Page 1

Quick Start Guide
Ethernet Switch Series
Intelligent Ethernet Switches
Versions: 3.79, 3.80, 3.90, 4.00, 4.10
Edition 3, 02/2014
CLI Reference Guide
Default Login Details
Out-Of-Band Mgt Port http://192.168.0.1
In-Band Ports http://192.168.1.1
User Name admin
Password 1234
www.zyxel.com
Copyright © 2011
Copyright © 2013 ZyXEL Communications Corporation
ZyXEL Communications Corporation
Page 2
IMPORTANT!
READ CAREFULLY BEFORE USE.
KEEP THIS GUIDE FOR FUTURE REFERENCE.
This is a Reference Guide for a series of products. Not all products support all firmware features.
Screenshots, graphics and commands in this book may differ slightly from your product due to
differences in your product firmware or your computer operating system. Every effort has been made
to ensure that the information in this manual is accurate.
Related Documentation
• User’s Guide
The User’s Guide explains how to use the Web Configurator to configure the Switch.
It is recommended you use the Web Configurator to configure the Switch.
Page 3
About This CLI Reference Guide
About This CLI Reference Guide
Intended Audience
This manual is intended for people who want to configure ZyXEL Switches via Command
Line Interface (CLI).
The version number on the cover page refers to the latest firmware version supported by the
ZyXEL Switches. This guide applies to version 3.79, 3.80, 3.90, 4.00 and 4.10 at the time of
writing.
This guide is intended as a command reference for a series of products.
Therefore many commands in this guide may not be available in your product.
See your User’s Guide for a list of supported features and details about feature
implementation.
Please refer to www.zyxel.com for product specific User Guides and product certifications.
How To Use This Guide
•Read the How to Access the CLI chapter for an overview of various ways you can get to
the command interface on your Switch.
• Use the Reference section in this guide for command syntax, description and examples.
Each chapter describes commands related to a feature.
• To find specific information in this guide, use the Contents Overview, the Index of
Commands, or search the PDF file. E-mail techwriters@zyxel.com.tw if you cannot find
the information you require.
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
3
Page 4

Document Conventions
Document Conventions
Warnings and Notes
These are how warnings and notes are shown in this CLI Reference Guide.
Warnings tell you about things that could harm you or your device. See your
User’s Guide for product specific warnings.
Notes tell you other important information (for example, other things you may
need to configure or helpful tips) or recommendations.
Syntax Conventions
This manual follows these general conventions:
• ZyXEL’s switches may be referred to as the “Switch”, the “device”, the “system” or the
“product” in this Reference Guide.
• Units of measurement may denote the “metric” value or the “scientific” value. For
example, “k” for kilo may denote “1000” or “1024”, “M” for mega may denote “1000000”
or “1048576” and so on.
Command descriptions follow these conventions:
• Commands are in
• Required input values are in angle brackets <>; for example,
must specify an IP address for this command.
• Optional fields are in square brackets []; for instance show logins [name], the name
field is optional.
The following is an example of a required field within an optional field: snmp-server
[contact <system contact>], the contact field is optional. However, if you
use contact, then you must provide the system contact information.
• Lists (such as <port-list>) consist of one or more elements separated by commas.
Each element might be a single value (1, 2, 3, ...) or a range of values (1-2, 3-5, ...)
separated by a dash.
•The | (bar) symbol means “or”.
• italic terms represent user-defined input values; for example, in snmp-server
[contact <system contact>], system contact can be replaced by the
administrator’s name.
• A key stroke is denoted by square brackets and uppercase text, for example, [ENTER]
means the “Enter” or “Return” key on your keyboard.
courier new font.
ping <ip> means that you
4
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
Page 5
Document Conventions
• <cr> means press the [ENTER] key.
• An arrow (-->) indicates that this line is a continuation of the previous line.
Command summary tables are organized as follows:
Table 1 Example: Command Summary Table
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
show vlan Displays the status of all VLANs. E 3
vlan <1-4094> Enters config-vlan mode for the specified VLAN. Creates the
VLAN, if necessary.
inactive Disables the specified VLAN. C 13
no inactive Enables the specified VLAN. C 13
no vlan <1-4094> Deletes a VLAN. C 13
C13
The Table title identifies commands or the specific feature that the commands configure.
The COMMAND column shows the syntax of the command.
• If a command is not indented, you run it in the enable or config mode. See Chapter 2 on
page 14 for more information on command modes.
• If a command is indented, you run it in a sub-command mode.
The DESCRIPTION column explains what the command does. It also identifies legal input
values, if necessary.
The M column identifies the mode in which you run the command.
• E: The command is available in enable mode. It is also available in user mode if the
privilege level (P) is less than 13.
• C: The command is available in config (not indented) or one of the sub-command modes
(indented).
The P column identifies the privilege level of the command. If you don’t have a high enough
privilege level you may not be able to view or execute some of the co mmands. See Chapter 2
on page 14 for more information on privilege levels.
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
5
Page 6

Contents Overview
Contents Overview
Introduction ..............................................................................................................................9
How to Access and Use the CLI .................................................................................................11
Privilege Level and Command Mode ......................................................................................... 14
Initial Setup ................................................................................................................................ 19
Reference A-G ........................................................................................................................22
AAA Commands ........................................................................................................................ 24
ARP Commands ................................. ... ... ... .... ................................................ ... .... ... ... ... ... ....... 27
ARP Inspection Commands ............................................... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... .......................... 29
ARP Learning Commands .................................. ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... .......................... 34
Bandwidth Commands ................................................. ... ... ... .... ... ............................................. 35
Broadcast Storm Commands ..................................................................................................... 38
CFM Commands ....................................................................................................................... 41
Classifier Commands ................................................................................................................ 50
Cluster Commands ................................ ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ................................................ ... ....... 53
Date and Time Commands ........................................................................................................56
Data Center Bridging Commands .............................................................................................. 59
DHCP Commands ..................................................................................................................... 67
DHCP Snooping & DHCP VLAN Commands ............................................................................ 72
DiffServ Commands ................................................................................................................... 76
Display Commands ................................................................................................................... 77
DVMRP Commands ........... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... ................................................. ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... 78
Error Disable and Recovery Commands ...................................................................................80
Ethernet OAM Commands ........................................................................................................ 84
External Alarm Commands ........................................................................................................90
GARP Commands ..................................................................................................................... 92
Green Ethernet Commands ....................................................................................................... 94
GVRP Commands ..................................................................................................................... 98
Reference H-M ........................................................................................................................99
HTTPS Server Commands ...................................................................................................... 101
IEEE 802.1x Authentication Commands ................................................................................. 105
IGMP and Multicasting Commands ......................................................................................... 108
IGMP Snooping Commands .....................................................................................................111
IGMP Filtering Commands .......................................................................................................118
Interface Commands ...............................................................................................................120
Interface Route-domain Mode ................................................................................................. 125
6
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
Page 7

Contents Overview
IP Commands .................................. ... ... ... ... ................................................. ... ... .... ... ... ... ........ 126
IP Source Binding Commands .................................................. ... ........................................... 130
IPv6 Commands ...................................................................................................................... 132
Layer 2 Protocol Tunnel (L2PT) Commands ........................................................................... 155
Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) Commands ................................................................. 158
Load Sharing Commands ................................... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ........................ 170
Logging Commands ................................................................................................................172
Login Account Commands .............................................. ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ..................... 173
Loopguard Commands ... ................................................. ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ..................... 175
MAC Address Commands ....................................................................................................... 177
MAC Authentication Commands .............................................................................................179
MAC Filter Commands ............................................................................................................181
MAC Forward Commands ....................................................................................................... 183
MAC Pinning Commands ........................................................................................................184
Mirror Commands .................................................................................................................... 186
MRSTP Commands .................................................................................................................190
MSTP Commands ...................................................................................................................192
Multiple Login Commands ....................................................................................................... 197
MVR Commands ..................................................................................................................... 198
Reference N-S ......................................................................................................................200
OSPF Commands .............................................. ... ... ................................................. ... ... ... ..... 202
Password Commands ............................................................................................................. 208
PoE Commands ...................................................................................................................... 210
Policy Commands ....................................................................................................................214
Policy Route Commands ......................................................................................................... 218
Port Security Commands ............. .... ... ... ... ... ................................................. ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .....220
Port-based VLAN Commands ................................................................................................. 222
PPPoE IA Commands .............................................................................................................223
Private VLAN Commands ...... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ................................................ .... ... ... ... ... .....229
Protocol-based VLAN Commands ........................................................................................... 234
Queuing Commands ................................................................................................................236
RADIUS Commands ................................................................................................................240
Remote Management Commands ........................................................................................... 242
RIP Commands ....................................................................................................................... 245
RMON .................................... ...................... ....................... ....................... .............................. 247
Running Configuration Commands .........................................................................................253
sFlow .......................................................................................................................................255
Smart Isolation Commands ..................................................................................................... 257
SNMP Server Commands .......................................................................................................261
STP and RSTP Commands .....................................................................................................265
SSH Commands ................................. ... ... ... .... ................................................ ... .... ... ... ... ... ..... 269
Static Multicast Commands ..................................................................................................... 271
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
7
Page 8

Contents Overview
Static Route Commands ..........................................................................................................273
Subnet-based VLAN Commands ....................................... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ........................... 276
Syslog Commands .................................................................................................................. 278
Reference T-Z .......................................................................................................................279
TACACS+ Commands ............................................................................... ... ... ... .... ... ... ...........281
Tech Support Commands ........................................................................................................ 282
TFTP Commands ........... .... ... ... ... .... ... ................................................ ... .... ... ... ... ..................... 285
Trunk Commands ........................................ .... ... ... ... ................................................. ... ... ... ..... 286
trTCM Commands ....... ... .... ... ................................................ .... ... ... ... ... .................................. 289
VLAN Commands .................................................................................................................... 292
VLAN IP Commands ...............................................................................................................298
VLAN Mapping Commands ..................................................................................................... 300
VLAN Port Isolation Commands .............................................................................................. 302
VLAN Stacking Commands ..................................................................................................... 303
VLAN Trunking Commands ..................................................................................................... 306
VRRP Commands ...................................................................................................................307
Additional Commands .................................................. ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ......................311
Appendices and Index of Commands ................................................................................323
8
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
Page 9

PART I
Introduction
How to Access and Use the CLI (11)
Privilege Level and Command Mode (14)
Initial Setup (19)
9
Page 10

10
Page 11
CHAPTER 1
How to Access and Use the CLI
This chapter introduces the command line interface (CLI).
1.1 Accessing the CLI
Use any of the following methods to access the CLI.
1.1.1 Console Port
1 Connect your computer to the console port on the Switch using the appropriate cable.
2 Use terminal emulation software with the following settings:
Table 2 Default Settings for the Console Port
SETTING DEFAULT VALUE
Terminal Emulation VT100
Baud Rate 9600 bps
Parity None
Number of Data Bits 8
Number of Stop Bits 1
Flow Control None
3 Press [ENTER] to open the login screen.
1.1.2 Telnet
1 Connect your computer to one of the Ethernet ports.
2 Open a T elnet session to the Switch’ s IP address. If this is your first login, use the default
values.
Table 3 Default Management IP Address
SETTING DEFAULT VALUE
IP Address 192.168.1.1
Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0
Make sure your computer IP address is in the same subnet, unless you are accessing the
Switch through one or more routers.
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
11
Page 12
Chapter 1 How to Access and Use the CLI
1.1.3 SSH
1 Connect your computer to one of the Ethernet ports.
2 Use a SSH client program to access the Switch. If this is your first login, use the default
values in Table 3 on page 11 and Table 4 on page 12. Make sure your computer IP
address is in the same subnet, unless you are accessing the Switch through one or more
routers.
1.2 Logging in
Use the administrator username and password. If this is your first login, use the default values.
Table 4 Default User Name and Password
SETTING DEFAULT VALUE
User Name admin
Password 1234
The Switch automatically logs you out of the management interface after five
minutes of inactivity. If this happens to you, simply log back in again.
1.3 Using Shortcuts and Getting Help
This table identifies some shortcuts in the CLI, as well as how to get help.
Table 5 CLI Shortcuts and Help
COMMAND / KEY(S) DESCRIPTION
history Displays a list of recently-used commands.
(up/down arrow keys) Scrolls through the list of recently-used commands. You can edit
[CTRL]+U Clears the current command.
[TAB] Auto-completes the keyword you are typing if possible. For
? Displays the keywords and/or input values that are allowed in
help Displays the (full) commands that are allowed in place of help.
any command or press [ENTER] to run it again.
example, type config, and press [TAB]. The Switch finishes the
word configure.
place of the ?.
12
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
Page 13

Chapter 1 How to Access and Use the CLI
1.4 Saving Your Configuration
When you run a command, the Switch saves any changes to its run-time memory. The Switch
loses these changes if it is turned off or loses power. Use the
enable mode to save the current configuration permanently to non-volatile memory.
sysname# write memory
write memory command in
You should save your changes after each CLI session. All unsaved
configuration changes are lost once you restart the Switch.
1.5 Logging Out
Enter logout to log out of the CLI. You have to be in user, enable, or config mode. See
Chapter 2 on page 14 for more information about modes.
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
13
Page 14

CHAPTER 2
Privilege Level and Command
Mode
This chapter introduces the CLI privilege levels and command modes.
• The privilege level determines whether or not a user can run a particular command.
• If a user can run a particular command, the user has to run it in the correct mode.
2.1 Privilege Levels
Every command has a privilege level (0-14). Users can run a command if the session’s
privilege level is greater than or equal to the command’s privilege level. The session’s
privilege level initially comes from the login account’s privilege level, though it is possible to
change the session’s privilege level after logging in.
2.1.1 Privilege Levels for Commands
The privilege level of each command is listed in the Reference A-G chapters on page 22.
At the time of writing, commands have a privilege level of 0, 3, 13, or 14. The following table
summarizes the types of commands at each of these privilege levels.
Table 6 Types of Commands at Different Privilege Levels
PRIVILEGE LEVEL T YPES OF COMMANDS AT THIS PRIVILEGE LEVEL
0 Display basic system information.
3 Display configuration or status.
13 Configure features except for login accounts, SNMP user accounts, the
authentication method sequence and authorization settings, multiple lo gins,
administrator and enable passwords, and configuration information display.
14 Configure login accounts, SNMP user accounts, the authentication method
sequence and authorization settings, multiple logins, and administrator and
enable passwords, and display configuration information.
2.1.2 Privilege Levels for Login Accounts
You can manage the privilege levels for login accounts in the following ways:
• Using commands. Login accounts can be configured by the admin account or any login
account with a privilege level of 14. See Chapter 40 on page 173.
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
14
Page 15

• Using vendor-specific attributes in an external authentication server. See the User’ s Guide
for more information.
The admin account has a privilege level of 14, so the administrator can run every command.
You cannot change the privilege level of the admin account.
2.1.3 Privilege Levels for Sessions
The session’s privilege level initially comes from the privilege level of the login account the
user used to log in to the Switch. After logging in, the user can use the following commands to
change the session’s privilege level.
2.1.3.1 enable Command
This command raises the session’s privilege level to 14. It also changes the session to enable
mode (if not already in enable mode). This command is available in user mode or enable
mode, and users have to know the enable password.
In the following example, the login account user0 has a privilege level of 0 but knows that the
enable password is 123456. Afterwards, the session’s privilege level is 14, instead of 0, and
the session changes to enable mode.
Chapter 2 Privilege Level and Command Mode
sysname> enable
Password: 123456
sysname#
The default enable password is 1234. Use this command to set the enable password.
password <password>
<password> consists of 1-32 alphanumeric characters. For example, the following
command sets the enable password to 123456. See Chapter 89 on page 311 for more
information about this command.
sysname(config)# password 123456
The password is sent in plain text and stored in the Switch’s buffers. Use this command to set
the cipher password for password encryption.
password cipher <password>
<password> consists of 32 alphanumeric characters. For example, the following command
encrypts the enable password with a 32-character cipher password. See Chapter 53 on page
208 for more information about this command.
sysname(config)# password cipher qwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnm123456
2.1.3.2 enable <0-14> Command
This command raises the session’s privilege level to the specified level. It also changes the
session to enable mode, if the specified level is 13 or 14. This command is available in user
mode or enable mode, and users have to know the password for the specified privilege level.
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
15
Page 16
Chapter 2 Privilege Level and Command Mode
In the following example, the login account user0 has a privilege level of 0 but knows that the
password for privilege level 13 is pswd13. Afterwards, the session’s privilege level is 13,
instead of 0, and the session changes to enable mode.
sysname> enable 13
Password: pswd13
sysname#
Users cannot use this command until you create passwords for specific privilege levels. Use
the following command to create passwords for specific privilege levels.
password <password> privilege <0-14>
<password> consists of 1-32 alphanumeric characters. For example, the following
command sets the password for privilege level 13 to pswd13. See Chapter 89 on page 311 for
more information about this command.
sysname(config)# password pswd13 privilege 13
2.1.3.3 disable Command
This command reduces the session’s privilege level to 0. It also changes the session to user
mode. This command is available in enable mode.
2.1.3.4 show privilege command
This command displays the session’s current privilege level. This command is available in
user mode or enable mode.
sysname# show privilege
Current privilege level : 14
2.2 Command Modes
The CLI is divided into several modes. If a user has enough privilege to run a particular
command, the user has to run the command in the correct mode. The modes that are available
depend on the session’s privilege level.
2.2.1 Command Modes for Privilege Levels 0-12
If the session’s privilege level is 0-12, the user and all of the allowed commands are in user
mode. Users do not have to change modes to run any allowed commands.
16
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
Page 17
Chapter 2 Privilege Level and Command Mode
2.2.2 Command Modes for Privilege Levels 13-14
If the session’s privilege level is 13-14, the allowed commands are in one of several modes.
Table 7 Command Modes for Privilege Levels 13-14 and the Types of Commands in Each One
MODE PROMPT COMMAND FUNCTIONS IN THIS MODE
enable sysname# Display current configuration, diagnostics, maintenance.
config sysname(config)# Configure features other than those below.
config-interface sysname(config-interface)# Configure ports.
config-mvr sysname(config-mvr)# Configure multicast VLAN.
config-route-
domain
config-dvmrp sysname(config-dvmrp)# Configure Distance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol
config-igmp sysname(config-igmp)# Configure Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP).
config-ma sysname(config-ma)# Configure an Maintenance Association (MA) in
config-ospf sysname(config-ospf)# Configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) protocol.
config-rip sysname(config-rip)# Configure Routing Information Protocol (RIP).
config-vrrp sysname(config-vrrp)# Configure Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP).
sysname(config-if)# Enable and enter configuration mode for an IPv4 or IPv6
routing domain.
(DVRMP).
Connectivity Fault Management (CFM).
Each command is usually in one and only one mode. If a user wants to run a particular
command, the user has to change to the appropriate mode. The command modes are organized
like a tree, and users start in enable mode. The following table explains how to change from
one mode to another.
Table 8 Changing Between Command Modes for Privilege Levels 13-14
MODE ENTER MODE LEAVE MODE
enable -- --
config configure exit
config-interface interface port-channel <port-list> exit
config-mvr mvr <1-4094> exit
config-vlan vlan <1-4094> exit
config-route-domain interface route domain <ip-address>/<mask-bits> exit
config-dvmrp router dvmrp exit
config-igmp router igmp exit
config-ospf router ospf <router-id> exit
config-rip router rip exit
config-vrrp router vrrp network <ip-address>/<mask-bits>
vr-id <1~7> uplink-gateway <ip-address>
exit
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
17
Page 18
Chapter 2 Privilege Level and Command Mode
2.3 Listing Available Commands
Use the help command to view the executable commands on the Switch. You must have the
highest privilege level in order to view all the commands. Follow these steps to create a list of
supported commands:
1 Log into the CLI. This takes you to the enable mode.
2 Type help and press [ENTER]. A list comes up which shows all the commands
available in enable mode. The example shown next has been edited for brevity’s sake.
sysname# help
Commands available:
help
logout
exit
history
enable <0-14>
enable <cr>
.
.
traceroute <ip|host-name> [vlan <vlan-id>][..]
traceroute help
ssh <1|2> <[user@]dest-ip> <cr>
ssh <1|2> <[user@]dest-ip> [command </>]
sysname#
3 Copy and paste the results into a text editor of your choice. This creates a list of all the
executable commands in the user and enable modes.
4 Type configure and press [ENTER]. This takes you to the config mode.
5 Type help and press [ENTER]. A list is displayed which shows all the commands
available in config mode and all the sub-commands. The sub-commands are preceded by
the command necessary to enter that sub-command mode. For example, the command
name <name-str> as shown next, is preceded by the command used to enter the
config-vlan sub-mode:
sysname# help
.
.
no arp inspection log-buffer logs
no arp inspection filter-aging-time
no arp inspection <cr>
vlan <1-4094>
vlan <1-4094> name <name-str>
vlan <1-4094> normal <port-list>
vlan <1-4094> fixed <port-list>
vlan <1-4094>.
6 Copy and paste the results into a text editor of your choice. This creates a list of all the
executable commands in config and the other submodes, for example, the config-vlan
mode.
18
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
Page 19
CHAPTER 3
Initial Setup
This chapter identifies tasks you might want to do when you first configure the Switch.
3.1 Changing the Administrator Password
It is recommended you change the default administrator password. You can
encrypt the password with a cipher password. See Chapter 53 on page 208 for
more information.
Use this command to change the administrator password.
admin-password <pw-string> <Confirm-string>
where <pw-string> may be 1-32 alphanumeric characters long.
sysname# configure
sysname(config)# admin-password t1g2y7i9 t1g2y7i9
3.2 Changing the Enable Password
It is recommended you change the default enable password. You can encrypt
the password with a cipher password. See Chapter 53 on page 208 for more
information.
Use this command to change the enable password.
password <password>
where <password> may be 1-32 alphanumeric characters long.
sysname# configure
sysname(config)# password k8s8s3dl0
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
19
Page 20

