Page 1

Conext™ SW Inverter/Charger
Conext SW 2524 120/240 Split-phase (865-2524)
Conext SW 4024 120/240 Split-phase (865-4024)
Conext SW 4048 120/240 Split-phase (865-4048)
Owner’s Guide
975-0638-01-01 Rev G
9-2018
solar.schneider-electric.com
Page 2

Page 3

Conext SW Inverter/Charger
Conext SW 2524 120/240 Split-phase (865-2524)
Conext SW 4024 120/240 Split-phase (865-4024)
Conext SW 4048 120/240 Split-phase (865-4048)
Owner’s Guide
http://solar.schneider-electric.com
Page 4

Copyright and Contact
Copyright © 2012-2018 Schneider Electric. All Rights Reserved. All trademarks are owned by Schneider Electric
Industries SAS or its affiliated companies.
Exclusion for Documentation
UNLESS SPECIFICALLY AGREED TO IN WRITING, SELLER
(A) MAKES NO WARRANTY AS TO THE ACCURACY, SUFFICIENCY OR SUITABILITY OF ANY TECHNICAL OR OTHER INFORMATION
PROVIDED IN ITS MANUALS OR OTHER DOCUMENTATION;
(B) ASSUMES NO RESPONSIBILITY OR LIABILITY FOR LOSSES, DAMAGES, COSTS OR EXPENSES, WHETHER SPECIAL, DIRECT,
INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL OR INCIDENTAL, WHICH MIGHT ARISE OUT OF THE USE OF SUCH INFORMATION.THE USE OF ANY
SUCH INFORMATION WILL BE ENTIRELY AT THE USER’S RISK; AND
(C) REMINDS YOU THAT IF THIS MANUAL IS IN ANY LANGUAGE OTHER THAN ENGLISH, ALTHOUGH STEPS HAVE BEEN TAKEN TO
MAINTAIN THE ACCURACY OF THE TRANSLATION, THE ACCURACY CANNOT BE GUARANTEED.APPROVED CONTENT IS
CONTAINED WITH THE ENGLISH LANGUAGE VERSION WHICH IS POSTED AT SOLAR.SCHNEIDER-ELECTRIC.COM.
Document Number: 975-0638-01-01 Revision: Rev G Date: 9-2018
Product Part Numbers: 865-2524, 865-4024, 865-4048
Contact Information solar.schneider-electric.com
Please contact your local Schneider Electric Sales Representative or visit our website at:
http://solar.schneider-electric.com/tech-support/
Information About Your System
As soon as you open your product, record the following information and be sure to keep your proof of purchase.
Serial Number
Product Number
Purchased From
Purchase Date
_________________________________
_________________________________
_________________________________
_________________________________
Page 5

About This Guide
Purpose
The purpose of this Owner’s Guide is to provide explanations and procedures for
operating, troubleshooting, and maintaining the Conext SW Inverter/Charger.
Scope
The Guide provides safety guidelines, as well as information about operating and
troubleshooting the unit. It does not provide details about particular brands of
batteries. You need to consult individual battery manufacturers for this
information.
Audience
The Guide is intended for users and operators of the Conext SW Inverter/
Charger.
Organization
This Guide is organized into the following chapters.
Chapter 1, “Introduction” covers material list, key features, and basic protection
features.
Chapter 2, “Components and Mechanical Features” provides detailed
information on system components and the product’s main features.
Chapter 3, “Operation” provides operational instructions from the Front Panel
including operation using the System Control Panel (SCP).
Chapter 4, “Configuration via SCP” provides instructions to change inverter and
charger settings using the System Control Panel (SCP).
Chapter 5, “Troubleshooting” covers normal troubleshooting guidelines that also
includes fault detection and warning codes and how to interpret them.
Chapter 6, “Specifications” covers product specifications.
975-0638-01-01 Rev G iii
Page 6
About This Guide
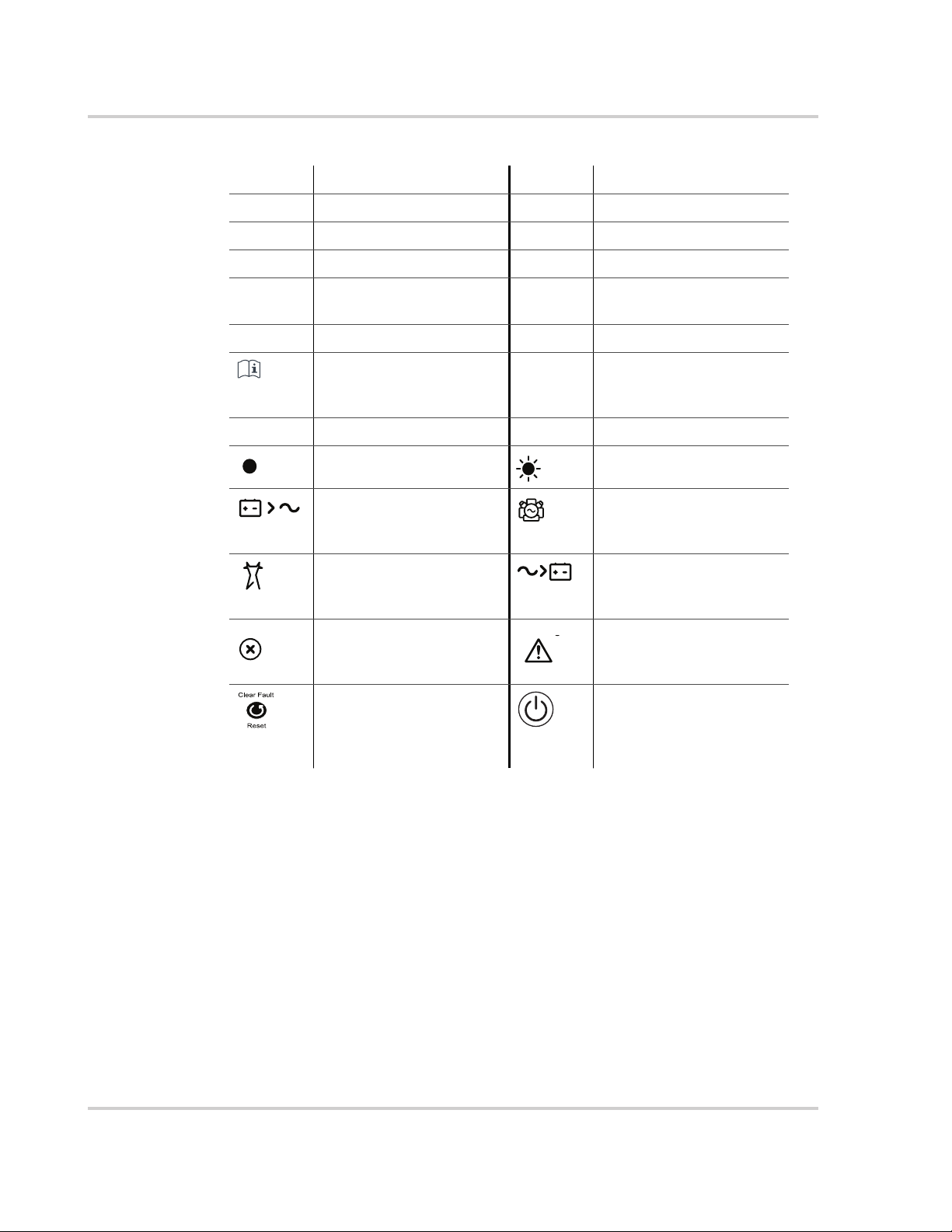
Abbreviations, Acronyms, and Symbols
AC Alternating Current LED Light Emitting Diode
AGS Automatic Generator Start SCP System Control Panel
BOS Balance of System SW Sine Wave
DC Direct Current VAC Volts, Alternating Current
PPE Personal Protective
Equipment
PV Photovoltaic IP20 Ingress protection rating
Reference to see guide
(or manual) for more
information
AC DC
Denotes a steady LED Denotes a flashing LED
Inv Enabled – see “Front
Panel LEDs” on page 3–4
for definition.
AC IN – see “Front Panel
LEDs” on page 3–4 for
definition
Fault – see “Front Panel
LEDs” on page 3–4 for
definition.
Clear Fault | Reset – see
“Conext SW Front and
Side Panels” on page 2–4
for definition.
.
VDC Volts, Direct Current
Ground
Gen Support – see “Front
Panel LEDs” on page 3–4
for definition.
Charging – see “Front
Panel LEDs” on page 3–4
for definition.
Warning – see “Front
Panel LEDs” on page 3–4
for definition.
Inv Enable – see “Conext
SW Front and Side
Panels” on page 2–4 for
definition.
Related Information
You can find more information about Schneider Electric as well as its products
and services at solar.schneider-electric.com.
iv 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
Page 7

Important Safety Instructions
READ AND SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS - DO NOT DISCARD
This guide contains important safety instructions for the Conext SW Inverter/
Charger that must be followed during operation and troubleshooting. Read and
keep this Owner’s Guide for future reference.
Read these instructions carefully and look at the equipment to become familiar
with the device before trying to install, operate, service or maintain it. The
following special messages may appear throughout this bulletin or on the
equipment to warn of potential hazards or to call attention to information that
clarifies or simplifies a procedure.
The addition of either symbol to a “Danger” or “Warning” safety label
indicates that an electrical hazard exists which will result in personal
injury if the instructions are not followed.
This is the safety alert symbol. It is used to alert you to potential
personal injury hazards. Obey all safety messages that follow this
symbol to avoid possible injury or death.
DANGER
DANGER indicates an imminently hazardous situation, which, if not avoided,
will result in death or serious injury.
WARNING
WARNING indicates a potentially hazardous situation, which, if not avoided,
can result in death or serious injury.
CAUTION
CAUTION indicates a potentially hazardous situation, which, if not avoided,
can result in moderate or minor injury.
NOTICE
NOTICE indicates a potentially hazardous situation, which, if not avoided, can
result in equipment damage.
975-0638-01-01 Rev G v
Page 8

Safety
Safety Information
ELECTRICAL SHOCK AND FIRE HAZARD
Installation must be done by qualified personnel to ensure compliance with all
applicable installation and electrical codes and regulations. Instructions for
installing the Conext SW are provided in a separate installation guide for use
by qualified installers only.
Failure to follow these instructions will result in death or serious injury.
ELECTRICAL SHOCK AND FIRE HAZARD
• Read all instructions, cautionary markings, and all other appropriate
sections of this guide before operating, troubleshooting, and performing
maintenance on the Conext SW.
• Exercise extreme caution at all times to prevent accidents.
• Do not cover or obstruct ventilation openings.
• Do not mount in a zero-clearance compartment. Overheating may result.
• Do not open nor disassemble the inverter/charger. There are no userserviceable parts inside.
• Do not expose to rain or spray.
• Disconnect and lockout all AC and DC sources before servicing. Servicing
includes maintenance or cleaning or working on any circuits connected to
the inverter/charger. See following note
Failure to follow these instructions will result in death or serious injury.
DANGER
DANGER
NOTE: Turning off inverter mode using the Inv Enable switch on the front panel,
disabling the inverter and charger functions using the SCP, and putting the unit in
Standby mode will not reduce an electrical shock hazard.
vi 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
Page 9

Safety
DANGER
ELECTRIC SHOCK HAZARD
• For indoor use only. This inverter/charger is designed for off-grid, solar,
backup, and hybrid applications. See the installation guide for information.
• Do not operate the inverter/charger if it has been damaged in any way.
• Do not operate the inverter/charger with damaged or substandard wiring.
Wiring must be done by qualified personnel to ensure compliance with all
applicable installation codes and regulations.
Failure to follow these instructions will result in death or serious injury.
WARNING
EXPLOSION AND FIRE HAZARD
• Charge properly rated lead-acid (GEL, AGM, Flooded, or lead-calcium)
rechargeable batteries because other battery types may explode.
• When using Lithium-Ion batteries, ensure that the battery pack being used
includes a certified Battery Management System (BMS) with safety
controls.
• Do not work in the vicinity of lead-acid batteries. Batteries generate
explosive gases during normal operation. See note #1.
• Do not install and/or operate in compartments containing flammable
materials or in locations that require ignition-protected equipment. See
notes #2 and #3.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in death or serious injury.
NOTES:
1. Follow these instructions and those published by the battery manufacturer
and the manufacturer of any equipment you intend to use in the vicinity of the
battery. Review cautionary markings on these products.
2. This inverter/charger contains components which tend to produce arcs or
sparks.
3. Locations include any space containing gasoline-powered machinery like a
generator, fuel tanks, as well as joints, fittings, or other connections between
components of the fuel system.
CAUTION
FIRE AND BURN HAZARD
Do not cover or obstruct the air intake vent openings and/or install in a zeroclearance compartment.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in moderate or minor injury.
975-0638-01-01 Rev G vii
Page 10
Safety
Precautions When Working With Batteries
IMPORTANT: Battery work and maintenance must be done by qualified
personnel knowledgeable about batteries to ensure compliance with battery
handling and maintenance safety precautions.
WARNING
BURN AND FIRE HAZARD
• Always wear proper, non-absorbent gloves, complete eye protection, and
clothing protection.
• Remove all personal metal items, like rings, bracelets, and watches when
working with batteries.
• Never smoke or allow a spark or flame near batteries.
• Batteries can produce a short circuit current high enough to weld a ring or
metal bracelet or the like to the battery terminal, causing a severe burn.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in death or serious injury.
WARNING
CHEMICAL, BURN, AND EXPLOSION HAZARD
• Never place the Conext SW Inverter/Charger unit in the same compartment
as batteries due to an explosive hazard.
• Make sure the area around the battery is well ventilated.
• Make sure the voltage of the batteries matches the output voltage of the
inverter/charger.
• Never allow battery acid to drip when reading specific gravity or filling
battery.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in death or serious injury.
WARNING
LIMITATIONS ON USE
Do not use in connection with life support systems or other medical
equipment.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in death or serious injury.
LI
viii 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
Page 11

Safety
NOTICE
RISK OF INVERTER/CHARGER DAMAGE
Do not exceed the maximum inverter load limit (power) on either single phase
(L1/N or L2/N). See “Inverter Specifications” on page 6–2.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in damage to equipment.
NOTICE
RISK OF INVERTER/CHARGER DAMAGE
Never place the Conext SW Inverter/Charger unit directly above batteries;
gases from a battery will corrode and damage the inverter/charger.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in damage to equipment.
NOTICE
RISK OF BATTERY DAMAGE
Study and follow all of the battery manufacturer's specific precautions, such
as removing or not removing cell caps while charging, whether equalization is
acceptable for your battery, and recommended rates of charge.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in damage to equipment.
975-0638-01-01 Rev G ix
Page 12

Safety
FCC Information to the User
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B
digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to
provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential
installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency
energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may
cause harmful interference to radio communications.
However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular
installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and
on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the
following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which
the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
x 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
Page 13

Contents
Important Safety Instructions
Safety Information ----------------------------------------------------------vi
Precautions When Working With Batteries ----------------------------------------viii
FCC Information to the User ---------------------------------------------------x
1 Introduction
Materials List ------------------------------------------------------------1–2
Key Features ------------------------------------------------------------1–3
Key Features Explained --------------------------------------------------1–4
Basic Protection Features ---------------------------------------------------1–5
Grid-interactive and Other Features --------------------------------------------1–6
Load Shaving ---------------------------------------------------------1–6
AC Support ----------------------------------------------------------1–8
AC Support Mode using SOC ------------------------------------------1–9
Enhanced AC Support ------------------------------------------------1–9
Regular AC Support without Xanbus devices ------------------------------1–11
Grid-Interactive Delay Feature --------------------------------------------1–11
AC Coupling ---------------------------------------------------------1–12
AC Couple Smart Charge -----------------------------------------------1–13
Storing the State of the Inverter Mode --------------------------------------- 1–15
NoLoadVD ----------------------------------------------------------1–15
Low Battery Cut Out Hysteresis -------------------------------------------1–15
LBCO Delay --------------------------------------------------------- 1–15
Lithium Ion Battery Type ------------------------------------------------ 1–16
2 Components and Mechanical Features
System Components-------------------------------------------------------2–2
Xanbus System --------------------------------------------------------2–2
Xanbus-enabled Products and Other Accessories -------------------------------2–3
Conext SW Inverter/Charger Mechanical Features----------------------------------2–4
Conext SW Front and Side Panels ------------------------------------------2–4
Front Panel Buttons and Status LEDs -------------------------------------2–5
Conext SW AC/DC/Ports Side Panel --------------------------------------2–6
3 Operation
Start Up Behavior ---------------------------------------------------------3–2
Inverter Operation Using the Front Panel ----------------------------------------3–3
Operating Limits for Inverter Operation ---------------------------------------3–5
Operating Limits for Charger Operation --------------------------------------3–7
975-0638-01-01 Rev G xi
Page 14

Contents
Inverter/Charger Operation using the System Control Panel (SCP) ---------------------- 3–8
SCP Features --------------------------------------------------------- 3–9
Using the Standby Button ----------------------------------------------- 3–10
SCP Navigation ------------------------------------------------------ 3–10
Startup Screen ---------------------------------------------------- 3–10
Viewing the SCP Home Screens --------------------------------------- 3–11
Viewing Other Screens ---------------------------------------------- 3–14
Changing Operational Settings ------------------------------------------- 3–16
4 Configuration via SCP
Viewing the Firmware Revision Number ----------------------------------------- 4–2
Setting the Time and Date--------------------------------------------------- 4–3
Viewing the Basic and Advanced Settings Menus---------------------------------- 4–4
Configuring Basic Settings -------------------------------------------------- 4–7
Configuring Advanced Settings----------------------------------------------- 4–9
Inverter Settings Menu -------------------------------------------------- 4–9
Using the Low Battery Cut Out and LBCO Delay Settings --------------------- 4–11
Low Battery Cut Out Hysteresis ---------------------------------------- 4–11
Using Search Mode ------------------------------------------------ 4–12
Using Inverter Block ------------------------------------------------ 4–13
Charger Settings Menu ------------------------------------------------- 4–13
Battery Charger Functions -------------------------------------------- 4–15
Multi-Stage Charging Process ----------------------------------------- 4–16
Equalize-Charging the Batteries --------------------------------------- 4–18
Using Charger Block ----------------------------------------------- 4–19
Custom Battery Settings Menu ----------------------------------------- 4–20
LithiumIon Battery Settings Menu --------------------------------------- 4–22
AC Settings --------------------------------------------------------- 4–24
AC Support Settings --------------------------------------------------- 4–25
AC Support Mode Setting -------------------------------------------- 4–27
Load Shaving Setting ----------------------------------------------- 4–29
Enhanced AC Support Setting ----------------------------------------- 4–31
Multi Unit Config Menu ------------------------------------------------- 4–32
Setting the Device Name --------------------------------------------- 4–33
Setting the Device Number ------------------------------------------- 4–34
Restoring Factory Default Settings ----------------------------------------- 4–36
Advanced Features Menu ----------------------------------------------- 4–37
EuroFreq Feature -------------------------------------------------- 4–37
xii 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
Page 15

