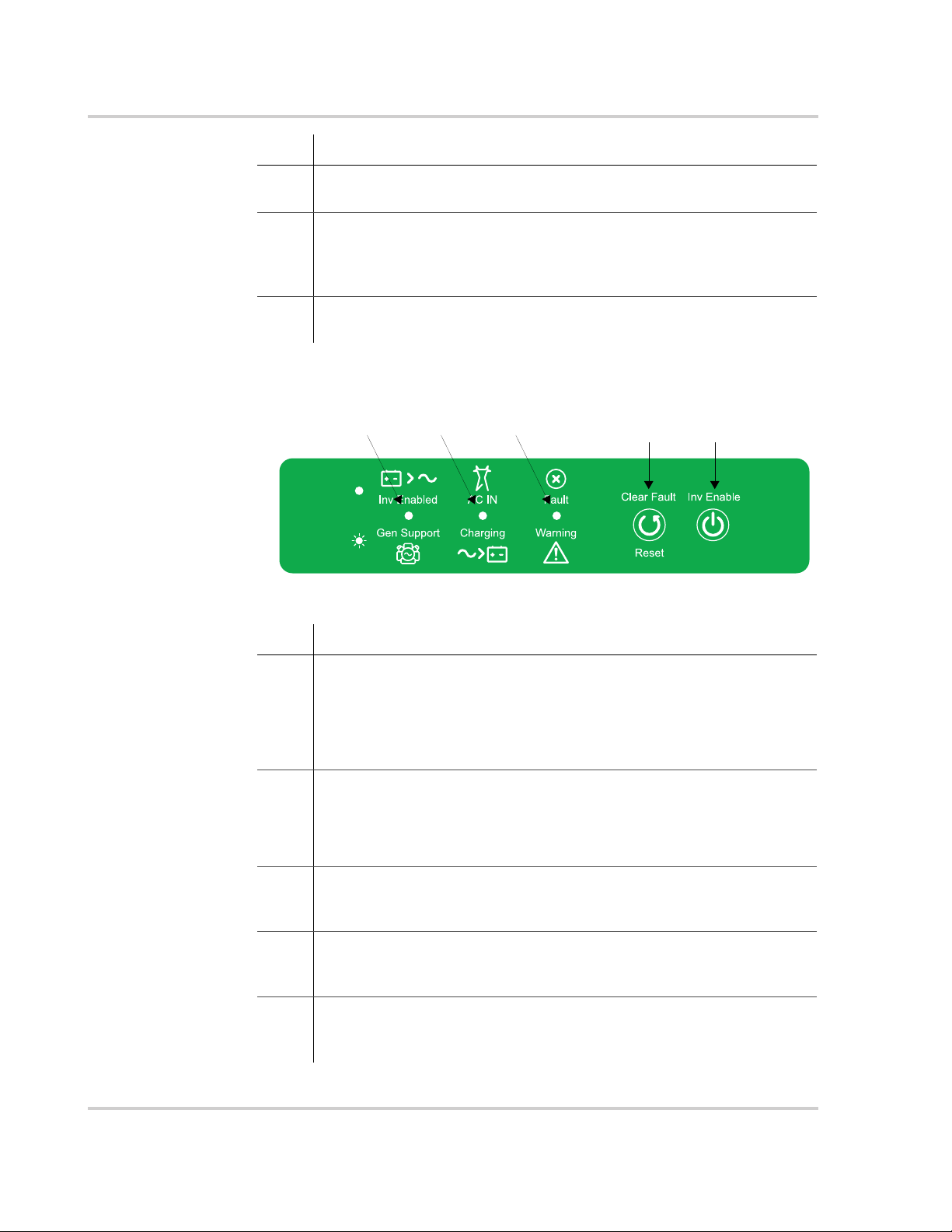
Front Panel Buttons and Status LEDs
54321
Figure 1-3 Front Panel Buttons and Status LEDs
Item Description
1 The Inv Enabled LED illuminates steadily when invert mode is enabled.
If AC is present and invert mode is enabled, this LED remains
illuminated even though AC power is being passed through.
Gen Support LED flashes intermittently when the inverter is in AC
support mode and load shaving mode.
2 When AC is present and qualified, the AC IN LED will illuminate steadily
indicating also that AC is passing through.
Charging LED flashes intermittently when the Conext SW is in charge
mode and is producing DC output to charge your batteries.
3 Fault | Warning LED illuminates steadily if a fault is detected (a fault
detection condition) and flashes intermittently when a warning
condition is active.
4 Clear Fault | Reset button is used to clear any detected faults if
pressed momentarily. If held down for more than three seconds, the
unit will reset (reboot) itself.
5 Inv Enable button is used to enable and disable inverter mode.
“Enabled” is different from the inverter being “on”. When enabled, the
inverter can be on or off. When disabled, the inverter is always off.
1–4 975-0639-01-01 Rev F
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 23
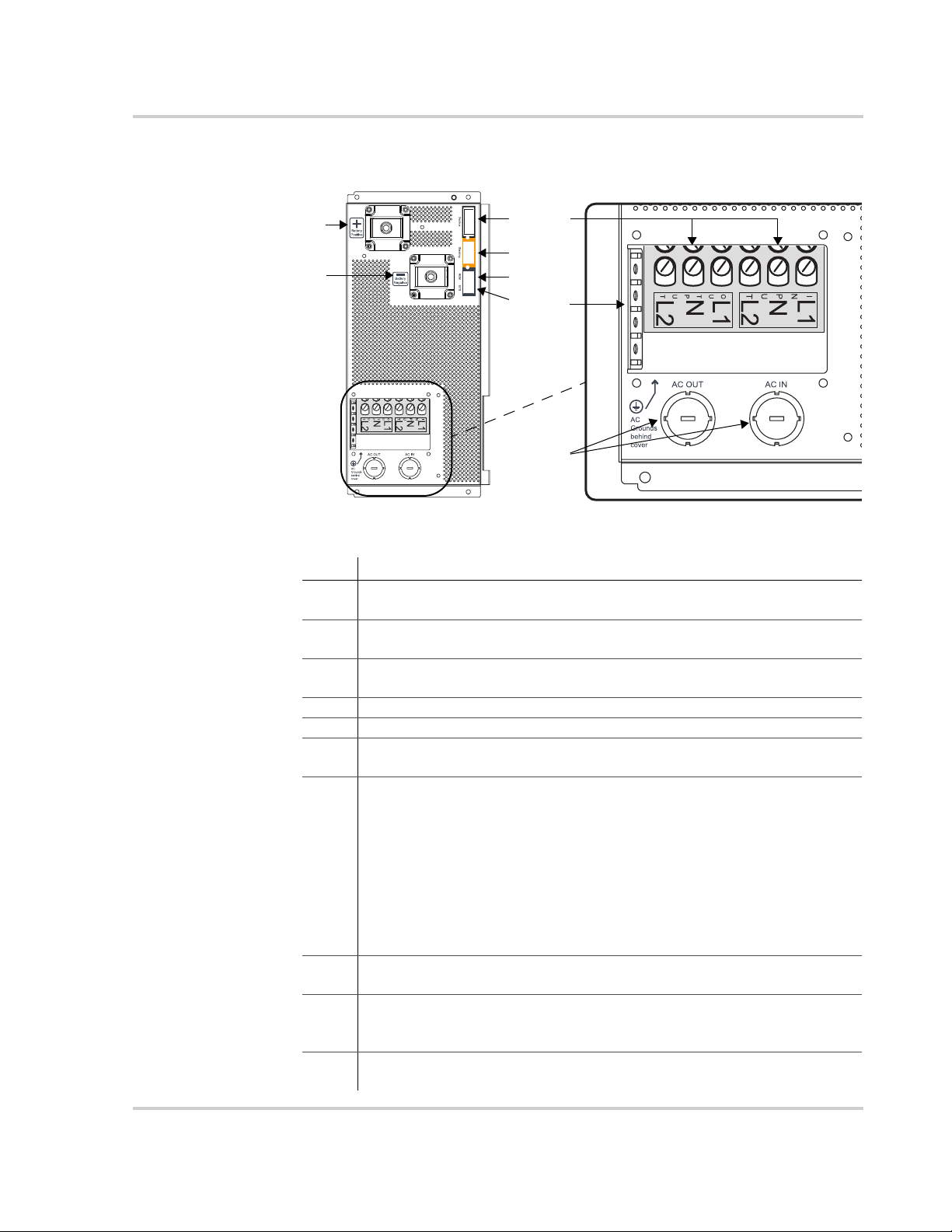
Conext SW AC/DC/Ports Side Panel
1
2
Figure 1-4 AC and DC Terminals, Network and Communication Ports Panel
Materials List
7
3
4
5
6
8
9
ab
Item Description
1 Battery Positive (+) (red) DC terminal connects to the positive bus bar
of the DC Switchgear.
2 Battery Negative (–) (black) DC terminal connects to the negative bus
bar of the DC Switchgear.
3 XANBUS interface ports are used to connect Xanbus-enabled devices
including the optional SCP and AGS.
4 STACKING port. Feature not available in this model.
5 Remote (REM) port provides connection for the on/off remote switch.
6 Battery temperature sensor (BTS) port provides connection for the
battery temperature sensor (supplied).
7 AC input/output lines wiring compartment access panel without the
compartment cover.
(a) AC Input terminal block is a screw-type terminal block for attaching
AC input wires. The terminals are labeled INPUT N for Neutral and
INPUT L1 and L2 for split-phase lines 1 and 2 respectively.
(b) AC Output terminal block is a screw-type terminal block for
attaching AC output wires. The terminals are labeled OUTPUT N for
Neutral and OUTPUT L1 and L2 for split-phase lines 1 and 2
respectively.
8 All Ground terminals are along the tab (as shown) of the AC wiring
compartment access panel opening.
9 AC knockouts (3/4" and 1") provide access for AC cables (both input
and output wiring). Detach the knockout covers and install strain-relief
clamps available in hardware and electrical stores.
Not
shown
AC wiring compartment cover that is taken out during wiring and put
back in when wiring has been completed.
975-0639-01-01 Rev F 1–5
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 24

