Page 1

CLI Reference Guide
T2600G Series Switches
T2600G-18TS(TL-SG3216) / T2600G-28TS (TL-SG3424)
T2600G-52TS (TL-SG3452) / T2600G-28MPS (TL-SG3424P)
1910012087 REV2.2.0
April 2017
Page 2

COPYRIGHT & TRADEMARKS
Specifications are subject to change without notice. is a registered trademark of
TP-Link Technologies Co., Ltd. Other brands and product names are trademarks or registered
trademarks of their respective holders.
No part of the specifications may be reproduced in any form or by any means or used to make
any derivative such as translation, transformation, or adaptation without permission from
TP-Link Technologies Co., Ltd. Copyright © 2017 TP-Link Technologies Co., Ltd. All rights
reserved.
http://www.tp-link.com
I
Page 3

CONTENTS
Preface ............................................................................................................................ 1
Chapter 1 Using the CLI ................................................................................................... 5
1.1 Accessing the CLI ..................................................................................................................................... 5
1.1.1 Logon by a console port ...................................................................................................... 5
1.1.2 Logon by Telnet ...................................................................................................................... 7
1.1.3 Logon by SSH ........................................................................................................................ 11
1.2 CLI Command Modes ............................................................................................................................ 16
1.3 Privilege Restrictions ............................................................................................................................. 19
1.4 Conventions .............................................................................................................................................. 19
1.4.1 Format Conventions ........................................................................................................... 19
1.4.2 Special Characters .............................................................................................................. 20
1.4.3 Parameter Format ................................................................................................................ 20
Chapter 2 User Interface .............................................................................................. 21
2.1 enable ............................................................................................................................................... 21
2.2 service password-encryption .................................................................................................. 21
2.3 enable password ........................................................................................................................... 22
2.4 enable secret ................................................................................................................................. 23
2.5 configure .......................................................................................................................................... 24
2.6 exit...................................................................................................................................................... 25
2.7 end ..................................................................................................................................................... 25
2.8 clipaging ........................................................................................................................................... 26
2.9 history ............................................................................................................................................... 26
2.10 history clear .................................................................................................................................... 27
Chapter 3 IEEE 802.1Q VLAN Commands ................................................................ 28
3.1 vlan ..................................................................................................................................................... 28
3.2 interface vlan .................................................................................................................................. 29
3.3 name .................................................................................................................................................. 29
3.4 switchport mode ........................................................................................................................... 30
3.5 switchport access vlan ............................................................................................................... 31
3.6 switchport trunk allowed vlan ................................................................................................... 31
3.7 switchport trunk allowed vlan all ............................................................................................. 32
3.8 switchport general allowed vlan .............................................................................................. 33
3.9 switchport pvid .............................................................................................................................. 34
II
Page 4

3.10 show vlan summary...................................................................................................................... 34
3.11 show vlan brief ............................................................................................................................... 35
3.12 show vlan ......................................................................................................................................... 35
3.13 show interface switchport ......................................................................................................... 36
Chapter 4 MAC-based VLAN Commands ................................................................. 37
4.1 mac-vlan mac-address ............................................................................................................... 37
4.2 mac-vlan .......................................................................................................................................... 38
4.3 show mac-vlan ............................................................................................................................... 38
4.4 show mac-vlan interface ............................................................................................................ 39
Chapter 5 Protocol-based VLAN Commands ......................................................... 40
5.1 protocol-vlan template (For T2600G-18TS only) .............................................................. 40
5.2 protocol-vlan template (For other switches) ....................................................................... 41
5.3 protocol-vlan vlan ......................................................................................................................... 42
5.4 protocol-vlan group ..................................................................................................................... 43
5.5 show protocol-vlan template .................................................................................................... 43
5.6 show protocol-vlan vlan ............................................................................................................. 44
Chapter 6 VLAN-VPN Commands .............................................................................. 45
6.1 dot1q-tunnel ................................................................................................................................... 45
6.2 dot1q-tunnel tpid .......................................................................................................................... 45
6.3 dot1q-tunnel mapping ................................................................................................................ 46
6.4 switchport dot1q-tunnel missdrop ......................................................................................... 47
6.5 switchport dot1q-tunnel mapping .......................................................................................... 47
6.6 switchport dot1q-tunnel mode ................................................................................................ 48
6.7 show dot1q-tunnel ....................................................................................................................... 49
6.8 show dot1q-tunnel
6.9 show dot1q-tunnel interface .................................................................................................... 50
mapping ..................................................................................................... 50
Chapter 7 Private VLAN Commands ......................................................................... 51
7.1 private-vlan primary ..................................................................................................................... 51
7.2 private-vlan community .............................................................................................................. 51
7.3 private-vlan isolated .................................................................................................................... 52
7.4 private-vlan association ............................................................................................................. 53
7.5 switchport private-vlan ............................................................................................................... 53
7.6 switchport private-vlan host-association ............................................................................ 54
7.7 switchport private-vlan mapping ............................................................................................ 55
7.8 show vlan private-vlan ................................................................................................................ 56
III
Page 5

7.9 show vlan private-vlan interface .............................................................................................. 56
Chapter 8 L2PT Commands ......................................................................................... 58
8.1 l2protocol-tunnel .......................................................................................................................... 58
8.2 l2protocol-tunnel type ................................................................................................................ 58
8.3 show l2protocol-tunnel global ................................................................................................. 60
8.4 show l2protocol-tunnel interface ............................................................................................ 60
Chapter 9 GVRP Commands ........................................................................................ 62
9.1 gvrp .................................................................................................................................................... 62
9.2 gvrp (interface)............................................................................................................................... 62
9.3 gvrp registration ............................................................................................................................ 63
9.4 gvrp timer ........................................................................................................................................ 64
9.5 show gvrp interface ..................................................................................................................... 65
9.6 show gvrp global ........................................................................................................................... 66
Chapter 10 Voice VLAN Commands ............................................................................ 67
10.1 voice vlan ......................................................................................................................................... 67
10.2 voice vlan aging ............................................................................................................................. 67
10.3 voice vlan priority .......................................................................................................................... 68
10.4 voice vlan mac-address ............................................................................................................. 69
10.5 switchport voice vlan mode ...................................................................................................... 70
10.6 switchport voice vlan security ................................................................................................. 70
10.7 show voice vlan ............................................................................................................................. 71
10.8 show voice vlan oui ...................................................................................................................... 71
10.9 show voice vlan switchport ....................................................................................................... 72
Chapter 11 Etherchannel Commands ......................................................................... 73
11.1 channel-group ............................................................................................................................... 73
11.2 port-channel load-balance ........................................................................................................ 74
11.3 lac
11.4 lacp port-priority ........................................................................................................................... 76
p system-priority ..................................................................................................................... 75
11.5 show etherchannel ....................................................................................................................... 76
11.6 show etherchannel load-balance ............................................................................................ 77
11.7 show lacp ......................................................................................................................................... 78
11.8 show lacp sys-id ............................................................................................................................ 78
Chapter 12 User Management Commands ................................................................ 80
12.1 user name (password) ................................................................................................................. 80
IV
Page 6

12.2 user name (secret) ........................................................................................................................ 81
12.3 service password-recovery ...................................................................................................... 82
12.4 user access-control ip-based .................................................................................................. 83
12.5 user access-control mac-based ............................................................................................. 84
12.6 user access-control port-based ............................................................................................. 85
12.7 line ...................................................................................................................................................... 85
12.8 password ......................................................................................................................................... 86
12.9 login ................................................................................................................................................... 88
12.10 login local ......................................................................................................................................... 88
12.11 media-type rj45 ............................................................................................................................. 89
12.12 telnet ................................................................................................................................................. 90
12.13 serial_port baud-rate ................................................................................................................... 90
12.14 show password-recovery .......................................................................................................... 91
12.15 show user account-list................................................................................................................ 91
12.16 show user configuration ............................................................................................................. 92
12.17 show telnet-status........................................................................................................................ 92
Chapter 13 HTTP and HTTPS Commands .................................................................. 94
13.1 ip http server .................................................................................................................................. 94
13.2 ip http max-users (For T2600G-18TS only) ......................................................................... 95
13.3 ip http max-users (For other switches) ................................................................................. 96
13.4 ip http session timeout ............................................................................................................... 96
13.5 ip http secure-server ................................................................................................................... 97
13.6 ip http secure-protocol............................................................................................................... 98
13.7 ip http secure-ciphersuite ......................................................................................................... 98
13.8 ip http secure-max-users .......................................................................................................... 99
13.9 ip
13.10 ip http secure-server download certificate ...................................................................... 101
13.11 ip http secure-server download key ................................................................................... 102
13.12 show ip http configuration ...................................................................................................... 103
http secure-session timeout ............................................................................................. 100
13.13 show ip http secure-server .................................................................................................... 103
Chapter 14 ARP Commands ......................................................................................... 104
14.1 arp ................................................................................................................................................... 104
14.2 clear arp-cache .......................................................................................................................... 105
14.3 arp timeout ................................................................................................................................... 105
14.4 show arp ........................................................................................................................................ 106
14.5 show ip arp (interface) .............................................................................................................. 106
V
Page 7

14.6 show ip arp summary................................................................................................................ 107
Chapter 15 Binding Table Commands ....................................................................... 108
15.1 ip source binding ....................................................................................................................... 108
15.2 ip dhcp snooping ....................................................................................................................... 109
15.3 ip dhcp snooping vlan .............................................................................................................. 110
15.4 ip dhcp snooping information option .................................................................................. 111
15.5 ip dhcp snooping information strategy .............................................................................. 111
15.6 ip dhcp snooping information format ................................................................................. 112
15.7 ip dhcp snooping information remote-id ........................................................................... 113
15.8 ip dhcp snooping information circuit-id ............................................................................. 114
15.9 ip dhcp snooping trust ............................................................................................................. 115
15.10 ip dhcp snooping mac-verify ................................................................................................. 115
15.11 ip dhcp snooping limit rate ..................................................................................................... 116
15.12 ip dhcp snooping decline rate ............................................................................................... 117
15.13 show ip source binding ............................................................................................................ 118
15.14 show ip dhcp snooping ............................................................................................................ 118
15.15 show ip dhcp snooping interface ......................................................................................... 119
15.16 show ip dhcp snooping information interface ................................................................. 119
Chapter 16 IPv6 Binding Table Commands .............................................................. 121
16.1 ipv6 source binding ................................................................................................................... 121
16.2 ipv6 dhcp snooping .................................................................................................................. 122
16.3 ipv6 dhcp snooping vlan ......................................................................................................... 123
16.4 ipv6 dhcp snooping trust ........................................................................................................ 123
16.5 ipv6 nd snooping ....................................................................................................................... 124
16.6 ipv6 nd snooping vlan .............................................................................................................. 125
16.7 ipv6 nd snooping max-entries ............................................................................................... 125
16.8 show ipv6 source binding ....................................................................................................... 126
16.9 show
16.10 show ipv6 dhcp snooping interface .................................................................................... 127
ipv6 dhcp snooping ....................................................................................................... 127
16.11 show ipv6 nd snooping ............................................................................................................ 128
16.12 show ipv6 nd snooping interface ......................................................................................... 128
Chapter 17 IP Verify Source Commands .................................................................. 130
17.1 ip verify source ........................................................................................................................... 130
17.2 show ip verify source ................................................................................................................ 131
17.3 show ip verify source interface ............................................................................................. 131
VI
Page 8

Chapter 18 IPv6 Verify Source Commands ............................................................. 133
18.1 ipv6 verify source ...................................................................................................................... 133
18.2 show ipv6 verify source ........................................................................................................... 134
18.3 show ipv6 verify source interface ........................................................................................ 134
Chapter 19 ND Detection Commands ....................................................................... 136
19.1 ipv6 nd detection ....................................................................................................................... 136
19.2 ipv6 nd detection vlan .............................................................................................................. 136
19.3 ipv6 nd detection trust ............................................................................................................. 137
19.4 show ipv6 nd detection ........................................................................................................... 138
19.5 show ipv6 nd detection interface ......................................................................................... 138
Chapter 20 ARP Inspection Commands .................................................................... 140
20.1 ip arp inspection(global) .......................................................................................................... 140
20.2 ip arp inspection trust .............................................................................................................. 140
20.3 ip arp inspection(interface)..................................................................................................... 141
20.4 ip arp inspection limit-rate ...................................................................................................... 142
20.5 ip arp inspection recover ........................................................................................................ 143
20.6 show ip arp inspection ............................................................................................................. 143
20.7 show ip arp inspection interface .......................................................................................... 144
20.8 show ip arp inspection statistics .......................................................................................... 144
20.9 clear ip arp inspection statistics ........................................................................................... 145
Chapter 21 DoS Defend Commands .......................................................................... 146
21.1 ip dos-prevent ............................................................................................................................ 146
21.2 ip dos-prevent type................................................................................................................... 146
21.3 show ip dos-prevent ................................................................................................................. 148
Chapter 22 IEEE 802.1X Commands .......................................................................... 149
22.1 dot1x system-auth-control .................................................................................................... 149
22.2 dot1x handshake ....................................................................................................................... 150
22.3 dot
22.4 dot1x accounting ....................................................................................................................... 151
22.5 dot1x vlan-assignment ............................................................................................................ 152
22.6 dot1x guest-vlan(global) .......................................................................................................... 153
22.7 dot1x quiet-period..................................................................................................................... 153
22.8 dot1x timeout supplicant-timeout ....................................................................................... 154
22.9 dot1x max-reauth-req .............................................................................................................. 155
22.10 dot1x .............................................................................................................................................. 156
1x auth-method ................................................................................................................... 150
VII
Page 9

22.11 dot1x guest-vlan(interface) .................................................................................................... 156
22.12 dot1x mab .................................................................................................................................... 157
22.13 dot1x port-control ..................................................................................................................... 158
22.14 dot1x port-method .................................................................................................................... 159
22.15 show dot1x global ..................................................................................................................... 159
22.16 show dot1x interface ................................................................................................................ 160
Chapter 23 PPPoE ID-Insertion Commands ............................................................ 161
23.1 pppoe id-insertion(global)....................................................................................................... 161
23.2 pppoe circuit-id(interface) ...................................................................................................... 162
23.3 pppoe circuit-id type ................................................................................................................ 162
23.4 pppoe remote-id ........................................................................................................................ 163
23.5 show pppoe id-insertion global ............................................................................................ 164
23.6 show pppoe id-insertion interface ....................................................................................... 164
Chapter 24 System Log Commands .......................................................................... 166
24.1 logging buffer .............................................................................................................................. 166
24.2 logging buffer level .................................................................................................................... 166
24.3 logging file flash ......................................................................................................................... 167
24.4 logging file flash frequency .................................................................................................... 168
24.5 logging file flash level ............................................................................................................... 169
24.6 logging host index ..................................................................................................................... 169
24.7 logging console .......................................................................................................................... 170
24.8 logging console level ................................................................................................................ 171
24.9 logging monitor .......................................................................................................................... 172
24.10 logging monitor level ................................................................................................................ 172
24.11 clear logging ................................................................................................................................ 173
24.12 show logging local-config....................................................................................................... 174
24.13 show logging loghost ............................................................................................................... 174
24.14 show logging buffer .................................................................................................................. 175
24.15 show logging flash ..................................................................................................................... 175
Chapter 25 SSH Commands ......................................................................................... 177
25.1 ip ssh server ................................................................................................................................ 177
25.2 ip ssh version .............................................................................................................................. 177
25.3 ip ssh algorithm .......................................................................................................................... 178
25.4 ip ssh timeout .............................................................................................................................. 179
25.5 ip ssh max-client ........................................................................................................................ 179
25.6 ip ssh download .......................................................................................................................... 180
VIII
Page 10