Configuration Sheet ------------------------------------------------------ 4–39
5 Troubleshooting
General Troubleshooting Guidelines -------------------------------------------5–2
Inverter Applications -------------------------------------------------------5–3
View Device Info Logs------------------------------------------------------5–4
Troubleshooting the Conext SW via the SCP --------------------------------------5–5
Fault Detection Types ---------------------------------------------------5–5
Warning Types --------------------------------------------------------5–6
6 Specifications
Inverter Specifications------------------------------------------------------6–2
Charger Specifications -----------------------------------------------------6–3
AC Transfer Specifications --------------------------------------------------6–4
Physical Specifications -----------------------------------------------------6–5
Environmental Specifications -------------------------------------------------6–5
Regulatory --------------------------------------------------------------6–6
Contents
975-0638-01-01 Rev G xiii
Page 16

xiv
Page 17

Figures
Figure 1-1 Materials List------------------------------------------------------1–2
Figure 1-2 Load Shaving in Action ----------------------------------------------1–7
Figure 1-3 AC Support Mode using SOC ------------------------------------------1–9
Figure 1-4 Enhanced AC Support -----------------------------------------------1–9
Figure 1-5 Enhanced AC Support Charge Cycle -----------------------------------1–10
Figure 1-6 Regular AC Support without Xanbus Devices------------------------------ 1–11
Figure 1-7 Load Shaving 2-Hour Delay Example -----------------------------------1–12
Figure 2-1 Xanbus System Components ------------------------------------------2–2
Figure 2-2 Conext SW Front and Side Panels---------------------------------------2–4
Figure 2-3 Front Panel Buttons and Status LEDs ------------------------------------2–5
Figure 2-4 AC and DC Terminals, Network and Communication Ports Panel-----------------2–6
Figure 3-1 Startup Screen --------------------------------------------------- 3–10
Figure 3-2 SCP Top Level Screens --------------------------------------------- 3–11
Figure 3-3 System Status Screen ----------------------------------------------3–12
Figure 3-4 Conext SW Home Screen --------------------------------------------3–12
Figure 3-5 Selecting a Device Setup Menu ---------------------------------------3–14
Figure 3-6 Viewing the Meters Screen -------------------------------------------3–15
Figure 3-7 Navigate To Conext SW Setup Menu------------------------------------ 3–16
Figure 3-8 Conext SW Setup Menu Operational Settings------------------------------ 3–18
Figure 4-1 Selecting Basic Settings---------------------------------------------- 4–4
Figure 4-2 Selecting Advanced Settings ------------------------------------------4–6
Figure 4-3 Menu Map of the Conext SW Basic Settings--------------------------------4–7
Figure 4-4 Inverter Settings Menu Screen -----------------------------------------4–9
Figure 4-5 Charger Settings Menu Screen ----------------------------------------4–13
Figure 4-6 Custom Settings Menu Screen ----------------------------------------4–20
Figure 4-7 LithiumIon Settings Menu Screen -------------------------------------- 4–22
Figure 4-8 AC Settings Menu Screen--------------------------------------------4–24
Figure 4-9 AC Support Menu Screen-------------------------------------------- 4–25
Figure 4-10 Multi Unit Config Menu Screen ----------------------------------------4–32
Figure 4-11 Setting a Device Number -------------------------------------------- 4–35
Figure 4-12 Adv Features Menu Screen ------------------------------------------4–37
Figure 5-1 View Device Info Log ------------------------------------------------5–4
Figure 6-1 Output Power versus Temperature Derating Graph --------------------------6–5
975-0638-01-01 Rev G xv
Page 18

xvi
Page 19

Tables
Table 3-1 Front Panel LEDs---------------------------------------------------3–4
Table 3-2 Conext SW Home Screen States ---------------------------------------3–13
Table 3-3 Meters Screen---------------------------------------------------- 3–15
Table 3-4 Conext SW Setup menu ---------------------------------------------3–17
Table 4-1 Setting Defaults and Ranges ------------------------------------------4–7
Table 4-2 Basic Settings -----------------------------------------------------4–8
Table 4-3 Setting Defaults and Ranges ------------------------------------------4–9
Table 4-4 Inverter Settings Description------------------------------------------ 4–10
Table 4-5 Setting Defaults and Ranges ----------------------------------------- 4–14
Table 4-6 Charger Settings Menu Description------------------------------------- 4–14
Table 4-7 Bulk Voltage Settings for Different Battery Types --------------------------- 4–16
Table 4-8 Preset Absorption Voltage Settings for Different Battery Types -----------------4–16
Table 4-9 Preset Float Voltage Settings for Different Battery Types ----------------------4–17
Table 4-10 Preset Equalization Voltage Settings for Different Battery Types ----------------4–18
Table 4-11 Setting Defaults and Ranges -----------------------------------------4–20
Table 4-12 Custom Battery Settings Menu Description ------------------------------- 4–21
Table 4-13 Setting Defaults and Ranges -----------------------------------------4–22
Table 4-14 LithiumIon Battery Settings Menu Description -----------------------------4–23
Table 4-15 Setting Defaults and Ranges -----------------------------------------4–24
Table 4-16 AC Settings menu ------------------------------------------------- 4–24
Table 4-17 AC Support Menu Description and Values --------------------------------4–25
Table 4-18 Multi Unit Menu Description and Values---------------------------------- 4–32
Table 4-19 Adv Features Description and Values ----------------------------------- 4–37
Table 5-1 Fault Detection Types and Behaviors ------------------------------------5–5
Table 5-2 Warning Types and Behavior ------------------------------------------5–6
Table 5-3 Fault Detection Messages --------------------------------------------5–7
Table 5-4 Warning Messages ------------------------------------------------5–12
975-0638-01-01 Rev G xvii
Page 20

xviii
Page 21

1 Introduction
The following topics will be covered in this
chapter.
• Material List
• Key Features
• Basic Protection Features
• Grid-interactive and Other Features
975-0638-01-01 Rev G 1–1
Page 22

Introduction
Materials List
Congratulations on your purchase of the Conext SW Inverter/Charger (called
Conext SW). The Conext SW has been designed to give you premium true sine
wave power, ease of use, and outstanding reliability for your off-grid and power
backup applications.
The Conext SW ships with the following items:
• One Conext SW unit
• One set of owner’s and installation guides
• One Battery Temperature Sensor (BTS)
• Two Xanbus network terminators
• Two sets of 5/16
• Two DC terminal covers (red and black) with two sets of #6-32 screws
• One Installation bracket with one set of M6 nuts for mounting (not shown)
NOTE: If any of the supplied accessories are missing, contact customer
service for replacement. For code-compliant installations in Canada and USA,
the DC Switch Gear accessory is required. See the Installation Guide for more
information.
"-18
nuts and washers for the DC terminals,
Figure 1-1 Materials List
1–2 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
Page 23

Key Features
Key Features
The Conext SW Inverter/Charger is a true sine wave inverter/charger that can be
used for off-grid, backup, solar, and hybrid applications. The Conext SW Inverter/
Chargers are designed to operate with a wide variety of generators and are
capable of operating in parallel with a generator for short durations to assist with
starting large loads. The Conext SW is a convenient combination of an inverter,
multi-stage battery charger, and transfer switch in one electronic device.
The Conext SW Inverter/Charger’s key features are:
True Sine Wave output
•
power for your microwave, entertainment system, computer, and other loads.
This power is identical to the AC source provided from the utility grid (power
company).
Some of the benefits of high efficiency true sine wave power include consistent
cooking in your microwave, handling of sensitive loads such as your TV set,
dimmer switches, and appliances with speed controls.
•
Multiple unit configuration
versatile platform capable of parallel multiple unit configuration1to increase
power levels.
•
High surge capacity
twice the maximum continuous output power rating to start difficult loads like well
pumps, refrigerators, or A/C compressors. See “Inverter Specifications” on
page 6–2.
•
Power factor correction
input current required for charging, increasing AC pass-through capacity.
•
Multi-stage charging
stage charging capability that minimizes charging time.
•
Adjustable frequency
from a 50Hz and 60Hz power source by extending the AC qualification frequency
range. See “AC Settings” on page 4–24.
•
Temperature-controlled, variable-speed internal cooling fans
on when the internal temperature reaches
speed at
104 °F (
•
Xanbus-enabled
which allows network compatibility and communication with other Xanbusenabled devices. See more information under “Xanbus System” on page 2–2.
158 °F (
40 °C).
70 °C). The fan turns off when the internal temperature falls to
- as an inverter, the Conext SW provides true sine wave
- the Conext SW Inverter/Charger has a highly
- the Conext SW Inverter/Charger has a surge rating that is
- Power factor-corrected (PFC) input minimizes AC
- the Conext SW Inverter/Charger has a high output, multi-
- the Conext SW Inverter/Charger is capable of operating
- the fans turn
113 °F (
- the Conext SW Inverter/Charger is also Xanbus-enabled
45 °C) and reaches maximum
1.In Conext SW Inverter/Chargers, multiple unit configuration (installation) is limited to two
units - one master unit and one slave unit.
975-0638-01-01 Rev G 1–3
Page 24

Introduction
Key Features Explained
Built-in Charge
Formulas
Battery
Temperature
Sensor
Dead Battery
Charging
Manual
Equalization
Load Management The Conext SW has a built-in transfer relay that connects your inverter output or
1
For the unit to perform at the highest level, the batteries must be charged
correctly. The Conext SW has optimized algorithms for flooded, gel, and AGM
batteries.
Since battery temperature is a key factor in correct charging, the charging
formula must be adjusted (automatically and in real time) according to the actual
battery temperature to ensure that batteries are fully charged, but not
overcharged. For this reason, a battery temperature sensor (BTS) is included
with the Conext SW that works with a temperature-compensated charge formula.
Another feature that the Conext SW includes is dead battery charging. The
Conext SW—unlike many chargers—has the ability to recharge batteries even if
the battery voltage is very low, that is, as low as 12 volts.
Over a period of time, the cells in a flooded battery can develop uneven
chemical states. This can result in a weak (undercharged) cell which, in turn, can
reduce the overall capacity of the battery. To improve the life and performance of
a non-sealed, flooded battery, the Conext SW’s multi-stage charging cycle
includes a manual equalize mode that can be used, if recommended by the
battery manufacturer.
AC input from the AC generator to your loads. Because the usual AC power
sources such as small generators often have limited current availability, having
the capability to manage your AC loads is extremely valuable. The Conext SW
provides a number of features to facilitate this.
• The charger is power factor corrected to use AC current as efficiently as
possible. Minimizing the AC current used by the charger means more
current is available for your AC loads.
• The Conext SW has a power share feature which prioritizes your AC
loads by reducing the charge current depending on the load current;
and programmed AC breaker setting.
Occasionally, AC input sources have low voltage. To avoid loading these weak
sources any further, the charger automatically reduces its AC current draw as the
AC voltage approaches the minimum acceptable level.
Multiple Unit
Configuration
1.Requires a 240V AC input. The feature does not work on 120V AC input only.
Conext SW Inverter/Charger supports multiple unit configuration to increase
capacity. Conext SW multiple unit configuration is limited to one master unit and
one slave unit.
Multiple Unit Inverting
Multiple unit configuration allows two inverter/chargers to operate in parallel
thereby doubling the capacity in inverter mode. The multiple inverters
communicate over the Xanbus network and intelligently manage the load
balance between the units.
1–4 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
Page 25

Multiple Unit Charging
Two Conext SW Inverter/Chargers synchronize charging stages to ensure
efficient charging of the battery bank. When a single unit transitions from bulk to
absorption so does the other unit. In absorption, the two units must complete the
absorption stage before transitioning to the next stage. Note that the two units do
not load share when charging except during the bulk stage. The Conext SW units
stop sharing charge current just before completing the bulk stage. The units do
not share charge current during the absorption and float stages.
Each unit charges batteries based on the Max Charge Rate setting and active
internal (temperature-based) deratings.
If equalization is enabled on one or more devices capable of equalization
charging, only those devices perform an equalize cycle after absorption. Other
devices transition to float (if three-stage charging is selected) or transition to AC
pass-through (if two-stage charging is selected).
Basic Protection Features
The Conext SW has the following protection features:
• Over temperature shutdown for critical components such as the transformer
and the power board
• Battery temperature sensor (BTS) failure/battery temperature out-of-range
fault protection
• DC output over voltage protection during charge mode
• AC output overload and short circuit protection during invert mode
Basic Protection Features
• AC backfeed1protection
The Battery Temperature Sensor (BTS) provides these protection features:
• battery over temperature charging protection preventing battery charging at
140 °F (60 °C) or higher, and
• charging voltage compensation based on the temperature of the battery the
BTS is connected to.
1.An AC backfeed error occurs when the AC output of the inverter/charger is connected or
routed back to the inverter/charger’sAC input terminalor ifthe ACinternal transferrelay error is
detected.
975-0638-01-01 Rev G 1–5
Page 26

Introduction
Grid-interactive and Other Features
Load Shaving
Load shaving (Load Shave) allows the Conext SW to support (or assist) the AC
source in powering local loads during a defined window of time (LoadShaveStart
and LoadShaveStop). See “Time-of-Use Metering” on page 1–7. It allows the
inverter to control how much current can be drawn from the AC source.
The Conext SW transitions to load shaving mode only when both the phase
currents exceed Load Shave Amps. It uses battery power to limit the peak load on
the AC input by providing the difference in amps between the actual load current
and the current limit set in Load Shave Amps. Some scenarios are presented
below to reflect this behavior.
Scenario 1
Load Shave Amps = 5A,
L1 = 7A of AC load,
L2 = 3A of AC load
Conext SW will not enter into the AC load shaving mode because one of the
phase currents (L1 or L2) is lower than the value of Load Shave Amps.
(L2 =3A) < (Load Shave Amps = 5A)
Scenario 2
Load Shave Amps = 5A,
L1 = 7A of AC load,
L2 = 9A of AC load
In this scenario, the Conext SW enters into the AC load shaving mode because
both phase currents exceed the value of Load Shave Amps.
(L1 =7A) > (Load Shave Amps = 5A)
The difference between these two values is 2A.
Conext SW will shave off 2A from each phase, meaning, the current draw from L1
will be limited to 5A and L2 limited to 7A.
However, when the battery is in charge mode, the total AC input current is limited
by 80% of Load Shave Amps to avoid the fluctuation between battery charge and
discharge.
This fluctuation is described as follows:
• If the AC input current limit is the same value as Load Shave Amps in battery
charge mode, the charge current can be higher than the limit value due to
the charge dynamics. Under this condition, the battery will enter into
discharge mode because the AC current is higher than Load Shave Amps.
After the battery is in discharge mode, the battery will go back into charge
mode again because the load current is smaller than Load Shave Amps.
1–6 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
Page 27
Grid-interactive and Other Features
• Therefore, the battery will fluctuate between the charge and discharge
modes. In order to avoid this fluctuation, a hysteresis band is set by limiting
the AC input current to 80% of Load Shave Amps when the battery is in the
charge mode.
In a grid-interactive backup system Load shaving combined with time-of-use
metering helps reduce utility peak demand surcharges.
In an off-grid system with generator Load shaving can be used to support the
generator. If the generator is unable to provide enough current to run loads in the
system, load shaving ensures that the system does not exceed the generator’s
current rating. This is done by matching the generator’s manufacturer
recommended current rating with the Load Shave Amps setting.
See “Load Shaving Setting” on page 4–29 for a sample scenario.
NOTE: Current is regulated by placing a limit (Load Shave Amps) on the current
of the AC source.
15 A10 A
5A
Figure 1-2 Load Shaving in Action
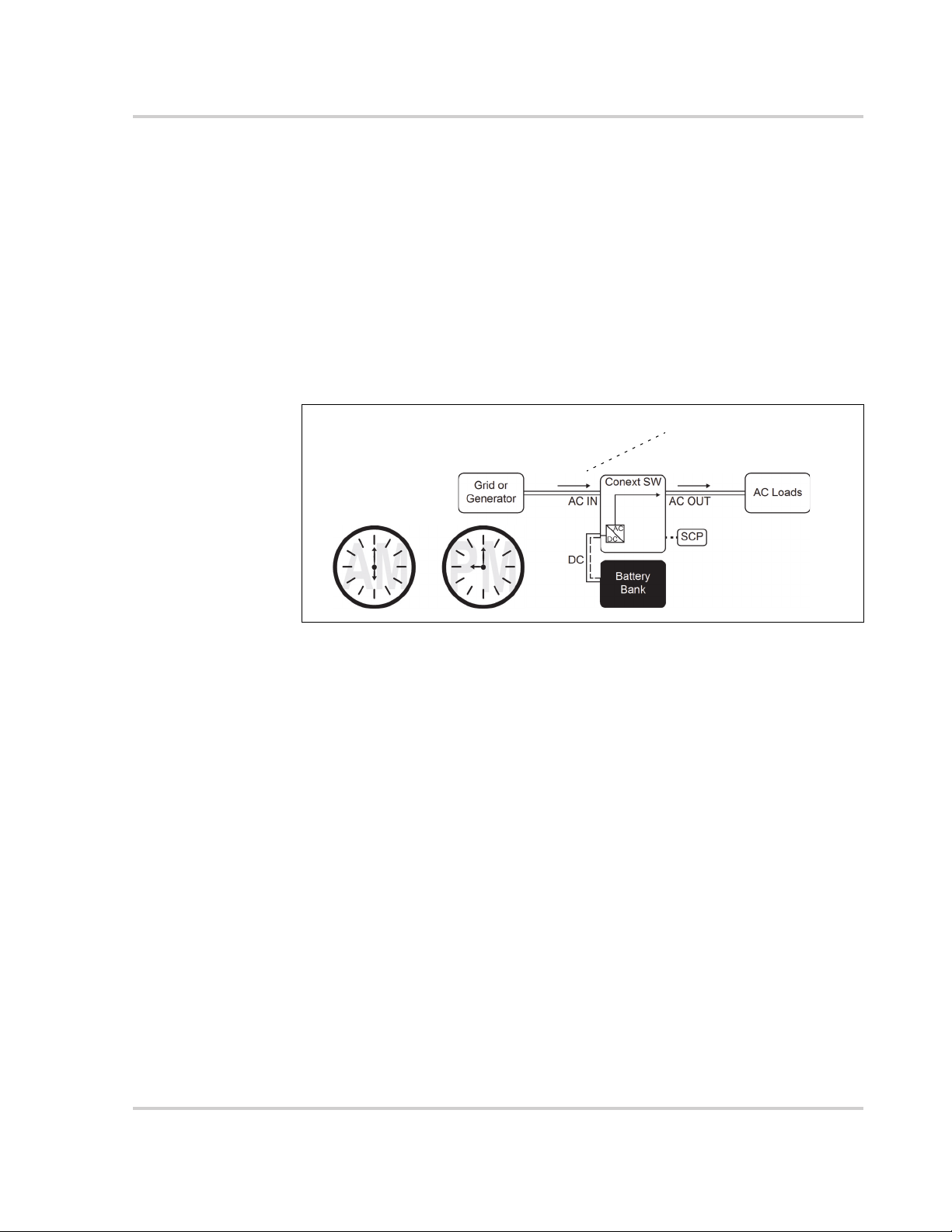
Time-of-Use Metering Utilities use time-of-use metering to set utility charges
during peak usage hours and to impose a surcharge. The Conext SW can be
configured (using the LoadShaveStart, LoadShaveStop and charger block [see
the Conext SW Owner’s Guide] settings) to overcome these peak charges by
using utility power to charge the battery bank during the inexpensive energy
hours and consuming the battery energy during expensive energy hours.
For example, if charger block is set between 9:00 AM and 10:00 PM and load
shaving is set between LoadShaveStart=6:00 PM and LoadShaveStop=9:00 PM,
charging on AC Input stops at 9:00 AM and the inverter continues to pass utility
AC through to the loads. If charging is required during the charger block period
then Conext SW can use an alternative external renewable energy source such
as an MPPT solar charge controller to charge the battery bank. The inverter
connects to the utility grid at 6:00 PM and supports running the loads using the
batteries. The inverter continues to run the loads until 9:00 PM.
The Conext SW then stops supporting the utility grid and passes utility AC
through to the loads at 9:01 PM. At the end of charger block at 10:00 PM utility
AC begins maintaining the batteries based on charger settings.
The above example allows an external renewable energy source to be utilized as
a primary charging source during a desired time window. The charger (using
utility power connected to AC Input) can then be used to supplement battery
charging when the utility rates are low.
975-0638-01-01 Rev G 1–7
Page 28

