Page 1
TI-89 / TI-92 Plus
TI
Calculus Tools
Getting Started
What is the Calculus T ools Application?
Before You Begin
Starting the Calculus Tools Application
Calculus Tools Menus
F1:Tools F4:Seq
F2:Deriv F5:Vector
F3:Integ F6:Advanced
More Infor m a t ion
Calculus Tools Application Functions
8/10/01 © 2001 Texas Instruments
Page 2

Important Information
Texas Instruments makes no warranty, either expressed or
implied, including but not limited to any implied warranties of
merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose, regarding
any programs or book materials and makes such materials
available solely on an "as-is" basis.
In no event shall Texas Instruments be liable to anyone for
special, collateral, incidental, or consequential damages in
connection with or arising out of the purchase or use of these
materials, and the sole and exclusive liability of Texas
Instruments, regardless of the form of action, shall not exceed
any applicable purchase price of this item or material. Moreover,
Texas Instruments shall not be liable for any claim of any kind
whatsoever against the use of these materials by any other
party.
Graphing product applications (Apps) are licensed. See the
terms of the
license agreementfor this product.
TI-GRAPH LINK is a trademark of Texas Instruments.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
TI-89 / TI-92 Plus Calculus Tools Page 2
Page 3

What is the Calculus Tools Application?
The Calculus Tools application (App) is a Concept software
application for the TI-89 / TI-92 Plus. Concept software
applications are calculator software application prototypes that
demonstrate a new concept area.
The Calculus Tools App extends the built-in power of your
TI-89 / TI-92 Plus by providing more specialized functionality.
Use the Calculus Tools App to investigate applications of
differentiation; compare numerical integration techniques; and
explore sequences, series, vector calculus, Fourier series, and
more.
The Calculus Tools App is based on programs written or
evaluated by CAS (Computer Algebra System) experts and
educators Bernhard Kutzler, Bhuvanesh Bhatt, David R.
Stoutemyer, Josef Böhm, Ray Barton, Ruth Dover, and
Wolfgang Pröpper. We appreciate their contributions and
evaluations.
Additional documentation for many of the Calculus Tools App
features can be found at series.bk-teachware.com
teaching and learning materials written for the TI-89 and
TI-92 Plus are also available at the Web site, including Exploring
Integration with the TI-89/92/92+ by Josef Böhm and Wolfgang
Pröpper.
TI-89 / TI-92 Plus Calculus Tools Page 3
. Other
Page 4

Before You Begin
Concept applications are shared with our customers, educators,
and students before product definition and testing is complete.
These applications may contain software imperfections and/or
incomplete coding areas. They are "alpha" software versions.
TI invites feedback from teachers and students concerning the
functionality and educational value of the Calculus Tools App.
Please send your comments and questions to
concept@list.ti.com
Mode settings
The Calculus Tools App requires specific mode settings to run
correctly. If you try to access the application with incorrect mode
settings, this error dialog box will appear:
.
TI-89 / TI-92 Plus Calculus Tools Page 4
Page 5

Before starting the Calculus Tools App, set modes to the
Mode
Setting
Graph
FUNCTION
Display Digits
FLOAT or FLOAT # (1 - 12)
Angle
RADIAN
Split Screen
FULL
Exact/Approx
AUTO or EXACT
Base
DEC
Language
ENGLISH
required values as follows:
1. From the Home screen, press
dialog box.
2. Ensure that the following modes are set as indicated:
3. Press
¸
MEMORY and VAR-LINK screens unavailable
The MEMORY and VAR-LINK screens, accessed by the
and
2 °
3
to display the MODE
. The Home screen displays.
2 ¯
keys, are unavailable for the Calculus Tools A pp.
TI-89 dialog boxes
The TI-89 Calculus Tools App dialog boxes default to alpha-lock.
Press
TI-89 / TI-92 Plus Calculus Tools Page 5
j
to turn alpha-lock off before entering numbers.
Page 6
Using variables from the Main folder
Menu option
Variable defined as …
F2F3F4F5F6
Independent var
1 and 2;
4-7
4
Dependent var
4
Angle Parameter
7
Index var
1
Coordinate variables
All
Integration variables
5-8
Var n
2 and 3
x3All
Using variables from the Main folder places those stored values
in the Calculus Tools App functions. The Calculus Tools App,
however, clears the following types of variables for specified
functions. As a result, the data stored in these variables is lost.
Viewing answers in split screen
The Calculus Tools App uses a split screen view to display the
numerical and graphical representations of selected solutions.
For answers that are partially hidden when viewed in a split
•
screen, press
For answers that are too long to be viewed in a full screen,
•
use the Display Answer
You cannot switch back and forth between the split screen
•
portions.
to view the answer in full screen.
N
option.
TI-89 / TI-92 Plus Calculus Tools Page 6
Page 7

