Perkins Engine 2806C-E16 Service Manual

Perkins 2800 Series
Model 2806C-E16
DIAGNOSTIC MANUAL
6 cylinder turbocharged diesel engine
Publication TSL4247, Preliminary.
© Proprietary information of Perkins Engines Company Limited, all rights reserved. The information is correct at the time of print.
Published in May 2001 by Technical Publications,
Perkins Engines Company Limited, Tixall Road, Stafford, ST16 3UB, England
i

Diagnostic code quick reference
CID-FMI |
Diagnostic code description |
Troubleshooting |
|
|
|
|
|
1-11 |
Injector Cylinder #1 Fault |
See Test 10 on page |
133 |
|
|
|
|
2-11 |
Injector Cylinder #2 Fault |
See Test 10 on page |
133 |
|
|
|
|
3-11 |
Injector Cylinder #3 Fault |
See Test 10 on page |
133 |
|
|
|
|
4-11 |
Injector Cylinder #4 Fault |
See Test 10 on page |
133 |
|
|
|
|
5-11 |
Injector Cylinder #5 Fault |
See Test 10 on page |
133 |
|
|
|
|
6-11 |
Injector Cylinder #6 Fault |
See Test 10 on page |
133 |
|
|
|
|
41-03 |
ECM 8 Volt DC Supply Open/Short to B+ |
See Test 6 on page 107 |
|
|
|
|
|
41-04 |
ECM 8 Volt DC Supply Short to ground |
See Test 6 on page 107 |
|
|
|
|
|
91-08 |
PWM Speed Control Abnormal |
See Test 6 on page 107 |
|
|
|
|
|
100-03 |
Engine Oil Pressure Sensor Open/Short to B+ |
See Test 3 on page |
88 |
|
|
|
|
100-04 |
Engine Oil Pressure Sensor Short to ground |
See Test 3 on page |
88 |
|
|
|
|
110-03 |
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Open/Short to B+ |
See Test 3 on page |
88 |
|
|
|
|
110-04 |
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Short to ground |
See Test 3 on page |
88 |
|
|
|
|
168-02 |
Intermittent Battery Power to the ECM |
See Test 2 on page |
85 |
|
|
|
|
172-03 |
Inlet Air Temperature Sensor Open/Short to B+ |
See Test 3 on page |
88 |
|
|
|
|
172-04 |
Inlet Air Temperature Sensor Short to ground |
See Test 3 on page |
88 |
|
|
|
|
174-03 |
Fuel Temperature Sensor Open/Short to B+ |
See Test 3 on page |
88 |
|
|
|
|
174-04 |
Fuel Temperature Sensor Short to ground |
See Test 3 on page |
88 |
|
|
|
|
190-02 |
Engine Speed Sensor Data Intermittent |
See Test 8 on page 121 |
|
|
|
|
|
190-09 |
Engine Speed Sensor Abnormal Update |
See Test 8 on page 121 |
|
|
|
|
|
190-11,190-12 |
Engine Speed Sensor Mechanical Fault |
See Test 8 on page 121 |
|
|
|
|
|
252-11 |
Incorrect Engine Software |
See page 23 |
|
|
|
|
|
253-02 |
Check Customer or System Parameters |
See page 26 |
|
|
|
|
|
261-13 |
Engine Timing Calibration Required |
See Test 9 on page 129 |
|
|
|
|
|
262-03 |
5 Volt Sensor Power Supply Open/Short to B+ |
See Test 5 on page 102 |
|
|
|
|
|
262-04 |
5 Volt Sensor Power Supply Short to ground |
See Test 5 on page 102 |
|
|
|
|
|
268-02 |
Check Programmable Parameters |
See page 26 |
|
|
|
|
|
273-03 |
Turbo Outlet Pressure Sensor Open/Short to B+ |
See Test 3 on page |
88 |
|
|
|
|
273-04 |
Turbo Outlet Pressure Sensor Short to ground |
See Test 3 on page |
88 |
|
|
|
|
274-03 |
Atmospheric Pressure Sensor Open/Short to B+ |
See Test 3 on page |
88 |
|
|
|
|
274-04 |
Atmospheric Pressure Sensor Short to ground |
See Test 3 on page |
88 |
|
|
|
|
281-03 |
Action Alert lamp Open/Short to B+ |
See Test 4 on page |
97 |
|
|
|
|
281-04 |
Action Alert lamp Short to ground |
See Test 4 on page |
97 |
|
|
|
|
281-05 |
Action Alert Lamp Open Circuit |
See Test 4 on page |
97 |
|
|
|
|
282-03 |
Overspeed lamp Open/Short to B+ |
See Test 4 on page |
97 |
|
|
|
|
282-04 |
Overspeed lamp Short to ground |
See Test 4 on page |
97 |
|
|
|
|
285-03 |
Coolant temperature lamp Open/Short to B+ |
See Test 4 on page |
97 |
|
|
|
|
285-04 |
Coolant temperature lamp Short to ground |
See Test 4 on page |
97 |
|
|
|
|
286-03 |
Lub oil pressure lamp Open/Short to B+ |
See Test 4 on page |
97 |
|
|
|
|
286-04 |
Lub oil pressure lamp Short to ground |
See Test 4 on page |
97 |
|
|
|
|
286-05 |
Lub Oil Pressure Lamp Open Circuit |
See Test 4 on page |
97 |
|
|
|
|
323-03 |
Shutdown lamp Open/Short to B+ |
See Test 4 on page |
97 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
iii

CID-FMI |
Diagnostic code description |
Troubleshooting |
|
|
|
323-04 |
Shutdown lamp Short to ground |
See Test 4 on page 97 |
|
|
|
323-05 |
Shutdown Lamp Open Circuit |
See Test 4 on page 97 |
|
|
|
324-03 |
Warning lamp Open/Short to B+ |
See Test 4 on page 97 |
|
|
|
324-04 |
Warning lamp Short to ground |
See Test 4 on page 97 |
|
|
|
324-05 |
Warning Lamp Open Circuit |
See Test 4 on page 97 |
|
|
|
342-02 |
Secondary Engine Speed Sensor Data Intermittent |
See Test 8 on page 121 |
|
|
|
342-11, 342-12 |
Secondary Engine Speed Sensor Mechanical Fault |
See Test 8 on page 121 |
|
|
|
861-03 |
Diagnostic lamp Open/Short to B+ |
See Test 4 on page 97 |
|
|
|
861-04 |
Diagnostic lamp Short to ground |
See Test 4 on page 97 |
|
|
|
iv

Contents
1 General information
Introduction ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 1
Safety precautions ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 2
2 Electronic system overview
System operation .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 3
Electronic controls ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 3
Engine governor ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 3
Timing considerations .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 3
Fuel injection . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 3
Engine monitoring ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 4
Fuel temperature monitoring ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 5
Self diagnostics ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 5
Effect of diagnostic codes on engine performance .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 5
Current totals stored in the ECM . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 6
Programmable parameters .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 6
Passwords . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 6
Engine component diagram . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 7
v

