Telefunken TSOP1140SB1, TSOP1156SB1, TSOP1133SB1, TSOP1137SB1, TSOP1138SB1 Datasheet
...
TSOP11..SB1
Vishay Telefunken
1 (8)Rev. 8, 29-Mar-01
www.vishay.com
Document Number 82010
Photo Modules for PCM Remote Control Systems
Available types for different carrier frequencies
Type fo Type fo
TSOP1130SB1 30 kHz TSOP1133SB1 33 kHz
TSOP1136SB1 36 kHz TSOP1137SB1 36.7 kHz
TSOP1138SB1 38 kHz TSOP1140SB1 40 kHz
TSOP1156SB1 56 kHz
Description
The TSOP1 1..SB1 – series are miniaturized receivers
for infrared remote control systems. PIN diode and
preamplifier are assembled on lead frame, the epoxy
package is designed as IR filter.
The demodulated output signal can directly be de-
coded by a microprocessor. The main benefit is the
operation with short burst transmission codes (e.g.
RECS 80) and high data rates.
96 12581
Features
D
Photo detector and preamplifier in one package
D
Internal filter for PCM frequency
D
Improved shielding against electrical field distur-
bance
D
TTL and CMOS compatibility
D
Output active low
D
Low power consumption
D
High immunity against ambient light
Special Features
D
Enhanced data rate of 3500 bit/s
D
Operation with short bursts possible
(≥6 cycles/burst)
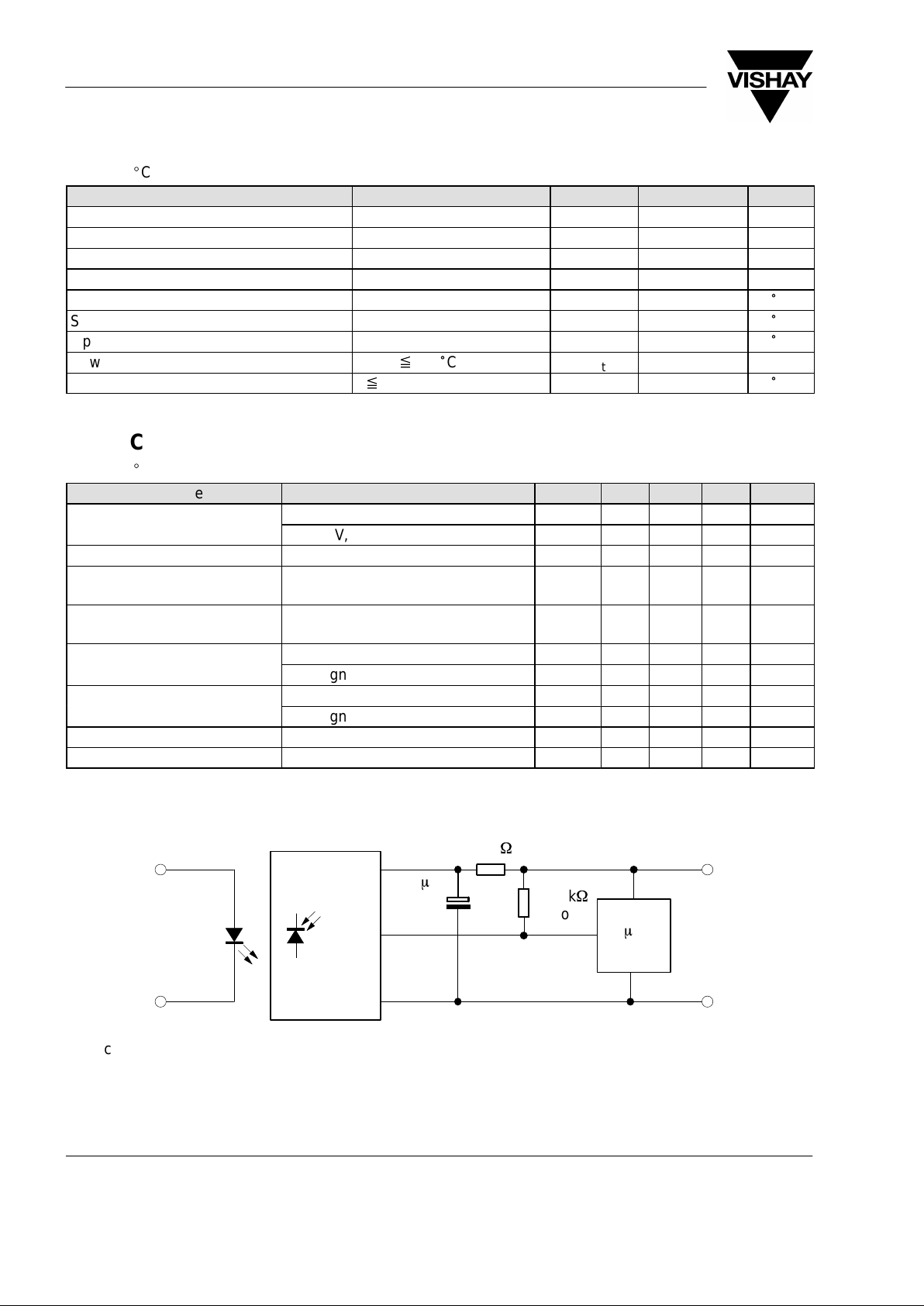
Block Diagram
94 8136
PIN
Input
AGC
Control
Circuit
Band
Pass
Demodu-
lator
80 k
W
1
2
3
V
S
OUT
GND
TSOP11..SB1
Vishay Telefunken
Rev. 8, 29-Mar-01
www.vishay.com
Document Number 82010
2 (8)
Absolute Maximum Ratings
T
amb
= 25
_
C
Parameter Test Conditions Symbol Value Unit
Supply Voltage (Pin 2) V
S
–0.3...6.0 V
Supply Current (Pin 2) I
S
5 mA
Output Voltage (Pin 3) V
O
–0.3...6.0 V
Output Current (Pin 3) I
O
5 mA
Junction Temperature T
j
100
°
C
Storage Temperature Range T
stg
–25...+85
°
C
Operating Temperature Range T
amb
–25...+85
°
C
Power Consumption (T
amb
x
85
°
C) P
tot
50 mW
Soldering Temperature t
x
10 s, 1 mm from case T
sd
260
°
C
Basic Characteristics
T
amb
= 25
_
C
Parameter Test Conditions Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Supply Current (Pin 2) V
S
= 5 V, E
v
= 0 I
SD
0.4 0.6 1.5 mA
y()
V
S
= 5 V, E
v
= 40 klx, sunlight I
SH
1 mA
Supply Voltage (Pin 2) V
S
4.5 5.5 V
Transmission Distance E
v
= 0, test signal see fig.8,
IR diode TSAL6200, I
F
= 0.4 A
d 35 m
Output Voltage Low (Pin 3) I
OSL
= 0.5 mA,E
e
= 0.7 mW/m
2
,
f = f
o
, test signal see fig.7
V
OSL
250 mV
