Ericsson AXE 810 Service Manual

Improvements Within APZ
Chapter 3
This chapter is designed to provide the student with knowledge about the main changes within the APZ system. The chapter describes important improvements within all different areas of APZ, not only the Central Processor.
OBJECTIVES:
Upon completion of this chapter the student will be able to:
•account for improvements in capacity in APZ 212 33
•account for improvements in capacity and footprint for all types of regional processors such as RPP, RPG, EMRP and RP
•account for improvements in the APG40.

AXE 810 Delta
Intentionally Blank
EN/LZT 123 6389 R1A

3 Improvements Within APZ
3 Improvements Within APZ
Table of Contents
|
|
Topic |
Page |
|
|
|
|
CENTRAL PROCESSORS, CP............................................................. |
1 |
CAPACITY...................................................................................................................... |
1 |
HARDWARE................................................................................................................... |
1 |
NEW HARDWARE ......................................................................................................... |
4 |
OTHER NEWS AND IMPROVEMENTS ........................................................................ |
4 |
COMPATIBILITY ............................................................................................................ |
5 |
REGIONAL PROCESSOR, RP ............................................................. |
6 |
RPP, PCI BUS BASED REGIONAL PROCESSOR .............................. |
7 |
THE BASIC CONFIGURATION ..................................................................................... |
7 |
THE MODEM CONFIGURATION .................................................................................. |
8 |
THE PMC CONFIGURATION ........................................................................................ |
8 |
THE EPSB, ETHERNET PACKET SWITCH BOARD.................................................... |
9 |
APPLICATIONS.............................................................................................................. |
9 |
RPG ..................................................................................................... |
11 |
EMRP................................................................................................... |
12 |
APG40 ................................................................................................. |
13 |
SYSTEM CAPABILITIES.............................................................................................. |
13 |
THE HARDWARE......................................................................................................... |
14 |
EN/LZT 123 6389 R1A |
– i – |

AXE 810 Delta
Intentionally Blank
– ii – |
EN/LZT 123 6389 R1A |

3 Improvements Within APZ
CENTRAL PROCESSORS, CP
CAPACITY
The main improvement within the CP area is a new Central Processor referred to as APZ 212 33. It is basically the same hardware as APZ 212 30 but with some improvements.
Increased clock speed and the removal of some internal bottlenecks are the two main reasons for the improved capacity.
The capacity increase from APZ 212 30 to 212 33 is some 70% and the first field trials of the system will be during end of year 2000.
A completely new central processor is being developed at the same time. The name will be APZ 212 40 (not part of AXE 810) and it will be the first CP from Ericsson built with a commercial micro processor. By using a commercial CPU, the hardware development of external CPUs can be followed and Ericsson does not need to keep up with this pace (doubled capacity every 18 month as in Moore’s law). The price for the processor can also be reduced with this solution. The capacity comparison between all available processors can be seen in the figure below. Please note that the capacity comparison is only valid within this figure and cannot be used to compare, for example, a CP with an RP.
|
212 11 |
212 20 |
212 25 |
212 30 |
212 33 |
212 40 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Relative |
1 |
4 |
1.7 |
14 |
23 |
42 |
Capacity |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DSMemory |
228 |
1532 |
252 |
4096 |
4096 |
8000 |
(M word) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Power (W) |
1750 |
800 |
60 |
470 |
470 |
510 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Number in |
3000 |
4500 |
1000 |
500 |
- |
- |
Service |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Figure 3- 1 Capacity of different APZ versions
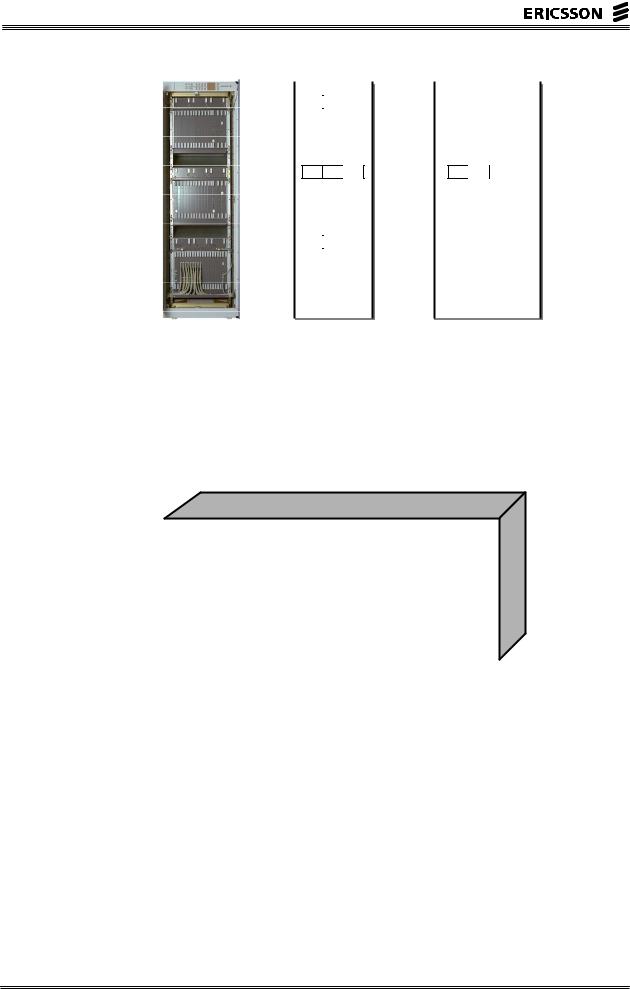
HARDWARE
The hardware of APZ 212 33 is on high level exactly the same as the hardware in APZ 212 30. The figure below gives an overview of the cabinet.
EN/LZT 123 6389 R1A |
– 1 – |
AXE 810 Delta
|
F r o n t Vie w |
|
|
S id e V ie w |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
FAN |
FAN |
FAN |
|
|
|
FAN |
FAN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C P U -A |
|
|
|
CPU-A |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FAN FAN FAN |
FAN FAN |
|
C P U -B |
|
|
|
|
CPU-B |
|
|
|
1800 mm |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
FAN |
FAN |
FAN |
|
|
|
|
FAN |
|
FAN |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R P H -A |
|
|
|
RPH-A |
|
RPH-B |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
600 mm |
|
|
|
800 mm |
||||||||||
Figure 3- 2 The APZ 212 33 cabinet
The CPU Subrack
On a subrack level, the hardware of the CPU Subrack looks like in the figure below.
MAU |
STUDI-0 |
STUDI-1 |
STUDI-2 |
STUDI-3 |
IPU |
STUDI-4 |
STUDI-5 |
STUDI-6 |
STUDI-7 |
SPU |
|
POWC (MAI) |
POU |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Figure 3- 3 The CPU Subrack
There are basically three processor boards:
•Instruction Processor Unit (IPU)
•Signal Processor Unit (SPU)
•Power Control Unit (POWC) including the Maintenance Interface (MAI)
There is one power unit (POU) in each subrack. The MAU, Maintenance Unit, is only present in the B-side (CP-B) as there is one MAU per CP pair. The eight slots for Data Store boards (STUD, Storage Unit Data) can either be of DRAM or SRAM type. In both APZ 212 30 and in 212 33 there are three different types of boards that can be used:
– 2 – |
EN/LZT 123 6389 R1A |
 Loading...
Loading...