OEM connection diagram . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 8
Sensor and connector location diagram . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 9
Engine wiring diagram .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 10
Machine wiring diagram (all options) .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 11
Electrical connectors and functions ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 12
Service tools and diagnostics .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 13
Required service tools .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 14
Optional service tools ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 15
Service tool illustrations ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 16
3 Programming parameters
Connecting the TIPSS-EST ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 17
Passwords .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 19
Programming a new ECM . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 20
Programming a Personality Module using flash programming ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 23
ECM date/time clock .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 24
ECM diagnostic clock ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 24
Injector codes ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 25
TIPSS-EST manual cylinder cutout test .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 25
Programming parameters . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 26
System configuration parameters ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 26
Customer specified parameters ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 28
vi

4 Troubleshooting without a diagnostic code |
|
Introduction ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . |
31 |
P-401 Engine will not crank ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . |
32 |
P-402 Engine cranks but will not start ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . |
33 |
P-403 Engine misfires, runs rough or is unstable .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . |
34 |
P-404 Low power/poor or no response to throttle . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . |
35 |
P-405 Intermittent engine shutdowns ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . |
36 |
P-406 Intermittent low power or power cutouts . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . |
37 |
P-407 Electronic service tool will not communicate with the ECM ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . |
38 |
P-408 ECM will not accept factory passwords .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . |
39 |
P-409 Excessive black smoke ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . |
40 |
P-410 Excessive white smoke ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . |
41 |
P-411 Engine cannot reach correct rev/min .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . |
42 |
P-412 Poor acceleration or response ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . |
43 |
P-413 Poor fuel consumption ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . |
44 |
P-414 Too much vibration . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . |
45 |
P-415 Noise coming from cylinder ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . |
46 |
P-416 Excessive valve clearance .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . |
47 |
P-417 Valve rotocoil or spring lock is free . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . |
48 |
P-418 Mechanical noise (knock) in engine ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . |
49 |
P-419 Oil in cooling system ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . |
50 |
P-420 Fuel in cooling system ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . |
51 |
P-421 Coolant in lubricating oil .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . |
52 |
P-422 Fuel dilution of lubricating oil .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . |
53 |
P-423 Engine has early wear ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . |
54 |
P-424 Engine has low oil pressure ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . |
55 |
P-425 Engine uses too much lubricating oil .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . |
56 |
P-426 Engine coolant is too hot ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . |
57 |
P-427 Oil at the exhaust ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . |
58 |
P-428 Engine has a fuel supply problem ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . |
59 |
P-429 Indicator lamp not functioning correctly .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . |
60 |
P-430 Inlet air manifold temperature is too high ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . |
61 |
P-431 Engine has a high fuel temperature ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . |
62 |
5 Troubleshooting with an event code
General information .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . 63
Event codes ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . 64
E36-2 Low coolant temperature Action Alert . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . 65 E162-1 High boost pressure Warning ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . 66
E162-2 High boost pressure Action Alert .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . 66
E360-1 Low oil pressure Warning . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . 67
E360-2 Low oil pressure Action Alert ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . 67
E360-3 Low oil pressure Shutdown ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . 67
E361-1 High coolant temperature Warning ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . 68 E361-2 High coolant temperature Action Alert .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . 68
vii

E361-3 High coolant temperature Shutdown . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... |
68 |
|
E362-1 Engine overspeed Warning ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... |
69 |
|
E362-2 Engine overspeed Action Alert .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... |
69 |
|
E362-3 Engine overspeed Shutdown ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... |
69 |
|
E363-1 |
High fuel temperature Warning . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... |
70 |
E363-1 |
High fuel temperature Action Alert ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... |
70 |
E368-1 |
High inlet air temperature Warning ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... |
71 |
E368-2 |
High inlet air temperature Action Alert ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... |
71 |
6 Troubleshooting with a diagnostic code
Diagnostic codes ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... |
73 |
Diagnostic terminology . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 75
Quick reference for ECM diagnostic codes ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 76
7 Functional tests
General information .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... |
77 |
Connectors . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 77
Test 1 Inspecting electrical connectors .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 78
Test 2 Electrical power supply to the ECM ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 83 Test 3 Analogue sensor open or short circuit test .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 86
Test 4 ECM Status indicator output circuit test .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 95
Test 5 +5 V Sensor voltage supply circuit test ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 100 Test 6 PWM desired speed setting circuit test ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 105
Test 7 Perkins Data Link circuit test ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 112
Test 8 Engine speed/timing circuit test .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 119 Test 9 Engine speed/timing calibration .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 127
Test 10 Injector solenoids circuit test . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 131
8 Glossary
Glossary of terms .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 141
viii

2800 Series
1
General information
Introduction
The 2800 Series industrial diesel engines are the latest development from Perkins Engines Company Limited, a world leader in the design and manufacture of high performance diesel engines.
Read and remember the "Safety precautions" on page 2. They are given for your protection and must be applied at all times.
Danger is indicated in the text by two methods:
Warning! This indicates that there is a possible danger to the person.
Caution: This indicates that there is a possible danger to the engine.
Note: Is used where the information is important, but there is not a danger.
Ensure that all adjustments and repairs are done by personnel who have had the correct training.
Diagnostic Manual, TSL4247, Preliminary |
1 |

1 |
2800 Series |
Safety precautions |
|
These safety precautions are important.
Reference must also be made to the local regulations in the country of operation.
lOnly use these engines in the type of application for which they have been designed.
lDo not change the specification of the engine.
lDo not smoke when you put fuel in the tank.
lClean away fuel which has been spilt. Material which has been contaminated by fuel must be moved to a safe place.
lDo not put fuel in the tank while the engine runs (unless it is absolutely necessary).
lDo not clean, add lubricating oil, or adjust the engine while it runs (unless you have had the correct training; even then extreme caution must be used to prevent injury).
lDo not make adjustments that you do not understand.
lEnsure that the engine does not run in a location where it can cause a concentration of toxic emissions.
lOther persons must be kept at a safe distance while the engine or equipment is in operation.
lDo not permit loose clothing or long hair near moving parts.
lKeep away from moving parts during engine operation. Warning! Some moving parts cannot be seen clearly while the engine runs.
lDo not operate the engine if a safety guard has been removed.
lDo not remove the filler cap of the cooling system while the engine is hot and while the coolant is under pressure, because dangerous hot coolant can be discharged.
lDo not use salt water or any other coolant which can cause corrosion in the closed coolant circuit.
lDo not allow sparks or fire near the batteries (especially when the batteries are on charge) because the gases from the electrolyte are highly flammable. The battery fluid is dangerous to the skin and especially to the eyes.
lDisconnect the battery terminals before a repair is made to the electrical system.
lOnly one person must control the engine.
lEnsure that the engine is operated only from the control panel or from the operator’s position.
lIf your skin comes into contact with high-pressure fuel, obtain medical assistance immediately.
lDiesel fuel and lubricating oil (especially used lubricating oil) can damage the skin of certain persons. Protect your hands with gloves or a special solution to protect the skin.
lDo not wear clothing which is contaminated by lubricating oil. Do not put material which is contaminated with oil into the pockets.
lDiscard used lubricating oil in a safe place to prevent contamination.
lThe combustible material of some components of the engine (for example certain seals) can become extremely dangerous if it is burned. Never allow this burnt material to come into contact with the skin or with the eyes.
lFuel and oil pipes MUST be inspected for cracks or damage before they are fitted to the engine.
lFit only genuine Perkins parts.
2 |
Diagnostic Manual, TSL4247, Preliminary |

