NEC PD78F9210, PD78F9211, PD78F9212, PD78F9210-A, PD78F9211-A User Guide
...
User’s Manual
78K0S/KY1+
8-bit Single-Chip Microcontrollers
PD78F9210 PD78F9211 PD78F9212PD78F9210(A) PD78F9211(A) PD78F9212(A)PD78F9210(A2) PD78F9211(A2) PD78F9212(A2)
Document No. |
U16994EJ5V0UD00 (5th edition) |
Date Published |
January 2008 NS |
©


 2004 Printed in Japan
2004 Printed in Japan
[MEMO]
2 |
User’s Manual U16994EJ5V0UD |

NOTES FOR CMOS DEVICES
1VOLTAGE APPLICATION WAVEFORM AT INPUT PIN
Waveform distortion due to input noise or a reflected wave may cause malfunction. If the input of the CMOS device stays in the area between VIL (MAX) and VIH (MIN) due to noise, etc., the device may malfunction. Take care to prevent chattering noise from entering the device when the input level is fixed, and also in the transition period when the input level passes through the area between VIL (MAX) and VIH (MIN).
2HANDLING OF UNUSED INPUT PINS
Unconnected CMOS device inputs can be cause of malfunction. If an input pin is unconnected, it is possible that an internal input level may be generated due to noise, etc., causing malfunction. CMOS devices behave differently than Bipolar or NMOS devices. Input levels of CMOS devices must be fixed high or low by using pull-up or pull-down circuitry. Each unused pin should be connected to VDD or GND via a resistor if there is a possibility that it will be an output pin. All handling related to unused pins must be judged separately for each device and according to related specifications governing the device.
3PRECAUTION AGAINST ESD
A strong electric field, when exposed to a MOS device, can cause destruction of the gate oxide and ultimately degrade the device operation. Steps must be taken to stop generation of static electricity as much as possible, and quickly dissipate it when it has occurred. Environmental control must be adequate. When it is dry, a humidifier should be used. It is recommended to avoid using insulators that easily build up static electricity. Semiconductor devices must be stored and transported in an anti-static container, static shielding bag or conductive material. All test and measurement tools including work benches and floors should be grounded. The operator should be grounded using a wrist strap. Semiconductor devices must not be touched with bare hands. Similar precautions need to be taken for PW boards with mounted semiconductor devices.
4STATUS BEFORE INITIALIZATION
Power-on does not necessarily define the initial status of a MOS device. Immediately after the power source is turned ON, devices with reset functions have not yet been initialized. Hence, power-on does not guarantee output pin levels, I/O settings or contents of registers. A device is not initialized until the reset signal is received. A reset operation must be executed immediately after power-on for devices with reset functions.
5POWER ON/OFF SEQUENCE
In the case of a device that uses different power supplies for the internal operation and external interface, as a rule, switch on the external power supply after switching on the internal power supply. When switching the power supply off, as a rule, switch off the external power supply and then the internal power supply. Use of the reverse power on/off sequences may result in the application of an overvoltage to the internal elements of the device, causing malfunction and degradation of internal elements due to the passage of an abnormal current.
The correct power on/off sequence must be judged separately for each device and according to related specifications governing the device.
6INPUT OF SIGNAL DURING POWER OFF STATE
Do not input signals or an I/O pull-up power supply while the device is not powered. The current injection that results from input of such a signal or I/O pull-up power supply may cause malfunction and the abnormal current that passes in the device at this time may cause degradation of internal elements. Input of signals during the power off state must be judged separately for each device and according to related specifications governing the device.
User’s Manual U16994EJ5V0UD |
3 |

Windows is a registered trademark or a trademark of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other countries.
PC/AT is a trademark of International Business Machines Corporation.
HP9000 series 700 and HP-UX are trademarks of Hewlett-Packard Company.
SPARCstation is a trademark of SPARC International, Inc.
Solaris and SunOS are trademarks of Sun Microsystems, Inc.
SuperFlash is a registered trademark of Silicon Storage Technology, Inc. in several countries including the United States and Japan.
Caution: This product uses SuperFlash® technology licensed from Silicon Storage Technology, Inc.
4 |
User’s Manual U16994EJ5V0UD |

•The information in this document is current as of January, 2008. The information is subject to change without notice. For actual design-in, refer to the latest publications of NEC Electronics data sheets or data books, etc., for the most up-to-date specifications of NEC Electronics products. Not all products and/or types are available in every country. Please check with an NEC Electronics sales representative for availability and additional information.
•No part of this document may be copied or reproduced in any form or by any means without the prior written consent of NEC Electronics. NEC Electronics assumes no responsibility for any errors that may appear in this document.
•NEC Electronics does not assume any liability for infringement of patents, copyrights or other intellectual property rights of third parties by or arising from the use of NEC Electronics products listed in this document or any other liability arising from the use of such products. No license, express, implied or otherwise, is granted under any patents, copyrights or other intellectual property rights of NEC Electronics or others.
•Descriptions of circuits, software and other related information in this document are provided for illustrative purposes in semiconductor product operation and application examples. The incorporation of these circuits, software and information in the design of a customer's equipment shall be done under the full responsibility of the customer. NEC Electronics assumes no responsibility for any losses incurred by customers or third parties arising from the use of these circuits, software and information.
•While NEC Electronics endeavors to enhance the quality, reliability and safety of NEC Electronics products, customers agree and acknowledge that the possibility of defects thereof cannot be eliminated entirely. To minimize risks of damage to property or injury (including death) to persons arising from defects in NEC Electronics products, customers must incorporate sufficient safety measures in their design, such as redundancy, fire-containment and anti-failure features.
•NEC Electronics products are classified into the following three quality grades: "Standard", "Special" and "Specific".
The "Specific" quality grade applies only to NEC Electronics products developed based on a customerdesignated "quality assurance program" for a specific application. The recommended applications of an NEC Electronics product depend on its quality grade, as indicated below. Customers must check the quality grade of each NEC Electronics product before using it in a particular application.
"Standard": Computers, office equipment, communications equipment, test and measurement equipment, audio and visual equipment, home electronic appliances, machine tools, personal electronic equipment and industrial robots.
"Special": Transportation equipment (automobiles, trains, ships, etc.), traffic control systems, anti-disaster systems, anti-crime systems, safety equipment and medical equipment (not specifically designed for life support).
"Specific": Aircraft, aerospace equipment, submersible repeaters, nuclear reactor control systems, life support systems and medical equipment for life support, etc.
The quality grade of NEC Electronics products is "Standard" unless otherwise expressly specified in NEC Electronics data sheets or data books, etc. If customers wish to use NEC Electronics products in applications not intended by NEC Electronics, they must contact an NEC Electronics sales representative in advance to determine NEC Electronics' willingness to support a given application.
(Note)
(1)"NEC Electronics" as used in this statement means NEC Electronics Corporation and also includes its majority-owned subsidiaries.
(2)"NEC Electronics products" means any product developed or manufactured by or for NEC Electronics (as defined above).
M8E |
02. 11-1 |
User’s Manual U16994EJ5V0UD |
5 |
INTRODUCTION
Target Readers |
This manual is intended for user engineers who wish to understand the functions of |
|||
|
the 78K0S/KY1+ in order to design and develop its application systems and |
|||
|
programs. |
|
|
|
|
The target devices are the following subseries products. |
|||
|
• 78K0S/KY1+: PD78F9210, 78F9211, |
78F9212, 78F9210(A), 78F9211(A), |
||
|
78F9212(A), 78F9210(A2), 78F9211(A2), 78F9212(A2) |
|||
Purpose |
This manual is intended to give users on understanding of the functions described in |
|||
|
the Organization below. |
|
|
|
Organization |
Two manuals are available for 78K0S/KY1+: this manual and the Instruction Manual |
|||
|
(common to the 78K/0S Series). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
78K0S/KY1+ |
|
78K/0S Series |
|
|
|
Instructions |
|
|
|
User’s Manual |
|
|
|
|
|
User’s Manual |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
• Pin functions |
• CPU function |
||
|
• Internal block functions |
• Instruction set |
||
|
• Interrupts |
• Instruction description |
||
|
• Other internal peripheral functions |
|
|
|
|
• Electrical specifications |
|
|
|
How to Use This Manual |
It is assumed that the readers of this manual have general knowledge of electrical |
|||
|
engineering, logic circuits, and microcontrollers. |
|||
◊ To understand the overall functions of 78K0S/KY1+
→ Read this manual in the order of the CONTENTS. The mark <R> shows major revised points. The revised points can be easily searched by copying an “<R>” in the PDF file and specifying it in the “Find what:” field.
◊ How to read register formats
→ For a bit number enclosed in angle brackets (<>), the bit name is defined as a reserved word in the RA78K0S, and is defined as an sfr variable using the #pragma sfr directive in the CC78K0S.
◊ To learn the detailed functions of a register whose register name is known
→ See APPENDIX B REGISTER INDEX.
◊ To learn the details of the instruction functions of the 78K/0S Series
→ Refer to 78K/0S Series Instructions User’s Manual (U11047E) separately available.
◊ To learn the electrical specifications of the 78K0S/KY1+
→ See CHAPTER 19 and 20 ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS.
6 |
User’s Manual U16994EJ5V0UD |