Installation
Conext SW Supplied Accessories
Figure 1-5 Supplied Accessories
NOTE: If any of the supplied accessories are missing, contact customer service
for replacement. See “Contact Information solar.schneider-electric.com” on
page ii.
1
2
3
Item Description
1 BTS, the Battery Temperature Sensor consists of:
• Connector that plugs into the BTS port on the Conext SW.
• Sensor cable is 25 feet (7.6 meters).
• Sensor can be mounted on the side of the battery case or on
the negative battery terminal.
NOTE: The BTS continuously measures the temperature of the battery
and adjusts the charger output for a more accurate, temperaturecompensated charge.
2 Two sets of M6 nuts and washers are used to secure the DC
Switchgear’s bus bars to the DC battery terminals.
3 Two Xanbus network terminators are used to properly terminate each of
the two ends of the daisy-chained Xanbus network. For example, if the
SCP is connected to the inverter/charger, one terminator will be
plugged to the SCP, one network cable will connect both devices, and
one terminator will be plugged to the inverter/charger.
IMPORTANT: The SCP may perform erratically if the Xanbus network is
not properly terminated.
4 Two DC terminal covers (not shown) - not needed for installation with
the DC Switchgear which is required in Canada and the USA.
5 Installation bracket (not shown)
1–6 975-0639-01-01 Rev F
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 25

Conext SW Required Accessory
Figure 1-6 DC Switchgear
NOTE: The DC Switchgear is required by electrical code to be installed with the
Conext SW inverter/charger in installations within Canada and the USA.
Materials List
975-0639-01-01 Rev F 1–7
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 26

Installation
Installation Information
Before You Begin the Installation
Before beginning your installation:
• Read the entire Installation Guide so you can plan the installation from
beginning to end.
• Assemble all the tools and materials you require for the installation.
• Review the Important Safety Instructions on page v.
• Be aware of all safety and electrical codes which must be met.
ELECTRICAL SHOCK AND FIRE HAZARD
• All wiring must be done by qualified personnel to ensure compliance with
all applicable installation codes and regulations.
• Disconnect and lockout all AC and DC power sources.
• Disable and secure all AC and DC disconnect devices and automatic
generator starting devices.
Failure to follow these instructions will result in death or serious injury.
DANGER
Installation Codes
Applicable installation codes vary depending on the specific location and
application of the installation. Some examples are:
Applicable installation codes vary depending on the specific location and
application of the installation. Some examples are:
• National Electrical Code (NFPA 70)
• Canadian Electrical Code (CSA C22.1)
1–8 975-0639-01-01 Rev F
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 27

Xanbus Network System
Xanbus System
The Xanbus system includes the Conext SW and other Xanbus-enabled devices.
The Conext SW is the device in a Xanbus system that typically provides network
power—500 mA at 12 VDC. All of the Xanbus-enabled devices, such as the
Conext SW, the SCP, and the AGS are able to communicate their settings and
activity to each other.
Xanbus Network System
Xanbus Network ________
Solar
Charge
Controller
SCP
Xanbus System Control Panel
network terminator
Xanbus Automatic Generator Start
AGS
Conext
ComBox
Conext SW
network terminator
Figure 1-7 Xanbus System Diagram Example
The Xanbus-enabled designation (see below) means that this product works on a
Xanbus network. Xanbus-enabled products are:
• Simple to operate and routine tasks are automated.
• Controlled by software that eliminates analog signalling errors.
• Less susceptible to interference and line loss.
• Upgradable through new software releases.
NOTICE
EQUIPMENT DAMAGE
Do not remove Xanbus cables during system operation.
Failure to follow these instructions can damage connected equipment.
975-0639-01-01 Rev F 1–9
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 28

Installation
Xanbus-enabled Products and Other Accessories
5
6
3
Product/Accessory (Shown above) Product Number/s
1 Conext SW DC Switchgear* 865-1016*
2 Conext SW AC Switchgear 865-1017
3 MPPT 60 150 Solar Charge Controller 865-1030-1
MPPT 80 600 Solar Charge Controller (not shown) 865-1032
4 Conext SW On/Off Remote Switch (not shown) 865-1052
5 System Control Panel (SCP) 865-1050
6 Conext ComBox 865-1058
7 Automatic Generator Start (AGS) 865-1060
8 Conext Battery Monitor 865-1080-01
9 Battery Temperature Sensor (BTS) 808-0232-02
10 3-ft network cable (0.9 m) 809-0935
25-ft network cable (7.6 m) 809-0940
75-ft network cable (22.9 m) 809-0942
* required accessory for code-compliant installation in Canada and USA.
1
2
7
8
9
10
25-ft cable 75-ft cable3-ft cable
1–10 975-0639-01-01 Rev F
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 29

Installation Planning
Planning Preparations
This section provides information to help plan for a basic installation of the
Conext SW. There are two key factors that will have a major impact on system
performance.
1. Size and Length of DC Cables
To select the appropriate size and length of DC cables, see “DC Cabling” on
page 1–14.
The DC cables should be as short as possible and large enough to handle the
required current, in accordance with the electrical codes or regulations
applicable to your installation. If there are long battery cables which are in
excess of 3 meters each and not of sufficient size, the voltage drop across the
cables will have a negative impact on overall system performance.
2. Mounting Location of the Conext SW
See “Step 1: Choosing a Location for the Inverter/Charger” on page 1–19.
Installation Planning
Components of the Inverter Power System
Inverter power systems vary depending on the power requirements of the user
and where the user is located. Inverter power systems typically involve one AC
source, one DC source, one inverter/charger, and a control and monitoring
device.
One example is an off the grid house with an AC generator, a battery, and a
Conext SW inverter/charger with a System Control Panel (SCP). Another example
is a house in the city, that is connected to the power grid but needs a power
backup solution to cope with rolling blackouts during summer. Some power
systems involve harvesting renewable energy such as solar energy in
conjunction with off-grid or power backup solutions.
Before installing a Conext SW inverter/charger, know your power requirements
then divide the components of the power system into AC, DC, and Xanbus
network devices. Xanbus network devices control and monitor the Conext SW
inverter/charger as well as AC generators and solar panels.
975-0639-01-01 Rev F 1–11
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 30

Installation
AC, DC, and Network Components
The illustration below shows the different components that can go into a Conext
SW inverter/charger installation.
/
DC Sources
AC Loads
Inverter panel
Figure 1-8 AC, DC, and Network Components
AC Generator for
off-grid applications
Xanbus Network
Devices
AC Sources
Grid for power backup
applications
1–12 975-0639-01-01 Rev F
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 31

The illustration below shows which components you may need before you begin
your installation.
DC Components Xanbus Network Components
•
24- or 48-volt battery
Component -Batteries” on page 1–14.
• DC-rated fuse and/or circuit breaker,
see “DC Disconnects and Overcurrent
Devices” on page 1–15.
• Conext SW DC Switchgear (required
component in Canada and USA)
• Battery Temperature Sensor
(BTS, supplied)
• DC cables, see “DC
Cabling” on page 1–14.
• solar panel for renewable
energy application
or batteries, see “DC
• System Control Panel (SCP)
• Automatic Generator Start (AGS)
• Battery Monitor
• Solar charge controller
• Conext ComBox
• CAT-5 network cables
• Xanbus network terminators
(supplied)
Installation Planning
120/240-volt split-phase, 60 Hz
AC Loads (AC OUTPUT)
• Inverter electrical
distribution panel
• AC-rated 30-amp circuit
breakers to provide overcurrent
protection and means of disconnect
• Conext SW AC Switchgear
(recommended)
• AC cable (4-wire) and connectors, see
“AC Wiring” on page 1–13.
Figure 1-9 AC, DC, and Network Components
AC Wiring Definition AC wiring includes input wiring (all the wires and connectors
between the main AC source panel and the inverter/charger AC INPUT) and
output wiring (all the wires between the inverter/charger AC OUTPUT and the AC
load panels, circuit breakers, and loads).
protection and means of disconnect
• Transfer switch (between two AC
sources, if applicable)
• Conext SW AC Switchgear
(recommended)
• AC cable (4-wire) and connectors, see
“AC Wiring” on page 1–13.
120/240-volt split-phase, 60 Hz
AC Source (AC INPUT)
• Main electrical distribution
panel (grid and/or generator)
• AC-rated 30-amp circuit
breakers to provide overcurrent
Type The type of wiring required varies according to the electrical codes or
regulations applicable to your installation. Wiring may be solid in multi-conductor
cables, but stranded wire is required if single conductors are used. All wiring
must be rated 90 °C or higher.
975-0639-01-01 Rev F 1–13
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 32