2800 Series
2
Electronic system overview
System operation
The 2800 Series industrial diesel engines are designed for electronic control. The injection pump, fuel lines and nozzles used in mechanical engines have been replaced with an electronic unit injector in each cylinder. A solenoid on each injector controls the amount of fuel that is delivered by the injector. An Engine Control Module (ECM) sends a signal to each injector solenoid in order to provide complete control of the engine.
Electronic controls
The electronic system consists of the Engine Control Module (ECM), the engine sensors and the OEM interface. The ECM is the computer which controls the engine. The Personality Module in the ECM contains the software which controls how the ECM behaves (the Personality Module stores the operating maps that define power, rev/min, etc).
Engine governor
The electronic controls on the engine serve as the engine governor, determining when and how much fuel to deliver to the cylinders based on the actual and desired conditions at any given time.
The ECM uses one of three possible speed control inputs to determine the desired engine speed and compares this to the actual engine speed determined through the crankshaft position sensor. If the desired engine speed is greater than the actual engine speed, more fuel is injected in order to increase engine speed.
Timing considerations
Once the ECM has determined how much fuel is required, it must next determine when to inject the fuel. Injection timing is determined by the ECM after considering input from the following components:
lCoolant temperature sensor
lIntake manifold air temperature sensor
lAtmospheric pressure sensor
lBoost pressure sensor
The ECM determines where top centre on cylinder number one is located from the engine camshaft position sensor signal. The ECM decides when injection should occur relative to top centre and provides the signal to the injector at the desired time. The ECM adjusts timing for the best engine performance, fuel economy and white smoke control.
Note: Actual or desired timing cannot be viewed with an electronic service tool.
Fuel injection
The ECM controls the amount of fuel injected by varying the signals to the injectors. The injectors will pump fuel only if the injector solenoid is energized. The ECM sends a high voltage signal to energize the solenoid. By controlling the timing and duration of the high voltage signal, the ECM can control injection timing and the amount of fuel that is injected.
The Personality Module inside the ECM sets certain limits on the amount of fuel that can be injected. The FRC Fuel Limit is a limit based on boost pressure to control the air/fuel ratio for control of emissions. When the ECM senses a higher boost pressure (more air into cylinder) it increases the FRC Fuel Limit (allows more fuel into cylinder).
Diagnostic Manual, TSL4247, Preliminary |
3 |
2 |
2800 Series |
The Rated Fuel Limit is a limit that is based on the power rating of the engine and engine rev/min. It is similar to the rack stops and torque spring on a mechanically governed engine. It provides power and torque curves for a specific engine family and rating.
Note: All of these limits are determined at the factory in the Personality Module and cannot be changed.
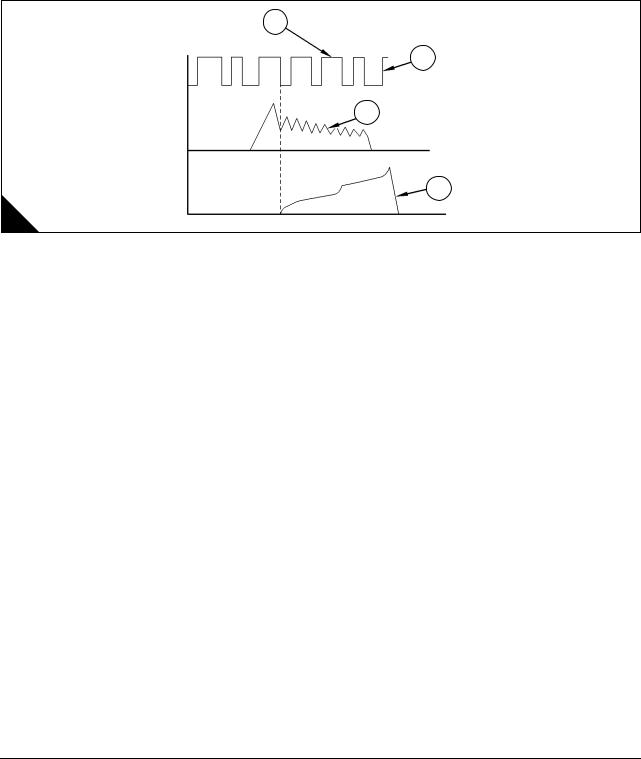
Example of EUI system
1TC reference
2Speed/timing signal
3Electrical current to the injector solenoid
4Injection pressure curve
1
2
3
4
A
Note: Signals and timing are not to scale.
Engine monitoring
Perkins provides a factory installed engine monitoring system. The Perkins engine monitoring system monitors the following parameters:
lEngine oil pressure
lCoolant temperature
lIntake manifold air temperature
lEngine speed
lBoost pressure
lFuel temperature
The Perkins engine monitoring system has three levels of operation, WARNING, ACTION ALERT and SHUTDOWN as described below.
Perkins engine monitoring WARNING operation
In the WARNING condition the ECM causes the Warning lamp to turn ON to indicate a problem has been detected by the Engine Monitoring System. No further ECM or engine action occurs.
Perkins engine monitoring ACTION ALERT operation
In the ACTION ALERT condition the ECM begins by activating the Action Alert lamp ON to indicate a problem has been detected by the Engine Monitoring System. This is also normally wired to cause a shutdown via the OEM control panel.
Perkins engine monitoring SHUTDOWN operation
If the fault reaches the SHUTDOWN condition the ECM activates the shutdown lamp and unless the engine is in CRITICAL OVERRIDE condition, the engine will shutdown.
4 |
Diagnostic Manual, TSL4247, Preliminary |

2800 Series |
2 |
Fuel temperature monitoring |
|
The fuel temperature sensor monitors the fuel temperature, adjusting the ECM calculated fuel rate to compensate for fuel temperature changes and to adjust the fuel rate for constant power. The sensor is also used to warn the operator of excessive fuel temperature with a diagnostic event code because excessive fuel temperatures can adversely affect engine performance.
Self diagnostics
The electronic system has the ability to diagnose problems. When a problem is detected, a diagnostic code is generated and stored in permanent memory (logged) in the ECM. The diagnostic lamp is also activated.
When diagnostic codes occur, the diagnostic codes are referred to as Active diagnostic codes. They indicate that a problem of some kind currently exists.
Diagnostic codes that are stored in memory are called Logged diagnostic codes. Since the problem may have been temporary, or may have been repaired since the problem was logged, logged codes do not necessarily mean that something needs to be repaired. They are instead meant to be an indication of probable causes for intermittent problems.
Diagnostic codes that identify operating conditions outside the normal operating range are called Events. Event codes are not typically an indication of an electronic system problem.
Note: Some of the diagnostic codes require passwords to clear.
Effect of diagnostic codes on engine performance
The discussion on engine monitoring mentions that the diagnostic lamp activates when a specific condition exists. When the ECM detects an engine problem, it generates an active diagnostic code and also logs the diagnostic code in order to indicate when, and if appropriate, how many times the problem occurred. There are two types of diagnostic codes, Fault codes and Event codes.
Diagnostic fault codes
These are provided in order to indicate that an electrical or electronic problem has been detected by the ECM. In some cases the engine performance can be affected when the condition causing the code exists. More frequently, however, no difference in the engine performance can be detected.
Diagnostic event codes
Diagnostic event codes are used to indicate that some operational problem has been detected in the engine by the ECM. This usually does not indicate an electronic malfunction.
The ECM also provides an ECM clock with date/time to date and time stamp the following critical event codes:
l362-3 Engine overspeed Shutdown
l360-3 Low oil pressure Shutdown
l361-3 High coolant temperature Shutdown
For a listing all of the CID-FMI Diagnostic codes, along with the page number where details regarding the cause, performance effect, and troubleshooting of the code can be located, refer to "Quick reference for ECM diagnostic codes" on page 76.
Diagnostic Manual, TSL4247, Preliminary |
5 |