Irradiance (30 – 40 kHz) Test signal see fig.7 E
e
min
0.4 0.6 mW/m
2
()
Test signal see fig.8 E
e
min
0.35 0.5 mW/m
2
Irradiance (56 kHz) Test signal see fig.7 E
e
min
0.45 0.7 mW/m
2
()
Test signal see fig.8 E
e
min
0.40 0.6 mW/m
2
Irradiance Test signal see fig.7 E
e
max
30 W/m
2
Directivity Angle of half transmission distance ϕ
1/2
±45 deg
Application Circuit
12755
TSAL62..
TSOP11..
2
3
1
4.7
m
F *)
m
C
>10 k
W
optional
100
W
*)
+5V
*) recommended to suppress power supply disturbances
GND
**) The output voltage should not be hold continuously at a voltage below 3.3V by the external circuit.
**)

TSOP11..SB1
Vishay Telefunken
3 (8)Rev. 8, 29-Mar-01
www.vishay.com
Document Number 82010
Suitable Data Format
The circuit of the TSOP11..SB1 is designed in that
way that unexpected output pulses due to noise or
disturbance signals are avoided. A bandpassfilter, an
integrator stage and an automatic gain control are
used to suppress such disturbances.
The distinguishing mark between data signal and
disturbance signal are carrier frequency, burst length
and duty cycle.
The data signal should fullfill the following condition:
• Carrier frequency should be close to center
frequency of the bandpass (e.g. 38kHz).
• Burst length should be 6 cycles/burst or longer.
• After each burst which is between 6 cycles and 70
cycles a gap time of at least 10 cycles is neccessary.
• For each burst which is longer than 1.8ms a
corresponding gap time is necessary at some time in
the data stream. This gap time should have at least
same length as the burst.
• Up to 2200 short bursts per second can be received
continuously .
Some examples for suitable data format are:
NEC Code, T oshiba Micom Format, Sharp Code, RC5
Code, RC6 Code, RCMM Code, R–2000 Code,
RECS–80 Code.
When a disturbance signal is applied to the
TSOP11..SB1 it can still receive the data signal.
However the sensitivity is reduced to that level that no
unexpected pulses will occure.
Some examples for such disturbance signals which
are suppressed by the TSOP11..SB1 are:
• DC light (e.g. from tungsten bulb or sunlight)
• Continuous signal at 38kHz or at any other
frequency
• Signals from fluorescent lamps with electronic
ballast (an example of the signal modulation is in the
figure below).
0 5 10 15 20
time [ms]
IR Signal from Fluorescent Lamp with low Modulation
 Loading...
Loading...