Chapter 3 Initial Setup
3.3 Prohibiting Concurrent Logins
By default, multiple CLI sessions are allowed via the console port or Telnet. See the User’s
Guide for the maximum number of concurrent sessions for your Switch . Use this comman d to
prohibit concurrent logins.
no multi-login
Console port has higher priority than Telnet. See Chapter 50 on page 197 for more multi-
login
commands.
sysname# configure
sysname(config)# no multi-login
3.4 Changing the Management IP Address
The Switch has a different IP address in each VLAN. By default, the Switch has VLAN 1 with
IP address 192.168.1.1 and subnet mask 255.255.255.0. Use this command in config-vlan
mode to change the management IP address in a specific VLAN.
ip address <ip> <mask>
This example shows you how to change the management IP address in VLAN 1 to 172.16.0.1
with subnet mask 255.255.255.0.
sysname# configure
sysname(config)# vlan 1
sysname(config-vlan)# ip address default-management 172.16.0.1 255.255.255.0
Afterwards, you have to use the new IP address to access the Switch.
3.5 Changing the Out-of-band Management IP Address
If your Switch has a MGMT port (also referred to as the out-of-band management port), then
the Switch can also be managed via this interface. By default, the MGMT port IP address is
192.168.0.1 and the subnet mask is 255.255.255.0. Use this command in config mode to
change the out-of-band management IP address.
ip address <ip> <mask>
This example shows you how to change the out-of-band management IP address to 10.10.10.1
with subnet mask 255.255.255.0 and the default gateway 10.10.10.254
20
sysname# configure
sysname(config)# ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0
sysname(config)# ip address default-gateway 10.10.10.254
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
Page 21

3.6 Looking at Basic System Information
Use this command to look at general system information about the Switch.
show system-information
This is illustrated in the following example.
sysname# show system-information
System Name : sysname
System Contact :
System Location :
Ethernet Address : 00:13:49:ae:fb:7a
ZyNOS F/W Version : V3.80(AII.0)b0 | 04/18/2007
RomRasSize : 1746416
System up Time : 280:32:52 (605186d ticks)
Bootbase Version : V1.00 | 05/17/2006
ZyNOS CODE : RAS Apr 18 2007 19:59:49
Product Model : ES-2024PWR
Chapter 3 Initial Setup
See Chapter 89 on page 311 for more information about these attributes.
3.7 Looking at the Operating Configuration
Use this command to look at the current operating configuration.
show running-config
This is illustrated in the following example.
sysname# show running-config
Building configuration...
Current configuration:
vlan 1
name 1
normal ""
fixed 1-9
forbidden ""
untagged 1-9
ip address default-management 172.16.37.206 255.255.255.0
ip address default-gateway 172.16.37.254
exit
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
21
Page 22

PART II
Reference A-G
AAA Commands (24)
ARP Commands (27)
ARP Inspection Commands (29)
ARP Learning Commands (34)
Bandwidth Commands (35)
Broadcast Storm Commands (38)
CFM Commands (41)
Classifier Commands (50)
Cluster Commands (53)
Date and Time Commands (56)
Data Center Bridging Commands (59)
DHCP Commands (67)
DHCP Snooping & DHCP VLAN Commands (72)
DiffServ Commands (76)
Display Commands (77)
DVMRP Commands (78)
Error Disable and Recovery Commands (80)
Ethernet OAM Commands (84)
External Alarm Commands (90)
GARP Commands (92)
Green Ethernet Commands (94)
GVRP Commands (98)
22
Page 23

23
Page 24
CHAPTER 4
AAA Commands
Use these commands to configure authentication, authorization and accounting on the Switch.
4.1 Command Summary
The following section lists the commands for this feature.
Table 9 aaa authentication Command Summary
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
show aaa authentication Displays what methods are used for authentication. E 3
show aaa authentication enable Displays the authentication method(s) for checking privilege
level of administrators.
aaa authentication enable
<method1> [<method2> ...]
no aaa authentication enable Resets the method list for checking privileges to its default
show aaa authentication login Displays the authentication methods for administrator login
aaa authentication login
<method1> [<method2> ...]
no aaa authentication login Resets the method list for the authentication of login accounts
Specifies which method should be used first, second, and
third for checking privileges.
method: enable, radius, or tacacs+.
value.
accounts.
Specifies which method should be used first, second, and
third for the authentication of login accounts.
method: local, radius, or tacacs+.
to its default value.
E3
C14
C14
E3
C14
C14
Table 10 Command Summary: aaa accounting
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
show aaa accounting Displays accounting settings configured on the Switch. E 3
show aaa accounting update Display the update period setting on the Switch for
accounting sessions.
aaa accounting update periodic
<1-2147483647>
no aaa accounting update Resets the accounting update interval to the default value. C 13
show aaa accounting commands Displays accounting settings for recording command events. E 3
aaa accounting commands
<privilege> stop-only tacacs+
[broadcast]
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
Sets the update period (in minutes) for accounting sessions.
This is the time the Switch waits to send an update to an
accounting server after a session starts.
Enables accounting of command sessions and specifies the
minimum privilege level (0-14) for the command sessions that
should be recorded. Optionally, sends accounting information
for command sessions to all configured accounting servers at
the same time.
E3
C13
C13
24
Page 25
Chapter 4 AAA Commands
Table 10 Command Summary: aaa accounting (continued)
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
no aaa accounting commands Disables accounting of command sessions on the Switch. C 13
show aaa accounting dot1x Displays accounting settings for recording IEEE 802.1x
aaa accounting dot1x <startstop|stop-only>
<radius|tacacs+> [broadcast]
no aaa accounting dot1x Disables accounting of IEEE 802.1x authentication sessions
show aaa accounting exec Displays accounting settings for recording administrative
aaa accounting exec <startstop|stop-only>
<radius|tacacs+> [broadcast]
no aaa accounting exec Disables accounting of administrative sessions via SSH,
show aaa accounting system Displays accounting settings for recording system events, for
aaa accounting system
<radius|tacacs+> [broadcast]
no aaa accounting system Disables accounting of system events on the Switch. C 13
session events.
Enables accounting of IEEE 802.1x authentication sessions
and specifies the mode and protocol method. Optionally,
sends accounting information for IEEE 802.1x authentication
sessions to all configured accounting servers at the same
time.
on the Switch.
sessions via SSH, Telnet or the console port.
Enables accounting of administrative sessions via SSH,
Telnet and console port an d specifies the mode and protocol
method. Optionally, sends accounting information for
administrative sessions via SSH, Telnet and console port to
all configured accounting servers at the same time.
Telnet or console on th e Switch.
example system shut down, start up, accounting enabled or
accounting disabled.
Enables accounting of system events and specifies the
protocol method. Optionally, sends accounting information for
system events to all configured accounting servers at the
same time.
E3
C13
C13
E3
C13
C13
E3
C13
Table 11 aaa authorization Command Summary
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
show aaa authorization Displays authorization settings configured on the Switch. E 3
show aaa authorization dot1x Displays the authorization method used to allow an IEEE
802.1x client to have different bandwidth limit or VLAN ID
assigned via the external server.
show aaa authorization exec Displays the authorization method used to allow an
administrator which logs in the Switch through Telnet or SSH
to have different access privilege level assigned via the
external server.
aaa authorization console Enables authorization of allowing an administrator which logs
in the Switch through the console port to have different
access privilege level assigned via the external server.
aaa authorization dot1x radius Enables authorization for IEEE 802.1x clients using RADIUS. C 14
aaa authorization exec
<radius|tacacs+>
no aaa authorization console Disables authorization of allowing an administrator which logs
Specifies which method (radius or tacacs+) should be
used for administrator authorization.
in the Switch through the console port to have different
access privilege level assigned via the external server.
E3
E3
C14
C14
C14
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
25
Page 26
Chapter 4 AAA Commands
Table 11 aaa authorization Command Summary (continued)
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
no aaa authorization dot1x Disables authorization of allowing an IEEE 802.1x client to
have different bandwidth limit or VLAN ID assigned via the
external server.
no aaa authorization exec Disables authorization of allowing an administrator which logs
in the Switch through Telnet or SSH to have different access
privilege level assigned via the external server.
C14
C14
26
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
Page 27
CHAPTER 5
ARP Commands
Use these commands to look at IP-to-MAC address mapping(s).
5.1 Command Summary
The following section lists the commands for this feature.
Table 12 arp Command Summary
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
arp aging-time <60-1000000> Sets how long dynamically learned ARP entries remain in the
ARP table before they age out (and must be relearned).
arp name <name> ip <ip-address>
mac <mac-addr> vlan <vlan-id>
interface port-channel <port-
list>
arp name <name> ip <ip-address>
mac <mac-addr> vlan <vlan-id>
interface port-channel <port-
list> inactive
no arp ip <ip-address> mac <mac-
addr> vlan <vlan-id>
no arp ip <ip-address> mac <mac-
addr> vlan <vlan-id> inactive
show ip arp Displays the ARP table. E 3
clear ip arp Removes all of the dynamic entries from the ARP table. E 13
clear ip arp interface port-
channel <port-list>
clear ip arp ip <ip-address> Removes the dynamic entries learned with the specified IP
no arp Flushes the ARP table entries. E 1 3
Creates a static ARP entry which will not age out. C 13
Creates a static ARP entry but disables it. C 13
Deletes a static ARP entry from the ARP table. C 13
Enables the specified static ARP entry. C 13
Removes the dynamic entries learned on the specified port. E 13
address.
C13
E13
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
27
Page 28

Chapter 5 ARP Commands
5.2 Command Examples
This example creates a static ARP entry and shows the ARP tahle on the Switch.
sysname# config
sysname(config)# arp name test ip 192.168.1.99 mac 00:c5:d8:01:23:45 vlan
1 interface port-channel 3
sysname(config)# exit
sysname# show ip arp
Index IP MAC VLAN Port Age(s) Type
1 192.168.1.1 00:19:cb:37:00:49 1 CPU 0 static
2 192.168.1.99 00:c5:d8:01:23:45 1 3 0 sta tic
3 192.168.2.1 00:19:cb:37:00:49 465 CPU 0 static
sysname#
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 13 show ip arp
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Index This field displays the index number.
IP This field displays the learned IP address of the device.
MAC This field displays the MAC address of the device.
VLAN This field displ ays the VLAN to which the device belongs.
Port This field displays the number of the port from which the IP address was learned.
CPU indicates this IP address is the Switch’s management IP address.
Age(s) This field displays how long the entry remains valid.
Type This field displays how the entry was learned.
dynamic: The Switch learned this entry from ARP packets.
28
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
Page 29
CHAPTER 6
ARP Inspection Commands
Use these commands to filter unauthorized ARP packets in your network.
6.1 Command Summary
The following section lists the commands for this feature.
Table 14 arp inspection Command Summary
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
arp inspection Enables ARP inspection on the Switch. You still have to
enable ARP inspection on specific VLAN and specify trusted
ports.
no arp inspection Disables ARP inspection on the Switch. C 13
show arp inspection Displays ARP inspection configuration details. E 3
clear arp inspection statistics Removes all ARP inspection statistics on the Switch. E 3
clear arp inspection statistics
vlan <vlan-list>
show arp inspection statistics Displays all ARP inspection statistics on the Switch. E 3
show arp inspection statistics
vlan <vlan-list>
Removes ARP inspection statistics for the specified VLAN(s). E 3
Displays ARP inspection statistics for the specified VLAN(s). E 3
C13
Table 15 Command Summary: arp inspection filter
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
show arp inspection filter
[<mac-addr>] [vlan <vlan-id>]
no arp inspection filter <mac-
addr> vlan <vlan-id>
clear arp inspection filter Delete all ARP inspection filters from the Switch. E 13
arp inspection filter-aging-time
<1-2147483647>
arp inspection filter-aging-time
none
no arp inspection filter-agingtime
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
Displays the current list of MAC address filters that were
created because the Switch identified an unauthorized ARP
packet. Optionally, lists MAC address filters based on the
MAC address or VLAN ID in the filter.
Specifies the ARP inspection record you want to delete from
the Switch. The ARP inspection record is identified by the
MAC address and VLAN ID pair.
Specifies how long (1-2147483647 seconds) MAC address
filters remain in the Switch after the Switch identifies an
unauthorized ARP packet. The Switch automatically deletes
the MAC address filter afterwards.
Specifies the MAC address filter to be permanent. C 13
Resets how long (1-2147483647 seconds) the MAC address
filter remains in the Switch after the Switch identifies an
unauthorized ARP packet to the default value.
E3
E13
C13
C13
29
Page 30
Chapter 6 ARP Inspection Commands
Table 16 Command Summary: arp inspection log
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
show arp inspection log Displays the log settings configured on the Switch. It also
displays the log entries recorded on the Switch.
clear arp inspection log Delete all ARP inspection log entries from the Switch. E 13
arp inspection log-buffer
entries <0-1024>
arp inspection log-buffer logs
<0-1024> interval <0-86400>
no arp inspection log-buffer
entries
no arp inspection log-buffer
logs
Specifies the maximum number (1-1024) of log messages
that can be generated by ARP packets and not sent to the
syslog server.
If the number of log messages in the Switch exceeds this
number, the Switch stops recording log messages and simply
starts counting the number of entries that were dropped due
to unavailable buffer.
Specifies the number of syslog messages that can be sent to
the syslog server in one batch and how often (1-86400
seconds) the Switch sends a batch of syslog messages to the
syslog server.
Resets the maximum number (1-1024) of log messages that
can be generated by ARP packets and not sent to the syslog
server to the default value.
Resets the maximum number of syslog messages the Switch
can send to the syslog server in one batch to the default
value.
E3
C13
C13
C13
C13
Table 17 Command Summary: interface arp inspection
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
show arp inspection interface
port-channel <port-list>
interface port-channel <port-
list>
arp inspection trust Sets the port to be a trusted port for arp inspection. The
no arp inspection trust Disables this port from being a trusted port for ARP
Displays the ARP inspection settings for the specified port(s). E 3
Enters config-interface mode for the specified port(s). C 13
C13
Switch does not discard ARP packets on trusted ports for any
reason.
C13
inspection.
Table 18 Command Summary: arp inspection vlan
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
show arp inspection vlan <vlanlist>
arp inspection vlan <vlan-list> Enables ARP inspection on the specified VLAN(s). C 13
no arp inspection vlan <vlan-
list>
arp inspection vlan <vlan-list>
logging [all|none|permit|deny]
no arp inspection vlan <vlan-
list> logging
Displays ARP inspection settings for the specified VLAN(s). E 3
Disables ARP inspection on the specified VLAN(s). C 13
Enables logging of ARP inspection events on the specified
VLAN(s). Optionally specifies which types of events to log.
Disables logging of messages generated by ARP inspection
for the specified VLAN(s).
C13
C13
30
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
Page 31