25.7 remove public-key ..................................................................................................................... 181
25.8 show ip ssh................................................................................................................................... 181
Chapter 26 MAC Address Commands ....................................................................... 183
26.1 mac address-table static ........................................................................................................ 183
26.2 mac address-table aging-time .............................................................................................. 184
26.3 mac address-table filtering .................................................................................................... 184
26.4 mac address-table notification ............................................................................................. 185
26.5 mac address-table max-mac-count ................................................................................... 186
26.6 mac address-table notification (interface) ........................................................................ 187
26.7 mac address-table security ................................................................................................... 188
26.8 show mac address-table ......................................................................................................... 189
26.9 clear mac address-table ......................................................................................................... 190
26.10 show mac address-table aging-time .................................................................................. 190
26.11 show mac address-table max-mac-count ........................................................................ 191
26.12 show mac address-table interface ...................................................................................... 191
26.13 show mac address-table count ............................................................................................ 192
26.14 show mac address-table address ....................................................................................... 193
26.15 show mac address-table vlan ................................................................................................ 193
26.16 show mac address-table notification ................................................................................. 194
26.17 show mac address-table security ........................................................................................ 194
Chapter 27 System Configuration Commands ....................................................... 196
27.1 system-time manual ................................................................................................................. 196
27.2 system-time ntp ......................................................................................................................... 196
27.3 system-time dst predefined .................................................................................................. 198
27.4 syst
27.5 system-time dst recurring ...................................................................................................... 200
27.6 hostname ...................................................................................................................................... 201
27.7 location .......................................................................................................................................... 202
27.8 contact-info ................................................................................................................................. 202
em-time dst date ............................................................................................................... 199
27.9 ip address ..................................................................................................................................... 203
27.10 ip address-alloc .......................................................................................................................... 204
27.11 reset ............................................................................................................................................... 205
27.12 reboot ............................................................................................................................................ 205
27.13 reboot-schedule ........................................................................................................................ 206
27.14 copy running-config startup-config .................................................................................... 207
27.15 copy startup-config tftp .......................................................................................................... 207
IX
Page 11

27.16 copy tftp startup-config .......................................................................................................... 208
27.17 boot application ......................................................................................................................... 209
27.18 remove backup-image ............................................................................................................. 209
27.19 firmware upgrade ....................................................................................................................... 210
27.20 boot autoinstall start ................................................................................................................. 211
27.21 boot autoinstall persistent-mode ........................................................................................ 211
27.22 boot autoinstall auto-save ...................................................................................................... 212
27.23 boot autoinstall auto-reboot .................................................................................................. 212
27.24 boot autoinstall retry-count ................................................................................................... 213
27.25 show boot autoinstall ............................................................................................................... 214
27.26 show boot autoinstall downloaded-config ....................................................................... 214
27.27 ping ................................................................................................................................................. 215
27.28 tracert ............................................................................................................................................ 216
27.29 show system-info ...................................................................................................................... 217
27.30 show system-info interface ................................................................................................... 217
27.31 show image-info ......................................................................................................................... 218
27.32 show boot ..................................................................................................................................... 218
27.33 show running-config ................................................................................................................. 219
27.34 show running-config | ............................................................................................................... 219
27.35 show startup-config ................................................................................................................. 220
27.36 show system-time ..................................................................................................................... 220
27.37 show system-time dst .............................................................................................................. 221
27.38 show system-time ntp ............................................................................................................. 221
27.39 show cable-diagnostics interface gigabitEthernet ........................................................ 222
27.40 show cable-diagnostics careful interface ......................................................................... 222
27.41 sho
w cpu-utilization .................................................................................................................. 223
27.42 show memory-utilization ......................................................................................................... 223
Chapter 28 IPv6 Address Configuration Commands ............................................ 225
28.1 ipv6 enable ................................................................................................................................... 225
28.2 ipv6 address autoconfig.......................................................................................................... 225
28.3 ipv6 address link-local ............................................................................................................. 226
28.4 ipv6 address dhcp ..................................................................................................................... 227
28.5 ipv6 address ra ........................................................................................................................... 227
28.6 ipv6 address eui-64 .................................................................................................................. 228
28.7 ipv6 address ................................................................................................................................ 229
28.8 show ipv6 interface ................................................................................................................... 230
X
Page 12

Chapter 29 Ethernet Configuration Commands ..................................................... 231
29.1 interface gigabitEthernet ........................................................................................................ 231
29.2 interface range gigabitEthernet............................................................................................ 231
29.3 description ................................................................................................................................... 232
29.4 shutdown ...................................................................................................................................... 233
29.5 flow-control ................................................................................................................................. 234
29.6 duplex ............................................................................................................................................ 234
29.7 jumbo ............................................................................................................................................. 235
29.8 jumbo-size .................................................................................................................................... 235
29.9 speed ............................................................................................................................................. 236
29.10 storm-control pps ..................................................................................................................... 237
29.11 storm-control .............................................................................................................................. 237
29.12 bandwidth ..................................................................................................................................... 238
29.13 clear counters ............................................................................................................................. 239
29.14 show interface status ............................................................................................................... 240
29.15 show interface counters ......................................................................................................... 240
29.16 show interface configuration ................................................................................................. 241
29.17 show storm-control .................................................................................................................. 242
29.18 show bandwidth ......................................................................................................................... 242
Chapter 30 QoS Commands ......................................................................................... 244
30.1 qos (For T2600G-18TS only) ................................................................................................. 244
30.2 qos (For other switches) .......................................................................................................... 245
30.3 qos cos .......................................................................................................................................... 245
30.4 qos dscp ....................................................................................................................................... 246
30.5 qos queue cos-map .................................................................................................................. 247
30.6 qos queue dscp-map (For T2600G-18TS only) ............................................................... 248
30.7 qos q
30.8 qos queue mode ........................................................................................................................ 250
30.9 qos queue weight ...................................................................................................................... 251
ueue dscp-map (For other switches) ....................................................................... 249
30.10 show qos interface .................................................................................................................... 252
30.11 show qos cos-map .................................................................................................................... 253
30.12 show qos dscp-map ................................................................................................................. 253
30.13 show qos queue mode ............................................................................................................. 254
30.14 show qos status ......................................................................................................................... 254
Chapter 31 Port Mirror Commands ............................................................................ 255
31.1 monitor session destination interface................................................................................ 255
XI
Page 13

31.2 monitor session source interface ........................................................................................ 256
31.3 show monitor session .............................................................................................................. 257
Chapter 32 Port Isolation Commands ....................................................................... 258
32.1 port isolation................................................................................................................................ 258
32.2 show port isolation interface ................................................................................................. 259
Chapter 33 Loopback Detection Commands .......................................................... 260
33.1 loopback-detection (global) ................................................................................................... 260
33.2 loopback-detection interval ................................................................................................... 260
33.3 loopback-detection recovery-time ..................................................................................... 261
33.4 loopback-detection (interface) ............................................................................................. 262
33.5 loopback-detection config process-mode ...................................................................... 262
33.6 loopback-detection config recovery-mode ..................................................................... 263
33.7 loopback-detection recover .................................................................................................. 264
33.8 show loopback-detection global.......................................................................................... 264
33.9 show loopback-detection interface .................................................................................... 265
Chapter 34 DDM Commands ....................................................................................... 266
34.1 ddm state enable ....................................................................................................................... 266
34.2 ddm shutdown ............................................................................................................................ 266
34.3 ddm temperature_threshold .................................................................................................. 267
34.4 ddm voltage_threshold ............................................................................................................ 268
34.5 ddm bias_current_threshold ................................................................................................. 269
34.6 ddm tx_power_threshold ........................................................................................................ 270
34.7 ddm rx_power_threshold ........................................................................................................ 271
34.8 show ddm configuration.......................................................................................................... 272
34.9 show ddm status ........................................................................................................................ 273
Chapter 35 ACL Commands ......................................................................................... 274
35.1 time-range .................................................................................................................................... 274
35.2 absolute ........................................................................................................................................ 274
35.3 periodic ......................................................................................................................................... 275
35.4 holiday ........................................................................................................................................... 276
35.5 holiday (global) ............................................................................................................................ 277
35.6 access-list create ...................................................................................................................... 277
35.7 mac access-list .......................................................................................................................... 278
35.8 access-list standard ................................................................................................................. 279
35.9 access-list extended ................................................................................................................ 280
XII
Page 14

35.10 access-list combined ............................................................................................................... 281
35.11 access-list ipv6 .......................................................................................................................... 283
35.12 rule .................................................................................................................................................. 284
35.13 access-list policy name ........................................................................................................... 286
35.14 access-list policy action .......................................................................................................... 286
35.15 redirect interface ....................................................................................................................... 287
35.16 s-condition ................................................................................................................................... 288
35.17 s-mirror.......................................................................................................................................... 288
35.18 qos-remark .................................................................................................................................. 289
35.19 access-list bind acl (interface) .............................................................................................. 290
35.20 access-list bind acl (vlan) ........................................................................................................ 290
35.21 access-list bind (interface) ..................................................................................................... 291
35.22 access-list packet-content profile ...................................................................................... 292
35.23 access-list packet-content config ...................................................................................... 292
35.24 access-list bind (vlan) ............................................................................................................... 293
35.25 show access-list ........................................................................................................................ 294
35.26 show access-list status ........................................................................................................... 295
35.27 show access-list policy ........................................................................................................... 295
35.28 show access-list bind ............................................................................................................... 296
Chapter 36 MSTP Commands ...................................................................................... 297
36.1 debug spanning-tree ................................................................................................................ 297
36.2 spanning-tree (global) .............................................................................................................. 298
36.3 spanning-tree (interface) ........................................................................................................ 298
36.4 spanning-tree common-config ............................................................................................. 299
36.5 spa
36.6 spanning-tree mst configuration ......................................................................................... 301
36.7 instance ......................................................................................................................................... 301
36.8 name ............................................................................................................................................... 302
36.9 revision .......................................................................................................................................... 303
nning-tree mode ................................................................................................................. 300
36.10 spanning-tree mst instance ................................................................................................... 304
36.11 spanning-tree mst ..................................................................................................................... 304
36.12 spanning-tree priority .............................................................................................................. 305
36.13 spanning-tree timer .................................................................................................................. 306
36.14 spanning-tree hold-count ....................................................................................................... 307
36.15 spanning-tree max-hops ......................................................................................................... 307
36.16 spanning-tree bpdufilter ......................................................................................................... 308
36.17 spanning-tree bpduguard ....................................................................................................... 309
XIII
Page 15

36.18 spanning-tree guard loop ....................................................................................................... 309
36.19 spanning-tree guard root ........................................................................................................ 310
36.20 spanning-tree guard tc ............................................................................................................ 311
36.21 spanning-tree mcheck ............................................................................................................. 311
36.22 show spanning-tree active ..................................................................................................... 312
36.23 show spanning-tree bridge .................................................................................................... 312
36.24 show spanning-tree interface ............................................................................................... 313
36.25 show spanning-tree interface-security ............................................................................. 314
36.26 show spanning-tree mst ......................................................................................................... 314
Chapter 37 Ethernet OAM Commands ...................................................................... 316
37.1 ethernet-oam .............................................................................................................................. 316
37.2 ethernet-oam mode .................................................................................................................. 316
37.3 ethernet-oam link-monitor symbol-period ....................................................................... 317
37.4 ethernet-oam link-monitor frame ........................................................................................ 318
37.5 ethernet-oam link-monitor frame-period .......................................................................... 319
37.6 ethernet-oam link-monitor frame-seconds...................................................................... 320
37.7 ethernet-oam remote-failure ................................................................................................. 321
37.8 ethernet-oam remote-loopback received-remote- loopback ................................... 322
37.9 ethernet-oam remote-loopback .......................................................................................... 323
37.10 clear ethernet-oam statistics ................................................................................................ 324
37.11 clear ethernet-oam event-log ............................................................................................... 324
37.12 show ethernet-oam configuration ....................................................................................... 325
37.13 show ethernet-oam event-log .............................................................................................. 326
37.14 show
37.15 show ethernet-oam status ..................................................................................................... 327
ethernet-oam statistics ............................................................................................... 326
Chapter 38 DLDP Commands ...................................................................................... 328
38.1 dldp (global) ................................................................................................................................. 328
38.2 dldp interval ................................................................................................................................. 328
38.3 dldp shut-mode .......................................................................................................................... 329
38.4 dldp reset (global) ...................................................................................................................... 330
38.5 dldp(interface) ............................................................................................................................. 330
38.6 dldp reset (interface) ................................................................................................................ 331
38.7 show dldp ..................................................................................................................................... 331
38.8 show dldp interface................................................................................................................... 332
Chapter 39 IGMP Snooping Commands.................................................................... 333
39.1 ip igmp snooping (global) ........................................................................................................ 333
XIV
Page 16

39.2 ip igmp snooping (interface) .................................................................................................. 333
39.3 ip igmp snooping rtime ............................................................................................................ 334
39.4 ip igmp snooping mtime .......................................................................................................... 335
39.5 ip igmp snooping report-suppression ................................................................................ 335
39.6 ip igmp snooping immediate-leave ..................................................................................... 336
39.7 ip igmp snooping drop-unknown ......................................................................................... 336
39.8 ip igmp snooping last-listener query-inteval .................................................................... 337
39.9 ip igmp snooping last-listener query-count ..................................................................... 338
39.10 ip igmp snooping vlan-config ................................................................................................ 338
39.11 ip igmp snooping vlan-config (router-port-forbidden) ................................................. 340
39.12 ip igmp snooping multi-vlan-config ..................................................................................... 341
39.13 ip igmp snooping multi-vlan-config (router-port-forbidden) ...................................... 342
39.14 ip igmp snooping multi-vlan-config (source-ip-replace) ............................................. 343
39.15 ip igmp snooping querier vlan ............................................................................................... 343
39.16 ip igmp snooping querier vlan (general query) ................................................................ 344
39.17 ip igmp snooping max-groups .............................................................................................. 345
39.18 ip igmp snooping authentication .......................................................................................... 346
39.19 ip igmp snooping accounting ................................................................................................ 347
39.20 ip igmp profile ............................................................................................................................. 347
39.21 deny ................................................................................................................................................ 348
39.22 permit ............................................................................................................................................. 349
39.23 range .............................................................................................................................................. 349
39.24 ip igmp filter ................................................................................................................................. 350
39.25 clear ip igmp snooping statistics ......................................................................................... 350
39.26 show ip igmp snooping ............................................................................................................ 351
39.27 show
ip igmp snooping interface ......................................................................................... 351
39.28 show ip igmp snooping vlan ................................................................................................... 352
39.29 show ip igmp snooping multi-vlan ....................................................................................... 353
39.30 show ip igmp snooping groups ............................................................................................. 353
39.31 show ip igmp snooping querier ............................................................................................. 354
39.32 show ip igmp profile .................................................................................................................. 355
Chapter 40 MLD Snooping Commands ..................................................................... 356
40.1 ipv6 mld snooping (global) ...................................................................................................... 356
40.2 ipv6 mld snooping (interface) ................................................................................................ 356
40.3 ipv6 mld snooping rtime .......................................................................................................... 357
40.4 ipv6 mld snooping mtime ........................................................................................................ 357
40.5 ipv6 mld snooping report-suppression ............................................................................. 358
XV
Page 17