Introduction
AC Support
When using the system for time-of-use metering, the system should be designed
with a battery capacity large enough to support loads during the entire peak rate
period without reaching the low battery cut out (Low Batt Cut Out) setting.
Load shaving can also be used with time-of-use metering and enhanced AC
support feature (see “Enhanced AC Support” on page 1–9 and “Enhanced AC
Support Setting” on page 4–31) to support self-consumption.
AC Support is similar to load shaving because in both cases the Conext SW
inverter supplements AC current. However, unlike load shaving, AC Support
minimizes the AC input current to the Conext SW as long as the battery’s SOC
(state-of-charge) or battery voltage conditions allow it. AC Support allows the
Conext SW to support local loads by converting excess power from external DC
sources connected to its battery bank. Examples of external DC sources are
MPPT solar charge controllers. When local loads demand more energy from the
external DC sources then extra current can be pulled in from the AC source as a
last resort. When operating without a solar charge controller in the system, set
the battery charge cycle to 2StgNoFloat to allow AC Support to function
immediately after the absorption charge stage.
When Conext SW is operating in AC support mode, it only compensates AC
loads which are connected to both phases and having equal power. The
difference in power between the two phases will be drawn from the AC source.
Some scenarios are presented below to reflect this behavior.
Scenario 1
L1 = 3A of AC load,
L2 = 3A of AC load
In this scenario, the Conext SW injects 3A into each phase to offset both loads.
Scenario 2
L1 = 5A of AC load,
L2 = 3A of AC load
In this second scenario where power from the two loads is unequal, the Conext
SW still injects 3A (the lesser of the two AC loads) into each phase. However, the
difference of 2A on L1 shall be drawn from the grid.
AC Support behaves three different ways depending on the type of equipment
that is installed in the Xanbus network with the Conext SW.
• SOC - Xanbus-enabled Conext Battery Monitor is installed
• Enhanced - Xanbus-enabled MPPT solar charge controller is installed
• Regular - neither Xanbus-enabled battery monitor nor MPPT solar charge
controller is installed
1–8 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
Page 29
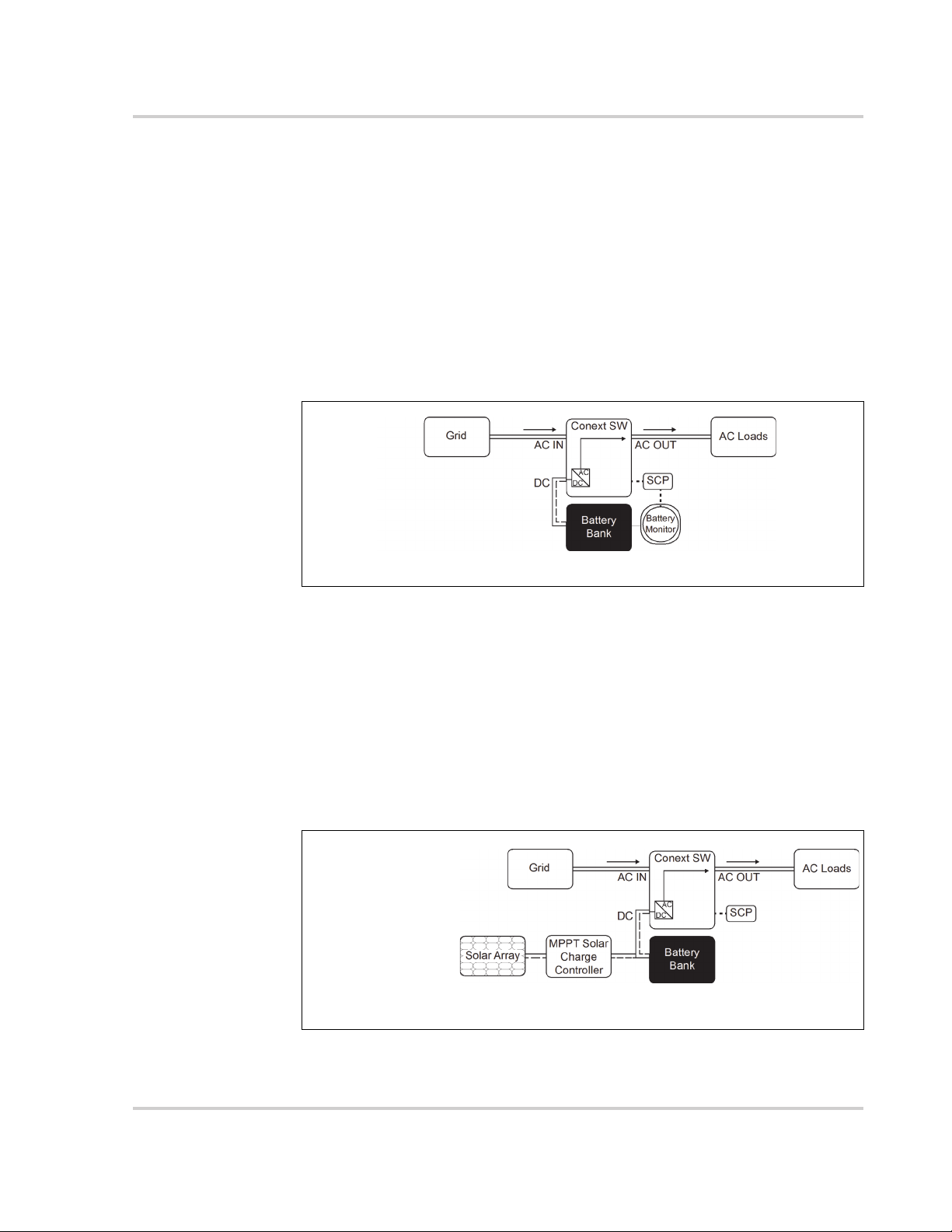
AC Support Mode using SOC
With AC support on SOC (AC Supp on SOC) enabled (default setting), Conext SW
maximizes power utilization using stored energy in a battery bank within a gridinteractive backup power system. AC support mode allows the Conext SW to
accurately determine when grid power can be used to supply energy to the
loads by knowing the state-of-charge (SOC) of the battery bank.
The SOC of a battery bank is monitored by using a Xanbus-enabled battery
monitor. SOC entry and exit points are determined by the user. The SOC entry
point (AC Supp Start Soc) which is a high percentage value determines when
AC support mode is engaged and the SOC exit point (AC Supp Stop Soc) which
is a low percentage value determines when AC support mode is disengaged.
See “AC Support Settings” on page 4–25.
Grid-interactive and Other Features
15 A<2A*
>13A
NOTE: Entry and exit into AC Support
Mode is determined by the SOC. In this
case, AC support mode is engaged.
Figure 1-3 AC Support Mode using SOC
Enhanced AC Support
Enhanced AC Support (EnhancedACSup) works when power systems are DC
coupled with a Xanbus-enabled MPPT Solar Charge Controller. This means that
DC power from a renewable source such as an MPPT Solar Charge Controller is
used to charge the battery bank while simultaneously utilizing its power (by way
of inverting) to power loads. Entry and exit to enhanced AC support are
controlled by the MPPT charger so that they can control the state-of-charge of
the batteries. AC power from the grid is utilized only when load demand exceeds
power available from the MPPT charger for charging and supplying the loads.
NOTE: Entry and exit into
Enhanced AC Support is
determined by the MPPT.
SOC Entry = 80%
actual SOC = 75%
SOC Exit = 50%
* To prevent injecting current into the grid from the inverter, there is less than 2 amps of offset allowed
from the grid to flow into AC IN under all conditions.
15 A<2A*
>13A
* To prevent injecting current into the grid from the inverter, there is less than 2 amps of offset allowed
from the grid to flow into AC IN under all conditions.
Figure 1-4 Enhanced AC Support
975-0638-01-01 Rev G 1–9
Page 30
Introduction
When enhanced AC support mode is enabled, the Conext SW automatically
tracks the MPPT solar charge controller’s charging voltage as it transitions from
bulk to absorption to float. By tracking the voltage, the Conext SW is then able to
execute and finish the charging cycle using DC power from the solar charge
controller while converting its excess DC power to AC power to support the grid
by supplying more current. Conext SW only uses excess DC power not required
by the battery to support the grid thus, it prioritizes charging the battery before
supporting the loads. Battery health is improved because the system always
executes a three stage charging of the battery that ensures battery SOC is as
close as possible to 100% at all times. Systems that use a fixed voltage for AC
support (or similar) start to support loads sooner and may not fully charge the
battery bank, leaving the battery in a partial SOC. Prolonged periods of partial
SOC can degrade battery performance. Enhanced AC support limits this
degrading effect.
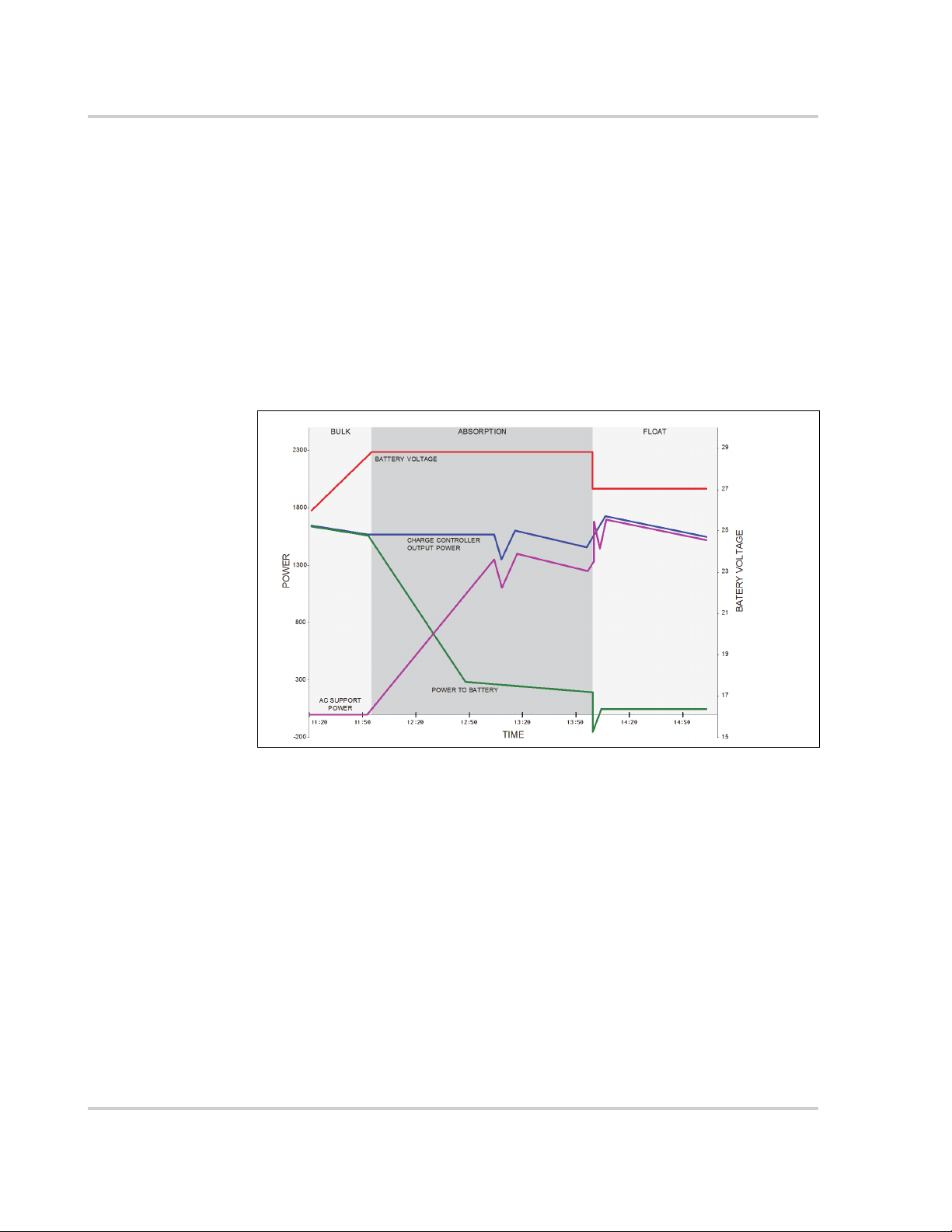
Figure 1-5 Enhanced AC Support Charge Cycle
Enhanced AC Support Charging Stages
• BULK Phase - During this phase, all PV energy from the charge controller is
diverted to the battery for maximum charging. During this phase, the Conext
SW does not engage AC support.
• ABSORPTION Phase - Once the charge controller is in absorption phase,
the charge controller output is split between the battery and Conext SW for
supporting AC loads. As the battery approaches full charge, more power
from the charge controller is diverted to Conext SW for AC support.
• FLOAT Phase - Once the battery is full and the charge controller transitions
to float phase, almost all the charge controller output is used by Conext SW
to support AC loads. The battery only receives a trickle charge to maintain a
healthy state of charge.
See “Enhanced AC Support Setting” on page 4–31.
1–10 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
Page 31

Regular AC Support without Xanbus devices
If no Xanbus-enabled devices, such as an MPPT charge controller, are
connected to the power system, then entry and exit into AC support mode is
based solely on battery voltage monitored by Conext SW. If the battery voltage is
above a set limit (AC Supp Volts), then AC support mode is engaged.
Grid-interactive and Other Features
NOTE: Entry and exit into AC Support Mode
is determined by the battery voltage. In this
case, AC support mode is engaged because
actual battery voltage is above the AC
support voltage level.
* To prevent injecting current into the grid from the inverter, there is less than 2 amps of offset allowed
from the grid to flow into AC IN under all conditions.
Figure 1-6 Regular AC Support without Xanbus Devices
With its charger enabled, the Conext SW enters AC support mode only after
completing a charge cycle when it is first powered up or reconnected to the grid.
For regular AC support mode set the Conext SW’s battery charge cycle to
2StgNoFloat to allow AC Support feature to function immediately after the
absorption charge stage.
Grid-Interactive Delay Feature
Conext SW has a delay feature that postpones the engagement of two gridinteractive features, namely load shaving and AC support, until a connected
MPPT solar charge controller has had a chance to charge the battery for two
hours in Float mode. The delay feature is called PLSDelay in SCP. The delay
feature prioritizes the MPPT solar charge controller’s ability to sufficiently charge
the battery bank. The feature works by inhibiting grid-interactive operation for two
hours from the time the charge controller transitions from Absorption to Float
charging. This allows the battery to be fully charged before either load shaving or
AC support mode is engaged. This feature is useful in applications where battery
micro-cycling is to be minimized in order to maximize battery life. See below.
<2A*
15 A
>13A
actual battery voltage = 25V
AC support voltage = 24V
Example: Load Shave = Enabled
LoadShaveStart = 10:00AM
PLSDelay = Enabled
Absorption to float charging starts at 7:00 AM and load shaving is set to start at
10:00 AM. Absorption transitions to float at 9:00 AM but because PLSDelay is
enabled, the 2-hour delay inhibits load shaving to actually start at 10:00 AM.
Because of the 2-hour delay, load shaving does not start until 11:00 AM. See
“Load Shaving 2-Hour Delay Example” on page 1–12.
975-0638-01-01 Rev G 1–11
Page 32

Introduction
Figure 1-7 Load Shaving 2-Hour Delay Example
The feature also ensures that self-consumption of harvested solar energy is
optimized. The 2-hour delay works only under the following conditions:
• Conext SW’s battery charge cycle must be set to 2StgNoFloat
• PLSDelay must be set to Enabled
• an MPPT solar charge controller must be connected and detected in the
Xanbus network
• the feature must not have been activated within that day
AC Coupling
This configuration can be enabled or disabled in “Advanced Features Menu” on
page 4–37. The default setting for PLSDelay is Disabled.
Off-grid AC Coupled system architecture is often used to create a stand-alone
grid. Commonly this means that PV inverters are connected to the output of a
battery-based inverter/charger putting both on the same AC bus along with the
AC loads. In this scenario, the battery powered inverter charger provides the
necessary frequency and voltage to enable the PV inverter to produce power.
This type of system must be able to maintain power generation in balance with
power consumption at all times. If there is more power being generated than can
be consumed by the loads, power will flow to the inverter/charger and be
converted to DC power which flows into the battery. Once the battery reaches
capacity, power generation by the PV inverter must be curtailed to maintain the
balance between generation and consumption. As the battery bank reaches
capacity, Conext SW curtails PV inverter generation by raising the AC line
frequency causing compatible PV inverters to reduce their power output in an
orderly manner. This is called Active Frequency Shift Power Curtailment.
During a grid outage even a home with a grid-tie PV inverter system will be
without power because PV inverters cannot produce power without the presence
of a reference voltage and frequency. To enable the PV inverter to provide power
during a grid outage the Conext SW is retrofitted in front of the PV inverter. The PV
inverter is rewired from the grid connection to a critical load (sub) panel and the
AC Couple is on the Conext SW AC Output port.
1–12 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
Page 33

Grid-interactive and Other Features
Consult the manufacturer's specifications to determine if your PV inverter is
compatible with Active Frequency Shift Power Curtailment. Conext SW’s AC
coupling function is enabled by default (see “Advanced Features Menu” on
page 4–37).
NOTICE
AC COUPLED PV INVERTER COMPATIBILITY
AC power generated by AC coupling PV inverters with Conext SW must be
consumed by AC loads or used to charge batteries. As an alternative, the
excess power produced from a PV inverter can be routed to dump loads. Do
not AC couple PV inverters with the Conext SW that are unable to reduce,
derate or cease the excess PV inverter power in response to the changes in
AC line frequency controlled by the Conext SW. Consult the manufacturer's
specifications of your PV inverter and confirm compatibility.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in equipment damage.
The AC coupling advanced setting should remain enabled except in cases when
the DC voltage level is allowed to have large variations and the line frequency
needs to remain constant.
Further details about AC Coupling can be found in the document “AC Coupling
Solutions Guide (Document Number: 976-0240-01-01)” available at
solar.schneider-electric.com.
AC Couple Smart Charge
AC Couple Smart Charge is a feature of the Conext SW that prioritizes battery
charging over energy export to local AC loads connected upstream of the
Conext CSW battery inverter. AC Coupling must be enabled for this feature to be
functional.
In AC-coupled configuration and with grid present, the Conext SW monitors flow
of power from its load port (AC Output) to the utility grid input (AC Input). When
power flow to the grid is detected and the battery needs charging after a short
delay, the Conext SW initiates a bulk charging cycle by switching to charge
mode and drawing AC power to charge the battery. It only draws enough energy
to keep the flow of power to the grid to zero. As long as the battery is able to
accept the energy, the Conext SW will continue diverting excess PV production
to the battery. Once the battery bank is at a level such that not all excess energy
from the PV Inverter is being absorbed, the balance will then flow out to upstream
loads in the house that are not connected to the Conext SW’s AC output port.
If PV production is lost for a prolonged period of time and the battery bank
discharges below the Recharge Volts setting, the Conext SW will initiate a normal
charge cycle and use power from the grid to charge the battery. For information
on this setting, see “Configuring Basic Settings” on page 4–7. In all of the above
modes of operation, only the PV Inverter exports energy to the grid. The Conext
975-0638-01-01 Rev G 1–13
Page 34