Conventions |
Data significance: |
Higher digits on the left and lower digits on the right |
|
Active low representation: ××× (overscore over pin or signal name) |
|
|
Note: |
Footnote for item marked with Note in the text |
|
Caution: |
Information requiring particular attention |
|
Remark: |
Supplementary information |
|
Numerical representation: Binary ... ×××× or ××××B |
|
|
|
Decimal ... ×××× |
|
|
Hexadecimal ... ××××H |
Related Documents |
The related documents indicated in this publication may include preliminary versions. |
|
|
However, preliminary versions are not marked as such. |
|
Documents Related to Devices
Document Name |
Document No. |
|
|
78K0S/KY1+ User’s Manual |
This manual |
|
|
78K/0S Series Instructions User’s Manual |
U11047E |
|
|
Documents Related to Development Software Tools (User’s Manuals)
|
Document Name |
Document No. |
|
|
|
|
|
RA78K0S Assembler Package |
|
Operation |
U16656E |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Language |
U14877E |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Structured Assembly Language |
U11623E |
|
|
|
|
CC78K0S C Compiler |
|
Operation |
U16654E |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Language |
U14872E |
|
|
|
|
ID78K0S-QB Ver. 2.81 Integrated Debugger |
|
Operation |
U17287E |
|
|
|
|
PM plus Ver.5.20 |
|
|
U16934E |
|
|
|
|
Documents Related to Development Hardware Tools (User’s Manuals)
Document Name |
Document No. |
|
|
QB-78K0SKX1 In-Circuit Emulator |
U18219E |
|
|
QB-MINI2 On-Chip Debug Emulator with Programming Function |
U18371E |
|
|
Caution The related documents listed above are subject to change without notice. Be sure to use the latest version of each document for designing.
User’s Manual U16994EJ5V0UD |
7 |
Documents Related to Flash Memory Writing
Document Name |
Document No. |
|
|
PG-FP4 Flash Memory Programmer User’s Manual |
U15260E |
|
|
PG-FP5 Flash Memory Programmer User’s Manual |
U18865E |
|
|
Other Related Documents
Document Name |
Document No. |
|
|
SEMICONDUCTOR SELECTION GUIDE - Products and Packages - |
X13769X |
|
|
Semiconductor Device Mount Manual |
Note |
|
|
Quality Grades on NEC Semiconductor Devices |
C11531E |
|
|
NEC Semiconductor Device Reliability/Quality Control System |
C10983E |
|
|
Guide to Prevent Damage for Semiconductor Devices by Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) |
C11892E |
|
|
Note See the “Semiconductor Device Mount Manual” website (http://www.necel.com/pkg/en/mount/index.html).
Caution The related documents listed above are subject to change without notice. Be sure to use the latest version of each document for designing.
8 |
User’s Manual U16994EJ5V0UD |
CONTENTS
CHAPTER 1 |
OVERVIEW......................................................................................................................... |
15 |
|||
1.1 |
Features ...................................................................................................................................... |
15 |
|||
1.2 |
Ordering Information ................................................................................................................. |
17 |
|||
1.3 |
Pin Configuration (Top View) ................................................................................................... |
18 |
|||
1.4 |
78K0S/Kx1+ Product Lineup..................................................................................................... |
20 |
|||
1.5 |
Block Diagram............................................................................................................................ |
21 |
|||
1.6 |
Functional Outline ..................................................................................................................... |
22 |
|||
CHAPTER 2 |
PIN FUNCTIONS............................................................................................................... |
23 |
|||
2.1 |
Pin Function List........................................................................................................................ |
23 |
|||
2.2 |
Pin Functions ............................................................................................................................. |
25 |
|||
|
2.2.1 P20 to P23 (Port 2) ....................................................................................................................... |
25 |
|||
|
2.2.2 P32 and P34 (Port 3) .................................................................................................................... |
26 |
|||
|
2.2.3 P40 to P47 (Port 4) ....................................................................................................................... |
26 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.2.4 |
|
RESET .......................................................................................................................................... |
26 |
|
|
2.2.5 |
|
X1 and X2 ..................................................................................................................................... |
26 |
|
|
2.2.6 |
|
VDD................................................................................................................................................ |
26 |
|
|
2.2.7 |
|
VSS ................................................................................................................................................ |
26 |
|
2.3 |
Pin I/O Circuits and Connection of Unused Pins ................................................................... |
27 |
|||
CHAPTER 3 |
CPU ARCHITECTURE...................................................................................................... |
29 |
|||
3.1 |
Memory Space............................................................................................................................ |
29 |
|||
|
3.1.1 Internal program memory space ................................................................................................... |
32 |
|||
|
3.1.2 Internal data memory space.......................................................................................................... |
33 |
|||
|
3.1.3 Special function register (SFR) area ............................................................................................. |
33 |
|||
|
3.1.4 |
|
Data memory addressing .............................................................................................................. |
33 |
|
3.2 |
Processor Registers.................................................................................................................. |
36 |
|||
|
3.2.1 |
|
Control registers............................................................................................................................ |
36 |
|
|
3.2.2 |
|
General-purpose registers............................................................................................................. |
39 |
|
|
3.2.3 Special function registers (SFRs).................................................................................................. |
40 |
|||
3.3 |
Instruction Address Addressing .............................................................................................. |
43 |
|||
|
3.3.1 |
|
Relative addressing....................................................................................................................... |
43 |
|
|
3.3.2 |
|
Immediate addressing................................................................................................................... |
44 |
|
|
3.3.3 |
|
Table indirect addressing .............................................................................................................. |
44 |
|
|
3.3.4 |
|
Register addressing ...................................................................................................................... |
45 |
|
3.4 |
Operand Address Addressing.................................................................................................. |
46 |
|||
|
3.4.1 |
|
Direct addressing .......................................................................................................................... |
46 |
|
|
3.4.2 |
|
Short direct addressing ................................................................................................................. |
47 |
|
|
3.4.3 Special function register (SFR) addressing ................................................................................... |
48 |
|||
|
3.4.4 |
|
Register addressing ...................................................................................................................... |
49 |
|
|
3.4.5 |
|
Register indirect addressing.......................................................................................................... |
50 |
|
|
|
|
|
User’s Manual U16994EJ5V0UD |
9 |
3.4.6 Based addressing.......................................................................................................................... |
51 |
3.4.7Stack addr
10 |
User’s Manual U16994EJ5V0UD |
7.2 |
Configuration of 8-bit Timer H1.............................................................................................. |
124 |
|
7.3 |
Registers Controlling 8-bit Timer H1 ..................................................................................... |
127 |
|
7.4 |
Operation of 8-bit Timer H1 .................................................................................................... |
129 |
|
|
7.4.1 |
Operation as interval timer/square-wave output.......................................................................... |
129 |
|
7.4.2 |
Operation as PWM output mode ................................................................................................. |
133 |
CHAPTER 8 |
WATCHDOG TIMER ....................................................................................................... |
139 |
|
8.1 |
Functions of Watchdog Timer ................................................................................................ |
139 |
|
8.2 |
Configuration of Watchdog Timer.......................................................................................... |
141 |
|
8.3 |
Registers Controlling Watchdog Timer................................................................................. |
142 |
|
8.4 |
Operation of Watchdog Timer ................................................................................................ |
144 |
|
|
8.4.1 |
Watchdog timer operation when “low-speed internal oscillator cannot be stopped” is |
|
|
|
selected by option byte................................................................................................................ |
144 |
|
8.4.2 |
Watchdog timer operation when “low-speed internal oscillator can be stopped by |
|
|
|
software” is selected by option byte ............................................................................................ |
146 |
|
8.4.3 |
Watchdog timer operation in STOP mode (when “low-speed internal oscillator can be |
|
|
|
stopped by software” is selected by option byte)......................................................................... |
148 |
|
8.4.4 |
Watchdog timer operation in HALT mode (when “low-speed internal oscillator can be |
|
|
|
stopped by software” is selected by option byte)......................................................................... |
149 |
CHAPTER 9 |
A/D CONVERTER ........................................................................................................... |
150 |
|
9.1 |
Functions of A/D Converter .................................................................................................... |
150 |
|
9.2 |
Configuration of A/D Converter.............................................................................................. |
152 |
|
9.3 |
Registers Used by A/D Converter .......................................................................................... |
154 |
|
9.4 |
A/D Converter Operations....................................................................................................... |
159 |
|
|
9.4.1 |
Basic operations of A/D converter............................................................................................... |
159 |
|
9.4.2 |
Input voltage and conversion results........................................................................................... |
161 |
|
9.4.3 |
A/D converter operation mode .................................................................................................... |
162 |
9.5 |
How to Read A/D Converter Characteristics Table .............................................................. |
164 |
|
9.6 |
Cautions for A/D Converter .................................................................................................... |
166 |
|
CHAPTER 10 |
INTERRUPT FUNCTIONS ............................................................................................ |
170 |
|
10.1 |
Interrupt Function Types......................................................................................................... |
170 |
|
10.2 |
Interrupt Sources and Configuration..................................................................................... |
170 |
|
10.3 |