2 |
2800 Series |
Current totals stored in the ECM |
|
The ECM maintains engine total data for the following parameters:
Total time
The total time is the engine's operating hours. This does not include operating time when the ECM is powered ON but the engine is not running.
Programmable parameters
Certain parameters affecting engine operation may be changed with electronic service tools. The parameters are stored in the ECM, and are protected from unauthorized changes by passwords. These parameters are either System Configuration Parameters or Customer Parameters.
System configuration parameters
These are set at the factory and affect emissions or power ratings within an engine family. Factory passwords must be obtained and used to change the system configuration parameters.
Customer parameters
These are variable and can be used to tailor the engine to customer requirements within the limits set by the factory and Perkins engine monitoring operation. Customer passwords may be required to change customer parameters.
Caution: Some of the parameters may affect engine operation. Without adequate training, these parameters may lead to power or performance complaints even when the engine is performing to specification.
Refer to "Programming parameters" on page 26 for further information.
Passwords
System configuration parameters are protected by Factory passwords. Factory passwords are calculated on a computer system that is available only to Perkins dealers.
Customer parameters can be protected by Customer passwords. The customer passwords are programmed by the customer. Factory passwords can be used to change customer passwords if they are lost.
Refer to "System configuration parameters" on page 26 for further information when passwords are needed and how to obtain them.
6 |
Diagnostic Manual, TSL4247, Preliminary |
2800 Series |
2 |
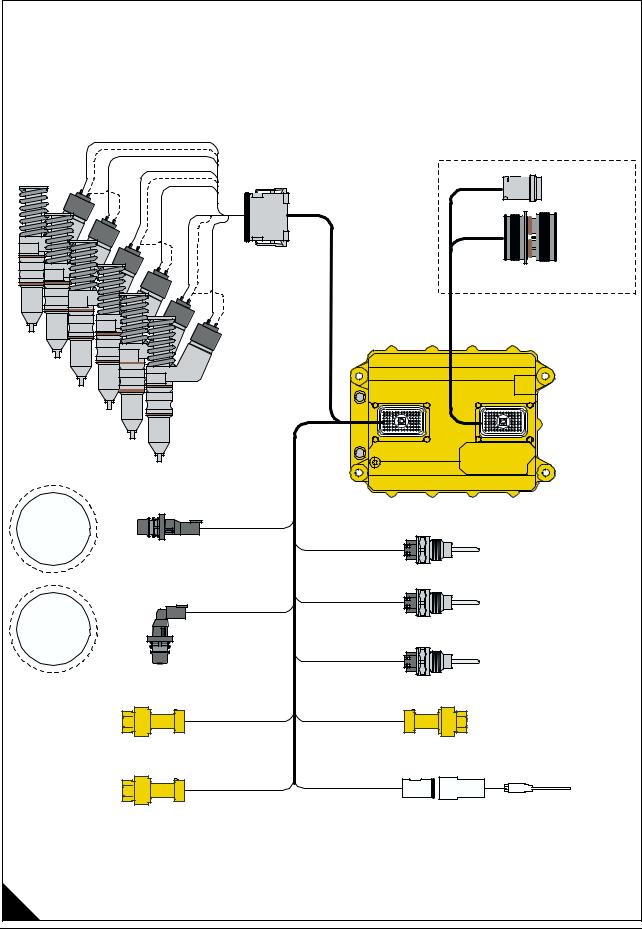
Engine component diagram |
|
Internal Injector Harness |
|
|
12PIN Connector |
Service |
|
|
Tool |
|
|
Connector |
|
|
Interface |
|
|
Connector |
|
|
OEM Interface Connectors |
|
Main Engine Harness |
|
|
|
A3 ECM |
|
Crank Speed/Timing |
|
|
36+1 TOOTH |
|
|
CRANK |
|
|
GEAR |
Inlet Air Manifold Temperature |
|
|
||
Cam Speed/Timing |
|
|
|
Fuel Temperature |
|
36+1 TOOTH |
|
|
CAM GEAR |
|
|
|
Coolant Temperature |
|
Boost |
Atmospheric Pressure Sensor |
|
Pres Sensor |
||
|
||
|
Calibration |
|
Lub Oil Pressure |
Probe |
|
|
||
Sensor |
|
|
A |
|
|
Diagnostic Manual, TSL4247, Preliminary |
7 |
2 |
2800 Series |
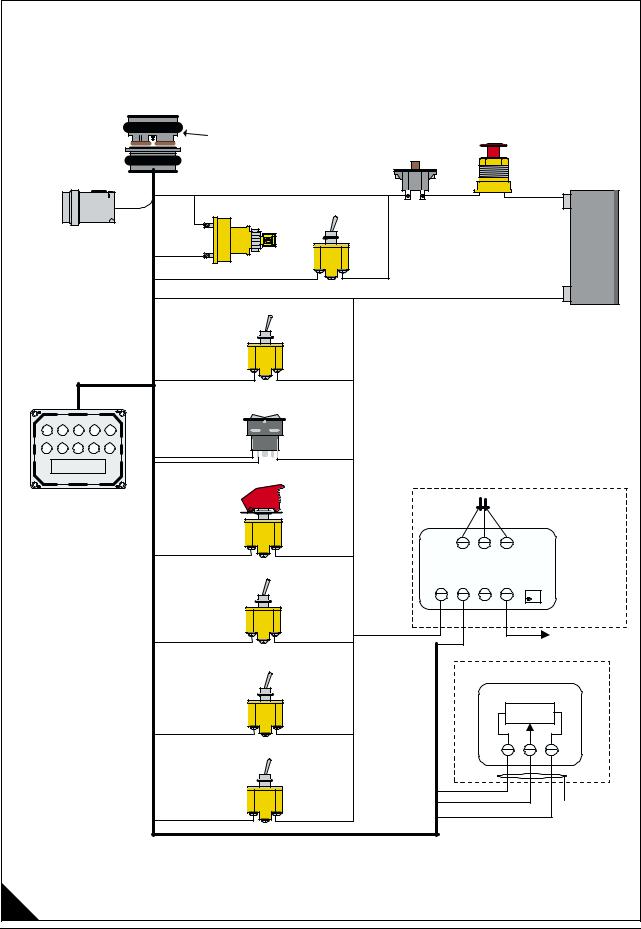
OEM connection diagram |
|
|
To ECM J1 Connector |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Customer connecter |
(If fitted) |
|
E-Stop |
|
|
|
|
|
16A Breaker |
|
|
|
|
|
Service |
|
|
|
|
|
|
+ |
Tool |
Keyswitch |
Injector Disable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Connector |
|
Optional |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
24V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
Digital Speed Control |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Optional |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Optional |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Speed |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Raise/Lower |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Critical Override |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Optional |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Lamp Box |
|
|
|
|
Throttle Adjust |
Optional |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pot |
|
|
1: Diagnostics |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2: Caution |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Speed |
3: Warning |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Control |
4: Shutdown |
|
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
|
5: Overspeed |
Shutdown Reset |
|
|
|
|
droop |
|
6: High Coolant Temp |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
-B |
S |
D |
+B |
|
||
Optional |
adjust |
|
|||||
7: Low Pressure |
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Switched |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Battery +ve |
|
|
Optional |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Droop/Isoch |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Optional |
|
|
|
|
|
Potentiometer |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.5-4.5V |
|
|
Speed Selection |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Optional |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Screen tied to |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ECM -VE |
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
Diagnostic Manual, TSL4247, Preliminary |
|||||