Installation
Size of AC Input Wiring Wire size must be coordinated with the overcurrent
protection provided ahead of the wire involved, in accordance with the electrical
codes or regulations applicable to your installation.
Therefore, the wiring used between the main AC source panel’s circuit breaker
and the inverter/charger AC INPUT must be sized to match the input breaker
rating.
Table 1-1 AC Wire Size In and Out of the Inverter/Charger
Conext SW
Breaker Size Used 30 amps per line
Wire Size No. 8 AWG
Color Coding L1/L2: red or black
N: white or gray
: green or bare
Size of AC Output Wiring Wire size must be coordinated with the current the
wiring will carry. For example, this current may be determined by the 15-amp
maximum inverter current, or by the bypass current, which is determined by the
overcurrent protection provided ahead of the Conext SW 4024 120/240.
Size of Wiring Downstream of the AC Output Breaker The wiring used
between the AC output breaker and your loads must be sized to match the
output breaker.
DC Component Batteries
DC Cabling Definition DC cabling and connectors between the batteries, the DC
The Conext SW system requires a 24-volt or 48-volt, lead-acid deep-cycle
battery or group of batteries to provide the DC current that the inverter/charger
converts to AC power. The battery may be a flooded, gel, or AGM type.
See “Battery Information” on page 1–39 for information on:
• Estimating the battery size that will meet your requirements.
• Designing battery banks.
• Restrictions on the size of appliances.
For information on cabling and hooking up batteries, see “Battery Cabling and
Hook-up Configurations” on page 1–43.
For detailed information about specific brands of batteries, consult individual
battery manufacturers or a local battery distributor.
disconnect and overcurrent protection device, and the inverter/charger.
Type All installations require multi-strand insulated cables. The DC cables must
be copper and must be sized based on 75 °C ampacity and must have an
insulation rating of at least 75 °C.
Size and Length See Table 1-2 for required DC cable length, cable size and
required fuse size for the Conext SW. Wire size is usually marked on the cables.
1–14 975-0639-01-01 Rev F
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 33

Installation Planning
Table 1-2 Recommended Battery Cable Sizes
Model Maximum
Current (A)
a
Conduit
b
Cable Length
<5ft
Cable Length
5to10ft
SW 2524 120/240 120 1 AWG
SW 4024 120/240 200 3/0 AWG
SW 4048 120/240 120 1 AWG
a.From National Electrical Code (NEC) requirements.
b.Per NEC Table 310.16 for 177 °F (75 °C) rated copper conductor.
IMPORTANT: Using a smaller gauge cable or a longer cable may cause the
inverter to shut down under heavy load.
WARNING
FIRE AND BURN HAZARD
Do not use battery cables that are insufficiently sized for expected current.
Check local electrical codes carefully.
Failure to follow this instruction can result in death or serious injury.
DC Disconnects
and Overcurrent
Devices
Conext SW DC
Switchgear
The DC circuit from the battery to the inverter/charger must be equipped with a
disconnect and overcurrent protection device. Refer to your applicable
installation code.
TypeThis device usually consists of a circuit breaker, a “fused-disconnect,” or a
separate fuse (installed at each positive cable near the battery terminal) and DC
disconnect. Do not confuse AC circuit breakers with DC circuit breakers. They
are not interchangeable.
RatingThe rating of the fuse or breaker must be matched to the size of cables
used in accordance with the applicable installation codes.
LocationThe breaker or fuse and disconnect should be located as close as
possible to the battery in the positive cable. Applicable codes may limit how far
the protection can be from the battery.
Table 1-3 Recommended Fuse and Breaker Sizes
Model Fuse Size (A) Minimum Breaker Size (A)
SW 2524 120/240 250 250
SW 4024 120/240 250 250
SW 4048 120/240 250 250
The DC Switchgear (part number: 865-1016) provides complete DC disconnect
and overcurrent protection for the Conext SW Inverter/Charger. The Conext DC
Switchgear contains a master DC breaker that stops DC power from the main DC
source. The DC Switchgear must be installed with the Conext SW Inverter/
Charger in Canada and USA.
975-0639-01-01 Rev F 1–15
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 34

Installation
Unpacking and Inspecting the Conext SW Inverter/Charger
CAUTION
HEAVY LOAD HAZARD
Do not lift the unit by yourself. Use two people to lift and mount the unit. Always
use proper lifting techniques during installation to prevent injury.
Failure the follow these instructions can result in injury.
To unpack and inspect:
IMPORTANT: Keep the carton and packing material in case you need to return
the Conext SW for servicing.
1. Unpack the unit and check the materials list. If anything is missing from the
shipping box, contact your local Schneider Electric customer service
representative. See page ii for information.
2. Record the serial number of the Conext SW and other purchase information
in the beginning section under Information About Your System of the Conext
SW Inverter/Charger Owner’s Guide.
3. Save your purchase receipt to use as proof of purchase. This receipt is
required if the inverter/charger requires warranty service.
4. Save the original shipping carton and packing materials. If the inverter/
charger needs to be returned for service, it should be shipped in the original
carton. Packing the Conext SW in the original shipping carton is also a good
way to protect the inverter/charger if it ever needs to be moved.
1–16 975-0639-01-01 Rev F
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 35

Installation Tools and Materials
Tools
You will need the following tools to install the Conext SW and the battery
temperature sensor.
❐ Wire stripper
❐ Crimping tools for fastening lugs and terminals on DC cables
❐ Phillips screwdriver: #2
❐ Slot screwdriver (1/4" [6mm] wide blade max.)
❐ Needle-nose pliers
❐ Wrench for DC terminals and Installation bracket: 5/16" and M6
❐ Power drill/driver
Materials
You will need the following materials to complete your installation:
❐ DC Switchgear
❐ Strain-relief clamp(s) for AC cables (not provided): 3/4" and/or 1"
❐ DC battery cables sized according to Table 1-2 on page 1–15
❐ Terminals and/or crimp connectors for DC cables (3/8" [9.5mm] stud size)
❐ AC and DC disconnect switches and overcurrent protective devices and
connectors as required. See page 1–14
❐ AC output and input wire. See “AC Wiring” on page 1–13
❐ If the AC ground wire is stranded, each ground wire requires a ring terminal
❐ Four M6 nuts to secure the unit to the installation bracket (supplied)
❐ Four #12 (or equivalent) screws or bolts to mount the installation bracket to a
non-flammable wall (see page 1–19 for definition)
❐ Four #10 (or equivalent) screws for securing the DC Switchgear to the
installation bracket
Installation Planning
975-0639-01-01 Rev F 1–17
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 36

Installation
Inverter/Charger Installation
Overview
This section provides detailed information on installing the Conext SW. The
overall procedure is divided into seven steps:
Step 1: Choosing a Location for the Inverter/Charger on page 1–19
Step 2: Mounting the Inverter/Charger on page 1–20
Step 3: Connecting the AC Input and AC Output Wires on page 1–22
Step 4: Installing the DC Switchgear and Connecting the DC Cables on page 1–25
Step 5: Connecting the BTS and Xanbus-enabled Components on page 1–29
Step 6: Performing Checks Prior to Initial Start-Up on page 1–31
Step 7: Testing Your Installation on page 1–31
1–18 975-0639-01-01 Rev F
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 37

Step 1: Choosing a Location for the Inverter/Charger
WARNING
FIRE HAZARD
For indoor use only.
• Do not install and/or operate in compartments containing flammable
materials or in locations that require ignition-protected equipment.
• Do not cover or obstruct the ventilation openings.
• Do not install this unit in a compartment with limited airflow.
• Do not install where access to disconnecting means is obstructed.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in death or serious injury.
\
Flammable or combustible materials are defined as “any material containing
wood, compressed paper, cellulose, plant fibers, plastics, liquids, or other
material that will ignite and burn, whether flame-proofed or not” according to the
NFPA. Flammable liquids are defined as “any liquid whose flash point does not
exceed 100 °F (38 °C).” Examples of flammable liquids are gasoline, methanol,
and ether.
Inverter/Charger Installation
When choosing a wall to install the Conext SW, choose a wall that is not
considered a flammable material such as concrete, brick, or metal.
The inverter should only be installed in a location that meets the following
requirements:
Dry Do not allow water or other fluids to drip or splash on the
inverter/charger. Do not expose to rain, snow or water.
Cool Normal ambient air temperature should be between
32 °F and 77 °F (0 °C and 25 °C).
Close to battery
but not in the
same
compartment
Clearance Allow as much space around the inverter/charger as
The length and size of your DC cables will affect
performance. Use the DC cables recommended in
Table 1-2 on page 1–15. The unit should not be installed
in the battery compartment due to the possible presence
of explosive hydrogen gas from the batteries.
possible. It is recommended that other objects and
surfaces be at least 10" (254 mm) away from the
ventilation openings for best performance.
975-0639-01-01 Rev F 1–19
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 38

Installation
Step 2: Mounting the Inverter/Charger
HEAVY LOAD HAZARD
• Do not lift the unit by yourself. Use two people to lift and mount the unit.
Always use proper lifting techniques during installation to prevent injury.
• Do not install in drywall using drywall anchors.
Failure the follow these instructions can result in injury.
IMPORTANT: Mount the inverter/charger before connecting any wires or cables.
CAUTION
1–20 975-0639-01-01 Rev F
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 39

Inverter/Charger Installation
NOTE: These mounting instructions are general guidelines and are provided here for information purposes only.
You must install with care and heed precautions and warnings as stated beginning in “Step 1: Choosing a
Location for the Inverter/Charger” on page 1–19 and all subsequent steps.
(1) Place the
installation bracket flat
on non-flammable wall
(see page 1–19 for
definition) and mark
the positions of the
5 7/8 in.
mounting holes on the
wall.
(2)
149.0 mm
(2) Pilot drill the four
mounting holes on the
wall. Install the
appropriate anchors.
(3) Fasten the
installation bracket to
the mounting surface
with four #12 (or
equivalent) screws (or
bolts).
(4) With two people,
hang the Conext SW to
the installation bracket
carefully aligning the
Conext SW’s mounting
holes to the threaded
bolts on the installation
bracket.
(5) Secure the Conext
SW to the installation
bracket using the
supplied M6 nuts.
Figure 1-10 Conext SW Mounting Instructions
TIP: Use these
mounting holes.
975-0639-01-01 Rev F 1–21
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 40