Introduction
SW itself cannot sell to the grid - it simply passes energy from the PV inverter to
the grid. For this reason, the PV Inverter must be fully grid code compliant as it
assumes responsibility for anti-islanding protection.
NOTICE
RISK OF INCOMPATIBLE EQUIPMENT
Check that the PV Inverter warranty covers off-grid applications, specifically
AC coupling with a battery- based inverter.
Check that the PV Inverter is capable of operating when it is AC-Coupled with
the inverter/charger which forms the local grid. PV Inverters with an
impedance sensing anti-islanding scheme are not compatible with the
inverter/charger.
Check that the PV Inverter can be configured to curtail power when the grid
frequency rises above 50.5 Hz and that power ceases to flow when the
frequency reaches 52.0 Hz.
Failure to follow these instructions could result in damage to equipment
not covered by warranty.
NOTICE
RISK OF DAMAGE TO THE GENERATOR
Never connect a generator to the AC Input terminal of a battery inverter
configured for AC coupling. The inverter will not be able to regulate the current
being backfed into the AC input and may backfeed AC current into the
generator.
Failure to follow this instruction can result in equipment damage.
NOTICE
RISK OF BATTERY DAMAGE
• To prevent battery damage in a micro-grid AC system, use only firmware
which has the AC coupling feature implemented. Always be sure to use the
latest firmware available for your inverter. For firmware upgrade
instructions, see the Conext Configuration Tool User’s Guide (document
part number: 975-0365-01-01) available on solar.schneider-electric.com.
• Do not use a Lithium Ion battery pack in AC-Coupled inverters.
Failure to follow this instruction can result in battery damage.
1–14 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
Page 35

Storing the State of the Inverter Mode
You can enable or disable a feature called StoreInvState which, when enabled
remembers the state of the inverter mode prior to a power down (that is, when AC
and DC power sources are disconnected). When the Conext SW is powered up
again, the inverter mode reverts back to its prior state.
See “Advanced Features Menu” on page 4–37.
NoLoadVD
The No Load Voltage Derating (NoLoadVD) feature further reduces tare loss by
adjusting output voltage by +4%/-5% of nominal, over the full load range. That
means at 50% load, the output voltage is at nominal but 5% below nominal at no
load and up to 4% at full load. The feature results in slight increase on overall
operating efficiency but may result in visible flicker of incandescent or similar
lights during large sudden load changes.
See “Advanced Features Menu” on page 4–37.
Low Battery Cut Out Hysteresis
Low battery cut out (Low Batt Cut Out) (LBCO) preserves battery life by
stopping the inverter when battery voltage drops down to the LBCO value for a
few seconds (see LBCO Delay below), then battery charging commences. When
charging starts, the voltage level jumps a little but enough that inverting might
resume abruptly. Then, battery voltage goes down again and charging starts
abruptly. To prevent the inverter from switching abruptly between inverting and
charging, the LBCO Hysteresis value is added to the LBCO value to allow the
battery voltage to reach a sufficient energy capacity level before inverting
resumes. This feature contributes to battery health.
Grid-interactive and Other Features
See “Advanced Features Menu” on page 4–37.
LBCO Delay
LBCO Delay (LBCO Delay) is the amount of time in seconds before inverting is
interrupted due to low battery voltage.
See “Advanced Features Menu” on page 4–37.
975-0638-01-01 Rev G 1–15
Page 36

Introduction
Lithium Ion Battery Type
See “LithiumIon Battery Settings Menu” on page 4–22.
Further details about Lithium Ion support can be found in the document “Lithium
Ion Application Note (Document Number: 976-0319-01-01)” available at
solar.schneider-electric.com.
BATTERY TYPE HAZARD
When using Lithium Ion batteries, ensure that the battery pack being used
includes a certified Battery Management System (BMS) with safety protocols.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in property damage, death
or serious injury.
WARNING
1–16 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
Page 37

2 Components and
Mechanical Features
The following topics will be covered in this
chapter.
• System Components
• Mechanical Features
975-0638-01-01 Rev G 2–1
Page 38

Components and Mechanical Features
System Components
The Conext SW uses Xanbus, a network communications protocol developed to
send Conext SW’s operational settings and status to other Xanbus-enabled
devices. You can configure and monitor the Conext SW and every Xanbusenabled device in the system using an optional System Control Panel (SCP).
Another component is the optional Automatic Generator Start (AGS) which allows
operation with a wide range of generators, supported through a dedicated
generator input. Simply, the AGS automatically starts and stops your generator.
Solar charge controllers allow renewable energy collected from the sun to charge
batteries as might be the case in an off-grid application of Conext SW. The
charge controllers form part of the Xanbus network.
See “Xanbus-enabled Products and Other Accessories” on page 2–3 for part
numbers.
Xanbus System
The Xanbus system includes the Conext SW and other Xanbus-enabled devices.
The Conext SW is the device in a Xanbus system that typically provides network
power—500 mA at 12 VDC. All of the Xanbus-enabled devices, such as the
Conext SW, the SCP, and the AGS are able to communicate their settings and
activity to each other.
Conext SWXanbus Network ________
MPPT 60150
Solar Charge
Controller
network terminator network terminator
SCP
Xanbus System Control Panel
AGS
Xanbus Automatic Generator Start
Conext
ComBox
Figure 2-1 Xanbus System Components
The Xanbus-enabled designation (see left) means that this product works on a
Xanbus network. Xanbus-enabled products are:
• Simple to operate and routine tasks are automated.
• Controlled by software that eliminates analog signalling errors.
• Less susceptible to interference and line loss.
• Upgradable through new software releases.
2–2 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
Page 39

For detailed instructions and a complete list of Xanbus-enabled devices, visit
www.schneider-electric.com.
Xanbus-enabled Products and Other Accessories
1
System Components
5
6
3
2
Product/Accessory (Shown above) Product Number/s
1 Conext SW DC Switch Gear* 865-1016*
2 Conext SW AC Switch Gear 865-1017
3 MPPT 60 150 Solar Charge Controller 865-1030-1
MPPT 80 600 Solar Charge Controller (not shown) 865-1032
4 Conext SW On/Off Remote Switch (not shown) 865-1052
5 System Control Panel (SCP) 865-1050
6 Conext CM (not shown) 865-1058
7 Automatic Generator Start (AGS) 865-1060
8 Conext Battery Monitor 865-1080-01
9 Battery Temperature Sensor (BTS) 808-0232-02
10 3-ft network cable (0.9 m) 809-0935
25-ft network cable (7.6 m) 809-0940
75-ft network cable (22.9 m) 809-0942
* required accessory for code-compliant installation in Canada and USA.
7
8
9
10
7.6 m cable 22.9 m cable0.9 m cable
975-0638-01-01 Rev G 2–3
Page 40

Components and Mechanical Features
Conext SW Inverter/Charger Mechanical Features
1
2
TOP TOP
3
77
4
5
Figure 2-2 Conext SW Front and Side Panels
Conext SW Front and Side Panels
Before you begin to operate the Conext SW, review the front panel features
shown in Figure 2-3 and described in the next table. A detailed view of the lights
and buttons on the front panel is also shown.
Item Description
1 Front Panel contains the Inv Enable and Clear Fault | Reset buttons, as
well as various LEDs (status indicator lights). See “Front Panel Buttons
and Status LEDs” on page 2–5.
2 Network and communications ports. See “AC and DC Terminals,
Network and Communication Ports Panel” on page 2–6.
3 DC battery terminals. See “AC and DC Terminals, Network and
Communication Ports Panel” on page 2–6.
6
2–4 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
Page 41

Item Description
4 AC Ground terminals. See “AC and DC Terminals, Network and
Communication Ports Panel” on page 2–6.
5 AC line terminals. See “AC and DC Terminals, Network and
Communication Ports Panel” on page 2–6.
6 Two variable-speed cooling fans maintain a cool internal temperature
of critical components. The two fans control airflow through the
transformer and power compartments of the unit. Ensure at least
6" (152 mm) of clearance for proper ventilation.
7 Mounting holes for permanent installation.
Front Panel Buttons and Status LEDs
Conext SW Inverter/Charger Mechanical Features
1
Figure 2-3 Front Panel Buttons and Status LEDs
Item Description
1 The Inv Enabled LED illuminates steadily when invert mode is enabled.
If AC is present and invert mode is enabled, this LED remains
illuminated even though AC power is being passed through.
Gen Support LED flashes intermittently when the inverter is in AC
Support mode or Load Shave mode.
2 When AC is present and qualified, the AC IN LED will illuminate steadily
indicating also that AC is passing through.
Charging LED flashes intermittently when the Conext SW is in charge
mode and is producing DC output to charge your batteries.
32
54
3 Fault | Warning LED illuminates steadily if a fault is detected (a fault
detection condition) and flashes intermittently when a warning
condition is active.
4 Clear Fault | Reset button is used to clear any fault detections if
pressed momentarily. If held down for more than three seconds, the
unit will reset (reboot) itself.
5 Inv Enable button is used to enable and disable inverter mode.
“Enabled” is different from the inverter being “on”. When enabled, the
inverter can be on or off. When disabled, the inverter is always off.
975-0638-01-01 Rev G 2–5
Page 42

Components and Mechanical Features
Conext SW AC/DC/Ports Side Panel
ELECTRICAL SHOCK AND FIRE HAZARD
Installation must be done by qualified personnel to ensure compliance with all
applicable installation and electrical codes and regulations. Instructions for
installing the Conext SW are provided in a separate installation guide for use
by qualified installers only.
Failure to follow these instructions will result in death or serious injury.
1
2
DANGER
7
3
4
5
6
8
Figure 2-4 AC and DC Terminals, Network and Communication Ports Panel
Item Description
1 Battery Positive (+)
2 Battery Negative (–)
3 XANBUS interface ports are used to connect Xanbus-enabled devices
including the optional SCP and AGS.
4 STACKING port. Feature not available in these models.
5 Remote (REM) port provides connection for the on/off remote switch.
6 Battery temperature sensor (BTS) port provides connection for the
battery temperature sensor (supplied).
7 AC input/output wiring compartment access panel with the
compartment cover
8 AC knockouts
DC terminal connects to the positive battery cable (red).
DC terminal connects to the negative battery cable (black).
2–6 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
Page 43

3 Operation
The following topics will be covered in this
chapter.
• Start Up Behavior
• Conext SW Front Panel
• Conext SW with the SCP – System Control Panel
• Battery Charging Reference
975-0638-01-01 Rev G 3–1
Page 44

Operation
Start Up Behavior
When the Conext SW is powered up (energized) or has been reset (using the
Reset button on the front panel), all of the front panel LEDs illuminate and remain
on for a minimum of five seconds. During this interval, the fans also turn on as the
unit executes internal diagnostics.
The Conext SW inverter function is initially disabled (meaning the unit will not
invert even if there is sufficient battery voltage) every time the Conext SW is
energized for the first time. After being energized, the Inv Enable button on the
front panel can be used to enable or disable the inverter. A separate control
device called a System Control Panel (or SCP) may also be used to enable or
disable the inverter. However, the unit will remember its inverter function setting in
succeeding operations. This means that if the inverter function is left enabled
before a reset or power down-power up cycle, the inverter function will remain
enabled.
When a function is enabled, it generally means that it is “standing by” and other
conditions may have to be met before the function is utilized. For example, the
charger function on the Conext SW may be enabled, but it will not charge unless
qualified AC power is present. Similarly, even if the inverter function is enabled,
inverting may not occur if the batteries cannot supply the energy required for the
loads.
IMPORTANT: Review the “Important Safety Instructions” on page v before
operating the inverter/charger.
3–2 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
Page 45

Inverter Operation Using the Front Panel
Inverter Operation Using the Front Panel
IMPORTANT: Review the “Important Safety Instructions” on page v before
operating the inverter/charger.
Once the inverter/charger is installed, you can operate it in invert mode. The
steps below will test the unit for normal operation using the front panel.
To test the inverter using the front panel:
1. Press the Inv Enable button on the Conext SW on the front panel. The
Inv Enabled LED illuminates.
2. Turn on the main AC breaker or AC disconnect to supply AC input power to
the inverter.
NOTE: The Inv Enabled LED will remain lit. However, AC will continue to be
passed through (also called AC bypass) to the loads until conditions exist that
cause AC to be disqualified, in which case the unit will start inverting. The AC
IN LED should also illuminate. The Charging LED will start flashing to
indicate that the unit is charging the battery. The charger automatically starts
when qualified AC power is connected and when the battery is not fully
charged.
3. Turn off the main AC breaker or AC disconnect to stop AC input power from
going into the inverter.
4. Place a load on the inverter. This also usually means turning on the inverter’s
AC distribution sub-panel’s breaker switch.
5. Connect a load such as a lamp into an outlet connected to the sub-panel
circuit and turn it on. The lamp lights up.
6. Repeat step #2. The lamp will remain lit up.
7. Repeat step #3. The inverter/charger should invert immediately. The transfer
relay will make a clicking sound and the Inv Enabled LED will illuminate.
The lamp should remain lit up. If any part of this test does not happen
correctly, determine the cause before continuing to use the unit.
8. Monitor the Conext SW front panel.
The indicator LEDs on the front panel show you the operating status of the
Conext SW. A description of the LEDs is provided in Table 3-1.
If none of the front panel LEDs are on, see “General Troubleshooting
Guidelines” on page 5–2.
975-0638-01-01 Rev G 3–3
Page 46

Operation
Table 3-1 Front Panel LEDs
Icon LED Status Action (or Status Item)
Steady
Green
If generator or grid AC is unavailable
and operating conditions are met,
the Conext SW will produce AC
voltage to power loads.
You can run your appliances from
the inverter.
Flashing
Green
Steady
Green
Flashing
Green
Steady
Red
Flashing
Red
The inverter is in AC Support or
Load Shave mode.
When the Conext SW is connected
to a generator or grid and is
producing qualified AC, the AC IN
light illuminates.
Conext SW is connected to a
qualified AC source, is charging and
passing-through power to AC loads.
A fault has been detected on the
network.
A warning is detected. Investigate by examining warning
You can run your appliances from
the inverter.
You can run your appliances using
passed-through AC.
Your battery bank is being
replenished and AC loads are
receiving power from a qualified AC
source.
Investigate and clear the fault
detection condition.
logs on SCP.
Fault Detections and Warnings A fault detection condition affects the
operation of the unit. A fault detection sometimes requires user intervention by
clearing the condition using the Clear Fault button on the inverter/charger’s front
panel. Press the button once to clear the condition. See “Troubleshooting” on
page 5–1 for information on clearing fault detections from the SCP.
A warning alerts you to a condition that could possibly affect operation of the
unit. A warning usually precedes a fault detection condition.
IMPORTANT: If you are having problems with any of your loads, refer to “Inverter
Applications” on page 5–3.
3–4 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
Page 47

Operating Limits for Inverter Operation
Temperature The Conext SW series of inverter/chargers will operate at rated
power continuously at 77 °F (25 °C) with some models capable of continuous
operation at much higher ambient temperature. However, the continuous power
rating at elevated ambient temperature may differ between models. See
“Environmental Specifications” on page 6–5 for full details. In higher ambient
temperatures, if the loads draw full power for an extended period of time, the unit
may shut down to protect itself against overheating.
Surge Power The Conext SW series of inverter chargers feature a surge rating
of 200% of rated power for five seconds at 77 °F (25 °C). See “Inverter
Specifications” on page 6–2 for full details. Operating the inverter/charger in
conditions outside of normal rated power and temperature limits, however, will
result in thermal shutdown and/or significantly decreased performance. See
“Inverter Specifications” on page 6–2 for information on continuous operation at
higher than rated power.
Difficulty on starting loads The inverter/charger should be able to operate all
AC loads rated at or below its power rating. Some high horsepower induction
motors used in pumps and other motor-operated equipment require very high
surge currents to start, and the inverter/charger may have difficulty starting these
loads.
Inverter Operation Using the Front Panel
If you have problems starting certain loads, ensure that:
• The battery connections are tight and clean.
• The DC cabling is no longer than the recommended length. Refer to the
Conext SW Inverter/Charger Installation Guide for this information.
• The AC wiring is of recommended size. Refer to the Conext SW Inverter/
Charger Installation Guide for this information.
• The battery is of sufficient capacity and is fully charged.
Split-phase output during invert mode and AC bypass The Conext SW always
yields a split-phase output when inverting and during AC bypass.
• A split-phase input through L1 and L2 yields a split-phase output of L1
and L2.
• Single-phase input through L1 yields a split-phase output of L1 and L2.
• A single-phase input through L2 does not produce any output. Only the
input in Line 1 is capable of qualifying the AC coming from the power
source.
975-0638-01-01 Rev G 3–5
Page 48

Operation
Battery power during AC bypass When sufficient AC is detected by the
inverter/charger and the battery is sufficiently charged, the AC is automatically
passed through to the loads. However, if the battery is less than 12 V (for 24-volt
models), 24 V (for 48-volt model), or had been disconnected, the inverter/
charger will not pass grid AC through to the loads.
NOTICE
EQUIPMENT DAMAGE
Do not energize and operate the inverter/charger with an AC source before
connecting a battery. Do not rely solely on AC bypass power to provide energy
to connected loads. Always operate with a battery connected to the inverter/
charger.
Failure to follow these instructions can damage the inverter/charger.
NOTICE
EQUIPMENT DAMAGE
Always try to balance load between lines L1 and L2. Damage to the internal
power transformer may occur if one line is overloaded when the other line is
unloaded.
Failure to follow these instructions can damage the inverter/charger.
3–6 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
Page 49

Operating Limits for Charger Operation
By default, the maximum charger output current is the rated charger output
current for the particular model. Using the SCP, you can reduce the total output if
you change the maximum charge rate (Max Chg Rate) on the Conext SW Basic
Settings menu or Charger Settings menu under Advanced Settings.
The charger can charge batteries when the AC input voltage line-to-neutral is
within the minimum and maximum range of 95 to 135 VAC. They are the default
minimum and maximum settings. The minimum range setting can be adjusted
from 78 to 115 VAC and the maximum range setting from 125 to 140 VAC.
The charger can also be configured to accept and operate from a wide AC
source frequency of 44–70 Hz. The default setting is 55 Hz for low frequency and
65 Hz for high frequency. This wide range allows the Conext SW to charge your
batteries even when incoming AC voltage is less than the typical 60 Hz.
Power Share The Conext SW charger uses both split-phase lines AC INPUT L1
and L2 to charge the batteries at full capacity. However, if only AC INPUT L1 is
used, charge capacity is reduced to 50%. Consequently, the Conext SW charger
shares incoming power with AC loads on both split-phase lines with a current
limit of 30 amps for charging and pass-through AC. However, when AC is
qualified only on one line at AC INPUT L1, the current draw from that input is
limited to 15 amps (SW 4024 120/240) and 13 amps (SW 2524 120/240) for
charging and AC pass-through. The AC loads have priority, which means that the
charger will reduce its output with large AC loads and increase the output again
when the AC load decreases. The regulatory maximum for continuous AC loads
is 80% of the breaker rating that the loads are connected to.
Inverter Operation Using the Front Panel
The Conext SW senses pass-through current going to the AC load. The
difference between the pass-through (load) and 80% of the Power Share setting
is the current that is available for charging the batteries.
For example, if the AC input of the Conext SW is from an AC panel with a 30-amp
breaker, the Power Share setting on the SCP should be selected as 30-amp.
Based on this, the charger will control the charge current so that the total current
draw is equal to or less than 24 amps in this case. Should the load current be
more than about 24 amps, the charger output will reduce to zero (0) amp, but the
Conext SW will continue to supply the loads. The Conext SW will continue to
pass-through power to the loads, even if the load current exceeds the Power
Share setting. In this case, it will be up to the user to remove/disconnect loads if
tripping the AC input breaker supplying the Conext SW is to be avoided.
975-0638-01-01 Rev G 3–7
Page 50

