Page 1

User‘s Manual
PROFIBUS-DP
Interface for Encoders
English (en)
7/2014
Page 2

Contents
Contents
List of tables .......................................................................................................................... 4
List of figures ......................................................................................................................... 5
1 General information ....................................................................................................... 6
1. 1 Encoder gateway .................................................................................................... 6
1. 2 Absolute encoders ................................................................................................. 6
1. 3 PROFIBUS technology ........................................................................................... 7
1.3.1 PROFIBUS DP functionality levels ............................................................. 7
1.3.2 References .................................................................................................. 8
1.3.3 Abbreviations .............................................................................................. 8
2 Encoder gateway installation ....................................................................................... 9
2.1 Settings inside the gateway ................................................................................... 9
2.1. 1 Node address ............................................................................................ 10
2.1.2 Bus termination ......................................................................................... 11
2.2 Power supply ......................................................................................................... 12
2.3 BUS lines ............................................................................................................... 14
2.4 Shielding philosophy .............................................................................................. 16
2.5 GSD file .................................................................................................................. 16
2.6 LED indication ....................................................................................................... 18
3 Absolute encoder installation .................................................................................... 19
3.1 Settings inside the encoder .................................................................................. 19
3.1.1 Node address ............................................................................................ 19
3.1.2 Bus termination ........................................................................................ 20
3.2 Connecting the encoder ....................................................................................... 21
3.2.1 Bus lines ................................................................................................... 23
3.3 Shielding philosophy ............................................................................................. 25
3.4 GSD file ................................................................................................................. 25
3.5 LED indication ....................................................................................................... 27
4 Profile overview, DPV0 version 1.1. ............................................................................ 28
4.1 DPV0 encoder classes ......................................................................................... 29
2
Page 3

Contents
5 Encoder and Gateway functionality, DPV0 .............................................................. 31
5.1 Basic functionality ................................................................................................. 31
5.2 PROFIBUS data transfer principle ........................................................................ 31
5.2.1 During Configuration (DDLM_Chk_Cfg mode) ........................................ 31
5.2.2 During Parameterization (DDLM_Set_Prm mode) .................................. 31
5.2.3 Normal operation (DDLM_Data_Exchange mode) .................................. 32
5.3 Configuration, DPV0 ............................................................................................. 32
5.4 Parameterization, DPV0 ....................................................................................... 32
5.4.1 Code sequence......................................................................................... 34
5.4.2 Class 2 functionality .................................................................................. 34
5.4.3 Commissioning diagnostics ..................................................................... 34
5.4.4 Scaling function control ............................................................................ 35
5.4.5 Measuring units per revolution ................................................................ 35
5.4.6 Total measuring range (units) ................................................................... 37
5.4.7 Velocity control.......................................................................................... 38
5.4.8 Velocity calculation .................................................................................... 39
5.5 Data transfer in normal operation (DDLM_Data_Exchange) ............................... 40
5.5.1 Data exchange mode ............................................................................... 40
5.5.2 Preset function ......................................................................................... 41
5.6 Diagnostics ........................................................................................................... 43
5.6.1 Diagnostic Header .................................................................................... 45
5.6.2 Alarms ....................................................................................................... 45
5.6.3 Operating Status ....................................................................................... 47
5.6.4 Encoder type............................................................................................. 48
5.6.5 Singleturn resolution or measuring step .................................................. 49
5.6.6 Number of distinguishable revolutions .................................................... 49
5.6.7 Additional alarms ...................................................................................... 50
5.6.8 Supported alarms ..................................................................................... 50
5.6.9 Warnings ................................................................................................... 51
5.6.10 Supported warnings ................................................................................. 52
5.6.11 Profile Version ........................................................................................... 53
5.6.12 Software Version ....................................................................................... 53
5.6.13 Operating time .......................................................................................... 54
5.6.14 Offset value ............................................................................................... 55
5.6.15 Offset value of the encoder manufacturer............................................... 55
5.6.16 Scaling parameters settings ..................................................................... 56
5.6.17 Encoder serial number ............................................................................. 57
6 Encoder commissioning example, DPV0 ................................................................. 58
7 Revision history ............................................................................................................ 61
3
Page 4

List of tables
List of tables
Table 1 Termination switch settings ......................................................................... 11
Table 2 Pinning M12 power supply connector ....................................................... 12
Table 3 Pinning M12 bus in/out connectors ........................................................... 14
Table 4 Available GSD file for DPV0 gateway ......................................................... 16
Table 5 LED indication ............................................................................................. 18
Table 6 Te rminating switch settings ........................................................................ 20
Table 7 Pinning M12 power supply connector ....................................................... 21
Table 8 Pinning M12 bus in/out lines ...................................................................... 23
Table 9 Available GSD file for DPV0 encoders ........................................................ 25
Table 10 LED indication encoder .............................................................................. 27
Table 11 Operating parameters in DPV0 .................................................................. 32
Table 12 Octet9, Parameter definition ...................................................................... 33
Table 13 Singleturn scaling parameters format ........................................................ 36
Table 14 Multiturn scaling parameters format .......................................................... 36
Table 15 Octet 39 Velocity Control ............................................................................ 39
Table 16 Data exchange 32-bits ................................................................................ 40
Table 17 Data exchange -16 b its ............................................................................... 41
Table 18 Preset value, 32-bit format ......................................................................... 42
Table 19 Preset value, 16-bit format.......................................................................... 42
Table 20 Diagnostic message, DPV0 ........................................................................ 44
Table 21 Diagnostic header ....................................................................................... 45
Table 22 Alarms ......................................................................................................... 46
Table 23 Operating status ......................................................................................... 47
Table 24 Diagnostic, encoder .................................................................................... 48
Table 25 Diagnostic, singleturn resolution ................................................................ 49
Table 26 Diagnostics, number of distinguishable revolutions .................................. 49
Table 27 Diagnostics, additional alarms .................................................................... 50
Table 28 Diagnostics, supported alarms ................................................................... 50
Table 29 Diagnostics, warnings ................................................................................ 51
Table 30 Diagnostics, supported warnings ............................................................... 52
Table 31 Diagnostics, profile version ........................................................................ 53
Table 32 Diagnostics, software version .................................................................... 54
Table 33 Diagnostic, operating time ......................................................................... 54
Table 34 Diagnostics, offset value ............................................................................ 55
Table 35 Diagnostics, offset value of the encoder manufacturer ............................ 55
Table 36 Diagnostics, scaling parameter setting ...................................................... 56
Table 37 Diagnsotics, encoder serial number........................................................... 57
Table 38 Revision history........................................................................................... 61
4
Page 5

General information
List of figures
Figure 1 Placement of screws .................................................................................... 9
Figure 2 PCB-view of a cable gland PROFIBUS gateway ........................................ 10
Figure 3 Orientation of M12 power supply connector ............................................. 12
Figure 4 Terminal connections of power supply cables ........................................... 13
Figure 5 Orientation of M12 bus connectors ........................................................... 14
Figure 6 Terminal connections of bus line cables .................................................... 15
Figure 7 PCB-view of a cable gland encoder ........................................................... 19
Figure 8 Orientation of M12 power supply connector ............................................. 21
Figure 9 Terminal connections of power supply cables ........................................... 22
Figure 10 Orientation of M12 bus connectors ........................................................... 23
Figure 11 Terminal connections of bus line cables .................................................... 24
Figure 12 Overview encoder profile and related documents .................................... 28
Figure 13 Basic functionality ....................................................................................... 31
Figure 14 Cyclic scaling ............................................................................................... 37
Figure 15 Non-cyclic scaling ........................................................................................ 38
5
Page 6

General information
1 General information
This manual describes the installation procedures and
configuration of HEIDENHAIN absolute encoders and encoder
gateways with PROFIBUS DPV0 functionality.
1.1 Encoder gateway
The advantages of the gateway concept is that it allows the use
of small and very robust EnDat encoders, which make the
encoder gateway solution suitable in applications where very high
ambient temperature is a limiting factor.
Another benefit with the gateway solution is that in case of an
encoder error occurs, the EnDat encoder can easily be replaced
without the need to disconnect the PROFIBUS line. The encoder
gateway supports singleturn encoders with up to 31 bit resolution
and multiturn encoders with up to 37 bits resolution with the
limitations described in this manual.
1.2 Absolute encoders
With an absolute encoder each angular position is assigned a
coded position value generated by a code disc equipped with
several parallel fine graduations tracks which are scanned
individually. On singleturn encoders, i.e. an encoder producing
absolute positions within one revolution, the absolute position
information repeats itself with every revolution. So called multiturn
encoders can also distinguish between revolutions. The numbers
of unique revolutions is determined by the resolution of the
multiturn scanning and repeats itself after the total resolution is
reached.
6
Page 7

1.3 PROFIBUS technology
PROFIBUS is a powerful and versatile 2-wire non-proprietary open
field bus standard defined by several international standards such
as EN 50170, IEC 61158 together with different device profiles.
There are 3 different PROFIBUS versions available today, DP, FMS
and PA. HEIDENHAIN products support the Decentralized
Peripherals (DP) version. In addition to manufacturer-specific
functions, the HEIDENHAIN devices described in this manual
supports class 1 and 2 according to the encoder profile 3.062. The
encoder device profile describing encoder functionality and
additional information about PROFIBUS can be ordered from
PROFIBUS User Organization, PNO.
PROFIBUS User Organization
Haid-und-Neu Straße 7
D 76131 Karlsruhe, Germany
Te l : + 4 9 721 96 58 590
Fax: + 49 721 96 58 589
www.profibus.com
Web:
1.3.1 PROFIBUS DP functionality levels
The main functions of the different levels are as follows:
DPV0: Supports the basic functionality for the PROFIBUS
protocol. In principal this means the cyclical I/O communication
and diagnostics. This manual only covers DPV0 functionality.
DPV1: The most important benefits with DPV1 are the expanded
functions for the acyclical data communication and alarm
handling. This is a precondition for parameterization and calibration
of field devices over the bus in runtime. HEIDENHAIN have a
separate manual for DPV1/DPV2 devices.
DPV2: In addition to the functionality above, DPV2 includes
expansions that are required for time critical applications such as
motion control. This means functions such as slave-to-slave
communications and isochronous data exchange (time
synchronization). HEIDENHAIN have a separate manual for
DPV1/DPV2 devices.
General information
7
Page 8