Interrupt Function Control Registers..................................................................................... |
172 |
|
10.4 |
Interrupt Servicing Operation................................................................................................. |
175 |
|
|
10.4.1 |
Maskable interrupt request acknowledgment operation .............................................................. |
175 |
|
10.4.2 |
Multiple interrupt servicing........................................................................................................... |
177 |
|
10.4.3 |
Interrupt request pending ............................................................................................................ |
179 |
CHAPTER 11 |
STANDBY FUNCTION.................................................................................................. |
180 |
|
11.1 |
Standby Function and Configuration .................................................................................... |
180 |
|
|
11.1.1 |
Standby function ......................................................................................................................... |
180 |
|
11.1.2 |
Registers used during standby.................................................................................................... |
182 |
|
|
User’s Manual U16994EJ5V0UD |
11 |
11.2 |
Standby Function Operation................................................................................................... |
183 |
|||||
|
11.2.1 |
|
HALT mode ................................................................................................................................. |
183 |
|||
|
11.2.2 |
|
STOP mode................................................................................................................................. |
186 |
|||
CHAPTER 12 |
RESET FUNCTION ....................................................................................................... |
190 |
|||||
12.1 |
Register for Confirming Reset Source................................................................................... |
197 |
|||||
CHAPTER 13 |
POWER-ON-CLEAR CIRCUIT ..................................................................................... |
198 |
|||||
13.1 |
Functions of Power-on-Clear Circuit ..................................................................................... |
198 |
|||||
13.2 |
Configuration of Power-on-Clear Circuit ............................................................................... |
199 |
|||||
13.3 |
Operation of Power-on-Clear Circuit...................................................................................... |
199 |
|||||
13.4 |
Cautions for Power-on-Clear Circuit...................................................................................... |
200 |
|||||
CHAPTER 14 |
LOW-VOLTAGE DETECTOR ....................................................................................... |
202 |
|||||
14.1 |
Functions of Low-Voltage Detector ....................................................................................... |
202 |
|||||
14.2 |
Configuration of Low-Voltage Detector ................................................................................. |
202 |
|||||
14.3 |
Registers Controlling Low-Voltage Detector ........................................................................ |
203 |
|||||
14.4 |
Operation of Low-Voltage Detector........................................................................................ |
205 |
|||||
14.5 |
Cautions for Low-Voltage Detector........................................................................................ |
209 |
|||||
CHAPTER 15 |
OPTION BYTE................................................................................................................ |
212 |
|||||
15.1 |
Functions of Option Byte ........................................................................................................ |
212 |
|||||
15.2 |
Format of Option Byte ............................................................................................................. |
213 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15.3 |
Caution When the RESET Pin Is Used as an Input-Only Port Pin (P34)............................. |
214 |
|||||
CHAPTER 16 |
FLASH MEMORY.......................................................................................................... |
215 |
|||||
16.1 |
Features .................................................................................................................................... |
215 |
|||||
16.2 |
Memory Configuration............................................................................................................. |
216 |
|||||
16.3 |
Functional Outline.................................................................................................................... |
216 |
|||||
16.4 |
Writing with Flash Memory Programmer............................................................................... |
217 |
|||||
16.5 |
Programming Environment..................................................................................................... |
218 |
|||||
16.6 |
Processing of Pins on Board .................................................................................................. |
220 |
|||||
|
16.6.1 X1 and X2 pins ............................................................................................................................ |
220 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
16.6.2 |
|
RESET pin................................................................................................................................... |
221 |
|||
|
16.6.3 |
|
Port pins ...................................................................................................................................... |
222 |
|||
|
16.6.4 |
|
Power supply............................................................................................................................... |
222 |
|||
16.7 |
On-Board and Off-Board Flash Memory Programming ....................................................... |
223 |
|||||
|
16.7.1 Flash memory programming mode.............................................................................................. |
223 |
|||||
|
16.7.2 |
|
Communication commands ......................................................................................................... |
223 |
|||
|
16.7.3 |
|
Security settings .......................................................................................................................... |
224 |
|||
16.8 |
Flash Memory Programming by Self Programming ............................................................. |
225 |
|||||
|
16.8.1 Outline of self programming ........................................................................................................ |
225 |
|||||
|
16.8.2 Cautions on self programming function ....................................................................................... |
228 |
|||||
|
16.8.3 Registers used for self programming function ............................................................................. |
228 |
|||||
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
User’s Manual U16994EJ5V0UD |
|
16.8.4 |
Example of shifting normal mode to self programming mode...................................................... |
235 |
16.8.5 |
Example of shifting self programming mode to normal mode...................................................... |
238 |
16.8.6 |
Example of block erase operation in self programming mode..................................................... |
241 |
16.8.7 |
Example of block blank check operation in self programming mode ........................................... |
244 |
16.8.8 |
Example of byte write operation in self programming mode........................................................ |
247 |
16.8.9 |
Example of internal verify operation in self programming mode.................................................. |
250 |
16.8.10 |
Examples of operation when command execution time should be minimized in self |
|
|
programming mode .................................................................................................................... |
254 |
16.8.11 |
Examples of operation when interrupt-disabled time should be minimized in self |
|
|
programming mode ..................................................................................................................... |
261 |
CHAPTER 17 |
ON-CHIP DEBUG FUNCTION....................................................................................... |
272 |
|
17.1 |
Connecting QB-MINI2 to 78K0S/KY1+ ................................................................................... |
272 |
|
|
17.1.1 Connection of INTP1 pin ............................................................................................................. |
273 |
|
|
17.1.2 Connection of X1 and X2 pins..................................................................................................... |
274 |
|
17.2 |
Securing of user resources .................................................................................................... |
275 |
|
CHAPTER 18 |
INSTRUCTION SET OVERVIEW................................................................................. |
276 |
|
18.1 |
Operation .................................................................................................................................. |
276 |
|
|
18.1.1 Operand identifiers and description methods .............................................................................. |
276 |
|
|
18.1.2 Description of “Operation” column............................................................................................... |
277 |
|
|
18.1.3 Description of “Flag” column ....................................................................................................... |
277 |
|
18.2 |
Operation List........................................................................................................................... |
278 |
|
18.3 |
Instructions Listed by Addressing Type ............................................................................... |
283 |
|
CHAPTER 19 |
ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS (Standard product, (A) grade product) ................ |
286 |
|
CHAPTER 20 |
ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS (TARGET VALUES) ((A2) grade product) ............ |
298 |
|
CHAPTER 21 |
PACKAGE DRAWING .................................................................................................. |
312 |
|
CHAPTER 22 |
RECOMMENDED SOLDERING CONDITIONS .......................................................... |
315 |
|
APPENDIX A |
DEVELOPMENT TOOLS .............................................................................................. |
317 |
|
A.1 |
Software Package .................................................................................................................... |
320 |
|
A.2 |
Language Processing Software ............................................................................................. |
320 |
|
A.3 |
Control Software ...................................................................................................................... |
321 |
|
A.4 |
Flash Memory Writing Tools................................................................................................... |
321 |
|
A.5 |
Debugging Tools (Hardware).................................................................................................. |
322 |
|
|
A.5.1 When using in-circuit emulator QB-78K0SKX1 ........................................................................... |
322 |
|
|
A.5.2 |
When using on-chip debug emulator QB-MINI2......................................................................... |
322 |
A.6 |
Debugging Tools (Software)................................................................................................... |
322 |
|
|
|
User’s Manual U16994EJ5V0UD |
13 |
APPENDIX B |
NOTES ON DESIGNING TARGET SYSTEM................................................................. |
323 |
|
APPENDIX C |
REGISTER INDEX ......................................................................................................... |
325 |
|
C.1 |
Register Index (Register Name).............................................................................................. |
325 |
|
C.2 |
Register Index (Symbol) .......................................................................................................... |
327 |
|
APPENDIX D |
LIST OF CAUTIONS..................................................................................................... |
329 |
|
APPENDIX E |
REVISION HISTORY...................................................................................................... |
344 |
|
E.1 |
Major Revisions in This Edition.............................................................................................. |
344 |
|
E.2 |
Revision History up to Previous Editions ............................................................................. |
345 |
|
14 |
User’s Manual U16994EJ5V0UD |