6.2 Command Examples
This example looks at the current list of MAC address filters that were created because the
Switch identified an unauthorized ARP packet. When the Switch identifies an unauthorized
ARP packet, it automatically creates a MAC address filter to block traffic from the source
MAC address and source VLAN ID of the unauthorized ARP packet.
sysname# show arp inspection filter
Filtering aging timeout : 300
MacAddress VLAN Port Expiry (sec) Reason
----------------- ---- ----- ------------ ------------- Total number of bindings: 0
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 19 show arp inspection filter
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Filtering aging timeout This field displays how long the MAC address filters remain in the Switch
after the Switch identifies an unauthorized ARP packet. The Switch
automatically deletes the MAC address filter afterwards.
MacAddress This field displays the source MAC address in the MAC address filter.
VLAN This field displays the source VLAN ID in the MAC address filter.
Port This field displays the source port of the discarded ARP packet.
Expiry (sec) This field displays how long (in seconds) the MAC address filter remains in
the Switch. You can also delete the record manually (Delete).
Reason This field displays the reason the ARP packet was discarded.
MAC+VLAN: The MAC address and VLAN ID were not in the binding table.
IP: The MAC address and VLAN ID were in the binding table, but the IP
address was not valid.
Port: The MAC address, VLAN ID, and IP address were in the binding
table, but the port number was not valid.
Chapter 6 ARP Inspection Commands
This example looks at log messages that were generated by ARP packets and that have not
been sent to the syslog server yet.
sysname# show arp inspection log
Total Log Buffer Size : 32
Syslog rate : 5 entries per 1 seconds
Port Vlan Sender MAC Sender IP Pkts Reason
Time
---- ---- ----------------- --------------- ---- ---------- ----
-------------------- Total number of logs: 0
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
31
Page 32

Chapter 6 ARP Inspection Commands
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 20 show arp inspection log
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Total Log Buffer Size This field displays the maximum number (1-1024) of log messages that
Syslog rate This field displays the maximum number of syslog messages the Switch
Port This field displays the source port of the ARP packet.
Vlan This field displays the source VLAN ID of the ARP packet.
Sender MAC This field displays the source MAC address of the ARP packet.
Sender IP This field displays the source IP address of the ARP packet.
Pkts This field displays the number of ARP packets that were consolidated into
Reason This field displays the reason the log message was generated.
Time This field displays when the log message was generated.
Total number of logs This field displays the number of log messages that were generated by
were generated by ARP packets and have not been sent to the syslog
server yet.
If the number of log messages in the Switch exceeds this number, the
Switch stops recording log messages and simply starts counting the
number of entries that were dropped due to unavailable buffer.
can send to the syslog server in one batch. This number is expressed as a
rate because the batch frequency is determined by the Log Interval.
this log message. The Switch consolidates identical log messages
generated by ARP packets in the log consolidation interval into one log
message.
dhcp deny: An ARP packet was discarded because it violated a dynamic
binding with the same MAC address and VLAN ID.
static deny: An ARP packet was discarded because it violated a static
binding with the same MAC address and VLAN ID.
deny: An ARP packet was discarded because there were no bindings with
the same MAC address and VLAN ID.
static permit: An ARP packet was forwarded because it matched a static
binding.
dhcp permit: An ARP packet was forwarded because it matched a
dynamic binding.
ARP packets and that have not been sent to the syslog server yet. If one or
more log messages are dropped due to unavailable buffer, there is an entry
called overflow with the current number of dropped log messages.
32
This example displays whether ports are trusted or untrusted ports for ARP inspection.
sysname# show arp inspection interface port-channel 1
Interface Trusted State Rate (pps) Burst Interval
--------- ------------- ---------- ------------- 1 Untrusted 15 1
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
Page 33

Chapter 6 ARP Inspection Commands
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 21 show arp inspection interface port-channel
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Interface This field displays the port number. If you configure the * port, the settings
Trusted State This field displays whether this port is a trusted port (Trusted) or an
Rate (pps) This field displays the maximum number for DHCP packets that the Switch
Burst Interval This field displays the length of time over which the rate of ARP packets is
are applied to all of the ports.
untrusted port (Untrusted).
Trusted ports are connected to DHCP servers or other switches, and the
Switch discards DHCP packets from trusted ports only if the rate at which
DHCP packets arrive is too high.
receives from each port each second. The Switch discards any additional
DHCP packets.
monitored for each port. For example, if the Rate is 15 pps and the burst
interval is 1 second, then the Switch accepts a maximum of 15 ARP
packets in every one-second interval. If the burst interval is 5 seconds, then
the Switch accepts a maximum of 75 ARP packets in every five-second
interval.
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
33
Page 34

CHAPTER 7
ARP Learning Commands
Use these commands to configure how the Switch updates the ARP table.
7.1 Command Summary
The following section lists the commands for this feature.
Table 22 arp-learning Command Summary
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
interface port-channel <portlist>
arp-learning <arpreply|gratuitous-arp|arprequest>
no arp-learning Resets the ARP learning mode to its default setting (arp-
Enters config-interface mode for the specified port(s). C 13
Sets the ARP learning mode the Switch uses on the port.
arp-reply: the Switch updates the ARP table only with the
ARP replies to the ARP requests sent by the Switch.
gratuitous-arp: the Switch updates its ARP table with
either an ARP reply or a gratuitous ARP request. A gratuitous
ARP is an ARP request in which both the source and
destination IP address fields are set to the IP address of the
device that sends this request and the destination MAC
address field is set to the broadcast address.
arp-request: the Switch updates the ARP table with both
ARP replies, gratuitous ARP requests and ARP requests.
reply).
C13
C13
7.2 Command Examples
This example changes the ARP learning mode on port 8 from arp-reply to arp-request.
sysname# configure
sysname(config)# interface port-channel 8
sysname(config-interface)# arp-learning arp-request
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
34
Page 35

CHAPTER 8
Bandwidth Commands
Use these commands to configure the maximum allowable bandwidth for incoming or
outgoing traffic flows on a port.
Bandwidth management implementation differs across Switch models.
• Some models use a single command (bandwidth-limit ingress) to control the
incoming rate of traffic on a port.
• Other models use two separate commands (bandwidth-limit cir and
bandwidth-limit pir) to control the Committed Information Rate (CIR) and the
Peak Information Rate (PIR) allowed on a port.
The CIR and PIR should be set for all ports that use the same uplink bandwidth. If the CIR
is reached, packets are sent at the rate up to the PIR. When network congestion occurs,
packets through the ingress port exceeding the CIR will be marked for drop.
The CIR should be less than the PIR.
See Section 8.2 on page 36 and Section 8.3 on page 37 for examples.
See also Chapter 81 on page 289 for information on how to use trTCM (T wo Rate Three Color
Marker) to control traffic flow.
8.1 Command Summary
The following table describes user-input values available in multiple commands for this
feature.
Table 23 User-input Values: running-config
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
port-list The port number or a range of port numbers that you want to configure.
rate The rate represents a bandwidth limit. Different models support different rate
limiting incremental steps. See your User’s Guide for more information.
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
35
Page 36

Chapter 8 Bandwidth Commands
The following section lists the commands for this feature.
Table 24 Command Summary: bandwidth-control & bandwidth-limit
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
show interfaces config <portlist> bandwidth-control
bandwidth-control Enables bandwidth control on the Switch. C 13
no bandwidth-control Disables bandwidth control on the Switch. C 13
interface port-channel <port-
list>
bandwidth-limit ingress Enables bandwidth limits for incoming traffic on the port(s). C 13
bandwidth-limit ingress
<rate>
bandwidth-limit egress Enables bandwidth limits for outgoing traffic on the port(s). C 13
bandwidth-limit egress
<rate>
no bandwidth-limit ingress Disables ingress bandwidth limits on the specified port(s). C 13
no bandwidth-limit egress Disables egress bandwidth limits on the specified port(s). C 13
bandwidth-limit cir Enables commit rate limits on the specified port(s). C 13
bandwidth-limit cir <rate> Sets the guaranteed bandwidth allowed for the incoming
Displays the current settings for interface bandwidth control. E 3
Enters subcommand mode for configuring the specified ports. C 13
Sets the maximum bandwidth allowed for incoming traffic on
the port(s).
Sets the maximum bandwidth allowed for outgoing traffic on
the port(s).
traffic flow on a port. The commit rate should be less than the
peak rate. The sum of commit rates cannot be greater than or
equal to the uplink bandwidth.
C13
C13
C13
Note: The sum of CIRs cannot be greater than or
equal to the uplink bandwidth.
bandwidth-limit pir Enables peak rate limits on the specified port(s). C 13
bandwidth-limit pir <rate> Sets the maximum bandwidth allowed for the incoming traffic
flow on the specified port(s).
no bandwidth-limit cir Disables commit rate limits on the specified port(s). C 13
no bandwidth-limit pir Disables peak rate limits on the specified port(s). C 13
8.2 Command Examples: ingress
This example sets the outgoing traffic bandwidth limit to 5000 Kbps and the incoming traffic
bandwidth limit to 4000 Kbps for port 1.
sysname# configure
sysname(config)# bandwidth-control
sysname(config)# interface port-channel 1
sysname(config-interface)# bandwidth-limit egress 5000
sysname(config-interface)# bandwidth-limit ingress 4000
sysname(config-interface)# exit
sysname(config)# exit
C13
36
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
Page 37

This example deactivates the outgoing bandwidth limit on port 1.
sysname# configure
sysname(config)# interface port-channel 1
sysname(config-interface)# no bandwidth-limit egress
sysname(config-interface)# exit
sysname(config)# exit
8.3 Command Examples: cir & pir
This example sets the guaranteed traffic bandwidth limit on port 1 to 4000 Kbps and the
maximum traffic bandwidth limit to 5000 Kbps for port 1.
sysname# configure
sysname(config)# bandwidth-control
sysname(config)# interface port-channel 1
sysname(config-interface)# bandwidth-limit cir
sysname(config-interface)# bandwidth-limit cir 4000
sysname(config-interface)# bandwidth-limit pir
sysname(config-interface)# bandwidth-limit pir 5000
sysname(config-interface)# exit
sysname(config)# exit
Chapter 8 Bandwidth Commands
This example displays the bandwidth limits configured on port 1.
sysname# show running-config interface port-channel 1 bandwidth-limit
Building configuration...
Current configuration:
interface port-channel 1
bandwidth-limit cir 4000
bandwidth-limit cir
bandwidth-limit pir 5000
bandwidth-limit pir
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
37
Page 38

CHAPTER 9
Broadcast Storm Commands
Use these commands to limit the number of broadcast, multicast and destination lookup failure
(DLF) packets the Switch receives per second on the ports.
Broadcast storm control implementation differs across Switch models.
• Some models use a single command (bmstorm-limit) to control the combined rate of
broadcast, multicast and DLF packets accepted on Switch ports.
• Other models use three separate commands (broadcast-limit, multicast-
limit, dlf-limit) to control the number of individual types of packets accepted on
Switch ports.
See Section 9.2 on page 39 and Section 9.3 on page 39 for examples.
9.1 Command Summary
The following table describes user-input values available in multiple commands for this
feature.
Table 25 User-input Values: broadcast-limit, multicast-limit & dlf-limit
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
pkt/s Specifies the maximum number of packets per second accepted by a Switch
port.
The following section lists the commands for this feature.
Table 26 Command Summary: storm-control, bmstorm-limit, and bstorm-control
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
show interfaces config <portlist> bstorm-control
storm-control Enables broadcast storm control on the Switch. C 13
no storm-control Disables broadcast storm control on the Switch. C 13
interface port-channel <port-
list>
bmstorm-limit Enables broadcast storm control on the specified port(s). C 13
Displays the current settings for broadcast storm control. E 3
Enters subcommand mode for configuring the specified ports. C 13
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
38
Page 39

Chapter 9 Broadcast Storm Commands
Table 26 Command Summary: storm-control, bmstorm-limit, and bstorm-control (continued)
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
bmstorm-limit <rate> Specifies the maximum rate at which the Switch receives
broadcast, multicast, and destination lookup failure (DLF)
packets on the specified port(s).
Different models support different rate limiting incremental
steps. See your User’s Guide for more information.
no bmstorm-limit Disables broadcast storm control on the specified port(s). C 13
broadcast-limit Enables the broadcast packet limit on the specified port(s). C 13
broadcast-limit <pkt/s> Specifies the maximum number of broadcast packets the
Switch accepts per second on the specified port(s).
no broadcast-limit Disables broadcast packet limit no the specified port(s). C 13
multicast-limit Enables the multicast packet limit on the specified port(s). C 13
multicast-limit <pkt/s> Specifies the maximum number of multicast packets the
Switch accepts per second on the specified port(s).
no multicast-limit Disables multicast packet limit on the specified port(s). C 13
dlf-limit Enables the DLF packet limit on the specified port(s). C 13
dlf-limit <pkt/s> Specifies the maximum number of DLF packets the Switch
accepts per second on the specified port(s).
no dlf-limit Disables DLF packet limits no the specified port(s). C 13
C13
C13
C13
C13
9.2 Command Example: bmstorm-limit
This example enables broadcast storm control on port 1 and limits the combined maximum
rate of broadcast, multicast and DLF packets to 128 Kbps.
sysname# configure
sysname(config)# storm-control
sysname(config)# interface port-channel 1
sysname(config-interface)# bmstorm-limit
sysname(config-interface)# bmstorm-limit 128
sysname(config-interface)# exit
sysname(config)# exit
9.3 Command Example: broadcast-limit, multicast-limit & dlflimit
This example enables broadcast storm control on the Switch, and configures port 1 to accept
up to:
• 128 broadcast packets per second,
• 256 multicast packets per second,
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
39
Page 40

Chapter 9 Broadcast Storm Commands
• 64 DLF packets per second.
sysname# configure
sysname(config)# storm-control
sysname(config)# interface port-channel 1
sysname(config-interface)# broadcast-limit
sysname(config-interface)# broadcast-limit 128
sysname(config-interface)# multicast-limit
sysname(config-interface)# multicast-limit 256
sysname(config-interface)# dlf-limit
sysname(config-interface)# dlf-limit 64
sysname(config)# exit
sysname# show interfaces config 1 bstorm-control
Broadcast Storm Control Enabled: Yes
Port Broadcast|Enabled Multicast|Enabled DLF-Limit|Enabled
1 128 pkt/s|Yes 256 pkt/s|Yes 64 pkt/s|Yes
40
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
Page 41

CHAPTER 10
CPE
Service Provider Network
CPE
CFM Commands
Use these commands to configure the Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) on the Switch.
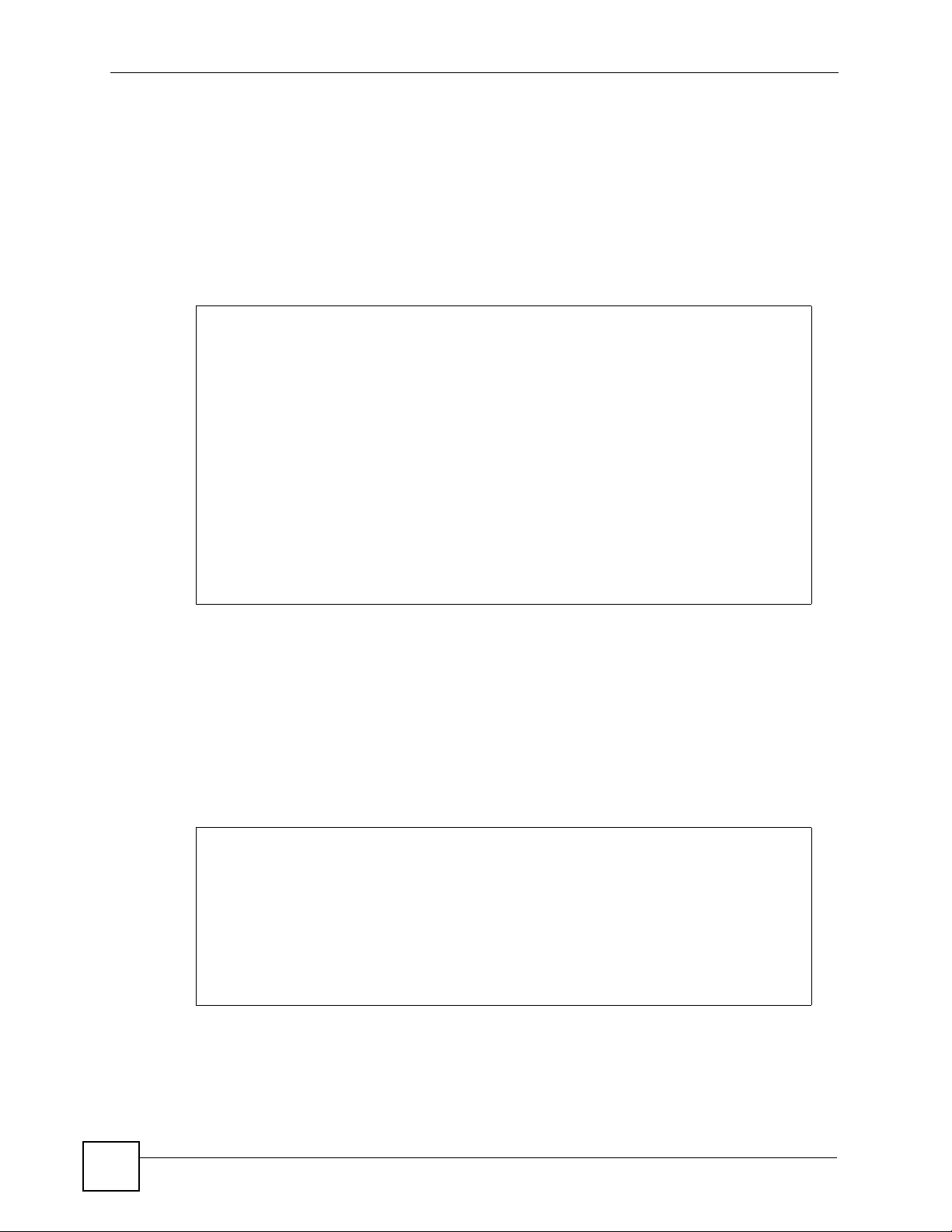
10.1 CFM Overview
The route between two users may go through aggregated switches, routers and/or DSLAMs
owned by independent organizations. A connectivity fault point generally takes time to
discover and impacts subscribers’ network access. IEEE 802.1ag is a Connectivity Fault
Management (CFM) specification which allows network administrators to identify and
manage connection faults in order to ease management and maintenance. Through discovery
and verification of the path, CFM can detect and analyze connectivity faults in bridged LANs.
The figure shown below is an example of a connection fault between switches in the service
provider’s network. CFM can be used to identify and management this kind of connection
problem.
Figure 1 Connectivity Fault Example
10.1.1 How CFM Works
CFM sends pro-active Connectivity Check (CC) packets between two CFM-aware devices in
the same MD (Maintenance Domain) network. An MA (Maintenance Association) defines a
VLAN and associated ports on the device under an MD level. In this MA, a port can be an
MEP (Maintenance End Point) port or an MIP (Maintenance Intermediate Point) port.
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
41
Page 42