88VVLLQJQJ&&DDOOFXFXOOXXVV77RRRROOVV$$SSSS00HQXHQXVV
Access the Calculus Tools App menus using the F1 through F6
function keys. F1 menu options let you change the configuration
of what you see on the screen, such as viewing the complete
answer or data entered as a string, changing split screen
settings, and restoring window defaults.
F2 through F6 menu options let you access calculus operations
and are organized under the broad categories of derivatives,
integrals, sequences, vectors, and advanced functions.
Most F2 through F6 options access a problem-entry dialog box
that includes an example problem to help you get started. Work
through the example problem, or replace it as desired.
Dialog boxes for most F2 through F6 menu options revert to
default values after data is entered. Dialog boxes for the F3
menu options, however, display the values entered last.
This is the problem-entry dialog box for
TI-89 / TI-92 Plus Calculus Tools Page 7
1:Tangent Line
.
Page 8
F1:Tools
Tip
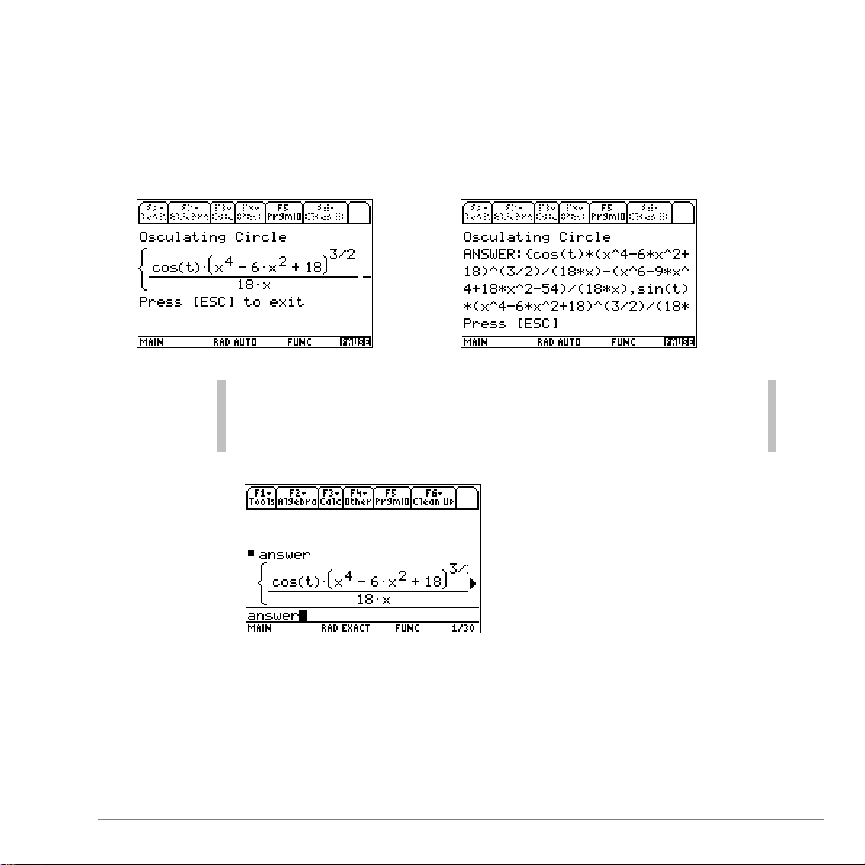
You can also go to the Home screen, type
answer
, and
press
¸
. Scroll to see the complete answer displayed
in Pretty Print.
F1 1:Display ANSWER
Lets you view an answer that is too long to fit on the screen.
(Answers are displayed as a string.)
TI-89 / TI-92 Plus Calculus Tools Page 8
Page 9
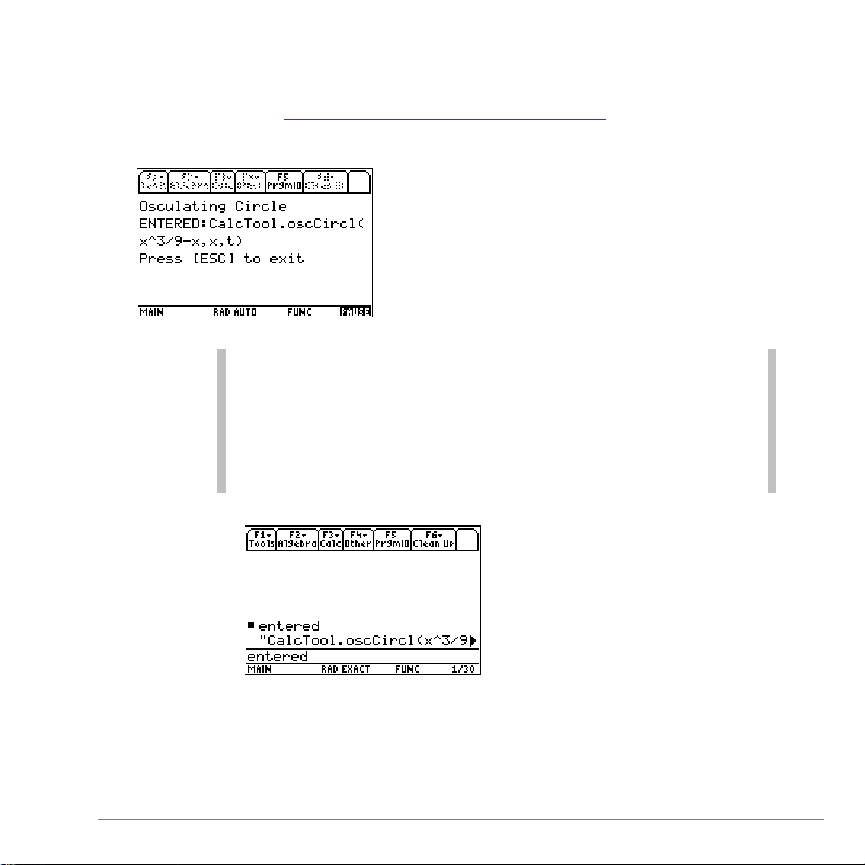
F1 2:Display ENTERED
Tip
To run a Calculus Tools App function from the Home
screen, type
entered
and press
¸
. The last command
(function and instructions) executed appears.
Be sure to remove the quotes from the string before
executing the command.
Lets you view executed commands or functions as a string,
including the Calculus Tools App functions
entered from the problem-entry dialog box.
and operations
TI-89 / TI-92 Plus Calculus Tools Page 9
Page 10