Operation
Inverter/Charger Operation using the System Control Panel (SCP)
This section contains detailed information and procedures for using your Conext
SW in conjunction with the SCP.
If you’re using the SCP to operate or monitor the status of the unit, you may also
refer to the System Control Panel Owner’s Guide.
WARNING
LI
LIMITATIONS ON USE
Do not use in connection with life support systems or other medical
equipment.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in death or serious injury.
The SCP provides operating, configuring, and monitoring capability for your
Xanbus system.
The System Control Panel:
• Monitors activity throughout your power system.
• Displays the latest information about your inverter/charger, battery voltage
level, battery charge output, and generator start and stop activity.
• Displays the settings for each Xanbus-enabled device in the system.
• Enables you to adjust the settings for each Xanbus-enabled device in the
system.
• Preserves all of its settings if system power is interrupted. After power is
restored, you don’t have to reconfigure the SCP or any of the Xanbusenabled devices connected to it.
The SCP provides remote configuration and monitoring capabilities for the
Conext SW and other Xanbus-enabled devices in the power system. Please refer
to the System Control Panel Owner’s Guide for complete information on using the
System Control Panel.
You can monitor Conext SW operation on the SCP using the:
• System Status screen (see page 3–11)
• Conext SW Home screen (see page 3–12)
• Conext SW Meters Menu (see page 3–15)
3–8 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
Page 51

SCP Features
Inverter/Charger Operation using the System Control Panel (SCP)
7
1
2345
Feature Description
1 Fault/Warning light indicates a device has a fault detection or warning
condition and requires attention. The light flashes when a warning
occurs and turns on steadily when a fault detection occurs.
2 Enter button confirms selection of a menu item or displays the next
screen.
3 Up arrow button scrolls upward through screen text or increases a
selected value.
4 Down arrow button scrolls downward through screen text or
decreases a selected value.
5 Exit button cancels selection of a menu item or displays the previous
screen.
6 Screen shows menus, settings, and system information.
6
7 Standby button disables inverting and charging on all Conext SW
units in the system when pressed and held for one to two seconds. To
enable inverting and charging, press and hold the Standby button
again for one to two seconds.
975-0638-01-01 Rev G 3–9
Page 52

Operation
Using the Standby Button
The Standby button has two functions, depending on how it is pressed. First,
when only the Standby button is pressed, it can disable inverting and charging
for all Conext SW units in the system. Second, when it is pressed simultaneously
with the Exit button, this action puts the entire system into Standby mode.
Pressing the Standby button produces the same result as disabling “Invert” and
“AC Charge” from the System Settings menu on the SCP. Pressing the Standby
button momentarily affects only Conext SW units; it does not affect charge
controller operation. After disabling inverting and charging with the Standby
button, the system continues to pass AC input through to the loads.
Pressing the Exit and Standby buttons at the same time puts the entire Xanbus
network system (including charge controllers) into Standby mode. In Standby
mode, the Conext SW stops passing AC input through to the loads.
After the keypress command to enter Standby mode, the AGS – Automatic
Generator Start (if installed) shuts down the generator (if it is running) after a
cool-down cycle.
SCP Navigation
Startup Screen
This section describes the different types of screens and menus on the SCP. To
monitor Conext SW operation and change settings, it is helpful to know how to
locate these screens and menus.
This screen is shown when the SCP first receives power from the Xanbus
network.
Figure 3-1 Startup Screen
3–10 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
Page 53

Viewing the SCP Home Screens
The top level screens on the SCP are the Startup screen, the System Status
screen, and the Device Home screens. After power is applied and the Startup
screen appears, the SCP displays the System Status screen. You can view the
Device Home screens for the Conext SW and other devices in the system by
pressing the up and down arrows, as shown in Figure 3-2.
Startup Screen
System Status
Screen
Inverter/Charger
Home Screen
Inverter/Charger Operation using the System Control Panel (SCP)
Appears for a few seconds after the system starts
up or when the system has been reset.
Press Enter to view
Select Device menu.
Select Device
Screen
Select device from list
and press Enter to view
device Setup menu.
System Status
Screen
Device 2
Home Screen
Device 3
Home Screen
Device n
Home Screen
Press Enter from a Device Home screen
to view the Device Setup menu.
The number of Home screens depends
on the number of Xanbus-enabled
devices installed in the system.
Figure 3-2 SCP Top Level Screens
The System Status screen appears after the Startup screen. The System Status
screen displays aggregated status information for the entire power system. For
example, a single system may have three Xanbus network-connected Conext
SWs, two MPPT Solar Charge Controllers, one AGS–Automatic Generator Start
module, and one SCP–System Control Panel all connected to a single battery
bank and a single AC generator.
The System Status screen always features a “Menu” arrow pointing to the Enter
button. Pressing Enter takes you to the Select Device menu.
975-0638-01-01 Rev G 3–11
Page 54

Operation
IMPORTANT: If you are uncertain which SCP screen or menu you are viewing,
you can always return to the starting point—the System Status screen—by
pressing Exit repeatedly until the screens stop changing.
The System Status screen displays:
• Qualified AC source (if applicable) and total power to and from the source
• Battery capacity and voltage level
• Net battery input or output current
• Total inverter loading
• Time and date
Line 1: Battery input/output current and voltage
Line 2: Battery level meter
Line 3: Power supplied to loads
Line 4: AC input source and line-to-line voltage
The menu arrow indicates the
Enter button. Press Enter to
display the Select Device menu.
Conext SW Home
Screen
Figure 3-3 System Status Screen
The Conext SW Home screen is the first of the Device Home screens. Each Conext
SW installed in the system has its own Home screen. The screen appearance
varies with the status of each inverter/charger. The Conext SW Home screen
displays real-time operating data specific to the Conext SW. The Conext SW
status changes according to the states described in Table 3-2 on page 3–13.
To display the Conext SW Home screen:
◆ While viewing the System Status screen, press the down arrow key.
Top Line: Device name and number
Line 1: Inverter/charger status
Line 2: Battery current (in + or out –) and voltage
Line 3: Power supplied to loads
Line 4: AC input status
The setup arrow indicates the Enter
button. Press Enter to display the
inverter/charger setup menu.
Figure 3-4 Conext SW Home Screen
The system arrow indicates the
Exit button. Press Exit to display
the System Home screen.
3–12 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
Page 55

Inverter/Charger Operation using the System Control Panel (SCP)
Pressing the down arrow button from the Conext SW Home screen displays the
Home screens for other Conext SW units and other Xanbus-enabled devices in
the system.
Table 3-2 Conext SW Home Screen States
Conext SW
Status Displayed When...
Invert The Conext SW is supplying power to loads by inverting power
from the batteries. AC input from the AC generator or grid is
absent or out of nominal range.
Qualifying ACThe Conext SW is determining if AC input from the AC
generator or grid is within a usable voltage and frequency
range. It is also displayed when the Conext SW is awaiting
application of AC power or a command to enable invert mode.
AC Support Conext SW powers critical loads by taking power from the
battery before any AC source.
See “AC Support Settings” on page 4–25.
Load Shave There is limited AC input from the AC source and the Conext
SW is supporting the AC source by supplying additional power
to the critical loads.
See “Load Shaving Setting” on page 4–29.
Bulk The Conext SW is bulk-charging the batteries from qualified
AC input from an AC generator or grid. AC input is also passed
through to the load while bulk-charging.
Absorption The Conext SW is absorption-charging the batteries from
qualified AC input from an AC generator or grid. AC input is
also passed through to the load while absorption-charging.
ABS Finish The Conext SW has completed the absorption stage and is
waiting for other Conext SWs in the system to complete
absorption. This status can occur only when there is another
Conext SW also charging the battery.
Equalize Equalization has been turned on, and the Conext SW is
equalizing the batteries after completing a full charge cycle.
Equalization time is fixed at 60 minutes.
Float The Conext SW is float-charging the batteries from qualified
AC input from an AC generator or grid. The Conext SW is set
for three-stage charging. AC input is also passed through to
the load while float-charging.
NoFloat The Conext SW finishes the absorption stage and the Conext
SW is set for two-stage charging.
ACGood The Conext SW has determined that AC input is within a usable
voltage and frequency range.
LdSenseActv Search Mode is enabled and the Conext SW is standing by
waiting to begin inverting. See “Using Search Mode” on
page 4–12.
ACCB/ACCA AC coupling is engaged.
975-0638-01-01 Rev G 3–13
Page 56

Operation
Viewing Other Screens
This section describes the next level of screens and menus on the SCP.
Select Device
Menu
Device Setup
Menus
The Select Device menu displays a list of Xanbus-enabled devices in the
system, including the Conext SW and the SCP. The Select Device menu is
where you can access the Setup menus for each device in the system. The
length of the Select Device menu depends on how many Xanbus-enabled
devices are installed.
The Select Device menu also contains the Clock menu (where the time and
date are set) and the System Settings menu (where system-level settings can
be configured). The System Settings, SCP, and Clock menus are always
available from the Select Device menu, regardless of the number of Xanbusenabled devices installed.
To display the Select Device menu:
◆ While viewing the System Status screen, press Enter.
Device Setup menus display status information (on the Meters screen) and
changeable settings. Changeable settings are identified by the square brackets
[ ] around values in the right-hand column.
To display the Setup menu for a device:
◆ Highlight the device name on the Select Device menu by using the up and
down arrow buttons, and then press Enter on the highlighted device.
-Or-
From the Home screen menu, simply press Enter.
Select Device menu Inverter/Charger Setup menu
Select device from list,
and then press Enter to
view device Setup menu
NOTE: The SCP only displays four lines of
the Setup menu at one time. To view
additional settings, press the down arrow
button.
Figure 3-5 Selecting a Device Setup Menu
When a particular device is selected, it is possible to change its settings and operate
the device using the Device Setup menu screen. For more information on how to
operate the Conext SW, see “Changing Operational Settings” on page 3–16.
3–14 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
Page 57

Inverter/Charger Operation using the System Control Panel (SCP)
Meters Screen The Meters screen displays total system power production, generator voltage
and current status, and load voltage and current status.
To view the Meters screen:
◆ On the Conext SW Setup menu highlight Meters, and then press Enter.
Figure 3-6 Viewing the Meters Screen
Table 3-3 Meters Screen
Screen Item Description
Mode Operating state of the Conext SW. See also “Conext SW Home
Screen States” on page 3–13.
Battery Displays battery voltage, charging current and battery
temperature. The battery temperature comes from the BTS,
connected to the Conext SW. If the BTS is not installed, Battery
shows as N/A (not available).
Load Displays power consumption (watts), voltage, and current
(amps) supplied to the AC loads.
AC Quality Displays the quality of the AC input. A good quality AC input
generally means that it falls between the high and low voltage
range set in “AC Settings” on page 4–24.
AC In L1 AC input current, voltage, and frequency connected to the
Conext SW AC INPUT L1 terminal.
AC In L2 AC input current, voltage, and frequency connected to the
Conext SW AC INPUT L2 terminal.
AC In L1L2 Combined L1 and L2 input voltage and frequency.
975-0638-01-01 Rev G 3–15
Page 58

Operation
Changing Operational Settings
The following table shows the various settings you can change to effectively
operate the Conext SW inverter/charger.
To navigate to the Conext SW Setup menu:
1. From the System Status screen (see 1A), press Enter to view the Select
Device menu. Go to step 2.
Or
From the Conext SW Home screen (see1B), press Enter. The Conext SW Setup
menu appears.
2. Highlight the Conext SW device name, and then press Enter.
1A 1B
2
Figure 3-7 Navigate To Conext SW Setup Menu
3–16 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
Page 59

Inverter/Charger Operation using the System Control Panel (SCP)
Table 3-4 Conext SW Setup menu
Menu Item Description
Inverter Enables or disables the inverter. See “To change an
operational setting” on page 3–18.
NOTE: When changing the operational setting for Inverter,
remember that enabling the inverter is not the same as the
inverter being turned on. An “enabled” inverter can either be
on or off, that is inverting or not inverting, respectively. A
“disabled” inverter cannot be turned on.
Search Mode Enables or disables Search Mode. See “To change an
operational setting” on page 3–18. For more information on this
setting see “Using Search Mode” on page 4–12.
Charger Enables or disables the charger. See “To change an
operational setting” on page 3–18.
NOTE: When changing the operational setting for Charger,
remember that enabling the charger is not the same as the
charger being turned on. An “enabled” charger can either be
on or off, that is charging or not charging, respectively. A
“disabled” charger cannot be turned on except when the
Auto Chg Enable is set to Enabled. See “Charger Settings
Menu” on page 4–13 for details.
Force Chg
State
Equalize Enables or disables battery equalization. See “To change an
Mode Selects the Conext SW operating mode: Operating or Standby.
Clear
Faults/
Warnings
View Device
Info
Meters Displays the Meters screen. See “To view the Meters screen:”
Basic
Settings
Advanced
Settings
Manually changes the charge stage to either Bulk or Float
(when 3-Stage cycle is selected) or Bulk or NoFloat (when 2Stage cycle is selected). See “To change an operational
setting” on page 3–18.
operational setting” on page 3–18.
The red Standby button on the SCP has similar functionality.
See “To change an operational setting” on page 3–18.
Clears any active faults that were detected or warnings. If the
fault detection or warning condition is still present, the fault
detection or warning message may reappear. See “To clear
fault detections/warnings:” on page 3–18.
Displays the View Device Info logs screen. On the Device Info
screen you can view the Warning, fault detection, and Event
Logs. See “View Device Info Logs” on page 5–4.
on page 3–15.
Select to display and/or adjust the basic Conext SW settings.
See “Configuring Basic Settings” on page 4–7.
Select to display and/or adjust the advanced Conext SW
settings. See “Configuring Advanced Settings” on page 4–9.
NOTE: Meters and View Device Info are not operational settings rather they
are informational. Basic and Advanced Settings are covered in another section of
the guide.
975-0638-01-01 Rev G 3–17
Page 60

Operation
CSW4024 00: Setup
Meters
Inverter
Search Mode
Charger
Force Chg State
Equalize
Mode
Clear Faults/Warnings
View Device Info
Basic Settings
[Enabled]
[Disabled]
[Enabled]
[Bulk]
[Disabled]
[Operating]
[*Enabled] [Disabled]
[*Enabled] [Disabled]
[*Enabled] [Disabled]
[*Bulk] [Float] [NoFloat]
[*Enabled] [Disabled]
[*Operating] [Standby]
Figure 3-8 Conext SW Setup Menu Operational Settings
To change an operational setting
1. From the device Setup menu screen, use the up or down arrow buttons to
highlight any operational setting you wish to change.
2. Press Enter then use the up or down arrow buttons to move between
selections. For example, the inverter setting can be changed to either
Enabled or Disabled.
3. Press Enter to confirm the selection.
4. Press Exit (twice) to go back to the System Status menu screen.
To clear fault detections/warnings:
1. From the device Setup menu screen, use the up or down arrow buttons to
highlight Clear Faults/Warnings.
2. Press Enter to clear the highlighted selection.
3–18 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
Page 61

4 Configuration via
SCP
The following topics will be covered in this
chapter.
• Viewing Conext SW’s Firmware Version
• Setting System Time and Date
• Viewing Basic and Advanced Settings
• Configuring Basic Settings
• Configuring Advanced Settings
975-0638-01-01 Rev G 4–1
Page 62

Configuration via SCP
Viewing the Firmware Revision Number
You may need to view the firmware revision number (F/W Rev.) of the Conext SW
when troubleshooting the unit with authorized service personnel.
To view the firmware revision number:
1. From the System Status screen, press the Enter button.
The Select Device menu screen appears.
2. From the Select Device screen, press the Enter button.
The System Settings menu screen appears.
3. From the System Settings screen, press the down arrow button to highlight
View Device Info then press Enter.
The Device Info screen appears.
4. Read the displayed information.
The series of numbers and letters opposite F/W Rev. is the firmware revision
number.
5. Press Exit (three times) to return to the System Status screen.
4–2 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
Page 63

Setting the Time and Date
The system time and date are set using the SCP. Time-stamped events such as
fault detections and warnings and logged historical data require that the system
be set to the correct time.
The SCP has an internal clock that controls the time for all Xanbus-enabled
devices in the system. You can set the time, time format, and date on the Clock
menu. The Clock menu is accessible on the Select Device menu.
To set the time and date:
1. From the System Status screen, press the Enter button.
The Select Device menu screen appears.
2. From the Select Device screen, press the down arrow button to highlight
Clock then press Enter.
The Clock screen appears and Set Time is highlighted.
3. Press Enter and use the up and down arrow buttons to change the hour
setting.
4. Press Enter and use the up and down arrow buttons to change the minute
setting.
5. Press Enter and use the up and down arrow buttons to select AM or PM.
This is not applicable if the 12/24 Hour setting is set to 24.
6. Press the down arrow button to highlight Set Date.
7. Press Enter and use the up and down arrow buttons to change the month
setting.
8. Press Enter and use the up and down arrow buttons to change the day
setting.
9. Press Enter and use the up and down arrow buttons to change the year
setting.
10. Press Enter to confirm the changes.
11. Press Exit (twice) to return to the System Status screen.
Setting the Time and Date
975-0638-01-01 Rev G 4–3
Page 64

Configuration via SCP
Viewing the Basic and Advanced Settings Menus
Basic Settings
menu
The Conext SW configuration settings can be viewed in Basic and Advanced
formats. The Basic Settings include configuration items you may have to adjust
routinely or as part of initial setup. The Basic Settings option appears by default
on the Setup menu screen.
The Conext SW Basic settings include menus for configuring:
• Battery type setting (see page 4–7).
• Battery capacity setting (see page 4–7).
• Maximum charging rate setting (see page 4–7).
• Charging cycle setting (see page 4–7).
• Recharge volts setting (see page 4–7)
• AC priority setting (see page 4–7).
• AC In Breaker settings (see page 4–7).
• Low battery cutout setting (see page 4–7).
To view the Basic Settings menu:
◆ From the Setup menu, scroll to the bottom of the screen to highlight Basic
Settings and press Enter. See Figure 4-2.
Figure 4-1 Selecting Basic Settings
To select and change a configurable setting:
1. On the desired configuration menu, press the up arrow or down arrow button
to highlight the setting you want to change.
2. Press Enter to highlight the current value of the setting.
3. Press the up arrow or the down arrow button to change the value. Hold down
the button to scroll through a large range of values quickly.
The previously set value appears with an asterisk (*) beside it.
4. Press Enter to select the value.
5. If you have another setting to change, return to step 1.
Or
If you have no more settings to change, press Exit until the SCP displays the
desired screen or menu.
4–4 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
Page 65