General information
PROFIBUS
Process Field Bus
PI
PROFIBUS and Profinet International
PNO
PROFIBUS Nutzerorganisation e.V.
GSD
German term "Gerätestammdaten". A GSD is the
device database file, also called device
datasheet.
DP
Decentral Periphery
Input data
Data which the master receives from the
encoder
Output data
Data which the encoder receives from the
master.
PDU
Protocol Data Unit
DDLM
Direct Data Link Mapper, the interface between
PROFIBUS
software
DDLM_Set_Prm
Interface during parameterization
DDLM_Data_Exchange
DDLM_Slave_Diag
DDLM_Chk_Cfg
Interface during data exchange
Interface during diagnostics data transfer
Interface during configuration
1.3.2 References
1.3.3 Abbreviations
Profile Encoder V1.1, Order No. 3.062
-DP functions and the encoder
8
Page 9
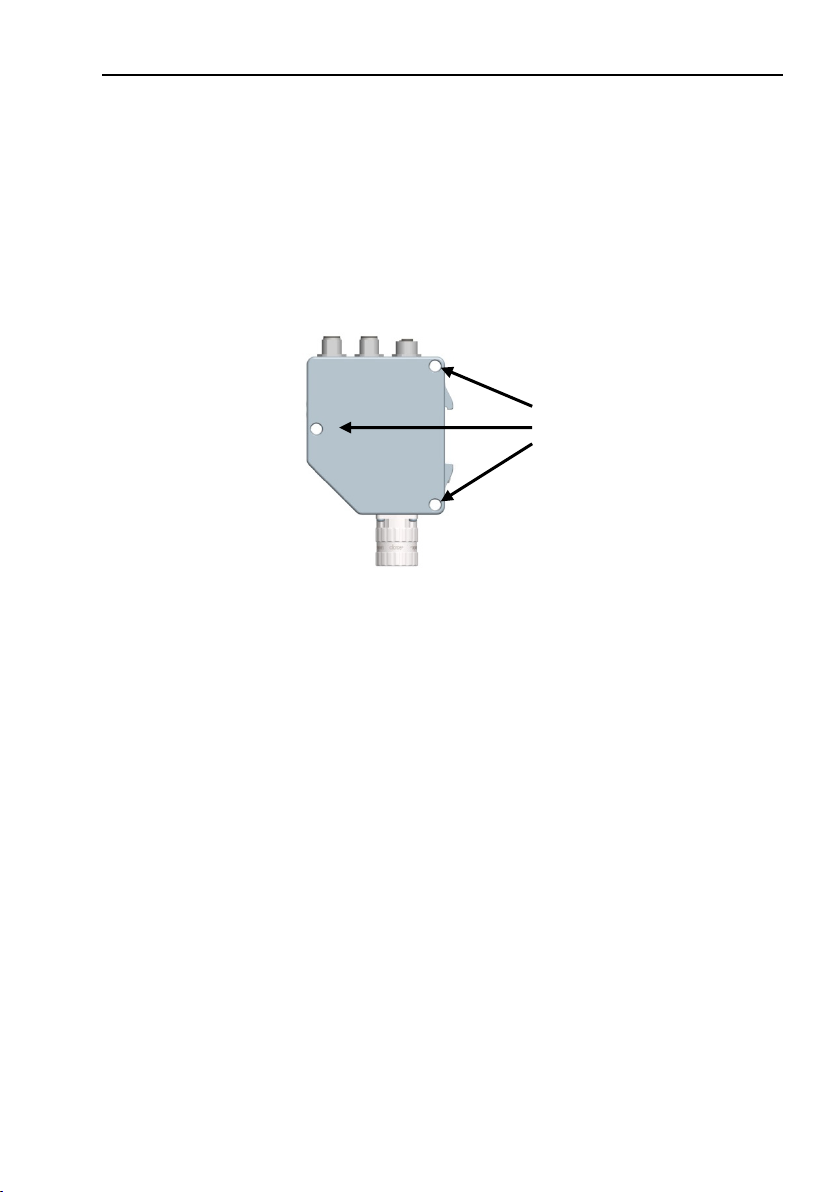
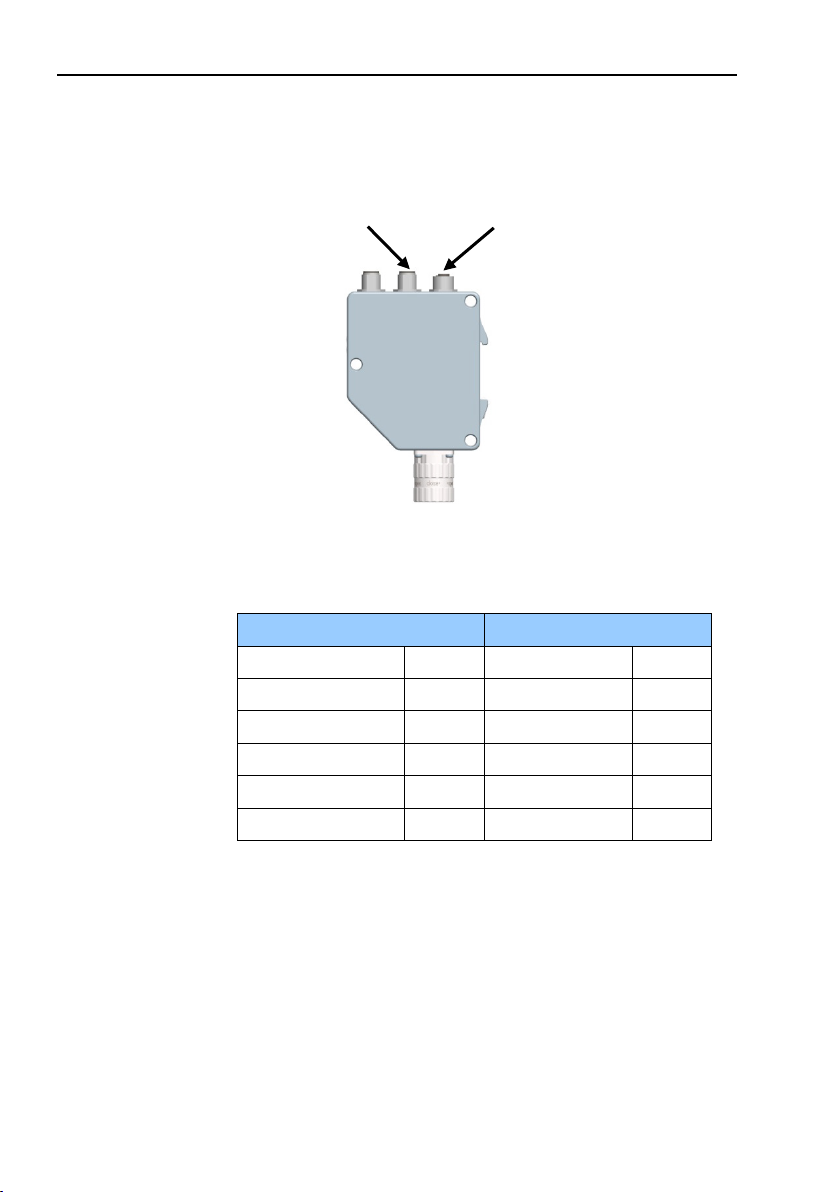
2 Encoder gateway installation
2.1 Settings inside the gateway
The encoder gateway addressing switches and bus termination
must be configured during commissioning of the device. This is
done by removing the back cover, i.e. screwing off the three
screws at the rear of the gateway.
Figure 1 Placement of screws
Encoder gateway installation
Screws to remove
ba ck cover
9
Page 10
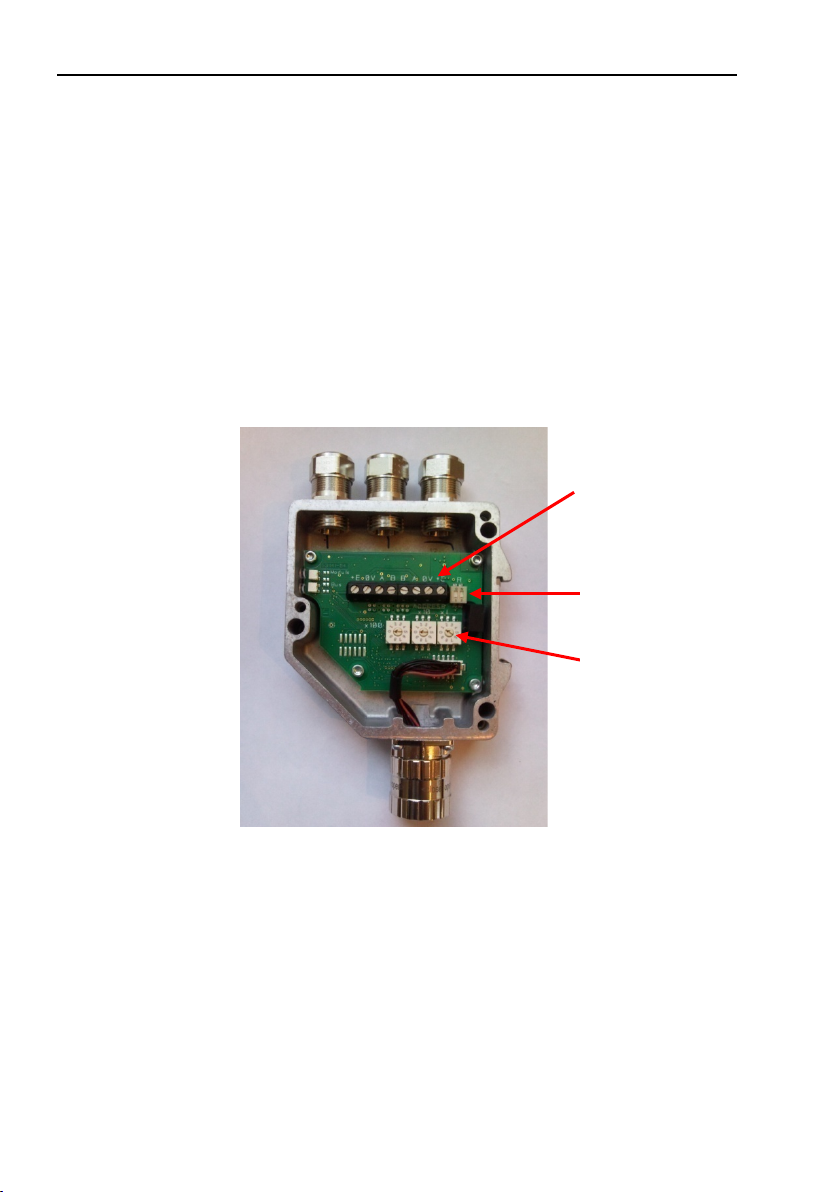
Encoder gateway installation
Screw terminals
Bus termination
switch (on/off)
Node address
2.1.1 Node address
The node address of the encoder gateway can be set via three
decimal rotary switches located inside the back cover. The
weighting, x100, x10 and x1 are specified on the circuit board
besides the switches. Permissible address range is between 0
and 126 but the lower addresses 0 to 2 are usually used by the
master and not recommended to be used by the device. Each
address used in a PROFIBUS network must be unique and may
not be used by other devices.
The device address is only read and adopted when the gateway
power supply is switched on. A restart of the gateway is therefore
required in order to adopt changes done to the address settings.
10
switches ()
Figure 2 PCB-view of a cable gland PROFIBUS gateway
Example: To set the node address to 115, the switch to the left
(x100) shall be set to 1, the switch in the middle(x10)
should also be set to 1 and the switch to the right(x1)
shall be set to 5.
Page 11
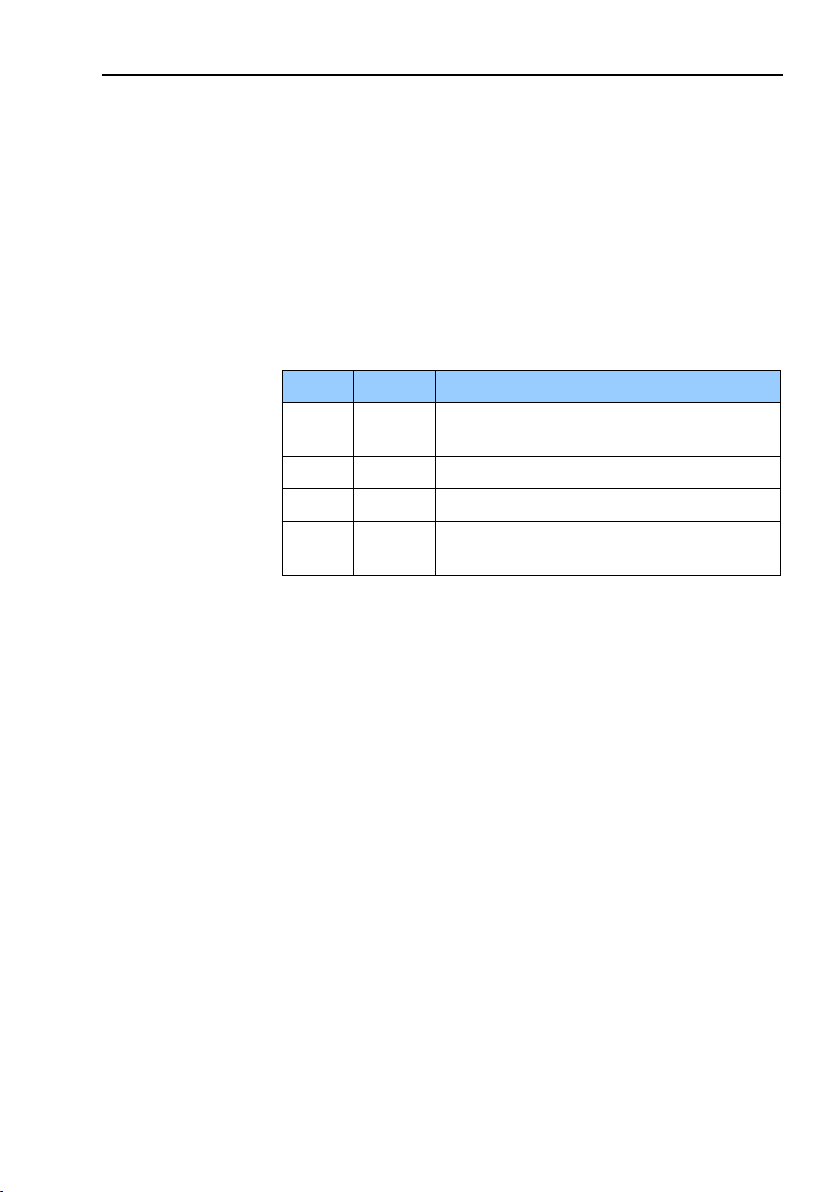
2.1.2 Bus termination
Bit1
Bit2
Effect
On
On
There is a 220 ohms resistor between bus
A and bus B line.
On
Off
Not a valid setting
Off
On
Not a valid setting
Off
Off
There is no resistor between bus A and
bus B line.
In a PROFIBUS net, all devices are connected in a bus structure.
Up to 32 devices (master and/or slaves) can be connected in one
segment. When more devices are needed repeaters should be
used to amplify the signals between segments. An active
termination must be added in the beginning and the end of each
bus segment in order to ensure error-free operation. In case of the
gateway with cable glands such terminators are integrated inside
the back cover and can be activated via dip switches as shown in
figure 2. If the device is un-powered the A and B lines are
internally terminated by a 220 Ω resistor.
Table 1 Termination switch settings
When encoder gateways with M12 connectors are used the
termination should be done using a M12 terminating resistor plug.
Note: When M12 terminating resistor plugs are used, the
internal terminating switch shall not be activated.
Encoder gateway installation
11
Page 12
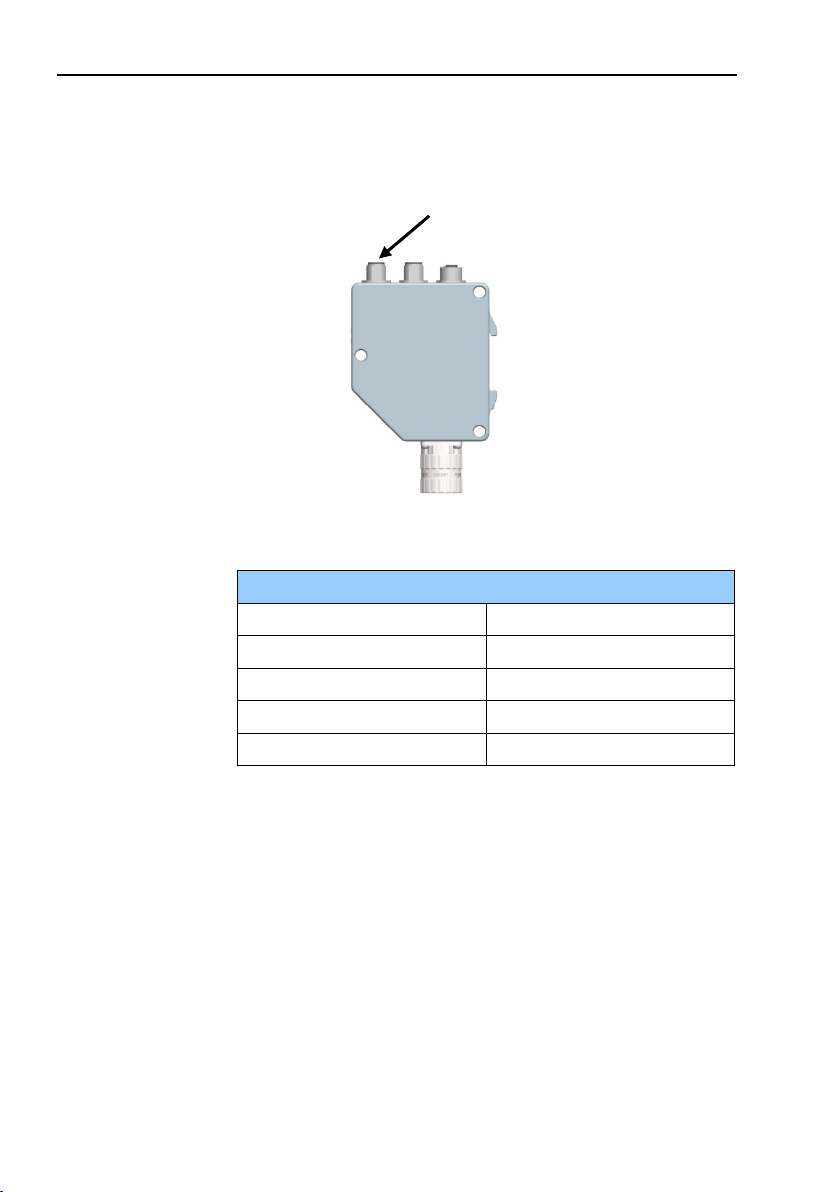
Encoder gateway installation
Power supply M12 version
Function
Pin
+E Volt
1
Not connected
2
0 Volt
3
Not connected
4
Power supply
2.2 Power supply
The power supply connection of M12 equipped gateways are
constituted by a male A-coded 4 pin M12 connector.
Figure 3 Orientation of M12 power supply connector
12
Table 2 Pinning M12 power supply connector
Page 13