F1 3:Change Split Screen
Lets you choose between left-right (default) and top-bottom
split screens.
The TI-92 Plus lets you change the ratio of the split screen
views.
1:1 displays the answer and graph views at the same size.
•
1:2 displays the answer view at half the size of the graph
•
view.
2:1 displays the answer view at twice the size of the graph
•
view.
TI-89 / TI-92 Plus Calculus Tools Page 10
Page 11

F1 4:Restore Window Defaults
Parameter
Default Value
xmin
-3.55102040816
xmax
3.55102040816
xscl
1
ymin
L
3
ymax
3
yscl
1
xres
2
F1 5:Special Thanks
F1 6:About
Restores the Calculus Tools App window parameters to
default values. Dialog boxes accessed using the F3 menu
options are also restored to default values.
Function Graph Window Parameters
Acknowledges some of the Calculus Tools App contributors.
Displays a variety of information about the application,
including the version number.
TI-89 / TI-92 Plus Calculus Tools Page 11
Page 12
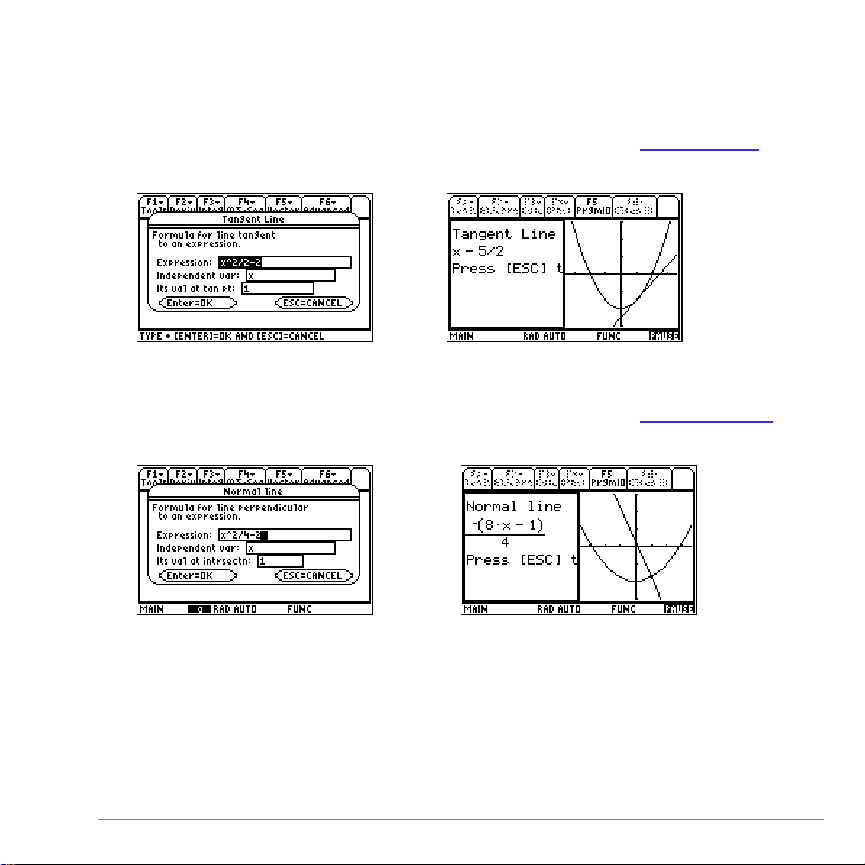
F2:Deriv
F2 1:Tangent Line
Displays the problem-entry dialog box for the tanLine(...)
function along with an example problem (page 35).
F2 2:Normal Line
Displays the problem-entry dialog box for the prpendic(...)
function along with an example problem (page 34).
TI-89 / TI-92 Plus Calculus Tools Page 12
Page 13