Viewing the Basic and Advanced Settings Menus
Advanced Settings
menu
The Advanced Settings option gives you access to the full range of Conext SW
settings, including everything displayed on the Basic menu. As a safeguard
against unintended Advanced configuration, the SCP displays the Basic settings
by default. To view the Advanced settings, you must perform a special keypress.
NOTICE
EQUIPMENT DAMAGE
The advanced settings are intended for qualified installation/service personnel
only. Before changing advanced settings, you must be familiar with the
settings and the system-wide impact of changing those settings. Setting
parameters incorrectly could damage connected equipment (such as
batteries) or could severely affect the performance of your system. Incorrect
charging configuration can lead to battery damage.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in equipment damage.
To select the Advanced Settings menu:
1. On the Select Device menu, select a Conext SW device.
2. Press Enter. The Setup menu screen appears.
3. Press Enter + up arrow + down arrow at the same time.
NOTES:
• This keypress (Enter + up arrow + down arrow) enables the Advanced
settings for every device in the system.
• After performing the keypress, “Advanced Settings” appears at the top of
the Setup menu (see Figure 4-2). When the keypress is performed again, the
Setup menu displays “Basic Settings” as the last item on the menu (see
Figure 4-1).
The Conext SW Advanced settings include menus for configuring:
• Inverter settings (see page 4–9).
• Charger settings (see page 4–13).
• AC transfer limit settings (see page 4–24).
• AC support settings (see page 4–25).
Multiple unit operation, including customizing the default model name of the
inverter/charger and setting its network device number. Setting the device
number is important when multiple Conext SW units are on the Xanbus network
and sharing connections such as AC loads and AC generator. The device
number is also used when configuring paralleled Conext SW units for masterslave operation (see page 4–32).
Additionally, from Conext SW Advanced settings, you can:
• Restore factory defaults
975-0638-01-01 Rev G 4–5
Page 66

Configuration via SCP
• Access other advanced features
To view the Advanced Settings menu:
◆ From the Setup menu, with Advanced Settings highlighted, press Enter. See
Figure 4-2.
Figure 4-2 Selecting Advanced Settings
To select and change a configurable setting:
1. On the desired configuration menu, press the up arrow or down arrow button
to highlight the setting you want to change.
2. Press Enter to highlight the current value of the setting.
3. Press the up arrow or the down arrow button to change the value. Hold down
the button to scroll through a large range of values quickly.
The previously set value appears with an asterisk (*) beside it.
4. Press Enter to select the value.
5. If you have another setting to change, return to step 1.
Or
If you have no more settings to change, press Exit until the SCP displays the
desired screen or menu.
IMPORTANT: If you have no more settings to change, it is recommended to
leave the Setup menu in the Basic Settings format to help prevent unintended
configuration. If the Setup menu displays “Advanced Settings,” press Enter + up
arrow + down arrow at the same time. The Setup menu should then display Basic
Settings as the last item on the menu.
4–6 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
Page 67

Configuring Basic Settings
EQUIPMENT DAMAGE
Transition the Conext SW to Standby modea(see page 3–10) before making
changes to the device settings. You may transition the unit back to Operating
mode after enacting the changes.
Failure to follow these instructions can damage equipment.
a.Critical loads will lose power and disconnect from the grid (or generator) when the Conext
SW transitions to Standby mode.
An overview of the Conext SW Basic Settings menu structure is shown below.
Configuring Basic Settings
NOTICE
Follow procedures on “To select and change a configurable setting:” on
page 4–4 to change the settings.
Figure 4-3 Menu Map of the Conext SW Basic Settings
Table 4-1 Setting Defaults and Ranges
Model 24-volt Models 48-volt Model
Setting Default Min Max Default Min Max
Batt Type Flooded Flooded, Gel,
AGM, Custom
Batt Capacity 250Ah 50Ah 100Ah 250Ah 50Ah 1000Ah
Max Chg Rate 100% 10% 100% 100% 10% 100%
Charge Cycle 3Stage 3Stage,
2StgNoFloat
ReCharge Volts 25.0V 22.0V 29.0V 50.0V 44.0V 58.0V
AC In Breaker 30A 5A 30A 30A 5A 30A
Flooded Flooded, Gel,
AGM, Custom
3Stage 3Stage,
2StgNoFloat
975-0638-01-01 Rev G 4–7
Page 68

Configuration via SCP
Table 4-1 Setting Defaults and Ranges
Model 24-volt Models 48-volt Model
Setting Default Min Max Default Min Max
Low Batt Cut
Out
Table 4-2 Basic Settings
Setting Description
Batt Type Sets the system battery chemistry and type: Flooded,
Batt Capacity Selects the system battery capacity in amp hours.
Max Chg Rate Sets the percentage of the maximum DC output current
Charge Cycle Sets the charging method: 3-Stage (bulk, absorption,
ReCharge Volts Sets the recharging volts to tell the charger to initiate
AC In Breaker Sets the breaker limit of incoming AC (generator or grid).
Low Batt Cut Out Low Battery Cut Out (LBCO) controls when the inverter
21.0V 20.0V 24.0V 42.0V 40.0V 48.0V
AGM, Gel, and Custom.
that is available to the charger. The maximum DC output
current for different models is:
SW 2524 120/240 — 65 ADC
SW 4024 120/240 — 90 ADC
SW 4048 120/240 — 45 ADC
If multiple Conext SWs are charging the same battery
bank, set each inverter's Max Chg Rate to 1/n of the
desired charge rate (where n is the number of inverter/
chargers).
float) or 2StgNoFloat (bulk, absorption, no float).
charging when the battery drains past the value setting.
stops producing AC output due to a low battery voltage
condition. The inverter will stop producing AC output only
after this level has been reached for the period of time set
by the LBCO Delay. This setting is not temperature
compensated.
4–8 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
Page 69

Configuring Advanced Settings
RISK OF DAMAGE TO CONNECTED DEVICES
The advanced settings are intended for qualified installation/service personnel
only. Before changing advanced settings, you must be familiar with the
settings and the system-wide impact of changing those settings. Setting
parameters incorrectly could damage connected equipment (such as
batteries) or could severely affect the performance of your system. Incorrect
charging configuration can lead to battery damage.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in equipment damage.
EQUIPMENT DAMAGE
Transition the Conext SW to Standby mode (see page 3–10) before making
changes to the device settings. You may transition the unit back to Operating
mode after enacting the changes.
Failure to follow these instructions can damage equipment.
Configuring Advanced Settings
NOTICE
NOTICE
Inverter Settings Menu
The Inverter Settings menu contains settings that control when the Conext SW
starts and stops producing AC output.
CSW4024 00: Adv
Inverter Settings
Charger Settings
AC Settings
Gen Support
Multi Unit Config
Restore Defaults
Adv Features
Follow procedures on “To select and change a configurable setting:” on page 4–6 to
change the settings.
Figure 4-4 Inverter Settings Menu Screen
Table 4-3 Setting Defaults and Ranges
Model 24-volt Models 48-volt Model
Setting Default Min Max Default Min Max
Low Batt Cut
Out
LBCO Hysteresis 2.0V 0.5V 5.0V 2.0V 0.5V 5.0V
LBCO Delay 10sec 0sec 600sec 10sec 0sec 600sec
Hi Batt Cut Out 29.0V 29.0V 34.0V 68.0V 58.0V 68.0V
CSW4024 00: Inv
Low Batt Cut Out
LBCO Hysteresis
LBCO Delay
Hi Batt Cut Out
Search Watts
Search Delay
Inv Block Start
Inv Block Stop
[21.0]
[2.0V]
[10sec]
[29.0V]
[50W]
[2sec]
[hh:mm AM]
[hh:mm AM]
[*21.0V] [20.0V] to [24.0V]
[*2.0V] [0.5V] to [5.0V]
[*10sec] [0sec] to [600sec]
[*29.0V] [29.0V] to [34.0V]
[*50W] [5W] to [250W]
[*2sec] [1sec] to [25sec]
21.0V 20.0V 24.0V 44.0V 40.0V 48.0V
975-0638-01-01 Rev G 4–9
Page 70

Configuration via SCP
Table 4-3 Setting Defaults and Ranges
Model 24-volt Models 48-volt Model
Setting Default Min Max Default Min Max
Search Watts 50W 5W 250W 50W 5W 250W
Search Delay 2sec 1sec 25sec 2sec 1sec 25sec
Inv Block Start 12:00AM n/a 12:00AM n/a
Inv Block Stop 12:00AM n/a 12:00AM n/a
NOTE: When charging is enabled for single-phase configuration,(120 VAC
output) the minimum charging voltage starts at 43.0 V for the 48-volt model.
Similarly, for the dual-phase configuration (120/240 VAC output) the minimum
charging voltage starts at 32.0 V,
Table 4-4 Inverter Settings Description
Setting Description
Low Batt Cut
Out
LBCO Hysteresis See “Low Battery Cut Out Hysteresis” on page 4–11.
LBCO Delay LBCO Delay controls how long the inverter is allowed to
Hi Batt Cut Out Hi Batt Cut Out sets the maximum battery voltage at which
Search Watts Search Watts sets the Conext SW’s search sensitivity when
Same description as “Basic Settings” on page 4–8.
operate at or below the Low Batt Cut Out level before
turning off due to a low battery voltage condition. The
inverter will stop producing AC output only after the
Low Batt Cut Out level has been reached for this
uninterrupted period of time.
Once the inverter has shut off, the battery voltage must rise
2 volts above the Low Batt Cut Out setting for inverter
operation to resume.
the inverter will operate. If the battery voltage exceeds this
limit for more than one minute, the Conext SW displays a
fault message and shuts down. The inverter will not support
AC loads when in this condition. If a qualified AC source is
present, the unit passes AC through to the loads. The
inverter automatically restarts when the voltage drops to
3 volts below the Hi Batt Cut Out setting. If battery
voltage continues to rise after shutdown, an external
charger may still be charging the batteries. The Conext SW
cannot control how external chargers operate.
search mode is enabled. When a load larger than this
setting is present, the inverter starts producing AC output.
Enabling search mode from the Setup menu can minimize
power draw from the battery during periods of low demand
from loads. Also see “Using Search Mode” on page 4–12.
4–10 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
Page 71

Table 4-4 Inverter Settings Description
Setting Description
Search Delay Search Delay sets the time between search pulses. When
searching for loads, the Conext SW sends out search
pulses to determine if a load is present. If the Conext SW
finds a load above the Search Watts setting, the inverter
turns on. Conext SW power draw while in search mode
decreases when Search Delay is increased, but the Conext
SW’s response time to active loads is slower.
Inv Block Start Sets the time to halt inverting. See “Using Inverter Block” on
page 4–13 for more information.
Inv Block Stop Sets the time to resume inverting. See “Using Inverter
Block” on page 4–13 for more information.
Using the Low Battery Cut Out and LBCO Delay Settings
The Low Batt Cut Out setting is the lowest battery voltage level acceptable for
use by the inverter. When the batteries discharge to the Low Batt Cut Out setting
and are held at or below this level for the LBCO Delay time, the inverter output
shuts down and transfers any available AC source (like an AC generator) to the
charger to bring the battery level back above the Low Batt Cut Out setting. After
shutdown, the inverter does not support any AC loads, and AC loads must be
powered by an AC generator.
Configuring Advanced Settings
If using an automatic generator starting system, it is recommended to set the
Xanbus AGS voltage trigger setting higher than the Conext SW Low Batt Cut Out
voltage. Otherwise, inverter output turns off before the generator automatically
starts, causing the battery voltage to recover slightly. This may then stop the
Xanbus AGS from starting the generator or result in the inverter cycling on and off
multiple times before the generator automatically starts.
If using an automatic generator starting system with the start trigger set to the
same voltage as the LBCO voltage, do not set the LBCO Delay for less than the
amount of time it takes the generator to start and connect. Otherwise, inverter
output turns off before the generator automatically starts, causing the battery
voltage to recover slightly. This may then stop the Xanbus AGS from starting the
generator or result in the inverter cycling on and off multiple times before the
generator automatically starts.
Low Battery Cut Out Hysteresis
Low battery cut out (Low Batt Cut Out) (LBCO) preserves battery life by
stopping the inverter when battery voltage drops down to the LBCO value for a
few seconds then battery charging commences. When charging starts, the
voltage level jumps a little but enough that inverting might resume abruptly. Then,
battery voltage goes down again and charging starts abruptly. To prevent the
inverter from switching abruptly between inverting and charging, the LBCO
Hysteresis value is added to the LBCO value to allow the battery voltage to
reach a sufficient energy capacity level before inverting resumes. This feature
contributes to battery health.
975-0638-01-01 Rev G 4–11
Page 72

Configuration via SCP
Using Search Mode
Why use Search
mode?
Single units When a single Conext SW has Search mode enabled, the inverter sends
Multiple units Search mode is automatically enabled in multiple unit installations with two
When to set up
Search mode
Search mode allows the inverter to selectively power only items that draw more
than a certain amount of power, which can result in power savings.
The Conext SW has a no-load power draw of about 38 W (SW 2524 120/240) and
40 W (SW 4024 120/240). Enabling Search mode reduces this power draw to
less than 8 W for all models.
Search mode operates differently in single-unit and multiple unit installations.
electrical search pulses through its AC output. These search pulses search for
connected AC loads. The delay between search pulses is set using the Search
Delay setting.
After a load larger than the Search Watts setting is detected, the inverter
turns on.
paralleled Conext SW units. Only the master Conext SW operates, and the slave
unit comes online only when the load exceeds approximately 60% of the rated
output of the master unit. When the load drops below 20% of the master’s rated
output, the slave unit turns off.
The Search mode feature is only valuable if the inverter can spend a couple of
hours “sleeping” each day. Therefore, if Search mode is to be used it must be
adjusted properly. The initial adjustment should be made so that the inverter
comes on only when needed.
Certain types of loads can cause Search mode not to work as expected. These
types of loads are described on “Problem Loads” on page 5–3 of the
Troubleshooting chapter. If these kinds of loads are in the system, follow the
suggestions given to eliminate the problem. If the problem loads cannot be
eliminated, there are two work-around solutions:
1. Disable Search Mode from the main Conext SW Setup menu, causing the
inverter to always remain at full output voltage.
2. Use a search-friendly companion load whose only purpose is to be switched
on to wake up the inverter to power the load that is unable to bring the
inverter out of Search mode.
NOTES:
• Search mode, by function, cannot work with clocks and timers or devices
that need power 24 hours a day. Examples of devices with timers include
video recorders, coffee makers with brew timers, refrigerators, and freezers
with defrost timers. Examples of devices that need power 24 hours a day
include telephone answering machines, alarm systems, motion detection
lights, and some thermostats.
• When the inverter is searching the output for loads, lights that have a
wattage lower than this setting may flash momentarily.
4–12 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
Page 73

Using Inverter Block
The Inverter Block feature halts inverter function for a period of time each day.
This period of time is defined by the Inv Block Start and Inv Block Stop
settings. Inverter Block allows you to control which time period is not ideal for
inverting. This can be a time period when conserving battery power is more
important than running loads.
The Inverter setting must be initially Enabled in order for the Inverter Block to
work as intended. The Inv Block Start setting disables inverter function if the
inverter is initially enabled and then Inv Block Stop enables the inverter
function. However, if the Inverter setting is initially Disabled when Inv Block
Start commences, then the succeeding Inv Block Stop will not enable inverter
function automatically. The inverter will remain disabled.
Setting the Inv Block Start and Inv Block Stop to the same time disables
Inverter Block. Disabling Inverter Block means that inverting is allowed to occur
at any time when the right conditions for inverting exist.
NOTE: In a multiple unit configuration, set the same Inverter Block settings to
both the master and slave units.
Charger Settings Menu
Configuring Advanced Settings
The Charger Settings menu provides options for configuring the Conext SW to
operate from your battery bank.
CSW4024 00: Adv
Inverter Settings
Charger Settings
AC Settings
AC Support
Multi Unit Config
Restore Defaults
Adv Features
Follow procedures on “To select and change a configurable setting:” on page 4–6 to
change the settings.
CSW4024 00: Chg
Batt Type
Custom Settings
LithiumIon Settings
Batt Capacity
Max Chg Rate
Charge Cycle
Default Batt Temp
ReCharge Volts
Absorb Time
Auto Chg Enable
Chg Block Start
Chg Block Stop
[Flooded]
[220Ah]
[100%]
[3-Stage]
[Warm]
[25.0V]
[180min]
[Enabled]
[hh:mm AM]
[hh:mm AM]
[*Flooded] [Gel] [AGM] [Custom] [LithiumIon]
[*220Ah] [50Ah] to [1000Ah]
[*80%] [10%] to [100%]
[*3-Stage] or [2StgNoFloat]
[*Warm] [Hot] [Cold]
[*25.0V] [22.0V] to [29.0V]
[*180min] [1min] to [480min]
[*Enabled] or [Disabled]
Figure 4-5 Charger Settings Menu Screen
975-0638-01-01 Rev G 4–13
Page 74

Configuration via SCP
Table 4-5 Setting Defaults and Ranges
Model 24-Volt Models 48-Volt Model
Setting Default Min Max Default Min Max
Batt Type Flooded Flooded, Gel,
AGM, Custom,
LithiumIon
Custom Settings See page 4–20. See page 4–20.
LithiumIon
Settings
Batt Capacity See page 4–7. See page 4–7.
Max Chg Rate 100% 10% 100% 100% 10% 100%
Charge Cycle 3Stage 3Stage,
Default Batt
Temp
ReCharge Volts 25.0V 22.0V 27.0 50.0V 44.0V 58.0V
Absorb Time 180min 1min 480min 180min 1min 480min
Auto Chg Enable
Chg Block Start 12:00AM n/a 12:00AM n/a
Chg Block Stop 12:00AM n/a 12:00AM n/a
See page 4–22. See page 4–22.
2StgNoFloat
Warm Hot, Warm, Cold Warm Hot, Warm, Cold
Disabled
Enabled,
Disabled
Flooded Flooded, Gel,
AGM, Custom,
LithiumIon
3Stage 3Stage,
2StgNoFloat
Disabled
Enabled,
Disabled
Table 4-6 Charger Settings Menu Description
Setting Description
Batt Type Sets the system battery chemistry and type: Flooded, AGM, Gel,
and Custom.
Selecting Custom displays the Custom Settings item, which
allows you to adjust the settings for each charging stage.
Custom
Settings
LithiumIon
Settings
Batt
Capacity
Max Chg
Rate
Charge
Cycle
4–14 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
See page 4–20.
See page 4–22.
See page 4–7.
Same description as “Basic Settings” on page 4–8.
Sets the charging method: 3Stage (bulk, absorption, float) or
2StgNoFloat (bulk and absorption only, no float).
Page 75

Table 4-6 Charger Settings Menu Description
Setting Description
Configuring Advanced Settings
Default
Batt Temp
ReCharge
Volts
Absorb
Time
Auto
Charge
Enable
Chg Block
Start
Chg Block
Stop
Selects the battery temperature charging compensation if a
battery temperature sensor is not installed. In the absence of a
battery temperature sensor, the charger uses one of three
settings:
Cold (50 °F/10 °C), Warm (77 °F/25 °C), or Hot (104 °F/40 °C).
Sets the recharging volts to tell the charger to initiate charging
when the battery drains past the value setting.
Sets the maximum time spent in the absorption stage, before
transitioning to float or no float.
NOTE: The Absorb Time setting resets to its default value of 180
minutes when the Battery Type is changed except when changing
to Custom Settings. In Custom Settings, the Absorb Time setting
will not reset to its default value.
When this setting is enabled, it overrides the “Charger” function to
begin charging automatically when qualified AC is present. This
happens even when the charger function is previously disabled.
Sets the time to halt charging. See “Using Charger Block” on
page 4–19 for more information.
Sets the time to resume charging. See “Using Charger Block” on
page 4–19 for more information.
Battery Charger Functions
When AC power is available, the Conext SW can operate as a battery charger.
Different battery types and chemistries require different charging voltage levels.
Not charging batteries at the required levels can shorten battery life or damage
the batteries. The Conext SW is configured at the factory to work with the battery
types recommended for inverter applications. If the default settings do not work
for your specific installation, you can adjust the charge stage settings (as
recommended by the battery manufacturer) on the Custom (Battery) Settings
menu (see page 4–20).
IMPORTANT: This information is provided for guidance only. Variations in
battery chemistry and site-specific environmental considerations mean that you
should consult your system designer or battery manufacturer for specific
recommendations for appropriate battery voltage and current settings.
975-0638-01-01 Rev G 4–15
Page 76