2800 Series |
2 |
Sensor and connector location diagram |
|
Key
1Electronic Control Module (ECM)
2J1/P1 Machine connector
3J2/P2 Engine connector
4Atmospheric pressure sensor
5Oil pressure sensor
6Crankshaft position sensor
7Fuel temperature sensor
8Camshaft position sensor
9Coolant temperature sensor
10Boost pressure sensor
11Intake manifold air temperature sensor
12Electronic unit injector connector
13Timing calibration pickup connector
9
12
10 |
11 |
|
13 |
|
1 |
8 |
2 |
|
|
|
7 |
5 4
3
6
A
Diagnostic Manual, TSL4247, Preliminary |
9 |
2 |
2800 Series |
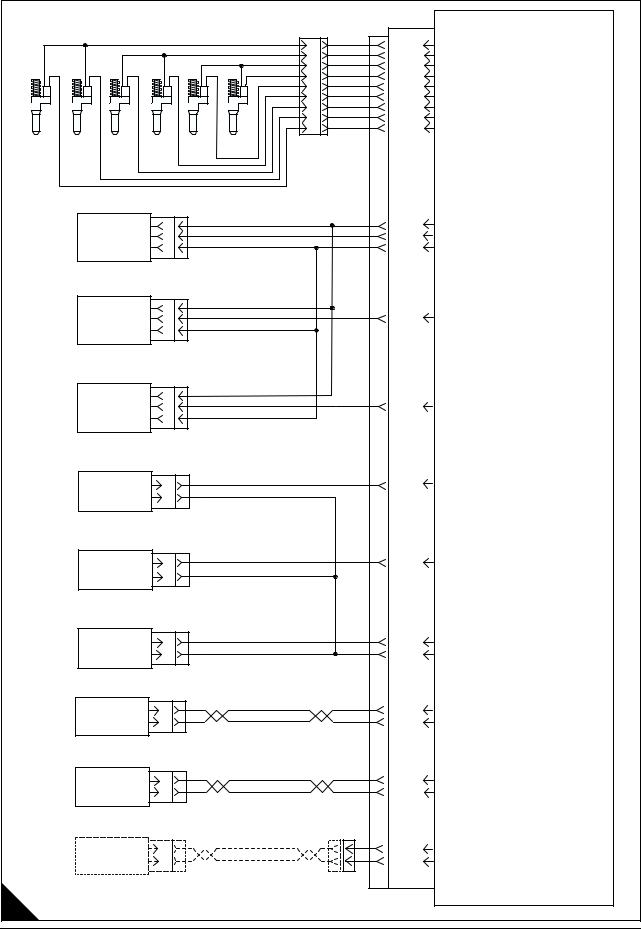
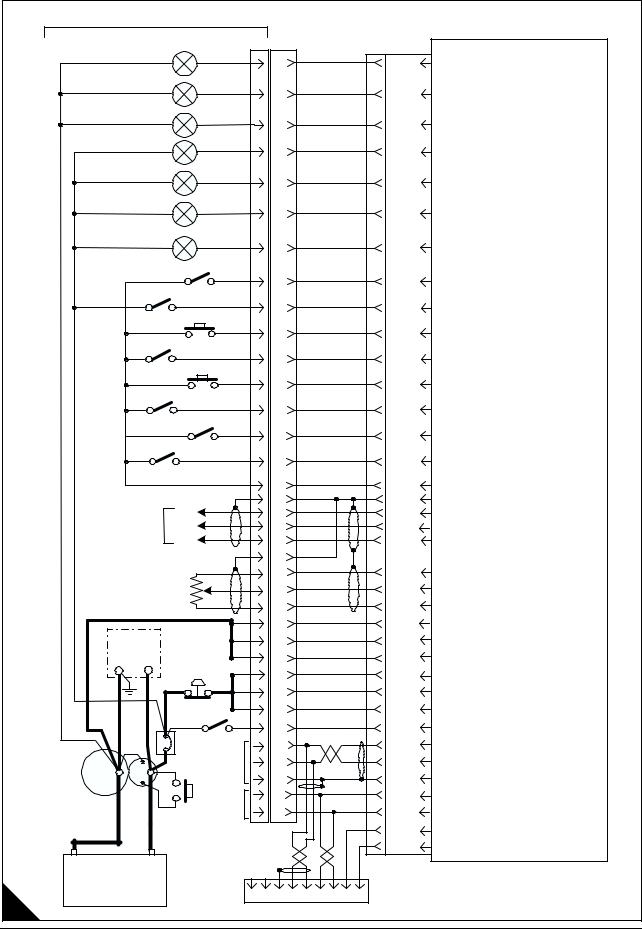
Engine wiring diagram |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ECM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
J2/44 |
Injector Common Cylinders 1 & 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
J2/45 |
Injector Common Cylinders 3 & 4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
J2/46 |
Injector Common Cylinders 5 & 6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
J2/55 |
Injector Cylinder 6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
J2/54 |
Injector Cylinder 5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
J2/39 |
Injector Cylinder 4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
J2/38 |
Injector Cylinder 3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
J2/37 |
Injector Cylinder 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
J2/36 |
Injector Cylinder 1 |
Injector |
Injector |
Injector |
Injector |
Injector |
Injector |
J300 P300 |
|
|
|
Cyl 1 |
Cyl 2 |
Cyl 3 |
|
Cyl 4 |
Cyl 5 |
Cyl 6 |
|
|
|
|
Atmospheric Pressure Sensor |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
+5V |
A |
|
|
|
J2/2 |
+5VDC Supply |
|
|
|
Signal |
|
C |
|
|
|
J2/14 |
Atmospheric Pressure |
|
|
Return |
|
B |
|
|
|
J2/3 |
Analogue Return |
|
|
|
|
P203 J203 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Turbo Outlet Pressure Sensor |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
+5V |
A |
|
|
|
J2/40 |
Turbo Outlet Pressure |
|
|
|
Signal |
|
C |
|
|
|
||
|
|
Return |
|
B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P200 J200 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Oil Pressure Sensor |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
+5V |
A |
|
|
|
J2/24 |
|
|
|
|
Signal |
|
C |
|
|
|
Oil Pressure |
|
|
|
Return |
|
B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P201 J201 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Coolant Temperature Sensor |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
Signal |
|
C |
|
|
|
J2/32 |
Coolant Temperature |
|
|
Return |
B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
J100 P100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fuel Temperature Sensor |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Signal |
|
C |
|
|
|
J2/33 |
Fuel Temperature |
|
|
Return |
B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
J105 P105 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Inlet Air Temperature Sensor |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
Signal |
|
C |
|
|
|
J2/35 |
Inlet Air Temperature |
|
|
Return |
|
B |
|
|
|
J2/18 |
Return |
|
|
|
|
J103 P103 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Crankshaft Position Sensor |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
Signal |
|
2 |
|
|
|
J2/48 |
Crank Speed Timing + |
|
|
Return |
|
1 |
|
|
|
J2/49 |
Crank Speed Timing - |
|
|
|
|
J401 P401 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Camshaft Position Sensor |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
Signal |
|
2 |
|
|
|
J2/58 |
Cam Speed timing + |
|
|
Return |
|
1 |
|
|
|
J2/59 |
Cam speed timing - |
|
|
|
|
J402 P402 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Calibration Probe |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Signal |
|
1 |
|
|
|
J2/22 |
Calibration Probe + |
|
|
Return |
|
2 |
|
|
|
J2/23 |
Calibration Probe - |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
J400 P400 |
|
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P2 J2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Diagnostic Manual, TSL4247, Preliminary |
|
2800 Series |
2 |
Machine wiring diagram (all options)
This Wiring Supplied By OEM |
|
Customer |
|
Outputs may be used to |
J3 P3 |
Interface |
|
Connector |
|||
drive lamps or relays |
|||
|
|
||
Shutdown |
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Action Alert |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Warning |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Diagnostics |
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Oil Pressure |
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Coolant Temp |
17 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Overspeed |
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Digital Speed |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Control Enable |
34 |
|
|
|
|
|
Injection |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Disable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Lower |
29 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Speed |
35 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shutdown |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Emergency Override |
|
28 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Raise |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Speed |
25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1500/1800 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
rpm Select |
|
26 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Droop/ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Isochronous |
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fault Reset |
|
23 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
27 |
|
|
|
|
To PWM |
Ground |
|
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
36 |
|
|
|
|
||
Speed Control |
PWM |
|
|
|
|
|
||
(If Required) |
+8V |
|
21 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
23 |
|
|
|
|
Analogue Speed |
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
Setting |
|
24 |
|
|
|
|
|
Potentiometer or |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Input from Load |
|
19 |
|
|
|
|
||
Sharer/Synchroniser |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
38 |
|
|
|
|
Charging |
|
|
39 |
|
|
|
|
|
Alternator |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
GRD |
POS |
Emergency |
40 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Stop Button |
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
33 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Key |
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Switch |
31 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Circuit |
J1939 |
32 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Breaker |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Data |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Link |
11 |
|
|
|
|
Starter |
|
|
Perkins |
7 |
|
|
|
|
Motor |
|
Start |
Data |
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Link |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Button |
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Battery |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
24V DC |
|
|
J |
H C G |
F |
D |
E A |
B |
A
|
ECM |
J1/10 |
Shutdown lamp Output |
J1/19 |
Action Alert Lamp Output |
J1/20 |
Warning Lamp Output |
J1/31 |
System Fault Lamp Output |
J1/28 |
Oil Pressure Lamp Output |
J1/29 |
Coolant Temperature Lamp Output |
J1/30 |
Overspeed Lamp Output |
J1/49 |
Digital Speed Control Enable |
J1/62 |
Injection Disable |
J1/59 |
Lower Speed |
J1/58 |
Shutdown Emergency Override |
J1/7 |
Raise Speed |
J1/56 |
1500/1800 rpm Select |
J1/46 |
Droop/Isochronous |
J1/41 |
Fault Reset |
J1/18 |
Digital Ground |
J1/67 |
- Battery |
J1/5 |
Ground |
J1/66 |
PWM Input |
J1/4 |
+8V |
J1/3 |
Analogue Ground |
J1/15 |
Analogue Speed Input |
J1/2 |
+5V |
J1/61 |
- Battery |
J1/63 |
- Battery |
J1/65 |
- Battery |
J1/48 |
Unswitched + Battery |
J1/52 |
Unswitched + Battery |
J1/53 |
Unswitched + Battery |
J1/70 |
Switched + Battery |
J1/50 |
J1939 Data Link + |
J1/34 |
J1939 Data Link - |
J1/42 |
J1939 Screen |
J1/8 |
Perkins Data Link + |
J1/9 |
Perkins Data Link - |
J1/55 |
Unswitched + Battery |
J1/69 |
- Battery |
P1 J1
9 Pin Perkins Data
Link Connector
Diagnostic Manual, TSL4247, Preliminary |
11 |