F2 3:Newton’s Method
Note
The number of iterations must be an integer
1.
Displays the problem-entry dialog box for Newton's Method
along with an example problem. Enter a function f (x), Initial
guess, and Number of iterations.
The solution appears in a split screen. One portion of the split
screen displays a sequence of approximations to a real root
of the functions.
The other portion of the split screen displays a graph of the
function and draws tangent lines corresponding to
consecutive iterations.
The application draws the first guess for you. Press either
¸
or
to view the consecutive guesses. This example
N
shows four iterations.
TI-89 / TI-92 Plus Calculus Tools Page 13
Page 14

F2 4:Implicit Derivative
Displays the problem-entry dialog box for the impDifN(...)
function along with an example problem (page 32).
F2 5:Curvature
Displays the problem-entry dialog box for the curvatur(...)
function along with an example problem (page 31).
TI-89 / TI-92 Plus Calculus Tools Page 14
Page 15

F2 6:Center of Curvature
Displays the problem-entry dialog box for the cntrCurv(...)
function along with an example problem (page 30).
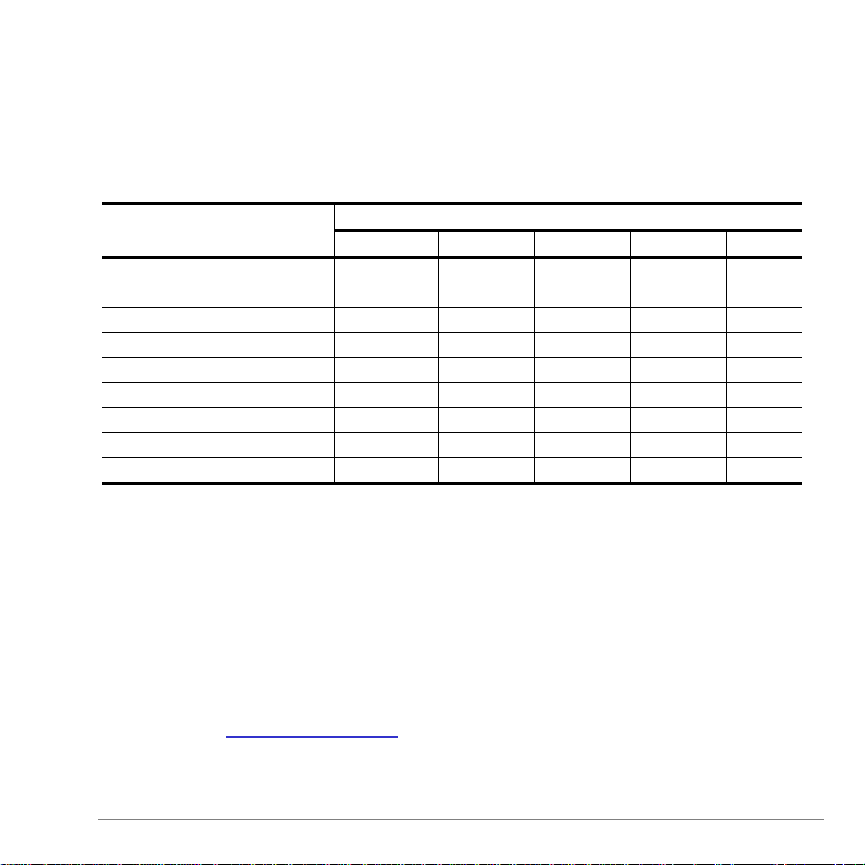
F2 7:Osculating Circle
Displays the problem-entry dialog box for the oscCircl(...)
function along with an example problem (page 33).
TI-89 / TI-92 Plus Calculus Tools Page 15
Page 16