CHAPTER 1 OVERVIEW
<R> 1.1 Features
O 78K0S CPU core
O ROM and RAM capacities
|
Item |
Program Memory (Flash Memory) |
Memory (Internal High-Speed RAM) |
Part number |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PD78F9210 |
|
1 KB |
128 bytes |
|
|
|
|
PD78F9211 |
|
2 KB |
|
|
|
|
|
PD78F9212 |
|
4 KB |
|
|
|
|
|
O Minimum instruction execution time: 0.2 s (with 10 MHz@4.0 to 5.5 V operation)
OClock
• High-speed system clock … Selected from the following three sources
- Ceramic/crystal resonator: |
2 to 10 MHz (Standard product, (A) grade product) |
||
|
2 to 8 MHz ((A2) grade product) |
||
- External clock: |
2 to 10 MHz (Standard product, (A) grade product) |
||
|
2 to 8 MHz ((A2) grade product) |
||
- High-speed internal oscillator: |
8 |
MHz ±3% |
(−10 to +70°C), |
|
8 |
MHz ±5% |
(Standard product, (A) grade product: −40 to +85°C, (A2) |
grade product: −40 to +125°C)
•Low-speed internal oscillator 240 kHz (TYP.) … Watchdog timer, timer clock in intermittent operation O I/O ports: 14 (CMOS I/O: 13, CMOS input: 1)
O Timer: 3 channels
•16-bit timer/event counter: 1 channel … Timer output × 1, capture input × 2
• 8-bit timer: |
1 channel … PWM output × 1 |
• Watchdog timer: |
1 channel … Operable with low-speed internal oscillation clock |
O On-chip power-on-clear (POC) circuit (A reset is automatically generated when the voltage drops to 2.1 V (TYP.)
or below)
O On-chip low voltage detector (LVI) circuit (An interrupt/reset (selectable) is generated when the detection voltage
is reached)
•Detection voltage: Selectable from ten levels between 2.35 and 4.3 V O Single-power-supply flash memory
•Flash self programming enabled
•Software protection function: Protected from outside party copying (no flash reading command)
•Time required for writing by dedicated flash memory programmer: Approximately 3 seconds (4 KB)
Flash programming on mass production lines supported
O Safety function
•Watchdog timer operated by clock independent from CPU
…A hang-up can be detected even if the system clock stops
•Supply voltage drop detectable by LVI
…Appropriate processing can be executed before the supply voltage drops below the operation voltage
•Equipped with option byte function
…Important system operation settings set in hardware
O Assembler and C language supported
User’s Manual U16994EJ5V0UD |
15 |