Configuration via SCP
Multi-Stage Charging Process
The charging cycle is a multi-stage process. Whenever qualified AC power is
present at the inverter’s input, it passes power through to the connected load and
begins charging the batteries.
NOTE: If the AC input fails or drops below the lower VAC limit (as set in AC
Settings), the complete multi-stage charge cycle (Bulk, Absorption, Float/No
Float) restarts once the source AC returns to within tolerance condition. If the
batteries are already nearly full, the charge cycle will take little time to complete.
Bulk Stage Bulk charge is the first stage in the charging process and provides the batteries
with a controlled, constant current. Once the battery voltage rises to the bulk
voltage threshold, the charger switches to the Absorption stage.
Table 4-7 Bulk Voltage Settings for Different Battery Types
24-Volt Models (Bulk Voltage) 48-Volt Model (Bulk Voltage)
Battery Type
Flooded 28.4V 28.8V 56.8V 57.6V
Gel 28.0V 28.4V 56.0V 56.8V
AGM 28.2V 28.6V 56.4V 57.2V
Custom 28.8V (changeable) 57.6V (changeable)
LithiumIon 29.0V (changeable) 58.0V (changeable)
Absorption Stage Absorption charge is the second stage of battery charging and provides the
batteries with a controlled, constant voltage. During this stage, the current drawn
by the batteries slowly decreases. When this current falls below 2% of the battery
capacity, or when the configurable Absorb Time expires, the charger switches to
the Float or NoFloat stage, depending on the selected charge cycle. The timer
begins when the battery voltage is above the bulk termination voltage for three
minutes.
NOTE: If there are DC loads on the batteries, the charger’s current may never
decrease to a level to initiate the next stage of charging. In this case, the
charger would stay in absorption until the Absorb Time setting is reached.
To make sure the charger does not remain in absorption for too long, adjust
Absorb Time on the Charger Settings menu.
Termination Preset Bulk Termination Preset Bulk
Also, the Absorption Time setting resets to its default value of 180 minutes when
the Battery Type is changed.
Table 4-8 Preset Absorption Voltage Settings for Different Battery Types
Battery Type 24-Volt Models 48-Volt Model
Flooded 28.8V 57.6V
Gel 28.4V 56.8V
4–16 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
Page 77

Configuring Advanced Settings
Table 4-8 Preset Absorption Voltage Settings for Different Battery Types
Battery Type 24-Volt Models 48-Volt Model
AGM 28.6V 57.2V
Custom 28.8V (changeable) 57.6V (changeable)
LithiumIon 29.0V (changeable) 58.0V (changeable)
Float Stage Float charge maintains a trickle charge on the batteries whenever AC is present
on the Conext SW input. Float charging reduces battery gassing, minimizes
watering requirements (for flooded batteries), and makes sure the batteries are in
a constant state of readiness. When three-stage charging is selected, the
charger automatically switches to the float stage after the batteries have received
a bulk and absorption charge. The batteries will be maintained at the default float
voltage level for the selected battery type or the voltage selected under Float
Voltage on the custom battery Settings menu.
NOTE: The battery voltage can increase above the float voltage when using an
external charging device such as PV arrays, wind turbines, or micro-hydro
generators. Be sure to include appropriate charge management equipment
with all external DC sources.
Table 4-9 Preset Float Voltage Settings for Different Battery Types
24-Volt Models
Battery Type
Flooded 27.0V 54.0V
Gel 27.6V 55.20V
AGM 26.8V 53.6V
Custom 27.0V (changeable) 54.0V (changeable)
LithiumIon 26.85V (changeable) 53.6V (changeable)
Two-Stage Two-stage (bulk and absorption only, no float) mode differs from an ordinary
three-stage charge mode in that it does not continuously maintain the battery at
float voltage. Instead, the Conext SW begins charging the battery in bulk mode
whenever the battery voltage drops below the recharge level. While the battery
voltage is above the recharge level, the inverter continues to pass power through
from the AC source to the loads but does not actively charge the batteries.
Preset Float Voltage
48-Volt Model
Preset Float Voltage
975-0638-01-01 Rev G 4–17
Page 78

Configuration via SCP
Equalize-Charging the Batteries
Many battery manufacturers recommend periodic equalize charging to level out the
voltage between individual cells, improving battery performance and lifespan.
Over time, the battery’s electrolyte can become stratified, causing inactive areas
in the plate material. If this condition is allowed to continue for extended periods,
the battery plates can sulfate and become unusable. Equalizing the batteries is a
controlled overcharging method that mixes up the electrolyte and reactivates the
unused areas of the plate material, restoring batteries to a full state of charge.
Consult the battery manufacturer’s recommendation for equalize voltage
settings. Equalization time is fixed at 60 minutes.
Table 4-10 Preset Equalization Voltage Settings for Different Battery Types
24-Volt Models
Preset Equalization
Battery Type
Flooded 32.0V 64.0V
Gel not applicable not applicable
AGM not applicable not applicable
Custom 32.0V (changeable) 64.0V (changeable)
LithiumIon not applicable not applicable
To start equalizing the batteries:
Voltage
48-Volt Model
Preset Equalization
Voltage
◆ On the device Setup menu, highlight Equalize and select Enabled.
NOTE: Only flooded or vented batteries should be equalize-charged.
Hydrogen and oxygen gases are produced when batteries are equalizecharged. See warning below.
WARNING
EXPLOSION HAZARD
Provide adequate ventilation and remove all sources of ignition to prevent
explosion.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in death or serious injury.
IMPORTANT: In a system where more than one device is capable of equalizing
batteries (such as a system including multiple Conext SW units and Solar Charge
Controllers), there is no system-wide equalization command for all devices. To
equalize with multiple devices, each would have to be enabled individually.
Alternatively, equalization can be performed using only one device. During the
equalization process, one device applies the equalization charge while the other
devices continue to operate in synchronized charge mode, typically in float
(three-stage charging) or no-float (two-stage charging).
4–18 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
Page 79

Using Charger Block
Configuring Advanced Settings
The Charger Block feature halts charging for a period of time each day. This
period of time is defined by the Chg Block Start and Chg Block Stop settings.
In areas where the utility charges variable rates for electricity, it is preferable to
use utility power for charging only during non-peak hours. Charger Block can
prevent utility power from being used for battery charging during peak billing
periods. During the time period set between Chg Block Start and Chg Block
Stop, AC input continues to be passed through to the loads. Inverter operation
remains unaffected during the charger block period. During the Charger Block
period, no charging occurs even if the batteries discharge below the ReCharge
Volts setting. However, a Solar Charge Controller may charge batteries during
the Charger Block period.
If the charger is operating (that is, in Float, Absorption, Bulk, or Equalize stage) at
the Chg Block Start time, charging stops immediately and the charger enters
an idle state identical to No Float (see “Two-Stage” on page 4–17). When the
Charger Block period is over, the charger does not resume the charge stage that
Chg Block Start interrupted. Instead, if the batteries are above the ReCharge
Volts setting, the charger remains idle. If the battery voltage falls below the
ReCharge Volts setting during the Charger Block period, the Conext SW
Inverter/Charger begins a new charge cycle with the Bulk stage after the
Charger Block period has expired (at the Chg Block Stop time).
Setting the Chg Block Start and Chg Block Stop to the same time disables
Charger Block. Disabling Charger Block means that charging is allowed to occur
at any time when the right conditions for charging exist.
975-0638-01-01 Rev G 4–19
Page 80

Configuration via SCP
C
Custom Battery Settings Menu
EQUIPMENT DAMAGE
Consult your battery manufacturer and associated documentation before
setting a custom battery type and before battery charging or equalization.
Failure to follow this instruction may cause damage to the battery.
CSW4024 00: Chg
Batt Type
Custom Settings
Batt Capacity
Max Chg Rate
Charge Cycle
Follow procedures on “To select and change a configurable setting:” on page 4–6 to
change the settings.
[Custom]
[220Ah]
[100%]
[3-Stage]
NOTICE
ustomSettings appears only when
Batt Type is set to Custom.
CSW4024 00: Cust
Eqlz Support
Eqlz Voltage
Bulk Voltage
Bulk Termination Voltage
Absorb Voltage
Float Voltage
BattTempComp
[Enabled]
[32.0V]
[28.8V]
[28.4V]
[28.8V]
[27.0V]
[-54mV/C]
Eqlz Voltage appearsonly
when Eqlz Support is
Enabled.
Figure 4-6 Custom Settings Menu Screen
Table 4-11 Setting Defaults and Ranges
Model 24-Volt Models 48-Volt Model
Setting Default Min Max Default Min Max
Eqlz Support Enabled Enabled,
Disabled
Enabled Enabled,
Disabled
Eqlz Voltage 32.0V 27.0V 32.0V 64.0V 54.0V 64.0V
Bulk Voltage 28.8V 22.4V 32.0V 57.6V 50.8V 64.0V
Bulk
28.4V 22.0V 31.6V 56.8V 50.0V 63.2V
Termination
Voltage
Absorb Voltage 28.8V 24.0V 32.0V 57.6V 40.0V 64.0V
Float Voltage 27.0V 22.0V 32.0V 54.0V 50.0V 64.0V
Batt Temp Comp -54mV/C -0mV/C -90mV/C
-108mV/C
-0mV/C
-108mV/C
The Custom Battery Settings menu can be viewed if Custom is selected as the
Batt Type. This menu allows you to adjust charging and equalization voltage for
batteries with specifications that fall outside the default settings for the battery
types the Conext SW offers. You can also adjust the temperature compensation
constant for the battery temperature sensor on this menu.
IMPORTANT: All settings for configuring a custom battery type are based on the
default settings for a flooded battery type.
4–20 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
Page 81

Configuring Advanced Settings
Table 4-12 Custom Battery Settings Menu Description
Setting Description
Eqlz Support Enables or disables the ability to enter an equalization cycle.
Refer to the battery manufacturer’s specifications to determine
whether equalization is recommended.
Eqlz
Voltage
a
Selects the equalization voltage. Consult your battery
manufacturer for equalization voltage setting.
Bulk Voltage Sets the bulk voltage for a custom battery type. This setting
must be 0.8 V or more for the 48-volt model (or 0.4 or more for
the 24-volt models) than the Bulk Termination Voltage. See note
below.
Bulk
Termination
Voltage
Sets the bulk termination voltage for a custom battery type.
This setting must be 0.8 V or less for the 48-volt model (or 0.4
or less for the 24-volt models) than the Bulk Voltage. See note
below.
Absorb
Sets the absorption voltage for a custom battery type.
Voltage
Float
Voltage
Batt Temp
Comp
Sets the float voltage for a custom battery type. See note
below.
Battery temperature compensation for a custom battery type.
This setting is the reference that the BTS uses to adjust the
charging voltage when the temperature is above or below
77 °F (25 °C).
a.The Eqlz Voltage setting is displayed when Eqlz Support is set to Enabled.
NOTE: If a warning is received indicating that a setting is not accepted by the
SCP, gradually increase the value of the setting until the SCP accepts it. This
type of warning means that an internal minimum threshold value is being crossed
and therefore the setting cannot be saved.
975-0638-01-01 Rev G 4–21
Page 82

Configuration via SCP
LithiumIon Battery Settings Menu
BATTERY TYPE HAZARD
When using Lithium Ion batteries, ensure that the battery pack being used
includes a certified Battery Management System (BMS) with safety controls.
Failure to follow this instruction can result in property damage, death
or serious injury.
CSW4024 00: Chg
Batt Type
LithiumIon Settings
Batt Capacity
Max Chg Rate
Charge Cycle
Follow procedures on “To select and change a configurable setting:” on page 4–6 to
change the settings.
[LithiumIon]
[250Ah]
[100%]
[3-Stage]
WARNING
LithiumIon Settings appears only
when Batt Type is set to LithiumIon.
CSW4024 00: LithiumIon
Control
Bulk Voltage
Max Bulk Current
Absorb Voltage
Max Absorb Current
Float Voltage
Max Float Current
DisChgImax
DisChgImax Timer
[3-Stage]
[29.0V]
[90A]
[29.0V]
[90A]
[26.8V]
[90A]
[150%]
[10s]
Figure 4-7 LithiumIon Settings Menu Screen
Table 4-13 Setting Defaults and Ranges
Model 24-Volt Models 48-Volt Model
Setting Default Min Max Default Min Max
Control 3-Stage Ext BMS,
2-Stage,
3-Stage
3-Stage Ext BMS,
2-Stage,
3-Stage
Bulk Voltage 29.0V 28.2V 32.5V 58.0V 56.2V 65.0V
Max Bulk
90A 15A 90A 45A 10A 45A
Current
Absorb Voltage 29.0V 20.0V 32.5V 58.0V 40.0V 65.0V
Max Absorb
90A 15A 90A 45A 10A 45A
Current
Float Voltage 26.8V 23.6V 32.0V 53.6V 47.2V 64.0V
Max Float
90A 1A 90A 45A 1A 45A
Current
DisChgImax 150% 20% 500% 150% 20% 500%
4–22 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
Page 83

Configuring Advanced Settings
Table 4-13 Setting Defaults and Ranges
Model 24-Volt Models 48-Volt Model
Setting Default Min Max Default Min Max
DisChgImax
Timer
The LithiumIon Settings menu can be viewed if LithiumIon is selected as the
Batt Type. This menu allows you to adjust charging and equalization voltage for
batteries with specifications that fall outside the default settings for the battery
types the Conext SW offers.
Table 4-14 LithiumIon Battery Settings Menu Description
Setting Description
Control Identifies the kind of battery management system.
Bulk Voltage Sets the bulk voltage for a LithiumIon battery type.
Max Bulk
Current
Absorb
Voltage
Max Absorb
Current
Float
Voltage
10s 1S 300s 10s 1s 300s
Sets the maximum bulk current for a LithiumIon battery type.
Sets the absorption voltage for a LithiumIon battery type.
Sets the maximum absorption current for a LithiumIon battery
type.
Sets the float voltage for a LithiumIon battery type.
Max Float
Current
DisChgImax Sets the maximum current discharge in percentage.
DisChgImax
Timer
975-0638-01-01 Rev G 4–23
Sets the maximum float current for a LithiumIon battery type.
Sets the maximum current discharge timer.
Page 84

Configuration via SCP
AC Settings
The AC Settings menu configures the voltage and frequency limits for AC In.
These are the limits at which the Conext SW considers input voltage qualified—
that is, suitable for charging batteries or powering loads. If the input voltage is
not qualified according to these settings, the Conext SW transfers from using AC
input to inverting.
CSW4024 00: Adv
Inverter Settings
Charger Settings
AC Settings
AC Support
Multi Unit Config
Restore Defaults
Adv Features
CSW4024 00: AC
ACIn Breaker
ACIn Lo Volt
ACIn Hi Volt
ACIn Lo Freq
ACIn Hi Freq
[30.0A]
[190.0V]
[270.0V]
[55Hz]
[65Hz]
[*30A] [5A] to [30A]
[*190.0V] [156.0V] to [230.0V]
[*270.0V] [250.0V] to [280.0V]
[*55Hz] [44Hz] to [59Hz]
[*55Hz] [61Hz] to [70Hz]
Follow procedures on “To select and change a configurable setting:” on page 4–6 to
change the settings.
Figure 4-8 AC Settings Menu Screen
Table 4-15 Setting Defaults and Ranges
Model All Models
Setting Default Min Max
ACIn Breaker 30A 5A 30A
ACIn Lo Volt 95V 78V 115V
ACIn Hi Volt 135V 125V 140V
ACIn Lo Freq 55Hz 44Hz 59Hz
ACIn Hi Freq 65Hz 61Hz 70Hz
Table 4-16 AC Settings menu
Setting Description
ACIn Breaker Sets the AC Input breaker size, based on the size of the
installed AC breaker at the source. The Breaker size setting
must not exceed the capacity of the AC source such as the
grid or a generator. The Conext SW limits the maximum input
current to this setting by derating its charging current. If the
connected loads exceed the breaker setting, the AC breaker
trips. The breaker may not trip if Load Shave is enabled and
Load Shave Amps is configured not to exceed the AC source’s
rated output current.
4–24 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
Page 85

Table 4-16 AC Settings menu
Setting Description
ACIn Lo Volt Sets the minimum acceptable AC input voltage level from the
ACIn Hi Volt Sets the maximum acceptable AC input voltage level from the
ACIn Lo Freq Sets the minimum acceptable AC input frequency from the AC
ACIn Hi Freq Sets the maximum acceptable AC input frequency from the AC
AC Support Settings
AC Support settings contain configuration options for grid-interactive operation
including AC support mode, load shaving (also applicable to generator only AC
source), and enhanced AC support for DC coupled systems.
Configuring Advanced Settings
AC source (generator or grid).
NOTE: It is recommended to leave this setting to its default
value and not to set it to the maximum allowed. Doing so might
inadvertently derate charging power in jurisdictions where the
nominal AC mains voltage or generator output is at 110 volts.
AC source (generator or grid).
source (generator or grid).
source (generator or grid).
Follow procedures on the Conext SW Owner’s Guide to change the settings.
Figure 4-9 AC Support Menu Screen
NOTE: To prevent injecting current into the grid from the inverter, set Load Shave
Amps to a value that is greater than there is less than 2 amps of offset allowed
from the grid to flow into AC IN even when Load Shave Amps is set to 0.
Table 4-17 AC Support Menu Description and Values
a
Setting Description Default Range
AC Supp Mode
AC Supp Volts
For 24-volt models
Turns AC Support Mode feature
on and off.
Battery voltage threshold in
order to engage regular AC
Support Mode.
Enabled Disabled,
Enabled
26.5V
For 24-volt models
23.0V to 35.0V
cannot be set below
Low Batt Cut Out +
2 volts
975-0638-01-01 Rev G 4–25
Page 86

Configuration via SCP
Table 4-17 AC Support Menu Description and Values
a
Setting Description Default Range
AC Supp Volts
For 48-volt model
Load Shave
Load Shave
Amps
LoadShave
Start
LoadShave
Stop
AC Supp on
Soc
AC Supp Start
Soc
AC Supp Stop
Soc
a.Applies to all Conext SW models.
Battery voltage threshold in
order to engage regular AC
Support Mode.
Enables or disables the load
shaving feature. When in this
mode, the Conext SW operates
until the batteries discharge to
the Low Batt Cut Out
threshold, after which the unit
starts charging the batteries.
The charger is automatically
blocked during the load
shaving time window.
Sets the maximum amount of
current that can be drawn from
the AC source input by the
loads and battery charger
combined. This setting
determines the amperage level
at which the inverter starts
drawing power from the
batteries to add to the power to
meet load demands. Typically,
this value is set to the peak
usage surcharge threshold
imposed by the utility, if
applicable. See NOTE above.
Sets the time for when load
shaving is engaged.
Sets the time for when load
shaving is disengaged.
Enables or disables the SOC
monitoring for AC Support
Mode.
This setting must be enabled for
AC Supp Start Soc and AC
Supp Stop Soc to take effect.
Sets the high percentage value
of the SOC of the battery for AC
Support Mode to engage.
Applicable only when AC Supp
on Soc is enabled.
Sets the low percentage value
of the SOC of the battery for AC
Support Mode to disengage.
Applicable only when AC Supp
on Soc is enabled.
53.0V
For 48-volt model
46.0V to 70.0V
cannot be set below
Low Batt Cut Out +
2 volts
Disabled Disabled,
Enabled
24A 1A to 24A
12:00 AM
12:00 AM
Setting the Load
Shave Start and Load
Shave Stop to the
same time disables
scheduling.
Enabled Disabled,
Enabled
80% 70% to 100%
50% 20% to 60%
4–26 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
Page 87