Encoder gateways equipped with cable glands are delivered with
a dust protection foil from the factory. The protection foil needs to
be removed prior to installing the cables.
It is recommended that gateways equipped with cable glands are
equipped with a shielded power supply cable with conductor area
between 0,34 mm
is ø 6 mm to ø 8 mm for the power supply cable. The power
supply screw terminal is located inside the back cover of the
gateway.
In the case were the gateway is the last node in the bus-structure
and only the cable glands for Supply and Bus-in is in use, the Bus
out cable gland should be replaced with a M16 filler plug to
ensure proper sealing.
The +E terminal shall be used to connect +E Volt.
The 0 V terminal shall be used to connect 0 Volt.
Figure 4 Terminal connections of power supply cables
Note: Tighten all screws in the terminal, even if no cable
has been attached.
Note: The two +E terminals are connected to each other
and the two 0 V terminals are also connected to
each other, i.e it does not matter to which pair the
+E Volt and 0 Volt are connected to.
Encoder gateway installation
2
to 1. 5 m m2. Permissible outer cable diameter
13
Page 14
Encoder gateway installation
Bus in line
Bus out line
Function
Pin
Function
Pin
Not connected
1
VP 1 A 2 A
2
Not connected
3
DGND
3
B 4 B
4
Chassis
5
Chassis
5
Bus in
Bus out
2.3 BUS lines
The PROFIBUS bus line connections of the M12 equipped
devices are constituted by a male B-coded 5 pin M12 connector
(bus in), and a female B-coded 5 pin M12 connector (bus out).
Figure 5 Orientation of M12 bus connectors
14
Table 3 Pinning M12 bus in/out connectors
Page 15