CHAPTER 1 OVERVIEW
O Enhanced development environment
• Support for full-function emulator (IECUBE), simplified emulator (MINICUBE2), and simulator
O Supply voltage: VDD = 2.0 to 5.5 V
Use these products in the following voltage range because the detection voltage (VPOC) of the POC circuit is the supply voltage range.
Standard product, (A) grade product: 2.2 to 5.5 V, (A2) grade product: 2.26 to 5.5 V
O Operating temperature range:
•Standard product, (A) grade product: TA = −40 to +85°C
•(A2) grade product: TA = −40 to +125°C
16 |
User’s Manual U16994EJ5V0UD |

CHAPTER 1 OVERVIEW
1.2 Ordering Information
Part Number
PD78F9 ××× - ×× (×) - ××× -A
Semiconductor component
Blank Conventional
-A Lead-free
<R>
<R>
|
|
|
Quality grades |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Blank |
|
Standard |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(A) |
|
Special |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(A2) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Package type |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
GR-JJG |
Plastic SSOP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CS-CAB |
Plastic SDIP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FH-2A2 |
WLBGA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Number of pins |
High-speed RAM |
|
Flash memory |
||||
210 |
|
16 pins |
128 bytes |
1 |
K byte |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
211 |
|
16 pins |
128 bytes |
2 |
K bytes |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
212 |
|
16 pins |
128 bytes |
4 |
K bytes |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Product type |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
F |
Flash memory versions |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Please refer to "Quality Grades on NEC Semiconductor Devices" (Document No . C11531E) p u b l i s h e d b y NEC Electronics Corporation to know the specification of the quality grade on the device and its recommended applications.
<R>
<R>
[Part number list]
PD78F9210GR-JJG
PD78F9210GR(A)-JJG
PD78F9210GR(A2)-JJGNote
PD78F9210GR-JJG-A
PD78F9210GR(A)-JJG-A
PD78F9210GR(A2)-JJG-ANote
PD78F9210CS-CAB-A
PD78F9210FH-2A2-A
Note Under development
PD78F9211GR-JJG
PD78F9211GR(A)-JJG
PD78F9211GR(A2)-JJGNote
PD78F9211GR-JJG-A
PD78F9211GR(A)-JJG-A
PD78F9211GR(A2)-JJG-ANote
PD78F9211CS-CAB-A
PD78F9211FH-2A2-A
PD78F9212GR-JJG
PD78F9212GR(A)-JJG
PD78F9212GR(A2)-JJGNote
PD78F9212GR-JJG-A
PD78F9212GR(A)-JJG-A
PD78F9212GR(A2)-JJG-ANote
PD78F9212CS-CAB-A
PD78F9212FH-2A2-A
User’s Manual U16994EJ5V0UD |
17 |
CHAPTER 1 OVERVIEW
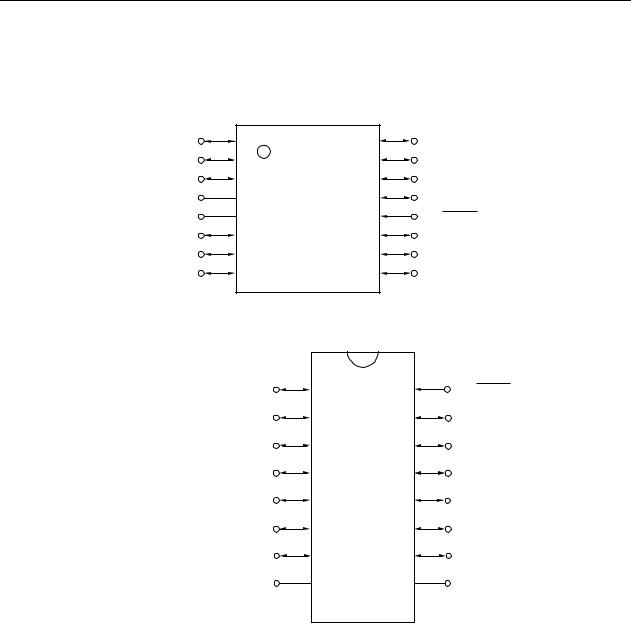
1.3Pin Configuration (Top View)
•16-pin plastic SSOP
P20/ANI0/TI000/TOH1 |
1 |
16 |
P21/ANI1/TI010/TO00/INTP0 |
P41 |
2 |
15 |
P42 |
P40 |
3 |
14 |
P43 |
VSSNote 1 |
4 |
13 |
P32/INTP1 |
VDDNote 2 |
5 |
12 |
P34/RESET |
P47 |
6 |
11 |
P44 |
P46 |
7 |
10 |
P45 |
P23/X1/ANI3 |
8 |
9 |
P22/X2/ANI2 |
<R> |
• 16-pin plastic SDIP |
|
|
|
|
P32/INTP1 |
1 |
16 |
P34/RESET |
|
P43 |
2 |
15 |
P44 |
|
P42 |
3 |
14 |
P45 |
|
P21/ANI1/TI010/TO00/INTP0 |
4 |
13 |
P22/X2/ANI2 |
|
P20/ANI0/TI000/TOH1 |
5 |
12 |
P23/X1/ANI3 |
|
P41 |
6 |
11 |
P46 |
|
P40 |
7 |
10 |
P47 |
|
VSSNote 1 |
8 |
9 |
VDDNote 2 |
Notes 1. In the 78K0S/KY1+, VSS functions alternately as the ground potential of the A/D converter. Be sure to connect VSS to a stabilized GND (= 0 V).
2.In the 78K0S/KY1+, VDD functions alternately as the A/D converter reference voltage input. When using the A/D converter, stabilize VDD at the supply voltage used (2.7 to 5.5 V).
18 |
User’s Manual U16994EJ5V0UD |