Installation
Step 3: Connecting the AC Input and AC Output Wires
DANGER
ELECTRICAL SHOCK AND FIRE HAZARD
Make sure wiring being connected to the inverter/charger is disconnected
(physically or by opening and locking out the breaker) from all electrical
sources before handling. All wiring must be done in accordance with local and
national electrical wiring codes.
Failure to follow these instructions will result in death or serious injury.
General AC Wiring Considerations
AC and DC Wiring Separation Do not mix AC and DC wiring in the same
conduit or panel. Consult the applicable installation code for details.
AC Knockouts There are two dual 3/4" /1" trade-size knockouts on the side
panel and another two on the bottom panel for AC wiring. Use the same trade
size of strain relief as the trade size of the knockout(s) you are using.
AC Wiring Terminals The AC wiring terminals accept cables of a specific size.
See “AC Wiring” on page 1–13 for required sizes.
NOTICE
EQUIPMENT DAMAGE
Do not mix input and output wires. The terminal block is split into INPUT and
OUTPUT sections. Damage may occur if the unit is wired incorrectly.
Failure to follow these instructions can damage the inverter/charger.
WARNING
ELECTRICAL SHOCK AND FIRE HAZARD
Turn off all electrical sources (by opening and locking out main and inverter
panel breakers) before connecting wires to and from the inverter/charger. All
wiring must be done in accordance with local and national electrical wiring
codes.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in death or serious injury.
1–22 975-0639-01-01 Rev F
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 41

AC System Bonding
MULTIPLE AC NEUTRAL-TO-GROUND BONDS
Verify that only one neutral-to-ground bond exists in the system. Having more
than one neutral-to-ground bond in a system violates local electrical codes,
may create a shock or fire hazard, and may cause some sensitive equipment
to malfunction.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in death or serious injury.
System bonding refers to connection (bonding) of one of the current-carrying
conductors of an electrical system to ground. This creates a "grounded
conductor" or "neutral" that is at ground potential, but is separate from the
equipment ground conductor. System bonding must be done at only one
location. Procedures for system bonding vary between on-grid and off-grid
systems.
Inverter/Charger Installation
WARNING
System bonding for
on-grid systems
System bonding for
off-grid systems
The Conext SW does not connect the neutral to ground. The AC input neutral is
already bonded to ground by the incoming utility grid system. Do not connect the
neutral to ground in any additional location.
The Conext SW does not switch or disconnect the AC neutral in any mode of
operation, so even in invert (back-up) mode, the inverter load sub-panel neutral
is bonded to ground by the utility grid system. It must not be grounded again in
the inverter load sub-panel.
In a system without a generator, or with a generator that does not provide a
grounded neutral, you must make the connection from neutral to ground in the
inverter load sub-panel or main distribution panel, as applicable.
In a system with a generator that provides a grounded neutral, no additional
connection from neutral to ground is needed. Do not connect neutral to ground in
the inverter load sub-panel or main distribution panel, as applicable.
975-0639-01-01 Rev F 1–23
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 42

Installation
(1) Make the wiring connections to the AC
source main panel.
(2) Route the AC cable to the inverter/
charger.
(3) Remove the wiring compartment cover
panel on the inverter/charger.
(4) Remove the AC knockouts from the side
or bottom (or both). Do not leave the
knockout inside the wiring compartment.
(5) Install strain-relief clamps in the AC
knockouts.
(6) Route the AC input cable through the AC
input knockouts and inside the wiring
compartment.
(7) Connect Lines1&2toL1 & L2, Neutral
to N, ground to on the AC input terminals.
If solid ground wire is being used, the wire
can be connected directly under the screw
heads. If stranded ground wire is being
used, ring terminals must be used.
(8) Tighten the terminal screws. Leave a
service loop in the wires inside the wiring
box.
(9) Route the AC output cable through the
AC output knockouts and inside the wiring
compartment.
(10) Connect Lines 1 & 2 to
L1 & L2, Neutral to N,
ground to on the AC
output terminals. If solid
ground wire is being used,
the wire can be connected
directly under the screw
heads. If stranded ground
wire is being used, ring
terminals must be used.
(3)
strip at least
1/2” (13mm)
side AC
knockouts
(4)
bottom AC
knockouts
strip at least
2” (50mm)
L1
N
L2
AC Cable
to Inverter
AC INPUT
(2)
(11) Tighten the terminal
(9)
screws. Leave a service
loop in the wires inside the
wiring box.
(12) Make the wiring
connections to the inverter
load panel.
(1)
AC Source
Main Panel
(13) Replace the wiring
Inverter Load Panel
compartment cover panel
on the inverter/charger.
Transfer switch
Figure 1-11 Conext SW AC INPUT and OUTPUT Connections
1–24 975-0639-01-01 Rev F
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 43

Inverter/Charger Installation
Step 4: Installing the DC Switchgear and Connecting the DC Cables
DC Connection Precautions
WARNING
BURN AND FIRE HAZARD
Connect and disconnect DC wiring only after opening and locking out the
disconnect switches or breakers at all AC and DC sources.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in death or serious injury.
Recommended
Cable Sizes and
Lengths and Fuse
Size
Preparing the
Cables
Guidelines for
Routing the DC
Cables
For recommended DC cables and fuse sizes, see Table 1-2 and Table 1-3 on
page 1–15.
Cut the negative and positive cables to the required length. Strip off enough
insulation so you can install the terminals you will be using.
Use of crimp connectors – The connector should have a 3/8" stud size to
connect to the Conext SW. If a crimp connector is used, it should be crimped
using the tool indicated by the connector manufacturer.
Attach the connectors to the ends of both cables. Make sure no stray wire
strands protrude from the connectors.
Follow these guidelines to ensure maximum performance.
WARNING
FIRE HAZARD
Route the cables away from sharp edges that can cut into or scrape the
insulation. Wires can become exposed. Avoid sharp bends in the cable.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in death or serious injury.
To reduce the chance of radio frequency interference, keep the positive and
negative cables close together—ideally, held together by straps, loom, or
insulated clamps at regular intervals.
975-0639-01-01 Rev F 1–25
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 44

Installation
Installing the DC Switchgear next to Conext SW Inverter/Charger
T
WARNING
FIRE HAZARD
• Make sure the supplied nuts on the inverter/charger are tightened to a
torque of 10–11 ft-lbs (13.5–14.9 Nm). Torque all other connections to the
manufacturer’s specifications.
• Make sure the bus bar, washer, and nut are assembled in the order shown
in Figure 1-12 on page 1–26.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in death or serious injury.
(1) Unpack the DC Switchgear
from its box, if not already.
(2) Prepare four #10 (M5)
machine screws. Use two
screws to secure the DC
Switchgear to the installation
brackets of the Conext SW
and two screws to secure the
connecting bracket. The
connecting bracket attaches
to the Conext SW and DC
Switchgear.
(3) Remove the nuts and
washers from the inverter/
charger’s DC terminals, if
present.
(4) Position the DC Switchgear
next to the inverter/charger
carefully aligning the
mounting holes with the precut mounting holes on the
installation bracket and the
copper bus bar connectors
with the inverter/charger’s DC
terminals.
(5) Fasten the screws to the
mounting holes on the DC
Switchgear with the pre-cut
mounting holes on the
installation bracket of the
inverter/charger.
(6) Fasten the screws to the
connecting bracket to join the
DC Switchgear and the
Conext SW together.
(7) Fasten the nuts and
washers of the inverter/
charger’s DC terminal bolts to
secure the copper bus bars.
connecting
bracket
mounting hole
copper bus bar
connector
copper bus bar
connector (+)
copper bus bar
connector (–)
flat washer
nut
(5)
(5)
(6)
pre-cut
mounting hole
(7)
pre-cut
mounting hole
positive (+) DC
terminal (red)
negative (–) DC
terminal (black)
DC terminal
Figure 1-12 Installing the DC Switchgear
1–26 975-0639-01-01 Rev F
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 45

Connecting the DC Cables to the DC Switchgear
WARNING
FIRE HAZARD
• Use only appropriately sized copper cable. Loose connections, improper
connections, and under-rated cables will overheat.
• Make sure the supplied nuts on the inverter/charger are tightened to a
torque of 10–11 ft-lbs (13.5–14.9 Nm). Torque all other connections to the
manufacturer’s specifications.
• Make sure the DC cables, washers, and nuts are assembled in the order
shown in Terminal Connection in Figure 1-13 on page 1–28.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in death or serious injury.
REVERSE POLARITY DAMAGE
Check cable polarity at both the battery and the inverter/charger before
making the final DC connection or closing the DC breaker or disconnect.
Positive (+) must be connected to positive (+). Negative (–) must be
connected to negative (–).
Failure to follow these instructions can damage the inverter/charger.
Inverter/Charger Installation
NOTICE
975-0639-01-01 Rev F 1–27
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 46

Installation
(1) Route the DC cables from the battery bank to the DC Switchgear.
(2) Install a DC fuse (a) on the positive cable near the battery terminal.
(3) Open the DC circuit breaker on the DC Switchgear.
(4) Connect one connector on the POSITIVE (+) cable to the POSITIVE terminal on the DC
Switchgear. The connector goes on first, then the flat washer (steel), then the 3/8”
(9.5mm) bolt (brass).
(5) Connect the other connector to the POSITIVE (+) terminal on the battery.
(6) Connect one connector on the NEGATIVE (–) cable to the BATTERY NEGATIVE
terminal on the DC Switchgear.
(7) Connect the other end of the cable to the NEGATIVE (–) terminal on the battery.
(6)
(4)
(2)(a)
Terminal Connection
(7)
(5)
Battery or Battery
Enclosure
Figure 1-13 Conext SW DC Connections
1–28 975-0639-01-01 Rev F
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 47