40.6 ipv6 mld snooping immediate-leave ................................................................................... 359
40.7 ipv6 mld snooping drop-unknown ....................................................................................... 359
40.8 ipv6 mld snooping last-listener query-inteval ................................................................. 360
40.9 ipv6 mld snooping last-listener query-count ................................................................... 360
40.10 ipv6 mld snooping vlan-config .............................................................................................. 361
40.11 ip mld snooping vlan-config (router-port-forbidden) .................................................... 362
40.12 ipv6 mld snooping multi-vlan-config .................................................................................. 363
40.13 ipv6 mld snooping multi-vlan-config (router-port-forbidden).................................... 364
40.14 ipv6 mld snooping multi-vlan-config (source-ip-replace) ........................................... 365
40.15 ipv6 mld snooping querier vlan ............................................................................................. 366
40.16 ipv6 mld snooping querier vlan (general query) .............................................................. 366
40.17 ipv6 mld snooping max-groups ............................................................................................ 367
40.18 ipv6 mld profile ........................................................................................................................... 369
40.19 deny ................................................................................................................................................ 369
40.20 permit ............................................................................................................................................. 370
40.21 range .............................................................................................................................................. 370
40.22 ipv6 mld filter ............................................................................................................................... 371
40.23 clear ipv6 mld snooping statistics ....................................................................................... 371
40.24 show ipv6 mld snooping .......................................................................................................... 372
40.25 show ipv6 mld snooping interface ....................................................................................... 372
40.26 show ipv6 mld snooping vlan ................................................................................................. 373
40.27 show ipv6 mld snooping multi-vlan ..................................................................................... 374
40.28 show ipv6 mld snooping groups .......................................................................................... 374
40.29 show ipv6 mld snooping querier .......................................................................................... 375
40.30 show ipv6 mld profile ................................................................................................................ 375
Chapter 41 SNMP Commands ..................................................................................... 377
41.1 snmp-server ................................................................................................................................ 377
41.2 snmp-server view ...................................................................................................................... 377
41.3 snmp-server group ................................................................................................................... 378
41.4 snmp-server user ...................................................................................................................... 380
41.5 snmp-server community ......................................................................................................... 381
41.6 snmp-server host ...................................................................................................................... 382
41.7 snmp-server engineID ............................................................................................................. 384
41.8 snmp-server traps snmp ......................................................................................................... 384
41.9 snmp-server traps link-status ............................................................................................... 385
41.10 snmp-server traps ..................................................................................................................... 386
41.11 snmp-server traps ddm ........................................................................................................... 387
XVI
Page 18

41.12 snmp-server traps vlan ............................................................................................................ 388
41.13 snmp-server traps security dhcp-snoop .......................................................................... 389
41.14 rmon history ................................................................................................................................ 390
41.15 rmon event ................................................................................................................................... 391
41.16 rmon alarm ................................................................................................................................... 392
41.17 rmon statistics ............................................................................................................................ 393
41.18 show snmp-server..................................................................................................................... 394
41.19 show snmp-server view ........................................................................................................... 395
41.20 show snmp-server group ........................................................................................................ 395
41.21 show snmp-server user ........................................................................................................... 395
41.22 show snmp-server community ............................................................................................. 396
41.23 show snmp-server host ........................................................................................................... 396
41.24 show snmp-server engineID .................................................................................................. 397
41.25 show rmon history ..................................................................................................................... 397
41.26 show rmon event ....................................................................................................................... 398
41.27 show rmon alarm ........................................................................................................................ 398
41.28 show rmon statistics ................................................................................................................ 399
Chapter 42 LLDP Commands ....................................................................................... 400
42.1 lldp................................................................................................................................................... 400
42.2 lldp forward_message .............................................................................................................. 400
42.3 lldp hold-multiplier ..................................................................................................................... 401
42.4 lldp timer ....................................................................................................................................... 402
42.5 lldp receive ................................................................................................................................... 403
42.6 lldp transmit ................................................................................................................................. 403
42.7 lldp snmp-trap ............................................................................................................................. 404
42.8 lldp t
42.9 lldp management address ...................................................................................................... 405
42.10 lldp med-fast-count .................................................................................................................. 406
42.11 lldp med-status ........................................................................................................................... 407
lv-select ............................................................................................................................... 405
42.12 lldp med-tlv-select .................................................................................................................... 407
42.13 lldp med-location ....................................................................................................................... 408
42.14 show lldp ....................................................................................................................................... 409
42.15 show lldp interface .................................................................................................................... 410
42.16 show lldp local-information interface ................................................................................. 410
42.17 show lldp neighbor-information interface ......................................................................... 411
42.18 show lldp traffic interface ....................................................................................................... 411
XVII
Page 19

Chapter 43 sFlow Commands ...................................................................................... 413
43.1 sflow address .............................................................................................................................. 413
43.2 sflow enable ................................................................................................................................. 414
43.3 sflow collector collector-ID .................................................................................................... 414
43.4 sflow sampler .............................................................................................................................. 415
43.5 show sflow global ...................................................................................................................... 416
43.6 show sflow collector ................................................................................................................. 417
43.7 show sflow sampler .................................................................................................................. 417
Chapter 44 Static Routes Commands ....................................................................... 418
44.1 interface vlan ............................................................................................................................... 418
44.2 interface loopback .................................................................................................................... 418
44.3 switchport .................................................................................................................................... 419
44.4 interface range port-channel ................................................................................................. 420
44.5 description ................................................................................................................................... 420
44.6 shutdown ...................................................................................................................................... 421
44.7 interface port-channel ............................................................................................................. 422
44.8 ip route .......................................................................................................................................... 422
44.9 ipv6 routing .................................................................................................................................. 423
44.10 ipv6 route ...................................................................................................................................... 424
44.11 show interface vlan ................................................................................................................... 424
44.12 show ip interface ........................................................................................................................ 425
44.13 show ip interface brief .............................................................................................................. 426
44.14 show ip route ............................................................................................................................... 426
44.15 show ip route specify ............................................................................................................... 427
44.16 show ip route summary ........................................................................................................... 428
44.17 show ipv6 interface ................................................................................................................... 428
44.18 show
44.19 show ipv6 route summary ...................................................................................................... 429
ipv6 route .......................................................................................................................... 429
Chapter 45 SDM Template Commands ..................................................................... 431
45.1 sdm prefer .................................................................................................................................... 431
45.2 show sdm prefer ........................................................................................................................ 432
Chapter 46 AAA Commands ........................................................................................ 433
46.1 aaa enable .................................................................................................................................... 433
46.2 tacacas-server host .................................................................................................................. 434
46.3 show tacacs-server .................................................................................................................. 435
XVIII
Page 20

46.4 radius-server host ..................................................................................................................... 435
46.5 show radius-server ................................................................................................................... 437
46.6 aaa group ...................................................................................................................................... 437
46.7 server ............................................................................................................................................. 438
46.8 show aaa group .......................................................................................................................... 439
46.9 aaa authentication login .......................................................................................................... 439
46.10 aaa authentication enable....................................................................................................... 440
46.11 aaa authentication dot1x default .......................................................................................... 441
46.12 aaa accounting dot1x default ................................................................................................ 442
46.13 show aaa authentication ......................................................................................................... 443
46.14 show aaa accounting ................................................................................................................ 443
46.15 line console .................................................................................................................................. 444
46.16 login authentication (console) ............................................................................................... 444
46.17 enable authentication (console) ........................................................................................... 445
46.18 line telnet ...................................................................................................................................... 446
46.19 login authentication (telnet) .................................................................................................... 446
46.20 line ssh ........................................................................................................................................... 447
46.21 login authentication (ssh) ........................................................................................................ 447
46.22 enable authentication (telnet) ................................................................................................ 448
46.23 enable authentication (ssh) .................................................................................................... 449
46.24 ip http login authentication ..................................................................................................... 450
46.25 ip http enable authentication ................................................................................................. 450
46.26 show aaa global .......................................................................................................................... 451
Chapter 47 DHCP Server Commands ........................................................................ 452
47.1 service dhcp server .................................................................................................................. 452
47.2 ip dhcp server extend-option capwap-ac-ip.................................................................... 452
47.3 ip dhcp server extend-opti
47.4 ip dhcp server exclude-address ........................................................................................... 454
47.5 ip dhcp server pool ................................................................................................................... 454
on vendor-class-id ............................................................... 453
47.6 ip dhcp server ping timeout ................................................................................................... 455
47.7 ip dhcp server ping packets ................................................................................................... 456
47.8 network ......................................................................................................................................... 456
47.9 lease ............................................................................................................................................... 457
47.10 address hardware-address .................................................................................................... 458
47.11 address client-identifier .......................................................................................................... 458
47.12 default-gateway ......................................................................................................................... 459
47.13 dns-server .................................................................................................................................... 460
XIX
Page 21

47.14 netbios-name-server ............................................................................................................... 461
47.15 netbios-node-type .................................................................................................................... 461
47.16 next-server ................................................................................................................................... 462
47.17 domain-name .............................................................................................................................. 463
47.18 bootfile .......................................................................................................................................... 463
47.19 show ip dhcp server status .................................................................................................... 464
47.20 show ip dhcp server statistics............................................................................................... 464
47.21 show ip dhcp server extend-option .................................................................................... 465
47.22 show ip dhcp server pool ........................................................................................................ 465
47.23 show ip dhcp server excluded-address ............................................................................ 466
47.24 show ip dhcp server manual-binding .................................................................................. 466
47.25 show ip dhcp server binding .................................................................................................. 467
47.26 clear ip dhcp server statistics ............................................................................................... 467
47.27 clear ip dhcp server binding ................................................................................................... 468
Chapter 48 DHCP Relay Commands .......................................................................... 469
48.1 service dhcp relay ..................................................................................................................... 469
48.2 ip helper-address....................................................................................................................... 469
48.3 ip dhcp relay information ........................................................................................................ 470
48.4 ip dhcp relay information policy ........................................................................................... 471
48.5 ip dhcp relay information format .......................................................................................... 471
48.6 ip dhcp relay information custom ........................................................................................ 472
48.7 ip dhcp relay information circuit-id ...................................................................................... 473
48.8 ip dhcp relay information remote-id .................................................................................... 473
48.9 ip dhcp relay default-interface .............................................................................................. 474
48.10 ip dhcp relay vlan ....................................................................................................................... 475
48.11 show ip dhcp relay ..................................................................................................................... 475
Chapter 49 PoE Commands ......................................................................................... 477
49.1 power inline consumption (global) ....................................................................................... 477
49.2 power inline disconnect-method ......................................................................................... 477
49.3 power profile ............................................................................................................................... 478
49.4 power time-range ...................................................................................................................... 479
49.5 power holiday .............................................................................................................................. 480
49.6 absolute ........................................................................................................................................ 481
49.7 periodic ......................................................................................................................................... 481
49.8 holiday ........................................................................................................................................... 482
49.9 power inline consumption (interface) ................................................................................. 483
XX
Page 22

49.10 power inline priority ................................................................................................................... 484
49.11 power inline supply .................................................................................................................... 484
49.12 power inline profile .................................................................................................................... 485
49.13 power inline time-range ........................................................................................................... 486
49.14 show power inline ...................................................................................................................... 486
49.15 show power inline configuration interface ........................................................................ 487
49.16 show power inline information interface ........................................................................... 487
49.17 show power profile .................................................................................................................... 488
49.18 show power holiday .................................................................................................................. 488
49.19 show power time-range ........................................................................................................... 489
XXI
Page 23

Preface
This Guide is intended for network administrator to provide referenced information about CLI
(Command Line Interface). The device mentioned in this Guide stands for T2600G-18TS/
T2600G-28TS/ T2600G-52TS/ T2600G-28MPS JetStream Gigabit L2 Managed Switch without
any explanation. The commands in this guilde apply to these models if not specially noted, and
T2600G-28TS is taken as an example model in the example commands.
Some models featured in this guide may be unavailable in your country or region. For local
sales information, visit http://www.tp-link.com.
Overview of this Guide
Chapter 1: Using the CLI
Provide information about how to use the CLI, CLI Command Modes, Security Levels and some
Conventions.
Chapter 2: User Interface
Provide information about the commands used to switch between five CLI Command Modes.
Chapter 3: IEEE 802.1Q VLAN Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring IEEE 802.1Q VLAN.
Chapter 4: MAC-based VLAN Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring MAC-based VLAN.
Chapter 5: Protocol VLAN Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring Protocol VLAN.
Chapter 6: VLAN-VPN Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring VLAN-VPN (Virtual Private
Network) function.
Chapter 7: Private VLAN Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring Private VLAN.
Chapter 8: L2PT Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring L2PT (Layer 2 Portocol
Tunneling).
Chapter 9: GVRP Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring GVRP (GARP VLAN registration
protocol).
Chapter 10: Voice VLAN Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring Voice VLAN.
1
Page 24

Chapter 11: Etherchannel Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring LAG (Link Aggregation Group)
and LACP (Link Aggregation Control Protocol).
Chapter 12: User Management Commands
Provide information about the commands used for user management.
Chapter 13: HTTP and HTTPS Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring the HTTP and HTTPS logon.
Chapter 14: ARP Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring the ARP (Address Resolution
Protocol) functions.
Chapter 15: Binding Table Commands
Provide information about the commands used for binding the IP address, MAC address, VLAN
and the connected Port number of the Host together.
Chapter 16: IPv6 Binding Table Commands
Provide information about the commands used for binding the IPv6 address, MAC address,
VLAN and the connected Port number of the Host together.
Chapter 17: IP Verify Source Commands
Provide information about the commands used for guarding the IP Source by filtering the IP
packets based on the IP-MAC Binding entries.
Chapter 18: IPv6 Verify Source Commands
Provide information about the commands used for guarding the IPv6 Source by filtering the IP
packets based on the IP-MAC Binding entries.
Chapter 19: ND Detection Commands
Provide information about the commands used for congifuring ND detection.
Chapter 20: ARP Inspection Commands
Provide information about the commands used for protecting the switch from the ARP
cheating or ARP Attack.
Chapter 21: DoS Defend Command
Provide information about the commands used for DoS defend and detecting the DoS attack.
Chapter 22: IEEE 802.1X Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring IEEE 802.1X function.
Chapter 23 PPPoE ID Insertion Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring PPPoE ID Insertion.
Chapter 24: System Log Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring system log.
2
Page 25

Chapter 25: SSH Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring and managing SSH (Security
Shell).
Chapter 26: MAC Address Commands
Provide information about the commands used for Address configuration.
Chapter 27: System Configuration Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring the System information and
System IP, reboot and reset the switch, upgrade the switch system and commands used for
cable test.
Chapter 28: IPv6 Address Configuration Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring the System IPv6 addresses.
Chapter 29: Ethernet Configuration Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring the Bandwidth Control,
Negotiation Mode, and Storm Control for enthernet ports.
Chapter 30: QoS Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring the QoS function.
Chapter 31: Port Mirror Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring the Port Mirror function.
Chapter 32: Port Isolation Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring Port Isolation function.
Chapter 33: Loopback Detection Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring the Loopback Detection
function.
Chapter 34: DDM Commands
Provide information about the commands used for DDM (Digtal Diagnostic Monitoring)
function.
Chapter 35: ACL Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring the ACL (Access Control List).
Chapter 36: MSTP Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring the MSTP (Multiple Spanning
Tree Protocol).
Chapter 37 Ethernet OAM Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring the Ethernet OAM (Operation,
Administration, and Maintenance) function.
3
Page 26