Chapter 10 CFM Commands
C
(port 17, MIP)
(port 2, MEP)
(port 18, MIP)
B
(port 8, MEP)
A
• MEP port - has the ability to send pro-active connectivity check (CC) packets and get
other MEP port information from neighbor switches’ CC packets within an MA.
• MIP port - only forwards the CC packets.
CFM provides two tests to discover connectivity faults.
• Loopback test - similar to using “ping” in Microsoft DOS mode to check connectivity
from your computer to a host. In a loopback test, a MEP port sends a LBM (Loop Back
Message) to a MIP port and checks for an LBR (Loop Back Response). If no response is
received, there might be a connectivity fault between them.
• Link trace test - similar to using “tracert” in the Microsoft DOS mode to check
connectivity from your computer to a host. A link trace test provides additional
connectivity fault analysis to get more information on where the fault is. In a link trace
test, a MEP port sends a L TM (Link T race Message) to a MIP port and checks for an LTR
(Link Trace Response). If an MIP or MEP port does not respond to the source MEP, this
may indicate a fault. Administrators can take further action to check the fault and r esume
services according to the line connectivity status report.
An example is shown next. A user cannot access the Internet. To check the problem, the
administrator starts the link trace test from A which is an MEP port to B which is also an MEP
port. Each aggregation MIP port between aggregated devices responds to the L TM packets and
also forwards them to the next port. A fault occurs at port C. A discovers the fault since it only
gets the LTR packets from the ports before port C.
Figure 2 MIP and MEP Example
10.2 CFM Term Definition
This section lists the common term definition which appears in this chapter. Refer to User’s
Guide for more detailed information about CFM.
Table 27 CFM Term Definitions
TERM DESCRIPTION
CFM CFM (Connectivity Fault Ma nagement) is used to detect and analyze connectivity
faults in bridged LANs.
MD An MD (Maintena nce Domain) is part of a network, where CFM can be done. The
MA An MA (Maintenance Association) is a group of MEPs and identified by a VLAN
MD is identified by a level number and contains both MEPs and MIPs. The Switch
supports up to eight MD levels (0 ~ 7) in a network. You can create multiple MDs
on one MD level and multiple MA groups in one MD.
ID. One MA should belong to one and only one MD group.
42
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
Page 43

Chapter 10 CFM Commands
Table 27 CFM Term Definitions
TERM DESCRIPTION
MEP An MEP (Maintenance End Point) port has the abil ity to send and reply to the
CCMs, LBMs and LTMs. It also gets other MEP port information from neighbor
switches’ CCMs in an MA.
MIP An MIP (Maintenance Intermediate Point) port forwards the CCMs, LBMs, and
LTMs and replies the LBMs and LTMs by sending Loop Back Responses (LBRs)
and Link Trace Responses (LTRs).
Connectivity
Check
Loop Back Test Loop Back Test (LBT) checks if an MEP port receives its LBR (Loop Back
Link Trace Test Link Trace Test (LT T) provi des additional connectivity fault analysis to get more
Connectivity Check (CC) enables an MEP port sending Connectivity Check
Messages (CCMs) periodically to other MEP ports. An MEP port collects CCMs to
get other MEP information within an MA.
Response) from its target after it sends the LBM (Loop Back Message). If no
response is received, there might be a connectivity fault between them.
information on where the fault is. In the link trace test, MIP ports also send LTR
(Link Trace Response) to response the source MEP port’s LTM (Link Trace
Message). If an MIP or MEP port does not respond to the source MEP, this may
indicate a fault. Administrators can take further action to check and resume
services from the fault according to the line connectivity status report.
10.3 User Input Values
This section lists the common term definition appears in this chapter. Refer to User’ s Guide for
more detailed information about CFM.
Table 28 CFM command user input values
USER INPUT DESCRIPTION
mep-id This is the maintenance endpoint identifier (1~8191).
ma-index This is the maintenance association (MA) index number
md-index This is the maintenance domain (MD) index number
mac-address This is the remote maintenance endpoint’s MAC address or a
(1~4294967295).
(1~4294967295).
virtual MAC address assigned to a port.
A Switch has one or two MAC addresses only. If you do not use
virtual MAC addresses with CFM, all CFM ports will use the
Switch’s MAC address and appear as one port. If you want
unique CFM ports, you need to assign virtual MAC addresses. If
you use virtual MAC addresses, make sure that all virtual MAC
addresses are unique in both the Switch and the network to which
it belongs.
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
43
Page 44

Chapter 10 CFM Commands
10.4 Command Summary
The following section lists the commands for this feature.
Table 29 CFM Command Summary
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
clear ethernet cfm linktrace Clears the link trace database. E 13
clear ethernet cfm mep-ccmdb Clears the MEP CCM database. E 13
clear ethernet cfm mip-ccmdb Clears the MIP CCM database. E 13
clear ethernet cfm mep-defects Clears the MEP-defects database. E 13
ethernet cfm Enables CFM on the Switch. C 13
ethernet cfm loopback remote-mep
<mep-id> mep <mep-id> ma <ma-index>
md <md-index> [size <0-1500>][count
<1-1024>]
ethernet cfm loopback mac <mac-
address> mep <mep-id> ma <ma-index>
md <md-index> [size <0-1500>][count
<1-1024>]
ethernet cfm linktrace remote-mep
<mep-id> mep <mep-id> ma <ma-index>
md <md-index> [mip-ccmdb][[ttl
<ttl>]
ethernet cfm linktrace mac <mac-
address> mep <mep-id> ma <ma-index>
md <md-index> [mip-ccmdb][[ttl
<ttl
>]
Specifies the remote MEP ID, local MEP ID, MA index
and MD index to perform a loopback test.
This enables the MEP port (with the specified MEP ID) in
a specified CFM domain to send the LBMs (Loop Back
Messages) to a specified remote end point.
You can also define the packet size (from 0 to 1500
bytes) and how many times the Switch sends the LBMs.
Specifies the destination MAC address, local MEP ID,
MA index and MD index to perform a loopback test.
This enables the MEP port (with the specified MEP ID) in
a specified CFM domain to send the LBMs (Loop Back
Messages) to a specified remote end point.
You can also define the packet size (from 0 to 1500
bytes) and how many times the Switch sends the LBMs.
Specifies the remote MEP ID, local MEP ID, MA index
and MD index to perform a link trace test.
This enables the MEP port (with the specified MEP ID) in
a specified CFM domain to send the LTMs (Link Trace
Messages) to a specified remote end point.
mip-ccmdb: Specifies the MIP CCM DB, a database that
stores information (tuples of {Port, VID, MAC address})
about MEPs in the MD when receiving CCMs. The MIP
CCM DB is used for fault isolation, such as link trace and
loop back. An entry can remains in the MIP CCM DB for
at least 24 hours.
ttl: This is the time-to-live value (the number of
transmissions, 64 hops by default). Sets this to stop a
test once it exceeds the time duration without receiving
any response.
Specifies the destination MAC address, local MEP ID,
MA index and MD index to perform a link trace test.
This enables the MEP port (with the specified MEP ID) in
a specified CFM domain to send the LTMs (Link Trace
Messages) to a specified remote end point.
mip-ccmdb: Specifies the MIP CCM DB, a database that
stores information (tuples of {Port, VID, MAC address})
about MEPs in the MD when receiving CCMs. The MIP
CCM DB is used for fault isolation, such as link trace and
loop back. An entry can remains in the MIP CCM DB for
at least 24 hours.
ttl: This is the time-to-live value (the number of
transmissions, 64 hops by default). Sets this to stop a
test once it exceeds the time duration without receiving
any response.
E13
E13
E13
E13
44
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
Page 45

Chapter 10 CFM Commands
Table 29 CFM Command Summary (continued)
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
ethernet cfm ma <ma-index> format
<vid|string|integer> name <ma-name>
md <md-index> primary-vlan <1-4094>
Creates an MA (Maintenance Association) and defines
its VLAN ID under the MD. You can also define the
format which the Switch uses to send this MA information
in the domain (MD).
ma-name: Enters a VLAN ID, a descriptive name or a 2octet integer for the MA.
C13
Note: If you set the format to vid, the VLAN
ID should be the same as the VLAN ID
you use to identify the MA.
cc-interval
<100ms|1s|10s|1min|10min>
mhf-creation < none | default |
explicit>
id-permission < none | chassis
| management | chassismanagement>
exit Exits from the config-ma mode. C 13
remote-mep <mep-id> Sets a remote MEP in an MA. C 13
mep <mep-id> interface port-
channel <port> direction
<up|down> priority <0-7>
mep <mep-id> interface portchannel <port> direction
<up|down> priority <0-7>
inactive
mep <mep-id> interface portchannel <port> direction
<up|down> priority <0-7> ccenable
no remote-mep <mep-id> Dele tes a specified destination MEP. C 13
no mep <mep-id> Deletes a specified MEP. C 13
no mep <mep-id> inactive Enables an MEP . C 13
no mep <mep-id> cc-enable Disallows an MEP sending Connectivity Check
Sets how often an MEP sends a connectivity check
message (CCM).
Sets MHF (MIP Half Function).
Select none and no MIP can be created automatically for
this MA.
Select default to automatically create MIPs for this MA
and on the ports belonging to this MA’s VLAN when there
are no lower configured MD levels or there is an MEP at
the next lower configured MD level on the port.
Select explicit to automatically create MIPs for this
MA and on the ports belonging to this MA’s VLAN only
when there is an MEP at the next lower configured MD
level on the port.
Sets what’s to be included in the sender ID TLV (TypeLength-Value) transmitted by CFM packets.
Select none to not include the sender ID TLV.
Select chassis to include the chassis information.
Select management to include the management
information.
Select chassis-management to include both chassis
and management information.
Sets an MEP in an MA.
up|down: The traffic direction.
0-7: The priority value of the CCMs or LTMs transmitted
by the MEP. 1 is the lowest, then 2, 0 and 3 ~ 7.
Disables a specified MEP. C 13
Enables Connectivity Check (CC) to allow an MEP
sending Connectivity Check Messages (CCMs)
periodically to other MEPs.
Messages (CCMs) periodically to other MEPs.
C13
C13
C13
C13
C13
C13
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
45
Page 46

Chapter 10 CFM Commands
Table 29 CFM Command Summary (continued)
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
ethernet cfm md <md-index> format
<dns|mac|string> name <md-name>
level <0-7>
ethernet cfm management-addressdomain ip [<ip-addr>]
interface port-channel <port-list> Enters config-interface mode for configuring the specified
ethernet cfm virtual-mac <mac-
addr>
no ethernet cfm virtual-mac Removes the virtual MAC address(es) and sets the
no ethernet cfm Disables CFM on the Switch. C 13
no ethernet cfm md <md-index> Deletes the specified MD. C 13
no ethernet cfm ma <ma-index> md
<md-index>
no ethernet cfm management-address-
domain
show ethernet cfm linktrace Displays the CFM link trace database information. E 13
show ethernet cfm local Displays the detailed settings of the configured MD(s)
show ethernet cfm local stack Displays a list of all maintenance points, such as MIP
show ethernet cfm local stack mep Displays a list of the MEP(s). E 13
show ethernet cfm local stack mep
<mep-id> ma <ma-index> md <md-
index>
show ethernet cfm local stack mep
<mep-id> ma <ma-index> md <md-
index> mep-ccmdb [remote-mep <mepid
>]
show ethernet cfm local stack mip Displays a list of the MIP(s). E 13
show ethernet cfm local stack mip
mip-ccmdb
show ethernet cfm remote Displays a list of MA(s), MEP(s) and the remote MEP(s)
show ethernet cfm virtual-mac Displays all virtual MAC addresses. E 13
show ethernet cfm virtual-mac port
<port-list>
Creates an MD (Maintenance Domain) with the specified
name and level number.
md-name: Enters a domain name, MAC address or a
descriptive name for the MD.
Sets the Switch to carry the host name and management
IP address for the VLAN to which an MEP belongs or the
specified IP address in CFM packets.
This helps you to easily identify a remote MEP by its host
name and management IP address showed in the link
trace database and MEP-CCM database.
port(s).
Assigns a virtual MAC address(es) to the specified
port(s) so that each specified port can have its own MAC
address for CFM.
You cannot use the copy running-config
interface port-channel command to copy the
virtual MAC address from the specified port to other
ports.
port(s) to use the default system MAC address.
Deletes an MA from the specified MD. C 13
Sets the Switch to not carry the host name and
management IP address in CFM packets.
and MA(s).
and MEP.
Displays the specified MEP’s general, fault notification
generator, continuity-check, loopback and link trace
information.
Displays the specified MEP’s MEP-CCM database
information. Each MEP maintains an MEP CCM
database which stores information about remote MEPs in
the MA when receiving CCMs.
Displays the MIP-CCM database. E 13
under the configured MD(s).
Displays the MAC address(es) of the specified port(s). E 13
C13
C13
C13
C13
C13
C13
E13
E13
E13
E13
E13
46
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
Page 47

Chapter 10 CFM Commands
10.5 Command Examples
This example creates MD1 (with MD index 1 and level 1) and MA2 (with MA index 2 and
VLAN ID 2) under MD1 that defines a CFM domain.
sysname# config
sysname(config)# ethernet cfm md 1 format string name MD1 level 1
sysname(config)# ethernet cfm ma 2 format string name MA2 md 1 primaryvlan 2
sysname(config-ma)# exit
sysname(config)# exit
sysname# write memory
Remember to save new settings using the write memory command.
This example deletes MA2 (with MA index 2) from MD1 (with MD index 1).
sysname# config
sysname(config)# no ethernet cfm ma 2 md 1
sysname(config)# exit
sysname# write mem
This example creates MA3 (with MA index 3 and VLAN ID 123) under MD1, and associates
port 1 as an MEP port with MEP ID 301 in the specified CFM domain. This also sets MHF
(MIP half function) to default to have the Switch automatically create MIPs for this MA and
on the ports belonging to this MA's VLAN when there are no lower configured MD levels or
there is a MEP at the next lower configur ed MD level on the port. This also sets a remote MEP
in MA3.
sysname# config
sysname(config)# ethernet cfm ma 3 format string name MA3 md 1 primary-vlan
123
sysname(config-ma)# mep 301 interface port-channel 1 direction up priority 2
sysname(config-ma)# mep 301 interface port-channel 1 direction up priority 2
cc-enable
sysname(config-ma)# mhf-creation default
sysname(config-ma)# remote-mep 117
sysname(config-ma)# exit
sysname(config)# exit
sysname# write mem
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
47
Page 48

Chapter 10 CFM Commands
This example lists all CFM domains. In this example, only one MD ( MD1) is configured. The
MA3 with the associated MEP port 1 is under this MD1.
sysname# show ethernet cfm local
MD Index: 1
MD Name: MD1(string)
MD Level: 1
MA Index: 3
MA Name: MA3(string)
Primary Vlan: 123
CC Interval: 1000 millisecond(s)
MHF Creation: default
ID Permission: none
MEP:301 (ACTIVE ) Port:1 Direction:DOWN Priority:5 CC-Enable:FALSE
sysname#
This example starts a loopback test and displays the test result on the console.
sysname# ethernet cfm loopback remote-mep 2 mep 1 ma 1 md 1
Sending 5 Ethernet CFM Loopback messages to remote-mepid 2, timeout is 5
seconds .....
sysname# Loopback: Successful
Success rate is 100 percent, round-trip min/avg/max = 0/0/0 ms
sysname#
This example displays all neighbors’ MEP port information in the MIP-CCM databases.
sysname# show ethernet cfm local stack mip mip-ccmdb
MIP CCM DB
Port VID Source Address Retained
---- ---- ----------------- -------- 2 1 00:19:cb:00:00:04 0 hr(s)
7 1 00:19:cb:00:00:06 0 hr(s)
sysname#
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 30 show cfm-action mipccmdb
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Port Displays the number of the port on which this CCM was received.
VID Displays the MA VLAN ID of the last received CCM.
Source Address Displays the MAC address of the remote MEP.
Retained Displays how long an entry has been kept in the database.
48
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
Page 49

Chapter 10 CFM Commands
This example assigns a virtual MAC address to port 3 and displays the MAC addresses of the
ports 2 ~ 4. The assigned virtual MAC address should be unique in both the Switch and the
network to which it belongs.
sysname# config
sysname(config)# interface port-channel 3
sysname(config-interface)# ethernet cfm virtual-mac 00:19:cb:12:34:56
sysname(config-interface)# exit
sysname(config)# exit
sysname# show ethernet cfm virtual-mac port 2-4
Virtual MACPort MAC
---- ----------------2 00:19:cb:00:00:02
3 00:19:cb:12:34:56
4 00:19:cb:00:00:02
sysname#
This example sets the Switch to carry its host name and management IP address 192.168.100.1
in CFM packets.
sysname# config
sysname(config)# ethernet cfm management-address-domain ip 192.168.100.1
This example shows remote MEP database information. The remote MEP has been configured
to carry its host name and a specified IP address in CFM packets.
sysnam# show ethernet cfm remote
MD Index: 1
MD Name: customer123(string)
MD Level: 2
MA Index: 1
MA Name: 123(vid)
Primary Vlan: 123
MEP: 11
Remote MEP ID: 1
MAC Address: 00:19:cb:6f:91:5a
Chassis Id: MGS-3712F
Management Address: 192.168.100.1:161
sysname#
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
49
Page 50