CHAPTER 1 OVERVIEW
• 16-pin WLBGA (2.24×1.93)
User’s Manual U16994EJ5V0UD |
19 |
CHAPTER 1 OVERVIEW
1.4 78K0S/Kx1+ Product Lineup
The following table shows the product lineup of the 78K0S/Kx1+.
|
Part Number |
78K0S/KU1+ |
78K0S/KY1+ |
78K0S/KA1+ |
78K0S/KB1+ |
|
Item |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Number of pins |
10 pins |
16 pins |
20 pins |
|
30/32 pins |
|
Internal |
Flash memory |
1 KB, 2 KB, 4 KB |
2 KB |
4 KB |
4 KB, 8 KB |
|
memory |
RAM |
|
128 bytes |
128 |
256 |
256 bytes |
|
|
|
|
bytes |
bytes |
|
Supply voltage |
|
VDD = 2.0 to 5.5 VNote 1 |
|
|
||
Minimum instruction |
|
|
0.20 s (10 MHz, VDD = 4.0 to 5.5 V) |
|
||||||
execution time |
|
|
0.33 s (6 MHz, VDD = 3.0 to 5.5 V) |
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.40 s (5 MHz, VDD = 2.7 to 5.5 V) |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.0 s (2 MHz, VDD = 2.0 to 5.5 V) |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
System clock |
|
|
High-speed internal oscillation (8 MHz (TYP.)) |
|
||||||
(oscillation frequency) |
|
|
Crystal/ceramic oscillation (2 to 10 MHz) Note 2 |
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
External clock input oscillation (2 to 10 MHz) |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Clock for TMH1 and WDT |
|
|
Low-speed internal oscillation (240 kHz (TYP.)) |
|
||||||
(oscillation frequency) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Port |
|
CMOS I/O |
7 |
|
13 |
|
15 |
|
24 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CMOS input |
1 |
|
1 |
|
1 |
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CMOS output |
− |
|
− |
|
1 |
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Timer |
|
16-bit (TM0) |
|
|
|
1 ch Note 3 |
|
|||
|
|
8-bit (TMH) |
|
|
|
1 ch |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8-bit (TM8) |
|
− |
|
1 ch |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
WDT |
|
|
|
1 ch |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Serial interface |
|
− |
|
LIN-Bus-supporting UART: 1 ch |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
A/D converter Note 4 |
|
|
10 bits: 4 ch (2.7 to 5.5V) |
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Multiplier (8 bits × 8 bits) |
|
|
− |
|
|
|
Provided |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interrupts |
|
Internal |
|
5 Note 5 |
|
9 |
|
|||
|
|
External |
|
2 |
|
4 |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Reset |
|
RESET pin |
|
|
|
Provided |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
POC |
|
|
|
2.1 V (TYP.) |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
LVI |
|
|
Provided (selectable by software) |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
WDT |
|
|
|
Provided |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Operating temperature range |
Standard products: |
|
Standard products, (A) grade products: −40 to +85°C |
|
||||||
−40 to +85°C |
|
(A2) grade products: −40 to +125°C |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Notes 1 |
Use these products in the following voltage range because the detection voltage (VPOC) of the power-on- |
|
|
|
clear (POC) circuit is the supply voltage range. |
|
|
Standard product, (A) grade product: 2.2 to 5.5 V, (A2) grade product: 2.26 to 5.5 V |
<R> |
2 |
PD78F95xx does not support the crystal/ceramic oscillation. |
<R> |
3 |
|
|
The product without A/D converter ( PD78F950x) in the 78K0S/KU1+ is not supported. |
|
<R> |
4 |
The product without A/D converter ( PD78F95xx) is provided for the 78K0S/KU1+ and 78K0S/KY1+ |
|
|
respectively. This product has A/D converter. |
<R> |
5 |
There are 2 and 4 factors for the products without A/D converter in the 78K0S/KU1+ and 78K0S/KY1+, |
|
|
respectively. |
20 |
User’s Manual U16994EJ5V0UD |
|
|
|
CHAPTER 1 |
OVERVIEW |
|
|
|
|
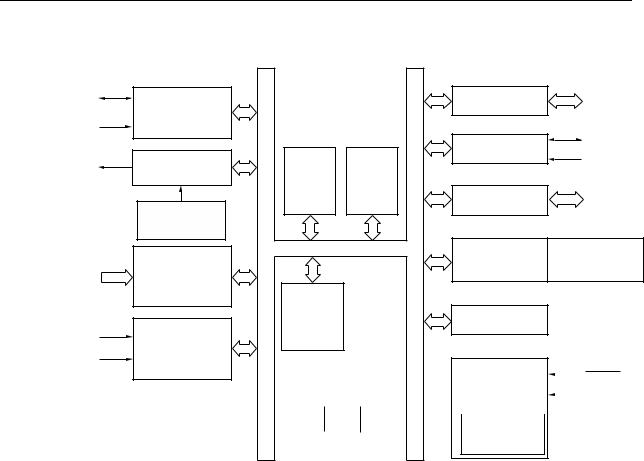
1.5 Block Diagram |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TO00/TI010/P21 |
|
16-bit timer/ |
|
|
|
Port 2 |
4 |
P20 to P23 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TI000/P20 |
|
event counter 00 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Port 3 |
|
P32 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P34 |
|
TOH1/P20 |
|
8-bit timer H1 |
78K0S |
|
|
|
||
|
Flash |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
CPU |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
memory |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
core |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Port 4 |
8 |
P40 to P47 |
|
|
|
Low-speed |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
internal |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
oscillator |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Power on clear/ |
|
POC/LVI |
|
|
|
|
|
|
low voltage |
|
|
ANI0/P20 to |
|
|
|
|
|
|
control |
|
4 |
A/D converter |
|
|
|
indicator |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
||||
ANI3/P23 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Internal |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
high-speed |
|
Reset control |
|
|
|
INTP0/P21 |
|
|
RAM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interrupt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
INTP1/P32 |
|
control |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
System |
|
|
|
RESET/P34 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
control |
|
|
|
X1/P23 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
X2/P22 |
|
|
|
|
High-speed VDDNote 1 VSSNote 2 internal
oscillator
Notes 1. In the 78K0S/KY1+, VDD functions alternately as the A/D converter reference voltage input. When using
the A/D converter, stabilize VDD at the supply voltage used (2.7 to 5.5 V).
2.In the 78K0S/KY1+, VSS functions alternately as the ground potential of the A/D converter. Be sure to connect VSS to a stabilized GND (= 0 V).
User’s Manual U16994EJ5V0UD |
21 |