2 |
2800 Series |
Electrical connectors and functions |
|
|
|
Connector |
Function |
|
|
J1/P1 |
ECM connector (70-Pin OEM harness) |
|
|
J2/P2 |
ECM connector (70-Pin Engine harness) |
|
|
J3/P3 |
Machine wiring connector (40-Pin connector) - optional |
|
|
J100/P100 |
Engine coolant temperature sensor (2-pin connector) |
|
|
J103/P103 |
Engine inlet air temperature sensor (2-pin connector) |
|
|
J105/P105 |
Engine fuel temperature sensor (2-pin connector) |
|
|
J200/P200 |
Engine turbo outlet pressure sensor (3-pin connector) |
|
|
J201/P201 |
Engine oil pressure sensor (3-pin connector) |
|
|
J203/P203 |
Engine atmospheric pressure sensor connector (3-pin connector) |
|
|
J300/P300 |
Injector solenoid harness (12-pin connector) |
|
|
J400/P400 |
Engine timing calibration probe (2-pin connector) |
|
|
J401/P401 |
Crankshaft position sensor (2-pin connector) |
|
|
J402/P402 |
Camshaft position sensor (2-pin connector) |
|
|
12 |
Diagnostic Manual, TSL4247, Preliminary |

2800 Series |
2 |
Service tools and diagnostics |
|
The Perkins TIPSS-EST service tools are designed to help the service technician analyze and locate faults or problems within the system. They are required to perform calibrations and to read or change engine parameters.
Perkins TIPSS-EST is a software program that runs on a personal computer and requires a communication adapter to translate information from the Perkins Data Link to the computer RS232 port.
Perkins TIPSS-EST can be used to display the following information:
lProgrammable parameter settings
lActive and logged diagnostic codes
lLogged events
lEngine rating history
lHistograms
lCustom data
lECM date/time clock
Perkins TIPSS-EST can also be used to perform the following functions:
lDiagnostic tests
lSensor calibrations
lFlash programming
lParameter programming
lCopy configuration (ECM replacement)
lData logging
lReal time graphing
There are several adapter cables, breakout T cables, etc that are used in order to access measurements of signals. A heavy duty multimeter is suitable in order to make the necessary measurements. A multimeter that has the ability to measure duty cycle may also be required. Other special tools include those needed to measure pressure and temperature.
Diagnostic Manual, TSL4247, Preliminary |
13 |