Chapter 38: DLDP Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring the DLDP (Device Link
Detection Protocol).
Chapter 39: IGMP Snooping Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring the IGMP Snooping (Internet
Group Management Protocol Snooping).
Chapter 40: MLD Snooping Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring the MLD Snooping (Multicast
Listener Discovery Snooping).
Chapter 41: SNMP Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring the SNMP (Simple Network
Management Protocol) functions.
Chapter 42: LLDP Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring LLDP function.
Chapter 43: sFlow Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring the Sampled Flow function.
Chapter 44: Static Routes Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring the Static Route function.
Chapter 45: SDM Template Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring the SDM templates.
Chapter 46: AAA Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring AAA (authentication,
authorization and accounting).
Chapter 47: DHCP Server Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring the DHCP Server function.
Chapter 48: DHCP Relay Commands
Provide information about the commands used for configuring the DHCP Relay function.
Chapter 49: PoE Commands(For T2600G-28MPS only)
Provide information about the commands used for configuring PoE function.
4
Page 27

Chapter 1 Using the CLI
1.1 Accessing the CLI
You can log on to the switch and access the CLI by the following three methods:
1. Log on to the switch by the console port on the switch.
2. Log on to the switch remotely by a Telnet connection through an Ethernet port.
3. Log on to the switch remotely by an SSH connection through an Ethernet port.
1.1.1 Logon by a console port
Console Port
The switch has two console ports: an RJ-45 console port and a Micro-USB console port.
Console output is active on devices connected to both console ports, but console input is only
active on one console port at a time.
The Micro-USB connector takes precedence over the RJ-45 connector. When the switch
detects a valid connection on the Micro-USB console port, input from the RJ-45 console port is
immediately disabled, and input from the Micro-USB console port is enabled. Removing the
Micro-USB connection immediately reenables input from the RJ-45 console connection.
USB Console Driver
If you are using the USB port on the MAC OS X or Linux OS for console connection, there is no
need to run a USB driver.
If you are using the switch’s Micro-USB console port with the USB port of a Windows PC, a
driver for the USB port is required. The USB driver is provided on the resource CD. Follow the
InstallSheild Wizard to accomplish the installation.
The TP-Link USB Console Driver supports the following Windows operating systems:
32-bit Windows XP SP3
64-bit Windows XP
32-bit Windows Vista
64-bit Windows Vista
32-bit Windows 7
64-bit Windows 7
32-bit Windows 8
5
Page 28
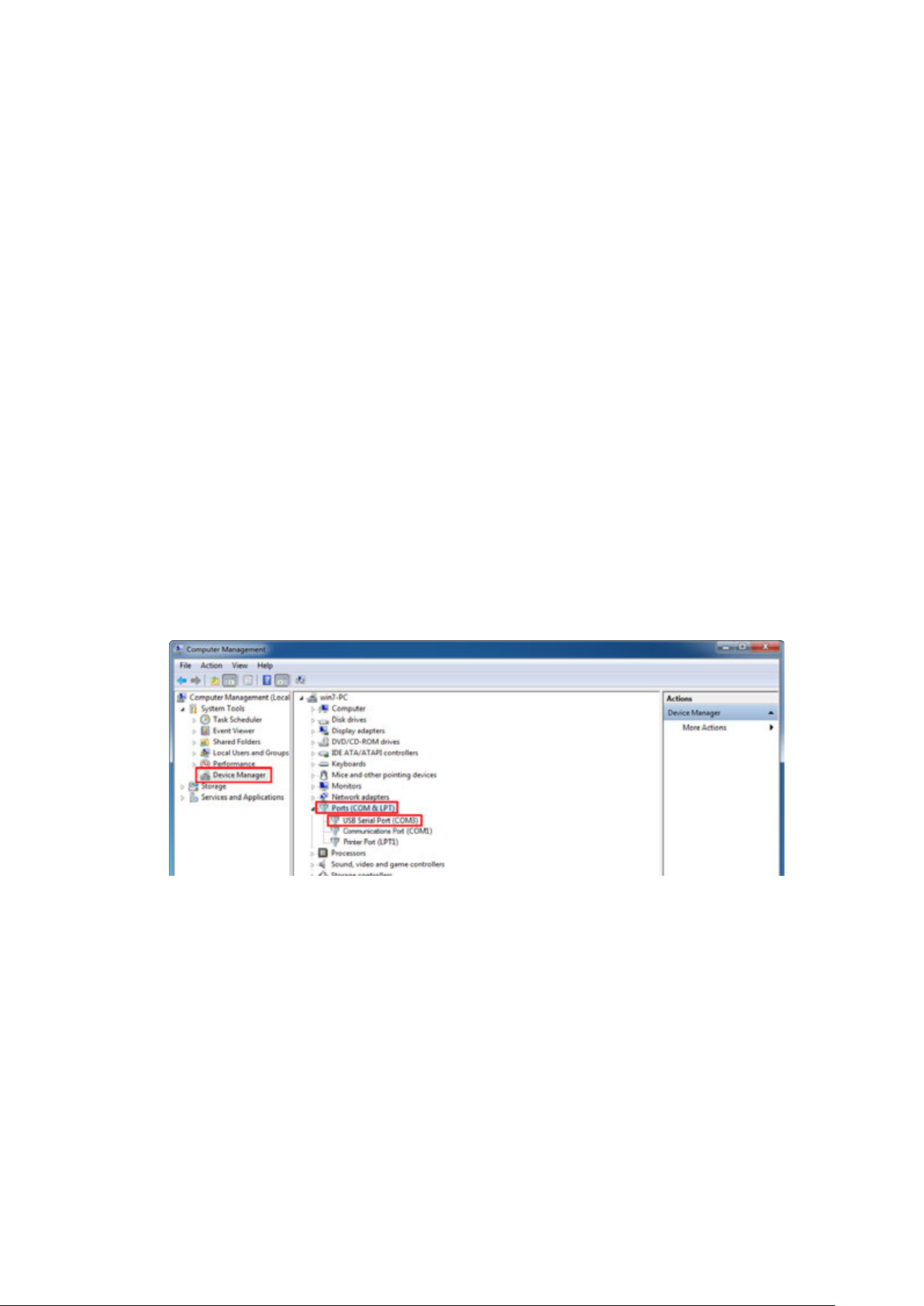
64-bit Windows 8
32-bit Windows 8.1
64-bit Windows 8.1
After the TP-Link USB Console Driver is installed, the PC’s USB port will act as RS-232 serial
port when the PC’s USB port is connected to the switch’s Micro-USB console port. And the
PC’s USB port will act as standard USB port when the PC’s USB port is unplugged from the
switch.
Logon
Take the following steps to log on to the switch by the console port.
1. Connect the PCs or Terminals to the console port on the switch by the provided cable.
2. Start the terminal emulation program (such as the HyperTerminal) on the PC.
3. Specify the connection COM port in the terminal emulation program. If the Micro-USB
Console port is used, you can view which port is assigned to the USB serial port in the
following path:
Control Panel -> Hardware and Sound -> Device Manager -> Ports ->USB Serial Port.
Figure 1-1 USB Serial Port Number
4. Configure the terminal emulation program or the terminal to use the following settings:
Baud rate: 38400 bps
Data bits: 8
Parity: none
Stop bits: 1
Flow control: none
6
Page 29
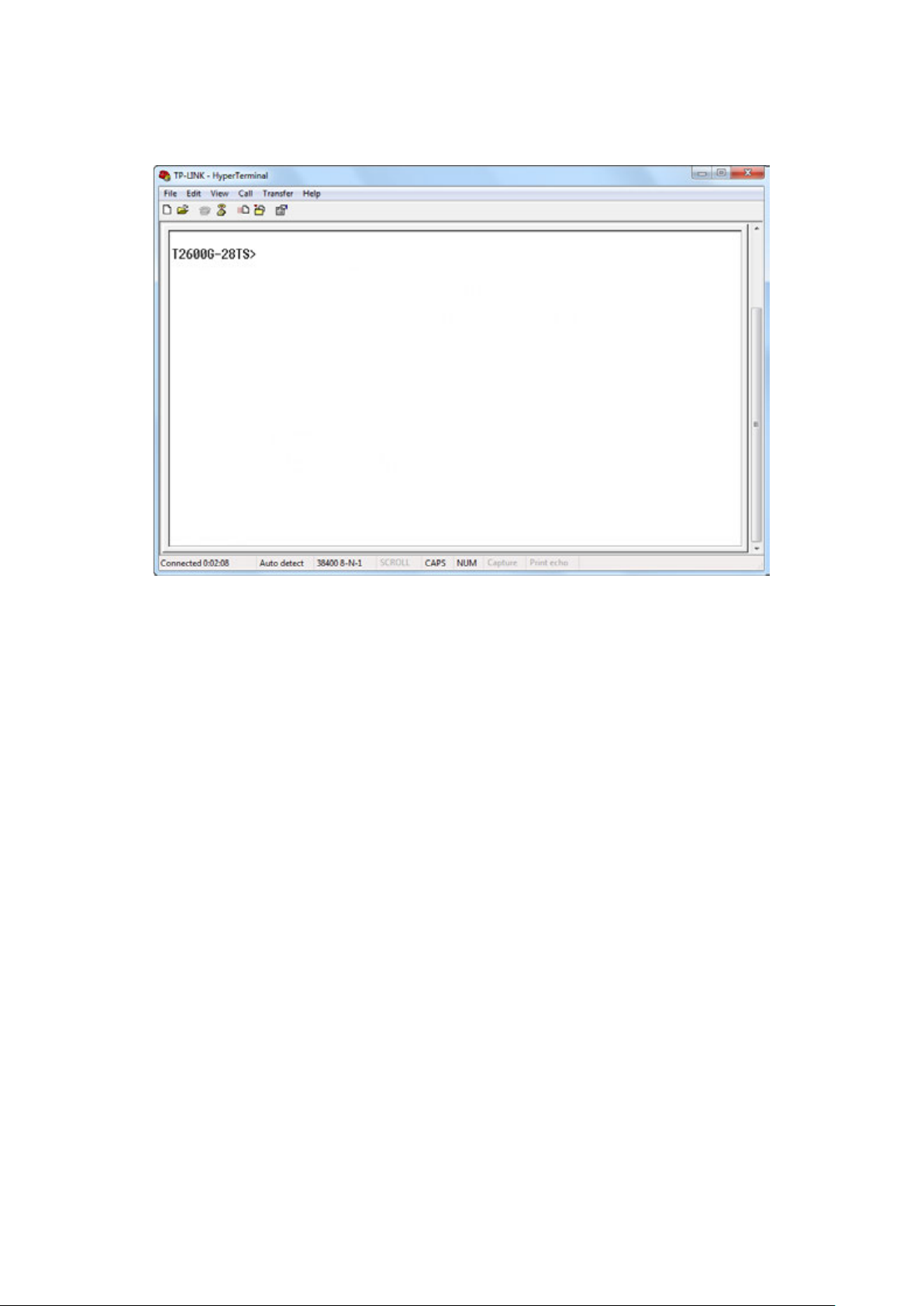
5. The DOS prompt ”T2600G-28TS>” will appear after pressing the Enter button as shown in
Figure 1-2. It indicates that you can use the CLI now.
Figure 1-2 Log in the Switch
1.1.2 Logon by Telnet
For Telnet connection, you should also configure the Telnet login mode and login
authentication information through console connection.
Telnet login has the following two modes. You can choose one according to your needs:
Login local Mode: It requires username and password, which are both admin by default.
Login Mode: It doesn’t require username and password, but a connection password is
required.
Before Telnet login, you are required to configure Telnet login mode and login authentication
information through console connection.
7
Page 30
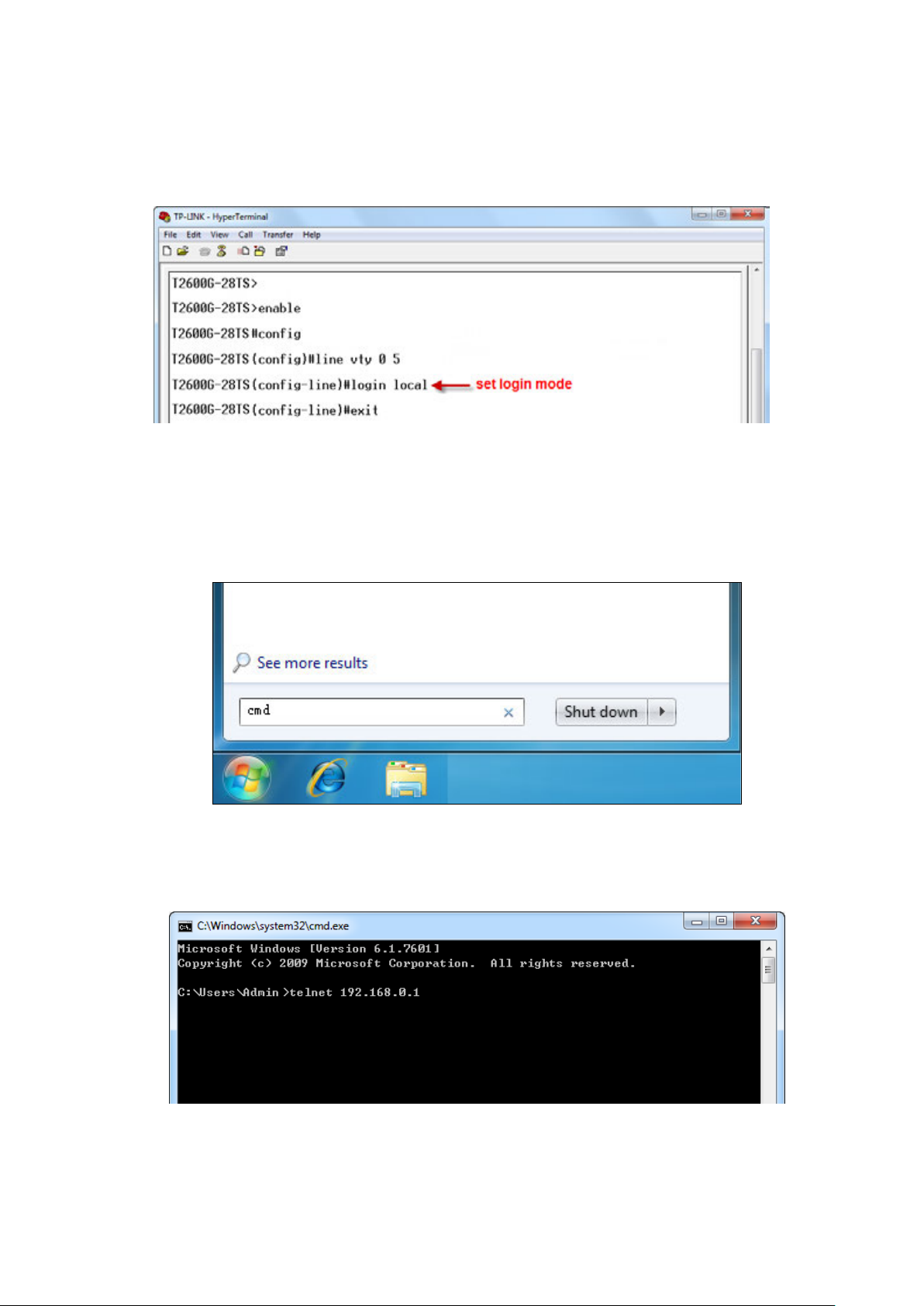
Login Local Mode
Firstly, configure the Telnet login mode as “login local” in the prompted DOS screen shown in
Figure 1-3.
Figure 1-3 Configure login local mode
Now, you can logon by Telnet in login local mode.
1. Make sure the switch and the PC are in the same LAN. Click Start and type in cmd in the
Search programs and files window and press the Enter button.
Figure 1-4 Run Window
2. Type telnet 192.168.0.1 in the command prompt shown as Figure 1-5, and press the Enter
button.
Figure 1-5 Connecting to the Switch
8
Page 31