The cable gland gateway shall be equipped with twisted pair
shielded cable in accordance with EN 50170 and PROFIBUS
guidelines. The guidelines recommend a conductor area higher
than 0,34 mm
ø 10 mm for the bus lines cables. Located inside the back cover
are four screw terminals containing the required bus line
terminals marked A and B. Cable glands not used, should be
replaced with a M16 filler plug to ensure proper sealing.
Figure 6 Terminal connections of bus line cables
Note: Tighten all screws in the terminal, even if no cable
has been attached.
Note: The two A terminals are internally connected to
each other and the two B terminals are also
connected to each other so it does not matter to
which the bus lines are connected to.
Encoder gateway installation
2
. Permissible outer cable diameter is ø 8 mm to
15
Page 16
Encoder gateway installation
GSD file
Gateway functionality
GSD file
Gateway PROFIBUS DPV0
(For rotary encoders)
ENC_A400
2.4 Shielding philosophy
To achieve the highest possible noise immunity and resistance
against other EMI related disturbances the bus and power supply
cables shall always be shielded. The screen should be connected
to ground on both ends of the cable. In certain cases
compensation current might flow over the screen. Therefore a
potential compensation wire is recommended.
2.5 GSD file
PROFIBUS Gateways can be configured and parameterized
corresponding to the requirements of the user. When the system
is started, the PROFIBUS devices are set and configured in
DDLM_Set_Prm mode, i.e the application class set by means of
the GSD file in the configuration tool and the operating
parameters are transferred to the respective slave.
Available GSD files can be downloaded from
www.heidenhain.com
16
Table 4 Available GSD file for DPV0 gateway
When configuring the gateways two device classes (Class 1
or Class 2) can be selected as described in chapter 4.
Selectable parameters and functionality of the device depend
on the selected encoder class. This data, saved in the
PROFIBUS master is transferred once to the gateway when
the system is powered on. If the gateway has been started
with one GSD file and a new GSD file with a different IDnumber shall be used, the gateway needs to be restarted
before it can use the new GSD file.
After the configuration and parameter data have been received,
the gateway enters normal operation with cyclic data transfer i.e.
“DDLM_Data_Exchange mode”.
Page 17

Encoder gateway installation
Installation of GSD-files:
1) Select and save the GSD file for the respective device from
www.heidenhain.com and then copy the *.gsd file into the respective
directory of the PROFIBUS configuration tool.
2) Select the bitmap file of the respective device and copy the *.bmp file into the
respective directory of the PROFIBUS configuration tool.
3) Update the GSD files (SCAN).
17
Page 18
Encoder gateway installation
Bus status
Module
Meaning
Cause
Off
Off
No power
Red
Green
No connection to other
exchange
- Bus disconnected
available/switched off
Red2)
Red2)
No connection to other
PROFIBUS PCB.
No connection to EnDat
Blinking1)
Green
Parameterization or
- Configuration received
parameterization.
Green
Red
System failure
- Diagnosis exists, slave in
data exchange mode.
Green
Green
Data exchange and encoder
function properly.
2.6 LED indication
In order to determine the status of the gateway two LEDs are
visible on the front of the gateway. The module LED indicates
status of the module itself. The bus LED indicates the status of
the bus. The table below defines the diagnostic messages using a
bi-colored red/green LED for bus and module.
device. Criteria: No data
device. No connection
- Master not
encoder at power up.
between EnDat encoder and
configuration fault
differs from the supported
configuration.
- Parameter error in the
Table 5 LED indication
1)
The blinking frequency is 0.5 Hz. Minimal indication time is 3 sec.
2)
Position error is when an alarm occurs in the encoder or if the EnDat encoder is
disconnected from the PROFIBUS interface PCB.
18
Page 19
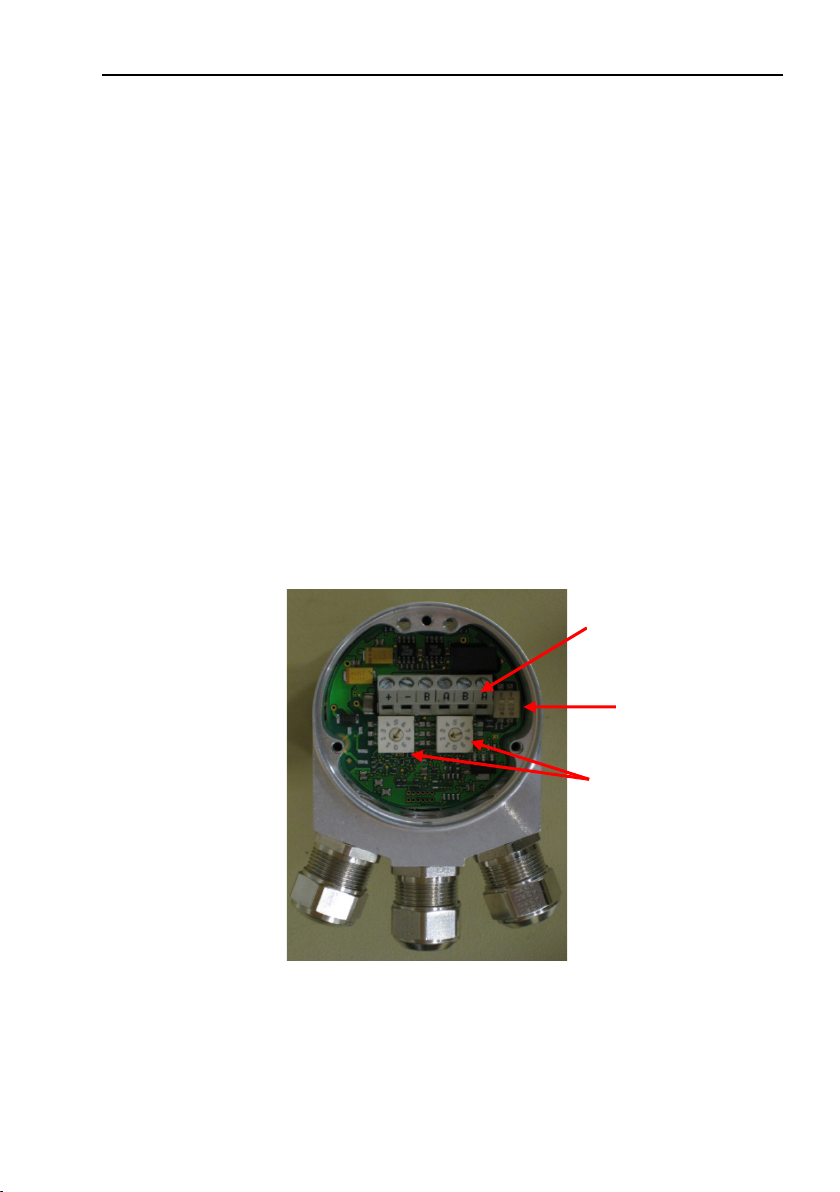
3 Absolute encoder installation
Screw terminals
Bus termination
Node address
switches
3.1 Settings inside the encoder
The encoder node address and bus termination must be
configured during commissioning of the device. This is done by
removing the back cover, i.e. screwing off the three screws at the
rear of the encoder.
3.1.1 Node address
The node address of the encoder can be set via two decimal
rotary switches located inside the back cover. The weighting, x10
or x1 are specified beside the switches. Permissible address
range is between 0 and 99 but the lower addresses 0 to 2 are
usually used by the master and not recommended to be used by
the device. Each address used in a PROFIBUS network must be
unique and may not be used by other devices.
The device address is only read and adopted when the encoder
power supply is switched on. A restart of the encoder is therefore
required in order to adopt changes done to the address settings.
Absolute encoder installation
switch (on/off)
Figure 7 PCB-view of a cable gland encoder
Example: If the node address shall be set to 85, the left (x10)
switch shall be set to 8 and the right (x1) switch shall
be set to 5.
19
Page 20