<R>
<R>
CHAPTER 1 OVERVIEW
1.6 Functional Outline
|
|
Item |
|
PD78F9210 |
|
PD78F9211 |
PD78F9212 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Internal |
Flash memory |
|
1 KB |
|
|
|
2 KB |
4 KB |
|||
memory |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
High-speed RAM |
|
128 bytes |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Memory space |
|
|
64 KB |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
X1 input clock (oscillation frequency) |
|
Crystal/ceramic/external clock input: |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
10 MHz (VDD = 2.0 to 5.5 V) |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Internal |
|
High speed (oscillation |
|
Internal oscillation: 8 MHz (TYP.) |
|
||||||
oscillation |
|
frequency) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
clock |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Low speed (for TMH1 |
|
Internal oscillation: 240 kHz (TYP.) |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
and WDT) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
General-purpose registers |
|
8 bits × 8 registers |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Instruction execution time |
|
0.2 s/0.4 s/0.8 s/1.6 s/3.2 s (X1 input clock: fX = 10 MHz) |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
I/O port |
|
|
|
Total: |
14 pins |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
CMOS I/O: |
13 pins |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
CMOS input: |
1 pin |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Timer |
|
|
|
• 16-bit timer/event counter: |
1 channel |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
• 8-bit timer (timer H1): |
1 channel |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
• Watchdog timer: |
|
|
|
1 channel |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Timer output |
|
2 pins (PWM: 1 pin) |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
A/D converter |
|
|
10-bit resolution × 4 channels |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Vectored |
|
External |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
interrupt sources |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Internal |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
• Reset by |
|
pin |
|
|
|||
Reset |
|
|
RESET |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
• Internal reset by watchdog timer |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
• Internal reset by power-on-clear |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
• Internal reset by low-voltage detector |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Supply voltage |
|
|
VDD = 2.0 to 5.5 VNote |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Operating temperature range |
|
Standard product, (A) grade product: −40 to +85°C |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
(A2) grade product: −40 to +125°C |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Package |
|
|
|
• 16-pin plastic SSOP |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
• 16-pin plastic SDIP |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
• 16-pin WLBGA (2.24 × 1.93) |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note Use these products in the following voltage range because the detection voltage (VPOC) of the power-on-clear (POC) circuit is the supply voltage range.
Standard product, (A) grade product: 2.2 to 5.5 V, (A2) grade product: 2.26 to 5.5 V
22 |
User’s Manual U16994EJ5V0UD |
CHAPTER 2 PIN FUNCTIONS
2.1Pin Function List
(1)Port pins
Pin Name |
I/O |
|
Function |
After Reset |
|
Alternate-Function |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pin |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P20 |
I/O |
Port 2. |
|
Input |
|
ANI0/TI000/TOH1 |
|
|
|
4-bit I/O port. |
|
|
|
|
|
P21 |
|
|
|
|
ANI1/TI010/ |
||
|
Can be set to input or output mode in 1-bit units. |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
TO00/INTP0 |
|||
|
|
An on-chip pull-up resistor can be connected by setting |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
P22Note |
|
|
|
X2/ANI2Note |
|||
|
software. |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P23Note |
|
|
|
|
|
X1/ANI3Note |
|
P32 |
I/O |
Port 3 |
Can be set to input or output mode in |
Input |
|
INTP1 |
|
|
|
|
1-bit units. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
An on-chip pull-up resistor can be |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
connected by setting software. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P34Note |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note |
Input |
|
Input only |
Input |
|
RESET |
||
P40 to P47 |
I/O |
Port 4. |
|
Input |
|
|
− |
|
|
8-bit I/O port. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Can be set to input or output mode in 1-bit units. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
An on-chip pull-up resistor can be connected by setting |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
software. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note For the setting method for pin functions, see CHAPTER 15 OPTION BYTE.
Caution The P22/X2/ANI2 and P23/X1/ANI3 pins are pulled down during reset.
User’s Manual U16994EJ5V0UD |
23 |

CHAPTER 2 PIN FUNCTIONS
(2) Non-port pins
|
Pin Name |
I/O |
Function |
After Reset |
Alternate- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function Pin |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
INTP0 |
Input |
External interrupt input for which the valid edge (rising edge, |
Input |
P21/ANI1/TI010/ |
||
|
|
|
|
falling edge, or both rising and falling edges) can be specified |
|
TO00 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
INTP1 |
|
|
|
P32 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TI000 |
Input |
External count clock input to 16-bit timer/event counter 00. |
Input |
P20/ANI0/TOH1 |
||
|
|
|
|
Capture trigger input to capture registers (CR000 and CR010) of |
|
|
|
|
|
|
16-bit timer/event counter 00 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TI010 |
|
Capture trigger input to capture register (CR000) of 16-bit |
|
P21/ANI1/TO00/ |
||
|
|
|
|
timer/event counter 00 |
|
INTP0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TO00 |
Output |
16-bit timer/event counter 00 output |
Input |
P21/ANI1/TI010/ |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
INTP0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TOH1 |
Output |
8-bit timer H1 output |
Input |
P20/ANI0/TI000 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ANI0 |
Input |
Analog input of A/D converter |
Input |
P20/TI000/TOH1 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ANI1 |
|
|
|
P21/TI010/TO00/ |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
INTP0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ANI2Note |
|
|
|
P22/X2Note |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ANI3Note |
|
|
|
P23/X1Note |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note |
|
|
|
P34Note |
RESET |
Input |
System reset input |
Input |
|||
X1Note |
Input |
Connection of crystal/ceramic oscillator for system clock |
− |
P23/ANI3Note |
||
|
|
|
|
oscillation. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
External clock input |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
X2Note |
− |
Connection of crystal/ceramic oscillator for system clock |
− |
P22/ANI2Note |
||
|
|
|
|
oscillation. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VDD |
− |
Positive power supply |
− |
− |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VSS |
− |
Ground potential |
− |
− |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note For the setting method for pin functions, see CHAPTER 15 OPTION BYTE.
Caution The P22/X2/ANI2 and P23/X1/ANI3 pins are pulled down during reset.
24 |
User’s Manual U16994EJ5V0UD |

CHAPTER 2 PIN FUNCTIONS
2.2 Pin Functions
2.2.1 P20 to P23 (Port 2)
P20 to P23 constitute a 4-bit I/O port. In addition to the function as I/O port pins, these pins also have a function to input an analog signal to the A/D converter, input/output a timer signal, and input an external interrupt request signal.
P22 and P23 also function as the X2/ANI2 and X1/ANI3, respectively. For the setting method for pin functions, see
CHAPTER 15 OPTION BYTE.
These pins can be set to the following operation modes in 1-bit units.
(1)Port mode
P20 to P23 function as a 4-bit I/O port. Each bit of this port can be set to the input or output mode by using port mode register 2 (PM2). In addition, an on-chip pull-up resistor can be connected to the port by using pullup resistor option register 2 (PU2).
(2)Control mode
P20 to P23 function to input an analog signal to the A/D converter, input/output a timer signal, and input an external interrupt request signal.
(a)ANI0 to ANI3
These are the analog input pins of the A/D converter. When using these pins as analog input pins, refer to 9.6 Cautions for A/D converter (5) ANI0/P20 to ANI3/P23.
(b)TI000
This pin inputs an external count clock to 16-bit timer/event counter 00, or a capture trigger signal to the capture registers (CR000 and CR010) of 16-bit timer/event counter 00.
(c)TI010
This pin inputs a capture trigger signal to the capture register (CR000) of 16-bit timer/event counter 00.
(d)TO00
This pin outputs a signal from 16-bit timer/event counter 00.
(e)TOH1
This pin outputs a signal from 8-bit timer H1.
(f)INTP0
This is an external interrupt request input pin for which the valid edge (rising edge, falling edge, or both rising and falling edges) can be specified.
Caution The P22/X2/ANI2 and P23/X1/ANI3 pins are pulled down during reset.
User’s Manual U16994EJ5V0UD |
25 |