3. Type the default user name and password (both of them are admin), then press the Enter
button so as to enter User EXEC Mode.
Figure 1-6 Enter into the User EXEC Mode
4. Type enable command to enter Privileged EXEC Mode.
Figure 1-7 Enter into the Priviledged EXEC Mode
Now you can manage your switch with CLI commands through Telnet connection.
Login Mode
Firstly configure the Telnet login mode as “login” and the connection password as 456 in the
prompted DOS screen shown in Figure 1-8.
Figure 1-8 Configure login mode
9
Page 32

Now, you can logon by Telnet in login mode:
1. Make sure the switch and the PC are in the same LAN. Click Start and type in cmd in the
Search programs and files window and press the Enter button.
Figure 1-9 Run Window
2. Type telnet 192.168.0.1 in the command prompt shown as Figure 1-10, and press the
Enter button.
Figure 1-10 Connecting to the Switch
3. You are prompted to enter the connection password 456 you have set through Console
port connection, and then you are in User EXEC Mode.
Figure 1-11 Enter into the User EXEC Mode
10
Page 33

4. Type enable command to enter Privileged EXEC Mode.
Figure 1-12 Enter into the Privileged EXEC Mode
Now you can manage your switch with CLI commands through Telnet connection.
Note:
You can refer to Chapter 11 User Management Commands for detailed commands
information of the Telnet connection configuration.
1.1.3 Logon by SSH
To log on by SSH, a Putty client software is recommended. There are two authentication modes
to set up an SSH connection:
Password Authentication Mode: It requires username and password, which are both admin by
default.
Key Authentication Mode: It requires a public key for the switch and a private key for the SSH
client software. You can generate the public key and the private key through Putty Key
Generator.
Note:
Before SSH login, please follow the steps shown in Figure 1-13 to enable the SSH function
through Telnet connection.
Figure 1-13 Enable SSH function
11
Page 34

Password Authentication Mode
1. Open the software to log on to the interface of PuTTY. Enter the IP address of the switch
into Host Name field; keep the default value 22 in the Port field; select SSH as the
Connection type.
Figure 1-14 SSH Connection Config
2. Click the Open button in the above figure to log on to the switch. Enter the login user name
and password to log on the switch, and then enter enable to enter Privileged EXEC Mode,
so you can continue to configure the switch.
Figure 1-15 Log on the Switch
12
Page 35

Key Authentication Mode
1. Select the key type and key length, and generate SSH key.
Figure 1-16 Generate SSH Key
Note:
1. The key length is in the range of 512 to 3072 bits.
2. During the key generation, randomly moving the mouse quickly can accelerate the key
generation.
13
Page 36

2. After the key is successfully generated, please save the public key and private key to a
TFTP server.
Figure 1-17 Save the Generated Key
3. Log on to the switch by Telnet and download the public key file from the TFTP server to the
switch, as the following figure shows:
Figure 1-18 Download the Public Key
14
Page 37

Note:
1. The key type should accord with the type of the key file.
2. The SSH key downloading can not be interrupted.
4. After the public key is downloaded, please log on to the interface of PuTTY and enter the IP
address for login.
Figure 1-19 SSH Connection Config
15
Page 38

5. Click Browse to download the private key file to SSH client software and click Open.
Figure 1-20 Download the Private Key
6. After successful authentication, please enter the login user name. If you log on to the
switch without entering password, it indicates that the key has been successfully
downloaded.
Figure 1-21 Log on the Switch
1.2 CLI Command Modes
The CLI is divided into different command modes: User EXEC Mode, Privileged EXEC Mode,
Global Configuration Mode, Interface Configuration Mode and VLAN Configuration Mode.
16
Page 39

mode.
VLAN Configuration mode.
mode.
Interface Configuration Mode can also be divided into Interface Ethernet, Interface
link-aggregation and some other modes, which is shown as the following diagram.
The following table gives detailed information about the Accessing path, Prompt of each mode
and how to exit the current mode and access the next mode.
Mode Accessing Path Prompt
User EXEC
Mode
Privileged
EXEC Mode
Global
Configuration
Mode
Primary mode once
it is connected with
the switch.
Use the enable
command to enter
this mode from User
EXEC mode.
Use the configure
command to enter
this mode from
Privileged EXEC
mode.
T2600G-28TS>
T2600G-28TS#
T2600G-28TS(config)#
Logout or Access the next
mode
Use the exit command to
disconnect the switch.
Use the enable command to
access Privileged EXEC mode.
Enter the disable or the exit
command to return to User
EXEC mode.
Enter configure command to
access Global Configuration
Use the exit or the end
command or press Ctrl+Z to
return to Privileged EXEC mode.
Use the interface
port
gigabitEthernet
interface range
gigabitEthernet
command to access interface
Configuration mode.
or
port-list
Interface
Configuration
Mode
Layer 2 Interface:
Use the interface
gigabitEthernet
port,
interface
port-channel
port-channel-id
interface range
gigabitEthernet
port-list
enter this mode from
Global Configuration
or
command to
T2600G-28TS (config-if)#
or
T2600G-28TS(config-if-range)#
17
Use the vlan
Use the end command or press
Ctrl+Z to return to Privileged
EXEC mode.
Enter the exit or the # command
to return to Global Configuration
mode.
A port number must be specified
in the interface command.
vlan-list
to access
Page 40

Configuration mode.
list
configuration mode.
Mode Accessing Path Prompt
Layer 3 Interface:
Use the no
switchport
command to enter
Routed Port mode
from Interface
Configuration mode.
Interface
Configuration
Mode
Use the interface
vlan-id
vlan
command to enter
VLAN Interface
mode from Global
Configuration mode.
Use the interface
loopback
command to enter
Loopback Interface
mode from Global
id
T2600G-28TS (config-if)#
T2600G-28TS(config-if-range)#
or
Logout or Access the next
mode
Use the switchport command to
switch to the Layer 2 interface
mode.
Use the end command or press
Ctrl+Z to return to Privileged
EXEC mode.
Enter the exit or the # command
to return to Global Configuration
mode.
Use the end command or press
Ctrl+Z to return to Privileged
EXEC mode.
Enter the exit command or the #
command to return to Global
VLAN
Configuration
Mode
Use the vlan
command to enter
this mode from
Global Configuration
mode.
vlan-
T2600G-28TS (config-vlan)#
Note:
1. The user is automatically in User EXEC Mode after the connection between the PC and the
switch is established by a Telnet/SSH connection.
2. Each command mode has its own set of specific commands. To configure some
commands, you should access the corresponding command mode firstly.
Global Configuration Mode: In this mode, global commands are provided, such as the
Spanning Tree, Schedule Mode and so on.
Interface Configuration Mode: In this mode, users can configure one or several ports,
different ports corresponds to different commands
a). Interface gigabitEthernet: Configure parameters for an Ethernet port, such as
Duplex-mode, flow control status.
b). Interface range gigabitEthernet: Configure parameters for several Ethernet ports.
18
Page 41

c). Interface link-aggregation: Configure parameters for a link-aggregation, such as
broadcast storm.
d). Interface range link-aggregation: Configure parameters for multi-trunks.
e). Interface vlan: Configure parameters for the vlan-port.
VLAN Configuration Mode: In this mode, users can create a VLAN and add a specified
port to the VLAN.
3. Some commands are global, that means they can be performed in all modes:
show: Display all information of switch, for example: statistic information, port
information, VLAN information.
history: Display the commands history.
1.3 Privilege Restrictions
This switch’s security is divided into four privilege levels: User level, Power User level, Operator
level and Admin level. You can define username and password pairs, and assign a specific
privilege level to each pair. Different privilege levels have access to specified commands,
which is illustrated in the Privilege Requirement in each command. For details about how to
configure usename and password pairs, please refer to user name (password) and
(secret).
Users can enter Privileged EXEC mode from User EXEC mode by using the enable command. In
default case, no password is needed. In Global Configuration Mode, you can configure
password for Admin level by enable password command. Once password is configured, you
are required to enter it to access Privileged EXEC mode.
user name
1.4 Conventions
1.4.1 Format Conventions
The following conventions are used in this Guide:
Items in square brackets [ ] are optional
Items in braces { } are required
Alternative items are grouped in braces and separated by vertical bars. For example:
speed {10 | 100 | 1000 }
Bold indicates an unalterable keyword. For example: show logging
19
Page 42

Normal Font indicates a constant (several options are enumerated and only one can be
selected). For example: mode {dynamic | static | permanent}
Italic Font indicates a variable (an actual value must be assigned). For example: bridge
aging-time
aging-time
1.4.2 Special Characters
You should pay attentions to the description below if the variable is a character string:
These six characters ” < > , \ & can not be input.
If a blank is contained in a character string, single or double quotation marks should be
used, for example ’hello world’, ”hello world”, and the words in the quotation marks will be
identified as a string. Otherwise, the words will be identified as several strings.
1.4.3 Parameter Format
Some parameters must be entered in special formats which are shown as follows:
MAC address must be enter in the format of xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx.
One or several values can be typed for a port-list or a vlan-list using comma to separate.
Use a hyphen to designate a range of values, for instance,1/0/1,1/0/3-5,1/0/7 indicates
choosing port 1/0/1,1/0/3,1/0/4,1/0/5,1/0/7.
20
Page 43

Chapter 2 User Interface
2.1 enable
Description
The enable command is used to access Privileged EXEC Mode from User
EXEC Mode.
Syntax
enable
Command Mode
User EXEC Mode
Privilege Requirement
None.
Example
If you have set the password to access Privileged EXEC Mode from User
EXEC Mode:
T2600G-28TS>enable
Enter password:
T2600G-28TS#
2.2 service password-encryption
Description
The service password-encryption command is used to encrypt the
password when the password is defined or when the configuration is written,
using the symmetric encryption algorithm. Encryption prevents the password
from being readable in the configuration file. To disable the global encryption
Syntax
function, please use no service password-encryption command.
service password-encryption
no service password-encryption
21
Page 44

Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin level users have access to these commands.
Example
Enable the global encryption function:
T2600G-28TS(config)# service password-encryption
2.3 enable password
Description
The enable password command is used to set or change the password for
users to access Privileged EXEC Mode from User EXEC Mode. To remove the
password, please use no enable password command. This command uses
the symmetric encryption.
Syntax
enable password { [ 0 ]
no enable password
Parameter
0 —— Specify the encryption type. 0 indicates that an unencrypted password
will follow. By default, the encryption type is 0.
password
characters or symbols. The password is case sensitive, allows digits, English
letters (case sensitive), underlines and sixteen special characters
( !$%'()*,-./[]{|} ). By default, it is empty.
7 —— Indicates a symmetric encrypted password with fixed length will follow.
encrypted-password
password
—— Super password, a string from 1 to 31 alphanumeric
—— A symmetric encrypted password with fixed length,
| 7
encrypted-password
}
which you can copy from another switch’s configuration file. After the
encrypted password is configured, you should use the corresponding
unencrypted password if you re-enter this mode.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
22
Page 45

Privilege Requirement
Only Admin level users have access to these commands.
User Guidelines
If the password you configured here is unencrypted and the global
encryption function is enabled in service password-encryption
password in the configuration file will be displayed in the symmetric
encrypted form.
Example
Set the super password as “admin” and unencrypted to access Privileged
EXEC Mode from User EXEC Mode:
T2600G-28TS(config)#enable password 0 admin
2.4 enable secret
Description
The enable secret command is used to set a secret password, which is using
an MD5 encryption algorithm, for users to access Privileged EXEC Mode from
User EXEC Mode. To return to the default configuration, please use no enable
, the
secret command. This command uses the MD5 encryption.
Syntax
enable secret { [ 0 ]
no enable secret
Parameter
0 —— Specify the encryption type. 0 indicates that an unencrypted password
will follow. By default, the encryption type is 0.
password
characters or symbols. The password is case sensitive, allows digits, English
letters (case sensitive), underlines and sixteen special characters
( !$%'()*,-./[]{|} ). By default, it is empty. The password in the configuration file
will be displayed in the MD5 encrypted form.
5 —— Indicates an MD5 encrypted password with fixed length will follow.
encrypted-password
password
—— Super password, a string from 1 to 31 alphanumeric
—— An MD5 encrypted password with fixed length,
| 5
encrypted-password
}
which you can copy from another switch’s configuration file. After the
23
Page 46

encrypted password is configured, you should use the corresponding
unencrypted password if you re-enter this mode.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin level users have access to these commands.
User Guidelines
If both the enable password and enable secret are defined, you must enter
the password set in enable secret.
Example
Set the secret password as “admin” and unencrypted to access Privileged
EXEC Mode from User EXEC Mode. The password will be displayed in the
encrypted form.
T2600G-28TS(config)#enable secret 0 admin
2.5 configure
Description
The configure command is used to access Global Configuration Mode from
Privileged EXEC Mode.
Syntax
configure
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin, Operator and Power User level users have access to these
commands.
Example
Access Global Configuration Mode from Privileged EXEC Mode:
T2600G-28TS# configure
T2600G-28TS(config)#
24
Page 47

2.6 exit
Description
The exit command is used to return to the previous Mode from the current
Mode.
Syntax
exit
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Privilege Requirement
None.
Example
Return to Global Configuration Mode from Interface Configuration Mode, and
then return to Privileged EXEC Mode:
T2600G-28TS(config-if)# exit
T2600G-28TS(config)#exit
T2600G-28TS#
2.7 end
Description
The end command is used to return to Privileged EXEC Mode.
Syntax
end
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin level users have access to these commands.
Example
Return to Privileged EXEC Mode from Interface Configuration Mode:
T2600G-28TS(config-if)#end
T2600G-28TS#
25
Page 48

2.8 clipaging
Description
The clipaging command is used to enable the pause function for the screen
display. If you want to display all the related information of the switch at once
when using the show command, please use no clipaging command.
Syntax
clipaging
no clipaging
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Privilege Requirement
None.
Example
Disable the pause function for the screen display:
T2600G-28TS(config)#no clipaging
2.9 history
Description
The history command is used to show the latest 20 commands you entered
in the current mode since the switch is powered.
Syntax
history
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and any Configuration Mode
Privilege Requirement
None.
Example
Show the commands you have entered in the current mode:
T2600G-28TS (config)# history
1 history
26
Page 49

2.10 history clear
Description
The history clear command is used to clear the commands you have entered
in the current mode, therefore these commands will not be shown next time
you use the history command.
Syntax
history clear
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and any Configuration Mode
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin, Operator and Power User level users have access to these
commands.
Example
Clear the commands you have entered in the current mode:
T2600G-28TS(config)#history clear
27
Page 50

Chapter 3 IEEE 802.1Q VLAN Commands
VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) technology is developed for the switch to divide the LAN
into multiple logical LANs flexibly. Hosts in the same VLAN can communicate with each other,
regardless of their physical locations. VLAN can enhance performance by conserving
bandwidth, and improve security by limiting traffic to specific domains.
3.1 vlan
Description
The vlan command is used to create IEEE 802.1Q VLAN and enter VLAN
Configuration Mode. To delete the IEEE 802.1Q VLAN, please use no vlan
command.
Syntax
vlan
vlan-list
no vlan
vlan-list
Parameter
vlan-list
format of 2-3, 5. It is multi-optional.
—— Specify IEEE 802.1Q VLAN ID list, ranging from 2 to 4094, in the
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin, Operator and Power User level users have access to these
commands.
Example
Create VLAN 2-10 and VLAN 100:
T2600G-28TS(config)# vlan 2-10,100
Delete VLAN 2:
T2600G-28TS(config)# no vlan 2
28
Page 51