Absolute encoder installation
Bit1
Bit2
Effect
On
On
There is a 220 ohms resistor between bus
A and bus B line.
On
Off
Not a valid setting
Off
On
Not a valid setting
Off
Off
There is no resistor between bus A and bus
B line.
3.1.2 Bus termination
In a PROFIBUS net, all devices are connected in a bus structure.
Up to 32 devices (master and/or slaves) can be connected in one
segment. When more devices are needed repeaters should be
used to amplify the signals between segments. An active
termination must be added in the beginning and end of each bus
segment in order to ensure error-free operation.
In case of the encoder with cable glands such terminators are
integrated inside the back cover and can be activated via dip
switches as shown in figure 7. If the device is un-powered the A
and B lines are internally terminated by a 220 Ω resistor.
Table 6 Terminating switch settings
When encoders with M12 connectors are used the termination
should be done using a terminating resistor plug.
Note: When encoders with M12 terminating resistor
plugs are used, the internal terminating switch
shall not be activated.
20
Page 21

3.2 Connecting the encoder
Power supply M12 version
Function
Pin
+E Volt
1
Not connected
2
0 Volt
3
Not connected
4
Power supply
The power supply connection of M12 equipped encoders are
constituted by a male A-coded 4 pin M12 connector.
Figure 8 Orientation of M12 power supply connector
Absolute encoder installation
Table 7 Pinning M12 power supply connector
21
Page 22

Absolute encoder installation
Encoders equipped with cable glands are delivered with a dust
protection foil from the factory. The protection foil needs to be
removed prior to install the cables.
It is recommended that encoders with cable gland are equipped
with a shielded power supply cable with conductor area between
0,34 mm
2
to 1. 5 mm2. Permissible outer cable diameter is
ø 6 mm to ø 8 mm for the power supply cable. Located inside the
back cover are two screw terminals containing the required power
supply terminals marked (+) and (-). In the case were the encoder
is the last node in the bus-structure and only the cable glands for
Supply and Bus-in is in use, the Bus out cable gland should be
replaced with a M16 filler plug to ensure proper sealing.
The (+) terminal shall be used to connect the +EV-line.
The (-) terminal shall be used to connect the 0 V-line.
Figure 9 Terminal connections of power supply cables
Note: Tighten all screws in the terminal, even if no cable
has been attached.
22
Page 23

3.2.1 Bus lines
Bus in line
Bus out line
Function
Pin
Function
Pin
Not connected
1
VP
1
A 2 A
2
Not connected
3
DGND
3
B 4 B
4
Chassis
5
Chassis
5
Bus in
Bus out
Absolute encoder installation
Figure 10 Orientation of M12 bus connectors
Table 8 Pinning M12 bus in/out lines
23
Page 24

Absolute encoder installation
The cable gland encoders shall be equipped with twisted pair
shielded cable in accordance with EN 50170 and PROFIBUS
guidelines. The guidelines recommend a conductor area higher
than 0,34 mm
ø 10 mm for the bus line cables. Located inside the back cover are
four screw terminals containing the required bus line terminals
marked (A) and (B). Cable glands not used should be replaced
with a M16 filler plug to ensure proper sealing.
The (A) terminal shall be used to connect the A-line.
The (B) terminal shall be used to connect the B-line.
Figure 11 Terminal connections of bus line cables
Note: Tighten all screws in the terminal, even if no cable
has been attached.
Note: The two A terminals are internally connected to
each other and the two B terminals are also
connected to each other so it does not matter to
which terminal the bus lines are connected to.
2
. Permissible outer cable diameter is ø 8 mm to
24
Page 25

3.3 Shielding philosophy
GSD file
Gateway functionality
GSD file
Absolute encoder PROFIBUS DPV0
Enc_A 4 01
To achieve the highest possible noise immunity and resistance
against other EMI related disturbances the bus and power supply
cables shall always be shielded. The screen should be connected
to ground on both ends of the cable. In certain cases
compensation current might flow over the screen. Therefore a
potential compensation wire is recommended.
3.4 GSD file
Absolute encoders with PROFIBUS can be configured and
parameterized corresponding to the requirements of the user.
When the system is started, the PROFIBUS devices are set and
configured in DDLM_Set_Prm mode, i.e. the encoder class set by
means of the GSD file in the configuration tool and the operating
parameters are transferred to the respective slave.
Available GSD files can be downloaded from
www.heidenhain.com.
Absolute encoder installation
Table 9 Available GSD file for DPV0 encoders
The GSD data is saved in the PROFIBUS master and transferred
once to the encoder when the system is powered on. If the
encoder has been started with one GSD file and a new GSD file
with a different ID-number shall be used, the encoder needs to be
restarted before it can use the new GSD file.
After the configuration and parameter data have been
received, the gateway enters normal operation with cyclic
data transfer i.e. “DDLM_Data_Exchange mode”.
25
Page 26

Absolute encoder installation
Installation of GSD-files:
1) Select and save the GSD file for the respective device from
www.heidenhain.com and then copy the *.gsd file into the respective
directory of the PROFIBUS configuration tool.
2) Select the bitmap file of the respective device and copy the *.bmp file into the
respective directory of the PROFIBUS configuration tool.
3) Update the GSD files (SCAN).
26
Page 27

3.5 LED indication
Bus status
Module
Meaning
Cause
Off
Off
No power
Red
Green
No connection to other
exchange
- Bus disconnected
switched off
Red2)
Red2)
No connection to other
and PROFIBUS PCB.
No connection to EnDat
Blinking1)
Green
Parameterization or
- Configuration received
parameterization.
Green
Red
System failure
- Diagnosis exists, slave in
- Position error
Green
Green
Data exchange. Slave and
operation OK
Absolute encoder installation
In order to determine the status of the encoder two LEDs are
visible from the rear end of the encoder. The module LED
indicates status of the module itself. The bus LED indicates the
status of the bus. The table below defines the diagnostic
messages using a red (BUS) and a bicolor, Red/Green, LED
(MODULE).
device. Criteria :No data
device. No connection
- Master not available/
encoder at power up.
between EnDat encoder
configuration fault
differs from the supported
configuration.
- Parameter error in the
data exchange mode.
Table 10 LED indication encoder
1)
The blinking frequency is 0.5 Hz. Minimal indication time is 3 sec.
2)
Position error is when an alarm occurs in the encoder or if the EnDat encoder is
disconnected from the PROFIBUS interface PCB.
27
Page 28

Profile overview, DPV0 ve rsion 1.1.
4 Profile overview, DPV0 version 1.1.
The operating function in this profile is divided into two device
classes named Class 1 and Class 2. Class 1 encoders offer basic
functions that all PROFIBUS-DP encoders must support.
Encoders of Class 2 must support all functions of Class 1 as well
as the additional functionality of Class 2. In addition to the two
classes, parameters and diagnostic ranges are reserved for
manufacturer-specific functions.
For further information regarding the encoder functionality refer to
the device profile. The profile and PROFIBUS technical information
can be ordered from
www.profibus.com.
28
Figure 12 Overview encoder profile and related documents
Page 29

4.1 DPV0 encoder classes
The device can be configured as a class 1 or class 2
PROFIBUS slave device. Class 2 configuration is extended to
optionally access velocity information from the encoder.
CLASS 1
In the CLASS 1 configuration, only input data are assigned.
Depending on the encoder resolution, this is one input data
word (16 bits) or two (32 bits).
The following functions can be performed:
1) Changed direction of counting
(Code sequence)
2) Diagnostic data up to octet 16
Configuration data:
Singleturn Class 1 – 16 Bit: D0hex, 1 input data word,
data consistency
Multiturn Class 1 – 32 Bit: D1hex, 2 input data words,
data consistency
CLASS 2
In the CLASS 2 configuration output data values and input
data words are transferred. Depending on the encoder
resolution, this is one input data word (16 bits) and one output
data word (16 bits) or two input data words (32 bits) and two
output data words (32 bits).
The following functions are available in addition to the class 1
functions:
1) Scaling function
2) Preset Value Function
3) Velocity read-out
4) Extended diagnostic data
Profile overview, DPV0 ve rsion 1.1.
29
Page 30

Profile overview, DPV0 ve rsion 1.1.
Configuration data:
Singleturn Class 2 – 16 bits: F0hex, 1 input data word,
1 output data word for preset value,data consistency
Multiturn Class 2 – 32 bits: F1hex, 2 input data word,
2 output data words for preset value,data
consistency
Position + Velocity, Class 2 – 32+16 bits: F1+D0hex,
3 input data word, 2 output velocity data words
Velocity for preset value, data consistency
The selection of class depends on the demands required
by the application but for enabling full functionality of the
device it is recommended to choose: Encoder class 2 32
bit + velocity.
30
Page 31

Encoder and Gateway functionality, DPV0
5 Encoder and Gateway functionality, DPV0
5.1 Basic functionality
The picture below gives an overview of the basic encoder and
gateway functions and how the functionality is conducted within
the device.
Figure 13 Basic functionality
5.2 PROFIBUS data transfer principle
The PROFIBUS-DP devices can be configured and parameters
can be set according to the user’s needs.
In this context it is useful to know that with PROFIBUS there are
different types of data transmission.
5.2.1 During Configuration (DDLM_Chk_Cfg mode)
The configuration function allows the DP-Master to send the
configuration data to the DP-device for checking. The main
purpose is to define the number of bytes used for Data_Exchange
function.
5.2.2 During Parameterization (DDLM_Set_Prm mode)
When the system is started, the PROFIBUS devices are
parameterized (DDLM_Set_Prm mode), i.e. the encoder class set
by means of the GSD file in the configuration tool) and the set
operating parameters are transferred to the respective slave.
31
Page 32