CHAPTER 2 PIN FUNCTIONS
2.2.2 P32 and P34 (Port 3)
P32 is a 1-bit I/O port. In addition to the function as an I/O port pin, this pin also has a function to input an external interrupt request signal.
P34 is a 1-bit input-only port. This pin is also used as a RESET pin, and when the power is turned on, this is the reset function.
For the setting method for pin functions, see CHAPTER 15 OPTION BYTE.
When P34 is used as an input port pin, connect the pull-up resistor.
P32 and P34 can be set to the following operation modes in 1-bit units.
(1)Port mode
P32 functions as a 1-bit I/O port. This pin can be set to the input or output mode by using port mode register 3 (PM3). In addition, an on-chip pull-up resistor can be connected to the port by using pull-up resistor option register 3 (PU3).
P34 functions as a 1-bit input-only port.
(2)Control mode
P32 functions as an external interrupt request input pin (INTP1) for which the valid edge (rising edge, falling edge, or both rising and falling edges) can be specified.
2.2.3P40 to P47 (Port 4)
P40 to P47 constitute an 8-bit I/O port. Each bit of this port can be set to the input or output mode by using port mode register 4 (PM4). In addition, an on-chip pull-up resistor can be connected to the port by using pull-up resistor option register 4 (PU4).
2.2.4 RESET
This pin inputs an active-low system reset signal. When the power is turned on, this is the reset function, regardless of the option byte setting.
2.2.5 X1 and X2
These pins connect an oscillator to oscillate the X1 input clock.
X1 and X2 also function as the P23/ANI3 and P22/ANI2, respectively. For the setting method for pin functions, see
CHAPTER 15 OPTION BYTE.
Supply an external clock to X1.
Caution The P22/X2/ANI2 and P23/X1/ANI3 pins are pulled down during reset.
2.2.6 VDD
This is the positive power supply pin.
In the 78K0S/KY1+, VDD functions alternately as the A/D converter reference voltage input. When using the A/D converter, stabilize VDD at the supply voltage used (2.7 to 5.5 V).
2.2.7 VSS
This is the ground pin.
In the 78K0S/KY1+, VSS functions alternately as the ground potential of the A/D converter. Be sure to connect VSS to a stabilized GND (= 0 V).
26 |
User’s Manual U16994EJ5V0UD |

CHAPTER 2 PIN FUNCTIONS
2.3 Pin I/O Circuits and Connection of Unused Pins
Table 2-1 shows I/O circuit type of each pin and the connections of unused pins.
For the configuration of the I/O circuit of each type, refer to Figure 2-1.
Table 2-1. Types of Pin I/O Circuits and Connection of Unused Pins
|
Pin Name |
I/O Circuit Type |
I/O |
|
Recommended Connection of Unused Pin |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P20/ANI0/TI000/TOH1 |
11 |
I/O |
Input: |
Individually connect to VDD or VSS via resistor. |
||
|
|
|
|
|
Output: Leave open. |
|
P21/ANI1/TI010/TO00/ |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|||
INTP0 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P22/ANI2/X2 |
36 |
|
Input: |
Individually connect to VSS via resistor. |
||
|
|
|
|
|
Output: Leave open. |
|
P23/ANI3/X1 |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P32/INTP1 |
8-A |
|
Input: |
Individually connect to VDD or VSS via resistor. |
||
|
|
|
|
|
Output: Leave open. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P34/RESET |
2 |
Input |
Connect to VDD via resistor. |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P40 to P47 |
8-A |
I/O |
Input: |
Individually connect to VDD or VSS via resistor. |
||
|
|
|
|
|
Output: |
Leave open. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
User’s Manual U16994EJ5V0UD |
27 |
CHAPTER 2 PIN FUNCTIONS
|
Figure 2-1. |
Pin I/O Circuits |
|
|
Type 2 |
|
Type 36 |
|
|
|
|
|
feedback |
|
IN |
|
|
cut-off |
|
|
|
|
P-ch |
|
Schmitt-triggered input with hysteresis characteristics |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OSC |
|
|
|
X1, |
enable |
X2, |
|
|
IN/OUT |
|
IN/OUT |
Type 8-A |
|
|
|
VDD |
|
VDD |
pullup |
|
P-ch |
|
|
enable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pull up |
|
|
|
VDD |
P-ch |
|
|
|
|
enable |
data |
|
P-ch |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VDD |
output |
|
|
|
|
|
N-ch |
|
Data |
|
disable |
|
VSS |
P-ch |
|
|
||
|
Comparator |
|
||
|
|
|
P-ch |
|
|
IN/OUT |
+ |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
N-ch |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
Output |
N-ch |
|
|
|
Comparison |
VSS |
|
||
disable |
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
voltage |
|
|
|
|
|
|
VDD |
|
|
pullup |
|
P-ch |
|
|
enable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Type 11 |
|
|
|
VDD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
VDD |
data |
|
P-ch |
|
|
|
||
Pull up |
P-ch |
output |
|
N-ch |
enable |
|
|||
|
VDD |
disable |
|
VSS |
|
|
|
|
|
Data |
P-ch |
Comparator |
|
P-ch |
|
|
|
||
|
|
+ |
|
|
|
IN/OUT |
|
N-ch |
|
|
- |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
Output |
N-ch |
Comparison |
VSS |
|
disable |
VSS |
voltage |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Comparator |
P-ch |
|
|
|
+ |
|
|
|
|
N-ch |
|
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Comparison |
VSS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
voltage |
|
|
|
|
Input |
|
|
|
|
enable |
|
|
|
|
28 |
User’s Manual U16994EJ5V0UD |
|
|
|
CHAPTER 3 CPU ARCHITECTURE
3.1Memory Space
The 78K0S/KY1+ can access up to 64 KB of memory space. Figures 3-1 to 3-3 show the memory maps.
Figure 3-1. Memory Map ( PD78F9210)
F F F F H
F F 0 0 H
F E F F H
F E 8 0 H
F E 7 F H
Data memory space
0 4 0 0 H
0 3 F F H
Program memory space
0 0 0 0 H
Special function registers (SFR)
256 × 8 bits
Internal high-speed RAM 128 × 8 bits
Use prohibited
0 3 F F H
0 0 8 2 H
0 0 8 1 H
0 0 8 0 H Flash memory 0 0 7 F H
1,024 × 8 bits
0 0 4 0 H
0 0 3 F H
0 0 1 4 H
0 0 1 3 H
0 0 0 0 H
Program area
Protect byte area
Option byte area
CALLT table area
Program area
Vector table area
Remark The option byte and protect byte are 1 byte each.
User’s Manual U16994EJ5V0UD |
29 |

CHAPTER 3 CPU ARCHITECTURE
Figure 3-2. Memory Map ( PD78F9211)
F F F F H
F F 0 0 H
F E F F H
F E 8 0 H
F E 7 F H
Data memory space
0 8 0 0 H
0 7 F F H
Program memory space
0 0 0 0 H
Special function registers (SFR)
256 × 8 bits
Internal high-speed RAM 128 × 8 bits
Use prohibited
0 7 F F H
|
0 0 8 2 H |
|
Flash memory |
0 0 8 1 H |
|
0 0 8 0 H |
||
2,048 × 8 bits |
||
0 0 7 F H |
||
|
||
|
0 0 4 0 H |
|
|
0 0 3 F H |
|
|
0 0 1 4 H |
|
|
0 0 1 3 H |
|
|
0 0 0 0 H |
Remark The option byte and protect byte are 1 byte each.
Program area
Protect byte area
Option byte area
CALLT table area
Program area
Vector table area
30 |
User’s Manual U16994EJ5V0UD |
 Loading...
Loading...