2 |
2800 Series |
|
Required service tools |
||
|
|
|
Part No. |
Description |
|
|
|
|
|
IBM PC Compatible: |
|
|
Minimum - Pentium 100 MHz processor or greater, 32 Mb RAM, 200 Mb of available hard disk |
|
|
space, VGA monitor or display, CD-ROM, 3.5 in 1.44 Mb diskette drive, Windows 95 or greater, |
|
|
Windows NT, Windows 2000, RS232 port with 16550AF UART, Built in pointing device or |
|
- |
mouse. |
|
|
Recommended - Pentium 200 MHz processor, 64 Mb RAM, 1Gb of available hard disk space, |
|
|
Super VGA monitor or display, 12X CD-ROM, 3.5 in 1.44 Mb diskette drive, Windows 95 or |
|
|
greater, Windows NT, Windows 2000, RS232 port with 16550AF UART, Built in pointing |
|
|
device or mouse |
|
|
|
|
- |
Single user license for TIPSS |
|
All engine data subscription |
||
|
||
|
|
|
|
Communication adapter II group |
|
27610164 |
(Communication adapter II, harness cables, software program, users manual and storage |
|
|
case) |
|
|
|
|
27610165 |
Communication adapter |
|
|
|
|
27610167 |
Communication adapter software |
|
|
|
|
27610169 |
RS232 cable (connects communication adapter to PC) |
|
|
|
|
27610168 |
Connector cable (connects communication adapter to diagnostic connector) |
|
|
|
|
- |
Terminal removal tool (14 AWG wire) used for removing pin and socket terminals |
|
|
|
|
- |
Terminal removal tool (16 and 18 AWG wire) used for removing pin and socket terminals |
|
|
|
|
- |
Heavy duty digital multimeter |
|
Digital multimeter capable of reading duty cycle |
||
|
||
|
|
|
- |
Service tool bypass harness |
|
|
|
|
- |
70-terminal “AMP” breakout T |
|
|
|
|
- |
Engine timing probe |
|
|
|
|
- |
Timing probe adapter |
|
|
|
|
- |
Deutsch “DT” timing probe cable |
|
|
|
|
- |
Slotted socket for removing coolant temperature sensor |
|
|
|
|
- |
Voltage test lamp |
|
|
|
|
14 |
Diagnostic Manual, TSL4247, Preliminary |

2800 Series |
2 |
|
Optional service tools |
||
|
|
|
Part No. |
Description |
|
|
|
|
27610181 |
Harness repair tool kit (includes crimping tool) |
|
|
|
|
27610182 |
Harness repair tool kit top-up |
|
|
|
|
- |
3-Pin "DT" breakout T (breakout T harness is inserted in series between a harness jack and |
|
plug to permit voltage measurement on an operating system) |
||
|
||
|
|
|
- |
3-Pin "HD" breakout T (for remote mounted throttle sensor only) |
|
|
|
|
- |
Signal reading probes |
|
|
|
|
- |
Extraction pump used to pull a vacuum for atmospheric pressure test |
|
|
|
|
- |
Suction tube attachment to 1U-5718 |
|
|
|
|
- |
Bottle assembly attachment to 1U-5718 |
|
|
|
|
- |
Turning tool permits turning engine by hand |
|
|
|
|
- |
Pressure group used to measure oil pressure |
|
|
|
|
- |
Temperature adapter group |
|
|
|
|
- |
3-terminal Packard breakout T |
|
|
|
|
- |
3-Pin "DT" harness bypass T (used to bypass the harness signal lines for engine pressure |
|
sensors) |
||
|
||
|
|
|
Diagnostic Manual, TSL4247, Preliminary |
15 |

Service tool illustrations
Engine Timing Probe |
Voltage Test Lamp 5P-7277 |
125-3662 Engine Sensor Harness Bypass
167-9225 Service Tool Bypass Harness
7X-6370 3-Pin DT Breakout T
140-2266 70-Terminal Breakout T
124-5643 3-Terminal Packard Breakout T
A
16

2800 Series
3
Programming parameters
Connecting the TIPSS-EST
The communications adapter is powered by 24 volts DC from the engine battery. This permits operation beside the engine to allow use during engine operation.
Use the following procedures to connect the service tool to the engine.
1Turn the key switch to the OFF position
2The PC (with the TIPSS-EST software installed) should be connected to the engine system through the diagnostics connector.
3Connect the opposite end of the service tool harness cable to the communication adapter. Refer "Connecting TIPSS-EST using a TIPSS communication adapter" on page 18.
4Connect the communication adapter to the PC using the appropriate cable.
5Turn the key switch to the ON position in order to begin testing. The service tool will operate while the engine is running or with the engine OFF and the key switch ON. If the tool does not communicate with the ECM disconnect and reconnect the diagnostics connector cable. Check the communication. If the problem is still present refer to Test 7: Perkins Data Link circuit test on page 114.
Notes:
lThe service tool may restart during engine cranking due to a voltage dip on the battery line.
lThe TIPSS-EST must be configured to communicate with the specific type of communication adapter used. Go to the ‘Preferences’ menu that is located under ‘Settings’ in order to select the appropriate communication adapter.
Diagnostic Manual, TSL4247, Preliminary |
17 |
3 |
2800 Series |
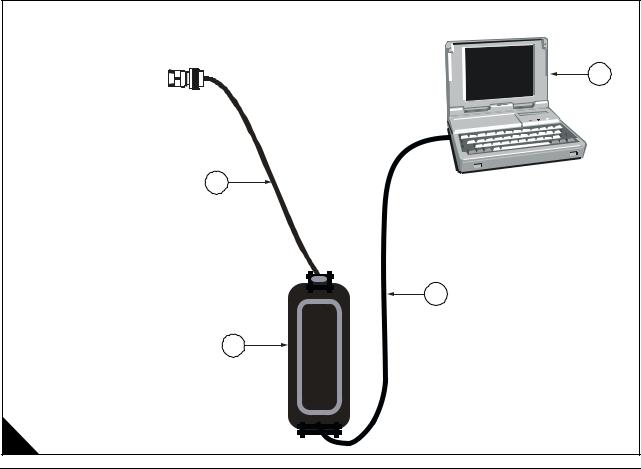
Connecting TIPSS-EST using a TIPSS communication adapter |
|
Q PC with TIPSS-EST installed
R 27610169 PC to communication adapter cable
S 27610165 communication adapter
T 27610168 service tool harness cable
1
4
2
3
A
18 |
Diagnostic Manual, TSL4247, Preliminary |