Encoder and Gateway functionality, DPV0
Parameters
Data type
Parameter
Device
Code sequence
Bit 9 1
Class 2 functionality
Bit 9 2
Commissioning diagnostics
Bit 9 Optional
Scaling function control
Bit 9 2
Measuring units per revolution
Unsigned 32 bits
10-13
2
Total measuring range in
measuring units
Unsigned 32 bits
14-17
2
Manufacturer specific functions
Bit
26-28
Optional
Velocity control
2 bit
39
2.ext
5.2.3 Normal operation (DDLM_Data_Exchange mode)
In the normal mode (DDLM_Data_Exchange mode), data are
exchanged between master and slaves. The preset function can
be carried out only in this operating mode. The data exchange is
described in chapter 5.5.
5.3 Configuration, DPV0
The configuration of a DPV0 device is conducted by choosing
encoder class, i.e. setting the input/output data structure. The
configuration options are 16-bit, 32-bit or 32-bit + 16-bit
velocity input data, for explanation view chapter 4.1.
5.4 Parameterization, DPV0
The PROFIBUS-DPV0 device is parameterized by means of
the operating parameters. The values selected in the
configuration tool are saved in the DP master and are
transferred to the PROFIBUS-DP slave each time the network
is started. The following table lists all available parameters:
Table 11 Operating parameters in DPV0
32
octet number
class
Page 33

Encoder and Gateway functionality, DPV0
Octet
9
Bits
7-0
Data
27-20 Operating parameters
Bits
Definition
=0
=1
0
Code sequence
Clockwise (CW) Increasing
ange
Counter clockwise
flange side)
1
Class 2
functionality
Disable
Enable
2
Commissioning
diagnostics
No
Ye s
3
Scaling function
Disable scaling
Enable scaling. Scaling
into octets 10 to 17.
4
Reserved
...
7
position
values when rotated
clockwise (seen from fl
side)
control
Table 12 Octet 9, Parameter definition
(CCW) Increasing
position values when
rotated counter
clockwise (seen from
parameters are taken
33
Page 34

Encoder and Gateway functionality, DPV0
5.4.1 Code sequence
The code sequence defines whether the absolute position value
should increase during clockwise or counter clockwise rotation of
the encoder shaft seen fromflange side. The code sequence is by
default set to increase the absolute position value when the shaft
is turned clockwise (0).
Note: The position value will be affected when the code
sequence is changed during operation. It might be
necessary to perform a preset after the code
sequence has been changed.
5.4.2 Class 2 functionality
This bit enables or disables class 2 functionality. The Class 2
functionality bit for PROFIBUS-DP devices is by default disabled
(0). This means that this control bit must be activated during
parameterization in order to support the class 2 functions.
Note: If a class 1 device uses some optional class 2
functions, the class 2 control bit must be set.
5.4.3 Commissioning diagnostics
The commissioning diagnostics function makes enable the device
to perform internal diagnostic test of the encoder components
responsible for position detection during a standstill of the
encoder (i.e. light unit, photovoltaic cells etc.). In conjunction
with the position alarms, it enables thorough checking of
whether the position values provided by the absolute encoder
are correct. The commissioning diagnostics function is started
by the commissioning bit in the operating parameters. If an
error is found within the absolute encoder, this is indicated in
the diagnostic function by the commissioning diagnostics
alarm bit (see chapter 5.6.2).
The commissioning diagnostics function is an option. To find out
whether the device supports commissioning diagnostics, the
“operating status” should be read by the diagnostic function
and the commissioning diagnostics bit should be checked.
34
Page 35

Encoder and Gateway functionality, DPV0
5.4.4 Scaling function control
The scaling function converts the encoder’s physical absolute
position value by means of software in order to change the
resolution of the encoder. Class 2 functionality must be enabled in
order to use the scaling function. The parameters “Measuring
units per revolution” and “Total measuring range in measuring
steps” are the scaling parameters set by the parameter function
in octet 10 to 17. Scaling is active only if the control bit for the
scaling function is set. When the scaling function control bit is set
to 0, the scaling function is disabled.
Singleturn encoders up to 31 bit and multiturn encoders up to
37 bits resolution are supported by the PROFIBUS gateway.
When using encoders with higher resolution than 31 bits, the
singleturn resolution of the encoder will automatically be reduced
as much as needed to fit into the 32 bit structure.
For example, if a 37 bit encoder with a 25 bit singleturn and 12 bit
multiturn resolution is used, the singleturn resolution will be
reduced from 25 to 19 bit, and the multiturn resolution will still be
12 bit. (19 bit singleturn+12 bit multiturn = 31 bit total resolution).
Note: After downloading new scaling parameters the
Preset function must be used to set the encoder
starting point to absolute position 0 or to any
required starting position within the scaled
operating range.
5.4.5 Measuring units per revolution
The total measuring range is calculated by multiplying the
singleturn resolution with the number of distinguishable
revolutions.
The default settings for singleturn encoders are:
Measuring units per revolution= 8192 (2
Total measuring range in measuring units= 8192
13
)
(2
13
x 20)
The default settings for 25 bit multiturn encoders are:
Measuring units per revolution= 8192 (2
Total measuring range in measuring units= 33554432 (2
13
)
13
12
x 2
)
35
Page 36

Encoder and Gateway functionality, DPV0
Octet
10
11
12
13
Bits
31-24
23-16
15-8
7-0
Data
231-224
223-216
215-28
27-20
Measuring units per revolution
Octet
10
11
12
13
Bits
31-24
23-16
15-8
7-0
Data
231-224
223-216
215-28
27-20
Measuring units per revolution
Format of the scaling parameters:
Table 13 Singleturn scaling parameters format
Table 14 Multiturn scaling parameters format
The data format for both scaling parameters is 32 bits without
sign, with a value range from 2
range is limited by the resolution of the encoder. For a 25-bit
encoder with a singleturn resolution of 13 bits the permissible
value range for “Measuring units per revolution” is between 2
13
and 2
(8192) and for the “Total measuring range in measuring
steps” the permissible value range is between 2
(33554432). The scaling parameters are securely stored in the
PROFIBUS-DP master and are reloaded into the encoder at each
power-up. Both parameters are output data in 32-bit format.
Example of scaling and entry:
If the user wants to scale the encoder to a single turn resolution
of 4000 unique positions per revolution and a total number of turn
count equal to 3200 revolutions shall the configuration be as:
Measuring units per revolution = 4000 steps
Total measuring range in measuring units
= 4000 steps x 3200 revolutions
= 12800000
Entry in the master configuration software:
Measuring units per revolution = 4000
Total measuring range (steps) = 12800000
0
31
to 2
. The permissible value
0
and 225
0
36
Page 37

5.4.6 Total measuring range (units)
The total measuring range is defined by the parameter “Total
measuring range in measuring units.” The device has two
different operating modes, depending on the specified measuring
range. When the device receives a parameter message, it checks
the scaling parameters if a binary scaling can be used. If binary
scaling can be used, the device selects operating mode A (see
following explanation). If not, operating mode B is selected.
A. Cyclic operation (Binary scaling)
Cyclic operation is used when operating with 2
(2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256, 512, 1024, 2048. 4096.. number of
turns). If the desired total measuring range is equal to the
specified single turn resolution * 2
operates in endless cyclic operation (0 - max - 0 -max..). If the
position value increases above the maximum value by rotating the
encoder shaft, the encoder continues from 0.
Example of a cyclic scaling:
Total measuring range = Measuring units per revolution x number
of revolutions
Measuring units per revolution = 1000
Total measuring range = 32000 (2
Encoder and Gateway functionality, DPV0
x
number of turns
x
(where x<= 12) the encoder
5
= number of revolution 32)
Figure 14 Cyclic scaling
37
Page 38

Encoder and Gateway functionality, DPV0
B. Non-cyclic scaling
If the measuring range is used to limit the encoder value
range to a value not equal to the specified singleturn
resolution * 2
X
, the output position value is limited within the
operating range. If the position value increases or decreases
outside the measuring range by rotating the encoder shaft
beyond the maximum value or below 0, the device outputs
the total measuring range value.
Example of non-cyclic scaling:
Measuring units per revolution = 100
Total measuring range = 5000 (number of revolutions 50)
Figure 15 Non-cyclic scaling
5.4.7 Vel o c ity control
The velocity data can be accessed if
class 2 32-bit + velocity configuration is used. In this case the
input data consists of 32-position data plus 16-bit signed velocity
data. The input velocity value is negative in CCW direction if code
sequence is set to CW. If the measured velocity is higher then
what is possible to present with the selected velocity unit the
value is set to 0x7FFF (32768) or 0x8000 (-32768) depending on
direction of shaft rotation.
Note: If the velocity control function is used and scaling is
38
set to the device the velocity calculation is based
on the scaled position value. Consequently the
accuracy of the velocity value is dependent of the
scaling set to the device.
Page 39

5.4.8 Velocity calculation
Octet
39
Bits
7-0
Data
27-20
Velocity control
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Velocity unit
0 0
Steps/s
0 1
Steps/100 ms
1 0
Steps/10 ms
1 1
RPM (revolutions
per minute)
The velocity calculations are made with a maximum of
19 bits resolution. If the resolution is higher than 219, the value
used for velocity calculations is automatically reduced to 2
multiturn encoder with 2
singleturn value will be 2
the same resolution as presented in the diagnostic structure. For
a singleturn encoder the resolution can be up to 31 bit, but the
velocity calculations will be made on maximum 19 bits. This
means that in the diagnostic structure, the value 2
presented, but the resolution used for velocity calculations is not
presented if the singleturn resolution is higher than 2
The parameter for velocity unit, octet 39 can be seen below:
Encoder and Gateway functionality, DPV0
19
can be
19
.
. For a
12
multiturn resolution, the maximum
19
and the velocity will be calculated on
31
Table 15 Octet 39, Velocity Control
In case of steps/s unit, an average is made over 200 ms, and the value is multiplied by 5.
39
Page 40