Inverter/Charger Installation
Step 5: Connecting the BTS and Xanbus-enabled Components
WARNING
ELECTRICAL SHOCK HAZARD
Connect and disconnect DC wiring only after opening and locking out the
disconnect switches or breakers at all AC and DC sources.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in death or serious injury.
Battery
Temperature
Sensor (BTS)
Xanbus-enabled
Components
Installing a BTS extends the life of a battery by preventing overcharging in warm
temperatures and undercharging in cold temperatures. With a BTS monitoring
the battery temperature, the voltage delivered to the battery is adjusted
according to the battery’s actual temperature.
The BTS has a self-adhesive backing and attaches to the side of the battery. The
BTS also comes with a metal tab. A 25-ft (7.6-m) cable is supplied with the BTS.
These include the SCP, the AGS, Conext ComBox, and a solar charge controller.
The order in which the components are connected to the inverter/charger does
not matter. The most important aspect of the installation of these components is
the attachment of network terminators at each end of the network.
NOTICE
EQUIPMENT DAMAGE
Do not remove Xanbus cables during system operation.
Failure to follow these instructions can damage connected equipment.
975-0639-01-01 Rev F 1–29
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 48

Installation
WARNING
FIRE HAZARD
Follow the stacking of wires as shown in 1(a) of the illustration below.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in death or serious injury.
(1) Install the BTS sensor on the
battery.
Method
sensor to the negative battery post
which allows the internal battery
temperature to be sensed providing
the most accurate results.
Method
side of the battery using the selfadhesive backing which also
provides good results in most
situations.
(2) Plug the BTS connector to the BTS
port of the inverter/charger.
(a) involves mounting the
(b) attaches the sensor to the
(3) Connect the Xanbus-enabled devices
using the provided network cable. Terminate
each end of the network with a network
terminator
(c) and (d).
/
Battery
Positive
Battery
Negative
Xanbus Stacking REM BTS
(c)
(3)
(2)
(1)(a)
BTS
battery cable
battery terminal
Figure 1-14 Conext SW BTS and Xanbus Connections
(d)
(1)(b)
1–30 975-0639-01-01 Rev F
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 49

Step 6: Performing Checks Prior to Initial Start-Up
WARNING
ELECTRICAL SHOCK HAZARD
The Inv Enable button on the Conext SW front panel and the SCP do not
disconnect DC or AC input power to the Conext SW. Open and lockout the
disconnect switches or breakers at all AC and DC sources. Test with a
multimeter before tightening electrical connections.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in death or serious injury.
Before testing your installation, ensure these conditions are met.
❐ AC ground are properly installed.
❐ AC input connections and AC output connections are wired correctly on the
terminal block and not reversed.
❐ Positive (+) battery cable from the DC Switchgear is connected to the
positive (+) battery terminal through the DC fuse.
❐ Negative (–) battery cable from the DC Switchgear is connected to the
negative (–) battery terminal.
❐ Battery voltage is within the proper range for this unit: 20–34 volts DC for 24-
volt models and 42–66 VDC for the 48-volt model.
❐ DC disconnect switch or breaker is turned off.
❐ AC input and output breakers are turned off.
❐ All connections are tight.
Inverter/Charger Installation
Step 7: Testing Your Installation
WARNING
ELECTRICAL SHOCK HAZARD
The Inv Enable button on the Conext SW front panel and the SCP do not
disconnect DC or AC input power to the Conext SW. Isolate energy by turning
off and locking out all AC and DC circuit breakers and test with a multimeter
before checking or tightening electrical connections.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in death or serious injury.
There are several tests to be performed for testing your installation. These tests
will verify that:
• The Conext SW works in invert mode.
• The Conext SW works in charge mode.
• The Conext SW works in AC bypass mode.
975-0639-01-01 Rev F 1–31
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 50

Installation
If the test fails at any point, go to “Step 6: Performing Checks Prior to Initial StartUp” on page 1–31 and go through the checklist again to check the installation.
Then perform the test again. If the test fails again, see the troubleshooting
section in the Conext SW Inverter/Charger Owner’s Guide.
Figure 1-15 Conext SW Front Panel
Testing in Invert Mode
To test the Conext SW in invert mode, using a 100 watt light bulb as the test
load:
1. Close the DC disconnect switch or the DC circuit breaker to supply DC
2. After initialization, observe that none of the lights on the front panel should
3. Press the Inv Enable button. Verify that the green Inv Enabled LED
4. Connect the Conext SW to the test load by closing the AC breaker that
5. Press the Inv Enable button to disable inverter mode. The Inv Enabled LED
power to the Conext SW.
Wait for the LEDs on the front panel to flash on and off, indicating that the unit
is successfully initializing (10 to 30 seconds). The LEDs will turn off after
initialization.
If none of the LEDs come on or flash intermittently, make sure the voltage at
the DC terminals on the Conext SW is correct, as described in “Step 6:
Performing Checks Prior to Initial Start-Up” on page 1–31.
remain illuminated.
illuminates.
controls the circuit that the test load is connected to.
If the light bulb illuminates, the Invert mode is working.
goes off.
Testing in Charge Mode and AC Bypass Mode
1. Start the AC generator, if off-grid. If grid-connected proceed to step #2.
2. Close the main breaker in the AC input panel (the AC input panel feeds
power from either the generator or grid) in order to supply AC power to the
unit.
Verifying charging: 3. After a few seconds, verify that the AC IN / Charging LED on the front panel is
turned on and that it starts flashing indicating that the batteries are being
charged.
Verifying AC
bypass:
1–32 975-0639-01-01 Rev F
4. Disable the AC source by opening the main breaker in the AC input panel
and turn off inverter mode by pressing the Inv Enable button.
5. Connect the test load to the AC output connection of the unit.
6. Enable the AC source by closing main breaker in the AC input panel and the
test load should turn on after ten seconds.
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 51

Installation Complete
Your installation is now complete. The inverter/charger is ready for use.
The preceding tests use a light test load (a light bulb) as a test case. If you
encounter problems when using a load over 1000 watts (for example, a hair dryer
or microwave), see the troubleshooting information in the Conext SW Inverter/
Charger Owner’s Guide.
Inverter/Charger Installation
975-0639-01-01 Rev F 1–33
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 52

Installation
Multiple Unit Configuration
The Conext SW inverter/chargers support multiple unit configuration to increase
power output. This gives the system engineer and/or installer more options to
work with when tailoring a system to meet load demands.
In a multiple unit configuration, only two Conext SW inverter/chargers of the same
model can be used. For example, two Conext SW 4024 120/240 units can be
configured because both units each have a 24-volt rating and a continuous
power rating of up to 3500 watts.
In this configuration, the inverter and charger capacity of a system is doubled. In
the case of two Conext SW 4024 120/240 units, the inverter power rating doubles
to 7000 watts and the charging output current doubles to 180 amps. However,
the AC transfer relay rating of 30-amps remains the same. Inverter/chargers can
operate from different battery banks, meaning each unit is connected to its own
battery bank. However, it is highly recommended to use only a single battery
bank. See “DC Connections for Multiple Unit Configuration” on page 1–36.
IMPORTANT: In a multiple unit configuration where two Conext SW units are set
up together, the AC transfer relay rating remains the same at 30 amps. This AC
transfer relay rating does not double to become 60 amps.
WARNING
FIRE HAZARD
Do not power multiple loads in excess of 30 amps even in a multiple unit
configuration.
Failure to follow this instruction can result in death or serious injury.
1–34 975-0639-01-01 Rev F
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 53

Multiple Unit Configuration
The Input and Output Neutrals are electrically tied at the inverter terminals. Only a
Neutral wire (from the AC Out cable) is necessary from each inverter.
AC Out
Cable
AC Out
Cable
AC In
Cable
AC In
Cable
AC Output Breakers AC Input Breakers
AC Bypass breakers are not shown. For detailed wiring illustration, see “DualInverter System Renewable Energy (Solar) Wiring” on page 3–8.
Figure 1-16 Multiple (Dual) Unit Configuration Using Two Conext SW Units
975-0639-01-01 Rev F 1–35
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 54