3.2 interface vlan
Description
The interface vlan command is used to create VLAN Interface and enter
Interface VLAN Mode. To delete VLAN Interface, please use no interface
vlan command.
Syntax
interface vlan
no interface vlan
vlan-id
Parameter
vlan-id
—— Specify IEEE 802.1Q VLAN ID, ranging from 1 to 4094.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin, Operator and Power User level users have access to these
commands.
Example
Create VLAN Interface 2:
T2600G-28TS(config)# interface vlan 2
vlan-id
3.3 name
Description
The name command is used to assign a description to a VLAN. To clear the
description, please use no name command.
Syntax
name
no name
Parameter
descript
most.
Command Mode
VLAN Configuration Mode(VLAN)
descript
——String to describe the VLAN, which contains 16 characters at
29
Page 52

Privilege Requirement
Only Admin, Operator and Power User level users have access to these
commands.
Example
Specify the name of VLAN 2 as “group1”:
T2600G-28TS(config)# vlan 2
T2600G-28TS(config-vlan)# name group1
3.4 switchport mode
Description
The switchport mode command is used to configure the Link Types for the
ports.
Syntax
switchport mode { access | trunk | general }
Parameter
access | trunk | general —— Link Types. There are three Link Types for the
ports.
Command Mode
Interface Configuration Mode (interface gigabitEthernet / interface range
gigabitEthernet / interface port-channel / interface range port-channel)
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin, Operator and Power User level users have access to these
commands.
Example
Specify the Link Type of Gigabit Ethernet port 1/0/3 as “trunk”:
T2600G-28TS(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 1/0/3
T2600G-28TS(config-if)#switchport mode trunk
30
Page 53

3.5 switchport access vlan
Description
The switchport access vlan command is used to add the desired Access
port to IEEE 802.1Q VLAN, or to remove a port from the corresponding VLAN.
Syntax
switchport access vlan
no switchport access vlan
Parameter
vlan-id
—— Specify IEEE 802.1Q VLAN ID, ranging from 2 to 4094.
Command Mode
Interface Configuration Mode (interface gigabitEthernet / interface range
gigabitEthernet / interface port-channel / interface range port-channel)
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin, Operator and Power User level users have access to these
commands.
Example
Configure Gigabit Ethernet port 1/0/3 whose link type is “access” to VLAN 2:
T2600G-28TS(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 1/0/3
vlan-id
T2600G-28TS(config-if)#switchport access vlan 2
3.6 switchport trunk allowed vlan
Description
The switchport trunk allowed vlan command is used to add the desired
trunk port to IEEE 802.1Q VLAN. To remove a trunk port from the
corresponding VLAN, please use no switchport trunk allowed vlan
command.
Syntax
switchport trunk allowed vlan {
no switchport trunk allowed vlan {
vlan-list }
31
vlan-list
}
Page 54

Parameter
vlan-list
multi-optional.
—— VLAN ID list, ranging from 2 to 4094, in the format of 2-3, 5. It is
Command Mode
Interface Configuration Mode (interface gigabitEthernet / interface range
gigabitEthernet / interface port-channel / interface range port-channel)
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin, Operator and Power User level users have access to these
commands.
Example
Configure the link type of port 2 as trunk and add it to VLAN 2:
T2600G-28TS(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 1/0/2
T2600G-28TS(config-if)#switchport mode trunk
T2600G-28TS(config-if)#switchport trunk allowed vlan 2
3.7 switchport trunk allowed vlan all
Description
The switchport trunk allowed vlan all command is used to add the desired
trunk port to all the IEEE 802.1Q VLANs. To remove a trunk port from all the
IEEE 802.1Q VLANs, please use no switchport trunk allowed vlan all
command.
Syntax
switchport trunk allowed vlan all
no switchport trunk allowed vlan all
Command Mode
Interface Configuration Mode (interface gigabitEthernet / interface range
gigabitEthernet / interface port-channel / interface range port-channel)
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin, Operator and Power User level users have access to these
commands.
32
Page 55

Example
Configure the link type of port 2 as trunk and add it to all the VLANs:
T2600G-28TS(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 1/0/2
T2600G-28TS(config-if)#switchport mode trunk
T2600G-28TS(config-if)# switchport trunk allowed vlan all
3.8 switchport general allowed vlan
Description
The switchport general allowed vlan command is used to add the desired
General port to IEEE 802.1Q VLAN, or to remove a port from the
corresponding VLAN.
Syntax
switchport general allowed vlan
no switchport general allowed vlan
Parameter
vlan-list
multi-optional.
tagged | untagged —— egress-rule.
—— VLAN ID list, ranging from 2 to 4094, in the format of 2-3, 5. It is
Command Mode
Interface Configuration Mode (interface gigabitEthernet / interface range
gigabitEthernet / interface port-channel / interface range port-channel)
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin, Operator and Power User level users have access to these
commands.
Example
vlan-list
vlan-list
{ tagged | untagged }
Configure Gigabit Ethernet port 1/0/4 whose link type is “general” to VLAN 2
and its egress-rule as “tagged”:
T2600G-28TS(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 1/0/4
T2600G-28TS(config-if)#switchport mode general
T2600G-28TS(config-if)#switchport general allowed vlan 2 tagged
33
Page 56

3.9 switchport pvid
Description
The switchport pvid command is used to configure the PVID for the switch
ports.
Syntax
switchport pvid
Parameter
vlan-id
—— VLAN ID, ranging from 1 to 4094.
Command Mode
Interface Configuration Mode (interface gigabitEthernet / interface range
gigabitEthernet / interface port-channel / interface range port-channel)
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin, Operator and Power User level users have access to these
commands.
Example
Specify the PVID of port 1/0/2 as 2:
T2600G-28TS(config)# interface gigabitEthernet 1/0/2
T2600G-28TS(config-if)# switchport pvid 2
vlan-id
3.10 show vlan summary
Description
The show vlan summary command is used to display the summarized
information of IEEE 802.1Q VLAN.
Syntax
show vlan summary
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Privilege Requirement
None.
34
Page 57

Example
Display the summarized information of IEEE 802.1Q VLAN:
T2600G-28TS(config)# show vlan summary
3.11 show vlan brief
Description
The show vlan brief command is used to display the brief information of IEEE
802.1Q VLAN.
Syntax
show vlan brief
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Privilege Requirement
None.
Example
Display the brief information of IEEE 802.1Q VLAN:
T2600G-28TS(config)# show vlan brief
3.12 show vlan
Description
The show vlan command is used to display the information of IEEE 802.1Q
VLAN.
Syntax
show vlan [ id
Parameter
vlan-id
]
vlan-id
multi-optional. Using the show vlan command without parameter displays the
detailed information of all VLANs.
—— Specify IEEE 802.1Q VLAN ID, ranging from 1 to 4094. It is
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
35
Page 58

Privilege Requirement
None.
Example
Display the information of vlan 5:
T2600G-28TS(config)# show vlan id 5
3.13 show interface switchport
Description
The show interface switchport command is used to display the IEEE 802.1Q
VLAN configuration information of the specified port/port channel.
Syntax
show interface switchport [ gigabitEthernet
port-channel-id
]
Parameter
port
—— The port number.
port-channel-id
—— The ID of the port channel.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Privilege Requirement
None.
Example
Display the VLAN configuration information of all ports and port channels:
T2600G-28TS(config)# show interface switchport
port
| port-channel
36
Page 59

Chapter 4 MAC-based VLAN Commands
MAC VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) is the way to classify the VLANs based on MAC
Address. A MAC address is relative to a single VLAN ID. The untagged packets and the
priority-tagged packets coming from the MAC address will be tagged with this VLAN ID.
4.1 mac-vlan mac-address
Description
The mac-vlan mac-address command is used to create a MAC-based VLAN
entry. To delete a MAC-based VLAN entry, please use the no mac-vlan
mac-address command.
Syntax
mac-vlan mac-address
no mac-vlan mac-address
Parameter
mac-addr
vlan-id
descript
contains 8 characters at most.
—— MAC address, in the format of XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX.
—— Specify IEEE 802.1Q VLAN ID, ranging from 1 to 4094.
—— Give a description to the MAC address for identification, which
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin, Operator and Power User level users have access to these
commands.
Example
mac-addr
mac-addr
vlan
vlan-id
[description
descript
]
Create VLAN 2 with the MAC address 00:11:11:01:01:12 and the name “TP”:
T2600G-28TS(config)#mac-vlan mac-address 00:11:11:01:01:12 vlan 2
description TP
37
Page 60

4.2 mac-vlan
Description
The mac-vlan command is used to enable a port for the MAC-based VLAN
feature. Only the port is enabled can the configured MAC-based VLAN take
effect. To disable the MAC-based VLAN function, please use no mac-vlan
command. All the ports are disabled by default.
Syntax
mac-vlan
no mac-vlan
Command Mode
Interface Configuration Mode (interface gigabitEthernet / interface range
gigabitEthernet / interface port-channel / interface range port-channel)
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin, Operator and Power User level users have access to these
commands.
Example
Enable the Gigabit Ethernet port 1/0/3 for the MAC-based VLAN feature:
T2600G-28TS(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 1/0/3
T2600G-28TS(config-if)#mac-vlan
4.3 show mac-vlan
Description
The show mac-vlan command is used to display the information of the
MAC-based VLAN entry. MAC address and VLAN ID can be used to filter the
displayed information.
Syntax
show mac-vlan { all | mac-address
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
38
mac-addr
| vlan
vlan-id
}
Page 61

Privilege Requirement
None.
Parameter
mac-addr
vlan-id
—— MAC address, in the format of XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX.
—— Specify IEEE 802.1Q VLAN ID, ranging from 1 to 4094.
Example
Display the information of all the MAC-based VLAN entry:
T2600G-28TS(config)#show mac-vlan all
4.4 show mac-vlan interface
Description
The show mac-vlan interface command is used to display the port state of
MAC-based VLAN.
Syntax
show mac-vlan interface
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Privilege Requirement
None.
Example
Display the enable state of all the ports:
T2600G-28TS(config)#show mac-vlan interface
39
Page 62

Chapter 5 Protocol-based VLAN Commands
Protocol VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) is the way to classify VLANs based on Protocols. A
Protocol is relative to a single VLAN ID. The untagged packets and the priority-tagged packets
matching the protocol template will be tagged with this VLAN ID.
5.1 protocol-vlan template (For T2600G-18TS
only)
Description
The protocol-vlan template command is used to create Protocol-based
VLAN template. To delete Protocol-based VLAN template, please use no
protocol-vlan template command.
Syntax
protocol-vlan template name
type
}
no protocol-vlan template
Parameter
protocol-name
which contains 8 characters at most.
ether_2 ether-type
template-idx
can get the template corresponding to the number by the show
protocol-vlan template command.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
protocol-name
template-idx
—— Give a name for the Protocol-based VLAN Template ,
type
—— Specify the Ethernet type.
—— The number of the Protocol-based VLAN Template. You
frame { ether_2 ether-type
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin, Operator and Power User level users have access to these
commands.
Example
Create a Protocol-based VLAN template named “TP” whose Ethernet
protocol type is 0x2024:
40
Page 63

T2600G-18TS(config)#protocol-vlan template name TP frame ether_2
ether-type 2024
5.2 protocol-vlan template (For other switches)
Description
The protocol-vlan template command is used to create Protocol-based
VLAN template. To delete Protocol-based VLAN template, please use no
protocol-vlan template command.
Syntax
protocol-vlan template name
type
| snap ether-type
no protocol-vlan template
Parameter
protocol-name
which contains 8 characters at most.
ether_2 ether-type
snap ether-type
llc dsap
SSAP type.
dsap_type
template-idx
can get the template corresponding to the number by the
protocol-vlan template command.
Command Mode
protocol-name
type
| llc dsap
template-idx
—— Give a name for the Protocol-based VLAN Template ,
type
—— Specify the Ethernet type.
type
—— Specify the Ethernet type.
ssap
ssap_type
dsap_type
—— Specify the DSAP type and the
frame { ether_2 ether-type
ssap
ssap_type
}
—— The number of the Protocol-based VLAN Template. You
show
Global Configuration Mode
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin, Operator and Power User level users have access to these
commands.
Example
Create a Protocol-based VLAN template named “TP” whose Ethernet
protocol type is 0x2024:
41
Page 64

T2600G-28TS(config)#protocol-vlan template name TP frame ether_2
ether-type 2024
5.3 protocol-vlan vlan
Description
The protocol-vlan vlan command is used to create a Protocol-based VLAN
entry. To delete a Protocol-based VLAN entry, please use no protocol-vlan
vlan command.
Syntax
protocol-vlan vlan
no protocol-vlan vlan
Parameter
vlan-id
template-idx
get the template corresponding to the number by the show protocol-vlan
template command.
group-idx
the Protocol-based VLAN entry corresponding to the number by the show
protocol-vlan vlan command.
—— Specify IEEE 802.1Q VLAN ID, ranging from 1-4094.
——The number of the Protocol-based VLAN Template. You can
——The number of the Protocol-based VLAN entry. You can get
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Privilege Requirement
vlan-id
group-idx
template
template-idx
Only Admin, Operator and Power User level users have access to these
commands.
Example
Create Protocol-based VLAN 2 and bind it with Protocol-based VLAN Template
3:
T2600G-28TS(config)#protocol-vlan vlan 2 template 3
42
Page 65

5.4 protocol-vlan group
Description
The protocol-vlan command is used to add the port to a specified protocol
group. To remove the port from this protocol group, please use no
protocol-vlan group command.
Syntax
protocol-vlan group
no protocol-vlan group
Parameter
index
—— Specify the protocol group ID.
Command Mode
Interface Configuration Mode (interface gigabitEthernet / interface range
gigabitEthernet / interface port-channel / interface range port-channel)
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin, Operator and Power User level users have access to these
commands.
Example
Add Gigabit Ethernet port 20 to protocol group 1:
T2600G-28TS(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 1/0/20
index
index
T2600G-28TS(config-if)#protocol-vlan group 1
5.5 show protocol-vlan template
Description
The show protocol-vlan template command is used to display the
information of the Protocol-based VLAN templates.
Syntax
show protocol-vlan template
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
43
Page 66

Privilege Requirement
None.
Example
Display the information of the Protocol-based VLAN templates:
T2600G-28TS(config)#show protocol-vlan template
5.6 show protocol-vlan vlan
Description
The show protocol-vlan vlan command is used to display the information
about Protocol-based VLAN entry.
Syntax
show protocol-vlan vlan
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Privilege Requirement
None.
Example
Display information of the Protocol-based VLAN entry:
T2600G-28TS(config)#show protocol-vlan vlan
44
Page 67

Chapter 6 VLAN-VPN Commands
VLAN-VPN (Virtual Private Network) function, the implement of a simple and flexible Layer 2
VPN technology, allows the packets with VLAN tags of private networks to be encapsulated
with VLAN tags of public networks at the network access terminal of the Internet Service
Provider. And these packets will be transmitted with double-tag across the public networks.
6.1 dot1q-tunnel
Description
The dot1q-tunnel command is used to enable the VLAN-VPN function
globally. To disable the VLAN-VPN function, please use the no dot1q-tunnel
command.
Syntax
dot1q-tunnel
no dot1q-tunnel
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin, Operator and Power User level users have access to these
commands.
Example
Enable the VLAN-VPN function globally:
T2600G-28TS(config)#dot1q-tunnel
6.2 dot1q-tunnel tpid
Description
The dot1q-tunnel tpid command is used to configure Global TPID of the
VLAN-VPN. To restore to the default value, please use the no dot1q-tunnel
tpid command.
45
Page 68