F3:Integ
F3 1:Left Sum
Displays the problem-entry dialog box for the Left Sum
integration method along with an example problem. Enter a
function f (x), Lower bound, Upper bound, and Number of
intervals.
The answer appears in a split screen. One portion of the split
screen displays the sum of the areas of the rectangles.
The other portion of the split screen displays the graph of the
function and draws the rectangles.
F3 2:Right Sum
Displays the problem-entry dialog box for the Right Sum
integration method along with an example problem. Enter a
function f (x), Lower bound, Upper bound, and Number of
intervals.
The answer appears in a split screen. One portion of the split
screen displays the sum of the areas of the rectangles.
TI-89 / TI-92 Plus Calculus Tools Page 16
Page 17

The other portion of the split screen displays the graph of the
function and draws the rectangles.
F3 3:Midpoint Rule
Displays the problem-entry dialog box for the Midpoint Rule
along with an example problem. Enter a function f (x), Lower
bound, Upper bound, and Number of intervals.
The answer appears in a split screen. One portion of the split
screen displays the sum of the areas of the rectangles.
The other portion of the split screen displays the graph of the
function and draws the rectangles.
TI-89 / TI-92 Plus Calculus Tools Page 17
Page 18

F3 4:Trapezoidal Rule
Note
The number of intervals must be an even integer 2.
Displays the problem-entry dialog box for the Trapezoidal
Rule along with an example problem. Enter a function f (x),
Lower bound, Upper bound, and Number of intervals.
The answer appears in a split screen. One portion of the split
screen displays the sum of the areas of the trapezoids.
The other portion of the split screen displays the graph of the
function and draws the trapezoids.
F3 5:Simpson’s Rule
Displays the problem-entry dialog box for Simpson's Rule
along with an example problem. Enter a function f (x), Lower
bound, Upper bound, and Number of intervals.
The answer appears in a split screen. One portion of the split
screen displays the Simpson’s Rule approximation to the
definite integral by using parabolic arcs.
TI-89 / TI-92 Plus Calculus Tools Page 18
Page 19

The other portion of the split screen displays the graph of the
function and draws the parabolic arcs.
F3 6:Comparison
Returns the approximation to the definite integral using these
previously mentioned methods: Left Sum
Midpoint Rule
, Trapezoidal Rule, and Simpson’s Rule (pages
, Right Sum,
16 through 18).
TI-89 / TI-92 Plus Calculus Tools Page 19
Page 20

F4:Seq (infinite series, sequences)
F4 1:Ratio Convergence Test
Displays the problem-entry dialog box for the ratioTst(...)
function (page 34) along with an example problem.
F4 2:1st-Order Sequence
Displays the problem-entry dialog box for the seq1Solv(...)
function (page 34) along with an example problem.
TI-89 / TI-92 Plus Calculus Tools Page 20
Page 21

F4 3:2nd-Order Sequence
Displays the problem-entry dialog box for the seq2Solv(...)
function (page 35) along with an example problem.
F5:Vector
F5 1:Gradient
Displays the problem-entry dialog box for the grad(...)
function (page 32) along with an example problem.
TI-89 / TI-92 Plus Calculus Tools Page 21
Page 22

F5 2:Divergence
Note
The number of components in
exprList
must equal the
number of variables in
varList
.
Displays the problem-entry dialog box for the div(...)
function (page 31) along with an example problem.
F5 3:Curl
Displays the problem-entry dialog box for the curl(...)
function (page 30) along with an example problem.
TI-89 / TI-92 Plus Calculus Tools Page 22
Page 23

F5 4:Potential
Displays the problem-entry dialog box for the potentl(...)
function (page 33) along with an example problem.
F6:Advanced
F6 1:Error Function, erf
Displays the problem-entry dialog box for the erf(...)
function
(page 31) along with an example problem.
TI-89 / TI-92 Plus Calculus Tools Page 23
Page 24

F6 2:Comp. Error Function
Displays the problem-entry dialog box for the erfc(...)
(page 31) along with an example problem.
F6 3:Gamma Function
Displays the problem-entry dialog box for the gamma(...)
function (page 32) along with an example problem.
function
TI-89 / TI-92 Plus Calculus Tools Page 24
Page 25

F6 4:Fourier Series
Displays the problem-entry dialog box for the fourirCf(...)
function (page 32) along with an example problem.
F6 5:Integral of Density
F6 5:Integral of Density > 1:over a Surface
Displays the problem-entry dialog box for the surfIntg(...)
function (page 35) along with an example problem.
TI-89 / TI-92 Plus Calculus Tools Page 25
Page 26

F6 5:Integral of Density > 2:over a Polar Region
Displays the problem-entry dialog box and example
problem to set up an iterated integral to integrate a density
over a region in polar coordinates. Use
density
unweighted polar area.
F6 6:Centroid of Density
Displays the problem-entry dialog box for the aCntroid(...)
function (page 29) along with an example problem.
1 for an
TI-89 / TI-92 Plus Calculus Tools Page 26
Page 27