CHAPTER 11
Classifier Commands
Use these commands to classify packets into traffic flows. After classifying traffic, policy
commands (Chapter 55 on page 214) can be used to ensure that a traffic flow gets the
requested treatment in the network.
11.1 Command Summary
The following section lists the commands for this feature.
Table 31 Command Summary: classifier
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
show classifier [<name>] Displays classifier configuration details. E 3
classifier <name> <[packet-
format <802.3untag|802.3tag|
EtherIIuntag|EtherIItag>]
[priority <0-7>] [vlan <vlan-
id>] [ethernet-type <ethernum|ip|ipx|arp|rarp|appletalk|d
ecnet|ipv6>] [source-mac <srcmac-addr>] [source-port <portnum>] [destination-mac <destmac-addr>] [dscp <0-63>] [ipv6-
dscp <0-63>] [ip-protocol
<protocol-num|tcp|udp|icmp|egp|
ospf|rsvp|igmp|igp|pim|ipsec>
[establish-only]] [ipv6-nextheader <protocol-
num|tcp|udp|icmpv6> [establishonly]] [source-ip <src-ip-addr>
[mask-bits <mask-bits>]] [ipv6source-ip <src-ipv6-addr>
[prefix-length <prefix-
length>]] [source-socket
<socket-num>] [destination-ip
<dest-ip-addr> [mask-bits <mask-
bits>]] [ipv6-destination-ip
<dest-ipv6-addr> [prefix-length
<prefix-length>]] [destination-
socket <socket-num>] [inactive]>
no classifier <name> Deletes the classifier.
no classifier <name> inactive Enables a classifier. C 13
Configures a classifier. Specify the parameters to identify the
traffic flow:
ethernet-type - enter one of the Ethernet types or type the
hexadecimal number that identifies an Ethernet type (see
Table 32 on page 51)
ip-protocol : enter one of the protocols or type the port
number that identifies the protocol (see Table 33 on page 51)
establish-only : enter this to identify only TCP packets
used to establish TCP connections.
source-socket : (for UDP or TCP protocols only) specify
the protocol port number.
destination-socket : (for UDP or TCP protocols only)
specify the protocol port number.
inactive : disables this classifier.
ipv6-next-header : enter an 8-bit next header in the IPv6
packet. The Next Header field is similar to the IPv4 Protocol
field. The IPv6 protocol number ranges from 1 to 255 (see
Table 34 on page 51).
See Chapter 35 on page 132 for more information about IPv6.
If you delete a classifier you cannot use policy rule relate d
information.
C13
C13
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
50
Page 51

Chapter 11 Classifier Commands
The following table shows some other common Ethernet types and the co rresponding protocol
number.
Table 32 Common Ethernet Types and Protocol Number
ETHERNET TYPE PROTOCOL NUMBER
IP ETHII 0800
X.75 Internet 0801
NBS Internet 0802
ECMA Internet 0803
Chaosnet 0804
X.25 Level 3 0805
XNS Compat 0807
Banyan Systems 0BAD
BBN Simnet 5208
IBM SNA 80D5
AppleTalk AARP 80F3
In an IPv4 packet header, the “Protocol” field identifies the next level protocol. The following
table shows some common IPv4 protocol types and the corresponding protocol number. Refer
to http://www.iana.org/assignments/protocol-numbers for a complete list.
Table 33 Common IPv4 Protocol Types and Protocol Numbers
PROTOCOL TYPE PROTOCOL NUMBER
ICMP 1
TCP 6
UDP 17
EGP 8
L2TP 115
In an IPv6 packet header, the "Next Header" field identifies the next level protocol. The
following table shows some common IPv6 Next Header values.
Table 34 Common IPv6 Next Header Values
PROTOCOL TYPE VALUE
IPv6 Hop-by-Hop Option 0
IPv4 4
TCP 6
UDP 17
IPv6 41
Routing Header for IPv6 43
Fragment Header for IPv6 44
Encapsulation Security Payload 50
Authentication Header 51
ICMP for IPv6 58
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
51
Page 52

Chapter 11 Classifier Commands
Table 34 Common IPv6 Next Header Values
PROTOCOL TYPE VALUE
No Next Header for IPv6 59
Destination Options for IPv6 60
11.2 Command Examples
This example creates a classifier for packets with a VLAN ID of 3. The resulting traffic flow is
identified by the name VLAN3. The policy command can use the name VLAN3 to apply
policy rules to this traffic flow. See the policy example in Chapter 55 on page 214.
sysname# config
sysname(config)# classifier VLAN3 vlan 3
sysname(config)# exit
sysname# show classifier
Index Active Name Rule
1 Yes VLAN3 VLAN = 3;
This example creates a classifier (Class1) for packets which have a source MAC address of
11:22:33:45:67:89 and are received on port 1. You can then use the policy command and the
name Class1 to apply policy rules to this traffic flow. See the policy example in Chapter 55 on
page 214.
sysname# config
sysname(config)# classifier Class1 source-mac 11:22:33:45:67:89 source-port
1
sysname(config)# exit
sysname# show classifier
Index Active Name Rule
1 Yes Class1 SrcMac = 11:22:33:45:67:89; S...
52
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
Page 53

CHAPTER 12
Cluster Commands
Use these commands to configure cluster mana gement.
12.1 Command Summary
The following section lists the commands for this feature.
Table 35 cluster Command Summary
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
show cluster Displays cluster management status. E 3
cluster <vlan-id> Enables clustering in the specified VLAN group. C 13
no cluster Disables cluster management on the Switch. C 13
cluster name <cluster name> Sets a descriptive name for the cluster.
<cluster name>: You may use up to 32 printable
characters (spaces are allowed).
show cluster candidates Displays the switches that are potential cluster members. The
cluster member <mac> password
<password>
show cluster member Displays the cluster member(s) and their running status. E 3
show cluster member config Displays the current cluster member(s). E 3
show cluster member mac <mac> Displays the running status of the cluster member(s). E 3
cluster rcommand <mac> Logs into the CLI of the specified cluster member. C 13
no cluster member <mac> Removes the cluster member. C 13
switches must be directly connected.
Adds the specified device to the cluster. You have to specify
the password of the device too.
C13
E3
C13
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
53
Page 54

Chapter 12 Cluster Commands
12.2 Command Examples
This example creates the cluster CManage in VLAN 1. Then, it looks at the current list of
candidates for membership in this cluster and adds two switches to cluster.
sysname# configure
sysname(config)# cluster 1
sysname(config)# cluster name CManage
sysname(config)# exit
sysname# show cluster candidates
Clustering Candidates:
Index Candidates(MAC/HostName/Model)
0 00:13:49:00:00:01/ES-2108PWR/ES-2108PWR
1 00:13:49:00:00:02/GS-3012/GS-3012
2 00:19:cb:00:00:02/ES-3124/ES-3124
sysname# configure
sysname(config)# cluster member 00:13:49:00:00:01 password 1234
sysname(config)# cluster member 00:13:49:00:00:02 password 1234
sysname(config)# exit
sysname# show cluster member
Clustering member status:
Index MACAddr Name Status
1 00:13:49:00:00:01 ES-2108PWR Online
2 00:13:49:00:00:02 GS-3012 Online
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 36 show cluster member
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Index This field displays an entry number for each member.
MACAddr This field displays the member’s MAC address.
Name This field displays the member’s system name.
Status This field displays the current status of the member in the cluster.
Online: The member is accessible.
Error: The member is connected but not accessible. For example, the
member’s password has changed, or the member was set as the manager
and so left the member list. This status also appears while the Switch
finishes adding a new member to the cluster.
Offline: The member is disconnected. It takes approximately 1.5 minutes
after the link goes down for this status to appear.
54
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
Page 55

Chapter 12 Cluster Commands
This example logs in to the CLI of member 00:13:49:00:00:01, looks at the current firmware
version on the member
Switch, logs out of the member’s CLI, and returns to the CLI of the
manager.
sysname# configure
sysname(config)# cluster rcommand 00:13:49:00:00:01
Connected to 127.0.0.2
Escape character is '^]'.
User name: admin
Password: ****
Copyright (c) 1994 - 2007 ZyXEL Communications Corp.
ES-2108PWR# show version
Current ZyNOS version: V3.80(ABS.0)b2 | 05/28/2007
ES-2108PWR# exit
Telnet session with remote host terminated.
Closed
sysname(config)#
This example looks at the current status of the Switch’s cluster.
sysname# show cluster
Cluster Status: Manager
VID: 1
Manager: 00:13:49:ae:fb:7a
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 37 show cluster
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Cluster Status This field displays the role of this Switch within the cluster.
Manager: This Switch is the device through which you manage the cluster
member switches.
Member: This Switch is managed by the specified manager.
None: This Switch is not in a cluster.
VID This field displays the VLAN ID used by the cluster.
Manager Thi s field displays the cluster manager’s MAC address.
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
55
Page 56

CHAPTER 13
Date and Time Commands
Use these commands to configure the date and time on the Switch.
13.1 Command Summary
The following table describes user-input values available in multiple commands for this
feature.
Table 38 time User-input Values
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
week Possible values (daylight-saving-time commands only): first, second,
day Possible values (daylight-saving-time commands only): Sunday,
month Possible values (daylight-saving-time commands only): January,
o’clock Possible values (daylight-saving-time commands only): 0-23
third, fourth, last.
Monday, Tuesday, ....
February, March, ....
The following section lists the commands for this feature.
Table 39 time Command Summary
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
show time Displays current system time and date. E 3
time <hour:min:sec> Sets the current time on the Switch.
hour: 0-23
min: 0-59
sec: 0-59
Note: If you configure Daylight Saving Time
after you configure the time, the Switch
will apply Daylight Saving Time.
time date <month/day/year> Sets the current date on the Switch.
month: 1-12
day: 1-31
year: 1970-2037
time timezone <-1200|...|1200> Selects the time difference between UTC (formerly
known as GMT) and your time zone.
time daylight-saving-time Enables daylight saving time. The current time is
updated if daylight saving time has started.
C13
C13
C13
C13
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
56
Page 57

Chapter 13 Date and Time Commands
Table 39 time Command Summary (continued)
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
time daylight-saving-time startdate <week> <day> <month> <o’clock>
time daylight-saving-time end-date
<week> <day> <month> <o’clock>
no time daylight-saving-time Disables daylight saving on the Switch. C 13
time daylight-saving-time help Provides more information about the specified command. C 13
Sets the day and time when Daylight Saving Time starts.
In most parts of the United States, Daylight Saving Time
starts on the second Sunday of March at 2 A.M. local
time. In the European Union, Daylight Saving Time starts
on the last Sunday of March at 1 A.M. GMT or UTC, so
the o’clock field depends on your time zone.
Sets the day and time when Daylight Saving Time ends.
In most parts of the United States, Daylight Saving Time
ends on the first Sunday of November at 2 A.M. local
time. In the European Union, Daylight Saving Time ends
on the last Sunday of October at 1 A.M. GMT or UTC, so
the o’clock field depends on your time zone.
C13
C13
Table 40 timesync Command Summary
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
show timesync Displays time server information. E 3
timesync server <ip> Sets the IP address of your time server. The Switch
synchronizes with the time server in the following
situations:
• When the Switch starts up.
• Every 24 hours after the Switch starts up.
• When the time server IP address or protocol is
updated.
timesync <daytime|time|ntp> Sets the time server protocol. You have to configure a
time server before you can specify the protocol.
no timesync Disables timeserver settings. C 13
C13
C13
13.2 Command Examples
This example sets the current date, current time, time zone, and daylight savings time.
sysname# configure
sysname(config)# time date 06/04/2007
sysname(config)# time timezone -600
sysname(config)# time daylight-saving-time
sysname(config)# time daylight-saving-time start-date second Sunday
--> March 2
sysname(config)# time daylight-saving-time end-date first Sunday
--> November 2
sysname(config)# time 13:24:00
sysname(config)# exit
sysname# show time
Current Time 13:24:03 (UTC-05:00 DST)
Current Date 2007-06-04
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
57
Page 58

Chapter 13 Date and Time Commands
This example looks at the current time server settings.
sysname# show timesync
Time Configuration
---------------------------- Time Zone :UTC -600
Time Sync Mode :USE_DAYTIME
Time Server IP Address :172.16.37.10
Time Server Sync Status:CONNECTING
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 41 show timesync
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Time Zone This field displays the time zone.
Time Sync Mode This field displays the time server protocol the Switch uses. It displays
Time Server IP Address This field displays the IP address of the time server.
Time Server Sync St atus This field displays the status of the connection with the time server.
NO_TIMESERVICE if the time server is disabled.
NONE: The time server is disabled.
CONNECTING: The Switch is trying to connect with the specified time
server.
OK: Synchronize with time server done.
FAIL: Synchronize with time server fail.
58
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
Page 59

CHAPTER 14
Data Center Bridging
Commands
At the time of writing, data center bridging can only be configured using commands on the
Switch.
14.1 Overview
A traditional Ethernet network is best-effort, that is, frames may be dropped due to network
congestion. FCoE (Fiber Channel over Ethernet) transparently encapsulates fiber channel
traffic into Ethernet, so that you don’t need separate fiber channel and Ethernet switches.
Data Center Bridging (DCB) enhances Ethernet technology to adapt to the FCoE. It supports
lossless Ethernet traffic (no frames discarded when there is network congestion) and can
allocate bandwidth for different traffic classes, based on IEEE802.1p priority with a
guaranteed minimum bandwidth. LAN traffic (large number of flows and not latencysensitive), SAN traffic (Storage Area Network, large packet sizes and requires lossless
performance), and IPC traffic (Inter-Process Communication, latency-sensitive messages) can
share the same physical connection while still having their own priority and guaranteed
minimum bandwidth.
You should configure DCB on any port that has both Ethernet and fiber channel traffic.
14.1.1 PFC, ETS, and DCBX Standards
DCB may use PFC, ETS, application priority and DCBX to adapt to the FCoE.
• PFC (Priority-based Flow Control, IEEE 802.1Qbb -2011) is a flow control mechanism
that uses a PAUSE frame to suspend traffic of a certain priority rather than drop it when
there is network congestion (lossless). If an outgoing (egress) port buffer is almost full, the
Switch transmits a PAUSE frame to the sender who just transmitted traffic requesting it to
stop sending traffic of a certain priority to that port. For example, say outgoing port 8 is
receiving too much traffic of priorities 3-6 from port 1. Then if port 1 is configured with
PFC priorities 3-6, port 1 can request the sender to suspend traffic with priorities 3-6.
Similarly , if the outgoing (egress) port 8 receives a PAUSE frame with PFC priorities 0-1,
then if port 8 is configured with PFC, it can suspend sending traffic with PFC priorities 0-
1.
• ETS (Enhanced Transmission Selection, IEEE 802.1Qaz -2011) is used to allocate
bandwidth for different traffic classes, based on IEEE802.1p priority (0 to 7, allowing for
eight types of traffic) with a guaranteed minimum bandwidth.
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
59
Page 60

Chapter 14 Data Center Bridging Commands
• Application priority is used to globally assign a priority to all FCoE traffic on the Switch.
• DCBX (Data Center Bridging capability eXchange, IEEE 802.1Qaz -2011) uses LLDP
(Link Layer Discovery Protocol) to advertize PFC, ETS and application priority
information between switches. PFC information should be consistent between connected
switches, so PFC can be configured automatically using DCBX.
The following table describes user-input values available in multiple commands for this
feature.
Table 42 dcb User-input Values
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
<priority-list> Possible values range from 0 to 7.
<port-list> Possible values range from 1 to the number of ports on your Switch.
<id> Possible values for traffic class ID range from 1 to 100. 0 is a default traffic
class and cannot be modified or deleted.
<tc-idN> The traffic class ID for priority N (0 to 7). The traffic class ID range is from 1 to
100.
<name> Up to 32 printable ASCII characters. Names with spaces must be enclosed in
<weight> Possible values range from 1 to 127 for unicast or multicast weights.
quotes. For example, “My Class”.
Possible values range from 1 to 100 for WFQ traffic class weight.
14.2 Command Summary
This section shows the commands and examples for PFC, ETS, Application Priority and
DCBX.
14.2.1 PFC
PFC should be configured the same on connected switch ports. If DCBX is used, then one
switch port must be configured to accept network configuration from the peer switch port
(auto). If both switch ports are configured to accept configuration (auto on both switch
ports), then the configuration of the switch port with the lowest MAC address hex value sum is
used.
The following table lists the commands for this feature.
Table 43 priority-flow-control Command Summary
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
interface port-channel <port-list> Enters config-interface mode for the specified port(s). C 13
priority-flow-control Enables PFC on the specified port(s). C 13
no priority-flow-control Disables PFC on the specified port(s). C 13
priority-flow-control auto Sets the port to accept PFC configuration from the
priority-flow-control priority
<priority-list>
no priority-flow-control
priority
connected Switch port.
Sets the priority value(s) on the specified port(s). C 13
Clears the priority value(s) on the specified port(s). C 13
C13
60
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
Page 61

Chapter 14 Data Center Bridging Commands
Table 43 priority-flow-control Command Summary (continued)
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
show priority-flow-control Displays PFC settings. E 3
show priority-flow-control
statistics interface port-channel
<port-list>
clear priority-flow-control
statistics interface port-channel
<port-list>
Displays PFC statistics on the specified port(s). E 3
Clears PFC statistics on the specified port(s). E 13
14.2.2 PFC Command Examples
In the following example, PFC on switch A, port 1, is set to auto, so that it can accept the
priority configuration from the peer switch B. If switch A did not receive PFC PDU from
switch B, then priority 2, will be used by switch A.
switchA# configure
switchA(config)# interface port-channel 1
switchA(config-interface)# priority-flow-control auto
switchA(config-interface)# priority-flow-control priority 2
switchB# configure
switchB(config)# interface port-channel 1
switchB(config-interface)# priority-flow-control
switchB(config-interface)# priority-flow-control priority 3-5
Use the show command to see the PFC configuration. Operation-Priority shows whether
switch A is using switch B’s configured priorities or not.
In the following example, Switch A is using Switch B’s configured priorities.
switchA# show priority-flow-control
Port Admin Operation Admin-Priority Operation-Priority
-------------------------------------------------------------------1 Auto On 2 3-5
In the following example, Switch A is NOT using Switch B’s configured priorities.
switchA# show priority-flow-control
Port Admin Operation Admin-Priority Operation-Priority
------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 Auto On 2 2
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
61
Page 62