Syntax
dot1q-tunnel tpid
no dot1q-tunnel tpid
Parameter
tpid
—— The value of Global TPID. It must be 4 Hex integers. By default, it is
8100.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin, Operator and Power User level users have access to these
commands.
Example
Configure Global TPID of the VLAN-VPN as 0x9100:
T2600G-28TS(config)#dot1q-tunnel tpid 9100
tpid
6.3 dot1q-tunnel mapping
Note: T2600G-18TS doesn’t support this command.
Description
The dot1q-tunnel mapping command is used to enable the VLAN Mapping
feature globally. To disable this function, please use the no dot1q-tunnel
mapping command. By default, the VLAN Mapping feature is disabled.
Syntax
dot1q-tunnel mapping
no dot1q-tunnel mapping
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin, Operator and Power User level users have access to these
commands.
46
Page 69

Example
Enable the VLAN mapping feature globally:
T2600G-28TS(config)#dot1q-tunnel mapping
6.4 switchport dot1q-tunnel missdrop
Description
The switchport dot1q-tunnel missdrop command is used to enable the
VLAN-VPN missdrop function for a specific port. To disable the VLAN-VPN
missdrop function, please use the no switchport dot1q-tunnel missdrop
command.
Syntax
switchport dot1q-tunnel missdrop
no switchport dot1q-tunnel missdrop
Command Mode
Interface Configuration Mode (interface gigabitEthernet / interface range
gigabitEthernet / interface port-channel / interface range port-channel)
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin, Operator and Power User level users have access to these
commands.
Example
Enable the VLAN-VPN missdrop function for Gigabit Ethernet port 1/0/3:
T2600G-28TS(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 1/0/3
T2600G-28TS(config-if)#switchport dot1q-tunnel missdrop
6.5 switchport dot1q-tunnel mapping
Description
The switchport dot1q-tunnel mapping command is used add the VLAN
Mapping entry on a specified port. To delete the VLAN Mapping entry on this
port, please use the no switchport dot1q-tunnel mapping command.
47
Page 70

Syntax
switchport dot1q-tunnel mapping
no switchport dot1q-tunnel mapping
Parameter
c-vlan
sp-vlan
descript
15 characters at most.
—— Customer VLAN ID, ranging from 1 to 4094.
—— Service Provider VLAN ID, ranging from 1 to 4094.
—— Give a description to the VLAN Mapping entry, which contains
Command Mode
Interface Configuration Mode (interface gigabitEthernet / interface range
gigabitEthernet / interface port-channel / interface range port-channel)
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin, Operator and Power User level users have access to these
commands.
c-vlan sp-vlan [descript
c-vlan
]
Example
Add a VLAN Mapping entry on the Gigabit Ethernet port 1/0/3 with the
Customer VLAN as VLAN 2 and the Service Provider VLAN as VLAN 3:
T2600G-28TS(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 1/0/3
T2600G-28TS(config-if)#switchport dot1q-tunnel mapping 2 3
6.6 switchport dot1q-tunnel mode
Description
The switchport dot1q-tunnel mode command is used to configure the VPN
port’s mode. To close this VPN port, please use the no switchport
dot1q-tunnel mode command. By default, no port has been configured as
the VPN port. The VPN port mode uni and nni cannot switch to each other
directly, so please close the VPN port and switch to the other mode if
needed.
Syntax
switchport dot1q-tunnel mode { uni/nni }
no switchport dot1q-tunnel mode
48
Page 71

Parameter
uni
——The port connected to the clients.
(Note: T2600G-18TS does’t support
nni
——The port connected to the ISP.
Command Mode
Interface Configuration Mode (interface gigabitEthernet / interface range
gigabitEthernet / interface port-channel / interface range port-channel)
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin, Operator and Power User level users have access to these
commands.
Example
Configure the Gigabit Ethernet port 1/0/3 as the VPN UNI ports:
T2600G-28TS(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 1/0/3
T2600G-28TS(config-if)#switchport dot1q-tunnel mode uni
uni
port setting.)
6.7 show dot1q-tunnel
Description
The show dot1q-tunnel command is used to display the global configuration
information of the VLAN VPN.
Syntax
show dot1q-tunnel
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Privilege Requirement
None.
Example
Display the global configuration information of the VLAN VPN:
T2600G-28TS(config)#show dot1q-tunnel
49
Page 72

6.8 show dot1q-tunnel mapping
Description
The show dot1q-tunnel mapping command is used to display the
information of VLAN Mapping entry.
Syntax
show dot1q-tunnel mapping
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Privilege Requirement
None.
Example
Display the information of VLAN Mapping entry:
T2600G-28TS(config)#show dot1q-tunnel mapping
6.9 show dot1q-tunnel interface
Description
The show dot1q-tunnel mapping interface command is used to display the
VLAN VPN port type.
Syntax
show dot1q-tunnel interface
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Privilege Requirement
None.
Example
Display the port type of all VLAN VPN ports:
T2600G-28TS(config)#show dot1q-tunnel interface
50
Page 73

Chapter 7 Private VLAN Commands
Note: T2600G-18TS doesn't support Private VLAN feature.
Private VLANs are configured specially for saving VLAN resource of uplink devices and
decreasing broadcast.
7.1 private-vlan primary
Description
The private-vlan primary command is used to configure the designated
VLAN as the primary VLAN of the Private VLAN. To remove the primary VLAN
property pf the current VLAN, please use no private-vlan primary command.
Syntax
private-vlan primary
no private-vlan primary
Command Mode
VLAN Configuration Mode (VLAN)
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin and Operator level users have access to these commands.
Example
Configure the VLAN 3 as the primary VLAN of the private VLAN:
T2600G-28TS(config)#vlan 3
T2600G-28TS(config-vlan)#private-vlan primary
7.2 private-vlan community
Description
The private-vlan community command is used to configure the designated
VLAN as the community VLAN of the Private VLAN. To remove the
community VLAN property pf the current VLAN, please use no private-vlan
community command.
51
Page 74

Syntax
private-vlan community
no private-vlan community
Command Mode
VLAN Configuration Mode (VLAN)
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin and Operator level users have access to these commands.
Example
Configure the VLAN 4 as the community VLAN of the private VLAN:
T2600G-28TS(config)#vlan 4
T2600G-28TS(config-vlan)#private-vlan community
7.3 private-vlan isolated
Description
The private-vlan isolated command is used to configure the designated
VLAN as the isolated VLAN of the Private VLAN. To remove the isolated VLAN
property pf the current VLAN, please use no private-vlan isolated command.
Syntax
private-vlan isolated
no private-vlan isolated
Command Mode
VLAN Configuration Mode (VLAN)
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin and Operator level users have access to these commands.
Example
Configure the VLAN 3 as the isolated VLAN of the private VLAN:
T2600G-28TS(config)#vlan 3
T2600G-28TS(config-vlan)#private-vlan isolated
52
Page 75

7.4 private-vlan association
Description
The private-vlan association command is used to associate primary VLAN
with secondary VLAN. To exterminate the currently association, please use
no private-vlan association command.
Syntax
private-vlan association
no private-vlan association
Parameter
vlan_list
—— Secondary VLAN ID, ranging from 2 to 4094.
Command Mode
VLAN Configuration Mode (VLAN)
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin and Operator level users have access to these commands.
Example
Associate primary VLAN 3 with community VLAN 4 as a private VLAN:
T2600G-28TS(config)#vlan 3
T2600G-28TS(config-vlan)#private-vlan association 4
vlan_list
vlan_list
7.5 switchport private-vlan
Description
The switchport private-vlan command is used to configure the private VLAN
mode for the switchport. To invalid the configuration, please use no
switchport private-vlan command.
Syntax
switchport private-vlan { promiscuous | host }
no switchport private-vlan
Parameter
promiscuous | host —— Configure the private VLAN mode for the switchport.
53
Page 76

Command Mode
Interface Configuration Mode (interface gigabitEthernet / interface range
gigabitEthernet / interface port-channel / interface range port-channel)
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin and Operator level users have access to these commands.
Example
Configure Gigabit Ethernet port 3 as “host”:
T2600G-28TS(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 1/0/3
T2600G-28TS(config-if)#switchport private-vlan host
7.6 switchport private-vlan host-association
Description
The switchport private-vlan host-association command is used to add host
type port to private VLAN. To remove the port from Private VLAN, please use
no switchport private-vlan host-association command.
Syntax
switchport private-vlan host-association
secondary_vlan_id vlantype
no switchport private-vlan host-association
Parameter
primary-vlan-id
secondary-vlan-id
vlantype
isolated
primary_vlan_id
—— Primary VLAN ID, ranging from 2 to 4094.
—— Secondary VLAN ID, ranging from 2 to 4094.
—— Specify the type of the secondary VLAN, either
.
community
or
Command Mode
Interface Configuration Mode (interface gigabitEthernet / interface range
gigabitEthernet / interface port-channel / interface range port-channel)
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin and Operator level users have access to these commands.
54
Page 77

Example
Configure host type Gigabit Ethernet port 1/0/3 as a member of primary
VLAN 3 and secondary VLAN 4, with the type of VLAN 4 as community:
T2600G-28TS(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 1/0/3
T2600G-28TS(config-if)#switchport private-vlan host-association 3 4
community
7.7 switchport private-vlan mapping
Description
The switchport private-vlan mapping command is used to add promiscuous
type port to private VLAN. To remove the port from Private VLAN, please use
no switchport private-vlan mapping command.
Syntax
switchport private-vlan mapping
no switchport private-vlan mapping
Parameter
primary-vlan-id
secondary-vlan-id
—— Primary VLAN ID, ranging from 2 to 4094.
Command Mode
Interface Configuration Mode (interface gigabitEthernet / interface range
gigabitEthernet / interface port-channel / interface range port-channel)
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin and Operator level users have access to these commands.
Example
primary_vlan_id secondary_vlan_id
—— Secondary VLAN ID, ranging from 2 to 4094.
Configure promiscuous type Gigabit Ethernet port 1/0/3 as a member of
primary VLAN 3 and secondary VLAN 4:
T2600G-28TS(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 1/0/3
T2600G-28TS(config-if)#switchport private-vlan mapping 3 4
55
Page 78

7.8 show vlan private-vlan
Description
The show vlan private-vlan command is used to display the Private VLAN
configuration information of the switch.
Syntax
show vlan private-vlan
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin and Operator level users have access to these commands.
Example
Display the configuration information of all Private VLAN:
T2600G-28TS(config)#show vlan private-vlan
7.9 show vlan private-vlan interface
Description
The show vlan private-vlan interface command is used to display the
Private VLAN configuration information of the specified port(s).
Syntax
show vlan private-vlan interface [gigabitEthernet
port-channel-id
Parameter
port
port-channel-id
—— The port number.
]
—— The ID of the port channel.
port
| port-channel
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin and Operator level users have access to these commands.
56
Page 79

Example
Display the configuration information of all the Ethernet ports:
T2600G-28TS(config)#show vlan private-vlan interface
57
Page 80

Chapter 8 L2PT Commands
L2PT (Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling) is a feature for service providers to transmit packets from
different customers across their ISP networks and maintain Layer 2 protocol configurations of
each customer. The supported Layer 2 protocols are STP (Spanning Tree Protocol), GVRP
(GARP VLAN Registration Protocol), CDP (Cisco Discovery Protocol), VTP (VLAN Trunking
Protocol), PAgP (Port Aggregation Protocol), UDLD (UniDirectional Link Detection) and
PVST+(Per VLAN Spanning Tree Plus).
8.1 l2protocol-tunnel
Description
The l2protocol-tunnel command is used to enable the layer 2 protocol
tunneling (L2PT) function globally. To disable the L2PT function, please use
no l2protocol-tunnel command.
Syntax
l2protocol-tunnel
no l2protocol-tunnel
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin and Operator level users have access to these commands.
Example
Enable the L2PT function globally:
T2600G-28TS(config)# l2protocol-tunnel
8.2 l2protocol-tunnel type
Description
The l2protocol-tunnel type command is used to configure the L2PT function
on a specified port. To disable the L2PT function on the specified port, please
use no l2protocol-tunnel command.
58
Page 81

Syntax
l2protocol-tunnel type nni
l2protocol-tunnel type uni { 01000ccccccc | 01000ccccccd | gvrp | stp | lacp
| all } [ threshold
no l2protocol-tunnel
Parameter
nni —— Specify the port type according to its connecting device in the
network. Specify the port’s type as NNI if it is connecting to the ISP network.
uni —— Specify the port type according to its connecting device in the
network. Specify the port’s type as UNI if it is connecting to the user’s local
network.
01000ccccccc | 01000ccccccd | gvrp | stp | lacp | all —— Select the
supported Layer 2 protocol type. Packets of the specified protocol will be
encapsulated with their destination MAC address before they are sent to the
ISP network. Packets will be decapsulated to restore their Layer 2 protocol
and MAC address information before they are sent to the customer network.
• 01000ccccccc: Enable protocol tunneling for the packets with
destination MAC address 01-00-0C-CC-CC-CC. 01-00-0CC-CC-CC-CC is
threshold ]
used as the destination MAC address of the CDP/VTP/PAgP/UDLD packets.
• 01000ccccccd: Enable protocol tunneling for the packets with
destination MAC address 01-00-0C-CC-CC-CD. 01-00-0CC-CC-CC-CD is
used as the destination MAC address of Cisco PVST+ BPDUs.
• gvrp: Enable protocol tunneling for the GVRP packets.
• stp: Enable protocol tunneling for the STP packets.
lacp: Enable protocol tunneling for the LACP packets.
• all: All the above Layer 2 protocols are supported for tunneling.
threshold
encapsulation. Packets beyond the threshold will be dropped. It ranges from
0 to 1000.
Command Mode
Interface Configuration Mode (interface gigabitEthernet / interface range
gigabitEthernet / interface port-channel / interface range port-channel)
——Configure the threshold for packets-per-second accepted for
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin and Operator level users have access to these commands.
59
Page 82

Example
Configure port 1/0/3 as a UNI port for STP packets with the threshold as 1000
packets/second:
T2600G-28TS(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 1/0/3
T2600G-28TS(config-if)# l2protocol-tunnel type uni stp threshold 1000
8.3 show l2protocol-tunnel global
Description
The show l2protocol-tunnel global command is used to display the global
L2PT status.
Syntax
show l2protocol-tunnel global
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Privilege Requirement
None.
Example
Display the global L2PT status:
T2600G-28TS(config)# show l2protocol-tunnel global
8.4 show l2protocol-tunnel interface
Description
The show l2protocol-tunnel interface command is used to display the L2PT
configuration information of a specified Ethernet port or of all Ethernet ports.
Syntax
show l2protocol-tunnel interface [ gigabitEthernet
port-channel-id
Parameter
port
port-channel-id
]
—— The port number.
—— The ID of the port channel.
60
port
| port-channel
Page 83

Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Privilege Requirement
None.
Example
Display the L2PT configuration information of Gigabit Ethernet port 1/0/1:
T2600G-28TS(config)#show l2protocol-tunnel interface gigabitEthernet
1/0/1
Display the L2PT configuration information of all Ethernet ports:
T2600G-28TS(config)#show l2protocol-tunnel interface
61
Page 84