F6 7:Inertia Tensor
Displays the problem-entry dialog box for the aInertia(...)
function (page 30) along with an example problem.
F6 8:Arc Displacement
Displays the problem-entry dialog box for the plrArcLn(...)
function along with an example problem (page 33).
TI-89 / TI-92 Plus Calculus Tools Page 27
Page 28

Working with Calculus Tools App Functions
Note
Calculus Tools App functions cannot be called from within
the application. If you try to call a function using the
application’s problem-entry dialog boxes, the error
message,
Protected memory violation
, will appear. Exit
and re-enter the application to ensure normal operation.
Tip
To view help for a function, select a function from the
catalog and press
.
Use Calculus Tools App functions outside the application when
working with programs or other built-in, user-defined, and Flash
application functions.
Accessing Calculus Tools App functions from the Catalog
1. From the Home screen, press
(TI-92 Plus). The catalog appears.
2. Press c. The list of Flash application functions appears.
3. Scroll through the list and select the function you want to use.
4. Press
¸
line in the form
CalcTool
. The function appears on the Home screen entry
.function name
5. Add the required arguments to complete the command and
press
TI-89 / TI-92 Plus Calculus Tools Page 28
¸
.
½
(TI-89) /
Page 29

Accessing Calculus Tools App functions from VAR-LINK
1. From the Home screen, press
VAR-LINK [ALL]
2. Press
2
screen appears.
(TI-89) / g(TI-92 Plus). The list of Flash
2 °
. The
application functions appears.
3. Scroll through the list and select the function you want to use.
You may need to expand the application's folder before you
can view its functions.
4. Press
CalcTool
¸
. The function appears on the entry line as
.function name
5. Add the required arguments to complete the command and
press
¸
.
List of Calculus Tools App Functions
aCntroid
(density, var1, lower1, upper1, var2, lower2(var1), upper2(var1))
Returns a two-element list denoting the
of the centroid of a
to
lower1
var2
upper1
varies from expression
might depend on
, which must be independent of
var1
density
over a 2D region.
lower2
. Use
density
{var1, var2}
to expression
coordinates
varies from
var1
and
var1
upper2
1 for an area centroid.
.
var2
, which
Use F6 6:Centroid of Density
to display the problem-entry
dialog box and example for this function.
TI-89 / TI-92 Plus Calculus Tools Page 29
Page 30

alnertia
(density, var1, lower1, upper1, var2, lower2(var1), upper2(var1))
Returns a 2x2 matrix denoting the inertia tensor of a density
over a two-dimensional region.
upper1
from expression
depend on
, which must be independent of
to expression
lower2
var1
. Use
density
1 for an area inertia tensor.
varies from
var1
var1
upper2
lower1
and
var2. var2
, which might
Use F6 7:Inertia Tensor to display the problem-entry dialog
box and example for this function.
to
varies
cntrCurv
(expression, var)
Returns a two-element list that is a parametric representation
of the center of curvature of
Use F2 6:Center of Curvature
expression
to display the problem-entry
with respect to
var
.
dialog box and example for this function.
curl
(exprList, xVar, yVar, zVar)
Returns the three-dimensional rectangular Cartesian curl of
the vector represented by
coordinate variables
xVar, yVar, zVar
exprList
with respect to the
.
Use F5 3:Curl to display the problem-entry dialog box and
example for this function.
TI-89 / TI-92 Plus Calculus Tools Page 30
Page 31

curvatur
Note
The number of components in
exprList
must equal the
number of variables in
varList
.
(expression, var)
Returns the curvature of
Use F2 5:Curvature to display the problem-entry dialog box
and example for this function.
div
(exprList, varList)
Returns the rectangular Cartesian n-dimensional divergence
of the vector represented by
coordinate variables in
Use F5 2:Divergence to display the problem-entry dialog box
and example for this function.
erf
(complexNumber)
Returns the approximate numeric error function of
complexNumber
Use F6 1:Error Function, erf to display the problem-entry
dialog box and example for this function.
.
expression
exprList
VarList
.
with respect to
var
with respect to the
.
n
erfc
(complexNumber)
Returns the approximate complementary error function of
complexNumber
TI-89 / TI-92 Plus Calculus Tools Page 31
.
Page 32