2800 Series |
3 |
Passwords |
|
Factory passwords
Factory passwords are required to perform each of the following five functions:
1 Program a new ECM
When an ECM is replaced the system configuration parameters must be programmed into the new ECM. A new ECM will allow these parameters to be programmed once without factory passwords. After the initial programming these parameters are protected by factory passwords.
2 Rerate to another engine family
This requires changing the Personality Module code, which is protected by factory passwords.
3 Read customer passwords
If the owner loses his customer passwords, he will not be able to program customer parameters. By using factory passwords, one can read customer passwords, then use those customer passwords to program customer parameters.
4 Clear certain diagnostic codes
Critical event codes require the use of factory passwords in order to clear the code once it is logged. Diagnostic code 252-11 (Incorrect Engine Software) also requires factory passwords. This diagnostic code should be cleared only if you are certain that the Personality Module is for the specific engine.
Caution: Operating the engine with a Personality Module not designed for that engine will result in engine damage. Be sure the Personality Module is correct for your engine.
Certain other codes require customer passwords. The majority of logged codes do not require passwords to be cleared. To obtain factory passwords, proceed as if you already have the password. At some point, if the factory passwords are actually needed, TIPSS-EST will request the factory passwords and display the information required to obtain the passwords.
Customer passwords
If customer passwords have been entered, they are then required to change ANY customer parameter.
TIPSS-EST can be used to change customer parameters. To obtain customer passwords, contact the supplier of the equipment. If the owner has lost the passwords, customer passwords may be read by using TIPSS-EST (factory passwords are required in order to read customer passwords) by using the following procedure.
1In TIPSS-EST access “View Passwords” under the “Utilities” menu.
2When the Factory Password screen appears, record the information listed.
3Obtain the factory passwords. The information recorded above must be provided, and generates a permanent record at Perkins of the access.
4From the Factory Password screen, enter the factory passwords.
5When the View Customer Passwords screen appears, record the customer passwords. The customer passwords may then be used to change customer parameters.
Diagnostic Manual, TSL4247, Preliminary |
19 |

3 |
2800 Series |
Programming a new ECM |
|
The Engine Control Module or ECM is the brain of the system. When a problem occurs, it is easy to assume that the ECM is responsible. This is usually the wrong conclusion.
Most failures occur at the wiring and connectors or at a sensor input/output. Follow the troubleshooting procedures, and do not replace an ECM on speculation.
However, when your troubleshooting indicates that a failure has in fact occurred in the ECM, the following procedure outlines the steps required to replace a faulty ECM.
Note: If an ECM replacement is required, the ECM parameters, injector trim codes, and timing calibration can be transferred from the suspect ECM to the replacement ECM. Timing calibration will NOT be necessary. This feature requires TIPSS-EST and is only possible if the suspect ECM can communicate with the TIPSS-EST.
Replacing the ECM using TIPSS-EST ECM replacement feature
1Ensure that the ECM is the problem by first temporarily connecting a test ECM. Hang the test ECM on the side of the engine. Flash program the identical Personality Module that was used in the suspect ECM into the test ECM. Use the TIPSS-EST ECM Replacement feature to copy the parameter configuration of the suspect ECM into the test ECM. Ensure that the parameters in the test ECM are programmed the same as the parameters in the suspect one.
2If the test ECM repairs the problem, reconnect the suspect ECM. Verify that the problem returns when the suspect ECM is reconnected.
3Select the ECM Replacement feature under the Service/Copy Configuration menu and load the parameters from the failed ECM.
4Temporarily connect the new ECM by connecting both ECM connectors. Do not mount the ECM on the engine yet.
5Flash program the Personality Module into the new ECM if the Personality Module is not already installed.
Note: The new ECM may be shipped with a blank Personality Module, or may have been pre-flashed at the factory.
6Use the TIPSS-EST ECM Replacement feature to program the new ECM
7Enter Rating Number parameter into the new ECM
8Check for active codes. Program any required parameters that have not been programmed.
Note: On initial power-up of a new ECM, the Rating Number parameter must be programmed to avoid a 253-02 Check Customer Or System Parameters diagnostic code.
If a 261-13 Check Timing Sensor Calibration diagnostic code is not active, install the new ECM on the engine, otherwise perform a timing calibration first.
20 |
Diagnostic Manual, TSL4247, Preliminary |

2800 Series |
3 |
Replacing the ECM (if ECM replacement feature cannot be used)
1Ensure that the ECM is the problem by first temporarily connecting a test ECM. Hang the test ECM on the side of the engine. Flash program the identical Personality Module that was used in the suspect ECM into the test ECM. Program any parameters that are necessary to use the ECM for the test. Program the parameters exactly the same as they are in the suspect ECM.
2If the test ECM repairs the problem, reconnect the suspect ECM. Verify that the problem returns when the suspect ECM is reconnected.
3Obtain customer parameters from the failed ECM
Obtain and record the customer passwords. If the customer has lost or forgotten their passwords, obtain factory passwords to get them.
Use TIPSS-EST to access customer specified parameters from the ECM that is being replaced. If the ECM does not communicate with the electronic service tool, obtain the required parameter list from the OEM.
Record the customer parameters
4Record ECM current totals
5Temporarily connect the new ECM by connecting both ECM connectors. Do not mount the ECM to the engine until the timing calibration has been performed.
6Flash program the Personality Module into the new ECM if the Personality Module is not already installed.
Note: The new ECM may be shipped with a blank Personality Module, or may have been pre-flashed at the factory.
7 Obtain factory passwords if required.
The following parameters can be programmed on a new ECM without factory passwords:
lFull Load Setting (FLS)
lFull Torque Setting (FTS)
lEngine serial number
System configuration parameters must be entered before the customer specified parameters are entered
If customer parameters are entered before the system configuration parameters, the total tattletale will change. It will then be necessary to obtain another set of factory passwords in order to access system configuration parameters.
8 Record the following information from the engine information plate:
lFull Load Setting (FLS)
lFull Torque Setting (FTS)
lEngine serial number
Use TIPSS-EST to access system configuration parameters. When the Factory Specified Passwords screen appears record the following information:
lECM serial number
lEngine serial number
lTIPSS-EST serial number
lTotal tattletale
lReason code
Leave TIPSS-EST on the Factory Specified Passwords screen and obtain the factory passwords.
9 Program the new ECM
Note: On initial powerup of a new ECM the following five parameters must be programmed to avoid a 253-02 Check Customer Or System Parameters diagnostic code:
lFull Load Setting (FLS)
lFull Torque Setting (FTS)
lRating number
lEngine serial number
lInjector trim codes
Continued
Diagnostic Manual, TSL4247, Preliminary |
21 |

3 |
2800 Series |
Use TIPSS-EST to access system configuration parameters. Enter the recorded values for the following parameters:
lFull Load Setting (FLS)
lFull Torque Setting (FTS)
lEngine serial number
Use TIPSS-EST to access customer specified parameters. Enter the customer specified parameters and the original customer passwords.
Use TIPSS-EST to access current totals from the Read/Change Current Totals main menu. Using the recorded factory passwords enter the totals from the original ECM.
Use the Service\Calibrations\Timing Calibration menu to calibrate the timing. Refer to Test 8: Engine speed/timing circuit test on page 121.
10 Install the new ECM on the engine.
22 |
Diagnostic Manual, TSL4247, Preliminary |
 Loading...
Loading...