Chapter 9 GVRP Commands
GVRP (GARP VLAN registration protocol) is an implementation of GARP (generic attribute
registration protocol). GVRP allows the switch to automatically add or remove the VLANs via
the dynamic VLAN registration information and propagate the local VLAN registration
information to other switches, without having to individually configure each VLAN.
9.1 gvrp
Description
The gvrp command is used to enable the GVRP function globally. To disable
the GVRP function, please use no gvrp command.
Syntax
gvrp
no gvrp
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin, Operator and Power User level users have access to these
commands.
Example
Enable the GVRP function globally:
T2600G-28TS(config)#gvrp
9.2 gvrp (interface)
Description
The gvrp command is used to enable the GVRP function for the desired port.
To disable it, please use no gvrp command. The GVRP feature can only be
enabled for the trunk-type ports.
Syntax
gvrp
62
Page 85

no gvrp
Command Mode
Interface Configuration Mode (interface gigabitEthernet / interface range
gigabitEthernet / interface port-channel / interface range port-channel)
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin, Operator and Power User level users have access to these
commands.
Example
Enable the GVRP function for Gigabit Ethernet ports 1/0/2-6:
T2600G-28TS(config)#interface range gigabitEthernet 1/0/2-6
T2600G-28TS(config-if-range)#gvrp
9.3 gvrp registration
Description
The gvrp registration command is used to configure the GVRP registration
type for the desired port. To restore to the default value, please use no gvrp
registration command.
Syntax
gvrp registration { normal | fixed | forbidden }
no gvrp registration
Parameter
normal | fixed | forbidden —— Registration mode. By default, the registration
mode is “normal”.
Command Mode
Interface Configuration Mode (interface gigabitEthernet / interface range
gigabitEthernet / interface port-channel / interface range port-channel)
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin, Operator and Power User level users have access to these
commands.
63
Page 86

Example
Configure the GVRP registration mode as “fixed” for Gigabit Ethernet ports
1/0/2-6:
T2600G-28TS(config)#interface range gigabitEthernet 1/0/2-6
T2600G-28TS(config-if-range)#gvrp registration fixed
9.4 gvrp timer
Description
The gvrp timer command is used to set a GVRP timer for the desired port. To
restore to the default setting of a GARP timer, please use no gvrp timer
command.
Syntax
gvrp timer { leaveall | join | leave }
no gvrp timer [leaveall | join | leave]
Parameter
leaveall | join | leave —— They are the three timers: leave All, join and leave.
Once the LeaveAll Timer is set, the port with GVRP enabled can send a
LeaveAll message after the timer times out, so that other GARP ports can
re-register all the attribute information. After that, the LeaveAll timer will start
to begin a new cycle. To guarantee the transmission of the Join messages, a
GARP port sends each Join message two times. The Join Timer is used to
define the interval between the two sending operations of each Join
message. Once the Leave Timer is set, the GARP port receiving a Leave
message will start its Leave timer, and deregister the attribute information if it
does not receive a Join message again before the timer times out.
value
30000 centiseconds and the default value is 1000 centiseconds. The Join
value
——The value of the timer. The LeaveAll Timer ranges from 1000 to
Timer ranges from 20 to 1000 centiseconds and the default value is 20
centiseconds. The Leave Timer ranges from 60 to 3000 centiseconds and
the default value is 60 centiseconds.
Command Mode
Interface Configuration Mode (interface gigabitEthernet / interface range
gigabitEthernet / interface port-channel / interface range port-channel)
64
Page 87

Privilege Requirement
Only Admin, Operator and Power User level users have access to these
commands.
Example
Set the GARP leaveall timer of Gigabit Ethernet port 1/0/6 as 2000
centiseconds and restore the join timer of it to the default value:
T2600G-28TS(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 1/0/6
T2600G-28TS(config-if)#gvrp timer leaveall 2000
T2600G-28TS(config-if)#no gvrp timer join
9.5 show gvrp interface
Description
The show gvrp interface command is used to display the GVRP
configuration information of a specified Ethernet port or of all Ethernet ports.
Syntax
show gvrp interface [ gigabitEthernet
Parameter
port
—— The port number.
port-channel-id
—— The ID of the port channel.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Privilege Requirement
None.
Example
port
| port-channel
port-channel-id
]
Display the GVRP configuration information of Gigabit Ethernet port 1:
T2600G-28TS(config)#show gvrp interface gigabitEthernet 1/0/1
Display the GVRP configuration information of all Ethernet ports:
T2600G-28TS(config)#show gvrp interface
65
Page 88

9.6 show gvrp global
Description
The show gvrp global command is used to display the global GVRP status.
Syntax
show gvrp global
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Privilege Requirement
None.
Example
Display the global GVRP status:
T2600G-28TS(config)#show gvrp global
66
Page 89

Chapter 10 Voice VLAN Commands
Voice VLANs are configured specially for voice data stream. By configuring Voice VLANs and
adding the ports with voice devices attached to voice VLANs, you can perform QoS-related
configuration for voice data, ensuring the transmission priority of voice data stream and voice
quality.
10.1 voice vlan
Description
The voice vlan command is used to enable Voice VLAN function. To disable
Voice VLAN function, please use no voice vlan command.
Syntax
voice vlan
no voice vlan
vlan-id
Parameter
vlan-id
—— Specify IEEE 802.1Q VLAN ID, ranging from 2 to 4094.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin, Operator and Power User level users have access to these
commands.
Example
Enable the Voice VLAN function for VLAN 10:
T2600G-28TS(config)# voice vlan 10
10.2 voice vlan aging
Description
The voice vlan aging command is used to set the aging time for a voice
VLAN. To restore to the default aging time for the Voice VLAN, please use no
voice vlan aging command.
67
Page 90

Syntax
voice vlan aging
no voice vlan aging
Parameter
time
—— Aging time (in minutes) to be set for the Voice VLAN. It ranges from
1 to 43200 minutes and the default value is 1440 minutes.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin, Operator and Power User level users have access to these
commands.
Example
Set the aging time for the Voice VLAN as 1 minute:
T2600G-28TS(config)# voice vlan aging 1
time
10.3 voice vlan priority
Description
The voice vlan priority command is used to configure the priority for the
Voice VLAN. To restore to the default priority, please use no voice vlan
priority command.
Syntax
voice vlan priority
no voice vlan priority
Parameter
pri
—— Priority, ranging from 0 to 7, and the default value is 6.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
pri
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin, Operator and Power User level users have access to these
commands.
68
Page 91

Example
Configure the priority of the Voice VLAN as 5:
T2600G-28TS(config)# voice vlan priority 5
10.4 voice vlan mac-address
Description
The voice vlan mac-address command is used to create Voice VLAN OUI. To
delete the specified Voice VLAN OUI, please use no voice vlan mac-address
command.
Syntax
voice vlan mac-address
no voice vlan mac-address
Parameter
mac-addr
XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX.
mask
XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX.
descript
characters at most.
—— The OUI address of the voice device, in the format of
—— The OUI address mask of the voice device, in the format of
——Give a description to the OUI for identification which contains 16
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin, Operator and Power User level users have access to these
commands.
mac-addr
mac-addr
mask
mask
[ description
descript
]
Example
Create a Voice VLAN OUI described as TP-Phone with the OUI address
00:11:11:11:11:11 and the mask address FF:FF:FF:00:00:00:
T2600G-28TS(config)#voice vlan mac-address 00:11:11:11:11:11 mask
FF:FF:FF:00:00:00 description TP-Phone
69
Page 92

10.5 switchport voice vlan mode
Description
The switchport voice vlan mode command is used to configure the Voice
VLAN mode for the Ethernet port.
Syntax
switchport voice vlan mode { manual | auto }
Parameter
manual | auto —— Port mode.
Command Mode
Interface Configuration Mode (interface gigabitEthernet / interface range
gigabitEthernet / interface port-channel / interface range port-channel)
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin, Operator and Power User level users have access to these
commands.
Example
Configure the port 1/0/3 to operate in the auto voice VLAN mode:
T2600G-28TS(config)# interface gigabitEthernet 1/0/3
T2600G-28TS(config-if)# switchport voice vlan mode auto
10.6 switchport voice vlan security
Description
The switchport voice vlan security command is used to enable the Voice
VLAN security feature. To disable the Voice VLAN security feature, please
use no switchport voice vlan security command.
Syntax
switchport voice vlan security
no switchport voice vlan security
Command Mode
Interface Configuration Mode (interface gigabitEthernet / interface range
gigabitEthernet / interface port-channel / interface range port-channel)
70
Page 93

Privilege Requirement
Only Admin, Operator and Power User level users have access to these
commands.
Example
Enable port 1/0/3 for the Voice VLAN security feature:
T2600G-28TS(config)# interface gigabitEthernet 1/0/3
T2600G-28TS(config-if)# switchport voice vlan security
10.7 show voice vlan
Description
The show voice vlan command is used to display the global configuration
information of Voice VLAN.
Syntax
show voice vlan
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin, Operator and Power User level users have access to these
commands.
Example
Display the configuration information of Voice VLAN globally:
T2600G-28TS(config)# show voice vlan
10.8 show voice vlan oui
Description
The show voice vlan oui command is used to display the configuration
information of Voice VLAN OUI.
Syntax
show voice vlan oui
71
Page 94

Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin, Operator and Power User level users have access to these
commands.
Example
Display the configuration information of Voice VLAN OUI:
T2600G-28TS(config)# show voice vlan oui
10.9 show voice vlan switchport
Description
The show voice vlan switchport command is used to display the Voice VLAN
configuration information of a specified port/port channel.
Syntax
show voice vlan switchport [ gigabitEthernet
port-channel-id
]
Parameter
port
—— The Ethernet port number.
port-channel-id
—— The ID of the port channel.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin, Operator and Power User level users have access to these
commands.
Example
port
| port-channel
Display the Voice VLAN configuration information of all ports and port
channels:
T2600G-28TS(config)# show voice vlan switchport
Display the Voice VLAN configuration information of port 1/0/2:
T2600G-28TS(config)# show voice vlan switchport gigabitEthernet 1/0/2
72
Page 95

Chapter 11 Etherchannel Commands
Etherchannel Commands are used to configure LAG and LACP function.
LAG (Link Aggregation Group) is to combine a number of ports together to make a single
high-bandwidth data path, which can highly extend the bandwidth. The bandwidth of the LAG is
the sum of bandwidth of its member port.
LACP (Link Aggregation Control Protocol) is defined in IEEE802.3ad and enables the dynamic
link aggregation and disaggregation by exchanging LACP packets with its partner. The switch
can dynamically group similarly configured ports into a single logical link, which will highly
extend the bandwidth and flexibly balance the load.
11.1 channel-group
Description
The channel-group command is used to add a port to the EtherChannel
Group and configure its mode. To delete the port from the EtherChannel
Group, please use no channel-group command.
Syntax
channel-group
no channel-group
Parameter
num
—— The number of the EtherChannel Group, ranging from 1 to 14.
on —— Enable the static LAG.
active —— Enable the active LACP mode.
passive —— Enable the passive LACP mode.
Command Mode
Interface Configuration Mode (interface gigabitEthernet / interface range
num
mode { on | active | passive }
gigabitEthernet)
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin, Operator and Power User level users have access to these
commands.
73
Page 96

Example
Add ports 2-4 to EtherChannel Group 1 and enable the static LAG:
T2600G-28TS(config)# interface range gigabitEthernet 1/0/2-4
T2600G-28TS(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode on
11.2 port-channel load-balance
Description
The port-channel load-balance command is used to configure the
Aggregate Arithmetic for LAG. To return to the default configurations, please
use no port-channel load-balance command.
Syntax
port-channel load-balance { src-mac | dst-mac | src-dst-mac | src-ip | dst-ip |
src-dst-ip }
no port-channel load-balance
Parameter
src-mac —— The source MAC address. When this option is selected, the
Aggregate Arithmetic will be based on the source MAC address of the
packets.
dst-mac —— The destination MAC address. When this option is selected, the
Aggregate Arithmetic will be based on the destination MAC address of the
packets.
src-dst-mac —— The source and destination MAC address. When this option
is selected, the Aggregate Arithmetic will be based on the source and
destination MAC addresses of the packets. The Aggregate Arithmetic for
LAG is “src-dst-mac” by default.
src-ip —— The source IP address. When this option is selected, the
Aggregate Arithmetic will be based on the source IP address of the packets.
dst-ip —— The destination IP address. When this option is selected, the
Aggregate Arithmetic will be based on the destination IP address of the
packets.
src-dst-ip —— The source and destination IP address. When this option is
selected, the Aggregate Arithmetic will be based on the source and
destination IP addresses of the packets.
74
Page 97

Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin, Operator and Power User level users have access to these
commands.
Example
Configure the Aggregate Arithmetic for LAG as “src-dst-ip”:
T2600G-28TS(config)# port-channel load-balance src-dst-ip
11.3 lacp system-priority
Description
The lacp system-priority command is used to configure the LACP system
priority globally. To return to the default configurations, please use no lacp
system-priority command.
Syntax
lacp system-priority
no lacp system-priority
Parameter
pri
—— The system priority, ranging from 0 to 65535. It is 32768 by default.
Command Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin, Operator and Power User level users have access to these
commands.
Example
pri
Configure the LACP system priority as 1024 globally:
T2600G-28TS(config)# lacp system-priority 1024
75
Page 98

11.4 lacp port-priority
Description
The lacp port-priority command is used to configure the LACP port priority
for specified ports. To return to the default configurations, please use no lacp
port-priority command.
Syntax
lacp port-priority
no lacp port-priority
Parameter
pri
—— The port priority, ranging from 0 to 65535. It is 32768 by default.
Command Mode
Interface Configuration Mode (interface gigabitEthernet / interface range
gigabitEthernet)
Privilege Requirement
Only Admin, Operator and Power User level users have access to these
commands.
Example
Configure the LACP port priority as 1024 for ports 1-3:
T2600G-28TS(config)# interface range gigabitEthernet 1/0/1-3
pri
T2600G-28TS(config-if-range)# lacp port-priority 1024
Configure the LACP port priority as 2048 for port 4:
T2600G-28TS(config)# interface gigabitEthernet 1/0/4
T2600G-28TS(config-if)# lacp port-priority 2048
11.5 show etherchannel
Description
The show etherchannel command is used to display the EtherChannel
information.
Syntax
show etherchannel [
channel-group-num
] { detail | summary }
76
Page 99

Parameter
channel-group-num
14. By default, it is empty, and will display the information of all EtherChannel
Groups.
detail —— The detailed information of EtherChannel.
summary —— The EtherChannel information in summary.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Privilege Requirement
None.
Example
Display the detailed information of EtherChannel Group 1:
T2600G-28TS(config)# show etherchannel 1 detail
—— The EtherChannel Group number, ranging from 1 to
11.6 show etherchannel load-balance
Description
The show etherchannel load-balance command is used to display the
Aggregate Arithmetic of LAG.
Syntax
show etherchannel load-balance
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Privilege Requirement
None.
Example
Display the Aggregate Arithmetic of LAG:
T2600G-28TS(config)# show etherchannel load-balance
77
Page 100

11.7 show lacp
Description
The show lacp command is used to display the LACP information for a
specified EtherChannel Group.
Syntax
show lacp [
channel-group-num
Parameter
channel-group-num
14. By default, it is empty, and will display the information of all LACP groups.
internal —— The internal LACP information.
neighbor —— The neighbor LACP information.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Privilege Requirement
None.
Example
Display the internal LACP information of EtherChannel Group 1:
T2600G-28TS(config)# show lacp 1 internal
] { internal
—— The EtherChannel Group number, ranging from 1 to
|
neighbor }
11.8 show lacp sys-id
Description
The show lacp sys-id command is used to display the LACP system priority
globally.
Syntax
show lacp sys-id
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC Mode and Any Configuration Mode
Privilege Requirement
None.
78
 Loading...
Loading...