Chapter 14 Data Center Bridging Commands
This is an example showing how many pause frames of certain priorities were temporarily
stopped (transmitted or received) on port 1.
sysname# show priority-flow-control statistics interface port-channel 1
Port Number: 1
PFC Tx
Priority 0: 0
Priority 1: 0
Priority 2: 0
Priority 3: 0
Priority 4: 0
Priority 5: 0
Priority 6: 0
Priority 7: 0
PFC Rx
Priority 0: 0
Priority 1: 0
Priority 2: 0
Priority 3: 0
Priority 4: 0
Priority 5: 0
Priority 6: 0
Priority 7: 0
sysname#
14.2.3 ETS
An IEEE 802.1p priority is assigned to a traffic class with guaranteed minimum bandwidth. A
traffic class can use SP (Strict Priority) or WFQ (Weighted Fair Queue) queuing method.
Available link bandwidth is reserved first for SP traffic. The guaranteed minimum bandwidth
for non-SP traffic (WFQ) is its weight value by remaining available bandwidth. If a non-strictpriority-traffic-class does not consume its allocated bandwidth, other non-strict-prioritytraffic-classes can share the unused bandwidth according to the weight ratio.
14.2.3.1 Notes on ETS
• Priority 0 does not mean the highest or lowest priority. Priority level of importance is
mapped to a queue level (with queue level 0, the lowest importance).
• You don’t automatically configure ETS using DCBX negotiation. ETS is configured
manually on each Switch.
• All priorities are mapped to traffic class ID 0 by default.
• The default traffic class (named Default) has ID 0, and is an SP traffic-class. It cannot
be modified or deleted.
• You can create up to 100 traffic class profiles, with ID from 1 to 100.
• The weight range of WFQ traffic-class can be from 1 to 100.
• Bandwidth can also be prioritized depending on whether traffic is unicast traffic or nonunicast (broadcast, multicast, DLF) traffic. For example, 100:50 means twice as much
unicast traffic to non-unicast traffic is allowed when there is network congestion. The
weight ranges of unicast and non-unicast traffic can be from 1 to 127.
62
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
Page 63

Chapter 14 Data Center Bridging Commands
The following table lists the commands for this feature.
Table 44 ets Command Summary
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
traffic-class <id> scheduler <sp |
ets <weight>> [name <name>]
no traffic-class <id> Delete s the SP/WFQ traffic class with specified ID. C 13
show traffic-class Shows a summary of traffic class(es) created on the
interface port-channel <port-list> Enters config-interface mode for the specified port(s). C 13
ets Enable Enhanced Transmission Selection (ETS) queuing
ets traffic-class binding <tcid0> <tc-id1> <tc-id2> <tc-id3>
<tc-id4> <tc-id5> <tc-id6> <tcid7>
no ets traffic-class binding Resets traffic class binding priorities to default settings
unicast-nonunicast-weight
<weight> <weight>
Creates a WFQ or SP traffic class with ID, weight and
(optional) name.
Switch.
method. See Chapter 62 on page 236 for other queuing
methods.
Binds priorities to a traffic class(es) on the specified
port(s).
on the specified port(s).
Sets the unicast to non-unicast traffic weight ratio on the
specified port(s).
C13
E3
C13
C13
C13
C13
14.2.4 ETS Command Example 1
This is an example where the non-editable default traffic class, ID 0, uses SP queuing. LAN
and SAN traffic uses WFQ queuing with equal weighting of 50 each.
Table 45 ETS Example Traffic Classes
TRAFFIC CLASS ID GUARANTEED BANDWIDTH NAME
0SPDefault
1 50 SAN
250LAN
The guaranteed minimum bandwidth for both SAN and LAN traffic is 2.5Gbps with a link
bandwidth of 10Gbps.
Table 46 ETS Example Traffic Bandwidths
NAME
Default 5 5 (SP) 5
SAN 3 (10-5) * (50/(50+50)) =
LAN 4 (10-5) * (50/(50+50)) =
Create and name traffic class IDs, with weights for the non-SP traffic type.
INCOMING TRAFFIC
BANDWIDTH (GBPS)
GUARANTEED
MINIMUM BANDWIDTH
2.5
2.5
OUTGOING TRAFFIC
BANDWIDTH (GBPS)
2.5
2.5
sysname# configure
sysname(config)# traffic-class 1 scheduler ets 50 name LAN
sysname(config)# traffic-class 2 scheduler ets 50 name SAN
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
63
Page 64

Chapter 14 Data Center Bridging Commands
This command shows traffic class.
switch# show traffic-class
Traffic Class Profile Configuration:
Traffic Class ID Scheduler Weight Name
---------------- --------- ------ ------------------------------ 0 sp - Default
1 ets 50 LAN
2 ets 50 SAN
Next, configure a port for traffic class(es) and bind priorities to traffic classes on a port. In the
next example, we configure port 1 and bind priorities 0, 1 and 2 to traffic class 2 (LAN), 3, 4,
5 and 6 to class 1 (SAN) and 7 to class 0, the default traffic class.
Table 47 ETS Example Priority Traffic Class ID Mapping
PRIORITY TRAFFIC CLASS ID NAME
02LAN
12LAN
22LAN
3 1 SAN
4 1 SAN
5 1 SAN
6 1 SAN
7 0 Default
sysname(config)# interface port-channel 1
sysname(config-interface)# ets
sysname(config-interface)# ets traffic-class binding 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 0
sysname(config-interface)# unicast-nonunicast-weight 100 100
sysname(config-interface)# exit
14.2.5 Application Priority
Use the application priority command to assign a priority to all FCoE traffic on a switch.
The following table lists the commands for this feature.
Table 48 application priority Command Summary
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
lldp dcbx application <ethertype><fcoe> priority <0-7>
no lldp dcbx application <ethertype > <fcoe>
Assigns the specified priority value to all FCoE traffic on
the Switch.
Clears priority value for all FCoE traffic on the Switch. C 13
C13
64
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
Page 65

Chapter 14 Data Center Bridging Commands
14.2.6 Application Priority Command Examples
In the following example, all FCoE traffic on the switch is assigned with priority 3.
switchA# configure
switchA(config)# lldp dcbx application ether-type fcoe priority 3
Application priority can then be used in conjunction with ETS and PFC as shown in the
following examples.
This is an application priority command example with PFC.
switchA(config)# interface port-channel 5
switchA(config-interface)# priority-flow-control
switchA(config-interface)# priority-flow-control priority 3
switchB(config)# interface port-channel 6
switchB(config-interface)# priority-flow-control
switchB(config-interface)# priority-flow-control priority 3
This is an application priority command example with ETS.
• Default traffic class 0 with strict priority for priorities 0, 1, 2, 6, 7
• Traffic class 3 (for legacy Ethernet traffic): Guarantee bandwidth 40% for priority 4, 5
• Traffic class 4 (for FCoE traffic): Guarantee bandwidth 60% for priority 3
• Unicast to Non-Unicast weight ratio is 100:100
Table 49 ETS Example 2 Traffic Classes
PRIORITY TRAFFIC CLASS ID NAME
0 0 Default
1 0 Default
2 0 Default
34 FCoE
4 3 Ethernet
5 3 Ethernet
6 0 Default
7 0 Default
sysname# configure
sysname(config)# traffic-class 3 scheduler ets 40 name ethernet
sysname (config)# traffic-class 4 scheduler ets 60 name fcoe
sysname (config)# interface port-channel 6
sysname (config-interface)# ets
sysname (config-interface)# ets traffic-class binding 0 0 0 4 3 3 0 0
sysname (config-interface)# unicast-nonunicast-weight 100 100
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
65
Page 66

Chapter 14 Data Center Bridging Commands
14.2.7 DCBX
DCBX uses LLDP (Link Layer Discovery Protocol) to exchange PFC, ETS and application
priority information between switches. PFC information should be consistent between
switches, so this can be configured automatically using DCBX.
See Chapter 37 on page 158 for more information on LLDP.
In order for switches to exchange information, they must send their type-length values (TL Vs)
in order to be able to read each other’s information.
The following table lists the commands for this feature.
Table 50 dcbx Command Summary
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
interface port-channel <port-list> Enters config-interface mode for the specified port(s). C 13
lldp org-specific-tlv dot1
dcbx-ets-configuration
lldp org-specific-tlv dot1
dcbx-pfc-configuration
lldp org-specific-tlv dot1
dcbx-application-priority
Enables the sending of ETS TLVs on the specified
port(s).
Enables the sending of PFC TLVs on the specified
port(s).
Enables the sending of application priority TLVs on the
specified port(s).
C13
C13
C13
This is a DCBX command example.
sysname# configure
sysname(config)# lldp
interface port-channel 2
sysname(config-interface)# lldp admin-status tx-rx
sysname(config-interface)# lldp org-specific-tlv dot1 dcbx-etsconfiguration
sysname(config-interface)# lldp org-specific-tlv dot1 dcbx-pfcconfiguration
sysname(config-interface)# lldp org-specific-tlv dot1 dcbx-applicationpriority
sysname(config-interface)#exit
sysname(config)# exit
sysname#
See Chapter 37 on page 158 for LLDP command examples.
66
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
Page 67

CHAPTER 15
DHCP Commands
Use these commands to configure DHCP features on the Switch.
• Use the dhcp option commands to configure DHCP Option 82 profiles.
• Use the dhcp relay commands to configure DHCP relay for specific VLAN.
• Use the dhcp smart-relay commands to configure DHCP relay for all broadcast
domains.
• Use the dhcp server commands to configure the Switch as a DHCP server. (This
command is available on a layer 3
15.1 Command Summary
The following section lists the commands for this feature.
Switch only.)
Table 51 dhcp option Command Summary
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
dhcp option profile <name>
[ circuit-id [slot-port] [vlan]
[hostname] [string <string>] ] [
remote-id [mac] [string
<string>] ]
no dhcp option profile <name> Deletes the specified DHCPv4 option 82 profile. C 1 3
show dhcp option profile Displays DHCP option 82 profile settings. E 3
Table 52 dhcp relay Command Summary
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
show dhcp relay <vlan-id> Displays DHCP relay settings for the specified VLAN. E 3
dhcp relay <vlan-id> helper-
address <remote-dhcp-server1>
[<remote-dhcp-server2>]
[<remote-dhcp-server3>]
[option] [information]
Creates a DHCPv4 option 82 profile. C 13
Enables DHCP relay on the specified VLAN and sets the IP
address of up to 3 DHCP servers. Optionally, sets the Switch
to add relay agent information and system name.
Note: You have to configure the VLAN before you
configure a DHCP relay for the VLAN. You
have to disable dhcp smart-relay
before you can enable dhcp relay.
C13
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
67
Page 68

Chapter 15 DHCP Commands
Table 52 dhcp relay Command Summary (continued)
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
dhcp relay <vlan-id> helperaddress <remote-dhcp-server1>
[<remote-dhcp-server2>]
[<remote-dhcp-server3>] [option
profile <name>]
Enables DHCP relay on the specified VLAN and sets the IP
address of up to 3 DHCP servers. Optionally, specify a predefined DHCP option 82 profile that the Switch applies to all
ports in this VLAN.
C13
Note: You have to configure the VLAN before you
configure a DHCP relay for the VLAN. You
have to disable dhcp smart-relay
before you can enable dhcp relay.
dhcp relay <vlan-id> interface
port-channel <port-list> option
profile <name>
no dhcp relay <vlan-id> Disables DHCP relay. C 13
no dhcp relay <vlan-id>
information
no dhcp relay <vlan-id>
interface port-channel <port-
list> option
no dhcp relay <vlan-id> option Disables the relay agent information option 82. C 13
Specifies a pre-defined DHCP option 82 profile that the
Switch applies to the specified port(s) in this VLAN. The
Switch adds the Circuit ID sub-option and/or Remote ID suboption specified in the profile to DHCP requests that it relays
to a DHCP server.
System name is not appended to option 82 information field. C 13
Sets the Switch to not apply a DHCP option 82 profile to the
specified port(s) in this VLAN.
C13
C13
Table 53 dhcp relay-broadcast Command Summary
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
dhcp relay-broadcast The broadcast behavior of DHCP packets will not be
terminated by the Switch.
no dhcp relay-broadcast The Switch terminates the broadcast behavior of DHCP
packets.
C13
C13
Table 54 dhcp smart-relay Command Summary
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
show dhcp smart-relay Displays global DHCP relay settings. E 3
dhcp smart-relay Enables DHCP relay for all broadcast domains on the Switch.
C13
Note: You have to disable dhcp relay before
you can enable dhcp smart-relay.
no dhcp smart-relay Disables global DHCP relay settings. C 13
dhcp smart-relay helper-address
<remote-dhcp-server1> [<remote-
dhcp-server2>] [<remote-dhcpserver3>]
dhcp smart-relay information Allows the Switch to add system name to agent information. C 13
no dhcp smart-relay information System name is not appended to option 82 information field
Sets the IP addresses of up to 3 DHCP servers. C 13
C13
for global dhcp settings.
68
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
Page 69

Chapter 15 DHCP Commands
Table 54 dhcp smart-relay Command Summary (continued)
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
dhcp smart-relay interface portchannel <port-list> option
profile <name>
Specifies a pre-defined DHCP option 82 profile that the
Switch applies to the specified port(s).
C13
Note: The profile you specify here has priority over
the one you set using the dhcp smart-
relay option profile <name>
command.
dhcp smart-relay option Allows the Switch to add DHCP relay agent information. C 13
dhcp smart-relay option profile
<name>
no dhcp smart-relay interface
port-channel <port-list>
no dhcp smart-relay option Disables the relay agent information option 82 for global dhcp
Table 55 dhcp server Command Summary
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
dhcp server <vlan-id> startingaddress <ip-addr> <subnet-mask>
size-of-client-ip-pool <1-253>
dhcp server <vlan-id> startingaddress <ip-addr> <subnet-mask>
size-of-client-ip-pool <1-253>
[default-gateway <ip-addr>]
[primary-dns <ip-addr>]
[secondary-dns <ip-addr>]
no dhcp server <vlan-id> Disables DHCP server for the specified VLAN. C 13
no dhcp server <vlan-id>
default-gateway
no dhcp server <vlan-id>
primary-dns
no dhcp server <vlan-id>
secondary-dns
show dhcp server Displays DHCP server settings. E 13
show dhcp server <vlan-id> Displays DHCP server settings in a specified VLAN. E 13
Specifies a pre-defined DHCPv4 option 82 profile that the
Switch applies to all ports. The Switch adds the Circuit ID
sub-option and/or Remote ID sub-option specified in the
profile to DHCP requests that it relays to a DHCP server.
Sets the Switch to not apply a DHCP option 82 profile to the
specified port(s).
settings.
Enables DHCP server for the specified VLAN and specifies
the TCP/IP configuration details to send to DHCP clients.
Enables DHCP server for the specified VLAN and specifies
the TCP/IP configuration details to send to DHCP clients.
Including default gateway IP address and DNS server
information.
Disables DHCP server default gateway settings. C 13
Disables DHCP primary DNS server settings. C 13
Disables DHCP server secondary DNS settings. C 13
C13
C13
C13
C13
C13
15.2 Command Examples
In this example, the Switch relays DHCP requests for the VLAN1 and VLAN2 domains.
There is only one DHCP server for DHCP clients in both domains.
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
69
Page 70

Chapter 15 DHCP Commands
VLAN1
VLAN2
192.168.1.100
DHCP Server:
VLAN 1
VLAN 2
DHCP:
192.168.1.100
DHCP:
172.16.10.100
Figure 3 Example: Global DHCP Relay
This example shows how to configure the Switch for this configuration. DHCP relay agent
information option 82 is also enabled.
sysname# configure
sysname(config)# dhcp smart-relay
sysname(config)# dhcp smart-relay helper-address 192.168.1.100
sysname(config)# dhcp smart-relay option
sysname(config)# exit
sysname# show dhcp smart-relay
DHCP Relay Agent Configuration
Active: Yes
Remote DHCP Server 1:192.168.1.100
Remote DHCP Server 2: 0.0.0.0
Remote DHCP Server 3: 0.0.0.0
Option82: Enable Option82Inf: Disable
In this example, there are two VLANs (VIDs 1 and 2) in a campus network. Two DHCP
servers are installed to serve each VLAN. The Switch forwards DHCP requests from the
dormitory rooms (VLAN 1) to the DHCP server with IP address 192.168.1.100. DHCP
requests from the academic buildings (VLAN 2) are sent to the other DHCP server with IP
address 172.16.10.100.
Figure 4 Example: DHCP Relay for Two VLANs
70
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
Page 71

Chapter 15 DHCP Commands
VLAN 1
VLAN 2
DHCP Pool:
192.168.1.100-192.168.1.200
DHCP Pool:
172.16.1.30-172.16.1.130
This example shows how to configure these DHCP servers. The VLANs are already
configured.
sysname# configure
sysname(config)# dhcp relay 1 helper-address 192.168.1.100
sysname(config)# dhcp relay 2 helper-address 172.16.10.100
sysname(config)# exit
In this example, the Switch is a DHCP server for clients on VLAN 1 and VLAN 2. The DHCP
clients in VLAN 1 are assigned IP addresses in the range 192.168.1.100 to 192.168.1.200 and
clients on VLAN 2 are assigned IP addresses in the range 172.16.1.30 to 172.16.1.130.
Figure 5 Example: DHCP Relay for Two VLANs
This example shows how to configure the DHCP server for VLAN 1 with the configuration
shown in Figure 5 on page 71. It also provides the DHCP clients with the IP address of the
default gateway and the DNS server.
sysname# configure
sysname(config)# dhcp server 1 starting-address 192.168.1.100
255.255.255.0 size-of-client-ip-pool 100 default-gateway 192.168.1.1
primary-dns 192.168.5.1
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
71
Page 72