Use F6 2:Comp. Error Function to display the problem-entry
dialog box and example for this function.
fourirCf
(expression, var, lowerLimit, upperLimit, n)
Returns the truncated Fourier series of
lowerLimit
to
upperLimit
, through the nth harmonic.
expression
for
var
Use F6 4:Fourier Series to display the problem-entry dialog
box and example for this function.
gamma
(complexNumber)
Returns the approximate gamma function of
Use F6 3:Gamma Function, Γ(z)
complexNumber
to display the problem-entry
dialog box and example for this function.
grad
(expression, VarList)
Returns the rectangular Cartesian n-dimensional gradient of
expression
with respect to the ncoordinate variables in
Use F5 1:Gradient to display the problem-entry dialog box
and example for this function.
impDifN
(equation, IndependentVar, DependentVar, n)
Returns the nth derivative of the function implicitly defined by
equation
.
from
VarList
.
.
Use F2 4:Implicit Derivative to display the problem-entry
dialog box and example for this function.
TI-89 / TI-92 Plus Calculus Tools Page 32
Page 33

oscCircl
Note
Does not verify that
exprList
is a gradient, so first see if
curl
(exprList, xVar, yVar, zVar)
simplifies to {0,0,0}, as it
should for a gradient.
(expression, var, circleParameter)
Returns a two-element list that is a parametric representation
of the circle that osculates
expression
.
Use F2 7:Osculating Circle to display the problem-entry
dialog box and example for this function.
plrArcLn
Returns the weighted arc displacement in polar coordinates,
where var
and
Use
Use F6 8:Arc Displacement to display the problem-entry
dialog box and example for this function.
potentl
Returns the scalar potential of the three-dimensional
rectangular Cartesian gradient represented by
the potential = 0 at
Use F5 4:Potential to display the problem-entry dialog box
and example for this function.
(r(qVar), qVar, low, up, weight(qVar))
q
Var
varies from
weight(qVar)
weight
(exprList, xVar, yVar, zVar, x0, y0, z0)
being expressions that might depend on
1 for an unweighted arc displacement.
{x0, y0, z0}
lowerLimit
.
to
upperLimit
, with
exprList
r(qVar)
q
, with
Var
.
TI-89 / TI-92 Plus Calculus Tools Page 33
Page 34

prpendic
(expression, var, varValue)
Returns an expression for the line that is normal to
at
var
=
varValue
.
expression
Use F2 2:Normal Line to display the problem-entry dialog box
and example for this function.
ratioTst
(expression, indexVar)
Conducts the ratio test for the convergence of an infinite
series, returning one of the strings
, or
inconclusive
unable to complete test
converges, diverges, test
.
Use F4 1:Ratio Convergence Test to display the problem-
entry dialog box and example for this function.
seq1Solv
(p(n), r(n), n, nMin, ui)
Attempts to return an exact symbolic expression for u(n) that
satisfies the linear 1st-order sequence equation
u(n)=p(n)
Use F4 2:1st-Order Sequence
u(n-1)+r(n) with u(nMin)=ui.
to display the problem-entry
dialog box and example for this function.
TI-89 / TI-92 Plus Calculus Tools Page 34
Page 35

seq2Solv
(k, c, r(n), n, nMin, {u(nMin), u(nMin-1)})
Attempts to return an exact symbolic expression for u(n) that
satisfies the linear 2nd-order constant-coefficient sequence
equation
u(n)=k
u(n-1)+cu(n-2)+r(n) and ui={u(nMin) , u(nMin-1)}.
Use F4 3:2nd-Order Sequence
to display the problem-entry
dialog box and example for this function.
surfIntg
(density, height, var1, lower1, upper1, var2, lower2(var1), upper2(var1))
Returns the integral of a
might vary with
var1
and
density
var2. var1
which must be independent of
expression
. Use
var1
density
to expression
lower2
1 for a surface area.
over surface whose
varies from
and
var1
upper2
var2. var2
, which might depend on
lower1
varies from
to
height
upper1
Use F6 5:Integral of Density > 1:over a Surface to display the
problem-entry dialog box and example for this function.
tanLine
(expression, var, varValue)
Returns an expression for the line that is tangent to
at
var
=
varValue
. (In contrast, the built-in LineTan command
expression
draws the tangent line but does not reveal its formula.)
Use F2 1:Tangent Line
to display the problem-entry dialog
box and example for this function.
,
TI-89 / TI-92 Plus Calculus Tools Page 35
Page 36

Installing the Calculus Tools App
Detailed Flash application installation instructions are available
from education.ti.com/guides.
You will need:
A TI-89 / TI-92 Plus with the latest Advanced Mathematics
•
Software Operating System. Download a free copy from
education.ti.com/softwareupdates
.
A computer using either Microsoft
•
Macintoshëoperating system software.
A TI-GRAPH LINK™ computer-to-calculator cable, available
•
for purchase from the TI Online Store at
education.ti.com/buy
TI-GRAPH LINK connectivity software for the
•
TI-89 / TI-92 Plus. Download a free copy from
education.ti.com/softwareupdates
TI-89 / TI-92 Plus Calculus Tools Page 36
.
Windowsëor Apple
ë
.
ë
Page 37