Encoder and Gateway functionality, DPV0
Octet
1 2 3 4 Bits
31-24
23-16
15-8
7-0
Data
231-224
223-216
215-28
27-20
Data_Exchange -32 bits
5.5 Data transfer in normal operation (DDLM_Data_Exchange)
The DDLM_Data_Exchange mode is the normal status of the
device when operated. In this mode the position value is
transmitted from the device in a cyclic manner. Output data can
also be sent to the device i.e. preset commands.
5.5.1 Data exchange mode
The actual position value is transferred to the master as 32-bit
values (double word) or optional, the device supports
a position value length of 16-bit for singleturn encoder. The
position value is right-aligned in the data field.
DDLM_Data_Exchange mode
Standard configuration:
Table 16 Data exchange -32-bits
Configuration data:
40
Device class 1: D1hex 2 input data words, data consistency
Device class 2: F1hex 2 input data words, 2 output data words for
preset value, data consistency
Page 41

Octet
1
2
Bits
15-8
7-0
Data
215-28
27-20
Data_Exchange -16 bits
Table 17 Data exchange -16 b its
Configuration data:
5.5.2 Preset function
Encoder and Gateway functionality, DPV0
Device class 1: D0hex 1 input data word, data consistency
Device class 2: F0hex 1 input data word, 1 output data word for
preset value, data consistency
The preset function enables adaptation of the position value
from the encoder to a known mechanical reference point of
the system. The preset function sets the actual position of
the encoder to zero or to the selected preset value. The
preset value is written to the encoder as output data in the
Data_Exchange function. If scaling is used the preset function
shall be used after the scaling function, to ensure that the
preset value is entered in the current measuring unit. The
most significant bit (MSB) of the preset value controls the
preset function as follows:
Normal operating mode: MSB = 0 (bit 31, optionally bit 15)
The encoder will not change the preset value.
Activated mode: MSB = 1 (bit 31, optionally bit 15) With
MSB = 1, the encoder accepts the transferred value (bits 0 –
30) as a preset value in binary code. The encoder reads the
current position value and calculates an offset value from the
preset value and the read position value. The position value is
shifted by the calculated offset value. If the input position
value equals the preset value, the preset mode is terminated
and the MSB can be set to 0 by the master. The offset value
can be read with the diagnostic function and is securely
stored in case of a power interruption and is reloaded at each
start-up.
Note: The preset function should only be used at encoder
standstill.
41
Page 42

Encoder and Gateway functionality, DPV0
Octet
1 2 3
4
Bits
31
30-24
23-16
15-8
7-0
Data
0/1
230-224
223-216
215-28
27-20
Preset control
bit
Preset value – Max. 31 bits
Octet
1
2
Bits
15
14-8
7-0
Data
0/1
214-28
27-20
Preset control
bit
Preset value – Max . 15 bits
Preset value format (2 words, 32 bits)
Table 18 Preset value, 32-bit format
Preset value format (1 words, 16 bits)
Table 19 Preset value, 16-bit format
42
Page 43

5.6 Diagnostics
Diagnostic function
Data type
Diagnostic
Octet number
Device
class
Station status 1
Bits 1 1
Station status 2
Bits 2 1
Station status 3
Bits 3 1
Diagnostics master address
Bits 4 1
PNO identification number
Bits
5-6
1
Extended diagnostic header
Octet string
7 1 Alarms
Octet string
8
1
Operating status
Octet string
9
1
Encoder type
Octet string
10
1
Singleturn resolution(encoder)
Measuring unit (linear encoder)
32 without sign
11-14
1
Number of distinguishable revolutions
16 without sign
15-16
1
Additional alarms
Octet string
17 2 Supported alarms
Octet string
18-19
2
Warnings
Octet string
20-21
2
Supported warnings
Octet string
22-23
2
Profile version
Octet string
24-25
2
DDLM_Slave_Diag
Encoder and Gateway functionality, DPV0
The diagnostic information contains diagnostic data which are
defined in the PROFIBUS-DP specification (octets 1 to 6) but
also encoder specific diagnostic data:
43
Page 44

Encoder and Gateway functionality, DPV0
Diagnostic function
Data type
Diagnostic
Octet number
Device
class
Software version
Octet string
26-27
2
Operating time
32 without sign
28-31
2
Offset value
32 with sign
32-35
2
Manufacturer offset value
32 with sign
36-39
2
Measuring units per revolution
32 without sign
40-43
2
Total measuring range in measuring
units
32 without sign
44-47
2
Serial number
ASCII string
48-57
2
Reserved for future
58-61
2
Table 20 Diagnostic message, DPV0
Note: The length of the diagnostic information of class 1
is limited to 16 bytes, compatible with previos DP
version. For PROFIBUS-DP encoders of class 2, the
length of the encoder specific diagnostic data
including the extended diagnostic header is
57 bytes.
44
Page 45

5.6.1 Diagnostic Header
Octet
7
Alarms
7 6 5-0
Data
0 0 xxh
Set to 00
Length incl. header
Extended diagnosis
The header byte specifies the length of the encoder diagnostics
including the header byte. The format of the transmission length
is hexadecimal. For the PROFIBUS-DP encoder of class 1 the
length of the encoder-specific diagnostic data is 10 bytes (0Ahex).
DDLM_Slave_Diag
Table 21 Diagnostic header
5.6.2 Alarms
Alarm is generated by the device when failure occurs which
effects the position value. Octet 8 in the diagnostic function
(DDLM_Slave_Diag) indicates the status of the alarms.
Additional alarms for device class 2 are addedin the diagnostic
octet 17.
If an alarm is given, the Ext_Diag bit and the Stat_Diag bit in
the diagnostic function are set to high and remain high until
the alarm is cleared and the encoder can provide a correct
position value. Alarms are cleared when the functionality is
within the specifi- cation and the position value is correct.
Note: Not every encoder supports every alarm. For
encoders of class 2 the diagnostic information
“supported alarms” (see Chapter 5.6.8) makes it
possible to find out which individual alarm bits are
supported.
Encoder and Gateway functionality, DPV0
45
Page 46

Encoder and Gateway functionality, DPV0
Octet
8
Bits
7-0
Alarms
Bits
Definition
=0
=1 0 Position error
No
Ye s 1 Voltage supply error
No
Ye s 2 Current is too high
No
Ye s 3 Commissioning diagnostics
OK
Error
4
Memory error
No
Ye s
5-7
Currently not assign
DDLM_Slave_Diag
Table 22 Alarms
46
Page 47

5.6.3 Operating Status
Octet
9
Bits
7-0 Operating status
Bits
Definition
=0
=1
0
Code sequence
Increasing position
flange side)
Increasing position
(Seen from flange side)
1
Class 2
functionality
No, not supported
Ye s
2
Commissioning
diagnostics
No, not supported
Ye s
3
Scaling function
status
Scaling disabled
Scaling enabled
4-7
Currently not assigned
DDLM_Slave_Diag
Encoder and Gateway functionality, DPV0
Octet 9 in the diagnostic function provides information
about encoder-specific parameters. A class 2 encoder
sets the functionality bit for class 2 commands in order to
show the DP master that all class 2 commands are
supported. The DP master must activate the class 2
functionality bit in the parameter message (DDLM_Set_Prm)
to enable the use of class 2 functions. The status bit of
the scaling function is set when the scaling function is
activated and the resolution of the encoder is calculated
by means of the scaling parameters.
Table 23 Operating status
values for clockwise
revolutions (Seen from
values for counter
clockwise revolutions
47
Page 48

Encoder and Gateway functionality, DPV0
Octet
10
Bits
0-FF Encoder type
Bits
Definition
00
Absolute singleturn encoder
01
Absolute multiturn encoder
02
Absolute singleturn encoder with electronic revolution counter
03
Incremental rotary encoder
04
Incremental rotary encoder with battery buffer
05
Incremental linear encoder
06
Incremental linear encoder with battery buffer
07
Absolute linear encoder
08
Absolute linear encoder with periodic coding
09-FF
Currently not assigned
5.6.4 Encoder type
The type of encoder can be read in octet 10 of the diagnostic
function. The type of encoder is defined in hex-code in the range
from 0 to FF.
DDLM_Slave_Diag
Table 24 Diagnostic, encoder
48
Page 49

Encoder and Gateway functionality, DPV0
Octet
11
12
13
14
Bits
31-24
23-16
15-8
7-0
Data
231-224
223-216
215-28
27-20
Singleturn resolution
Octet
15
16
Bits
15-8
7-0 Number of distinguishable revolutions
5.6.5 Singleturn resolution or measuring step
The singleturn resolution in the diagnostic function has different
meanings depending on the type of encoder.
For rotary or angle encoders, the diagnostic octets 11 to 14
indicate the physical resolution in number of measuring steps per
revolution which is transferred for the absolute singleturn position
value. The maximum singleturn resolution is 2
encoders the measuring steps is presented with respect to the
resolution of the linear encoder, i.e. each increment of the
measuring step is equal the actual resolution for the linear
encoder in use. Typical values for the linear resolution are
1µm - 40 µm.
DDLM_Slave_Diag
Table 25 Diagnostic, singleturn resolution
5.6.6 Number of distinguishable revolutions
The number of distinguishable revolutions that the
encoder can transfer is defined by octets 15 and 16 of
the diagnostic function. In accordance with the formula
below, the measuring range for an encoder results from
the number of distinguishable revolutions multiplied by
the singleturn resolution. The maximum number of
distinguishable revolutions is 65536-1(16 bits).
Measuring range = number of distinguishable revolutions
x singleturn resolution
DDLM_Slave_Diag
31
. For linear
Table 26 Diagnostics, number of distinguishable revolutions
49
Page 50