CHAPTER 16
DHCP Snooping & DHCP VLAN
Commands
Use the dhcp snooping commands to configure the DHCP snooping on the Switch and the
dhcp vlan commands to specify a DHCP VLAN on your network. DHCP snooping filters
unauthorized DHCP packets on the network and builds the binding table dynamically.
16.1 Command Summary
The following section lists the commands for this feature.
Table 56 dhcp snooping Command Summary
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
show dhcp snooping Displays DHCP snooping configuration on the Switch. E 3
show dhcp snooping binding Displays the DHCP binding table. E 3
show dhcp snooping database Displays DHCP snooping database update statistics and
settings.
show dhcp snooping database
detail
show dhcp snooping option [vlan
<vlan-list>][interface <port-
list>]
dhcp snooping Enables DHCP Snooping on the Switch. C 13
no dhcp snooping Disables DHCP Snooping on the Switch. C 13
dhcp snooping database <tftp://
host/filename>
no dhcp snooping database Removes the location of the DHCP snooping database. C 13
dhcp snooping database timeout
<seconds>
no dhcp snooping database
timeout
dhcp snooping database writedelay <seconds>
Displays DHCP snooping database update statistics in full
detail form.
Displays the DHCP option 82 profile that the Switch applies to
ports in the specified VLAN or to the specified port(s).
Specifies the location of the DHCP snooping database. The
location should be expressed like this: tftp://{domain name
or IP address}/directory, if applicable/file name; for
example, tftp://192.168.10.1/database.txt.
Specifies how long (10-65535 seconds) the Switch tries to
complete a specific update in the DHCP snooping database
before it gives up.
Resets how long (10-65535 seconds) the Switch tries to
complete a specific update in the DHCP snooping database
before it gives up to the default value (300).
Specifies how long (10-65535 seconds) the Switch waits to
update the DHCP snooping database the first time the current
bindings change after an update.
E3
E3
E3
C13
C13
C13
C13
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
72
Page 73

Chapter 16 DHCP Snooping & DHCP VLAN Commands
Table 56 dhcp snooping Command Summary (continued)
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
no dhcp snooping database writedelay
dhcp snooping vlan <vlan-list> Specifies the VLAN IDs for VLANs you want to enable DHCP
no dhcp snooping vlan <vlan-
list>
dhcp snooping vlan <vlan-list>
information
no dhcp snooping vlan <vlan-
list> information
dhcp snooping vlan <vlan-list>
interface port-channel <port-
list> option profile <name>
no dhcp snooping vlan <vlan-
list> interface port-channel
<port-list> option
dhcp snooping vlan <vlan-list>
option
no dhcp snooping vlan <vlan-
list> option
dhcp snooping vlan <vlan-list>
option profile <name>
no dhcp snooping vlan <vlan-
list> option
clear dhcp snooping database
statistics
renew dhcp snooping database Loads dynamic bindings from the default DHCP snooping
renew dhcp snooping database
<tftp://host/filename>
interface port-channel <port-
list>
dhcp snooping trust Sets this port as a trusted DHCP snooping port. Trusted ports
dhcp snooping limit rate
<pps>
no dhcp snooping trust Disables this port from being a trusted port for DHCP
no dhcp snooping limit rate Resets the DHCP snooping rate to the default (0). C 13
Resets how long (10-65535 seconds) the Switch waits to
update the DHCP snooping database the first time the current
bindings change after an update to the default value (300).
snooping on.
Specifies the VLAN IDs for VLANs you want to disable DHCP
snooping on.
Sets the Switch to add the system name to DHCP requests
that it broadcasts to the DHCP VLAN, if specified, or VLAN.
Sets the Switch to not add the system name to DHCP
requests that it broadcasts to the DHCP VLAN, if specified, or
VLAN.
Specifies a pre-defined DHCP option 82 profile that the
Switch applies to the specified port(s) in the specified VLAN.
Sets the Switch to not apply a DHCP option 82 profile to the
specified port(s).
Sets the Switch to add the slot number, port number and
VLAN ID to DHCP requests that it broadcasts to the DHCP
VLAN, if specified, or VLAN.
Sets the Switch to not add the slot number, port number and
VLAN ID to DHCP requests that it broadcasts to the DHCP
VLAN, if specified, or VLAN.
Specifies a pre-defined DHCP option 82 profile that the
Switch applies to all ports in the specified VLAN.
Sets the Switch to not apply a DHCP option 82 profile to all
ports in the specified VLAN.
Delete all statistics records of DHCP requests going through
the Switch.
database.
Loads dynamic bindings from the specified DHCP snooping
database.
Enables a port or a list of ports for configuration. C 13
are connected to DHCP servers or other switches, and the
Switch discards DHCP packets from trusted ports only if the
rate at which DHCP packets arrive is too high.
Sets the maximum rate in packets per second (pps) that
DHCP packets are allowed to arrive at a trusted DHCP
snooping port.
snooping.
C13
C13
C13
C13
C13
C13
C13
C13
C13
C13
C13
E13
E13
E13
C13
C13
C13
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
73
Page 74

Chapter 16 DHCP Snooping & DHCP VLAN Commands
The following table describes the dhcp-vlan commands.
Table 57 dhcp-vlan Command Summary
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
dhcp dhcp-vlan <vlan-id> Specifies the VLAN ID of the DHCP VLAN. C 13
no dhcp dhcp-vlan Disables DHCP VLAN on the Switch. C 13
16.2 Command Examples
This example:
• Enables DHCP snooping Switch.
• Sets up an external DHCP snooping database on a network server with IP address
172.16.37.17.
• Enables DHCP snooping on VLANs 1,2,3,200 and 300.
• Sets the Switch to add the slot number, port number and VLAN ID to DHCP requests that
it broadcasts to the DHCP VLAN.
• Sets ports 1 - 5 as DHCP snooping trusted ports.
• Sets the maximum number of DHCP packets that can be received on ports 1 - 5 to 100
packets per second.
• Configures a DHCP VLAN with a VLAN ID 300.
74
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
Page 75

Chapter 16 DHCP Snooping & DHCP VLAN Commands
• Displays DHCP snooping configuration details.
sysname(config)# dhcp snooping
sysname(config)# dhcp snooping database tftp://172.16.37.17/
snoopdata.txt
sysname(config)# dhcp snooping vlan 1,2,3,200,300
sysname(config)# dhcp snooping vlan 1,2,3,200,300 option
sysname(config)# interface port-channel 1-5
sysname(config-interface)# dhcp snooping trust
sysname(config-interface)# dhcp snooping limit rate 100
sysname(config-interface)# exit
sysname(config)# dhcp dhcp-vlan 300
sysname(config)# exit
sysname# show dhcp snooping
Switch DHCP snooping is enabled
DHCP Snooping is configured on the following VLANs:
1-3,200,300
Option 82 is configured on the following VLANs:
1-3,200,300
Appending system name is configured on the following VLANs:
DHCP VLAN is enabled on VLAN 300
Interface Trusted Rate Limit (pps)
--------- ------- --------------- 1 yes 100
2 yes 100
3 yes 100
4 yes 100
5 yes 100
6 no unlimited
7 no unlimited
8 no unlimited
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
75
Page 76

CHAPTER 17
DiffServ Commands
Use these commands to configure Di fferentiated Services (DiffServ) on the Switch.
17.1 Command Summary
The following section lists the commands for this feature.
Table 58 diffserv Command Summary
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
show diffserv Displays general DiffServ settings. E 3
diffserv Enables DiffServ on the Switch. C 13
no diffserv Disables DiffServ on the Switch. C 13
diffserv dscp <0-63> priority
<0-7>
interface port-channel <port-
list>
diffserv Enables DiffServ on the port(s). C 13
no diffserv Disables DiffServ on the port(s). C 13
Sets the DSCP-to-IEEE 802.1q mappings. C 13
Enters config-interface mode for the specified port(s). C 13
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
76
Page 77

CHAPTER 18
Display Commands
Use these commands to display configuration information.
18.1 Command Summary
The following section lists the commands for this feature.
Table 59 display Command Summary
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
display user <[system][snmp]> Displays all or specific user account information in the
configuration file.
system: Displays system account information, such as
admin, enable or login username and password.
snmp: Displays SNMP user account information.
no display user <[system][snmp]> Hide all or specific user account information in the
configuration file.
display aaa
<[authentication][authorization][s
erver]>
no display aaa
<[authentication][authorization][s
erver]>
Displays all or specific AAA information in the
configuration file.
authentication: Displays authentication information in
the configuration file.
authorization: Displays authorization information in
the configuration file.
server: Displays authentication server information in the
configuration file.
Hide all or specific AAA information in the configuration
file.
C14
C14
C14
C14
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
77
Page 78

CHAPTER 19
DVMRP Commands
This chapter explains how to use commands to activate the Distance V ector Multicast Routing
Protocol (DVMRP) on the Switch.
19.1 DVMRP Overview
DVMRP (Distance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol) is a protocol used for routing multicast
data. DVMRP is used when a router receives multicast traffic and it wants to find out if other
multicast routers it is connected to need to receive the data. DVMRP sends the data to all
attached routers and waits for a reply. Routers which do not need to receive the data (do not
have multicast group member connected) return a “prune” message, which stops further
multicast traffic for that group from reaching the router.
19.2 Command Summary
The following section lists the commands for this feature.
Table 60 Command Summary: DVMRP
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
show ip dvmrp group Displays DVMRP group information. E 3
show ip dvmrp interface Displays DVMRP interface information. E 3
show ip dvmrp neighbor Displays DVMRP neighbor information. E 3
show ip dvmrp prune Displays the DVMRP prune information. E 3
show ip dvmrp route Displays the DVMRP routes. E 3
show router dvmrp Displays DVMRP settings. E 3
router dvmrp Enables and enters the DVMRP
configuration mode.
exit Leaves the DVMRP configuration mode. C 13
threshold <ttl-value> Sets the DVMRP threshold value. Multicast
packets with TTL (Time-To-Live) value
lower than the threshold are not forwarded
by the Switch.
no router dvmrp Disables DVMRP on the Switch. C 13
interface route-domain <ip-address>/<mask-
bits>
Enters the configuration mode for this
routing domain.
C13
C13
C13
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
78
Page 79

Chapter 19 DVMRP Commands
A
B
C
D
E
10.10.10.254
172.16.1.254
Table 60 Command Summary: DVMRP (continued)
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
ip dvmrp Activates this routing domain in
participating in DVMRP.
no ip dvmrp Disables this routing domain from
participating in DVMRP.
C13
C13
19.3 Command Examples
In this example, the Switch is configured to exchange DVMRP information with other
DVMRP enabled routers as shown next. The Switch is a DVMRP router (C). DVMRP is
activated on IP routing domains 10.10.10.1/24 and 172.16.1.1/24 so that it can exchange
DVMRP information with routers A and B.
Figure 6 DVMRP Network Example
sysname(config)# router igmp
sysname(config-igmp)# exit
sysname(config)# router dvmrp
sysname(config-dvmrp)# exit
sysname(config)# interface route-domain 10.10.10.1/24
sysname(config-if)# ip dvmrp
sysname(config-if)# exit
sysname(config)# interface route-domain 172.16.1.1/24
sysname(config-if)# ip dvmrp
sysname(config-if)# exit
sysname(config)# exit
sysname# show router dvmrp
TTL threshold: 50
IP Address Subnet Mask Active
----------------------------------------
10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0 Yes
172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 Yes
192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 No
• Enables IGMP and DVMRP on the Switch.
• Enables DVMRP on the following routing domains: 10.10.10.1/24, 172.16.1.1/24.
• Displays DVMRP settings configured on the Switch.
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
79
Page 80

CHAPTER 20
Error Disable and Recovery
Commands
Use these commands to configure the CPU protection and error disable recovery features on
the Switch.
20.1 CPU Protection Overview
Switches exchange protocol control packets in a network to get the latest networking
information. If a
IGMP packets, which are to be processed by the CPU, the CPU may become overloaded and
be unable to handle regular tasks properly.
Switch receives large numbers of control packets, such as ARP, BPDU or
The CPU protection feature allows you to limit the rate of ARP, BPDU and IGMP packets to
be delivered to the CPU on a port. This enhances the CPU efficiency and protects against
potential DoS attacks or errors from other network(s). You then can choose to drop control
packets that exceed the specified rate limit or disable a port on which the packets are received.
20.2 Error-Disable Recovery Overview
Some features, such as loop guard or CPU protection, allow the Switch to shut down a port or
discard specific packets on a port when an error is detected on the port. For example, if the
Switch detects that packets sent out the port(s) loop back to the Switch, the Switch can shut
down the port(s) automatically. After that, you need to enable the port(s) or allow the packets
on a port manually via the web configurator or the commands. With error-disable recovery,
you can set the disabled port(s) to become active or start receiving the packets again after the
time interval you specify.
20.3 User Input Values
This section lists the common term definition appears in this chapter.
Table 61 errdisable recovery command user input values
USER INPUT DESCRIPTION
port-list The port number or a range of port numbers that you want to configure.
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
80
Page 81

Chapter 20 Error Disable and Recovery Commands
20.4 Command Summary
The following section lists the commands for this feature.
Table 62 cpu-protection Command Summary
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
interface port-channel <portlist>
cpu-protection cause
<ARP|BPDU|IGMP> rate-limit
<0-256>
clear cpu-protection interface
port-channel <port-list> cause
<ARP|BPDU|IGMP>
reset cpu-protection interface
port-channel <port-list> cause
<ARP|BPDU|IGMP>
show cpu-protection interface
port-channel <port-list>
Enables a port or a list of ports for configuration. C 13
Sets the maximum number of ARP, BPDU or IGMP packets
that the specified port(s) are allowed to receive or transmit
per second. 0 means no rate limit.
Resets the “Total Drop” counters for the specified port(s) to
zero (0). You can see the counter using the show cpu-
protection command. The “Total Drops” means the
number of ARP, BPDU or IGMP packets that have been
dropped due to the Error Disable feature in rate-
limitation mode.
Sets the specified port(s) to handle all ARP, BPDU or IGMP
packets in stead of ignoring them, if the port(s) are in
inactive-reason mode (set by using the errdisable
detet cause command).
Shows the CPU Protection settings and the number of ARP,
BPDU and/or IGMP packets that has been dropped by the
Error Disable feature for the specified port(s).
C13
E13
E13
E13
Table 63 errdisable recovery Command Summary
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
errdisable detect cause
<ARP|BPDU|IGMP>
errdisable detect cause
<ARP|BPDU|IGMP> mode <inactiveport|inactive-reason|ratelimitation>
errdisable recovery Turns on the disabled port recovery function on the Switch. C 13
errdisable recovery cause
<loopguard|ARP|BPDU|IGMP>
errdisable recovery cause
<loopguard|ARP|BPDU|IGMP>
interval <30-2592000>
no errdisable detect cause
<ARP|BPDU|IGMP>
no errdisable recovery Turns off the disabled port recovery function on the Switch. C 13
no errdisable recovery cause
<loopguard|ARP|BPDU|IGMP>
Sets the Switch to detect if the number of ARP, BPDU or
IGMP packets exceeds the rate limit on port(s) (set by using
the cpu-protection cause command).
Sets the action that the Switch takes when the number of
ARP, BPDU or IGMP packets exceeds the rate limit on
port(s).
inactive-port: The Switch shuts down the port.
inactive-reason: The Switch bypasses the processing of
the specified control packets (such as ARP or IGMP packets),
or drops all the specified control packets (such as BPDU) on
the port.
rate-limitation: The Switch drops the additional control
packets the port(s) have to handle in every one second.
Enables the recovery timer for the specified feature that
causes the Switch to shut down port(s).
Sets how many seconds the Switch waits before enabling the
port(s) which was shut down.
Disables the rate limit for ARP, BPDU or IGMP packets on
port(s), set by using the cpu-protection cause
command.
Disables the recovery timer for the specified feature that
causes the Switch to shut down a port.
C13
C13
C13
C13
C13
C13
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
81
Page 82

Chapter 20 Error Disable and Recovery Commands
Table 63 errdisable recovery Command Summary (continued)
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
show errdisable Displays which port(s) are detected (by Error Disable), the
mode of the ports, and which packets (ARP, BPDU or IGMP)
are being detected.
show errdisable detect Displays the Error Disable settings including the available
protocol of packets (ARP, BPDU or IGMP), the current status
(enabled or disabled), and the corresponding action the
Switch takes when a detected port is handling packets over
the limit.
show errdisable recovery Displays the disabled port recovery settings and after how
many seconds which port(s) will be activated.
E13
E13
E13
20.5 Command Examples
This example shows you how to configure the following:
• limit the number of ARP packets that port 7 can handle to 100 packets per second.
• set to shut down port 7 when the number ARP packets the port should handle exceeds the
rate limit.
• display the CPU protection settings that you just set for port 7.
• display the Error Disable status and action mode for ARP packet handling.
systemname# config
systemname(config)# interface port-channel 7
systemname(config-interface)# cpu-protection cause ARP rate-limit 100
systemname(config-interface)# exit
systemname(config)# errdisable detect cause ARP
systemname(config)# errdisable detect cause ARP mode inactive-port
systemname(config)# exit
systemname# show cpu-protection interface port-channel 7
Port : 7
Reason Rate Mode Total Drops
------ ------- --------------- ---------- ARP 100 inactive-port BPDU 0 inactive-port IGMP 0 inactive-port -
systemname# show errdisable detect
Reason Status Mode
------ ------- -------------- ARP enable inactive-port
BPDU enable rate-limitation
IGMP enable inactive-port
systemname#
82
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
Page 83

Chapter 20 Error Disable and Recovery Commands
This example enables the disabled port recovery function and the recovery timer for the
loopguard feature on the Switch. If a port is shut dow n due to the sp ecif ied reason, the Switch
activates the port 300 seconds (the default value) later. This example also shows the number of
the disabled port(s) and the time left before the port(s) becomes active.
sysname# configure
sysname(config)# errdisable recovery
sysname(config)# errdisable recovery cause loopguard
sysname(config)# exit
sysname# show errdisable recovery
Errdisable Recovery Status:Enable
Reason Timer Status Time
---------- ------------ ------ loopguard Enable 300
ARP Disable 300
BPDU Disable 300
IGMP Disable 300
Interfaces that will be enabled at the next timeout:
Interface Reason Time left(sec) Mode
--------- ---------- -------------- --------------sysname#
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
83
Page 84