AC Support Mode Setting
When AC Support Mode is enabled, the Conext SW does not ordinarily draw a
large amount of current from the grid. If the Conext SW is drawing more current
than expected, notice that it cannot distinguish between real power and reactive
power. Large current draw will only affect reactive power and not real power, and
utility companies generally only charge by real power consumed.
When AC Support Mode is enabled, the Conext SW primarily supplies local loads
by converting capacity from its battery bank and then only utilizing grid power
when the loads demand more capacity. In addition to AC Support Mode, the
Conext SW also has the enhanced AC support feature. See “Enhanced AC
Support Setting” on page 4–31.
When AC Support Mode is enabled during multiple unit operation, only one of the
units will charge when battery voltage falls below the ReCharge Volts setting.
To use the AC Support Mode feature:
1. Enable AC support mode. AC support mode is enabled by default. Check
only to see if it is enabled. If not, enable it.
Go to Advanced Settings -> AC Support -> AC Supp Mode
Configuring Advanced Settings
2. Set the battery voltage threshold for AC support mode to engage.
NOTE: Applicable only when there are no Xanbus devices attached as
described in “Regular AC Support without Xanbus devices” on page 1–11.
an
From AC Support -> AC Supp Volts
Press Enter, then select a value using the up
and down arrow buttons. Press Enter.
3. Enable state-of-charge (SOC) monitoring if you have a Conext Battery
Monitor installed. AC support on SOC is disabled by default.
975-0638-01-01 Rev G 4–27
Page 88

Configuration via SCP
an
From AC Support -> AC Support on SOC
Press Enter, then select Enabled using the
up and down arrow buttons. Press Enter.
4. Set the battery SOC thresholds for when AC support mode is engaged.
From AC Support -> AC Supp Start Soc
Press Enter, then select a value using the up
and down arrow buttons. Press Enter.
From AC Support -> AC Supp Stop Soc
Press Enter, then select a value using the up
and down arrow buttons. Press Enter.
4–28 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
Page 89

Load Shaving Setting
For Load shaving to be effective, all loads must be connected to the inverter. To
help the batteries supplement the power requirements of the connected load, an
additional source of power (like solar, wind, or hydroelectric) is recommended
but not required.
To demonstrate a scenario where load shaving takes effect on the Conext SW,
the following settings are programmed into the SCP.
Scenario Settings: Load Shave=Enabled
LoadShaveAmps=10A
LoadShaveStart=6:00AM
LoadShaveStop=9:00PM
PLSDelay=Enabled
To use the Load Shaving feature:
1. Enable load shaving.
Go to Advanced Settings -> AC Support -> Load Shave
Press Enter, then select Enabled using the up and down arrow
buttons. Press Enter.
Configuring Advanced Settings
2. Set the load shaving amps.
From AC Support -> Load Shave Amps
Press Enter, then select a value of 10 using
the up and down arrow buttons. Press Enter.
3. Set the load shaving start and stop times.
975-0638-01-01 Rev G 4–29
Page 90

Configuration via SCP
From AC Support -> LoadShaveStart
Press Enter, then a time of 6:00 AM using the
up and down arrow buttons. Press Enter.
From AC Support -> LoadShaveStop
Press Enter, then a time of 9:00 PM using the
up and down arrow buttons. Press Enter.
4. Enable the grid-interactive delay feature.
Go back to Advanced Settings -> Adv Features -> PLSDelay
Press Enter, then select Enabled using the up and down arrow
buttons. Press Enter.
In this scenario, load shaving is only entered and exited as programmed within
the time window (from 6 AM to 9 PM).
Additionally, with these scenario settings, the Conext SW would enter load
shaving within the configured time and also only if the battery has been charged
from an MPPT charge controller in Float (including Absorption) for 2 hours.
NOTE: In the absence of an MPPT charge controller, charger block stop and
start settings must be set at the same times as the load shaving stop and start
settings. Otherwise, charging may start even during load shaving.
4–30 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
Page 91

Configuring Advanced Settings
Enhanced AC Support Setting
Self-consumption The goal of the enhanced AC support (EnhancedACSup) feature is to make sure
that the power system self-consumes the power it harvests from a PV array. It
does this by keeping the battery bank charged up and ready to supply power to
the loads.
When EnhancedACSup is enabled, the Conext SW supports local loads by
converting excess capacity from external DC sources connected to its battery
bank. An example of an external DC source is the Conext MPPT solar charge
controller like the MPPT 80 600.
To use the Enhanced AC Support feature:
1. Enable AC support mode. AC support mode is enabled by default. Check
only to see if it is enabled. If not, enable it.
Go to Advanced Settings -> AC Support -> AC Supp Mode
2. Enable enhanced AC support.
Go back to Advanced Settings -> Adv Features -> EnhancedAcSup
Press Enter, then select Enabled using the up
and down arrow buttons. Press Enter.
975-0638-01-01 Rev G 4–31
Page 92

Configuration via SCP
Multi Unit Config Menu
The Multi Unit Config menu configures the Conext SW to operate as a part of
a multiple unit installation1.
CSW4024 00: Adv
Inverter Settings
Charger Settings
AC Settings
AC Support
Multi Unit Config
Restore Defaults
Adv Features
CSW4024 00: Multi
Dev Name
Dev Number
Invtr Mode
AC In
Battery
[CSW4024]
[00]
[Master]
[Gen1]
[HouseBatt1]
[*Master] [Slave]
[*Gen1] [Grid1]
[*HouseBatt1]...[HouseBatt5]
Follow procedures on “To select and change a configurable setting:” on page 4–6 to
change the settings.
Figure 4-10 Multi Unit Config Menu Screen
IMPORTANT: Accessing this menu automatically places the Conext SW in
standby mode. When entering the Multi Unit Config menu, the unit identifies
itself by flashing all front panel LEDs. After exiting the Multi Unit Config menu,
the Conext SW returns to operating mode and the front panel LEDs stop flashing.
Table 4-18 Multi Unit Menu Description and Values
a
Setting Description Default Range
Dev Name Allows the customizing
of the default name for
the inverter/charger.
CSW4024
will vary from model
to model.
Can be
changed by
the user.
This setting is optional
and does not affect
operation. See “Setting
the Device Name” on
page 4–33.
Dev Number Allows setting of a
unique unit number in a
multiple-unit system.
See “Setting the Device
Number” on page 4–34.
Invtr Mode For this to operate, one
Conext SW must be
00 usually for a
00–31
single unit or for two
units, this will
designate the
master.
Master Master,
Slave
configured to Master
and the other as Slave,
otherwise a system-wide
fault is asserted.
1.In Conext SW Inverter/Chargers, multiple unit configuration (installation) is limited to two
units - one master unit and one slave unit.
4–32 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
Page 93

Configuring Advanced Settings
Table 4-18 Multi Unit Menu Description and Values
a
Setting Description Default Range
AC In For identifying the type
Gen1 Gen1, Grid1
of AC source when two
power sources are
available and an AGS is
also present.
Battery For identifying batteries
only.
a.Applies to all Conext SW models.
HouseBatt1 HouseBatt1..
HouseBatt5
When installing a multiple unit system, every setting on the Multi Unit Config
menu (except for Dev Name) must be configured for each of the two Conext SW
units in the system. The settings should be configured in the following order: Dev
Number then Invtr Mode.
AC In setting The Conext SW accepts only a single AC source - either from the grid or from a
generator. In a power system where the Conext SW is solely connected to the
grid and an AGS is neither present nor required, the AC In setting can be either
Gen1 or Grid1. Therefore, the default value of Gen1 need not be changed.
In a situation where the AC source is a generator and the AGS is being used to
start the generator to produce AC power, the AC In setting must be set to Gen1.
Therefore, the default value of Gen1 must remain unchanged.
In a power system where the two AC sources are available but only one AC
source can be used, an external transfer switch becomes necessary. When an
external transfer switch is used and an AGS (with a B+ signal connection) is also
present, change the AC In setting to Grid1.
Setting the Device Name
The Dev Name setting allows you to customize the name of the Conext SW as it is
displayed on other screens and menus.
The available characters are:
• A to Z
• a to z
• 0 to 9
• space
NOTE: Increasing the number of characters in a device name may cause other
text on the same line to run off the edge of the screen. Device names should be
limited to 10 characters or less.
975-0638-01-01 Rev G 4–33
Page 94

Configuration via SCP
To customize the Conext SW name:
1. On the device setup menu, select Advanced Settings.
If Basic Settings appears instead of Advanced Settings on the Setup
menu, display Advanced Settings by pressing Enter + up arrow + down
arrow simultaneously.
On the Advanced Settings menu, select Multi Unit Config, and then
press Enter.
2. Select Dev Name, and then press Enter.
The last letter of the Conext SW name is highlighted.
3. Begin customizing the device name.
• To change the character, press the up or down arrow button. Holding
down the button causes the characters to scroll more quickly.
• To delete the character, press Exit.
• To add characters, press Enter.
4. When the correct character is shown, press Enter to select it.
5. After pressing Enter to select the last character of your customized device
name, press Enter again to return to the menu.
Setting the Device Number
Setting the device number gives a Xanbus-enabled device a unique identity
when several devices of the same type are installed in the networked power
system. When each identical device has a unique number, the SCP can correctly
identify and display status information for each device. A device number consists
of two digits ranging from 00 (default) to 31.
If only one of each device is installed in the networked power system, you do not
need to set the device number. However, setting the device number to a value
other than 00 is recommended in case you need to use the Restore Defaults
command. After performing the command, checking that the device number has
returned to 00 indicates that the command was successfully completed.
To set the Conext SW device number:
1. On the Conext SW Setup menu, select Advanced Settings.
If Basic Settings appears instead of Advanced Settings on the Setup
menu, display Advanced Settings by pressing Enter + up arrow + down
arrow simultaneously.
On the Advanced Settings menu, select Multi Unit Config, and then
press Enter.
2. On the Multi Unit Config menu, select Dev Number. See Figure 4-11.
3. Press Enter to highlight the instance number.
4. Use the up and down arrow buttons to adjust the two-digit identifier number.
5. Press Enter.
4–34 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
Page 95

Configuring Advanced Settings
Follow procedures on “To select and change a configurable setting:” on page 4–6 to
change the settings.
Figure 4-11 Setting a Device Number
NOTICE
DAMAGE FROM HAVING DIFFERENT CHARGER SETTINGS
Make sure that all Conext SW Inverter/Charger units in a multi-unit setup in a
power system has the same Charger Settings. For example, if one Conext SW
unit has a Battery Type of Flooded, all Conext SW units must have the same
Battery Type. See NOTE below.
Failure to follow these instructions may damage the battery/batteries.
Note: If Cascading is Enabled in SCP, the charger settings will cascade to
other Conext SW devices with the same DC Associations. However they will not
cascade to other device types such as Conext Battery Monitor even if they have
the same DC associations. Make sure that the charger settings are configured
correctly on the other device types.
975-0638-01-01 Rev G 4–35
Page 96

Configuration via SCP
Restoring Factory Default Settings
The Restore Defaults command returns the Conext SW to factory default
settings. After using the Restore Defaults command, the Conext SW is no
longer configured for the power system.
EQUIPMENT DAMAGE
Do not use the Restore Defaults command while the Conext SW is
operating. De-energize the power system and disconnect the Conext SW AC
input before using the Restore Defaults command. Reconfigure the Conext
SW before reconnecting the AC input and re-energizing the power system.
Failure to follow these instructions can damage the inverter/charger.
To restore Conext SW default settings:
1. On the Advanced Setup menu, select Restore Defaults.
Event code W252 appears, asking to confirm the Restore Defaults
command.
2. To cancel the command, press Exit. To continue with the Restore Defaults
command, press Enter.
NOTICE
IMPORTANT: If a warning is already active in the system, selecting Restore
Defaults brings up the Warning List, with warning W252 at the top. Press Enter to
view W252 and continue with the Restore Defaults process.
IMPORTANT: Restoring to default may mean that the AC output frequency will
change back to 60 Hz. When the change happens, event code W298 appears.
See “EuroFreq Feature” on page 4–37 for information on changing the AC output
frequency to 50 Hz, if desired.
4–36 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
Page 97

Advanced Features Menu
See “To select and change a configurable setting:” on page 4–
6 to change the settings.
Figure 4-12 Adv Features Menu Screen
Configuring Advanced Settings
EuroFreq Feature
Table 4-19 Adv Features Description and Values
a
Setting Description Default Range
EuroFreq
StoreInv
State
AcCouple
Enhanced
ACSup
PLSDelay
NoLoadVD
a.Applies to all Conext SW models.
When enabled, sets the AC
output frequency to a constant
50Hz.
See “Storing the State of the
Inverter Mode” on page 1–15.
For information on this feature
refer to the AC Coupling
Solutions Guide.
See “Enhanced AC Support”
on page 1–9.
Delays load shaving and AC
support features until the
MPPT has charged the battery
in float mode for 2 hours. See
“Grid-Interactive Delay
Feature” on page 1–11.
See “NoLoadVD” on page 1–
15.
Disabled Enabled,
Disabled
Enabled Enabled,
Disabled
Disabled Enabled,
Disabled
Disabled Disabled,
Enabled
Disabled Disabled,
Enabled
Disabled Enabled,
Disabled
The default inverter AC output frequency is 60 Hz.
To change the inverter AC output frequency to 50 Hz:
1. Put the system in Standby mode. See “To change an operational setting” on
page 3–18.
2. Change the EuroFreq to Enabled. See “To select and change a configurable
setting:” on page 4–6.
975-0638-01-01 Rev G 4–37
Page 98

Configuration via SCP
NOTICE
EQUIPMENT DAMAGE
Do not change the frequency to 50 Hz unless the equipment and appliances
connected to the inverter’s output can operate in this frequency setting.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in equipment damage.
3. Restore the system to Operating mode. See “To change an operational
setting” on page 3–18.
IMPORTANT: Restoring to default (see “Restoring Factory Default Settings” on
page 4–36) means that the AC output frequency will change back to 60 Hz.
4–38 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
Page 99

Configuration Sheet
Configuration Sheet
SETTING DESCRIPTION
Inverter
Settings
Charger
Settings
AC
Settings
AC
Support
Low Batt Cut Out
LBCO Delay
Hi Batt Cut Out
Search Watts
Search Delay
Inv Block Start
Inv Block Stop
Batt Type
Custom Settings
Eqlz Support
Eqlz Voltage
Bulk Voltage
Bulk Termination
Voltage
Absorb Voltage
Float Voltage
Batt Temp Comp
Batt Capacity
Max Chg Rate
Charge Cycle
Default Batt Temp
ReCharge Volts
Absorb Time
Auto Chg Enable
Chg Block Start
Chg Block Stop
AC Breaker
AC Lo Volt
AC Hi Volt
AC Lo Freq
AC Hi Freq
AC Supp Mode
AC Supp Volts
Load Shave
Load Shave Amps
Load Shave Start
Load Shave Stop
AC Supp on Soc
AC Supp Start Soc
AC Supp Stop Soc
Select battery voltage below which batteries will be cut out
Select the time delay before low battery cut out is engaged
Select the voltage above which batteries will be cut out
Select Watts at which level Search Mode triggers on
Select delay time before Search Mode triggers on
Sets the time to halt inverting
Sets the time to resume inverting
Select your battery type (FLOODED, GEL, AGM, Custom)
Makes BATTERY CUSTOM SETTINGS screen visible
Enable battery EQUALIZE function
Select maximum EQUALIZE voltage
Select maximum BULK charge voltage
Select maximum BULK TERMINATION charge voltage
Select maximum ABSORPTION charge voltage
Select maximum FLOAT charge voltage
Select BATTERY TEMPERATURE COMP coefficient
Select battery bank capacity
Select maximum charge rate
Select 2 or 3 stage charge cycle
Select system default battery temp setting
Select voltage at which charger will initiate a charge cycle
Sets the maximum Absorption time
Select automatic charging, overrides Charger setup
Sets the time to halt charging
Sets the time to resume charging
Select AC Input current limit
Select lowest acceptable AC voltage
Select highest acceptable AC voltage
Select lowest acceptable AC frequency
Select highest acceptable AC frequency
Sets the AC Support feature
Sets the AC support voltage
Sets the load shaving feature
Sets the current for load shaving
Sets the start time for load shaving
Sets the stop time for load shaving
Sets the AC Support feature based on SOC
Sets the start time for SOC AC support
Sets the stop time for SOC AC support
DEFAULT
24-volt
21.0V 42.0V
10sec 10sec
29.0V 58.0V
50W 50W
2sec 2sec
12:00AM 12:00AM
12:00AM 12:00AM
Flooded Flooded
-- --
Enabled Enabled
32.0V 62.0V
28.8V 57.6V
28.4V 56.8V
28.8V 57.6V
27.0V 54.0V
-54mV/C -108mV/C
250Ah 250Ah
100% 100%
3Stage 3Stage
Warm Warm
25.0V 50.0V
180min 180min
Disabled Disabled
12:00AM 12:00AM
12:00AM 12:00AM
30A 30A
95V 95V
135V 135V
55Hz 55Hz
65Hz 65Hz
Enabled Enabled
26.5V 53.0V
Disabled Disabled
24A 24A
12:00AM 12:00AM
12:00AM 12:00AM
Enabled Enabled
80% 80%
50% 50%
DEFAULT
48-volt
YOUR
SETTING
975-0638-01-01 Rev G 4–39
Page 100

Configuration via SCP
SETTING DESCRIPTION
Multi
Unit
Config
Restore
Defaults
Advanced
Features
Dev Name
Dev Number
Invtr Mode
AC In
Battery
Restore Defaults
EuroFreq
StoreInv
State
AcCouple
Enhanced ACSup
PLSDelay
NoLoadVD
Select unique device Name for each unit
Select unique device number for each unit
Select Master or Slave designation for each unit
Select AC source type
Identify batteries
Restores all system default settings
Sets AC output frequency to 50 Hertz
Sets inverter mode state feature.
Sets AC Coupling feature. See “AC Coupling” on page 1–12.
Sets enhanced AC Support feature. See “Enhanced AC
Support” on page 1–9.
Sets load shaving delay for 2 hours. See “Grid-Interactive
Delay Feature” on page 1–11.
Sets no load voltage derating feature. See “NoLoadVD” on
page 1–15.
DEFAULT
24-volt
CSW4024
CSW2524
00 00
Master Master
Gen1 Gen1
HouseBatt1 HouseBatt1
-- --
Disabled Disabled
Enabled Enabled
Disabled Disabled
Disabled Disabled
Disabled Disabled
Disabled Disabled
DEFAULT
48-volt
CSW4048
YOUR
SETTING
4–40 975-0638-01-01 Rev G
 Loading...
Loading...