Encoder and Gateway functionality, DPV0
Octet
17
Bits
7-0
Additional alarms
Octet
Definition
=0
=1
Bits
Currently not assigned
0..7
Octet
18
19
Bits
15-8
7-0 Supported alarms
Octet
Definition
=0
=1
0
Position error
Not supported
Supported
1
Voltage supply error
Not supported
Supported
2
Current is too high
Not supported
Supported
3
Commissioning diagnostics
Not supported
Supported
4
Memory error
Not supported
Supported
5..15
Currently not assigned
5.6.7 Additional alarms
The diagnostic octet 17 indicates additional alarms for device
class 2.
Table 27 Diagnostics, additional alarms
5.6.8 Supported alarms
The diagnostics octet 18 and 19 contain information on the
supported alarms.
Table 28 Diagnostics, supported alarms
50
Page 51

5.6.9 Warnings
Octet
20
21
Bits
15-8
7-0
Warnings
Octet
Definition
=0
=1 0 Frequency exceeded
No
Ye s 1 Temperature exceeded
No
Ye s 2 Light control reserve
Not reached
Reached
3
CPU monitoring status
OK
Reset
4
Maximum operating time
exceeded
No
Ye s
5
Battery charging
OK
Too low
6
Reference point
Reached
Not reached
7..15
Currently not assigned
Encoder and Gateway functionality, DPV0
Warnings indicate that tolerances for certain internal parameters
of the device have been exceeded. Contrary to alarms, no faulty
position values are expected in case of warnings. Octets 20 and
21 of the diagnostic function indicate the status of the warnings.
If a warning is set, the Ext_Diag bit in the diagnostic function is
logically set to 1 until the warning is cleared. All warnings are
deleted when the diagnostic message of the device has been
read. However, if the tolerances are still exceeded, the warning is
activated again. The warning “Maximum operating time exceeded”
(bit 4) is not activated before the system is switched on again.
Note: Not every encoder supports every warning.
Please refer to the diagnostic information under
“Supported Warnings”, see chapter 5.6.10, for
information on the support of specific warnings.
Table 29 Diagnostics, warnings
51
Page 52

Encoder and Gateway functionality, DPV0
Octet
22
23
Bits
15-8
7-0 Supported Warnings
Octet
Definition
=0
=1 0 Frequency warning
Not supported
Supported
1
Temperature warning
Not supported
Supported
2
Light control reserve warning
Not supported
Supported
3
CPU monitoring status warning
Not supported
Supported
4
Maximum operating time
exceeded warning
Not supported
Supported
5
Battery charging warning
Not supported
Supported
6
Reference point warning
Not supported
Supported
7..15
Currently not assigned
5.6.10 Supported warnings
The diagnostics octet 22 and 23 contain information about
supported warnings.
Table 30 Diagnostics, supported warnings
52
Page 53

Encoder and Gateway functionality, DPV0
Octet
24
25
Bits
15-8
7-0
Data
27-20
27-20
Revision number
Index
Profile Version
5.6.11 Profile Version
Octets 24 and 25 of the diagnostic function provide the
PROFIBUS-DP encoder profile version that is implemented in the
device. The octet’s revision number and index are combined.
Example:
Profile version 1. 4 0
Octet no. 24 25
Binary code. 00000001 01000000
Hex. 1 40
DDLM_Slave_Diag
Table 31 Diagnostics, profile version
5.6.12 Software Version
Octets 26 and 27 of the DDLM_Slave_Diag function provide the
software version of the device. The octet’s revision number and
index are combined.
Example:
Software version 1.4 0
Octet no. 26 27
Binary code. 00000001 01000000
Hex. 1 40
53
Page 54

Encoder and Gateway functionality, DPV0
Octet
26
27
Bits
15-8
7-0
Data
27-20
27-20
Revision number
Index
Software Version
Octet
28
29
30
31
Bits
31-24
23-16
15-8
7-0
Data
231-224
223-216
215-28
27-20
Operating time
DDLM_Slave_Diag
Table 32 Diagnostics, software version
5.6.13 Operating time
The operating time monitor stores the operating time for the
device in operating hours. The operating time is saved every six
minutes in the non-volatile memory in the device. This happens
as long as the device is under power. The operating time is
displayed as a 32-bit value without sign in 0.1 h by the
DDLM_Slave_Diag function.If the operating time function is
not supported by the device, it is set to the maximum value
(FFFF FFFF hex).
DDLM_Slave_Diag
Table 33 Diagnostic, operating time
54
Page 55

Encoder and Gateway functionality, DPV0
Octet
32
33
34
35
Bits
31-24
23-16
15-8
7-0
Data
231-224
223-216
215-28
27-20
Offset value
Octet
36
37
38
39
Bits
31-24
23-16
15-8
7-0
Data
231-224
223-216
215-28
27-20
Offset value of the encoder manufacturer
5.6.14 Offset value
The offset value is calculated by the preset function and shifts the
position value by the calculated value.
The offset value is stored in the device and can be provided by
the diagnostic octets 32 to 35. The data type for the offset value
is a 32-bit binary value with sign, whereby the offset value range
is equal to the measuring range of the device. The preset function
is used after the scaling function. This means that the offset value
is indicated according to the scaled resolution of the device.
DDLM_Slave_Diag
Table 34 Diagnostics, offset value
5.6.15 Offset value of the encoder manufacturer
The manufacturer offset value indicates the encoder offset set by
the manufacturer. This value gives information on the shift of the
position zero point in number of positions from the physical zero
point of the encoder. The data type for the offset value is a 32-bit
binary value with sign. The value range corresponds to the
measuring range of the encoder. The offset value of the
manufacturer of the encoder is indicated in the number of units
according to the basic resolution of the encoder. The value is
stored in write-protected memory, which can be changed only by
the encoder manufacturer. This value has practically no
importance for the user.
Table 35 Diagnostics, offset value of the encoder manufacturer
55
Page 56

Encoder and Gateway functionality, DPV0
Octet
40
41
42
43
Bits
31-24
23-16
15-8
7-0
Data
231-224
223-216
215-28
27-20
Measuring units per revolution
Octet
44
45
46
47
Bits
31-24
23-16
15-8
7-0
Data
231-224
223-216
215-28
27-20
Total measuring range in measuring units
5.6.16 Scaling parameters settings
The scaling parameters are set in the DDLM_Set_Prm function.
The parameters are stored in the octets 40 to 47 of the diagnostic
data. The “Measuring units per revolution” and “Total measuring
range in measuring units” parameters define the selected
resolution of the encoders. The status bit of the scaling function in
the operating status (octet 9 of the diagnostic data) indicates
whether the scaling function is enabled.
Values preset by the manufacturer of the encoder:
Measuring units per revolution = singleturn resolution.
Total measuring range in measuring units = singleturn
resolution x number of distinguishable revolutions.
The data type for both values is unsigned 32 bits.
DDLM_Slave_Diag
DDLM_Slave_Diag
Table 36 Diagnostics, scaling parameter setting
56
Page 57

Encoder and Gateway functionality, DPV0
Octet
48-57
Bits
79-0
Data
ASCII
Serial number
Octet
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
ASCII string
30
30
30
35
39
46
38
44
45
35
Serial (hex)
0 0 0 5 9 F 8 D E
5
Serial (Dec)
94342629
5.6.17 Encoder serial number
Octet 48 to 57 of the diagnostic function provides the serial
number of the encoder as a 10-character ASCII string.
DDLM_Slave_Diag
Example of a serial number
Table 37 Diagnsotics, encoder serial number
57
Page 58

Encoder commissioning example, DPV0
6 Encoder commissioning example, DPV0
This example uses a Siemens master software. The example is
intended to illustrate the commissioning of a PROFIBUS-DPV0
encoder with a 25 bit absolute rotary encoder and velocity
information.
Copying the GSD file
First, copy the GSD file and bitmap file into the corresponding
directory in the configuration
software,...\GSD. Then install the GSD file into your system.
58
Page 59

Encoder commissioning example, DPV0
Selecting the DPV0 Slave
To select the encoder click on the “PROFIBUS Encoder” icon in
the map structure on the right side of the window. Use “dragand-drop” to add the encoder on the BUS, upper left view.
When dropping the encoder on the BUS a PROFIBUS address
must be assigned, naturally this address must be the same as
assigned on the hardware address switches on the back of the
encoder. See chapter 3.1.1.
Configuration of DPV0 Slave
To configure the encoder for 25-bit position value plus
velocity data choose the “Encoder Class 2 32-bit velocity”
configuration option in the map structure. Add the chosen
configuration by “drag-and-drop” to the configuration
window in lower left view.
59
Page 60

Encoder commissioning example, DPV0
Assigning parameters to the DPV0 slave
By “double-clicking” on the configuration row in the
configuration view the parameterization view will be opened.
Add or change the data in the “value” field to the desired
parameter values. Chapter 5,4 describes the functionality and
possibility of each parameter. Then save and compile the setting
by clicking Save and compile on the Station tab.
60
Page 61

7 Revision history
Revision
Date
changes
Rev. 1. 0
2014-07-01
First release
Table 38 Revision history
Revision history
61
Page 62

DR. JOHANNES HEIDENHAIN GmbH
Dr.-Johannes-Heidenhain-Straße 5
83301 Traunreut, Germany
{ +49 8669 31-0
| +49 8669 5061
E-mail: info@heidenhain.de
www.heidenhain.de
1111895-20 · Ver00 · 7/2014 · PDF
 Loading...
Loading...