Installation
DC Connections for Multiple Unit Configuration
Individual overcurrent devices are to be used between the battery positive and each
positive cable leading to the DC Switchgear. Keep cable lengths to the two DC
switchgears the same in order to balance cable losses.
Connect the units as follows:
1. Connect the positive cables.
Follow the steps in “Connecting the DC Cables to the DC Switchgear” on page 1–
27.
Also, do not tie the positives in series together between inverters.
2. Connect the negative cables.
Follow the steps in “Connecting the DC Cables to the DC Switchgear” on page 1–
27.
3. Connect the battery temperature sensors (BTS), if needed.
Follow the steps in “Step 5: Connecting the BTS and Xanbus-enabled Components”
on page 1–29.
Xanbus Stacking REM BTS Xanbus Stacking REM BTS
A DC fuse for
each (+) cable
1
24 V
2
3
Figure 1-17 Connecting Battery Cables
1–36 975-0639-01-01 Rev F
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 55
Configuring the System for Multiple Unit Operation
Verify all DC and AC connections. Check Xanbus network connections and ensure that
terminators are installed at devices at each end of the network. The simplest system
includes a Xanbus SCP, the two multi-unit-configured Conext SW inverter/chargers, and
two Xanbus terminators.
For both units to operate in multiple unit configuration, a Master and Slave have to be
assigned. The default out-of-box configuration for all Conext SW inverter/chargers is
Master which causes a conflict the first time the system is powered up. The installer will
need to change configuration on one of the inverter/chargers to Slave mode.
To configure the system for multiple unit configuration:
1. Apply DC power to both inverter/chargers.
Power up order has no impact. Because there are now two Master units in the
system, the SCP will detect an F71 fault, a “system configuration fault”.
2. From the SCP System Status screen, press Enter. The Select Device screen
appears.
3. Select the inverter to configure as a Slave unit from the list, then press Enter.
4. Bring up the Advanced Settings screen by pressing Enter, Up, and Down arrow
buttons all together.
5. Select Advanced Settings and press Enter. The Advanced Settings screen
appears.
6. Scroll down to select Multi Unit Config.
At this point all devices in the system will be automatically placed in standby mode.
All three LEDs on the inverter to be configured will start flashing
Multiple Unit Configuration
CSW4024 00: Adv
Inverter Settings
Charger Settings
AC Settings
Gen Support
Multi Unit Config
Restore Defaults
Adv Features
CSW4024 00: Multi
Dev Name
Dev Number
Invtr Mode
Battery
[00]
[01]
[Master]
[HouseBatt1]
[*Master] [Slave]
[*HouseBatt1]...[HouseBatt5]
Figure 1-18 Multi Menu Screen
7. Select Invtr Mode and press Enter.
8. Select Slave and press Enter.
9. Press the Exit button repeatedly until the System Status screen appears.
NOTE: The only situation in which the Slave may shut down the Master inverter is
during fault detection conditions such as high or low battery voltage, overcurrent, or
over-temperature conditions. Both inverters will auto reset after a fault detection
condition has been cleared. The exception is that an overcurrent condition will generate
a shutdown for both inverters that will require a manual restart of the system.
975-0639-01-01 Rev F 1–37
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 56

Installation
Search Mode Operation in Multiple Unit Configuration
Search mode is automatically enabled in multiple unit installations with two
paralleled Conext SW units. Only the master Conext SW operates, and the slave
unit comes online only when the load exceeds approximately 60% of the rated
output of the master unit. When the load drops below 20% of the master’s rated
output, the slave unit turns off.
For more information on when to set up the Search mode, refer to the Conext SW
Inverter/Charger Owner’s Guide (document part number: 975-0638-01-01) under
Chapter 4 -> Configuring Advanced Settings -> Using Search Mode.
Wiring Schematic
NOTE: Please refer to “Multiple Unit Configuration” on page 1–34 that shows the
wiring schematic employed between two Conext SW inverter/chargers.
IMPORTANT: Follow the same guidelines in “Inverter/Charger Installation” on
page 1–18 when choosing cables and/or wires for AC and DC connections.
WARNING
FIRE, ELECTRICAL SHOCK, AND EXPLOSION HAZARD
Make sure all wiring being used to make multiple unit configurations between
inverter/chargers is disconnected (physically or by opening and locking out
the breaker) from all electrical sources before handling. All wiring must be
done in accordance with local and national electrical wiring codes.
Failure to follow these instructions will result in death or serious injury.
1–38 975-0639-01-01 Rev F
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 57

Battery Information
Battery Bank Sizing
Battery capacity Battery size or capacity is just as important as the battery type
selected for use with the Conext SW. The batteries are the most important part of your
system, so it is recommended that you purchase as much battery capacity as possible.
A large battery will extend running time and ensure that your inverter/charger delivers
full rated surge.
It is recommended to have a minimum battery size of 100 amp-hours (Ah) for moderate
loads (<1000W) and greater than 200 Ah for heavy loads.
See “Estimating Battery Requirements” for information on a more detailed calculation.
About Amp-hours A number of different standards are used to rate battery energy
storage capacity. Automotive starting batteries are normally rated in cranking amps.
This is not a relevant rating for continuous loads like an inverter. Deep-cycle batteries
use a more suitable rating system such as amp-hours (Ah).
Amp-hour capacity is the number of amps a battery can continuously deliver during a
specified number of hours. It is represented by the product of the two —amps
multiplied by hours.
Battery Information
A battery rated for 100 Ah can deliver 5 amps for 20 hours (5 amps × 20 hours = 100
Ah). Depending on the battery chemistry, this battery can deliver a higher or lower
current for less or more time.
975-0639-01-01 Rev F 1–39
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 58

Installation
Estimating Battery Requirements
Calculating Battery Size
Step 1: Compute
Amp-hours
Step 2: Calculate
Battery Size
For each appliance, compute the number of amp-hours that will be used
between charging cycles, as follows:
1. Obtain the wattage. If the wattage is marked on the nameplate rating, use
that. Otherwise, multiply the marked voltage and amperage:
WATTS = VOLTS × AMPS.
2. Obtain the Watt-hours by multiplying that amount by the hours the appliance
will be used:
WATT-HOURS = WATTS × HOURS.
3. Obtain the amp-hours that the appliance requires by dividing that amount by
20 (the factor for the Conext SW, which is a 24-volt system):
BATTERY AMP-HOURS USED = AC WATT-HOURS/20
For example, a 100 W light bulb that is used for 4 hours will use 400 watt-hours
(Wh) and the inverter will consume approximately 20 Ah from a 24-volt battery.
4. Enter this information on the blank calculation worksheet (page 1–42).
5. Complete the rest of the worksheet; see Table 1-4, “Battery Sizing Example”
on page 1–41 for an example.
Size the batteries for approximately twice the estimated total amp-hour usage.
Doubling the expected amp-hour usage ensures that the batteries will not be
overly discharged and extends battery life.
Do not skip this doubling step. More capacity is better since you will have more
reserve capacity, be better able to handle large loads and surge loads, and your
battery won’t be discharged as deeply. Battery life is largely dependent on how
deeply the battery is discharged. The deeper the discharge, the shorter the
battery life.
Troubleshooting If you find that the system shuts down when appliances with
large motors are started, the problem may be that this motor is too much for the
battery. Even though you calculated the amp-hour requirements appropriately,
the startup of a large motor makes high demands on the battery. You may find
that adding more amp-hours (in the form of extra batteries or replacement with a
bigger battery) solves the problem.
1–40 975-0639-01-01 Rev F
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 59

Table 1-4 Battery Sizing Example
Daily watt-hours
needed for this
appliance
(A) Power
Appliance
TV & VCR 200 W 2 hours 400 Wh
Small microwave oven 800 W 15 min = 1/4 hour 200 Wh
3 lamps, 60 W each 180 W 4 hours 720 Wh
Coffee maker 600 W 15 min = 1/4 hour 150 Wh
Hair dryer 1500 W 6 min = 1/10 hour 150 Wh
Total daily watt-hours of AC load 1620 Wh
× Number of days between charges 3
= Total watt-hours of AC load between charges 4860 Wh
Battery Ah used between charges (divide by 20 for 24 volt system) 243 Ah
Recommended Battery Bank Size in Ah (multiply by 2) 486 Ah
Consumption (Watts)
(B) Operating Time per
Day (Hours)
(=A×B)
Battery Information
This example illustrates how quickly your battery needs can escalate. To reduce the
required battery bank size, you can either conserve energy by eliminating or reducing
the use of some loads, or recharge more frequently.
Battery Banks
As your power requirements increase, you may need to use more than one battery to
obtain sufficient capacity. Batteries can be connected in parallel, in series, or in seriesparallel to create higher capacity systems.
See “Battery Cabling and Hook-up Configurations” on page 1–43 for more information
about battery inter-connection schemes.
Mixing Batteries Batteries connected in parallel should be of the same type and amphour rating and from the same manufacturer.
It is not recommended to connect batteries of different types, amp-hour ratings or
manufacturers. Improper charging and decreased battery life will result.
Battery Bank Sizing Worksheet
The following worksheet is a guide to help you determine your battery needs. Be
generous in estimating the time for which you will run each of the loads to ensure
sufficient battery capacity.
975-0639-01-01 Rev F 1–41
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 60

Installation
Restrictions on Motor Size
An appliance may require three to six times its normal running current in order to start.
The Conext SW can handle surges up to twice its rated amount (surge current) for five
seconds. For example, the model Conext SW 4024 120/240 is rated as having a
maximum continuous output current of 15 amps and a surge capability of 32 amps. In
motors, the locked rotor amp (also called its starting current) may be specified on the
motor nameplate as “LRA” or “LRI”. The LRA must not exceed the surge current rating
of 32 amps.
When considering appliances with large motors, follow these guidelines:
• Make sure that the motor’s LRA rating is no more than surge current amps. The
Conext SW may not be able to start a motor with a higher LRA, and the Conext SW
will shut down if the attempt is made.
• Make sure the battery bank, DC cables and DC fuses are capable of handling up to
600 amps DC for five seconds. A weaker circuit may not be able to provide
sufficient power to the Conext SW to allow the Conext SW to start up the appliance.
Again, if the circuit cannot deliver the required current, the system may shut down
or the fuse may open.
• In a multiple unit configuration, two Conext SW units do not double up the surge
current rating. If a motor’s starting current exceeds the surge capacity of one
Conext SW unit, it will also exceed the surge capacity of two Conext SW units.
Table 1-5 Battery Sizing Worksheet
(A) Power
Appliance
Total daily watt-hours of AC load Wh
× Number of days between charges
= Total watt-hours of AC load between charges Wh
Battery Ah used between charges (divide by 20 for 24 volt system) Ah
Consumption (Watts)
W hours Wh
W hours Wh
W hours Wh
W hours Wh
W hours Wh
W hours Wh
W hours Wh
W hours Wh
Recommended Battery Bank Size in Ah (multiply by 2) Ah
(B) Operating Time per
Day (Hours)
Daily watt-hours
needed for this
appliance
(=A×B)
1–42 975-0639-01-01 Rev F
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 61