Starting and Quitting the Application
Starting the Calculus Tools App
The instructions in this guidebook refer to this Flash application
only. For help using the TI-89 / TI-92 Plus, refer to the
comprehensive guidebook at education.ti.com/guides
.
1. Ensure modes
2. Press
3. Press
¸
are set to the required values.
1:FlashApps
and select
Calculus Tools
. The Hint screen displays.
.
Quitting the Calculus Tools App
Press
TI-89 / TI-92 Plus Calculus Tools Page 37
2 K
from the Calculus Tools App Hint screen.
Page 38

Deleting an Application
Deleting an application removes it from the calculator and
increases space for other applications. Before deleting an
application, consider storing it on a computer for reinstallation
later.
1. Quit
2. Press
3. Press
the application.
2 °
2
(TI-89) / (TI-92 Plus) to display the list of
to display the
VAR-LINK [ALL]
applications.
4. Select the application you want to delete.
5. Press
1:Delete
. The
VAR-LINK
delete confirmation dialog
box displays.
6. Press
¸
to delete the application.
screen.
TI-89 / TI-92 Plus Calculus Tools Page 38
Page 39

Concept Application Evaluation License Agreement
(Including Preview, Prototype, and Demo APPS)
By downloading the software and/or documentation you agree to abide by
the following provisions.
1.
Copyright:
Licensee agrees that he/she wi l l not delete the copyright notic e, trademarks or protective
notices from the Licensed Materials or copies made during installation.
2.
Support:
limited support for this concept application may be available from TI.
3.
Testing:
subjected concept appli cations to rigorous testing and that the concept application may
cause problems with his/ her calculator, including its use in any kind of shared environment.
Further, it is possi bl e for a concept application to c ause calculator crashes or lock ups
which may be difficult to recover from. You are advis ed that use of the concept application
is AT YOUR OWN RISK.
4.
Warranty:
meet your specific requi rem ents.
The Licensed Materials are mad e available "AS IS" to Licen see.
5.
Limitations: TI makes no warranty or condition, either express or implied, including
but not limited to any implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a
particular purpose, regard i n g th e Licensed Materials.
In no event shall TI, any third party licensor, or TI's suppliers be liable for any
indirect, incidental or consequential damages, loss of profits, loss of use or data, or
interruption of business, w heth er the alleged damages are labeled in tor t, co n tract
or indemnity.
Some states do not allow the exclusion or limitation of incidental or consequential
damages, so the above lim itation may not apply.
6.
Restricted Rights:
duplication or disclos ure by the United States Government is subject to restric tions as set
forth in subparagraph [c](1)(ii) of the Rights in Technical Data and Comput er S oftware
clause at DFARS 252.227-7013 or in s ubparagraph [ c](1) and (2) of the Commercial
Computer Software - Restrict ed Ri ghts at 48 CFR 52.227-19, as applicable.
The Licensed Materials are copyrighted by TI or the third party l i censor.
The Licensed Materials are provided by TI with the understanding that onl y
Licensee acknowledges that he/ she understands that TI has not in al l cases
TI does not warrant that the Licensed Materials will be free from errors or will
The Licensed Materials are provided with Restricted Rights. Us e,
TI-89 / TI-92 Plus Calculus Tools Page 39
Page 40

Page Reference
This PDF document contains electronic bookmarks designed for
easy on-screen navigation. If you decide to print this document,
please use the page numbers below to find specific topics.
Important Information............................................................................................. 2
What is the Calculus Tools Application?................................................................ 3
Before You Begin................................................................................................... 4
Mode settings ....................................................................................................4
MEMORY and VAR-LINK screens inactive.......................................................5
TI-89 dialog boxes.............................................................................................5
Using variables from the Main folder.................................................................6
Viewing answers in split screen......................................................................... 6
Using Calculus Tools App Menus.......................................................................... 7
F1:Tools............................................................................................................. 8
F2:Deriv ........................................................................................................... 12
F3:Integ............................................................................................................ 16
F4:Seq (infinite series, sequences) ................................................................. 20
F5:Vector ......................................................................................................... 21
F6:Advanced.................................................................................................... 23
Working with Calculus Tools App Functions........................................................ 28
Accessing Calculus Tools App functions from the Catalog............................. 28
Accessing Calculus Tools App functions from VAR-LINK...............................29
List of Calculus Tools App Functions .............................................................. 29
Installing the Calculus Tools App......................................................................... 36
Starting and Quitting the Application....................................................................37
Starting the Calculus Tools App ...................................................................... 37
Quitting the Calculus Tools App ...................................................................... 37
Deleting an Application.........................................................................................38
Concept Application Evaluation License Agreement ...........................................39
TI-89 / TI-92 Plus Calculus Tools Page 40
 Loading...
Loading...