CHAPTER 21
Ethernet OAM Commands
Use these commands to use the link monitoring protocol IEEE 802.3ah Link Layer Ethernet
OAM (Operations, Administration and Maintenance).
21.1 IEEE 802.3ah Link Layer Ethernet OAM Implementation
Link layer Ethernet OAM (Operations, Administration and Maintenance) as described in IEEE
802.3ah is a link monitoring protocol. It utilizes OAM Protocol Data Units or OAM PDU’s to
transmit link status information between directly connected Ethernet devices. Both devices
must support IEEE 802.3ah. Because link layer Ethernet OAM operates at layer two of the
OSI (Open Systems Interconnection Basic Reference) model, neither IP or SNMP are
necessary to monitor or troubleshoot network connection problems.
The Switch supports the following IEEE 802.3ah features:
• Discovery - this identifies the devices on each end of the Ethernet link and their OAM
configuration.
• Remote Loopback - this can initiate a loopback test between Ethernet devices.
21.2 Command Summary
The following section lists the commands for this feature.
Table 64 ethernet oam Command Summary
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
show ethernet oam discovery
<port-list>
show ethernet oam statistics
<port-list>
show ethernet oam summary Displays the configuration details of each OAM activated port. E 3
ethernet oam Enables Ethernet OAM on the Switch. C 13
no ethernet oam Disables Ethernet OAM on the Switch. C 13
ethernet oam remote-loopback
start <port>
ethernet oam remote-loopback
stop <port>
Displays OAM configuration details and operational status of
the specified ports.
Displays the number of OAM packets transferred for the
specified ports.
Initiates a remote-loopback test from the specified port by
sending Enable Loopback Control PDUs to the remote
device.
Terminates a remote-loopback test from the specified port by
sending Disable Loopback Control PDUs to the remote
device.
E3
E3
E13
E13
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
84
Page 85

Chapter 21 Ethernet OAM Commands
Table 64 ethernet oam Command Summary (continued)
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
ethernet oam remote-loopback
test <port> [<number-of-packets>
[<packet-size>]]
interface port-channel <port-
list>
ethernet oam Enables Ethernet OAM on the port(s). C 13
no ethernet oam Disables Ethernet OAM on the port(s). C 13
ethernet oam mode
<active|passive>
ethernet oam remote-loopback
ignore-rx
ethernet oam remote-loopback
supported
no ethernet oam remoteloopback ignore-rx
no ethernet oam remoteloopback supported
no ethernet oam mode Resets the OAM mode to the default value. C 13
Performs a remote-loopback test from the specified port. You
can also define the allowable packet number and packet size
of the loopback test frames.
Enters config-interface mode for the specified port(s). C 13
Specifies the OAM mode on the ports.
active: Allows the port to issue and respond to Ethernet
OAM commands.
passive: Allows the port to respond to Ethernet OAM
commands.
Sets the Switch to ignore loopback commands received on
the ports.
Enables the remote loopback feature on the ports. C 13
Sets the Switch to process loopback commands received on
the ports.
Disables the remote loopback feat ure on the ports. C 13
E13
C13
C13
C13
21.3 Command Examples
This example enables Ethernet OAM on port 7 and sets the mode to active.
sysname# configure
sysname(config)# ethernet oam
sysname(config)# interface port-channel 7
sysname(config-interface)# ethernet oam
sysname(config-interface)# ethernet oam mode active
sysname(config-interface)# exit
sysname(config)# exit
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
85
Page 86

Chapter 21 Ethernet OAM Commands
This example performs Ethernet OAM discovery from port 7.
sysname# show ethernet oam discovery 7
Port 7
Local client
----------- OAM configurations:
Mode : Active
Unidirectional : Not supported
Remote loopback : Not supported
Link events : Not supported
Variable retrieval: Not supported
Max. OAMPDU size : 1518
Operational status:
Link status : Down
Info. revision : 3
Parser state : Forward
Discovery state : Active Send Local
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 65 show ethernet oam discovery
LABEL DESCRIPTION
OAM configurations The remote device uses this information to determine what functions are
Mode This field displays the OAM mode. The device in active mode (typically the
Unidirectional This field indicates whether or not the Switch can send information PDUs to
Remote loopback This field indicates whether or not the Switch can use loopback control
Link events This field indicates whether or not the Switch can interpret link events, such
Variable retrieval This field indicates whether or not the Switch can respond to requests for
Max. OAMPDU size This field displays the maximum size of PDU for receipt and delivery.
Operational status
Link status This field indicates that the link is up or down.
supported.
service provider's device) controls the device in p assive mode (typically the
subscriber's device).
Active: The Switch initiates OAM discovery; sends information PDUs; and
may send event notification PDUs, variable request/response PDUs, or
loopback control PDUs.
Passive: The Switch waits for the remote device to initiate OAM discovery;
sends information PDUs; may send event notification PDUs; and may
respond to variable request PDUs or loopback control PDUs.
The Switch might not support some types of PDUs, as indicated in the
fields below.
transmit fault information when the receive path is non-operational.
PDUs to put the remote device into loopback mode.
as link fault and dying gasp. Link events are sent in event notification PDUs
and indicate when the number of errors in a given interval (time, number of
frames, number of symbols, or number of errored frame seconds) exceeds
a specified threshold. Organizations may create organization-specific link
event TLVs as well.
more information, such as requests for Ethernet counters and statistics,
about link events.
86
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
Page 87

Chapter 21 Ethernet OAM Commands
Table 65 show ethernet oam discovery (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Info. revision This field displays the current version of local state and configuration. This
two-octet value starts at zero and increments every time the local state or
configuration changes.
Parser state This field indicates the current state of the parser.
Forward: The packet is forwarding packets normally.
Loopback: The Switch is in loopback mode.
Discard: The Switch is discarding non-OAMPDUs because it is trying to or
has put the remote device into loopback mode.
Discovery state This field indicates the state in the OAM discovery process. OAM-enabled
devices use this process to detect each other and to exchange information
about their OAM configuration and capabilities. OAM discovery is a
handshake protocol.
Fault: One of the devices is transmitting OAM PDUs with link fault
information, or the interface is not operational.
Active Send Local: The Switch is in active mode and is trying to see if the
remote device supports OAM.
Passive Wait: The Switch is in passive mode and is waiting for the remote
device to begin OAM discovery.
Send Local Remote: This state occurs in the following circumstances.
• The Switch has discovered the remote device but has not accepted or
rejected the connection yet.
• The Switch has discovered the remote device and rejected the
connection.
Send Local Remote OK: The Switch has discovered the remote device
and has accepted the connection. In addition, the remote device has not
accepted or rejected the connection yet, or the remote device has rejected
the connected.
Send Any: The Switch and the remote device have accepted the
connection. This is the operating state for OAM links that are fully
operational.
This example looks at the number of OAM packets transferred on port 1.
sysname# show ethernet oam statistics 1
Port 1
Statistics:
---------- Information OAMPDU Tx : 0
Information OAMPDU Rx : 0
Event Notification OAMPDU Tx : 0
Event Notification OAMPDU Rx : 0
Loopback Control OAMPDU Tx : 0
Loopback Control OAMPDU Rx : 0
Variable Request OAMPDU Tx : 0
Variable Request OAMPDU Rx : 0
Variable Response OAMPDU Tx : 0
Variable Response OAMPDU Rx : 0
Unsupported OAMPDU Tx : 0
Unsupported OAMPDU Rx : 0
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
87
Page 88

Chapter 21 Ethernet OAM Commands
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 66 show ethernet oam statistics
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Information OAMPDU Tx This field displays the number of OAM PDUs sent on the port.
Information OAMPDU Rx This field displays the number of OAM PDUs received on the port.
Event Notification
OAMPDU Tx
Event Notification
OAMPDU Rx
Loopback Control
OAMPDU Tx
Loopback Control
OAMPDU Rx
Variable Request
OAMPDU Tx
Variable Request
OAMPDU Rx
Variable Response
OAMPDU Tx
Variable Response
OAMPDU Rx
Unsupported OAMPDU TxThis field displays the number of unsupported OAM PDUs sent on the port.
This field displays the number of unique or duplicate OAM event notification
PDUs sent on the port.
This field displays the number of unique or duplicate OAM event notification
PDUs received on the port.
This field displays the number of loopback control OAM PDUs sent on the
port.
This field displays the number of loopback control OAM PDUs received on
the port.
This field displays the number of OAM PDUs sent to request MIB objects
on the remote device.
This field displays the number of OAM PDUs received requesting MIB
objects on the Switch.
This field displays the number of OAM PDUs sent by the Switch in
response to requests.
This field displays the number of OAM PDUs sent by the remote device in
response to requests.
Unsupported OAMPDU RxThis field displays the number of unsupported OAM PDUs received on the
port.
This example looks at the configuration of ports on which OAM is enabled.
sysname# show ethernet oam summary
OAM Config: U : Unidirection, R : Remote Loopback
L : Link Events , V : Variable Retrieval
Local Remote
------------- ----------------------------------------Port Mode MAC Addr OUI Mode Config
----- ------- ----------------- ------ ------- -------1 Active
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 67 show ethernet oam summary
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Local This section displays information about the ports on the Switch.
Port This field displays the port number.
Mode This field displays the operational state of the port.
Remote This section displa ys information about the remote device.
MAC Addr This field displays the MAC address of the remote device.
88
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
Page 89

Chapter 21 Ethernet OAM Commands
Table 67 show ethernet oam summary (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
OUI This field displays the OUI (first three bytes of the MAC address) of the
remote device.
Mode This field displays the operational state of the remote device.
Config This field displays the capabilities of the Switch and remote device. THe
capabilities are identified in the OAM Config section.
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
89
Page 90

CHAPTER 22
External Alarm Commands
Use these commands to configure the external alarm features on the Switch.
22.1 Command Summary
The following section lists the commands for this feature.
Table 68 external-alarm Command Summary
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
external-alarm <index> name
<name_string>
no external-alarm <index> Removes the name of the specified external alarm. C 13
no external-alarm all Removes the name of all external alarms. C 13
show external-alarm Displays external alarm settings and status. E 13
Sets the name of the specified external alarm.
index: 1 ~ 4
name_string: Enters a name of up to 32 ASCII characters.
C13
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
90
Page 91

22.2 Command Examples
This example configures and shows the name and status of the external alarm(s).
sysname# configure
sysname(config)# external-alarm 1 name dooropen
sysname(config)# exit
sysname# show external-alarm
External Alarm 1
Status: Not asserted
Name: dooropen
External Alarm 2
Status: Not asserted
Name:
External Alarm 3
Status: Not asserted
Name:
Chapter 22 External Alarm Commands
External Alarm 4
Status: Not asserted
Name:
sysname#
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
91
Page 92

CHAPTER 23
GARP Commands
Use these commands to configure GARP.
23.1 GARP Overview
Switches join VLANs by making a declaration. A declaration is made by issuing a Join
message using GARP. Declarations are withdrawn by issuing a Leave message. A Leave All
message terminates all registrations. GARP timers set declaration timeout values.
23.2 Command Summary
The following section lists the commands for this feature.
Table 69 garp Command Summary
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
show garp Displays GARP information. E 3
garp join <100-65535> leave
<200-65535> leaveall <200-65535>
Configures GARP time settings (in milliseconds), including
the join, leave and leave all timers for each port. Leave Time
must be at least two times larger than Join Timer, and Leave
All Timer must be larger than Leave Timer.
C13
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
92
Page 93

23.3 Command Examples
In this example, the administrator looks at the Switch’s GARP timer settings and decides to
change them. The administrator sets the Join Timer to 300 milliseconds, the Leave Timer to
800 milliseconds, and the Leave All Timer to 1 1000 milliseconds.
sysname# show garp
GARP Timer
-----------------------Join Timer :200
Leave Timer :600
Leave All Timer :10000
sysname# configure
sysname(config)# garp join 300 leave 800 leaveall 11000
sysname(config)# exit
sysname# show garp
GARP Timer
-----------------------Join Timer :300
Leave Timer :800
Leave All Timer :11000
Chapter 23 GARP Commands
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
93
Page 94

CHAPTER 24
Green Ethernet Commands
Use these commands to configure green Ethernet.
24.1 Green Ethernet Overview
Green Ethernet reduces Switch port power consumption in the following ways.
• IEEE 802.3az Energy Efficient Ethernet (EEE)
If EEE is enabled, both sides of a link support EEE and there is no traffic, the port enters
Low Power Idle (LPI) mode. LPI mode turns off some functions of the physical layer
(becomes quiet) to save power. Periodically the port transmits a REFRESH signal to allow
the link partner keep the link alive. When there is traffic to be sent, a WAKE signal is sent
to the link partner to return the link to active mode.
• Auto Power Down
Auto Power Down turns off almost all functions of the port’s physical layer functions
when the link is down, so the port only uses power to check for a link up pulse from the
link partner. After the link up pulse is detected, the port wakes up from Auto Power Down
and operates normally.
• Short Reach
Traditional Ethernet transmits all data with enough power to reach the maximum cable
length. Shorter cables lose less power, so Short Reach saves power by adjusting the
transmit power of each port according to the length of cable attached to that port.
Not all Switches supports Green Ethernet completely. Some may only support
EEE.
First configure Green Ethernet on the Switch, then configure it on an interface.
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
94
Page 95

Chapter 24 Green Ethernet Commands
24.2 Command Summary
The following section lists the commands for this feature.
Table 70 green-ethernet Command Summary
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
green-ethernet auto-power-down Enables automatic power down on the Switch. E 13
no green-ethernet auto-power-down Disables automatic power down on the Switch. E 13
green-ethernet eee Enables IEEE 802.3az Energy Efficient Ethernet on
no green-ethernet eee Disables eee on the Switch. E 13
green-ethernet short-reach Enables adjusting the transmission power of each
no green-ethernet short-reach Disables short-reach on the Switch. E 13
interface port-channel <port-list> Enters config-interface mode for the specified port(s). C 13
green-ethernet auto-power-down Enables automatic power down on the specified port(s). C 13
no green-ethernet auto-power-
down
green-ethernet eee Enables IEEE 802.3az Energy Efficient Ethernet on
no green-ethernet eee Disable IEEE 802.3az Energy Efficient Ethernet on
green-ethernet short-reach Enables adjusting the transmit power of the
no green-ethernet short-reach Disables adjusting the transmit power of the
show green-ethernet auto-power-down Shows automatic power down information. E3
show green-ethernet eee Shows Energy Efficient Ethernet information. E3
show green-ethernet short-reach Shows short reach information. E3
the Switch.
port according to the length of cable attached to
a port on the Switch.
Disables automatic power down on the specified port(s). C 13
the the specified port(s).
the the specified port(s).
specified port(s) according to the length of cable
attached to the port.
specified port(s) according to the length of cable
attached to the port.
E13
E13
C13
C13
C13
C13
24.3 Green Ethernet Command Example
In this example, the Switch supports EEE and auto power down per port, and short reach
globally. The following are explanations of the Status parameters:
EEE
• Active displays when EEE is enabled and the EEE port is up
• Inactive displays when EEE is enabled but the EEE port is down or the device
connected to this port does not support EEE
• Unsupported means the Switch cannot display the status.
• - means EEE is not enabled
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
95
Page 96

Chapter 24 Green Ethernet Commands
Auto power down
• Normal means auto power down has not reduced the power on this link
• Power down means auto power down has reduced the power on this link
• Unsupported means the Switch cannot display the status.
• - means auto power down is not enabled
Short reach
• Normal means short reach has not reduced the power on this link
• Low power means short reach has reduced the power on this link
• Unsupported means the Switch cannot display the status.
• - means short reach is not enabled
sysname# configure
sysname(config)# green-ethernet eee
sysname(config)# green-ethernet short-reach
sysname(config)# green-ethernet auto-power-down
sysname(config)# interface port-channel 1-4
sysname(config-interface)# green-ethernet eee
sysname(config-interface)# green-ethernet auto-power-down
sysname(config-interface)# exit
sysname(config)# exit
sysname# show green-ethernet eee
EEE globally configuration : Enable
Port Port status Config Status
---- --------------- ------- -------- 1 100M/F Enable Active
2 Down Enable Inactive
3 100M/F Enable Unsupported
4 Down Disable -
sysname# show green-ethernet auto-power-down
Auto Power Down globally configuration : Enable
Port Config Status
---- ------- --------- 1 Enable Power down
2 Enable Normal
3 Enable Unsupported
4 Disable -
sysname# show green-ethernet short-reach
Short Reach globally configuration : Enable
sysname#
96
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
Page 97

Chapter 24 Green Ethernet Commands
The following example shows how to configure short reach if the Switch supports short reach
per port
sysname# configure
sysname(config)# green-ethernet short-reach
sysname# configure
sysname(config)# interface port-channel 1-4
sysname(config-interface)# green-ethernet short-reach
The following example shows the display for short reach if the Switch supports short reach per
port and showing the status
sysname# show green-ethernet short-reach
Global configuration : Enable
Port Config Status
---- ----------- ------------- 1 Enable Low power
2 Disable 3 Enable Unsupported
4 Enable Normal
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
97
Page 98

CHAPTER 25
GVRP Commands
Use these commands to configure GVRP.
25.1 Command Summary
The following section lists the commands for this feature.
Table 71 gvrp Command Summary
COMMAND DESCRIPTION M P
show vlan1q gvrp Displays GVRP settings. E 13
vlan1q gvrp Enables GVRP. C 13
no vlan1q gvrp Disables GVRP on the Switch. C 13
interface port-channel <port-
list>
gvrp Enables this function to permit VLAN groups beyond the local
no gvrp Disable GVRP on the port(s). C 13
Enters config-interface mode for the specified port(s). C 13
C13
Switch.
25.2 Command Examples
This example shows the Switch’s GVRP settings.
sysname# show vlan1q gvrp
GVRP Support
----------------------gvrpEnable = YES
gvrpPortEnable:
This example turns off GVRP on ports 1-5.
sysname# configure
sysname(config)# interface port-channel 1-5
sysname(config-interface)# no gvrp
sysname(config-interface)# exit
sysname(config)# exit
Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Guide
98
Page 99

PART III
Reference H-M
HTTPS Server Commands (101)
IEEE 802.1x Authentication Commands (105)
IGMP and Multicasting Commands (108)
IGMP Snooping Commands (111)
IGMP Filtering Commands (118)
Interface Commands (120)
Interface Route-domain Mode (125)
IP Commands (126)
IP Source Binding Commands (130)
IPv6 Commands (132)
Layer 2 Protocol Tunnel (L2PT) Commands (155)
Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) Commands (158)
Load Sharing Commands (170)
Logging Commands (172)
Login Account Commands (173)
Loopguard Commands (175)
MAC Address Commands (177)
MAC Authentication Commands (179)
MAC Filter Commands (181)
MAC Forward Commands (183)
MAC Pinning Commands (184)
Mirror Commands (186)
MRSTP Commands (190)
99
Page 100

MSTP Commands (192)
Multiple Login Commands (197)
MVR Commands (198)
100
 Loading...
Loading...