Battery Cabling and Hook-up Configurations
Several smaller batteries can be connected to create a battery bank of substantial size.
You can connect batteries in three ways: in parallel, series, or series-parallel.
To make a larger battery bank, connect individual batteries with heavy cables. The
actual size of the cable depends on whether the batteries are connected in parallel or
series. Generally, the cable should not be smaller than the inverter cables—if the main
cables are 4/0 AWG, the battery interconnects should be 4/0 AWG.
The best configuration is to connect the batteries in series and parallel. This requires
additional cables, but reduces imbalances in the battery bank and can improve the
overall performance. Consult your battery supplier for more information regarding the
hook-up configuration required for your system.
Battery Parallel Connection
Batteries are connected in parallel when all the positive terminals of a group of batteries
are connected and then, separately, all the negative terminals are connected. In a
parallel configuration, the battery bank has the same voltage as a single battery, but an
Ah rating equal to the sum of the individual batteries. See below.
Battery Information
Figure 1-19 Batteries Connected in Parallel
975-0639-01-01 Rev F 1–43
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 62

Installation
Battery Series Connection
When batteries are connected with the positive terminal of one battery to the negative
terminal of the next battery, they are connected in series. In a series configuration, the
battery bank has the same Ah rating of a single battery, but an overall voltage equal to
the sum of the individual batteries. See below.
Figure 1-20 Batteries Connected in Series
Battery Series-Parallel Connections
As the name series-parallel implies, both the series and parallel configurations are used
in combination. The result is an increase in both the voltage and the capacity of the total
battery bank. The smaller, lower voltage batteries are first connected in series to obtain
the necessary voltage, and then these “batteries connected-in-series” sets are
connected in parallel to increase the battery bank capacity. See below.
Figure 1-21 Batteries in Series-Parallel Connections
1–44 975-0639-01-01 Rev F
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 63

2 Specifications
NOTE: Specifications are subject to change without prior notice.
975-0639-01-01 Rev F 2–1
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 64

Specifications
Inverter Specifications
NOTE: All inverter specifications are at nominal conditions: ambient temperature
of 77 °F (25 °C), 24 VDC, unless otherwise specified.
AC Output
SW 2524 120/240 SW 4024 120/240 SW 4048 120/240
Output waveform true sine wave true sine wave true sine wave
Continuous output power (AC)
- Maximum
- 30 minutes
Maximum load power on a
3000 W
3300 W
a
b
3400 W
4000 W
c
4400 W
3800 W
1800 W 2550 W 2700 W
a
a
single phase (L1/N or L2/N)
Maximum continuous output
12.5 A 15 A 15.2 A
current
Surge power rating (5
5000 W
d
7000 W
e
7000 W
seconds)
Inverter peak output current 24.3 A 41 A 41 A
AC OUTPUT connection Split-phase
(L1/L2)
Split-phase
(L1/L2)
Split-phase
(L1/L2)
Peak efficiency 91.5% 92% 94%
Output power factor
0.5 - 1.0 0.6 - 1.0 0.6 - 1.0
(capacitive or inductive)
Operating voltage range
single-phase/split-phase
104/208 VAC
to 127/
254 VAC
104/208 VAC
to 127/
254 VAC
104/208 VAC
to 127/
254 VAC
Nominal voltage
120/240 VAC 120/240 VAC 120/240 VAC
single-phase/split-phase
Operating frequency range selectable
50 or 60 Hz
selectable
50 or 60 Hz
selectable
50 or 60 Hz
Default output frequency 60 Hz 60 Hz 60 Hz
a.Only when NoLoadVD is enabled.
b.Duty cycle 3300 W for 30 minutes, 0 W for 45 minutes, NoLoadVD is enabled.
c.Duty cycle 4000 W for 30 minutes, 0 W for 45 minutes.
d.Duty cycle 5000 W for 5 seconds, 3000 W for 300 seconds.
e.Duty cycle 7000 W for 5 seconds, 3400 W for 300 seconds.
DC Input
SW 2524 120/240 SW 4024 120/240 SW 4048 120/240
Voltage range 20–34 VDC 20–34 VDC 40–64 VDC
Maximum continuous power
22–27 VDC 22–28 VDC 46–48 VDC
voltage range
Maximum battery current 150 A 230 A 105 A
2–2 975-0639-01-01 Rev F
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 65

Charger Specifications
DC Input
No-load power draw (Inverter
On)
Low battery voltage shutdown
cut-off
(other values selectable)
High battery voltage shutdown
cut-off
(other values selectable)
Charger Specifications
NOTE: All charging specifications are at nominal conditions: ambient
temperature of 77 °F (25 °C), split-phase 120/240 VAC, 60 Hz unless otherwise
specified.
DC Output
Maximum output current 65 A 90 A
Nominal output voltage 24 VDC 24 VDC 48 VDC
Charging output voltage
operation range
SW 2524 120/240 SW 4024 120/240 SW 4048 120/240
21 W 26 W 27 W
21.0 V
(default)
33.0 V
(default)
SW 2524 120/240 SW 4024 120/240 SW 4048 120/240
12.0–
b
32.0 VDC
21.0 V
(default)
33.0 V
(default)
a
12.0–
32.0 VDC
42.0 V
(default)
62.0 V
(default)
45 A
24.0–
64.0 VDC
Equalization cycle Automatic,
Manual by
SCP
Optimal charging efficiency 90% 90% 92%
Dead battery charge voltage > 12.0 VDC > 12.0 VDC > 24.0 VDC
Charging methods (two
settings)
Without a battery temperature
sensor (three settings)
Three-stage charge (Bulk, Absorption, Float) [default]
Two-stage charge (Bulk, Absorption)
Cool 50 °F (10 °C)
Warm 77 °F (25 °C) [default]
Hot 104 °F (40 °C)
Automatic,
Manual by
SCP
Automatic,
Manual by
SCP
975-0639-01-01 Rev F 2–3
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 66

Specifications
DC Output
With a battery temperature
sensor (provided)
a.Charging current derates up to 5% between 35 to 60 °C.
b.Recharging does not occur when battery voltage is below 12 V.
AC Input
SW 2524 120/240 SW 4024 120/240 SW 4048 120/240
The temperature compensation coefficients on a
24-volt battery
are as follows:
Flooded: 54 mV × (25 °C – BTS °C)
Gel: 54 mV × (25 °C – BTS °C)
AGM: 42 mV × (25 °C – BTS °C)
The temperature compensation coefficients on a
48-volt battery
are as follows:
Flooded: 108 mV × (25 °C – BTS °C)
Gel: 54 mV × (25 °C – BTS °C)
AGM: 42 mV × (25 °C – BTS °C)
SW 2524 120/240 SW 4024 120/240 SW 4048 120/240
Power factor at full charge rate > 0.98 > 0.98 > 0.98
Current 9 A 13 A 12 A
Voltage 120/240 VAC 120/240 VAC 120/240 VAC
Voltage range
single-phase/split-phase
Frequency range 44–70Hz 44–70 Hz 44–70 Hz
AC INPUT Connection Split-phase
AC Transfer Specifications
NOTE: All transfer specifications are at nominal conditions: ambient temperature
of 77 °F (25 °C), split-phase 120/240 VAC, 60 Hz input, unless otherwise
specified.
Transfer time—utility to invert < 20 ms
Relay current rating 30 A
Minimum line-to-neutral AC input
voltage for transfer
Maximum
voltage for transfer
Minimum AC input frequency for transfer
Maximum AC input frequency for transfer
Cooling Fan-cooled, temperature controlled
line-to-neutral
a.Limited by SCP to 24 A due to CEC/NEC regulatory requirements.
AC input
95/190 VAC to
135/270 VAC
(L1/L2)
95/190 VAC to
135/270 VAC
Split-phase
(L1/L2)
All Models
95 VAC RMS
135 VAC RMS
44 Hz
70 Hz
95/190 VAC to
135/270 VAC
Split-phase
(L1/L2)
a
2–4 975-0639-01-01 Rev F
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 67

Physical Specifications
Physical Specifications
SW 2524 120/240 SW 4024 120/240 SW 4048 120/240
L×W×H
15.2×13.5×7.6 in
(387×343×197 mm)
Unit Net
50.7 lbs. (23 kg) 67.2 lbs. (30.5 kg) 67.2 lbs. (30.5 kg)
Weight
Environmental Specifications
Nominal ambient temperature 77 °F (25 °C)
Operating temperature range
Storage temperature range –40 to 185 °F (–40 to 85 °C)
Humidity: Operation/Storage 95% RH, non-condensing
Ingress protection rating Indoor only, IP 20
Pollution degree 3
Over voltage category (AC mains) CAT III
Altitude: Operating 6,562 ft. (2,000 m)
Mounting wall mount using installation bracket
15.2×13.5×7.6 in
(387×343×197 mm)
15.2×13.5×7.6 in
(387×343×197 mm)
All Models
–4 to 140 °F (–20 to 60 °C)
starts derating above 77 °F (25 °C) (see following graph)
Full power at ambient
W
3750
3500
3250
3000
2750
2500
SW 4048 120/240
SW 4024 120/240
SW 2524 120/240
3400W
3000W
3800W
3600W
2750W
3400W
3200W
3000W
2800W
2500W
2250
2000
1750
1500
-4 14 32 41 50 59 68 77 86 95 104 113 122 131 140 °F
-20 -10 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 °C
Figure 2-1 Output Power versus Temperature Derating Graph
975-0639-01-01 Rev F 2–5
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 68

Specifications
Regulatory
All Models
Safety UL 1741 Ed. 2,
UL 1778 Ed. 4
CSA C22.2 NO. 107.1-01,
CSA C22.2 NO. 107 3-05
EMC FCC Part 15, Class B
Industry Canada ICES-0003, Class B
2–6 975-0639-01-01 Rev F
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 69

3 Wiring Diagrams
“Wiring Diagrams” illustrate the most basic
BOS configurations and are for reference only.
Specific installations may require additional
equipment to meet national or local electric
codes. Ensure all safety requirements are
strictly followed.
For...... See....
“Single-Inverter System (Off-Grid/Backup) Overview” page 3–3
“Single-Inverter System Renewable Energy (Solar) Overview”
975-0639-01-01 Rev F 3–1
page 3–5
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 70

Wiring Diagrams
3–2 975-0639-01-01 Rev F
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 71

Single-Inverter System (Off-Grid/Power Backup)
Communication
Loads
Vented Battery
Enclosure
Battery Bank
Inverter AC
Distribution
Panel
Utility Grid
AC Source(s)
AC Generator
DC Charging
and DC In
AC Out
AC In
Conext SW AC Switchgear
Conext SW DC Switchgear
Conext SW DC Switchgear
Automatic Generator
Start (optional)
System Control Panel
(optional)
Accessories
System Control Panel
Enter Exit
Fault/Warning
System Status
Battery 20.4 A 53.9V
BatLev E --F
Load 1235W
AC 1 115 W 3202V
Menu
Standby
12: 00 AM Jan 01
Power
Generator On
Network
Fault
Automatic Generator Start
Conext ComBox
(optional)
Remote Switch
(optional)
Battery Temperature
Sensor
(optional)
DANGER
ELECTRICAL SHOCK AND FIRE HAZARD
Installation must be done by qualified personnel to ensure compliance with all
applicable installation codes and regulations. Instructions for installing the
Conext SW are provided in this installation guide for use by qualified installers
only.
Failure to follow these instructions will result in death or serious injury.
Single-Inverter System (Off-Grid/Power Backup)
Figure 3-1 Single-Inverter System (Off-Grid/Backup) Overview
975-0639-01-01 3–3
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 72

L1
L2
Inverter
AC Distribution Panel
NEUTRAL
GROUND
Neutral
HOT L1
HOT L2
Ground
AC LEGEND
AC Cable
Generator
Disconnect
G
N
L2
L1
System Control
Panel (optional)
Vented Battery
Enclosure
Battery Temperature Sensor
(BTS)
24-volt Battery Bank Enclosure
Bypass INV 1 OUT
INV IN
AC Breakers
Bypass
Utility
Grid
Grounding
Electrode
Conductor
Main
AC Distribution
Panel
H
a
n
d
l
e
I
n
t
e
r
l
o
c
k
Conext SW DC Switchgear
DC Disconnect
Battery
Negative
Battery
Positive
Xanbus Stacking REM BTS
N
120/240 Vac or
240 Vac only
AC Generator
Conext SW Inverter/Charger
Conext SW AC Switchgear
Negative (–)
Positive (+)
BATTERY
LEGEND
Ground
'&Bus Bar
Neutral-to-Ground
Bond inside.
NOTE: Be sure to check the
generator for a neutral-toground bond and remove it.
There can only be one neutr alto-ground bond in the system.
System Control Panel
Ente
r
Exit
Fault/Warning System S tatus
Battery 20.4 A 53.9V
BatLev E --F
Load 1235W
AC 1 115 W 3202V
Menu
Standby
12:00 AM Jan 01
INV OUT
Xanbus
Network
Terminator
This AC Switch is a
customer-supplied
component.
Battery System
Ground
Ensure DC Switchgear
chassis is properly
bonded to Inverter
chassis using supplied
bonding busbar.
The actual positions of the Neutral bus and the Ground bus may be different than what is shown he re. This drawing is for illustration purpose only.
NOTE: If no Grid
is available, the
generator can be
connected to the
AC breakers in the
Conext SW AC
Switchgear,
instead of to a
separate AC
Generator
Disconnect.
The actual positions of the Negative shu nt and
Ground bus may be different tha n what is shown
here. This drawing is for illustration pur pose only.
Automatic Generator
Start (optional)
Xanbus
Network
Terminator
Power
Generator On
Network
Fault
Automatic Generator Start
Conext ComBox
(optional)
AC
TRANSFER
SWITCH
Remote Switch
(optional)
Battery
Negative
Battery
Positive
Communication Cable
(Category 5)
BTS
ACCESSORIES
Communication Cable
(6-conductor telephone cable)
20-contact wiring harness
24-volt or 48-volt
Battery Bank Enclosure
Figure 3-2 Single-Inverter System (Off-Grid/Backup) Wiring
3–4 975-0639-01-01
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 73

Single-Inverter System Renewable Energy (Solar)
Renewable Energy
Conext SW
Inverter/Charger
BA
T +
PV+BAT–PV
–
Solar Charge Controller
DC Charging
and DC In
Conext SW AC Switchgear
Conext SW DC Switchgear
Inverter AC
Distribution
Panel
Utility Grid
AC Source(s)
AC Generator
DC In
AC Out
AC In
Communication
Vented Battery
Enclosure
Battery Bank
DC
Combiner
Box
Photovoltaic
Conext SW DC Switchgear
Conext SW DC Switchgear
Automatic Generator
Start (optional)
System Control Panel
(optional)
Accessories
System Control Panel
Enter Exit
Fault/Warning
System Status
Battery 20.4 A 53.9V
BatLev E --F
Load 1235W
AC 1 115 W 3202V
Menu
Standby
12: 00 AM Jan 01
Power
Generator On
Network
Fault
Automatic Generator Start
Conext ComBox
(optional)
Remote Switch
(optional)
Battery Temperature
Sensor
(optional)
DANGER
ELECTRICAL SHOCK AND FIRE HAZARD
Installation must be done by qualified personnel to ensure compliance with all
applicable installation codes and regulations. Instructions for installing the
Conext SW are provided in this installation guide for use by qualified installers
only.
Failure to follow these instructions will result in death or serious injury.
Single-Inverter System Renewable Energy (Solar)
Figure 3-3 Single-Inverter System Renewable Energy (Solar) Overview
975-0639-01-01 3–5
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 74

L1
L2
Inverter
AC Distribution Panel
NEUTRAL
GROUND
Neutral
HOT L1
HOT L2
Ground
AC LEGEND
AC Cable
Solar Charge Controller
BATT+BATT–PV–PV
+
System Control
Panel (optional)
Renewable
Energy
Vented Battery
Enclosure
Battery Temperature Sensor
(BTS)
24-volt Battery Bank Enclosure
Bypass INV 1 OUT
INV IN
AC Breakers
Bypass
Utility
Grid
Grounding
Electrode
Conductor
Main
AC Distribution
Panel
H
a
n
d
l
e
I
n
t
e
r
l
o
c
k
Conext SW DC Switchgear
DC Disconnect
Battery
Negative
Battery
Positive
Xanbus Stacking REM BTS
Photovoltaic
DC
Combiner Box
Negative (–)
Positive (+)
Ground
DC LEGEND
DC Cable
N
120/240 Vac or
240 Vac only
AC Generator
Conext SW Inverter/Charger
Negative (–)
Positive (+)
BATTERY
LEGEND
Ground
'&Bus Bar
Neutral-to-Ground
Bond inside.
NOTE: Be sure to check the
generator for a neutral-toground bond and remove it.
There can only be one neutra lto-ground bond in the system.
System Control Panel
Ente
r
Exit
Fault/Warning
System Status
Battery 20.4 A 53. 9V
BatLev E --F
Load 1235W
AC 1 115 W 3202V
Menu
Standby
12:00 AM Jan 01
INV OUT
Xanbus
Network
Terminator
Generator
Disconnect
G
N
L2
L1
This AC Switch is a
customer-supplied
component.
Battery System
Ground
The actual positions of the Neutral bus and the Ground bus may be different than what is shown here. This drawing is for illustration purpose only.
NOTE: If no Grid is
available, the generator
can be connected to
the AC breakers in the
Conext SW AC
Switchgear, instead of
to a separate AC
Generator Disconnect.
Install a DC breaker
on the positive line.
Automatic Generator
Start (optional)
Xanbus
Network
Terminator
Power
Generator On
Network
Fault
Automatic Generator Start
Conext ComBox
(optional)
AC
TRANSFER
SWITCH
The actual positions of the Negative sh unt and
Ground bus may be different than what is shown
here. This drawing is for illustration purpose only.
Ensure DC Switchgear
chassis is properly
bonded to Inverter
chassis using supplied
bonding busbar.
Remote Switch
(optional)
Conext SW AC Switchgear
Charge Controller
Disconnect
CC
+
Battery
Negative
Battery
Positive
Communication Cable
(Category 5)
BTS
ACCESSORIES
Communication Cable
(6-conductor telephone cable)
20-contact wiring harness
24-volt or 48-volt
Battery Bank Enclosure
Figure 3-4 Single-Inverter System Renewable Energy (Solar) Wiring
3–6 975-0639-01-01
This guide for use by qualified personnel only
Page 75

Page 76

Schneider Electric
solar.schneider-electric.com
As standards, specifications, and designs
change from time to time, please ask for
confirmation of the information given in this
publication.
© 2015 Schneider Electric. All rights reserved.
975-0639-01-01 Rev F
Printed in China
 Loading...
Loading...